Relative Velocity. Exercise
|
|
|
- Collin Bennett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHYSICS 0 Lecture 06 Projectile Motion Tetbook Sections 4. Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 1 Relative Velocit We often assume that our reference frame is attached to the Earth. What happen when the reference frame is moving at a constant velocit with respect to the Earth? The motion can be eplained b including the relative velocit of the reference frame in the description of the motion. The ground velocit of an airplane is the vector sum of the air velocit and the wind velocit. Using the air as the intermediate reference frame, ground speed is: Eample airplane V(PG)=V(PA) +V(AG) Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 Eercise Three swimmers can swim equall fast relative to the water. The have a race to see who can swim across a river in the least time. Relative to the water, Beth (B) swims perpendicular to the flow, Ann (A) swims upstream, and Carl (C) swims downstream. Which swimmer wins the race? Eercise What angle should Ann take to get directl to the other side if she can swim 5 mph relative to the water, and the river is flowing at 3 mph? A) Ann B) Beth C) Carl correct V Ann,ground = V ann,water +V water,ground t = d / v Ann v = v cos() Beth v = v Carl v = v cos() A B C Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 3 -direction: sin() = V water,ground / V ann,water A B C sin() = 3/5 Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 4
2 X and Y are -Dimensions INDEPENDENT No component of one F or v on other The don t have to be vertical and horizontal just at right angles to each other Break -D problem into two 1-D problems Demo 1D-1 was done in L04 Velocit in Two Dimensions A ball is rolling on a horizontal surface at 5 m/s. It then rolls up a ramp at a 5 degree angle. After 0.5 seconds, the ball has slowed to 3 m/s. What is the magnitude of the change in velocit? -direction v i = 5 m/s v f = 3 m/s cos(5) "v = 3cos(5) 5 =-.8m/s v = v + v =.6 m/s 5 m/s -direction v i = 0 m/s v f = 3 m/s sin(5) "v = 3sin(5)=+1.7 m/s 3 m/s Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 5 Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 6 Acceleration in Two Dimensions A ball is rolling on a horizontal surface at 5 m/s. It then rolls up a ramp at a 5 degree angle. After 0.5 seconds, the ball has slowed to 3 m/s. What is the average acceleration? -direction a =.8m/s 0.5 s -direction = 4.56 m/s a = 1.7m/s 0.5 s =.54 m/s Kinematics in Two Dimensions = 0 + v 0 t + 1/ a t = 0 + v 0 t + 1/ a t v = v 0 + a t v = v 0 + a t v = v 0 + a " v = v 0 + a " a = a + a 5 m/s = 5.1 m/s 3 m/s and motions are independent The share a common time t Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 7 Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 8
3 Projectile Motion Velocit of a Projectile -direction: a = 0 -direction: a = -g = 0 + v 0 t v = v 0 = 0 + v 0 t - gt v = v 0 g t v = v 0 g " Velocit components of a projectile Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 9 Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 10 Independence of the Vertical and Horizontal motion of Projectiles A place-kicker kicks a football at an angle of =40 0 above the horizontal ais. The initial speed of the ball is v 0 = m/s. Ignore air resistance and find the range R that the ball attains. v 0 =m/s =40 0 H R Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 11 Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 1
4 Use the equations = 0 + v 0 t v = v 0 v 0 = v 0 cos = (m/s)cos 40 0 = 17 m/s = 0 + v 0 t - 1/ gt v = v 0 - gt v = v 0 - g " The range is a characteristic of the horizontal motion You need v 0 and v 0 but ou have been given v 0 v 0 v 0 v 0 Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 13 We could be done if we know the time of flight of the kickoff = R = v 0 t The time of flight can be determined from equations. For eample the time to get to height H is v 0 v 0 v = v 0 gt v 0 t h = v v 0 = 14m / s v 0 =v 0 sin = g 9.8m / s = 1.48s (m/s)sin 40 0 =14 m/s Therefore the time to determine the range is #.9 s = R = v 0 t = (17m / s)(.9s) = 49m The range depends on the angle at which the football is kicked. Maimum range is reached for =45 0 Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 14 Range of a Projectile Demo 1D- Two was to hit a target ecept at limit Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 15
5 Shooting the Monke You are a vet tring to shoot a tranquilizer dart into a monke hanging from a branch in a distant tree. You know that the monke is ver nervous, and will let go of the branch and start to fall as soon as our gun goes off. On the other hand, ou also know that the dart will not travel in a straight line, but rather in a parabolic path like an other projectile. In order to hit the monke with the dart, where should ou point the gun before shooting? A) Right at the monke B) Below the monke C) Above the monke Demo 1D-3 = v 0 t - 1 / g t Shooting the Monke = 0-1 / g t Dart hits the monke Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 17 Lecture 6 Purdue Universit, Phsics 0 18
Lecture 02: 2D Kinematics. Physics 2210 Fall Semester 2014
 Lecture 02: 2D Kinematics Physics 2210 Fall Semester 2014 Announcements Note that all Prelectures, Checkpoint Quizzes, and Homeworks are available one week before due date. You should have done Prelecture
Lecture 02: 2D Kinematics Physics 2210 Fall Semester 2014 Announcements Note that all Prelectures, Checkpoint Quizzes, and Homeworks are available one week before due date. You should have done Prelecture
1-D and 2-D Motion Test Friday 9/8
 1-D and -D Motion Test Frida 9/8 3-1 Vectors and Scalars A vector has magnitude as well as direction. Some vector quantities: displacement, velocit, force, momentum A scalar has onl a magnitude. Some scalar
1-D and -D Motion Test Frida 9/8 3-1 Vectors and Scalars A vector has magnitude as well as direction. Some vector quantities: displacement, velocit, force, momentum A scalar has onl a magnitude. Some scalar
Review! Kinematics: Free Fall, A Special Case. Review! A Few Facts About! Physics 101 Lecture 3 Kinematics: Vectors and Motion in 1 Dimension
 Phsics 101 Lecture 3 Kinematics: Vectors and Motion in 1 Dimension What concepts did ou find most difficult, or what would ou like to be sure we discuss in lecture? Acceleration vectors. Will ou go over
Phsics 101 Lecture 3 Kinematics: Vectors and Motion in 1 Dimension What concepts did ou find most difficult, or what would ou like to be sure we discuss in lecture? Acceleration vectors. Will ou go over
Bell Ringer. x- direction: Ball and car start with same position and velocity, a=0, so always have same position
 Objectives Students should be able to add, subtract, and resolve displacement and velocity vectors so they can: Determine the components of a vector along two specified, mutually perpendicular axes. Determine
Objectives Students should be able to add, subtract, and resolve displacement and velocity vectors so they can: Determine the components of a vector along two specified, mutually perpendicular axes. Determine
Phys 201, Lecture 5 Feb.2. Chapter 3: Mo;on in Two and Three Dimensions
 Phys 201, Lecture 5 Feb.2 Chapter 3: Mo;on in Two and Three Dimensions Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Displacement describes the location change of a particle Velocity is rate of change of displacement
Phys 201, Lecture 5 Feb.2 Chapter 3: Mo;on in Two and Three Dimensions Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Displacement describes the location change of a particle Velocity is rate of change of displacement
Classical Mechanics Lecture 2
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 2 Today's Concepts: a) Vectors b) Projec@le mo@on c) Reference frames Mechanics Lecture 2, Slide 1 Unit 6 Activity Guide Today Not everyone is doing the pre-lecture This is
Classical Mechanics Lecture 2 Today's Concepts: a) Vectors b) Projec@le mo@on c) Reference frames Mechanics Lecture 2, Slide 1 Unit 6 Activity Guide Today Not everyone is doing the pre-lecture This is
CHAPTER 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 HAPTER 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Solution Guide to WebAssign Problems 3.1 [] The truck has a displacement of 18 + (16) blocks north and 1 blocks east. The resultant has a magnitude of +
HAPTER 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Solution Guide to WebAssign Problems 3.1 [] The truck has a displacement of 18 + (16) blocks north and 1 blocks east. The resultant has a magnitude of +
Components of a Vector
 Vectors (Ch. 1) A vector is a quantity that has a magnitude and a direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, force, acceleration, momentum Examples of scalars: speed, temperature, mass, length, time.
Vectors (Ch. 1) A vector is a quantity that has a magnitude and a direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, force, acceleration, momentum Examples of scalars: speed, temperature, mass, length, time.
Classical Mechanics Lecture 2
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 2 Today's Concepts: a) Vectors b) Projec@le mo@on c) Reference frames Mechanics Lecture 2, Slide 1 Unit 6 Activity Guide Today Name Date (YY/MM/DD) / / SFU e-mail @sfu.ca Section
Classical Mechanics Lecture 2 Today's Concepts: a) Vectors b) Projec@le mo@on c) Reference frames Mechanics Lecture 2, Slide 1 Unit 6 Activity Guide Today Name Date (YY/MM/DD) / / SFU e-mail @sfu.ca Section
Solutions to Physics: Principles with Applications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 3 CHAPTER 3
 Solutions to Phsics: Principles with Applications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 3 CHAPTE 3 1. We choose the west and south coordinate sstem shown. For the components of the resultant we have W W = D 1 + D cos
Solutions to Phsics: Principles with Applications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 3 CHAPTE 3 1. We choose the west and south coordinate sstem shown. For the components of the resultant we have W W = D 1 + D cos
Announcements. Unit 1 homework due tomorrow 11:59 PM Quiz 1 on 3:00P Unit 1. Units 2 & 3 homework sets due 11:59 PM
 Announcements Unit 1 homework due tomorrow (Tuesday) @ 11:59 PM Quiz 1 on Wednesday @ 3:00P Unit 1 Ø First 12 minutes of class: be on time!!! Units 2 & 3 homework sets due Sunday @ 11:59 PM Ø Most homework
Announcements Unit 1 homework due tomorrow (Tuesday) @ 11:59 PM Quiz 1 on Wednesday @ 3:00P Unit 1 Ø First 12 minutes of class: be on time!!! Units 2 & 3 homework sets due Sunday @ 11:59 PM Ø Most homework
Welcome back to Physics 211
 Welcome back to Physics 211 The room is very full please move toward the center and help others find a seat. Be patient. The registration database is only updated twice per week. Get to know the people
Welcome back to Physics 211 The room is very full please move toward the center and help others find a seat. Be patient. The registration database is only updated twice per week. Get to know the people
Projectile Motion trajectory Projectile motion
 Projectile Motion The path that a moving object follows is called its trajectory. An object thrown horizontally is accelerated downward under the influence of gravity. Gravitational acceleration is only
Projectile Motion The path that a moving object follows is called its trajectory. An object thrown horizontally is accelerated downward under the influence of gravity. Gravitational acceleration is only
physics Chapter 4 Lecture a strategic approach randall d. knight FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS Chapter 4_Lecture1 THIRD EDITION
 Chapter 4 Lecture physics FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS a strategic approach THIRD EDITION randall d. knight Chapter 4_Lecture1 1 Chapter 4 Kinematics in 2D: Projectile Motion (Sec. 4.2) Which fountain
Chapter 4 Lecture physics FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS a strategic approach THIRD EDITION randall d. knight Chapter 4_Lecture1 1 Chapter 4 Kinematics in 2D: Projectile Motion (Sec. 4.2) Which fountain
3.4 Projectile Motion
 3.4 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion A projectile is anything launched, shot or thrown---i.e. not self-propelled. Examples: a golf ball as it flies through the air, a kicked soccer ball, a thrown football,
3.4 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion A projectile is anything launched, shot or thrown---i.e. not self-propelled. Examples: a golf ball as it flies through the air, a kicked soccer ball, a thrown football,
Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions
 Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions Textbook Sign-Out Put your name in it and let s go! Check-In Any questions from last day s homework? Vector Addition 1. Find the resultant displacement
Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions Textbook Sign-Out Put your name in it and let s go! Check-In Any questions from last day s homework? Vector Addition 1. Find the resultant displacement
Chapter 2. Kinematics in One Dimension. continued
 Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension continued 2.6 Freely Falling Bodies Example 10 A Falling Stone A stone is dropped from the top of a tall building. After 3.00s of free fall, what is the displacement
Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension continued 2.6 Freely Falling Bodies Example 10 A Falling Stone A stone is dropped from the top of a tall building. After 3.00s of free fall, what is the displacement
Chapter 4 MOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS
 Chapter 4 MTIN IN TW AND THREE DIMENSINS Section 4-5, 4-6 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion Analzed Important skills from this lecture: 1. Identif the projectile motion and its velocit and acceleration
Chapter 4 MTIN IN TW AND THREE DIMENSINS Section 4-5, 4-6 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion Analzed Important skills from this lecture: 1. Identif the projectile motion and its velocit and acceleration
PHYS-2010: General Physics I Course Lecture Notes Section IV
 PHYS-010: General Phsics I Course Lecture Notes Section IV Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State Universit Edition.3 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
PHYS-010: General Phsics I Course Lecture Notes Section IV Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State Universit Edition.3 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and students
Motion in Two and Three Dimensions
 chapter 4 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions Projectile motion (Section 4.3) 1. Which target got hit first? Contet of the tetbook: Before Eample 4. 2. Projectile range problem comparable to Eample 7, ecept
chapter 4 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions Projectile motion (Section 4.3) 1. Which target got hit first? Contet of the tetbook: Before Eample 4. 2. Projectile range problem comparable to Eample 7, ecept
Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16)
 Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16) 1. An object moves around a circular path of radius R. The object starts from point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle.
Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16) 1. An object moves around a circular path of radius R. The object starts from point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle.
When we throw a ball :
 PROJECTILE MOTION When we throw a ball : There is a constant velocity horizontal motion And there is an accelerated vertical motion These components act independently of each other PROJECTILE MOTION A
PROJECTILE MOTION When we throw a ball : There is a constant velocity horizontal motion And there is an accelerated vertical motion These components act independently of each other PROJECTILE MOTION A
PHY 1114: Physics I. Quick Question 1. Quick Question 2. Quick Question 3. Quick Question 4. Lecture 5: Motion in 2D
 PHY 1114: Physics I Lecture 5: Motion in D Fall 01 Kenny L. Tapp Quick Question 1 A child throws a ball vertically upward at the school playground. Which one of the following quantities is (are) equal
PHY 1114: Physics I Lecture 5: Motion in D Fall 01 Kenny L. Tapp Quick Question 1 A child throws a ball vertically upward at the school playground. Which one of the following quantities is (are) equal
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors & Scalars!! Scalars They are specified only by a number and units and have no direction associated with them, such as time, mass, and temperature.!! Vectors
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors & Scalars!! Scalars They are specified only by a number and units and have no direction associated with them, such as time, mass, and temperature.!! Vectors
Vector and Relative motion discussion/ in class notes. Projectile Motion discussion and launch angle problem. Finish 2 d motion and review for test
 AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
Problem: Projectile (CM-1998) Justify your answer: Problem: Projectile (CM-1998) 5 10 m/s 3. Show your work: 3 m/s 2
 Physics C -D Kinematics Name: AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors Specify
Physics C -D Kinematics Name: AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors Specify
10. The vectors are V 1 = 6.0i + 8.0j, V 2 = 4.5i 5.0j. (a) For the magnitude of V 1 we have 2 1x + V 1y2 ) 1/2 = [( 6.0) 2 + (8.0) 2 ] 1/2 = 10.0.
![10. The vectors are V 1 = 6.0i + 8.0j, V 2 = 4.5i 5.0j. (a) For the magnitude of V 1 we have 2 1x + V 1y2 ) 1/2 = [( 6.0) 2 + (8.0) 2 ] 1/2 = 10.0. 10. The vectors are V 1 = 6.0i + 8.0j, V 2 = 4.5i 5.0j. (a) For the magnitude of V 1 we have 2 1x + V 1y2 ) 1/2 = [( 6.0) 2 + (8.0) 2 ] 1/2 = 10.0.](/thumbs/72/66768579.jpg) 10. The vectors are V 1 = 6.0i + 8.0j, V 2 = 4.5i 5.0j. (a) For the magnitude of V 1 we have V 1 = (V 2 1x + V 1y2 ) 1/2 = [( 6.0) 2 + (8.0) 2 ] 1/2 = 10.0. We find the direction from tan θ 1 = V 1y /V
10. The vectors are V 1 = 6.0i + 8.0j, V 2 = 4.5i 5.0j. (a) For the magnitude of V 1 we have V 1 = (V 2 1x + V 1y2 ) 1/2 = [( 6.0) 2 + (8.0) 2 ] 1/2 = 10.0. We find the direction from tan θ 1 = V 1y /V
PHYS 1114, Lecture 10, February 8 Contents:
 PHYS 1114, Lecture 10, February 8 Contents: 1 Example of projectile motion: Man shooting a gun firing a bullet horizontally. 2 Example of projectile motion: Man shooting an arrow at a monkey in a tree.
PHYS 1114, Lecture 10, February 8 Contents: 1 Example of projectile motion: Man shooting a gun firing a bullet horizontally. 2 Example of projectile motion: Man shooting an arrow at a monkey in a tree.
Vectors. Graphical Method. Graphical Method. SEEMS SIMPLE? = 30.5 m/s. Graphical Method. Graphical Method (TIP TO TAIL) S
 Vectors Graphical Method General discussion. Vector - A quantity which has magnitude and direction. Velocity, acceleration, Force, E Field, Mag Field, calar - A quantity which has magnitude only. (temp,
Vectors Graphical Method General discussion. Vector - A quantity which has magnitude and direction. Velocity, acceleration, Force, E Field, Mag Field, calar - A quantity which has magnitude only. (temp,
Chapter 3. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Vectors. Section 2 Vector Operations. Section 3 Projectile Motion. Section 4 Relative Motion
 Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Section 1 Introduction to Vectors
Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Section 1 Introduction to Vectors
MOTION OF A PROJECTILE
 MOTION OF A PROJECTILE Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Analyze the free-flight motion of a projectile. In-Class Activities: Check Homework Reading Quiz Applications Kinematic Equations
MOTION OF A PROJECTILE Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Analyze the free-flight motion of a projectile. In-Class Activities: Check Homework Reading Quiz Applications Kinematic Equations
Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball.
 Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball. I-clicker question 3-1: A particle moves with the position-versus-time graph shown. Which graph best illustrates the velocity of the particle as a function
Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball. I-clicker question 3-1: A particle moves with the position-versus-time graph shown. Which graph best illustrates the velocity of the particle as a function
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS
 CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
Pearson Physics Level 20 Unit I Kinematics: Chapter 2 Solutions
 Pearson Phsics Leel 0 Unit I Kinematics: Chapter Solutions Student Book page 71 Skills Practice Students answers will ar but ma consist of: (a) scale 1 cm : 1 m; ector will be 5 cm long scale 1 m forward
Pearson Phsics Leel 0 Unit I Kinematics: Chapter Solutions Student Book page 71 Skills Practice Students answers will ar but ma consist of: (a) scale 1 cm : 1 m; ector will be 5 cm long scale 1 m forward
2 MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE
 MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE Download full Solution manual for Universit phsics with modern phsics 14t http://testbankcollection.com/download/solution-manual-for-universit-phsics-withmodern-phsics-14th.1.
MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE Download full Solution manual for Universit phsics with modern phsics 14t http://testbankcollection.com/download/solution-manual-for-universit-phsics-withmodern-phsics-14th.1.
Q3.1. A. 100 m B. 200 m C. 600 m D m E. zero. 500 m. 400 m. 300 m Pearson Education, Inc.
 Q3.1 P 400 m Q A bicyclist starts at point P and travels around a triangular path that takes her through points Q and R before returning to point P. What is the magnitude of her net displacement for the
Q3.1 P 400 m Q A bicyclist starts at point P and travels around a triangular path that takes her through points Q and R before returning to point P. What is the magnitude of her net displacement for the
AP* PHYSICS B DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS &VECTORS
 AP* PHYSICS B DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS &VECTORS The moment of truth has arrived! To discuss objects that move in something other than a straight line we need vectors. VECTORS Vectors
AP* PHYSICS B DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS &VECTORS The moment of truth has arrived! To discuss objects that move in something other than a straight line we need vectors. VECTORS Vectors
Honors Physics Acceleration and Projectile Review Guide
 Honors Physics Acceleration and Projectile Review Guide Major Concepts 1 D Motion on the horizontal 1 D motion on the vertical Relationship between velocity and acceleration Difference between constant
Honors Physics Acceleration and Projectile Review Guide Major Concepts 1 D Motion on the horizontal 1 D motion on the vertical Relationship between velocity and acceleration Difference between constant
Multiple-Choice Questions
 Multiple-Choice Questions 1. A rock is thrown straight up from the edge of a cliff. The rock reaches the maximum height of 15 m above the edge and then falls down to the bottom of the cliff 35 m below
Multiple-Choice Questions 1. A rock is thrown straight up from the edge of a cliff. The rock reaches the maximum height of 15 m above the edge and then falls down to the bottom of the cliff 35 m below
Problem: Projectile (CM-1998)
 Physics C -D Kinematics Name: ANSWER KEY AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors
Physics C -D Kinematics Name: ANSWER KEY AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Optional Problems for Quiz 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The components of vectors B and C are given as follows: 1) Bx
Optional Problems for Quiz 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The components of vectors B and C are given as follows: 1) Bx
PS 11 GeneralPhysics I for the Life Sciences
 PS 11 GeneralPhysics I for the Life Sciences M E C H A N I C S I D R. B E N J A M I N C H A N A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R P H Y S I C S D E P A R T M E N T N O V E M B E R 0 1 3 Definition Mechanics
PS 11 GeneralPhysics I for the Life Sciences M E C H A N I C S I D R. B E N J A M I N C H A N A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R P H Y S I C S D E P A R T M E N T N O V E M B E R 0 1 3 Definition Mechanics
Motion in Two or Three Dimensions
 Chapter 3 Motion in Two or Three Dimensions PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 3 To use vectors
Chapter 3 Motion in Two or Three Dimensions PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 3 To use vectors
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
3.2 Projectile Motion
 Motion in 2-D: Last class we were analyzing the distance in two-dimensional motion and revisited the concept of vectors, and unit-vector notation. We had our receiver run up the field then slant Northwest.
Motion in 2-D: Last class we were analyzing the distance in two-dimensional motion and revisited the concept of vectors, and unit-vector notation. We had our receiver run up the field then slant Northwest.
2-D Kinematics. In general, we have the following 8 equations (4 per dimension): Notes Page 1 of 7
 2-D Kinematics The problem we run into with 1-D kinematics, is that well it s one dimensional. We will now study kinematics in two dimensions. Obviously the real world happens in three dimensions, but
2-D Kinematics The problem we run into with 1-D kinematics, is that well it s one dimensional. We will now study kinematics in two dimensions. Obviously the real world happens in three dimensions, but
Methods of Integration
 U96-b)! Use the substitution u = - to evaluate U95-b)! 4 Methods of Integration d. Evaluate 9 d using the substitution u = + 9. UNIT MATHEMATICS (HSC) METHODS OF INTEGRATION CSSA «8» U94-b)! Use the substitution
U96-b)! Use the substitution u = - to evaluate U95-b)! 4 Methods of Integration d. Evaluate 9 d using the substitution u = + 9. UNIT MATHEMATICS (HSC) METHODS OF INTEGRATION CSSA «8» U94-b)! Use the substitution
Physics 11 Chapter 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions. Problem Solving
 Physics 11 Chapter 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions The only thing in life that is achieved without effort is failure. Source unknown "We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence, therefore, is not an act,
Physics 11 Chapter 3: Kinematics in Two Dimensions The only thing in life that is achieved without effort is failure. Source unknown "We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence, therefore, is not an act,
Projectile Motion. v = v 2 + ( v 1 )
 What do the following situations have in common? Projectile Motion A monkey jumps from the branch of one tree to the branch of an adjacent tree. A snowboarder glides at top speed off the end of a ramp
What do the following situations have in common? Projectile Motion A monkey jumps from the branch of one tree to the branch of an adjacent tree. A snowboarder glides at top speed off the end of a ramp
Projectile Motion. Chin- Sung Lin STEM GARAGE SCIENCE PHYSICS
 Projectile Motion Chin- Sung Lin Introduction to Projectile Motion q What is Projectile Motion? q Trajectory of a Projectile q Calculation of Projectile Motion Introduction to Projectile Motion q What
Projectile Motion Chin- Sung Lin Introduction to Projectile Motion q What is Projectile Motion? q Trajectory of a Projectile q Calculation of Projectile Motion Introduction to Projectile Motion q What
INTRODUCTION. 3. Two-Dimensional Kinematics
 INTRODUCTION We now extend our study of kinematics to motion in two dimensions (x and y axes) This will help in the study of such phenomena as projectile motion Projectile motion is the study of objects
INTRODUCTION We now extend our study of kinematics to motion in two dimensions (x and y axes) This will help in the study of such phenomena as projectile motion Projectile motion is the study of objects
Physics 10. Lecture 4A. "It is good to have an end to journey towards, but it is the journey that matters in the end." -- Ursula K.
 Physics 10 Lecture 4A "It is good to have an end to journey towards, but it is the journey that matters in the end." -- Ursula K. LeGuin Mass and Weight Mass is a measure of how much inertia an object.
Physics 10 Lecture 4A "It is good to have an end to journey towards, but it is the journey that matters in the end." -- Ursula K. LeGuin Mass and Weight Mass is a measure of how much inertia an object.
Vocabulary Preview. Oct 21 9:53 AM. Projectile Motion. An object shot through the air is called a projectile.
 Projectile Trajectory Range Launch angle Vocabulary Preview Projectile Motion Projectile Motion An object shot through the air is called a projectile. A projectile can be a football, a bullet, or a drop
Projectile Trajectory Range Launch angle Vocabulary Preview Projectile Motion Projectile Motion An object shot through the air is called a projectile. A projectile can be a football, a bullet, or a drop
Linear and Non Linear Motion. Reading: Supplemental Textbook Materials, pages
 Linear and Non Linear Motion Reading: Supplemental Textbook Materials, pages 73-87 Acceleration Rate of increase of a rate d/t t Increases rate for each increment in time that has passed So there is an
Linear and Non Linear Motion Reading: Supplemental Textbook Materials, pages 73-87 Acceleration Rate of increase of a rate d/t t Increases rate for each increment in time that has passed So there is an
Physics 207, Lecture 4, Sept. 15
 Phsics 07, Lecture 4, Sept. 15 Goals for hapts.. 3 & 4 Perform vector algebra (addition & subtraction) graphicall or b, & z components Interconvert between artesian and Polar coordinates Distinguish position-time
Phsics 07, Lecture 4, Sept. 15 Goals for hapts.. 3 & 4 Perform vector algebra (addition & subtraction) graphicall or b, & z components Interconvert between artesian and Polar coordinates Distinguish position-time
Chapter 3. Kinematics in Two Dimensions
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions 3.1 Trigonometry 3.1 Trigonometry sin! = h o h cos! = h a h tan! = h o h a 3.1 Trigonometry tan! = h o h a tan50! = h o 67.2m h o = tan50! ( 67.2m) = 80.0m 3.1 Trigonometry!
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions 3.1 Trigonometry 3.1 Trigonometry sin! = h o h cos! = h a h tan! = h o h a 3.1 Trigonometry tan! = h o h a tan50! = h o 67.2m h o = tan50! ( 67.2m) = 80.0m 3.1 Trigonometry!
Exam 1 Practice SOLUTIONS Physics 111Q.B
 Exam 1 Practice SOLUTIONS Physics 111Q.B Instructions This is a collection of practice problems for the first exam. The first exam will consist of 7-10 multiple choice questions followed by 1-3 problems
Exam 1 Practice SOLUTIONS Physics 111Q.B Instructions This is a collection of practice problems for the first exam. The first exam will consist of 7-10 multiple choice questions followed by 1-3 problems
New Course Webpage (To be setup by this weekend) h>p://people.physics.tamu.edu/tyana/phys218/
 Important Informa+on Instructor: Dr. Ty S(egler Office: ENPH 211 (Office Hours TBD) Email: tyana@physics.tamu.edu New Course Webpage (To be setup by this weekend) h>p://people.physics.tamu.edu/tyana/phys218/
Important Informa+on Instructor: Dr. Ty S(egler Office: ENPH 211 (Office Hours TBD) Email: tyana@physics.tamu.edu New Course Webpage (To be setup by this weekend) h>p://people.physics.tamu.edu/tyana/phys218/
2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics. f i i
 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = v + at f i 1 r = r + v t+ at f i i 2 2 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = viˆ+ v ˆj f x y = ( v + ati ) ˆ+ ( v +
2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = v + at f i 1 r = r + v t+ at f i i 2 2 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = viˆ+ v ˆj f x y = ( v + ati ) ˆ+ ( v +
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I
 PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 4 Main points of last lecture Scalars vs. Vectors Vectors A: (A x, A y ) or A & θ Addition/Subtraction Projectile Motion X-direction: a x = 0 (v x = constant)
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 4 Main points of last lecture Scalars vs. Vectors Vectors A: (A x, A y ) or A & θ Addition/Subtraction Projectile Motion X-direction: a x = 0 (v x = constant)
Bell Ringer: What is constant acceleration? What is projectile motion?
 Bell Ringer: What is constant acceleration? What is projectile motion? Can we analyze the motion of an object on the y-axis independently of the object s motion on the x-axis? NOTES 3.2: 2D Motion: Projectile
Bell Ringer: What is constant acceleration? What is projectile motion? Can we analyze the motion of an object on the y-axis independently of the object s motion on the x-axis? NOTES 3.2: 2D Motion: Projectile
Exam. Name. 1) For general projectile motion with no air resistance, the horizontal component of a projectile's velocity A) B) C) D)
 Exam Name 1) For general projectile motion with no air resistance, the horizontal component of a projectile's velocity 2) An athlete participates in an interplanetary discus throw competition during an
Exam Name 1) For general projectile motion with no air resistance, the horizontal component of a projectile's velocity 2) An athlete participates in an interplanetary discus throw competition during an
For use only in [the name of your school] 2014 M2 Note. M2 Notes (Edexcel)
![For use only in [the name of your school] 2014 M2 Note. M2 Notes (Edexcel) For use only in [the name of your school] 2014 M2 Note. M2 Notes (Edexcel)](/thumbs/74/69628193.jpg) For use onl in [the name of our school] 014 M Note M Notes (Edecel) Copright www.pgmaths.co.uk - For AS, A notes and IGCSE / GCSE worksheets 1 For use onl in [the name of our school] 014 M Note Copright
For use onl in [the name of our school] 014 M Note M Notes (Edecel) Copright www.pgmaths.co.uk - For AS, A notes and IGCSE / GCSE worksheets 1 For use onl in [the name of our school] 014 M Note Copright
Kinematics and Dynamics
 AP PHYS 1 Test Review Kinematics and Dynamics Name: Other Useful Site: http://www.aplusphysics.com/ap1/ap1- supp.html 2015-16 AP Physics: Kinematics Study Guide The study guide will help you review all
AP PHYS 1 Test Review Kinematics and Dynamics Name: Other Useful Site: http://www.aplusphysics.com/ap1/ap1- supp.html 2015-16 AP Physics: Kinematics Study Guide The study guide will help you review all
Trigonometry Basics. Which side is opposite? It depends on the angle. θ 2. Y is opposite to θ 1 ; Y is adjacent to θ 2.
 Trigonometry Basics Basic Terms θ (theta) variable for any angle. Hypotenuse longest side of a triangle. Opposite side opposite the angle (θ). Adjacent side next to the angle (θ). Which side is opposite?
Trigonometry Basics Basic Terms θ (theta) variable for any angle. Hypotenuse longest side of a triangle. Opposite side opposite the angle (θ). Adjacent side next to the angle (θ). Which side is opposite?
Section 2-2: Constant velocity means moving at a steady speed in the same direction
 Section 2-2: Constant velocity means moving at a steady speed in the same direction 1. A particle moves from x 1 = 30 cm to x 2 = 40 cm. The displacement of this particle is A. 30 cm B. 40 cm C. 70 cm
Section 2-2: Constant velocity means moving at a steady speed in the same direction 1. A particle moves from x 1 = 30 cm to x 2 = 40 cm. The displacement of this particle is A. 30 cm B. 40 cm C. 70 cm
GALILEAN RELATIVITY. Projectile motion. The Principle of Relativity
 GALILEAN RELATIVITY Projectile motion The Principle of Relativity When we think of the term relativity, the person who comes immediately to mind is of course Einstein. Galileo actually understood what
GALILEAN RELATIVITY Projectile motion The Principle of Relativity When we think of the term relativity, the person who comes immediately to mind is of course Einstein. Galileo actually understood what
Welcome back to PHY101: Major Concepts in Physics I. Photo: J. M. Schwarz
 Welcome back to PHY101: Major Concepts in Phsics I Photo: J. M. Schwarz Announcements Course Website: jmschwarztheorgroup.org/ph101/ HW on Chapter is due at the beginning of lecture on Wednesda. HW 3 on
Welcome back to PHY101: Major Concepts in Phsics I Photo: J. M. Schwarz Announcements Course Website: jmschwarztheorgroup.org/ph101/ HW on Chapter is due at the beginning of lecture on Wednesda. HW 3 on
13.1. For further details concerning the physics involved and animations of the trajectories of the particles, see the following websites:
 8 CHAPTER VECTOR FUNCTIONS N Some computer algebra sstems provide us with a clearer picture of a space curve b enclosing it in a tube. Such a plot enables us to see whether one part of a curve passes in
8 CHAPTER VECTOR FUNCTIONS N Some computer algebra sstems provide us with a clearer picture of a space curve b enclosing it in a tube. Such a plot enables us to see whether one part of a curve passes in
UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion
 IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
Two-Dimensional and Projectile Motion
 Two-Dimensional and Projectile Motion James H Dann, Ph.D. James Dann, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this
Two-Dimensional and Projectile Motion James H Dann, Ph.D. James Dann, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this
Two Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems
 Two Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems Problem 1: Suppose a MIT student wants to row across the Charles River. Suppose the water is moving downstream at a constant rate of 1.0 m/s. A second boat
Two Dimensional Kinematics Challenge Problems Problem 1: Suppose a MIT student wants to row across the Charles River. Suppose the water is moving downstream at a constant rate of 1.0 m/s. A second boat
Introduction to 2-Dimensional Motion
 Introduction to 2-Dimensional Motion 2-Dimensional Motion! Definition: motion that occurs with both x and y components.! Example:! Playing pool.! Throwing a ball to another person.! Each dimension of the
Introduction to 2-Dimensional Motion 2-Dimensional Motion! Definition: motion that occurs with both x and y components.! Example:! Playing pool.! Throwing a ball to another person.! Each dimension of the
Circular motion. Announcements:
 Circular motion Announcements: Clicker scores through Wednesday are now posted on DL. Scoring is points for a wrong answer, 3 points for a right answer. 13 clicker questions so far, so max is 39 points.
Circular motion Announcements: Clicker scores through Wednesday are now posted on DL. Scoring is points for a wrong answer, 3 points for a right answer. 13 clicker questions so far, so max is 39 points.
Physics 231. Topic 3: Vectors and two dimensional motion. Alex Brown September MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physics 231 Topic 3: Vectors and two dimensional motion Alex Brown September 14-18 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2014 1 What s up? (Monday Sept 14) 1) Homework set 01 due Tuesday Sept 15 th 10 pm 2) Learning
Physics 231 Topic 3: Vectors and two dimensional motion Alex Brown September 14-18 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2014 1 What s up? (Monday Sept 14) 1) Homework set 01 due Tuesday Sept 15 th 10 pm 2) Learning
Projectile motion. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment. Equations. Physics terms 5/20/14. Identify examples of projectile motion.
 Projectile motion Objectives Identify examples of projectile motion. Solve projectile motion problems. problems Graph the motion of a projectile. 1. Which of the events described below cannot be an example
Projectile motion Objectives Identify examples of projectile motion. Solve projectile motion problems. problems Graph the motion of a projectile. 1. Which of the events described below cannot be an example
MOTION IN A PLANE. Chapter Four MCQ I. (a) 45 (b) 90 (c) 45 (d) 180
 Chapter Four MOTION IN A PLANE MCQ I 4.1 The angle between A = ˆi + ˆj and B = ˆi ˆj is (a) 45 (b) 90 (c) 45 (d) 180 4.2 Which one of the following statements is true? (a) A scalar quantity is the one
Chapter Four MOTION IN A PLANE MCQ I 4.1 The angle between A = ˆi + ˆj and B = ˆi ˆj is (a) 45 (b) 90 (c) 45 (d) 180 4.2 Which one of the following statements is true? (a) A scalar quantity is the one
Full file at
 Section 3-1 Constructing Complex Motions from Simple Motion *1. In Figure 3-1, the motion of a spinning wheel (W) that itself revolves in a circle is shown. Which of the following would not be represented
Section 3-1 Constructing Complex Motions from Simple Motion *1. In Figure 3-1, the motion of a spinning wheel (W) that itself revolves in a circle is shown. Which of the following would not be represented
Projectile Motion. x = v ox t (1)
 Projectile Motion Theory Projectile motion is the combination of different motions in the x and y directions. In the x direction, which is taken as parallel to the surface of the earth, the projectile
Projectile Motion Theory Projectile motion is the combination of different motions in the x and y directions. In the x direction, which is taken as parallel to the surface of the earth, the projectile
Two-Dimensional Kinematics: Heading North (Solutions)
 Two-Dimensional Kinematics: Heading North (Solutions) You are the navigator of a TWA flight scheduled to fly from New Orleans due north to St. Louis, a distance of 673 miles. Your instruments tell you
Two-Dimensional Kinematics: Heading North (Solutions) You are the navigator of a TWA flight scheduled to fly from New Orleans due north to St. Louis, a distance of 673 miles. Your instruments tell you
Motion in Two Dimensions Sections Covered in the Text: Chapters 6 & 7, except 7.5 & 7.6
 Motion in Two Dimensions Sections Covered in the Tet: Chapters 6 & 7, ecept 7.5 & 7.6 It is time to etend the definitions we developed in Note 03 to describe motion in 2D space. In doin so we shall find
Motion in Two Dimensions Sections Covered in the Tet: Chapters 6 & 7, ecept 7.5 & 7.6 It is time to etend the definitions we developed in Note 03 to describe motion in 2D space. In doin so we shall find
Kinematics. Vector solutions. Vectors
 Kinematics Study of motion Accelerated vs unaccelerated motion Translational vs Rotational motion Vector solutions required for problems of 2- directional motion Vector solutions Possible solution sets
Kinematics Study of motion Accelerated vs unaccelerated motion Translational vs Rotational motion Vector solutions required for problems of 2- directional motion Vector solutions Possible solution sets
Name: Class: Date: Solution x 1 = units y 1 = 0. x 2 = d 2 cos = = tan 1 y
 Assessment Chapter Test B Teacher Notes and Answers Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors CHAPTER TEST B (ADVANCED) 1. b 2. d 3. d x 1 = 3.0 10 1 cm east y 1 = 25 cm north x 2 = 15 cm west x tot = x 1 + x
Assessment Chapter Test B Teacher Notes and Answers Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors CHAPTER TEST B (ADVANCED) 1. b 2. d 3. d x 1 = 3.0 10 1 cm east y 1 = 25 cm north x 2 = 15 cm west x tot = x 1 + x
Bill s ball goes up and comes back down to Bill s level. At that point, it is
 ConcepTest 2.1 Up in the Air Alice and Bill are at the top of a cliff of height H.. Both throw a ball with initial speed v 0, Alice straight down and Bill straight up. The speeds of the balls when they
ConcepTest 2.1 Up in the Air Alice and Bill are at the top of a cliff of height H.. Both throw a ball with initial speed v 0, Alice straight down and Bill straight up. The speeds of the balls when they
Physics 201 Homework 1
 Physics 201 Homework 1 Jan 9, 2013 1. (a) What is the magnitude of the average acceleration of a skier who, starting (a) 1.6 m/s 2 ; (b) 20 meters from rest, reaches a speed of 8.0 m/s when going down
Physics 201 Homework 1 Jan 9, 2013 1. (a) What is the magnitude of the average acceleration of a skier who, starting (a) 1.6 m/s 2 ; (b) 20 meters from rest, reaches a speed of 8.0 m/s when going down
CHAPTER-OPENING QUESTION
 g B This snowboarder fling through the air shows an eample of motion in two dimensions. In the absence of air resistance, the path would be a perfect parabola. The gold arrow represents the downward acceleration
g B This snowboarder fling through the air shows an eample of motion in two dimensions. In the absence of air resistance, the path would be a perfect parabola. The gold arrow represents the downward acceleration
Physics 114A Introduction to Mechanics (without calculus)
 Physics 114A Introduction to Mechanics (without calculus) A course about learning basic physics concepts and applying them to solve real-world, quantitative, mechanical problems Lecture 8 More Kinematics
Physics 114A Introduction to Mechanics (without calculus) A course about learning basic physics concepts and applying them to solve real-world, quantitative, mechanical problems Lecture 8 More Kinematics
Unit 2 Projectile Motion
 Name: Hr: Unit 2 Projectile Motion Vocabulary Projectile: a moving object that is acted upon only by the earth s gravity A projectile may start at a given height and move toward the ground in an arc. For
Name: Hr: Unit 2 Projectile Motion Vocabulary Projectile: a moving object that is acted upon only by the earth s gravity A projectile may start at a given height and move toward the ground in an arc. For
Write these equations in your notes if they re not already there. You will want them for Exam 1 & the Final.
 Tuesday January 24 Assignment 3: Due Friday, 11:59pm.like every Friday Pre-Class Assignment: 15min before class like every class Office Hours: Wed. 10-11am, 204 EAL Help Room: Wed. & Thurs. 6-9pm, here
Tuesday January 24 Assignment 3: Due Friday, 11:59pm.like every Friday Pre-Class Assignment: 15min before class like every class Office Hours: Wed. 10-11am, 204 EAL Help Room: Wed. & Thurs. 6-9pm, here
Review Exercises for Chapter 2
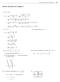 Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
Chapter 4. Motion in Two Dimensions. Position and Displacement. General Motion Ideas. Motion in Two Dimensions
 Motion in Two Dimensions Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Using + or signs is not always sufficient to fully describe motion in more than one dimension Vectors can be used to more fully describe motion
Motion in Two Dimensions Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Using + or signs is not always sufficient to fully describe motion in more than one dimension Vectors can be used to more fully describe motion
Unit 1 Motion. Projectile Motion
 Unit 1 Motion Projectile Motion Motion to Date Uniform Motion Accelerated Motion Relative Motion Uniform Motion Motion with a constant velocity - Constant speed - Same direction Equation: v d t Problems
Unit 1 Motion Projectile Motion Motion to Date Uniform Motion Accelerated Motion Relative Motion Uniform Motion Motion with a constant velocity - Constant speed - Same direction Equation: v d t Problems
Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration
 Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration 1. If the acceleration vector of an object is perpendicular to its velocity vector, which of the following must be true? (a) The speed is changing. (b) The direction
Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration 1. If the acceleration vector of an object is perpendicular to its velocity vector, which of the following must be true? (a) The speed is changing. (b) The direction
Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy. 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall Lecture 4. Home Page. Title Page. Page 1 of 35.
 Rutgers Uniersit Department of Phsics & Astronom 01:750:271 Honors Phsics I Fall 2015 Lecture 4 Page 1 of 35 4. Motion in two and three dimensions Goals: To stud position, elocit, and acceleration ectors
Rutgers Uniersit Department of Phsics & Astronom 01:750:271 Honors Phsics I Fall 2015 Lecture 4 Page 1 of 35 4. Motion in two and three dimensions Goals: To stud position, elocit, and acceleration ectors
In this activity, we explore the application of differential equations to the real world as applied to projectile motion.
 Applications of Calculus: Projectile Motion ID: XXXX Name Class In this activity, we explore the application of differential equations to the real world as applied to projectile motion. Open the file CalcActXX_Projectile_Motion_EN.tns
Applications of Calculus: Projectile Motion ID: XXXX Name Class In this activity, we explore the application of differential equations to the real world as applied to projectile motion. Open the file CalcActXX_Projectile_Motion_EN.tns
This Week. 1/15/2015 Physics 214 Spring
 This Week Gravity: Dropping and throwing objects From Baseballs to satellites What causes motion. All changes involve motion Extinction of the dinosaurs 1/15/2015 Physics 214 Spring 2015 1 One dimensional
This Week Gravity: Dropping and throwing objects From Baseballs to satellites What causes motion. All changes involve motion Extinction of the dinosaurs 1/15/2015 Physics 214 Spring 2015 1 One dimensional
VECTORS AND MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS 3
 VECTORS AND MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS 3 Q3.. Reason: (a) If one component of the vector is zero, then the other component must not be zero (unless the whole vector is zero). Thus the magnitude of the vector
VECTORS AND MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS 3 Q3.. Reason: (a) If one component of the vector is zero, then the other component must not be zero (unless the whole vector is zero). Thus the magnitude of the vector
F13--HPhys--Q4 Practice POST
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A F13--HPhys--Q4 Practice POST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not an example of projectile
Name: Class: Date: ID: A F13--HPhys--Q4 Practice POST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not an example of projectile
Physics 201 Quiz 1. Jan 14, 2013
 Physics 201 Quiz 1 Jan 14, 2013 1. A VW Beetle goes from 0 to 60.0 mph with an acceleration of 2.35 m/s 2. (a) How much time does it take for the Beetle to reach this speed? (b) A top-fuel dragster can
Physics 201 Quiz 1 Jan 14, 2013 1. A VW Beetle goes from 0 to 60.0 mph with an acceleration of 2.35 m/s 2. (a) How much time does it take for the Beetle to reach this speed? (b) A top-fuel dragster can
