Chapter. Part 1: Consider the function
|
|
|
- Jean Howard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter Analysing rational Functions Pages Part 1: Consider the function a) What value of x is important to consider when analysing this function? b) Now look at the graph of this function below. 1
2 Notice there is a point of discontinuity at (2, 3). point of discontinuity a point, described by an ordered pair, at which the graph of a function is not continuous. How can you simplify the function? ***NOTE: When you cancel the like factors from the top and the bottom, that x value can give you the point of discontinuity, and the intercepts. 2
3 Determine the x and y intercept for the function 3
4 Part 2: Consider the function What value of x is important to consider when analysing this function? Now look at the graph of this function below. 4
5 What is happening at x = 2? How can you simplify the function? *** NOTE: Because you cannot cancel any like factors from the top and the bottom, the nonpermissible value found from the bottom gives you a vertical asymptote without having to graph. 5
6 Determine the x and y intercept for the function 6
7 Example 2 Page 448 Rational Functions: Points of Discontinuity Versus Asymptotes a) Compare the behaviour of the functions and near any non permissible values. b) Explain any differences. 7
8 Example 2: Your Turn Page 449 Compare the functions and explain any differences. and Answer 8
9 Determining Asymptotes for Rational Functions: #1 Vertical Asymptotes occur at the value(s) of x which make(s) the denominator of the simplified expression equal 0. Example: Determine the vertical asymptote(s) for 9
10 #2 Horizontal Asymptotes occur when the degree of the numerator the degree of the denominator. Case #1: d of n < d of d => y = 0 Case #2: d of n = d of d => y = division of leading coefficients Example: Determine the horizontal asymptote for the following: 10
11 #3 Oblique(slant) Asymptotes occur when the degree of the numerator is more than the degree of the denominator. Example: Determine the oblique asymptote for the following: 11
12 Examples: For each of the following rational functions, predict the locations of any asymptotes, points of discontinuity, and intercepts. 12
13 Example 3 Page 449 Match Graphs and Equations for Rational Functions Match the equation of each rational function with the most appropriate graph. For each of the rational functions, predict the locations of any asymptotes, points of discontinuity, and intercepts. 13
14 Example 3: Your Turn Page 450 Match the equation of each rational function with the most appropriate graph. For each of the rational functions, predict the locations of any asymptotes, points of discontinuity, and intercepts. Answer 14
15 More Examples: Write the equation of a possible rational function with each set of characteristics. a) vertical asymptote of x = 2, a point of discontinuity at x intercept of 0 and y intercept of 0. b) vertical asymptote of x = 3, no point of discontinuity, x intercepts of 1 and 6, and y intercept of 2. c) no vertical asymptote, point of discontinuity at x intercept of 2 and y intercept of 2 15
Analyzing Rational Functions
 Analyzing Rational Functions These notes are intended as a summary of section 2.3 (p. 105 112) in your workbook. You should also read the section for more complete explanations and additional examples.
Analyzing Rational Functions These notes are intended as a summary of section 2.3 (p. 105 112) in your workbook. You should also read the section for more complete explanations and additional examples.
7.4 RECIPROCAL FUNCTIONS
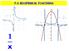 7.4 RECIPROCAL FUNCTIONS x VOCABULARY Word Know It Well Have Heard It or Seen It No Clue RECIPROCAL FUNCTION ASYMPTOTE VERTICAL ASYMPTOTE HORIZONTAL ASYMPTOTE RECIPROCAL a mathematical expression or function
7.4 RECIPROCAL FUNCTIONS x VOCABULARY Word Know It Well Have Heard It or Seen It No Clue RECIPROCAL FUNCTION ASYMPTOTE VERTICAL ASYMPTOTE HORIZONTAL ASYMPTOTE RECIPROCAL a mathematical expression or function
Rational Functions. A rational function is a function that is a ratio of 2 polynomials (in reduced form), e.g.
 Rational Functions A rational function is a function that is a ratio of polynomials (in reduced form), e.g. f() = p( ) q( ) where p() and q() are polynomials The function is defined when the denominator
Rational Functions A rational function is a function that is a ratio of polynomials (in reduced form), e.g. f() = p( ) q( ) where p() and q() are polynomials The function is defined when the denominator
Rational Functions 4.5
 Math 4 Pre-Calculus Name Date Rational Function Rational Functions 4.5 g ( ) A function is a rational function if f ( ), where g ( ) and ( ) h ( ) h are polynomials. Vertical asymptotes occur at -values
Math 4 Pre-Calculus Name Date Rational Function Rational Functions 4.5 g ( ) A function is a rational function if f ( ), where g ( ) and ( ) h ( ) h are polynomials. Vertical asymptotes occur at -values
Introduction. A rational function is a quotient of polynomial functions. It can be written in the form
 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS Introduction A rational function is a quotient of polynomial functions. It can be written in the form where N(x) and D(x) are polynomials and D(x) is not the zero polynomial. 2 In general,
RATIONAL FUNCTIONS Introduction A rational function is a quotient of polynomial functions. It can be written in the form where N(x) and D(x) are polynomials and D(x) is not the zero polynomial. 2 In general,
Department of Mathematics, University of Wisconsin-Madison Math 114 Worksheet Sections (4.1),
 Department of Mathematics, University of Wisconsin-Madison Math 114 Worksheet Sections (4.1), 4.-4.6 1. Find the polynomial function with zeros: -1 (multiplicity ) and 1 (multiplicity ) whose graph passes
Department of Mathematics, University of Wisconsin-Madison Math 114 Worksheet Sections (4.1), 4.-4.6 1. Find the polynomial function with zeros: -1 (multiplicity ) and 1 (multiplicity ) whose graph passes
Chapter 9 BLM Answers
 Chapter 9 BLM Answers BLM 9 Prerequisite Skills. a) x 5x4 x x x x x x 5x x 5x 5x 4x 4x 0 g(x) x 5x 4. a) g(5 g) g(f 4g) c) (x 5)(x ) d) (x )(x 5) e) (a )(a ) f) (x 0.)(x 0.) g) 5(xy )(xy ). a),, and h(x)
Chapter 9 BLM Answers BLM 9 Prerequisite Skills. a) x 5x4 x x x x x x 5x x 5x 5x 4x 4x 0 g(x) x 5x 4. a) g(5 g) g(f 4g) c) (x 5)(x ) d) (x )(x 5) e) (a )(a ) f) (x 0.)(x 0.) g) 5(xy )(xy ). a),, and h(x)
UNIT 3. Rational Functions Limits at Infinity (Horizontal and Slant Asymptotes) Infinite Limits (Vertical Asymptotes) Graphing Rational Functions
 UNIT 3 Rational Functions Limits at Infinity (Horizontal and Slant Asymptotes) Infinite Limits (Vertical Asymptotes) Graphing Rational Functions Recall From Unit Rational Functions f() is a rational function
UNIT 3 Rational Functions Limits at Infinity (Horizontal and Slant Asymptotes) Infinite Limits (Vertical Asymptotes) Graphing Rational Functions Recall From Unit Rational Functions f() is a rational function
Graphing Rational Functions KEY. (x 4) (x + 2) Factor denominator. y = 0 x = 4, x = -2
 6 ( 6) Factor numerator 1) f ( ) 8 ( 4) ( + ) Factor denominator n() is of degree: 1 -intercepts: d() is of degree: 6 y 0 4, - Plot the -intercepts. Draw the asymptotes with dotted lines. Then perform
6 ( 6) Factor numerator 1) f ( ) 8 ( 4) ( + ) Factor denominator n() is of degree: 1 -intercepts: d() is of degree: 6 y 0 4, - Plot the -intercepts. Draw the asymptotes with dotted lines. Then perform
2.6 Rational Functions
 2.6 Rational Functions Pre-Calculus Mr. Niedert Pre-Calculus 2.6 Rational Functions Mr. Niedert 1 / 20 2.6 Rational Functions 1 Rational Functions Pre-Calculus 2.6 Rational Functions Mr. Niedert 2 / 20
2.6 Rational Functions Pre-Calculus Mr. Niedert Pre-Calculus 2.6 Rational Functions Mr. Niedert 1 / 20 2.6 Rational Functions 1 Rational Functions Pre-Calculus 2.6 Rational Functions Mr. Niedert 2 / 20
UNIT 3. Recall From Unit 2 Rational Functions
 UNIT 3 Recall From Unit Rational Functions f() is a rational function if where p() and q() are and. Rational functions often approach for values of. Rational Functions are not graphs There various types
UNIT 3 Recall From Unit Rational Functions f() is a rational function if where p() and q() are and. Rational functions often approach for values of. Rational Functions are not graphs There various types
6.1 Polynomial Functions
 6.1 Polynomial Functions Definition. A polynomial function is any function p(x) of the form p(x) = p n x n + p n 1 x n 1 + + p 2 x 2 + p 1 x + p 0 where all of the exponents are non-negative integers and
6.1 Polynomial Functions Definition. A polynomial function is any function p(x) of the form p(x) = p n x n + p n 1 x n 1 + + p 2 x 2 + p 1 x + p 0 where all of the exponents are non-negative integers and
of multiplicity two. The sign of the polynomial is shown in the table below
 161 Precalculus 1 Review 5 Problem 1 Graph the polynomial function P( ) ( ) ( 1). Solution The polynomial is of degree 4 and therefore it is positive to the left of its smallest real root and to the right
161 Precalculus 1 Review 5 Problem 1 Graph the polynomial function P( ) ( ) ( 1). Solution The polynomial is of degree 4 and therefore it is positive to the left of its smallest real root and to the right
MAC1105-College Algebra
 MAC1105-College Algebra Chapter -Polynomial Division & Rational Functions. Polynomial Division;The Remainder and Factor Theorems I. Long Division of Polynomials A. For f ( ) 6 19 16, a zero of f ( ) occurs
MAC1105-College Algebra Chapter -Polynomial Division & Rational Functions. Polynomial Division;The Remainder and Factor Theorems I. Long Division of Polynomials A. For f ( ) 6 19 16, a zero of f ( ) occurs
GUIDED NOTES 5.6 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS
 GUIDED NOTES 5.6 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Use arrow notation. Solve applied problems involving rational functions. Find the domains of rational functions. Identify
GUIDED NOTES 5.6 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Use arrow notation. Solve applied problems involving rational functions. Find the domains of rational functions. Identify
Math 111 Lecture Notes
 A rational function is of the form R() = p() q() where p and q are polnomial functions. The zeros of a rational function are the values of for which p() = 0, as the function s value is zero where the value
A rational function is of the form R() = p() q() where p and q are polnomial functions. The zeros of a rational function are the values of for which p() = 0, as the function s value is zero where the value
Graphing Rational Functions
 Unit 1 R a t i o n a l F u n c t i o n s Graphing Rational Functions Objectives: 1. Graph a rational function given an equation 2. State the domain, asymptotes, and any intercepts Why? The function describes
Unit 1 R a t i o n a l F u n c t i o n s Graphing Rational Functions Objectives: 1. Graph a rational function given an equation 2. State the domain, asymptotes, and any intercepts Why? The function describes
RADICAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS REVIEW
 RADICAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS REVIEW Name: Block: Date: Total = % 2 202 Page of 4 Unit 2 . Sketch the graph of the following functions. State the domain and range. y = 2 x + 3 Domain: Range: 2. Identify
RADICAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS REVIEW Name: Block: Date: Total = % 2 202 Page of 4 Unit 2 . Sketch the graph of the following functions. State the domain and range. y = 2 x + 3 Domain: Range: 2. Identify
( ) = 1 x. g( x) = x3 +2
 Rational Functions are ratios (quotients) of polynomials, written in the form f x N ( x ) and D x ( ) are polynomials, and D x ( ) does not equal zero. The parent function for rational functions is f x
Rational Functions are ratios (quotients) of polynomials, written in the form f x N ( x ) and D x ( ) are polynomials, and D x ( ) does not equal zero. The parent function for rational functions is f x
To get horizontal and slant asymptotes algebraically we need to know about end behaviour for rational functions.
 Concepts: Horizontal Asymptotes, Vertical Asymptotes, Slant (Oblique) Asymptotes, Transforming Reciprocal Function, Sketching Rational Functions, Solving Inequalities using Sign Charts. Rational Function
Concepts: Horizontal Asymptotes, Vertical Asymptotes, Slant (Oblique) Asymptotes, Transforming Reciprocal Function, Sketching Rational Functions, Solving Inequalities using Sign Charts. Rational Function
Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 8 3) CCSS Then/Now New Vocabulary Key Concept: Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes Example 1: Graph with No Horizontal
 Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 8 3) CCSS Then/Now New Vocabulary Key Concept: Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes Example 1: Graph with No Horizontal Asymptote Example 2: Real-World Example: Use Graphs
Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 8 3) CCSS Then/Now New Vocabulary Key Concept: Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes Example 1: Graph with No Horizontal Asymptote Example 2: Real-World Example: Use Graphs
Midterm Review. Name: Class: Date: ID: A. Short Answer. 1. For each graph, write the equation of a radical function of the form y = a b(x h) + k.
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Midterm Review Short Answer 1. For each graph, write the equation of a radical function of the form y = a b(x h) + k. a) b) c) 2. Determine the domain and range of each function.
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Midterm Review Short Answer 1. For each graph, write the equation of a radical function of the form y = a b(x h) + k. a) b) c) 2. Determine the domain and range of each function.
Making Connections with Rational Functions and Equations
 Section 3.5 Making Connections with Rational Functions and Equations When solving a problem, it's important to read carefully to determine whether a function is being analyzed (Finding key features) or
Section 3.5 Making Connections with Rational Functions and Equations When solving a problem, it's important to read carefully to determine whether a function is being analyzed (Finding key features) or
Section 5.1 Determine if a function is a polynomial function. State the degree of a polynomial function.
 Test Instructions Objectives Section 5.1 Section 5.1 Determine if a function is a polynomial function. State the degree of a polynomial function. Form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given. Graph
Test Instructions Objectives Section 5.1 Section 5.1 Determine if a function is a polynomial function. State the degree of a polynomial function. Form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given. Graph
4.3 Division of Polynomials
 4.3 Division of Polynomials Learning Objectives Divide a polynomials by a monomial. Divide a polynomial by a binomial. Rewrite and graph rational functions. Introduction A rational epression is formed
4.3 Division of Polynomials Learning Objectives Divide a polynomials by a monomial. Divide a polynomial by a binomial. Rewrite and graph rational functions. Introduction A rational epression is formed
Section 2.6 Limits at infinity and infinite limits 2 Lectures. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 2.6 Limits at infinity and infinite its 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS 0: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Infinite Limits / 29 Finite its as ±. 2 Horizontal Asympotes. 3 Infinite its. 4
Section 2.6 Limits at infinity and infinite its 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS 0: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Infinite Limits / 29 Finite its as ±. 2 Horizontal Asympotes. 3 Infinite its. 4
Chapter 9 Prerequisite Skills
 Name: Date: Chapter 9 Prerequisite Skills BLM 9. Consider the function f() 3. a) Show that 3 is a factor of f(). If f() ( 3)g(), what is g()?. Factor each epression fully. a) 30g 4g 6fg 8g c) 6 5 d) 5
Name: Date: Chapter 9 Prerequisite Skills BLM 9. Consider the function f() 3. a) Show that 3 is a factor of f(). If f() ( 3)g(), what is g()?. Factor each epression fully. a) 30g 4g 6fg 8g c) 6 5 d) 5
Review: Limits of Functions - 10/7/16
 Review: Limits of Functions - 10/7/16 1 Right and Left Hand Limits Definition 1.0.1 We write lim a f() = L to mean that the function f() approaches L as approaches a from the left. We call this the left
Review: Limits of Functions - 10/7/16 1 Right and Left Hand Limits Definition 1.0.1 We write lim a f() = L to mean that the function f() approaches L as approaches a from the left. We call this the left
MATH section 4.4 Concavity and Curve Sketching Page 1. is increasing on I. is decreasing on I. = or. x c
 MATH 0100 section 4.4 Concavity and Curve Sketching Page 1 Definition: The graph of a differentiable function y = (a) concave up on an open interval I if df f( x) (b) concave down on an open interval I
MATH 0100 section 4.4 Concavity and Curve Sketching Page 1 Definition: The graph of a differentiable function y = (a) concave up on an open interval I if df f( x) (b) concave down on an open interval I
Horizontal and Vertical Asymptotes from section 2.6
 Horizontal and Vertical Asymptotes from section 2.6 Definition: In either of the cases f(x) = L or f(x) = L we say that the x x horizontal line y = L is a horizontal asymptote of the function f. Note:
Horizontal and Vertical Asymptotes from section 2.6 Definition: In either of the cases f(x) = L or f(x) = L we say that the x x horizontal line y = L is a horizontal asymptote of the function f. Note:
Questions From Old Exams
 MATH 0 OLD EXAM QUESTIONS FOR EXAM 3 ON CHAPTERS 3 AND 4 PAGE Questions From Old Eams. Write the equation of a quadratic function whose graph has the following characteristics: It opens down; it is stretched
MATH 0 OLD EXAM QUESTIONS FOR EXAM 3 ON CHAPTERS 3 AND 4 PAGE Questions From Old Eams. Write the equation of a quadratic function whose graph has the following characteristics: It opens down; it is stretched
Section 3.3 Limits Involving Infinity - Asymptotes
 76 Section. Limits Involving Infinity - Asymptotes We begin our discussion with analyzing its as increases or decreases without bound. We will then eplore functions that have its at infinity. Let s consider
76 Section. Limits Involving Infinity - Asymptotes We begin our discussion with analyzing its as increases or decreases without bound. We will then eplore functions that have its at infinity. Let s consider
L43-Mon-12-Dec-2016-Rev-Cpt-4-for-Final-HW44-and-Rev-Cpt-5-for-Final-HW45 Page 27. L43-Mon-12-Dec-2016-Rev-Cpt-4-HW44-and-Rev-Cpt-5-for-Final-HW45
 L43-Mon-1-Dec-016-Rev-Cpt-4-for-Final-HW44-and-Rev-Cpt-5-for-Final-HW45 Page 7 L43-Mon-1-Dec-016-Rev-Cpt-4-HW44-and-Rev-Cpt-5-for-Final-HW45 L43-Mon-1-Dec-016-Rev-Cpt-4-for-Final-HW44-and-Rev-Cpt-5-for-Final-HW45
L43-Mon-1-Dec-016-Rev-Cpt-4-for-Final-HW44-and-Rev-Cpt-5-for-Final-HW45 Page 7 L43-Mon-1-Dec-016-Rev-Cpt-4-HW44-and-Rev-Cpt-5-for-Final-HW45 L43-Mon-1-Dec-016-Rev-Cpt-4-for-Final-HW44-and-Rev-Cpt-5-for-Final-HW45
Mission 1 Simplify and Multiply Rational Expressions
 Algebra Honors Unit 6 Rational Functions Name Quest Review Questions Mission 1 Simplify and Multiply Rational Expressions 1) Compare the two functions represented below. Determine which of the following
Algebra Honors Unit 6 Rational Functions Name Quest Review Questions Mission 1 Simplify and Multiply Rational Expressions 1) Compare the two functions represented below. Determine which of the following
PreCalculus Notes. MAT 129 Chapter 5: Polynomial and Rational Functions. David J. Gisch. Department of Mathematics Des Moines Area Community College
 PreCalculus Notes MAT 129 Chapter 5: Polynomial and Rational Functions David J. Gisch Department of Mathematics Des Moines Area Community College September 2, 2011 1 Chapter 5 Section 5.1: Polynomial Functions
PreCalculus Notes MAT 129 Chapter 5: Polynomial and Rational Functions David J. Gisch Department of Mathematics Des Moines Area Community College September 2, 2011 1 Chapter 5 Section 5.1: Polynomial Functions
Chapter 3.5: Rational Functions
 Chapter.5: Rational Functions A rational number is a ratio of two integers. A rational function is a quotient of two polynomials. All rational numbers are, therefore, rational functions as well. Let s
Chapter.5: Rational Functions A rational number is a ratio of two integers. A rational function is a quotient of two polynomials. All rational numbers are, therefore, rational functions as well. Let s
Practice Test - Chapter 2
 Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
4.5 Rational functions.
 4.5 Rational functions. We have studied graphs of polynomials and we understand the graphical significance of the zeros of the polynomial and their multiplicities. Now we are ready to etend these eplorations
4.5 Rational functions. We have studied graphs of polynomials and we understand the graphical significance of the zeros of the polynomial and their multiplicities. Now we are ready to etend these eplorations
Chapter 5B - Rational Functions
 Fry Texas A&M University Math 150 Chapter 5B Fall 2015 143 Chapter 5B - Rational Functions Definition: A rational function is The domain of a rational function is all real numbers, except those values
Fry Texas A&M University Math 150 Chapter 5B Fall 2015 143 Chapter 5B - Rational Functions Definition: A rational function is The domain of a rational function is all real numbers, except those values
MAT116 Final Review Session Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 MAT116 Final Review Session Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions Quadratic Function A quadratic function is defined by a quadratic or second-degree polynomial. Standard Form f x = ax 2 + bx + c,
MAT116 Final Review Session Chapter 3: Polynomial and Rational Functions Quadratic Function A quadratic function is defined by a quadratic or second-degree polynomial. Standard Form f x = ax 2 + bx + c,
3 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 3 Polynomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Polynomial Functions and their Graphs So far, we have learned how to graph polynomials of degree 0, 1, and. Degree 0 polynomial functions are things like f(x) =,
3 Polynomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Polynomial Functions and their Graphs So far, we have learned how to graph polynomials of degree 0, 1, and. Degree 0 polynomial functions are things like f(x) =,
Things to remember: x n a 1. x + a 0. x n + a n-1. P(x) = a n. Therefore, lim g(x) = 1. EXERCISE 3-2
 lim f() = lim (0.8-0.08) = 0, " "!10!10 lim f() = lim 0 = 0.!10!10 Therefore, lim f() = 0.!10 lim g() = lim (0.8 - "!10!10 0.042-3) = 1, " lim g() = lim 1 = 1.!10!0 Therefore, lim g() = 1.!10 EXERCISE
lim f() = lim (0.8-0.08) = 0, " "!10!10 lim f() = lim 0 = 0.!10!10 Therefore, lim f() = 0.!10 lim g() = lim (0.8 - "!10!10 0.042-3) = 1, " lim g() = lim 1 = 1.!10!0 Therefore, lim g() = 1.!10 EXERCISE
MHF4U. Advanced Functions Grade 12 University Mitchell District High School. Unit 3 Rational Functions & Equations 6 Video Lessons
 MHF4U Advanced Functions Grade 12 University Mitchell District High School Unit 3 Rational Functions & Equations 6 Video Lessons Allow no more than 15 class days for this unit! This includes time for review
MHF4U Advanced Functions Grade 12 University Mitchell District High School Unit 3 Rational Functions & Equations 6 Video Lessons Allow no more than 15 class days for this unit! This includes time for review
Practice Test - Chapter 2
 Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
Section 3.7 Rational Functions
 Section 3.7 Rational Functions A rational function is a function of the form where P and Q are polynomials. r(x) = P(x) Q(x) Rational Functions and Asymptotes The domain of a rational function consists
Section 3.7 Rational Functions A rational function is a function of the form where P and Q are polynomials. r(x) = P(x) Q(x) Rational Functions and Asymptotes The domain of a rational function consists
Rational Functions. Elementary Functions. Algebra with mixed fractions. Algebra with mixed fractions
 Rational Functions A rational function f (x) is a function which is the ratio of two polynomials, that is, Part 2, Polynomials Lecture 26a, Rational Functions f (x) = where and are polynomials Dr Ken W
Rational Functions A rational function f (x) is a function which is the ratio of two polynomials, that is, Part 2, Polynomials Lecture 26a, Rational Functions f (x) = where and are polynomials Dr Ken W
Section 5.1 Model Inverse and Joint Variation
 108 Section 5.1 Model Inverse and Joint Variation Remember a Direct Variation Equation y k has a y-intercept of (0, 0). Different Types of Variation Relationship Equation a) y varies directly with. y k
108 Section 5.1 Model Inverse and Joint Variation Remember a Direct Variation Equation y k has a y-intercept of (0, 0). Different Types of Variation Relationship Equation a) y varies directly with. y k
Homework on Rational Functions - Solutions
 Homework on Rational Functions - Solutions Group Work 1 Consider f () = 1. Answer the questions below, eplain your answers. 1. What is the domain of f? f is a fraction, hence to be defined, its denominator
Homework on Rational Functions - Solutions Group Work 1 Consider f () = 1. Answer the questions below, eplain your answers. 1. What is the domain of f? f is a fraction, hence to be defined, its denominator
Limits Involving Infinity (Horizontal and Vertical Asymptotes Revisited)
 Limits Involving Infinity (Horizontal and Vertical Asymptotes Revisited) Limits as Approaches Infinity At times you ll need to know the behavior of a function or an epression as the inputs get increasingly
Limits Involving Infinity (Horizontal and Vertical Asymptotes Revisited) Limits as Approaches Infinity At times you ll need to know the behavior of a function or an epression as the inputs get increasingly
f ( x ) = x Determine the implied domain of the given function. Express your answer in interval notation.
 Test Review Section.. Given the following function: f ( ) = + 5 - Determine the implied domain of the given function. Epress your answer in interval notation.. Find the verte of the following quadratic
Test Review Section.. Given the following function: f ( ) = + 5 - Determine the implied domain of the given function. Epress your answer in interval notation.. Find the verte of the following quadratic
MTH4100 Calculus I. Lecture notes for Week 4. Thomas Calculus, Sections 2.4 to 2.6. Rainer Klages
 MTH4100 Calculus I Lecture notes for Week 4 Thomas Calculus, Sections 2.4 to 2.6 Rainer Klages School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary University of London Autumn 2009 One-sided its and its at infinity
MTH4100 Calculus I Lecture notes for Week 4 Thomas Calculus, Sections 2.4 to 2.6 Rainer Klages School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary University of London Autumn 2009 One-sided its and its at infinity
1. Reduce. 2. Intercepts. x x x. L27-Fri-4-Nov-2016-Sec-4-3-Rational-Graphs-Start-Moodle-Q23. Cannot reduce so no holes.
 L7-Fri-4-Nov-016-Sec-4-3-Rational-Graphs-Start-Moodle-Q3 8 L7-Fri-4-Nov-016-Sec-4-3-Rational-Graphs-Start-Moodle-Q3 1. Reduce x x 9 3 3 x x x Domain: x x 3, x 3 Cannot reduce so no holes.. Intercepts x-intercepts
L7-Fri-4-Nov-016-Sec-4-3-Rational-Graphs-Start-Moodle-Q3 8 L7-Fri-4-Nov-016-Sec-4-3-Rational-Graphs-Start-Moodle-Q3 1. Reduce x x 9 3 3 x x x Domain: x x 3, x 3 Cannot reduce so no holes.. Intercepts x-intercepts
56 CHAPTER 3. POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS
 56 CHAPTER 3. POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 4 Rational functions and inequalities 4.1 Rational functions Textbook section 4.7 4.1.1 Basic rational functions and asymptotes As a first step towards understanding
56 CHAPTER 3. POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 4 Rational functions and inequalities 4.1 Rational functions Textbook section 4.7 4.1.1 Basic rational functions and asymptotes As a first step towards understanding
TEST 150 points Write neatly. Show all work. Write all responses on separate paper. Clearly label the exercises.
 Math 130 Fall 007 Name: TEST # @ 150 points Write neatly. Show all work. Write all responses on separate paper. Clearly label the exercises. 1. Consider the polynomial function 4 3 f ( x) = x 19x + 57x
Math 130 Fall 007 Name: TEST # @ 150 points Write neatly. Show all work. Write all responses on separate paper. Clearly label the exercises. 1. Consider the polynomial function 4 3 f ( x) = x 19x + 57x
Name: Class: Date: A. 70 B. 62 C. 38 D. 46
 Class: Date: Test 2 REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Divide: (4x 2 49y 2 ) (2x 7y) A. 2x 7y B. 2x 7y C. 2x 7y D. 2x 7y 2. What is
Class: Date: Test 2 REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Divide: (4x 2 49y 2 ) (2x 7y) A. 2x 7y B. 2x 7y C. 2x 7y D. 2x 7y 2. What is
1. Find the domain of the following functions. Write your answer using interval notation. (9 pts.)
 MATH- Sample Eam Spring 7. Find the domain of the following functions. Write your answer using interval notation. (9 pts.) a. 9 f ( ) b. g ( ) 9 8 8. Write the equation of the circle in standard form given
MATH- Sample Eam Spring 7. Find the domain of the following functions. Write your answer using interval notation. (9 pts.) a. 9 f ( ) b. g ( ) 9 8 8. Write the equation of the circle in standard form given
Example 1a ~ Like # 1-39
 Example 1a ~ Like # 1-39 f(x) = A. The domain is {x x 2 1 0} = {x x 1} DOM: (, 1) ( 1, 1) (1, ) B. The x- and y-intercepts are both 0. C. Since f( x) = f(x), the function f is even. The curve is symmetric
Example 1a ~ Like # 1-39 f(x) = A. The domain is {x x 2 1 0} = {x x 1} DOM: (, 1) ( 1, 1) (1, ) B. The x- and y-intercepts are both 0. C. Since f( x) = f(x), the function f is even. The curve is symmetric
Asymptotes are additional pieces of information essential for curve sketching.
 Mathematics 00a Summary Notes page 57 4. Curve Sketching Asymptotes are additional pieces of information essential for curve sketching. Vertical Asymptotes The line a is a vertical asymptote of the graph
Mathematics 00a Summary Notes page 57 4. Curve Sketching Asymptotes are additional pieces of information essential for curve sketching. Vertical Asymptotes The line a is a vertical asymptote of the graph
QUIZ ON CHAPTERS 1 AND 2 - SOLUTIONS REVIEW / LIMITS AND CONTINUITY; MATH 150 SPRING 2017 KUNIYUKI 105 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 100 POINTS = 100%
 QUIZ ON CHAPTERS AND 2 - SOLUTIONS REVIEW / LIMITS AND CONTINUITY; MATH 50 SPRING 207 KUNIYUKI 05 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 00 POINTS = 00% ) For a), b), and c) below, bo in the correct answer. (6 points total;
QUIZ ON CHAPTERS AND 2 - SOLUTIONS REVIEW / LIMITS AND CONTINUITY; MATH 50 SPRING 207 KUNIYUKI 05 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 00 POINTS = 00% ) For a), b), and c) below, bo in the correct answer. (6 points total;
Chapter 2. Polynomial and Rational Functions. 2.6 Rational Functions and Their Graphs. Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions.6 Rational Functions and Their Graphs Copyright 014, 010, 007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Find the domains of rational functions. Use arrow notation.
Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions.6 Rational Functions and Their Graphs Copyright 014, 010, 007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Find the domains of rational functions. Use arrow notation.
Math 1051, Robertson, Exam 3 on Chapters 3 & 4 on Friday 12 November 2010 KEY page 1
 Math, Robertson, Eam on Chapters & on Friday November 0 KEY page. You earned points out of. Ans: f 6 Write the equation of a quadratic function whose graph has the following characteristics: It opens down;
Math, Robertson, Eam on Chapters & on Friday November 0 KEY page. You earned points out of. Ans: f 6 Write the equation of a quadratic function whose graph has the following characteristics: It opens down;
3.7 Part 1 Rational Functions
 7 Part 1 Rational Functions Rational functions are used in science and engineering to model complex equations in areas such as 1) fields and forces in physics, 2) electronic circuitry, 3) aerodynamics,
7 Part 1 Rational Functions Rational functions are used in science and engineering to model complex equations in areas such as 1) fields and forces in physics, 2) electronic circuitry, 3) aerodynamics,
Calculus I Sample Exam #01
 Calculus I Sample Exam #01 1. Sketch the graph of the function and define the domain and range. 1 a) f( x) 3 b) g( x) x 1 x c) hx ( ) x x 1 5x6 d) jx ( ) x x x 3 6 . Evaluate the following. a) 5 sin 6
Calculus I Sample Exam #01 1. Sketch the graph of the function and define the domain and range. 1 a) f( x) 3 b) g( x) x 1 x c) hx ( ) x x 1 5x6 d) jx ( ) x x x 3 6 . Evaluate the following. a) 5 sin 6
Simplifying Rationals 5.0 Topic: Simplifying Rational Expressions
 Simplifying Rationals 5.0 Topic: Simplifying Rational Expressions Date: Objectives: SWBAT (Simplify Rational Expressions) Main Ideas: Assignment: Rational Expression is an expression that can be written
Simplifying Rationals 5.0 Topic: Simplifying Rational Expressions Date: Objectives: SWBAT (Simplify Rational Expressions) Main Ideas: Assignment: Rational Expression is an expression that can be written
Rational and Radical Functions. College Algebra
 Rational and Radical Functions College Algebra Rational Function A rational function is a function that can be written as the quotient of two polynomial functions P(x) and Q(x) f x = P(x) Q(x) = a )x )
Rational and Radical Functions College Algebra Rational Function A rational function is a function that can be written as the quotient of two polynomial functions P(x) and Q(x) f x = P(x) Q(x) = a )x )
Final Exam Review Part 2
 Final Exam Review Part 2 Exponential & Logarithmic Functions and Equations Polynomial & Sinusoidal Functions Rational Expressions and Equations Exponential Functions To describe, orally and in written
Final Exam Review Part 2 Exponential & Logarithmic Functions and Equations Polynomial & Sinusoidal Functions Rational Expressions and Equations Exponential Functions To describe, orally and in written
STUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY
 STUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY 1) (LT 4A) Graph and indicate the Vertical Asymptote, Horizontal Asymptote, Domain, -intercepts, and y- intercepts of this rational function. 3 2 + 4 Vertical Asymptote: Set the
STUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY 1) (LT 4A) Graph and indicate the Vertical Asymptote, Horizontal Asymptote, Domain, -intercepts, and y- intercepts of this rational function. 3 2 + 4 Vertical Asymptote: Set the
( x) f = where P and Q are polynomials.
 9.8 Graphing Rational Functions Lets begin with a deinition. Deinition: Rational Function A rational unction is a unction o the orm ( ) ( ) ( ) P where P and Q are polynomials. Q An eample o a simple rational
9.8 Graphing Rational Functions Lets begin with a deinition. Deinition: Rational Function A rational unction is a unction o the orm ( ) ( ) ( ) P where P and Q are polynomials. Q An eample o a simple rational
9.5. Polynomial and Rational Inequalities. Objectives. Solve quadratic inequalities. Solve polynomial inequalities of degree 3 or greater.
 Chapter 9 Section 5 9.5 Polynomial and Rational Inequalities Objectives 1 3 Solve quadratic inequalities. Solve polynomial inequalities of degree 3 or greater. Solve rational inequalities. Objective 1
Chapter 9 Section 5 9.5 Polynomial and Rational Inequalities Objectives 1 3 Solve quadratic inequalities. Solve polynomial inequalities of degree 3 or greater. Solve rational inequalities. Objective 1
Chapter 2. Limits and Continuity 2.6 Limits Involving Infinity; Asymptotes of Graphs
 2.6 Limits Involving Infinity; Asymptotes of Graphs Chapter 2. Limits and Continuity 2.6 Limits Involving Infinity; Asymptotes of Graphs Definition. Formal Definition of Limits at Infinity.. We say that
2.6 Limits Involving Infinity; Asymptotes of Graphs Chapter 2. Limits and Continuity 2.6 Limits Involving Infinity; Asymptotes of Graphs Definition. Formal Definition of Limits at Infinity.. We say that
Rational Functions. Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University. October 19, 2000
 Rational Functions Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University October 19, 2000 Abstract This handout is a quick review of rational functions. It also contains a set of problems to guide the student
Rational Functions Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University October 19, 2000 Abstract This handout is a quick review of rational functions. It also contains a set of problems to guide the student
MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 20
 official website http://uoft.me/mat137 MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 20 Today: 4.6 Concavity 4.7 Asypmtotes Next: 4.8 Curve Sketching Indeterminate Forms for Limits Which of the following are indeterminate
official website http://uoft.me/mat137 MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 20 Today: 4.6 Concavity 4.7 Asypmtotes Next: 4.8 Curve Sketching Indeterminate Forms for Limits Which of the following are indeterminate
3.5 Graphs of Rational Functions
 Math 30 www.timetodare.com Eample Graph the reciprocal unction ( ) 3.5 Graphs o Rational Functions Answer the ollowing questions: a) What is the domain o the unction? b) What is the range o the unction?
Math 30 www.timetodare.com Eample Graph the reciprocal unction ( ) 3.5 Graphs o Rational Functions Answer the ollowing questions: a) What is the domain o the unction? b) What is the range o the unction?
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. A) 6 B) 14 C) 10 D) Does not exist
 Assn 3.1-3.3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the limit, if it exists. 1) Find: lim x -1 6x + 5 5x - 6 A) -11 B) - 1 11 C)
Assn 3.1-3.3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the limit, if it exists. 1) Find: lim x -1 6x + 5 5x - 6 A) -11 B) - 1 11 C)
1 DL3. Infinite Limits and Limits at Infinity
 Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 78 Mark Sparks 01 Infinite Limits and Limits at Infinity In our graphical analysis of its, we have already seen both an infinite
Daily Lessons and Assessments for AP* Calculus AB, A Complete Course Page 78 Mark Sparks 01 Infinite Limits and Limits at Infinity In our graphical analysis of its, we have already seen both an infinite
Flip-Flop Functions KEY
 For each rational unction, list the zeros o the polynomials in the numerator and denominator. Then, using a calculator, sketch the graph in a window o [-5.75, 6] by [-5, 5], and provide an end behavior
For each rational unction, list the zeros o the polynomials in the numerator and denominator. Then, using a calculator, sketch the graph in a window o [-5.75, 6] by [-5, 5], and provide an end behavior
Pre-calculus 12 Curriculum Outcomes Framework (110 hours)
 Curriculum Outcomes Framework (110 hours) Trigonometry (T) (35 40 hours) General Curriculum Outcome: Students will be expected to develop trigonometric reasoning. T01 Students will be expected to T01.01
Curriculum Outcomes Framework (110 hours) Trigonometry (T) (35 40 hours) General Curriculum Outcome: Students will be expected to develop trigonometric reasoning. T01 Students will be expected to T01.01
MAT 129 Precalculus Chapter 5 Notes
 MAT 129 Precalculus Chapter 5 Notes Polynomial and Rational Functions David J. Gisch and Models Example: Determine which of the following are polynomial functions. For those that are, state the degree.
MAT 129 Precalculus Chapter 5 Notes Polynomial and Rational Functions David J. Gisch and Models Example: Determine which of the following are polynomial functions. For those that are, state the degree.
#1, 2, 3ad, 4, 5acd, 6, 7, 8, 9bcd, 10, 11, 12a, 13, 15, 16 #1-5
 MHF4U Unit 3 Rational Functions Section Pages Questions Prereq Skills 146-147 #1, 2, 3bf, 4ac, 6, 7ace, 8cdef, 9bf, 10abe 3.1 153-155 #1ab, 2, 3, 5ad, 6ac, 7cdf, 8, 9, 14* 3.2 164-167 #1ac, 2, 3ab, 4ab,
MHF4U Unit 3 Rational Functions Section Pages Questions Prereq Skills 146-147 #1, 2, 3bf, 4ac, 6, 7ace, 8cdef, 9bf, 10abe 3.1 153-155 #1ab, 2, 3, 5ad, 6ac, 7cdf, 8, 9, 14* 3.2 164-167 #1ac, 2, 3ab, 4ab,
The Intermediate Value Theorem If a function f (x) is continuous in the closed interval [ a,b] then [ ]
![The Intermediate Value Theorem If a function f (x) is continuous in the closed interval [ a,b] then [ ] The Intermediate Value Theorem If a function f (x) is continuous in the closed interval [ a,b] then [ ]](/thumbs/94/120320387.jpg) Lecture 4-6B1 Evaluating Limits Limits x ---> a The Intermediate Value Theorem If a function f (x) is continuous in the closed interval [ a,b] then [ ] the y values f (x) must take on every value on the
Lecture 4-6B1 Evaluating Limits Limits x ---> a The Intermediate Value Theorem If a function f (x) is continuous in the closed interval [ a,b] then [ ] the y values f (x) must take on every value on the
Calculus I Exam 1 Review Fall 2016
 Problem 1: Decide whether the following statements are true or false: (a) If f, g are differentiable, then d d x (f g) = f g. (b) If a function is continuous, then it is differentiable. (c) If a function
Problem 1: Decide whether the following statements are true or false: (a) If f, g are differentiable, then d d x (f g) = f g. (b) If a function is continuous, then it is differentiable. (c) If a function
NONLINEAR FUNCTIONS A. Absolute Value Exercises: 2. We need to scale the graph of Qx ( )
 NONLINEAR FUNCTIONS A. Absolute Value Eercises:. We need to scale the graph of Q ( ) f ( ) =. The graph is given below. = by the factor of to get the graph of 9 - - - - -. We need to scale the graph of
NONLINEAR FUNCTIONS A. Absolute Value Eercises:. We need to scale the graph of Q ( ) f ( ) =. The graph is given below. = by the factor of to get the graph of 9 - - - - -. We need to scale the graph of
2.6. Graphs of Rational Functions. Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc.
 2.6 Graphs of Rational Functions Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc. Rational Functions What you ll learn about Transformations of the Reciprocal Function Limits and Asymptotes Analyzing Graphs of Rational Functions
2.6 Graphs of Rational Functions Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc. Rational Functions What you ll learn about Transformations of the Reciprocal Function Limits and Asymptotes Analyzing Graphs of Rational Functions
October 27, 2018 MAT186 Week 3 Justin Ko. We use the following notation to describe the limiting behavior of functions.
 October 27, 208 MAT86 Week 3 Justin Ko Limits. Intuitive Definitions of Limits We use the following notation to describe the iting behavior of functions.. (Limit of a Function A it is written as f( = L
October 27, 208 MAT86 Week 3 Justin Ko Limits. Intuitive Definitions of Limits We use the following notation to describe the iting behavior of functions.. (Limit of a Function A it is written as f( = L
Math 1314 Lesson 1: Prerequisites. Example 1: Simplify and write the answer without using negative exponents:
 Math 1314 Lesson 1: Prerequisites 1. Exponents 1 m n n n m Recall: x = x = x n x Example 1: Simplify and write the answer without using negative exponents: a. x 5 b. ( x) 5 Example : Write as a radical:
Math 1314 Lesson 1: Prerequisites 1. Exponents 1 m n n n m Recall: x = x = x n x Example 1: Simplify and write the answer without using negative exponents: a. x 5 b. ( x) 5 Example : Write as a radical:
Assessment Exemplars: Polynomials, Radical and Rational Functions & Equations
 Class: Date: Assessment Exemplars: Polynomials, Radical and Rational Functions & Equations 1 Express the following polynomial function in factored form: P( x) = 10x 3 + x 2 52x + 20 2 SE: Express the following
Class: Date: Assessment Exemplars: Polynomials, Radical and Rational Functions & Equations 1 Express the following polynomial function in factored form: P( x) = 10x 3 + x 2 52x + 20 2 SE: Express the following
Section Properties of Rational Expressions
 88 Section. - Properties of Rational Expressions Recall that a rational number is any number that can be written as the ratio of two integers where the integer in the denominator cannot be. Rational Numbers:
88 Section. - Properties of Rational Expressions Recall that a rational number is any number that can be written as the ratio of two integers where the integer in the denominator cannot be. Rational Numbers:
MATH CALCULUS I 1.5: Continuity
 MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 1.5: Continuity Professor Donald L. White Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. White (Kent State University) 1 / 12 Definition of Continuity Intuitively,
MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 1.5: Continuity Professor Donald L. White Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. White (Kent State University) 1 / 12 Definition of Continuity Intuitively,
Summer Mathematics Prep
 Summer Mathematics Prep Entering Calculus Chesterfield County Public Schools Department of Mathematics SOLUTIONS Domain and Range Domain: All Real Numbers Range: {y: y } Domain: { : } Range:{ y : y 0}
Summer Mathematics Prep Entering Calculus Chesterfield County Public Schools Department of Mathematics SOLUTIONS Domain and Range Domain: All Real Numbers Range: {y: y } Domain: { : } Range:{ y : y 0}
MATH 150 CHAPTER3 Polynomials Section 3.1
 MATH 50 CHAPTER Polynomials ------- Section. 4 Degree of a Polynomial 4 Identify the following polynomials: 4 4 Descending order 7 5 4 Leading Term Leading Coefficient The constant (no variable) LEFT AND
MATH 50 CHAPTER Polynomials ------- Section. 4 Degree of a Polynomial 4 Identify the following polynomials: 4 4 Descending order 7 5 4 Leading Term Leading Coefficient The constant (no variable) LEFT AND
Math 106 Answers to Test #1 11 Feb 08
 Math 06 Answers to Test # Feb 08.. A projectile is launched vertically. Its height above the ground is given by y = 9t 6t, where y is the height in feet and t is the time since the launch, in seconds.
Math 06 Answers to Test # Feb 08.. A projectile is launched vertically. Its height above the ground is given by y = 9t 6t, where y is the height in feet and t is the time since the launch, in seconds.
10/22/16. 1 Math HL - Santowski SKILLS REVIEW. Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions. Lesson Objectives. (A) Rational Functions
 Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions SKILLS REVIEW! Use function composition to prove that the following two funtions are inverses of each other. 2x 3 f(x) = g(x) = 5 2 x 1 1 2 Lesson Objectives! The
Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions SKILLS REVIEW! Use function composition to prove that the following two funtions are inverses of each other. 2x 3 f(x) = g(x) = 5 2 x 1 1 2 Lesson Objectives! The
= lim. (1 + h) 1 = lim. = lim. = lim = 1 2. lim
 Math 50 Exam # Solutions. Evaluate the following its or explain why they don t exist. (a) + h. h 0 h Answer: Notice that both the numerator and the denominator are going to zero, so we need to think a
Math 50 Exam # Solutions. Evaluate the following its or explain why they don t exist. (a) + h. h 0 h Answer: Notice that both the numerator and the denominator are going to zero, so we need to think a
Rational number = one real number divided by another, as in 2/3, = constant/constant
 RATIONAL FN S & EQN S CHEAT SHEET MATH1314/GWJ/08 Rational = ratio = fraction Rational number = one real number divided by another, as in 2/3, = constant/constant Generalize constants to polynomials: p(x)/q(x)
RATIONAL FN S & EQN S CHEAT SHEET MATH1314/GWJ/08 Rational = ratio = fraction Rational number = one real number divided by another, as in 2/3, = constant/constant Generalize constants to polynomials: p(x)/q(x)
PART 1: USING SCIENTIFIC CALCULATORS (41 PTS.) 1) The Vertex Form for the equation of a parabola in the usual xy-plane is given by y = 3 x + 4
 MIDTERM SOLUTIONS (CHAPTERS AND 3: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, EXP L, LOG FUNCTIONS) MATH 141 FALL 018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 41 FOR PART 1, AND 109 FOR PART PART 1: USING SCIENTIFIC CALCULATORS (41 PTS.)
MIDTERM SOLUTIONS (CHAPTERS AND 3: POLYNOMIAL, RATIONAL, EXP L, LOG FUNCTIONS) MATH 141 FALL 018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 41 FOR PART 1, AND 109 FOR PART PART 1: USING SCIENTIFIC CALCULATORS (41 PTS.)
LIMITS AT INFINITY MR. VELAZQUEZ AP CALCULUS
 LIMITS AT INFINITY MR. VELAZQUEZ AP CALCULUS RECALL: VERTICAL ASYMPTOTES Remember that for a rational function, vertical asymptotes occur at values of x = a which have infinite its (either positive or
LIMITS AT INFINITY MR. VELAZQUEZ AP CALCULUS RECALL: VERTICAL ASYMPTOTES Remember that for a rational function, vertical asymptotes occur at values of x = a which have infinite its (either positive or
INDEX UNIT 3 TSFX REFERENCE MATERIALS 2014 ALGEBRA AND ARITHMETIC
 INDEX UNIT 3 TSFX REFERENCE MATERIALS 2014 ALGEBRA AND ARITHMETIC Surds Page 1 Algebra of Polynomial Functions Page 2 Polynomial Expressions Page 2 Expanding Expressions Page 3 Factorising Expressions
INDEX UNIT 3 TSFX REFERENCE MATERIALS 2014 ALGEBRA AND ARITHMETIC Surds Page 1 Algebra of Polynomial Functions Page 2 Polynomial Expressions Page 2 Expanding Expressions Page 3 Factorising Expressions
Section 4.3 Concavity and Curve Sketching 1.5 Lectures. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 4.3 Concavity and Curve Sketching 1.5 Lectures College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Concavity 1 / 29 Concavity Increasing Function has three cases (University of Bahrain)
Section 4.3 Concavity and Curve Sketching 1.5 Lectures College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Concavity 1 / 29 Concavity Increasing Function has three cases (University of Bahrain)
Curve Sketching. The process of curve sketching can be performed in the following steps:
 Curve Sketching So ar you have learned how to ind st and nd derivatives o unctions and use these derivatives to determine where a unction is:. Increasing/decreasing. Relative extrema 3. Concavity 4. Points
Curve Sketching So ar you have learned how to ind st and nd derivatives o unctions and use these derivatives to determine where a unction is:. Increasing/decreasing. Relative extrema 3. Concavity 4. Points
( ) c. m = 0, 1 2, 3 4
 G Linear Functions Probably the most important concept from precalculus that is required for differential calculus is that of linear functions The formulas you need to know backwards and forwards are:
G Linear Functions Probably the most important concept from precalculus that is required for differential calculus is that of linear functions The formulas you need to know backwards and forwards are:
