A New SPH Equations Including Variable Smoothing Lengths Aspects and Its Implementation
|
|
|
- Whitney Cory Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMPUTATIOAL MECHAICS ISCM007, July 30-August 1, 007, Beng,Chna 007 Tsnghua Unversty Press & Sprnger A ew SPH Equatons Includng Varable Smoothng Lengths Aspects and Its Implementaton Hongfu Qang*, Weran Gao Faculty of Mechancal & Propulson Engneerng, X an H-Tech Insttute, X an, Shaanx, Chna Emal: qang@63.net Abstract ew SPH equatons ncludng fully varable smoothng length aspects and ts mplementaton are proposed n ths paper. Unlke the exstng adaptve kernel SPH method, the fully varable smoothng lengths effects have been consdered essentally n the scheme based on the adaptve symmetrcal kernel estmaton. Among the new equatons, the evoluton equaton of densty s derved n essence, t s mplctly coupled wth varable smoothng length equaton; the momentum equaton and energy equaton are derved from Sprngel s fully conservatve formulaton SPH usng the symmetrcal kernel estmaton nstead of the scatter kernel estmaton algorthm. Because the new SPH densty evoluton equaton s mplctly coupled wth varable smoothng length equaton, an addtonal teraton process s employed necessary to solve the evoluton equatons of densty and the varable smoothng lengths equaton, and the SPH momentum equaton and the energy equaton s solved n nature, only the lttle cost s used n the teraton algorthm. The new equatons and ts algorthm are tested va two 1D shock-tube problems and a D Sedov problem, t s showed that the new algorthm corrects the varable smoothng lengths effect farly well, especally n the D Sedov problem, the pressure peak s captured by the presented method more accurately than that of Sprngel s scheme, and the accuracy of pressure at the center n Sedov problem s mproved also. The new method can deal wth the large densty gradent and large smoothng length gradent problems well, such as large deformaton and serous dstorton problems n hgh velocty mpact and blastng phenomenon. Key words: SPH, meshless, algorthm, shock-tube, Sedov problem ITRODUCTIO Usually the local nterpolaton resoluton s determned by the smoothng length h n SPH method. Early SPH smulatons used a fxed h for all partcles [1] or h s taken as a globally tme-dependent functon of the mean number densty of partcles n the system []. However, SPH method usng the constant smoothng length n space would yeld more accurately estmate n hgh partcle neghborhood regons than n low regons, and would furthermore not take full advantages of the partcle local dstrbuton. Consderng both the consstency and effcency, an SPH method wth local varable smoothng length algorthms was frstly presented by Gngold & Monaghan [3], whch adapts h accordng to the local number densty of partcles. Evard [4] also proposed the local varable smoothng length algorthms n SPH, he ponted out the h effects, whch refers to the effects of the varable spatal h on the estmaton of gradents, and ths knds of effects can be gnored safely. But accordng to research by Hernqust et al [5], the ntroducton of varyng smoothng length can lead to serous problems wth badly energy conservaton n certan stuatons. elson [6] conducted the research n detal on how the h affects the result, he ndcated that the addtonal h terms should appear n the partcle equatons of moton. Serna et al [7] also dd the smlar analyss. However, the above approach to correct the h effects leads to somewhat complex forms for the dynamcal equatons and 817
2 ntroduces nose nto smoothed estmates, and such verson of SPH method has not found wdespread usage fnally. Another dea to treat the nconsstent problems of varyng smoothng length s proposed by Sprngel et al [8], they derved a new formulaton of SPH whch employs varable smoothng lengths and conserves energy and entropy by usng the Lagrangan formalsm, and the method s equvalent to Thomas [9] equatons when constant smoothng length algorthm s adopted. Then Monaghan [10] also presented new SPH equatons va smlar way, whch mproves the relatonshp between the smoothng length and densty, and the conservaton propertes of the new equatons was analyzed n hs paper. The Sprngel SPH equatons [8] used the scatter kernel estmaton, but the scatter kernel estmaton produces more errors than the symmetrcal kernel estmaton method [11]. We found that the Sprngel s method corrects the h effects well, but worses the precson n the smulaton both at the front of expand waves and the contact dscontnues, where the smoothng length are not dstrbuted smoothly. In ths paper, new SPH equatons ncludng fully varable smoothng length aspects s presented, and the adaptve symmetrcal kernel estmaton algorthm s adopted. Among the new equatons, the evoluton equaton of densty s derved n essence, t s mplctly coupled wth varable smoothng length equaton; the momentum equaton and energy equaton are derved from Sprngel s fully conservatve formulaton SPH usng the symmetrcal kernel estmaton nstead of the scatter kernel estmaton algorthm. The mplementaton of new SPH equatons s also dscussed n ths paper, an addtonal teraton process s employed to solve the coupled densty equaton and varable smoothng length equaton, and the momentum equaton and energy equaton are solved n nature, only lttle cost s used n the teraton calculaton. Three test problems are presented to verfy the new equatons, there are the 1D Blast-Wave shock-tube problem, 1D Sögreen shock-tube problem and D Sedov problem. The numerc results show that the new equaton corrects the varable smoothng length effect farly well, especally n the D Sedov problem, the pressure peak s captured by the presented method more accurately than that of Sprngel s scheme, and the accuracy of pressure at the center n Sedov problem s mproved also. The new method can deal wth the large densty gradent and large smoothng length gradent problems well, such as large deformaton and serous dstorton problems n hgh velocty mpact and blastng phenomenon. SPH EQUATIOS WITH VARIABLE SMOOTHIG LEGTH 1. Evoluton Equaton of Densty As n SPH calculatons, the contnuous densty feld at the locaton r s evaluated as Eq. (1), ( ) = mw (, h) ρ r r r (1) = 1 r r s a smooth functon, usually referred to as the nterpolatng kernel, h s the smoothng length, or named as bandwdth of the kernel, whch determnes the kernel estmatng precson, and s the number of neghbors of partcle. W, h d = 1 lm W r r, h = δ r r. Where ρ s the densty of flud partcle, m s the mass of partcle, W(, h) The kernel functon satsfes the condtons ( r r ) r, and ( ) ( ) Ω Usually the smoothng lengths should vared to keep the number of neghbors for each partcle mantaned at a nearly fxed value, here, we select smoothng lengths by requrng that a fxed mass s contaned wthn the volume n h radus[8], vz. Eq. () σh ρ = M () d sph Where the d s the number of dmensons, and σ s constant number wth the values, π, 4 3 π correspond to dfferent dmensons. The use of Eq. () leads to the nconsstence spatal and temporal dstrbutng of h h r, t. smoothng length,.e., the smoothng length s both the functon of poston and tme, ( ) 818 h 0 = For the kernel estmaton wth varable smoothng length, the symmetrcal kernel estmaton can get hgher
3 order precson compared to the scatter kernel estmaton [11], we adopt the symmetrcal kernel estmaton, and the symmetrcal kernel estmaton form of Eq. () s ρ ( r ) = mw (3) = 1 1 Where W = W( r, h ), r = r r, h = ( h + h ) By dfferentatng Eq. (3) wth respect to tme, we get dρ d 1 dh dh W = mw = m W dt dt v + + dt dt h (4) Where v = v v, v s the velocty of partcle, ths s the new SPH evoluton equaton of densty ncludng varable smoothng length, and t equals to normal SPH evoluton equaton of densty when the smoothng length keep constant.. Equaton of Moton ow, we derved the new SPH equaton of moton based on Sprngel s fully conservatve formulaton of SPH [8], and replace the scatter kernel estmaton algorthm by the symmetrcal kernel estmaton. The Lagrangan L for the non-dsspatve moton of a flud s [10] 1 = ρ ( ρ, ) (5) L v u s dq Where v s the velocty, u s the thermal energy per unt mass, ρ s the densty and s s the entropy. For the strctly adabatc flow, from the frst law of thermodynamcs we know that u P = ρ ρ s Where P s pressure.. The SPH form of Eq. (5) s 1 L ( qq&, ) = mb vb u( ρb, sb) (7) b Where q = ( r1, Kr, h1, K h),ncludng the poston and smoothng length of partcles. Such process s consdered as dscretely approxmatng of contnues flud phase space to dmensonal. The second half of q,.e., smoothng length, s provded constrans Eq. (), n order to mantan the typcal number of smoothng neghbors for partcles. d ( ) = = 0, = 1 φ q σh ρ M K (8) sph We now obtan the equatons of moton from the Lagrangan equaton wth constrants Eq. (9) d L L φ =, = 1K dt q& q q λ = 1 Where λ s Lagrange multples. The second half of these equatons gves P ρ m d h h ρ d 1 d = σ ρλ + σ λ ρ h = 1 h (10) Where (6) (9) 819
4 ρ = mk Wk = m W (11) h k h h Among Eq. (11), the symmetrcal kernel estmaton s ntroduced, and W W(, h ) From the frst equatons of Eq. (6), we get 80 = r. dv P 1 ρ d m = m 1 σλ h ρ (1) dt = 1 ρ m P Usng ρ m W δ mk Wk k = 1 = + (13) The fnal equatons of moton are obtaned as dv P P = m f + f W dt = 1 ρ ρ (14) Where 1 ρ d f = 1 σλ h m P (15) ρ The λ n Eq. (15) s calculated from Eq. (10). Because of h s zero except the neghbor partcles, and the value of W ρ s lttle outsde one smoothng length from the center of partcle, we gnore the h h and smplfy the Eq. (15) nto Eq. (16). The result of numercal smulaton also support ths dea. 1 h ρ f = 1 + (16) dρ h The corrected SPH equaton of moton (14) s equal to the standard SPH equaton of moton f the effect of λ are gnored 3. Equaton of Thermal Energy From the frst law of thermodynamcs, we know that P Tds = du + Pdv = du d ρ (17) ρ Where T s the temperature, s s the entropy per unt mass, u s the thermal energy per unt mass, P s the pressure and v s the volume per unt mass. If the entropy mantans constant, the tme rate of change of thermal energy s du P d ρ = (18) dt ρ dt The SPH form of Eq. (18) s du P d ρ = (19) dt ρ dt 4. Varable Smoothng Length Equaton and Implementaton of Equatons The smoothng length h s the functon both of space and tme, by dfferentatng Eq. () wth respect to tme, we obtaned dh 1 h dρ = (0) dt d ρ dt
5 Because the dh dt s related to dρ dt, and the dρ dt s related to all ts neghbors dh dt and dh dt, t s dffcult to solve evoluton equaton of densty Eq. (4) and varable smoothng length equaton Eq. (0) drectly, here we employ an teraton process to solve these two equatons. Frstly let dh dt, and calculate the dρ dt through Eq. (4), then usng the ntermedate values of dρ dt to get dh dt from Eq. (0), and update the new dρ dt usng the value of dh dt va Eq. (4). Repeat the above process untl dρ dt has no sgnfcant change n one loop. The equaton of moton and equaton of energy are solved n nature. Usually only a lttle cost s spent n the teraton calculaton. UMERICAL TESTS In order to verfy the capabltes of the present method, two 1D shock problems and one D Sedov problems are tested, whch the smoothng length has changes sgnfcantly n the smulatons. Amongst them, the gas equaton of state as P = ( γ 1) ρu s used, where γ = 1.4. The cubc splne kernel s used [1] also. The correcton term of equaton of moton Eq. (14) n ths paper s calculated from Eq. (16), that means the effect of ρ h are gnored. The approprate artfcal vscosty [13] and artfcal heat [14] are ntroduced to stable the smulaton of shock, and the smulaton s updated usng a standard leapfrog ntegrator. 1. Blast-Wave Problem The Blast-Wave problem s a dffcult test whch nvolves extremely supersonc 5 flows, and the ntal pressure of the left sde to the dscontnuty s 10 tmes to the rght sde. The ntal condton s the deal gas wth Eq. (1). There are 800 partcles of equal mass mplementng n ths smulaton, and the ntal contact dscontnues s set at x = 0. The dscontnuous of physcal parameters are smoothed ntally [15]. ( ρ, u, p) = ( 1,0,1000 ) L (1) ( ρ, u, p) = ( 1,0,0.01) R The densty vs poston, velocty vs poston and pressure vs poston are showed n Fg 1. In ths test, the densty peak value s overestmated by about 10% and the energy conserves badly when standard SPH method s adopt. Compared wth the former, both the Sprngel s method and the present method n the paper performs well, and the smulaton error n densty peak value less than 1%. Furthermore, f the correcton on equaton of moton s gnored when f = 1, the new method also can get the correct results, unforturnately, the Sprngel s method can not obtan. Fgure 1: Results for the one-dmensonal blast-wave problem at t = s 800 partcles of equal mass are arranged on each sde of the ntal nterface. Results for dfferent SPH formulatons are compared wth densty profle (left), velocty profle (mddle) and pressure profle (rght). The Sprngel s method (trangles) new method presented n ths paper (dots) compares very well wth exact soluton (sold lne), however the standard SPH (squares) overestmated the densty peakvalue by about 10%.. Sögreen Problem The exact soluton of Sögreen problem contans two expand wave and a week constant contact dscontnues, the pressure value at contact s very lttle. Ths problem can check the ablty 81
6 of numercal method when smulate the low densty and low energy problem. The ntal condton s descrbe as Eq. (), and the setup of smulaton s same as above problem. ( ρ, u, p) = ( 1,,0.4 ) L () ρ, u, p = 1,,0.4 ( ) ( ) R The densty vs poston, velocty vs poston and pressure vs poston are showed n Fg 1. The standard SPH, Sprngel s method and the new method n ths paper all perform well. Among the result obtaned by Sprngel s method, there are small umps at the front of expand waves of densty and nternal profle, whereas the new method n ths paper and the standard SPH do not have ths problem. The new method get the lowest densty 0.04 at x = 0 (exact value s 0.015), yet the Standard SPH and Sprngel s method get the lowest densty great than Fgure : Results for the one-dmensonal Sögreen problem at t = 0.3s 800 partcles of equal mass are arraged on each sde of the ntal nterface. Results for dfferent SPH formulatons are compared wth densty profle (left), velocty profle (mddle) and pressure profle (rght), and all methods perform well. There are small umps at the front of expand waves of densty and pressure profle obtaned by Sprngel SPH (trangles), whereas the new method (dots) n ths paper do not have ths problem. And the new method get the lowest densty 0.04 at x = 0 (exact value s 0.015), yet the Standard SPH (squares) and Sprngel s method get the lowest densty great than D Sedov Problem The D Sedov Problem nvolves a cylndrcal blast wave from a δ functon ntal pressure perturbaton n a homogeneous medum at the rest. The analytcal soluton of ths problem was frstly derved by Sedov[16]. In ths test, there are = partcles arranged n a rectangle area, the ntal condton s Eq. (3), 5 T ρ ( 1, 0,1 10 ), x 0 T v = ( γ 1) e (3) P 1, 0,, x = 0 V0 Where e = 1 s the quantty of energy deposted at r = 0, V 0 s the volume of the center partcle. The standard SPH solved wth the evoluton equaton of densty cannot smulate ths problem successfully. The partcle dstrbuton at the tme t=0.05s s showed n Fg. 3, by comparson we fnd that the present method n ths paper gets more smoothng dstrbuton of partcles than Sprngel s method. Then the comparson of radal profles of densty and pressure s llustrated n Fg. 4, that the poston of the densty and pressure peak s captured by the presented method at r 0.3, t s very close to the exact soluton, however t s mproperly captured by Sprngel s method ( r 0.3 ). The accuracy of pressure at the center n Sedov problem s mproved also by usng the new method, but the center pressure get by Sprngel s method s much hgher than exact soluton. 8
7 Fgure 3: Partcle dstrbuton plot for D cylndrcal Sedov blast wave wth partcles at tme t=0.05s The sze of partcle crcle represents the smoothng length scale. Left: the results from Sprngel method. Rght: the results from the new method n ths paper. It shows that the smulated results by the new method get more smoothng partcle dstrbuton than that by Sprngel s method. Fgure 4: Radal profles of mass densty (left) and pressure (rght) for the D cylndrcal Sedov blast wave smulaton at t=0.05s The numercal results by the Sprngel s method (trangles) and the new method presented n ths paper (dots) are compared wth the exact soluton (sold lne). It shows that the new method obtaned more accurate than Sprngel s method both at poston of densty peak and the center pressure. COCLUSIOS We have derved a corrected SPH equaton ncludng varable smoothng length essentally, among the new equatons, the symmetrcal kernel estmaton s employed, that lead n mplctly couplng relaton of the evoluton equaton of densty and varable smoothng length equaton, the equaton of moton and equaton of energy are derved n the smlar way as Sprngel s fully conservatve formulaton of SPH. An teraton process s used to solve the coupled evoluton equaton of densty and the varable smoothng length equaton, and other equatons are solved drectly, only a lttle calculaton s needed n the teraton calculatons. 83
8 Two 1D shock problems and the D Sedov problems are presented to test the behavor of new formulaton and compared wth standard SPH method and Sprngel s method. The smulaton result demonstrates the new algorthms corrects the varable smoothng lengths effect farly well, especally n the D Sedov problem, the pressure peak s captured by the presented method more accurately than that of Sprngel s scheme, and the accuracy of pressure at the center n Sedov problem s mproved also. Ths new method can deal wth the large densty gradent and large smoothng length gradent problems well, such as large deformaton and serous dstorton problems n hgh velocty mpact and blastng phenomenon. Acknowledgements The support of ew Century Excellent Talents n Unversty (CET) and o for atonal 973 Program n Chna s gratefully acknowledged. REFERECES 1. Lucy LB. A numercal approach to the testng of the fsson hypothess. The Astronomcal Journal, 1977; 8(1): Gngold RA, Monaghan JJ. Smoothed partcle hydrodynamcs: theory and applcaton to non-sphercal stars. Mon. ot. R. astr. Soc., 1977; 181: Gngold RA, Monaghan JJ. Kernel estmates as a bass for general partcle methods n hydrodynamcs. Comput. Phys., 198; 46: Evrard AE. Beyond n-body: 3D cosmologcal gas dynamcs. Mon. ot. R. astr. Soc., 1988; 35: Hernqust L. Some cautonary remarks about smoothed partcle hydrodynamcs. The Astronomcal Journal, 1993; 404: elson RP, Papalozou JC. Varable smoothng lengths and energy conservaton n smoothed partcle hydrodynamcs. Mon. ot. R. astr. Soc., 1994; 70: Serna A, Alm JM, Cheze JP. Adaptve smooth partcle hydrodynamcs and partcle-partcle coupled codes: energy and entropy conservaton. The Astronomcal Journal, 1996; 461: Sprngel V, Hernqust L. Cosmologcal smoothed partcle hydrodynamcs smulatons: the entropy equaton. Mon. ot. R. Astr. Soc., 00; 333: Thomas PA, Couchman HMP. Smulatng the formaton of a cluster of galaxes. Mon. ot. R. Astr. Soc., 199; 57: Monaghan JJ. SPH compressble turbulence. Mon. ot. R. astr. Soc., 00; 335(5): Hernqust L, Katz. TreeSPH: a unfcaton of SPH wth the herarchcal tree method. The Astronomcal Journal Supplement Seres, 1989; 70: Monaghan JJ. Smoothed partcle hydrodynamcs. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys., 199; 30: Monaghan JJ. Gngold RA. Shock smulaton by the partcle method SPH. J. Comput. Phys., 1983; 5: Monaghan JJ. SPH meets the shocks of noh. 1988, (unpublshed preprnt). 15. Monaghan JJ. SPH and Remann solver. J. Comput. Phys., 1997; 136: Sedov LI. Smlarty and Dmensonal Methods n Mechancs. Academc Press Inc., ew York, USA,
Tensor Smooth Length for SPH Modelling of High Speed Impact
 Tensor Smooth Length for SPH Modellng of Hgh Speed Impact Roman Cherepanov and Alexander Gerasmov Insttute of Appled mathematcs and mechancs, Tomsk State Unversty 634050, Lenna av. 36, Tomsk, Russa RCherepanov82@gmal.com,Ger@npmm.tsu.ru
Tensor Smooth Length for SPH Modellng of Hgh Speed Impact Roman Cherepanov and Alexander Gerasmov Insttute of Appled mathematcs and mechancs, Tomsk State Unversty 634050, Lenna av. 36, Tomsk, Russa RCherepanov82@gmal.com,Ger@npmm.tsu.ru
arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 16 Sep 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 16 Sep 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 16 Sep 2013](/thumbs/71/66225386.jpg) Three-Dmensonal Smoothed Partcle Hydrodynamcs Method for Smulatng Free Surface Flows Rzal Dw Prayogo a,b, Chrstan Fredy Naa a a Faculty of Mathematcs and Natural Scences, Insttut Teknolog Bandung, Jl.
Three-Dmensonal Smoothed Partcle Hydrodynamcs Method for Smulatng Free Surface Flows Rzal Dw Prayogo a,b, Chrstan Fredy Naa a a Faculty of Mathematcs and Natural Scences, Insttut Teknolog Bandung, Jl.
Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer
 Master degree n Mechancal Engneerng Numercal Heat and Mass Transfer 06-Fnte-Dfference Method (One-dmensonal, steady state heat conducton) Fausto Arpno f.arpno@uncas.t Introducton Why we use models and
Master degree n Mechancal Engneerng Numercal Heat and Mass Transfer 06-Fnte-Dfference Method (One-dmensonal, steady state heat conducton) Fausto Arpno f.arpno@uncas.t Introducton Why we use models and
Computational Fluid Dynamics. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Simulations. Smoothing Kernels and Basis of SPH
 Computatonal Flud Dynamcs If you want to learn a bt more of the math behnd flud dynamcs, read my prevous post about the Naver- Stokes equatons and Newtonan fluds. The equatons derved n the post are the
Computatonal Flud Dynamcs If you want to learn a bt more of the math behnd flud dynamcs, read my prevous post about the Naver- Stokes equatons and Newtonan fluds. The equatons derved n the post are the
N-Body Simulation. Typical uncertainty: π = 4 Acircle/Asquare! 4 ncircle/n. πest π = O(n
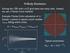 N-Body Smulaton Solvng the CBE wth a 6-D grd takes too many cells. Instead, we use a Monte-Carlo method. Example: Monte-Carlo calculaton of π. Scatter n ponts n square; count number ncrcle fallng wthn
N-Body Smulaton Solvng the CBE wth a 6-D grd takes too many cells. Instead, we use a Monte-Carlo method. Example: Monte-Carlo calculaton of π. Scatter n ponts n square; count number ncrcle fallng wthn
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION
 NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 Introducton Dfferentaton s a method to compute the rate at whch a dependent output y changes wth respect to the change n the ndependent nput x. Ths rate of change s called the
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 Introducton Dfferentaton s a method to compute the rate at whch a dependent output y changes wth respect to the change n the ndependent nput x. Ths rate of change s called the
COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD
 COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD Ákos Jósef Lengyel, István Ecsed Assstant Lecturer, Professor of Mechancs, Insttute of Appled Mechancs, Unversty of Mskolc, Mskolc-Egyetemváros,
COMPOSITE BEAM WITH WEAK SHEAR CONNECTION SUBJECTED TO THERMAL LOAD Ákos Jósef Lengyel, István Ecsed Assstant Lecturer, Professor of Mechancs, Insttute of Appled Mechancs, Unversty of Mskolc, Mskolc-Egyetemváros,
CONTROLLED FLOW SIMULATION USING SPH METHOD
 HERI COADA AIR FORCE ACADEMY ROMAIA ITERATIOAL COFERECE of SCIETIFIC PAPER AFASES 01 Brasov, 4-6 May 01 GEERAL M.R. STEFAIK ARMED FORCES ACADEMY SLOVAK REPUBLIC COTROLLED FLOW SIMULATIO USIG SPH METHOD
HERI COADA AIR FORCE ACADEMY ROMAIA ITERATIOAL COFERECE of SCIETIFIC PAPER AFASES 01 Brasov, 4-6 May 01 GEERAL M.R. STEFAIK ARMED FORCES ACADEMY SLOVAK REPUBLIC COTROLLED FLOW SIMULATIO USIG SPH METHOD
(Online First)A Lattice Boltzmann Scheme for Diffusion Equation in Spherical Coordinate
 Internatonal Journal of Mathematcs and Systems Scence (018) Volume 1 do:10.494/jmss.v1.815 (Onlne Frst)A Lattce Boltzmann Scheme for Dffuson Equaton n Sphercal Coordnate Debabrata Datta 1 *, T K Pal 1
Internatonal Journal of Mathematcs and Systems Scence (018) Volume 1 do:10.494/jmss.v1.815 (Onlne Frst)A Lattce Boltzmann Scheme for Dffuson Equaton n Sphercal Coordnate Debabrata Datta 1 *, T K Pal 1
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM
 ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
High resolution entropy stable scheme for shallow water equations
 Internatonal Symposum on Computers & Informatcs (ISCI 05) Hgh resoluton entropy stable scheme for shallow water equatons Xaohan Cheng,a, Yufeng Ne,b, Department of Appled Mathematcs, Northwestern Polytechncal
Internatonal Symposum on Computers & Informatcs (ISCI 05) Hgh resoluton entropy stable scheme for shallow water equatons Xaohan Cheng,a, Yufeng Ne,b, Department of Appled Mathematcs, Northwestern Polytechncal
Module 1 : The equation of continuity. Lecture 1: Equation of Continuity
 1 Module 1 : The equaton of contnuty Lecture 1: Equaton of Contnuty 2 Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer: Modules 1. THE EQUATION OF CONTINUITY : Lectures 1-6 () () () (v) (v) Overall Mass Balance Momentum
1 Module 1 : The equaton of contnuty Lecture 1: Equaton of Contnuty 2 Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer: Modules 1. THE EQUATION OF CONTINUITY : Lectures 1-6 () () () (v) (v) Overall Mass Balance Momentum
STUDY ON TWO PHASE FLOW IN MICRO CHANNEL BASED ON EXPERI- MENTS AND NUMERICAL EXAMINATIONS
 Blucher Mechancal Engneerng Proceedngs May 0, vol., num. www.proceedngs.blucher.com.br/evento/0wccm STUDY ON TWO PHASE FLOW IN MICRO CHANNEL BASED ON EXPERI- MENTS AND NUMERICAL EXAMINATIONS Takahko Kurahash,
Blucher Mechancal Engneerng Proceedngs May 0, vol., num. www.proceedngs.blucher.com.br/evento/0wccm STUDY ON TWO PHASE FLOW IN MICRO CHANNEL BASED ON EXPERI- MENTS AND NUMERICAL EXAMINATIONS Takahko Kurahash,
NON-CENTRAL 7-POINT FORMULA IN THE METHOD OF LINES FOR PARABOLIC AND BURGERS' EQUATIONS
 IJRRAS 8 (3 September 011 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol8issue3/ijrras_8_3_08.pdf NON-CENTRAL 7-POINT FORMULA IN THE METHOD OF LINES FOR PARABOLIC AND BURGERS' EQUATIONS H.O. Bakodah Dept. of Mathematc
IJRRAS 8 (3 September 011 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol8issue3/ijrras_8_3_08.pdf NON-CENTRAL 7-POINT FORMULA IN THE METHOD OF LINES FOR PARABOLIC AND BURGERS' EQUATIONS H.O. Bakodah Dept. of Mathematc
Finite Element Modelling of truss/cable structures
 Pet Schreurs Endhoven Unversty of echnology Department of Mechancal Engneerng Materals echnology November 3, 214 Fnte Element Modellng of truss/cable structures 1 Fnte Element Analyss of prestressed structures
Pet Schreurs Endhoven Unversty of echnology Department of Mechancal Engneerng Materals echnology November 3, 214 Fnte Element Modellng of truss/cable structures 1 Fnte Element Analyss of prestressed structures
STATISTICAL MECHANICS
 STATISTICAL MECHANICS Thermal Energy Recall that KE can always be separated nto 2 terms: KE system = 1 2 M 2 total v CM KE nternal Rgd-body rotaton and elastc / sound waves Use smplfyng assumptons KE of
STATISTICAL MECHANICS Thermal Energy Recall that KE can always be separated nto 2 terms: KE system = 1 2 M 2 total v CM KE nternal Rgd-body rotaton and elastc / sound waves Use smplfyng assumptons KE of
Power law and dimension of the maximum value for belief distribution with the max Deng entropy
 Power law and dmenson of the maxmum value for belef dstrbuton wth the max Deng entropy Bngy Kang a, a College of Informaton Engneerng, Northwest A&F Unversty, Yanglng, Shaanx, 712100, Chna. Abstract Deng
Power law and dmenson of the maxmum value for belef dstrbuton wth the max Deng entropy Bngy Kang a, a College of Informaton Engneerng, Northwest A&F Unversty, Yanglng, Shaanx, 712100, Chna. Abstract Deng
Flow equations To simulate the flow, the Navier-Stokes system that includes continuity and momentum equations is solved
 Smulaton of nose generaton and propagaton caused by the turbulent flow around bluff bodes Zamotn Krll e-mal: krart@gmal.com, cq: 958886 Summary Accurate predctons of nose generaton and spread n turbulent
Smulaton of nose generaton and propagaton caused by the turbulent flow around bluff bodes Zamotn Krll e-mal: krart@gmal.com, cq: 958886 Summary Accurate predctons of nose generaton and spread n turbulent
Grand canonical Monte Carlo simulations of bulk electrolytes and calcium channels
 Grand canoncal Monte Carlo smulatons of bulk electrolytes and calcum channels Thess of Ph.D. dssertaton Prepared by: Attla Malascs M.Sc. n Chemstry Supervsor: Dr. Dezső Boda Unversty of Pannona Insttute
Grand canoncal Monte Carlo smulatons of bulk electrolytes and calcum channels Thess of Ph.D. dssertaton Prepared by: Attla Malascs M.Sc. n Chemstry Supervsor: Dr. Dezső Boda Unversty of Pannona Insttute
829. An adaptive method for inertia force identification in cantilever under moving mass
 89. An adaptve method for nerta force dentfcaton n cantlever under movng mass Qang Chen 1, Mnzhuo Wang, Hao Yan 3, Haonan Ye 4, Guola Yang 5 1,, 3, 4 Department of Control and System Engneerng, Nanng Unversty,
89. An adaptve method for nerta force dentfcaton n cantlever under movng mass Qang Chen 1, Mnzhuo Wang, Hao Yan 3, Haonan Ye 4, Guola Yang 5 1,, 3, 4 Department of Control and System Engneerng, Nanng Unversty,
A large scale tsunami run-up simulation and numerical evaluation of fluid force during tsunami by using a particle method
 A large scale tsunam run-up smulaton and numercal evaluaton of flud force durng tsunam by usng a partcle method *Mtsuteru Asa 1), Shoch Tanabe 2) and Masaharu Isshk 3) 1), 2) Department of Cvl Engneerng,
A large scale tsunam run-up smulaton and numercal evaluaton of flud force durng tsunam by usng a partcle method *Mtsuteru Asa 1), Shoch Tanabe 2) and Masaharu Isshk 3) 1), 2) Department of Cvl Engneerng,
Smoothed particle hydrodynamics modelling of fluids and solids
 Appled and Computatonal Mechancs 1 (2007) 521-530 Smoothed partcle hydrodynamcs modellng of fluds and solds L. Lobovský a,, J. Křen a a Department of Mechancs, Faculty of Appled Scences, UWB n Plsen, Unverztní
Appled and Computatonal Mechancs 1 (2007) 521-530 Smoothed partcle hydrodynamcs modellng of fluds and solds L. Lobovský a,, J. Křen a a Department of Mechancs, Faculty of Appled Scences, UWB n Plsen, Unverztní
Thermal-Fluids I. Chapter 18 Transient heat conduction. Dr. Primal Fernando Ph: (850)
 hermal-fluds I Chapter 18 ransent heat conducton Dr. Prmal Fernando prmal@eng.fsu.edu Ph: (850) 410-6323 1 ransent heat conducton In general, he temperature of a body vares wth tme as well as poston. In
hermal-fluds I Chapter 18 ransent heat conducton Dr. Prmal Fernando prmal@eng.fsu.edu Ph: (850) 410-6323 1 ransent heat conducton In general, he temperature of a body vares wth tme as well as poston. In
Effect of loading frequency on the settlement of granular layer
 Effect of loadng frequency on the settlement of granular layer Akko KONO Ralway Techncal Research Insttute, Japan Takash Matsushma Tsukuba Unversty, Japan ABSTRACT: Cyclc loadng tests were performed both
Effect of loadng frequency on the settlement of granular layer Akko KONO Ralway Techncal Research Insttute, Japan Takash Matsushma Tsukuba Unversty, Japan ABSTRACT: Cyclc loadng tests were performed both
Suppose that there s a measured wndow of data fff k () ; :::; ff k g of a sze w, measured dscretely wth varable dscretzaton step. It s convenent to pl
 RECURSIVE SPLINE INTERPOLATION METHOD FOR REAL TIME ENGINE CONTROL APPLICATIONS A. Stotsky Volvo Car Corporaton Engne Desgn and Development Dept. 97542, HA1N, SE- 405 31 Gothenburg Sweden. Emal: astotsky@volvocars.com
RECURSIVE SPLINE INTERPOLATION METHOD FOR REAL TIME ENGINE CONTROL APPLICATIONS A. Stotsky Volvo Car Corporaton Engne Desgn and Development Dept. 97542, HA1N, SE- 405 31 Gothenburg Sweden. Emal: astotsky@volvocars.com
Chapter 3 Differentiation and Integration
 MEE07 Computer Modelng Technques n Engneerng Chapter Derentaton and Integraton Reerence: An Introducton to Numercal Computatons, nd edton, S. yakowtz and F. zdarovsky, Mawell/Macmllan, 990. Derentaton
MEE07 Computer Modelng Technques n Engneerng Chapter Derentaton and Integraton Reerence: An Introducton to Numercal Computatons, nd edton, S. yakowtz and F. zdarovsky, Mawell/Macmllan, 990. Derentaton
Normally, in one phase reservoir simulation we would deal with one of the following fluid systems:
 TPG4160 Reservor Smulaton 2017 page 1 of 9 ONE-DIMENSIONAL, ONE-PHASE RESERVOIR SIMULATION Flud systems The term sngle phase apples to any system wth only one phase present n the reservor In some cases
TPG4160 Reservor Smulaton 2017 page 1 of 9 ONE-DIMENSIONAL, ONE-PHASE RESERVOIR SIMULATION Flud systems The term sngle phase apples to any system wth only one phase present n the reservor In some cases
χ x B E (c) Figure 2.1.1: (a) a material particle in a body, (b) a place in space, (c) a configuration of the body
 Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
SIMULATION OF WAVE PROPAGATION IN AN HETEROGENEOUS ELASTIC ROD
 SIMUATION OF WAVE POPAGATION IN AN HETEOGENEOUS EASTIC OD ogéro M Saldanha da Gama Unversdade do Estado do o de Janero ua Sào Francsco Xaver 54, sala 5 A 559-9, o de Janero, Brasl e-mal: rsgama@domancombr
SIMUATION OF WAVE POPAGATION IN AN HETEOGENEOUS EASTIC OD ogéro M Saldanha da Gama Unversdade do Estado do o de Janero ua Sào Francsco Xaver 54, sala 5 A 559-9, o de Janero, Brasl e-mal: rsgama@domancombr
CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE
 CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE Analytcal soluton s usually not possble when exctaton vares arbtrarly wth tme or f the system s nonlnear. Such problems can be solved by numercal tmesteppng
CHAPTER 5 NUMERICAL EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE Analytcal soluton s usually not possble when exctaton vares arbtrarly wth tme or f the system s nonlnear. Such problems can be solved by numercal tmesteppng
Lecture Notes on Linear Regression
 Lecture Notes on Lnear Regresson Feng L fl@sdueducn Shandong Unversty, Chna Lnear Regresson Problem In regresson problem, we am at predct a contnuous target value gven an nput feature vector We assume
Lecture Notes on Lnear Regresson Feng L fl@sdueducn Shandong Unversty, Chna Lnear Regresson Problem In regresson problem, we am at predct a contnuous target value gven an nput feature vector We assume
Inductance Calculation for Conductors of Arbitrary Shape
 CRYO/02/028 Aprl 5, 2002 Inductance Calculaton for Conductors of Arbtrary Shape L. Bottura Dstrbuton: Internal Summary In ths note we descrbe a method for the numercal calculaton of nductances among conductors
CRYO/02/028 Aprl 5, 2002 Inductance Calculaton for Conductors of Arbtrary Shape L. Bottura Dstrbuton: Internal Summary In ths note we descrbe a method for the numercal calculaton of nductances among conductors
CHAPTER 14 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY
 CHAPTER 4 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY 4 Introducton A partcle n orbt around a pont mass or a sphercally symmetrc mass dstrbuton s movng n a gravtatonal potental of the form GM / r In ths potental t moves
CHAPTER 4 GENERAL PERTURBATION THEORY 4 Introducton A partcle n orbt around a pont mass or a sphercally symmetrc mass dstrbuton s movng n a gravtatonal potental of the form GM / r In ths potental t moves
Fast Calculation for Particle Interactions in SPH Simulations: Outlined Sub-Domain Technique
 Internatonal Journal of Cvl and Envronmental Engneerng 6 0 Fast Calculaton for Partcle Interactons n SPH Smulatons: Outlned Sub-Doman Technque Buntara Sthenly Gan and Naohro Kawada Abstract A smple and
Internatonal Journal of Cvl and Envronmental Engneerng 6 0 Fast Calculaton for Partcle Interactons n SPH Smulatons: Outlned Sub-Doman Technque Buntara Sthenly Gan and Naohro Kawada Abstract A smple and
One-sided finite-difference approximations suitable for use with Richardson extrapolation
 Journal of Computatonal Physcs 219 (2006) 13 20 Short note One-sded fnte-dfference approxmatons sutable for use wth Rchardson extrapolaton Kumar Rahul, S.N. Bhattacharyya * Department of Mechancal Engneerng,
Journal of Computatonal Physcs 219 (2006) 13 20 Short note One-sded fnte-dfference approxmatons sutable for use wth Rchardson extrapolaton Kumar Rahul, S.N. Bhattacharyya * Department of Mechancal Engneerng,
The Study of Teaching-learning-based Optimization Algorithm
 Advanced Scence and Technology Letters Vol. (AST 06), pp.05- http://dx.do.org/0.57/astl.06. The Study of Teachng-learnng-based Optmzaton Algorthm u Sun, Yan fu, Lele Kong, Haolang Q,, Helongang Insttute
Advanced Scence and Technology Letters Vol. (AST 06), pp.05- http://dx.do.org/0.57/astl.06. The Study of Teachng-learnng-based Optmzaton Algorthm u Sun, Yan fu, Lele Kong, Haolang Q,, Helongang Insttute
A Fast Computer Aided Design Method for Filters
 2017 Asa-Pacfc Engneerng and Technology Conference (APETC 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-443-1 A Fast Computer Aded Desgn Method for Flters Gang L ABSTRACT *Ths paper presents a fast computer aded desgn method
2017 Asa-Pacfc Engneerng and Technology Conference (APETC 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-443-1 A Fast Computer Aded Desgn Method for Flters Gang L ABSTRACT *Ths paper presents a fast computer aded desgn method
Solution Thermodynamics
 Soluton hermodynamcs usng Wagner Notaton by Stanley. Howard Department of aterals and etallurgcal Engneerng South Dakota School of nes and echnology Rapd Cty, SD 57701 January 7, 001 Soluton hermodynamcs
Soluton hermodynamcs usng Wagner Notaton by Stanley. Howard Department of aterals and etallurgcal Engneerng South Dakota School of nes and echnology Rapd Cty, SD 57701 January 7, 001 Soluton hermodynamcs
Turbulent Flow. Turbulent Flow
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xoll2kedog&feature=related http://br.youtube.com/watch?v=7kkftgx2any http://br.youtube.com/watch?v=vqhxihpvcvu 1. Caothc fluctuatons wth a wde range of frequences and
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xoll2kedog&feature=related http://br.youtube.com/watch?v=7kkftgx2any http://br.youtube.com/watch?v=vqhxihpvcvu 1. Caothc fluctuatons wth a wde range of frequences and
Physics 181. Particle Systems
 Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
Amplification and Relaxation of Electron Spin Polarization in Semiconductor Devices
 Amplfcaton and Relaxaton of Electron Spn Polarzaton n Semconductor Devces Yury V. Pershn and Vladmr Prvman Center for Quantum Devce Technology, Clarkson Unversty, Potsdam, New York 13699-570, USA Spn Relaxaton
Amplfcaton and Relaxaton of Electron Spn Polarzaton n Semconductor Devces Yury V. Pershn and Vladmr Prvman Center for Quantum Devce Technology, Clarkson Unversty, Potsdam, New York 13699-570, USA Spn Relaxaton
Transfer Functions. Convenient representation of a linear, dynamic model. A transfer function (TF) relates one input and one output: ( ) system
 Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Open Systems: Chemical Potential and Partial Molar Quantities Chemical Potential
 Open Systems: Chemcal Potental and Partal Molar Quanttes Chemcal Potental For closed systems, we have derved the followng relatonshps: du = TdS pdv dh = TdS + Vdp da = SdT pdv dg = VdP SdT For open systems,
Open Systems: Chemcal Potental and Partal Molar Quanttes Chemcal Potental For closed systems, we have derved the followng relatonshps: du = TdS pdv dh = TdS + Vdp da = SdT pdv dg = VdP SdT For open systems,
Physics 607 Exam 1. ( ) = 1, Γ( z +1) = zγ( z) x n e x2 dx = 1. e x2
 Physcs 607 Exam 1 Please be well-organzed, and show all sgnfcant steps clearly n all problems. You are graded on your wor, so please do not just wrte down answers wth no explanaton! Do all your wor on
Physcs 607 Exam 1 Please be well-organzed, and show all sgnfcant steps clearly n all problems. You are graded on your wor, so please do not just wrte down answers wth no explanaton! Do all your wor on
Kernel Methods and SVMs Extension
 Kernel Methods and SVMs Extenson The purpose of ths document s to revew materal covered n Machne Learnng 1 Supervsed Learnng regardng support vector machnes (SVMs). Ths document also provdes a general
Kernel Methods and SVMs Extenson The purpose of ths document s to revew materal covered n Machne Learnng 1 Supervsed Learnng regardng support vector machnes (SVMs). Ths document also provdes a general
Simulation of Hypervelocity Spacecrafts And Orbital Debris Collisions using Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics in LS-DYNA
 Smulaton of Hypervelocty Spacecrafts And Orbtal Debrs Collsons usng Smoothed Partcle Hydrodynamcs n LS-DYNA J.L.Lacome a, Ch. Espnosa b, C. Gallet b, a Consultant LSTC Rue des Pyrénées, F-31330 Grenade
Smulaton of Hypervelocty Spacecrafts And Orbtal Debrs Collsons usng Smoothed Partcle Hydrodynamcs n LS-DYNA J.L.Lacome a, Ch. Espnosa b, C. Gallet b, a Consultant LSTC Rue des Pyrénées, F-31330 Grenade
Bindel, Spring 2014 Applications of Parallel Computers (CS 5220)
 Bndel, Sprng 2014 Applcatons of Parallel Computers (CS 5220) 1 Dervng SPH The Naver-Stokes equatons wth gravty are ρa = p + µ 2 v + ρg. The acceleraton s the materal dervatve of velocty, and we usually
Bndel, Sprng 2014 Applcatons of Parallel Computers (CS 5220) 1 Dervng SPH The Naver-Stokes equatons wth gravty are ρa = p + µ 2 v + ρg. The acceleraton s the materal dervatve of velocty, and we usually
Note 10. Modeling and Simulation of Dynamic Systems
 Lecture Notes of ME 475: Introducton to Mechatroncs Note 0 Modelng and Smulaton of Dynamc Systems Department of Mechancal Engneerng, Unversty Of Saskatchewan, 57 Campus Drve, Saskatoon, SK S7N 5A9, Canada
Lecture Notes of ME 475: Introducton to Mechatroncs Note 0 Modelng and Smulaton of Dynamc Systems Department of Mechancal Engneerng, Unversty Of Saskatchewan, 57 Campus Drve, Saskatoon, SK S7N 5A9, Canada
Kinematics of Fluids. Lecture 16. (Refer the text book CONTINUUM MECHANICS by GEORGE E. MASE, Schaum s Outlines) 17/02/2017
 17/0/017 Lecture 16 (Refer the text boo CONTINUUM MECHANICS by GEORGE E. MASE, Schaum s Outlnes) Knematcs of Fluds Last class, we started dscussng about the nematcs of fluds. Recall the Lagrangan and Euleran
17/0/017 Lecture 16 (Refer the text boo CONTINUUM MECHANICS by GEORGE E. MASE, Schaum s Outlnes) Knematcs of Fluds Last class, we started dscussng about the nematcs of fluds. Recall the Lagrangan and Euleran
Implicit Integration Henyey Method
 Implct Integraton Henyey Method In realstc stellar evoluton codes nstead of a drect ntegraton usng for example the Runge-Kutta method one employs an teratve mplct technque. Ths s because the structure
Implct Integraton Henyey Method In realstc stellar evoluton codes nstead of a drect ntegraton usng for example the Runge-Kutta method one employs an teratve mplct technque. Ths s because the structure
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Physics 53. Rotational Motion 3. Sir, I have found you an argument, but I am not obliged to find you an understanding.
 Physcs 53 Rotatonal Moton 3 Sr, I have found you an argument, but I am not oblged to fnd you an understandng. Samuel Johnson Angular momentum Wth respect to rotatonal moton of a body, moment of nerta plays
Physcs 53 Rotatonal Moton 3 Sr, I have found you an argument, but I am not oblged to fnd you an understandng. Samuel Johnson Angular momentum Wth respect to rotatonal moton of a body, moment of nerta plays
Parameter Estimation for Dynamic System using Unscented Kalman filter
 Parameter Estmaton for Dynamc System usng Unscented Kalman flter Jhoon Seung 1,a, Amr Atya F. 2,b, Alexander G.Parlos 3,c, and Klto Chong 1,4,d* 1 Dvson of Electroncs Engneerng, Chonbuk Natonal Unversty,
Parameter Estmaton for Dynamc System usng Unscented Kalman flter Jhoon Seung 1,a, Amr Atya F. 2,b, Alexander G.Parlos 3,c, and Klto Chong 1,4,d* 1 Dvson of Electroncs Engneerng, Chonbuk Natonal Unversty,
2 Finite difference basics
 Numersche Methoden 1, WS 11/12 B.J.P. Kaus 2 Fnte dfference bascs Consder the one- The bascs of the fnte dfference method are best understood wth an example. dmensonal transent heat conducton equaton T
Numersche Methoden 1, WS 11/12 B.J.P. Kaus 2 Fnte dfference bascs Consder the one- The bascs of the fnte dfference method are best understood wth an example. dmensonal transent heat conducton equaton T
4DVAR, according to the name, is a four-dimensional variational method.
 4D-Varatonal Data Assmlaton (4D-Var) 4DVAR, accordng to the name, s a four-dmensonal varatonal method. 4D-Var s actually a drect generalzaton of 3D-Var to handle observatons that are dstrbuted n tme. The
4D-Varatonal Data Assmlaton (4D-Var) 4DVAR, accordng to the name, s a four-dmensonal varatonal method. 4D-Var s actually a drect generalzaton of 3D-Var to handle observatons that are dstrbuted n tme. The
A Hybrid Variational Iteration Method for Blasius Equation
 Avalable at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol. 10, Issue 1 (June 2015), pp. 223-229 Applcatons and Appled Mathematcs: An Internatonal Journal (AAM) A Hybrd Varatonal Iteraton Method
Avalable at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol. 10, Issue 1 (June 2015), pp. 223-229 Applcatons and Appled Mathematcs: An Internatonal Journal (AAM) A Hybrd Varatonal Iteraton Method
Design and Optimization of Fuzzy Controller for Inverse Pendulum System Using Genetic Algorithm
 Desgn and Optmzaton of Fuzzy Controller for Inverse Pendulum System Usng Genetc Algorthm H. Mehraban A. Ashoor Unversty of Tehran Unversty of Tehran h.mehraban@ece.ut.ac.r a.ashoor@ece.ut.ac.r Abstract:
Desgn and Optmzaton of Fuzzy Controller for Inverse Pendulum System Usng Genetc Algorthm H. Mehraban A. Ashoor Unversty of Tehran Unversty of Tehran h.mehraban@ece.ut.ac.r a.ashoor@ece.ut.ac.r Abstract:
Chapter 12. Ordinary Differential Equation Boundary Value (BV) Problems
 Chapter. Ordnar Dfferental Equaton Boundar Value (BV) Problems In ths chapter we wll learn how to solve ODE boundar value problem. BV ODE s usuall gven wth x beng the ndependent space varable. p( x) q(
Chapter. Ordnar Dfferental Equaton Boundar Value (BV) Problems In ths chapter we wll learn how to solve ODE boundar value problem. BV ODE s usuall gven wth x beng the ndependent space varable. p( x) q(
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
Module 3 LOSSY IMAGE COMPRESSION SYSTEMS Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Lesson 6 Theory of Quantzaton Verson ECE IIT, Kharagpur Instructonal Objectves At the end of ths lesson, the students should be able to:
The Feynman path integral
 The Feynman path ntegral Aprl 3, 205 Hesenberg and Schrödnger pctures The Schrödnger wave functon places the tme dependence of a physcal system n the state, ψ, t, where the state s a vector n Hlbert space
The Feynman path ntegral Aprl 3, 205 Hesenberg and Schrödnger pctures The Schrödnger wave functon places the tme dependence of a physcal system n the state, ψ, t, where the state s a vector n Hlbert space
Interconnect Modeling
 Interconnect Modelng Modelng of Interconnects Interconnect R, C and computaton Interconnect models umped RC model Dstrbuted crcut models Hgher-order waveform n dstrbuted RC trees Accuracy and fdelty Prepared
Interconnect Modelng Modelng of Interconnects Interconnect R, C and computaton Interconnect models umped RC model Dstrbuted crcut models Hgher-order waveform n dstrbuted RC trees Accuracy and fdelty Prepared
APPROXIMATE ANALYSIS OF RIGID PLATE LOADING ON ELASTIC MULTI-LAYERED SYSTEMS
 6th ICPT, Sapporo, Japan, July 008 APPROXIMATE ANALYSIS OF RIGID PLATE LOADING ON ELASTIC MULTI-LAYERED SYSTEMS James MAINA Prncpal Researcher, Transport and Infrastructure Engneerng, CSIR Bult Envronment
6th ICPT, Sapporo, Japan, July 008 APPROXIMATE ANALYSIS OF RIGID PLATE LOADING ON ELASTIC MULTI-LAYERED SYSTEMS James MAINA Prncpal Researcher, Transport and Infrastructure Engneerng, CSIR Bult Envronment
Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics
 Introducton to Computatonal Flud Dynamcs M. Zanub 1, T. Mahalakshm 2 1 (PG MATHS), Department of Mathematcs, St. Josephs College of Arts and Scence for Women-Hosur, Peryar Unversty 2 Assstance professor,
Introducton to Computatonal Flud Dynamcs M. Zanub 1, T. Mahalakshm 2 1 (PG MATHS), Department of Mathematcs, St. Josephs College of Arts and Scence for Women-Hosur, Peryar Unversty 2 Assstance professor,
CSci 6974 and ECSE 6966 Math. Tech. for Vision, Graphics and Robotics Lecture 21, April 17, 2006 Estimating A Plane Homography
 CSc 6974 and ECSE 6966 Math. Tech. for Vson, Graphcs and Robotcs Lecture 21, Aprl 17, 2006 Estmatng A Plane Homography Overvew We contnue wth a dscusson of the major ssues, usng estmaton of plane projectve
CSc 6974 and ECSE 6966 Math. Tech. for Vson, Graphcs and Robotcs Lecture 21, Aprl 17, 2006 Estmatng A Plane Homography Overvew We contnue wth a dscusson of the major ssues, usng estmaton of plane projectve
Extension of Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH), Mathematical Background of Vortex Blob Method (VBM) and Moving Particle Semi-Implicit (MPS)
 Amercan Journal of Computatonal athematcs, 04, 5, 44-445 Publshed Onlne December 04 n ScRes. http://www.scrp.org/ournal/acm http://dx.do.org/0.436/acm.04.45036 Extenson of Smoothed Partcle Hydrodynamcs
Amercan Journal of Computatonal athematcs, 04, 5, 44-445 Publshed Onlne December 04 n ScRes. http://www.scrp.org/ournal/acm http://dx.do.org/0.436/acm.04.45036 Extenson of Smoothed Partcle Hydrodynamcs
Ionization fronts in HII regions
 Ionzaton fronts n HII regons Intal expanson of HII onzaton front s supersonc, creatng a shock front. Statonary frame: front advances nto neutral materal In frame where shock front s statonary, neutral
Ionzaton fronts n HII regons Intal expanson of HII onzaton front s supersonc, creatng a shock front. Statonary frame: front advances nto neutral materal In frame where shock front s statonary, neutral
SHEAR FLOWS IN SMOOTHED PARTICLE HYDRODYNAMICS Yusuke Imaeda. and Shu-ichiro Inutsuka
 The Astrophyscal Journal, 569:501 518, 2002 Aprl 10 # 2002. The Amercan Astronomcal Socety. All rghts reserved. Prnted n U.S.A. SHEAR FLOWS IN SMOOTHE PARTICLE HYROYNAMICS Yusuke Imaeda vson of Theoretcal
The Astrophyscal Journal, 569:501 518, 2002 Aprl 10 # 2002. The Amercan Astronomcal Socety. All rghts reserved. Prnted n U.S.A. SHEAR FLOWS IN SMOOTHE PARTICLE HYROYNAMICS Yusuke Imaeda vson of Theoretcal
DETERMINATION OF TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION FOR ANNULAR FINS WITH TEMPERATURE DEPENDENT THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY BY HPM
 Ganj, Z. Z., et al.: Determnaton of Temperature Dstrbuton for S111 DETERMINATION OF TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION FOR ANNULAR FINS WITH TEMPERATURE DEPENDENT THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY BY HPM by Davood Domr GANJI
Ganj, Z. Z., et al.: Determnaton of Temperature Dstrbuton for S111 DETERMINATION OF TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION FOR ANNULAR FINS WITH TEMPERATURE DEPENDENT THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY BY HPM by Davood Domr GANJI
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. D Alembert s Principle and The Lagrangian-1
 P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
Integrals and Invariants of Euler-Lagrange Equations
 Lecture 16 Integrals and Invarants of Euler-Lagrange Equatons ME 256 at the Indan Insttute of Scence, Bengaluru Varatonal Methods and Structural Optmzaton G. K. Ananthasuresh Professor, Mechancal Engneerng,
Lecture 16 Integrals and Invarants of Euler-Lagrange Equatons ME 256 at the Indan Insttute of Scence, Bengaluru Varatonal Methods and Structural Optmzaton G. K. Ananthasuresh Professor, Mechancal Engneerng,
Lecture 20: Noether s Theorem
 Lecture 20: Noether s Theorem In our revew of Newtonan Mechancs, we were remnded that some quanttes (energy, lnear momentum, and angular momentum) are conserved That s, they are constant f no external
Lecture 20: Noether s Theorem In our revew of Newtonan Mechancs, we were remnded that some quanttes (energy, lnear momentum, and angular momentum) are conserved That s, they are constant f no external
in a horizontal wellbore in a heavy oil reservoir
 498 n a horzontal wellbore n a heavy ol reservor L Mngzhong, Wang Ypng and Wang Weyang Abstract: A novel model for dynamc temperature dstrbuton n heavy ol reservors s derved from and axal dfference equatons
498 n a horzontal wellbore n a heavy ol reservor L Mngzhong, Wang Ypng and Wang Weyang Abstract: A novel model for dynamc temperature dstrbuton n heavy ol reservors s derved from and axal dfference equatons
Workshop: Approximating energies and wave functions Quantum aspects of physical chemistry
 Workshop: Approxmatng energes and wave functons Quantum aspects of physcal chemstry http://quantum.bu.edu/pltl/6/6.pdf Last updated Thursday, November 7, 25 7:9:5-5: Copyrght 25 Dan Dll (dan@bu.edu) Department
Workshop: Approxmatng energes and wave functons Quantum aspects of physcal chemstry http://quantum.bu.edu/pltl/6/6.pdf Last updated Thursday, November 7, 25 7:9:5-5: Copyrght 25 Dan Dll (dan@bu.edu) Department
A new Approach for Solving Linear Ordinary Differential Equations
 , ISSN 974-57X (Onlne), ISSN 974-5718 (Prnt), Vol. ; Issue No. 1; Year 14, Copyrght 13-14 by CESER PUBLICATIONS A new Approach for Solvng Lnear Ordnary Dfferental Equatons Fawz Abdelwahd Department of
, ISSN 974-57X (Onlne), ISSN 974-5718 (Prnt), Vol. ; Issue No. 1; Year 14, Copyrght 13-14 by CESER PUBLICATIONS A new Approach for Solvng Lnear Ordnary Dfferental Equatons Fawz Abdelwahd Department of
Calculating the Quasi-static Pressures of Confined Explosions Considering Chemical Reactions under the Constant Entropy Assumption
 Appled Mechancs and Materals Onlne: 202-04-20 ISS: 662-7482, ol. 64, pp 396-400 do:0.4028/www.scentfc.net/amm.64.396 202 Trans Tech Publcatons, Swtzerland Calculatng the Quas-statc Pressures of Confned
Appled Mechancs and Materals Onlne: 202-04-20 ISS: 662-7482, ol. 64, pp 396-400 do:0.4028/www.scentfc.net/amm.64.396 202 Trans Tech Publcatons, Swtzerland Calculatng the Quas-statc Pressures of Confned
A Solution of the Harry-Dym Equation Using Lattice-Boltzmannn and a Solitary Wave Methods
 Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vol. 11, 2017, no. 52, 2579-2586 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hkar.com https://do.org/10.12988/ams.2017.79280 A Soluton of the Harry-Dym Equaton Usng Lattce-Boltzmannn and a Soltary Wave
Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vol. 11, 2017, no. 52, 2579-2586 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hkar.com https://do.org/10.12988/ams.2017.79280 A Soluton of the Harry-Dym Equaton Usng Lattce-Boltzmannn and a Soltary Wave
ME 501A Seminar in Engineering Analysis Page 1
 umercal Solutons of oundary-value Problems n Os ovember 7, 7 umercal Solutons of oundary- Value Problems n Os Larry aretto Mechancal ngneerng 5 Semnar n ngneerng nalyss ovember 7, 7 Outlne Revew stff equaton
umercal Solutons of oundary-value Problems n Os ovember 7, 7 umercal Solutons of oundary- Value Problems n Os Larry aretto Mechancal ngneerng 5 Semnar n ngneerng nalyss ovember 7, 7 Outlne Revew stff equaton
THE EFFECT OF TORSIONAL RIGIDITY BETWEEN ELEMENTS ON FREE VIBRATIONS OF A TELESCOPIC HYDRAULIC CYLINDER SUBJECTED TO EULER S LOAD
 Journal of Appled Mathematcs and Computatonal Mechancs 7, 6(3), 7- www.amcm.pcz.pl p-issn 99-9965 DOI:.75/jamcm.7.3. e-issn 353-588 THE EFFECT OF TORSIONAL RIGIDITY BETWEEN ELEMENTS ON FREE VIBRATIONS
Journal of Appled Mathematcs and Computatonal Mechancs 7, 6(3), 7- www.amcm.pcz.pl p-issn 99-9965 DOI:.75/jamcm.7.3. e-issn 353-588 THE EFFECT OF TORSIONAL RIGIDITY BETWEEN ELEMENTS ON FREE VIBRATIONS
Brownian-Dynamics Simulation of Colloidal Suspensions with Kob-Andersen Type Lennard-Jones Potentials 1
 Brownan-Dynamcs Smulaton of Collodal Suspensons wth Kob-Andersen Type Lennard-Jones Potentals 1 Yuto KIMURA 2 and Mcho TOKUYAMA 3 Summary Extensve Brownan-dynamcs smulatons of bnary collodal suspenton
Brownan-Dynamcs Smulaton of Collodal Suspensons wth Kob-Andersen Type Lennard-Jones Potentals 1 Yuto KIMURA 2 and Mcho TOKUYAMA 3 Summary Extensve Brownan-dynamcs smulatons of bnary collodal suspenton
Lecture 12: Discrete Laplacian
 Lecture 12: Dscrete Laplacan Scrbe: Tanye Lu Our goal s to come up wth a dscrete verson of Laplacan operator for trangulated surfaces, so that we can use t n practce to solve related problems We are mostly
Lecture 12: Dscrete Laplacan Scrbe: Tanye Lu Our goal s to come up wth a dscrete verson of Laplacan operator for trangulated surfaces, so that we can use t n practce to solve related problems We are mostly
Visco-Rubber Elastic Model for Pressure Sensitive Adhesive
 Vsco-Rubber Elastc Model for Pressure Senstve Adhesve Kazuhsa Maeda, Shgenobu Okazawa, Koj Nshgch and Takash Iwamoto Abstract A materal model to descrbe large deformaton of pressure senstve adhesve (PSA
Vsco-Rubber Elastc Model for Pressure Senstve Adhesve Kazuhsa Maeda, Shgenobu Okazawa, Koj Nshgch and Takash Iwamoto Abstract A materal model to descrbe large deformaton of pressure senstve adhesve (PSA
Chapter 13: Multiple Regression
 Chapter 13: Multple Regresson 13.1 Developng the multple-regresson Model The general model can be descrbed as: It smplfes for two ndependent varables: The sample ft parameter b 0, b 1, and b are used to
Chapter 13: Multple Regresson 13.1 Developng the multple-regresson Model The general model can be descrbed as: It smplfes for two ndependent varables: The sample ft parameter b 0, b 1, and b are used to
Lecture Note 3. Eshelby s Inclusion II
 ME340B Elastcty of Mcroscopc Structures Stanford Unversty Wnter 004 Lecture Note 3. Eshelby s Incluson II Chrs Wenberger and We Ca c All rghts reserved January 6, 004 Contents 1 Incluson energy n an nfnte
ME340B Elastcty of Mcroscopc Structures Stanford Unversty Wnter 004 Lecture Note 3. Eshelby s Incluson II Chrs Wenberger and We Ca c All rghts reserved January 6, 004 Contents 1 Incluson energy n an nfnte
Linear Approximation with Regularization and Moving Least Squares
 Lnear Approxmaton wth Regularzaton and Movng Least Squares Igor Grešovn May 007 Revson 4.6 (Revson : March 004). 5 4 3 0.5 3 3.5 4 Contents: Lnear Fttng...4. Weghted Least Squares n Functon Approxmaton...
Lnear Approxmaton wth Regularzaton and Movng Least Squares Igor Grešovn May 007 Revson 4.6 (Revson : March 004). 5 4 3 0.5 3 3.5 4 Contents: Lnear Fttng...4. Weghted Least Squares n Functon Approxmaton...
The Expectation-Maximization Algorithm
 The Expectaton-Maxmaton Algorthm Charles Elan elan@cs.ucsd.edu November 16, 2007 Ths chapter explans the EM algorthm at multple levels of generalty. Secton 1 gves the standard hgh-level verson of the algorthm.
The Expectaton-Maxmaton Algorthm Charles Elan elan@cs.ucsd.edu November 16, 2007 Ths chapter explans the EM algorthm at multple levels of generalty. Secton 1 gves the standard hgh-level verson of the algorthm.
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. Principle of Virtual Work-1
 P. Guterrez 1 Introducton Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs Prncple of Vrtual Work The frst varatonal prncple we encounter n mechancs s the prncple of vrtual work. It establshes the equlbrum condton of a mechancal
P. Guterrez 1 Introducton Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs Prncple of Vrtual Work The frst varatonal prncple we encounter n mechancs s the prncple of vrtual work. It establshes the equlbrum condton of a mechancal
Irregular vibrations in multi-mass discrete-continuous systems torsionally deformed
 (2) 4 48 Irregular vbratons n mult-mass dscrete-contnuous systems torsonally deformed Abstract In the paper rregular vbratons of dscrete-contnuous systems consstng of an arbtrary number rgd bodes connected
(2) 4 48 Irregular vbratons n mult-mass dscrete-contnuous systems torsonally deformed Abstract In the paper rregular vbratons of dscrete-contnuous systems consstng of an arbtrary number rgd bodes connected
Annexes. EC.1. Cycle-base move illustration. EC.2. Problem Instances
 ec Annexes Ths Annex frst llustrates a cycle-based move n the dynamc-block generaton tabu search. It then dsplays the characterstcs of the nstance sets, followed by detaled results of the parametercalbraton
ec Annexes Ths Annex frst llustrates a cycle-based move n the dynamc-block generaton tabu search. It then dsplays the characterstcs of the nstance sets, followed by detaled results of the parametercalbraton
SIMULATION OF SOUND WAVE PROPAGATION IN TURBULENT FLOWS USING A LATTICE-BOLTZMANN SCHEME. Abstract
 SIMULATION OF SOUND WAVE PROPAGATION IN TURBULENT FLOWS USING A LATTICE-BOLTZMANN SCHEME PACS REFERENCE: 43.20.Mv Andreas Wlde Fraunhofer Insttut für Integrerte Schaltungen, Außenstelle EAS Zeunerstr.
SIMULATION OF SOUND WAVE PROPAGATION IN TURBULENT FLOWS USING A LATTICE-BOLTZMANN SCHEME PACS REFERENCE: 43.20.Mv Andreas Wlde Fraunhofer Insttut für Integrerte Schaltungen, Außenstelle EAS Zeunerstr.
Least squares cubic splines without B-splines S.K. Lucas
 Least squares cubc splnes wthout B-splnes S.K. Lucas School of Mathematcs and Statstcs, Unversty of South Australa, Mawson Lakes SA 595 e-mal: stephen.lucas@unsa.edu.au Submtted to the Gazette of the Australan
Least squares cubc splnes wthout B-splnes S.K. Lucas School of Mathematcs and Statstcs, Unversty of South Australa, Mawson Lakes SA 595 e-mal: stephen.lucas@unsa.edu.au Submtted to the Gazette of the Australan
18.1 Introduction and Recap
 CS787: Advanced Algorthms Scrbe: Pryananda Shenoy and Shjn Kong Lecturer: Shuch Chawla Topc: Streamng Algorthmscontnued) Date: 0/26/2007 We contnue talng about streamng algorthms n ths lecture, ncludng
CS787: Advanced Algorthms Scrbe: Pryananda Shenoy and Shjn Kong Lecturer: Shuch Chawla Topc: Streamng Algorthmscontnued) Date: 0/26/2007 We contnue talng about streamng algorthms n ths lecture, ncludng
Robert Eisberg Second edition CH 09 Multielectron atoms ground states and x-ray excitations
 Quantum Physcs 量 理 Robert Esberg Second edton CH 09 Multelectron atoms ground states and x-ray exctatons 9-01 By gong through the procedure ndcated n the text, develop the tme-ndependent Schroednger equaton
Quantum Physcs 量 理 Robert Esberg Second edton CH 09 Multelectron atoms ground states and x-ray exctatons 9-01 By gong through the procedure ndcated n the text, develop the tme-ndependent Schroednger equaton
CS 468 Lecture 16: Isometry Invariance and Spectral Techniques
 CS 468 Lecture 16: Isometry Invarance and Spectral Technques Justn Solomon Scrbe: Evan Gawlk Introducton. In geometry processng, t s often desrable to characterze the shape of an object n a manner that
CS 468 Lecture 16: Isometry Invarance and Spectral Technques Justn Solomon Scrbe: Evan Gawlk Introducton. In geometry processng, t s often desrable to characterze the shape of an object n a manner that
The Finite Element Method
 The Fnte Element Method GENERAL INTRODUCTION Read: Chapters 1 and 2 CONTENTS Engneerng and analyss Smulaton of a physcal process Examples mathematcal model development Approxmate solutons and methods of
The Fnte Element Method GENERAL INTRODUCTION Read: Chapters 1 and 2 CONTENTS Engneerng and analyss Smulaton of a physcal process Examples mathematcal model development Approxmate solutons and methods of
Week 11: Chapter 11. The Vector Product. The Vector Product Defined. The Vector Product and Torque. More About the Vector Product
 The Vector Product Week 11: Chapter 11 Angular Momentum There are nstances where the product of two vectors s another vector Earler we saw where the product of two vectors was a scalar Ths was called the
The Vector Product Week 11: Chapter 11 Angular Momentum There are nstances where the product of two vectors s another vector Earler we saw where the product of two vectors was a scalar Ths was called the
Markov Chain Monte Carlo Lecture 6
 where (x 1,..., x N ) X N, N s called the populaton sze, f(x) f (x) for at least one {1, 2,..., N}, and those dfferent from f(x) are called the tral dstrbutons n terms of mportance samplng. Dfferent ways
where (x 1,..., x N ) X N, N s called the populaton sze, f(x) f (x) for at least one {1, 2,..., N}, and those dfferent from f(x) are called the tral dstrbutons n terms of mportance samplng. Dfferent ways
Study on Non-Linear Dynamic Characteristic of Vehicle. Suspension Rubber Component
 Study on Non-Lnear Dynamc Characterstc of Vehcle Suspenson Rubber Component Zhan Wenzhang Ln Y Sh GuobaoJln Unversty of TechnologyChangchun, Chna Wang Lgong (MDI, Chna [Abstract] The dynamc characterstc
Study on Non-Lnear Dynamc Characterstc of Vehcle Suspenson Rubber Component Zhan Wenzhang Ln Y Sh GuobaoJln Unversty of TechnologyChangchun, Chna Wang Lgong (MDI, Chna [Abstract] The dynamc characterstc
Electrical double layer: revisit based on boundary conditions
 Electrcal double layer: revst based on boundary condtons Jong U. Km Department of Electrcal and Computer Engneerng, Texas A&M Unversty College Staton, TX 77843-318, USA Abstract The electrcal double layer
Electrcal double layer: revst based on boundary condtons Jong U. Km Department of Electrcal and Computer Engneerng, Texas A&M Unversty College Staton, TX 77843-318, USA Abstract The electrcal double layer
A Numerical Study of Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow past Single Tube
 A Numercal Study of Heat ransfer and Flud Flow past Sngle ube ZEINAB SAYED ABDEL-REHIM Mechancal Engneerng Natonal Research Center El-Bohos Street, Dokk, Gza EGYP abdelrehmz@yahoo.com Abstract: - A numercal
A Numercal Study of Heat ransfer and Flud Flow past Sngle ube ZEINAB SAYED ABDEL-REHIM Mechancal Engneerng Natonal Research Center El-Bohos Street, Dokk, Gza EGYP abdelrehmz@yahoo.com Abstract: - A numercal
Application of B-Spline to Numerical Solution of a System of Singularly Perturbed Problems
 Mathematca Aeterna, Vol. 1, 011, no. 06, 405 415 Applcaton of B-Splne to Numercal Soluton of a System of Sngularly Perturbed Problems Yogesh Gupta Department of Mathematcs Unted College of Engneerng &
Mathematca Aeterna, Vol. 1, 011, no. 06, 405 415 Applcaton of B-Splne to Numercal Soluton of a System of Sngularly Perturbed Problems Yogesh Gupta Department of Mathematcs Unted College of Engneerng &
