Convergence Analysis of the LCCMA in an Asynchronous DS-CDMA System
|
|
|
- Melissa Craig
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Convergence naysis of the LCCM in an synchronous DS-CDM System James Whitehead and Fambirai aaira Schoo of Eectrica Eectronic and Computer Engineering University of Nata Durban South frica bstract he proof of goba convergence of the ineary constrained constant moduus agorithm (LCCM in the absence of noise for an asynchronous DS-CDM system is given. fter initia convergence by LCCM sitch over to decision directed (DD agorithms is standard practice. measure of the non-idea properties of the channe is used to modify the sitch over to the DD-LMS agorithm to improve its on stabiity and steady-state performance. Simuation resuts are used to demonstrate the increase in performance. I. INRODUCION he performance of persona ireess communications systems using direct sequence code division mutipe access (DS-CDM can be greaty enhanced by using signa processing techniques such as mutiuser detection (MUD []. MUD improves the performance by reducing the amount of mutipe access interference (MI at the receiver. he MUD considered in this paper is categorized as a inear scheme and is appicabe hen short spreading codes are used. In this paper bind indicates that ony the timing and spreading code information of the desired user is non at the receiver. Bind impementations are desirabe because they are spectray more efficient than their trained counter parts (they circumvent the need for piot channes. daptive schemes are desirabe because they offer a oer computationa compexity and have the abiity to trac a time varying channe. he constant moduus agorithm (CM is perhaps the most idey studied and used practica bind equaization agorithm [] [3] due to its computationa simpicity and robustness. he CM has recenty been appied to the bind adaptive MUD probem here the various versions: ineary constrained (LC- CM [] [5] mutiuser (MU- CM [6] cross correation (CC- CM [7] and ineary constrained differentia (LCD- CM [8] have modified the CM cost function to ensure that the desired user is captured. he LCCM scheme is considered in this paper because of its reative simpicity and proven resiience under mismatch conditions []. he upin of a future generation mobie ireess communications system oud typicay mae use of an asynchronous DS-CDM system ith short spreading codes. he his or as partiay supported by cate tech eecoms and eom S as part of the Centres of Exceence Programme. he financia assistance of the Department of Labour (DoL toards this research is hereby acnoedged. Opinions expressed and concusions arrived at are those of the author and are not necessariy to be attributed to the DoL. goba convergence in the mean of the LCCM as proven in [5] but ony for the synchronous case. his paper extends the proof of [5] to the asynchronous case by using a unique boc matrix formuation of the Hessian matrix of the LCCM cost function. he Hessian matrix defines the curvature of the cost surface at every point. Goba convergence is proved by shoing that the Hessian matrix is positive definite. positive definite Hessian matrix indicates that the cost surface is convex hich in turn proves that there is a unique goba minimum to the cost function. If the cost function has a unique minimum then a stochastic gradient agorithm is guaranteed to converge to the goba minimum irrespective of the initiaization of the adaptive fiter. he LCCM is a poerfu agorithm for converging to the MMSE receiver in a competey unnon operating environment. Once the LCCM agorithm has converged to the neighborhood of the MMSE receiver there are hoever better agorithms to sitch over to that i have a oer excess mean square error (EMSE in the tracing and steady-state phases of the adaptive agorithm. hese agorithms convergence properties are not as robust as that of the LCCM hich is hy LCCM is required to get the receiver into the neighborhood of the MMSE receiver. One idey touted agorithm [9] to use is the decision-directed LMS agorithm. he DD-LMS agorithm as originay formuated for the bind equaization of intersymbo-interference (ISI channes. hese happen to be quite different from the mutiuser CDM channe and hence their performance is reduced. his paper suggests a method of quantifying the deviation aay from the idea conditions that the DD-LMS as intended to operate in. his metric is then used to improve the performance of DD-LMS hen appied to the bind MUD appication. Improvements in both stabiity and steady-state EMSE of the modified DD-LMS are demonstrated via simuation. his paper is organized as foos: section II outines the signa mode and LCCM section III proves the goba convergence of the LCCM in an asynchronous DS-CDM system and section IV outines the modifications made to the DD-LMS agorithm. Simuation resuts are given in section V and concuding remars are made in section VI. II. SYSEM MODEL. ransmitter n asynchronous (ideband DS-CDM transmitter mode for the upin of a mobie radio netor is considered. he baseband representation of the th user s transmitted
2 signa is given by i x ( t b ( i s ( t i τ ( here and s denote the ampitude and normaised spreading aveform of the th user respectivey and is the data symbo duration. he reative offset of the th user s asynchronous signa is given byτ hich taes on integer vaues in the range 3. he th user s ith transmitted symbo b ( i taes on the vaues { + } ith equa probabiity. he spreading aveform taes the form N c n s ( t c ( n ψ ( t n t [ ] ( here N is the processing gain and c is the th user s spreading code sequence of ± s ψ ( t is the chip puse shape of duration c N. It is noted that s ( t ony taes on vaues in the interva [ ]. B. Receiver he received signa is passed through a chip-matched fiter and samped at the chip-rate. hese sampes are concatenated into a ength N vector of received sampes. Let s [ ] ( ( τ s s N τ be the don shifted (by amountτ version of discrete signature sequence vector s of ength N. Define ( N c ( c ( N s (3 [ ] [ ] [ τ ] [ τ ] S s s s ( S[ ] s ( N τ s ( N τ here ( N τ (5 s is the up shifted version of s aso padded ith zeros. he first entry in (5 is the zero vector as the receiver is bit synchronized to the desired user ( τ. Using this notation the received vector of sampes from the chip-matched fiter is given by [ ] ( i + [ ] ( i+ + b ( i b ( i b ( i diag ([ ] r S b S b n (6 is a diagona matrix ith the users ampitudes aong the main diagona and n ( i is an additive hite Gaussian noise vector ith covariance matrix σ I N. he vector r ( i is fitered by a finite impuse response (FIR fiter structure hose coefficients form the vector ( i ( i N ( i. he desired user from here on i be user. he output of the fiter hich constitutes the decision statistic is given by ( ( (. y i i r i (7 C. LCCM he non-canonicay constrained LCCM is based on the CM- [] agorithm and attempts to minimize the cost function ( J( ( i E ( i ( i r (8 subject to the inear constraint s. he LCCM uses its estimate of the desired user s signature sequence s to prevent the capture of unanted users. he cost func- tion as it stands is not amenabe to conventiona stochastic gradient techniques due to the constraint but by maing use of the canonica representation of the MMSE fiter [9] it is possibe to spit the fiter coefficients into to orthogona components: a fixed (or non-adaptive part and an adaptive part given by ( i + ( i s (9. he fiter component orthogona to the spreading code is adapted ithout a constraint. he update step of the adaptive agorithm is given by ( ( µ (( ( ( ( i+ i + y i y i r i ( here µ is a sma positive constant (step size. he orthogona projection of the received vector r ( i ( i ( i r s r s ( is used in ( to ensure that remains orthogona to s this in turn ensures that the constraint s is aays met. Reference [5] shoed that the LCCM converges to a scaed version of the MMSE fiter hich is given by opt C s sc s { ( (} [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] σ C E r i r i S S + S S + I. ( (3 III. CONVERGENCE NLYSIS FOR SYNCHRONOUS DS-CDM he technique used to prove the goba convergence property of the LCCM in an asynchronous DS-CDM system foos the same technique as that presented in []. his paper differs in the definition of the u and u vectors as e as the boc matrix notation used for the first and second derivatives of the LCCM cost function in order to accommodate the asynchronous data transmission of the various users. Define vectors u and u hose eements correspond to the contribution at the output of the fiter of the users current and successive transmitted bits ( [ ] ( [] u S and u S. ( he th eement of u and u are given by respectivey ( [ τ ] ( τ ( u s and u s N. (5 he output of the chip-matched matched fiter may no be ritten as r bu. + bu (6 Expanding the cost function in (8 e have { } ( E ( ( J r r +. (7 Using the reationship in (6 the cost function J ( may be expressed in terms of u and u {( } E r uu + uu (8
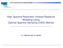
3 6 5 φ(u u 3 E u u Fig.. Surface Pot of LCCM cost function ( for a to user asynchronous system. {( r } E ( bubu + ubbu + ubbu 3( uu ( u { } ( uu ( u ( uu ( uu (9 since the inear constraint in (8 is equivaent to u the cost function in (7 can be ritten as u ( u u ( uu ( u + ( uu min φ 3 3 ( u ( uu ( uu ( uu uu ( We need to find the stationary points of the cost function to do this define a ne coumn vector u u ( u here u u u and u u u. Define a ne cost function in terms of u hich is equivaent to ( φ u φ u u ( ( ( he first derivative taes the form (using boc matrix notation u u u here the eements of are given by u (3 u ( ( uu ( uu ( ( u ( u 3 u + u u 3 uu + 3 uu ( u ( 3 + u + 3 u j + 3 u j j j j and simiary for : u ( u u ( 3 + u + 3 u j + 3 u j u j j j for. From ( and (5 ceary if ( stationary point is hen (5 3 then the ony u u (6 hich corresponds to the decorreating detector since the MI has been competey removed. he goba convexity of the cost function can be assured by anaysing the Hessian matrix of φ ( u. Using boc matrix notation the Hessian matrix taes the form φ φ u uu. u φ φ uu u φ Where the eements of the sub matrices are given by 3 ( ( uu 3( uu + u u u u u u u u and simiary for (7 (8 (9
4 3 ( ( uu 3( uu + u u u u (3 u u. (3 u u When 3 and thus u then the main diagona of the Hessian matrix equas 3 ( and off diagona eements equa. Ceary under this condition the Hessian matrix is positive definite the decorreating detector is the ony stationary point hich is aso the goba minimum and thus goba convergence is guaranteed. his is the same condition hich appies to the synchronous system hich as proved in [] he cost function as given in ( is potted in Fig. for a to user asynchronous system. In this case u and u as it is assumed that the spreading code and timing of the desired user is non perfecty. he height of the surface in Fig. is equa to the cost function of the remaining to degrees of freedom u and u. It can be seen that athough the curvature of the cost surface is not constant there does exist a unique goba minimum corresponding to u u the decorreating receiver. (he decorreating receiver competey removes MI. he terms u and u are a measure of the residua MI corresponding to user and hen they equa it indicates that a MI has been removed and thus the receiver is operating as the decorreating receiver. IV. IMPROVING SWICH OVER O DD-LMS. Reationship beteen LCCM and MMSE fiter coefficients It is e non that the optimum tap eight vector of the MMSE fiter is given by ( C s (3 M. Mutipying the optima tap eight vector of the non-canonicay constrained LCCM as given in ( by e get: opt C sc ( s ( s M s M (33 here it is non that the receiver gain is defined as (. θ " M s Substituting the s term of (33 using the receiver gain definition e get M opt θ (3 M θ hich shos that the LCCM and the MMSE fiter coefficients are coinear and are reated via the scaing factorθ. B. DD-LMS he update step of the DD-LMS agorithm is given by ( i+ ( i + µ ( sgn( y y r (35 he DD-LMS agorithm as originay formuated for the bind equaization of ISI channes. he presupposed operating conditions ere high SNR and perfecty bind equaizabiity of the channe. hese assumptions differ from the conditions found hen performing bind adaptive MUD in a DS-CDM communications system. For exampe in a ireess communications channe phenomena such as fading and shadoing can significanty oer the SNR. so there is residua MI at the output of a MMSE MUD and the amount increases as SNR decreases. hus the perfect equaization condition is vioated. It is proposed in this paper that the receiver gain is used to tae into account the deviation of the channe aay from the idea conditions expected by DD-LMS. Under idea conditions the SNR increases to infinity and the receiver approaches the decorreating receiver. When this occurs the residua MI goes to and θ approaches. Under non-idea conditions θ is in the range ( ith corresponding to a SNR of infinity. he optima tap eight vector of the DD-LMS agorithm is the MMSE tap eight vector. he reationship beteen the MMSE and LCCM optima tap eight vector as derived in this paper and given in (3 in terms of the receiver gainθ. he receiver gain is then used to scae the fiter coefficients in a once-off manner at the moment of sitch over to DD-LMS. his has the effect of removing the scaing beteen the optima DD-LMS fiter coefficients (hich are the MMSE fiter coefficients and the optima LCCM fiter coefficients. he scaing coud possiby ead to instabiity at sitch over or convergence toards oca minima (scaed MMSE. C. Estimation of Receiver Gain he receiver gain θ can be estimated by maing use of an approximation of the MMSE given in [9] and the expression for the MMSE achievabe ith a inear transformation ε given in [] as: min ε min sc s. (36 Using the definition of the receiver gain (36 can be ritten as ε min θ. (37 he approximation given in [9] for ε min hods hen the signa vectors are approximatey orthogona and is ε. min + σ Comparing (37 and (38 it is cear that (38 θ. (39 + σ his bound is asymptoticay tight ith SNR (see Fig. and upper bounds the true vaue as MI increases. he LCCM requires the estimation of to compute step (9 of the adaptive agorithm. he added compexity to estimate θ is tantamount to estimating the SNR hich is a common operation in error decoding and maxima ratio combining. It thus constitutes a margina increase in overa receiver compexity.
5 Exact vaue of θ pproximate vaue of θ SNR (db Fig.. Pot of θ and the estimate of θ using (39 as function of SNR. user system ith MI eve of 3dB s is used. V. RESULS the resuts ere generated using ength 3 God codes. he MI ratio is defined as here a the interfering users transmit at the same ampitude. he reative timing offsets of the users ere initiaized in the range [ 3 at the start of a particuar simuation and then fixed for the duration of the simuation. he output SINR at time instant i is defined as ( SINR i ( ( i s ( i + ( i σ s ( ( and as obtained from simuating the received vector of sampes given in (6 and impementing the LCCM as given in (. In Figs. 3-5 the LCCM is seen to converge correcty in an asynchronous DS-CDM system as proved in section III. Fig. 3 iustrates the performance increase obtained hen sitching over to DD-LMS from LCCM. he ensembe average SINR of independent simuation runs of the receiver agorithm is potted as a function of iterations (bits here the sitch over to DD-LMS is made at each time. user system ith MI ratio of 5dB s and SNR of 3 db s is considered. fixed step of is used. he LCCM is initiaized to the singe user matched fiter (MF and thus the output SINR is seen to start at the MF eve and converge toards the optima (MMSE SINR. It is observed that the LCCM requires approximatey bits to converge under this system configuration. It is assumed there is a 5% error in the estimate of the desired user s ampitude. his yieds a arge EMSE at steady-state. he DD-LMS agorithm does not require any ampitude estimation and its steady-state EMSE is significanty oer than the LCCM as it is observed that as soon as the sitch over to DD-LMS is made the output SINR immediatey increases. In Fig. the use of θ to correct the magnitude of the LCCM fiter coefficients at sitch over is seen to mae the DD-LMS mode of operation possibe as the DD-LMS agorithm is no stabe. he SINR of DD-LMS agorithm ithout the use of θ at sitch over is seen to decrease hich indicates that it is unstabe. system ith users 5dB MI ratio 5dB SNR and step size of 5 5 as considered. Fig. 5 demonstrates the performance gain hen θ is used on sitch over in the situation here DD-LMS is stabe ithout the use of θ. he system here θ as used has a higher output SINR as the DD-LMS agorithms converges to the correcty scaed version of the MMSE fiter coefficients. he system considered had users db SNR 5dB MI ratio and a step size of. VI. CONCLUSION In this paper the LCCM as proven to be gobay convergent in an asynchronous DS-CDM system here the receiver has enough degrees of freedom to competey suppress a MI. his paper aso derived the reationship beteen the optima non-canonicay constrained LCCM tap eight vector and the MMSE tap eight vector in terms of the receiver gain. his reationship as expoited at the sitch over to the DD-LMS mode of operation to both enhance the stabiity and increase the output SINR of the DD-LMS mode. simpe method for estimating the receiver gain as aso presented. 5 MMSE SINR Output SINR (db 5 LCCM DD LMS 5 Singe user matched fiter DD LMS sitch over No DD LMS sitch over Iterations x Fig. 3. Improvement in SINR hen sitching over to DD-LMS for a user asynchronous system.
6 Output SINR (db 3 MMSE SINR LCCM DD LMS 5 Singe user matched fiter θ used θ not used Iterations x Fig.. Stabiity due to the use of θ at the point of sitch over to DD-LMS. REFERENCES [] S. Verdú Mutiuser Detection Cambridge University Press 998. [] S. Hayin ed. Unsupervised daptive Fitering Chapter : he Core of FSE-CM Behavior heory Wiey 999. [3] C. R. Johnson Jr. P. Schniter. J. Endres J. D. Behn D. R. Bron R.. Casas Bind Equaization Using the Constant Moduus Criterion: Revie Proc. of IEEE Vo. 86 No. pp Oct [] J. Miguez L. Castedo Lineary Constrained Constant Moduus pproach to Bind daptive Mutiuser Interference Suppression IEEE Commun. Letters Vo. No. 8 pp. 7-9 ug [5] Changjiang Xu Guangzeng Feng yung Sup a modified constrained constant moduus approach to bind adaptive mutiuser detection IEEE rans. Commun. Vo. 9 No. 9 pp Sep.. [6] C. B. Papadias. J. Pauraj Constant Moduus gorithm for Mutiuser Signa Separation in Presence of Deay Spread Using ntenna rrays IEEE Sign. Proc. Lett. Vo. No. 6 pp May 997. [7] P. rasaratnam S. Zhu and. G. Constantinides "Fast Convergent mutiuser constant moduus agorithm for use in mutiuser DS/CDM Environments" IEEE Proc. Int. Conf. coust. Speech Signa Process. (ICSSP Orando Forida pp May. [8].Miyajima Bind daptive Detection Using Differentia CM for CDM Systems rans IEICE. Vo.J83- No. pp Nov.. Output SINR (db MMSE SINR. LCCM DD LMS θ used θ not used.5.5 Iterations x Fig. 5. Increased Performance due to the use of θ at the point of sitch over to DD-LMS. [9] M. Honig U. Madho S. Verdú Bind daptive Mutiuser Detection IEEE rans. On Information heory Vo. No. pp Juy 995. [] C. Xu G. Feng Comments on Lineary Constrained Constant Moduus pproach to Bind daptive Mutiuser Interference Suppression IEEE Commun. Letters Vo. No. 9 pp. 8-8 Sept.. James Whitehead hods a BScEng (Eectronic and MscEng degree from the University of Nata. t present he is studying a PhD at the University of Nata. His research interests incude CDM systems ith emphasis on mutiuser detection and muti-antenna systems. Fambirai aaira hods a PhD degree from Cambridge University Cambridge U.. He is presenty a Professor at and the head of the Schoo of Eectrica and Eectronic Engineering at the University of Nata Durban South frica. His research interests are in digita communication systems and netors ith particuar emphasis on CDM ceuar systems
ESTIMATION OF SAMPLING TIME MISALIGNMENTS IN IFDMA UPLINK
 ESTIMATION OF SAMPLING TIME MISALIGNMENTS IN IFDMA UPLINK Aexander Arkhipov, Michae Schne German Aerospace Center DLR) Institute of Communications and Navigation Oberpfaffenhofen, 8224 Wessing, Germany
ESTIMATION OF SAMPLING TIME MISALIGNMENTS IN IFDMA UPLINK Aexander Arkhipov, Michae Schne German Aerospace Center DLR) Institute of Communications and Navigation Oberpfaffenhofen, 8224 Wessing, Germany
Source and Relay Matrices Optimization for Multiuser Multi-Hop MIMO Relay Systems
 Source and Reay Matrices Optimization for Mutiuser Muti-Hop MIMO Reay Systems Yue Rong Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering, Curtin University, Bentey, WA 6102, Austraia Abstract In this paper,
Source and Reay Matrices Optimization for Mutiuser Muti-Hop MIMO Reay Systems Yue Rong Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering, Curtin University, Bentey, WA 6102, Austraia Abstract In this paper,
MC-CDMA CDMA Systems. Introduction. Ivan Cosovic. Stefan Kaiser. IEEE Communication Theory Workshop 2005 Park City, USA, June 15, 2005
 On the Adaptivity in Down- and Upink MC- Systems Ivan Cosovic German Aerospace Center (DLR) Institute of Comm. and Navigation Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany Stefan Kaiser DoCoMo Euro-Labs Wireess Soution Laboratory
On the Adaptivity in Down- and Upink MC- Systems Ivan Cosovic German Aerospace Center (DLR) Institute of Comm. and Navigation Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany Stefan Kaiser DoCoMo Euro-Labs Wireess Soution Laboratory
FRST Multivariate Statistics. Multivariate Discriminant Analysis (MDA)
 1 FRST 531 -- Mutivariate Statistics Mutivariate Discriminant Anaysis (MDA) Purpose: 1. To predict which group (Y) an observation beongs to based on the characteristics of p predictor (X) variabes, using
1 FRST 531 -- Mutivariate Statistics Mutivariate Discriminant Anaysis (MDA) Purpose: 1. To predict which group (Y) an observation beongs to based on the characteristics of p predictor (X) variabes, using
High Spectral Resolution Infrared Radiance Modeling Using Optimal Spectral Sampling (OSS) Method
 High Spectra Resoution Infrared Radiance Modeing Using Optima Spectra Samping (OSS) Method J.-L. Moncet and G. Uymin Background Optima Spectra Samping (OSS) method is a fast and accurate monochromatic
High Spectra Resoution Infrared Radiance Modeing Using Optima Spectra Samping (OSS) Method J.-L. Moncet and G. Uymin Background Optima Spectra Samping (OSS) method is a fast and accurate monochromatic
T.C. Banwell, S. Galli. {bct, Telcordia Technologies, Inc., 445 South Street, Morristown, NJ 07960, USA
 ON THE SYMMETRY OF THE POWER INE CHANNE T.C. Banwe, S. Gai {bct, sgai}@research.tecordia.com Tecordia Technoogies, Inc., 445 South Street, Morristown, NJ 07960, USA Abstract The indoor power ine network
ON THE SYMMETRY OF THE POWER INE CHANNE T.C. Banwe, S. Gai {bct, sgai}@research.tecordia.com Tecordia Technoogies, Inc., 445 South Street, Morristown, NJ 07960, USA Abstract The indoor power ine network
First-Order Corrections to Gutzwiller s Trace Formula for Systems with Discrete Symmetries
 c 26 Noninear Phenomena in Compex Systems First-Order Corrections to Gutzwier s Trace Formua for Systems with Discrete Symmetries Hoger Cartarius, Jörg Main, and Günter Wunner Institut für Theoretische
c 26 Noninear Phenomena in Compex Systems First-Order Corrections to Gutzwier s Trace Formua for Systems with Discrete Symmetries Hoger Cartarius, Jörg Main, and Günter Wunner Institut für Theoretische
DIGITAL FILTER DESIGN OF IIR FILTERS USING REAL VALUED GENETIC ALGORITHM
 DIGITAL FILTER DESIGN OF IIR FILTERS USING REAL VALUED GENETIC ALGORITHM MIKAEL NILSSON, MATTIAS DAHL AND INGVAR CLAESSON Bekinge Institute of Technoogy Department of Teecommunications and Signa Processing
DIGITAL FILTER DESIGN OF IIR FILTERS USING REAL VALUED GENETIC ALGORITHM MIKAEL NILSSON, MATTIAS DAHL AND INGVAR CLAESSON Bekinge Institute of Technoogy Department of Teecommunications and Signa Processing
Radar/ESM Tracking of Constant Velocity Target : Comparison of Batch (MLE) and EKF Performance
 adar/ racing of Constant Veocity arget : Comparison of Batch (LE) and EKF Performance I. Leibowicz homson-csf Deteis/IISA La cef de Saint-Pierre 1 Bd Jean ouin 7885 Eancourt Cede France Isabee.Leibowicz
adar/ racing of Constant Veocity arget : Comparison of Batch (LE) and EKF Performance I. Leibowicz homson-csf Deteis/IISA La cef de Saint-Pierre 1 Bd Jean ouin 7885 Eancourt Cede France Isabee.Leibowicz
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF MULTIPLE ACCESS CHAOTIC-SEQUENCE SPREAD-SPECTRUM COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS USING PARALLEL INTERFERENCE CANCELLATION RECEIVERS
 Internationa Journa of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vo. 14, No. 10 (2004) 3633 3646 c Word Scientific Pubishing Company PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF MULTIPLE ACCESS CHAOTIC-SEQUENCE SPREAD-SPECTRUM COMMUNICATION
Internationa Journa of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vo. 14, No. 10 (2004) 3633 3646 c Word Scientific Pubishing Company PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF MULTIPLE ACCESS CHAOTIC-SEQUENCE SPREAD-SPECTRUM COMMUNICATION
Scalable Spectrum Allocation for Large Networks Based on Sparse Optimization
 Scaabe Spectrum ocation for Large Networks ased on Sparse Optimization innan Zhuang Modem R&D Lab Samsung Semiconductor, Inc. San Diego, C Dongning Guo, Ermin Wei, and Michae L. Honig Department of Eectrica
Scaabe Spectrum ocation for Large Networks ased on Sparse Optimization innan Zhuang Modem R&D Lab Samsung Semiconductor, Inc. San Diego, C Dongning Guo, Ermin Wei, and Michae L. Honig Department of Eectrica
Optimality of Gaussian Fronthaul Compression for Uplink MIMO Cloud Radio Access Networks
 Optimaity of Gaussian Fronthau Compression for Upink MMO Coud Radio Access etworks Yuhan Zhou, Yinfei Xu, Jun Chen, and Wei Yu Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering, University of oronto, Canada
Optimaity of Gaussian Fronthau Compression for Upink MMO Coud Radio Access etworks Yuhan Zhou, Yinfei Xu, Jun Chen, and Wei Yu Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering, University of oronto, Canada
LINEAR DETECTORS FOR MULTI-USER MIMO SYSTEMS WITH CORRELATED SPATIAL DIVERSITY
 LINEAR DETECTORS FOR MULTI-USER MIMO SYSTEMS WITH CORRELATED SPATIAL DIVERSITY Laura Cottateucci, Raf R. Müer, and Mérouane Debbah Ist. of Teecommunications Research Dep. of Eectronics and Teecommunications
LINEAR DETECTORS FOR MULTI-USER MIMO SYSTEMS WITH CORRELATED SPATIAL DIVERSITY Laura Cottateucci, Raf R. Müer, and Mérouane Debbah Ist. of Teecommunications Research Dep. of Eectronics and Teecommunications
A Brief Introduction to Markov Chains and Hidden Markov Models
 A Brief Introduction to Markov Chains and Hidden Markov Modes Aen B MacKenzie Notes for December 1, 3, &8, 2015 Discrete-Time Markov Chains You may reca that when we first introduced random processes,
A Brief Introduction to Markov Chains and Hidden Markov Modes Aen B MacKenzie Notes for December 1, 3, &8, 2015 Discrete-Time Markov Chains You may reca that when we first introduced random processes,
Transmit Antenna Selection for Physical-Layer Network Coding Based on Euclidean Distance
 Transmit ntenna Seection for Physica-Layer Networ Coding ased on Eucidean Distance 1 arxiv:179.445v1 [cs.it] 13 Sep 17 Vaibhav Kumar, arry Cardiff, and Mar F. Fanagan Schoo of Eectrica and Eectronic Engineering,
Transmit ntenna Seection for Physica-Layer Networ Coding ased on Eucidean Distance 1 arxiv:179.445v1 [cs.it] 13 Sep 17 Vaibhav Kumar, arry Cardiff, and Mar F. Fanagan Schoo of Eectrica and Eectronic Engineering,
Maximizing Sum Rate and Minimizing MSE on Multiuser Downlink: Optimality, Fast Algorithms and Equivalence via Max-min SIR
 1 Maximizing Sum Rate and Minimizing MSE on Mutiuser Downink: Optimaity, Fast Agorithms and Equivaence via Max-min SIR Chee Wei Tan 1,2, Mung Chiang 2 and R. Srikant 3 1 Caifornia Institute of Technoogy,
1 Maximizing Sum Rate and Minimizing MSE on Mutiuser Downink: Optimaity, Fast Agorithms and Equivaence via Max-min SIR Chee Wei Tan 1,2, Mung Chiang 2 and R. Srikant 3 1 Caifornia Institute of Technoogy,
Turbo Codes. Coding and Communication Laboratory. Dept. of Electrical Engineering, National Chung Hsing University
 Turbo Codes Coding and Communication Laboratory Dept. of Eectrica Engineering, Nationa Chung Hsing University Turbo codes 1 Chapter 12: Turbo Codes 1. Introduction 2. Turbo code encoder 3. Design of intereaver
Turbo Codes Coding and Communication Laboratory Dept. of Eectrica Engineering, Nationa Chung Hsing University Turbo codes 1 Chapter 12: Turbo Codes 1. Introduction 2. Turbo code encoder 3. Design of intereaver
A Simple and Efficient Algorithm of 3-D Single-Source Localization with Uniform Cross Array Bing Xue 1 2 a) * Guangyou Fang 1 2 b and Yicai Ji 1 2 c)
 A Simpe Efficient Agorithm of 3-D Singe-Source Locaization with Uniform Cross Array Bing Xue a * Guangyou Fang b Yicai Ji c Key Laboratory of Eectromagnetic Radiation Sensing Technoogy, Institute of Eectronics,
A Simpe Efficient Agorithm of 3-D Singe-Source Locaization with Uniform Cross Array Bing Xue a * Guangyou Fang b Yicai Ji c Key Laboratory of Eectromagnetic Radiation Sensing Technoogy, Institute of Eectronics,
Gokhan M. Guvensen, Member, IEEE, and Ender Ayanoglu, Fellow, IEEE. Abstract
 A Generaized Framework on Beamformer esign 1 and CSI Acquisition for Singe-Carrier Massive MIMO Systems in Miimeter Wave Channes Gokhan M. Guvensen, Member, IEEE, and Ender Ayanogu, Feow, IEEE arxiv:1607.01436v1
A Generaized Framework on Beamformer esign 1 and CSI Acquisition for Singe-Carrier Massive MIMO Systems in Miimeter Wave Channes Gokhan M. Guvensen, Member, IEEE, and Ender Ayanogu, Feow, IEEE arxiv:1607.01436v1
Throughput Optimal Scheduling for Wireless Downlinks with Reconfiguration Delay
 Throughput Optima Scheduing for Wireess Downinks with Reconfiguration Deay Vineeth Baa Sukumaran vineethbs@gmai.com Department of Avionics Indian Institute of Space Science and Technoogy. Abstract We consider
Throughput Optima Scheduing for Wireess Downinks with Reconfiguration Deay Vineeth Baa Sukumaran vineethbs@gmai.com Department of Avionics Indian Institute of Space Science and Technoogy. Abstract We consider
A GENERAL METHOD FOR EVALUATING OUTAGE PROBABILITIES USING PADÉ APPROXIMATIONS
 A GENERAL METHOD FOR EVALUATING OUTAGE PROBABILITIES USING PADÉ APPROXIMATIONS Jack W. Stokes, Microsoft Corporation One Microsoft Way, Redmond, WA 9852, jstokes@microsoft.com James A. Ritcey, University
A GENERAL METHOD FOR EVALUATING OUTAGE PROBABILITIES USING PADÉ APPROXIMATIONS Jack W. Stokes, Microsoft Corporation One Microsoft Way, Redmond, WA 9852, jstokes@microsoft.com James A. Ritcey, University
Approximate Minimum Bit-Error Rate Multiuser Detection
 Approximate Minimum Bit-Error Rate Multiuser Detection Chen-Chu Yeh, Renato R. opes, and John R. Barry School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0250
Approximate Minimum Bit-Error Rate Multiuser Detection Chen-Chu Yeh, Renato R. opes, and John R. Barry School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0250
FREQUENCY modulated differential chaos shift key (FM-
 Accepted in IEEE 83rd Vehicuar Technoogy Conference VTC, 16 1 SNR Estimation for FM-DCS System over Mutipath Rayeigh Fading Channes Guofa Cai, in Wang, ong ong, Georges addoum Dept. of Communication Engineering,
Accepted in IEEE 83rd Vehicuar Technoogy Conference VTC, 16 1 SNR Estimation for FM-DCS System over Mutipath Rayeigh Fading Channes Guofa Cai, in Wang, ong ong, Georges addoum Dept. of Communication Engineering,
LINK BETWEEN THE JOINT DIAGONALISATION OF SYMMETRICAL CUBES AND PARAFAC: AN APPLICATION TO SECONDARY SURVEILLANCE RADAR
 LINK BETWEEN THE JOINT DIAGONALISATION OF SYMMETRICAL CUBES AND PARAFAC: AN APPLICATION TO SECONDARY SURVEILLANCE RADAR Nicoas PETROCHILOS CReSTIC, University of Reims Mouins de a Housse, BP 1039 51687
LINK BETWEEN THE JOINT DIAGONALISATION OF SYMMETRICAL CUBES AND PARAFAC: AN APPLICATION TO SECONDARY SURVEILLANCE RADAR Nicoas PETROCHILOS CReSTIC, University of Reims Mouins de a Housse, BP 1039 51687
Adaptive Joint Self-Interference Cancellation and Equalization for Space-Time Coded Bi-Directional Relaying Networks
 1 Adaptive Joint Sef-Interference Canceation and Equaization for Space-Time Coded Bi-Directiona Reaying Networs Jeong-Min Choi, Jae-Shin Han, and Jong-Soo Seo Department of Eectrica and Eectronic Engineering,
1 Adaptive Joint Sef-Interference Canceation and Equaization for Space-Time Coded Bi-Directiona Reaying Networs Jeong-Min Choi, Jae-Shin Han, and Jong-Soo Seo Department of Eectrica and Eectronic Engineering,
Distributed average consensus: Beyond the realm of linearity
 Distributed average consensus: Beyond the ream of inearity Usman A. Khan, Soummya Kar, and José M. F. Moura Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering Carnegie Meon University 5 Forbes Ave, Pittsburgh,
Distributed average consensus: Beyond the ream of inearity Usman A. Khan, Soummya Kar, and José M. F. Moura Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering Carnegie Meon University 5 Forbes Ave, Pittsburgh,
Asynchronous Control for Coupled Markov Decision Systems
 INFORMATION THEORY WORKSHOP (ITW) 22 Asynchronous Contro for Couped Marov Decision Systems Michae J. Neey University of Southern Caifornia Abstract This paper considers optima contro for a coection of
INFORMATION THEORY WORKSHOP (ITW) 22 Asynchronous Contro for Couped Marov Decision Systems Michae J. Neey University of Southern Caifornia Abstract This paper considers optima contro for a coection of
BICM Performance Improvement via Online LLR Optimization
 BICM Performance Improvement via Onine LLR Optimization Jinhong Wu, Mostafa E-Khamy, Jungwon Lee and Inyup Kang Samsung Mobie Soutions Lab San Diego, USA 92121 Emai: {Jinhong.W, Mostafa.E, Jungwon2.Lee,
BICM Performance Improvement via Onine LLR Optimization Jinhong Wu, Mostafa E-Khamy, Jungwon Lee and Inyup Kang Samsung Mobie Soutions Lab San Diego, USA 92121 Emai: {Jinhong.W, Mostafa.E, Jungwon2.Lee,
sensors Beamforming Based Full-Duplex for Millimeter-Wave Communication Article
 sensors Artice Beamforming Based Fu-Dupex for Miimeter-Wave Communication Xiao Liu 1,2,3, Zhenyu Xiao 1,2,3, *, Lin Bai 1,2,3, Jinho Choi 4, Pengfei Xia 5 and Xiang-Gen Xia 6 1 Schoo of Eectronic and Information
sensors Artice Beamforming Based Fu-Dupex for Miimeter-Wave Communication Xiao Liu 1,2,3, Zhenyu Xiao 1,2,3, *, Lin Bai 1,2,3, Jinho Choi 4, Pengfei Xia 5 and Xiang-Gen Xia 6 1 Schoo of Eectronic and Information
Methods for Ordinary Differential Equations. Jacob White
 Introduction to Simuation - Lecture 12 for Ordinary Differentia Equations Jacob White Thanks to Deepak Ramaswamy, Jaime Peraire, Micha Rewienski, and Karen Veroy Outine Initia Vaue probem exampes Signa
Introduction to Simuation - Lecture 12 for Ordinary Differentia Equations Jacob White Thanks to Deepak Ramaswamy, Jaime Peraire, Micha Rewienski, and Karen Veroy Outine Initia Vaue probem exampes Signa
Doubly Iterative Receiver for Block Transmissions with EM-Based Channel Estimation
 656 IEEE RANSACIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICAIONS, VOL. 8, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2009 Douby Iterative Receiver for Bock ransmissions with EM-Based Channe Estimation he-hanh Pham, Ying-Chang Liang, Senior Member,
656 IEEE RANSACIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICAIONS, VOL. 8, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2009 Douby Iterative Receiver for Bock ransmissions with EM-Based Channe Estimation he-hanh Pham, Ying-Chang Liang, Senior Member,
Title Sinusoidal Signals. Author(s) Sakai, Hideaki; Fukuzono, Hayato. Conference: Issue Date DOI
 Tite Anaysis of Adaptive Fiters in Fee Sinusoida Signas Authors) Sakai, Hideaki; Fukuzono, Hayato Proceedings : APSIPA ASC 2009 : Asi Citation Information Processing Association, Conference: 430-433 Issue
Tite Anaysis of Adaptive Fiters in Fee Sinusoida Signas Authors) Sakai, Hideaki; Fukuzono, Hayato Proceedings : APSIPA ASC 2009 : Asi Citation Information Processing Association, Conference: 430-433 Issue
A. Distribution of the test statistic
 A. Distribution of the test statistic In the sequentia test, we first compute the test statistic from a mini-batch of size m. If a decision cannot be made with this statistic, we keep increasing the mini-batch
A. Distribution of the test statistic In the sequentia test, we first compute the test statistic from a mini-batch of size m. If a decision cannot be made with this statistic, we keep increasing the mini-batch
Introduction to Simulation - Lecture 13. Convergence of Multistep Methods. Jacob White. Thanks to Deepak Ramaswamy, Michal Rewienski, and Karen Veroy
 Introduction to Simuation - Lecture 13 Convergence of Mutistep Methods Jacob White Thans to Deepa Ramaswamy, Micha Rewiensi, and Karen Veroy Outine Sma Timestep issues for Mutistep Methods Loca truncation
Introduction to Simuation - Lecture 13 Convergence of Mutistep Methods Jacob White Thans to Deepa Ramaswamy, Micha Rewiensi, and Karen Veroy Outine Sma Timestep issues for Mutistep Methods Loca truncation
A Novel Approach to Security Enhancement of Chaotic DSSS Systems
 A Nove Approach to Security Enhancement of Chaotic DSSS Systems Nguyen Xuan Quyen 1, Chuyen T. Nguyen 1, Pere Baret-Ros 2, and Reiner Dojen 3 1 Schoo of Eectronics and Teecommunications, Hanoi University
A Nove Approach to Security Enhancement of Chaotic DSSS Systems Nguyen Xuan Quyen 1, Chuyen T. Nguyen 1, Pere Baret-Ros 2, and Reiner Dojen 3 1 Schoo of Eectronics and Teecommunications, Hanoi University
Polite Water-filling for the Boundary of the Capacity/Achievable Regions of MIMO MAC/BC/Interference Networks
 2011 IEEE Internationa Symposium on Information Theory Proceedings Poite Water-fiing for the Boundary of the Capacity/Achievabe Regions of MIMO MAC/BC/Interference Networks An iu 1, Youjian iu 2, Haige
2011 IEEE Internationa Symposium on Information Theory Proceedings Poite Water-fiing for the Boundary of the Capacity/Achievabe Regions of MIMO MAC/BC/Interference Networks An iu 1, Youjian iu 2, Haige
Linear Network Coding for Multiple Groupcast Sessions: An Interference Alignment Approach
 Linear Network Coding for Mutipe Groupcast Sessions: An Interference Aignment Approach Abhik Kumar Das, Siddhartha Banerjee and Sriram Vishwanath Dept. of ECE, The University of Texas at Austin, TX, USA
Linear Network Coding for Mutipe Groupcast Sessions: An Interference Aignment Approach Abhik Kumar Das, Siddhartha Banerjee and Sriram Vishwanath Dept. of ECE, The University of Texas at Austin, TX, USA
Smoothers for ecient multigrid methods in IGA
 Smoothers for ecient mutigrid methods in IGA Cemens Hofreither, Stefan Takacs, Water Zuehner DD23, Juy 2015 supported by The work was funded by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF): NFN S117 (rst and third
Smoothers for ecient mutigrid methods in IGA Cemens Hofreither, Stefan Takacs, Water Zuehner DD23, Juy 2015 supported by The work was funded by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF): NFN S117 (rst and third
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL TO INNOVATED SCALABLE EFFICIENT ESTIMATION IN ULTRA-LARGE GAUSSIAN GRAPHICAL MODELS
 ISEE 1 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL TO INNOVATED SCALABLE EFFICIENT ESTIMATION IN ULTRA-LARGE GAUSSIAN GRAPHICAL MODELS By Yingying Fan and Jinchi Lv University of Southern Caifornia This Suppementary Materia
ISEE 1 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL TO INNOVATED SCALABLE EFFICIENT ESTIMATION IN ULTRA-LARGE GAUSSIAN GRAPHICAL MODELS By Yingying Fan and Jinchi Lv University of Southern Caifornia This Suppementary Materia
Precoding for the Sparsely Spread MC-CDMA Downlink with Discrete-Alphabet Inputs
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL.*, NO.*, MONTH 2016 1 Precoding for the Sparsey Spread MC-CDMA Downin with Discrete-Aphabet Inputs Min Li, Member, IEEE, Chunshan Liu, Member, IEEE, and Stephen
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL.*, NO.*, MONTH 2016 1 Precoding for the Sparsey Spread MC-CDMA Downin with Discrete-Aphabet Inputs Min Li, Member, IEEE, Chunshan Liu, Member, IEEE, and Stephen
Bayesian Unscented Kalman Filter for State Estimation of Nonlinear and Non-Gaussian Systems
 Bayesian Unscented Kaman Fiter for State Estimation of Noninear and Non-aussian Systems Zhong Liu, Shing-Chow Chan, Ho-Chun Wu and iafei Wu Department of Eectrica and Eectronic Engineering, he University
Bayesian Unscented Kaman Fiter for State Estimation of Noninear and Non-aussian Systems Zhong Liu, Shing-Chow Chan, Ho-Chun Wu and iafei Wu Department of Eectrica and Eectronic Engineering, he University
Sum Capacity and TSC Bounds in Collaborative Multi-Base Wireless Systems
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL X, NO X, DECEMBER 004 1 Sum Capacity and TSC Bounds in Coaborative Muti-Base Wireess Systems Otiia Popescu, Student Member, IEEE, and Christopher Rose, Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL X, NO X, DECEMBER 004 1 Sum Capacity and TSC Bounds in Coaborative Muti-Base Wireess Systems Otiia Popescu, Student Member, IEEE, and Christopher Rose, Member,
OPPORTUNISTIC SPECTRUM ACCESS (OSA) [1], first. Cluster-Based Differential Energy Detection for Spectrum Sensing in Multi-Carrier Systems
![OPPORTUNISTIC SPECTRUM ACCESS (OSA) [1], first. Cluster-Based Differential Energy Detection for Spectrum Sensing in Multi-Carrier Systems OPPORTUNISTIC SPECTRUM ACCESS (OSA) [1], first. Cluster-Based Differential Energy Detection for Spectrum Sensing in Multi-Carrier Systems](/thumbs/86/93514187.jpg) Custer-Based Differentia Energy Detection for Spectrum Sensing in Muti-Carrier Systems Parisa Cheraghi, Student Member, IEEE, Yi Ma, Senior Member, IEEE, Rahim Tafazoi, Senior Member, IEEE, and Zhengwei
Custer-Based Differentia Energy Detection for Spectrum Sensing in Muti-Carrier Systems Parisa Cheraghi, Student Member, IEEE, Yi Ma, Senior Member, IEEE, Rahim Tafazoi, Senior Member, IEEE, and Zhengwei
Adaptive Fuzzy Sliding Control for a Three-Link Passive Robotic Manipulator
 Adaptive Fuzzy Siding Contro for a hree-link Passive Robotic anipuator Abstract An adaptive fuzzy siding contro (AFSC scheme is proposed to contro a passive robotic manipuator. he motivation for the design
Adaptive Fuzzy Siding Contro for a hree-link Passive Robotic anipuator Abstract An adaptive fuzzy siding contro (AFSC scheme is proposed to contro a passive robotic manipuator. he motivation for the design
Introduction to Simulation - Lecture 14. Multistep Methods II. Jacob White. Thanks to Deepak Ramaswamy, Michal Rewienski, and Karen Veroy
 Introduction to Simuation - Lecture 14 Mutistep Methods II Jacob White Thans to Deepa Ramaswamy, Micha Rewiensi, and Karen Veroy Outine Sma Timestep issues for Mutistep Methods Reminder about LTE minimization
Introduction to Simuation - Lecture 14 Mutistep Methods II Jacob White Thans to Deepa Ramaswamy, Micha Rewiensi, and Karen Veroy Outine Sma Timestep issues for Mutistep Methods Reminder about LTE minimization
Optimality of Inference in Hierarchical Coding for Distributed Object-Based Representations
 Optimaity of Inference in Hierarchica Coding for Distributed Object-Based Representations Simon Brodeur, Jean Rouat NECOTIS, Département génie éectrique et génie informatique, Université de Sherbrooke,
Optimaity of Inference in Hierarchica Coding for Distributed Object-Based Representations Simon Brodeur, Jean Rouat NECOTIS, Département génie éectrique et génie informatique, Université de Sherbrooke,
An Algorithm for Pruning Redundant Modules in Min-Max Modular Network
 An Agorithm for Pruning Redundant Modues in Min-Max Moduar Network Hui-Cheng Lian and Bao-Liang Lu Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1954 Hua Shan Rd., Shanghai
An Agorithm for Pruning Redundant Modues in Min-Max Moduar Network Hui-Cheng Lian and Bao-Liang Lu Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University 1954 Hua Shan Rd., Shanghai
MARKOV CHAINS AND MARKOV DECISION THEORY. Contents
 MARKOV CHAINS AND MARKOV DECISION THEORY ARINDRIMA DATTA Abstract. In this paper, we begin with a forma introduction to probabiity and expain the concept of random variabes and stochastic processes. After
MARKOV CHAINS AND MARKOV DECISION THEORY ARINDRIMA DATTA Abstract. In this paper, we begin with a forma introduction to probabiity and expain the concept of random variabes and stochastic processes. After
Symbolic models for nonlinear control systems using approximate bisimulation
 Symboic modes for noninear contro systems using approximate bisimuation Giordano Poa, Antoine Girard and Pauo Tabuada Abstract Contro systems are usuay modeed by differentia equations describing how physica
Symboic modes for noninear contro systems using approximate bisimuation Giordano Poa, Antoine Girard and Pauo Tabuada Abstract Contro systems are usuay modeed by differentia equations describing how physica
Partial permutation decoding for MacDonald codes
 Partia permutation decoding for MacDonad codes J.D. Key Department of Mathematics and Appied Mathematics University of the Western Cape 7535 Bevie, South Africa P. Seneviratne Department of Mathematics
Partia permutation decoding for MacDonad codes J.D. Key Department of Mathematics and Appied Mathematics University of the Western Cape 7535 Bevie, South Africa P. Seneviratne Department of Mathematics
FREQUENCY-DOMAIN EQUALIZATION OF SINGLE CARRIER TRANSMISSIONS OVER DOUBLY SELECTIVE CHANNELS
 FREQUENCY-DOMAIN EQUALIZATION OF SINGLE CARRIER TRANSMISSIONS OVER DOUBLY SELECTIVE CHANNELS DISSERTATION Presented in Partia Fufiment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Phiosophy in the Graduate
FREQUENCY-DOMAIN EQUALIZATION OF SINGLE CARRIER TRANSMISSIONS OVER DOUBLY SELECTIVE CHANNELS DISSERTATION Presented in Partia Fufiment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Phiosophy in the Graduate
LOW-COMPLEXITY LINEAR PRECODING FOR MULTI-CELL MASSIVE MIMO SYSTEMS
 LOW-COMPLEXITY LINEAR PRECODING FOR MULTI-CELL MASSIVE MIMO SYSTEMS Aba ammoun, Axe Müer, Emi Björnson,3, and Mérouane Debbah ing Abduah University of Science and Technoogy (AUST, Saudi Arabia Acate-Lucent
LOW-COMPLEXITY LINEAR PRECODING FOR MULTI-CELL MASSIVE MIMO SYSTEMS Aba ammoun, Axe Müer, Emi Björnson,3, and Mérouane Debbah ing Abduah University of Science and Technoogy (AUST, Saudi Arabia Acate-Lucent
ASummaryofGaussianProcesses Coryn A.L. Bailer-Jones
 ASummaryofGaussianProcesses Coryn A.L. Baier-Jones Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge caj@mrao.cam.ac.uk Introduction A genera prediction probem can be posed as foows. We consider that the variabe
ASummaryofGaussianProcesses Coryn A.L. Baier-Jones Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge caj@mrao.cam.ac.uk Introduction A genera prediction probem can be posed as foows. We consider that the variabe
Subspace Estimation and Decomposition for Hybrid Analog-Digital Millimetre-Wave MIMO systems
 Subspace Estimation and Decomposition for Hybrid Anaog-Digita Miimetre-Wave MIMO systems Hadi Ghauch, Mats Bengtsson, Taejoon Kim, Mikae Skogund Schoo of Eectrica Engineering and the ACCESS Linnaeus Center,
Subspace Estimation and Decomposition for Hybrid Anaog-Digita Miimetre-Wave MIMO systems Hadi Ghauch, Mats Bengtsson, Taejoon Kim, Mikae Skogund Schoo of Eectrica Engineering and the ACCESS Linnaeus Center,
Iterative Decoding Performance Bounds for LDPC Codes on Noisy Channels
 Iterative Decoding Performance Bounds for LDPC Codes on Noisy Channes arxiv:cs/060700v1 [cs.it] 6 Ju 006 Chun-Hao Hsu and Achieas Anastasopouos Eectrica Engineering and Computer Science Department University
Iterative Decoding Performance Bounds for LDPC Codes on Noisy Channes arxiv:cs/060700v1 [cs.it] 6 Ju 006 Chun-Hao Hsu and Achieas Anastasopouos Eectrica Engineering and Computer Science Department University
A Generalized Framework on Beamformer Design and CSI Acquisition for Single-Carrier Massive MIMO Systems in Millimeter-Wave Channels
 1 A Generaized Framework on Beamformer esign and CSI Acquisition for Singe-Carrier Massive MIMO Systems in Miimeter-Wave Channes Gokhan M. Guvensen, Member, IEEE and Ender Ayanogu, Feow, IEEE Abstract
1 A Generaized Framework on Beamformer esign and CSI Acquisition for Singe-Carrier Massive MIMO Systems in Miimeter-Wave Channes Gokhan M. Guvensen, Member, IEEE and Ender Ayanogu, Feow, IEEE Abstract
Group Sparse Precoding for Cloud-RAN with Multiple User Antennas
 entropy Artice Group Sparse Precoding for Coud-RAN with Mutipe User Antennas Zhiyang Liu ID, Yingxin Zhao * ID, Hong Wu and Shuxue Ding Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoeectronic Sensor and Sensing Networ
entropy Artice Group Sparse Precoding for Coud-RAN with Mutipe User Antennas Zhiyang Liu ID, Yingxin Zhao * ID, Hong Wu and Shuxue Ding Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoeectronic Sensor and Sensing Networ
Haar Decomposition and Reconstruction Algorithms
 Jim Lambers MAT 773 Fa Semester 018-19 Lecture 15 and 16 Notes These notes correspond to Sections 4.3 and 4.4 in the text. Haar Decomposition and Reconstruction Agorithms Decomposition Suppose we approximate
Jim Lambers MAT 773 Fa Semester 018-19 Lecture 15 and 16 Notes These notes correspond to Sections 4.3 and 4.4 in the text. Haar Decomposition and Reconstruction Agorithms Decomposition Suppose we approximate
Target Location Estimation in Wireless Sensor Networks Using Binary Data
 Target Location stimation in Wireess Sensor Networks Using Binary Data Ruixin Niu and Pramod K. Varshney Department of ectrica ngineering and Computer Science Link Ha Syracuse University Syracuse, NY 344
Target Location stimation in Wireess Sensor Networks Using Binary Data Ruixin Niu and Pramod K. Varshney Department of ectrica ngineering and Computer Science Link Ha Syracuse University Syracuse, NY 344
DISTRIBUTION OF TEMPERATURE IN A SPATIALLY ONE- DIMENSIONAL OBJECT AS A RESULT OF THE ACTIVE POINT SOURCE
 DISTRIBUTION OF TEMPERATURE IN A SPATIALLY ONE- DIMENSIONAL OBJECT AS A RESULT OF THE ACTIVE POINT SOURCE Yury Iyushin and Anton Mokeev Saint-Petersburg Mining University, Vasiievsky Isand, 1 st ine, Saint-Petersburg,
DISTRIBUTION OF TEMPERATURE IN A SPATIALLY ONE- DIMENSIONAL OBJECT AS A RESULT OF THE ACTIVE POINT SOURCE Yury Iyushin and Anton Mokeev Saint-Petersburg Mining University, Vasiievsky Isand, 1 st ine, Saint-Petersburg,
Maximum Ratio Combining of Correlated Diversity Branches with Imperfect Channel State Information and Colored Noise
 Maximum Ratio Combining of Correated Diversity Branches with Imperfect Channe State Information and Coored Noise Lars Schmitt, Thomas Grunder, Christoph Schreyoegg, Ingo Viering, and Heinrich Meyr Institute
Maximum Ratio Combining of Correated Diversity Branches with Imperfect Channe State Information and Coored Noise Lars Schmitt, Thomas Grunder, Christoph Schreyoegg, Ingo Viering, and Heinrich Meyr Institute
Improved Min-Sum Decoding of LDPC Codes Using 2-Dimensional Normalization
 Improved Min-Sum Decoding of LDPC Codes sing -Dimensiona Normaization Juntan Zhang and Marc Fossorier Department of Eectrica Engineering niversity of Hawaii at Manoa Honouu, HI 968 Emai: juntan, marc@spectra.eng.hawaii.edu
Improved Min-Sum Decoding of LDPC Codes sing -Dimensiona Normaization Juntan Zhang and Marc Fossorier Department of Eectrica Engineering niversity of Hawaii at Manoa Honouu, HI 968 Emai: juntan, marc@spectra.eng.hawaii.edu
Timing and Carrier Synchronization with Channel Estimation in Multi-Relay Cooperative Networks
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING VOL XX NO XX XXXX 20 Timing and Carrier Synchronization with Channe Estimation in Muti-Reay Cooperative Networs Ai A Nasir Student Member IEEE Hani Mehrpouyan Member
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING VOL XX NO XX XXXX 20 Timing and Carrier Synchronization with Channe Estimation in Muti-Reay Cooperative Networs Ai A Nasir Student Member IEEE Hani Mehrpouyan Member
MASSIVE multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems,
 Non-coherent assive SIO Systems in ISI Channes: Consteation Design and Performance Anaysis Huiqiang Xie, Weiyang Xu, ember, IEEE, Wei Xiang, Senior ember, IEEE, e Shao, Shengbo Xu arxiv:89946v [eesssp]
Non-coherent assive SIO Systems in ISI Channes: Consteation Design and Performance Anaysis Huiqiang Xie, Weiyang Xu, ember, IEEE, Wei Xiang, Senior ember, IEEE, e Shao, Shengbo Xu arxiv:89946v [eesssp]
Sequential Decoding of Polar Codes with Arbitrary Binary Kernel
 Sequentia Decoding of Poar Codes with Arbitrary Binary Kerne Vera Miosavskaya, Peter Trifonov Saint-Petersburg State Poytechnic University Emai: veram,petert}@dcn.icc.spbstu.ru Abstract The probem of efficient
Sequentia Decoding of Poar Codes with Arbitrary Binary Kerne Vera Miosavskaya, Peter Trifonov Saint-Petersburg State Poytechnic University Emai: veram,petert}@dcn.icc.spbstu.ru Abstract The probem of efficient
arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 29 Nov 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 29 Nov 2010 arxiv: v1 [cs.it] 29 Nov 2010](/thumbs/82/86655437.jpg) SUBMITTED TO IEEE TRANS ON INFORMATION THEORY, 1 arxiv:10116121v1 [csit] 29 Nov 2010 On Beamformer Design for Mutiuser MIMO Interference Channes Juho Par, Student Member, IEEE, Youngchu Sung, Senior Member,
SUBMITTED TO IEEE TRANS ON INFORMATION THEORY, 1 arxiv:10116121v1 [csit] 29 Nov 2010 On Beamformer Design for Mutiuser MIMO Interference Channes Juho Par, Student Member, IEEE, Youngchu Sung, Senior Member,
Interactive Fuzzy Programming for Two-level Nonlinear Integer Programming Problems through Genetic Algorithms
 Md. Abu Kaam Azad et a./asia Paciic Management Review (5) (), 7-77 Interactive Fuzzy Programming or Two-eve Noninear Integer Programming Probems through Genetic Agorithms Abstract Md. Abu Kaam Azad a,*,
Md. Abu Kaam Azad et a./asia Paciic Management Review (5) (), 7-77 Interactive Fuzzy Programming or Two-eve Noninear Integer Programming Probems through Genetic Agorithms Abstract Md. Abu Kaam Azad a,*,
A Statistical Framework for Real-time Event Detection in Power Systems
 1 A Statistica Framework for Rea-time Event Detection in Power Systems Noan Uhrich, Tim Christman, Phiip Swisher, and Xichen Jiang Abstract A quickest change detection (QCD) agorithm is appied to the probem
1 A Statistica Framework for Rea-time Event Detection in Power Systems Noan Uhrich, Tim Christman, Phiip Swisher, and Xichen Jiang Abstract A quickest change detection (QCD) agorithm is appied to the probem
Discrete Techniques. Chapter Introduction
 Chapter 3 Discrete Techniques 3. Introduction In the previous two chapters we introduced Fourier transforms of continuous functions of the periodic and non-periodic (finite energy) type, as we as various
Chapter 3 Discrete Techniques 3. Introduction In the previous two chapters we introduced Fourier transforms of continuous functions of the periodic and non-periodic (finite energy) type, as we as various
Tracking Control of Multiple Mobile Robots
 Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Internationa Conference on Robotics & Automation Seou, Korea May 21-26, 2001 Tracking Contro of Mutipe Mobie Robots A Case Study of Inter-Robot Coision-Free Probem Jurachart
Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Internationa Conference on Robotics & Automation Seou, Korea May 21-26, 2001 Tracking Contro of Mutipe Mobie Robots A Case Study of Inter-Robot Coision-Free Probem Jurachart
THE ROLE OF ENERGY IMBALANCE MANAGEMENT ON POWER MARKET STABILITY
 Proceedings of HICSS-31, Big Isand of Hawaii, January 6-9, 1998, Voume III, pp. 4-8. THE ROLE OF ENERGY IMBALANCE MANAGEMENT ON POWER MARKET STABILITY Fernando L. Avarado Department of Eectrica and C.
Proceedings of HICSS-31, Big Isand of Hawaii, January 6-9, 1998, Voume III, pp. 4-8. THE ROLE OF ENERGY IMBALANCE MANAGEMENT ON POWER MARKET STABILITY Fernando L. Avarado Department of Eectrica and C.
Worst Case Analysis of the Analog Circuits
 Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS Internationa Conference on CIRCUITS, Agios Nikoaos, Crete Isand, Greece, Juy 3-5, 7 9 Worst Case Anaysis of the Anaog Circuits ELENA NICULESCU*, DORINA-MIOARA PURCARU* and
Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS Internationa Conference on CIRCUITS, Agios Nikoaos, Crete Isand, Greece, Juy 3-5, 7 9 Worst Case Anaysis of the Anaog Circuits ELENA NICULESCU*, DORINA-MIOARA PURCARU* and
(This is a sample cover image for this issue. The actual cover is not yet available at this time.)
 (This is a sampe cover image for this issue The actua cover is not yet avaiabe at this time) This artice appeared in a journa pubished by Esevier The attached copy is furnished to the author for interna
(This is a sampe cover image for this issue The actua cover is not yet avaiabe at this time) This artice appeared in a journa pubished by Esevier The attached copy is furnished to the author for interna
Adaptive Noise Cancellation Using Deep Cerebellar Model Articulation Controller
 daptive Noise Canceation Using Deep Cerebear Mode rticuation Controer Yu Tsao, Member, IEEE, Hao-Chun Chu, Shih-Wei an, Shih-Hau Fang, Senior Member, IEEE, Junghsi ee*, and Chih-Min in, Feow, IEEE bstract
daptive Noise Canceation Using Deep Cerebear Mode rticuation Controer Yu Tsao, Member, IEEE, Hao-Chun Chu, Shih-Wei an, Shih-Hau Fang, Senior Member, IEEE, Junghsi ee*, and Chih-Min in, Feow, IEEE bstract
Pilot Contamination Problem in Multi-Cell. TDD Systems
 Piot Contamination Probem in Muti-Ce 1 TDD Systems Jubin Jose, Aexei Ashikhmin, Thomas L. Marzetta, and Sriram Vishwanath Laboratory for Informatics, Networks and Communications LINC) Department of Eectrica
Piot Contamination Probem in Muti-Ce 1 TDD Systems Jubin Jose, Aexei Ashikhmin, Thomas L. Marzetta, and Sriram Vishwanath Laboratory for Informatics, Networks and Communications LINC) Department of Eectrica
8 Digifl'.11 Cth:uits and devices
 8 Digif'. Cth:uits and devices 8. Introduction In anaog eectronics, votage is a continuous variabe. This is usefu because most physica quantities we encounter are continuous: sound eves, ight intensity,
8 Digif'. Cth:uits and devices 8. Introduction In anaog eectronics, votage is a continuous variabe. This is usefu because most physica quantities we encounter are continuous: sound eves, ight intensity,
12.2. Maxima and Minima. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Maima and Minima 1. Introduction In this Section we anayse curves in the oca neighbourhood of a stationary point and, from this anaysis, deduce necessary conditions satisfied by oca maima and oca minima.
Maima and Minima 1. Introduction In this Section we anayse curves in the oca neighbourhood of a stationary point and, from this anaysis, deduce necessary conditions satisfied by oca maima and oca minima.
Efficient Generation of Random Bits from Finite State Markov Chains
 Efficient Generation of Random Bits from Finite State Markov Chains Hongchao Zhou and Jehoshua Bruck, Feow, IEEE Abstract The probem of random number generation from an uncorreated random source (of unknown
Efficient Generation of Random Bits from Finite State Markov Chains Hongchao Zhou and Jehoshua Bruck, Feow, IEEE Abstract The probem of random number generation from an uncorreated random source (of unknown
ORTHOGONAL MULTI-WAVELETS FROM MATRIX FACTORIZATION
 J. Korean Math. Soc. 46 2009, No. 2, pp. 281 294 ORHOGONAL MLI-WAVELES FROM MARIX FACORIZAION Hongying Xiao Abstract. Accuracy of the scaing function is very crucia in waveet theory, or correspondingy,
J. Korean Math. Soc. 46 2009, No. 2, pp. 281 294 ORHOGONAL MLI-WAVELES FROM MARIX FACORIZAION Hongying Xiao Abstract. Accuracy of the scaing function is very crucia in waveet theory, or correspondingy,
Fast Blind Recognition of Channel Codes
 Fast Bind Recognition of Channe Codes Reza Moosavi and Erik G. Larsson Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When citing this work, cite the origina artice. 213 IEEE. Persona use of this materia is permitted.
Fast Bind Recognition of Channe Codes Reza Moosavi and Erik G. Larsson Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When citing this work, cite the origina artice. 213 IEEE. Persona use of this materia is permitted.
Duality, Polite Water-filling, and Optimization for MIMO B-MAC Interference Networks and itree Networks
 Duaity, Poite Water-fiing, and Optimization for MIMO B-MAC Interference Networks and itree Networks 1 An Liu, Youjian Eugene) Liu, Haige Xiang, Wu Luo arxiv:1004.2484v3 [cs.it] 4 Feb 2014 Abstract This
Duaity, Poite Water-fiing, and Optimization for MIMO B-MAC Interference Networks and itree Networks 1 An Liu, Youjian Eugene) Liu, Haige Xiang, Wu Luo arxiv:1004.2484v3 [cs.it] 4 Feb 2014 Abstract This
Discrete Techniques. Chapter Introduction
 Chapter 3 Discrete Techniques 3. Introduction In the previous two chapters we introduced Fourier transforms of continuous functions of the periodic and non-periodic (finite energy) type, we as various
Chapter 3 Discrete Techniques 3. Introduction In the previous two chapters we introduced Fourier transforms of continuous functions of the periodic and non-periodic (finite energy) type, we as various
HYDROGEN ATOM SELECTION RULES TRANSITION RATES
 DOING PHYSICS WITH MATLAB QUANTUM PHYSICS Ian Cooper Schoo of Physics, University of Sydney ian.cooper@sydney.edu.au HYDROGEN ATOM SELECTION RULES TRANSITION RATES DOWNLOAD DIRECTORY FOR MATLAB SCRIPTS
DOING PHYSICS WITH MATLAB QUANTUM PHYSICS Ian Cooper Schoo of Physics, University of Sydney ian.cooper@sydney.edu.au HYDROGEN ATOM SELECTION RULES TRANSITION RATES DOWNLOAD DIRECTORY FOR MATLAB SCRIPTS
Power Control and Transmission Scheduling for Network Utility Maximization in Wireless Networks
 ower Contro and Transmission Scheduing for Network Utiity Maximization in Wireess Networks Min Cao, Vivek Raghunathan, Stephen Hany, Vinod Sharma and. R. Kumar Abstract We consider a joint power contro
ower Contro and Transmission Scheduing for Network Utiity Maximization in Wireess Networks Min Cao, Vivek Raghunathan, Stephen Hany, Vinod Sharma and. R. Kumar Abstract We consider a joint power contro
Efficiently Generating Random Bits from Finite State Markov Chains
 1 Efficienty Generating Random Bits from Finite State Markov Chains Hongchao Zhou and Jehoshua Bruck, Feow, IEEE Abstract The probem of random number generation from an uncorreated random source (of unknown
1 Efficienty Generating Random Bits from Finite State Markov Chains Hongchao Zhou and Jehoshua Bruck, Feow, IEEE Abstract The probem of random number generation from an uncorreated random source (of unknown
arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 31 Oct 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 31 Oct 2017 arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 31 Oct 2017](/thumbs/86/93671836.jpg) ACCELERATED SPARSE SUBSPACE CLUSTERING Abofaz Hashemi and Haris Vikao Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA arxiv:7.26v [cs.lg] 3 Oct 27 ABSTRACT
ACCELERATED SPARSE SUBSPACE CLUSTERING Abofaz Hashemi and Haris Vikao Department of Eectrica and Computer Engineering, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA arxiv:7.26v [cs.lg] 3 Oct 27 ABSTRACT
Melodic contour estimation with B-spline models using a MDL criterion
 Meodic contour estimation with B-spine modes using a MDL criterion Damien Loive, Ney Barbot, Oivier Boeffard IRISA / University of Rennes 1 - ENSSAT 6 rue de Kerampont, B.P. 80518, F-305 Lannion Cedex
Meodic contour estimation with B-spine modes using a MDL criterion Damien Loive, Ney Barbot, Oivier Boeffard IRISA / University of Rennes 1 - ENSSAT 6 rue de Kerampont, B.P. 80518, F-305 Lannion Cedex
Maximum likelihood decoding of trellis codes in fading channels with no receiver CSI is a polynomial-complexity problem
 1 Maximum ikeihood decoding of treis codes in fading channes with no receiver CSI is a poynomia-compexity probem Chun-Hao Hsu and Achieas Anastasopouos Eectrica Engineering and Computer Science Department
1 Maximum ikeihood decoding of treis codes in fading channes with no receiver CSI is a poynomia-compexity probem Chun-Hao Hsu and Achieas Anastasopouos Eectrica Engineering and Computer Science Department
Data Search Algorithms based on Quantum Walk
 Data Search Agorithms based on Quantum Wak Masataka Fujisaki, Hiromi Miyajima, oritaka Shigei Abstract For searching any item in an unsorted database with items, a cassica computer takes O() steps but
Data Search Agorithms based on Quantum Wak Masataka Fujisaki, Hiromi Miyajima, oritaka Shigei Abstract For searching any item in an unsorted database with items, a cassica computer takes O() steps but
Alberto Maydeu Olivares Instituto de Empresa Marketing Dept. C/Maria de Molina Madrid Spain
 CORRECTIONS TO CLASSICAL PROCEDURES FOR ESTIMATING THURSTONE S CASE V MODEL FOR RANKING DATA Aberto Maydeu Oivares Instituto de Empresa Marketing Dept. C/Maria de Moina -5 28006 Madrid Spain Aberto.Maydeu@ie.edu
CORRECTIONS TO CLASSICAL PROCEDURES FOR ESTIMATING THURSTONE S CASE V MODEL FOR RANKING DATA Aberto Maydeu Oivares Instituto de Empresa Marketing Dept. C/Maria de Moina -5 28006 Madrid Spain Aberto.Maydeu@ie.edu
STABILITY OF A PARAMETRICALLY EXCITED DAMPED INVERTED PENDULUM 1. INTRODUCTION
 Journa of Sound and Vibration (996) 98(5), 643 65 STABILITY OF A PARAMETRICALLY EXCITED DAMPED INVERTED PENDULUM G. ERDOS AND T. SINGH Department of Mechanica and Aerospace Engineering, SUNY at Buffao,
Journa of Sound and Vibration (996) 98(5), 643 65 STABILITY OF A PARAMETRICALLY EXCITED DAMPED INVERTED PENDULUM G. ERDOS AND T. SINGH Department of Mechanica and Aerospace Engineering, SUNY at Buffao,
VALIDATED CONTINUATION FOR EQUILIBRIA OF PDES
 VALIDATED CONTINUATION FOR EQUILIBRIA OF PDES SARAH DAY, JEAN-PHILIPPE LESSARD, AND KONSTANTIN MISCHAIKOW Abstract. One of the most efficient methods for determining the equiibria of a continuous parameterized
VALIDATED CONTINUATION FOR EQUILIBRIA OF PDES SARAH DAY, JEAN-PHILIPPE LESSARD, AND KONSTANTIN MISCHAIKOW Abstract. One of the most efficient methods for determining the equiibria of a continuous parameterized
Recursive Asymptotic Hybrid Matrix Method for Acoustic Waves in Multilayered Piezoelectric Media
 Open Journa o Acoustics, 2,, 27-33 doi:.4236/oja.2.4 Pubished Onine September 2 (http://.scirp.org/journa/oja) Recursive Asymptotic Hybrid Matrix Method or Acoustic Waves in Mutiayered Piezoeectric Media
Open Journa o Acoustics, 2,, 27-33 doi:.4236/oja.2.4 Pubished Onine September 2 (http://.scirp.org/journa/oja) Recursive Asymptotic Hybrid Matrix Method or Acoustic Waves in Mutiayered Piezoeectric Media
Compression Ratio Expansion for Complementary Code Set Compressing a Signal to a Width of Several Sub-pulses
 Compression Ratio Expansion for Compementary Code Set Compressing a Signa to a Width of Severa Sub-puses Reiji Sato 2nd Research Center, Technica R and D Institute Japan Defense Agency 1-2-24 Ikejiri,
Compression Ratio Expansion for Compementary Code Set Compressing a Signa to a Width of Severa Sub-puses Reiji Sato 2nd Research Center, Technica R and D Institute Japan Defense Agency 1-2-24 Ikejiri,
Approximated MLC shape matrix decomposition with interleaf collision constraint
 Approximated MLC shape matrix decomposition with intereaf coision constraint Thomas Kainowski Antje Kiese Abstract Shape matrix decomposition is a subprobem in radiation therapy panning. A given fuence
Approximated MLC shape matrix decomposition with intereaf coision constraint Thomas Kainowski Antje Kiese Abstract Shape matrix decomposition is a subprobem in radiation therapy panning. A given fuence
Simplified Algorithms for Optimizing Multiuser Multi-Hop MIMO Relay Systems
 2896 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VO. 59, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2011 Simpified Agorithms for Optimizing Mutiuser Muti-op MIMO Reay Systems Yue Rong, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract In this paper, we address
2896 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VO. 59, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2011 Simpified Agorithms for Optimizing Mutiuser Muti-op MIMO Reay Systems Yue Rong, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract In this paper, we address
EasyChair Preprint. Time-Domain Channel Estimation for the LTE-V System Over High-Speed Mobile Channels
 EasyChair Preprint 184 Time-Domain Channe Estimation for the LTE-V System Over High-Speed Mobie Channes Qu Huiyang, Liu Guanghui, Wang Yanyan, Wen Shan and Chen Qiang EasyChair preprints are intended for
EasyChair Preprint 184 Time-Domain Channe Estimation for the LTE-V System Over High-Speed Mobie Channes Qu Huiyang, Liu Guanghui, Wang Yanyan, Wen Shan and Chen Qiang EasyChair preprints are intended for
Nonlinear Gaussian Filtering via Radial Basis Function Approximation
 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Contro December 10-13 01 Maui Hawaii USA Noninear Gaussian Fitering via Radia Basis Function Approximation Huazhen Fang Jia Wang and Raymond A de Caafon Abstract This
51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Contro December 10-13 01 Maui Hawaii USA Noninear Gaussian Fitering via Radia Basis Function Approximation Huazhen Fang Jia Wang and Raymond A de Caafon Abstract This
Unconditional security of differential phase shift quantum key distribution
 Unconditiona security of differentia phase shift quantum key distribution Kai Wen, Yoshihisa Yamamoto Ginzton Lab and Dept of Eectrica Engineering Stanford University Basic idea of DPS-QKD Protoco. Aice
Unconditiona security of differentia phase shift quantum key distribution Kai Wen, Yoshihisa Yamamoto Ginzton Lab and Dept of Eectrica Engineering Stanford University Basic idea of DPS-QKD Protoco. Aice
Published in: Proceedings of the Twenty Second Nordic Seminar on Computational Mechanics
 Aaborg Universitet An Efficient Formuation of the Easto-pastic Constitutive Matrix on Yied Surface Corners Causen, Johan Christian; Andersen, Lars Vabbersgaard; Damkide, Lars Pubished in: Proceedings of
Aaborg Universitet An Efficient Formuation of the Easto-pastic Constitutive Matrix on Yied Surface Corners Causen, Johan Christian; Andersen, Lars Vabbersgaard; Damkide, Lars Pubished in: Proceedings of
