Response surface designs using the generalized variance inflation factors
|
|
|
- Lily Leonard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STATISTICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Response surface designs using the generalized variance inflation factors Diarmuid O Driscoll and Donald E Ramirez 2 * Received: 22 December 204 Accepted: 5 May 205 Published: 4 June 205 *Corresponding author: Donald E Ramirez, Department of Mathematics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA 22904, USA der@virginiaedu Reviewing editor: Guohua Zou, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Additional information is available at the end of the article Abstract: We study response surface designs using the generalized variance inflation factors for subsets as an extension of the variance inflation factors Subjects: Mathematics & Statistics; Science; Statistical Computing; Statistical Theory & Methods; Statistics; Statistics & Probability Keywords: variance inflation factors; generalized variance inflation factors; response surface designs Introduction We consider a linear regression Y β + ε with a full rank n p matrix and (ε) N(0, σ 2 I n ) The variance inflation factor VIF, Belsley (986), measures the penalty for adding one non-orthogonal additional explanatory variable to a linear regression model, and they can be computed as a ratio of determinants The extension of VIF to a measure of the penalty for adding a subset of variables to a model is the generalized variance inflation factor GVIF of Fox and Monette (992), which will be used to study response surface designs, in particular, as the penalty for adding the quadratic terms to the model 2 Variance inflation factors For our linear model Y β + ε, let D be the diagonal matrix with entries on the diagonal D [i, i ( ) 2 When the design has been standardized D i,i, the VIFs are the diagonal entries of the inverse of S D ( )D That is, the VIFs are the ratios of the actual variances for ABOUT THE AUTHORS Diarmuid O Driscoll is the head of the Mathematics and Computer Studies Department at Mary Immaculate College, Limerick He was awarded a Travelling Studentship for his MSc at University College Cork in 977 He has taught at University College Cork, Cork Institute of Technology, University of Virginia, and Frostburg State University His research interests are in mathematical education, errors in variables regression, and design criteria In 204, he was awarded a Teaching Heroes Award by the National Forum for the Enhancement of Teaching and Learning (Ireland) Donald E Ramirez is a full professor in the Department of Mathematics at the University of Virginia in Charlottesville, Virginia He received his PhD in Mathematics from Tulane University in New Orleans, Louisiana His research is in harmonic analysis and mathematical statistics His current research interests are in statistical outliers and ridge regression PUBLIC INTEREST STATEMENT Response surface designs are a mainstay in applied statistics The variance inflation factors VIF are a measure of collinearity for a single variable in a linear regression model The generalization to subsets of variables is the generalized variance inflation factor GVIF This research introduces GVIF as a penalty measure for extending a linear response model to a response surface with the included quadratic terms The methodology is demonstrated with case studies, and, in particular, it is shown that using GVIF, the H30 design can be improved for the standard global optimality criteria of A, D, and E 205 The Author(s) This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 40 license Page of
2 the explanatory variables to the ideal variances had the columns of been orthogonal Note that we follow Stewart (987) and do not necessarily center the explanatory variables For our linear model Y β + ε, view [ [p, x p with x p the p th column of and [p the matrix formed by the remaining columns The variance inflation factor VIF p measures the effect of adding column x p to [p For notational convenience, we demonstrate VIF p with the last column p An ideal column would be orthogonal to the previous columns with the entries in the off-diagonal elements of the p th row and p th column of all zeros Denote by M p the idealized moment matrix [ [p M p [p 0 p 0 p x x p p The VIFs are the diagonal entries of S D ( ) D It remains to note that the inverse, S, can be computed using cofactors C i,j In particular, VIF p [S p,p [D ( ) D p,p (x p x p ) 2 det(c p,p ) det( ) (x p x p ) 2 det(m p ) det( ) the ratio of the determinant of the idealized moment matrix M p to the determinant of the moment matrix This definition extends naturally to subsets and is discussed in the next section For an alternate view of the how collinearities in the explanatory variables inflate the model variances of the regression coefficients when compared to a fictitious orthogonal reference design, consider the formula for the model variance Var M ( β j ) where R 2 j is the square of the multiple correlation from the regression of the jth column of [x ij on the remaining columns as in Liao and Valliant (202) The first term σ 2 (x ij x j ) 2 is the model variance for β j had the j th explanatory variable been orthogonal to the remaining variables The second term ( R 2 j ) is a standard definition of the jth VIF as in Thiel (97) 3 Generalized variance inflation factors In this section, we introduce the GVIFs as an extension of the classical variance inflation factors VIF from Equation For the linear model Y β + ε, view [, 2 partitioned with of dimension n r usually consisting of the lower order terms and 2 of dimension n s usually consisting of the higher order terms The idealized moment matrix for the (r, s) partitioning of is M (r,s) σ 2 n i (x ij x j )2 R 2 j [ 0 r s 0 s r 2 2 () Following Equation, to measure the effect of adding 2 to the design, that is for 2, we define the generalized variance inflation factor as GVIF( 2 ) det(m (r,s) ) det( ) det( ) det( 2 2 ) det( ) as in Equation 0 of Fox and Monette (992), who compared the sizes of the joint confidence regions for β for partitioned designs and noted when [ [p, x p that GVIF[x p [p VIF p Equation 2 is in the spirit of the efficiency comparisons in linear inferences introduced in Theorems 4 and 5 of Jensen and Ramirez (993) A similar measure of collinearity is mentioned in Note 2 in Wichers (975), (2) Page 2 of
3 Theorem of Berk (977), and Garcia, Garcia, and Soto (20) For the simple linear regression model with p 2, Equation 2 gives VIF ρ 2 with ρ the correlation coefficient as required Fox and Monette (992) suggested that contains the variables which are of simultaneous interest, while 2 contains additional variables selected by the investigator We will set for the constant and main effects and set 2 the (optional) quadratic terms with values from Willan and Watts (978) measured the effect of collinearity using the ratio of the volume of the actual joint confidence region for β to the volume of the joint confidence region in the fictitious orthogonal reference design Their ratio is in the spirit of GVIF as det( ) is inversely proportional to the square of the volume of the joint confidence region for β They also introduced a measure of relative predictability and they note: The existence of near linear relations in the independent variables of the actual data reduces the overall predictive efficiency by this factor For a simple case study, consider the simple linear regression model with n 4, x [ 2,,, 2, and y [4,,, 4 The 95% prediction interval for x 0 is 25 ± 020 If the model also includes [ 200, 00, 00, 200, then the 95% prediction interval for (x, )(0, 0) is 25 ± 4602 demonstrating the loss of predictive efficiency due to the collinearity introduced by For the (r, s) partition of [, 2 with of dimension n r and 2 of dimension n s, set [ ( D (r,s) 2 ) 0 ( 0 ) 2, 2 2 and denote the canonical moment matrix as R D (r,s) ( )D (r,s) [ ( I r r ) 2 ( ) ( ) 2 ( ) ( ) ( 2 ) 2 ; I s s with determinant det(r) equivalently, det( ) det( ) det( 2 2 ) GVIF( 2 ) ; det(r) det(i r r B r s B s r )det(i s s B s r B r s ) where B r s ( ) 2 ( ) ( ) (3) In the case {r p, s }, 2 x p is a n vector and the partitioned design [, x p has det(r) [x ( p ) ) x p (x x p p From standard facts for the inverse of a partitioned matrix, for example, Myers (990, p 459), VIF p [R p,p [D (p,) ( ) D (p,) p,p can be computed directly as ( ) 2 ( ) 2 x x p p ( ) p,p x x x x p p p p x x p p x ( p ) x p [x ( p ) ) x p (x x p p det(r) GVIF( ) 2 Page 3 of
4 We study the eigenvalue structure ( of M (r,s) in Appendix Let {λ λ 2 λ min(r,s) 0} be the non-negative singular values of ) 2 ( ) ( ) It is shown in Appendix that an alternative formulation for GVIF is GVIF( 2 ) ( λ 2 i ) min(r,s) i (4) 4 Quadratic model with p 3 For the partitioning [ r s, the canonical moment matrix, Equation 3, has the identity matrices I r, I ( s down the diagonal and off-diagonal array ) 2 ( ) For the quadratic model y β 0 + β x + β 2 and partitioning [, x, we have R 0 ρ 0 ρ 2 ρ ρ 2 From Equation 4, GVIF(, x) ( λ 2 ) where λ value of [ρ, ρ 2 Denote γ 2 ρ2 + ρ2 2 ρ 2 + ρ2 2 is the unique positive singular as the canonical index with GVIF(, x) Surprisingly, many higher order designs γ 2 det(r) also have the off-diagonal entry of the canonical moment matrix with a unique positive singular value with GVIF( 2 ) with the collinearity between the lower order terms and the upper γ 2 order terms as a function of the canonical index γ 2 5 Central composite and factorial designs for quadratic models (p 6) In this section, we compare the central composite design (CCD) of Box and Wilson (95) and the factorial design Z The design points are shown in Table B of Appendi Both designs are 9 6 and use the quadratic response model y β 0 + β x + β 2 + β + β 22 x2 + β x x + ε The CCD traditionally uses the value a 2 in four entries, while the factorial design uses the value a To study the difference in the designs with these different values, we computed the GVIF to compare the orthogonality between the lower order terms of dimension 9 3 and the higher order quadratic terms 2 of dimension 9 3 The off-diagonal B 3 3 entry of R from Equation 3 in Section 3 has the form B 3 3 ρ ρ Table CCD with parameter a, canonical index γ 2, and GVIF a GVIF( 2 ) γ Page 4 of
5 2+a 2 with ρ ρ a 4, canonical index γ2 ρ2 + ρ2 2 and GVIF( ) 2 as in the quadratic γ 2 model case with p 3 shown in the Section 4 For Table, if a, then ρ ρ 2 2 0, γ 2 8 0, and GVIF( 2 )5 Surprisingly, the classical choice of a 2 gives the largest value for GVIF( 2 ), that is the worst value, indicating the greatest collinearity between the lower and higher order terms, as noted in O Driscoll and Ramirez (in press) 6 Larger designs (p 0) We consider the quadratic response surface designs for y β 0 + β x + β 2 + β 3 + β + β 22 x2 2 + β 33 x2 3 + β 2 x + β 3 x + β 23 + ε with n responses and with partitioned into [ 2 with the four lower order terms (r 4) and 2 the six quadratic terms (s 6) Four popular designs are given in Appendi They are the hybrid designs (H30 and H3B) of Roquemore (976) Tables B2 and B3, the Box and Behnken (960) (BBD) design Table B4, and the CCD of Box and Wilson (95) Table B5 For each design, we compute the 0 0 canonical moment matrix It is striking that, for all these designs, the off-diagonal 4 6 array in R has only one non-zero singular value with its square the canonical index γ 2 It follows that GVIF( ) 2 γ 2 Table 2 reports that the design H30 is the most conditioned with respect to the GVIF with the least amount of collinearity between the lower and higher order terms 7 More complicated designs with ordered singular values Let be the minimal design of Box and Draper (974) BDD with n from Table B6, and let Z be the small composite design of Hartley (959) SCD with n from Table B7 for the quadratic response surface model (r 4 and s 6) as in Equation (5) Let α {α α r 0} and β {β β r 0} be the non-negative singular values of the off-diagonal array for R and R Z, respectively As α i β i ( i r) (Table 3), it follows that GVIF( 2 ) GVIF(Z 2 Z ) showing less collinearity between the lower and higher order terms for the BDD design Table 2 Hybrid designs H30, H3B, Box and Behnken BBD, and CCD Design n r γ 2 GVIF( 2 ) H H3B BBD CCD (5) Table 3 Singular values for off-diagonal array of R for BDD and SCD with GVIF BDD SCD α β GVIF Page 5 of
6 8 An improved H30 design When the diagonal matrix Λ r s in Equation 6 in Appendix has only one non-zero entry, we have denoted the square of this value the canonical index We extend this definition to the case when ( ) 2 ( ) ( ) has multiple positive singular values The Frobenious norm for a rectangular matrix A r s is defined by A 2 r s F i j a2 ij trace(a A) For a design matrix, we extend the definition of the canonical index with γ 2 Λ r s 2 F Alternatively, γ 2 trace(( ) 2 2 ( ) ( 2 ) ( 2 )) as in Equation 7 We examine, in detail, the H30 design matrix 0, Table B2 in Appendi, with our attention to the value of 0360 in row 2 for In succession, we will replace the values {736, 06386, 09273, 0000, 2906, 0360} by a free parameter and use γ 2 to determine an optimal value For example, replacing the four entries which are 736 with c, we calculate the minimum value for γ with c 768 denoted c min in Table 4 These values are within the four digit accuracy of the data We performed a similar calculation with c 2 using the four entries which are 06386; with c 3 with the four entries which are 09273; with c 4 with the eight entries which are ; and with c 5 with the single entry 2906 The original design has γ The entries in the H30 design are given to four significant digits With this precision, the original design is nearly optimal with respect to the canonical index γ 2 for the first five entries in Table 4 The sixth entry of c was not optimal with γ with c min 00264, a magnitude value smaller Denote the improved H30 design as the H30 design with the value of c The improved H30 also has a unique positive singular value for the off-diagonal of R with its square the canonical index γ 2 All of the standard design criteria favor the improved H30 design over the H30 design, which was originally constructed based on the rotatability criterion to maintain equal variances for predicted responses for points that have the same distance from the design center As usual A() tr(( ) ), D() det(( ) ), and E() max{eigenvalues of ( ) } The small relative changes Δ in the design criteria are shown in Table 5 in Column 4 The abnormality of the second row in H30 has been noted in Jensen (998) who showed that the design is least sensitive to the second row of, the row containing the value c Table 4 Optimal values c min for γ 2 Design entries c min γ 2 c c c c c c Table 5 Design criteria for the improved H30 with Δ the relative change c c Δ A % D % E % γ % Page 6 of
7 9 Conclusions The VIF measure the penalty for adding a non-orthogonal variable to a linear regression The VIF can be computed as a ratio of determinant as in Equation A similar ratio criterion was studied by Fox and Monette (992) to measure the effect of adding a subset of new variables to a design and they dubbed it the generalized variance inflation factor GVIF, Equation 2 We have noted the relationship between GVIF and the singular values of the off-diagonal array in the canonical moment matrix and have used GFIV to study standard quadratic response designs The H30 design of Roquemorer (976) was shown not to be optimal with respect to GFIV and an improved H30 design was introduced which was favored over H30 using the standard design criteria A, D, and E Funding The authors received no direct funding for this research Author details Diarmuid O Driscoll diarmuidodriscoll@miculie Donald E Ramirez 2 der@virginiaedu Department of Mathematics and Computer Studies, Mary Immaculate College, Limerick, Ireland 2 Department of Mathematics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, 22904, USA Citation information Cite this article as: Response surface designs using the generalized variance inflation factors, Diarmuid O Driscoll & Donald E Ramirez, Cogent Mathematics (205), 2: References Belsley, D A (986) Centering, the constant, firstdifferencing, and assessing conditioning In E Kuh & D A Belsley (Eds), Model reliability (pp 7 53) Cambridge: MIT Press Berk, K (977) Tolerance and condition in regression computations Journal of the American Statistical Association, 72, Box, G E P, & Behnken, D W (960) Some new threelevel designs for the study of quantitative variables Technometrics, 2, Box, M J, & Draper, N R (974) On minimum-point second order design Technometrics, 6, Appendix Box, G E P, & Wilson, K B (95) On the experimental attainment of optimum conditions Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 3, 45 Eaton, M L (983) Multivariate statistics New York, NY: Wiley Fox, J, & Monette, G (992) Generalized collinearity diagnostics Journal of the American Statistical Association, 87, Garcia, C B, Garcia, J, & Soto, J (20) The raise method: An alternative procedure to estimate the parameters in presence of collinearity Quality and Quantity, 45, Hartley, H O (959) Smallest composite design for quadratic response surfaces Biometrics, 5, Jensen, D R (998) Principal predictors and efficiency in small second-order designs Biometrical Journal, 40, Jensen, D R, & Ramirez, D E (993) Efficiency comparisons in linear inference Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 37, 5 68 Liao, D, & Valliant, R (202) Variance inflation in the analysis of complex survey data Survey Methodology, 38, Myers, R (990) Classical and modern regression with applications (2nd ed) Boston, MA: PWS-Kent O Driscoll, D, & Ramirez, D E (in press) Revisiting some design criteria (under review) Roquemorer, K G (976) Hybrid designs for quadratic response surfaces Technometrics, 8, Stewart, G W (987) Collinearity and least squares regression Statistical Science, 2, Thiel, H (97) Principles of econometrics New York, NY: Wiley Wichers, R (975) The detection of multicollinearity: A comment Review of Economics and Statistics, 57, Willan, A R, & Watts, D G (978) Meaningful multicollinearity measures Technometrics, 20, We study the eigenvalue ( structure of M (r,s) Let {λ λ 2 λ min(r,s) 0} be the non-negative singular values of ) 2 ( ) ( ) As with the canonical correlation coefficients Eaton (983), write the off-diagonal rectangular array B r s of R as PΛQ with P and Q orthogonal matrices and Λ r s the rectangular diagonal matrix with the non-negative singular values down the diagonal Set [ Pr r 0 L r s 0 s r Q s s For notational convenience, we assume r s The matrix L is orthogonal and transforms R L RL into diagonal matrices: [ I r Λ s r Λ r s I s [ I r [SV r r 0 r (s r) [SV r r 0 r (s r) I s (A) Page 7 of
8 with Λ r s [SV r r 0 r (s r) where SV r r is the diagonal matrix of the non-negative singular values Since L is orthogonal, this transformation has not changed the eigenvalues To compute the determinant of R, convert the matrix in Equation 6 into an upper diagonal matrix by Gauss Elimination on Λ s r This changes r of the s on the diagonal in rows r + to r + r into λ 2 i, and thus det(r) min(r,s) ( λ 2 ) i i with GVIF( 2 ) min(r,s) i λ 2 i The singular values of R 2 ( ) 2 ( ) ( ) are the non-negative square roots of the eigenvalues of Λ Λ denoted by eigvals(λ Λ)eigvals((Q R 2 P)(P R 2 Q))) eigvals( ( ) )( ) ( 2 ) 2 2 ( )) 2 If the trace of the inverse of the matrix in Equation 6 is required, then we note that [ I r Λ s r Λ r s I s with trace given by tr((l RL) ) r s + 2 min(r,s) i Appendi [ (I r Λ r s Λ s r ) Λ r s (I s Λ Λ s r r s ) Λ (I Λ s r r r s Λ s r ) (I s Λ Λ s r r s ) Table B The lower order matrix for the CCD with center run with a 2, n 9 and the lower order matrix for the factorial design with center run n 9 Central composite design Factorial design x x a 0 0 a a 0 0 a λ 2 i (A2) Page 8 of
9 Table B2 The lower order matrix for the hybrid (H30) design of Roquemore (976) with center run, n x Table B3 The lower order matrix for the hybrid (H3B) design of Roquemore (976) with center run, n x Table B4 The lower order matrix for the Box and Behnken (960) design (BBD) with center run, n 3 x Page 9 of
10 Table B5 The lower order matrix for the Box and Wilson (95) CCD for α 732 with center run, n 5 x Table B6 The lower order matrix for the Box and Draper (974) minimal design (BDD) with center run, n x Table B7 The Lower order matrix for the small composite design of Hartley (959) (SCD) for α 732 with center run, n x Page 0 of
11 205 The Author(s) This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 40 license You are free to: Share copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format Adapt remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms Under the following terms: Attribution You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use No additional restrictions You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits Cogent Mathematics (ISSN: ) is published by Cogent OA, part of Taylor & Francis Group Publishing with Cogent OA ensures: Immediate, universal access to your article on publication High visibility and discoverability via the Cogent OA website as well as Taylor & Francis Online Download and citation statistics for your article Rapid online publication Input from, and dialog with, expert editors and editorial boards Retention of full copyright of your article Guaranteed legacy preservation of your article Discounts and waivers for authors in developing regions Submit your manuscript to a Cogent OA journal at wwwcogentoacom Page of
Mitigating collinearity in linear regression models using ridge, surrogate and raised estimators
 STATISTICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Mitigating collinearity in linear regression models using ridge, surrogate and raised estimators Diarmuid O Driscoll 1 and Donald E. Ramirez 2 * Received: 21 October 2015 Accepted:
STATISTICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Mitigating collinearity in linear regression models using ridge, surrogate and raised estimators Diarmuid O Driscoll 1 and Donald E. Ramirez 2 * Received: 21 October 2015 Accepted:
A note on the unique solution of linear complementarity problem
 COMPUTATIONAL SCIENCE SHORT COMMUNICATION A note on the unique solution of linear complementarity problem Cui-Xia Li 1 and Shi-Liang Wu 1 * Received: 13 June 2016 Accepted: 14 November 2016 First Published:
COMPUTATIONAL SCIENCE SHORT COMMUNICATION A note on the unique solution of linear complementarity problem Cui-Xia Li 1 and Shi-Liang Wu 1 * Received: 13 June 2016 Accepted: 14 November 2016 First Published:
Revisting Some Design Criteria
 Revisting Some Design Criteria Diarmuid O Driscoll diarmuid.odriscoll@mic.ul.ie Head, Department of Mathematics and Computer Studies Mary Immaculate College, Ireland Donald E. Ramirez der@virginia.edu
Revisting Some Design Criteria Diarmuid O Driscoll diarmuid.odriscoll@mic.ul.ie Head, Department of Mathematics and Computer Studies Mary Immaculate College, Ireland Donald E. Ramirez der@virginia.edu
The plastic number and its generalized polynomial
 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE The plastic number and its generalized polynomial Vasileios Iliopoulos 1 * Received: 18 December 2014 Accepted: 19 February 201 Published: 20 March 201 *Corresponding
PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE The plastic number and its generalized polynomial Vasileios Iliopoulos 1 * Received: 18 December 2014 Accepted: 19 February 201 Published: 20 March 201 *Corresponding
Matrix l-algebras over l-fields
 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Matrix l-algebras over l-fields Jingjing M * Received: 05 January 2015 Accepted: 11 May 2015 Published: 15 June 2015 *Corresponding author: Jingjing Ma, Department of
PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Matrix l-algebras over l-fields Jingjing M * Received: 05 January 2015 Accepted: 11 May 2015 Published: 15 June 2015 *Corresponding author: Jingjing Ma, Department of
On a mixed interpolation with integral conditions at arbitrary nodes
 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE On a mixed interpolation with integral conditions at arbitrary nodes Srinivasarao Thota * and Shiv Datt Kumar Received: 9 October 5 Accepted: February 6 First Published:
PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE On a mixed interpolation with integral conditions at arbitrary nodes Srinivasarao Thota * and Shiv Datt Kumar Received: 9 October 5 Accepted: February 6 First Published:
Finding the strong defining hyperplanes of production possibility set with constant returns to scale using the linear independent vectors
 Rafati-Maleki et al., Cogent Mathematics & Statistics (28), 5: 447222 https://doi.org/.8/233835.28.447222 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Finding the strong defining hyperplanes
Rafati-Maleki et al., Cogent Mathematics & Statistics (28), 5: 447222 https://doi.org/.8/233835.28.447222 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Finding the strong defining hyperplanes
Some aspects on hesitant fuzzy soft set
 Borah & Hazarika Cogent Mathematics (2016 3: 1223951 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Some aspects on hesitant fuzzy soft set Manash Jyoti Borah 1 and Bipan Hazarika 2 * Received:
Borah & Hazarika Cogent Mathematics (2016 3: 1223951 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Some aspects on hesitant fuzzy soft set Manash Jyoti Borah 1 and Bipan Hazarika 2 * Received:
Graded fuzzy topological spaces
 Ibedou, Cogent Mathematics (06), : 8574 http://dxdoiorg/0080/85068574 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Graded fuzzy topological spaces Ismail Ibedou, * Received: August 05 Accepted: 0 January 06 First
Ibedou, Cogent Mathematics (06), : 8574 http://dxdoiorg/0080/85068574 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Graded fuzzy topological spaces Ismail Ibedou, * Received: August 05 Accepted: 0 January 06 First
Derivation, f-derivation and generalized derivation of KUS-algebras
 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Derivation, -derivation and generalized derivation o KUS-algebras Chiranjibe Jana 1 *, Tapan Senapati 2 and Madhumangal Pal 1 Received: 08 February 2015 Accepted: 10 June
PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Derivation, -derivation and generalized derivation o KUS-algebras Chiranjibe Jana 1 *, Tapan Senapati 2 and Madhumangal Pal 1 Received: 08 February 2015 Accepted: 10 June
Petrović s inequality on coordinates and related results
 Rehman et al., Cogent Mathematics 016, 3: 1798 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Petrović s inequality on coordinates related results Atiq Ur Rehman 1 *, Muhammad Mudessir 1, Hafiza Tahira Fazal Ghulam
Rehman et al., Cogent Mathematics 016, 3: 1798 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Petrović s inequality on coordinates related results Atiq Ur Rehman 1 *, Muhammad Mudessir 1, Hafiza Tahira Fazal Ghulam
Draft of an article prepared for the Encyclopedia of Social Science Research Methods, Sage Publications. Copyright by John Fox 2002
 Draft of an article prepared for the Encyclopedia of Social Science Research Methods, Sage Publications. Copyright by John Fox 00 Please do not quote without permission Variance Inflation Factors. Variance
Draft of an article prepared for the Encyclopedia of Social Science Research Methods, Sage Publications. Copyright by John Fox 00 Please do not quote without permission Variance Inflation Factors. Variance
Non-linear unit root testing with arctangent trend: Simulation and applications in finance
 STATISTICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Non-linear unit root testing with arctangent trend: Simulation and applications in finance Deniz Ilalan 1 * and Özgür Özel 2 Received: 24 October 2017 Accepted: 18 March 2018
STATISTICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Non-linear unit root testing with arctangent trend: Simulation and applications in finance Deniz Ilalan 1 * and Özgür Özel 2 Received: 24 October 2017 Accepted: 18 March 2018
Multicollinearity and A Ridge Parameter Estimation Approach
 Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods Volume 15 Issue Article 5 11-1-016 Multicollinearity and A Ridge Parameter Estimation Approach Ghadban Khalaf King Khalid University, albadran50@yahoo.com
Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods Volume 15 Issue Article 5 11-1-016 Multicollinearity and A Ridge Parameter Estimation Approach Ghadban Khalaf King Khalid University, albadran50@yahoo.com
A detection for patent infringement suit via nanotopology induced by graph
 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE A detection for patent infringement suit via nanotopology induced by graph M. Lellis Thivagar 1 *, Paul Manuel 2 and. Sutha Devi 1 Received: 08 October 2015 Accepted:
PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE A detection for patent infringement suit via nanotopology induced by graph M. Lellis Thivagar 1 *, Paul Manuel 2 and. Sutha Devi 1 Received: 08 October 2015 Accepted:
Existence and uniqueness of a stationary and ergodic solution to stochastic recurrence equations via Matkowski s FPT
 Arvanitis, Cogent Mathematics 2017), 4: 1380392 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Existence and uniqueness of a stationary and ergodic solution to stochastic recurrence equations
Arvanitis, Cogent Mathematics 2017), 4: 1380392 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Existence and uniqueness of a stationary and ergodic solution to stochastic recurrence equations
Response Surface Methodology
 Response Surface Methodology Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments Second Edition RAYMOND H. MYERS Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University DOUGLAS C. MONTGOMERY Arizona
Response Surface Methodology Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments Second Edition RAYMOND H. MYERS Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University DOUGLAS C. MONTGOMERY Arizona
Wiley. Methods and Applications of Linear Models. Regression and the Analysis. of Variance. Third Edition. Ishpeming, Michigan RONALD R.
 Methods and Applications of Linear Models Regression and the Analysis of Variance Third Edition RONALD R. HOCKING PenHock Statistical Consultants Ishpeming, Michigan Wiley Contents Preface to the Third
Methods and Applications of Linear Models Regression and the Analysis of Variance Third Edition RONALD R. HOCKING PenHock Statistical Consultants Ishpeming, Michigan Wiley Contents Preface to the Third
Useful Numerical Statistics of Some Response Surface Methodology Designs
 Journal of Mathematics Research; Vol. 8, No. 4; August 20 ISSN 19-9795 E-ISSN 19-9809 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Useful Numerical Statistics of Some Response Surface Methodology
Journal of Mathematics Research; Vol. 8, No. 4; August 20 ISSN 19-9795 E-ISSN 19-9809 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Useful Numerical Statistics of Some Response Surface Methodology
ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING RESEARCH ARTICLE
 Received: 21 June 2018 Accepted: 04 December 2018 First Published: 18 December 2018 *Corresponding author: Shantanu Sarkar, Machinery, L&T Technology Services, Houston, TX, USA E-mail: Shantanu75@gmail.com
Received: 21 June 2018 Accepted: 04 December 2018 First Published: 18 December 2018 *Corresponding author: Shantanu Sarkar, Machinery, L&T Technology Services, Houston, TX, USA E-mail: Shantanu75@gmail.com
Efficient Choice of Biasing Constant. for Ridge Regression
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 3, 008, no., 57-536 Efficient Choice of Biasing Constant for Ridge Regression Sona Mardikyan* and Eyüp Çetin Department of Management Information Systems, School of
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 3, 008, no., 57-536 Efficient Choice of Biasing Constant for Ridge Regression Sona Mardikyan* and Eyüp Çetin Department of Management Information Systems, School of
Experimental designs for multiple responses with different models
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2015 Experimental designs for multiple responses with different models Wilmina Mary Marget Iowa State University Follow this and additional works at:
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2015 Experimental designs for multiple responses with different models Wilmina Mary Marget Iowa State University Follow this and additional works at:
Ridge Regression and Ill-Conditioning
 Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods Volume 3 Issue Article 8-04 Ridge Regression and Ill-Conditioning Ghadban Khalaf King Khalid University, Saudi Arabia, albadran50@yahoo.com Mohamed Iguernane
Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods Volume 3 Issue Article 8-04 Ridge Regression and Ill-Conditioning Ghadban Khalaf King Khalid University, Saudi Arabia, albadran50@yahoo.com Mohamed Iguernane
Double domination in signed graphs
 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Double domination in signed graphs P.K. Ashraf 1 * and K.A. Germina 2 Received: 06 March 2016 Accepted: 21 April 2016 Published: 25 July 2016 *Corresponding author: P.K.
PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Double domination in signed graphs P.K. Ashraf 1 * and K.A. Germina 2 Received: 06 March 2016 Accepted: 21 April 2016 Published: 25 July 2016 *Corresponding author: P.K.
Classes of Second-Order Split-Plot Designs
 Classes of Second-Order Split-Plot Designs DATAWorks 2018 Springfield, VA Luis A. Cortés, Ph.D. The MITRE Corporation James R. Simpson, Ph.D. JK Analytics, Inc. Peter Parker, Ph.D. NASA 22 March 2018 Outline
Classes of Second-Order Split-Plot Designs DATAWorks 2018 Springfield, VA Luis A. Cortés, Ph.D. The MITRE Corporation James R. Simpson, Ph.D. JK Analytics, Inc. Peter Parker, Ph.D. NASA 22 March 2018 Outline
Response Surface Methodology:
 Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments RAYMOND H. MYERS Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University DOUGLAS C. MONTGOMERY Arizona State University
Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments RAYMOND H. MYERS Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University DOUGLAS C. MONTGOMERY Arizona State University
Relationship between ridge regression estimator and sample size when multicollinearity present among regressors
 Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 59 (016) 1-3 EISSN 39-19 elationship between ridge regression estimator and sample size when multicollinearity present among regressors ABSTACT M. C.
Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 59 (016) 1-3 EISSN 39-19 elationship between ridge regression estimator and sample size when multicollinearity present among regressors ABSTACT M. C.
Minimizing Oblique Errors for Robust Estimating
 Irish Math. Soc. Bulletin 62 (2008), 71 78 71 Minimizing Oblique Errors for Robust Estimating DIARMUID O DRISCOLL, DONALD E. RAMIREZ, AND REBECCA SCHMITZ Abstract. The slope of the best fit line from minimizing
Irish Math. Soc. Bulletin 62 (2008), 71 78 71 Minimizing Oblique Errors for Robust Estimating DIARMUID O DRISCOLL, DONALD E. RAMIREZ, AND REBECCA SCHMITZ Abstract. The slope of the best fit line from minimizing
Generalizations on Humbert polynomials and functions
 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Generalizations on Humbert polynomials and functions Clemente Cesarano 1 * Received: 19 October 2016 Accepted: 20 March 2017 First Published: 24
APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Generalizations on Humbert polynomials and functions Clemente Cesarano 1 * Received: 19 October 2016 Accepted: 20 March 2017 First Published: 24
Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments, 3rd Edition
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/705963/ Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments, 3rd Edition Description: Identifying
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/705963/ Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments, 3rd Edition Description: Identifying
Geometric View of Measurement Errors
 This article was downloaded by: [University of Virginia, Charlottesville], [D. E. Ramirez] On: 20 May 205, At: 06:4 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number:
This article was downloaded by: [University of Virginia, Charlottesville], [D. E. Ramirez] On: 20 May 205, At: 06:4 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number:
On some properties of p-ideals based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets
 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE On some properties of p-ideals based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets Muhammad Touqeer 1 * and Naim Çağman 2 Received: 13 June 2016 Accepted: 23 June 2016 First Published:
PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE On some properties of p-ideals based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets Muhammad Touqeer 1 * and Naim Çağman 2 Received: 13 June 2016 Accepted: 23 June 2016 First Published:
EIGENVALUES AND SINGULAR VALUE DECOMPOSITION
 APPENDIX B EIGENVALUES AND SINGULAR VALUE DECOMPOSITION B.1 LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INVERSES Problems of linear estimation can be written in terms of a linear matrix equation whose solution provides the required
APPENDIX B EIGENVALUES AND SINGULAR VALUE DECOMPOSITION B.1 LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INVERSES Problems of linear estimation can be written in terms of a linear matrix equation whose solution provides the required
On the complex k-fibonacci numbers
 Falcon, Cogent Mathematics 06, 3: 0944 http://dxdoiorg/0080/33835060944 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE On the complex k-fibonacci numbers Sergio Falcon * ceived: 9 January 05
Falcon, Cogent Mathematics 06, 3: 0944 http://dxdoiorg/0080/33835060944 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE On the complex k-fibonacci numbers Sergio Falcon * ceived: 9 January 05
Comparison of Some Improved Estimators for Linear Regression Model under Different Conditions
 Florida International University FIU Digital Commons FIU Electronic Theses and Dissertations University Graduate School 3-24-2015 Comparison of Some Improved Estimators for Linear Regression Model under
Florida International University FIU Digital Commons FIU Electronic Theses and Dissertations University Graduate School 3-24-2015 Comparison of Some Improved Estimators for Linear Regression Model under
Bounds on Hankel determinant for starlike and convex functions with respect to symmetric points
 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Bounds on Hankel determinant for starlike convex functions with respect to symmetric points Ambuj K. Mishra 1, Jugal K. Prajapat * Sudhana Maharana Received: 07 November
PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Bounds on Hankel determinant for starlike convex functions with respect to symmetric points Ambuj K. Mishra 1, Jugal K. Prajapat * Sudhana Maharana Received: 07 November
Multivariate Statistical Analysis
 Multivariate Statistical Analysis Fall 2011 C. L. Williams, Ph.D. Lecture 4 for Applied Multivariate Analysis Outline 1 Eigen values and eigen vectors Characteristic equation Some properties of eigendecompositions
Multivariate Statistical Analysis Fall 2011 C. L. Williams, Ph.D. Lecture 4 for Applied Multivariate Analysis Outline 1 Eigen values and eigen vectors Characteristic equation Some properties of eigendecompositions
Review of Linear Algebra
 Review of Linear Algebra Definitions An m n (read "m by n") matrix, is a rectangular array of entries, where m is the number of rows and n the number of columns. 2 Definitions (Con t) A is square if m=
Review of Linear Algebra Definitions An m n (read "m by n") matrix, is a rectangular array of entries, where m is the number of rows and n the number of columns. 2 Definitions (Con t) A is square if m=
Definitive Screening Designs with Added Two-Level Categorical Factors *
 Definitive Screening Designs with Added Two-Level Categorical Factors * BRADLEY JONES SAS Institute, Cary, NC 27513 CHRISTOPHER J NACHTSHEIM Carlson School of Management, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis,
Definitive Screening Designs with Added Two-Level Categorical Factors * BRADLEY JONES SAS Institute, Cary, NC 27513 CHRISTOPHER J NACHTSHEIM Carlson School of Management, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis,
Optimality of Central Composite Designs Augmented from One-half Fractional Factorial Designs
 of Central Composite Designs Augmented from One-half Fractional Factorial Designs Anthony F. Capili Department of Mathematics and Statistics, College of Arts and Sciences, University of Southeastern Philippines
of Central Composite Designs Augmented from One-half Fractional Factorial Designs Anthony F. Capili Department of Mathematics and Statistics, College of Arts and Sciences, University of Southeastern Philippines
Regression Diagnostics for Survey Data
 Regression Diagnostics for Survey Data Richard Valliant Joint Program in Survey Methodology, University of Maryland and University of Michigan USA Jianzhu Li (Westat), Dan Liao (JPSM) 1 Introduction Topics
Regression Diagnostics for Survey Data Richard Valliant Joint Program in Survey Methodology, University of Maryland and University of Michigan USA Jianzhu Li (Westat), Dan Liao (JPSM) 1 Introduction Topics
Intermediate Algebra. Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technology
 Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technology c 2017 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. The essence of the license
Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technology c 2017 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. The essence of the license
Linear Models 1. Isfahan University of Technology Fall Semester, 2014
 Linear Models 1 Isfahan University of Technology Fall Semester, 2014 References: [1] G. A. F., Seber and A. J. Lee (2003). Linear Regression Analysis (2nd ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. [2] A. C. Rencher and
Linear Models 1 Isfahan University of Technology Fall Semester, 2014 References: [1] G. A. F., Seber and A. J. Lee (2003). Linear Regression Analysis (2nd ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. [2] A. C. Rencher and
Singular Value Decomposition Compared to cross Product Matrix in an ill Conditioned Regression Model
 International Journal of Statistics and Applications 04, 4(): 4-33 DOI: 0.593/j.statistics.04040.07 Singular Value Decomposition Compared to cross Product Matrix in an ill Conditioned Regression Model
International Journal of Statistics and Applications 04, 4(): 4-33 DOI: 0.593/j.statistics.04040.07 Singular Value Decomposition Compared to cross Product Matrix in an ill Conditioned Regression Model
Mathematics. EC / EE / IN / ME / CE. for
 Mathematics for EC / EE / IN / ME / CE By www.thegateacademy.com Syllabus Syllabus for Mathematics Linear Algebra: Matrix Algebra, Systems of Linear Equations, Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Probability
Mathematics for EC / EE / IN / ME / CE By www.thegateacademy.com Syllabus Syllabus for Mathematics Linear Algebra: Matrix Algebra, Systems of Linear Equations, Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Probability
The combined reproducing kernel method and Taylor series to solve nonlinear Abel s integral equations with weakly singular kernel
 Alvandi & Paripour, Cogent Mathematics (6), 3: 575 http://dx.doi.org/.8/33835.6.575 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE The combined reproducing kernel method and Taylor series to
Alvandi & Paripour, Cogent Mathematics (6), 3: 575 http://dx.doi.org/.8/33835.6.575 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE The combined reproducing kernel method and Taylor series to
Single and multiple linear regression analysis
 Single and multiple linear regression analysis Marike Cockeran 2017 Introduction Outline of the session Simple linear regression analysis SPSS example of simple linear regression analysis Additional topics
Single and multiple linear regression analysis Marike Cockeran 2017 Introduction Outline of the session Simple linear regression analysis SPSS example of simple linear regression analysis Additional topics
Minimax design criterion for fractional factorial designs
 Ann Inst Stat Math 205 67:673 685 DOI 0.007/s0463-04-0470-0 Minimax design criterion for fractional factorial designs Yue Yin Julie Zhou Received: 2 November 203 / Revised: 5 March 204 / Published online:
Ann Inst Stat Math 205 67:673 685 DOI 0.007/s0463-04-0470-0 Minimax design criterion for fractional factorial designs Yue Yin Julie Zhou Received: 2 November 203 / Revised: 5 March 204 / Published online:
Dynamics of the equation complex plane
 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Dynamics of the equation in the complex plane Sk. Sarif Hassan 1 and Esha Chatterjee * Received: 0 April 015 Accepted: 08 November 015 Published:
APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Dynamics of the equation in the complex plane Sk. Sarif Hassan 1 and Esha Chatterjee * Received: 0 April 015 Accepted: 08 November 015 Published:
Moment Aberration Projection for Nonregular Fractional Factorial Designs
 Moment Aberration Projection for Nonregular Fractional Factorial Designs Hongquan Xu Department of Statistics University of California Los Angeles, CA 90095-1554 (hqxu@stat.ucla.edu) Lih-Yuan Deng Department
Moment Aberration Projection for Nonregular Fractional Factorial Designs Hongquan Xu Department of Statistics University of California Los Angeles, CA 90095-1554 (hqxu@stat.ucla.edu) Lih-Yuan Deng Department
DIMENSION REDUCTION OF THE EXPLANATORY VARIABLES IN MULTIPLE LINEAR REGRESSION. P. Filzmoser and C. Croux
 Pliska Stud. Math. Bulgar. 003), 59 70 STUDIA MATHEMATICA BULGARICA DIMENSION REDUCTION OF THE EXPLANATORY VARIABLES IN MULTIPLE LINEAR REGRESSION P. Filzmoser and C. Croux Abstract. In classical multiple
Pliska Stud. Math. Bulgar. 003), 59 70 STUDIA MATHEMATICA BULGARICA DIMENSION REDUCTION OF THE EXPLANATORY VARIABLES IN MULTIPLE LINEAR REGRESSION P. Filzmoser and C. Croux Abstract. In classical multiple
Some inequalities for unitarily invariant norms of matrices
 Wang et al Journal of Inequalities and Applications 011, 011:10 http://wwwjournalofinequalitiesandapplicationscom/content/011/1/10 RESEARCH Open Access Some inequalities for unitarily invariant norms of
Wang et al Journal of Inequalities and Applications 011, 011:10 http://wwwjournalofinequalitiesandapplicationscom/content/011/1/10 RESEARCH Open Access Some inequalities for unitarily invariant norms of
8 RESPONSE SURFACE DESIGNS
 8 RESPONSE SURFACE DESIGNS Desirable Properties of a Response Surface Design 1. It should generate a satisfactory distribution of information throughout the design region. 2. It should ensure that the
8 RESPONSE SURFACE DESIGNS Desirable Properties of a Response Surface Design 1. It should generate a satisfactory distribution of information throughout the design region. 2. It should ensure that the
Improved Ridge Estimator in Linear Regression with Multicollinearity, Heteroscedastic Errors and Outliers
 Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods Volume 15 Issue 2 Article 23 11-1-2016 Improved Ridge Estimator in Linear Regression with Multicollinearity, Heteroscedastic Errors and Outliers Ashok Vithoba
Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods Volume 15 Issue 2 Article 23 11-1-2016 Improved Ridge Estimator in Linear Regression with Multicollinearity, Heteroscedastic Errors and Outliers Ashok Vithoba
The successive raising estimator and its relation with the ridge estimator
 The successive raising estimator and its relation with the ridge estimator J. García and D.E. Ramirez July 27, 206 Abstract The raise estimators are used to reduce collinearity in linear regression models
The successive raising estimator and its relation with the ridge estimator J. García and D.E. Ramirez July 27, 206 Abstract The raise estimators are used to reduce collinearity in linear regression models
Available online at (Elixir International Journal) Statistics. Elixir Statistics 49 (2012)
 10108 Available online at www.elixirpublishers.com (Elixir International Journal) Statistics Elixir Statistics 49 (2012) 10108-10112 The detention and correction of multicollinearity effects in a multiple
10108 Available online at www.elixirpublishers.com (Elixir International Journal) Statistics Elixir Statistics 49 (2012) 10108-10112 The detention and correction of multicollinearity effects in a multiple
((n r) 1) (r 1) ε 1 ε 2. X Z β+
 Bringing Order to Outlier Diagnostics in Regression Models D.R.JensenandD.E.Ramirez Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University and University of Virginia der@virginia.edu http://www.math.virginia.edu/
Bringing Order to Outlier Diagnostics in Regression Models D.R.JensenandD.E.Ramirez Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University and University of Virginia der@virginia.edu http://www.math.virginia.edu/
I L L I N O I S UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN
 Canonical Edps/Soc 584 and Psych 594 Applied Multivariate Statistics Carolyn J. Anderson Department of Educational Psychology I L L I N O I S UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN Canonical Slide
Canonical Edps/Soc 584 and Psych 594 Applied Multivariate Statistics Carolyn J. Anderson Department of Educational Psychology I L L I N O I S UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN Canonical Slide
Multilevel modeling and panel data analysis in educational research (Case study: National examination data senior high school in West Java)
 Multilevel modeling and panel data analysis in educational research (Case study: National examination data senior high school in West Java) Pepi Zulvia, Anang Kurnia, and Agus M. Soleh Citation: AIP Conference
Multilevel modeling and panel data analysis in educational research (Case study: National examination data senior high school in West Java) Pepi Zulvia, Anang Kurnia, and Agus M. Soleh Citation: AIP Conference
University, Wuhan, China c College of Physical Science and Technology, Central China Normal. University, Wuhan, China Published online: 25 Apr 2014.
 This article was downloaded by: [0.9.78.106] On: 0 April 01, At: 16:7 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 10795 Registered office: Mortimer House,
This article was downloaded by: [0.9.78.106] On: 0 April 01, At: 16:7 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 10795 Registered office: Mortimer House,
An Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis
 An Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis Third Edition T. W. ANDERSON Stanford University Department of Statistics Stanford, CA WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION Contents
An Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis Third Edition T. W. ANDERSON Stanford University Department of Statistics Stanford, CA WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION Contents
1 Data Arrays and Decompositions
 1 Data Arrays and Decompositions 1.1 Variance Matrices and Eigenstructure Consider a p p positive definite and symmetric matrix V - a model parameter or a sample variance matrix. The eigenstructure is
1 Data Arrays and Decompositions 1.1 Variance Matrices and Eigenstructure Consider a p p positive definite and symmetric matrix V - a model parameter or a sample variance matrix. The eigenstructure is
Exercises * on Principal Component Analysis
 Exercises * on Principal Component Analysis Laurenz Wiskott Institut für Neuroinformatik Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Germany, EU 4 February 207 Contents Intuition 3. Problem statement..........................................
Exercises * on Principal Component Analysis Laurenz Wiskott Institut für Neuroinformatik Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Germany, EU 4 February 207 Contents Intuition 3. Problem statement..........................................
Day 4: Shrinkage Estimators
 Day 4: Shrinkage Estimators Kenneth Benoit Data Mining and Statistical Learning March 9, 2015 n versus p (aka k) Classical regression framework: n > p. Without this inequality, the OLS coefficients have
Day 4: Shrinkage Estimators Kenneth Benoit Data Mining and Statistical Learning March 9, 2015 n versus p (aka k) Classical regression framework: n > p. Without this inequality, the OLS coefficients have
component risk analysis
 273: Urban Systems Modeling Lec. 3 component risk analysis instructor: Matteo Pozzi 273: Urban Systems Modeling Lec. 3 component reliability outline risk analysis for components uncertain demand and uncertain
273: Urban Systems Modeling Lec. 3 component risk analysis instructor: Matteo Pozzi 273: Urban Systems Modeling Lec. 3 component reliability outline risk analysis for components uncertain demand and uncertain
Multicollinearity Exercise
 Multicollinearity Exercise Use the attached SAS output to answer the questions. [OPTIONAL: Copy the SAS program below into the SAS editor window and run it.] You do not need to submit any output, so there
Multicollinearity Exercise Use the attached SAS output to answer the questions. [OPTIONAL: Copy the SAS program below into the SAS editor window and run it.] You do not need to submit any output, so there
Linear Regression. In this problem sheet, we consider the problem of linear regression with p predictors and one intercept,
 Linear Regression In this problem sheet, we consider the problem of linear regression with p predictors and one intercept, y = Xβ + ɛ, where y t = (y 1,..., y n ) is the column vector of target values,
Linear Regression In this problem sheet, we consider the problem of linear regression with p predictors and one intercept, y = Xβ + ɛ, where y t = (y 1,..., y n ) is the column vector of target values,
Lecture 1: OLS derivations and inference
 Lecture 1: OLS derivations and inference Econometric Methods Warsaw School of Economics (1) OLS 1 / 43 Outline 1 Introduction Course information Econometrics: a reminder Preliminary data exploration 2
Lecture 1: OLS derivations and inference Econometric Methods Warsaw School of Economics (1) OLS 1 / 43 Outline 1 Introduction Course information Econometrics: a reminder Preliminary data exploration 2
APPLICATION OF RIDGE REGRESSION TO MULTICOLLINEAR DATA
 Journal of Research (Science), Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan, Pakistan. Vol.15, No.1, June 2004, pp. 97-106 ISSN 1021-1012 APPLICATION OF RIDGE REGRESSION TO MULTICOLLINEAR DATA G. R. Pasha 1 and
Journal of Research (Science), Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan, Pakistan. Vol.15, No.1, June 2004, pp. 97-106 ISSN 1021-1012 APPLICATION OF RIDGE REGRESSION TO MULTICOLLINEAR DATA G. R. Pasha 1 and
Nonlinear least squares algorithm for identification of hazards
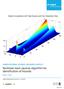 COMPUTATIONAL SCIENCE RESEARCH ARTICLE Nonlinear least squares algorithm for identification of hazards Robert E White Cogent Mathematics (2015, 2: 1118219 Page 1 of 16 White, Cogent Mathematics (2015,
COMPUTATIONAL SCIENCE RESEARCH ARTICLE Nonlinear least squares algorithm for identification of hazards Robert E White Cogent Mathematics (2015, 2: 1118219 Page 1 of 16 White, Cogent Mathematics (2015,
Appendix A: Matrices
 Appendix A: Matrices A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers Such arrays have rows and columns The numbers of rows and columns are referred to as the dimensions of a matrix A matrix with, say, 5 rows
Appendix A: Matrices A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers Such arrays have rows and columns The numbers of rows and columns are referred to as the dimensions of a matrix A matrix with, say, 5 rows
Next is material on matrix rank. Please see the handout
 B90.330 / C.005 NOTES for Wednesday 0.APR.7 Suppose that the model is β + ε, but ε does not have the desired variance matrix. Say that ε is normal, but Var(ε) σ W. The form of W is W w 0 0 0 0 0 0 w 0
B90.330 / C.005 NOTES for Wednesday 0.APR.7 Suppose that the model is β + ε, but ε does not have the desired variance matrix. Say that ε is normal, but Var(ε) σ W. The form of W is W w 0 0 0 0 0 0 w 0
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY (formerly the Examinations of the Institute of Statisticians) GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 2007
 EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY (formerly the Examinations of the Institute of Statisticians) GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 2007 Applied Statistics I Time Allowed: Three Hours Candidates should answer
EXAMINATIONS OF THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY (formerly the Examinations of the Institute of Statisticians) GRADUATE DIPLOMA, 2007 Applied Statistics I Time Allowed: Three Hours Candidates should answer
Machine learning for pervasive systems Classification in high-dimensional spaces
 Machine learning for pervasive systems Classification in high-dimensional spaces Department of Communications and Networking Aalto University, School of Electrical Engineering stephan.sigg@aalto.fi Version
Machine learning for pervasive systems Classification in high-dimensional spaces Department of Communications and Networking Aalto University, School of Electrical Engineering stephan.sigg@aalto.fi Version
Using Ridge Least Median Squares to Estimate the Parameter by Solving Multicollinearity and Outliers Problems
 Modern Applied Science; Vol. 9, No. ; 05 ISSN 9-844 E-ISSN 9-85 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Using Ridge Least Median Squares to Estimate the Parameter by Solving Multicollinearity
Modern Applied Science; Vol. 9, No. ; 05 ISSN 9-844 E-ISSN 9-85 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Using Ridge Least Median Squares to Estimate the Parameter by Solving Multicollinearity
AN IMPROVEMENT TO THE ALIGNED RANK STATISTIC
 Journal of Applied Statistical Science ISSN 1067-5817 Volume 14, Number 3/4, pp. 225-235 2005 Nova Science Publishers, Inc. AN IMPROVEMENT TO THE ALIGNED RANK STATISTIC FOR TWO-FACTOR ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE
Journal of Applied Statistical Science ISSN 1067-5817 Volume 14, Number 3/4, pp. 225-235 2005 Nova Science Publishers, Inc. AN IMPROVEMENT TO THE ALIGNED RANK STATISTIC FOR TWO-FACTOR ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE
Stochastic Design Criteria in Linear Models
 AUSTRIAN JOURNAL OF STATISTICS Volume 34 (2005), Number 2, 211 223 Stochastic Design Criteria in Linear Models Alexander Zaigraev N. Copernicus University, Toruń, Poland Abstract: Within the framework
AUSTRIAN JOURNAL OF STATISTICS Volume 34 (2005), Number 2, 211 223 Stochastic Design Criteria in Linear Models Alexander Zaigraev N. Copernicus University, Toruń, Poland Abstract: Within the framework
Variable Selection in Restricted Linear Regression Models. Y. Tuaç 1 and O. Arslan 1
 Variable Selection in Restricted Linear Regression Models Y. Tuaç 1 and O. Arslan 1 Ankara University, Faculty of Science, Department of Statistics, 06100 Ankara/Turkey ytuac@ankara.edu.tr, oarslan@ankara.edu.tr
Variable Selection in Restricted Linear Regression Models Y. Tuaç 1 and O. Arslan 1 Ankara University, Faculty of Science, Department of Statistics, 06100 Ankara/Turkey ytuac@ankara.edu.tr, oarslan@ankara.edu.tr
Theorems. Least squares regression
 Theorems In this assignment we are trying to classify AML and ALL samples by use of penalized logistic regression. Before we indulge on the adventure of classification we should first explain the most
Theorems In this assignment we are trying to classify AML and ALL samples by use of penalized logistic regression. Before we indulge on the adventure of classification we should first explain the most
Forecast comparison of principal component regression and principal covariate regression
 Forecast comparison of principal component regression and principal covariate regression Christiaan Heij, Patrick J.F. Groenen, Dick J. van Dijk Econometric Institute, Erasmus University Rotterdam Econometric
Forecast comparison of principal component regression and principal covariate regression Christiaan Heij, Patrick J.F. Groenen, Dick J. van Dijk Econometric Institute, Erasmus University Rotterdam Econometric
Researchers often record several characters in their research experiments where each character has a special significance to the experimenter.
 Dimension reduction in multivariate analysis using maximum entropy criterion B. K. Hooda Department of Mathematics and Statistics CCS Haryana Agricultural University Hisar 125 004 India D. S. Hooda Jaypee
Dimension reduction in multivariate analysis using maximum entropy criterion B. K. Hooda Department of Mathematics and Statistics CCS Haryana Agricultural University Hisar 125 004 India D. S. Hooda Jaypee
Math Camp Lecture 4: Linear Algebra. Xiao Yu Wang. Aug 2010 MIT. Xiao Yu Wang (MIT) Math Camp /10 1 / 88
 Math Camp 2010 Lecture 4: Linear Algebra Xiao Yu Wang MIT Aug 2010 Xiao Yu Wang (MIT) Math Camp 2010 08/10 1 / 88 Linear Algebra Game Plan Vector Spaces Linear Transformations and Matrices Determinant
Math Camp 2010 Lecture 4: Linear Algebra Xiao Yu Wang MIT Aug 2010 Xiao Yu Wang (MIT) Math Camp 2010 08/10 1 / 88 Linear Algebra Game Plan Vector Spaces Linear Transformations and Matrices Determinant
φ-contractive multivalued mappings in complex valued metric spaces and remarks on some recent papers
 Joshi et al., Cogent Mathematics 2016, 3: 1162484 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE φ-contractive multivalued mappings in complex valued metric spaces and remarks on some recent papers Received: 25 October
Joshi et al., Cogent Mathematics 2016, 3: 1162484 PURE MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE φ-contractive multivalued mappings in complex valued metric spaces and remarks on some recent papers Received: 25 October
The Precise Effect of Multicollinearity on Classification Prediction
 Multicollinearity and Classification Prediction The Precise Effect of Multicollinearity on Classification Prediction Mary G. Lieberman John D. Morris Florida Atlantic University The results of Morris and
Multicollinearity and Classification Prediction The Precise Effect of Multicollinearity on Classification Prediction Mary G. Lieberman John D. Morris Florida Atlantic University The results of Morris and
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear Algebra
 SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 1.1. Introduction Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 1.1. Introduction Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
Psychology Seminar Psych 406 Dr. Jeffrey Leitzel
 Psychology Seminar Psych 406 Dr. Jeffrey Leitzel Structural Equation Modeling Topic 1: Correlation / Linear Regression Outline/Overview Correlations (r, pr, sr) Linear regression Multiple regression interpreting
Psychology Seminar Psych 406 Dr. Jeffrey Leitzel Structural Equation Modeling Topic 1: Correlation / Linear Regression Outline/Overview Correlations (r, pr, sr) Linear regression Multiple regression interpreting
Vector control of asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor
 Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: 11344 ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING RESEARCH ARTICLE Vector control of asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor Arif Iqbal 1 *, G.K. Singh 1 and Vinay Pant
Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: 11344 ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING RESEARCH ARTICLE Vector control of asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor Arif Iqbal 1 *, G.K. Singh 1 and Vinay Pant
Linear Algebra: Matrix Eigenvalue Problems
 CHAPTER8 Linear Algebra: Matrix Eigenvalue Problems Chapter 8 p1 A matrix eigenvalue problem considers the vector equation (1) Ax = λx. 8.0 Linear Algebra: Matrix Eigenvalue Problems Here A is a given
CHAPTER8 Linear Algebra: Matrix Eigenvalue Problems Chapter 8 p1 A matrix eigenvalue problem considers the vector equation (1) Ax = λx. 8.0 Linear Algebra: Matrix Eigenvalue Problems Here A is a given
USING REGULAR FRACTIONS OF TWO-LEVEL DESIGNS TO FIND BASELINE DESIGNS
 Statistica Sinica 26 (2016, 745-759 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5705/ss.202014.0099 USING REGULAR FRACTIONS OF TWO-LEVEL DESIGNS TO FIND BASELINE DESIGNS Arden Miller and Boxin Tang University of Auckland
Statistica Sinica 26 (2016, 745-759 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5705/ss.202014.0099 USING REGULAR FRACTIONS OF TWO-LEVEL DESIGNS TO FIND BASELINE DESIGNS Arden Miller and Boxin Tang University of Auckland
ISyE 691 Data mining and analytics
 ISyE 691 Data mining and analytics Regression Instructor: Prof. Kaibo Liu Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering UW-Madison Email: kliu8@wisc.edu Office: Room 3017 (Mechanical Engineering Building)
ISyE 691 Data mining and analytics Regression Instructor: Prof. Kaibo Liu Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering UW-Madison Email: kliu8@wisc.edu Office: Room 3017 (Mechanical Engineering Building)
JORDAN NORMAL FORM NOTES
 18.700 JORDAN NORMAL FORM NOTES These are some supplementary notes on how to find the Jordan normal form of a small matrix. First we recall some of the facts from lecture, next we give the general algorithm
18.700 JORDAN NORMAL FORM NOTES These are some supplementary notes on how to find the Jordan normal form of a small matrix. First we recall some of the facts from lecture, next we give the general algorithm
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear Algebra
 1.1. Introduction SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
1.1. Introduction SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
Full terms and conditions of use:
 This article was downloaded by:[rollins, Derrick] [Rollins, Derrick] On: 26 March 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 770393152] Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and
This article was downloaded by:[rollins, Derrick] [Rollins, Derrick] On: 26 March 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 770393152] Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and
Detection of Influential Observation in Linear Regression. R. Dennis Cook. Technometrics, Vol. 19, No. 1. (Feb., 1977), pp
 Detection of Influential Observation in Linear Regression R. Dennis Cook Technometrics, Vol. 19, No. 1. (Feb., 1977), pp. 15-18. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0040-1706%28197702%2919%3a1%3c15%3adoioil%3e2.0.co%3b2-8
Detection of Influential Observation in Linear Regression R. Dennis Cook Technometrics, Vol. 19, No. 1. (Feb., 1977), pp. 15-18. Stable URL: http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0040-1706%28197702%2919%3a1%3c15%3adoioil%3e2.0.co%3b2-8
MSE Performance and Minimax Regret Significance Points for a HPT Estimator when each Individual Regression Coefficient is Estimated
 This article was downloaded by: [Kobe University] On: 8 April 03, At: 8:50 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 07954 Registered office: Mortimer House,
This article was downloaded by: [Kobe University] On: 8 April 03, At: 8:50 Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 07954 Registered office: Mortimer House,
Effects of Outliers and Multicollinearity on Some Estimators of Linear Regression Model
 204 Effects of Outliers and Multicollinearity on Some Estimators of Linear Regression Model S. A. Ibrahim 1 ; W. B. Yahya 2 1 Department of Physical Sciences, Al-Hikmah University, Ilorin, Nigeria. e-mail:
204 Effects of Outliers and Multicollinearity on Some Estimators of Linear Regression Model S. A. Ibrahim 1 ; W. B. Yahya 2 1 Department of Physical Sciences, Al-Hikmah University, Ilorin, Nigeria. e-mail:
Checking model assumptions with regression diagnostics
 @graemeleehickey www.glhickey.com graeme.hickey@liverpool.ac.uk Checking model assumptions with regression diagnostics Graeme L. Hickey University of Liverpool Conflicts of interest None Assistant Editor
@graemeleehickey www.glhickey.com graeme.hickey@liverpool.ac.uk Checking model assumptions with regression diagnostics Graeme L. Hickey University of Liverpool Conflicts of interest None Assistant Editor
MS-C1620 Statistical inference
 MS-C1620 Statistical inference 10 Linear regression III Joni Virta Department of Mathematics and Systems Analysis School of Science Aalto University Academic year 2018 2019 Period III - IV 1 / 32 Contents
MS-C1620 Statistical inference 10 Linear regression III Joni Virta Department of Mathematics and Systems Analysis School of Science Aalto University Academic year 2018 2019 Period III - IV 1 / 32 Contents
Linear Regression Models
 Linear Regression Models Model Description and Model Parameters Modelling is a central theme in these notes. The idea is to develop and continuously improve a library of predictive models for hazards,
Linear Regression Models Model Description and Model Parameters Modelling is a central theme in these notes. The idea is to develop and continuously improve a library of predictive models for hazards,
Least Squares Estimation-Finite-Sample Properties
 Least Squares Estimation-Finite-Sample Properties Ping Yu School of Economics and Finance The University of Hong Kong Ping Yu (HKU) Finite-Sample 1 / 29 Terminology and Assumptions 1 Terminology and Assumptions
Least Squares Estimation-Finite-Sample Properties Ping Yu School of Economics and Finance The University of Hong Kong Ping Yu (HKU) Finite-Sample 1 / 29 Terminology and Assumptions 1 Terminology and Assumptions
