Chapter 5. Integration
|
|
|
- Leo Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Itrodutio The term "itegrtio" hs severl meigs It is usully met s the reverse proess to differetitio, ie fidig ti-derivtive to futio A ti-derivtive of futio f is futio F suh tht its derivtive F' stisfies F' = f o some suitle domi I mehis the veloity of ojet i motio my e determied from its elertio y ti-differetitio I Busiess, reveue futio my e omputed from give Mrgil Reveue futio y usig ti-differetitio I these d other emples, the questio of how to fid ti-derivtive of prtiulr futio f leds to other meig of the term "itegrtio" relted to re uder grph, defiite itegrtio These two meigs uder pproprite oditio re lied y the so lled "fudmetl theorem of lulus" There re other sutle mthemtil formultios lso lled itegrtio some of whih re geerliztios of the defiite itegrtio 5 Ati-derivtive Defiitio Let I e ope itervl Suppose F :I R is differetile o I d tht F' = f The F is lled ti-derivtive, idefiite itegrl or primitive of f Remr For give f :I R, there my e my or oe suh F with F' = f If F' = f, the let G = F + C, where C is ostt The G' = F' = f Thus y two ti-derivtives differ y ostt We reple I i Defiitio y y itervl if we te the derivtives t the ed poits of I to e the pproprite oe-sided limits (See Chpter 3 for osequees) Theorem If F is prtiulr ti-derivtive of f o ope itervl I, the every ti-derivtive of f o I is give y F() + C, where C is ostt, tht is, the set of ll ti-derivtives of f o I is { F() + C: C R} Proof Suppose G is other ti-derivtive of f o I Let h = G F o I The h' = G' F'= 0 o I Therefore, y Theorem 6 Chpter 4, h is ostt futio, sy h = C The h = G F = C d so G = F + C We ormlly write f d F C to deote fidig ti-derivtive of f, d wheever futio F with F'() = f () or d F f is foud Not every futio hs ti-derivtive s the followig emple will show Emple 3 The futio f :R R defied y f, 0 does ot hve, 0 ti-derivtive This is see s follows Suppose f hs ti-derivtive F :R R with F' = f The for > 0, F'() = f () = Therefore, y Theorem, for > 0, F() = + for some ostt i R For < 0, F'() = f () = Thus, lso y Theorem, for < 0, F() = + for some ostt i R Thus, lim F d lim F Sie F is differetile, F is otiuous d is therefore otiuous t 0 0 Ng Tze Beg
2 Chpter 5 Itegrtio = 0 Thus lim F lim F F 0 Hee = =, sy Therefore, F() = But the this implies tht F is ot differetile t = 0 sie the futio is ot differetile t = 0 This otrditio shows tht f does ot hve ti-derivtive The futio f i the ove emple is ot otiuous t = 0 But ot every disotiuous futio does ot hve ti-derivtive s the followig emple shows Emple 4 The futio f :R R defied y f si ( ) os( ), 0 0, 0 hs ti-derivtive F :R R, defied y F si( ), 0 eve though f 0, 0 is ot otiuous t = 0 We te the sequee ( ), where The 0 The f si ( ) os( ) for eh i P Therefore, f ( ) f (0) Hee the sequee ( f ( )) does ot overge to f (0) Therefore, y Defiitio of Chpter 3, f is ot otiuous t = 0 Theorem 5 d C; If f hs ti-derivtive o ope itervl I, the for y ostt, f lso hs ti-derivtive o I d f d f d 3 If f d f hve ti-derivtives o I, the for y rel umers d, [ f f ]d f d f d Theorem 5 is proved y diret verifitio d is left to the reder Theorem 6 For y rtiol umer, d C, Proof For, d d Remr Usig Theorem 5 d Theorem 6, we fid ti-derivtive of y polyomil futio Emple d 3 d 5 d 3 C 5 C 3 5 3C 5C 3 5 C, where C 3C 5C d C C d C C 4 d 3 d 3 3 C 5 5 C We shll ow eted our method of fidig ti-derivtive This is pplitio of the hi rule Suppose I d J re ope itervls, g: I R d F : J R re differetile futios with g(i ) J The F d g re omposle The Chi Ng Tze Beg
3 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Rule sys (F g )'() = F'(g())g'() for every i I (Referee: Theorem 8 Chpter 4) If we write f for F', we hve (F g )'() = f (g())g'() for every i I This shows tht F g is ti-derivtive of f (g())g'() I this wy, owig the ti-derivtive of f will ele us to determie the ti-derivtive of more omple futio f (g())g'() However, to pply this method of fidig ti-derivtive, we eed to put our futio i the form of f (g())g'() for suitle differetile futio g d futio f whose ti-derivtive is ow Hee, we hve the followig theorem Theorem 8 (Chge of Vrile, Sustitutio) Suppose g: I R is differetile d f : J R is suh tht f hs ti-derivtive F : J R d g(i ) J The f g g d F g C Moreover, F e hose to e y ti-derivtive of f If we write y = g (), the the theorem is usully lso rememered s f y dy d d f y dy = F y C Remr This is theorem out ti-derivtive It gives us etesio to fidig ti-derivtives y elrgig our "looup" tle through differetitio of omposite futios Emple 9 dy Fid 3 4 d Let y = The d 3 Here we let f (y) = y d g()= 3 +4 A ti-derivtive of f is F y d g'() = 3 y 3 y d d 3 f 3 4 g d 3 f g g d 3 3 g 3 C C Fid 3 d Let g d so g'()=, g 3 d d d g g g d g g g d y 3 y dy y Theorem 8, where y = g() is to e sustituted, y y C 5 y 5 3 y 3 C 3 3 C 3 Fid si d Let g() = d f () = si() The g'() = 3 Therefore, si d si d si g g d os g C os C sie ti-derivtive of si() is os() Ng Tze Beg 3
4 Chpter 5 Itegrtio 5 Riem Itegrls Are uder grph my e omputed y Riem itegrl If the veloity of ojet is ow umerilly over time itervl from time = 0 to sy, time = T, the diste trveled i this time itervl my e omputed y determiig the re uder the veloity-time grph of the ojet usig Riem itegrtio This pproh is differet from usig ti-derivtive of the veloity futio, whih my ot e ville Wht is ow lled the Riem itegrl of futio f is mthemtilly rigorous formultio of the ituitive otio of the re uder the grph of f Are uder urve We ow give desriptio of proedure to ompute the re of regio uder urve Cosider otiuous futio f defied o [, ] whose grph is give s follows y = = 0 The re uder the urve etwee = d = d y = f () is pproimted y the retgles show elow the grph of f We hve prtitioed [, ] ito smller itervls [ i, i+ ], i =0,,, with P: = 0 < < < = We ow defie the lower sum with respet to the 'prtitio' P to e the qutity give y i m i, where m i = mi{ f (): [ i-, i ]} By the Etreme Vlue Theorem, there eists i i [ i-, i ] suh tht m i = f ( i ) Now we let the prtitio e eqully sped, sy i for ll i The the lower sum with respet to the prtitio is f i f i If we te the ommo width of the retgles to e s smll s we wish we shll evetully pproimte the re uder the urve Tht is to sy, the re uder the urve A lim f i lim 0 f i Ie Give > 0, there eists positive iteger N suh tht for y iteger N f i A f i A Note here tht the i 's re geerlly differet for differet This gives pproh of fidig re from elow Ng Tze Beg 4
5 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Similrly we defie the upper sum with respet to the 'prtitio' P to e the summtio i M i, where M i = m{ f (): [ i-, i ]} = f (d i ) for some d i i [ i-, i ] y the Etreme Vlue Theorem If we te the prtitio to e regulr prtitio s efore, suh tht i, the re uder the urve my e give y A lim f d i lim 0 f d i This is pproh to fidig re uder urve from ove Emple 0 Fid the re of the regio ouded y y = d the -is d the lie = 3 Let f () = Suppose is positive iteger Let 0 = 0 d = 3 [We re goig to prtitio [0,3] ito equl prts] Let 3 0, Sie i 0 i 3i is iresig futio o [0, ), m i mi f :, i f 3 i () Therefore, A lim f lim 3 y () i 3 lim 7 3 i lim 7 3 i lim lim 3 9 lim 9 9 y = y 0 3 Typilly Emple 0 illustrtes the method of fidig re from elow Similrly, y tig the upper sum we should get the sme vlue for the re of the regio i Emple 0 Now if isted of tig the miimum or mimum i eh suitervl [ i-, i ], we simply hoose y vlue e i i [ i-, i ], the y the otiuity of f, the sum i f e i will lie etwee the upper sum d the lower sum I this wy, s the size of the suitervls, teds to 0, the sum i f e i would ted to the sme vlue s the re uder the urve This pproh hs some dvtges Firstly we do ot eed to fid the mimum or the miimum i eh suitervl Seodly we do ot eed to ofie to otiuous futios so log s the futio is defied However we eed to impose o hvig the sum Ng Tze Beg 5
6 Chpter 5 Itegrtio i f e i to e ouded d tht for meigful defiitio of re, the sum should ehve just lie the se for the otiuous futio Thus we wt the sum i f e i lled Riem sum to pproh fiite vlue s the prtitio of the itervl [, ] gets fier d fier Riem Sum d Riem Itegrl We ow formlize the ove disussio We will eve e etedig the defiitio to disotiuous futios The dvtge of the followig defiitio med fter the Germ mthemtii George Friedrih Berhrd Riem (86-866), is tht it voids the eed to fid the mimum or miimum of the futio over eh suitervl Let f e defied o the losed itervl [, ] We shll sudivide [, ] ito suitervls y hoosig - itermedite poits etwee d Defiitio A prtitio of [, ] is fiite set of umers { 0,,, } suh tht : = 0 < < < = Let i e the legth of the i-th suitervl [ i-, i ], ie i = i i- The orm or mesh of the prtitio is m{ i : i =,, } d is deoted y Thus = m{ i i- :i =,, } Suppose ow : = 0 < < < = is prtitio Let e poit i [ i-, i ], for i =,,, The Riem sum S of f with respet to is defied y S f i i f i We deote S y R( f,, ), where =(,, ) is the hoie of i i [ i-, i ] We sy the futio f is Riem itegrle o [, ] if d oly if there eists umer L suh tht give y > 0, there eists > 0 suh tht for ll prtitio of [, ] with orm <, we hve for every Riem sum S for S L <, ie, f i i L R f,, L where is the prtitio : = 0 < < < = d =(,, ) is give y y hoie of i [ i-, i ] If f is Riem itegrle o [,], we the write limit is deoted y f lim 0, f i i Ld this Ng Tze Beg 6
7 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Defiitio If f : [, ] R is itegrle o [, ], the the defiite itegrl of f or Riem itegrl of f from to is deoted y, f d lim f i i 0 is lled the lower limit, is lled the upper limit d f () is lled the itegrd Remr Though Defiitio is remrle elegt defiitio, it is ot esy to use it to prove the properties of the Riem itegrl Thus, we shll loo t pproh y Drou usig his so lled Drou sums, whih re geerliztio of the upper d lower sums This pproh is prtiulrly useful for verifitio of the properties of the Riem itegrl We shll develop this fter the followig emple Emple 3 0 d Te y prtitio: P: 0 =0 < < < = Let i e y poit i [ i-, i ] Let f () = The Riem sum, R f, P, Therefore, Liewise, R f, P, f i i i i It follows tht f i i f i i R f, P, i i f i i i i i i i P P R f, P, P These two iequlities () d () implies tht () i i i i P R f, P, P () P P Now give y > 0, just te = The for y prtitio P with P < R f, P, P [0, ] d 0 f d Hee, y Defiitio, f is Riem itegrle o Ng Tze Beg 7
8 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Let f : [, ] R e futio We rell tht the futio f is ouded if its rge is ouded This mes there eist rel umers d suh tht f () for ll i [, ] or equivletly, there eists positive rel umer K suh tht f () K for ll i [, ] If f is ot ouded, the oe hve ritrrily lrge Riem sum or ritrrily egtively lrge Riem sum d so f would ot e Riem itegrle (Referee: my rtile, "Riem Itegrl d Bouded Futio" o My Clulus We ) Thus y uouded futio is ot Riem itegrle 53 Upper d Lower Drou Sums, Upper d Lower Itegrls Suppose ow f : [, ] R is ouded futio Let P : = 0 < < < = e prtitio for [, ] The upper Drou sum with respet to the prtitio P is defied y U f, P M i i, where M i = sup{ f () : [ i-, i ]} Note tht sie f is ouded o [, ], f is ouded o eh [ i-, i ] d so the supremum M i eists for eh i Lie wise for eh i, m i = if{ f () : [ i-, i ]} eists sie f is ouded o eh [ i-, i ] We defie the lower Drou sum with respet to the prtitio P y L f, P m i i Beuse for eh iteger i suh tht i, m i M i, L( f, P) U( f, P) Sie f is ouded, there eist rel umers m d M suh tht m f () M for ll i [, ] Hee m M i M d m m i M for i =,,, Therefore, for y prtitio P the upper Drou sum U f, P M i i m i m Hee the set of ll upper Drou sums (over ll prtitios of [, ]) is ouded elow y m( ) Liewise, the lower Drou sum L f, P m i i M i M We olude tht the set of ll lower Drou sums (over ll prtitios of [, ]) is ouded ove y M( ) We my ow me the followig defiitio followig Drou Defiitio 4 Suppose f : [, ] R is ouded futio The the upper Drou itegrl or upper itegrl is defied to e U f if U f, P : P prtitio of, The lower Drou itegrl or lower itegrl is defied to e L f sup L f, P : P prtitio of, Ng Tze Beg 8
9 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Note tht y the ompleteess property of the rel umers, the upper itegrl eists, euse the set of ll upper Drou sum is ouded elow d the lower itegrl eists euse the set of ll lower Drou sum is ouded ove We ow oserve some ovious properties of the Drou sums with respet to prtitio Suppose Q d P re prtitios of [, ] We sy Q is refiemet of P if eh prtitio poit of P is lso prtitio of Q, more preisely if P Q Lemm 5 The Refiemet Lemm Suppose f : [, ] R is ouded futio Suppose Q d P re prtitios of [, ] suh tht Q is refiemet of P The L( f, P) L( f, Q) d U( f, Q) U( f, P) Proof First we shll prove the lemm whe Q otis just oe dditiol poit y th P Let P e deoted y P : = 0 < < < = Suppose y ( j-, j ) for some j etwee d The Q is the prtitio Q : = 0 < < < j- < y < j < < = Let m j ' = if{ f () : [ j-, y]}, m j '' = if{ f () : [y, j]} The m j = if{ f () : [ j-, j ]} m j ', m j '' Therefore, j L f, P m i i m i i m j y j m j j y m i i i j j m i i m j y j m j j y i j m i i L f, Q Let M j ' = sup{ f () : [ j-, y]}, M j '' = sup{ f () : [y, j]} The M j = sup{ f () : [ j-, j ]} M j ', M j '' Therefore, U f, P j j M i i M i i M j y j M j j y i j M i i M j y j M j j y i j M i i M i i U f, Q This proves the lemm for the se whe Q hs just oe dditiol prtitio poit th P For the geerl se, if Q otis poits ot i P, the there is sequee of prtitios, P = P 0, P, P,, P = Q where Q is otied y ddig oe poit t time Tht is P i+, is otied y ddig oe poit i Q ot i P i to P i Thus y the speil se, L( f, P)=L( f, P 0 ) L( f, P ) L( f, P ) ( f, P ) =L( f, Q) d U( f, P)=U( f, P 0 ) U( f, P ) U( f, P ) U( f, P ) =U( f, Q) This ompletes the proof The et result is oservtio tht y lower Drou sum is less th or equl to y upper Drou sum Ng Tze Beg 9
10 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Theorem 6 Suppose f : [, ] R is ouded futio Suppose Q d P re prtitios of [, ] L( f, P) U( f, Q) Proof The prtitio P Q is refiemet of oth P d Q Therefore, y Lemm 5, L( f, P) L( f, P Q) d U( f, P Q) U( f, Q) Therefore, L( f, P) L( f, P Q) U( f, P Q) U( f, Q) Theorem 7 Suppose f : [, ] R is ouded futio The L f U f Proof By Theorem 6 for y prtitio P of [, ], L( f, P) is lower oud of {U( f, Q): Q prtitio of [, ] } Therefore, L f, P if U f, Q : Q prtitio of, U f Thus the upper itegrl U f is upper oud of {L( f, P): P prtitio of [, ] } Therefore, U f sup L f, P : P prtitio of, L f 54 Drou Itegrl For ouded futio we hve defied the upper d lower itegrls So isted of oe itegrl we hve two Arhimedes hd devised strtegy to ompute the re of o-polygol geometri ojet y ostrutig outer d ier polygol pproimtios of the ojet We hve defied the upper d lower itegrls, similr i philosophy to the pproh of fidig suessive outer d ier polygol pproimtios of geometri ojet Ulie the o-polygol geometri ojets, where the outer d ier polygol pproimtios will ted to the sme vlue, there is o gurtee tht the two itegrls re the sme Whe they re the sme it gives meig to geerliztio of re Defiitio 8 Suppose f : [, ] R is ouded futio We sy f is Drou itegrle if the lower d upper itegrls re the sme, ie, L f U f Remr This is Drou's versio of the itegrility of ouded futio ompletig the formultio of Riem We shll show tht this is equivlet to Riem itegrility Emple 9 The Dirihlet futio h : [0, ] R, defied y h 0, if is rtiol, if is irrtiol is ot Drou itegrle Let P : 0 = 0 < < < < = e y prtitio for the itervl [0, ] By the desity of the rtiol umers d irrtiol umers, i eh of the suitervl, Ng Tze Beg 0
11 Chpter 5 Itegrtio [ i -, i ], (i =,, ) we lwys fid rtiol umer d irrtiol umer Hee for i =,,, {h(): [ i -, i ]} = {0, } It follows tht, for eh i =,,, M i (h, P) = sup{h(): [ i -, i ]} = sup{0, }= m{0, }= d m i (h, P) = if{h(): [ i -, i ]} = if{0, }= mi{0, }= 0 Therefore, the upper Drou sum with respet to the Prtitio P is U h, P M i h, P i i d the lower Drou sum with respet to the Prtitio P is L h, P m i h, P i 0 The ove sttemet is true for y prtitio P for [0, ] Hee the lower Drou itegrl of h, L h sup L h, P : P is prtitio for 0, m 0 0 d the upper Drou itegrl of h, U h if U h, P : P is prtitio for 0, m Therefore, the lower Drou itegrl L h is ot equl to the upper Drou itegrl U h d so h is ot Drou itegrle over [0, ] y Defiitio 8 We oserve lso tht y the ove remr out desity of the rtiol d irrtiol umers, for y prtitio P with P < we hoose rtiol poits i for eh i d so the Riem sum R(h, P, ) = 0 d if we hoose irrtiol poits i for eh i, the Riem sum R(h, P, ) = Hee y Defiitio, h is ot Riem itegrle The futio f : [0, ] defied y f () = is Drou itegrle Let P : 0 = 0 < < < < = e y prtitio for the itervl [0, ] For eh i =,,, M i ( f, P) = sup{ f (): [ i -, i ]} = i d m i ( f, P) = if{ f (): [ i -, i ]} = i - Therefore, the upper Drou sum with respet to the Prtitio P is U f, P M i f, P i i i 3 i i 3 i i 3 6 i P i P 3 6 P P euse i i Therefore, sie we hoose the orm of the prtitio P ritrrily smll, U 0 f 3 Similrly the lower Drou sum with respet to the prtitio P L f, P m i f, P i i Ng Tze Beg
12 Chpter 5 Itegrtio 3 i i 3 i i 3 6 i 3 i P 3 P Therefore, L 0 f L f, P 3 P Sie P e hose to e ritrrily smll, It follows the from Theorem 7 tht L 0 f 3 U 0 f L 0 f sie L 3 f U f 55 Itegrility Criteri Drou itegrility is equivlet to Riem itegrility s we shll show i this setio It is ot lwys esy to ompute the lower d upper itegrls just to he whether they re the sme to deide o itegrility This mouts to tully omputig the itegrl It is suffiiet to he o the ehviour of the lower d upper sums to see if they re very lose to some vlue or ltertively if their differees re gettig smller d smller This is ruil to formulte itegrility riteri We strt y givig et very useful hrteriztio of the upper d lower itegrls i terms of sequees Propositio 0 Suppose f : [, ] R is ouded futio The there eists sequee of prtitios (P ) of [, ] suh tht P P +, L f, P L f d U f, P U f lim P 0 d Proof By defiitio of the lower itegrl d upper itegrl, there eist prtitios P ' d P '' of [, ] suh tht L f L f, P L f d U f U f, P U f Let P e ommo refiemet of P ' d P '' for whih P < The y the Refiemet Lemm (Lemm 5) L f L f, P L f d U f U f, P U f Similrly, there eist prtitios P ' d P '' of [, ] suh tht d L f L f, P L f U f U f, P U f Ng Tze Beg
13 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Let P e ommo refiemet of P, P ' d P '' for whih P < / The d L f L f, P L f U f U f, P U f We ow defie the sequee {P } y repetig the ove proess Suppose we hve defied prtitio P suh tht P - P, P < / By the defiitio of the lower d upper itegrls, there eist prtitios P + ' d P + '' of [, ] suh tht L f d L f, P L f U f U f, P U f Let P + e ommo refiemet of P, P + ' d P + '' for whih P + < /(+) The y the Refiemet Lemm, L f L f, P L f d U f U f, P U f d P P + I this wy we oti the sequee of prtitios {P } of [, ] suh tht P P + d lim P 0 I prtiulr, y the defiitio of overgee of sequee or y the Compriso Test (Propositio 8 Chpter ), L f, P L f d U f, P U f This ompletes the proof Theorem Suppose f : [, ] R is ouded futio The followig sttemets re equivlet () f is Drou itegrle () There is sequee (P ) of prtitios of [, ] suh tht lim U f, P L f, P 0 Furthermore, for y suh sequee, L f, P f d U f, P (3) Give > 0, there eists prtitio P for the itervl [, ] suh tht the differee U( f,p) L( f, P) < (4) f is Riem itegrle, ie, there eists umer L suh tht give y > 0, we fid > 0 suh tht for y prtitio P for [, ] with orm P <, d for y Riem sum S with respet to P, S L < f Ng Tze Beg 3
14 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Proof () () Suppose f is Drou itegrle, tht is, the lower d upper itegrls re the sme Te the sequee of prtitios (P ) of [, ] give y Propositio 0 suh tht L f, P L f d U f, P U f Sie L f U f, lim U f, P L f, P 0 () () Suppose there is sequee (P ) of prtitios of [, ] suh tht lim U f, P L f, P 0 For eh iteger, y Theorem 7, L f, P L f U f U f, P Therefore, 0 U f L f U f, P L f, P d so 0 U f L f lim U f, P L f, P 0 Hee, U f L f 0 d so L f U f d f is Drou itegrle Moreover, sie 0 U f, P U f U f, P L f, P for eh iteger, d so y the Compriso Test, U f, P U f f Similrly, sie 0 L f L f, P U f, P L f, P for eh iteger, y the Compriso Test for sequees, L f, P L f f () (3) Suppose there is sequee (P ) of prtitios of [, ] suh tht lim U f, P L f, P 0 The, give > 0, there eists positive iteger N, suh tht N U( f,p ) L( f, P ) < Let P = P N d we hve U( f,p ) L( f, P ) < (3) () Suppose for y > 0, there eists prtitio P for the itervl [, ] suh tht the differee U( f,p) L( f, P) < Thus, for y > 0, 0 U f L f U f, P L f, P Therefore, U f L f It follows the y Theorem 7 tht L f U f d so f is Drou itegrle (4) (3) Assume f is Riem itegrle Give > 0, the there eists > 0 suh tht for y prtitio P for [, ] with orm P <, d for y Riem sum S with respet to P, S L < /4 Let T ={ Riem sum S: S hs the sme prtitio P} The for y S i T, L /4< S < L + / () Ng Tze Beg 4
15 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Let P: = 0 < < < = e prtitio of [, ] with P < Let M i = sup{ f () : [ i-, i ]} for i =,, By the defiitio of supremum, for eh i, i, there eists i i [ i-, i ] suh tht f ( i ) > M i 4 Usig this iequlity, the Riem sum R f, P, C f i i M i 4 i M i i U f, P, 4 4 where, C=(,, ) Therefore, U f, P R f, P, C L L () y iequlity () Now let m i = if{ f () : [ i-, i ]} for i =,, By the defiitio of ifimum, for eh i suh tht i, there eists d i i [ i-, i ] stisfyig f (d i ) < m i 4 The Riem sum R f, P, d f d i i m i 4 i m i i L f, P 4 4 where d=(d,,d ) It follows tht L f, P R f, P, d L L (3) y iequlity () Iequlity () d (3) implies tht, U( f, P) L( f, P) < Hee () follows () (4) Suppose there is sequee (P ) of prtitios of [, ] suh tht lim U f, P L f, P 0 This mes give > 0, there eists prtitio P j : = 0 < < < L = with L > suh tht U f, P j L f, P j Deote the prtitio P j y P Let K = mi { i i- : i =,, L } Sie f is ouded, there eists M 0 suh tht f () < M First we shll speify our for the prtitio Let R: = y 0 < y < < y N = e y prtitio suh tht R, where mi K, ML The euse R < K, the umer of suitervls of R, N must e stritly igger th L, whih is the umer of suitervls of P Moreover euse K = mi { i i- : i =,, L } d for eh i =,,, N, y i y i- R < K, eh suitervl [y i-, y i ] oti t most oe poit from P Therefore, eh i for i =,,, L must elog to oe d oly oe suitervl y ji, y ji for some j i, j i N, ie, for i =,,, L, y ji i y ji Let I = {j i : i =,,L } I j i : i,, L The for y Riem sum with respet to the prtitio R, R f, R, N f i y i y, where i [y i-, y i ], =(,, ) f i y i y L f ji y ji y ji i I i I Ng Tze Beg f i y i y L f i y ji y ji 5 L f ji f i y ji y ji
16 Chpter 5 Itegrtio i I f i y i y L L f i y ji i f ji f i y ji y ji L f i i y ji Note tht the reted term is Riem sum S for the prtitio R P Thus R f, R, S L f ji f i y ji y ji U f, R P L M y ji y ji U f, P L M y ji y ji y the Refiemet Lemm L f, P L M R L f, P ML R L f ML L sie ML f R ML We hve thus proved tht R f, R, L f (4) Similrly, R f, R, N f i y i y S L f ji f i y ji y ji L f, R P L f ji f i y ji y ji L f, P L f ji f i y ji y ji U f, P L M y ji y ji U P, f L M R U f ML R U f ML ML U f ie R f, R, U f (5) Sie L f U f C (euse () ()), it follows from iequlities (4) d (5) tht R f, R, L We hve thus show tht there eists rel umer C suh tht for y prtitio R with orm R < d for y Riem sum S =R( f, R, ) with respet to R, S C Hee, f is Riem itegrle, Remr Note tht we hve give the proof of Theorem i more th oe wys Most oftely used prt of the theorem will e the equivlee of sttemets () to (3) Note tht (4) () Theorem is very useful tool for further developmet of the itegrl 3 I view of Theorem, we shll simply sy futio is itegrle wheever yoe of the equivlet oditios i Theorem is met Itegrility of Mootoe Futio Theorem Suppose f : [, ] R is mootoe futio The f is Riem itegrle Proof Sie f is mootoe o the losed d ouded itervl [, ], f is ouded Suppose tht f is iresig Let P : = 0 < < < = e prtitio for [, ] The Ng Tze Beg 6
17 Chpter 5 Itegrtio U f, P L f, P M i m i i Sie f is iresig, M i = f ( i ) d m i = f ( i- ) Therefore, U f, P L f, P P P M i m i f i f P f f If f () = f (), the give y > 0, for y prtitio P, U( f, P) L( f, P) = 0 < If f () f (), te y prtitio P suh tht P < /( f () f ()) The U f, P L f, P P f f Therefore, y Theorem, f is Riem itegrle The proof is similr whe f is deresig Itegrility of Cotiuous Futio Net we hve theorem whih ofirms tht defiite itegrls do eist t lest o otiuous futios Theorem 3 Every futio whih is otiuous o the losed itervl [, ] is (Riem) itegrle o [, ] Proof If f : [, ] R is otiuous, the it is lso uiformly otiuous (Referee: Theorem 9 Chpter 3) Therefore, give y > 0, there eists > 0 suh tht for ll, y i [, ], y < f () f (y) < Let P : = 0 < < < < = e prtitio with orm P < whih is give y () ove For i =,,, let M i = sup{ f () : [ i-, i ]} Sie f is otiuous o [ i-, i ], for eh i, y the Etreme Vlue Theorem, M i = f ( i ) for some i i [ i-, i ] Similrly for eh i =,,, let m i = if { f () : [ i-, i ]} Agi y the Etreme Vlue Theorem, for eh i =,,, there eists d i i [ i-, i ] suh tht m i = f (d i ) The upper Drou sum with respet to P is U f, P M i i d the lower Drou sum with respet to P is L f, P It follows tht the differee U f, P L f, P m i i f i f d i i f i i f d i i f i f d i i Ng Tze Beg 7
18 Chpter 5 Itegrtio y () sie i - d i P i i Therefore, U f, P L f, P i 0 Thus, y Theorem, f is Riem itegrle This ompletes the proof Remr More geerlly, suppose f : [, ] R is ouded futio, tht is, for some rel umers M d L, M < f () < L for ll i [, ] Suppose f is otiuous eept possily o suset of "mesure zero" The f is itegrle Ideed the overse is lso true: f is itegrle implies tht f is otiuous eept o suset of "mesure zero" This result is stted y Drou ut is ofte referred to s Leesgue Theorem By set of mesure zero we me tht the poits of disotiuity e elosed y t most outly ifiite set of itervls whose totl legth is ritrrily smll Ay fiite or outle set is of mesure zero The set of rtiol umers is of mesure zero (See Chpter 4 for defiitio of the Leesgue mesure of set) This gives other wy of provig Theorem sie y mootoe futio o [, ] hve t most outle umer of disotiuities Emple 4 [,] f 0, 0, 0 f is ot otiuous t 0 ut f is itegrle o Let P : = 0 < < < < = e prtitio of [,] Let i = i i- Let R f, P, f i i f i i () e Riem sum with respet to the prtitio P d =(,, ), where i is i [ i-, i ] If i 0 for i =,,, the f ( i ) 0 for ll i =,,, d so R f, P, f i i 0 If j 0 for some j, the f ( i ) 0 fo i j, j or i j, j+, whihever mes sese The Riem sum R f, P, f j j f j j or R f, P, f j j f j j Sie f () for ll i [, ], R f, P, Give y > 0, we te y prtitio P with j j P or j j P P < Therefore, f is Riem itegrle o [, ] d f 0 d R( f, P, ) 0 Ng Tze Beg 8
19 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Emple 5 d Proof Let f () =, Let P : = 0 < < < < = e prtitio of [, ] Sie for y ostt futio, mimum d miimum re the sme d so the upper Drou sum d the lower Drou sum for the prtitio P re the sme d it follows tht y ostt futio is Riem itegrle Therefore, f is Riem itegrle d the itegrl is give y the limit of sequee of lower sums of sequee of prtitios y Theorem Ay lower sum L f, P m i i i 0 e (P ) to e sequee of prtitios suh tht P 0 The L( f, P ) ( ) sie L( f, P ) is ostt sequee d so d 56 Properties of the Riem Drou itegrl Theorem 6 Suppose f : [, ] R is ouded futio If f is ouded d itegrle o the losed itervls [, ] d [, ], where < <, the f is itegrle o [, ] d f d f d f d Proof By Theorem, there eists sequee (P ) of prtitios of [, ] suh tht lim U f, P L f, P 0 d L f, P f Similrly, there eists sequee ( Q ) of prtitios of [, ] suh tht lim U f, Q L f, Q 0 d L f, Q f The (P Q ) is sequee of prtitios of [, ] Note tht U( f, P Q ) = U( f, P ) + U( f, Q ) d L( f, P Q ) = L( f, P ) + L( f, Q ) Therefore, lim U f, P Q L f, P Q lim U f, P U f, Q L f, P L f, Q lim U f, P L f, P lim U f, Q L f, Q It follows y Theorem tht f is Riem itegrle o [, ] Moreover, L f, P Q L f, P L f, Q f Hee f d f d f d f Theorem 7 Suppose f : [, ] R is ouded futio If f is itegrle o [, ], the for y i (, ), f is itegrle o [, ] d o [, ] d Ng Tze Beg 9
20 Chpter 5 Itegrtio f d f d f d Proof By Theorem, sie f is Riem itegrle, there is sequee (P ) of prtitios of [, ] suh tht lim U f, P L f, P 0 We my ssume tht the poit elogs to eh prtitio P We epli this s follows Let Q = P {}, the y the Refiemet Lemm, for eh positive iteger, U( f, Q ) L( f, Q ) U( f, P ) L( f, P ) Therefore, y the Compriso Test for sequees, lim U f, Q L f, Q 0 If P, we reple P y Q Hee we my ssume tht elogs to prtitio P for eh positive iteger Therefore, eh prtitio P is uio of prtitio P ' for [, ] d prtitio P '' for [, ] I prtiulr, U( f, P ) = U( f, P ' ) + U( f,p '' ) d L( f, P ) = L( f, P ' ) + L( f,p '' ) Thus, U( f, P ) L( f, P ) = U( f, P ' ) L( f, P ' ) + U( f,p '' ) L( f,p '' ) d so U( f, P ' ) L( f, P ' ) U( f, P ) L( f, P ) d U( f, P '' ) L( f, P '' ) U( f, P ) L( f, P ) Therefore, y the Compriso Test for sequees, lim U f, P L f, P 0 d lim U f, P L f, P 0 It follows y Theorem tht f is Riem itegrle o [, ] d o [, ] Moreover, L f, P L f, P L f, P Thus, f d f d f d f f Net we shll list the properties of the Drou sums whih we shll use lter Lemm 8 Suppose f : [, ] R d g : [, ] R re ouded futios Let P : = 0 < < < < = e prtitio of [, ] The L( f, P) + L( g, P) L( f + g, P) d U( f, P) + U( g, P) U( f + g, P) (A) Furthermore, for y rel umer, L( f, P) = L( f, P) d U( f, P) = U( f, P) if 0 U( f, P) = L( f, P) d L( f, P) = U( f, P) if (B) Proof These re oservtio regrdig properties of ifimum d supremum First we set up some ottio Suppose h : [, ] R is ouded futio d P : = 0 < < < < = is prtitio of [, ] For eh i =,,, let M i (h, P) = sup{h(): [ i -, i ]} d m i (h, P) = if{h(): [ i -, i ]} We egi y emiig the ompoets of the lower sums Ng Tze Beg 0
21 Chpter 5 Itegrtio m i ( f, P) = if{ f (): [ i -, i ]} is lower oud of { f (): [ i -, i ]}d m i (g, P) = if{ g(): [ i -, i ]} is lower oud of { g(): [ i -, i ]} Therefore, m i ( f, P) + m i (g, P) f () + g() for ll [ i -, i ] It follows tht m i ( f, P) + m i (g, P) is lower oud of { f () + g(): [ i -, i ]} Therefore, m i ( f, P) + m i (g, P) if { (f + g)() : [ i -, i ]} = m i ( f + g, P) () y the defiitio of ifimum, d so L( f, P) + L( g, P) = m i f, P i m i g, P i m i f g, P i L f g, P This proves the first iequlity of (A) We proeed with the seod iequlity of (A) similrly By defiitio M i ( f, P) is upper oud of { f (): [ i -, i ]} d M i (g, P) is upper oud of { g(): [ i -, i ]} Therefore, for ll [ i -, i ], M i ( f, P) + M i (g, P) f () + g() It follows tht M i ( f, P) + M i (g, P) is upper oud for the set { (f + g)() : [ i -, i ]} Hee, y the defiitio of supremum, M i ( f, P) + M i (g, P) sup{ (f + g)() : [ i -, i ]} = M i ( f + g, P) () The U( f, P) + U( g, P) = M i f, P i M i g, P i M i f g, P i U f g, P y () This proves the seod iequlity of (A) To prove the iequlity (B), ote tht for ouded set of rel umers, A, for y 0, if( A) = if(a), sup(a) = sup(a) Also for < 0, if( A) = sup(a), sup(a) = if(a) It follows tht for eh i =,,, m i ( f, P) = m i ( f, P) d M i ( f, P) = M i ( f, P) if 0 d m i ( f, P) = M i ( f, P) d M i ( f, P) = m i ( f, P) if < 0 Therefore, it follows from this set of equlities tht L( f, P) = L( f, P) d U( f, P) = U( f, P) if 0 ; U( f, P) = L( f, P) d L( f, P) = U( f, P) if 0 Theorem 9 Suppose f : [, ] R is ouded futio If f is Riem itegrle, the for y rel umer, f is Riem itegrle d f d f d Proof By Theorem, sie f is itegrle, there is sequee (P ) of prtitios of [, ] suh tht lim U f, P L f, P 0 d tht L f, P d f U f, P f If 0, the lim U f, P L f, P lim U f, P L f, P lim U f, P L f, P 0 Ng Tze Beg
22 Chpter 5 Itegrtio If < 0, the lim U f, P L f, P lim L f, P U f, P lim U f, P L f, P 0 Therefore, y Theorem, f is itegrle d L f, P L f, P f 0 d L f, P U f, P f if < 0 d so f f if Theorem 30 Suppose f : [, ] R d g : [, ] R re ouded futios If f d g re itegrle, the f + g is itegrle d f g f g Proof Sie f d g re itegrle, y Theorem there eist sequee (P ) of prtitios of [, ] suh tht lim U f, P L f, P 0 d sequee (Q ) of prtitios of [, ] suh tht lim U g, Q L g, Q 0 Te the sequee of prtitio (R ), where R = P Q for eh positive iteger By the Refiemet Lemm, for eh positive iteger, L( f, P ) L( f, R ) U( f, R ) U( f, P ) d L( g, Q ) L(g, R ) U( g, R ) U( g, Q ) It follows tht 0 U( f, R ) L( f, R ) U( f, P ) L( f, P ) () d 0 U( g, R ) L(g, R ) U( g, Q ) L( g, Q ) () Beuse of iequlities () d (), lim U f, P L f, P 0 d tht lim U g, Q L g, Q 0, y the Compriso Test for sequees, lim U f, R L f, R 0 d L g, R 0 Cosequetly, (see for emple Theorem ()), we hve tht L f, R, f U f, R f L g, R Now y Lemm 8, for eh positive iteger, g, U g, R (3) g L( f, R ) + L( g, R ) L( f + g, R ) U( f + g, R ) U( f, R ) + U( g, R ) (4) Therefore, 0 U( f + g, R ) - L( f + g, R ) U( f, R ) L( f, R ) + U( g, R ) L( g, R ) ---- (5) Sie lim U f, R L f, R U g, R L g, R lim U f, R, L f, R lim U g, R L g, R 0 it follows from the iequlity (5) d the Compriso Test for sequees, lim U f g, R L f g, R 0 Therefore, y Theorem (), f + g is itegrle By the iequlity (4), the limits i (3) d the Squeeze Theorem for sequees, L f g, R But f g L f g, R f g d so f g f g Remr A proof usig Theorem (4) is preseted i Ng Tze Beg's "Clulus, itrodutio", 943 Theorem 3 Suppose f : [, ] R is ouded futios If f 0 d itegrle, the f 0 Ng Tze Beg
23 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Proof Sie f is itegrle, y Theorem (), there eists sequee (P ) of prtitios of [, ] suh tht L f, P f Sie f 0, L( f, P ) 0 for eh positive iteger th or equl to 0 f eig the limit of the sequee (L( f, P ) ) is therefore greter Theorem 3 Suppose f : [, ] R d g : [, ] R re ouded futios If f d g re itegrle o [, ] d f () g() for ll i [, ], the g f Proof Sie f () g() for ll i [, ], f g 0 d so y Theorem 3 f g 0 But y Theorem 9 d Theorem 30, f g f g f g It follows tht f g 0 d so f g Remr Oe give proof usig either the upper Drou sum or the lower Drou sum d Theorem () We et stte useful oservtio Propositio 33 Suppose f : [, ] R is ouded d itegrle If g : [, ] R is futio suh tht g = f eept o fiite set of poits i [, ], the g is itegrle d g f Proof g() f () = 0 for ll ut fiite set of poits i [, ] This mes g f is lier omitio of futios of the type osidered i emple 4 Therefore, y Emple 4, Theorem 9 d 30, g - f is itegrle d g f 0 Sie g = (g f ) + f d oth (g f ) d f re itegrle, y Theorem 30, g is itegrle d g f g f f g f f 0 f This ompletes the proof Remr I ft muh more is true By Leesgue Theorem, if g = f eept o set of "mesure" 0 i [, ], d if f is itegrle, the g is itegrle d g f Theorem 34 Suppose f : [, ] R is ouded futio Suppose f is otiuous o (, ) The f is itegrle d the itegrl does ot deped o the vlues t the ed poits of the itervl Proof We shll use the equivlet oditio (3) for itegrility i Theorem Tht is, we shll show tht give y > 0, there is prtitio P for the itervl [, ] suh tht the differee U( f,p) L( f, P) < Sie f is ouded, there eists K > 0 suh tht f () K for ll i [, ] Let ( ) e deresig sequee i (, ( +)/) suh tht Let ( ) e iresig sequee i (( +)/, ) suh tht Give y > 0, there eists positive iteger N suh tht N implies tht 0 < < / (8K) d 0 < < Ng Tze Beg 3
24 Chpter 5 Itegrtio / (8K) Let m e y fied iteger Sie f is otiuous, f is otiuous o the losed d ouded suitervl [ m, m ] Therefore, y Theorem 3, the restritio of f to [ m, m ] is itegrle By Theorem (3), there eists prtitio P for the itervl [ m, m ] suh tht U f m,m, P L f m,m, P / Addig i the two ed poits d we get prtitio Q for [, ] Tht is, Q = P {, } The the upper Drou sum with respet to Q is U f, Q sup f :, m m U f m,m, P sup f : m, m K m K m U f m,m, P /4 U f m,m, P Liewise, the lower Drou sum with respet to Q is L f, Q if f :, m m L f m,m, P if f : m, m K m L f m,m, P K m /4 L f m,m, P Therefore, U f, Q L f, Q / U f m,m, P L f m,m, P / / It follows y Theorem (3) tht f is itegrle By Propositio 33 the itegrl is idepedet of the vlues of f t the ed poits of the itervl We show muh more Give y iteger i P, there eist itegers d m suh tht 0 8K d 0 m By Theorem (3), there eists prtitio P for the 8K itervl, m suh tht U f, m, P L f, m, P Without loss of geerlity we my ssume tht < + d m < m + for eh iteger i P Let Q = P {, } The, we show similrly s ove tht U f, Q L f, Q Hee lim U f, Q L f, Q 0 Therefore, y Theorem (), f U f, Q But U f, Q sup f :, U f, m, P sup f : m, m d sup f :, sup f : m, m 4 Sie lim, y the Compriso Test, 4 0 lim (sup f :, sup f : m, m ) 0 It follows tht lim U f, m, P lim U f, Q It is ler tht U f, m, P is idepedet of the ed poits of the itervl [, ] Similrly, we show tht L f, m, P f Sie L f, m, P m sequees, lim f f m f f U f, m, P, y the Squeeze Theorem for Ng Tze Beg 4
25 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Remr Note tht the oly use of the otiuity of f o (, ) i the proof ove is to dedue the itegrility of f o the suitervls [ m, m ] Emple 35 () Let f, 0, 0 By Propositio 33, f d d ssumig the Fudmetl 0 Theorem of Clulus () Let f, 0 3, f d 0 f d f d y Theorem 34 d Theorem 6 0 Clulus 0 d 3 d d ssumig the Fudmetl Theorem of (3) 03 d 0 d d 3 d 0 0d d 3 d y Propositio Riem Sums Covergee Theorem We hve see i Theorem () tht if f : [, ] R is itegrle, the the itegrl is the limit of sequee of lower Drou sums with respet to sequee of prtitios of [, ] We shll show et tht the itegrl is the limit of y sequee of Riem sums with respet to sequee of prtitios {P } of [, ] so log s P 0 Theorem 36 Suppose f : [, ] R is Riem itegrle o [, ] d (P ) is sequee of Prtitio of [, ] Let R( f, P, C ) e Riem sum with respet to the prtitio P with C eig y hoie of poits i the suitervls of P If P overges to 0 s teds to ifiity, the the sequee of Riem sums teds to f (R( f, P, C ) ) Proof Sie f is itegrle, y Theorem (4) give y > 0, we fid > 0 suh tht for y prtitio P for [, ] with orm P <, d for y Riem sum S with respet to P, S f Sie P overges to 0, we fid iteger N suh tht for y N, P < Therefore, euse eh R( f, P, C ) is Riem sum with respet to P, R f, P, C f for ll N This mes the sequee (R( f, P, C ) ) overges to s teds to ifiity Remr The usul pplitio of the ove theorem is to sequee of prtitios ( P ), where P = ( )/ s is the se whe P is regulr prtitio d the f Ng Tze Beg 5
26 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Riem sum R( f, P, C ) with respet to P is hose suh tht C the hoie of poits i the suitervls of P is hose either to e the ed poit or egiig poit of the suitervl I more detil, the pplitio is stted elow Corollry 37 Suppose we re give limit of the form lim g i If we write g i f i, where either i i or i i, the lim g i lim f i, f d if f is Riem itegrle o [, ] Therefore, if we fid ti-derivtive F of f, the lim g i F F y the Fudmetl Theorem of Clulus Emple 38 5 i lim 3 lim 0 5 i 5 d 3 [ 5 3/ ] / 5 3/ Drou Sums Covergee Theorem It is turl questio to s tht if the futio f is itegrle o [, ], the does the sme olusio s i Theorem 36 holds true for either the upper Drou sums or lower Drou sums, tht is, does the sequee of either upper Drou sum or lower Drou with respet to y sequee of prtitios overge to the itegrl of f if the orm of the prtitios ted to 0 Theorem 39 Suppose f : [, ] R is itegrle d (P ) is sequee of prtitios of [, ] If P overges to 0 s teds to ifiity, the lim U f, P L f, P 0 d osequetly L f, P f d U f, P f Proof Sie f is itegrle, y Theorem (4), give > 0, the there eists > 0 suh tht for y prtitio P for [, ] with orm P <, d for y Riem sum S with respet to P, S L < /4 Let T = { Riem sum S : S hs the sme prtitio P} The for y S i T, L /4 < S < L + / () Let P: = 0 < < < = e prtitio of [, ] with P < Let M i = sup{ f () : [ i-, i ]} for i =,, By the defiitio of supremum, for eh i, i, there eists i i [ i-, i ] suh tht f ( i ) > M i 4 The, usig this iequlity the Riem sum Ng Tze Beg 6
27 Chpter 5 Itegrtio R f, P, C f i i M i 4 i M i i U f, P, 4 4 where, C=(,, ) Therefore, U f, P R f, P, C L L () y iequlity () Now let m i = if{ f () : [ i-, i ]} for i =,, By the defiitio of ifimum, for eh i, i, there eists d i i [ i-, i ] suh tht f (d i ) < m i 4 The, usig this iequlity, the Riem sum R f, P, d f d i i m i, 4 i m i i L f, P 4 4 where d=(d,,d ) Therefore, L f, P R f, P, d L L (3) It follows from () d (3) tht if P <, the U( f, P) L( f, P) < Now sie P 0, there eists iteger N suh tht N P < Therefore, y wht we hve just proved, N U( f, P ) L( f, P ) < This mes lim U f, P L f, P 0 Remr The rgumet i the proof of Theorem 39 is i the proof of Theorem (4) (3) d is reprodued here for oveiee Me Vlue Theorem Theorem 40 Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls Suppose f is otiuous o the losed itervl [, ] with < The there eists poit i [, ] suh tht f f Proof Sie f is otiuous o [, ], y the Etreme Vlue Theorem, there eists, d i [, ] suh tht m = f () f () f (d) = M for ll i [, ] Therefore, y Theorem 3, m f M d so f f f d Dividig the ove iequlity y ( ), we get f f f d Ng Tze Beg 7
28 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Therefore, sie f is otiuous, y the Itermedite Vlue Theorem, there eists etwee d d, ie i [, ] suh tht f (The left hd side of the equtio ove is ow s the me vlue) Hee f f Emple 4 We estimte Itegrls It sys there eists i f 3 si 8 d usig the Me Vlue Theorem for 6 6, 3 suh tht 6 si 8 Sie the futio sie is iresig o 6, 3, 3 si 8 d si si 6 si si 3 3 It follows tht si 8 d so si 8 3 d 4 6 Therefore, 3 si 8 7 d Fudmetl Theorem of Clulus The most importt theorem i Clulus is the fudmetl theorem euse it provides the li etwee differetitio d Riem itegrtio Our et result is theorem of Drou whih gives the fudmetl theorem without the ssumptio of the otiuity of the derived futio f ' of f Theorem 4 Drou Fudmetl Theorem of Clulus Suppose F : [, ] R is futio otiuous o [, ] d differetile o (, ) Suppose the derived futio F' : (, ) R is itegrle i the sese tht y etesio of F' to the ed poits d is itegrle The F F F Proof For eh iteger let the regulr prtitio P for [, ] e P : = 0 < < < =, with P = ( )/, for = 0,,, For eh =,,, sie F is otiuous o [, ] d differetile o (, ), y the Me Vlue Theorem (Theorem 5 Chpter 4), there eist i (, ) suh tht F' ( ) ( ) F( ) F( ) () Let R( F', P, C ) e the Riem sum with respet to the prtitio P, where C =(,, ) is the hoie of i i [ i-, i ] give y () The R F, P, C F F F F F 0 F F Sie P = ( )/ 0, y Theorem 36, the sequee of Riem sums (R( F', P, C ) ) teds to F But the sequee is ostt d so R( F', P, C ) F() F() Therefore, F F F The followig is the more fmilir form of the fudmetl theorem of lulus Theorem 43 (First Fudmetl Theorem of Clulus) Ng Tze Beg 8
29 Chpter 5 Itegrtio Suppose F : [, ] R is futio otiuous o [, ] d differetile o (, ) Suppose F' : (, ) R is otiuous d ouded The F F F Proof F' : (, ) R is otiuous d ouded implies tht F' is itegrle y Theorem 34 d tht the itegrl does ot deped o the vlues of the etesio of F' t the ed poits Hee, the theorem follows from Theorem 4 Remr Suppose f : [, ] R is itegrle d hs "ti-derivtive" F : [, ] R, whih is otiuous o [, ] d F'() = f () for ll i (, ) Note tht F eed ot e differetile t the ed poits of the itervl The y Theorem 4, f F F The sigifie of Theorem 43 is tht we use y "ti-derivtive" to ompute defiite itegrl Let f e futio otiuous o [, ] d so itegrle o [, ] For y otiuous futio F defied o [, ] suh tht F'() = f () for ll i (, ), (ie F is "ti-derivtive" of f i the sese give ove), f F F F This is the usul form tht the theorem is used Emple d Let f () = The f is otiuous o [0, ] We reogize immeditely tht F is ti-derivtive of f Thus 3 6 d Remr Not ll otiuous futios hve ti-derivtives epressile i terms of elemetry futios By elemetry futio, we me y futio formed from rel ostt, the idetity futio, the epoetil futio, the logrithmi futio, the trigoometri futios d the iverse trigoometri futios, y ddig, multiplyig, dividig or formig ompositio Not ll itegrle futios hve ti-derivtives For emple, the futio does ot hve /4 ti-derivtive i terms of elemetry futios o [-, ] d the futio f, 0 does ot hve ti-derivtive o [-, ] ut is itegrle We, 0 still ompute whih is 0 f Theorem 45 (Seod Fudmetl Theorem of Clullus) Suppose f : [, ] R is itegrle Defie F: [, ] R y F f for i [, ] The F is otiuous o [, ] If f is otiuous t i [, ], the F is differetile t d F'() = f () Proof Sie f is itegrle, f is ouded o [, ] Thus, there eists positive rel umer K suh tht K f () K for ll i [, ] We shll show tht F is Ng Tze Beg 9
30 Chpter 5 Itegrtio uiformly otiuous d hee otiuous For y < y suh tht y we hve tht K f (t) K for ll t i [, y] Hee, tig itegrls, y Theorem 3, y K y f K y d so y K( y ) = K y () f For y < y suh tht y, y y y F y f f f F f Therefore, y F y F f () Similrly, if y, y iterhgig the role of d y ove, we get, F F y y f (3) It follows from (), () d (3) tht, for y y, F F y K y Hee for y > 0, te to e y rel umer suh tht 0 < < /K The for ll, y i [, ], y < F() F(y) K y < K /K = This mes F is uiformly otiuous o [, ] d so otiuous o [, ] Prt () Suppose f is otiuous t 0 [, ] We shll show tht F f t dt is differetile t 0 For > 0, F F 0 f 0 f 0 f 0 f 0 f 0 f d for < 0, F F 0 f 0 f f f 0 f 0 f 0 f where we use the ovetio tht whe < d i [, ], d f d f For 0, let H F F 0 0 f 0 0 The y the defiitio of the derivtive, lim, where the limit is te to e the pproprite left or 0 H F 0 right limit whe 0 = or We shll show tht H() teds to f ( 0 ) s teds to 0 Sie f is otiuous t 0, give > 0 there eists > 0 suh tht 0 f f 0 f 0 f f 0 Tht is to sy, for ll i [, ] with 0, 0, we hve f 0 f f (4) Now we osider the right limit first For i ( 0, 0 + ), usig (4) d Theorem 3, we oti 0 f 0 0 Tht is to sy, for y i ( 0, 0 + ), f f 0 f 0 f t dt f 0 0 Dividig the ove iequlity y ( 0 ) > 0, we oti f 0 0 f t dt 0 H f 0 Therefore, H f 0 This shows tht lim H f 0 Similrly, for the left limit, we te i ( 0, 0 ) The from (4) d Theorem 3, we oti for y i ( 0, 0 ), 0 0 f 0 0 f 0 f 0 Ng Tze Beg 30
31 Chpter 5 Itegrtio 0 f t dt As efore we get f 0 0 f t dt 0 0 H f 0 This shows tht the left limit lim Therefore, if 0, is i (, ), the H f 0 0 lim H d so By the ove rgumet 0 lim 0 H f 0 F 0 lim 0 H f 0 F lim H f d F lim H f This shows tht for ll i [, ], F'() = f () This ompletes the proof Corollry 46 Suppose f : [, ] R is otiuous Defie F: [, ] R y F f for i [, ] The F is differetile d F'() = f () for ll i [, ], ie, F is ti-derivtive of f Defiitio 47 Suppose f : [, ] R is itegrle Suppose d d re two poits d i [, ] suh tht < d We defie With this defiitio, we hve the d f f y for y, y i [, ], f y f I prtiulr, for y, y d z i [, ], z y z f f y f Corollry 48 Suppose f : [, ] R is otiuous Let e i (, ] Defie F: [, ] R y F f for i [, ] The F is differetile d F'() = f () for ll i [, ], ie, F is ti-derivtive of f Proof Note tht F f f f Therefore, y Corollry 46, F d d f d d f f for ll i [, ] Hee F' = f Corollry 49 Suppose I is ope itervl d f : I R is otiuous Let 0 e i I d defie F: I R y F f for i I The F'() = f () for eh i I 0 Emple 50 () Let g: R R e defied y g t dt Let f t t The g f t dt F Thus y Corollry 49, g F f () Let h: R R e defied y h t dt Therefore, h F, where F is defied i emple () By the Chi Rule for differetitio, h F f, where the futio f is defied i Emple () Hee h 4 Corollry 49 provides wy to fid the ti-derivtive of otiuous futio It is the turl questio to s whether if we rel the otiuity oditio to oe of itegrility, the the olusio of Corollry 49 holds The swer is o i geerl A outeremple is is provided y the futio i Emple 5 Emple 5 Let g : [0, ] R, e futio defied y Ng Tze Beg 3
32 Chpter 5 Itegrtio 0 if is irrtiol g q if 0 is rtiol d p q i its lowest terms if 0 or The g is ouded, itegrle d 0 g 0 We shll ow show tht g is itegrle y usig oe of the equivlet oditios for itegrility i Theorem Give y > 0, y the Arhimede property of R, there eists positive iteger m > suh tht /m < Oserve tht there oly e fiite umer of reiprols of itegers tht re greter th or equl to /m: Te y rtiol umer p/q with p/q i its lowest terms d 0 < p/q This mes tht p q d the gretest ommo divisor of p d q is g(p/q) /m if d oly if /q /m if d oly if q m Thus, the umer of rtiol umers i [0, ] tht hve vlues greter th or equl to /m is fiite d this set iludes the poit 0 sie g(0) = Tht is the fiite set S m = { p/q: q =,, m; p =,, q} {0} is preisely the set o whih the vlues of g re greter th or equl to /m We shll show tht g stisfies oditio (3) of Theorem Rell tht the fiite set S m is preisely the set {y [0, ]: g(y) /m} Note tht 0, S m Let the umer of poits of S m e + Order the elemets y 0, y, y,, y of S m s follows: 0 = y 0 < y < y < y < y = Choose pir of poits, eh pir ostitute itervl otiig eh y i i its iterior d of legth < / for i =,,, d suh tht they re ll mutully disjoit Tht is, we hoose < < < suh tht 0 = y 0 y 3 y y y = We hoose further two more poits, 0 d d me y 0 s, y s suh tht 0 = = y 0 0 d = y = We further require tht j j () j 0 Oviously, P: 0 = = forms prtitio for [0, ] Now y the desity of the irrtiol umers i y itervl, for i = 0,,, m i( g, P ) = if{g(): [ i -, i ]}= () Now sie for eh j = 0,,,,, y j [ j j ] d so y the defiitio of S m, M j (g, P) = sup{g(): [ j -, j ]}= g (y j ) (3) for j = 0,,,, Now euse for j =,,,, [ j -, j ] S m =, M j - (g, P ) = sup{ g (): [ j -, j ]} /m (4) for j =,,, U(g, P) L(g, P) = M i g, P i m i g, P i, i 0 i 0 = M i g, P i y () i 0 Ng Tze Beg 3
33 Chpter 5 Itegrtio = j 0 M j g, P j j 0 M j g, P j g y j j m j y (3) d (4) j 0 j 0 j j m sie g (y j ) j 0 j 0 < / + y () m j 0 j < / + /m sie j 0 j < / + / = Therefore, give y we fid prtitio P suh tht, U(g, P) L(g, P) < By Theorem (), g is itegrle Furthermore y Theorem 39, for y sequee of prtitios ( P ) of [0, ] with P 0 (te ( P ) to e the sequee of regulr prtitios), L g, P But for eh positive iteger, y the desity of the 0 g irrtiol umers, L(g, P ) = 0 Therefore, 0 g 0 Remr Sie g is o-egtive d, the futio G :[0,] R defied y 0 g 0 G 0 g = 0 for eh i [0,] Hee, G'() = 0 d so G'() g() for ll rtiol i [0,] Thus G is ot ti-derivtive of g This gives outeremple to relig the otiuity oditio i Corollry 50 The futio g i Emple 5 is otiuous t every irrtiol poits d disotiuous t every rtiol poits i [0, ] Therefore, we pply Leesgue Theorem (referee: Theorem 33 Chpter 4) to olude tht g is itegrle euse the rtiol poits ostitute set of mesure zero We show elow tht g is otiuous t irrtiol poits Give y > 0, hoose positive iteger m suh tht /m < Te irrtiol umer i [0, ] Let = mi{ y : y S m } The > 0 sie is irrtiol Oviously the ope itervl (, + ) do ot meet S m This is, euse if (, + ) S m, the there eists p/q i S m suh tht - p/q < otrditig tht - p/q mi{ y : y S m } = Tht mes for ll y i (, + ) [0, ], y S m d osequetly, g(y) < /m < Therefore, g(y) g() = g(y) 0 = g(y) < We hve thus show tht for ll y i [0, ] suh tht y < we hve g(y) g() < It follows y defiitio tht g is otiuous t Sie is ritrry, g is otiuous t every irrtiol poit i [0, ] Now we shll show tht g is disotiuous t y rtiol poit For y rtiol poit i [0, ], y defiitio g() > 0 Let = g()/ > 0 For y > 0, y the desity of the irrtiol umers i y itervl, there eists irrtiol umer y i (, + ) [0, ] The g( y ) g() = 0 g() = g() > g()/ = We hve thus show tht for y > 0, we fid y i (, + ) [0, ] suh tht g( y ) g() > g()/ = This mes g is ot otiuous t, if is rtiol Hee g Ng Tze Beg 33
Riemann Integral Oct 31, such that
 Riem Itegrl Ot 31, 2007 Itegrtio of Step Futios A prtitio P of [, ] is olletio {x k } k=0 suh tht = x 0 < x 1 < < x 1 < x =. More suitly, prtitio is fiite suset of [, ] otiig d. It is helpful to thik of
Riem Itegrl Ot 31, 2007 Itegrtio of Step Futios A prtitio P of [, ] is olletio {x k } k=0 suh tht = x 0 < x 1 < < x 1 < x =. More suitly, prtitio is fiite suset of [, ] otiig d. It is helpful to thik of
Limit of a function:
 - Limit of fuctio: We sy tht f ( ) eists d is equl with (rel) umer L if f( ) gets s close s we wt to L if is close eough to (This defiitio c e geerlized for L y syig tht f( ) ecomes s lrge (or s lrge egtive
- Limit of fuctio: We sy tht f ( ) eists d is equl with (rel) umer L if f( ) gets s close s we wt to L if is close eough to (This defiitio c e geerlized for L y syig tht f( ) ecomes s lrge (or s lrge egtive
Riemann Integral and Bounded function. Ng Tze Beng
 Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
Week 13 Notes: 1) Riemann Sum. Aim: Compute Area Under a Graph. Suppose we want to find out the area of a graph, like the one on the right:
 Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
MATH 104: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 2008/09 PROBLEM SET 10 SOLUTIONS. f m. and. f m = 0. and x i = a + i. a + i. a + n 2. n(n + 1) = a(b a) +
 MATH 04: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 008/09 PROBLEM SET 0 SOLUTIONS Throughout this problem set, B[, b] will deote the set of ll rel-vlued futios bouded o [, b], C[, b] the set of ll rel-vlued futios
MATH 04: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 008/09 PROBLEM SET 0 SOLUTIONS Throughout this problem set, B[, b] will deote the set of ll rel-vlued futios bouded o [, b], C[, b] the set of ll rel-vlued futios
12.2 The Definite Integrals (5.2)
 Course: Aelerted Egieerig Clulus I Istrutor: Mihel Medvisky. The Defiite Itegrls 5. Def: Let fx e defied o itervl [,]. Divide [,] ito suitervls of equl width Δx, so x, x + Δx, x + jδx, x. Let x j j e ritrry
Course: Aelerted Egieerig Clulus I Istrutor: Mihel Medvisky. The Defiite Itegrls 5. Def: Let fx e defied o itervl [,]. Divide [,] ito suitervls of equl width Δx, so x, x + Δx, x + jδx, x. Let x j j e ritrry
The Real Numbers. RATIONAL FIELD Take rationals as given. is a field with addition and multiplication defined. BOUNDS. Addition: xy= yx, xy z=x yz,
 MAT337H Itrodutio to Rel Alysis The Rel Numers RATIONAL FIELD Tke rtiols s give { m, m, R, } is field with dditio d multiplitio defied Additio: y= y, y z= yz, There eists Q suh tht = For eh Q there eists
MAT337H Itrodutio to Rel Alysis The Rel Numers RATIONAL FIELD Tke rtiols s give { m, m, R, } is field with dditio d multiplitio defied Additio: y= y, y z= yz, There eists Q suh tht = For eh Q there eists
AP Calculus AB AP Review
 AP Clulus AB Chpters. Re limit vlues from grphsleft-h Limits Right H Limits Uerst tht f() vlues eist ut tht the limit t oes ot hve to.. Be le to ietify lel isotiuities from grphs. Do t forget out the 3-step
AP Clulus AB Chpters. Re limit vlues from grphsleft-h Limits Right H Limits Uerst tht f() vlues eist ut tht the limit t oes ot hve to.. Be le to ietify lel isotiuities from grphs. Do t forget out the 3-step
Crushed Notes on MATH132: Calculus
 Mth 13, Fll 011 Siyg Yg s Outlie Crushed Notes o MATH13: Clculus The otes elow re crushed d my ot e ect This is oly my ow cocise overview of the clss mterils The otes I put elow should ot e used to justify
Mth 13, Fll 011 Siyg Yg s Outlie Crushed Notes o MATH13: Clculus The otes elow re crushed d my ot e ect This is oly my ow cocise overview of the clss mterils The otes I put elow should ot e used to justify
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
General properties of definite integrals
 Roerto s Notes o Itegrl Clculus Chpter 4: Defiite itegrls d the FTC Sectio Geerl properties of defiite itegrls Wht you eed to kow lredy: Wht defiite Riem itegrl is. Wht you c ler here: Some key properties
Roerto s Notes o Itegrl Clculus Chpter 4: Defiite itegrls d the FTC Sectio Geerl properties of defiite itegrls Wht you eed to kow lredy: Wht defiite Riem itegrl is. Wht you c ler here: Some key properties
Approximate Integration
 Study Sheet (7.7) Approimte Itegrtio I this sectio, we will ler: How to fid pproimte vlues of defiite itegrls. There re two situtios i which it is impossile to fid the ect vlue of defiite itegrl. Situtio:
Study Sheet (7.7) Approimte Itegrtio I this sectio, we will ler: How to fid pproimte vlues of defiite itegrls. There re two situtios i which it is impossile to fid the ect vlue of defiite itegrl. Situtio:
Numerical Methods. Lecture 5. Numerical integration. dr hab. inż. Katarzyna Zakrzewska, prof. AGH. Numerical Methods lecture 5 1
 Numeril Methods Leture 5. Numeril itegrtio dr h. iż. Ktrzy Zkrzewsk, pro. AGH Numeril Methods leture 5 Outlie Trpezoidl rule Multi-segmet trpezoidl rule Rihrdso etrpoltio Romerg's method Simpso's rule
Numeril Methods Leture 5. Numeril itegrtio dr h. iż. Ktrzy Zkrzewsk, pro. AGH Numeril Methods leture 5 Outlie Trpezoidl rule Multi-segmet trpezoidl rule Rihrdso etrpoltio Romerg's method Simpso's rule
Definition Integral. over[ ab, ] the sum of the form. 2. Definite Integral
![Definition Integral. over[ ab, ] the sum of the form. 2. Definite Integral Definition Integral. over[ ab, ] the sum of the form. 2. Definite Integral](/thumbs/83/87856510.jpg) Defiite Itegrl Defiitio Itegrl. Riem Sum Let f e futio efie over the lose itervl with = < < < = e ritrr prtitio i suitervl. We lle the Riem Sum of the futio f over[, ] the sum of the form ( ξ ) S = f Δ
Defiite Itegrl Defiitio Itegrl. Riem Sum Let f e futio efie over the lose itervl with = < < < = e ritrr prtitio i suitervl. We lle the Riem Sum of the futio f over[, ] the sum of the form ( ξ ) S = f Δ
MATH 104: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 2009/10 PROBLEM SET 8 SOLUTIONS. and x i = a + i. i + n(n + 1)(2n + 1) + 2a. (b a)3 6n 2
 MATH 104: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 2009/10 PROBLEM SET 8 SOLUTIONS 6.9: Let f(x) { x 2 if x Q [, b], 0 if x (R \ Q) [, b], where > 0. Prove tht b. Solutio. Let P { x 0 < x 1 < < x b} be regulr prtitio
MATH 104: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 2009/10 PROBLEM SET 8 SOLUTIONS 6.9: Let f(x) { x 2 if x Q [, b], 0 if x (R \ Q) [, b], where > 0. Prove tht b. Solutio. Let P { x 0 < x 1 < < x b} be regulr prtitio
Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals By Ng Tze Beng. The Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals (SMVT) Statement of the Theorem
 Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
Review of the Riemann Integral
 Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Linford 1. Kyle Linford. Math 211. Honors Project. Theorems to Analyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of a Function Involving a Radical (A4)
 Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
Liford 1 Kyle Liford Mth 211 Hoors Project Theorems to Alyze: Theorem 2.4 The Limit of Fuctio Ivolvig Rdicl (A4) Theorem 2.8 The Squeeze Theorem (A5) Theorem 2.9 The Limit of Si(x)/x = 1 (p. 85) Theorem
a f(x)dx is divergent.
 Mth 250 Exm 2 review. Thursdy Mrh 5. Brig TI 30 lultor but NO NOTES. Emphsis o setios 5.5, 6., 6.2, 6.3, 3.7, 6.6, 8., 8.2, 8.3, prt of 8.4; HW- 2; Q-. Kow for trig futios tht 0.707 2/2 d 0.866 3/2. From
Mth 250 Exm 2 review. Thursdy Mrh 5. Brig TI 30 lultor but NO NOTES. Emphsis o setios 5.5, 6., 6.2, 6.3, 3.7, 6.6, 8., 8.2, 8.3, prt of 8.4; HW- 2; Q-. Kow for trig futios tht 0.707 2/2 d 0.866 3/2. From
B. Examples 1. Finite Sums finite sums are an example of Riemann Sums in which each subinterval has the same length and the same x i
 Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
Mth 06 Clculus Sec. 5.: The Defiite Itegrl I. Riem Sums A. Def : Give y=f(x):. Let f e defied o closed itervl[,].. Prtitio [,] ito suitervls[x (i-),x i ] of legth Δx i = x i -x (i-). Let P deote the prtitio
f(t)dt 2δ f(x) f(t)dt 0 and b f(t)dt = 0 gives F (b) = 0. Since F is increasing, this means that
 Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES. To a 2π-periodic function f(x) we will associate a trigonometric series. a n cos(nx) + b n sin(nx),
 FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
Important Facts You Need To Know/Review:
 Importt Fcts You Need To Kow/Review: Clculus: If fuctio is cotiuous o itervl I, the its grph is coected o I If f is cotiuous, d lim g Emple: lim eists, the lim lim f g f g d lim cos cos lim 3 si lim, t
Importt Fcts You Need To Kow/Review: Clculus: If fuctio is cotiuous o itervl I, the its grph is coected o I If f is cotiuous, d lim g Emple: lim eists, the lim lim f g f g d lim cos cos lim 3 si lim, t
Introduction to Matrix Algebra
 Itrodutio to Mtri Alger George H Olso, Ph D Dotorl Progrm i Edutiol Ledership Applhi Stte Uiversit Septemer Wht is mtri? Dimesios d order of mtri A p q dimesioed mtri is p (rows) q (olums) rr of umers,
Itrodutio to Mtri Alger George H Olso, Ph D Dotorl Progrm i Edutiol Ledership Applhi Stte Uiversit Septemer Wht is mtri? Dimesios d order of mtri A p q dimesioed mtri is p (rows) q (olums) rr of umers,
( ) dx ; f ( x ) is height and Δx is
 Mth : 6.3 Defiite Itegrls from Riem Sums We just sw tht the exct re ouded y cotiuous fuctio f d the x xis o the itervl x, ws give s A = lim A exct RAM, where is the umer of rectgles i the Rectgulr Approximtio
Mth : 6.3 Defiite Itegrls from Riem Sums We just sw tht the exct re ouded y cotiuous fuctio f d the x xis o the itervl x, ws give s A = lim A exct RAM, where is the umer of rectgles i the Rectgulr Approximtio
Riemann Integration. Chapter 1
 Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
1. (25 points) Use the limit definition of the definite integral and the sum formulas to compute. [1 x + x2
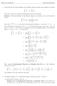 Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Chapter 5. The Riemann Integral. 5.1 The Riemann integral Partitions and lower and upper integrals. Note: 1.5 lectures
 Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Thomas J. Osler Mathematics Department Rowan University Glassboro NJ Introduction
 Ot 0 006 Euler s little summtio formul d speil vlues of te zet futio Toms J Osler temtis Deprtmet Row Uiversity Glssboro J 0608 Osler@rowedu Itrodutio I tis ote we preset elemetry metod of determiig vlues
Ot 0 006 Euler s little summtio formul d speil vlues of te zet futio Toms J Osler temtis Deprtmet Row Uiversity Glssboro J 0608 Osler@rowedu Itrodutio I tis ote we preset elemetry metod of determiig vlues
1.3 Continuous Functions and Riemann Sums
 mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
The Reimann Integral is a formal limit definition of a definite integral
 MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
0 otherwise. sin( nx)sin( kx) 0 otherwise. cos( nx) sin( kx) dx 0 for all integers n, k.
 . Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
. Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
MAS221 Analysis, Semester 2 Exercises
 MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS
 Chpter 4 EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS If the defiite itegrl represets re betwee curve d the x-xis, d if you c fid the re by recogizig the shpe of the regio, the you c evlute the defiite itegrl. Those
Chpter 4 EVALUATING DEFINITE INTEGRALS If the defiite itegrl represets re betwee curve d the x-xis, d if you c fid the re by recogizig the shpe of the regio, the you c evlute the defiite itegrl. Those
EXPONENTS AND LOGARITHMS
 978--07-6- Mthemtis Stdrd Level for IB Diplom Eerpt EXPONENTS AND LOGARITHMS WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW The rules of epoets: m = m+ m = m ( m ) = m m m = = () = The reltioship etwee epoets d rithms: = g where
978--07-6- Mthemtis Stdrd Level for IB Diplom Eerpt EXPONENTS AND LOGARITHMS WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW The rules of epoets: m = m+ m = m ( m ) = m m m = = () = The reltioship etwee epoets d rithms: = g where
MATH 104 FINAL SOLUTIONS. 1. (2 points each) Mark each of the following as True or False. No justification is required. y n = x 1 + x x n n
 MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
Math 201 (Introduction to Analysis) Fall
 Mth (Itrodutio to Alysis) Fll 4-5 Istrutor: Dr. Ki Y. Li Offie: Room 47 Offie Phoe: 58 74 e-mil ddress: myli@ust.h Offie Hours: Tu. :pm - 4:pm (or y ppoitmets) Prerequisite: A-level Mth or Oe Vrile Clulus
Mth (Itrodutio to Alysis) Fll 4-5 Istrutor: Dr. Ki Y. Li Offie: Room 47 Offie Phoe: 58 74 e-mil ddress: myli@ust.h Offie Hours: Tu. :pm - 4:pm (or y ppoitmets) Prerequisite: A-level Mth or Oe Vrile Clulus
Project 3: Using Identities to Rewrite Expressions
 MAT 5 Projet 3: Usig Idetities to Rewrite Expressios Wldis I lger, equtios tht desrie properties or ptters re ofte lled idetities. Idetities desrie expressio e repled with equl or equivlet expressio tht
MAT 5 Projet 3: Usig Idetities to Rewrite Expressios Wldis I lger, equtios tht desrie properties or ptters re ofte lled idetities. Idetities desrie expressio e repled with equl or equivlet expressio tht
Taylor Polynomials. The Tangent Line. (a, f (a)) and has the same slope as the curve y = f (x) at that point. It is the best
 Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
AIEEE CBSE ENG A function f from the set of natural numbers to integers defined by
 AIEEE CBSE ENG. A futio f from the set of turl umers to itegers defied y, whe is odd f (), whe is eve is (A) oe oe ut ot oto (B) oto ut ot oe oe (C) oe oe d oto oth (D) either oe oe or oto. Let z d z e
AIEEE CBSE ENG. A futio f from the set of turl umers to itegers defied y, whe is odd f (), whe is eve is (A) oe oe ut ot oto (B) oto ut ot oe oe (C) oe oe d oto oth (D) either oe oe or oto. Let z d z e
The Basic Properties of the Integral
 The Bsic Properties of the Itegrl Whe we compute the derivtive of complicted fuctio, like x + six, we usully use differetitio rules, like d [f(x)+g(x)] d f(x)+ d g(x), to reduce the computtio dx dx dx
The Bsic Properties of the Itegrl Whe we compute the derivtive of complicted fuctio, like x + six, we usully use differetitio rules, like d [f(x)+g(x)] d f(x)+ d g(x), to reduce the computtio dx dx dx
{ } { S n } is monotonically decreasing if Sn
 Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
4. When is the particle speeding up? Why? 5. When is the particle slowing down? Why?
 AB CALCULUS: 5.3 Positio vs Distce Velocity vs. Speed Accelertio All the questios which follow refer to the grph t the right.. Whe is the prticle movig t costt speed?. Whe is the prticle movig to the right?
AB CALCULUS: 5.3 Positio vs Distce Velocity vs. Speed Accelertio All the questios which follow refer to the grph t the right.. Whe is the prticle movig t costt speed?. Whe is the prticle movig to the right?
 n. A Very Interesting Example + + = d. + x3. + 5x4. math 131 power series, part ii 7. One of the first power series we examined was. 2!
 mth power series, prt ii 7 A Very Iterestig Emple Oe of the first power series we emied ws! + +! + + +!! + I Emple 58 we used the rtio test to show tht the itervl of covergece ws (, ) Sice the series coverges
mth power series, prt ii 7 A Very Iterestig Emple Oe of the first power series we emied ws! + +! + + +!! + I Emple 58 we used the rtio test to show tht the itervl of covergece ws (, ) Sice the series coverges
We will begin by supplying the proof to (a).
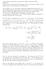 (The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
(The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
SPH3UW Unit 7.5 Snell s Law Page 1 of Total Internal Reflection occurs when the incoming refraction angle is
 SPH3UW Uit 7.5 Sell s Lw Pge 1 of 7 Notes Physis Tool ox Refrtio is the hge i diretio of wve due to hge i its speed. This is most ommoly see whe wve psses from oe medium to other. Idex of refrtio lso lled
SPH3UW Uit 7.5 Sell s Lw Pge 1 of 7 Notes Physis Tool ox Refrtio is the hge i diretio of wve due to hge i its speed. This is most ommoly see whe wve psses from oe medium to other. Idex of refrtio lso lled
Numerical Solutions of Fredholm Integral Equations Using Bernstein Polynomials
 Numericl Solutios of Fredholm Itegrl Equtios Usig erstei Polyomils A. Shiri, M. S. Islm Istitute of Nturl Scieces, Uited Itertiol Uiversity, Dhk-, gldesh Deprtmet of Mthemtics, Uiversity of Dhk, Dhk-,
Numericl Solutios of Fredholm Itegrl Equtios Usig erstei Polyomils A. Shiri, M. S. Islm Istitute of Nturl Scieces, Uited Itertiol Uiversity, Dhk-, gldesh Deprtmet of Mthemtics, Uiversity of Dhk, Dhk-,
Math1242 Project I (TI 84) Name:
 Mth4 Project I (TI 84) Nme: Riem Sums d Defiite Itegrls The re uder the grph of positive fuctio is give y the defiite itegrl of the fuctio. The defiite itegrl c e pproimted y the followig sums: Left Riem
Mth4 Project I (TI 84) Nme: Riem Sums d Defiite Itegrls The re uder the grph of positive fuctio is give y the defiite itegrl of the fuctio. The defiite itegrl c e pproimted y the followig sums: Left Riem
the midpoint of the ith subinterval, and n is even for
 Mth4 Project I (TI 89) Nme: Riem Sums d Defiite Itegrls The re uder the grph of positive fuctio is give y the defiite itegrl of the fuctio. The defiite itegrl c e pproimted y the followig sums: Left Riem
Mth4 Project I (TI 89) Nme: Riem Sums d Defiite Itegrls The re uder the grph of positive fuctio is give y the defiite itegrl of the fuctio. The defiite itegrl c e pproimted y the followig sums: Left Riem
ON n-fold FILTERS IN BL-ALGEBRAS
 Jourl of Alger Numer Theor: Adves d Applitios Volume 2 Numer 29 Pges 27-42 ON -FOLD FILTERS IN BL-ALGEBRAS M. SHIRVANI-GHADIKOLAI A. MOUSSAVI A. KORDI 2 d A. AHMADI 2 Deprtmet of Mthemtis Trit Modres Uiversit
Jourl of Alger Numer Theor: Adves d Applitios Volume 2 Numer 29 Pges 27-42 ON -FOLD FILTERS IN BL-ALGEBRAS M. SHIRVANI-GHADIKOLAI A. MOUSSAVI A. KORDI 2 d A. AHMADI 2 Deprtmet of Mthemtis Trit Modres Uiversit
lecture 16: Introduction to Least Squares Approximation
 97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
Addendum. Addendum. Vector Review. Department of Computer Science and Engineering 1-1
 Addedum Addedum Vetor Review Deprtmet of Computer Siee d Egieerig - Coordite Systems Right hded oordite system Addedum y z Deprtmet of Computer Siee d Egieerig - -3 Deprtmet of Computer Siee d Egieerig
Addedum Addedum Vetor Review Deprtmet of Computer Siee d Egieerig - Coordite Systems Right hded oordite system Addedum y z Deprtmet of Computer Siee d Egieerig - -3 Deprtmet of Computer Siee d Egieerig
INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
 Mthemtics Revisio Guides Itegrtig Trig, Log d Ep Fuctios Pge of MK HOME TUITION Mthemtics Revisio Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C Edecel: C OCR: C OCR MEI: C INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
Mthemtics Revisio Guides Itegrtig Trig, Log d Ep Fuctios Pge of MK HOME TUITION Mthemtics Revisio Guides Level: AS / A Level AQA : C Edecel: C OCR: C OCR MEI: C INTEGRATION TECHNIQUES (TRIG, LOG, EXP FUNCTIONS)
Chapter 2. LOGARITHMS
 Chpter. LOGARITHMS Dte: - 009 A. INTRODUCTION At the lst hpter, you hve studied bout Idies d Surds. Now you re omig to Logrithms. Logrithm is ivers of idies form. So Logrithms, Idies, d Surds hve strog
Chpter. LOGARITHMS Dte: - 009 A. INTRODUCTION At the lst hpter, you hve studied bout Idies d Surds. Now you re omig to Logrithms. Logrithm is ivers of idies form. So Logrithms, Idies, d Surds hve strog
MA123, Chapter 9: Computing some integrals (pp )
 MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
MA13, Chpter 9: Computig some itegrls (pp. 189-05) Dte: Chpter Gols: Uderstd how to use bsic summtio formuls to evlute more complex sums. Uderstd how to compute its of rtiol fuctios t ifiity. Uderstd how
Course 121, , Test III (JF Hilary Term)
 Course 2, 989 9, Test III (JF Hilry Term) Fridy 2d Februry 99, 3. 4.3pm Aswer y THREE questios. Let f: R R d g: R R be differetible fuctios o R. Stte the Product Rule d the Quotiet Rule for differetitig
Course 2, 989 9, Test III (JF Hilry Term) Fridy 2d Februry 99, 3. 4.3pm Aswer y THREE questios. Let f: R R d g: R R be differetible fuctios o R. Stte the Product Rule d the Quotiet Rule for differetitig
Theorem 5.3 (Continued) The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part 2: ab,, then. f x dx F x F b F a. a a. f x dx= f x x
 Chpter 6 Applictios Itegrtio Sectio 6. Regio Betwee Curves Recll: Theorem 5.3 (Cotiued) The Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus, Prt :,,, the If f is cotiuous t ever poit of [ ] d F is tiderivtive of f o [ ] (
Chpter 6 Applictios Itegrtio Sectio 6. Regio Betwee Curves Recll: Theorem 5.3 (Cotiued) The Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus, Prt :,,, the If f is cotiuous t ever poit of [ ] d F is tiderivtive of f o [ ] (
The Weierstrass Approximation Theorem
 The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
REVIEW OF CHAPTER 5 MATH 114 (SECTION C1): ELEMENTARY CALCULUS
 REVIEW OF CHAPTER 5 MATH 4 (SECTION C): EEMENTARY CACUUS.. Are.. Are d Estimtig with Fiite Sums Emple. Approimte the re of the shded regio R tht is lies ove the -is, elow the grph of =, d etwee the verticl
REVIEW OF CHAPTER 5 MATH 4 (SECTION C): EEMENTARY CACUUS.. Are.. Are d Estimtig with Fiite Sums Emple. Approimte the re of the shded regio R tht is lies ove the -is, elow the grph of =, d etwee the verticl
Infinite Series Sequences: terms nth term Listing Terms of a Sequence 2 n recursively defined n+1 Pattern Recognition for Sequences Ex:
 Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
Ifiite Series Sequeces: A sequece i defied s fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers. Usully it s esier to deote sequece i subscript form rther th fuctio ottio.,, 3, re the terms of the sequece
1.1 The FTC and Riemann Sums. An Application of Definite Integrals: Net Distance Travelled
 mth 3 more o the fudmetl theorem of clculus The FTC d Riem Sums A Applictio of Defiite Itegrls: Net Distce Trvelled I the ext few sectios (d the ext few chpters) we will see severl importt pplictios of
mth 3 more o the fudmetl theorem of clculus The FTC d Riem Sums A Applictio of Defiite Itegrls: Net Distce Trvelled I the ext few sectios (d the ext few chpters) we will see severl importt pplictios of
Accuplacer Elementary Algebra Study Guide
 Testig Ceter Studet Suess Ceter Aupler Elemetry Alger Study Guide The followig smple questios re similr to the formt d otet of questios o the Aupler Elemetry Alger test. Reviewig these smples will give
Testig Ceter Studet Suess Ceter Aupler Elemetry Alger Study Guide The followig smple questios re similr to the formt d otet of questios o the Aupler Elemetry Alger test. Reviewig these smples will give
Content: Essential Calculus, Early Transcendentals, James Stewart, 2007 Chapter 1: Functions and Limits., in a set B.
 Review Sheet: Chpter Cotet: Essetil Clculus, Erly Trscedetls, Jmes Stewrt, 007 Chpter : Fuctios d Limits Cocepts, Defiitios, Lws, Theorems: A fuctio, f, is rule tht ssigs to ech elemet i set A ectly oe
Review Sheet: Chpter Cotet: Essetil Clculus, Erly Trscedetls, Jmes Stewrt, 007 Chpter : Fuctios d Limits Cocepts, Defiitios, Lws, Theorems: A fuctio, f, is rule tht ssigs to ech elemet i set A ectly oe
MTH 146 Class 16 Notes
 MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
MTH 46 Clss 6 Notes 0.4- Cotiued Motivtio: We ow cosider the rc legth of polr curve. Suppose we wish to fid the legth of polr curve curve i terms of prmetric equtios s: r f where b. We c view the cos si
REAL ANALYSIS STUDY MATERIAL. B.Sc. Mathematics VI SEMESTER CORE COURSE. (2011 Admission) UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
 REAL ANALYSIS STUDY MATERIAL BSc Mthemtics VI SEMESTER CORE COURSE ( Admissio) UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION THENJIPALAM, CALICUT UNIVERSITY PO, MALAPPURAM, KERALA - 67 65 57 UNIVERSITY
REAL ANALYSIS STUDY MATERIAL BSc Mthemtics VI SEMESTER CORE COURSE ( Admissio) UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION THENJIPALAM, CALICUT UNIVERSITY PO, MALAPPURAM, KERALA - 67 65 57 UNIVERSITY
Introduction of Fourier Series to First Year Undergraduate Engineering Students
 Itertiol Jourl of Adved Reserh i Computer Egieerig & Tehology (IJARCET) Volume 3 Issue 4, April 4 Itrodutio of Fourier Series to First Yer Udergrdute Egieerig Studets Pwr Tejkumr Dtttry, Hiremth Suresh
Itertiol Jourl of Adved Reserh i Computer Egieerig & Tehology (IJARCET) Volume 3 Issue 4, April 4 Itrodutio of Fourier Series to First Yer Udergrdute Egieerig Studets Pwr Tejkumr Dtttry, Hiremth Suresh
( ) 2 3 ( ) I. Order of operations II. Scientific Notation. Simplify. Write answers in scientific notation. III.
 Assessmet Ceter Elemetry Alger Study Guide for the ACCUPLACER (CPT) The followig smple questios re similr to the formt d otet of questios o the Aupler Elemetry Alger test. Reviewig these smples will give
Assessmet Ceter Elemetry Alger Study Guide for the ACCUPLACER (CPT) The followig smple questios re similr to the formt d otet of questios o the Aupler Elemetry Alger test. Reviewig these smples will give
f(bx) dx = f dx = dx l dx f(0) log b x a + l log b a 2ɛ log b a.
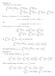 Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Math 104: Final exam solutions
 Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
5.3. The Definite Integral. Limits of Riemann Sums
 . The Defiite Itegrl 4. The Defiite Itegrl I Sectio. we ivestigted the limit of fiite sum for fuctio defied over closed itervl [, ] usig suitervls of equl width (or legth), s - d>. I this sectio we cosider
. The Defiite Itegrl 4. The Defiite Itegrl I Sectio. we ivestigted the limit of fiite sum for fuctio defied over closed itervl [, ] usig suitervls of equl width (or legth), s - d>. I this sectio we cosider
2. Infinite Series 3. Power Series 4. Taylor Series 5. Review Questions and Exercises 6. Sequences and Series with Maple
 Chpter II CALCULUS II.4 Sequeces d Series II.4 SEQUENCES AND SERIES Objectives: After the completio of this sectio the studet - should recll the defiitios of the covergece of sequece, d some limits; -
Chpter II CALCULUS II.4 Sequeces d Series II.4 SEQUENCES AND SERIES Objectives: After the completio of this sectio the studet - should recll the defiitios of the covergece of sequece, d some limits; -
[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.
![[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold. [ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.](/thumbs/78/77732161.jpg) [ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
[ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
f ( x) ( ) dx =
 Defiite Itegrls & Numeric Itegrtio Show ll work. Clcultor permitted o, 6,, d Multiple Choice. (Clcultor Permitted) If the midpoits of equl-width rectgles is used to pproximte the re eclosed etwee the x-xis
Defiite Itegrls & Numeric Itegrtio Show ll work. Clcultor permitted o, 6,, d Multiple Choice. (Clcultor Permitted) If the midpoits of equl-width rectgles is used to pproximte the re eclosed etwee the x-xis
The limit comparison test
 Roerto s Notes o Ifiite Series Chpter : Covergece tests Sectio 4 The limit compriso test Wht you eed to kow lredy: Bsics of series d direct compriso test. Wht you c ler here: Aother compriso test tht does
Roerto s Notes o Ifiite Series Chpter : Covergece tests Sectio 4 The limit compriso test Wht you eed to kow lredy: Bsics of series d direct compriso test. Wht you c ler here: Aother compriso test tht does
Section 2.2. Matrix Multiplication
 Mtri Alger Mtri Multiplitio Setio.. Mtri Multiplitio Mtri multiplitio is little more omplite th mtri itio or slr multiplitio. If A is the prout A of A is the ompute s follow: m mtri, the is k mtri, 9 m
Mtri Alger Mtri Multiplitio Setio.. Mtri Multiplitio Mtri multiplitio is little more omplite th mtri itio or slr multiplitio. If A is the prout A of A is the ompute s follow: m mtri, the is k mtri, 9 m
The Definite Riemann Integral
 These otes closely follow the presettio of the mteril give i Jmes Stewrt s textook Clculus, Cocepts d Cotexts (d editio). These otes re iteded primrily for i-clss presettio d should ot e regrded s sustitute
These otes closely follow the presettio of the mteril give i Jmes Stewrt s textook Clculus, Cocepts d Cotexts (d editio). These otes re iteded primrily for i-clss presettio d should ot e regrded s sustitute
AN INEQUALITY OF GRÜSS TYPE FOR RIEMANN-STIELTJES INTEGRAL AND APPLICATIONS FOR SPECIAL MEANS
 RGMIA Reserch Report Collectio, Vol., No., 998 http://sci.vut.edu.u/ rgmi/reports.html AN INEQUALITY OF GRÜSS TYPE FOR RIEMANN-STIELTJES INTEGRAL AND APPLICATIONS FOR SPECIAL MEANS S.S. DRAGOMIR AND I.
RGMIA Reserch Report Collectio, Vol., No., 998 http://sci.vut.edu.u/ rgmi/reports.html AN INEQUALITY OF GRÜSS TYPE FOR RIEMANN-STIELTJES INTEGRAL AND APPLICATIONS FOR SPECIAL MEANS S.S. DRAGOMIR AND I.
y udv uv y v du 7.1 INTEGRATION BY PARTS
 7. INTEGRATION BY PARTS Ever differetitio rule hs correspodig itegrtio rule. For istce, the Substitutio Rule for itegrtio correspods to the Chi Rule for differetitio. The rule tht correspods to the Product
7. INTEGRATION BY PARTS Ever differetitio rule hs correspodig itegrtio rule. For istce, the Substitutio Rule for itegrtio correspods to the Chi Rule for differetitio. The rule tht correspods to the Product
AP Calculus Notes: Unit 6 Definite Integrals. Syllabus Objective: 3.4 The student will approximate a definite integral using rectangles.
 AP Clculus Notes: Uit 6 Defiite Itegrls Sllus Ojective:.4 The studet will pproimte defiite itegrl usig rectgles. Recll: If cr is trvelig t costt rte (cruise cotrol), the its distce trveled is equl to rte
AP Clculus Notes: Uit 6 Defiite Itegrls Sllus Ojective:.4 The studet will pproimte defiite itegrl usig rectgles. Recll: If cr is trvelig t costt rte (cruise cotrol), the its distce trveled is equl to rte
1 Tangent Line Problem
 October 9, 018 MAT18 Week Justi Ko 1 Tget Lie Problem Questio: Give the grph of fuctio f, wht is the slope of the curve t the poit, f? Our strteg is to pproimte the slope b limit of sect lies betwee poits,
October 9, 018 MAT18 Week Justi Ko 1 Tget Lie Problem Questio: Give the grph of fuctio f, wht is the slope of the curve t the poit, f? Our strteg is to pproimte the slope b limit of sect lies betwee poits,
( a n ) converges or diverges.
 Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
n 2 + 3n + 1 4n = n2 + 3n + 1 n n 2 = n + 1
 Ifiite Series Some Tests for Divergece d Covergece Divergece Test: If lim u or if the limit does ot exist, the series diverget. + 3 + 4 + 3 EXAMPLE: Show tht the series diverges. = u = + 3 + 4 + 3 + 3
Ifiite Series Some Tests for Divergece d Covergece Divergece Test: If lim u or if the limit does ot exist, the series diverget. + 3 + 4 + 3 EXAMPLE: Show tht the series diverges. = u = + 3 + 4 + 3 + 3
18.01 Calculus Jason Starr Fall 2005
 18.01 Clculus Jso Strr Lecture 14. October 14, 005 Homework. Problem Set 4 Prt II: Problem. Prctice Problems. Course Reder: 3B 1, 3B 3, 3B 4, 3B 5. 1. The problem of res. The ciet Greeks computed the res
18.01 Clculus Jso Strr Lecture 14. October 14, 005 Homework. Problem Set 4 Prt II: Problem. Prctice Problems. Course Reder: 3B 1, 3B 3, 3B 4, 3B 5. 1. The problem of res. The ciet Greeks computed the res
Surds, Indices, and Logarithms Radical
 MAT 6 Surds, Idices, d Logrithms Rdicl Defiitio of the Rdicl For ll rel, y > 0, d ll itegers > 0, y if d oly if y where is the ide is the rdicl is the rdicd. Surds A umber which c be epressed s frctio
MAT 6 Surds, Idices, d Logrithms Rdicl Defiitio of the Rdicl For ll rel, y > 0, d ll itegers > 0, y if d oly if y where is the ide is the rdicl is the rdicd. Surds A umber which c be epressed s frctio
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL. Examination for the Degrees of B.Sc. and M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS 1B, SOLUTIONS MATH (Paper Code MATH-10006)
 UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
Thomas Whitham Sixth Form
 Thoms Whithm ith Form Pure Mthemtis Uit lger Trigoometr Geometr lulus lger equees The ifiite sequee of umers U U U... U... is si to e () overget if U L fiite limit s () iverget to if U s Emple The sequee...
Thoms Whithm ith Form Pure Mthemtis Uit lger Trigoometr Geometr lulus lger equees The ifiite sequee of umers U U U... U... is si to e () overget if U L fiite limit s () iverget to if U s Emple The sequee...
Integration. Table of contents
 Itegrtio Tle of cotets. Defiitio of Riem Itegrtio.................................. Prtitio of itervls........................................... Upper/lower Riem sum......................................3.
Itegrtio Tle of cotets. Defiitio of Riem Itegrtio.................................. Prtitio of itervls........................................... Upper/lower Riem sum......................................3.
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Lecture 17
 CS 70 Discrete Mthemtics d Proility Theory Sprig 206 Ro d Wlrd Lecture 7 Vrice We hve see i the previous ote tht if we toss coi times with is p, the the expected umer of heds is p. Wht this mes is tht
CS 70 Discrete Mthemtics d Proility Theory Sprig 206 Ro d Wlrd Lecture 7 Vrice We hve see i the previous ote tht if we toss coi times with is p, the the expected umer of heds is p. Wht this mes is tht
GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS. Linear Equations. x l ( 3,1 ) _x-axis. Origin ( 0, 0 ) Slope = change in y change in x. Equation for l 1.
 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS Qudrt II Qudrt I ORDERED PAIR: The first umer i the ordered pir is the -coordite d the secod umer i the ordered pir is the y-coordite. (, ) Origi ( 0, 0 ) _-is Lier Equtios Qudrt
GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS Qudrt II Qudrt I ORDERED PAIR: The first umer i the ordered pir is the -coordite d the secod umer i the ordered pir is the y-coordite. (, ) Origi ( 0, 0 ) _-is Lier Equtios Qudrt
Reversing the Arithmetic mean Geometric mean inequality
 Reversig the Arithmetic me Geometric me iequlity Tie Lm Nguye Abstrct I this pper we discuss some iequlities which re obtied by ddig o-egtive expressio to oe of the sides of the AM-GM iequlity I this wy
Reversig the Arithmetic me Geometric me iequlity Tie Lm Nguye Abstrct I this pper we discuss some iequlities which re obtied by ddig o-egtive expressio to oe of the sides of the AM-GM iequlity I this wy
Math 2414 Activity 17 (Due with Final Exam) Determine convergence or divergence of the following alternating series: a 3 5 2n 1 2n 1
 Mth 44 Activity 7 (Due with Fil Exm) Determie covergece or divergece of the followig ltertig series: l 4 5 6 4 7 8 4 {Hit: Loo t 4 } {Hit: } 5 {Hit: AST or just chec out the prtil sums} {Hit: AST or just
Mth 44 Activity 7 (Due with Fil Exm) Determie covergece or divergece of the followig ltertig series: l 4 5 6 4 7 8 4 {Hit: Loo t 4 } {Hit: } 5 {Hit: AST or just chec out the prtil sums} {Hit: AST or just
Fig. 1. I a. V ag I c. I n. V cg. Z n Z Y. I b. V bg
 ymmetricl Compoets equece impedces Although the followig focuses o lods, the results pply eqully well to lies, or lies d lods. Red these otes together with sectios.6 d.9 of text. Cosider the -coected lced
ymmetricl Compoets equece impedces Although the followig focuses o lods, the results pply eqully well to lies, or lies d lods. Red these otes together with sectios.6 d.9 of text. Cosider the -coected lced
Approximations of Definite Integrals
 Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
Numerical Integration
 Numericl tegrtio Newto-Cotes Numericl tegrtio Scheme Replce complicted uctio or tulted dt with some pproimtig uctio tht is esy to itegrte d d 3-7 Roerto Muscedere The itegrtio o some uctios c e very esy
Numericl tegrtio Newto-Cotes Numericl tegrtio Scheme Replce complicted uctio or tulted dt with some pproimtig uctio tht is esy to itegrte d d 3-7 Roerto Muscedere The itegrtio o some uctios c e very esy
Options: Calculus. O C.1 PG #2, 3b, 4, 5ace O C.2 PG.24 #1 O D PG.28 #2, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG #1, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.
 O C. PG.-3 #, 3b, 4, 5ce O C. PG.4 # Optios: Clculus O D PG.8 #, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG.3-33 #, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.36-37 #, 3 O G. PG.4 #c, 3c O G. PG.43 #, O H PG.49 #, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 O I. PG.53-54 #5, 8
O C. PG.-3 #, 3b, 4, 5ce O C. PG.4 # Optios: Clculus O D PG.8 #, 3, 4, 5, 7 O E PG.3-33 #, 3, 4, 5 O F PG.36-37 #, 3 O G. PG.4 #c, 3c O G. PG.43 #, O H PG.49 #, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 O I. PG.53-54 #5, 8
THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING
 OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
OLLSCOIL NA héireann, CORCAIGH THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND, CORK COLÁISTE NA hollscoile, CORCAIGH UNIVERSITY COLLEGE, CORK SUMMER EXAMINATION 2005 FIRST ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MA008 Clculus d Lier
EXERCISE a a a 5. + a 15 NEETIIT.COM
 - Dowlod our droid App. Sigle choice Type Questios EXERCISE -. The first term of A.P. of cosecutive iteger is p +. The sum of (p + ) terms of this series c be expressed s () (p + ) () (p + ) (p + ) ()
- Dowlod our droid App. Sigle choice Type Questios EXERCISE -. The first term of A.P. of cosecutive iteger is p +. The sum of (p + ) terms of this series c be expressed s () (p + ) () (p + ) (p + ) ()
Elementary Linear Algebra
 Elemetry Lier Alger Ato & Rorres, th Editio Lecture Set Chpter : Systems of Lier Equtios & Mtrices Chpter Cotets Itroductio to System of Lier Equtios Gussi Elimitio Mtrices d Mtri Opertios Iverses; Rules
Elemetry Lier Alger Ato & Rorres, th Editio Lecture Set Chpter : Systems of Lier Equtios & Mtrices Chpter Cotets Itroductio to System of Lier Equtios Gussi Elimitio Mtrices d Mtri Opertios Iverses; Rules
3.7 The Lebesgue integral
 3 Mesure d Itegrtio The f is simple fuctio d positive wheever f is positive (the ltter follows from the fct tht i this cse f 1 [B,k ] = for ll k, ). Moreover, f (x) f (x). Ideed, if x, the there exists
3 Mesure d Itegrtio The f is simple fuctio d positive wheever f is positive (the ltter follows from the fct tht i this cse f 1 [B,k ] = for ll k, ). Moreover, f (x) f (x). Ideed, if x, the there exists
