Phys 328 Nuclear Physics and Particles Introduction Murat
|
|
|
- Judith Sims
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phys 328 Nuclear Physics and Particles Introduction 1
2 Syllabus COURSE OUTLINE PHYS328 NUCLEAR PHYSICS AND PARTICLES Instructor: Prof. Dr. A. Murat Güler Room: 333, Class Schedule: Monday 9:00-11:30 in P350 Wednesday 9:40-10:30 in P350 Text Book B.R. Martin, Nuclear and Particle Physics 2
3 Syllabus Topics: Introduction Basic Concepts Nuclear Phenomenology Particle Phenomenology Experimental Methods Applications of Nuclear Physics 3
4 History Grading Midterm : 25 % Final : 40% Project work: 30 % Attandance : 5% Dates: Midterm Examination First week of May. 4
5 Basic Concepts -Provides historical introduction to the field of nuclear and particle physics. -A number of concepts and tools are introduced concerning the nuclear and particle physics. -Give the basic principles and interpretations in nuclear and particle physics 5
6 History 19th Century : atoms are indivisible 6
7 History Radioactivity In 1896: Henry Becquerel dicovers radioactivity (β-radiation from uranium salts) When the salts were placed near to a photographic plate covered with opaque paper, the plate was discovered to be fogged. The phenomenon was found to be common to all the uranium salts studied and was concluded to be a property of the uranium atom. Henri Becquerel The Nobel Prize in Physics
8 History Rutherford and Pierre & Marie Curie establish existence of α and β rays and nature of radiactivity Through a long series of experiments he realized that there were two kinds of radiation emitted from Uranium. Rutherford called them alpha and beta. In a few years it was concluded that beta rays were cathode rays, that is, electrons. The precise nature of alpha particles remained a mystery although both Rutherford and the Curies suspected they were particles, atoms electrically charged and projected at high speed. They also knew they could be stopped by extremely thin shields (e.g. paper) and were deflected to only a small extent in a magnetic field. 8
9 History In 1896 Roentgen discovered X-rays X-rays were first discovered accidentally by Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen. X-rays are waves of electromagnetic energy that have a shorter wavelength than normal light He discovered that these new invisible rays could pass through most objects that casted shadows including human tissue but not human bones and metals. Within a year of the discovery many scientists replicated the experiment Röntgen performed and began using it in clinical settings In 1901 Röntgen won the first Nobel Prize in Physics 9
10 X-ray production 10
11 History Television Computer Monitor Cathode ray tubes pass electricity through a gas that is contained at a very low pressure. 11
12 History In 1898 Pierre and Marie Curie α-radiation m 1 M m 2 12
13 History 1900 Villard γ-radiation Villard investigated the radiation from radium salts that escaped from a narrow aperture in a shielded container onto a photographic plate, through a thin layer of lead that was known to stop alpha rays. He was able to show that the remaining radiation consisted of a second and third type of rays. One of those was deflected by a magnetic field (as were the familiar "canal rays") and could be identified with Rutherford's beta rays. The last type was a very penetrating kind of radiation which had not been identified before... 13
14 History 1897: Thomson discovers the electron cathode rays, and measured mass and charge Plum pudding model of atom Poor agreement with experiment JJ Thomson Nobel Prize in Physics,
15 History 1911: Rutherford experiments > positive nucleus orbited by electrons (planetary model) Ernest Rutherford (Nobel Prize in Chemistry, 1908) 15
16 History Most of the particles passed right through A few particles were deflected VERY FEW were greatly deflected Conclusions: a) The nucleus is small b) The nucleus is dense c) The nucleus is positively charged 16
17 History Based on his experimental evidence: The atom is mostly empty space All the positive charge, and almost all the mass is concentrated in a small area in the center. He called this a nucleus The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons (they make the nucleus!) The electrons distributed around the nucleus, and occupy most of the volume His model was called a nuclear model 17
18 History 1913: Bohr model of atom: first window into quantum physics Atom was like a miniature planetry system with electrons circulating about the nucleus (like planets circulating about Sun). But accelerated charge radiates electromagnetic energy. As it radiates this energy its total energy would decrease and electron spirals in toward the nucleus and atom would collapse. Prize motivation: "for his services in the investigation of the structure of atoms and of the radiation emanating from them" Nobel prize in Physics in
19 History Bohr proposed that there are certain special states called stationary states. İn which angular momentum of electron may have magnitude h, 2h,...(quantization of angular momentum). Only orbits of certain radii and thus only certain only quantized energies are allowed. Allowed radii is n= 1,2,3... a 0 is Bohr radius Quantized radiation is emitted /absorbed if an electron changes its orbit. 19
20 Where does this go wrong? The Bohr model s successes are limited: Doesn t work for multi-electron atoms. The electron racetrack picture is incorrect. That said, the Bohr model was a pioneering, quantized picture of atomic energy levels. 20
21 Discovery of Neutron Discovery of the neutron, by J. Chadwick in 1932 Be 1) Neutral Gamma? No! protons too energetic 2) m n ~ m p Interpretation: non - ionizing radiation 4 2 He 9 4 Be 1 0 n 12 6 C James Chadwick Nobel Prize in 1935 Outside the nucleus, free neutrons are unstable and have a half life of ±1.0s. 21
22 Discovery of Isotopes Frederick Soddy ( ) proposed the idea of isotopes in 1912 Isotopes are atoms of the same element having different masses, due to varying numbers of neutrons. We can also put the mass number after the name of the element: carbon-12 carbon-14 uranium-235 Soddy won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1921 "for his contributions to our knowledge of the chemistry of radioactive substances, and his investigations into the origin and nature of isotopes". 22
23 Isotopes Atomic mass is the average of all the naturally occurring isotopes of that element Isotope Carbon- 12 Carbon- 13 Carbon- 14 Symbol Composition of the nucleus 12 C 6 protons 6 neutrons 13 C 6 protons 7 neutrons 14 C 6 protons 8 neutrons Carbon = % in nature 98.89% 1.11% <0.01% 23
24 Elementary particles 1930s The known 'Elementary Particles' were : electron proton neutron (inside the nucleus) 'neutrino' (now anti-neutrino) in beta decay photon (γ) the quantum of the electromagnetic field 24
25 Elementary particles Heisenberg et al applied QM to nucleons bound together byshort range strong nuclear force 1930 s: Nucleus is composite consisting of nucleons: protons and neutrons 1960 s: Nucleons are bound states of quarks which have fractional electric charge Gell Mann (NP 1969) 1930: Neutrino postulated by Pauli to save energy conservation in β decay 1956: Reines and Cowan discover neutrino (Reines NP 1995) 25
26 Elementary particles Questions that are asked since 2000 years What are the building blocks of matter? What forces act on matter? 400 v.chr Demokritos atom Newton forces Maxwell electromagnetism Einstein a lot 26
27 Standard Model Elementary particle: mass, charge, spin Fundamental forces: Electromagnetic Weak Strong Gravity Fundamental particles Fermions and bosons. There are also antiparticles. Proton (uud) and neutron (udd) are not elementary particles. 27
28 Relativity and Antiparticles We know that E=mc 2 and λ=h/p High energies are required to make new particles Proton radius is ~10 15 m, >10 3 m e energy required So relativistic effects are important Quantum Theory + Special Relativity: each particle must have an antiparticle with opposite quantum numbers: electric charge, spin, lepton charge, etc. Described by Dirac equation: Particle+antiparticle annihilation (γ s or other) Symmetry between particles and antiparticles Dirac made theoretical prediction of anti particles 1933 Anderson discovered positron (NP 1936) 1959 Segre & Chamberlain NP for discovery of anti proton 28
29 Space Time Symmetries and Conservation Laws Emmy Noether s theorem Space, time translation & orientation symmetries are all continuous symmetries Translational invariance p Rotational invariance L Time invariance E Additional symmetries of interest for nuclear and particle physics are: parity charge conjugation time reversal 29
30 Discrete Symmetries Parity, P Parity reflects a system through the origin. Converts right-handed coordinate systems to left-handed ones. Vectors change sign but axial vectors remain unchanged x -x, p -p, but L = x p L Charge Conjugation, C Charge conjugation turns a particle into its anti-particle e + e -, K - K + Time Reversal, T Changes, for example, the direction of motion of particles t -t 30
31 Parity Parity Refers to spatial reflection r r P eigenvalue is called intrinsic parity, or simply parity. Strong and EM interactions conserve parity. Weak interaction violates parity. Leptons and quarks have parity +1 Antileptons and antiquarks have parity 1 Additional contribution to parity from orbital angular momentum 31
32 Charge Conjugation Charge Conjugation Changes particles into antiparticles a electrically neutral particles, b electrically charged particles C a phase factor Weak interaction violates parity EM and strong preserve parity 32
33 Time Reversal t t = t If conserved T is not Hermitian, so it is not observable when conserved. However, rates of time reversed processes must be the same(if no weak interaction is present violates parity). There is a general CPT theorem any relativistic field theory is invariant under the combined CPT. 33
34 Particle Reactions Scattering Reactions 34
35 Decays 35
36 Feynman Diagrams 36
37 Feynman Rules 37
38 Feynman Rules How to calculate amplitude M? The drawing is a mathematical object! p 1 1/(q M= 2 -m 2 ) g g p 2 p 3 38
39 Weak Interactions 39
40 Strong Interactions 40
41 Four Vectors 41
42 Four Vectors 42
43 Particle Exchange 43
44 Klein-Gordon Equation 44
45 Yukowa Potential 45
46 Units 46
47 Units 47
Nuclear & Particle Physics
 AstroPhysics Notes Nuclear Physics Dr. Bill Pezzaglia A. Nuclear Structure Nuclear & Particle Physics B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions D. Particle Physics Updated: 03Aug9 (for physics 700) A. Nuclear
AstroPhysics Notes Nuclear Physics Dr. Bill Pezzaglia A. Nuclear Structure Nuclear & Particle Physics B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions D. Particle Physics Updated: 03Aug9 (for physics 700) A. Nuclear
What is Radiation? Física da Radiação MEBiom 2016/2017 Patrícia Gonçalves. Supporting Slides and images
 What is Radiation? Física da Radiação MEBiom 2016/2017 Patrícia Gonçalves Supporting Slides and images Radiation? Radiation is energy that comes from a source and travels through some material or through
What is Radiation? Física da Radiação MEBiom 2016/2017 Patrícia Gonçalves Supporting Slides and images Radiation? Radiation is energy that comes from a source and travels through some material or through
Radiation can be defined as the propagation of energy through matter or space. It can be in the form of electromagnetic waves or energetic particles.
 Lecture 1: Overview; History of Radiation Radiation can be defined as the propagation of energy through matter or space. It can be in the form of electromagnetic waves or energetic particles. Source: Lawrence
Lecture 1: Overview; History of Radiation Radiation can be defined as the propagation of energy through matter or space. It can be in the form of electromagnetic waves or energetic particles. Source: Lawrence
Lecture 21 Fundamentals of Physics Phys 120, Fall 2015 Nuclear Physics
 Lecture 21 Fundamentals of Physics Phys 120, Fall 2015 Nuclear Physics A. J. Wagner North Dakota State University, Fargo, ND 58102 Fargo, November 13, 2015 Overview Why care about nuclei? How do nuclei
Lecture 21 Fundamentals of Physics Phys 120, Fall 2015 Nuclear Physics A. J. Wagner North Dakota State University, Fargo, ND 58102 Fargo, November 13, 2015 Overview Why care about nuclei? How do nuclei
Nuclear & Particle Physics
 AstroPhysics Notes Nuclear Physics Dr. Bill Pezzaglia A. Nuclear Structure Nuclear & Particle Physics B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions D. Particle Physics Updated: 0Aug8 Rough draft A. Nuclear Structure
AstroPhysics Notes Nuclear Physics Dr. Bill Pezzaglia A. Nuclear Structure Nuclear & Particle Physics B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions D. Particle Physics Updated: 0Aug8 Rough draft A. Nuclear Structure
Atomic Theory Timeline
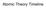 Atomic Theory Timeline Democritus 450 B.C. Democritus was a Greek philosopher who came to the conclusion that everything was made up of tiny particles. He used the term atomos. Unfortunately, since Democritus
Atomic Theory Timeline Democritus 450 B.C. Democritus was a Greek philosopher who came to the conclusion that everything was made up of tiny particles. He used the term atomos. Unfortunately, since Democritus
Chapter 30 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
 Chapter 30 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity 30.1 Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Nucleus is made of protons and neutrons Proton has positive charge: Neutron is electrically neutral: 30.1 Structure
Chapter 30 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity 30.1 Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Nucleus is made of protons and neutrons Proton has positive charge: Neutron is electrically neutral: 30.1 Structure
Democritus of Abdera. John Dalton. Dalton s Atom. Dalton s Atomic Theory Ancient Greece - 4th century BC. Eaglesfield, England
 Democritus of Abdera Ancient Greece - 4th century BC first suggested the existence of tiny fundamental particles that make up matter. atoms = indestructible did not agree with the current sci theory -
Democritus of Abdera Ancient Greece - 4th century BC first suggested the existence of tiny fundamental particles that make up matter. atoms = indestructible did not agree with the current sci theory -
Physics 30 Modern Physics Unit: Atomic Basics
 Physics 30 Modern Physics Unit: Atomic Basics Models of the Atom The Greeks believed that if you kept dividing matter into smaller and smaller pieces, you would eventually come to a bit of matter that
Physics 30 Modern Physics Unit: Atomic Basics Models of the Atom The Greeks believed that if you kept dividing matter into smaller and smaller pieces, you would eventually come to a bit of matter that
Updating the Atomic Theory
 Updating the Atomic Theory Three major differences between modern atomic theory and Dalton s atomic theory 1. Atoms are NOT indivisible. They are made up of smaller particles: electrons, protons and neutrons.
Updating the Atomic Theory Three major differences between modern atomic theory and Dalton s atomic theory 1. Atoms are NOT indivisible. They are made up of smaller particles: electrons, protons and neutrons.
Quantum Physics and Atomic Models Chapter Questions. 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge?
 Quantum Physics and Atomic Models Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently
Quantum Physics and Atomic Models Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently
PSI AP Physics How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge?
 PSI AP Physics 2 Name Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently named
PSI AP Physics 2 Name Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently named
Updating the Atomic Theory
 Updating the Atomic Theory On the basis of Dalton s Atomic Theory: An atom is the basic unit of an element that can enter into chemical combination. Three major differences between modern atomic theory
Updating the Atomic Theory On the basis of Dalton s Atomic Theory: An atom is the basic unit of an element that can enter into chemical combination. Three major differences between modern atomic theory
Alpha decay usually occurs in heavy nuclei such as uranium or plutonium, and therefore is a major part of the radioactive fallout from a nuclear
 Radioactive Decay Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of atomic nuclei. This phenomenon was first reported in 1896 by the French physicist Henri Becquerel. Marie Curie and her husband Pierre
Radioactive Decay Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of atomic nuclei. This phenomenon was first reported in 1896 by the French physicist Henri Becquerel. Marie Curie and her husband Pierre
Atomic Structure. Chemistry Mr. McKenzie
 Atomic Structure Chemistry Mr. McKenzie How was the understanding of the atom developed? John Dalton (1766-1844) - developed a model to explain observations made at the time 1. Elements are made of tiny
Atomic Structure Chemistry Mr. McKenzie How was the understanding of the atom developed? John Dalton (1766-1844) - developed a model to explain observations made at the time 1. Elements are made of tiny
Chapter 44. Nuclear Structure
 Chapter 44 Nuclear Structure Milestones in the Development of Nuclear Physics 1896: the birth of nuclear physics Becquerel discovered radioactivity in uranium compounds Rutherford showed the radiation
Chapter 44 Nuclear Structure Milestones in the Development of Nuclear Physics 1896: the birth of nuclear physics Becquerel discovered radioactivity in uranium compounds Rutherford showed the radiation
Nuclear Reactions: Chemistry 5.1 AN INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
 Nuclear Reactions: Chemistry 5.1 AN INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY Discovery of Radioactivity Roentgen In 1895 Wilhelm Konrad Roentgen discovered Xrays. Roentgen observed that a vacuum discharge tube
Nuclear Reactions: Chemistry 5.1 AN INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY Discovery of Radioactivity Roentgen In 1895 Wilhelm Konrad Roentgen discovered Xrays. Roentgen observed that a vacuum discharge tube
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Basic Concepts. 1.1 History
 1 Basic Concepts 1.1 History Although this book will not follow a strictly historical development, to set the scene this first chapter will start with a brief review of the most important discoveries that
1 Basic Concepts 1.1 History Although this book will not follow a strictly historical development, to set the scene this first chapter will start with a brief review of the most important discoveries that
Fundamental Forces. Range Carrier Observed? Strength. Gravity Infinite Graviton No. Weak 10-6 Nuclear W+ W- Z Yes (1983)
 Fundamental Forces Force Relative Strength Range Carrier Observed? Gravity 10-39 Infinite Graviton No Weak 10-6 Nuclear W+ W- Z Yes (1983) Electromagnetic 10-2 Infinite Photon Yes (1923) Strong 1 Nuclear
Fundamental Forces Force Relative Strength Range Carrier Observed? Gravity 10-39 Infinite Graviton No Weak 10-6 Nuclear W+ W- Z Yes (1983) Electromagnetic 10-2 Infinite Photon Yes (1923) Strong 1 Nuclear
H 1. Nuclear Physics. Nuclear Physics. 1. Parts of Atom. A. Nuclear Structure. 2b. Nomenclature. 2. Isotopes. AstroPhysics Notes
 AstroPhysics Notes Nuclear Physics Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Nuclear Physics A. Nuclear Structure B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions Updated: 0Feb07 Rough draft A. Nuclear Structure. Parts of Atom. Parts of
AstroPhysics Notes Nuclear Physics Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Nuclear Physics A. Nuclear Structure B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions Updated: 0Feb07 Rough draft A. Nuclear Structure. Parts of Atom. Parts of
Glencoe: Chapter 4. The Structure of the Atom
 Glencoe: Chapter 4 The Structure of the Atom Section One: Early Ideas about Matter Atomists and Democritus : 400 B.C. From Thrace in Greece. Atoms- Uncut-Table Indivisible parts which cannot be broken
Glencoe: Chapter 4 The Structure of the Atom Section One: Early Ideas about Matter Atomists and Democritus : 400 B.C. From Thrace in Greece. Atoms- Uncut-Table Indivisible parts which cannot be broken
Quantum Numbers. F. Di Lodovico 1 EPP, SPA6306. Queen Mary University of London. Quantum Numbers. F. Di Lodovico. Quantum Numbers.
 1 1 School of Physics and Astrophysics Queen Mary University of London EPP, SPA6306 Outline : Number Conservation Rules Based on the experimental observation of particle interactions a number of particle
1 1 School of Physics and Astrophysics Queen Mary University of London EPP, SPA6306 Outline : Number Conservation Rules Based on the experimental observation of particle interactions a number of particle
Chapter 4 The Atom. Philosophers and scientists have proposed many ideas on the structure of atoms.
 Chapter4 TheAtom 4.1 Early Models of the Atom An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction. Philosophers and scientists have proposed many ideas on the
Chapter4 TheAtom 4.1 Early Models of the Atom An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction. Philosophers and scientists have proposed many ideas on the
H 1. Nuclear Physics. Nuclear Physics. 1. Parts of Atom. 2. Isotopes. AstroPhysics Notes. Dr. Bill Pezzaglia. Rough draft. A.
 AstroPhysics Notes Tom Lehrer: Elements Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Nuclear Physics Updated: 0Feb Rough draft Nuclear Physics A. Nuclear Structure A. Nuclear Structure B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions. Parts
AstroPhysics Notes Tom Lehrer: Elements Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Nuclear Physics Updated: 0Feb Rough draft Nuclear Physics A. Nuclear Structure A. Nuclear Structure B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions. Parts
Isotopes of an element have the same symbol and same atomic number - Mass number refers to the protons plus neutrons in an isotope
 7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay Natural background radiation exists all around us. This radiation consists of high energy particles or waves being emitted from a variety of materials Radioactivity
7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay Natural background radiation exists all around us. This radiation consists of high energy particles or waves being emitted from a variety of materials Radioactivity
Radioactive Decay. Becquerel. Atomic Physics. In 1896 Henri Becquerel. - uranium compounds would fog photographic plates as if exposed to light.
 Radioactive Decay Atomic Physics Becquerel In 1896 Henri Becquerel - uranium compounds would fog photographic plates as if exposed to light. - a magnetic field could deflect the radiation that caused the
Radioactive Decay Atomic Physics Becquerel In 1896 Henri Becquerel - uranium compounds would fog photographic plates as if exposed to light. - a magnetic field could deflect the radiation that caused the
Quantum Numbers. Elementary Particles Properties. F. Di Lodovico c 1 EPP, SPA6306. Queen Mary University of London. Quantum Numbers. F.
 Elementary Properties 1 1 School of Physics and Astrophysics Queen Mary University of London EPP, SPA6306 Outline Most stable sub-atomic particles are the proton, neutron (nucleons) and electron. Study
Elementary Properties 1 1 School of Physics and Astrophysics Queen Mary University of London EPP, SPA6306 Outline Most stable sub-atomic particles are the proton, neutron (nucleons) and electron. Study
Chapter 3. Radioactivity. Table of Contents
 Radioactivity Table of Contents Introduction 1. Radioactivity 2. Types of Radioactive Decays 3. Natural Radioactivity 4. Artificial Radioactivity 5. The Rate of Radioactive Decay 6. The Effects of Radiation
Radioactivity Table of Contents Introduction 1. Radioactivity 2. Types of Radioactive Decays 3. Natural Radioactivity 4. Artificial Radioactivity 5. The Rate of Radioactive Decay 6. The Effects of Radiation
Books: - Martin, B.R. & Shaw, G Particle Physics (Wiley) (recommended) - Perkins, D.H. Introduction to High Energy Physics (CUP) (advanced)
 PC 3 Foundations of Particle Physics Lecturer: Dr F. Loebinger Books: - Martin, B.R. & Shaw, G Particle Physics (Wiley) (recommended) - Perkins, D.H. Introduction to High Energy Physics (CUP) (advanced)
PC 3 Foundations of Particle Physics Lecturer: Dr F. Loebinger Books: - Martin, B.R. & Shaw, G Particle Physics (Wiley) (recommended) - Perkins, D.H. Introduction to High Energy Physics (CUP) (advanced)
Atomic Structure. ppst.com
 Atomic Structure ppst.com Defining the Atom The Greek philosopher (460 B.C. 370 B.C.) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms (from the Greek word ) He believed that atoms were and His ideas
Atomic Structure ppst.com Defining the Atom The Greek philosopher (460 B.C. 370 B.C.) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms (from the Greek word ) He believed that atoms were and His ideas
Early Atomic Theories and the Origins of Quantum Theory. Chapter 3.1
 Early Atomic Theories and the Origins of Quantum Theory Chapter 3.1 What is Matter Made of? People have wondered about the answer to this question for thousands of years Philosophers Matter is composed
Early Atomic Theories and the Origins of Quantum Theory Chapter 3.1 What is Matter Made of? People have wondered about the answer to this question for thousands of years Philosophers Matter is composed
Radioactivity. The Nobel Prize in Physics 1903 for their work on radioactivity. Henri Becquerel Pierre Curie Marie Curie
 Radioactivity Toward the end of the 19 th century, minerals were found that would darken a photographic plate even in the absence of light. This phenomenon is now called radioactivity. Marie and Pierre
Radioactivity Toward the end of the 19 th century, minerals were found that would darken a photographic plate even in the absence of light. This phenomenon is now called radioactivity. Marie and Pierre
Introduction. Read: Ch 1 of M&S
 Introduction What questions does this field address? Want to know the basic law of nature. Can we unify all the forces with one equation or one theory? Read: Ch 1 of M&S K.K. Gan L1: Introduction 1 Particle
Introduction What questions does this field address? Want to know the basic law of nature. Can we unify all the forces with one equation or one theory? Read: Ch 1 of M&S K.K. Gan L1: Introduction 1 Particle
Atoms, nuclei, particles
 Atoms, nuclei, particles Nikolaos Kidonakis Physics for Georgia Academic Decathlon September 2016 Age-old questions What are the fundamental particles of matter? What are the fundamental forces of nature?
Atoms, nuclei, particles Nikolaos Kidonakis Physics for Georgia Academic Decathlon September 2016 Age-old questions What are the fundamental particles of matter? What are the fundamental forces of nature?
In 1808 John Dalton proposed that:
 In 1808 John Dalton proposed that: all matter is made up of atoms which cannot be subdivided atoms of the same element are identical atoms of different elements have different masses atoms combine together
In 1808 John Dalton proposed that: all matter is made up of atoms which cannot be subdivided atoms of the same element are identical atoms of different elements have different masses atoms combine together
The origins of atomic theory
 Models of the atom It is important to realise that a lot of what we know about the structure of atoms has been developed over a long period of time. This is often how scientific knowledge develops, with
Models of the atom It is important to realise that a lot of what we know about the structure of atoms has been developed over a long period of time. This is often how scientific knowledge develops, with
21/11/ /11/2017 Atomic Structure AQA Physics topic 4
 Atomic Structure AQA Physics topic 4 4.1 Atoms and Isotopes The structure of the atom ELECTRON negative, mass nearly nothing The nucleus is around 10,000 times smaller then the atom! NEUTRON neutral, same
Atomic Structure AQA Physics topic 4 4.1 Atoms and Isotopes The structure of the atom ELECTRON negative, mass nearly nothing The nucleus is around 10,000 times smaller then the atom! NEUTRON neutral, same
6. Atomic and Nuclear Physics
 6. Atomic and Nuclear Physics Chapter 6.2 Radioactivity From IB OCC, prepared by J. Domingues based on Tsokos Physics book Warm Up Define: nucleon atomic number mass number isotope. Radioactivity In 1896,
6. Atomic and Nuclear Physics Chapter 6.2 Radioactivity From IB OCC, prepared by J. Domingues based on Tsokos Physics book Warm Up Define: nucleon atomic number mass number isotope. Radioactivity In 1896,
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics
 Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics PHY-302 Dr. E. Rizvi Lecture 1 - Course Organiser: Deputy: Dr E. Rizvi (room 401) Prof. J. Emerson My Office hours 1000 1100 Thursday 3 lecture slots per week Thursday
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics PHY-302 Dr. E. Rizvi Lecture 1 - Course Organiser: Deputy: Dr E. Rizvi (room 401) Prof. J. Emerson My Office hours 1000 1100 Thursday 3 lecture slots per week Thursday
History of the Atom. Scientists and Their Contribution to the Model of an Atom
 History of the Atom Scientists and Their Contribution to the Model of an Atom 1700s 1800s 1900s History of the Atom Timeline 1766 1844 Antoine Lavoisier makes J.J. a substantial Thomson number discovers
History of the Atom Scientists and Their Contribution to the Model of an Atom 1700s 1800s 1900s History of the Atom Timeline 1766 1844 Antoine Lavoisier makes J.J. a substantial Thomson number discovers
Atomic Structure Discovered. Dalton s Atomic Theory. Discovery of the Electron 10/30/2012
 Atomic Structure Discovered Ancient Greeks Democritus (460-362 BC) - indivisible particles called atoms Prevailing argument (Plato and Aristotle) - matter is continuously and infinitely divisible John
Atomic Structure Discovered Ancient Greeks Democritus (460-362 BC) - indivisible particles called atoms Prevailing argument (Plato and Aristotle) - matter is continuously and infinitely divisible John
Hand of Anna Röntgen. From Life magazine,6 April 1896
 FROM ELECTRONS TO QUARKS The development of Particle Physics QUARKNET 2001, FSU Laura Reina Outline ffl What is Particle Physics? ffl The origins of Particle Physics: the atom (p,e ), radioactivity, and
FROM ELECTRONS TO QUARKS The development of Particle Physics QUARKNET 2001, FSU Laura Reina Outline ffl What is Particle Physics? ffl The origins of Particle Physics: the atom (p,e ), radioactivity, and
Sources of Radiation
 Radioactivity Sources of Radiation Natural Sources Cosmic Radiation The Earth is constantly bombarded by radiation from outside our solar system. interacts in the atmosphere to create secondary radiation
Radioactivity Sources of Radiation Natural Sources Cosmic Radiation The Earth is constantly bombarded by radiation from outside our solar system. interacts in the atmosphere to create secondary radiation
THE NUCLEUS OF AN ATOM
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE THE NUCLEUS OF AN ATOM Models of the atom positive charge uniformly distributed over a sphere J. J. Thomson model of the atom (1907) ~2x10-10 m plum-pudding model: positive charge
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE THE NUCLEUS OF AN ATOM Models of the atom positive charge uniformly distributed over a sphere J. J. Thomson model of the atom (1907) ~2x10-10 m plum-pudding model: positive charge
Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide Atomic Structure, Chapter 3
 Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide Atomic Structure, Chapter 3 Terms and definitions atom ion law of constant composition isotope atomic theory of matter mass number cathode ray tube atomic mass electron
Accelerated Chemistry Study Guide Atomic Structure, Chapter 3 Terms and definitions atom ion law of constant composition isotope atomic theory of matter mass number cathode ray tube atomic mass electron
25.1. Nuclear Radiation
 Nuclear Radiation Marie Curie was a Polish scientist whose research led to many discoveries about radiation and radioactive elements. In 1934 she died from leukemia caused by her long-term exposure to
Nuclear Radiation Marie Curie was a Polish scientist whose research led to many discoveries about radiation and radioactive elements. In 1934 she died from leukemia caused by her long-term exposure to
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN 7-3: THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER Questions From Reading Activity? Essential Idea: It is believed that all the matter around us is made up of fundamental
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS LSN 7-3: THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER Questions From Reading Activity? Essential Idea: It is believed that all the matter around us is made up of fundamental
ISP209 Spring Exam #3. Name: Student #:
 ISP209 Spring 2014 Exam #3 Name: Student #: Please write down your name and student # on both the exam and the scoring sheet. After you are finished with the exam, please place the scoring sheet inside
ISP209 Spring 2014 Exam #3 Name: Student #: Please write down your name and student # on both the exam and the scoring sheet. After you are finished with the exam, please place the scoring sheet inside
1. Based on Dalton s evidence, circle the drawing that demonstrates Dalton s model.
 Various models of the ATOM Dalton Model John Dalton developed the first atomic model in 1808. Before him people, mostly philosophers, had speculated about the smallest unit of matter and two theories prevailed.
Various models of the ATOM Dalton Model John Dalton developed the first atomic model in 1808. Before him people, mostly philosophers, had speculated about the smallest unit of matter and two theories prevailed.
Atomic Theory. Developing the Nuclear Model of the Atom. Saturday, January 20, 18
 Atomic Theory Developing the Nuclear Model of the Atom Democritus Theory: Atom, the indivisible particle c. 300 BC Democritus Problem: No scientific evidence c. 300 BC Dalton Theory: The solid sphere model
Atomic Theory Developing the Nuclear Model of the Atom Democritus Theory: Atom, the indivisible particle c. 300 BC Democritus Problem: No scientific evidence c. 300 BC Dalton Theory: The solid sphere model
Chapter 38 and Chapter 39
 Chapter 38 and Chapter 39 State of 19th and very early 20th century physics: Light: 1. E&M Maxwell s equations > waves; J. J. Thompson s double slit experiment with light 2. Does light need a medium? >
Chapter 38 and Chapter 39 State of 19th and very early 20th century physics: Light: 1. E&M Maxwell s equations > waves; J. J. Thompson s double slit experiment with light 2. Does light need a medium? >
HONORS CHEMISTRY. Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
 HONORS CHEMISTRY Chapter 4 Atomic Structure History of the Atomic Theory DEMOCRITUS (400 BC) 1st atomic theory World is made of empty space & tiny particles called atoms. Atomos - Greek for indivisible
HONORS CHEMISTRY Chapter 4 Atomic Structure History of the Atomic Theory DEMOCRITUS (400 BC) 1st atomic theory World is made of empty space & tiny particles called atoms. Atomos - Greek for indivisible
Introduction to Nuclear Reactor Physics
 Introduction to Nuclear Reactor Physics J. Frýbort, L. Heraltová Department of Nuclear Reactors 19 th October 2017 J. Frýbort, L. Heraltová (CTU in Prague) Introduction to Nuclear Reactor Physics 19 th
Introduction to Nuclear Reactor Physics J. Frýbort, L. Heraltová Department of Nuclear Reactors 19 th October 2017 J. Frýbort, L. Heraltová (CTU in Prague) Introduction to Nuclear Reactor Physics 19 th
INTRODUCTION TO THE STANDARD MODEL OF PARTICLE PHYSICS
 INTRODUCTION TO THE STANDARD MODEL OF PARTICLE PHYSICS Class Mechanics My office (for now): Dantziger B Room 121 My Phone: x85200 Office hours: Call ahead, or better yet, email... Even better than office
INTRODUCTION TO THE STANDARD MODEL OF PARTICLE PHYSICS Class Mechanics My office (for now): Dantziger B Room 121 My Phone: x85200 Office hours: Call ahead, or better yet, email... Even better than office
Topic III Quest Study Guide
 Topic III Quest Study Guide A. Early Concepts: Democritus: Democritus: Greek Philosopher 400 B.C. Matter is composed of atoms, which move through empty space Atoms are solid, homogeneous indestructible
Topic III Quest Study Guide A. Early Concepts: Democritus: Democritus: Greek Philosopher 400 B.C. Matter is composed of atoms, which move through empty space Atoms are solid, homogeneous indestructible
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics
 Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics PHY-302 Dr. E. Rizvi Lecture 1 - Course Organiser: Deputy: Dr E. Rizvi (room 401) Dr A. Bevan My Office hours 1000 1100 Thursday 3 lecture slots per week Thursday 0900-1000
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics PHY-302 Dr. E. Rizvi Lecture 1 - Course Organiser: Deputy: Dr E. Rizvi (room 401) Dr A. Bevan My Office hours 1000 1100 Thursday 3 lecture slots per week Thursday 0900-1000
Nuclear Chemistry. Atomic Structure Notes Start on Slide 20 from the second class lecture
 Nuclear Chemistry Atomic Structure Notes Start on Slide 20 from the second class lecture The Birth of an Idea Democritus, 400 B.C. coined the term atom If you divide matter into smaller and smaller pieces,
Nuclear Chemistry Atomic Structure Notes Start on Slide 20 from the second class lecture The Birth of an Idea Democritus, 400 B.C. coined the term atom If you divide matter into smaller and smaller pieces,
Option 212: UNIT 2 Elementary Particles
 Department of Physics and Astronomy Option 212: UNIT 2 Elementary Particles SCHEDULE 26-Jan-15 13.pm LRB Intro lecture 28-Jan-15 12.pm LRB Problem solving (2-Feb-15 1.am E Problem Workshop) 4-Feb-15 12.pm
Department of Physics and Astronomy Option 212: UNIT 2 Elementary Particles SCHEDULE 26-Jan-15 13.pm LRB Intro lecture 28-Jan-15 12.pm LRB Problem solving (2-Feb-15 1.am E Problem Workshop) 4-Feb-15 12.pm
Physics for Poets Lecture 2
 Physics for Poets Lecture 2 Gaurang Yodh Development of quantum theory (and relativity) was in response to Experimental Observations that defied explanation in terms of Classical Physics (Newton's Laws
Physics for Poets Lecture 2 Gaurang Yodh Development of quantum theory (and relativity) was in response to Experimental Observations that defied explanation in terms of Classical Physics (Newton's Laws
Atomic Theory. Democritus to the Planetary Model
 Atomic Theory Democritus to the Planetary Model Democritus Greek philosopher (460-370 BCE) Believed in the philosophy of materialism With Leucippus, they though that matter can not be divided infinitely.
Atomic Theory Democritus to the Planetary Model Democritus Greek philosopher (460-370 BCE) Believed in the philosophy of materialism With Leucippus, they though that matter can not be divided infinitely.
4.1 Structure of the Atom
 4.1 Structure of the Atom How do atoms differ from each other? What are atoms composed of? What are the subatomic particles? 2-1 Structure of the Atom Atoms actually are divisible. They are composed of
4.1 Structure of the Atom How do atoms differ from each other? What are atoms composed of? What are the subatomic particles? 2-1 Structure of the Atom Atoms actually are divisible. They are composed of
Populating nucleon states. From the Last Time. Other(less stable) helium isotopes. Radioactivity. Radioactive nuclei. Stability of nuclei.
 Nucleus: From the Last Time System of and neutrons bound by the strong force Proton number determines the element. Different isotopes have different # neutrons. Stable isotopes generally have similar number
Nucleus: From the Last Time System of and neutrons bound by the strong force Proton number determines the element. Different isotopes have different # neutrons. Stable isotopes generally have similar number
Study Sheet for Modern Physics
 Study Sheet for Modern Physics Classical mechanics was meant to provide the general rules that govern the dynamics of all material bodies, such as cannon balls, planets, and pendulums, and is defined as
Study Sheet for Modern Physics Classical mechanics was meant to provide the general rules that govern the dynamics of all material bodies, such as cannon balls, planets, and pendulums, and is defined as
Phys102 Lecture 29, 30, 31 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
 Phys10 Lecture 9, 30, 31 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity Key Points Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Alpha, Beta and Gamma Decays References 30-1,,3,4,5,6,7. Atomic Structure Nitrogen (N) Atom
Phys10 Lecture 9, 30, 31 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity Key Points Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Alpha, Beta and Gamma Decays References 30-1,,3,4,5,6,7. Atomic Structure Nitrogen (N) Atom
The Development of Atomic Theory
 The Development of Atomic Theory Democritus (400 BC) John Dalton (1803) J.J. Thomson (1897) Ernest Rutherford (1911) James Chadwick (1932) - suggested that matter is composed of indivisible particles called
The Development of Atomic Theory Democritus (400 BC) John Dalton (1803) J.J. Thomson (1897) Ernest Rutherford (1911) James Chadwick (1932) - suggested that matter is composed of indivisible particles called
FXA Candidates should be able to :
 1 Candidates should be able to : MATTER AND ANTIMATTER Explain that since protons and neutrons contain charged constituents called quarks, they are therefore, not fundamental particles. Every particle
1 Candidates should be able to : MATTER AND ANTIMATTER Explain that since protons and neutrons contain charged constituents called quarks, they are therefore, not fundamental particles. Every particle
History and Structure of the Atom. From Democritus to...
 1 History and Structure of the Atom From Democritus to... History of Atomic Theory 2 Democritus (from about 440 BC) coined the term atom which means uncuttable He felt that if you kept cutting matter smaller
1 History and Structure of the Atom From Democritus to... History of Atomic Theory 2 Democritus (from about 440 BC) coined the term atom which means uncuttable He felt that if you kept cutting matter smaller
Chapter 28. Atomic Physics
 Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Sir Joseph John Thomson J. J. Thomson 1856-1940 Discovered the electron Did extensive work with cathode ray deflections 1906 Nobel Prize for discovery of electron Early Models
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Sir Joseph John Thomson J. J. Thomson 1856-1940 Discovered the electron Did extensive work with cathode ray deflections 1906 Nobel Prize for discovery of electron Early Models
Exam 2 Development of Quantum Mechanics
 PHYS40 (Spring 00) Riq Parra Exam # (Friday, April 1 th, 00) Exam Development of Quantum Mechanics Do NOT write your name on this exam. Write your class ID number on the top right hand corner of each problem
PHYS40 (Spring 00) Riq Parra Exam # (Friday, April 1 th, 00) Exam Development of Quantum Mechanics Do NOT write your name on this exam. Write your class ID number on the top right hand corner of each problem
2 Atomic Theory Development of Theory
 Atomic Theory Development of Theory Historical Atomic Models Democritus Greek philosopher who postulated that matter is comprised of atoms as the smallest part (ca 400 BC) John Dalton Max Planck J.J. Thompson
Atomic Theory Development of Theory Historical Atomic Models Democritus Greek philosopher who postulated that matter is comprised of atoms as the smallest part (ca 400 BC) John Dalton Max Planck J.J. Thompson
Atomic emission & absorption spectra
 Name: Date: Modern Physics Models of the Atom The word atom comes from the Greek word atomos meaning indivisible We now know that this model of the atom is not accurate JJ Thompson Experiment and atomic
Name: Date: Modern Physics Models of the Atom The word atom comes from the Greek word atomos meaning indivisible We now know that this model of the atom is not accurate JJ Thompson Experiment and atomic
Chapter 3 Radioactivity
 Chapter 3 Radioactivity Marie Curie 1867 1934 Discovered new radioactive elements Shared Nobel Prize in physics in 1903 Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1911 Radioactivity Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission
Chapter 3 Radioactivity Marie Curie 1867 1934 Discovered new radioactive elements Shared Nobel Prize in physics in 1903 Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1911 Radioactivity Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission
Chemistry 6A F2007. Dr. J.A. Mack 12/3/07. What do I need to bring? Exam 3: Friday 12/7/07 (here in lecture)
 Chemistry 6A F2007 Dr. J.A. Mack Exam 3: Friday 12/7/07 (here in lecture) What will be covered on the exam? Chapter 6: 6.9-6.15 Chapter 7: All Chapter 8: All Chapter 9: 9.1-9.9 Any thing from lab as well
Chemistry 6A F2007 Dr. J.A. Mack Exam 3: Friday 12/7/07 (here in lecture) What will be covered on the exam? Chapter 6: 6.9-6.15 Chapter 7: All Chapter 8: All Chapter 9: 9.1-9.9 Any thing from lab as well
Nuclear Properties. Thornton and Rex, Ch. 12
 Nuclear Properties Thornton and Rex, Ch. 12 A pre-history 1896 Radioactivity discovered - Becquerel a rays + (Helium) b rays - (electrons) g rays 0 (EM waves) 1902 Transmutation observed - Rutherford and
Nuclear Properties Thornton and Rex, Ch. 12 A pre-history 1896 Radioactivity discovered - Becquerel a rays + (Helium) b rays - (electrons) g rays 0 (EM waves) 1902 Transmutation observed - Rutherford and
Particle Physics. All science is either physics or stamp collecting and this from a 1908 Nobel laureate in Chemistry
 Particle Physics JJ Thompson discovered electrons in 1897 Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus in 1911 and the proton in 1919 (idea of gold foil expt) All science is either physics or stamp collecting
Particle Physics JJ Thompson discovered electrons in 1897 Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus in 1911 and the proton in 1919 (idea of gold foil expt) All science is either physics or stamp collecting
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure. Chemistry- Lookabaugh Moore High School
 Chapter 4 Atomic Structure Chemistry- Lookabaugh Moore High School Section 4.1 Defining the Atom Democritus (460 B.C 370 B.C.) first used the term atomon to describe the smallest particle of matter possible.
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure Chemistry- Lookabaugh Moore High School Section 4.1 Defining the Atom Democritus (460 B.C 370 B.C.) first used the term atomon to describe the smallest particle of matter possible.
Overview. The quest of Particle Physics research is to understand the fundamental particles of nature and their interactions.
 Overview The quest of Particle Physics research is to understand the fundamental particles of nature and their interactions. Our understanding is about to take a giant leap.. the Large Hadron Collider
Overview The quest of Particle Physics research is to understand the fundamental particles of nature and their interactions. Our understanding is about to take a giant leap.. the Large Hadron Collider
The Building Blocks of Nature
 The Building Blocks of Nature PCES 15.1 Schematic picture of constituents of an atom, & rough length scales. The size quoted for the nucleus here (10-14 m) is too large- a single nucleon has size 10-15
The Building Blocks of Nature PCES 15.1 Schematic picture of constituents of an atom, & rough length scales. The size quoted for the nucleus here (10-14 m) is too large- a single nucleon has size 10-15
Quanta to Quarks. Science Teachers Workshop 2014 Workshop Session. Adrian Manning
 Quanta to Quarks Science Teachers Workshop 2014 Workshop Session Adrian Manning The Quanta to Quarks module! The Quanta to Quarks module ultimately deals with some of the most fundamental questions about
Quanta to Quarks Science Teachers Workshop 2014 Workshop Session Adrian Manning The Quanta to Quarks module! The Quanta to Quarks module ultimately deals with some of the most fundamental questions about
Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Reactions
 Slide 1 / 33 Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Reactions The Nucleus Slide 2 / 33 Proton: The charge on a proton is +1.6x10-19 C. The mass of a proton is 1.6726x10-27 kg. Neutron: The neutron is neutral. The
Slide 1 / 33 Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Reactions The Nucleus Slide 2 / 33 Proton: The charge on a proton is +1.6x10-19 C. The mass of a proton is 1.6726x10-27 kg. Neutron: The neutron is neutral. The
SECTION A: NUCLEAR AND PARTICLE PHENOMENOLOGY
 SECTION A: NUCLEAR AND PARTICLE PHENOMENOLOGY This introductory section covers some standard notation and definitions, and includes a brief survey of nuclear and particle properties along with the major
SECTION A: NUCLEAR AND PARTICLE PHENOMENOLOGY This introductory section covers some standard notation and definitions, and includes a brief survey of nuclear and particle properties along with the major
Basic Concepts. 1.1 History The origins of nuclear physics
 1 Basic Concepts 1.1 History Although this book will not follow a strictly historical development, to set the scene this first chapter will start with a brief review of the most important discoveries that
1 Basic Concepts 1.1 History Although this book will not follow a strictly historical development, to set the scene this first chapter will start with a brief review of the most important discoveries that
CHAPTER 7 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 94 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 7 TEST REVIEW 1. An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 10 kv.
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 94 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 7 TEST REVIEW 1. An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 10 kv.
The Nucleus Came Next
 The Nucleus Came Next Ernest Rutherford The New Zealand born British chemist and physicist who became known as the father of nuclear physics. He discovered the atomic nucleus, and thereby pioneered the
The Nucleus Came Next Ernest Rutherford The New Zealand born British chemist and physicist who became known as the father of nuclear physics. He discovered the atomic nucleus, and thereby pioneered the
7. Atomic & Nuclear Physics
 7. Atomic & Nuclear Physics Topic Outline Section Recommended Time Giancoli Sections 7.1 The Atom 2h 27.8, 27.9 7.2 Radioactive Decay 3h 30.1, 30.3-30.6, 30.8 7.3 Nuclear Reactions, Fission and Fusion
7. Atomic & Nuclear Physics Topic Outline Section Recommended Time Giancoli Sections 7.1 The Atom 2h 27.8, 27.9 7.2 Radioactive Decay 3h 30.1, 30.3-30.6, 30.8 7.3 Nuclear Reactions, Fission and Fusion
Chemistry Day 10. Monday, September 17 th Tuesday, September 18 th, 2018
 Chemistry Day 10 Monday, September 17 th Tuesday, September 18 th, 2018 Do-Now Title: Brainstorm: Unit 1 1. Write down today s FLT 2. Draw what an atom looks like according to Democritus and Dalton 3.
Chemistry Day 10 Monday, September 17 th Tuesday, September 18 th, 2018 Do-Now Title: Brainstorm: Unit 1 1. Write down today s FLT 2. Draw what an atom looks like according to Democritus and Dalton 3.
Where are we? Check-In
 Where are we? Check-In ü Building Blocks of Matter ü Moles, molecules, grams, gases, ü The Bohr Model solutions, and percent composition Coulomb s Law ü Empirical and Molecular formulas Photoelectron Spectroscopy
Where are we? Check-In ü Building Blocks of Matter ü Moles, molecules, grams, gases, ü The Bohr Model solutions, and percent composition Coulomb s Law ü Empirical and Molecular formulas Photoelectron Spectroscopy
The Four Fundamental Forces. The Four Fundamental Forces. Gravitational Force. The Electrical Force. The Photon (γ) Unification. Mass.
 The Four Fundamental Forces What are the four fundamental forces? The Four Fundamental Forces What are the four fundamental forces? Weaker Stronger Gravitational, Electromagnetic, Strong and Weak Nuclear
The Four Fundamental Forces What are the four fundamental forces? The Four Fundamental Forces What are the four fundamental forces? Weaker Stronger Gravitational, Electromagnetic, Strong and Weak Nuclear
Explain the term subshell. 5. Explain de-broglie equation (relationship). 6. Discuss the dual nature of electrons
 MODEL COLLEGE ASSIGNMENT SHEET FOR STRUCTURE OF ATOM. What are the main postulates of Bohr s theory of an atom?. Explain how the angular momentum of an electron in an atom is quantized? 3. What are the
MODEL COLLEGE ASSIGNMENT SHEET FOR STRUCTURE OF ATOM. What are the main postulates of Bohr s theory of an atom?. Explain how the angular momentum of an electron in an atom is quantized? 3. What are the
Atomic Models. A model uses familiar ideas to explain unfamiliar facts observed in nature. A model can be changed as new information is collected.
 This model of the atom may look familiar to you. This is the Bohr model. In this model, the nucleus is orbited by electrons, which are in different energy levels. Atomic Models A model uses familiar ideas
This model of the atom may look familiar to you. This is the Bohr model. In this model, the nucleus is orbited by electrons, which are in different energy levels. Atomic Models A model uses familiar ideas
Quantum and Atomic Physics - Multiple Choice
 PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. The Cathode Ray Tube experiment is associated with: (A) J. J. Thomson (B) J. S. Townsend (C) M. Plank (D) A. H. Compton 2. The electron charge was measured the first time in: (A)
PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. The Cathode Ray Tube experiment is associated with: (A) J. J. Thomson (B) J. S. Townsend (C) M. Plank (D) A. H. Compton 2. The electron charge was measured the first time in: (A)
da u g ht er + radiation
 RADIOACTIVITY The discovery of radioactivity can be attributed to several scientists. Wilhelm Roentgen discovered X-rays in 1895 and shortly after that Henri Becquerel observed radioactive behavior while
RADIOACTIVITY The discovery of radioactivity can be attributed to several scientists. Wilhelm Roentgen discovered X-rays in 1895 and shortly after that Henri Becquerel observed radioactive behavior while
THE NATURE OF THE ATOM. alpha particle source
 chapter THE NATURE OF THE ATOM www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) Section 30.1 Rutherford Scattering and the Nuclear Atom 1. Which model of atomic structure
chapter THE NATURE OF THE ATOM www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) Section 30.1 Rutherford Scattering and the Nuclear Atom 1. Which model of atomic structure
Franck-Hertz experiment, Bohr atom, de Broglie waves Announcements:
 Franck-Hertz experiment, Bohr atom, de Broglie waves Announcements: Problem solving sessions Tues. 1-3. Reading for Wednesday TZD 6.1-.4 2013 Nobel Prize Announcement Tomorrow Few slides on the Higgs Field
Franck-Hertz experiment, Bohr atom, de Broglie waves Announcements: Problem solving sessions Tues. 1-3. Reading for Wednesday TZD 6.1-.4 2013 Nobel Prize Announcement Tomorrow Few slides on the Higgs Field
Section 3.1 Substances Are Made of Atoms
 Section 3.1 Substances Are Made of Atoms Objectives: 1. State the three laws that support the existence of atoms. 2. List the five principles of John Dalton s atomic theory. Vocabulary: law of definite
Section 3.1 Substances Are Made of Atoms Objectives: 1. State the three laws that support the existence of atoms. 2. List the five principles of John Dalton s atomic theory. Vocabulary: law of definite
The Goals of Particle Physics
 The Goals of Particle Physics Richard (Ryszard) Stroynowski Department of Physics Southern Methodist University History of Elementary Particles Science as a field of study derives from the Western Civilization
The Goals of Particle Physics Richard (Ryszard) Stroynowski Department of Physics Southern Methodist University History of Elementary Particles Science as a field of study derives from the Western Civilization
CHEMISTRY. Matter and Change. Table Of Contents. Section 4.1 Early Ideas About Matter. Unstable Nuclei and Radioactive Decay
 CHEMISTRY 4 Table Of Contents Matter and Change Section 4.1 Early Ideas About Matter Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom Section 4.2 Section 4.3 Section 4.4 Defining the Atom How Atoms Differ Unstable
CHEMISTRY 4 Table Of Contents Matter and Change Section 4.1 Early Ideas About Matter Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom Section 4.2 Section 4.3 Section 4.4 Defining the Atom How Atoms Differ Unstable
Particle Nature of Matter. Chapter 4
 Particle Nature of Matter Chapter 4 Modern physics When my grandfather was born, atoms were just an idea. That year, 1897, was marked by the discovery of the electron by J.J. Thomson. The nuclear model
Particle Nature of Matter Chapter 4 Modern physics When my grandfather was born, atoms were just an idea. That year, 1897, was marked by the discovery of the electron by J.J. Thomson. The nuclear model
Nuclear Science A Teacher s Guide to the Nuclear Science Wall Chart 1998 Contemporary Physics Education Project (CPEP)
 Nuclear Science A Teacher s Guide to the Nuclear Science Wall Chart 1998 Contemporary Physics Education Project (CPEP) Chapter 3 Radioactivity In radioactive processes, particles or electromagnetic radiation
Nuclear Science A Teacher s Guide to the Nuclear Science Wall Chart 1998 Contemporary Physics Education Project (CPEP) Chapter 3 Radioactivity In radioactive processes, particles or electromagnetic radiation
Ch. 4 Notes THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics.
 Ch. 4 Notes THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. I. Early Ideas About Matter A. atom the smallest particle of an element retaining
Ch. 4 Notes THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. I. Early Ideas About Matter A. atom the smallest particle of an element retaining
