Review Packet 1 B 11 B 12 B 13 B = B 21 B 22 B 23 B 31 B 32 B 33 B 41 B 42 B 43
|
|
|
- Elvin Dawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Packet. For each of the following, write the vector or matrix that is specified: a. e 3 R 4 b. D = diag{, 3, } c. e R 3 d. I. For each of the following matrices and vectors, give their dimension. Label each as a matrix or vector. For each matrix, indicate whether the matrix is square or rectangular. a. b. c. d. 3 A = h = 4 B B B 3 B = B B B 3 B 3 B 3 B 33 B 4 B 4 B 43 A = [A ij ] where i =,, 3 and j =, 3. Specify whether the following augmented matrices are in row-echelon form (REF), reduced row-echelon form (RREF), or neither: 3 a b c d
2 4. (True/False) The normal equations are used to find the ordinary least-squares solution to an inconsistent system of equations. 5. If the matrix equation Mv = b is inconsistent, what alternative equation should I solve to find a solution v such that M v = b is as close to b as possible in the sense that it minimizes the sum of squared error: SSE = n ( b i b i ) 6. Answer the following questions about each matrix A = 5 3 B = a. Is the matrix square? A B b. What is the transpose of the matrix? A T = B T = c. Is the matrix symmetric? A B d. If possible, name the diagonal elements of the matrix. A B e. If possible, compute the Trace of the matrix. A B f. Can the product AB be computed? If so, what is the size of the result? g. Can the product BA be computed? If so, what is the size of the result? h. Can the product (B 3 ) T (A 3 ) T be computed? If so, what is the result?
3 7. What is the inverse of the matrix D = σi 3? 8. For the following graph, number the nodes and write the corresponding adjacency matrix: 9. Compute the outer product xy T where 3 x = 4 y = 5 xy T = 0. Can you say anything about the rank of an outer product in general? Explain your answer.. Briefly explain what it means for a matrix to be full rank.. For the following augmented matrices, circle the pivot elements and give the rank of the coefficient matrix along with the number of free variables. 3 a rank= # free var=
4 b. c rank= # free var= rank= # free var= Write the vector v as a linear combination of each given x and y, if possible. a. x = ( ) 0 y = ( ) 0 v = ( ) 3 b. x = ( ) 0 ( 0 y = ) c. x = ( ) y = ( ) 4. Suppose we measure the heights of 0 people, person, person,..., person 0. a. If we create a matrix S where S ij = height(person i ) height(person j ) is the matrix S symmetric? What is the trace(s)? b. If instead we create a matrix G where G ij = [height(person i ) height(person j )] is the matrix G symmetric? What is the trace(g)? 5. For the matrix H = X(X T Σ X) X T Σ, use the properties of matrix arithmetic to show that a. H = H b. H(I H) = 0
5 6. Let U = (U U U 3... U p ) and V T = V T V T V3 T. Write the matrix product UV T in terms of the columns of U and the rows of V T. V T p 7. Suppose that u is a unit vector. Then, u =? 0 8. Let x = and y =. Compute the following: 3 a. x b. y c. y d. x y e. x y 9. Suppose we have a dataset containing survey data. Individuals were asked to respond yes = or no =0 to twenty potential political referendums. Let a be the vector containing the numerical responses of Individual A and let b be the vector containing the numerical responses of Individual B (so a, b R 0 ). Explain in words the interpretation of the quantity a b.
6 0. Statistical Formulas Using Linear Algebra Notation. Almost every statistical formula can be written in a more compact fashion using linear algebra. Most of the elementary formulas involve vector inner products or the Euclidean norm. To begin, we ll introduce the concept of centering the data. Centering the data means that the mean of a variable is subtracted from each observation. For example, if we have some variable, x, and 3 observations on that variable: x = 3 4 then obviously, x = 3. The centered version of x would then be 3 x xe = 3 3 = We simply subtract the mean from every observation so that the new mean of the variable is 0. Most multivariate textbooks start by saying all variable vectors in this textbook are assumed to be centered to have mean zero unless otherwise specified. Looking at the most common statistical formulas helps us see why. Try to re-write the following formulas using linear algebra notation, using the vectors x and y to represent centered data: x x y ȳ x x y ȳ x = x 3 x, y = y 3 ȳ. x n x. y n ȳ For this exercise, keep in mind the following linear algebra constructs, which you should be very familiar with by now: a = a + a + a a n a T b = a b + a b + a 3 b a n b n a. Sample standard deviation: s = n (x i x) = n b. Sample covariance: covariance(x, y) = n n (x i x)(y i ȳ) =
7 c. Correlation coefficient: r xy = n n (x i x)(y i ȳ) = (x i x) n (y i ȳ)
8 . List of Key Words. You should be comfortable with the following vocabulary: linear matrix vector scalar A ij A j A i dimensions diagonal element square matrix rectangular matrix network graph adjacency matrix correlation matrix transpose symmetric matrix trace diagonal matrix identity matrix upper triangular matrix lower triangular matrix matrix addition matrix subtraction scalar multiplication inner product matrix product linear combination outer product matrix inverse systems of equations row operations row-echelon form pivot element Gaussian elimination Gauss-Jordan elimination reduced row-echelon form rank unique solution infinitely many solutions inconsistent back-substitution residual error least squares normal equations least squares solution parameter estimate linearly independent linearly dependent full rank perfect multicollinearity severe multicollinearity invertible nonsingular Distributive Property A(B + C) =? (A + B)(C + D) =? Associative Property Transpose of Product (ABC) T =? (αa) T =? Inverse of Transpose, A T Partitioned Matrices Vector Norm Magnitude/Length -norm x x T x Euclidean Norm Euclidean Distance Unit vector Create unit vector -norm x Manhattan distance Taxicab distance Cityblock distance x Max Distance Mahalanobis distance
Elementary Linear Algebra
 Elementary Linear Algebra Linear algebra is the study of; linear sets of equations and their transformation properties. Linear algebra allows the analysis of; rotations in space, least squares fitting,
Elementary Linear Algebra Linear algebra is the study of; linear sets of equations and their transformation properties. Linear algebra allows the analysis of; rotations in space, least squares fitting,
Chapter 1: Systems of linear equations and matrices. Section 1.1: Introduction to systems of linear equations
 Chapter 1: Systems of linear equations and matrices Section 1.1: Introduction to systems of linear equations Definition: A linear equation in n variables can be expressed in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2
Chapter 1: Systems of linear equations and matrices Section 1.1: Introduction to systems of linear equations Definition: A linear equation in n variables can be expressed in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2
Matrices and systems of linear equations
 Matrices and systems of linear equations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations and linear algebra - MA 262 Taken from Differential equations and linear algebra by Goode and Annin Samy T.
Matrices and systems of linear equations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations and linear algebra - MA 262 Taken from Differential equations and linear algebra by Goode and Annin Samy T.
If A is a 4 6 matrix and B is a 6 3 matrix then the dimension of AB is A. 4 6 B. 6 6 C. 4 3 D. 3 4 E. Undefined
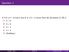 Question 1 If A is a 4 6 matrix and B is a 6 3 matrix then the dimension of AB is A. 4 6 B. 6 6 C. 4 3 D. 3 4 E. Undefined Quang T. Bach Math 18 October 18, 2017 1 / 17 Question 2 1 2 Let A = 3 4 1 2 3
Question 1 If A is a 4 6 matrix and B is a 6 3 matrix then the dimension of AB is A. 4 6 B. 6 6 C. 4 3 D. 3 4 E. Undefined Quang T. Bach Math 18 October 18, 2017 1 / 17 Question 2 1 2 Let A = 3 4 1 2 3
7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix
 7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Verify that two matrices are inverses of each other. Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find inverses
7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Verify that two matrices are inverses of each other. Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find inverses
MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS. + + x 1 x 2. x n 8 (4) 3 4 2
 MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS AND MATRICES Representation of a linear system The general system of m equations in n unknowns can be written a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n b a
MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS AND MATRICES Representation of a linear system The general system of m equations in n unknowns can be written a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n b a
Math 220: Summer Midterm 1 Questions
 Math 220: Summer 2015 Midterm 1 Questions MOST questions will either look a lot like a Homework questions This lists draws your attention to some important types of HW questions. SOME questions will have
Math 220: Summer 2015 Midterm 1 Questions MOST questions will either look a lot like a Homework questions This lists draws your attention to some important types of HW questions. SOME questions will have
Finite Mathematics Chapter 2. where a, b, c, d, h, and k are real numbers and neither a and b nor c and d are both zero.
 Finite Mathematics Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Systems of Linear Equations: An Introduction Systems of Equations Recall that a system of two linear equations in two variables may be written in the general form
Finite Mathematics Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Systems of Linear Equations: An Introduction Systems of Equations Recall that a system of two linear equations in two variables may be written in the general form
Math 4A Notes. Written by Victoria Kala Last updated June 11, 2017
 Math 4A Notes Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu Last updated June 11, 2017 Systems of Linear Equations A linear equation is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 +...
Math 4A Notes Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu Last updated June 11, 2017 Systems of Linear Equations A linear equation is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 +...
MAC Module 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices I
 MAC 2103 Module 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices I 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Represent a system of linear equations as an augmented matrix.
MAC 2103 Module 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices I 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Represent a system of linear equations as an augmented matrix.
Introduction to Matrices
 POLS 704 Introduction to Matrices Introduction to Matrices. The Cast of Characters A matrix is a rectangular array (i.e., a table) of numbers. For example, 2 3 X 4 5 6 (4 3) 7 8 9 0 0 0 Thismatrix,with4rowsand3columns,isoforder
POLS 704 Introduction to Matrices Introduction to Matrices. The Cast of Characters A matrix is a rectangular array (i.e., a table) of numbers. For example, 2 3 X 4 5 6 (4 3) 7 8 9 0 0 0 Thismatrix,with4rowsand3columns,isoforder
Review Questions REVIEW QUESTIONS 71
 REVIEW QUESTIONS 71 MATLAB, is [42]. For a comprehensive treatment of error analysis and perturbation theory for linear systems and many other problems in linear algebra, see [126, 241]. An overview of
REVIEW QUESTIONS 71 MATLAB, is [42]. For a comprehensive treatment of error analysis and perturbation theory for linear systems and many other problems in linear algebra, see [126, 241]. An overview of
Chapter 1 Matrices and Systems of Equations
 Chapter 1 Matrices and Systems of Equations System of Linear Equations 1. A linear equation in n unknowns is an equation of the form n i=1 a i x i = b where a 1,..., a n, b R and x 1,..., x n are variables.
Chapter 1 Matrices and Systems of Equations System of Linear Equations 1. A linear equation in n unknowns is an equation of the form n i=1 a i x i = b where a 1,..., a n, b R and x 1,..., x n are variables.
4 Elementary matrices, continued
 4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices are constructed
4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices are constructed
Matrix & Linear Algebra
 Matrix & Linear Algebra Jamie Monogan University of Georgia For more information: http://monogan.myweb.uga.edu/teaching/mm/ Jamie Monogan (UGA) Matrix & Linear Algebra 1 / 84 Vectors Vectors Vector: A
Matrix & Linear Algebra Jamie Monogan University of Georgia For more information: http://monogan.myweb.uga.edu/teaching/mm/ Jamie Monogan (UGA) Matrix & Linear Algebra 1 / 84 Vectors Vectors Vector: A
CHAPTER 8: Matrices and Determinants
 (Exercises for Chapter 8: Matrices and Determinants) E.8.1 CHAPTER 8: Matrices and Determinants (A) means refer to Part A, (B) means refer to Part B, etc. Most of these exercises can be done without a
(Exercises for Chapter 8: Matrices and Determinants) E.8.1 CHAPTER 8: Matrices and Determinants (A) means refer to Part A, (B) means refer to Part B, etc. Most of these exercises can be done without a
Math Camp II. Basic Linear Algebra. Yiqing Xu. Aug 26, 2014 MIT
 Math Camp II Basic Linear Algebra Yiqing Xu MIT Aug 26, 2014 1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations 2 Vectors and Vector Spaces 3 Matrices 4 Least Squares Systems of Linear Equations Definition A linear
Math Camp II Basic Linear Algebra Yiqing Xu MIT Aug 26, 2014 1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations 2 Vectors and Vector Spaces 3 Matrices 4 Least Squares Systems of Linear Equations Definition A linear
4 Elementary matrices, continued
 4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. To repeat the recipe: These matrices are constructed by performing the given row
4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. To repeat the recipe: These matrices are constructed by performing the given row
9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables
 9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two variables is an ordered
9.1 - Systems of Linear Equations: Two Variables Recall that a system of equations consists of two or more equations each with two or more variables. A solution to a system in two variables is an ordered
Chapter 2 Notes, Linear Algebra 5e Lay
 Contents.1 Operations with Matrices..................................1.1 Addition and Subtraction.............................1. Multiplication by a scalar............................ 3.1.3 Multiplication
Contents.1 Operations with Matrices..................................1.1 Addition and Subtraction.............................1. Multiplication by a scalar............................ 3.1.3 Multiplication
Chapter 1. Vectors, Matrices, and Linear Spaces
 1.4 Solving Systems of Linear Equations 1 Chapter 1. Vectors, Matrices, and Linear Spaces 1.4. Solving Systems of Linear Equations Note. We give an algorithm for solving a system of linear equations (called
1.4 Solving Systems of Linear Equations 1 Chapter 1. Vectors, Matrices, and Linear Spaces 1.4. Solving Systems of Linear Equations Note. We give an algorithm for solving a system of linear equations (called
CS123 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS. Linear Algebra 1/33
 Linear Algebra 1/33 Vectors A vector is a magnitude and a direction Magnitude = v Direction Also known as norm, length Represented by unit vectors (vectors with a length of 1 that point along distinct
Linear Algebra 1/33 Vectors A vector is a magnitude and a direction Magnitude = v Direction Also known as norm, length Represented by unit vectors (vectors with a length of 1 that point along distinct
Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide
 Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide Phil R. Smith, Ph.D. February 28, 20 Homework Problem Sets Organized by Learning Outcomes Test I: Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Lesson. Give examples of
Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide Phil R. Smith, Ph.D. February 28, 20 Homework Problem Sets Organized by Learning Outcomes Test I: Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Lesson. Give examples of
POLI270 - Linear Algebra
 POLI7 - Linear Algebra Septemer 8th Basics a x + a x +... + a n x n b () is the linear form where a, b are parameters and x n are variables. For a given equation such as x +x you only need a variable and
POLI7 - Linear Algebra Septemer 8th Basics a x + a x +... + a n x n b () is the linear form where a, b are parameters and x n are variables. For a given equation such as x +x you only need a variable and
Chapter 4. Solving Systems of Equations. Chapter 4
 Solving Systems of Equations 3 Scenarios for Solutions There are three general situations we may find ourselves in when attempting to solve systems of equations: 1 The system could have one unique solution.
Solving Systems of Equations 3 Scenarios for Solutions There are three general situations we may find ourselves in when attempting to solve systems of equations: 1 The system could have one unique solution.
Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued
 Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued Math 19620 Outline of Lecture Algorithm for putting a matrix in row reduced echelon form - i.e. Gauss-Jordan Elimination Number of Solutions
Lecture 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices, Continued Math 19620 Outline of Lecture Algorithm for putting a matrix in row reduced echelon form - i.e. Gauss-Jordan Elimination Number of Solutions
Linear Algebra. The analysis of many models in the social sciences reduces to the study of systems of equations.
 POLI 7 - Mathematical and Statistical Foundations Prof S Saiegh Fall Lecture Notes - Class 4 October 4, Linear Algebra The analysis of many models in the social sciences reduces to the study of systems
POLI 7 - Mathematical and Statistical Foundations Prof S Saiegh Fall Lecture Notes - Class 4 October 4, Linear Algebra The analysis of many models in the social sciences reduces to the study of systems
Midterm 1 Review. Written by Victoria Kala SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015
 Midterm 1 Review Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015 Summary This Midterm Review contains notes on sections 1.1 1.5 and 1.7 in your
Midterm 1 Review Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 12:30 1:30 pm Last updated 10/10/2015 Summary This Midterm Review contains notes on sections 1.1 1.5 and 1.7 in your
Math 314H EXAM I. 1. (28 points) The row reduced echelon form of the augmented matrix for the system. is the matrix
 Math 34H EXAM I Do all of the problems below. Point values for each of the problems are adjacent to the problem number. Calculators may be used to check your answer but not to arrive at your answer. That
Math 34H EXAM I Do all of the problems below. Point values for each of the problems are adjacent to the problem number. Calculators may be used to check your answer but not to arrive at your answer. That
A Review of Matrix Analysis
 Matrix Notation Part Matrix Operations Matrices are simply rectangular arrays of quantities Each quantity in the array is called an element of the matrix and an element can be either a numerical value
Matrix Notation Part Matrix Operations Matrices are simply rectangular arrays of quantities Each quantity in the array is called an element of the matrix and an element can be either a numerical value
Digital Workbook for GRA 6035 Mathematics
 Eivind Eriksen Digital Workbook for GRA 6035 Mathematics November 10, 2014 BI Norwegian Business School Contents Part I Lectures in GRA6035 Mathematics 1 Linear Systems and Gaussian Elimination........................
Eivind Eriksen Digital Workbook for GRA 6035 Mathematics November 10, 2014 BI Norwegian Business School Contents Part I Lectures in GRA6035 Mathematics 1 Linear Systems and Gaussian Elimination........................
CS123 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS. Linear Algebra /34
 Linear Algebra /34 Vectors A vector is a magnitude and a direction Magnitude = v Direction Also known as norm, length Represented by unit vectors (vectors with a length of 1 that point along distinct axes)
Linear Algebra /34 Vectors A vector is a magnitude and a direction Magnitude = v Direction Also known as norm, length Represented by unit vectors (vectors with a length of 1 that point along distinct axes)
MAC1105-College Algebra. Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices
 MAC05-College Algebra Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices 5. Systems of Equations in Two Variables Solving Systems of Two Linear Equations/ Two-Variable Linear Equations A system of equations is
MAC05-College Algebra Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices 5. Systems of Equations in Two Variables Solving Systems of Two Linear Equations/ Two-Variable Linear Equations A system of equations is
Inverting Matrices. 1 Properties of Transpose. 2 Matrix Algebra. P. Danziger 3.2, 3.3
 3., 3.3 Inverting Matrices P. Danziger 1 Properties of Transpose Transpose has higher precedence than multiplication and addition, so AB T A ( B T and A + B T A + ( B T As opposed to the bracketed expressions
3., 3.3 Inverting Matrices P. Danziger 1 Properties of Transpose Transpose has higher precedence than multiplication and addition, so AB T A ( B T and A + B T A + ( B T As opposed to the bracketed expressions
Chapter 1: Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices
 : Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Multiple Choice Questions. Which of the following equations is linear? (A) x + 3x 3 + 4x 4 3 = 5 (B) 3x x + x 3 = 5 (C) 5x + 5 x x 3 = x + cos (x ) + 4x 3 = 7.
: Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Multiple Choice Questions. Which of the following equations is linear? (A) x + 3x 3 + 4x 4 3 = 5 (B) 3x x + x 3 = 5 (C) 5x + 5 x x 3 = x + cos (x ) + 4x 3 = 7.
Elementary matrices, continued. To summarize, we have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding
 Elementary matrices, continued To summarize, we have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices
Elementary matrices, continued To summarize, we have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. If you check the previous examples, you ll find that these matrices
Linear Algebra I Lecture 10
 Linear Algebra I Lecture 10 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 30, 2019 Outline 1 Gauss-Jordan Algorithm ] Let A = [a ij m n be an m n matrix. To reduce A to a reduced row echelon form using elementary
Linear Algebra I Lecture 10 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 30, 2019 Outline 1 Gauss-Jordan Algorithm ] Let A = [a ij m n be an m n matrix. To reduce A to a reduced row echelon form using elementary
Elementary Row Operations on Matrices
 King Saud University September 17, 018 Table of contents 1 Definition A real matrix is a rectangular array whose entries are real numbers. These numbers are organized on rows and columns. An m n matrix
King Saud University September 17, 018 Table of contents 1 Definition A real matrix is a rectangular array whose entries are real numbers. These numbers are organized on rows and columns. An m n matrix
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra. Section 2.1 Matrix Operations. Definition: A : m n, B : n p. Example: Compute AB, if possible.
 MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 2.1 Matrix Operations Definition: A : m n, B : n p ( 1 2 p ) ( 1 2 p ) AB = A b b b = Ab Ab Ab Example: Compute AB, if possible. 1 Row-column rule: i-j-th entry of AB:
MATH 2331 Linear Algebra Section 2.1 Matrix Operations Definition: A : m n, B : n p ( 1 2 p ) ( 1 2 p ) AB = A b b b = Ab Ab Ab Example: Compute AB, if possible. 1 Row-column rule: i-j-th entry of AB:
3.4 Elementary Matrices and Matrix Inverse
 Math 220: Summer 2015 3.4 Elementary Matrices and Matrix Inverse A n n elementary matrix is a matrix which is obtained from the n n identity matrix I n n by a single elementary row operation. Elementary
Math 220: Summer 2015 3.4 Elementary Matrices and Matrix Inverse A n n elementary matrix is a matrix which is obtained from the n n identity matrix I n n by a single elementary row operation. Elementary
Math Computation Test 1 September 26 th, 2016 Debate: Computation vs. Theory Whatever wins, it ll be Huuuge!
 Math 5- Computation Test September 6 th, 6 Debate: Computation vs. Theory Whatever wins, it ll be Huuuge! Name: Answer Key: Making Math Great Again Be sure to show your work!. (8 points) Consider the following
Math 5- Computation Test September 6 th, 6 Debate: Computation vs. Theory Whatever wins, it ll be Huuuge! Name: Answer Key: Making Math Great Again Be sure to show your work!. (8 points) Consider the following
Review for Exam Find all a for which the following linear system has no solutions, one solution, and infinitely many solutions.
 Review for Exam. Find all a for which the following linear system has no solutions, one solution, and infinitely many solutions. x + y z = 2 x + 2y + z = 3 x + y + (a 2 5)z = a 2 The augmented matrix for
Review for Exam. Find all a for which the following linear system has no solutions, one solution, and infinitely many solutions. x + y z = 2 x + 2y + z = 3 x + y + (a 2 5)z = a 2 The augmented matrix for
Section 3.3. Matrix Rank and the Inverse of a Full Rank Matrix
 3.3. Matrix Rank and the Inverse of a Full Rank Matrix 1 Section 3.3. Matrix Rank and the Inverse of a Full Rank Matrix Note. The lengthy section (21 pages in the text) gives a thorough study of the rank
3.3. Matrix Rank and the Inverse of a Full Rank Matrix 1 Section 3.3. Matrix Rank and the Inverse of a Full Rank Matrix Note. The lengthy section (21 pages in the text) gives a thorough study of the rank
Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices
 Chapter 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices System of linear algebraic equations and their solution constitute one of the major topics studied in the course known as linear algebra. In the first
Chapter 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices System of linear algebraic equations and their solution constitute one of the major topics studied in the course known as linear algebra. In the first
Lecture Notes in Linear Algebra
 Lecture Notes in Linear Algebra Dr. Abdullah Al-Azemi Mathematics Department Kuwait University February 4, 2017 Contents 1 Linear Equations and Matrices 1 1.2 Matrices............................................
Lecture Notes in Linear Algebra Dr. Abdullah Al-Azemi Mathematics Department Kuwait University February 4, 2017 Contents 1 Linear Equations and Matrices 1 1.2 Matrices............................................
MTH Linear Algebra. Study Guide. Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education
 MTH 3 Linear Algebra Study Guide Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education June 3, ii Contents Table of Contents iii Matrix Algebra. Real Life
MTH 3 Linear Algebra Study Guide Dr. Tony Yee Department of Mathematics and Information Technology The Hong Kong Institute of Education June 3, ii Contents Table of Contents iii Matrix Algebra. Real Life
Online Exercises for Linear Algebra XM511
 This document lists the online exercises for XM511. The section ( ) numbers refer to the textbook. TYPE I are True/False. Lecture 02 ( 1.1) Online Exercises for Linear Algebra XM511 1) The matrix [3 2
This document lists the online exercises for XM511. The section ( ) numbers refer to the textbook. TYPE I are True/False. Lecture 02 ( 1.1) Online Exercises for Linear Algebra XM511 1) The matrix [3 2
Number of solutions of a system
 Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 3: Linear systems and matrices Section 7 Number of solutions of a system What you need to know already: How to solve a linear system by using Gauss- Jordan elimination.
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 3: Linear systems and matrices Section 7 Number of solutions of a system What you need to know already: How to solve a linear system by using Gauss- Jordan elimination.
Chapter 2: Matrices and Linear Systems
 Chapter 2: Matrices and Linear Systems Paul Pearson Outline Matrices Linear systems Row operations Inverses Determinants Matrices Definition An m n matrix A = (a ij ) is a rectangular array of real numbers
Chapter 2: Matrices and Linear Systems Paul Pearson Outline Matrices Linear systems Row operations Inverses Determinants Matrices Definition An m n matrix A = (a ij ) is a rectangular array of real numbers
Linear Algebra. Chapter Linear Equations
 Chapter 3 Linear Algebra Dixit algorizmi. Or, So said al-khwarizmi, being the opening words of a 12 th century Latin translation of a work on arithmetic by al-khwarizmi (ca. 78 84). 3.1 Linear Equations
Chapter 3 Linear Algebra Dixit algorizmi. Or, So said al-khwarizmi, being the opening words of a 12 th century Latin translation of a work on arithmetic by al-khwarizmi (ca. 78 84). 3.1 Linear Equations
Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices
 Chapter 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices System of linear algebraic equations and their solution constitute one of the major topics studied in the course known as linear algebra. In the first
Chapter 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices System of linear algebraic equations and their solution constitute one of the major topics studied in the course known as linear algebra. In the first
Extra Problems: Chapter 1
 MA131 (Section 750002): Prepared by Asst.Prof.Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 1 Extra Problems: Chapter 1 1. In each of the following answer true if the statement is always true and false otherwise in the space
MA131 (Section 750002): Prepared by Asst.Prof.Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 1 Extra Problems: Chapter 1 1. In each of the following answer true if the statement is always true and false otherwise in the space
Lecture 3: Gaussian Elimination, continued. Lecture 3: Gaussian Elimination, continued
 Definition The process of solving a system of linear equations by converting the system to an augmented matrix is called Gaussian Elimination. The general strategy is as follows: Convert the system of
Definition The process of solving a system of linear equations by converting the system to an augmented matrix is called Gaussian Elimination. The general strategy is as follows: Convert the system of
MASTER OF SCIENCE IN ANALYTICS 2014 EMPLOYMENT REPORT
 MASTER OF SCIENCE IN ANALYTICS 204 EMPLOYMENT REPORT! Results at graduation, May 204 Number of graduates: 79 MSA 205 Number of graduates seeking new employment: 75 Percent with one or more offers of employment
MASTER OF SCIENCE IN ANALYTICS 204 EMPLOYMENT REPORT! Results at graduation, May 204 Number of graduates: 79 MSA 205 Number of graduates seeking new employment: 75 Percent with one or more offers of employment
Math 313 Chapter 1 Review
 Math 313 Chapter 1 Review Howard Anton, 9th Edition May 2010 Do NOT write on me! Contents 1 1.1 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations 2 2 1.2 Gaussian Elimination 3 3 1.3 Matrices and Matrix Operations
Math 313 Chapter 1 Review Howard Anton, 9th Edition May 2010 Do NOT write on me! Contents 1 1.1 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations 2 2 1.2 Gaussian Elimination 3 3 1.3 Matrices and Matrix Operations
Section 6.2 Larger Systems of Linear Equations
 Section 6.2 Larger Systems of Linear Equations Gaussian Elimination In general, to solve a system of linear equations using its augmented matrix, we use elementary row operations to arrive at a matrix
Section 6.2 Larger Systems of Linear Equations Gaussian Elimination In general, to solve a system of linear equations using its augmented matrix, we use elementary row operations to arrive at a matrix
Gauss-Jordan Row Reduction and Reduced Row Echelon Form
 Gauss-Jordan Row Reduction and Reduced Row Echelon Form If we put the augmented matrix of a linear system in reduced row-echelon form, then we don t need to back-substitute to solve the system. To put
Gauss-Jordan Row Reduction and Reduced Row Echelon Form If we put the augmented matrix of a linear system in reduced row-echelon form, then we don t need to back-substitute to solve the system. To put
Chapter 6. Linear Independence. Chapter 6
 Linear Independence Linear Dependence/Independence A set of vectors {v, v 2,..., v p } is linearly dependent if we can express the zero vector, 0, as a non-trivial linear combination of the vectors. α
Linear Independence Linear Dependence/Independence A set of vectors {v, v 2,..., v p } is linearly dependent if we can express the zero vector, 0, as a non-trivial linear combination of the vectors. α
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra. A linear (algebraic) equation in. unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is. an equation of the form
 Chapter 5. Linear Algebra A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are real numbers. 1
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are real numbers. 1
Elementary Linear Algebra
 Matrices J MUSCAT Elementary Linear Algebra Matrices Definition Dr J Muscat 2002 A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, arranged in rows and columns a a 2 a 3 a n a 2 a 22 a 23 a 2n A = a m a mn We
Matrices J MUSCAT Elementary Linear Algebra Matrices Definition Dr J Muscat 2002 A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, arranged in rows and columns a a 2 a 3 a n a 2 a 22 a 23 a 2n A = a m a mn We
22A-2 SUMMER 2014 LECTURE 5
 A- SUMMER 0 LECTURE 5 NATHANIEL GALLUP Agenda Elimination to the identity matrix Inverse matrices LU factorization Elimination to the identity matrix Previously, we have used elimination to get a system
A- SUMMER 0 LECTURE 5 NATHANIEL GALLUP Agenda Elimination to the identity matrix Inverse matrices LU factorization Elimination to the identity matrix Previously, we have used elimination to get a system
Math 250B Midterm I Information Fall 2018
 Math 250B Midterm I Information Fall 2018 WHEN: Wednesday, September 26, in class (no notes, books, calculators I will supply a table of integrals) EXTRA OFFICE HOURS: Sunday, September 23 from 8:00 PM
Math 250B Midterm I Information Fall 2018 WHEN: Wednesday, September 26, in class (no notes, books, calculators I will supply a table of integrals) EXTRA OFFICE HOURS: Sunday, September 23 from 8:00 PM
MAC Module 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices II. Learning Objectives. Upon completing this module, you should be able to :
 MAC 0 Module Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices II Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to :. Find the inverse of a square matrix.. Determine whether a matrix is invertible..
MAC 0 Module Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices II Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to :. Find the inverse of a square matrix.. Determine whether a matrix is invertible..
MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra
 MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra Lecture Outlines Exam 2 Material Prof. M. Beauregard Department of Mathematics & Statistics Stephen F. Austin State University February 6, 2018 Linear Algebra (MTH
MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra Lecture Outlines Exam 2 Material Prof. M. Beauregard Department of Mathematics & Statistics Stephen F. Austin State University February 6, 2018 Linear Algebra (MTH
1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry Week 2: Jan , Gauss-Jordan, homogeneous matrices, intro matrix arithmetic
 1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry Week 2: Jan 14 18 1.2, 1.3... Gauss-Jordan, homogeneous matrices, intro matrix arithmetic R. Craigen Office: MH 523 Email: craigenr@umanitoba.ca Winter 2019 What
1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry Week 2: Jan 14 18 1.2, 1.3... Gauss-Jordan, homogeneous matrices, intro matrix arithmetic R. Craigen Office: MH 523 Email: craigenr@umanitoba.ca Winter 2019 What
Vector Spaces, Orthogonality, and Linear Least Squares
 Week Vector Spaces, Orthogonality, and Linear Least Squares. Opening Remarks.. Visualizing Planes, Lines, and Solutions Consider the following system of linear equations from the opener for Week 9: χ χ
Week Vector Spaces, Orthogonality, and Linear Least Squares. Opening Remarks.. Visualizing Planes, Lines, and Solutions Consider the following system of linear equations from the opener for Week 9: χ χ
1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry
 1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry R. Craigen Office: MH 523 Email: craigenr@umanitoba.ca May-June 2017 Introduction: linear equations Read 1.1 (in the text that is!) Go to course, class webpages.
1300 Linear Algebra and Vector Geometry R. Craigen Office: MH 523 Email: craigenr@umanitoba.ca May-June 2017 Introduction: linear equations Read 1.1 (in the text that is!) Go to course, class webpages.
Introduction. Vectors and Matrices. Vectors [1] Vectors [2]
![Introduction. Vectors and Matrices. Vectors [1] Vectors [2] Introduction. Vectors and Matrices. Vectors [1] Vectors [2]](/thumbs/77/76245607.jpg) Introduction Vectors and Matrices Dr. TGI Fernando 1 2 Data is frequently arranged in arrays, that is, sets whose elements are indexed by one or more subscripts. Vector - one dimensional array Matrix -
Introduction Vectors and Matrices Dr. TGI Fernando 1 2 Data is frequently arranged in arrays, that is, sets whose elements are indexed by one or more subscripts. Vector - one dimensional array Matrix -
Section 2.2: The Inverse of a Matrix
 Section 22: The Inverse of a Matrix Recall that a linear equation ax b, where a and b are scalars and a 0, has the unique solution x a 1 b, where a 1 is the reciprocal of a From this result, it is natural
Section 22: The Inverse of a Matrix Recall that a linear equation ax b, where a and b are scalars and a 0, has the unique solution x a 1 b, where a 1 is the reciprocal of a From this result, it is natural
Pre-Calculus I. For example, the system. x y 2 z. may be represented by the augmented matrix
 Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Chapter 2. Matrix Arithmetic. Chapter 2
 Matrix Arithmetic Matrix Addition and Subtraction Addition and subtraction act element-wise on matrices. In order for the addition/subtraction (A B) to be possible, the two matrices A and B must have the
Matrix Arithmetic Matrix Addition and Subtraction Addition and subtraction act element-wise on matrices. In order for the addition/subtraction (A B) to be possible, the two matrices A and B must have the
APPENDIX: MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION AND OTHER FORMS OF PROOF
 ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA WORKBOOK/FOR USE WITH RON LARSON S TEXTBOOK ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA CREATED BY SHANNON MARTIN MYERS APPENDIX: MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION AND OTHER FORMS OF PROOF When you are done
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA WORKBOOK/FOR USE WITH RON LARSON S TEXTBOOK ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA CREATED BY SHANNON MARTIN MYERS APPENDIX: MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION AND OTHER FORMS OF PROOF When you are done
Chapter 4 - MATRIX ALGEBRA. ... a 2j... a 2n. a i1 a i2... a ij... a in
 Chapter 4 - MATRIX ALGEBRA 4.1. Matrix Operations A a 11 a 12... a 1j... a 1n a 21. a 22.... a 2j... a 2n. a i1 a i2... a ij... a in... a m1 a m2... a mj... a mn The entry in the ith row and the jth column
Chapter 4 - MATRIX ALGEBRA 4.1. Matrix Operations A a 11 a 12... a 1j... a 1n a 21. a 22.... a 2j... a 2n. a i1 a i2... a ij... a in... a m1 a m2... a mj... a mn The entry in the ith row and the jth column
MAC Module 3 Determinants. Learning Objectives. Upon completing this module, you should be able to:
 MAC 2 Module Determinants Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to:. Determine the minor, cofactor, and adjoint of a matrix. 2. Evaluate the determinant of a matrix by cofactor
MAC 2 Module Determinants Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to:. Determine the minor, cofactor, and adjoint of a matrix. 2. Evaluate the determinant of a matrix by cofactor
GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION AND LU DECOMPOSITION (SUPPLEMENT FOR MA511)
 GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION AND LU DECOMPOSITION (SUPPLEMENT FOR MA511) D. ARAPURA Gaussian elimination is the go to method for all basic linear classes including this one. We go summarize the main ideas. 1.
GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION AND LU DECOMPOSITION (SUPPLEMENT FOR MA511) D. ARAPURA Gaussian elimination is the go to method for all basic linear classes including this one. We go summarize the main ideas. 1.
Chapter 6 Page 1 of 10. Lecture Guide. Math College Algebra Chapter 6. to accompany. College Algebra by Julie Miller
 Chapter 6 Page 1 of 10 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 6 to accompany College Algebra by Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared by Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
Chapter 6 Page 1 of 10 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 6 to accompany College Algebra by Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared by Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
Linear Algebra: Lecture Notes. Dr Rachel Quinlan School of Mathematics, Statistics and Applied Mathematics NUI Galway
 Linear Algebra: Lecture Notes Dr Rachel Quinlan School of Mathematics, Statistics and Applied Mathematics NUI Galway November 6, 23 Contents Systems of Linear Equations 2 Introduction 2 2 Elementary Row
Linear Algebra: Lecture Notes Dr Rachel Quinlan School of Mathematics, Statistics and Applied Mathematics NUI Galway November 6, 23 Contents Systems of Linear Equations 2 Introduction 2 2 Elementary Row
Basic Concepts in Linear Algebra
 Basic Concepts in Linear Algebra Grady B Wright Department of Mathematics Boise State University February 2, 2015 Grady B Wright Linear Algebra Basics February 2, 2015 1 / 39 Numerical Linear Algebra Linear
Basic Concepts in Linear Algebra Grady B Wright Department of Mathematics Boise State University February 2, 2015 Grady B Wright Linear Algebra Basics February 2, 2015 1 / 39 Numerical Linear Algebra Linear
Solving Systems of Linear Equations
 LECTURE 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Recall that we introduced the notion of matrices as a way of standardizing the expression of systems of linear equations In today s lecture I shall show how
LECTURE 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Recall that we introduced the notion of matrices as a way of standardizing the expression of systems of linear equations In today s lecture I shall show how
Example: 2x y + 3z = 1 5y 6z = 0 x + 4z = 7. Definition: Elementary Row Operations. Example: Type I swap rows 1 and 3
 Linear Algebra Row Reduced Echelon Form Techniques for solving systems of linear equations lie at the heart of linear algebra. In high school we learn to solve systems with or variables using elimination
Linear Algebra Row Reduced Echelon Form Techniques for solving systems of linear equations lie at the heart of linear algebra. In high school we learn to solve systems with or variables using elimination
8-15. Stop by or call (630)
 To review the basics Matrices, what they represent, and how to find sum, scalar product, product, inverse, and determinant of matrices, watch the following set of YouTube videos. They are followed by several
To review the basics Matrices, what they represent, and how to find sum, scalar product, product, inverse, and determinant of matrices, watch the following set of YouTube videos. They are followed by several
Math 302 Outcome Statements Winter 2013
 Math 302 Outcome Statements Winter 2013 1 Rectangular Space Coordinates; Vectors in the Three-Dimensional Space (a) Cartesian coordinates of a point (b) sphere (c) symmetry about a point, a line, and a
Math 302 Outcome Statements Winter 2013 1 Rectangular Space Coordinates; Vectors in the Three-Dimensional Space (a) Cartesian coordinates of a point (b) sphere (c) symmetry about a point, a line, and a
is a 3 4 matrix. It has 3 rows and 4 columns. The first row is the horizontal row [ ]
![is a 3 4 matrix. It has 3 rows and 4 columns. The first row is the horizontal row [ ] is a 3 4 matrix. It has 3 rows and 4 columns. The first row is the horizontal row [ ]](/thumbs/82/86615780.jpg) Matrices: Definition: An m n matrix, A m n is a rectangular array of numbers with m rows and n columns: a, a, a,n a, a, a,n A m,n =...... a m, a m, a m,n Each a i,j is the entry at the i th row, j th column.
Matrices: Definition: An m n matrix, A m n is a rectangular array of numbers with m rows and n columns: a, a, a,n a, a, a,n A m,n =...... a m, a m, a m,n Each a i,j is the entry at the i th row, j th column.
Linear Algebra and Matrix Inversion
 Jim Lambers MAT 46/56 Spring Semester 29- Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Section 63 in the text Linear Algebra and Matrix Inversion Vector Spaces and Linear Transformations Matrices are much
Jim Lambers MAT 46/56 Spring Semester 29- Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Section 63 in the text Linear Algebra and Matrix Inversion Vector Spaces and Linear Transformations Matrices are much
1 Last time: determinants
 1 Last time: determinants Let n be a positive integer If A is an n n matrix, then its determinant is the number det A = Π(X, A)( 1) inv(x) X S n where S n is the set of n n permutation matrices Π(X, A)
1 Last time: determinants Let n be a positive integer If A is an n n matrix, then its determinant is the number det A = Π(X, A)( 1) inv(x) X S n where S n is the set of n n permutation matrices Π(X, A)
Graduate Mathematical Economics Lecture 1
 Graduate Mathematical Economics Lecture 1 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University September 23, 2012 Outline 1 2 Course Outline ematical techniques used in graduate level economics courses Mathematics for Economists
Graduate Mathematical Economics Lecture 1 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University September 23, 2012 Outline 1 2 Course Outline ematical techniques used in graduate level economics courses Mathematics for Economists
Matrices and Matrix Algebra.
 Matrices and Matrix Algebra 3.1. Operations on Matrices Matrix Notation and Terminology Matrix: a rectangular array of numbers, called entries. A matrix with m rows and n columns m n A n n matrix : a square
Matrices and Matrix Algebra 3.1. Operations on Matrices Matrix Notation and Terminology Matrix: a rectangular array of numbers, called entries. A matrix with m rows and n columns m n A n n matrix : a square
OHSx XM511 Linear Algebra: Solutions to Online True/False Exercises
 This document gives the solutions to all of the online exercises for OHSx XM511. The section ( ) numbers refer to the textbook. TYPE I are True/False. Answers are in square brackets [. Lecture 02 ( 1.1)
This document gives the solutions to all of the online exercises for OHSx XM511. The section ( ) numbers refer to the textbook. TYPE I are True/False. Answers are in square brackets [. Lecture 02 ( 1.1)
Review of Basic Concepts in Linear Algebra
 Review of Basic Concepts in Linear Algebra Grady B Wright Department of Mathematics Boise State University September 7, 2017 Math 565 Linear Algebra Review September 7, 2017 1 / 40 Numerical Linear Algebra
Review of Basic Concepts in Linear Algebra Grady B Wright Department of Mathematics Boise State University September 7, 2017 Math 565 Linear Algebra Review September 7, 2017 1 / 40 Numerical Linear Algebra
MATH 212 Linear Algebra I
 MATH 212 Linear Algebra I Richard Taylor Thompson Rivers University last revision: January 16, 2008 Lec. #1 1 Systems of Linear Equations In your other courses you might have already met with a problem
MATH 212 Linear Algebra I Richard Taylor Thompson Rivers University last revision: January 16, 2008 Lec. #1 1 Systems of Linear Equations In your other courses you might have already met with a problem
MATH 213 Linear Algebra and ODEs Spring 2015 Study Sheet for Midterm Exam. Topics
 MATH 213 Linear Algebra and ODEs Spring 2015 Study Sheet for Midterm Exam This study sheet will not be allowed during the test Books and notes will not be allowed during the test Calculators and cell phones
MATH 213 Linear Algebra and ODEs Spring 2015 Study Sheet for Midterm Exam This study sheet will not be allowed during the test Books and notes will not be allowed during the test Calculators and cell phones
MAC Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives (Cont.) Module 10 System of Equations and Inequalities II
 MAC 1140 Module 10 System of Equations and Inequalities II Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. represent systems of linear equations with matrices. 2. transform a
MAC 1140 Module 10 System of Equations and Inequalities II Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. represent systems of linear equations with matrices. 2. transform a
CPE 310: Numerical Analysis for Engineers
 CPE 310: Numerical Analysis for Engineers Chapter 2: Solving Sets of Equations Ahmed Tamrawi Copyright notice: care has been taken to use only those web images deemed by the instructor to be in the public
CPE 310: Numerical Analysis for Engineers Chapter 2: Solving Sets of Equations Ahmed Tamrawi Copyright notice: care has been taken to use only those web images deemed by the instructor to be in the public
Matrix Algebra: Introduction
 Matrix Algebra: Introduction Matrices and Determinants were discovered and developed in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. Initially, their development dealt with transformation of geometric objects
Matrix Algebra: Introduction Matrices and Determinants were discovered and developed in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. Initially, their development dealt with transformation of geometric objects
MATRICES. knowledge on matrices Knowledge on matrix operations. Matrix as a tool of solving linear equations with two or three unknowns.
 MATRICES After studying this chapter you will acquire the skills in knowledge on matrices Knowledge on matrix operations. Matrix as a tool of solving linear equations with two or three unknowns. List of
MATRICES After studying this chapter you will acquire the skills in knowledge on matrices Knowledge on matrix operations. Matrix as a tool of solving linear equations with two or three unknowns. List of
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear Algebra
 SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 1.1. Introduction Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to 1.1. Introduction Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
The scope of the midterm exam is up to and includes Section 2.1 in the textbook (homework sets 1-4). Below we highlight some of the important items.
 AMS 10: Review for the Midterm Exam The scope of the midterm exam is up to and includes Section 2.1 in the textbook (homework sets 1-4). Below we highlight some of the important items. Complex numbers
AMS 10: Review for the Midterm Exam The scope of the midterm exam is up to and includes Section 2.1 in the textbook (homework sets 1-4). Below we highlight some of the important items. Complex numbers
Math Linear Algebra Final Exam Review Sheet
 Math 15-1 Linear Algebra Final Exam Review Sheet Vector Operations Vector addition is a component-wise operation. Two vectors v and w may be added together as long as they contain the same number n of
Math 15-1 Linear Algebra Final Exam Review Sheet Vector Operations Vector addition is a component-wise operation. Two vectors v and w may be added together as long as they contain the same number n of
SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear Algebra
 1.1. Introduction SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
1.1. Introduction SAMPLE OF THE STUDY MATERIAL PART OF CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Linear algebra is a specific branch of mathematics dealing with the study of vectors, vector spaces with functions that
Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2
 Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2 We have studied the properties of matrices and found out that there are more ways that we can solve Linear Systems. In Section 7.3, we learned that we can use
Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2 We have studied the properties of matrices and found out that there are more ways that we can solve Linear Systems. In Section 7.3, we learned that we can use
