QUIZ ON CHAPTERS 1 AND 2 - SOLUTIONS REVIEW / LIMITS AND CONTINUITY; MATH 150 SPRING 2017 KUNIYUKI 105 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 100 POINTS = 100%
|
|
|
- Anthony Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 QUIZ ON CHAPTERS AND 2 - SOLUTIONS REVIEW / LIMITS AND CONTINUITY; MATH 50 SPRING 207 KUNIYUKI 05 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 00 POINTS = 00% ) For a), b), and c) below, bo in the correct answer. (6 points total; 2 pts. each) a) Let f ( ) = 4 + cos( ). The function f is even odd neither Dom f b) Let g Dom g c) Let h =., f ( ) = ( ) 4 + cos( ) = 4 + cos( ) = f ( ). = + sin( ). The function g is even odd neither =., g( ) = + sin = sin = g( ). = 5 +. The function h is even odd neither. A countereample to h being even or odd: h 2 and h( 2) are neither equal nor opposite. h 2 =, but h( 2) = 29. 2) Fill in the blanks. Find rules for functions f and g so that ( f g) ( ) = f ( g( ) ) =. (We are decomposing a composite function.) 2 + g( ) = 2 +, f ( u) = u (Do not let f or g be the identity function.) (2 points) There are different possible answers, but the above would be a reasonable choice. ) Complete the Identities. Fill out the table below so that, for each row, the left side is equivalent to the right side, based on the type of identity (ID) given in the last column. (8 points total; 2 points each) Left Side Right Side Type of Identity (ID) + tan 2 u cos u sin u ( u) cos u + v sin u v cos 2 sec 2 ( u) Pythagorean ID cos( v) sin( u) sin( v) Sum ID cos( v) cos( u) sin( v) Difference ID + cos( 2u) 2 or 2 + cos( 2u) 2 Power-Reducing ID (PRI) 4) Write any two of the three different versions of the Double-Angle Identity (ID) for cos 2u that were listed in Chapter. (4 points) Any two of these three: = cos 2 ( u) sin 2 u cos 2u The Pythagorean Identity sin 2 ; cos 2u = 2sin 2 ( u); cos( 2u) = 2cos 2 ( u) ( u) + cos 2 ( u) = is used to get from the first to the others.
2 tan sin 2 5) Verify the identity sin( 2) tan( ) Q.E.D. = 2sin( )cos sin( cos = ( 2cos2 ) using the Chapter identities. (5 points) Double-Angle ID Quotient ID = 2 sin ( ) cos cos sin = 2cos 2 ( ) 6) Fill out the table below. Use interval form (the form using parentheses and/or brackets) ecept where indicated. You do not have to show work. (6 points) Domain Range f cos (, ), tan( ) csc( ) Use set-builder form. π 2 + πn ( n ) Use set-builder form. { πn ( n ) } 7) In parts a) through i), consider the function f, where f and the graph of y = f = in the usual y-plane. (28 points total) a) Find f 2. Show all rigorous work, as in class. (7 points) f = 2 2 b) Find f (5 points) = 4 7 Limit Form (, ) (,, ) , ( ) ( + 2) ( 2) ( +) 2. Show all rigorous work, as in class. Use the Division Method to find a long-run it as. Divide the numerator and the denominator by 2 (or by for the simplified form on the right), the highest power of in the denominator.
3 (cont.) f 2 4 = or ( from Part a) ) ( This is the ratio of the given leading coefficients; see f). ) c) Which of the following is true? Bo in one: (2 points) i. f is continuous at = 2. ii. f has a removable discontinuity at = 2. iii. f has a jump discontinuity at = 2. iv. f has an infinite discontinuity at = 2. f is a rational function, and 2 Dom( f ), so f is continuous at 2. d) Which of the following is true? Bo in one: (2 points) i. f is continuous at =. ii. f has a removable discontinuity at =. iii. f has a jump discontinuity at =. iv. f has an infinite discontinuity at =. f is rational, and = The corresponding problem factor, + yields the it form nonzero real number 0 (divided) out in the denominator when the original f + f , is not completely canceled epression is simplified. Limit Form 5/ = f Limit Form 5/ =. 0
4 e) Which of the following is true? Bo in one: (2 points) i. f is continuous at = 2. ii. f has a removable discontinuity at = 2. iii. f has a jump discontinuity at = 2. iv. f has an infinite discontinuity at = 2. In Part a), we determined that 2 f However, f 2 denominator of eists. is undefined ( 2 Dom( f )) because Therefore, f has a removable discontinuity at = 2. f) What is the horizontal asymptote of the graph of y = f equation. Answer only on f) is fine. ( points) is a factor of the? Write its f is a rational function, so its graph has at most one horizontal asymptote (HA). From Part b), f =, so the sole HA has equation: y =. Note: For both original and simplified epressions for f ( ), the numerator and denominator have equal degrees, and the ratio of their leading coefficients is. g) Where is the hole on the graph of y = f ( )? Use, y coordinates. Answer only on g) is fine. ( points) form to write its From Part a), f 2 = 4. f is discontinuous at = 2 (it is undefined there), 7 yet 2 f eists, so there is a hole at: 2, 4 7 Observe that the ( 2) factor is completely canceled (divided) out in the denominator when the original f ( ) epression is simplified. h) What is the -intercept of the graph of y = f ( )? (2 points) Set y = 0. The real zeros of f are those of = , or + 2 ( + 2 ): + 2 = 0 ( 2) = 2 The -intercept is at ( 2, 0). i) What is the y-intercept of the graph of y = f ( )? (2 points) Set = 0 y = f ( 0) = The y-intercept is at ( 0, 2) = = 2 = 2 = 0 0
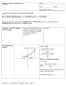
5 The graph of y = f ( ) is below. Note the horizontal asymptote (HA) at y =, the vertical asymptote (VA) at =, and the hole at 2, 4 7. There is continuity at = 2 ; in fact, the -intercept is at ( 2, 0). The y-intercept is at ( 0, 2). = ) Let f graph of y = f. What is the equation of the horizontal asymptote of the in the usual y-plane? ( points) The sole horizontal asymptote (HA) is given by y = 0, because = Alternatively, = 0. Note that is proper and rational, and we are taking its long-run its. (By proper, we mean that the numerator s degree, 4, is less than the denominator s degree, 0. Think: Bottom-heavy. ) 9) Find the following its. Bo in your final answers. (22 points total) a) r r r r r 2. Show all work, as in class. (0 points) r We have a 0 0 r 2 r it form. We will rationalize the numerator. ( r 2 ) ( r 2 + ) r r 2 + r ( r 2) 2 2 ( r) r 2 + Observe: r r ( r 2) 9 ( r) r 2 + ( r 2 is defined near r =. ) r and ( r) are opposites. Their quotient is. r 2 + = 2 + = 9 + = + = 6 ( ) r ( r) r 2 + ( )
6 b) cos ( ). Show all work, as in class. (6 points) cos( ) = 0. Prove this using the Sandwich / Squeeze Theorem: cos( ) ( ) More precisely: Observe that As, = 0 and > 0, > 0. cos So, by Sandwich/ Squeeze Thm. Divide all three parts by ( > 0) = 0, so by the Squeeze Theorem, 6 c). Show all work, as in class. (6 points) = 6 + ( ) ( + 2) + 5 cos Limit Form ( ) = 0. 0) (2 points). True or False: It is possible that for a function f, a f but f a = eists does not (meaning f ( a) is undefined). Bo in one: True False For eample, see Section 2., Eample 7; here, let s use the letter f instead of g. Let f ( ) = + ( ). f = 6 (the it eists), yet f is undefined. = L a, L ) Write a precise ε-δ definition of f a. Assume f is defined on a punctured neighborhood of a. (7 points) For every / any / all ε > 0, δ > 0 such that if 0 < a < δ, then f () L < ε. there eists Alternatively: then f ( ) is in ( L ε, L + ε)
7 2) Let f ( ) = 4, 2 2, > 2. (6 points total). (2 points) a) Evaluate 2 + f Since we are letting approach 2 from the right, the case > 2 is the only relevant case here, and the rule f ( ) = b) Evaluate f ( ). (2 points) 2 is the only relevant rule here. f ( 2 ) 2 + = 2 2 = Since we are letting approach 2 from the left, the case 2 is the only relevant case here, and the rule f = 4 is the only relevant rule here. 2 f = ( 2) 4 = c) Which of the following is true? Bo in one: (2 points) ) Let g( t) = i. f is continuous at = 2. ii. f has a removable discontinuity at = 2. iii. f has a jump discontinuity at = 2. iv. f has an infinite discontinuity at = 2. The right-hand it from a) and the left-hand it from b) as 2 both eist, but they are not equal. Therefore, f has a jump discontinuity at = 2. t 4 + t 7. What is the domain of g? Write your answer in interval form (the form using parentheses and/or brackets). Note: g is continuous on the domain interval(s). (4 points) The denominator, t 4, is real and nonzero t 4 > 0 t > 4. t 7 is real everywhere on. Dom( g) = ( 4, ) 4) (2 points). True or False: If f is a polynomial function on such that f = 0 and f ( 7) = 20, then the equation f ( ) = 5 has a real solution. Bo in one: True False f is polynomial on and hence continuous on, in particular on the interval, , 20. By the Intermediate Value Theorem (IVT), f in, 7. = 5 has a real solution
1) If f x symmetric about what? (Box in one:) (2 points) the x-axis the y-axis the origin none of these
 QUIZ ON CHAPTERS AND - SOLUTIONS REVIEW / LIMITS AND CONTINUITY; MATH 50 FALL 06 KUNIYUKI 05 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 00 POINTS = 00% = x /, then the graph of y = f ( x) in the usual (Cartesian) xy-plane is )
QUIZ ON CHAPTERS AND - SOLUTIONS REVIEW / LIMITS AND CONTINUITY; MATH 50 FALL 06 KUNIYUKI 05 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 00 POINTS = 00% = x /, then the graph of y = f ( x) in the usual (Cartesian) xy-plane is )
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART 1 MATH 150 FALL 2016 KUNIYUKI PART 1: 135 POINTS, PART 2: 115 POINTS, TOTAL: 250 POINTS
 SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART MATH 5 FALL 6 KUNIYUKI PART : 5 POINTS, PART : 5 POINTS, TOTAL: 5 POINTS No notes, books, or calculators allowed. 5 points: 45 problems, pts. each. You do not have to algebraically
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART MATH 5 FALL 6 KUNIYUKI PART : 5 POINTS, PART : 5 POINTS, TOTAL: 5 POINTS No notes, books, or calculators allowed. 5 points: 45 problems, pts. each. You do not have to algebraically
CALCULUS: THE ANSWERS MATH 150: CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRY I. VERSION 1.3 KEN KUNIYUKI and LALEH HOWARD SAN DIEGO MESA COLLEGE
 CALCULUS: THE ANSWERS MATH 150: CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRY I VERSION 1. KEN KUNIYUKI and LALEH HOWARD SAN DIEGO MESA COLLEGE 1) f 4 (Answers to Exercises for Chapter 1: Review) A.1.1. CHAPTER 1: REVIEW
CALCULUS: THE ANSWERS MATH 150: CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRY I VERSION 1. KEN KUNIYUKI and LALEH HOWARD SAN DIEGO MESA COLLEGE 1) f 4 (Answers to Exercises for Chapter 1: Review) A.1.1. CHAPTER 1: REVIEW
D sin x. (By Product Rule of Diff n.) ( ) D 2x ( ) 2. 10x4, or 24x 2 4x 7 ( ) ln x. ln x. , or. ( by Gen.
 SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART MATH 50 SPRING 07 KUNIYUKI PART : 35 POINTS, PART : 5 POINTS, TOTAL: 50 POINTS No notes, books, or calculators allowed. 35 points: 45 problems, 3 pts. each. You do not have
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL - PART MATH 50 SPRING 07 KUNIYUKI PART : 35 POINTS, PART : 5 POINTS, TOTAL: 50 POINTS No notes, books, or calculators allowed. 35 points: 45 problems, 3 pts. each. You do not have
Rational Functions 4.5
 Math 4 Pre-Calculus Name Date Rational Function Rational Functions 4.5 g ( ) A function is a rational function if f ( ), where g ( ) and ( ) h ( ) h are polynomials. Vertical asymptotes occur at -values
Math 4 Pre-Calculus Name Date Rational Function Rational Functions 4.5 g ( ) A function is a rational function if f ( ), where g ( ) and ( ) h ( ) h are polynomials. Vertical asymptotes occur at -values
SEE and DISCUSS the pictures on pages in your text. Key picture:
 Math 6 Notes 1.1 A PREVIEW OF CALCULUS There are main problems in calculus: 1. Finding a tangent line to a curve though a point on the curve.. Finding the area under a curve on some interval. SEE and DISCUSS
Math 6 Notes 1.1 A PREVIEW OF CALCULUS There are main problems in calculus: 1. Finding a tangent line to a curve though a point on the curve.. Finding the area under a curve on some interval. SEE and DISCUSS
3.5 Continuity of a Function One Sided Continuity Intermediate Value Theorem... 23
 Chapter 3 Limit and Continuity Contents 3. Definition of Limit 3 3.2 Basic Limit Theorems 8 3.3 One sided Limit 4 3.4 Infinite Limit, Limit at infinity and Asymptotes 5 3.4. Infinite Limit and Vertical
Chapter 3 Limit and Continuity Contents 3. Definition of Limit 3 3.2 Basic Limit Theorems 8 3.3 One sided Limit 4 3.4 Infinite Limit, Limit at infinity and Asymptotes 5 3.4. Infinite Limit and Vertical
Calculus I Exam 1 Review Fall 2016
 Problem 1: Decide whether the following statements are true or false: (a) If f, g are differentiable, then d d x (f g) = f g. (b) If a function is continuous, then it is differentiable. (c) If a function
Problem 1: Decide whether the following statements are true or false: (a) If f, g are differentiable, then d d x (f g) = f g. (b) If a function is continuous, then it is differentiable. (c) If a function
SECTION 2.5: THE INDETERMINATE FORMS 0 0 AND
 (Section 2.5: The Indeterminate Forms 0/0 and / ) 2.5. SECTION 2.5: THE INDETERMINATE FORMS 0 0 AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand what it means for a Limit Form to be indeterminate. Recognize indeterminate
(Section 2.5: The Indeterminate Forms 0/0 and / ) 2.5. SECTION 2.5: THE INDETERMINATE FORMS 0 0 AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand what it means for a Limit Form to be indeterminate. Recognize indeterminate
UNIT 3. Rational Functions Limits at Infinity (Horizontal and Slant Asymptotes) Infinite Limits (Vertical Asymptotes) Graphing Rational Functions
 UNIT 3 Rational Functions Limits at Infinity (Horizontal and Slant Asymptotes) Infinite Limits (Vertical Asymptotes) Graphing Rational Functions Recall From Unit Rational Functions f() is a rational function
UNIT 3 Rational Functions Limits at Infinity (Horizontal and Slant Asymptotes) Infinite Limits (Vertical Asymptotes) Graphing Rational Functions Recall From Unit Rational Functions f() is a rational function
4. (6 points) Express the domain of the following function in interval notation:
 Eam 1-A L. Ballou Name Math 131 Calculus I September 1, 016 NO Calculator Allowed BOX YOUR ANSWER! Show all work for full credit! 1. (4 points) Write an equation of a line with y-intercept 4 and -intercept
Eam 1-A L. Ballou Name Math 131 Calculus I September 1, 016 NO Calculator Allowed BOX YOUR ANSWER! Show all work for full credit! 1. (4 points) Write an equation of a line with y-intercept 4 and -intercept
PART 1: USING SCIENTIFIC CALCULATORS (41 PTS.) 1) The Vertex Form for the equation of a parabola in the usual xy-plane is given by y = 3 x + 4
 MIDTERM SOLUTIONS (CHAPTERS AND 3: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, EXP L, LOG FUNCTIONS) MATH 141 FALL 018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 41 FOR PART 1, AND 109 FOR PART PART 1: USING SCIENTIFIC CALCULATORS (41 PTS.)
MIDTERM SOLUTIONS (CHAPTERS AND 3: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, EXP L, LOG FUNCTIONS) MATH 141 FALL 018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 41 FOR PART 1, AND 109 FOR PART PART 1: USING SCIENTIFIC CALCULATORS (41 PTS.)
Pre-Calculus Mathematics Limit Process Calculus
 NOTES : LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON.1 THE TANGENT AND VELOCITY PROBLEMS Pre-Calculus Mathematics Limit Process Calculus The type of it that is used to find
NOTES : LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON.1 THE TANGENT AND VELOCITY PROBLEMS Pre-Calculus Mathematics Limit Process Calculus The type of it that is used to find
Rational Functions. A rational function is a function that is a ratio of 2 polynomials (in reduced form), e.g.
 Rational Functions A rational function is a function that is a ratio of polynomials (in reduced form), e.g. f() = p( ) q( ) where p() and q() are polynomials The function is defined when the denominator
Rational Functions A rational function is a function that is a ratio of polynomials (in reduced form), e.g. f() = p( ) q( ) where p() and q() are polynomials The function is defined when the denominator
of multiplicity two. The sign of the polynomial is shown in the table below
 161 Precalculus 1 Review 5 Problem 1 Graph the polynomial function P( ) ( ) ( 1). Solution The polynomial is of degree 4 and therefore it is positive to the left of its smallest real root and to the right
161 Precalculus 1 Review 5 Problem 1 Graph the polynomial function P( ) ( ) ( 1). Solution The polynomial is of degree 4 and therefore it is positive to the left of its smallest real root and to the right
1. Find the domain of the following functions. Write your answer using interval notation. (9 pts.)
 MATH- Sample Eam Spring 7. Find the domain of the following functions. Write your answer using interval notation. (9 pts.) a. 9 f ( ) b. g ( ) 9 8 8. Write the equation of the circle in standard form given
MATH- Sample Eam Spring 7. Find the domain of the following functions. Write your answer using interval notation. (9 pts.) a. 9 f ( ) b. g ( ) 9 8 8. Write the equation of the circle in standard form given
Chapter 3.5: Rational Functions
 Chapter.5: Rational Functions A rational number is a ratio of two integers. A rational function is a quotient of two polynomials. All rational numbers are, therefore, rational functions as well. Let s
Chapter.5: Rational Functions A rational number is a ratio of two integers. A rational function is a quotient of two polynomials. All rational numbers are, therefore, rational functions as well. Let s
MAC1105-College Algebra
 MAC1105-College Algebra Chapter -Polynomial Division & Rational Functions. Polynomial Division;The Remainder and Factor Theorems I. Long Division of Polynomials A. For f ( ) 6 19 16, a zero of f ( ) occurs
MAC1105-College Algebra Chapter -Polynomial Division & Rational Functions. Polynomial Division;The Remainder and Factor Theorems I. Long Division of Polynomials A. For f ( ) 6 19 16, a zero of f ( ) occurs
SECTION 2.4: LIMITS AND INFINITY II
 (Section 2.4: Limits and Infinity II) 2.4.1 SECTION 2.4: LIMITS AND INFINITY II LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand infinite limits at a point and relate them to vertical asymptotes of graphs. Be able to evaluate
(Section 2.4: Limits and Infinity II) 2.4.1 SECTION 2.4: LIMITS AND INFINITY II LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand infinite limits at a point and relate them to vertical asymptotes of graphs. Be able to evaluate
AP Calculus I Summer Packet
 AP Calculus I Summer Packet This will be your first grade of AP Calculus and due on the first day of class. Please turn in ALL of your work and the attached completed answer sheet. I. Intercepts The -intercept
AP Calculus I Summer Packet This will be your first grade of AP Calculus and due on the first day of class. Please turn in ALL of your work and the attached completed answer sheet. I. Intercepts The -intercept
PACKET Unit 4 Honors ICM Functions and Limits 1
 PACKET Unit 4 Honors ICM Functions and Limits 1 Day 1 Homework For each of the rational functions find: a. domain b. -intercept(s) c. y-intercept Graph #8 and #10 with at least 5 EXACT points. 1. f 6.
PACKET Unit 4 Honors ICM Functions and Limits 1 Day 1 Homework For each of the rational functions find: a. domain b. -intercept(s) c. y-intercept Graph #8 and #10 with at least 5 EXACT points. 1. f 6.
In this note we will evaluate the limits of some indeterminate forms using L Hôpital s Rule. Indeterminate Forms and 0 0. f(x)
 L Hôpital s Rule In this note we will evaluate the its of some indeterminate forms using L Hôpital s Rule. Indeterminate Forms and 0 0 f() Suppose a f() = 0 and a g() = 0. Then a g() the indeterminate
L Hôpital s Rule In this note we will evaluate the its of some indeterminate forms using L Hôpital s Rule. Indeterminate Forms and 0 0 f() Suppose a f() = 0 and a g() = 0. Then a g() the indeterminate
CHAPTER 1 Limits and Their Properties
 CHAPTER Limits and Their Properties Section. A Preview of Calculus................... 305 Section. Finding Limits Graphically and Numerically....... 305 Section.3 Evaluating Limits Analytically...............
CHAPTER Limits and Their Properties Section. A Preview of Calculus................... 305 Section. Finding Limits Graphically and Numerically....... 305 Section.3 Evaluating Limits Analytically...............
The main way we switch from pre-calc. to calc. is the use of a limit process. Calculus is a "limit machine".
 A Preview of Calculus Limits and Their Properties Objectives: Understand what calculus is and how it compares with precalculus. Understand that the tangent line problem is basic to calculus. Understand
A Preview of Calculus Limits and Their Properties Objectives: Understand what calculus is and how it compares with precalculus. Understand that the tangent line problem is basic to calculus. Understand
Limits and Their Properties
 Chapter 1 Limits and Their Properties Course Number Section 1.1 A Preview of Calculus Objective: In this lesson you learned how calculus compares with precalculus. I. What is Calculus? (Pages 42 44) Calculus
Chapter 1 Limits and Their Properties Course Number Section 1.1 A Preview of Calculus Objective: In this lesson you learned how calculus compares with precalculus. I. What is Calculus? (Pages 42 44) Calculus
An Intro to Limits Sketch to graph of 3
 Limits and Their Properties A Preview of Calculus Objectives: Understand what calculus is and how it compares with precalculus.understand that the tangent line problem is basic to calculus. Understand
Limits and Their Properties A Preview of Calculus Objectives: Understand what calculus is and how it compares with precalculus.understand that the tangent line problem is basic to calculus. Understand
TRIG REVIEW NOTES. Co-terminal Angles: Angles that end at the same spot. (sines, cosines, and tangents will equal)
 TRIG REVIEW NOTES Convert from radians to degrees: multiply by 0 180 Convert from degrees to radians: multiply by 0. 180 Co-terminal Angles: Angles that end at the same spot. (sines, cosines, and tangents
TRIG REVIEW NOTES Convert from radians to degrees: multiply by 0 180 Convert from degrees to radians: multiply by 0. 180 Co-terminal Angles: Angles that end at the same spot. (sines, cosines, and tangents
Chapter 5B - Rational Functions
 Fry Texas A&M University Math 150 Chapter 5B Fall 2015 143 Chapter 5B - Rational Functions Definition: A rational function is The domain of a rational function is all real numbers, except those values
Fry Texas A&M University Math 150 Chapter 5B Fall 2015 143 Chapter 5B - Rational Functions Definition: A rational function is The domain of a rational function is all real numbers, except those values
Directions: Please read questions carefully. It is recommended that you do the Short Answer Section prior to doing the Multiple Choice.
 AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Multiple Choice Section Directions: Please read questions carefully It is recommended that you do the Short Answer Section prior to doing the Multiple Choice Show all work
AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Multiple Choice Section Directions: Please read questions carefully It is recommended that you do the Short Answer Section prior to doing the Multiple Choice Show all work
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC. Complex Fractions
 Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
6.1 Polynomial Functions
 6.1 Polynomial Functions Definition. A polynomial function is any function p(x) of the form p(x) = p n x n + p n 1 x n 1 + + p 2 x 2 + p 1 x + p 0 where all of the exponents are non-negative integers and
6.1 Polynomial Functions Definition. A polynomial function is any function p(x) of the form p(x) = p n x n + p n 1 x n 1 + + p 2 x 2 + p 1 x + p 0 where all of the exponents are non-negative integers and
Math 31A Discussion Session Week 1 Notes January 5 and 7, 2016
 Math 31A Discussion Session Week 1 Notes January 5 and 7, 2016 This week we re discussing two important topics: its and continuity. We won t give a completely rigorous definition of either, but we ll develop
Math 31A Discussion Session Week 1 Notes January 5 and 7, 2016 This week we re discussing two important topics: its and continuity. We won t give a completely rigorous definition of either, but we ll develop
MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 FALL 2018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 47 FOR PART 1, AND 103 FOR PART
 Math 141 Name: MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 FALL 018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 47 FOR PART 1, AND 103 FOR PART Show all work, simplify as appropriate, and
Math 141 Name: MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 FALL 018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 47 FOR PART 1, AND 103 FOR PART Show all work, simplify as appropriate, and
MATH section 3.4 Curve Sketching Page 1 of 29
 MATH section. Curve Sketching Page of 9 The step by step procedure below is for regular rational and polynomial functions. If a function contains radical or trigonometric term, then proceed carefully because
MATH section. Curve Sketching Page of 9 The step by step procedure below is for regular rational and polynomial functions. If a function contains radical or trigonometric term, then proceed carefully because
Chapter 8: More on Limits
 Chapter 8: More on Limits Lesson 8.. 8-. a. 000 lim a() = lim = 0 b. c. lim c() = lim 3 +7 = 3 +000 lim b( ) 3 lim( 0000 ) = # = " 8-. a. lim 0 = " b. lim (#0.5 ) = # lim c. lim 4 = lim 4(/ ) = " d. lim
Chapter 8: More on Limits Lesson 8.. 8-. a. 000 lim a() = lim = 0 b. c. lim c() = lim 3 +7 = 3 +000 lim b( ) 3 lim( 0000 ) = # = " 8-. a. lim 0 = " b. lim (#0.5 ) = # lim c. lim 4 = lim 4(/ ) = " d. lim
4.3 Division of Polynomials
 4.3 Division of Polynomials Learning Objectives Divide a polynomials by a monomial. Divide a polynomial by a binomial. Rewrite and graph rational functions. Introduction A rational epression is formed
4.3 Division of Polynomials Learning Objectives Divide a polynomials by a monomial. Divide a polynomial by a binomial. Rewrite and graph rational functions. Introduction A rational epression is formed
Section 2.6 Limits at infinity and infinite limits 2 Lectures. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 2.6 Limits at infinity and infinite its 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS 0: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Infinite Limits / 29 Finite its as ±. 2 Horizontal Asympotes. 3 Infinite its. 4
Section 2.6 Limits at infinity and infinite its 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS 0: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Infinite Limits / 29 Finite its as ±. 2 Horizontal Asympotes. 3 Infinite its. 4
PART 1: USING SCIENTIFIC CALCULATORS (50 PTS.)
 Math 141 Name: MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 SPRING 2018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 50 FOR PART 1, AND 100 FOR PART 2 Show all work, simplify as appropriate,
Math 141 Name: MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 SPRING 2018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 50 FOR PART 1, AND 100 FOR PART 2 Show all work, simplify as appropriate,
Calculus Problem Sheet Prof Paul Sutcliffe. 2. State the domain and range of each of the following functions
 f() 8 6 4 8 6-3 - - 3 4 5 6 f().9.8.7.6.5.4.3.. -4-3 - - 3 f() 7 6 5 4 3-3 - - Calculus Problem Sheet Prof Paul Sutcliffe. By applying the vertical line test, or otherwise, determine whether each of the
f() 8 6 4 8 6-3 - - 3 4 5 6 f().9.8.7.6.5.4.3.. -4-3 - - 3 f() 7 6 5 4 3-3 - - Calculus Problem Sheet Prof Paul Sutcliffe. By applying the vertical line test, or otherwise, determine whether each of the
( ) is symmetric about the y - axis.
 (Section 1.5: Analyzing Graphs of Functions) 1.51 PART F: FUNCTIONS THAT ARE EVEN / ODD / NEITHER; SYMMETRY A function f is even f ( x) = f ( x) x Dom( f ) The graph of y = f x for every x in the domain
(Section 1.5: Analyzing Graphs of Functions) 1.51 PART F: FUNCTIONS THAT ARE EVEN / ODD / NEITHER; SYMMETRY A function f is even f ( x) = f ( x) x Dom( f ) The graph of y = f x for every x in the domain
(ii) y = ln 1 ] t 3 t x x2 9
![(ii) y = ln 1 ] t 3 t x x2 9 (ii) y = ln 1 ] t 3 t x x2 9](/thumbs/89/100579300.jpg) Study Guide for Eam 1 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its epression to be well-defined. Some eamples of the conditions are: What is inside
Study Guide for Eam 1 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its epression to be well-defined. Some eamples of the conditions are: What is inside
Chapter The function f and its graph are shown below: + < x. lim f ( x) (a) Calculate. (b) Which value is greater
 Chapter 1 1 1. The function f and its graph are shown below: f( ) = < 0 1 = 1 1< < 3 (a) Calculate lim f ( ) (b) Which value is greater lim f ( ) or f (1)? Justify your conclusion. (c) At what value(s)
Chapter 1 1 1. The function f and its graph are shown below: f( ) = < 0 1 = 1 1< < 3 (a) Calculate lim f ( ) (b) Which value is greater lim f ( ) or f (1)? Justify your conclusion. (c) At what value(s)
THS Step By Step Calculus Chapter 1
 Name: Class Period: Throughout this packet there will be blanks you are epected to fill in prior to coming to class. This packet follows your Larson Tetbook. Do NOT throw away! Keep in 3 ring binder until
Name: Class Period: Throughout this packet there will be blanks you are epected to fill in prior to coming to class. This packet follows your Larson Tetbook. Do NOT throw away! Keep in 3 ring binder until
Chapter. Part 1: Consider the function
 Chapter 9 9.2 Analysing rational Functions Pages 446 456 Part 1: Consider the function a) What value of x is important to consider when analysing this function? b) Now look at the graph of this function
Chapter 9 9.2 Analysing rational Functions Pages 446 456 Part 1: Consider the function a) What value of x is important to consider when analysing this function? b) Now look at the graph of this function
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School
 Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION
 4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.4 Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at
4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.4 Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at
MIDTERM 3 SOLUTIONS (CHAPTER 4) INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY; MATH 141 SPRING 2018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 30 FOR PART 1, AND 120 FOR PART 2
 MIDTERM SOLUTIONS (CHAPTER 4) INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY; MATH 4 SPRING 08 KUNIYUKI 50 POINTS TOTAL: 0 FOR PART, AND 0 FOR PART PART : USING SCIENTIFIC CALCULATORS (0 PTS.) ( ) = 0., where 0 θ < 0. Give
MIDTERM SOLUTIONS (CHAPTER 4) INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY; MATH 4 SPRING 08 KUNIYUKI 50 POINTS TOTAL: 0 FOR PART, AND 0 FOR PART PART : USING SCIENTIFIC CALCULATORS (0 PTS.) ( ) = 0., where 0 θ < 0. Give
Student s Printed Name:
 MATH 1060 Test 1 Fall 018 Calculus of One Variable I Version B KEY Sections 1.3 3. Student s Printed Name: Instructor: XID: C Section: No questions will be answered during this eam. If you consider a question
MATH 1060 Test 1 Fall 018 Calculus of One Variable I Version B KEY Sections 1.3 3. Student s Printed Name: Instructor: XID: C Section: No questions will be answered during this eam. If you consider a question
TAMU Spring Math 151, Spring 2019 Common Exam 1 Version A
 TAMU Spring 019 Math 151, Spring 019 Common Eam 1 Version A LAST NAME (print): FIRST NAME (print): INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NUMBER: STUDENT ID NUMBER: Directions: 1. No calculators, cell phones, or other electronic
TAMU Spring 019 Math 151, Spring 019 Common Eam 1 Version A LAST NAME (print): FIRST NAME (print): INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NUMBER: STUDENT ID NUMBER: Directions: 1. No calculators, cell phones, or other electronic
Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity
 Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity Functions Limits Continuity Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity 1 Functions Functions are the major tools for describing the real world in mathematical
Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity Functions Limits Continuity Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity 1 Functions Functions are the major tools for describing the real world in mathematical
MAT12X Intermediate Algebra
 MAT12X Intermediate Algebra Workshop 3 Rational Functions LEARNING CENTER Overview Workshop III Rational Functions General Form Domain and Vertical Asymptotes Range and Horizontal Asymptotes Inverse Variation
MAT12X Intermediate Algebra Workshop 3 Rational Functions LEARNING CENTER Overview Workshop III Rational Functions General Form Domain and Vertical Asymptotes Range and Horizontal Asymptotes Inverse Variation
DISCOVERING THE PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES LEARNING TASK:
 Name: Class Period: DISCOVERING THE PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES LEARNING TASK: An identity is an equation that is valid for all values of the variable for which the epressions in the equation are defined. You
Name: Class Period: DISCOVERING THE PYTHAGOREAN IDENTITIES LEARNING TASK: An identity is an equation that is valid for all values of the variable for which the epressions in the equation are defined. You
1.5 Inverse Trigonometric Functions
 1.5 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Remember that only one-to-one functions have inverses. So, in order to find the inverse functions for sine, cosine, and tangent, we must restrict their domains to intervals
1.5 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Remember that only one-to-one functions have inverses. So, in order to find the inverse functions for sine, cosine, and tangent, we must restrict their domains to intervals
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School
 Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
First Midterm Examination
 Çankaya University Department of Mathematics 016-017 Fall Semester MATH 155 - Calculus for Engineering I First Midterm Eamination 1) Find the domain and range of the following functions. Eplain your solution.
Çankaya University Department of Mathematics 016-017 Fall Semester MATH 155 - Calculus for Engineering I First Midterm Eamination 1) Find the domain and range of the following functions. Eplain your solution.
Math 111 Lecture Notes
 A rational function is of the form R() = p() q() where p and q are polnomial functions. The zeros of a rational function are the values of for which p() = 0, as the function s value is zero where the value
A rational function is of the form R() = p() q() where p and q are polnomial functions. The zeros of a rational function are the values of for which p() = 0, as the function s value is zero where the value
CHAPTER 5: Analytic Trigonometry
 ) (Answers for Chapter 5: Analytic Trigonometry) A.5. CHAPTER 5: Analytic Trigonometry SECTION 5.: FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Left Side Right Side Type of Identity (ID) csc( x) sin x Reciprocal
) (Answers for Chapter 5: Analytic Trigonometry) A.5. CHAPTER 5: Analytic Trigonometry SECTION 5.: FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Left Side Right Side Type of Identity (ID) csc( x) sin x Reciprocal
Review: Limits of Functions - 10/7/16
 Review: Limits of Functions - 10/7/16 1 Right and Left Hand Limits Definition 1.0.1 We write lim a f() = L to mean that the function f() approaches L as approaches a from the left. We call this the left
Review: Limits of Functions - 10/7/16 1 Right and Left Hand Limits Definition 1.0.1 We write lim a f() = L to mean that the function f() approaches L as approaches a from the left. We call this the left
1 DL3. Infinite Limits and Limits at Infinity
 Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 78 Mark Sparks 01 Infinite Limits and Limits at Infinity In our graphical analysis of its, we have already seen both an infinite
Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 78 Mark Sparks 01 Infinite Limits and Limits at Infinity In our graphical analysis of its, we have already seen both an infinite
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION
 4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.4 Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at
4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.4 Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at
Things to remember: x n a 1. x + a 0. x n + a n-1. P(x) = a n. Therefore, lim g(x) = 1. EXERCISE 3-2
 lim f() = lim (0.8-0.08) = 0, " "!10!10 lim f() = lim 0 = 0.!10!10 Therefore, lim f() = 0.!10 lim g() = lim (0.8 - "!10!10 0.042-3) = 1, " lim g() = lim 1 = 1.!10!0 Therefore, lim g() = 1.!10 EXERCISE
lim f() = lim (0.8-0.08) = 0, " "!10!10 lim f() = lim 0 = 0.!10!10 Therefore, lim f() = 0.!10 lim g() = lim (0.8 - "!10!10 0.042-3) = 1, " lim g() = lim 1 = 1.!10!0 Therefore, lim g() = 1.!10 EXERCISE
CHAPTER 1: Functions
 CHAPTER : Functions SECTION.: FUNCTIONS (Answers for Chapter : Functions) A.. f x 2) f x 3) = x = x 4) Input x Output f x 3 0 4 5 2 6 5 5 + 4 π π + 4 0/3 22/3 4.7 8.7 c c + 4 a + h a + h + 4 Input x Output
CHAPTER : Functions SECTION.: FUNCTIONS (Answers for Chapter : Functions) A.. f x 2) f x 3) = x = x 4) Input x Output f x 3 0 4 5 2 6 5 5 + 4 π π + 4 0/3 22/3 4.7 8.7 c c + 4 a + h a + h + 4 Input x Output
Graphing Rational Functions KEY. (x 4) (x + 2) Factor denominator. y = 0 x = 4, x = -2
 6 ( 6) Factor numerator 1) f ( ) 8 ( 4) ( + ) Factor denominator n() is of degree: 1 -intercepts: d() is of degree: 6 y 0 4, - Plot the -intercepts. Draw the asymptotes with dotted lines. Then perform
6 ( 6) Factor numerator 1) f ( ) 8 ( 4) ( + ) Factor denominator n() is of degree: 1 -intercepts: d() is of degree: 6 y 0 4, - Plot the -intercepts. Draw the asymptotes with dotted lines. Then perform
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals
 AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals 8. Basic Integration Rules In this section we will review various integration strategies. Strategies: I. Separate
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals 8. Basic Integration Rules In this section we will review various integration strategies. Strategies: I. Separate
Limits, Continuity, and Differentiability Solutions
 Limits, Continuity, and Differentiability Solutions We have intentionally included more material than can be covered in most Student Study Sessions to account for groups that are able to answer the questions
Limits, Continuity, and Differentiability Solutions We have intentionally included more material than can be covered in most Student Study Sessions to account for groups that are able to answer the questions
2.2 The Limit of a Function
 2.2 The Limit of a Function Introductory Example: Consider the function f(x) = x is near 0. x f(x) x f(x) 1 3.7320508 1 4.236068 0.5 3.8708287 0.5 4.1213203 0.1 3.9748418 0.1 4.0248457 0.05 3.9874607 0.05
2.2 The Limit of a Function Introductory Example: Consider the function f(x) = x is near 0. x f(x) x f(x) 1 3.7320508 1 4.236068 0.5 3.8708287 0.5 4.1213203 0.1 3.9748418 0.1 4.0248457 0.05 3.9874607 0.05
AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT. Dear future Calculus AB student
 AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Dear future Calculus AB student We are ecited to work with you net year in Calculus AB. In order to help you be prepared for this class, please complete the summer assignment.
AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Dear future Calculus AB student We are ecited to work with you net year in Calculus AB. In order to help you be prepared for this class, please complete the summer assignment.
A.P. Calculus Summer Assignment
 A.P. Calculus Summer Assignment This assignment is due the first day of class at the beginning of the class. It will be graded and counts as your first test grade. This packet contains eight sections and
A.P. Calculus Summer Assignment This assignment is due the first day of class at the beginning of the class. It will be graded and counts as your first test grade. This packet contains eight sections and
UNIT 3. Recall From Unit 2 Rational Functions
 UNIT 3 Recall From Unit Rational Functions f() is a rational function if where p() and q() are and. Rational functions often approach for values of. Rational Functions are not graphs There various types
UNIT 3 Recall From Unit Rational Functions f() is a rational function if where p() and q() are and. Rational functions often approach for values of. Rational Functions are not graphs There various types
Solutions to Math 41 First Exam October 12, 2010
 Solutions to Math 41 First Eam October 12, 2010 1. 13 points) Find each of the following its, with justification. If the it does not eist, eplain why. If there is an infinite it, then eplain whether it
Solutions to Math 41 First Eam October 12, 2010 1. 13 points) Find each of the following its, with justification. If the it does not eist, eplain why. If there is an infinite it, then eplain whether it
Math-3 Lesson 4-6 Polynomial and Rational Inequalities
 Math-3 Lesson 4-6 Polynomial and Rational Inequalities SM3 HANDOUT 4-6 Polynomial and Rational Inequalities Graph the general shape of the equation. y 4 1 Positive lead coefficient, even degree nd degree
Math-3 Lesson 4-6 Polynomial and Rational Inequalities SM3 HANDOUT 4-6 Polynomial and Rational Inequalities Graph the general shape of the equation. y 4 1 Positive lead coefficient, even degree nd degree
MATH section 3.1 Maximum and Minimum Values Page 1 of 7
 MATH section. Maimum and Minimum Values Page of 7 Definition : Let c be a number in the domain D of a function f. Then c ) is the Absolute maimum value of f on D if ) c f() for all in D. Absolute minimum
MATH section. Maimum and Minimum Values Page of 7 Definition : Let c be a number in the domain D of a function f. Then c ) is the Absolute maimum value of f on D if ) c f() for all in D. Absolute minimum
Continuity. The Continuity Equation The equation that defines continuity at a point is called the Continuity Equation.
 Continuity A function is continuous at a particular x location when you can draw it through that location without picking up your pencil. To describe this mathematically, we have to use limits. Recall
Continuity A function is continuous at a particular x location when you can draw it through that location without picking up your pencil. To describe this mathematically, we have to use limits. Recall
Calculus I Sample Exam #01
 Calculus I Sample Exam #01 1. Sketch the graph of the function and define the domain and range. 1 a) f( x) 3 b) g( x) x 1 x c) hx ( ) x x 1 5x6 d) jx ( ) x x x 3 6 . Evaluate the following. a) 5 sin 6
Calculus I Sample Exam #01 1. Sketch the graph of the function and define the domain and range. 1 a) f( x) 3 b) g( x) x 1 x c) hx ( ) x x 1 5x6 d) jx ( ) x x x 3 6 . Evaluate the following. a) 5 sin 6
CH 2: Limits and Derivatives
 2 The tangent and velocity problems CH 2: Limits and Derivatives the tangent line to a curve at a point P, is the line that has the same slope as the curve at that point P, ie the slope of the tangent
2 The tangent and velocity problems CH 2: Limits and Derivatives the tangent line to a curve at a point P, is the line that has the same slope as the curve at that point P, ie the slope of the tangent
Summer Assignment MAT 414: Calculus
 Summer Assignment MAT 414: Calculus Calculus - Math 414 Summer Assignment Due first day of school in September Name: 1. If f ( x) = x + 1, g( x) = 3x 5 and h( x) A. f ( a+ ) x+ 1, x 1 = then find: x+ 7,
Summer Assignment MAT 414: Calculus Calculus - Math 414 Summer Assignment Due first day of school in September Name: 1. If f ( x) = x + 1, g( x) = 3x 5 and h( x) A. f ( a+ ) x+ 1, x 1 = then find: x+ 7,
Section 5.1 Model Inverse and Joint Variation
 108 Section 5.1 Model Inverse and Joint Variation Remember a Direct Variation Equation y k has a y-intercept of (0, 0). Different Types of Variation Relationship Equation a) y varies directly with. y k
108 Section 5.1 Model Inverse and Joint Variation Remember a Direct Variation Equation y k has a y-intercept of (0, 0). Different Types of Variation Relationship Equation a) y varies directly with. y k
Chapter 2. Polynomial and Rational Functions. 2.6 Rational Functions and Their Graphs. Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions.6 Rational Functions and Their Graphs Copyright 014, 010, 007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Find the domains of rational functions. Use arrow notation.
Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions.6 Rational Functions and Their Graphs Copyright 014, 010, 007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Find the domains of rational functions. Use arrow notation.
Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule
 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at certain points. INDETERMINATE FORM TYPE
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION Indeterminate Forms and L Hospital s Rule In this section, we will learn: How to evaluate functions whose values cannot be found at certain points. INDETERMINATE FORM TYPE
Set 3: Limits of functions:
 Set 3: Limits of functions: A. The intuitive approach (.): 1. Watch the video at: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/differential-calculus/it-basics-dc/formal-definition-of-its-dc/v/itintuition-review. 3.
Set 3: Limits of functions: A. The intuitive approach (.): 1. Watch the video at: https://www.khanacademy.org/math/differential-calculus/it-basics-dc/formal-definition-of-its-dc/v/itintuition-review. 3.
Solutions Exam 4 (Applications of Differentiation) 1. a. Applying the Quotient Rule we compute the derivative function of f as follows:
 MAT 4 Solutions Eam 4 (Applications of Differentiation) a Applying the Quotient Rule we compute the derivative function of f as follows: f () = 43 e 4 e (e ) = 43 4 e = 3 (4 ) e Hence f '( ) 0 for = 0
MAT 4 Solutions Eam 4 (Applications of Differentiation) a Applying the Quotient Rule we compute the derivative function of f as follows: f () = 43 e 4 e (e ) = 43 4 e = 3 (4 ) e Hence f '( ) 0 for = 0
1.2 A List of Commonly Occurring Functions
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 2914: Calculus I Dr. Marcel B. Finan 1.2 A List of Commonly Occurring Functions In this section, we discuss the most common functions occurring in calculus. Linear Functions
Arkansas Tech University MATH 2914: Calculus I Dr. Marcel B. Finan 1.2 A List of Commonly Occurring Functions In this section, we discuss the most common functions occurring in calculus. Linear Functions
3.3 Limits and Infinity
 Calculus Maimus. Limits Infinity Infinity is not a concrete number, but an abstract idea. It s not a destination, but a really long, never-ending journey. It s one of those mind-warping ideas that is difficult
Calculus Maimus. Limits Infinity Infinity is not a concrete number, but an abstract idea. It s not a destination, but a really long, never-ending journey. It s one of those mind-warping ideas that is difficult
Precalculus Review. Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions. Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties. Constants. Linear.
 Precalculus Review Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties Constants Linear Quadratic Cubic Generalizations for Polynomial Functions - The domain
Precalculus Review Functions to KNOW! 1. Polynomial Functions Types: General form Generic Graph and unique properties Constants Linear Quadratic Cubic Generalizations for Polynomial Functions - The domain
Find the domain and range of each function. Use interval notation (parenthesis or square brackets).
 Page of 10 I. Functions & Composition of Functions A function is a set of points (x, y) such that for every x, there is one and only one y. In short, in a function, the x-values cannot repeat while the
Page of 10 I. Functions & Composition of Functions A function is a set of points (x, y) such that for every x, there is one and only one y. In short, in a function, the x-values cannot repeat while the
5.4 - Quadratic Functions
 Fry TAMU Spring 2017 Math 150 Notes Section 5.4 Page! 92 5.4 - Quadratic Functions Definition: A function is one that can be written in the form f (x) = where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0. (What
Fry TAMU Spring 2017 Math 150 Notes Section 5.4 Page! 92 5.4 - Quadratic Functions Definition: A function is one that can be written in the form f (x) = where a, b, and c are real numbers and a 0. (What
FINAL - PART 1 MATH 150 SPRING 2017 KUNIYUKI PART 1: 135 POINTS, PART 2: 115 POINTS, TOTAL: 250 POINTS No notes, books, or calculators allowed.
 Math 150 Name: FINAL - PART 1 MATH 150 SPRING 2017 KUNIYUKI PART 1: 135 POINTS, PART 2: 115 POINTS, TOTAL: 250 POINTS No notes, books, or calculators allowed. 135 points: 45 problems, 3 pts. each. You
Math 150 Name: FINAL - PART 1 MATH 150 SPRING 2017 KUNIYUKI PART 1: 135 POINTS, PART 2: 115 POINTS, TOTAL: 250 POINTS No notes, books, or calculators allowed. 135 points: 45 problems, 3 pts. each. You
MATH CALCULUS I 1.5: Continuity
 MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 1.5: Continuity Professor Donald L. White Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. White (Kent State University) 1 / 12 Definition of Continuity Intuitively,
MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 1.5: Continuity Professor Donald L. White Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. White (Kent State University) 1 / 12 Definition of Continuity Intuitively,
Infinite Limits. Infinite Limits. Infinite Limits. Previously, we discussed the limits of rational functions with the indeterminate form 0/0.
 Infinite Limits Return to Table of Contents Infinite Limits Infinite Limits Previously, we discussed the limits of rational functions with the indeterminate form 0/0. Now we will consider rational functions
Infinite Limits Return to Table of Contents Infinite Limits Infinite Limits Previously, we discussed the limits of rational functions with the indeterminate form 0/0. Now we will consider rational functions
MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I
 MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I Spring 2018, WEEK 3 JoungDong Kim Week 3 Section 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, Continuity, Limits at Infinity; Horizontal Asymptotes, Derivatives and Rates of Change. Section 2.5 Continuity
MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I Spring 2018, WEEK 3 JoungDong Kim Week 3 Section 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, Continuity, Limits at Infinity; Horizontal Asymptotes, Derivatives and Rates of Change. Section 2.5 Continuity
Continuity. MATH 161 Calculus I. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics
 Continuity MATH 161 Calculus I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2017 Intuitive Idea A process or an item can be described as continuous if it exists without interruption. The mathematical
Continuity MATH 161 Calculus I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2017 Intuitive Idea A process or an item can be described as continuous if it exists without interruption. The mathematical
Fundamental Theorem of Algebra (NEW): A polynomial function of degree n > 0 has n complex zeros. Some of these zeros may be repeated.
 .5 and.6 Comple Numbers, Comple Zeros and the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Pre Calculus.5 COMPLEX NUMBERS 1. Understand that - 1 is an imaginary number denoted by the letter i.. Evaluate the square root
.5 and.6 Comple Numbers, Comple Zeros and the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Pre Calculus.5 COMPLEX NUMBERS 1. Understand that - 1 is an imaginary number denoted by the letter i.. Evaluate the square root
AP Calculus Summer Packet
 AP Calculus Summer Packet Writing The Equation Of A Line Example: Find the equation of a line that passes through ( 1, 2) and (5, 7). ü Things to remember: Slope formula, point-slope form, slopeintercept
AP Calculus Summer Packet Writing The Equation Of A Line Example: Find the equation of a line that passes through ( 1, 2) and (5, 7). ü Things to remember: Slope formula, point-slope form, slopeintercept
Lecture 5: Finding limits analytically Simple indeterminate forms
 Lecture 5: Finding its analytically Simple indeterminate forms Objectives: (5.) Use algebraic techniques to resolve 0/0 indeterminate forms. (5.) Use the squeeze theorem to evaluate its. (5.3) Use trigonometric
Lecture 5: Finding its analytically Simple indeterminate forms Objectives: (5.) Use algebraic techniques to resolve 0/0 indeterminate forms. (5.) Use the squeeze theorem to evaluate its. (5.3) Use trigonometric
Midterm 1 Solutions. Monday, 10/24/2011
 Midterm Solutions Monday, 0/24/20. (0 points) Consider the function y = f() = e + 2e. (a) (2 points) What is the domain of f? Epress your answer using interval notation. Solution: We must eclude the possibility
Midterm Solutions Monday, 0/24/20. (0 points) Consider the function y = f() = e + 2e. (a) (2 points) What is the domain of f? Epress your answer using interval notation. Solution: We must eclude the possibility
Feedback D. Incorrect! Exponential functions are continuous everywhere. Look for features like square roots or denominators that could be made 0.
 Calculus Problem Solving Drill 07: Trigonometric Limits and Continuity No. of 0 Instruction: () Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully. () Do your work on a separate sheet of paper. (3)
Calculus Problem Solving Drill 07: Trigonometric Limits and Continuity No. of 0 Instruction: () Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully. () Do your work on a separate sheet of paper. (3)
EQ: What are limits, and how do we find them? Finite limits as x ± Horizontal Asymptote. Example Horizontal Asymptote
 Finite limits as x ± The symbol for infinity ( ) does not represent a real number. We use to describe the behavior of a function when the values in its domain or range outgrow all finite bounds. For example,
Finite limits as x ± The symbol for infinity ( ) does not represent a real number. We use to describe the behavior of a function when the values in its domain or range outgrow all finite bounds. For example,
2018 Pre-Cal Spring Semester Review Name: Per:
 08 Pre-Cal Spring Semester Review Name: Per: For # 4, find the domain of each function. USE INTERVAL NOTATION!!. 4 f ( ) 5. f ( ) 6 5. f( ) 5 4. f( ) 4 For #5-6, find the domain and range of each graph.
08 Pre-Cal Spring Semester Review Name: Per: For # 4, find the domain of each function. USE INTERVAL NOTATION!!. 4 f ( ) 5. f ( ) 6 5. f( ) 5 4. f( ) 4 For #5-6, find the domain and range of each graph.
Define a rational expression: a quotient of two polynomials. ..( 3 10) (3 2) Rational expressions have the same properties as rational numbers:
 1 UNIT 7 RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS & EQUATIONS Simplifying Rational Epressions Define a rational epression: a quotient of two polynomials. A rational epression always indicates division EX: 10 means..( 10)
1 UNIT 7 RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS & EQUATIONS Simplifying Rational Epressions Define a rational epression: a quotient of two polynomials. A rational epression always indicates division EX: 10 means..( 10)
1/100 Range: 1/10 1/ 2. 1) Constant: choose a value for the constant that can be graphed on the coordinate grid below.
 Name 1) Constant: choose a value or the constant that can be graphed on the coordinate grid below a y Toolkit Functions Lab Worksheet thru inverse trig ) Identity: y ) Reciprocal: 1 ( ) y / 1/ 1/1 1/ 1
Name 1) Constant: choose a value or the constant that can be graphed on the coordinate grid below a y Toolkit Functions Lab Worksheet thru inverse trig ) Identity: y ) Reciprocal: 1 ( ) y / 1/ 1/1 1/ 1
