Chapter 4: Summary. Solve lattice vibration equation of one atom/unitcellcase Consider a set of ions M separated by a distance a,
|
|
|
- Leslie Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 4: Summary Solve lattice vibration equation of one atom/unitcellcase case. Consider a set of ions M separated by a distance a, R na for integral n. Let u( na) be the displacement. Assuming only neighboring ions interact, we have 1 harm U Cu( na) u([ n1] a), n Newton's second law F Ma or harm du( na) U M ( ) ([ 1] ) ([ 1] ) ( ) C u na dt u na u n a u n a Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-1
2 For each of the N values of k there are thus two solutions, leading to a total of N normal modes. The two vs k curves are two branches of the dispersion relation. Acoustic and optical branches. Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-
3 Prob. 3, Consider a longitudinal wave u ucos( tska) which propagates in a monatomic linear lattice of atoms of mass M, spacing a, and nearest neighbor interaction C. a) show that the total energy of the wave is 1 1 E Mdus / dt Cus us 1, s where s runs over all atoms. s b)by substitution of u in this expression, show that the time average s total energy per atom is M u C 1cos Ka u M u, 4 where the last step we have used the dispersion relation for this problem. s Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-3
4 Chapter 5: Summary Planck distribution function: The average excitation ti quantum # of an oscillator is: n sexp( n/ ) 1 exp( s / ) exp( / ) 1 At low temperatures, 4 x 3 nx 1 dx 6, x x e dx 4 e 1 n1 n1 n T the heat capacity CV NkB. 5 3 Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-4
5 Einstein models of the density of states In the case of N oscillators of the same frequency in 1D, the Einstein density of states is D( ) N ( ) N. e 1 U N n / The heat capacity 0 U CV N NkB T V 0 e ( e 1) / Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-5
6 Thermal conductivity The thermal conductivity coefficient K of a solid is defined as, dt ju K, where ju is the flux of thermal energy, and dx x is distance. From the kinetic theory of gases we find 1 1 K Cvl Cv, where C is the heat capacity per volume, 3 3 v is the average particle velocity, and l is the mean free 1 path of a particle between collisions, is the phonon collision rate. Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-6
7 Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-7
8 Chapter 6: Free electron Fermi gas Under quantum theory and the Pauli exclusion principle, we consider N of single electron is ( r ), then 3 noninteracting electrons confined to a volume V( L ). If the wave function ( r ) ( r ) ( r ). m x y z m Applying boundary condition ( xyz,, L) ( xyz,, ); ( xy, Lz, ) ( xyz,, ); ( x Lyz,, L) ( xyz,, ). The solutions are 1 ik r k ( r K ) e, ( k ). Note the probability of V m finding the electron somewhere in the volume is 1 dr ( r ). Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-8
9 Note that K ( r ) is an eigenstate of the momentum operator, ik r ik r p, e ke i r i i r an electron in the level K ( r) has a momentum p k and a velocity v p / mk / m, where / k. Periodic boundary condition requires ik xl ikyl ikzl n n x y nz e e e 1 or k x, k y, k z L L L Thus in a 3-D k-space, the allowed wavevectors are those along the three axes given integer mutiples of. L Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-9
10 To calculate the allowed states in a region of k-space volume, V ( / L) ( ) 3 3 or the number of allowed k-values per unit volume of k-space (known as the k-space density of levels) is V. Because the electrons are noninteracting we can built up 3 ( ) the N-electron ground state by placing electrons into the allowed one-electron levels. Pauli exclusion principle allows each wavevector to have electronic levels with spins up and down. Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-10
11 Since the energy of a one-electron electron level is directly proportional to k, when N is enormous the occupied region will be indistinguishable from a sphere. The radius of this sphere is called k F (F for F ermi), 3 and its volume is 4 k / 3. The # of allowed k within the sphere is: 4 k V k F F 3 F V. Since each allowed k-value leads to two 3 3 kf kf one-electron levels, we must have N V V If electron density is n N / V, then we have n k / 3. F Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-11
12 The sphere of radius k F containing the occupied one eletron levels is called the Fermi sphere. The Surface of the Fermi sphere, which separate the occupied form the unoccupied levels is called the Fermi surface. 3 N The momentum pf kf= of the occupied V one-electron levels of highest energy is the Fermi momentum. 1/3 F 3 N kf / m is the Fermi energy; m V /3 3 N v F p F / m( ) m V 1/3 is the Fermi velocity. Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-1
13 Experimental heat capacity of metals 3 At sufficient low temperatures, CV T AT. Where is the Sommerfeld parameter. The ratio of the observed to the free electron values of the electronic heat capacity is related to thermal effective mass as: mth (observed) m (free) Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-13
14 Electrical l conductivity it and Ohm s law Considering Newton's second law, we have dv dk 1 F m e ( E v B ) dt dt c The displacement of the Fermi sphere, k eet/. If collision time is, the incremental velocity is v ee / m. In a constant e lectric field E and n electrons per volume,the electric current density is j nqv ne E / m E. The electrical conductivity ne / m. Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-14
15 Thermal conductivity of metals Wiedemann-Franz law Thermal conductivity for a Fermi gas 1 nk T nk T Kel Cvl v l 3 3 mv 3 B B F F m The Wiedemann-Franz law states that for metals at not too low temperatures the ratio of the thermal conductivity to the electrical conductivity is directly proportional to the temperature, independent of the particular metal. Kel nkbt /3m kb T ne / m 3 e LT. Lorenz number L.4510 watt-ohm/deg 8 Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-15
16 Chapter 7: Summary Bloch s theorem The eigenstates of the one-electron Hamiltonian H U( r), where U( r R) U( r) for all R in m a Bravias lattice, can be chosen to have the form of a plane wave times a function with the periodicity of the Bravias lattice: ik r ( r) e u ( r), where u ( r R) u ( r) nk nk nk nk for all R in the Bravias lattice. or ik R ( r R) e ( r) Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-16
17 The effect of a periodic potential The periodic potential has form: x U U0 U1cos, where a is lattice parameter a and U U. If U 0 then we have the free k electron gas case where m Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-17
18 Wave equation of electron in periodic potential U( x) U e U ( e e ) U cosgx igx igx igx G G G G G0 G0 1 H p U e x x igx ( G ) ( ) ( ) m G ikx ( x) C( k) e, k n/ L. k 1 ikx p ( x) k C( k) e, m m k igx igx ikx ( U e ) ( x ) U e C ( k ) e, G G G k ikx igx ikx kcke ( ) Ue G Cke ( ) C k m G k k k G ( ke ) ikx ( ) Ck ( ) UCk G ( G ) 0. k k / m. m G Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-18
19 Crystal momentum of an electron Under a crystal lattice translation we have ( ) ik T ik r ( ) ik r T e e u r T e T ( r). k k k If the lattice potential vanishes, the result recovers to that of free electron gas. k is called the crystal momentum of an electron. If an electron k absorbs in a collision a phonon of wavevector q, the selection rule is k q k ' G. Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-19
20 Approximate solution near a zone boundary At the zone boundary the kinetic energy of the waves 1 k G are equal. ( ) C( k) UGC( kg) 0. ( ) CG ( / ) UC( G/ ) 0 ( ) C ( G /) UC ( G /) 0 1 ( ) U ; U ( G) U. m Thus the potential energy has created an energy gap U at the zone boundary. G Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-0
21 Chapter 8: Summary A solid with an energy gap will be nonconducting at T 0 unless electric breakdown occurs or unless the AC field is of such high frequency that exceeds the energy gap. However, when T 0 some electrons will be thermally excited to unoccupied bands (conduction bands). If the enegy gap E the gap is of order g E e 0.5 ev, the fraction of electrons across g /k T B 10, and observable conductivity will occur. These materials are semiconductors. Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-1
22 Effective Mass 1 The group velocity vg d/ dk, /, so vg d / dk. dvg 1 d 1 d dk 1 d dk 1 d F dt dkdt dk dt dk dt dk F 1 1 d ma, then we have. * m dk Effective Mass in Semiconductors The angular rotation frequency c of the current carriers eb * is: c, where m is the effective mass. * mc Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-
23 In an intrinsic semiconductor, n p, E E E, 3/ kt B 3/4 n m m exp[( E / k T]. e h g B g c v Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-3
24 Chapter 9: Reduced zone scheme ik ' r For a Bloch function written as k' ( r) e uk' ( r), with k ' outside the first Brillouin zone, we have k k ' G. ' ( ) ik r ( ) ik r ig r e u r e e r u ( r) e ik r u ( r) ( r) k' k' k' k k Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-4
25 Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-5
26 Electron orbits, hole orbits, and open orbits An electron on the Fermi surface will move in a curve on the Fermi surface, because it is a surface of constant energy. Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-6
27 Tight banding method for energy bands Tight banding approximation deals with the case in which theovelapofatomicwavefunctionsisenough of atomic functions is enough to require corrections to the picture of isolated atoms, but not so much as to render the atomic description irrelevant. Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-7
28 Free electrons in a uniform magnetic field The orbital energy levels of an electron in a cubic box with sides of length L parallel to the x-, y-, and z-axes are determined in the presence of a uniform magnetic field H along the z-direction by two quantum numbers, and k : 1 eh kz kz ( ) c, c. m mc runs through all nonmagnetic integers, and kz takes on the same values as in the absence of a magnetic field: kz nz / L for any integral nz. The energy of motion perpendicular p to the field, which would be ( kx ky) / m if no field were present, is quantized in steps of ( eh / mc). This is orbit quantization. c c z Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-8
29 Origin of the oscillatory phenomena Most electronic properties of metals depend on the density of levels g at the Fermi energy, g. It follows that will be singular F whenever the value of H causes an extramal orbit on the Fermi surface to satisfy the quantization condition ( + ) A A e ( F ). 1 e 1 e H c A mck K / G. e F B Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-9 F
30 For a system of N electrons at absolute zero the Landau levels are filled to s. Orbitals at the next higher level s 1 will be partially filled. The Fermi level will lie between s and s1. As the magnetic field is increased the electrons move to lower levels because the area between successive circles are increased ( k ) ( k )( k ) eb/ c. Dai/PHYS 34/555 Spring 013 Review 1-30
Introduction to solid state physics
 PHYS 342/555 Introduction to solid state physics Instructor: Dr. Pengcheng Dai Professor of Physics The University of Tennessee (Room 407A, Nielsen, 974-1509) Chapter 5: Thermal properties Lecture in pdf
PHYS 342/555 Introduction to solid state physics Instructor: Dr. Pengcheng Dai Professor of Physics The University of Tennessee (Room 407A, Nielsen, 974-1509) Chapter 5: Thermal properties Lecture in pdf
Electrons in a periodic potential
 Chapter 3 Electrons in a periodic potential 3.1 Bloch s theorem. We consider in this chapter electrons under the influence of a static, periodic potential V (x), i.e. such that it fulfills V (x) = V (x
Chapter 3 Electrons in a periodic potential 3.1 Bloch s theorem. We consider in this chapter electrons under the influence of a static, periodic potential V (x), i.e. such that it fulfills V (x) = V (x
Nasser S. Alzayed.
 Lecture #4 Nasser S. Alzayed nalzayed@ksu.edu.sa ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY AND OHM'S LAW The momentum of a free electron is related to the wavevector by mv = ћk. In an electric field E and magnetic field
Lecture #4 Nasser S. Alzayed nalzayed@ksu.edu.sa ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY AND OHM'S LAW The momentum of a free electron is related to the wavevector by mv = ћk. In an electric field E and magnetic field
Nearly Free Electron Gas model - II
 Nearly Free Electron Gas model - II Contents 1 Lattice scattering 1 1.1 Bloch waves............................ 2 1.2 Band gap formation........................ 3 1.3 Electron group velocity and effective
Nearly Free Electron Gas model - II Contents 1 Lattice scattering 1 1.1 Bloch waves............................ 2 1.2 Band gap formation........................ 3 1.3 Electron group velocity and effective
PH575 Spring Lecture #26 & 27 Phonons: Kittel Ch. 4 & 5
 PH575 Spring 2009 Lecture #26 & 27 Phonons: Kittel Ch. 4 & 5 PH575 Spring 2009 POP QUIZ Phonons are: A. Fermions B. Bosons C. Lattice vibrations D. Light/matter interactions PH575 Spring 2009 POP QUIZ
PH575 Spring 2009 Lecture #26 & 27 Phonons: Kittel Ch. 4 & 5 PH575 Spring 2009 POP QUIZ Phonons are: A. Fermions B. Bosons C. Lattice vibrations D. Light/matter interactions PH575 Spring 2009 POP QUIZ
Lecture 14 The Free Electron Gas: Density of States
 Lecture 4 The Free Electron Gas: Density of States Today:. Spin.. Fermionic nature of electrons. 3. Understanding the properties of metals: the free electron model and the role of Pauli s exclusion principle.
Lecture 4 The Free Electron Gas: Density of States Today:. Spin.. Fermionic nature of electrons. 3. Understanding the properties of metals: the free electron model and the role of Pauli s exclusion principle.
Electrons in metals PHYS208. revised Go to Topics Autumn 2010
 Go to Topics Autumn 010 Electrons in metals revised 0.1.010 PHYS08 Topics 0.1.010 Classical Models The Drude Theory of metals Conductivity - static electric field Thermal conductivity Fourier Law Wiedemann-Franz
Go to Topics Autumn 010 Electrons in metals revised 0.1.010 PHYS08 Topics 0.1.010 Classical Models The Drude Theory of metals Conductivity - static electric field Thermal conductivity Fourier Law Wiedemann-Franz
PH575 Spring Lecture #26 & 27 Phonons: Kittel Ch. 4 & 5
 PH575 Spring 2014 Lecture #26 & 27 Phonons: Kittel Ch. 4 & 5 PH575 POP QUIZ Phonons are: A. Fermions B. Bosons C. Lattice vibrations D. Light/matter interactions PH575 POP QUIZ Phonon dispersion relation:
PH575 Spring 2014 Lecture #26 & 27 Phonons: Kittel Ch. 4 & 5 PH575 POP QUIZ Phonons are: A. Fermions B. Bosons C. Lattice vibrations D. Light/matter interactions PH575 POP QUIZ Phonon dispersion relation:
Three Most Important Topics (MIT) Today
 Three Most Important Topics (MIT) Today Electrons in periodic potential Energy gap nearly free electron Bloch Theorem Energy gap tight binding Chapter 1 1 Electrons in Periodic Potential We now know the
Three Most Important Topics (MIT) Today Electrons in periodic potential Energy gap nearly free electron Bloch Theorem Energy gap tight binding Chapter 1 1 Electrons in Periodic Potential We now know the
Non-Continuum Energy Transfer: Phonons
 Non-Continuum Energy Transfer: Phonons D. B. Go Slide 1 The Crystal Lattice The crystal lattice is the organization of atoms and/or molecules in a solid simple cubic body-centered cubic hexagonal a NaCl
Non-Continuum Energy Transfer: Phonons D. B. Go Slide 1 The Crystal Lattice The crystal lattice is the organization of atoms and/or molecules in a solid simple cubic body-centered cubic hexagonal a NaCl
Les états de bord d un. isolant de Hall atomique
 Les états de bord d un isolant de Hall atomique séminaire Atomes Froids 2/9/22 Nathan Goldman (ULB), Jérôme Beugnon and Fabrice Gerbier Outline Quantum Hall effect : bulk Landau levels and edge states
Les états de bord d un isolant de Hall atomique séminaire Atomes Froids 2/9/22 Nathan Goldman (ULB), Jérôme Beugnon and Fabrice Gerbier Outline Quantum Hall effect : bulk Landau levels and edge states
MP464: Solid State Physics Problem Sheet
 MP464: Solid State Physics Problem Sheet 1 Write down primitive lattice vectors for the -dimensional rectangular lattice, with sides a and b in the x and y-directions respectively, and a face-centred rectangular
MP464: Solid State Physics Problem Sheet 1 Write down primitive lattice vectors for the -dimensional rectangular lattice, with sides a and b in the x and y-directions respectively, and a face-centred rectangular
Problem Sheet 1 From material in Lectures 2 to 5
 lectrons in Solids ) Problem Sheet From material in Lectures to 5 ) [Standard derivation] Consider the free electron model for a - dimensional solid between x = and x = L. For this model the time independent
lectrons in Solids ) Problem Sheet From material in Lectures to 5 ) [Standard derivation] Consider the free electron model for a - dimensional solid between x = and x = L. For this model the time independent
Chapter 6 Free Electron Fermi Gas
 Chapter 6 Free Electron Fermi Gas Free electron model: The valence electrons of the constituent atoms become conduction electrons and move about freely through the volume of the metal. The simplest metals
Chapter 6 Free Electron Fermi Gas Free electron model: The valence electrons of the constituent atoms become conduction electrons and move about freely through the volume of the metal. The simplest metals
FYS Vår 2015 (Kondenserte fasers fysikk)
 FYS410 - Vår 015 (Kondenserte fasers fysikk) http://www.uio.no/studier/emner/matnat/fys/fys410/v15/index.html Pensum: Introduction to Solid State Physics by Charles Kittel (Chapters 1-9 and 17, 18, 0)
FYS410 - Vår 015 (Kondenserte fasers fysikk) http://www.uio.no/studier/emner/matnat/fys/fys410/v15/index.html Pensum: Introduction to Solid State Physics by Charles Kittel (Chapters 1-9 and 17, 18, 0)
Chapter 6 Free Electron Fermi Gas
 Chapter 6 Free Electron Fermi Gas Free electron model: The valence electrons of the constituent atoms become conduction electrons and move about freely through the volume of the metal. The simplest metals
Chapter 6 Free Electron Fermi Gas Free electron model: The valence electrons of the constituent atoms become conduction electrons and move about freely through the volume of the metal. The simplest metals
Free Electron Fermi Gas and Energy Bands
 PHYS 353 SOLID STATE PHYSICS STUDY GUIDE FOR PART 3 OUTLINE: Free Electron Fermi Gas and Energy Bands A. Quantum Theory and energy levels 1. Schrodinger's equation 2. quantum numbers and energy levels
PHYS 353 SOLID STATE PHYSICS STUDY GUIDE FOR PART 3 OUTLINE: Free Electron Fermi Gas and Energy Bands A. Quantum Theory and energy levels 1. Schrodinger's equation 2. quantum numbers and energy levels
7. FREE ELECTRON THEORY.
 7. FREE ELECTRON THEORY. Aim: To introduce the free electron model for the physical properties of metals. It is the simplest theory for these materials, but still gives a very good description of many
7. FREE ELECTRON THEORY. Aim: To introduce the free electron model for the physical properties of metals. It is the simplest theory for these materials, but still gives a very good description of many
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 5
 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 5 detector sample X-ray source monochromator David Ritchie http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home QCMP Lent/Easter 2019 5.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 5 detector sample X-ray source monochromator David Ritchie http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home QCMP Lent/Easter 2019 5.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical
In an electric field R and magnetic field B, the force on an electron (charge e) is given by:
 Lecture 17 Electric conduction Electrons motion in magnetic field Electrons thermal conductivity Brief review In solid state physics, we do not think about electrons zipping around randomly in real space.
Lecture 17 Electric conduction Electrons motion in magnetic field Electrons thermal conductivity Brief review In solid state physics, we do not think about electrons zipping around randomly in real space.
C. Show your answer in part B agrees with your answer in part A in the limit that the constant c 0.
 Problem #1 A. A projectile of mass m is shot vertically in the gravitational field. Its initial velocity is v o. Assuming there is no air resistance, how high does m go? B. Now assume the projectile is
Problem #1 A. A projectile of mass m is shot vertically in the gravitational field. Its initial velocity is v o. Assuming there is no air resistance, how high does m go? B. Now assume the projectile is
Phonons I - Crystal Vibrations (Kittel Ch. 4)
 Phonons I - Crystal Vibrations (Kittel Ch. 4) Displacements of Atoms Positions of atoms in their perfect lattice positions are given by: R 0 (n 1, n 2, n 3 ) = n 10 x + n 20 y + n 30 z For simplicity here
Phonons I - Crystal Vibrations (Kittel Ch. 4) Displacements of Atoms Positions of atoms in their perfect lattice positions are given by: R 0 (n 1, n 2, n 3 ) = n 10 x + n 20 y + n 30 z For simplicity here
Lecture 4: Basic elements of band theory
 Phys 769 Selected Topics in Condensed Matter Physics Summer 010 Lecture 4: Basic elements of band theory Lecturer: Anthony J. Leggett TA: Bill Coish 1 Introduction Most matter, in particular most insulating
Phys 769 Selected Topics in Condensed Matter Physics Summer 010 Lecture 4: Basic elements of band theory Lecturer: Anthony J. Leggett TA: Bill Coish 1 Introduction Most matter, in particular most insulating
Lecture 12: Phonon heat capacity
 Lecture 12: Phonon heat capacity Review o Phonon dispersion relations o Quantum nature of waves in solids Phonon heat capacity o Normal mode enumeration o Density of states o Debye model Review By considering
Lecture 12: Phonon heat capacity Review o Phonon dispersion relations o Quantum nature of waves in solids Phonon heat capacity o Normal mode enumeration o Density of states o Debye model Review By considering
Lecture contents. A few concepts from Quantum Mechanics. Tight-binding model Solid state physics review
 Lecture contents A few concepts from Quantum Mechanics Particle in a well Two wells: QM perturbation theory Many wells (atoms) BAND formation Tight-binding model Solid state physics review Approximations
Lecture contents A few concepts from Quantum Mechanics Particle in a well Two wells: QM perturbation theory Many wells (atoms) BAND formation Tight-binding model Solid state physics review Approximations
Phonon II Thermal Properties
 Phonon II Thermal Properties Physics, UCF OUTLINES Phonon heat capacity Planck distribution Normal mode enumeration Density of states in one dimension Density of states in three dimension Debye Model for
Phonon II Thermal Properties Physics, UCF OUTLINES Phonon heat capacity Planck distribution Normal mode enumeration Density of states in one dimension Density of states in three dimension Debye Model for
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
 A11046W1 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2015 Wednesday, 17 June, 2.30
A11046W1 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2015 Wednesday, 17 June, 2.30
Electrons in a periodic potential: Free electron approximation
 Dr. A. Sapelin, Jan 01 Electrons in a periodic potential: ree electron approximation ree electron ermi gas - gas of non-interacting electrons subject to Pauli principle Wealy bound electrons move freely
Dr. A. Sapelin, Jan 01 Electrons in a periodic potential: ree electron approximation ree electron ermi gas - gas of non-interacting electrons subject to Pauli principle Wealy bound electrons move freely
A few principles of classical and quantum mechanics
 A few principles of classical and quantum mechanics The classical approach: In classical mechanics, we usually (but not exclusively) solve Newton s nd law of motion relating the acceleration a of the system
A few principles of classical and quantum mechanics The classical approach: In classical mechanics, we usually (but not exclusively) solve Newton s nd law of motion relating the acceleration a of the system
2.57/2.570 Midterm Exam No. 1 April 4, :00 am -12:30 pm
 Name:.57/.570 Midterm Exam No. April 4, 0 :00 am -:30 pm Instructions: ().57 students: try all problems ().570 students: Problem plus one of two long problems. You can also do both long problems, and one
Name:.57/.570 Midterm Exam No. April 4, 0 :00 am -:30 pm Instructions: ().57 students: try all problems ().570 students: Problem plus one of two long problems. You can also do both long problems, and one
Phonons (Classical theory)
 Phonons (Classical theory) (Read Kittel ch. 4) Classical theory. Consider propagation of elastic waves in cubic crystal, along [00], [0], or [] directions. Entire plane vibrates in phase in these directions
Phonons (Classical theory) (Read Kittel ch. 4) Classical theory. Consider propagation of elastic waves in cubic crystal, along [00], [0], or [] directions. Entire plane vibrates in phase in these directions
The potential is minimum at the positive ion sites and maximum between the two ions.
 1. Bloch theorem: - A crystalline solid consists of a lattice, which is composed of a large number of ion cores at regular intervals, and the conduction electrons that can move freely through out the lattice.
1. Bloch theorem: - A crystalline solid consists of a lattice, which is composed of a large number of ion cores at regular intervals, and the conduction electrons that can move freely through out the lattice.
Section 10 Metals: Electron Dynamics and Fermi Surfaces
 Electron dynamics Section 10 Metals: Electron Dynamics and Fermi Surfaces The next important subject we address is electron dynamics in metals. Our consideration will be based on a semiclassical model.
Electron dynamics Section 10 Metals: Electron Dynamics and Fermi Surfaces The next important subject we address is electron dynamics in metals. Our consideration will be based on a semiclassical model.
Thermal and Statistical Physics Department Exam Last updated November 4, L π
 Thermal and Statistical Physics Department Exam Last updated November 4, 013 1. a. Define the chemical potential µ. Show that two systems are in diffusive equilibrium if µ 1 =µ. You may start with F =
Thermal and Statistical Physics Department Exam Last updated November 4, 013 1. a. Define the chemical potential µ. Show that two systems are in diffusive equilibrium if µ 1 =µ. You may start with F =
Problems. ECE 4070, Spring 2017 Physics of Semiconductors and Nanostructures Handout HW 1. Problem 1: Semiconductor History
 ECE 4070, Spring 2017 Physics of Semiconductors and Nanostructures Handout 4070 Problems Present your solutions neatly. Do not turn in rough unreadable worksheets - learn to take pride in your presentation.
ECE 4070, Spring 2017 Physics of Semiconductors and Nanostructures Handout 4070 Problems Present your solutions neatly. Do not turn in rough unreadable worksheets - learn to take pride in your presentation.
Summary: Thermodynamic Potentials and Conditions of Equilibrium
 Summary: Thermodynamic Potentials and Conditions of Equilibrium Isolated system: E, V, {N} controlled Entropy, S(E,V{N}) = maximum Thermal contact: T, V, {N} controlled Helmholtz free energy, F(T,V,{N})
Summary: Thermodynamic Potentials and Conditions of Equilibrium Isolated system: E, V, {N} controlled Entropy, S(E,V{N}) = maximum Thermal contact: T, V, {N} controlled Helmholtz free energy, F(T,V,{N})
3. LATTICE VIBRATIONS. 3.1 Sound Waves
 3. LATTIC VIBRATIONS Atoms in lattice are not stationary even at T 0K. They vibrate about particular equilibrium positions at T 0K ( zero-point energy). For T > 0K, vibration amplitude increases as atoms
3. LATTIC VIBRATIONS Atoms in lattice are not stationary even at T 0K. They vibrate about particular equilibrium positions at T 0K ( zero-point energy). For T > 0K, vibration amplitude increases as atoms
Chapter 5 Phonons II Thermal Properties
 Chapter 5 Phonons II Thermal Properties Phonon Heat Capacity < n k,p > is the thermal equilibrium occupancy of phonon wavevector K and polarization p, Total energy at k B T, U = Σ Σ < n k,p > ħ k, p Plank
Chapter 5 Phonons II Thermal Properties Phonon Heat Capacity < n k,p > is the thermal equilibrium occupancy of phonon wavevector K and polarization p, Total energy at k B T, U = Σ Σ < n k,p > ħ k, p Plank
Unit III Free Electron Theory Engineering Physics
 . Introduction The electron theory of metals aims to explain the structure and properties of solids through their electronic structure. The electron theory is applicable to all solids i.e., both metals
. Introduction The electron theory of metals aims to explain the structure and properties of solids through their electronic structure. The electron theory is applicable to all solids i.e., both metals
Classical Theory of Harmonic Crystals
 Classical Theory of Harmonic Crystals HARMONIC APPROXIMATION The Hamiltonian of the crystal is expressed in terms of the kinetic energies of atoms and the potential energy. In calculating the potential
Classical Theory of Harmonic Crystals HARMONIC APPROXIMATION The Hamiltonian of the crystal is expressed in terms of the kinetic energies of atoms and the potential energy. In calculating the potential
Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter
 Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter E E k=λ a k=λ b k=λ a k=λ b Topological Phases of Matter Many examples of topological band phenomena States adiabatically connected to independent electrons: - Quantum
Symmetry, Topology and Phases of Matter E E k=λ a k=λ b k=λ a k=λ b Topological Phases of Matter Many examples of topological band phenomena States adiabatically connected to independent electrons: - Quantum
Sommerfeld-Drude model. Ground state of ideal electron gas
 Sommerfeld-Drude model Recap of Drude model: 1. Treated electrons as free particles moving in a constant potential background. 2. Treated electrons as identical and distinguishable. 3. Applied classical
Sommerfeld-Drude model Recap of Drude model: 1. Treated electrons as free particles moving in a constant potential background. 2. Treated electrons as identical and distinguishable. 3. Applied classical
Concepts for Specific Heat
 Concepts for Specific Heat Andreas Wacker 1 Mathematical Physics, Lund University August 17, 018 1 Introduction These notes shall briefly explain general results for the internal energy and the specific
Concepts for Specific Heat Andreas Wacker 1 Mathematical Physics, Lund University August 17, 018 1 Introduction These notes shall briefly explain general results for the internal energy and the specific
FYS Vår 2017 (Kondenserte fasers fysikk)
 FYS3410 - Vår 2017 (Kondenserte fasers fysikk) http://www.uio.no/studier/emner/matnat/fys/fys3410/v16/index.html Pensum: Introduction to Solid State Physics by Charles Kittel (Chapters 1-9, 11, 17, 18,
FYS3410 - Vår 2017 (Kondenserte fasers fysikk) http://www.uio.no/studier/emner/matnat/fys/fys3410/v16/index.html Pensum: Introduction to Solid State Physics by Charles Kittel (Chapters 1-9, 11, 17, 18,
PHYSICS 4750 Physics of Modern Materials Chapter 5: The Band Theory of Solids
 PHYSICS 4750 Physics of Modern Materials Chapter 5: The Band Theory of Solids 1. Introduction We have seen that when the electrons in two hydrogen atoms interact, their energy levels will split, i.e.,
PHYSICS 4750 Physics of Modern Materials Chapter 5: The Band Theory of Solids 1. Introduction We have seen that when the electrons in two hydrogen atoms interact, their energy levels will split, i.e.,
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
 2753 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Wednesday, 22 June, 9.30 am 12.30
2753 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Wednesday, 22 June, 9.30 am 12.30
Electrons & Phonons. Thermal Resistance, Electrical Resistance P = I 2 R T = P R TH V = I R. R = f( T)
 lectrons & Phonons Ohm s & Fourier s Laws Mobility & Thermal Conductivity Heat Capacity Wiedemann-Franz Relationship Size ffects and Breadown of Classical Laws 1 Thermal Resistance, lectrical Resistance
lectrons & Phonons Ohm s & Fourier s Laws Mobility & Thermal Conductivity Heat Capacity Wiedemann-Franz Relationship Size ffects and Breadown of Classical Laws 1 Thermal Resistance, lectrical Resistance
PHY 140A: Solid State Physics. Solution to Midterm #2
 PHY 140A: Solid State Physics Solution to Midterm #2 TA: Xun Jia 1 December 4, 2006 1 Email: jiaxun@physics.ucla.edu Problem #1 (20pt)(20 points) Use the equation dp dt + p = ee for the electron momentum,
PHY 140A: Solid State Physics Solution to Midterm #2 TA: Xun Jia 1 December 4, 2006 1 Email: jiaxun@physics.ucla.edu Problem #1 (20pt)(20 points) Use the equation dp dt + p = ee for the electron momentum,
The properties of an ideal Fermi gas are strongly determined by the Pauli principle. We shall consider the limit:
 Chapter 13 Ideal Fermi gas The properties of an ideal Fermi gas are strongly determined by the Pauli principle. We shall consider the limit: k B T µ, βµ 1, which defines the degenerate Fermi gas. In this
Chapter 13 Ideal Fermi gas The properties of an ideal Fermi gas are strongly determined by the Pauli principle. We shall consider the limit: k B T µ, βµ 1, which defines the degenerate Fermi gas. In this
Thermal & Statistical Physics Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 6, 2017
 Thermal & Statistical Physics Study Questions for the Spring 018 Department Exam December 6, 017 1. a. Define the chemical potential. Show that two systems are in diffusive equilibrium if 1. You may start
Thermal & Statistical Physics Study Questions for the Spring 018 Department Exam December 6, 017 1. a. Define the chemical potential. Show that two systems are in diffusive equilibrium if 1. You may start
Electrons in a weak periodic potential
 Electrons in a weak periodic potential Assumptions: 1. Static defect-free lattice perfectly periodic potential. 2. Weak potential perturbative effect on the free electron states. Perfect periodicity of
Electrons in a weak periodic potential Assumptions: 1. Static defect-free lattice perfectly periodic potential. 2. Weak potential perturbative effect on the free electron states. Perfect periodicity of
Review of Semiconductor Physics
 Solid-state physics Review of Semiconductor Physics The daunting task of solid state physics Quantum mechanics gives us the fundamental equation The equation is only analytically solvable for a handful
Solid-state physics Review of Semiconductor Physics The daunting task of solid state physics Quantum mechanics gives us the fundamental equation The equation is only analytically solvable for a handful
Minimal Update of Solid State Physics
 Minimal Update of Solid State Physics It is expected that participants are acquainted with basics of solid state physics. Therefore here we will refresh only those aspects, which are absolutely necessary
Minimal Update of Solid State Physics It is expected that participants are acquainted with basics of solid state physics. Therefore here we will refresh only those aspects, which are absolutely necessary
Normal modes are eigenfunctions of T
 Quasiparticles Phonons N atom atoms in crystal 3N atom normal modes p atoms in the basis N atom /p unit cells N atom /p translational symmetries N atom /p k-vectors 3p modes for every k vector 3 acoustic
Quasiparticles Phonons N atom atoms in crystal 3N atom normal modes p atoms in the basis N atom /p unit cells N atom /p translational symmetries N atom /p k-vectors 3p modes for every k vector 3 acoustic
Metals: the Drude and Sommerfeld models p. 1 Introduction p. 1 What do we know about metals? p. 1 The Drude model p. 2 Assumptions p.
 Metals: the Drude and Sommerfeld models p. 1 Introduction p. 1 What do we know about metals? p. 1 The Drude model p. 2 Assumptions p. 2 The relaxation-time approximation p. 3 The failure of the Drude model
Metals: the Drude and Sommerfeld models p. 1 Introduction p. 1 What do we know about metals? p. 1 The Drude model p. 2 Assumptions p. 2 The relaxation-time approximation p. 3 The failure of the Drude model
Lecture 3: Electron statistics in a solid
 Lecture 3: Electron statistics in a solid Contents Density of states. DOS in a 3D uniform solid.................... 3.2 DOS for a 2D solid........................ 4.3 DOS for a D solid........................
Lecture 3: Electron statistics in a solid Contents Density of states. DOS in a 3D uniform solid.................... 3.2 DOS for a 2D solid........................ 4.3 DOS for a D solid........................
Solid State Physics. Lecture 10 Band Theory. Professor Stephen Sweeney
 Solid State Physics Lecture 10 Band Theory Professor Stephen Sweeney Advanced Technology Institute and Department of Physics University of Surrey, Guildford, GU2 7XH, UK s.sweeney@surrey.ac.uk Recap from
Solid State Physics Lecture 10 Band Theory Professor Stephen Sweeney Advanced Technology Institute and Department of Physics University of Surrey, Guildford, GU2 7XH, UK s.sweeney@surrey.ac.uk Recap from
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 9
 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 9 David Ritchie QCMP Lent/Easter 2018 http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home 9.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical and Semi-classical models for electrons
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 9 David Ritchie QCMP Lent/Easter 2018 http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home 9.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical and Semi-classical models for electrons
Electrical conduction in solids
 Equations of motion Electrical conduction in solids Electrical conduction is the movement of electrically charged particles through a conductor or semiconductor, which constitutes an electric current.
Equations of motion Electrical conduction in solids Electrical conduction is the movement of electrically charged particles through a conductor or semiconductor, which constitutes an electric current.
Nearly Free Electron Gas model - I
 Nearly Free Electron Gas model - I Contents 1 Free electron gas model summary 1 2 Electron effective mass 3 2.1 FEG model for sodium...................... 4 3 Nearly free electron model 5 3.1 Primitive
Nearly Free Electron Gas model - I Contents 1 Free electron gas model summary 1 2 Electron effective mass 3 2.1 FEG model for sodium...................... 4 3 Nearly free electron model 5 3.1 Primitive
Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics. Lecture notes for Physics 284 by Eugene Demler Harvard University
 Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics Lecture notes for Physics 284 by Eugene Demler Harvard University September 18, 2014 2 Chapter 5 Atoms in optical lattices Optical lattices
Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics Lecture notes for Physics 284 by Eugene Demler Harvard University September 18, 2014 2 Chapter 5 Atoms in optical lattices Optical lattices
The electronic structure of solids. Charge transport in solids
 The electronic structure of solids We need a picture of the electronic structure of solid that we can use to explain experimental observations and make predictions Why is diamond an insulator? Why is sodium
The electronic structure of solids We need a picture of the electronic structure of solid that we can use to explain experimental observations and make predictions Why is diamond an insulator? Why is sodium
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics
 QCMP-2017/18 Problem sheet 2: Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Band structure 1. Optical absorption of simple metals Sketch the typical energy-wavevector dependence, or dispersion relation, of electrons
QCMP-2017/18 Problem sheet 2: Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Band structure 1. Optical absorption of simple metals Sketch the typical energy-wavevector dependence, or dispersion relation, of electrons
Class 24: Density of States
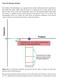 Class 24: Density of States The solution to the Schrödinger wave equation showed us that confinement leads to quantization. The smaller the region within which the electron is confined, the more widely
Class 24: Density of States The solution to the Schrödinger wave equation showed us that confinement leads to quantization. The smaller the region within which the electron is confined, the more widely
Calculating Band Structure
 Calculating Band Structure Nearly free electron Assume plane wave solution for electrons Weak potential V(x) Brillouin zone edge Tight binding method Electrons in local atomic states (bound states) Interatomic
Calculating Band Structure Nearly free electron Assume plane wave solution for electrons Weak potential V(x) Brillouin zone edge Tight binding method Electrons in local atomic states (bound states) Interatomic
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 22 Aug 1994
 Submitted to Phys. Rev. B Bound on the Group Velocity of an Electron in a One-Dimensional Periodic Potential arxiv:cond-mat/9408067v 22 Aug 994 Michael R. Geller and Giovanni Vignale Institute for Theoretical
Submitted to Phys. Rev. B Bound on the Group Velocity of an Electron in a One-Dimensional Periodic Potential arxiv:cond-mat/9408067v 22 Aug 994 Michael R. Geller and Giovanni Vignale Institute for Theoretical
In chapter 3, when we discussed metallic bonding, the primary attribute was that electrons are delocalized.
 Lecture 15: free electron gas Up to this point we have not discussed electrons explicitly, but electrons are the first offenders for most useful phenomena in materials. When we distinguish between metals,
Lecture 15: free electron gas Up to this point we have not discussed electrons explicitly, but electrons are the first offenders for most useful phenomena in materials. When we distinguish between metals,
Electromagnetism II. Instructor: Andrei Sirenko Spring 2013 Thursdays 1 pm 4 pm. Spring 2013, NJIT 1
 Electromagnetism II Instructor: Andrei Sirenko sirenko@njit.edu Spring 013 Thursdays 1 pm 4 pm Spring 013, NJIT 1 PROBLEMS for CH. 6 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/phys433/phys433eandm013.htm Can obtain
Electromagnetism II Instructor: Andrei Sirenko sirenko@njit.edu Spring 013 Thursdays 1 pm 4 pm Spring 013, NJIT 1 PROBLEMS for CH. 6 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/phys433/phys433eandm013.htm Can obtain
SOLID STATE PHYSICS. Second Edition. John Wiley & Sons. J. R. Hook H. E. Hall. Department of Physics, University of Manchester
 SOLID STATE PHYSICS Second Edition J. R. Hook H. E. Hall Department of Physics, University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Contents Flow diagram Inside front
SOLID STATE PHYSICS Second Edition J. R. Hook H. E. Hall Department of Physics, University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Contents Flow diagram Inside front
3.024 Electrical, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Materials Spring 2012 Recitation 8 Notes
 Overview 1. Electronic Band Diagram Review 2. Spin Review 3. Density of States 4. Fermi-Dirac Distribution 1. Electronic Band Diagram Review Considering 1D crystals with periodic potentials of the form:
Overview 1. Electronic Band Diagram Review 2. Spin Review 3. Density of States 4. Fermi-Dirac Distribution 1. Electronic Band Diagram Review Considering 1D crystals with periodic potentials of the form:
5 Problems Chapter 5: Electrons Subject to a Periodic Potential Band Theory of Solids
 E n = :75, so E cont = E E n = :75 = :479. Using E =!, :479 = m e k z =! j e j m e k z! k z = r :479 je j m e = :55 9 (44) (v g ) z = @! @k z = m e k z = m e :55 9 = :95 5 m/s. 4.. A ev electron is to
E n = :75, so E cont = E E n = :75 = :479. Using E =!, :479 = m e k z =! j e j m e k z! k z = r :479 je j m e = :55 9 (44) (v g ) z = @! @k z = m e k z = m e :55 9 = :95 5 m/s. 4.. A ev electron is to
Lattice Vibrations. Chris J. Pickard. ω (cm -1 ) 200 W L Γ X W K K W
 Lattice Vibrations Chris J. Pickard 500 400 300 ω (cm -1 ) 200 100 L K W X 0 W L Γ X W K The Breakdown of the Static Lattice Model The free electron model was refined by introducing a crystalline external
Lattice Vibrations Chris J. Pickard 500 400 300 ω (cm -1 ) 200 100 L K W X 0 W L Γ X W K The Breakdown of the Static Lattice Model The free electron model was refined by introducing a crystalline external
STM spectroscopy (STS)
 STM spectroscopy (STS) di dv 4 e ( E ev, r) ( E ) M S F T F Basic concepts of STS. With the feedback circuit open the variation of the tunneling current due to the application of a small oscillating voltage
STM spectroscopy (STS) di dv 4 e ( E ev, r) ( E ) M S F T F Basic concepts of STS. With the feedback circuit open the variation of the tunneling current due to the application of a small oscillating voltage
Free Electron Model. Assume N electrons that are non-interacting (identical) fermions Assume they are confined to a box of V=L 3
 As we mentioned previously, the Pauli exclusion principle plays an important role in the behavior of solids The first quantum model we ll look at is called the free electron model or the ermi gas model
As we mentioned previously, the Pauli exclusion principle plays an important role in the behavior of solids The first quantum model we ll look at is called the free electron model or the ermi gas model
Lecture 6 Photons, electrons and other quanta. EECS Winter 2006 Nanophotonics and Nano-scale Fabrication P.C.Ku
 Lecture 6 Photons, electrons and other quanta EECS 598-002 Winter 2006 Nanophotonics and Nano-scale Fabrication P.C.Ku From classical to quantum theory In the beginning of the 20 th century, experiments
Lecture 6 Photons, electrons and other quanta EECS 598-002 Winter 2006 Nanophotonics and Nano-scale Fabrication P.C.Ku From classical to quantum theory In the beginning of the 20 th century, experiments
sin[( t 2 Home Problem Set #1 Due : September 10 (Wed), 2008
 Home Problem Set #1 Due : September 10 (Wed), 008 1. Answer the following questions related to the wave-particle duality. (a) When an electron (mass m) is moving with the velocity of υ, what is the wave
Home Problem Set #1 Due : September 10 (Wed), 008 1. Answer the following questions related to the wave-particle duality. (a) When an electron (mass m) is moving with the velocity of υ, what is the wave
Spring 2010 MSE 111. Midterm Exam. Prof. Eugene E. Haller. University of California at Berkeley Department of Materials Science and Engineering
 Spring 00 MS Midterm xam Prof. ugene. Haller University of California at Berkeley Department of Materials Science and ngineering 3/6/0, 9:40 am 80 minutes, 74 points total, 0 pages ame: SID: Problem 3
Spring 00 MS Midterm xam Prof. ugene. Haller University of California at Berkeley Department of Materials Science and ngineering 3/6/0, 9:40 am 80 minutes, 74 points total, 0 pages ame: SID: Problem 3
Semiconductor Physics
 1 Semiconductor Physics 1.1 Introduction 2 1.2 The Band Theory of Solids 2 1.3 The Kronig Penney Model 3 1.4 The Bragg Model 8 1.5 Effective Mass 8 1.6 Number of States in a Band 10 1.7 Band Filling 12
1 Semiconductor Physics 1.1 Introduction 2 1.2 The Band Theory of Solids 2 1.3 The Kronig Penney Model 3 1.4 The Bragg Model 8 1.5 Effective Mass 8 1.6 Number of States in a Band 10 1.7 Band Filling 12
CHAPTER 9 Statistical Physics
 CHAPTER 9 Statistical Physics 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 Historical Overview Maxwell Velocity Distribution Equipartition Theorem Maxwell Speed Distribution Classical and Quantum Statistics Fermi-Dirac
CHAPTER 9 Statistical Physics 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 Historical Overview Maxwell Velocity Distribution Equipartition Theorem Maxwell Speed Distribution Classical and Quantum Statistics Fermi-Dirac
Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 10 The Free Electron Theory of Metals - Electrical Conductivity (Refer Slide Time: 00:20)
Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 10 The Free Electron Theory of Metals - Electrical Conductivity (Refer Slide Time: 00:20)
Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants are attached to this paper.
 Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants are attached to this paper. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Spring Semester (2016-2017) From Thermodynamics to Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants are attached to this paper. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Spring Semester (2016-2017) From Thermodynamics to Atomic and Nuclear Physics
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department Statistical Physics I Spring Term 2013
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department 8.044 Statistical Physics I Spring Term 2013 Problem 1: Ripplons Problem Set #11 Due in hand-in box by 4:00 PM, Friday, May 10 (k) We have seen
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department 8.044 Statistical Physics I Spring Term 2013 Problem 1: Ripplons Problem Set #11 Due in hand-in box by 4:00 PM, Friday, May 10 (k) We have seen
The Oxford Solid State Basics
 The Oxford Solid State Basics Steven H. Simon University of Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 About Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.1 What Is Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.2 Why Do We Study Condensed
The Oxford Solid State Basics Steven H. Simon University of Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 About Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.1 What Is Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.2 Why Do We Study Condensed
Chapter 1. From Classical to Quantum Mechanics
 Chapter 1. From Classical to Quantum Mechanics Classical Mechanics (Newton): It describes the motion of a classical particle (discrete object). dp F ma, p = m = dt dx m dt F: force (N) a: acceleration
Chapter 1. From Classical to Quantum Mechanics Classical Mechanics (Newton): It describes the motion of a classical particle (discrete object). dp F ma, p = m = dt dx m dt F: force (N) a: acceleration
Identical Particles. Bosons and Fermions
 Identical Particles Bosons and Fermions In Quantum Mechanics there is no difference between particles and fields. The objects which we refer to as fields in classical physics (electromagnetic field, field
Identical Particles Bosons and Fermions In Quantum Mechanics there is no difference between particles and fields. The objects which we refer to as fields in classical physics (electromagnetic field, field
Lecture 22 Metals - Superconductivity
 Lecture 22: Metals (Review and Kittel Ch. 9) and Superconductivity I (Kittel Ch. 1) Resistence Ω Leiden, Netherlands - 1911.1 4.6 K g sample < 1-5 Ω Outline metals Recall properties (From lectures 12,
Lecture 22: Metals (Review and Kittel Ch. 9) and Superconductivity I (Kittel Ch. 1) Resistence Ω Leiden, Netherlands - 1911.1 4.6 K g sample < 1-5 Ω Outline metals Recall properties (From lectures 12,
Lecture 11 - Phonons II - Thermal Prop. Continued
 Phonons II - hermal Properties - Continued (Kittel Ch. 5) Low High Outline Anharmonicity Crucial for hermal expansion other changes with pressure temperature Gruneisen Constant hermal Heat ransport Phonon
Phonons II - hermal Properties - Continued (Kittel Ch. 5) Low High Outline Anharmonicity Crucial for hermal expansion other changes with pressure temperature Gruneisen Constant hermal Heat ransport Phonon
Lecture 10 Waves in Periodic Potentials Today: Questions you should be able to address after today s lecture:
 Lecture 10 Waves in Periodic Potentials Today: 1. Direct lattice and periodic potential as a convolution of a lattice and a basis. 2. The discrete translation operator: eigenvalues and eigenfunctions.
Lecture 10 Waves in Periodic Potentials Today: 1. Direct lattice and periodic potential as a convolution of a lattice and a basis. 2. The discrete translation operator: eigenvalues and eigenfunctions.
Part II - Electronic Properties of Solids Lecture 12: The Electron Gas (Kittel Ch. 6) Physics 460 F 2006 Lect 12 1
 Part II - Electronic Properties of Solids Lecture 12: The Electron Gas (Kittel Ch. 6) Physics 460 F 2006 Lect 12 1 Outline Overview - role of electrons in solids The starting point for understanding electrons
Part II - Electronic Properties of Solids Lecture 12: The Electron Gas (Kittel Ch. 6) Physics 460 F 2006 Lect 12 1 Outline Overview - role of electrons in solids The starting point for understanding electrons
Phonons II: Thermal properties
 Phonons II: Thermal properties specific heat of a crystal density of state Einstein mode Debye model anharmonic effect thermal conduction A technician holding a silica fibre thermal insulation tile at
Phonons II: Thermal properties specific heat of a crystal density of state Einstein mode Debye model anharmonic effect thermal conduction A technician holding a silica fibre thermal insulation tile at
Carrier Mobility and Hall Effect. Prof.P. Ravindran, Department of Physics, Central University of Tamil Nadu, India
 Carrier Mobility and Hall Effect 1 Prof.P. Ravindran, Department of Physics, Central University of Tamil Nadu, India http://folk.uio.no/ravi/semi2013 calculation Calculate the hole and electron densities
Carrier Mobility and Hall Effect 1 Prof.P. Ravindran, Department of Physics, Central University of Tamil Nadu, India http://folk.uio.no/ravi/semi2013 calculation Calculate the hole and electron densities
Introduction to Condensed Matter Physics
 Introduction to Condensed Matter Physics The Reciprocal Lattice M.P. Vaughan Overview Overview of the reciprocal lattice Periodic functions Reciprocal lattice vectors Bloch functions k-space Dispersion
Introduction to Condensed Matter Physics The Reciprocal Lattice M.P. Vaughan Overview Overview of the reciprocal lattice Periodic functions Reciprocal lattice vectors Bloch functions k-space Dispersion
半導體元件與物理. Semiconductor Devices and physics 許正興國立聯合大學電機工程學系 聯大電機系電子材料與元件應用實驗室
 半導體元件與物理 Semiconductor Devices and physics 許正興國立聯合大學電機工程學系 1. Crystal Structure of Solids 2. Quantum Theory of Solids 3. Semiconductor in Equilibrium and Carrier Transport phenomena 4. PN Junction and
半導體元件與物理 Semiconductor Devices and physics 許正興國立聯合大學電機工程學系 1. Crystal Structure of Solids 2. Quantum Theory of Solids 3. Semiconductor in Equilibrium and Carrier Transport phenomena 4. PN Junction and
5.62 Physical Chemistry II Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.62 Physical Chemistry II Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.62 Spring 2008 Lecture
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.62 Physical Chemistry II Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.62 Spring 2008 Lecture
On the Heisenberg and Schrödinger Pictures
 Journal of Modern Physics, 04, 5, 7-76 Published Online March 04 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/ournal/mp http://dx.doi.org/0.436/mp.04.5507 On the Heisenberg and Schrödinger Pictures Shigei Fuita, James
Journal of Modern Physics, 04, 5, 7-76 Published Online March 04 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/ournal/mp http://dx.doi.org/0.436/mp.04.5507 On the Heisenberg and Schrödinger Pictures Shigei Fuita, James
Lecture 4 Recap: normal metals and the clectron-phonon interaction *
 Phys. 598SC Fall 2015 Prof. A. J. Leggett Lecture 4 Recap: normal metals and the clectron-phonon interaction * 1. Normal metals: Sommerfeld-Bloch picture 2. Screening 3. Fermi liquid theory 4. Electron-phonon
Phys. 598SC Fall 2015 Prof. A. J. Leggett Lecture 4 Recap: normal metals and the clectron-phonon interaction * 1. Normal metals: Sommerfeld-Bloch picture 2. Screening 3. Fermi liquid theory 4. Electron-phonon
introduction of thermal transport
 Subgroup meeting 2010.12.07 introduction of thermal transport members: 王虹之. 盧孟珮 introduction of thermal transport Phonon effect Electron effect Lattice vibration phonon Debye model of lattice vibration
Subgroup meeting 2010.12.07 introduction of thermal transport members: 王虹之. 盧孟珮 introduction of thermal transport Phonon effect Electron effect Lattice vibration phonon Debye model of lattice vibration
PH575 Spring Lecture #13 Free electron theory: Sutton Ch. 7 pp 132 -> 144; Kittel Ch. 6. 3/2 " # % & D( E) = V E 1/2. 2π 2.
 PH575 Spring 2014 Lecture #13 Free electron theory: Sutton Ch. 7 pp 132 -> 144; Kittel Ch. 6. E( k) = 2 k 2 D( E) = V 2π 2 " # $ 2 3/2 % & ' E 1/2 Assumption: electrons metal do not interact with each
PH575 Spring 2014 Lecture #13 Free electron theory: Sutton Ch. 7 pp 132 -> 144; Kittel Ch. 6. E( k) = 2 k 2 D( E) = V 2π 2 " # $ 2 3/2 % & ' E 1/2 Assumption: electrons metal do not interact with each
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics In order to understand the current-voltage characteristics, we need some knowledge of electron behavior in semiconductor when the electron is subjected to various potential
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics In order to understand the current-voltage characteristics, we need some knowledge of electron behavior in semiconductor when the electron is subjected to various potential
Condensed matter theory Lecture notes and problem sets 2012/2013
 Condensed matter theory Lecture notes and problem sets 2012/2013 Dmitri Ivanov Recommended books and lecture notes: [AM] N. W. Ashcroft and N. D. Mermin, Solid State Physics. [Mar] M. P. Marder, Condensed
Condensed matter theory Lecture notes and problem sets 2012/2013 Dmitri Ivanov Recommended books and lecture notes: [AM] N. W. Ashcroft and N. D. Mermin, Solid State Physics. [Mar] M. P. Marder, Condensed
