Energy dissipating structures generated by dipole-wall collisions at high Reynolds number
|
|
|
- Marlene Lambert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Energy dissipating structures generated by dipole-wall collisions at high Reynolds number Duncan Sutherland 1 Charlie Macaskill 1 David Dritschel 2 1. School of Mathematics and Statistics University of Sydney 2. School of Mathematical Sciences, University of St. Andrews ANZIAM 2012 Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
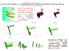
2 Introduction: Dipole wall collisions We are interested in a vortex dipole colliding with a wall in a viscous fluid in a periodic channel We compare energy dissipation results with a recent paper by Nguyen van yen, et al Figure: Dipole colliding with the wall at times 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
3 Introduction: Channel domain y L y /2 u = v = 0 ω t = J (ω, ψ) + ν 2 ω 2 ψ = ω N L y /2 0 ψ y = u, ψ x = v u = v = 0 J (ω, ψ) = ω ψ x y ω ψ y x L x x M Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
4 Introduction: Energy Dissipating Structures A recent study by Nguyen van yen, Schneider and Farge has indicated the existence of energy dissipating structures as the viscosity tends to zero Penalisation method: u t + (u )u = p + ν 2 u 1 η χu { 0 inside the fluid u = 0 χ = 1 elsewhere η is the penalisation parameter, chosen to be sufficiently small to ensure the velocity is zero outside of the fluid. These equations (in vorticity form) are then solved on a double-periodic domain using a Fourier-Fourier spectral method No-slip boundary conditions are approximated Navier boundary conditions with a slip length proportional to Re 1 Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
5 Introduction: Key Results of Nguyen van yen, et al Energy, E dissipation far from the wall is proportional to Re 1, as for unbounded flows Prandtl 1904: Energy dissipation close to the wall is proportional to Re 1/2, found to hold reasonably throughout the rebound Enstrophy, Z dissipation during the collision is proportional to Re 1, hence de dt = 2ZRe 1 tends to a constant as viscosity vanishes Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
6 Numerical Methods: Periodic direction and timestepping The periodic boundary conditions are dealt with using a Fourier Transform. The derivatives are calculated in spectral space and the nonlinear term is calculated in physical space The time equations are discretised using the Adams-Bashforth/Crank-Nicholson method This leaves N coupled Helmholtz problems for each Fourier wavenumber of ω and ψ Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
7 Numerical Methods: Helmholtz problems and boundary conditions d 2 ω dy 2 κ2 ω = S n,n 1 d 2 ψ dy 2 k2 ψ = ω u = v = 0 or equivalently ψ = dψ dy Coordinate transform: y = sin(η) sin π/2+1 = 0 on y = ±1 to deal with the Chebyshev grid Compact finite difference discretisation of derivative operators αf i 1 + βf i + αf i+1 = af i 1 + bf i + af i+1 This gives rise to a block tridiagonal matrix problem which may be solved in O(M) operations Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
8 Numerical Methods: Influence Matrix An influence matrix is used to treat the boundary conditions. Note the problem is linear, hence: ω n+1 = ω n 0 + α 1 ω 1 + α 2 ω 2 ψ n+1 = ψ n 0 + α 1 ψ 1 + α 2 ψ 2 = u n+1 = u n 0 + α 1 u 1 + α 2 u 2 Equipped with the following boundary conditions: ω 1 (±1) = 0, ω 1 (1) = 1, ω 1 ( 1) = 0, ω 2 (1) = 0, ω 2 ( 1) = 1,ψ i (±1) = 0 Then choose α 1,2 such that u(±1) = 0 This gives N 2 2 matrix problems of the form: ( ) ( ) ( u1 ( 1) u 2 ( 1) α1 u0 ( 1) = u 1 (1) u 2 (1) u 0 (1) α 2 ) Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
9 Simulations ri 2 = (x x i ) 2 + y 2 2 ) ω = ω e ( 1) (1 i r2 i r0 2 e r2 i /r2 0 i=1 L x = 2π, L y = 0.9 ω e = 300, x 1 = 0.05, x 2 = 0.05, r 0 = 0.05 Re N x N y The initial condition must be selected such that it is consistent with the no-slip boundary conditions. Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
10 Differences compared to Nguyen van yen, et al Our resolution is (apparently) lower, Nguyen van yen, et al demanded scales of Re 1 be resolved. (Work to get this resolution is in progress) Their test included higher Reynolds numbers up to 7880 They took L x = 1, we use L x = 2π. (Repeating the calculations on the shorter domain is in progress) Our initial condition will be slightly different, since we insure that the IC satisfies the boundary conditions exactly Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
11 Dipole-Wall Collision Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
12 Dipole-Wall Collision Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
13 Dipole-Wall Collision Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
14 Dipole-Wall Collision Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
15 Dipole-Wall Collision Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
16 Comparison: Energy Scaling Results Interior energy scaling Energy Dissipation E(0.2) E(0) Re 1 Wall region energy scaling Energy Dissipation E(0.495) E(0.39) Re 1/ Re Re The decay results are in agreement with Nguyen van yen, et al. Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
17 Comparison: Enstrophy Scaling Results Enstrophy Dissipation Z(0.495) Z(0.39) Re Re This is very close to linear, which implies the energy dissipation rate tends to a constant as viscosity vanishes. If Z is weakly sublinear then global energy dissipation 2ZRe 1 0 as the viscosity vanishes. Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
18 Further work to be done Conduct the tests at increased Reynolds number Increase the resolution (also helps with the higher Re) Nguyen van yen, et al tested dissipation in certain regions and examined Lagrangian trajectories Track and visualise the local energy dissipation Investigate the differences between the events at different Reynolds numbers Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
19 References and Acknowledgements Nguyen van yen, R, Farge, M, and Schneider, K, (2011) Energy Dissipating Structures Produced by Walls in Two-Dimensional Flows at Vanishing Viscosity. PRL 106, Kramer, W. PhD thesis 2007 Schneider, K, (2005), Numerical simulation of the transient flow behaviours in chemical reactors using a penalisation method, Computers & Fluids, 34, pp Clercx, H. J. H, and van Heijst G. J. F, (2002) Dissipation of kinetic energy in two-dimensional bounded flows, Physical Review E, 65, Lele, S. K. (1992), Compact finite difference schemes with spectral-like resolution. J. Comp. Phys. 103, pp Kraichnan, R, H and Montgomery D, (1980) Two Dimensional Turbulence. Rep. Prog. Phys. 43, pp Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
20 Questions Sutherland (Sydney) Influence Matrix ANZIAM / 16
On Decaying Two-Dimensional Turbulence in a Circular Container
 Frontiers of Computational Sciences Y. Kaneda, H. Kawamura and M. Sasai (Eds.) Springer, 2007, pp. 89-95 On Decaying Two-Dimensional Turbulence in a Circular Container Kai Schneider and Marie Farge Univesité
Frontiers of Computational Sciences Y. Kaneda, H. Kawamura and M. Sasai (Eds.) Springer, 2007, pp. 89-95 On Decaying Two-Dimensional Turbulence in a Circular Container Kai Schneider and Marie Farge Univesité
Decaying 2D Turbulence in Bounded Domains: Influence of the Geometry
 Computational Physics and New Perspectives in Turbulence Y. Kaneda (Ed.) Springer, 2007, pp. 241-246 Decaying 2D Turbulence in Bounded Domains: Influence of the Geometry Kai Schneider 1 and Marie Farge
Computational Physics and New Perspectives in Turbulence Y. Kaneda (Ed.) Springer, 2007, pp. 241-246 Decaying 2D Turbulence in Bounded Domains: Influence of the Geometry Kai Schneider 1 and Marie Farge
Lagrangian acceleration in confined 2d turbulent flow
 Lagrangian acceleration in confined 2d turbulent flow Kai Schneider 1 1 Benjamin Kadoch, Wouter Bos & Marie Farge 3 1 CMI, Université Aix-Marseille, France 2 LMFA, Ecole Centrale, Lyon, France 3 LMD, Ecole
Lagrangian acceleration in confined 2d turbulent flow Kai Schneider 1 1 Benjamin Kadoch, Wouter Bos & Marie Farge 3 1 CMI, Université Aix-Marseille, France 2 LMFA, Ecole Centrale, Lyon, France 3 LMD, Ecole
Energy dissipating structures in the vanishing viscosity limit of 2D incompressible flows with solid boundaries
 Energy dissipating structures in the vanishing viscosity limit of 2D incompressible flows with solid boundaries Wiko Berlin, 16.04.2010 Romain Nguyen van yen 1, Marie Farge 1, Kai Schneider 2 1 Laboratoire
Energy dissipating structures in the vanishing viscosity limit of 2D incompressible flows with solid boundaries Wiko Berlin, 16.04.2010 Romain Nguyen van yen 1, Marie Farge 1, Kai Schneider 2 1 Laboratoire
Energy dissipation caused by boundary layer instability at vanishing viscosity
 Energy dissipation caused by boundary layer instability at vanishing viscosity Marie Farge, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris Kai Schneider, Université d Aix-Marseille in collaboration with Romain Nguyen-Nouch
Energy dissipation caused by boundary layer instability at vanishing viscosity Marie Farge, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris Kai Schneider, Université d Aix-Marseille in collaboration with Romain Nguyen-Nouch
Energy dissipating structures in the vanishing viscosity limit of 2D incompressible flows with solid boundaries
 Energy dissipating structures in the vanishing viscosity limit of 2D incompressible flows with solid boundaries CIRM, Marseille, 2.09.2010 Romain Nguyen van yen 1, Marie Farge 1, Kai Schneider 2 1 Laboratoire
Energy dissipating structures in the vanishing viscosity limit of 2D incompressible flows with solid boundaries CIRM, Marseille, 2.09.2010 Romain Nguyen van yen 1, Marie Farge 1, Kai Schneider 2 1 Laboratoire
CVS filtering to study turbulent mixing
 CVS filtering to study turbulent mixing Marie Farge, LMD-CNRS, ENS, Paris Kai Schneider, CMI, Université de Provence, Marseille Carsten Beta, LMD-CNRS, ENS, Paris Jori Ruppert-Felsot, LMD-CNRS, ENS, Paris
CVS filtering to study turbulent mixing Marie Farge, LMD-CNRS, ENS, Paris Kai Schneider, CMI, Université de Provence, Marseille Carsten Beta, LMD-CNRS, ENS, Paris Jori Ruppert-Felsot, LMD-CNRS, ENS, Paris
Problem C3.5 Direct Numerical Simulation of the Taylor-Green Vortex at Re = 1600
 Problem C3.5 Direct Numerical Simulation of the Taylor-Green Vortex at Re = 6 Overview This problem is aimed at testing the accuracy and the performance of high-order methods on the direct numerical simulation
Problem C3.5 Direct Numerical Simulation of the Taylor-Green Vortex at Re = 6 Overview This problem is aimed at testing the accuracy and the performance of high-order methods on the direct numerical simulation
General introduction to Hydrodynamic Instabilities
 KTH ROYAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY General introduction to Hydrodynamic Instabilities L. Brandt & J.-Ch. Loiseau KTH Mechanics, November 2015 Luca Brandt Professor at KTH Mechanics Email: luca@mech.kth.se
KTH ROYAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY General introduction to Hydrodynamic Instabilities L. Brandt & J.-Ch. Loiseau KTH Mechanics, November 2015 Luca Brandt Professor at KTH Mechanics Email: luca@mech.kth.se
DNS of the Taylor-Green vortex at Re=1600
 DNS of the Taylor-Green vortex at Re=1600 Koen Hillewaert, Cenaero Corentin Carton de Wiart, NASA Ames koen.hillewaert@cenaero.be, corentin.carton@cenaero.be Introduction This problem is aimed at testing
DNS of the Taylor-Green vortex at Re=1600 Koen Hillewaert, Cenaero Corentin Carton de Wiart, NASA Ames koen.hillewaert@cenaero.be, corentin.carton@cenaero.be Introduction This problem is aimed at testing
Open boundary conditions in numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow
 Open boundary conditions in numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow M. P. Kirkpatrick S. W. Armfield Abstract In numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow, mass conservation can
Open boundary conditions in numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow M. P. Kirkpatrick S. W. Armfield Abstract In numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow, mass conservation can
A scaling limit from Euler to Navier-Stokes equations with random perturbation
 A scaling limit from Euler to Navier-Stokes equations with random perturbation Franco Flandoli, Scuola Normale Superiore of Pisa Newton Institute, October 208 Newton Institute, October 208 / Subject of
A scaling limit from Euler to Navier-Stokes equations with random perturbation Franco Flandoli, Scuola Normale Superiore of Pisa Newton Institute, October 208 Newton Institute, October 208 / Subject of
Transition to turbulence in plane Poiseuille flow
 Proceedings of the 55th Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, Tel-Aviv & Haifa, Israel, February 25-26, 2015 ThL2T5.1 Transition to turbulence in plane Poiseuille flow F. Roizner, M. Karp and
Proceedings of the 55th Israel Annual Conference on Aerospace Sciences, Tel-Aviv & Haifa, Israel, February 25-26, 2015 ThL2T5.1 Transition to turbulence in plane Poiseuille flow F. Roizner, M. Karp and
Numerical Simulations of a Stratified Oceanic Bottom Boundary Layer. John R. Taylor - MIT Advisor: Sutanu Sarkar - UCSD
 Numerical Simulations of a Stratified Oceanic Bottom Boundary Layer John R. Taylor - MIT Advisor: Sutanu Sarkar - UCSD Motivation Objective I: Assess and improve parameterizations of the bottom boundary
Numerical Simulations of a Stratified Oceanic Bottom Boundary Layer John R. Taylor - MIT Advisor: Sutanu Sarkar - UCSD Motivation Objective I: Assess and improve parameterizations of the bottom boundary
Stability of Shear Flow
 Stability of Shear Flow notes by Zhan Wang and Sam Potter Revised by FW WHOI GFD Lecture 3 June, 011 A look at energy stability, valid for all amplitudes, and linear stability for shear flows. 1 Nonlinear
Stability of Shear Flow notes by Zhan Wang and Sam Potter Revised by FW WHOI GFD Lecture 3 June, 011 A look at energy stability, valid for all amplitudes, and linear stability for shear flows. 1 Nonlinear
Turbulence modulation by fully resolved particles using Immersed Boundary Methods
 Turbulence modulation by fully resolved particles using Immersed Boundary Methods Abouelmagd Abdelsamie and Dominique Thévenin Lab. of Fluid Dynamics & Technical Flows University of Magdeburg Otto von
Turbulence modulation by fully resolved particles using Immersed Boundary Methods Abouelmagd Abdelsamie and Dominique Thévenin Lab. of Fluid Dynamics & Technical Flows University of Magdeburg Otto von
An iterative algorithm for nonlinear wavelet thresholding: Applications to signal and image processing
 An iterative algorithm for nonlinear wavelet thresholding: Applications to signal and image processing Marie Farge, LMD-CNRS, ENS, Paris Kai Schneider, CMI, Université de Provence, Marseille Alexandre
An iterative algorithm for nonlinear wavelet thresholding: Applications to signal and image processing Marie Farge, LMD-CNRS, ENS, Paris Kai Schneider, CMI, Université de Provence, Marseille Alexandre
Statistical Analysis of the Effect of Small Fluctuations on Final Modes Found in Flows between Rotating Cylinders
 Statistical Analysis of the Effect of Small Fluctuations on Final Modes Found in Flows between Rotating Cylinders Toshiki Morita 1, Takashi Watanabe 2 and Yorinobu Toya 3 1. Graduate School of Information
Statistical Analysis of the Effect of Small Fluctuations on Final Modes Found in Flows between Rotating Cylinders Toshiki Morita 1, Takashi Watanabe 2 and Yorinobu Toya 3 1. Graduate School of Information
Max Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik
 ASDEX Upgrade Max Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik 2D Fluid Turbulence Florian Merz Seminar on Turbulence, 08.09.05 2D turbulence? strictly speaking, there are no two-dimensional flows in nature approximately
ASDEX Upgrade Max Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik 2D Fluid Turbulence Florian Merz Seminar on Turbulence, 08.09.05 2D turbulence? strictly speaking, there are no two-dimensional flows in nature approximately
Nonlinear Evolution of a Vortex Ring
 Nonlinear Evolution of a Vortex Ring Yuji Hattori Kyushu Institute of Technology, JAPAN Yasuhide Fukumoto Kyushu University, JAPAN EUROMECH Colloquium 491 Vortex dynamics from quantum to geophysical scales
Nonlinear Evolution of a Vortex Ring Yuji Hattori Kyushu Institute of Technology, JAPAN Yasuhide Fukumoto Kyushu University, JAPAN EUROMECH Colloquium 491 Vortex dynamics from quantum to geophysical scales
DNS STUDY OF TURBULENT HEAT TRANSFER IN A SPANWISE ROTATING SQUARE DUCT
 10 th International Symposium on Turbulence and Shear Flow Phenomena (TSFP10), Chicago, USA, July, 2017 DNS STUDY OF TURBULENT HEAT TRANSFER IN A SPANWISE ROTATING SQUARE DUCT Bing-Chen Wang Department
10 th International Symposium on Turbulence and Shear Flow Phenomena (TSFP10), Chicago, USA, July, 2017 DNS STUDY OF TURBULENT HEAT TRANSFER IN A SPANWISE ROTATING SQUARE DUCT Bing-Chen Wang Department
Turbulent Rankine Vortices
 Turbulent Rankine Vortices Roger Kingdon April 2008 Turbulent Rankine Vortices Overview of key results in the theory of turbulence Motivation for a fresh perspective on turbulence The Rankine vortex CFD
Turbulent Rankine Vortices Roger Kingdon April 2008 Turbulent Rankine Vortices Overview of key results in the theory of turbulence Motivation for a fresh perspective on turbulence The Rankine vortex CFD
Scale interactions and scaling laws in rotating flows at moderate Rossby numbers and large Reynolds numbers
 Scale interactions and scaling laws in rotating flows at moderate Rossby numbers and large Reynolds numbers P.D. Mininni NCAR, Boulder, Colorado, USA, and Departamento de Física, Facultad de Cs. Exactas
Scale interactions and scaling laws in rotating flows at moderate Rossby numbers and large Reynolds numbers P.D. Mininni NCAR, Boulder, Colorado, USA, and Departamento de Física, Facultad de Cs. Exactas
Rapid generation of angular momentum in bounded magnetized plasma
 Rapid generation of angular momentum in bounded magnetized plasma Wouter J.T. Bos, Salah Neffaa, Kai Schneider To cite this version: Wouter J.T. Bos, Salah Neffaa, Kai Schneider. Rapid generation of angular
Rapid generation of angular momentum in bounded magnetized plasma Wouter J.T. Bos, Salah Neffaa, Kai Schneider To cite this version: Wouter J.T. Bos, Salah Neffaa, Kai Schneider. Rapid generation of angular
The behaviour of high Reynolds flows in a driven cavity
 The behaviour of high Reynolds flows in a driven cavity Charles-Henri BRUNEAU and Mazen SAAD Mathématiques Appliquées de Bordeaux, Université Bordeaux 1 CNRS UMR 5466, INRIA team MC 351 cours de la Libération,
The behaviour of high Reynolds flows in a driven cavity Charles-Henri BRUNEAU and Mazen SAAD Mathématiques Appliquées de Bordeaux, Université Bordeaux 1 CNRS UMR 5466, INRIA team MC 351 cours de la Libération,
Eigenmode resonance in a two-layer stratification
 J. Fluid Mech. (2002), vol. 460, pp. 223 240. c 2002 Cambridge University Press DOI: 10.1017/S0022112002008182 Printed in the United Kingdom 223 Eigenmode resonance in a two-layer stratification By ISAO
J. Fluid Mech. (2002), vol. 460, pp. 223 240. c 2002 Cambridge University Press DOI: 10.1017/S0022112002008182 Printed in the United Kingdom 223 Eigenmode resonance in a two-layer stratification By ISAO
Extraction of coherent structures out of turbulent flows : comparison between real-valued and complex-valued wavelets
 Extraction of coherent structures out of turbulent flows : comparison between real-valued and complex-valued wavelets Romain Nguyen van Yen and Marie Farge, LMD-CNRS, ENS, Paris In collaboration with:
Extraction of coherent structures out of turbulent flows : comparison between real-valued and complex-valued wavelets Romain Nguyen van Yen and Marie Farge, LMD-CNRS, ENS, Paris In collaboration with:
Two-dimensional turbulence in square and circular domains with no-slip walls
 Eur. J. Mech. B - Fluids 20 (2001) 557 576 2001 Éditions scientifiques et médicales Elsevier SAS. All rights reserved S0997-7546(01)01130-X/FLA Two-dimensional turbulence in square and circular domains
Eur. J. Mech. B - Fluids 20 (2001) 557 576 2001 Éditions scientifiques et médicales Elsevier SAS. All rights reserved S0997-7546(01)01130-X/FLA Two-dimensional turbulence in square and circular domains
Slide of the Seminar
 Slide of the Seminar! Dynamics of the Vortex Lines Density in Superfluid Turbulence!! Prof. Anna Pomyalov ERC Advanced Grant (N. 339032) NewTURB (P.I. Prof. Luca Biferale)! Università degli Studi di Roma
Slide of the Seminar! Dynamics of the Vortex Lines Density in Superfluid Turbulence!! Prof. Anna Pomyalov ERC Advanced Grant (N. 339032) NewTURB (P.I. Prof. Luca Biferale)! Università degli Studi di Roma
The need for de-aliasing in a Chebyshev pseudo-spectral method
 The need for de-aliasing in a Chebyshev pseudo-spectral method Markus Uhlmann Potsdam Institut für Klimafolgenforschung, D-442 Potsdam uhlmann@pik-potsdam.de (March 2) Abstract In the present report, we
The need for de-aliasing in a Chebyshev pseudo-spectral method Markus Uhlmann Potsdam Institut für Klimafolgenforschung, D-442 Potsdam uhlmann@pik-potsdam.de (March 2) Abstract In the present report, we
Multiscale Computation of Isotropic Homogeneous Turbulent Flow
 Multiscale Computation of Isotropic Homogeneous Turbulent Flow Tom Hou, Danping Yang, and Hongyu Ran Abstract. In this article we perform a systematic multi-scale analysis and computation for incompressible
Multiscale Computation of Isotropic Homogeneous Turbulent Flow Tom Hou, Danping Yang, and Hongyu Ran Abstract. In this article we perform a systematic multi-scale analysis and computation for incompressible
1. Comparison of stability analysis to previous work
 . Comparison of stability analysis to previous work The stability problem (6.4) can be understood in the context of previous work. Benjamin (957) and Yih (963) have studied the stability of fluid flowing
. Comparison of stability analysis to previous work The stability problem (6.4) can be understood in the context of previous work. Benjamin (957) and Yih (963) have studied the stability of fluid flowing
Simulating Drag Crisis for a Sphere Using Skin Friction Boundary Conditions
 Simulating Drag Crisis for a Sphere Using Skin Friction Boundary Conditions Johan Hoffman May 14, 2006 Abstract In this paper we use a General Galerkin (G2) method to simulate drag crisis for a sphere,
Simulating Drag Crisis for a Sphere Using Skin Friction Boundary Conditions Johan Hoffman May 14, 2006 Abstract In this paper we use a General Galerkin (G2) method to simulate drag crisis for a sphere,
Tutorial School on Fluid Dynamics: Aspects of Turbulence Session I: Refresher Material Instructor: James Wallace
 Tutorial School on Fluid Dynamics: Aspects of Turbulence Session I: Refresher Material Instructor: James Wallace Adapted from Publisher: John S. Wiley & Sons 2002 Center for Scientific Computation and
Tutorial School on Fluid Dynamics: Aspects of Turbulence Session I: Refresher Material Instructor: James Wallace Adapted from Publisher: John S. Wiley & Sons 2002 Center for Scientific Computation and
Coherent structures in stably stratified plane Couette flow
 Coherent structures in stably stratified plane Couette flow D. Olvera * & R. R. Kerswell School of Mathematics, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK. * do2542@bristol.ac.uk Abstract A large body of recent
Coherent structures in stably stratified plane Couette flow D. Olvera * & R. R. Kerswell School of Mathematics, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK. * do2542@bristol.ac.uk Abstract A large body of recent
Utilising high-order direct numerical simulation for transient aeronautics problems
 Utilising high-order direct numerical simulation for transient aeronautics problems D. Moxey, J.-E. Lombard, J. Peiró, S. Sherwin Department of Aeronautics, Imperial College London! WCCM 2014, Barcelona,
Utilising high-order direct numerical simulation for transient aeronautics problems D. Moxey, J.-E. Lombard, J. Peiró, S. Sherwin Department of Aeronautics, Imperial College London! WCCM 2014, Barcelona,
TURBULENCE IN FLUIDS AND SPACE PLASMAS. Amitava Bhattacharjee Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, Princeton University
 TURBULENCE IN FLUIDS AND SPACE PLASMAS Amitava Bhattacharjee Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, Princeton University What is Turbulence? Webster s 1913 Dictionary: The quality or state of being turbulent;
TURBULENCE IN FLUIDS AND SPACE PLASMAS Amitava Bhattacharjee Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, Princeton University What is Turbulence? Webster s 1913 Dictionary: The quality or state of being turbulent;
Chapter 7 The Time-Dependent Navier-Stokes Equations Turbulent Flows
 Chapter 7 The Time-Dependent Navier-Stokes Equations Turbulent Flows Remark 7.1. Turbulent flows. The usually used model for turbulent incompressible flows are the incompressible Navier Stokes equations
Chapter 7 The Time-Dependent Navier-Stokes Equations Turbulent Flows Remark 7.1. Turbulent flows. The usually used model for turbulent incompressible flows are the incompressible Navier Stokes equations
RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION IN A CYLINDER WITH AN ASPECT RATIO OF 8
 HEFAT01 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 01 Malta RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION IN A CYLINDER WITH AN ASPECT RATIO OF 8 Leong S.S. School of Mechanical
HEFAT01 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 01 Malta RAYLEIGH-BÉNARD CONVECTION IN A CYLINDER WITH AN ASPECT RATIO OF 8 Leong S.S. School of Mechanical
Advective and Diffusive Turbulent Mixing
 Advective and Diffusive Turulent Mixing J. J. Monaghan School of Mathematical Sciences Monash University, Clayton Melourne, Australia joe.monaghan@monash.edu J. B. Kajtar School of Mathematical Sciences
Advective and Diffusive Turulent Mixing J. J. Monaghan School of Mathematical Sciences Monash University, Clayton Melourne, Australia joe.monaghan@monash.edu J. B. Kajtar School of Mathematical Sciences
Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics
 Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics CDS 140b Joris Vankerschaver jv@caltech.edu CDS 01/29/08, 01/31/08 Joris Vankerschaver (CDS) Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics 01/29/08, 01/31/08 1 / 34 Outline
Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics CDS 140b Joris Vankerschaver jv@caltech.edu CDS 01/29/08, 01/31/08 Joris Vankerschaver (CDS) Hamiltonian aspects of fluid dynamics 01/29/08, 01/31/08 1 / 34 Outline
Recent progress on the vanishing viscosity limit in the presence of a boundary
 Recent progress on the vanishing viscosity limit in the presence of a boundary JIM KELLIHER 1 1 University of California Riverside The 7th Pacific RIM Conference on Mathematics Seoul, South Korea 1 July
Recent progress on the vanishing viscosity limit in the presence of a boundary JIM KELLIHER 1 1 University of California Riverside The 7th Pacific RIM Conference on Mathematics Seoul, South Korea 1 July
MULTISCALE ANALYSIS IN LAGRANGIAN FORMULATION FOR THE 2-D INCOMPRESSIBLE EULER EQUATION. Thomas Y. Hou. Danping Yang. Hongyu Ran
 DISCRETE AND CONTINUOUS Website: http://aimsciences.org DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS Volume 13, Number 5, December 2005 pp. 1153 1186 MULTISCALE ANALYSIS IN LAGRANGIAN FORMULATION FOR THE 2-D INCOMPRESSIBLE EULER
DISCRETE AND CONTINUOUS Website: http://aimsciences.org DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS Volume 13, Number 5, December 2005 pp. 1153 1186 MULTISCALE ANALYSIS IN LAGRANGIAN FORMULATION FOR THE 2-D INCOMPRESSIBLE EULER
Feedback control of transient energy growth in subcritical plane Poiseuille flow
 Feedback control of transient energy growth in subcritical plane Poiseuille flow Fulvio Martinelli, Maurizio Quadrio, John McKernan and James F. Whidborne Abstract Subcritical flows may experience large
Feedback control of transient energy growth in subcritical plane Poiseuille flow Fulvio Martinelli, Maurizio Quadrio, John McKernan and James F. Whidborne Abstract Subcritical flows may experience large
Intermittency of quasi-static magnetohydrodynamic turbulence: A wavelet viewpoint
 Intermittency of quasi-static magnetohydrodynamic turbulence: A wavelet viewpoint Naoya Okamoto 1, Katsunori Yoshimatsu 2, Kai Schneider 3 and Marie Farge 4 1 Center for Computational Science, Nagoya University,
Intermittency of quasi-static magnetohydrodynamic turbulence: A wavelet viewpoint Naoya Okamoto 1, Katsunori Yoshimatsu 2, Kai Schneider 3 and Marie Farge 4 1 Center for Computational Science, Nagoya University,
BOUNDARY LAYER ANALYSIS WITH NAVIER-STOKES EQUATION IN 2D CHANNEL FLOW
 Proceedings of,, BOUNDARY LAYER ANALYSIS WITH NAVIER-STOKES EQUATION IN 2D CHANNEL FLOW Yunho Jang Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 01002 Email:
Proceedings of,, BOUNDARY LAYER ANALYSIS WITH NAVIER-STOKES EQUATION IN 2D CHANNEL FLOW Yunho Jang Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 01002 Email:
GFD 2012 Lecture 1: Dynamics of Coherent Structures and their Impact on Transport and Predictability
 GFD 2012 Lecture 1: Dynamics of Coherent Structures and their Impact on Transport and Predictability Jeffrey B. Weiss; notes by Duncan Hewitt and Pedram Hassanzadeh June 18, 2012 1 Introduction 1.1 What
GFD 2012 Lecture 1: Dynamics of Coherent Structures and their Impact on Transport and Predictability Jeffrey B. Weiss; notes by Duncan Hewitt and Pedram Hassanzadeh June 18, 2012 1 Introduction 1.1 What
INFLUENCE OF THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS ON A TEMPERATURE FIELD IN THE TURBULENT FLOW NEAR THE HEATED WALL
 International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe 22 Kranjska Gora, Slovenia, September 9-2, 22 www.drustvo-js.si/gora22 INFLUENCE OF THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS ON A TEMPERATURE FIELD IN THE TURBULENT
International Conference Nuclear Energy for New Europe 22 Kranjska Gora, Slovenia, September 9-2, 22 www.drustvo-js.si/gora22 INFLUENCE OF THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS ON A TEMPERATURE FIELD IN THE TURBULENT
Topics in Fluid Dynamics: Classical physics and recent mathematics
 Topics in Fluid Dynamics: Classical physics and recent mathematics Toan T. Nguyen 1,2 Penn State University Graduate Student Seminar @ PSU Jan 18th, 2018 1 Homepage: http://math.psu.edu/nguyen 2 Math blog:
Topics in Fluid Dynamics: Classical physics and recent mathematics Toan T. Nguyen 1,2 Penn State University Graduate Student Seminar @ PSU Jan 18th, 2018 1 Homepage: http://math.psu.edu/nguyen 2 Math blog:
Validation of an Entropy-Viscosity Model for Large Eddy Simulation
 Validation of an Entropy-Viscosity Model for Large Eddy Simulation J.-L. Guermond, A. Larios and T. Thompson 1 Introduction A primary mainstay of difficulty when working with problems of very high Reynolds
Validation of an Entropy-Viscosity Model for Large Eddy Simulation J.-L. Guermond, A. Larios and T. Thompson 1 Introduction A primary mainstay of difficulty when working with problems of very high Reynolds
Vortex statistics for turbulence in a container with rigid boundaries Clercx, H.J.H.; Nielsen, A.H.
 Vortex statistics for turbulence in a container with rigid boundaries Clercx, H.J.H.; Nielsen, A.H. Published in: Physical Review Letters DOI: 0.03/PhysRevLett.85.752 Published: 0/0/2000 Document Version
Vortex statistics for turbulence in a container with rigid boundaries Clercx, H.J.H.; Nielsen, A.H. Published in: Physical Review Letters DOI: 0.03/PhysRevLett.85.752 Published: 0/0/2000 Document Version
Lagrangian intermittency in drift-wave turbulence. Wouter Bos
 Lagrangian intermittency in drift-wave turbulence Wouter Bos LMFA, Ecole Centrale de Lyon, Turbulence & Stability Team Acknowledgments Benjamin Kadoch, Kai Schneider, Laurent Chevillard, Julian Scott,
Lagrangian intermittency in drift-wave turbulence Wouter Bos LMFA, Ecole Centrale de Lyon, Turbulence & Stability Team Acknowledgments Benjamin Kadoch, Kai Schneider, Laurent Chevillard, Julian Scott,
Point Vortex Dynamics in Two Dimensions
 Spring School on Fluid Mechanics and Geophysics of Environmental Hazards 9 April to May, 9 Point Vortex Dynamics in Two Dimensions Ruth Musgrave, Mostafa Moghaddami, Victor Avsarkisov, Ruoqian Wang, Wei
Spring School on Fluid Mechanics and Geophysics of Environmental Hazards 9 April to May, 9 Point Vortex Dynamics in Two Dimensions Ruth Musgrave, Mostafa Moghaddami, Victor Avsarkisov, Ruoqian Wang, Wei
Final abstract for ONERA Taylor-Green DG participation
 1st International Workshop On High-Order CFD Methods January 7-8, 2012 at the 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Nashville, Tennessee Final abstract for ONERA Taylor-Green DG participation JB Chapelier,
1st International Workshop On High-Order CFD Methods January 7-8, 2012 at the 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Nashville, Tennessee Final abstract for ONERA Taylor-Green DG participation JB Chapelier,
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow
 Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research
FOUR-WAY COUPLED SIMULATIONS OF TURBULENT
 FOUR-WAY COUPLED SIMULATIONS OF TURBULENT FLOWS WITH NON-SPHERICAL PARTICLES Berend van Wachem Thermofluids Division, Department of Mechanical Engineering Imperial College London Exhibition Road, London,
FOUR-WAY COUPLED SIMULATIONS OF TURBULENT FLOWS WITH NON-SPHERICAL PARTICLES Berend van Wachem Thermofluids Division, Department of Mechanical Engineering Imperial College London Exhibition Road, London,
Generation of magnetic fields by large-scale vortices in rotating convection
 Generation of magnetic fields by large-scale vortices in rotating convection Céline Guervilly, David Hughes & Chris Jones School of Mathematics, University of Leeds, UK Generation of the geomagnetic field
Generation of magnetic fields by large-scale vortices in rotating convection Céline Guervilly, David Hughes & Chris Jones School of Mathematics, University of Leeds, UK Generation of the geomagnetic field
Direct Numerical Simulations of converging-diverging channel flow
 Intro Numerical code Results Conclusion Direct Numerical Simulations of converging-diverging channel flow J.-P. Laval (1), M. Marquillie (1) Jean-Philippe.Laval@univ-lille1.fr (1) Laboratoire de Me canique
Intro Numerical code Results Conclusion Direct Numerical Simulations of converging-diverging channel flow J.-P. Laval (1), M. Marquillie (1) Jean-Philippe.Laval@univ-lille1.fr (1) Laboratoire de Me canique
AER1310: TURBULENCE MODELLING 1. Introduction to Turbulent Flows C. P. T. Groth c Oxford Dictionary: disturbance, commotion, varying irregularly
 1. Introduction to Turbulent Flows Coverage of this section: Definition of Turbulence Features of Turbulent Flows Numerical Modelling Challenges History of Turbulence Modelling 1 1.1 Definition of Turbulence
1. Introduction to Turbulent Flows Coverage of this section: Definition of Turbulence Features of Turbulent Flows Numerical Modelling Challenges History of Turbulence Modelling 1 1.1 Definition of Turbulence
CHAPTER 11: REYNOLDS-STRESS AND RELATED MODELS. Turbulent Flows. Stephen B. Pope Cambridge University Press, 2000 c Stephen B. Pope y + < 1.
 1/3 η 1C 2C, axi 1/6 2C y + < 1 axi, ξ > 0 y + 7 axi, ξ < 0 log-law region iso ξ -1/6 0 1/6 1/3 Figure 11.1: The Lumley triangle on the plane of the invariants ξ and η of the Reynolds-stress anisotropy
1/3 η 1C 2C, axi 1/6 2C y + < 1 axi, ξ > 0 y + 7 axi, ξ < 0 log-law region iso ξ -1/6 0 1/6 1/3 Figure 11.1: The Lumley triangle on the plane of the invariants ξ and η of the Reynolds-stress anisotropy
What is Turbulence? Fabian Waleffe. Depts of Mathematics and Engineering Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison
 What is Turbulence? Fabian Waleffe Depts of Mathematics and Engineering Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison it s all around,... and inside us! Leonardo da Vinci (c. 1500) River flow, pipe flow, flow
What is Turbulence? Fabian Waleffe Depts of Mathematics and Engineering Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison it s all around,... and inside us! Leonardo da Vinci (c. 1500) River flow, pipe flow, flow
Quantum fluids are compressible In any compressible vortex cores have low density. Example: Tornados
 KITP, Santa Barbara 15 February 2011 Vortex Stretching as a Mechanism for Quantum Kinetic Energy Decay Robert M. Kerr, Warwick University Left: Classical Euler, isosurfaces of high vorticity magnitude.
KITP, Santa Barbara 15 February 2011 Vortex Stretching as a Mechanism for Quantum Kinetic Energy Decay Robert M. Kerr, Warwick University Left: Classical Euler, isosurfaces of high vorticity magnitude.
On the decay of two-dimensional homogeneous turbulence
 On the decay of two-dimensional homogeneous turbulence J. R. Chasnov a) The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Clear Water Bay, Kowloon, Hong Kong Received 19 June 1996; accepted 3 September
On the decay of two-dimensional homogeneous turbulence J. R. Chasnov a) The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Clear Water Bay, Kowloon, Hong Kong Received 19 June 1996; accepted 3 September
 http://www.springer.com/3-540-30725-7 Erratum Spectral Methods Fundamentals in Single Domains C. Canuto M.Y. Hussaini A. Quarteroni T.A. Zang Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2006 Due to a technical error
http://www.springer.com/3-540-30725-7 Erratum Spectral Methods Fundamentals in Single Domains C. Canuto M.Y. Hussaini A. Quarteroni T.A. Zang Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2006 Due to a technical error
Modeling of turbulence in stirred vessels using large eddy simulation
 Modeling of turbulence in stirred vessels using large eddy simulation André Bakker (presenter), Kumar Dhanasekharan, Ahmad Haidari, and Sung-Eun Kim Fluent Inc. Presented at CHISA 2002 August 25-29, Prague,
Modeling of turbulence in stirred vessels using large eddy simulation André Bakker (presenter), Kumar Dhanasekharan, Ahmad Haidari, and Sung-Eun Kim Fluent Inc. Presented at CHISA 2002 August 25-29, Prague,
Engineering. Spring Department of Fluid Mechanics, Budapest University of Technology and Economics. Large-Eddy Simulation in Mechanical
 Outline Geurts Book Department of Fluid Mechanics, Budapest University of Technology and Economics Spring 2013 Outline Outline Geurts Book 1 Geurts Book Origin This lecture is strongly based on the book:
Outline Geurts Book Department of Fluid Mechanics, Budapest University of Technology and Economics Spring 2013 Outline Outline Geurts Book 1 Geurts Book Origin This lecture is strongly based on the book:
Navier-Stokes equations
 1 Navier-Stokes equations Introduction to spectral methods for the CSC Lunchbytes Seminar Series. Incompressible, hydrodynamic turbulence is described completely by the Navier-Stokes equations where t
1 Navier-Stokes equations Introduction to spectral methods for the CSC Lunchbytes Seminar Series. Incompressible, hydrodynamic turbulence is described completely by the Navier-Stokes equations where t
Computational Fluid Dynamics 2
 Seite 1 Introduction Computational Fluid Dynamics 11.07.2016 Computational Fluid Dynamics 2 Turbulence effects and Particle transport Martin Pietsch Computational Biomechanics Summer Term 2016 Seite 2
Seite 1 Introduction Computational Fluid Dynamics 11.07.2016 Computational Fluid Dynamics 2 Turbulence effects and Particle transport Martin Pietsch Computational Biomechanics Summer Term 2016 Seite 2
Turbulent drag reduction by streamwise traveling waves
 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control December 10-13, 2012. Maui, Hawaii, USA Turbulent drag reduction by streamwise traveling waves Armin Zare, Binh K. Lieu, and Mihailo R. Jovanović Abstract For
51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control December 10-13, 2012. Maui, Hawaii, USA Turbulent drag reduction by streamwise traveling waves Armin Zare, Binh K. Lieu, and Mihailo R. Jovanović Abstract For
The JHU Turbulence Databases (JHTDB)
 The JHU Turbulence Databases (JHTDB) TURBULENT CHANNEL FLOW AT Re τ = 5200 DATA SET Data provenance: M. Lee 1 & R. D. Moser 1 Database ingest and Web Services: Z. Wu 2, G. Lemson 2, R. Burns 2, A. Szalay
The JHU Turbulence Databases (JHTDB) TURBULENT CHANNEL FLOW AT Re τ = 5200 DATA SET Data provenance: M. Lee 1 & R. D. Moser 1 Database ingest and Web Services: Z. Wu 2, G. Lemson 2, R. Burns 2, A. Szalay
Barotropic geophysical flows and two-dimensional fluid flows: Conserved Quantities
 Barotropic geophysical flows and two-dimensional fluid flows: Conserved Quantities Di Qi, and Andrew J. Majda Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Fall 2016 Advanced Topics in Applied Math Di Qi,
Barotropic geophysical flows and two-dimensional fluid flows: Conserved Quantities Di Qi, and Andrew J. Majda Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences Fall 2016 Advanced Topics in Applied Math Di Qi,
4.2 Concepts of the Boundary Layer Theory
 Advanced Heat by Amir Faghri, Yuwen Zhang, and John R. Howell 4.2 Concepts of the Boundary Layer Theory It is difficult to solve the complete viscous flow fluid around a body unless the geometry is very
Advanced Heat by Amir Faghri, Yuwen Zhang, and John R. Howell 4.2 Concepts of the Boundary Layer Theory It is difficult to solve the complete viscous flow fluid around a body unless the geometry is very
Before we consider two canonical turbulent flows we need a general description of turbulence.
 Chapter 2 Canonical Turbulent Flows Before we consider two canonical turbulent flows we need a general description of turbulence. 2.1 A Brief Introduction to Turbulence One way of looking at turbulent
Chapter 2 Canonical Turbulent Flows Before we consider two canonical turbulent flows we need a general description of turbulence. 2.1 A Brief Introduction to Turbulence One way of looking at turbulent
Nonequilibrium Dynamics in Astrophysics and Material Science YITP, Kyoto
 Nonequilibrium Dynamics in Astrophysics and Material Science 2011-11-02 @ YITP, Kyoto Multi-scale coherent structures and their role in the Richardson cascade of turbulence Susumu Goto (Okayama Univ.)
Nonequilibrium Dynamics in Astrophysics and Material Science 2011-11-02 @ YITP, Kyoto Multi-scale coherent structures and their role in the Richardson cascade of turbulence Susumu Goto (Okayama Univ.)
Review of fluid dynamics
 Chapter 2 Review of fluid dynamics 2.1 Preliminaries ome basic concepts: A fluid is a substance that deforms continuously under stress. A Material olume is a tagged region that moves with the fluid. Hence
Chapter 2 Review of fluid dynamics 2.1 Preliminaries ome basic concepts: A fluid is a substance that deforms continuously under stress. A Material olume is a tagged region that moves with the fluid. Hence
Candidates must show on each answer book the type of calculator used. Log Tables, Statistical Tables and Graph Paper are available on request.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Spring Semester Examination 2004 FLUID DYNAMICS Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt Question 1 and FOUR other questions. Candidates must show on each answer book
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Spring Semester Examination 2004 FLUID DYNAMICS Time allowed: 3 hours Attempt Question 1 and FOUR other questions. Candidates must show on each answer book
Chuichi Arakawa Graduate School of Interdisciplinary Information Studies, the University of Tokyo. Chuichi Arakawa
 Direct Numerical Simulations of Fundamental Turbulent Flows with the Largest Grid Numbers in the World and its Application of Modeling for Engineering Turbulent Flows Project Representative Chuichi Arakawa
Direct Numerical Simulations of Fundamental Turbulent Flows with the Largest Grid Numbers in the World and its Application of Modeling for Engineering Turbulent Flows Project Representative Chuichi Arakawa
arxiv: v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 2 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 2 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [physics.plasm-ph] 2 Nov 2018](/thumbs/89/100391610.jpg) Coherent nonlinear oscillations in magnetohydrodynamic plasma at Alfvén resonance Rupak Mukherjee, Rajaraman Ganesh, and Abhijit Sen Institute for Plasma Research, HBNI, Bhat, Gandhinagar - 382428, India
Coherent nonlinear oscillations in magnetohydrodynamic plasma at Alfvén resonance Rupak Mukherjee, Rajaraman Ganesh, and Abhijit Sen Institute for Plasma Research, HBNI, Bhat, Gandhinagar - 382428, India
Vorticity and Dynamics
 Vorticity and Dynamics In Navier-Stokes equation Nonlinear term ω u the Lamb vector is related to the nonlinear term u 2 (u ) u = + ω u 2 Sort of Coriolis force in a rotation frame Viscous term ν u = ν
Vorticity and Dynamics In Navier-Stokes equation Nonlinear term ω u the Lamb vector is related to the nonlinear term u 2 (u ) u = + ω u 2 Sort of Coriolis force in a rotation frame Viscous term ν u = ν
Kinematic and dynamic pair collision statistics of sedimenting inertial particles relevant to warm rain initiation
 Kinematic and dynamic pair collision statistics of sedimenting inertial particles relevant to warm rain initiation Bogdan Rosa 1, Hossein Parishani 2, Orlando Ayala 2, Lian-Ping Wang 2 & Wojciech W. Grabowski
Kinematic and dynamic pair collision statistics of sedimenting inertial particles relevant to warm rain initiation Bogdan Rosa 1, Hossein Parishani 2, Orlando Ayala 2, Lian-Ping Wang 2 & Wojciech W. Grabowski
Fluid Dynamics Exercises and questions for the course
 Fluid Dynamics Exercises and questions for the course January 15, 2014 A two dimensional flow field characterised by the following velocity components in polar coordinates is called a free vortex: u r
Fluid Dynamics Exercises and questions for the course January 15, 2014 A two dimensional flow field characterised by the following velocity components in polar coordinates is called a free vortex: u r
Engineering. Spring Department of Fluid Mechanics, Budapest University of Technology and Economics. Large-Eddy Simulation in Mechanical
 Outline Department of Fluid Mechanics, Budapest University of Technology and Economics Spring 2011 Outline Outline Part I First Lecture Connection between time and ensemble average Ergodicity1 Ergodicity
Outline Department of Fluid Mechanics, Budapest University of Technology and Economics Spring 2011 Outline Outline Part I First Lecture Connection between time and ensemble average Ergodicity1 Ergodicity
Formation and Long Term Evolution of an Externally Driven Magnetic Island in Rotating Plasmas )
 Formation and Long Term Evolution of an Externally Driven Magnetic Island in Rotating Plasmas ) Yasutomo ISHII and Andrei SMOLYAKOV 1) Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Ibaraki 311-0102, Japan 1) University
Formation and Long Term Evolution of an Externally Driven Magnetic Island in Rotating Plasmas ) Yasutomo ISHII and Andrei SMOLYAKOV 1) Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Ibaraki 311-0102, Japan 1) University
On the limiting behaviour of regularizations of the Euler Equations with vortex sheet initial data
 On the limiting behaviour of regularizations of the Euler Equations with vortex sheet initial data Monika Nitsche Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of New Mexico Collaborators: Darryl
On the limiting behaviour of regularizations of the Euler Equations with vortex sheet initial data Monika Nitsche Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of New Mexico Collaborators: Darryl
Wavelet-based methods to analyse, compress and compute turbulent flows
 Wavelet-based methods to analyse, compress and compute turbulent flows Marie Farge Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique Ecole Normale Supérieure Paris Mathematics of Planet Earth Imperial College, London
Wavelet-based methods to analyse, compress and compute turbulent flows Marie Farge Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique Ecole Normale Supérieure Paris Mathematics of Planet Earth Imperial College, London
FLOW-NORDITA Spring School on Turbulent Boundary Layers1
 Jonathan F. Morrison, Ati Sharma Department of Aeronautics Imperial College, London & Beverley J. McKeon Graduate Aeronautical Laboratories, California Institute Technology FLOW-NORDITA Spring School on
Jonathan F. Morrison, Ati Sharma Department of Aeronautics Imperial College, London & Beverley J. McKeon Graduate Aeronautical Laboratories, California Institute Technology FLOW-NORDITA Spring School on
Thomas Pierro, Donald Slinn, Kraig Winters
 Thomas Pierro, Donald Slinn, Kraig Winters Department of Ocean Engineering, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, Florida Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington Supported
Thomas Pierro, Donald Slinn, Kraig Winters Department of Ocean Engineering, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, Florida Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington Supported
arxiv:comp-gas/ v1 28 Apr 1993
 Lattice Boltzmann Thermohydrodynamics arxiv:comp-gas/9304006v1 28 Apr 1993 F. J. Alexander, S. Chen and J. D. Sterling Center for Nonlinear Studies and Theoretical Division Los Alamos National Laboratory
Lattice Boltzmann Thermohydrodynamics arxiv:comp-gas/9304006v1 28 Apr 1993 F. J. Alexander, S. Chen and J. D. Sterling Center for Nonlinear Studies and Theoretical Division Los Alamos National Laboratory
Helically forced MHD flows in confined cylindrical geometries
 Helically forced MHD flows in confined cylindrical geometries Malcolm Roberts 1, Matthieu Leroy 1, Jorge Morales 2, Wouter Bos 2, Kai Schneider 1 1 M2P2, Aix-Marseille University, 38 Rue Frédéric Joliot-Curie
Helically forced MHD flows in confined cylindrical geometries Malcolm Roberts 1, Matthieu Leroy 1, Jorge Morales 2, Wouter Bos 2, Kai Schneider 1 1 M2P2, Aix-Marseille University, 38 Rue Frédéric Joliot-Curie
Multiscale Computation of Isotropic Homogeneous Turbulent Flow
 Multiscale Computation of Isotropic Homogeneous Turbulent Flow Tom Hou, Danping Yang, and Hongyu Ran Abstract. In this article we perform a systematic multi-scale analysis and computation for incompressible
Multiscale Computation of Isotropic Homogeneous Turbulent Flow Tom Hou, Danping Yang, and Hongyu Ran Abstract. In this article we perform a systematic multi-scale analysis and computation for incompressible
Shear Turbulence. Fabian Waleffe. Depts. of Mathematics and Engineering Physics. Wisconsin
 Shear Turbulence Fabian Waleffe Depts. of Mathematics and Engineering Physics, Madison University of Wisconsin Mini-Symposium on Subcritical Flow Instability for training of early stage researchers Mini-Symposium
Shear Turbulence Fabian Waleffe Depts. of Mathematics and Engineering Physics, Madison University of Wisconsin Mini-Symposium on Subcritical Flow Instability for training of early stage researchers Mini-Symposium
New variables in spherical geometry. David G. Dritschel. Mathematical Institute University of St Andrews.
 New variables in spherical geometry David G Dritschel Mathematical Institute University of St Andrews http://www-vortexmcsst-andacuk Collaborators: Ali Mohebalhojeh (Tehran St Andrews) Jemma Shipton &
New variables in spherical geometry David G Dritschel Mathematical Institute University of St Andrews http://www-vortexmcsst-andacuk Collaborators: Ali Mohebalhojeh (Tehran St Andrews) Jemma Shipton &
Lecture 3: The Navier-Stokes Equations: Topological aspects
 Lecture 3: The Navier-Stokes Equations: Topological aspects September 9, 2015 1 Goal Topology is the branch of math wich studies shape-changing objects; objects which can transform one into another without
Lecture 3: The Navier-Stokes Equations: Topological aspects September 9, 2015 1 Goal Topology is the branch of math wich studies shape-changing objects; objects which can transform one into another without
Interfacial waves in steady and oscillatory, two-layer Couette flows
 Interfacial waves in steady and oscillatory, two-layer Couette flows M. J. McCready Department of Chemical Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556 Page 1 Acknowledgments Students: M.
Interfacial waves in steady and oscillatory, two-layer Couette flows M. J. McCready Department of Chemical Engineering University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556 Page 1 Acknowledgments Students: M.
Turbulence Modeling I!
 Outline! Turbulence Modeling I! Grétar Tryggvason! Spring 2010! Why turbulence modeling! Reynolds Averaged Numerical Simulations! Zero and One equation models! Two equations models! Model predictions!
Outline! Turbulence Modeling I! Grétar Tryggvason! Spring 2010! Why turbulence modeling! Reynolds Averaged Numerical Simulations! Zero and One equation models! Two equations models! Model predictions!
arxiv:nlin/ v2 [nlin.cd] 29 Jul 2001
![arxiv:nlin/ v2 [nlin.cd] 29 Jul 2001 arxiv:nlin/ v2 [nlin.cd] 29 Jul 2001](/thumbs/75/71786800.jpg) Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 Derivative moments in stationary homogeneous shear turbulence arxiv:nlin/0105034v2 [nlin.cd] 29 Jul 2001 By JÖRG SCHUMACHER Department of Mechanical
Under consideration for publication in J. Fluid Mech. 1 Derivative moments in stationary homogeneous shear turbulence arxiv:nlin/0105034v2 [nlin.cd] 29 Jul 2001 By JÖRG SCHUMACHER Department of Mechanical
The Turbulent Rotational Phase Separator
 The Turbulent Rotational Phase Separator J.G.M. Kuerten and B.P.M. van Esch Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, The Netherlands j.g.m.kuerten@tue.nl Summary. The Rotational
The Turbulent Rotational Phase Separator J.G.M. Kuerten and B.P.M. van Esch Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, The Netherlands j.g.m.kuerten@tue.nl Summary. The Rotational
Regularity diagnostics applied to a turbulent boundary layer
 Center for Turbulence Research Proceedings of the Summer Program 208 247 Regularity diagnostics applied to a turbulent boundary layer By H. J. Bae, J. D. Gibbon, R. M. Kerr AND A. Lozano-Durán Regularity
Center for Turbulence Research Proceedings of the Summer Program 208 247 Regularity diagnostics applied to a turbulent boundary layer By H. J. Bae, J. D. Gibbon, R. M. Kerr AND A. Lozano-Durán Regularity
Vortical control of forced two-dimensional turbulence
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 25, 1511 (213) Vortical control of forced two-dimensional turbulence Jérôme Fontane, 1,2 David G. Dritschel, 1 and Richard K. Scott 1 1 School of Mathematics and Statistics, University
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 25, 1511 (213) Vortical control of forced two-dimensional turbulence Jérôme Fontane, 1,2 David G. Dritschel, 1 and Richard K. Scott 1 1 School of Mathematics and Statistics, University
α 2 )(k x ũ(t, η) + k z W (t, η)
 1 3D Poiseuille Flow Over the next two lectures we will be going over the stabilization of the 3-D Poiseuille flow. For those of you who havent had fluids, that means we have a channel of fluid that is
1 3D Poiseuille Flow Over the next two lectures we will be going over the stabilization of the 3-D Poiseuille flow. For those of you who havent had fluids, that means we have a channel of fluid that is
