A Thermodynamic Formulation of the STZ Theory of Deformation in Amorphous Solids
|
|
|
- Blanche Summers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Thermodynamic Formulation of the STZ Theory of Deformation in Amorphous Solids Michael L. Falk Johns Hopkins University James S. Langer UC Santa Barbara E. Bouchbinder Weizmann Institute
2 Thermodynamics and STZs Briefly review the shear transformation zone theory of amorphous plasticity. Apply the non-equilibrium thermodynamics framework just presented to an STZ system in order to Constrain the theory Relate the microscopic degrees of freedom the relevant "effective temperature" associated with these degrees of freedom See Falk, Langer, Annual Reviews of Condensed Matter Physics (in press) arxiv:
3 Micro-mechanical Observations 1 Simulation by T.K. Haxton and A.J. Liu, PRL 99, (2007) 3
4 Shear Transformation Zones Falk, Maloney, EPJB (2010) Falk, Langer, PRE (1998) Postulates: STZs have a particular orientation. They are susceptible to shear to the extent that the shear is along this direction. STZs are reversible until their environment rearranges. They behave as 2-state systems. STZs are transient. They can be created and destroyed by neighboring plastic activity. 4
5 Deformation by STZs Next consider the shear response by assuming plastic strain rate to be proportional to STZ Flips ɛ pl = v 0 [R(s)n R( s)n + ] Flip Rates Shear Stress Bulk Material
6 Deformation by STZs Plastic Strain Rate Proportional to Flips ɛ pl = v 0 [R(s)n R( s)n + ] Master Equation for Densities ṅ ± = R(±s) n R( s) n ± + Γ(s, n ± ) Rate of Mechanical Mixing [ neq ] 2 n ±
7 Re-expressing the Master Eq Plastic Strain Rate Proportional to Flips ɛ pl = v 0 [R(s)n R( s)n + ] Master Equation for Densities [ neq ] ṅ + = +R(s) n R( s) n + + Γ 2 n + [ neq ] ṅ = R(s) n + R( s) n + + Γ 2 n Λ = n + + n (N/V ) m = n + n n + + n In a full tensorial model Λ would be a scalar, but m would be a tensor mij that describes the second moment of the STZ orientational distribution. 7
8 Re-expressing the Master Eq Plastic Strain Rate Proportional to Flips ɛ pl = ɛ 0 ΛC(s)[T (s) m] Master Equation for Densities Λ =ṅ + +ṅ = Γ(s, Λ,m)[Λ eq Λ] need to come up with way to obtain Λeq and Γ original guess for Γ was ṁ =2C(s)[T (s) m] Γ(s, Λ,m) Λ eq Λ m s ɛ pl 8
9 Thermodynamics of a Deforming System Bouchbinder, Langer PRE, , (2009) Consider a thermally isolated system consisting of a deforming subsystem with energy UC and entropy SC in contact with a thermal reservoir of energy UR and entropy SR. Define And χ By 1st Law ( UC S C ) σ,{λ} θ ( ) UR S R U tot = U C (S C, s, {Λ})+U R (S R ) 2 Vs ɛ tot = {Λ} represents all the internal state variables needed to describe the subsystem. U tot thermal reservior sheared subsystem 9
10 The First Law of Thermodynamics 2 Vs ɛ tot = If 2 Vs= ( U C / ɛ el) cancel and we find U tot 2 Vs( ɛ el + ɛ pl ) = U tot = ( UC ɛ el ) ɛ el +... then elastic terms 2 Vs ɛ pl = χṡc + α ( UC ) Λ α S C Λα + θṡr 10
11 How to Apply the Second Law? Clausius-Duhem Inequality states Ṡ 0 Coleman-Noll (1963) Axiomatic approach takes the Clausius- Duhem statement to be the definition of entropy and temperature. We can apply this to a system with two temperatures. See Bouchbinder, Langer (2009) for details. 11
12 Enforcing the Second Law This leaves us with the requirement that the work done exceeds the amount of energy stored in internal degrees of freedom. W(s, {Λ}) 2 Vs ɛ pl α And the first law becomes ( UC χṡc = W(s, {Λ})+Q Λ α but this is simply energy conservation, and when we define the specific heat as Vc eff χ( S C / χ) the first law reduces to Vc eff χ = W(s, {Λ})+Q ) S C Λα 0 thermal reservior Q sheared subsystem 12
13 Constraining Λeq and Γ We can write down an expression for configurational entropy S C = NΛ NΛ ln Λ + NΛψ(m)+S 1 (U 1 ) and the configurational energy U C = NΛ e Z + U 1 (S 1 ) from these and the equations of motion we derive an expression for the rate of plastic work W(s, {Λ}) 2 Vs ɛ pl ( ) UC Λα 0 Λ α α S C 13
14 Constraining Λeq and Γ W V [ = 2Λ C(s)[T (s) m] sv 0 + χ ψ ] m [ e z + χ ln Λ χψ(m)+χm ψ ] m Λ We can assure the work is non-negative if each term is non-negative. ψ ΓχΛm ψ m 0 must be an even function peaked at 0 14
15 Constraining Λeq and Γ W V Basic Form: F Z Λ Λ [ = 2Λ C(s)[T (s) m] sv 0 + χ ψ ] m [ e z + χ ln Λ χψ(m)+χm ψ ] m ΓχΛm ψ m 0 The second term will be even if the term in brackets goes to zero at Λ =Λ eq implying Λ eq = ν(m) exp( e z /χ) ] ν(m) = exp [ ψ(m) m ψ m Λ 15
16 Constraining Λeq and Γ W V [ = 2Λ C(s)[T (s) m] sv 0 + χ ψ ] m [ e z + χ ln Λ χψ(m)+χm ψ ] m Λ Similarly the first term will be even if the unknown term goes to zero when ψ m = v 0 χ ξ(m) ΓχΛm ψ m 0 T (s) =m T [ξ(m)] = m 16
17 Athermal Limit We will discuss the theory in the athermal limit; when annealing (aging) is negligible on the time scale of the experiment. In this limit there is only one relevant physical rate, the rate of plastic dissipation, which must be positive definite. The heat flow out of the system must also be proportional to the rate of plastic work, and we can write an equation for the evolution of χ. If we also assume we are in the low strain rate limit, there must be a well defined lower bound for χss, more than likely this value χ0=kbtg. c eff χ W [1 χχ0 ] The rate of mixing must also be proportional to the rate of work per STZ W V = 2Λ C(s)[T (s) m]sv 0 = ΓΛv 0 s 0 17
18 STZ Equations of Motion ɛ pl = ɛ 0 ΛC(s)[sign(s) m] ( ṁ = 2C(s)[sign(s) m] 1 sm ) s 0 Λ = 2C(s) s [sign(s) m][λ e ψ(0) ez/χ ] s 0 χ = 2 s ] ɛ 0 ΛC(s)[sign(s) m] [1 χχ0 c eff 18
19 Yield in the "Athermal" Limit ɛ pl = ɛ 0 ν(0)e ez/χ C(s)[sign(s) m] ( ṁ = 2C(s)[sign(s) m] 1 sm ) s 0 m uncrossable dynamical boundary s0 s 19
20 Development of a Shear Band 10% 20% 50% 100% Y Shi, MB Katz, H Li, MLF, PRL, 98, (2007) 20
21 Relating χ to the microstructure Consider a linear relation between the χ parameter and the local internal energy C 1 χ = U U 0 ɛ pl = exp( e Z /χ) f(s) Is there an underlying scaling? ɛ pl (y) ɛ b ( ɛ pl ) (y) ln ɛ b = exp ( ez χ b = e Z χ 0 ( ɛ pl ) e Z χ(y) ) C 1 e Z U(y) U 0 21
22 Scaling verifies the hypothesis ε SL χ 0 k B T g Assuming,, e Z =1.9ε Y Shi, MB Katz, H Li, MLF, PRL, 98, (2007) 22
23 Numerical Results (M Lisa Manning and JS Langer, PRE, 76, (2007) These equations closely reproduce the details of the strain rate and structural profiles during band formation 23
24 Metallic Glass Deformation Lu, Ravichandran, Johnson, Acta Mat 51, 3429 (2003) M 24
25 Shear Induced Anisotropy in Granular Media (experiments by W. Losert and M. Toyia) Taylor-Couette cell 102mm inner cylinder 44mm gap 1mm beads or 2mm beads Inner cylinder rotated 4-8 mm/s Top surface monitored with high speed camera Torque measured at inner cylinder MLF, M. Toiya, W. Losert, arxiv: (2008) 25
26 Comparison to Granular Flow Data The blue dots represent experimental measurements of displacement at a specified radial position, plotted as a function of the inner cylinder displacement subsequent to shear reversal. 1mm beads The red lines are the STZ predictions. 2mm beads MLF, M. Toiya, W. Losert, arxiv: (2008) 26
27 STZ Comparison to Shear of a-si Amorphous Silicon forms 5- fold coordinated liquid-like regions that facilitate shear. Requires χ dynamics Demkowicz and Argon, PRB 72, (2005). Bouchbinder, Langer and Procaccia, PRE 75, (2007). 27
28 Summing Up We need constitutive theories of plastic response in order to predict mechanical response past the elastic regime. Shear Transformation Zone Theory is an attempt to build a thermodynamically based phenomenological theory with a connection to the microscopic physics of deformation. The theory exhibits the following behaviors that are seen in simualtion and experiment A range of behavior from perfectly plastic to shear softening Plastic hysteresis (Bauschinger effects) Existence of a dynamically emerging yield stress (transition from creep to superplastic flow nonlinear rheology) Diverging time scale for deformation near the yield stress Are STZ's ephemeral or persistent? How can we more precisely connect atomic scale to parameters? What is the physically correct form for R(s)? 28
Strain localization in a shear transformation zone model for amorphous solids
 Strain localization in a shear transformation zone model for amorphous solids M. L. Manning,* J. S. Langer, and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara, California
Strain localization in a shear transformation zone model for amorphous solids M. L. Manning,* J. S. Langer, and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara, California
Athermal shear-transformation-zone theory of amorphous plastic deformation. I. Basic principles
 Athermal shear-transformation-zone theory of amorphous plastic deformation. I. Basic principles Eran Bouchbinder, 1 J. S. Langer, 2 and Itamar Procaccia 1 1 Department of Chemical Physics, The Weizmann
Athermal shear-transformation-zone theory of amorphous plastic deformation. I. Basic principles Eran Bouchbinder, 1 J. S. Langer, 2 and Itamar Procaccia 1 1 Department of Chemical Physics, The Weizmann
Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of driven amorphous materials. II. Effective-temperature theory
 Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of driven amorphous materials. II. Effective-temperature theory Eran Bouchbinder Racah Institute of Physics, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem 91904, Israel J. S.
Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of driven amorphous materials. II. Effective-temperature theory Eran Bouchbinder Racah Institute of Physics, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem 91904, Israel J. S.
Rate dependent shear bands in a shear transformation zone model of amorphous solids
 Rate dependent shear bands in a shear transformation zone model of amorphous solids M. L. Manning, E. G. Daub, J. S. Langer, and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara,
Rate dependent shear bands in a shear transformation zone model of amorphous solids M. L. Manning, E. G. Daub, J. S. Langer, and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara,
UNIVERSITY of CALIFORNIA Santa Barbara. Effective temperature and strain localization in amorphous solids
 UNIVERSITY of CALIFORNIA Santa Barbara Effective temperature and strain localization in amorphous solids A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of
UNIVERSITY of CALIFORNIA Santa Barbara Effective temperature and strain localization in amorphous solids A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of
Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of driven amorphous materials. I. Internal degrees of freedom and volume deformation
 Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of drien amorphous materials. I. Internal degrees of freedom and olume deformation Eran Bouchbinder Racah Institute of Physics, Hebrew Uniersity of Jerusalem, Jerusalem 91904,
Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of drien amorphous materials. I. Internal degrees of freedom and olume deformation Eran Bouchbinder Racah Institute of Physics, Hebrew Uniersity of Jerusalem, Jerusalem 91904,
Micromechanics of granular materials: slow flows
 Micromechanics of granular materials: slow flows Niels P. Kruyt Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Twente, n.p.kruyt@utwente.nl www.ts.ctw.utwente.nl/kruyt/ 1 Applications of granular
Micromechanics of granular materials: slow flows Niels P. Kruyt Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Twente, n.p.kruyt@utwente.nl www.ts.ctw.utwente.nl/kruyt/ 1 Applications of granular
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 3 Dec 2007
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 3 Dec 2007 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 3 Dec 2007](/thumbs/91/105334321.jpg) Shear-transformation-zone theory of plastic deformation near the glass transition J. S. Langer Dept. of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA 93106-9530 (Dated: October 28, 2018) arxiv:0712.0399v1
Shear-transformation-zone theory of plastic deformation near the glass transition J. S. Langer Dept. of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA 93106-9530 (Dated: October 28, 2018) arxiv:0712.0399v1
Athermal, Quasi-static Deformation of Amorphous Materials
 Athermal, Quasi-static Deformation of Amorphous Materials Anaël Lemaître 1 and Craig Maloney 2 1 Institut Navier France 2 Department of Physics UC Santa Barbara Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 016001 (2004) Phys.
Athermal, Quasi-static Deformation of Amorphous Materials Anaël Lemaître 1 and Craig Maloney 2 1 Institut Navier France 2 Department of Physics UC Santa Barbara Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 016001 (2004) Phys.
The response of an idealized granular material to an incremental shear strain
 The response of an idealized granular material to an incremental shear strain Luigi La Ragione and Vanessa Magnanimo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Bari, Italy E-mail: l.laragione@poliba.it;
The response of an idealized granular material to an incremental shear strain Luigi La Ragione and Vanessa Magnanimo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Bari, Italy E-mail: l.laragione@poliba.it;
Simulation of Thermomechanical Couplings of Viscoelastic Materials
 Simulation of Thermomechanical Couplings of Viscoelastic Materials Frank Neff 1, Thomas Miquel 2, Michael Johlitz 1, Alexander Lion 1 1 Institute of Mechanics Faculty for Aerospace Engineering Universität
Simulation of Thermomechanical Couplings of Viscoelastic Materials Frank Neff 1, Thomas Miquel 2, Michael Johlitz 1, Alexander Lion 1 1 Institute of Mechanics Faculty for Aerospace Engineering Universität
Continuum Mechanics Fundamentals
 Continuum Mechanics Fundamentals James R. Rice, notes for ES 220, 12 November 2009; corrections 9 December 2009 Conserved Quantities Let a conseved quantity have amount F per unit volume. Examples are
Continuum Mechanics Fundamentals James R. Rice, notes for ES 220, 12 November 2009; corrections 9 December 2009 Conserved Quantities Let a conseved quantity have amount F per unit volume. Examples are
THE PHYSICS OF FOAM. Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics. July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter. 1.
 THE PHYSICS OF FOAM Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter 1. Introduction Formation Microscopics 2. Structure Experiment Simulation
THE PHYSICS OF FOAM Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics July 1-26, 2002: Physics of Soft Condensed Matter 1. Introduction Formation Microscopics 2. Structure Experiment Simulation
3. General properties of phase transitions and the Landau theory
 3. General properties of phase transitions and the Landau theory In this Section we review the general properties and the terminology used to characterise phase transitions, which you will have already
3. General properties of phase transitions and the Landau theory In this Section we review the general properties and the terminology used to characterise phase transitions, which you will have already
Flow of Glasses. Peter Schall University of Amsterdam
 Flow of Glasses Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Liquid or Solid? Liquid or Solid? Example: Pitch Solid! 1 day 1 year Menkind 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 10 10 12 10 14 sec Time scale Liquid!
Flow of Glasses Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Liquid or Solid? Liquid or Solid? Example: Pitch Solid! 1 day 1 year Menkind 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 10 10 12 10 14 sec Time scale Liquid!
Curriculum Vitae. Smarajit Karmakar. Educational Qualifications : Computational Skill : Personal Information : Contact Information :
 Curriculum Vitae Smarajit Karmakar Contact Information : Department of Chemical Physics The Weizmann Institute of Science Rehovot 76100 Israel E-mail :smarajit.karmakar@weizmann.ac.il Personal Information
Curriculum Vitae Smarajit Karmakar Contact Information : Department of Chemical Physics The Weizmann Institute of Science Rehovot 76100 Israel E-mail :smarajit.karmakar@weizmann.ac.il Personal Information
A Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Damage Model for Unsaturated Geomaterials
 A Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Damage Model for Unsaturated Geomaterials Chloé Arson ALERT PhD Prize PhD Advisor : Behrouz Gatmiri Paris-Est University, U.R. Navier, geotechnical group (CERMES) This research
A Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Damage Model for Unsaturated Geomaterials Chloé Arson ALERT PhD Prize PhD Advisor : Behrouz Gatmiri Paris-Est University, U.R. Navier, geotechnical group (CERMES) This research
Lecture 7: Rheology and milli microfluidic
 1 and milli microfluidic Introduction In this chapter, we come back to the notion of viscosity, introduced in its simplest form in the chapter 2. We saw that the deformation of a Newtonian fluid under
1 and milli microfluidic Introduction In this chapter, we come back to the notion of viscosity, introduced in its simplest form in the chapter 2. We saw that the deformation of a Newtonian fluid under
Dynamics of viscoplastic deformation in amorphous solids
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 57, NUMBER 6 JUNE 1998 Dynamics of viscoplastic deformation in amorphous solids M. L. Falk and J. S. Langer Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara, Santa
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 57, NUMBER 6 JUNE 1998 Dynamics of viscoplastic deformation in amorphous solids M. L. Falk and J. S. Langer Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara, Santa
Linearized Theory: Sound Waves
 Linearized Theory: Sound Waves In the linearized limit, Λ iα becomes δ iα, and the distinction between the reference and target spaces effectively vanishes. K ij (q): Rigidity matrix Note c L = c T in
Linearized Theory: Sound Waves In the linearized limit, Λ iα becomes δ iα, and the distinction between the reference and target spaces effectively vanishes. K ij (q): Rigidity matrix Note c L = c T in
Viscoelasticity. Basic Notions & Examples. Formalism for Linear Viscoelasticity. Simple Models & Mechanical Analogies. Non-linear behavior
 Viscoelasticity Basic Notions & Examples Formalism for Linear Viscoelasticity Simple Models & Mechanical Analogies Non-linear behavior Viscoelastic Behavior Generic Viscoelasticity: exhibition of both
Viscoelasticity Basic Notions & Examples Formalism for Linear Viscoelasticity Simple Models & Mechanical Analogies Non-linear behavior Viscoelastic Behavior Generic Viscoelasticity: exhibition of both
The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature. Nikolai V. Priezjev
 The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature Nikolai V. Priezjev 5 March, 2018 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering Wright State University Movies,
The yielding transition in periodically sheared binary glasses at finite temperature Nikolai V. Priezjev 5 March, 2018 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering Wright State University Movies,
Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, 1 M. Lisa Manning, 1,2 and Jean M.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, 1 M. Lisa Manning, 1,2 and Jean M.
Non-linear Wave Propagation and Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics - Part 3
 Non-linear Wave Propagation and Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics - Part 3 Tommaso Ruggeri Department of Mathematics and Research Center of Applied Mathematics University of Bologna January 21, 2017 ommaso
Non-linear Wave Propagation and Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics - Part 3 Tommaso Ruggeri Department of Mathematics and Research Center of Applied Mathematics University of Bologna January 21, 2017 ommaso
On pore fluid pressure and effective solid stress in the mixture theory of porous media
 On pore fluid pressure and effective solid stress in the mixture theory of porous media I-Shih Liu Abstract In this paper we briefly review a typical example of a mixture of elastic materials, in particular,
On pore fluid pressure and effective solid stress in the mixture theory of porous media I-Shih Liu Abstract In this paper we briefly review a typical example of a mixture of elastic materials, in particular,
The Large Amplitude Oscillatory Strain Response of Aqueous Foam: Strain Localization and Full Stress Fourier Spectrum
 The Large Amplitude Oscillatory Strain Response of Aqueous Foam: Strain Localization and Full Stress Fourier Spectrum By F. Rouyer, S. Cohen-Addad, R. Höhler, P. Sollich, and S.M. Fielding The European
The Large Amplitude Oscillatory Strain Response of Aqueous Foam: Strain Localization and Full Stress Fourier Spectrum By F. Rouyer, S. Cohen-Addad, R. Höhler, P. Sollich, and S.M. Fielding The European
Viscoelastic Structures Mechanics of Growth and Aging
 Viscoelastic Structures Mechanics of Growth and Aging Aleksey D. Drozdov Institute for Industrial Mathematics Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Be'ersheba, Israel ACADEMIC PRESS San Diego London Boston
Viscoelastic Structures Mechanics of Growth and Aging Aleksey D. Drozdov Institute for Industrial Mathematics Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Be'ersheba, Israel ACADEMIC PRESS San Diego London Boston
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29750 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Wortel, Geert Title: Granular flows : fluidization and anisotropy Issue Date: 2015-11-19
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29750 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Wortel, Geert Title: Granular flows : fluidization and anisotropy Issue Date: 2015-11-19
06 - kinematic equations kinematic equations
 06 - - 06-1 continuum mechancis continuum mechanics is a branch of physics (specifically mechanics) that deals with continuous matter. the fact that matter is made of atoms and that it commonly has some
06 - - 06-1 continuum mechancis continuum mechanics is a branch of physics (specifically mechanics) that deals with continuous matter. the fact that matter is made of atoms and that it commonly has some
Steady Flow and its Instability of Gravitational Granular Flow
 Steady Flow and its Instability of Gravitational Granular Flow Namiko Mitarai Department of Chemistry and Physics of Condensed Matter, Graduate School of Science, Kyushu University, Japan. A thesis submitted
Steady Flow and its Instability of Gravitational Granular Flow Namiko Mitarai Department of Chemistry and Physics of Condensed Matter, Graduate School of Science, Kyushu University, Japan. A thesis submitted
1 Nonlinear deformation
 NONLINEAR TRUSS 1 Nonlinear deformation When deformation and/or rotation of the truss are large, various strains and stresses can be defined and related by material laws. The material behavior can be expected
NONLINEAR TRUSS 1 Nonlinear deformation When deformation and/or rotation of the truss are large, various strains and stresses can be defined and related by material laws. The material behavior can be expected
VISCOELASTIC PROPERTIES OF POLYMERS
 VISCOELASTIC PROPERTIES OF POLYMERS John D. Ferry Professor of Chemistry University of Wisconsin THIRD EDITION JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore Contents 1. The Nature of
VISCOELASTIC PROPERTIES OF POLYMERS John D. Ferry Professor of Chemistry University of Wisconsin THIRD EDITION JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore Contents 1. The Nature of
Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions Why do we have to make the assumption that plane sections plane? How about bars with non-axis symmetric cross section? The formulae derived look very similar to beam and axial
Frequently Asked Questions Why do we have to make the assumption that plane sections plane? How about bars with non-axis symmetric cross section? The formulae derived look very similar to beam and axial
Continuum mechanics V. Constitutive equations. 1. Constitutive equation: definition and basic axioms
 Continuum mechanics office Math 0.107 ales.janka@unifr.ch http://perso.unifr.ch/ales.janka/mechanics Mars 16, 2011, Université de Fribourg 1. Constitutive equation: definition and basic axioms Constitutive
Continuum mechanics office Math 0.107 ales.janka@unifr.ch http://perso.unifr.ch/ales.janka/mechanics Mars 16, 2011, Université de Fribourg 1. Constitutive equation: definition and basic axioms Constitutive
A phenomenological model for shear-thickening in wormlike micelle solutions
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 5 December 999 Europhys. Lett., 8 (6), pp. 76-7 (999) A phenomenological model for shear-thickening in wormlike micelle solutions J. L. Goveas ( ) and D. J. Pine Department of Chemical
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 5 December 999 Europhys. Lett., 8 (6), pp. 76-7 (999) A phenomenological model for shear-thickening in wormlike micelle solutions J. L. Goveas ( ) and D. J. Pine Department of Chemical
Lecture #10: Anisotropic plasticity Crashworthiness Basics of shell elements
 Lecture #10: 151-0735: Dynamic behavior of materials and structures Anisotropic plasticity Crashworthiness Basics of shell elements by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering,
Lecture #10: 151-0735: Dynamic behavior of materials and structures Anisotropic plasticity Crashworthiness Basics of shell elements by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering,
Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5
 Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, attilio.frangi@polimi.it Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5 1 Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5 2 Outline
Non-Linear Finite Element Methods in Solid Mechanics Attilio Frangi, attilio.frangi@polimi.it Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5 1 Politecnico di Milano, February 17, 2017, Lesson 5 2 Outline
Statistical Mechanics of Jamming
 Statistical Mechanics of Jamming Lecture 1: Timescales and Lengthscales, jamming vs thermal critical points Lecture 2: Statistical ensembles: inherent structures and blocked states Lecture 3: Example of
Statistical Mechanics of Jamming Lecture 1: Timescales and Lengthscales, jamming vs thermal critical points Lecture 2: Statistical ensembles: inherent structures and blocked states Lecture 3: Example of
Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field. Lecture 6-5. Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field Lecture 6-5 Transducers with cylindrical Geometry For a cylinder of radius r centered inside a shell with with an inner radius
Transduction Based on Changes in the Energy Stored in an Electrical Field Lecture 6-5 Transducers with cylindrical Geometry For a cylinder of radius r centered inside a shell with with an inner radius
Phase Transitions. Phys112 (S2012) 8 Phase Transitions 1
 Phase Transitions cf. Kittel and Krömer chap 10 Landau Free Energy/Enthalpy Second order phase transition Ferromagnetism First order phase transition Van der Waals Clausius Clapeyron coexistence curve
Phase Transitions cf. Kittel and Krömer chap 10 Landau Free Energy/Enthalpy Second order phase transition Ferromagnetism First order phase transition Van der Waals Clausius Clapeyron coexistence curve
Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids
 Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids Jean-Louis Barrat Université de Lyon Institut Universitaire de France Acknowledgements: Anne Tanguy, Fabien Chay Goldenberg, Léonforte, Michel Tsamados
Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids Jean-Louis Barrat Université de Lyon Institut Universitaire de France Acknowledgements: Anne Tanguy, Fabien Chay Goldenberg, Léonforte, Michel Tsamados
A New Approach in Material Modeling Towards Shear Cutting of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics
 DOI: 1.24352/UB.OVGU-218-8 TECHNISCHE MECHANIK, 38, 1, (218), 91 96 submitted: July 31, 217 A New Approach in Material Modeling Towards Shear Cutting of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics L. Poggenpohl,
DOI: 1.24352/UB.OVGU-218-8 TECHNISCHE MECHANIK, 38, 1, (218), 91 96 submitted: July 31, 217 A New Approach in Material Modeling Towards Shear Cutting of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics L. Poggenpohl,
Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.9/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, M. Lisa Manning, and Jean M. Carlson Abstract.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.9/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, M. Lisa Manning, and Jean M. Carlson Abstract.
Supplementary Figure 1: Approach to the steady state. Energy vs. cycle for different
 ( = ) -6.9-6.94 (a) N = 8 < y.2 (T = 1).4 (T = 1).6 (T = 1).7 (T = 1) ( = ) -6.94 (b).8 (T = 1).9 (T = 1).12 (T = 1).14 (T = 1).8 (T =.466).9 (T =.466).12 (T =.466).14 (T =.466) > y n * 12 8 (c) N = 8
( = ) -6.9-6.94 (a) N = 8 < y.2 (T = 1).4 (T = 1).6 (T = 1).7 (T = 1) ( = ) -6.94 (b).8 (T = 1).9 (T = 1).12 (T = 1).14 (T = 1).8 (T =.466).9 (T =.466).12 (T =.466).14 (T =.466) > y n * 12 8 (c) N = 8
Second-gradient theory : application to Cahn-Hilliard fluids
 Second-gradient theory : application to Cahn-Hilliard fluids P. Seppecher Laboratoire d Analyse Non Linéaire Appliquée Université de Toulon et du Var BP 132-83957 La Garde Cedex seppecher@univ-tln.fr Abstract.
Second-gradient theory : application to Cahn-Hilliard fluids P. Seppecher Laboratoire d Analyse Non Linéaire Appliquée Université de Toulon et du Var BP 132-83957 La Garde Cedex seppecher@univ-tln.fr Abstract.
Analytical formulation of Modified Upper Bound theorem
 CHAPTER 3 Analytical formulation of Modified Upper Bound theorem 3.1 Introduction In the mathematical theory of elasticity, the principles of minimum potential energy and minimum complimentary energy are
CHAPTER 3 Analytical formulation of Modified Upper Bound theorem 3.1 Introduction In the mathematical theory of elasticity, the principles of minimum potential energy and minimum complimentary energy are
Elements of Continuum Elasticity. David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II February 25, 2004
 Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
A hierarchy of higher order and higher grade continua Application to the plasticity and fracture of metallic foams
 A hierarchy of higher order and higher grade continua Application to the plasticity and fracture of metallic foams Samuel Forest Centre des Matériaux/UMR 7633 Mines Paris ParisTech /CNRS BP 87, 91003 Evry,
A hierarchy of higher order and higher grade continua Application to the plasticity and fracture of metallic foams Samuel Forest Centre des Matériaux/UMR 7633 Mines Paris ParisTech /CNRS BP 87, 91003 Evry,
Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II. Peter Schall University of Amsterdam
 Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Flow of glasses 1st Lecture Glass Phenomenology Basic concepts: Free volume, Dynamic correlations Apply Shear Glass? Soft
Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Flow of glasses 1st Lecture Glass Phenomenology Basic concepts: Free volume, Dynamic correlations Apply Shear Glass? Soft
Nonlinear stability of steady flow of Giesekus viscoelastic fluid
 Nonlinear stability of steady flow of Giesekus viscoelastic fluid Mark Dostalík, V. Průša, K. Tůma August 9, 2018 Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University Table of contents 1. Introduction
Nonlinear stability of steady flow of Giesekus viscoelastic fluid Mark Dostalík, V. Průša, K. Tůma August 9, 2018 Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Charles University Table of contents 1. Introduction
Vortex lattice pinning in high-temperature superconductors.
 Vortex lattice ning in high-temperature superconductors. Victor Vakaryuk. Abstract. Vortex matter in high temperature superconductors has many peculiar properties such as melting of the vortex lattice,
Vortex lattice ning in high-temperature superconductors. Victor Vakaryuk. Abstract. Vortex matter in high temperature superconductors has many peculiar properties such as melting of the vortex lattice,
A review of Continuum Thermodynamics
 A review of Continuum Thermodynamics Amabile Tatone 1 1 Disim, University of L Aquila, Italy November 2017 Summary Thermodynamics of continua is not a simple subject. It deals with the interplay between
A review of Continuum Thermodynamics Amabile Tatone 1 1 Disim, University of L Aquila, Italy November 2017 Summary Thermodynamics of continua is not a simple subject. It deals with the interplay between
Small-Scale Effect on the Static Deflection of a Clamped Graphene Sheet
 Copyright 05 Tech Science Press CMC, vol.8, no., pp.03-7, 05 Small-Scale Effect on the Static Deflection of a Clamped Graphene Sheet G. Q. Xie, J. P. Wang, Q. L. Zhang Abstract: Small-scale effect on the
Copyright 05 Tech Science Press CMC, vol.8, no., pp.03-7, 05 Small-Scale Effect on the Static Deflection of a Clamped Graphene Sheet G. Q. Xie, J. P. Wang, Q. L. Zhang Abstract: Small-scale effect on the
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 1 June 2006 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 76 NONLINEAR CONTINUUM MECHANICS Attempt FOUR questions. There are SIX questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. STATIONERY
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 1 June 2006 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 76 NONLINEAR CONTINUUM MECHANICS Attempt FOUR questions. There are SIX questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. STATIONERY
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017
 Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Module-4. Mechanical Properties of Metals
 Module-4 Mechanical Properties of Metals Contents ) Elastic deformation and Plastic deformation ) Interpretation of tensile stress-strain curves 3) Yielding under multi-axial stress, Yield criteria, Macroscopic
Module-4 Mechanical Properties of Metals Contents ) Elastic deformation and Plastic deformation ) Interpretation of tensile stress-strain curves 3) Yielding under multi-axial stress, Yield criteria, Macroscopic
Lecture 5. Chapters 3 & 4. Induced magnetization: that which is induced in the presence of an applied magnetic field. diamagnetic.
 Lecture 5 Induced magnetization: that which is induced in the presence of an applied magnetic field diamagnetic paramagnetic Remanent magnetization: that which remains in the absence of an external field
Lecture 5 Induced magnetization: that which is induced in the presence of an applied magnetic field diamagnetic paramagnetic Remanent magnetization: that which remains in the absence of an external field
Pulse like, crack like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006388, 2010 Pulse like, crack like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G.
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006388, 2010 Pulse like, crack like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G.
For an imposed stress history consisting of a rapidly applied step-function jump in
 Problem 2 (20 points) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 0239 2.002 MECHANICS AND MATERIALS II SOLUTION for QUIZ NO. October 5, 2003 For
Problem 2 (20 points) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 0239 2.002 MECHANICS AND MATERIALS II SOLUTION for QUIZ NO. October 5, 2003 For
cooperative motion in sheared granular matter Takahiro Hatano
 cooperative motion in sheared granular matter Takahiro Hatano (Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo) amorphous particulate systems: structure? 2D granular matter close to jamming spontaneous
cooperative motion in sheared granular matter Takahiro Hatano (Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo) amorphous particulate systems: structure? 2D granular matter close to jamming spontaneous
Exploiting pattern transformation to tune phononic band gaps in a two-dimensional granular crystal
 Exploiting pattern transformation to tune phononic band gaps in a two-dimensional granular crystal The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
Exploiting pattern transformation to tune phononic band gaps in a two-dimensional granular crystal The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
PSEUDO ELASTIC ANALYSIS OF MATERIAL NON-LINEAR PROBLEMS USING ELEMENT FREE GALERKIN METHOD
 Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, Vol. 27, No. 4, pp. 505-516 (2004) 505 PSEUDO ELASTIC ANALYSIS OF MATERIAL NON-LINEAR PROBLEMS USING ELEMENT FREE GALERKIN METHOD Raju Sethuraman* and Cherku
Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, Vol. 27, No. 4, pp. 505-516 (2004) 505 PSEUDO ELASTIC ANALYSIS OF MATERIAL NON-LINEAR PROBLEMS USING ELEMENT FREE GALERKIN METHOD Raju Sethuraman* and Cherku
Chapter 4. Electrostatic Fields in Matter
 Chapter 4. Electrostatic Fields in Matter 4.1. Polarization 4.2. The Field of a Polarized Object 4.3. The Electric Displacement 4.4. Linear Dielectrics 4.5. Energy in dielectric systems 4.6. Forces on
Chapter 4. Electrostatic Fields in Matter 4.1. Polarization 4.2. The Field of a Polarized Object 4.3. The Electric Displacement 4.4. Linear Dielectrics 4.5. Energy in dielectric systems 4.6. Forces on
Reference material Reference books: Y.C. Fung, "Foundations of Solid Mechanics", Prentice Hall R. Hill, "The mathematical theory of plasticity",
 Reference material Reference books: Y.C. Fung, "Foundations of Solid Mechanics", Prentice Hall R. Hill, "The mathematical theory of plasticity", Oxford University Press, Oxford. J. Lubliner, "Plasticity
Reference material Reference books: Y.C. Fung, "Foundations of Solid Mechanics", Prentice Hall R. Hill, "The mathematical theory of plasticity", Oxford University Press, Oxford. J. Lubliner, "Plasticity
Rheology of Soft Materials. Rheology
 Τ Thomas G. Mason Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Department of Physics and Astronomy California NanoSystems Institute Τ γ 26 by Thomas G. Mason All rights reserved. γ (t) τ (t) γ τ Δt 2π t γ
Τ Thomas G. Mason Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Department of Physics and Astronomy California NanoSystems Institute Τ γ 26 by Thomas G. Mason All rights reserved. γ (t) τ (t) γ τ Δt 2π t γ
Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming
 Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Tom Haxton Yair Shokef Tal Danino Ian Ono Corey S. O Hern Douglas Durian
Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Tom Haxton Yair Shokef Tal Danino Ian Ono Corey S. O Hern Douglas Durian
A unified flow theory for viscous fluids
 Laboratoire Jacques-Louis Lions, Paris 27/10/2015 A unified flow theory for viscous fluids ILYA PESHKOV CHLOE, University of Pau, France joint work with EVGENIY ROMENSKI Sobolev Institute of Mathematics,
Laboratoire Jacques-Louis Lions, Paris 27/10/2015 A unified flow theory for viscous fluids ILYA PESHKOV CHLOE, University of Pau, France joint work with EVGENIY ROMENSKI Sobolev Institute of Mathematics,
Summer School: Granular Materials from Simulations to Astrophysical Applications
 Summer School: Granular Materials from Simulations to Astrophysical Applications Hosted by CSCAMM and the University of Maryland Burgers Program in Fluid Dynamics Organizers: Derek Richardson, Astronomy
Summer School: Granular Materials from Simulations to Astrophysical Applications Hosted by CSCAMM and the University of Maryland Burgers Program in Fluid Dynamics Organizers: Derek Richardson, Astronomy
Supplementary Figures
 Fracture Strength (GPa) Supplementary Figures a b 10 R=0.88 mm 1 0.1 Gordon et al Zhu et al Tang et al im et al 5 7 6 4 This work 5 50 500 Si Nanowire Diameter (nm) Supplementary Figure 1: (a) TEM image
Fracture Strength (GPa) Supplementary Figures a b 10 R=0.88 mm 1 0.1 Gordon et al Zhu et al Tang et al im et al 5 7 6 4 This work 5 50 500 Si Nanowire Diameter (nm) Supplementary Figure 1: (a) TEM image
Modeling the Dynamic Propagation of Shear Bands in Bulk Metallic Glasses
 Modeling the Dynamic Propagation of Shear Bands in Bulk Metallic Glasses B.J. Edwards, K. Feigl, M.L. Morrison*, B. Yang*, P.K. Liaw*, and R.A. Buchanan* Dept. of Chemical Engineering, The University of
Modeling the Dynamic Propagation of Shear Bands in Bulk Metallic Glasses B.J. Edwards, K. Feigl, M.L. Morrison*, B. Yang*, P.K. Liaw*, and R.A. Buchanan* Dept. of Chemical Engineering, The University of
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS ABSTRACT : P Mata1, AH Barbat1, S Oller1, R Boroschek2 1 Technical University of Catalonia, Civil Engineering
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS ABSTRACT : P Mata1, AH Barbat1, S Oller1, R Boroschek2 1 Technical University of Catalonia, Civil Engineering
4 Constitutive Theory
 ME338A CONTINUUM MECHANICS lecture notes 13 Tuesday, May 13, 2008 4.1 Closure Problem In the preceding chapter, we derived the fundamental balance equations: Balance of Spatial Material Mass ρ t + ρ t
ME338A CONTINUUM MECHANICS lecture notes 13 Tuesday, May 13, 2008 4.1 Closure Problem In the preceding chapter, we derived the fundamental balance equations: Balance of Spatial Material Mass ρ t + ρ t
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. EQUATIONS AND THEOREMS
 1 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. EQUATIONS AND THEOREMS Version 2011-01-14 Stress tensor Definition of traction vector (1) Cauchy theorem (2) Equilibrium (3) Invariants (4) (5) (6) or, written in terms of principal
1 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. EQUATIONS AND THEOREMS Version 2011-01-14 Stress tensor Definition of traction vector (1) Cauchy theorem (2) Equilibrium (3) Invariants (4) (5) (6) or, written in terms of principal
arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.soft] 6 Nov 2012
![arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.soft] 6 Nov 2012 arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.soft] 6 Nov 2012](/thumbs/72/66260233.jpg) Microscopic Mechanism of Shear Bands in Amorphous Solids Ratul Dasgupta, H. George E. Hentschel and Itamar Procaccia Department of Chemical Physics, The Weizmann Institute of Science (Dated: November 7,
Microscopic Mechanism of Shear Bands in Amorphous Solids Ratul Dasgupta, H. George E. Hentschel and Itamar Procaccia Department of Chemical Physics, The Weizmann Institute of Science (Dated: November 7,
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol 10(59), No Series III: Mathematics, Informatics, Physics, 49-58
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol 10(59), No. 2-2017 Series III: Mathematics, Informatics, Physics, 49-58 THERMOELASTICITY WITH FRACTIONAL ORDER STRAIN FOR DIPOLAR MATERIALS WITH VOIDS
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol 10(59), No. 2-2017 Series III: Mathematics, Informatics, Physics, 49-58 THERMOELASTICITY WITH FRACTIONAL ORDER STRAIN FOR DIPOLAR MATERIALS WITH VOIDS
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering
 Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
ELASTOPLASTICITY THEORY by V. A. Lubarda
 ELASTOPLASTICITY THEORY by V. A. Lubarda Contents Preface xiii Part 1. ELEMENTS OF CONTINUUM MECHANICS 1 Chapter 1. TENSOR PRELIMINARIES 3 1.1. Vectors 3 1.2. Second-Order Tensors 4 1.3. Eigenvalues and
ELASTOPLASTICITY THEORY by V. A. Lubarda Contents Preface xiii Part 1. ELEMENTS OF CONTINUUM MECHANICS 1 Chapter 1. TENSOR PRELIMINARIES 3 1.1. Vectors 3 1.2. Second-Order Tensors 4 1.3. Eigenvalues and
STRONG CONFIGURATIONAL DEPENDENCE OF ELASTIC PROPERTIES OF A CU-ZR BINARY MODEL METALLIC GLASS
 Chapter 3 STRONG CONFIGURATIONAL DEPENDENCE OF ELASTIC PROPERTIES OF A CU-ZR BINARY MODEL METALLIC GLASS We report the strong dependence of elastic properties on configurational changes in a Cu-Zr binary
Chapter 3 STRONG CONFIGURATIONAL DEPENDENCE OF ELASTIC PROPERTIES OF A CU-ZR BINARY MODEL METALLIC GLASS We report the strong dependence of elastic properties on configurational changes in a Cu-Zr binary
F7. Characteristic behavior of solids
 F7. Characteristic behavior of solids F7a: Deformation and failure phenomena: Elasticity, inelasticity, creep, fatigue. à Choice of constitutive model: Issues to be considered è Relevance? Physical effect
F7. Characteristic behavior of solids F7a: Deformation and failure phenomena: Elasticity, inelasticity, creep, fatigue. à Choice of constitutive model: Issues to be considered è Relevance? Physical effect
ENGN 2340 Final Project Report. Optimization of Mechanical Isotropy of Soft Network Material
 ENGN 2340 Final Project Report Optimization of Mechanical Isotropy of Soft Network Material Enrui Zhang 12/15/2017 1. Introduction of the Problem This project deals with the stress-strain response of a
ENGN 2340 Final Project Report Optimization of Mechanical Isotropy of Soft Network Material Enrui Zhang 12/15/2017 1. Introduction of the Problem This project deals with the stress-strain response of a
PDLAMMPS - made easy
 PDLAMMPS - made easy R. Rahman 1, J. T. Foster 1, and S. J. Plimpton 2 1 The University of Texas at San Antonio 2 Sandia National Laboratory February 12, 2014 1 Peridynamic theory of solids The peridynamic
PDLAMMPS - made easy R. Rahman 1, J. T. Foster 1, and S. J. Plimpton 2 1 The University of Texas at San Antonio 2 Sandia National Laboratory February 12, 2014 1 Peridynamic theory of solids The peridynamic
Level Set Tumor Growth Model
 Level Set Tumor Growth Model Andrew Nordquist and Rakesh Ranjan, PhD University of Texas, San Antonio July 29, 2013 Andrew Nordquist and Rakesh Ranjan, PhD (University Level Set of Texas, TumorSan Growth
Level Set Tumor Growth Model Andrew Nordquist and Rakesh Ranjan, PhD University of Texas, San Antonio July 29, 2013 Andrew Nordquist and Rakesh Ranjan, PhD (University Level Set of Texas, TumorSan Growth
Nonlinear elasticity and gels
 Nonlinear elasticity and gels M. Carme Calderer School of Mathematics University of Minnesota New Mexico Analysis Seminar New Mexico State University April 4-6, 2008 1 / 23 Outline Balance laws for gels
Nonlinear elasticity and gels M. Carme Calderer School of Mathematics University of Minnesota New Mexico Analysis Seminar New Mexico State University April 4-6, 2008 1 / 23 Outline Balance laws for gels
12. Stresses and Strains
 12. Stresses and Strains Finite Element Method Differential Equation Weak Formulation Approximating Functions Weighted Residuals FEM - Formulation Classification of Problems Scalar Vector 1-D T(x) u(x)
12. Stresses and Strains Finite Element Method Differential Equation Weak Formulation Approximating Functions Weighted Residuals FEM - Formulation Classification of Problems Scalar Vector 1-D T(x) u(x)
International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 58 No ,
 International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 58 No. 2 2010, 195-208 A NOTE ON THE LINEARIZED FINITE THEORY OF ELASTICITY Maria Luisa Tonon Department of Mathematics University of Turin
International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 58 No. 2 2010, 195-208 A NOTE ON THE LINEARIZED FINITE THEORY OF ELASTICITY Maria Luisa Tonon Department of Mathematics University of Turin
Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems
 Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems Dr. Guillaume Ducard Fall 2017 Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control ETH Zurich, Switzerland G. Ducard c 1 / 34 Outline 1 Lecture 7: Recall on Thermodynamics
Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems Dr. Guillaume Ducard Fall 2017 Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control ETH Zurich, Switzerland G. Ducard c 1 / 34 Outline 1 Lecture 7: Recall on Thermodynamics
Rock Rheology GEOL 5700 Physics and Chemistry of the Solid Earth
 Rock Rheology GEOL 5700 Physics and Chemistry of the Solid Earth References: Turcotte and Schubert, Geodynamics, Sections 2.1,-2.4, 2.7, 3.1-3.8, 6.1, 6.2, 6.8, 7.1-7.4. Jaeger and Cook, Fundamentals of
Rock Rheology GEOL 5700 Physics and Chemistry of the Solid Earth References: Turcotte and Schubert, Geodynamics, Sections 2.1,-2.4, 2.7, 3.1-3.8, 6.1, 6.2, 6.8, 7.1-7.4. Jaeger and Cook, Fundamentals of
1.050 Engineering Mechanics. Lecture 22: Isotropic elasticity
 1.050 Engineering Mechanics Lecture 22: Isotropic elasticity 1.050 Content overview I. Dimensional analysis 1. On monsters, mice and mushrooms 2. Similarity relations: Important engineering tools II. Stresses
1.050 Engineering Mechanics Lecture 22: Isotropic elasticity 1.050 Content overview I. Dimensional analysis 1. On monsters, mice and mushrooms 2. Similarity relations: Important engineering tools II. Stresses
(Super) Fluid Dynamics. Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University
 (Super) Fluid Dynamics Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University Hydrodynamics Hydrodynamics (undergraduate version): Newton s law for continuous, deformable media. Fluids: Gases, liquids, plasmas,...
(Super) Fluid Dynamics Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University Hydrodynamics Hydrodynamics (undergraduate version): Newton s law for continuous, deformable media. Fluids: Gases, liquids, plasmas,...
An anisotropic continuum damage model for concrete
 An anisotropic continuum damage model for concrete Saba Tahaei Yaghoubi 1, Juha Hartikainen 1, Kari Kolari 2, Reijo Kouhia 3 1 Aalto University, Department of Civil and Structural Engineering 2 VTT 3 Tampere
An anisotropic continuum damage model for concrete Saba Tahaei Yaghoubi 1, Juha Hartikainen 1, Kari Kolari 2, Reijo Kouhia 3 1 Aalto University, Department of Civil and Structural Engineering 2 VTT 3 Tampere
Unit M1.5 Statically Indeterminate Systems
 Unit M1.5 Statically Indeterminate Systems Readings: CDL 2.1, 2.3, 2.4, 2.7 16.001/002 -- Unified Engineering Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Massachusetts Institute of Technology LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Unit M1.5 Statically Indeterminate Systems Readings: CDL 2.1, 2.3, 2.4, 2.7 16.001/002 -- Unified Engineering Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Massachusetts Institute of Technology LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Micro-macro Modeling of Particle Crushing Based on Branch Lengths. Esmaeel Bakhtiary 1, and Chloé Arson 2
 Micro-macro Modeling of Particle Crushing Based on Branch Lengths Esmaeel Bakhtiary 1, and Chloé Arson 2 1 PhD Student, Geosystems Group, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Georgia Institute
Micro-macro Modeling of Particle Crushing Based on Branch Lengths Esmaeel Bakhtiary 1, and Chloé Arson 2 1 PhD Student, Geosystems Group, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Georgia Institute
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing.
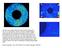 This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix. Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed
 Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONSHIPS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS In general, there are three types of relationships: Equilibrium
Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONSHIPS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS In general, there are three types of relationships: Equilibrium
Multi-mode revisited
 Multi-mode revisited Testing the application of shift factors S.J.M Hellenbrand 515217 MT 7.29 Coaches: Ir. L.C.A. van Breemen Dr. Ir. L.E. Govaert 2-7- 7 Contents Contents 1 Introduction 2 I Polymers
Multi-mode revisited Testing the application of shift factors S.J.M Hellenbrand 515217 MT 7.29 Coaches: Ir. L.C.A. van Breemen Dr. Ir. L.E. Govaert 2-7- 7 Contents Contents 1 Introduction 2 I Polymers
Dynamics of Supercooled Liquids The Generic Phase Diagram for Glasses
 Dynamics of Supercooled Liquids The Generic Phase Diagram for Glasses A normal liquid will crystallize at a melting temperature T m as it is cooled via a first-order phase transition (see figure above).
Dynamics of Supercooled Liquids The Generic Phase Diagram for Glasses A normal liquid will crystallize at a melting temperature T m as it is cooled via a first-order phase transition (see figure above).
Entropy current and equilibrium partition function in fluid dynam
 Entropy current and equilibrium partition function in fluid dynamics December 18, 2014 Aim of the talk In this talk we would analyse the relation between two apparently disjoint physical conditions that
Entropy current and equilibrium partition function in fluid dynamics December 18, 2014 Aim of the talk In this talk we would analyse the relation between two apparently disjoint physical conditions that
EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS FOR A THREE DIMENSIONAL MODEL OF FERROMAGNETISM
 1 EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS FOR A THREE DIMENSIONAL MODEL OF FERROMAGNETISM V. BERTI and M. FABRIZIO Dipartimento di Matematica, Università degli Studi di Bologna, P.zza di Porta S. Donato 5, I-4126, Bologna,
1 EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS FOR A THREE DIMENSIONAL MODEL OF FERROMAGNETISM V. BERTI and M. FABRIZIO Dipartimento di Matematica, Università degli Studi di Bologna, P.zza di Porta S. Donato 5, I-4126, Bologna,
Chapter 4. The Effect of Elastic Softening and Cooperativity on the Fragility of
 Chapter 4 The Effect of Elastic Softening and Cooperativity on the Fragility of Glass-Forming Metallic Liquids Key words: Amorphous metals, Shear transformation zones, Ultrasonic measurement, Compression
Chapter 4 The Effect of Elastic Softening and Cooperativity on the Fragility of Glass-Forming Metallic Liquids Key words: Amorphous metals, Shear transformation zones, Ultrasonic measurement, Compression
Inelastic constitutive equation of plasma-sprayed ceramic thermal barrier coatings
 Available online at www.amse.org.cn Acta Metall. Sin.(Engl. Lett.Vol.4 No. pp161-168 April 011 Inelastic constitutive equation of plasma-sprayed ceramic thermal barrier coatings Masayuki ARAI Materials
Available online at www.amse.org.cn Acta Metall. Sin.(Engl. Lett.Vol.4 No. pp161-168 April 011 Inelastic constitutive equation of plasma-sprayed ceramic thermal barrier coatings Masayuki ARAI Materials
