POLI270 - Linear Algebra
|
|
|
- Tiffany Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 POLI7 - Linear Algebra Septemer 8th Basics a x + a x a n x n b () is the linear form where a, b are parameters and x n are variables. For a given equation such as x +x you only need a variable and only the first power. Through substitution, elimination of variables, and matrix methods you get x + x 7 x + x () For n equations and n unknowns you get a x + a x... a n x n b a x + a x... a n x n b () Matrix arrays of numbers are treated as one mathematical object, and the elements of the matrix has it s own row and column number. For example, given the matrix 7 A (4) 7 8 we get a (order n, m is given in row, column format) A vector is an ordered set arranged in row or column. A symmetric matrix is defined by a ij a ji Diagonal matrix Scalar matrix (same value in all diagonals) Identity matrix Equality of matrices. For A B a ij b ij Transposition of matrix A is indicated by A and defined by making the nth row into the nth column (a ij a ji ) Addition and subtraction of matrices require the involved matrices to have the
2 same dimensions/comfortable for addition A + B B + A (A + B) + A A + (B + C) (A + B) A + B () Example: [ ] [ ] a a A b b, B a a b b [ ] (6) a + b A + B a + b a + b a + b Scalar multiplication KA ((Ka ij )) Vector multiplication ( ) a b c ( a b c ) (7) Matrix Multiplication: n by m matrix A and m by p matrix B gives n by p matrix C where each element is the dot product. [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] 6 ()() + ()(7) ()(6) + ()(8) 9 (8) ()() + (4)(7) ()(6) + (7)(8) 4 The number of columns in the first matrix must be equal to the number of rows in the second matrix in order for multiplication to make sense. Multiplication is not commutative. This means that for matrices A and B, AB does not equal BA Example: A [ ], B 4 [ ] 4 AB [ ] BA 6 4 Multiplication of matrices also follow these laws: (AB)C A(BC) 4 6 [ ] (9) A(B + C) AC + AC (AB) B A ()
3 [ ] The Identity Matrix is if post multiplied will be self Row Operators by premultiplying by modified identity matrices To interchange rows and : () To multiply a row by a scalar 8 8 () To add twice second to the first 4 ()!! Column operations are performed by postmultiplying. Echelon matrix - each row begins with more zeroes than previous row (upper triangle. Diagonals are pivots. (i.e. 4 reduced echelon form all ) 6 No division, but yes inverse (aa ( ) a ( ), a ) BA AB I so must be n by n If B exists, A is called invertable/nonsingular, otherwise B is called singular. If the determinant does not equal, then it is nonsingular (x multiply by cofactor) [ ] [ ] 6 4 inverse 4 4 (4) 4 Sequence of row operators that transform A into I is premultiplying matrix B To get a matrix into echelon form ( upper triangle approach of text ) [ ] () 4 Subtract x first row from second row [ ] [ ] 4 4 [ ] (6) Subtract second row from first [ ] [ 4 ] [ ] (7)
4 [ ] [ ] [ ] 4 Product of is inverse If row or column of A is all zero A ( ) does not exist If row or column is multiplie of another, then the inverse does not exist (A ) A (A ) (A ) (AB) B A (8) Gaussian Elimination Algorithm to Inversion and Systems of Equations Augmented matrix: A A I (9) Start at top row. Interchange rows to get non zero entry. If not possible, there is no inverse.. Divide each element by diagonal element/pivot to get I in pivot position. 4. Add multiples of row to lower rows to sweep on non zeros below pivot.. Do for all rows. 6. Begin at bottom and work to sweep out non zeros above pivot. (a) Subtract twice the first row from second and for times first row from third. () (b) Switch and (c) 8 second row, 8 4 () third row 8 () 4
5 (d) Subtract third row from first 8 () (d) Add second to first 8 8 (4) If initially x x + x x x x 4 x 4x + 4x + 4x x () Solving Systems of Linear Equations For we use x + x x x (6) giving us For example: A AX A B IX A B X A B [ ] as the coefficient matrix and [ ] as the column vector. (7) x a + x b c [ ] [ ] [ ] x + x x + x 4x + 9x [ ] ( ) [ x 4 9 x ] (8) (9)
6 To solve, we multiply both sides by the inverse giving us ( x ) x [ [ ] 4 9] () To get the inverse of the coefficient matrix, we first set up the augmented matrix A I: [ ] () 4 9 Subtract twice the first row from the second and divide. Then subtract. times the second row from the first: [ ] [ ] [ ] () Multiplying that through the column vector, we get ] is equal to [ ] [ () ( ) x + x (4) Example : x + x + x x + x + x x x + 9x 9 Finding the inverse of the coefficient matrix, we get: 9 x x x Finally, solving for the variables, we get x x x () (6) (7) 6
7 In order to have a unique solution, there must be no linear dependence. For example, the vectors, 6 are linearly dependent. These three matrices (call them a, b and c respectively) can be rewritten [ ] [ ] [ ] (8) 4 as a + b c all three are not linearly independent Form into a matrix, derive the echelon form and if one rows are all zeroes they are linearly dependent R + R 7R + R (9) R is 6 (4) 6 The rank of the matrix is the number of non zero rows in echelon matrix There is a unique solution if the rank is the same as the number of unknowns. If there is a greater rank to the echelon form, then there are more equations than unkowns and the matrix is overdetermined (no solution). If there is less rank than the variables the the matrix has an infinite number of solutions; underdetermined as there are more unknowns than equations. Example : x x x + x 6x + x (4) Augment 8 (4) Giving a unique solution of x and x (4) 7
8 Example : x + x 4 x + x x + x 4 x + x (44) Solution: (4) (46) Giving us x + x 4, x x 4, and x + x 4. This is undetermined and there are an infinite number of solutions. Example : a + b + c a + b + c a + b + c 6 (47) Solution: (48) 6 This gives us a+b+c. This is overdetermined, and thus has no solution. 8
Linear Algebra. The analysis of many models in the social sciences reduces to the study of systems of equations.
 POLI 7 - Mathematical and Statistical Foundations Prof S Saiegh Fall Lecture Notes - Class 4 October 4, Linear Algebra The analysis of many models in the social sciences reduces to the study of systems
POLI 7 - Mathematical and Statistical Foundations Prof S Saiegh Fall Lecture Notes - Class 4 October 4, Linear Algebra The analysis of many models in the social sciences reduces to the study of systems
Finite Mathematics Chapter 2. where a, b, c, d, h, and k are real numbers and neither a and b nor c and d are both zero.
 Finite Mathematics Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Systems of Linear Equations: An Introduction Systems of Equations Recall that a system of two linear equations in two variables may be written in the general form
Finite Mathematics Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Systems of Linear Equations: An Introduction Systems of Equations Recall that a system of two linear equations in two variables may be written in the general form
MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS. + + x 1 x 2. x n 8 (4) 3 4 2
 MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS AND MATRICES Representation of a linear system The general system of m equations in n unknowns can be written a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n b a
MATRIX ALGEBRA AND SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS AND MATRICES Representation of a linear system The general system of m equations in n unknowns can be written a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n b a
Section 12.4 Algebra of Matrices
 244 Section 2.4 Algebra of Matrices Before we can discuss Matrix Algebra, we need to have a clear idea what it means to say that two matrices are equal. Let's start a definition. Equal Matrices Two matrices
244 Section 2.4 Algebra of Matrices Before we can discuss Matrix Algebra, we need to have a clear idea what it means to say that two matrices are equal. Let's start a definition. Equal Matrices Two matrices
Topics. Vectors (column matrices): Vector addition and scalar multiplication The matrix of a linear function y Ax The elements of a matrix A : A ij
 Topics Vectors (column matrices): Vector addition and scalar multiplication The matrix of a linear function y Ax The elements of a matrix A : A ij or a ij lives in row i and column j Definition of a matrix
Topics Vectors (column matrices): Vector addition and scalar multiplication The matrix of a linear function y Ax The elements of a matrix A : A ij or a ij lives in row i and column j Definition of a matrix
Matrix & Linear Algebra
 Matrix & Linear Algebra Jamie Monogan University of Georgia For more information: http://monogan.myweb.uga.edu/teaching/mm/ Jamie Monogan (UGA) Matrix & Linear Algebra 1 / 84 Vectors Vectors Vector: A
Matrix & Linear Algebra Jamie Monogan University of Georgia For more information: http://monogan.myweb.uga.edu/teaching/mm/ Jamie Monogan (UGA) Matrix & Linear Algebra 1 / 84 Vectors Vectors Vector: A
Elementary maths for GMT
 Elementary maths for GMT Linear Algebra Part 2: Matrices, Elimination and Determinant m n matrices The system of m linear equations in n variables x 1, x 2,, x n a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n = b 1
Elementary maths for GMT Linear Algebra Part 2: Matrices, Elimination and Determinant m n matrices The system of m linear equations in n variables x 1, x 2,, x n a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n = b 1
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra. A linear (algebraic) equation in. unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is. an equation of the form
 Chapter 5. Linear Algebra A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are real numbers. 1
Chapter 5. Linear Algebra A linear (algebraic) equation in n unknowns, x 1, x 2,..., x n, is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n = b where a 1, a 2,..., a n and b are real numbers. 1
Chapter 1: Systems of linear equations and matrices. Section 1.1: Introduction to systems of linear equations
 Chapter 1: Systems of linear equations and matrices Section 1.1: Introduction to systems of linear equations Definition: A linear equation in n variables can be expressed in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2
Chapter 1: Systems of linear equations and matrices Section 1.1: Introduction to systems of linear equations Definition: A linear equation in n variables can be expressed in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2
Introduction to Matrices
 POLS 704 Introduction to Matrices Introduction to Matrices. The Cast of Characters A matrix is a rectangular array (i.e., a table) of numbers. For example, 2 3 X 4 5 6 (4 3) 7 8 9 0 0 0 Thismatrix,with4rowsand3columns,isoforder
POLS 704 Introduction to Matrices Introduction to Matrices. The Cast of Characters A matrix is a rectangular array (i.e., a table) of numbers. For example, 2 3 X 4 5 6 (4 3) 7 8 9 0 0 0 Thismatrix,with4rowsand3columns,isoforder
Basic Concepts in Linear Algebra
 Basic Concepts in Linear Algebra Grady B Wright Department of Mathematics Boise State University February 2, 2015 Grady B Wright Linear Algebra Basics February 2, 2015 1 / 39 Numerical Linear Algebra Linear
Basic Concepts in Linear Algebra Grady B Wright Department of Mathematics Boise State University February 2, 2015 Grady B Wright Linear Algebra Basics February 2, 2015 1 / 39 Numerical Linear Algebra Linear
Review of Basic Concepts in Linear Algebra
 Review of Basic Concepts in Linear Algebra Grady B Wright Department of Mathematics Boise State University September 7, 2017 Math 565 Linear Algebra Review September 7, 2017 1 / 40 Numerical Linear Algebra
Review of Basic Concepts in Linear Algebra Grady B Wright Department of Mathematics Boise State University September 7, 2017 Math 565 Linear Algebra Review September 7, 2017 1 / 40 Numerical Linear Algebra
ECON 186 Class Notes: Linear Algebra
 ECON 86 Class Notes: Linear Algebra Jijian Fan Jijian Fan ECON 86 / 27 Singularity and Rank As discussed previously, squareness is a necessary condition for a matrix to be nonsingular (have an inverse).
ECON 86 Class Notes: Linear Algebra Jijian Fan Jijian Fan ECON 86 / 27 Singularity and Rank As discussed previously, squareness is a necessary condition for a matrix to be nonsingular (have an inverse).
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination
 Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
Solving Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination DEFINITION: A linear equation in the variables x 1,..., x n is an equation that can be written in the form a 1 x 1 +...+a n x n = b, where a 1,...,a n
A matrix is a rectangular array of. objects arranged in rows and columns. The objects are called the entries. is called the size of the matrix, and
 Section 5.5. Matrices and Vectors A matrix is a rectangular array of objects arranged in rows and columns. The objects are called the entries. A matrix with m rows and n columns is called an m n matrix.
Section 5.5. Matrices and Vectors A matrix is a rectangular array of objects arranged in rows and columns. The objects are called the entries. A matrix with m rows and n columns is called an m n matrix.
A matrix is a rectangular array of. objects arranged in rows and columns. The objects are called the entries. is called the size of the matrix, and
 Section 5.5. Matrices and Vectors A matrix is a rectangular array of objects arranged in rows and columns. The objects are called the entries. A matrix with m rows and n columns is called an m n matrix.
Section 5.5. Matrices and Vectors A matrix is a rectangular array of objects arranged in rows and columns. The objects are called the entries. A matrix with m rows and n columns is called an m n matrix.
Linear Algebra and Matrix Inversion
 Jim Lambers MAT 46/56 Spring Semester 29- Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Section 63 in the text Linear Algebra and Matrix Inversion Vector Spaces and Linear Transformations Matrices are much
Jim Lambers MAT 46/56 Spring Semester 29- Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Section 63 in the text Linear Algebra and Matrix Inversion Vector Spaces and Linear Transformations Matrices are much
Section 9.2: Matrices.. a m1 a m2 a mn
 Section 9.2: Matrices Definition: A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers: a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A =...... a m1 a m2 a mn In general, a ij denotes the (i, j) entry of A. That is, the entry in
Section 9.2: Matrices Definition: A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers: a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A =...... a m1 a m2 a mn In general, a ij denotes the (i, j) entry of A. That is, the entry in
PH1105 Lecture Notes on Linear Algebra.
 PH05 Lecture Notes on Linear Algebra Joe Ó hógáin E-mail: johog@mathstcdie Main Text: Calculus for the Life Sciences by Bittenger, Brand and Quintanilla Other Text: Linear Algebra by Anton and Rorres Matrices
PH05 Lecture Notes on Linear Algebra Joe Ó hógáin E-mail: johog@mathstcdie Main Text: Calculus for the Life Sciences by Bittenger, Brand and Quintanilla Other Text: Linear Algebra by Anton and Rorres Matrices
Algebra & Trig. I. For example, the system. x y 2 z. may be represented by the augmented matrix
 Algebra & Trig. I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Algebra & Trig. I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Glossary of Linear Algebra Terms. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Glossary of Linear Algebra Terms Basis (for a subspace) A linearly independent set of vectors that spans the space Basic Variable A variable in a linear system that corresponds to a pivot column in the
Glossary of Linear Algebra Terms Basis (for a subspace) A linearly independent set of vectors that spans the space Basic Variable A variable in a linear system that corresponds to a pivot column in the
Chapter 4. Solving Systems of Equations. Chapter 4
 Solving Systems of Equations 3 Scenarios for Solutions There are three general situations we may find ourselves in when attempting to solve systems of equations: 1 The system could have one unique solution.
Solving Systems of Equations 3 Scenarios for Solutions There are three general situations we may find ourselves in when attempting to solve systems of equations: 1 The system could have one unique solution.
Matrix Algebra. Matrix Algebra. Chapter 8 - S&B
 Chapter 8 - S&B Algebraic operations Matrix: The size of a matrix is indicated by the number of its rows and the number of its columns. A matrix with k rows and n columns is called a k n matrix. The number
Chapter 8 - S&B Algebraic operations Matrix: The size of a matrix is indicated by the number of its rows and the number of its columns. A matrix with k rows and n columns is called a k n matrix. The number
7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix
 7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Verify that two matrices are inverses of each other. Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find inverses
7.6 The Inverse of a Square Matrix Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Verify that two matrices are inverses of each other. Use Gauss-Jordan elimination to find inverses
Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2
 Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2 We have studied the properties of matrices and found out that there are more ways that we can solve Linear Systems. In Section 7.3, we learned that we can use
Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2 We have studied the properties of matrices and found out that there are more ways that we can solve Linear Systems. In Section 7.3, we learned that we can use
Math Camp II. Basic Linear Algebra. Yiqing Xu. Aug 26, 2014 MIT
 Math Camp II Basic Linear Algebra Yiqing Xu MIT Aug 26, 2014 1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations 2 Vectors and Vector Spaces 3 Matrices 4 Least Squares Systems of Linear Equations Definition A linear
Math Camp II Basic Linear Algebra Yiqing Xu MIT Aug 26, 2014 1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations 2 Vectors and Vector Spaces 3 Matrices 4 Least Squares Systems of Linear Equations Definition A linear
Digital Workbook for GRA 6035 Mathematics
 Eivind Eriksen Digital Workbook for GRA 6035 Mathematics November 10, 2014 BI Norwegian Business School Contents Part I Lectures in GRA6035 Mathematics 1 Linear Systems and Gaussian Elimination........................
Eivind Eriksen Digital Workbook for GRA 6035 Mathematics November 10, 2014 BI Norwegian Business School Contents Part I Lectures in GRA6035 Mathematics 1 Linear Systems and Gaussian Elimination........................
Linear Algebra. Matrices Operations. Consider, for example, a system of equations such as x + 2y z + 4w = 0, 3x 4y + 2z 6w = 0, x 3y 2z + w = 0.
 Matrices Operations Linear Algebra Consider, for example, a system of equations such as x + 2y z + 4w = 0, 3x 4y + 2z 6w = 0, x 3y 2z + w = 0 The rectangular array 1 2 1 4 3 4 2 6 1 3 2 1 in which the
Matrices Operations Linear Algebra Consider, for example, a system of equations such as x + 2y z + 4w = 0, 3x 4y + 2z 6w = 0, x 3y 2z + w = 0 The rectangular array 1 2 1 4 3 4 2 6 1 3 2 1 in which the
3.4 Elementary Matrices and Matrix Inverse
 Math 220: Summer 2015 3.4 Elementary Matrices and Matrix Inverse A n n elementary matrix is a matrix which is obtained from the n n identity matrix I n n by a single elementary row operation. Elementary
Math 220: Summer 2015 3.4 Elementary Matrices and Matrix Inverse A n n elementary matrix is a matrix which is obtained from the n n identity matrix I n n by a single elementary row operation. Elementary
Linear Algebra V = T = ( 4 3 ).
 Linear Algebra Vectors A column vector is a list of numbers stored vertically The dimension of a column vector is the number of values in the vector W is a -dimensional column vector and V is a 5-dimensional
Linear Algebra Vectors A column vector is a list of numbers stored vertically The dimension of a column vector is the number of values in the vector W is a -dimensional column vector and V is a 5-dimensional
Chapter 2 Notes, Linear Algebra 5e Lay
 Contents.1 Operations with Matrices..................................1.1 Addition and Subtraction.............................1. Multiplication by a scalar............................ 3.1.3 Multiplication
Contents.1 Operations with Matrices..................................1.1 Addition and Subtraction.............................1. Multiplication by a scalar............................ 3.1.3 Multiplication
CHAPTER 6. Direct Methods for Solving Linear Systems
 CHAPTER 6 Direct Methods for Solving Linear Systems. Introduction A direct method for approximating the solution of a system of n linear equations in n unknowns is one that gives the exact solution to
CHAPTER 6 Direct Methods for Solving Linear Systems. Introduction A direct method for approximating the solution of a system of n linear equations in n unknowns is one that gives the exact solution to
Linear Equations and Matrix
 1/60 Chia-Ping Chen Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Linear Algebra Gaussian Elimination 2/60 Alpha Go Linear algebra begins with a system of linear
1/60 Chia-Ping Chen Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Linear Algebra Gaussian Elimination 2/60 Alpha Go Linear algebra begins with a system of linear
MAC Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives (Cont.) Module 10 System of Equations and Inequalities II
 MAC 1140 Module 10 System of Equations and Inequalities II Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. represent systems of linear equations with matrices. 2. transform a
MAC 1140 Module 10 System of Equations and Inequalities II Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. represent systems of linear equations with matrices. 2. transform a
Equality: Two matrices A and B are equal, i.e., A = B if A and B have the same order and the entries of A and B are the same.
 Introduction Matrix Operations Matrix: An m n matrix A is an m-by-n array of scalars from a field (for example real numbers) of the form a a a n a a a n A a m a m a mn The order (or size) of A is m n (read
Introduction Matrix Operations Matrix: An m n matrix A is an m-by-n array of scalars from a field (for example real numbers) of the form a a a n a a a n A a m a m a mn The order (or size) of A is m n (read
Linear Algebra (part 1) : Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations (by Evan Dummit, 2016, v. 2.02)
 Linear Algebra (part ) : Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations (by Evan Dummit, 206, v 202) Contents 2 Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations 2 Systems of Linear Equations 2 Elimination, Matrix Formulation
Linear Algebra (part ) : Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations (by Evan Dummit, 206, v 202) Contents 2 Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations 2 Systems of Linear Equations 2 Elimination, Matrix Formulation
Section 9.2: Matrices. Definition: A matrix A consists of a rectangular array of numbers, or elements, arranged in m rows and n columns.
 Section 9.2: Matrices Definition: A matrix A consists of a rectangular array of numbers, or elements, arranged in m rows and n columns. That is, a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A =...... a m1 a m2 a mn A
Section 9.2: Matrices Definition: A matrix A consists of a rectangular array of numbers, or elements, arranged in m rows and n columns. That is, a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n A =...... a m1 a m2 a mn A
Lecture 7: Introduction to linear systems
 Lecture 7: Introduction to linear systems Two pictures of linear systems Consider the following system of linear algebraic equations { x 2y =, 2x+y = 7. (.) Note that it is a linear system with two unknowns
Lecture 7: Introduction to linear systems Two pictures of linear systems Consider the following system of linear algebraic equations { x 2y =, 2x+y = 7. (.) Note that it is a linear system with two unknowns
Matrix Operations. Linear Combination Vector Algebra Angle Between Vectors Projections and Reflections Equality of matrices, Augmented Matrix
 Linear Combination Vector Algebra Angle Between Vectors Projections and Reflections Equality of matrices, Augmented Matrix Matrix Operations Matrix Addition and Matrix Scalar Multiply Matrix Multiply Matrix
Linear Combination Vector Algebra Angle Between Vectors Projections and Reflections Equality of matrices, Augmented Matrix Matrix Operations Matrix Addition and Matrix Scalar Multiply Matrix Multiply Matrix
Introduction to Matrices
 214 Analysis and Design of Feedback Control Systems Introduction to Matrices Derek Rowell October 2002 Modern system dynamics is based upon a matrix representation of the dynamic equations governing the
214 Analysis and Design of Feedback Control Systems Introduction to Matrices Derek Rowell October 2002 Modern system dynamics is based upon a matrix representation of the dynamic equations governing the
ANALYTICAL MATHEMATICS FOR APPLICATIONS 2018 LECTURE NOTES 3
 ANALYTICAL MATHEMATICS FOR APPLICATIONS 2018 LECTURE NOTES 3 ISSUED 24 FEBRUARY 2018 1 Gaussian elimination Let A be an (m n)-matrix Consider the following row operations on A (1) Swap the positions any
ANALYTICAL MATHEMATICS FOR APPLICATIONS 2018 LECTURE NOTES 3 ISSUED 24 FEBRUARY 2018 1 Gaussian elimination Let A be an (m n)-matrix Consider the following row operations on A (1) Swap the positions any
Chapter 7. Linear Algebra: Matrices, Vectors,
 Chapter 7. Linear Algebra: Matrices, Vectors, Determinants. Linear Systems Linear algebra includes the theory and application of linear systems of equations, linear transformations, and eigenvalue problems.
Chapter 7. Linear Algebra: Matrices, Vectors, Determinants. Linear Systems Linear algebra includes the theory and application of linear systems of equations, linear transformations, and eigenvalue problems.
MATRICES. knowledge on matrices Knowledge on matrix operations. Matrix as a tool of solving linear equations with two or three unknowns.
 MATRICES After studying this chapter you will acquire the skills in knowledge on matrices Knowledge on matrix operations. Matrix as a tool of solving linear equations with two or three unknowns. List of
MATRICES After studying this chapter you will acquire the skills in knowledge on matrices Knowledge on matrix operations. Matrix as a tool of solving linear equations with two or three unknowns. List of
CHAPTER 8: Matrices and Determinants
 (Exercises for Chapter 8: Matrices and Determinants) E.8.1 CHAPTER 8: Matrices and Determinants (A) means refer to Part A, (B) means refer to Part B, etc. Most of these exercises can be done without a
(Exercises for Chapter 8: Matrices and Determinants) E.8.1 CHAPTER 8: Matrices and Determinants (A) means refer to Part A, (B) means refer to Part B, etc. Most of these exercises can be done without a
Chapter 4 - MATRIX ALGEBRA. ... a 2j... a 2n. a i1 a i2... a ij... a in
 Chapter 4 - MATRIX ALGEBRA 4.1. Matrix Operations A a 11 a 12... a 1j... a 1n a 21. a 22.... a 2j... a 2n. a i1 a i2... a ij... a in... a m1 a m2... a mj... a mn The entry in the ith row and the jth column
Chapter 4 - MATRIX ALGEBRA 4.1. Matrix Operations A a 11 a 12... a 1j... a 1n a 21. a 22.... a 2j... a 2n. a i1 a i2... a ij... a in... a m1 a m2... a mj... a mn The entry in the ith row and the jth column
MATH.2720 Introduction to Programming with MATLAB Vector and Matrix Algebra
 MATH.2720 Introduction to Programming with MATLAB Vector and Matrix Algebra A. Vectors A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction, like velocity. The location of a vector is irrelevant;
MATH.2720 Introduction to Programming with MATLAB Vector and Matrix Algebra A. Vectors A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction, like velocity. The location of a vector is irrelevant;
A FIRST COURSE IN LINEAR ALGEBRA. An Open Text by Ken Kuttler. Matrix Arithmetic
 A FIRST COURSE IN LINEAR ALGEBRA An Open Text by Ken Kuttler Matrix Arithmetic Lecture Notes by Karen Seyffarth Adapted by LYRYX SERVICE COURSE SOLUTION Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA)
A FIRST COURSE IN LINEAR ALGEBRA An Open Text by Ken Kuttler Matrix Arithmetic Lecture Notes by Karen Seyffarth Adapted by LYRYX SERVICE COURSE SOLUTION Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA)
Chapter 1 Matrices and Systems of Equations
 Chapter 1 Matrices and Systems of Equations System of Linear Equations 1. A linear equation in n unknowns is an equation of the form n i=1 a i x i = b where a 1,..., a n, b R and x 1,..., x n are variables.
Chapter 1 Matrices and Systems of Equations System of Linear Equations 1. A linear equation in n unknowns is an equation of the form n i=1 a i x i = b where a 1,..., a n, b R and x 1,..., x n are variables.
Elementary Row Operations on Matrices
 King Saud University September 17, 018 Table of contents 1 Definition A real matrix is a rectangular array whose entries are real numbers. These numbers are organized on rows and columns. An m n matrix
King Saud University September 17, 018 Table of contents 1 Definition A real matrix is a rectangular array whose entries are real numbers. These numbers are organized on rows and columns. An m n matrix
Pre-Calculus I. For example, the system. x y 2 z. may be represented by the augmented matrix
 Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
Pre-Calculus I 8.1 Matrix Solutions to Linear Systems A matrix is a rectangular array of elements. o An array is a systematic arrangement of numbers or symbols in rows and columns. Matrices (the plural
1. Let m 1 and n 1 be two natural numbers such that m > n. Which of the following is/are true?
 . Let m and n be two natural numbers such that m > n. Which of the following is/are true? (i) A linear system of m equations in n variables is always consistent. (ii) A linear system of n equations in
. Let m and n be two natural numbers such that m > n. Which of the following is/are true? (i) A linear system of m equations in n variables is always consistent. (ii) A linear system of n equations in
1 Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations
 Linear Algebra (part ) : Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations (by Evan Dummit, 207, v 260) Contents Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations Systems of Linear Equations Elimination, Matrix Formulation
Linear Algebra (part ) : Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations (by Evan Dummit, 207, v 260) Contents Matrices and Systems of Linear Equations Systems of Linear Equations Elimination, Matrix Formulation
Introduction. Vectors and Matrices. Vectors [1] Vectors [2]
![Introduction. Vectors and Matrices. Vectors [1] Vectors [2] Introduction. Vectors and Matrices. Vectors [1] Vectors [2]](/thumbs/77/76245607.jpg) Introduction Vectors and Matrices Dr. TGI Fernando 1 2 Data is frequently arranged in arrays, that is, sets whose elements are indexed by one or more subscripts. Vector - one dimensional array Matrix -
Introduction Vectors and Matrices Dr. TGI Fernando 1 2 Data is frequently arranged in arrays, that is, sets whose elements are indexed by one or more subscripts. Vector - one dimensional array Matrix -
The matrix will only be consistent if the last entry of row three is 0, meaning 2b 3 + b 2 b 1 = 0.
 ) Find all solutions of the linear system. Express the answer in vector form. x + 2x + x + x 5 = 2 2x 2 + 2x + 2x + x 5 = 8 x + 2x + x + 9x 5 = 2 2 Solution: Reduce the augmented matrix [ 2 2 2 8 ] to
) Find all solutions of the linear system. Express the answer in vector form. x + 2x + x + x 5 = 2 2x 2 + 2x + 2x + x 5 = 8 x + 2x + x + 9x 5 = 2 2 Solution: Reduce the augmented matrix [ 2 2 2 8 ] to
MATH 315 Linear Algebra Homework #1 Assigned: August 20, 2018
 Homework #1 Assigned: August 20, 2018 Review the following subjects involving systems of equations and matrices from Calculus II. Linear systems of equations Converting systems to matrix form Pivot entry
Homework #1 Assigned: August 20, 2018 Review the following subjects involving systems of equations and matrices from Calculus II. Linear systems of equations Converting systems to matrix form Pivot entry
[ Here 21 is the dot product of (3, 1, 2, 5) with (2, 3, 1, 2), and 31 is the dot product of
 . Matrices A matrix is any rectangular array of numbers. For example 3 5 6 4 8 3 3 is 3 4 matrix, i.e. a rectangular array of numbers with three rows four columns. We usually use capital letters for matrices,
. Matrices A matrix is any rectangular array of numbers. For example 3 5 6 4 8 3 3 is 3 4 matrix, i.e. a rectangular array of numbers with three rows four columns. We usually use capital letters for matrices,
ENGI 9420 Lecture Notes 2 - Matrix Algebra Page Matrix operations can render the solution of a linear system much more efficient.
 ENGI 940 Lecture Notes - Matrix Algebra Page.0. Matrix Algebra A linear system of m equations in n unknowns, a x + a x + + a x b (where the a ij and i n n a x + a x + + a x b n n a x + a x + + a x b m
ENGI 940 Lecture Notes - Matrix Algebra Page.0. Matrix Algebra A linear system of m equations in n unknowns, a x + a x + + a x b (where the a ij and i n n a x + a x + + a x b n n a x + a x + + a x b m
3. Vector spaces 3.1 Linear dependence and independence 3.2 Basis and dimension. 5. Extreme points and basic feasible solutions
 A. LINEAR ALGEBRA. CONVEX SETS 1. Matrices and vectors 1.1 Matrix operations 1.2 The rank of a matrix 2. Systems of linear equations 2.1 Basic solutions 3. Vector spaces 3.1 Linear dependence and independence
A. LINEAR ALGEBRA. CONVEX SETS 1. Matrices and vectors 1.1 Matrix operations 1.2 The rank of a matrix 2. Systems of linear equations 2.1 Basic solutions 3. Vector spaces 3.1 Linear dependence and independence
System of Linear Equations
 Chapter 7 - S&B Gaussian and Gauss-Jordan Elimination We will study systems of linear equations by describing techniques for solving such systems. The preferred solution technique- Gaussian elimination-
Chapter 7 - S&B Gaussian and Gauss-Jordan Elimination We will study systems of linear equations by describing techniques for solving such systems. The preferred solution technique- Gaussian elimination-
n n matrices The system of m linear equations in n variables x 1, x 2,..., x n can be written as a matrix equation by Ax = b, or in full
 n n matrices Matrices Definitions Diagonal, Identity, and zero matrices Addition Multiplication Transpose and inverse The system of m linear equations in n variables x 1, x 2,..., x n a 11 x 1 + a 12 x
n n matrices Matrices Definitions Diagonal, Identity, and zero matrices Addition Multiplication Transpose and inverse The system of m linear equations in n variables x 1, x 2,..., x n a 11 x 1 + a 12 x
Math Linear Algebra Final Exam Review Sheet
 Math 15-1 Linear Algebra Final Exam Review Sheet Vector Operations Vector addition is a component-wise operation. Two vectors v and w may be added together as long as they contain the same number n of
Math 15-1 Linear Algebra Final Exam Review Sheet Vector Operations Vector addition is a component-wise operation. Two vectors v and w may be added together as long as they contain the same number n of
Inverting Matrices. 1 Properties of Transpose. 2 Matrix Algebra. P. Danziger 3.2, 3.3
 3., 3.3 Inverting Matrices P. Danziger 1 Properties of Transpose Transpose has higher precedence than multiplication and addition, so AB T A ( B T and A + B T A + ( B T As opposed to the bracketed expressions
3., 3.3 Inverting Matrices P. Danziger 1 Properties of Transpose Transpose has higher precedence than multiplication and addition, so AB T A ( B T and A + B T A + ( B T As opposed to the bracketed expressions
Department of Aerospace Engineering AE602 Mathematics for Aerospace Engineers Assignment No. 4
 Department of Aerospace Engineering AE6 Mathematics for Aerospace Engineers Assignment No.. Decide whether or not the following vectors are linearly independent, by solving c v + c v + c 3 v 3 + c v :
Department of Aerospace Engineering AE6 Mathematics for Aerospace Engineers Assignment No.. Decide whether or not the following vectors are linearly independent, by solving c v + c v + c 3 v 3 + c v :
7.5 Operations with Matrices. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 7.5 Operations with Matrices Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Decide whether two matrices are equal. Add and subtract matrices and multiply matrices by scalars. Multiply
7.5 Operations with Matrices Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Decide whether two matrices are equal. Add and subtract matrices and multiply matrices by scalars. Multiply
Matrices Gaussian elimination Determinants. Graphics 2009/2010, period 1. Lecture 4: matrices
 Graphics 2009/2010, period 1 Lecture 4 Matrices m n matrices Matrices Definitions Diagonal, Identity, and zero matrices Addition Multiplication Transpose and inverse The system of m linear equations in
Graphics 2009/2010, period 1 Lecture 4 Matrices m n matrices Matrices Definitions Diagonal, Identity, and zero matrices Addition Multiplication Transpose and inverse The system of m linear equations in
4 Elementary matrices, continued
 4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. To repeat the recipe: These matrices are constructed by performing the given row
4 Elementary matrices, continued We have identified 3 types of row operations and their corresponding elementary matrices. To repeat the recipe: These matrices are constructed by performing the given row
Definition of Equality of Matrices. Example 1: Equality of Matrices. Consider the four matrices
 IT 131: Mathematics for Science Lecture Notes 3 Source: Larson, Edwards, Falvo (2009): Elementary Linear Algebra, Sixth Edition. Matrices 2.1 Operations with Matrices This section and the next introduce
IT 131: Mathematics for Science Lecture Notes 3 Source: Larson, Edwards, Falvo (2009): Elementary Linear Algebra, Sixth Edition. Matrices 2.1 Operations with Matrices This section and the next introduce
GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION AND LU DECOMPOSITION (SUPPLEMENT FOR MA511)
 GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION AND LU DECOMPOSITION (SUPPLEMENT FOR MA511) D. ARAPURA Gaussian elimination is the go to method for all basic linear classes including this one. We go summarize the main ideas. 1.
GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION AND LU DECOMPOSITION (SUPPLEMENT FOR MA511) D. ARAPURA Gaussian elimination is the go to method for all basic linear classes including this one. We go summarize the main ideas. 1.
Relationships Between Planes
 Relationships Between Planes Definition: consistent (system of equations) A system of equations is consistent if there exists one (or more than one) solution that satisfies the system. System 1: {, System
Relationships Between Planes Definition: consistent (system of equations) A system of equations is consistent if there exists one (or more than one) solution that satisfies the system. System 1: {, System
Exercise Sketch these lines and find their intersection.
 These are brief notes for the lecture on Friday August 21, 2009: they are not complete, but they are a guide to what I want to say today. They are not guaranteed to be correct. 1. Solving systems of linear
These are brief notes for the lecture on Friday August 21, 2009: they are not complete, but they are a guide to what I want to say today. They are not guaranteed to be correct. 1. Solving systems of linear
MATRICES The numbers or letters in any given matrix are called its entries or elements
 MATRICES A matrix is defined as a rectangular array of numbers. Examples are: 1 2 4 a b 1 4 5 A : B : C 0 1 3 c b 1 6 2 2 5 8 The numbers or letters in any given matrix are called its entries or elements
MATRICES A matrix is defined as a rectangular array of numbers. Examples are: 1 2 4 a b 1 4 5 A : B : C 0 1 3 c b 1 6 2 2 5 8 The numbers or letters in any given matrix are called its entries or elements
MAC Module 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices I
 MAC 2103 Module 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices I 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Represent a system of linear equations as an augmented matrix.
MAC 2103 Module 1 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices I 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Represent a system of linear equations as an augmented matrix.
MATH 240 Spring, Chapter 1: Linear Equations and Matrices
 MATH 240 Spring, 2006 Chapter Summaries for Kolman / Hill, Elementary Linear Algebra, 8th Ed. Sections 1.1 1.6, 2.1 2.2, 3.2 3.8, 4.3 4.5, 5.1 5.3, 5.5, 6.1 6.5, 7.1 7.2, 7.4 DEFINITIONS Chapter 1: Linear
MATH 240 Spring, 2006 Chapter Summaries for Kolman / Hill, Elementary Linear Algebra, 8th Ed. Sections 1.1 1.6, 2.1 2.2, 3.2 3.8, 4.3 4.5, 5.1 5.3, 5.5, 6.1 6.5, 7.1 7.2, 7.4 DEFINITIONS Chapter 1: Linear
Graduate Mathematical Economics Lecture 1
 Graduate Mathematical Economics Lecture 1 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University September 23, 2012 Outline 1 2 Course Outline ematical techniques used in graduate level economics courses Mathematics for Economists
Graduate Mathematical Economics Lecture 1 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University September 23, 2012 Outline 1 2 Course Outline ematical techniques used in graduate level economics courses Mathematics for Economists
Undergraduate Mathematical Economics Lecture 1
 Undergraduate Mathematical Economics Lecture 1 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University September 15, 2014 Outline 1 Courses Description and Requirement 2 Course Outline ematical techniques used in economics courses
Undergraduate Mathematical Economics Lecture 1 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University September 15, 2014 Outline 1 Courses Description and Requirement 2 Course Outline ematical techniques used in economics courses
Phys 201. Matrices and Determinants
 Phys 201 Matrices and Determinants 1 1.1 Matrices 1.2 Operations of matrices 1.3 Types of matrices 1.4 Properties of matrices 1.5 Determinants 1.6 Inverse of a 3 3 matrix 2 1.1 Matrices A 2 3 7 =! " 1
Phys 201 Matrices and Determinants 1 1.1 Matrices 1.2 Operations of matrices 1.3 Types of matrices 1.4 Properties of matrices 1.5 Determinants 1.6 Inverse of a 3 3 matrix 2 1.1 Matrices A 2 3 7 =! " 1
Math 313 Chapter 1 Review
 Math 313 Chapter 1 Review Howard Anton, 9th Edition May 2010 Do NOT write on me! Contents 1 1.1 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations 2 2 1.2 Gaussian Elimination 3 3 1.3 Matrices and Matrix Operations
Math 313 Chapter 1 Review Howard Anton, 9th Edition May 2010 Do NOT write on me! Contents 1 1.1 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations 2 2 1.2 Gaussian Elimination 3 3 1.3 Matrices and Matrix Operations
Ack: 1. LD Garcia, MTH 199, Sam Houston State University 2. Linear Algebra and Its Applications - Gilbert Strang
 Gaussian Elimination CS6015 : Linear Algebra Ack: 1. LD Garcia, MTH 199, Sam Houston State University 2. Linear Algebra and Its Applications - Gilbert Strang The Gaussian Elimination Method The Gaussian
Gaussian Elimination CS6015 : Linear Algebra Ack: 1. LD Garcia, MTH 199, Sam Houston State University 2. Linear Algebra and Its Applications - Gilbert Strang The Gaussian Elimination Method The Gaussian
CS227-Scientific Computing. Lecture 4: A Crash Course in Linear Algebra
 CS227-Scientific Computing Lecture 4: A Crash Course in Linear Algebra Linear Transformation of Variables A common phenomenon: Two sets of quantities linearly related: y = 3x + x 2 4x 3 y 2 = 2.7x 2 x
CS227-Scientific Computing Lecture 4: A Crash Course in Linear Algebra Linear Transformation of Variables A common phenomenon: Two sets of quantities linearly related: y = 3x + x 2 4x 3 y 2 = 2.7x 2 x
Linear Algebra Practice Problems
 Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
Math 7, Professor Ramras Linear Algebra Practice Problems () Consider the following system of linear equations in the variables x, y, and z, in which the constants a and b are real numbers. x y + z = a
22A-2 SUMMER 2014 LECTURE 5
 A- SUMMER 0 LECTURE 5 NATHANIEL GALLUP Agenda Elimination to the identity matrix Inverse matrices LU factorization Elimination to the identity matrix Previously, we have used elimination to get a system
A- SUMMER 0 LECTURE 5 NATHANIEL GALLUP Agenda Elimination to the identity matrix Inverse matrices LU factorization Elimination to the identity matrix Previously, we have used elimination to get a system
Materials engineering Collage \\ Ceramic & construction materials department Numerical Analysis \\Third stage by \\ Dalya Hekmat
 Materials engineering Collage \\ Ceramic & construction materials department Numerical Analysis \\Third stage by \\ Dalya Hekmat Linear Algebra Lecture 2 1.3.7 Matrix Matrix multiplication using Falk s
Materials engineering Collage \\ Ceramic & construction materials department Numerical Analysis \\Third stage by \\ Dalya Hekmat Linear Algebra Lecture 2 1.3.7 Matrix Matrix multiplication using Falk s
Matrix Arithmetic. j=1
 An m n matrix is an array A = Matrix Arithmetic a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n a m1 a m2 a mn of real numbers a ij An m n matrix has m rows and n columns a ij is the entry in the i-th row and j-th column
An m n matrix is an array A = Matrix Arithmetic a 11 a 12 a 1n a 21 a 22 a 2n a m1 a m2 a mn of real numbers a ij An m n matrix has m rows and n columns a ij is the entry in the i-th row and j-th column
For comments, corrections, etc Please contact Ahnaf Abbas: Sharjah Institute of Technology. Matrices Handout #8.
 Matrices Handout #8 Topic Matrix Definition A matrix is an array of numbers: a a2... a n a2 a22... a 2n A =.... am am2... amn Matrices are denoted by capital letters : A,B,C,.. Matrix size or rank is determined
Matrices Handout #8 Topic Matrix Definition A matrix is an array of numbers: a a2... a n a2 a22... a 2n A =.... am am2... amn Matrices are denoted by capital letters : A,B,C,.. Matrix size or rank is determined
Matrices and systems of linear equations
 Matrices and systems of linear equations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations and linear algebra - MA 262 Taken from Differential equations and linear algebra by Goode and Annin Samy T.
Matrices and systems of linear equations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations and linear algebra - MA 262 Taken from Differential equations and linear algebra by Goode and Annin Samy T.
Fundamentals of Engineering Analysis (650163)
 Philadelphia University Faculty of Engineering Communications and Electronics Engineering Fundamentals of Engineering Analysis (6563) Part Dr. Omar R Daoud Matrices: Introduction DEFINITION A matrix is
Philadelphia University Faculty of Engineering Communications and Electronics Engineering Fundamentals of Engineering Analysis (6563) Part Dr. Omar R Daoud Matrices: Introduction DEFINITION A matrix is
1 Multiply Eq. E i by λ 0: (λe i ) (E i ) 2 Multiply Eq. E j by λ and add to Eq. E i : (E i + λe j ) (E i )
 Direct Methods for Linear Systems Chapter Direct Methods for Solving Linear Systems Per-Olof Persson persson@berkeleyedu Department of Mathematics University of California, Berkeley Math 18A Numerical
Direct Methods for Linear Systems Chapter Direct Methods for Solving Linear Systems Per-Olof Persson persson@berkeleyedu Department of Mathematics University of California, Berkeley Math 18A Numerical
Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition
 Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 2016 Also see the separate version of this with Matlab and R commands. Prof. Tesler Diagonalizing
Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 2016 Also see the separate version of this with Matlab and R commands. Prof. Tesler Diagonalizing
Linear Algebra M1 - FIB. Contents: 5. Matrices, systems of linear equations and determinants 6. Vector space 7. Linear maps 8.
 Linear Algebra M1 - FIB Contents: 5 Matrices, systems of linear equations and determinants 6 Vector space 7 Linear maps 8 Diagonalization Anna de Mier Montserrat Maureso Dept Matemàtica Aplicada II Translation:
Linear Algebra M1 - FIB Contents: 5 Matrices, systems of linear equations and determinants 6 Vector space 7 Linear maps 8 Diagonalization Anna de Mier Montserrat Maureso Dept Matemàtica Aplicada II Translation:
INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHEATHARLACH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CARLOW MATRICES
 1 CHAPTER 4 MATRICES 1 INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHEATHARLACH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CARLOW MATRICES 1 Matrices Matrices are of fundamental importance in 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional graphics programming
1 CHAPTER 4 MATRICES 1 INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHEATHARLACH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CARLOW MATRICES 1 Matrices Matrices are of fundamental importance in 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional graphics programming
Linear Systems and Matrices
 Department of Mathematics The Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 System of m linear equations in n unknowns (linear system) a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x 2 + + a 2n x n = b 2.......
Department of Mathematics The Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 System of m linear equations in n unknowns (linear system) a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x 2 + + a 2n x n = b 2.......
Matrix notation. A nm : n m : size of the matrix. m : no of columns, n: no of rows. Row matrix n=1 [b 1, b 2, b 3,. b m ] Column matrix m=1
![Matrix notation. A nm : n m : size of the matrix. m : no of columns, n: no of rows. Row matrix n=1 [b 1, b 2, b 3,. b m ] Column matrix m=1 Matrix notation. A nm : n m : size of the matrix. m : no of columns, n: no of rows. Row matrix n=1 [b 1, b 2, b 3,. b m ] Column matrix m=1](/thumbs/96/127103021.jpg) Matrix notation A nm : n m : size of the matrix m : no of columns, n: no of rows Row matrix n=1 [b 1, b 2, b 3,. b m ] Column matrix m=1 n = m square matrix Symmetric matrix Upper triangular matrix: matrix
Matrix notation A nm : n m : size of the matrix m : no of columns, n: no of rows Row matrix n=1 [b 1, b 2, b 3,. b m ] Column matrix m=1 n = m square matrix Symmetric matrix Upper triangular matrix: matrix
1 Last time: linear systems and row operations
 1 Last time: linear systems and row operations Here s what we did last time: a system of linear equations or linear system is a list of equations a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22
1 Last time: linear systems and row operations Here s what we did last time: a system of linear equations or linear system is a list of equations a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + + a 1n x n = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22
Lecture 3 Linear Algebra Background
 Lecture 3 Linear Algebra Background Dan Sheldon September 17, 2012 Motivation Preview of next class: y (1) w 0 + w 1 x (1) 1 + w 2 x (1) 2 +... + w d x (1) d y (2) w 0 + w 1 x (2) 1 + w 2 x (2) 2 +...
Lecture 3 Linear Algebra Background Dan Sheldon September 17, 2012 Motivation Preview of next class: y (1) w 0 + w 1 x (1) 1 + w 2 x (1) 2 +... + w d x (1) d y (2) w 0 + w 1 x (2) 1 + w 2 x (2) 2 +...
BASIC NOTIONS. x + y = 1 3, 3x 5y + z = A + 3B,C + 2D, DC are not defined. A + C =
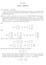 CHAPTER I BASIC NOTIONS (a) 8666 and 8833 (b) a =6,a =4 will work in the first case, but there are no possible such weightings to produce the second case, since Student and Student 3 have to end up with
CHAPTER I BASIC NOTIONS (a) 8666 and 8833 (b) a =6,a =4 will work in the first case, but there are no possible such weightings to produce the second case, since Student and Student 3 have to end up with
Lecture Notes in Linear Algebra
 Lecture Notes in Linear Algebra Dr. Abdullah Al-Azemi Mathematics Department Kuwait University February 4, 2017 Contents 1 Linear Equations and Matrices 1 1.2 Matrices............................................
Lecture Notes in Linear Algebra Dr. Abdullah Al-Azemi Mathematics Department Kuwait University February 4, 2017 Contents 1 Linear Equations and Matrices 1 1.2 Matrices............................................
Elementary Linear Algebra
 Elementary Linear Algebra Linear algebra is the study of; linear sets of equations and their transformation properties. Linear algebra allows the analysis of; rotations in space, least squares fitting,
Elementary Linear Algebra Linear algebra is the study of; linear sets of equations and their transformation properties. Linear algebra allows the analysis of; rotations in space, least squares fitting,
is a 3 4 matrix. It has 3 rows and 4 columns. The first row is the horizontal row [ ]
![is a 3 4 matrix. It has 3 rows and 4 columns. The first row is the horizontal row [ ] is a 3 4 matrix. It has 3 rows and 4 columns. The first row is the horizontal row [ ]](/thumbs/82/86615780.jpg) Matrices: Definition: An m n matrix, A m n is a rectangular array of numbers with m rows and n columns: a, a, a,n a, a, a,n A m,n =...... a m, a m, a m,n Each a i,j is the entry at the i th row, j th column.
Matrices: Definition: An m n matrix, A m n is a rectangular array of numbers with m rows and n columns: a, a, a,n a, a, a,n A m,n =...... a m, a m, a m,n Each a i,j is the entry at the i th row, j th column.
MAC1105-College Algebra. Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices
 MAC05-College Algebra Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices 5. Systems of Equations in Two Variables Solving Systems of Two Linear Equations/ Two-Variable Linear Equations A system of equations is
MAC05-College Algebra Chapter 5-Systems of Equations & Matrices 5. Systems of Equations in Two Variables Solving Systems of Two Linear Equations/ Two-Variable Linear Equations A system of equations is
Things we can already do with matrices. Unit II - Matrix arithmetic. Defining the matrix product. Things that fail in matrix arithmetic
 Unit II - Matrix arithmetic matrix multiplication matrix inverses elementary matrices finding the inverse of a matrix determinants Unit II - Matrix arithmetic 1 Things we can already do with matrices equality
Unit II - Matrix arithmetic matrix multiplication matrix inverses elementary matrices finding the inverse of a matrix determinants Unit II - Matrix arithmetic 1 Things we can already do with matrices equality
