Vector control of asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor
|
|
|
- Annabel Paul
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING RESEARCH ARTICLE Vector control of asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor Arif Iqbal 1 *, G.K. Singh 1 and Vinay Pant 1 Received: 22 October 215 Accepted: 9 December 215 First Published: 19 January 216 *Corresponding author: Arif Iqbal, Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee , Uttarakhand, India s: arif.iqbal.in@gmail.com, arif548@gmail.com Reviewing editor: Wei Meng, Wuhan University of Technology, China Additional information is available at the end of the article Abstract: Vector control scheme has been well adopted for higher performance applications of AC motor. Therefore, this paper presents an extensive development and investigation of vector control scheme for asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor in a new two-axis (M T coordinate system. Phasor diagram has also been developed in a simplified way, followed by its implementation technique. Analytical results have been presented for four-quadrant operation of synchronous motor, employing the developed vector control scheme. In analytical control model, common mutual leakage reactance between the two winding sets occupying same stator slot has been considered. Subjects: Automation Control; Mechatronics; Systems & Controls Keywords: six-phase synchronous motor; vector control; motor drive 1. Introduction The multiphase (more than three phase AC motor drives are used as a substitute of conventional three-phase motor in different applications particularly, in propulsion system of ship and vehicle, textile and steel industries, rolling mills, power plants, etc. This is because it offers certain potential advantages when compared with its three-phase counterpart, like reduction in space and time harmonics, reduced torque pulsation, increased power handling capability, higher reliability, etc. (Levi, 28; Singh, 22. Field-oriented control (i.e. vector control technique has been widely used in high performance of AC motor drives. In this regard, an abundant number of literatures are available for three-phase motor (Bose, 22; Das & Chattopadhyay, 1997; Jain & Ranganathan, 211; Krause, Wasynczuk, & Sudhoff, 24, but a few for six-phase induction motor (Bojoi, Lazzari, Profumo, & Tenconi, 23; Singh, Nam, & Lim, 25, wherein d q model of machine has been used in synchronously rotating Arif Iqbal ABOUT THE AUTHOR Arif Iqbal received his BTech and MTech degrees both in electrical engineering in 25 and 27, respectively, from Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India. After having experience in industry and teaching in the field AC drives and power system for a few years, he is currently pursuing his PhD from Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, India. His area of interest is multiphase AC machine and drives, power electronics, and renewable energy system. PUBLIC INTEREST STATEMENT It is always advantageous to use the electrical machine with its performance at higher level using a suitable technique. Among different techniques, vector control is widely used as it provides the decoupled control of torque and flux component of machine current. Therefore, the paper explores a detailed asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor operation employing this technique. Analysis and simulation of complete drive system has been carried out in Matlab/ Simulink environment, where dynamic behavior of motor was found to be substantially improved. It is believed that the paper will serve as a source toward higher performance of six-phase synchronous motor. 216 The Author(s. This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY 4. license. Page 1 of 1
2 Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: reference frame. But the utilization of this scheme has not been reported for field excited six-phase synchronous motor. Therefore, the paper is dedicated to explore and develop the control technique for asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor. In the control scheme, a new two axis (M T coordinate has been introduced along which the decoupled control of flux and torque is achieved. Following the inclusion of control technique, a detailed analytical results have been presented for motor operation in four quadrants. 2. Mathematical modeling For the purpose of realizing the six-phase motor, it is a common practice to split the existing threephase stator winding into two, namely a b c and a b c. Both splitted stator winding sets (a b c and a b c are physically displaced 3 apart to realize asymmetrical six-phase winding configuration. Asymmetrical six-phase winding configuration yields the reduced torque pulsation (Singh, 22, 211 due to the elimination of lower order harmonics. On the rotor side, it is equipped with field winding fr together with the damper windings K d and K q along d and q-axis, respectively. The equation of the motor can be written using machine variables. But this will yield a set of nonlinear differential equations. Nonlinearity is due to the existence of inductance term which is time varying in nature. Such equations are computationally complex and time-consuming. Therefore, to simplify the motor equations with constant inductance term, it will be conveniently written in rotor reference frame using Park s variables (Iqbal, Singh, & Pant, 214, in press; Schiferl & Ong, 1983; Singh, 211. v dqk r sk i dqk + ω r ω b ψ dqk + p ω b ψ dqk (1 v dqr r dqr i dqk + p ω b ψ dqr (2 v dqk v dk v qk (3 ψ dqk ψ dk ψ qk (4 r dqk r dk r qk (5 for k { 1, for winding set abc 2, for winding set a b c v dqr v Kd v Kq v fr (6 r fr v fr e xfd 3, 12] x md (7 ψ dqr ψ Kd ψ Kq ψ fr (8 r dqk r Kd r Kq r fr (9 Equations of motor flux linkage per second may be conveniently written as the function of currents, ψ xi (1 Page 2 of 1
3 Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: where i i dqk i dqk, ψ ψ dqk ψ dqk x is defined in Appendix 1. The developed motor torque is expressed as τ e τ e1 + τ e2 (11 where τ e1 and τ e2 are the developed motor torque associated with winding sets a b c and a b c, respectively, and expressed as τ e1 c(i q1 ψ d1 i d1 ψ q1 (12 τ e2 c(i q2 ψ d2 i d2 ψ q2 (13 with c 3 P ω b The rotor dynamics having P number of poles is expressed as ω r 1 1 P 1 ( ] τe τ ω b p ω b 2 J l (14 wherein, τ l is the load torque, p represents the derivative function w.r.t. time and all symbols stand to their usual meaning (Iqbal et al., in press. Evaluation of motor parameters is determined from the standard test procedure (Aghamohammadi & Pourgholi, 28; Alger, 197; Jones, Vector control scheme The operating performance of vector-controlled motor is greatly improved and similar to that of a separately excited DC motor (Bose, 22. This is because of decoupled control of both flux component and torque component of stator current. The inclusion of vector control scheme is not similar to that of induction motor drive. The main difference lies on the fact that the air gap flux is attributed by both stator flux as well as field flux. Therefore, the resultant air gap flux will align along the axis which is different from conventional d-axis. Hence, a new (M T coordinate axis has been introduced wherein, the resultant flux vector and torque current component will align along M and T axis, respectively. Machine variables in newly defined coordinate axis (M T axis may be readily transformed to its equivalent d q or vice versa by relation ] ] ] Mk cosδk sinδ k dk (15 T k sinδ k cosδ k q k In above relation, the torque angle δ 1 and δ 2 are associated with winding sets a b c and a b c, respectively, and defined as δ 1 δ δ 1 δ + +ξ (16 (17 δ is the initial value of load angle, whereas is the phase difference between voltage fed to phase a and a. Hence, torque attributed by each stator winding sets a b c and a b c is given by Equations (12 and (13 may be readily written in M T axes, τ e1 c(ψ M1 I T1 ψ T1 I M1 (18 Page 3 of 1
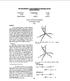
4 Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: Figure 1. Phasor diagram of vector-controlled six-phase synchronous motor. T 1 V a T 2, V a V a e j q s M 1 I M1 I s1 I s2 IT1 Ø I M2 I T2 r I m1 I T1 1 I m IT2, I fr s1 a s2 fr a, M 2 d s τ e2 c(ψ M2 I T2 ψ T2 I M2 (19 where, the flux linkage ψ Mk and ψ Tk, and stator current I Mk and I Tk are aligned along M k T k axes respectively, for winding sets a b c (for k 1 and a b c (for k 2. Since, the resultant armature air gap flux is only aligned along flux axis (i.e. M k axis. Therefore, ψ T1 and ψ M1 ψ s1, where ψ s1 ψ 2 M1 + ψ 2 T1 (2 ψ T2 and ψ M2 ψ s2, where ψ s2 ψ 2 M2 + ψ 2 T2 (21 Hence, motor torque equation may be simplified as τ e τ e1 + τ e2 c(ψ s1 I T1 + ψ s2 I T2 (22 The developed motor torque is dependent on flux linkage ψ s1 (and ψ s2 and current I T1 (and I T2 which are orthogonal. This is the introduction of vector-controlled six-phase synchronous motor. The motor operation during steady state has been shown in the developed phasor diagram in Figure Implementation of vector control scheme The implementation of developed vector-controlled synchronous motor drive system has been shown in Figure 2. In this paper, motor operation has been investigated in constant torque region up to base speed, but same may be extended in field weakening region above base speed. In the figure, the outer speed loop is used to generate the reference value torque component of stator current I Tk through a speed controller (PI controller, whereas the reference value magnetizing current I mk is generated by the flux controller (PI controller associated with each winding sets a b c (for k 1 and a b c (for k 2. The reference magnetizing current is used to establish the required flux ψ sk in air gap, which related to field current by the relation, } I m1 I cos δ fr 1 (23 I m2 I cos δ fr 2 In phasor diagram, current component I T1 (and I T2 is in the direction of T 1 (and T 2 axis along which the voltage vector is also aligned. Further, the magnetizing component of current I m1 (and I m2 is Page 4 of 1
5 Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: Figure 2. Schematic diagram of vector-controlled six-phase synchronous motor drive. aligned along M 1 (and M 2 axis which is used to establish the flux vector ψ s1 (and ψ s2. At steady state, both the stator flux and armature flux vectors are orthogonal to each other, i.e. ψ s1 (and ψ s2 is perpendicular to ψ a1 (and ψ a2 as shown in phasor diagram. Therefore, at steady state, both the vectors I Tk and I sk are equal i.e. I T1 I s1 for winding set a b c (and I T2 I s2 for winding set a b c and becomes in phase with voltage vector, signifying the motor operation at unity power factor. In control scheme, it may be noted that the magnetizing current component I m1 (and I m2 is related to field current I frk associated with winding sets a b c and a b c. Field current commands I fr1 and I fr2 are synthesized using Equation (23 in feedback loop. In field control loop, the field current error is fed to the field controller (PI controller to establish the required field excitation. It may be noted here that the magnitude of field current magnitude associated with each winding set a b c and a b c is assumed to be same I (.5I fr fr. Now, the flux component of stator current is generated by I M1 I cos δ m1 I fr 1 I M2 I cos δ m2 I fr 2 } (24 Above relation will yield a finite value of I M1 and I M2. But at steady state, it becomes zero (i.e. I M1 I M2 and Equation (23 will be satisfied. As soon as stator current component I Tk and I Mk are synthesized for winding sets a b c (k 1 and a b c (k 2, the reference value of current in stationary reference frame is generated. For this purpose, following two-step transformation is carried out. (1 Current component I Tk and I Mk are transformed to d q component in stationary reference frame, using angle α k in transformation in relation (15. (2 Above obtained stationary d q component of current is transformed into its equivalent threephase current (Krause et al., 24. The reference current generated in above steps in stationary reference frame are then compared with actual phase current of stator windings which results in current error. This current error is fed to the hysteresis current controller to regulate switching of inverter circuit feeding the motor. Page 5 of 1
6 Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: Simulation results The developed system of vector-controlled six-phase synchronous motor drive was implemented in Matlab/Simulink environment. For this purpose, a 3.7-kW motor (parameters are given in Appendix 1 was operated in four quadrant. Initially, speed command was given at time t.1 s. in ramp way, following to which motor starts to run at synchronous speed after time t.65 s, showing its operation in first quadrant. A load of 5% of base torque was applied at time t 1.5 s which results a small dip in speed by.3 rad/s, but regains its original speed (i.e. synchronous speed after time t.5 s, as shown in Figure 3. In order to examine the motor operation in second quadrant, the direction of load torque was reversed at time t 3 s, resulting in a small increase in rotor speed by.5 rad/s. A small change in rotor speed due to sudden change in load torque signifies the disturbance rejection property of the drive system. A zoomed view of speed variation has been shown in Figure 3(a. Following to the change in load torque, not only the variation in q-component of stator current but also resulted a small variation in d-component of current, as shown in Figure 5. Change in stator current is also reflected in T-axis component of motor current flowing in winding sets a b c and a b c, in Figures 4 and 6. In order to shift the motor operation to third quadrant, a speed reversal command was initiated at time t 4 s in ramp way. The motor is then finally operates in reverse motoring mode after time t 5 s at synchronous speed. Further, at time t 6 s the load torque is reversed to operate the drive in fourth quadrant. It is important to note here that the switching of motor operation to different quadrant results in a large variation in d-component stator current whose effect is compensated by rotor field current, as shown in Figure 7(b. But the field circuit has a larger time constant, making the response slow (Das & Chattopadhyay, 1997; Jain & Ranganathan, 211; Krause et al., 24. This sluggish response of field circuit is substantially improved due to the magnetizing current injection along flux direction, as depicted by reference value of current in Figure 4(b and c as well as in actual current in Figure 6(c and d. Input phase voltage fed to winding sets a b c and a b c, is shown in Figure 8(a and (b, respectively. 6. Conclusion The scheme of vector control applicable for asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor has been developed and extensively investigated in four quadrant operation. In this control technique, stator current is maintained for motor operation at unity power factor, which minimizes the stator current Figure 3. Motor response (a rotor speed ω r and (b torque T e. (a (b Page 6 of 1
7 Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: Figure 4. Reference current in M T coordinate (a I T1, (b I M1 and (c I M2. (a (b (c Figure 5. Stator current in d q coordinate (a i q1 (b i d1 (c i q2 (d i d2. (a (b (c (d Figure 6. Actual current in M T coordinate (a I T1, (b I T2 (c I M1 and (d I M2. (a (b (c (d Page 7 of 1
8 Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: Figure 7. Voltage current in field circuit (a reference I fr, (b actual I fr (c voltage E fr. (a (b (c Figure 8. Inverter output voltage (a phase a (b phase a'. (a (b and hence less losses. The dynamic behavior of six-phase synchronous motor in different quadrant operation was found to be substantially improved because of the decoupled/independent control of flux as well as torque component of current along M T axis, respectively. Furthermore, sluggish response of the rotor field circuit was also noted to be improved because of the magnetizing current injection from armature side. The present work may be further extended and investigated under different practical application with their experimental validation. Funding The authors received no direct funding for this research. Author details Arif Iqbal 1 arif.iqbal.in@gmail.com, arif548@gmail.com ORCID ID: G.K. Singh 1 gksngfee@gmail.com Vinay Pant 1 vpantfee@gmail.com 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee , Uttarakhand, India. Page 8 of 1
9 Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: Citation information Cite this article as: Vector control of asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor, Arif Iqbal, G.K. Singh & Vinay Pant, Cogent Engineering (216, 3: References Aghamohammadi, M. R., & Pourgholi, M. (28. Experience with SSSFR test for synchronous generator model identification using Hook Jeeves optimization method. International Journal of System Applications, Engineering and Development, 2, Alger, P. L. (197. Induction machine. New York, NY: Gorden and Breach. Bojoi, R., Lazzari, M., Profumo, F., & Tenconi, A. (23. Digital field-oriented control for dual three-phase induction motor drives. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 39, Bose, B. K. (22. Mordern power electronics and AC drives. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. Das, S. P., & Chattopadhyay, A. K. (1997. Observer based stator flux oriented vector control of cycloconverter-fed synchronous motor drive. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 33, Iqbal, A., Singh, G. K., & Pant, V. (214. Steady-state modeling and analysis of six-phase synchronous motor. System Science & Control Engineering, 2, Iqbal, A., Singh, G. K., & Pant, V. (in press. Stability analysis of asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences. Jain, A. K., & Ranganathan, V. T. (211. Modeling and field oriented control of salient pole wound field synchronous machine in stator flux coordinates. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 58, Jones, C. V. (1967. The unified theory of electric machine. London: Butterworths. Krause, P. C., Wasynczuk, O., & Sudhoff, S. D. (24. Analysis of electrical machinery and drive Systems. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press and Wiley. Levi, E. (28. Multiphase electric machines for variable-speed applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Applications, 38, Schiferl, R. F., & Ong, C. M. (1983. Six phase synchronous machine with AC and DC stator connections, part I: Equivalent circuit representation and steady-state analysis. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, 12, Singh, G. K. (22. Multi-phase induction machine drive research A survey. Electric Power Systems Research, 61, Singh, G. K. (211. Modeling and analysis of six-phase synchronous generator for stand-alone renewable energy generation. Energy, 36, Singh, G. K., Nam, K., & Lim, S. K. (25. A simple indirect field-oriented control scheme for multiphase induction machine. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 52, Appendix 1 Motor parameter of 3.7 kw, 6 poles, 36 slots are r 1.21 Ω x mq Ω r fr.56 Ω r 2.21 Ω x md Ω x ldq r Kq Ω x lkq.6697 Ω x lm.1652 Ω r Kd 14. Ω x lkd 1.55 Ω x lfr.242 Ω x l1 x l Ω x ( xl1 + x lm + x md ( xlm + x md x ldq ( x lm + x mq ( xlm + x md x ldq x md x md ( ( xl1 + x lm + x md x ldq x lm + x mq x mq ( x ldq xl2 + x lm + x md x md x md (x l2 + x lm + x mq x mq x md x md x md x mq x mq x md x md x md ( xlkd + x md (x lkq + x mq (x lfr + x md Page 9 of 1
10 Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: The Author(s. This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY 4. license. You are free to: Share copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format Adapt remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially. The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms. Under the following terms: Attribution You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use. No additional restrictions You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits. Cogent Engineering (ISSN: is published by Cogent OA, part of Taylor & Francis Group. Publishing with Cogent OA ensures: Immediate, universal access to your article on publication High visibility and discoverability via the Cogent OA website as well as Taylor & Francis Online Download and citation statistics for your article Rapid online publication Input from, and dialog with, expert editors and editorial boards Retention of full copyright of your article Guaranteed legacy preservation of your article Discounts and waivers for authors in developing regions Submit your manuscript to a Cogent OA journal at Page 1 of 1
MATLAB SIMULINK Based DQ Modeling and Dynamic Characteristics of Three Phase Self Excited Induction Generator
 628 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 MATLAB SIMULINK Based DQ Modeling and Dynamic Characteristics of Three Phase Self Excited Induction Generator A. Kishore,
628 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 MATLAB SIMULINK Based DQ Modeling and Dynamic Characteristics of Three Phase Self Excited Induction Generator A. Kishore,
A New Model Reference Adaptive Formulation to Estimate Stator Resistance in Field Oriented Induction Motor Drive
 A New Model Reference Adaptive Formulation to Estimate Stator Resistance in Field Oriented Induction Motor Drive Saptarshi Basak 1, Chandan Chakraborty 1, Senior Member IEEE and Yoichi Hori 2, Fellow IEEE
A New Model Reference Adaptive Formulation to Estimate Stator Resistance in Field Oriented Induction Motor Drive Saptarshi Basak 1, Chandan Chakraborty 1, Senior Member IEEE and Yoichi Hori 2, Fellow IEEE
On a mixed interpolation with integral conditions at arbitrary nodes
 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE On a mixed interpolation with integral conditions at arbitrary nodes Srinivasarao Thota * and Shiv Datt Kumar Received: 9 October 5 Accepted: February 6 First Published:
PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE On a mixed interpolation with integral conditions at arbitrary nodes Srinivasarao Thota * and Shiv Datt Kumar Received: 9 October 5 Accepted: February 6 First Published:
Finding the strong defining hyperplanes of production possibility set with constant returns to scale using the linear independent vectors
 Rafati-Maleki et al., Cogent Mathematics & Statistics (28), 5: 447222 https://doi.org/.8/233835.28.447222 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Finding the strong defining hyperplanes
Rafati-Maleki et al., Cogent Mathematics & Statistics (28), 5: 447222 https://doi.org/.8/233835.28.447222 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Finding the strong defining hyperplanes
Independent Control of Speed and Torque in a Vector Controlled Induction Motor Drive using Predictive Current Controller and SVPWM
 Independent Control of Speed and Torque in a Vector Controlled Induction Motor Drive using Predictive Current Controller and SVPWM Vandana Peethambaran 1, Dr.R.Sankaran 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of
Independent Control of Speed and Torque in a Vector Controlled Induction Motor Drive using Predictive Current Controller and SVPWM Vandana Peethambaran 1, Dr.R.Sankaran 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of
MODELING AND HIGH-PERFORMANCE CONTROL OF ELECTRIC MACHINES
 MODELING AND HIGH-PERFORMANCE CONTROL OF ELECTRIC MACHINES JOHN CHIASSON IEEE PRESS ü t SERIES ON POWER ENGINEERING IEEE Press Series on Power Engineering Mohamed E. El-Hawary, Series Editor The Institute
MODELING AND HIGH-PERFORMANCE CONTROL OF ELECTRIC MACHINES JOHN CHIASSON IEEE PRESS ü t SERIES ON POWER ENGINEERING IEEE Press Series on Power Engineering Mohamed E. El-Hawary, Series Editor The Institute
Direct Torque Control of Three Phase Induction Motor FED with Three Leg Inverter Using Proportional Controller
 Direct Torque Control of Three Phase Induction Motor FED with Three Leg Inverter Using Proportional Controller Bijay Kumar Mudi 1, Sk. Rabiul Hossain 2,Sibdas Mondal 3, Prof. Gautam Kumar Panda 4, Prof.
Direct Torque Control of Three Phase Induction Motor FED with Three Leg Inverter Using Proportional Controller Bijay Kumar Mudi 1, Sk. Rabiul Hossain 2,Sibdas Mondal 3, Prof. Gautam Kumar Panda 4, Prof.
Generalized Theory of Electrical Machines- A Review
 Generalized Theory of Electrical Machines- A Review Dr. Sandip Mehta Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, JIET Group of Institutions, Jodhpur Abstract:-This paper provides an overview
Generalized Theory of Electrical Machines- A Review Dr. Sandip Mehta Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, JIET Group of Institutions, Jodhpur Abstract:-This paper provides an overview
ANALYSIS OF ELECTRIC MACHINERY AND DRIVE SYSTEMS
 ANALYSIS OF ELECTRIC MACHINERY AND DRIVE SYSTEMS IEEE Press 445 Hoes Lane Piscataway, NJ 08854 IEEE Press Editorial Board 2013 John Anderson, Editor in Chief Linda Shafer Saeid Nahavandi George Zobrist
ANALYSIS OF ELECTRIC MACHINERY AND DRIVE SYSTEMS IEEE Press 445 Hoes Lane Piscataway, NJ 08854 IEEE Press Editorial Board 2013 John Anderson, Editor in Chief Linda Shafer Saeid Nahavandi George Zobrist
Mathematical Modelling of an 3 Phase Induction Motor Using MATLAB/Simulink
 2016 IJSRSET Volume 2 Issue 3 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology Mathematical Modelling of an 3 Phase Induction Motor Using MATLAB/Simulink ABSTRACT
2016 IJSRSET Volume 2 Issue 3 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology Mathematical Modelling of an 3 Phase Induction Motor Using MATLAB/Simulink ABSTRACT
Small Signal Stability Analysis of Six-phase Synchronous Generator
 Girish Kumar Singh 1, Derminder Singh 1 Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee, India (1) Small Signal Stability Analysis of Six-phase Synchronous Generator Abstract. In the present work, a higher
Girish Kumar Singh 1, Derminder Singh 1 Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee, India (1) Small Signal Stability Analysis of Six-phase Synchronous Generator Abstract. In the present work, a higher
The plastic number and its generalized polynomial
 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE The plastic number and its generalized polynomial Vasileios Iliopoulos 1 * Received: 18 December 2014 Accepted: 19 February 201 Published: 20 March 201 *Corresponding
PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE The plastic number and its generalized polynomial Vasileios Iliopoulos 1 * Received: 18 December 2014 Accepted: 19 February 201 Published: 20 March 201 *Corresponding
A note on the unique solution of linear complementarity problem
 COMPUTATIONAL SCIENCE SHORT COMMUNICATION A note on the unique solution of linear complementarity problem Cui-Xia Li 1 and Shi-Liang Wu 1 * Received: 13 June 2016 Accepted: 14 November 2016 First Published:
COMPUTATIONAL SCIENCE SHORT COMMUNICATION A note on the unique solution of linear complementarity problem Cui-Xia Li 1 and Shi-Liang Wu 1 * Received: 13 June 2016 Accepted: 14 November 2016 First Published:
DEVELOPMENT OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL MODELWITH USING SVI FOR THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR
 DEVELOPMENT OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL MODELWITH USING SVI FOR THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR MUKESH KUMAR ARYA * Electrical Engg. Department, Madhav Institute of Technology & Science, Gwalior, Gwalior, 474005,
DEVELOPMENT OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL MODELWITH USING SVI FOR THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR MUKESH KUMAR ARYA * Electrical Engg. Department, Madhav Institute of Technology & Science, Gwalior, Gwalior, 474005,
Modeling Free Acceleration of a Salient Synchronous Machine Using Two-Axis Theory
 1 Modeling ree Acceleration of a Salient Synchronous Machine Using Two-Axis Theory Abdullah H. Akca and Lingling an, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract This paper investigates a nonlinear simulation model of
1 Modeling ree Acceleration of a Salient Synchronous Machine Using Two-Axis Theory Abdullah H. Akca and Lingling an, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract This paper investigates a nonlinear simulation model of
Vector Controlled Power Generation in a Point Absorber Based Wave Energy Conversion System
 Vector Controlled Power Generation in a Point Absorber Based Wave Energy Conversion System Jisha Thomas Chandy 1 and Mr. Vishnu J 2 1,2 Electrical & Electronics Dept of Engineering, Sree Buddha College
Vector Controlled Power Generation in a Point Absorber Based Wave Energy Conversion System Jisha Thomas Chandy 1 and Mr. Vishnu J 2 1,2 Electrical & Electronics Dept of Engineering, Sree Buddha College
Matrix l-algebras over l-fields
 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Matrix l-algebras over l-fields Jingjing M * Received: 05 January 2015 Accepted: 11 May 2015 Published: 15 June 2015 *Corresponding author: Jingjing Ma, Department of
PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Matrix l-algebras over l-fields Jingjing M * Received: 05 January 2015 Accepted: 11 May 2015 Published: 15 June 2015 *Corresponding author: Jingjing Ma, Department of
DESIGN AND MODELLING OF SENSORLESS VECTOR CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR USING MODEL REFERENCE ADAPTIVE SYSTEMS
 DESIGN AND MODELLING OF SENSORLESS VECTOR CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR USING MODEL REFERENCE ADAPTIVE SYSTEMS Janaki Pakalapati 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE, Avanthi Institute of Engineering and Technology,
DESIGN AND MODELLING OF SENSORLESS VECTOR CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR USING MODEL REFERENCE ADAPTIVE SYSTEMS Janaki Pakalapati 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE, Avanthi Institute of Engineering and Technology,
EFFECTS OF LOAD AND SPEED VARIATIONS IN A MODIFIED CLOSED LOOP V/F INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE
 Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol. 31, No. 3, November, 2012, pp. 365 369. Copyright 2012 Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria. ISSN 1115-8443 EFFECTS OF LOAD AND SPEED VARIATIONS
Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol. 31, No. 3, November, 2012, pp. 365 369. Copyright 2012 Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria. ISSN 1115-8443 EFFECTS OF LOAD AND SPEED VARIATIONS
Modelling and Parameter Determination of an Induction Servo-Motor
 British Journal of Applied Science & Technology 13(2): 1-11, 2016, Article no.bjast.21969 ISSN: 2231-0843, NLM ID: 101664541 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Modelling and Parameter Determination
British Journal of Applied Science & Technology 13(2): 1-11, 2016, Article no.bjast.21969 ISSN: 2231-0843, NLM ID: 101664541 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Modelling and Parameter Determination
Graded fuzzy topological spaces
 Ibedou, Cogent Mathematics (06), : 8574 http://dxdoiorg/0080/85068574 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Graded fuzzy topological spaces Ismail Ibedou, * Received: August 05 Accepted: 0 January 06 First
Ibedou, Cogent Mathematics (06), : 8574 http://dxdoiorg/0080/85068574 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Graded fuzzy topological spaces Ismail Ibedou, * Received: August 05 Accepted: 0 January 06 First
Shanming Wang, Ziguo Huang, Shujun Mu, and Xiangheng Wang. 1. Introduction
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 215, Article ID 467856, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/467856 Research Article A Straightforward Convergence Method for ICCG Simulation of Multiloop and
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 215, Article ID 467856, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/467856 Research Article A Straightforward Convergence Method for ICCG Simulation of Multiloop and
Modelling of Closed Loop Speed Control for Pmsm Drive
 Modelling of Closed Loop Speed Control for Pmsm Drive Vikram S. Sathe, Shankar S. Vanamane M. Tech Student, Department of Electrical Engg, Walchand College of Engineering, Sangli. Associate Prof, Department
Modelling of Closed Loop Speed Control for Pmsm Drive Vikram S. Sathe, Shankar S. Vanamane M. Tech Student, Department of Electrical Engg, Walchand College of Engineering, Sangli. Associate Prof, Department
Parameter Estimation of Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor
 International Conference On Emerging Trends in Mechanical and Electrical Engineering RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Parameter Estimation of Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Sonakshi Gupta Department
International Conference On Emerging Trends in Mechanical and Electrical Engineering RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Parameter Estimation of Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Sonakshi Gupta Department
3 d Calculate the product of the motor constant and the pole flux KΦ in this operating point. 2 e Calculate the torque.
 Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) 11 November 011 from 14.00 to 17.00. This exam consists of 5 problems on 4 pages. Page 5 can be used to answer problem 4 question b. The number before a question
Parameter Prediction and Modelling Methods for Traction Motor of Hybrid Electric Vehicle
 Page 359 World Electric Vehicle Journal Vol. 3 - ISSN 232-6653 - 29 AVERE Parameter Prediction and Modelling Methods for Traction Motor of Hybrid Electric Vehicle Tao Sun, Soon-O Kwon, Geun-Ho Lee, Jung-Pyo
Page 359 World Electric Vehicle Journal Vol. 3 - ISSN 232-6653 - 29 AVERE Parameter Prediction and Modelling Methods for Traction Motor of Hybrid Electric Vehicle Tao Sun, Soon-O Kwon, Geun-Ho Lee, Jung-Pyo
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR 1 A.PANDIAN, 2 Dr.R.DHANASEKARAN 1 Associate Professor., Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Angel College of
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR 1 A.PANDIAN, 2 Dr.R.DHANASEKARAN 1 Associate Professor., Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Angel College of
Sensorless DTC-SVM of Induction Motor by Applying Two Neural Controllers
 Sensorless DTC-SVM of Induction Motor by Applying Two Neural Controllers Abdallah Farahat Mahmoud Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Al-Azhar University, Qena, Egypt engabdallah2012@azhar.edu.eg Adel S.
Sensorless DTC-SVM of Induction Motor by Applying Two Neural Controllers Abdallah Farahat Mahmoud Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Al-Azhar University, Qena, Egypt engabdallah2012@azhar.edu.eg Adel S.
A Power System Dynamic Simulation Program Using MATLAB/ Simulink
 A Power System Dynamic Simulation Program Using MATLAB/ Simulink Linash P. Kunjumuhammed Post doctoral fellow, Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Imperial College London, United Kingdom
A Power System Dynamic Simulation Program Using MATLAB/ Simulink Linash P. Kunjumuhammed Post doctoral fellow, Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Imperial College London, United Kingdom
Steady State Modeling of Doubly Fed Induction Generator
 Steady State Modeling of Douly Fed Induction Generator Bhola Jha 1, Dr. K. R. M Rao 2 1 Dept. of Electrical Engg., G. B. Pant Engg. College, Pauri-Garhwal, India 2 Dept. of Electrical Engg., M. J. College
Steady State Modeling of Douly Fed Induction Generator Bhola Jha 1, Dr. K. R. M Rao 2 1 Dept. of Electrical Engg., G. B. Pant Engg. College, Pauri-Garhwal, India 2 Dept. of Electrical Engg., M. J. College
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Electric Machines
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric Machines Problem Set 10 Issued November 11, 2013 Due November 20, 2013 Problem 1: Permanent
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.685 Electric Machines Problem Set 10 Issued November 11, 2013 Due November 20, 2013 Problem 1: Permanent
Some aspects on hesitant fuzzy soft set
 Borah & Hazarika Cogent Mathematics (2016 3: 1223951 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Some aspects on hesitant fuzzy soft set Manash Jyoti Borah 1 and Bipan Hazarika 2 * Received:
Borah & Hazarika Cogent Mathematics (2016 3: 1223951 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Some aspects on hesitant fuzzy soft set Manash Jyoti Borah 1 and Bipan Hazarika 2 * Received:
Dynamic d-q Model of Induction Motor Using Simulink
 Dynamic d-q Model of Induction Motor Using Simulink Anand Bellure #1, Dr. M.S Aspalli #2, #1,2 Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department, Poojya Doddappa Appa College of Engineering, Gulbarga,
Dynamic d-q Model of Induction Motor Using Simulink Anand Bellure #1, Dr. M.S Aspalli #2, #1,2 Electrical and Electronics Engineering Department, Poojya Doddappa Appa College of Engineering, Gulbarga,
Modeling and simulation aspects of AC machines
 ARCHIVES OF ELECRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 65(), pp. 35-36 (06) DOI 0.55/aee-06-003 Modeling and simulation aspects of AC machines MICHAEL POPP, PARICK LAZA, WOLFGANG MAHIS Leibniz Universität Hannover Institute
ARCHIVES OF ELECRICAL ENGINEERING VOL. 65(), pp. 35-36 (06) DOI 0.55/aee-06-003 Modeling and simulation aspects of AC machines MICHAEL POPP, PARICK LAZA, WOLFGANG MAHIS Leibniz Universität Hannover Institute
Comparative Analysis of Speed Control of Induction Motor by DTC over Scalar Control Technique
 Comparative Analysis of Speed Control of Induction Motor by DTC over Scalar Control Technique S.Anuradha 1, N.Amarnadh Reddy 2 M.Tech (PE), Dept. of EEE, VNRVJIET, T.S, India 1 Assistant Professor, Dept.
Comparative Analysis of Speed Control of Induction Motor by DTC over Scalar Control Technique S.Anuradha 1, N.Amarnadh Reddy 2 M.Tech (PE), Dept. of EEE, VNRVJIET, T.S, India 1 Assistant Professor, Dept.
Research on Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Control System Simulation *
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com AASRI Procedia 3 (2012 ) 262 269 2012 AASRI Conference on Modeling, Identification and Control Research on Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Control System
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com AASRI Procedia 3 (2012 ) 262 269 2012 AASRI Conference on Modeling, Identification and Control Research on Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Control System
Derivation, f-derivation and generalized derivation of KUS-algebras
 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Derivation, -derivation and generalized derivation o KUS-algebras Chiranjibe Jana 1 *, Tapan Senapati 2 and Madhumangal Pal 1 Received: 08 February 2015 Accepted: 10 June
PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Derivation, -derivation and generalized derivation o KUS-algebras Chiranjibe Jana 1 *, Tapan Senapati 2 and Madhumangal Pal 1 Received: 08 February 2015 Accepted: 10 June
Position with Force Feedback Control of Manipulator Arm
 Position with Force Feedback Control of Manipulator Arm 1 B. K. Chitra, 2 J. Nandha Gopal, 3 Dr. K. Rajeswari PG Student, Department of EIE Assistant Professor, Professor, Department of EEE Abstract This
Position with Force Feedback Control of Manipulator Arm 1 B. K. Chitra, 2 J. Nandha Gopal, 3 Dr. K. Rajeswari PG Student, Department of EIE Assistant Professor, Professor, Department of EEE Abstract This
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development SIMULATION OF FIELD ORIENTED CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 4, April -2015 SIMULATION
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 4, April -2015 SIMULATION
Nonlinear Electrical FEA Simulation of 1MW High Power. Synchronous Generator System
 Nonlinear Electrical FEA Simulation of 1MW High Power Synchronous Generator System Jie Chen Jay G Vaidya Electrodynamics Associates, Inc. 409 Eastbridge Drive, Oviedo, FL 32765 Shaohua Lin Thomas Wu ABSTRACT
Nonlinear Electrical FEA Simulation of 1MW High Power Synchronous Generator System Jie Chen Jay G Vaidya Electrodynamics Associates, Inc. 409 Eastbridge Drive, Oviedo, FL 32765 Shaohua Lin Thomas Wu ABSTRACT
Mathematical Modelling of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Rotor Frame of Reference
 Mathematical Modelling of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Rotor Frame of Reference Mukesh C Chauhan 1, Hitesh R Khunt 2 1 P.G Student (Electrical),2 Electrical Department, AITS, rajkot 1 mcchauhan1@aits.edu.in
Mathematical Modelling of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Rotor Frame of Reference Mukesh C Chauhan 1, Hitesh R Khunt 2 1 P.G Student (Electrical),2 Electrical Department, AITS, rajkot 1 mcchauhan1@aits.edu.in
Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Simulation of Direct Torque Control of Induction motor using Space Vector Modulation Methodology
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Simulation of Direct Torque Control of Induction motor using Space Vector Modulation Methodology Arpit S. Bhugul 1, Dr. Archana
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Simulation of Direct Torque Control of Induction motor using Space Vector Modulation Methodology Arpit S. Bhugul 1, Dr. Archana
Non-linear unit root testing with arctangent trend: Simulation and applications in finance
 STATISTICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Non-linear unit root testing with arctangent trend: Simulation and applications in finance Deniz Ilalan 1 * and Özgür Özel 2 Received: 24 October 2017 Accepted: 18 March 2018
STATISTICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Non-linear unit root testing with arctangent trend: Simulation and applications in finance Deniz Ilalan 1 * and Özgür Özel 2 Received: 24 October 2017 Accepted: 18 March 2018
Internal Model Control Approach to PI Tunning in Vector Control of Induction Motor
 Internal Model Control Approach to PI Tunning in Vector Control of Induction Motor Vipul G. Pagrut, Ragini V. Meshram, Bharat N. Gupta, Pranao Walekar Department of Electrical Engineering Veermata Jijabai
Internal Model Control Approach to PI Tunning in Vector Control of Induction Motor Vipul G. Pagrut, Ragini V. Meshram, Bharat N. Gupta, Pranao Walekar Department of Electrical Engineering Veermata Jijabai
VECTOR CONTROL OF INDUCTION MOTOR WITH SPLIT PHASE STATOR WINDINGS. K T. Ranganathan E. E. Professor
 VECTOR CONTROL OF INDUCTION MOTOR WITH SPLIT PHASE STATOR WINDINGS K Gopakumar CEDT Research stadent K T. Ranganathan E. E Professor S. R. Bhat CEDT Professor ABSTRACT A vector controlled scheme is described
VECTOR CONTROL OF INDUCTION MOTOR WITH SPLIT PHASE STATOR WINDINGS K Gopakumar CEDT Research stadent K T. Ranganathan E. E Professor S. R. Bhat CEDT Professor ABSTRACT A vector controlled scheme is described
Synchronous Machines
 Synchronous machine 1. Construction Generator Exciter View of a twopole round rotor generator and exciter. A Stator with laminated iron core C Slots with phase winding B A B Rotor with dc winding B N S
Synchronous machine 1. Construction Generator Exciter View of a twopole round rotor generator and exciter. A Stator with laminated iron core C Slots with phase winding B A B Rotor with dc winding B N S
Digitization of Vector Control Algorithm Using FPGA
 Digitization of Vector Control Algorithm Using FPGA M. P. Priyadarshini[AP] 1, K. G. Dharani[AP] 2, D. Kavitha[AP] 3 DEPARTMENT OF ECE, MVJ COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, BANGALORE Abstract: The paper is concerned
Digitization of Vector Control Algorithm Using FPGA M. P. Priyadarshini[AP] 1, K. G. Dharani[AP] 2, D. Kavitha[AP] 3 DEPARTMENT OF ECE, MVJ COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, BANGALORE Abstract: The paper is concerned
Modelling, Simulation and Nonlinear Control of Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor
 ISSN: 2278-8875 Modelling, Simulation and Nonlinear Control of Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Dr.K.Alicemary 1, Mrs. B. Arundhati 2, Ms.Padma.Maridi 3 Professor and Principal, Vignan s Institute
ISSN: 2278-8875 Modelling, Simulation and Nonlinear Control of Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Dr.K.Alicemary 1, Mrs. B. Arundhati 2, Ms.Padma.Maridi 3 Professor and Principal, Vignan s Institute
EFFICIENCY OPTIMIZATION OF VECTOR-CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE
 EFFICIENCY OPTIMIZATION OF VECTOR-CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE Hussein Sarhan Department of Mechatronics Engineering, Faculty of Engineering Technology, Amman, Jordan ABSTRACT This paper presents a
EFFICIENCY OPTIMIZATION OF VECTOR-CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE Hussein Sarhan Department of Mechatronics Engineering, Faculty of Engineering Technology, Amman, Jordan ABSTRACT This paper presents a
Synchronous Machines
 Synchronous Machines Synchronous Machines n 1 Φ f n 1 Φ f I f I f I f damper (run-up) winding Stator: similar to induction (asynchronous) machine ( 3 phase windings that forms a rotational circular magnetic
Synchronous Machines Synchronous Machines n 1 Φ f n 1 Φ f I f I f I f damper (run-up) winding Stator: similar to induction (asynchronous) machine ( 3 phase windings that forms a rotational circular magnetic
SIMULATION OF STEADY-STATE PERFORMANCE OF THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR BY MATLAB
 olume No.0, Issue No. 08, August 014 ISSN (online): 48 7550 SIMULATION OF STEADY-STATE PERFORMANCE OF THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR BY MATLAB Harish Kumar Mishra 1, Dr.Anurag Tripathi 1 Research Scholar,
olume No.0, Issue No. 08, August 014 ISSN (online): 48 7550 SIMULATION OF STEADY-STATE PERFORMANCE OF THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR BY MATLAB Harish Kumar Mishra 1, Dr.Anurag Tripathi 1 Research Scholar,
A GENERALISED OPERATIONAL EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT OF INDUCTION MACHINES FOR TRANSIENT/DYNAMIC STUDIES UNDER DIFFERENT OPERATING CONDITIONS
 A GENERALISED OPERATIONAL EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT OF INDUCTION MACHINES FOR TRANSIENT/DYNAMIC STUDIES UNDER DIFFERENT OPERATING CONDITIONS S. S. Murthy Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute
A GENERALISED OPERATIONAL EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT OF INDUCTION MACHINES FOR TRANSIENT/DYNAMIC STUDIES UNDER DIFFERENT OPERATING CONDITIONS S. S. Murthy Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute
Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS/IASME Int. Conf. on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Tenerife, Spain, December 16-18,
 Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS/IASME Int. Conf. on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Tenerife, Spain, December 16-18, 2006 196 A Method for the Modeling and Analysis of Permanent
Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS/IASME Int. Conf. on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Tenerife, Spain, December 16-18, 2006 196 A Method for the Modeling and Analysis of Permanent
Analysis of Field Oriented Control Strategy for Induction Motor
 Kalpa Publications in Engineering Volume 1, 2017, Pages 214 219 ICRISET2017. International Conference on Research and Innovations in Science, Engineering &Technology. Selected Papers in Engineering Analysis
Kalpa Publications in Engineering Volume 1, 2017, Pages 214 219 ICRISET2017. International Conference on Research and Innovations in Science, Engineering &Technology. Selected Papers in Engineering Analysis
EE 742 Chapter 3: Power System in the Steady State. Y. Baghzouz
 EE 742 Chapter 3: Power System in the Steady State Y. Baghzouz Transmission Line Model Distributed Parameter Model: Terminal Voltage/Current Relations: Characteristic impedance: Propagation constant: π
EE 742 Chapter 3: Power System in the Steady State Y. Baghzouz Transmission Line Model Distributed Parameter Model: Terminal Voltage/Current Relations: Characteristic impedance: Propagation constant: π
Simulations and Control of Direct Driven Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator
 Simulations and Control of Direct Driven Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator Project Work Dmitry Svechkarenko Royal Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering Electrical Machines and
Simulations and Control of Direct Driven Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator Project Work Dmitry Svechkarenko Royal Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering Electrical Machines and
PARAMETER SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR
 HUNGARIAN JOURNAL OF INDUSTRIAL CHEMISTRY VESZPRÉM Vol. 39(1) pp. 157-161 (2011) PARAMETER SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR P. HATOS, A. FODOR, A. MAGYAR University of Pannonia, Department of
HUNGARIAN JOURNAL OF INDUSTRIAL CHEMISTRY VESZPRÉM Vol. 39(1) pp. 157-161 (2011) PARAMETER SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR P. HATOS, A. FODOR, A. MAGYAR University of Pannonia, Department of
Nonlinear dynamic simulation model of switched reluctance linear machine
 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 1 (2009) 1320 1324 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia The 6 th International Conference on Mining Science & Technology Nonlinear
Procedia Earth and Planetary Science 1 (2009) 1320 1324 Procedia Earth and Planetary Science www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia The 6 th International Conference on Mining Science & Technology Nonlinear
CHAPTER 2 CAPACITANCE REQUIREMENTS OF SIX-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 9 CHAPTER 2 CAPACITANCE REQUIREMENTS OF SIX-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 2.. INTRODUCTION Rapidly depleting rate of conventional energy sources, has led the scientists to explore the possibility
9 CHAPTER 2 CAPACITANCE REQUIREMENTS OF SIX-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 2.. INTRODUCTION Rapidly depleting rate of conventional energy sources, has led the scientists to explore the possibility
ISSN: (Online) Volume 2, Issue 2, February 2014 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies
 ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 2, Issue 2, February 2014 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Paper / Case Study Available online at:
ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 2, Issue 2, February 2014 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Paper / Case Study Available online at:
Dynamic Behavior of Three phase Inductions Motors as Loads in an Electric Power System with Distributed Generation, a Case of Study.
 Dynamic Behavior of Three phase Inductions Motors as Loads in an Electric Power System with Distributed Generation, a Case of Study. Marcelo Rodrigo García Saquicela, Ernesto Ruppert Filho, José Luis Azcue
Dynamic Behavior of Three phase Inductions Motors as Loads in an Electric Power System with Distributed Generation, a Case of Study. Marcelo Rodrigo García Saquicela, Ernesto Ruppert Filho, José Luis Azcue
Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines
 Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines ET 332b Ac Motors, Generators and Power Systems Lesson 17_et332b.pptx 1 Learning Objectives After this presentation you will be able to: Explain how synchronous machines
Lesson 17: Synchronous Machines ET 332b Ac Motors, Generators and Power Systems Lesson 17_et332b.pptx 1 Learning Objectives After this presentation you will be able to: Explain how synchronous machines
Comparison Between Direct and Indirect Field Oriented Control of Induction Motor
 Comparison Between Direct and Indirect Field Oriented Control of Induction Motor Venu Gopal B T Research Scholar, Department of Electrical Engineering UVCE, Bangalore University, Bengaluru ABSTRACT - Vector
Comparison Between Direct and Indirect Field Oriented Control of Induction Motor Venu Gopal B T Research Scholar, Department of Electrical Engineering UVCE, Bangalore University, Bengaluru ABSTRACT - Vector
Modelling and Simulating a Three-Phase Induction Motor
 MURDOCH UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Modelling and Simulating a Three-Phase Induction Motor ENG460 Engineering Thesis Benjamin Willoughby 3/3/2014 Executive Summary This
MURDOCH UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Modelling and Simulating a Three-Phase Induction Motor ENG460 Engineering Thesis Benjamin Willoughby 3/3/2014 Executive Summary This
Response surface designs using the generalized variance inflation factors
 STATISTICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Response surface designs using the generalized variance inflation factors Diarmuid O Driscoll and Donald E Ramirez 2 * Received: 22 December 204 Accepted: 5 May 205 Published:
STATISTICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Response surface designs using the generalized variance inflation factors Diarmuid O Driscoll and Donald E Ramirez 2 * Received: 22 December 204 Accepted: 5 May 205 Published:
Three phase induction motor using direct torque control by Matlab Simulink
 Three phase induction motor using direct torque control by Matlab Simulink Arun Kumar Yadav 1, Dr. Vinod Kumar Singh 2 1 Reaserch Scholor SVU Gajraula Amroha, U.P. 2 Assistant professor ABSTRACT Induction
Three phase induction motor using direct torque control by Matlab Simulink Arun Kumar Yadav 1, Dr. Vinod Kumar Singh 2 1 Reaserch Scholor SVU Gajraula Amroha, U.P. 2 Assistant professor ABSTRACT Induction
AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm
 7th WSEAS International Conference on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Venice, Italy, November 21-23, 27 86 AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm PETR BLAHA
7th WSEAS International Conference on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Venice, Italy, November 21-23, 27 86 AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm PETR BLAHA
A Direct Torque Controlled Induction Motor with Variable Hysteresis Band
 UKSim 2009: th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation A Direct Torque Controlled Induction Motor with Variable Hysteresis Band Kanungo Barada Mohanty Electrical Engineering Department,
UKSim 2009: th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation A Direct Torque Controlled Induction Motor with Variable Hysteresis Band Kanungo Barada Mohanty Electrical Engineering Department,
Dynamic Modeling of Surface Mounted Permanent Synchronous Motor for Servo motor application
 797 Dynamic Modeling of Surface Mounted Permanent Synchronous Motor for Servo motor application Ritu Tak 1, Sudhir Y Kumar 2, B.S.Rajpurohit 3 1,2 Electrical Engineering, Mody University of Science & Technology,
797 Dynamic Modeling of Surface Mounted Permanent Synchronous Motor for Servo motor application Ritu Tak 1, Sudhir Y Kumar 2, B.S.Rajpurohit 3 1,2 Electrical Engineering, Mody University of Science & Technology,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Technology 25 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Technology 25 (2016 ) 801 807 Global Colloquium in Recent Advancement and Effectual Researches in Engineering, Science and Technology (RAEREST
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Technology 25 (2016 ) 801 807 Global Colloquium in Recent Advancement and Effectual Researches in Engineering, Science and Technology (RAEREST
Sensorless Sliding Mode Control of Induction Motor Drives
 Sensorless Sliding Mode Control of Induction Motor Drives Kanungo Barada Mohanty Electrical Engineering Department, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela-7698, India E-mail: kbmohanty@nitrkl.ac.in
Sensorless Sliding Mode Control of Induction Motor Drives Kanungo Barada Mohanty Electrical Engineering Department, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela-7698, India E-mail: kbmohanty@nitrkl.ac.in
Simulation of 3-Phase 2- Stator Induction Motor Using MATLAB Platform
 International Journal of Alied Engineering Research ISSN 0973-456 Volume 3, Number (08). 9437-944 Simulation of 3-Phase - Stator Induction Motor Using MATLAB Platform Pallavi R.Burande Deartment of Electrical
International Journal of Alied Engineering Research ISSN 0973-456 Volume 3, Number (08). 9437-944 Simulation of 3-Phase - Stator Induction Motor Using MATLAB Platform Pallavi R.Burande Deartment of Electrical
Accurate Joule Loss Estimation for Rotating Machines: An Engineering Approach
 Accurate Joule Loss Estimation for Rotating Machines: An Engineering Approach Adeeb Ahmed Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC, USA aahmed4@ncsu.edu
Accurate Joule Loss Estimation for Rotating Machines: An Engineering Approach Adeeb Ahmed Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC, USA aahmed4@ncsu.edu
Robust Controller Design for Speed Control of an Indirect Field Oriented Induction Machine Drive
 Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies ISSN 1583-1078 Issue 6, January-June 2005 p. 1-16 Robust Controller Design for Speed Control of an Indirect Field Oriented Induction Machine Drive
Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies ISSN 1583-1078 Issue 6, January-June 2005 p. 1-16 Robust Controller Design for Speed Control of an Indirect Field Oriented Induction Machine Drive
DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR USING TWO LEVEL INVERTER- SURVEY PAPER
 DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR USING TWO LEVEL INVERTER- SURVEY PAPER 1 PREETI SINGH, BHUPAL SINGH 1 M.Tech (scholar) Electrical Power & Energy System, lecturer Ajay Kumar
DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR USING TWO LEVEL INVERTER- SURVEY PAPER 1 PREETI SINGH, BHUPAL SINGH 1 M.Tech (scholar) Electrical Power & Energy System, lecturer Ajay Kumar
Petrović s inequality on coordinates and related results
 Rehman et al., Cogent Mathematics 016, 3: 1798 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Petrović s inequality on coordinates related results Atiq Ur Rehman 1 *, Muhammad Mudessir 1, Hafiza Tahira Fazal Ghulam
Rehman et al., Cogent Mathematics 016, 3: 1798 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Petrović s inequality on coordinates related results Atiq Ur Rehman 1 *, Muhammad Mudessir 1, Hafiza Tahira Fazal Ghulam
Dynamics of the synchronous machine
 ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability Dynamics of the synchronous machine Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2018 1 / 38 Time constants and
ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability Dynamics of the synchronous machine Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct October 2018 1 / 38 Time constants and
Anakapalli Andhra Pradesh, India I. INTRODUCTION
 Robust MRAS Based Sensorless Rotor Speed Measurement of Induction Motor against Variations in Stator Resistance Using Combination of Back Emf and Reactive Power Methods Srikanth Mandarapu Pydah College
Robust MRAS Based Sensorless Rotor Speed Measurement of Induction Motor against Variations in Stator Resistance Using Combination of Back Emf and Reactive Power Methods Srikanth Mandarapu Pydah College
The Enlarged d-q Model of Induction Motor with the Iron Loss and Saturation Effect of Magnetizing and Leakage Inductance
 The Enlarged d-q Model of Induction Motor with the Iron Loss and Saturation Effect of Magnetizing and Leakage Inductance Jan Otýpka, Petr Orság, Vítězslav Stýskala, Dmitrii Kolosov, Stanislav Kocman and
The Enlarged d-q Model of Induction Motor with the Iron Loss and Saturation Effect of Magnetizing and Leakage Inductance Jan Otýpka, Petr Orság, Vítězslav Stýskala, Dmitrii Kolosov, Stanislav Kocman and
Implementation of Twelve-Sector based Direct Torque Control for Induction motor
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 4 ǁ April. 2013 ǁ PP.32-37 Implementation of Twelve-Sector based Direct Torque Control
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 4 ǁ April. 2013 ǁ PP.32-37 Implementation of Twelve-Sector based Direct Torque Control
Transient Stability Analysis of Single Machine Infinite Bus System by Numerical Methods
 International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Research ISSN 348-6988 (online) Vol., Issue 3, pp: (58-66), Month: July - September 04, Available at: www.researchpublish.com Transient Stability Analysis
International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Research ISSN 348-6988 (online) Vol., Issue 3, pp: (58-66), Month: July - September 04, Available at: www.researchpublish.com Transient Stability Analysis
Open Access Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Vector Control Based on Weighted Integral Gain of Sliding Mode Variable Structure
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscienceae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 5, 7, 33-33 33 Open Access Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Vector Control Based on Weighted Integral
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscienceae The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 5, 7, 33-33 33 Open Access Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Vector Control Based on Weighted Integral
The Application of Anti-windup PI Controller, SIPIC on FOC of PMSM
 Electrical and Electronic Engineering 2016, 6(3): 39-48 DOI: 10.5923/j.eee.20160603.01 The Application of Anti-windup PI Controller, SIPIC on FOC of PMSM Hoo Choon Lih School of Engineering, Taylor s University,
Electrical and Electronic Engineering 2016, 6(3): 39-48 DOI: 10.5923/j.eee.20160603.01 The Application of Anti-windup PI Controller, SIPIC on FOC of PMSM Hoo Choon Lih School of Engineering, Taylor s University,
Offline Parameter Identification of an Induction Machine Supplied by Impressed Stator Voltages
 POSTER 2016, PRAGUE MAY 24 1 Offline Parameter Identification of an Induction Machine Supplied by Impressed Stator Voltages Tomáš KOŠŤÁL Dept. of Electric Drives and Traction, Czech Technical University,
POSTER 2016, PRAGUE MAY 24 1 Offline Parameter Identification of an Induction Machine Supplied by Impressed Stator Voltages Tomáš KOŠŤÁL Dept. of Electric Drives and Traction, Czech Technical University,
Sensorless Control for High-Speed BLDC Motors With Low Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF
 Sensorless Control for High-Speed BLDC Motors With Low Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF P.Suganya Assistant Professor, Department of EEE, Bharathiyar Institute of Engineering for Women Salem (DT). Abstract
Sensorless Control for High-Speed BLDC Motors With Low Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF P.Suganya Assistant Professor, Department of EEE, Bharathiyar Institute of Engineering for Women Salem (DT). Abstract
Introduction to Synchronous. Machines. Kevin Gaughan
 Introduction to Synchronous Machines Kevin Gaughan The Synchronous Machine An AC machine (generator or motor) with a stator winding (usually 3 phase) generating a rotating magnetic field and a rotor carrying
Introduction to Synchronous Machines Kevin Gaughan The Synchronous Machine An AC machine (generator or motor) with a stator winding (usually 3 phase) generating a rotating magnetic field and a rotor carrying
Analytical Model for Sizing the Magnets of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines
 Journal of Electrical Engineering 3 (2015) 134-141 doi: 10.17265/2328-2223/2015.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Analytical Model for Sizing Magnets of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines George Todorov and
Journal of Electrical Engineering 3 (2015) 134-141 doi: 10.17265/2328-2223/2015.03.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Analytical Model for Sizing Magnets of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines George Todorov and
Computer Aided Power Control for Wound Rotor Induction Generator
 Ozean Journal of Applied Sciences 2(1), 2009 ISSN 1943-2429 2009 Ozean Publication Computer Aided Power Control for Wound Rotor Induction Generator Fevzi Kentli Department of Electrical Education - Faculty
Ozean Journal of Applied Sciences 2(1), 2009 ISSN 1943-2429 2009 Ozean Publication Computer Aided Power Control for Wound Rotor Induction Generator Fevzi Kentli Department of Electrical Education - Faculty
Chapter 4. Synchronous Generators. Basic Topology
 Basic Topology Chapter 4 ynchronous Generators In stator, a three-phase winding similar to the one described in chapter 4. ince the main voltage is induced in this winding, it is also called armature winding.
Basic Topology Chapter 4 ynchronous Generators In stator, a three-phase winding similar to the one described in chapter 4. ince the main voltage is induced in this winding, it is also called armature winding.
EXPERIMENTAL COMPARISON OF LAMINATION MATERIAL CASE OF SWITCHING FLUX SYNCHRONOUS MACHINE WITH HYBRID EXCITATION
 EXPERIMENTAL COMPARISON OF LAMINATION MATERIAL CASE OF SWITCHING FLUX SYNCHRONOUS MACHINE WITH HYBRID EXCITATION Emmanuel Hoang, Sami Hlioui, Michel Lécrivain, Mohamed Gabsi To cite this version: Emmanuel
EXPERIMENTAL COMPARISON OF LAMINATION MATERIAL CASE OF SWITCHING FLUX SYNCHRONOUS MACHINE WITH HYBRID EXCITATION Emmanuel Hoang, Sami Hlioui, Michel Lécrivain, Mohamed Gabsi To cite this version: Emmanuel
DTC Based Induction Motor Speed Control Using 10-Sector Methodology For Torque Ripple Reduction
 DTC Based Induction Motor Speed Control Using 10-Sector Methodology For Torque Ripple Reduction S. Pavithra, Dinesh Krishna. A. S & Shridharan. S Netaji Subhas Institute of Technology, Delhi University
DTC Based Induction Motor Speed Control Using 10-Sector Methodology For Torque Ripple Reduction S. Pavithra, Dinesh Krishna. A. S & Shridharan. S Netaji Subhas Institute of Technology, Delhi University
Equivalent Circuits with Multiple Damper Windings (e.g. Round rotor Machines)
 Equivalent Circuits with Multiple Damper Windings (e.g. Round rotor Machines) d axis: L fd L F - M R fd F L 1d L D - M R 1d D R fd R F e fd e F R 1d R D Subscript Notations: ( ) fd ~ field winding quantities
Equivalent Circuits with Multiple Damper Windings (e.g. Round rotor Machines) d axis: L fd L F - M R fd F L 1d L D - M R 1d D R fd R F e fd e F R 1d R D Subscript Notations: ( ) fd ~ field winding quantities
Speed Control of Induction Motor Drives using Nonlinear Adaptive Controller
 Speed Control of Induction Motor Drives using Nonlinear Adaptive Controller 1 Sarojini.P, 2 Mr. R Issan Raj M.E Control and Instrumentation Engineering Valliammai Engineering College Kancheepuram District
Speed Control of Induction Motor Drives using Nonlinear Adaptive Controller 1 Sarojini.P, 2 Mr. R Issan Raj M.E Control and Instrumentation Engineering Valliammai Engineering College Kancheepuram District
Modeling and Simulation of Flux-Optimized Induction Motor Drive
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 2(6): 603-613, 2010 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2010 Submitted Date: July 21, 2010 Accepted Date: August 20, 2010 Published
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 2(6): 603-613, 2010 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2010 Submitted Date: July 21, 2010 Accepted Date: August 20, 2010 Published
PRINCIPLE OF DESIGN OF FOUR PHASE LOW POWER SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MACHINE AIMED TO THE MAXIMUM TORQUE PRODUCTION
 Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 55, NO. 5-6, 24, 138 143 PRINCIPLE OF DESIGN OF FOUR PHASE LOW POWER SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MACHINE AIMED TO THE MAXIMUM TORQUE PRODUCTION Martin Lipták This paper
Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 55, NO. 5-6, 24, 138 143 PRINCIPLE OF DESIGN OF FOUR PHASE LOW POWER SWITCHED RELUCTANCE MACHINE AIMED TO THE MAXIMUM TORQUE PRODUCTION Martin Lipták This paper
AXIAL FLUX INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR WITH SINUSOIDALLY SHAPED MAGNETS
 AXIAL FLUX INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR WITH SINUSOIDALLY SHAPED MAGNETS A. Parviainen, J. Pyrhönen, M. Niemelä Lappeenranta University of Technology, Department of Electrical Engineering
AXIAL FLUX INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR WITH SINUSOIDALLY SHAPED MAGNETS A. Parviainen, J. Pyrhönen, M. Niemelä Lappeenranta University of Technology, Department of Electrical Engineering
Design and Characteristic Analysis of LSM for High Speed Train System using Magnetic Equivalent Circuit
 IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 3, No. 1 / March 2010, pp. 14-18 The Korean Society for Railway Design and Characteristic Analysis of LSM for High Speed Train System using Magnetic Equivalent
IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 3, No. 1 / March 2010, pp. 14-18 The Korean Society for Railway Design and Characteristic Analysis of LSM for High Speed Train System using Magnetic Equivalent
Loss analysis of a 1 MW class HTS synchronous motor
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Loss analysis of a 1 MW class HTS synchronous motor To cite this article: S K Baik et al 2009 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 153 012003 View the article online for updates and
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Loss analysis of a 1 MW class HTS synchronous motor To cite this article: S K Baik et al 2009 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 153 012003 View the article online for updates and
CHAPTER 2 MODELLING OF INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
 21 CHAPTER 2 MODELLING OF INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR 2.1 INTRODUCTION The need for adjustable speed drives in industrial applications has been increasing progressively. The variable speed
21 CHAPTER 2 MODELLING OF INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR 2.1 INTRODUCTION The need for adjustable speed drives in industrial applications has been increasing progressively. The variable speed
