Motion. Slope. Slope. Distance and Displacement
|
|
|
- Avis Poppy Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Steepness or slope base (run), height (rise) slope = rise/run slope down (\) : - (rise/run) slope up (/) : + (rise/run) sudden change of slope curved hill - the slope is always changing procedure to find a slope of a curved hill - slope method tangent line Motion Slope Given 2 points (x 1,y 1 ) and (x 2,y 2 ) the slope of the straight line going though them is: Slope Distance and Displacement Slope of a vertical line Slope of a horizontal line y=mx+b m slope b - y-intercept Distance and displacement are two quantities which may seem to mean the same thing, yet they have distinctly different meanings and definitions. Distance is a scalar quantity which refers to "how much ground an object has covered" during its motion. Displacement is a vector quantity which refers to "how far out of place an object is"; it is the object's change in position.
2 Speed and Velocity Speed is a scalar quantity which refers to "how fast an object is moving." Instantaneous speed: the speed in an instant Average speed = total distance covered / duration Velocity is a vector quantity which refers to "the rate at which an object changes its position." Acceleration how does the velocity change, vector quantity Velocity: speed + direction of motion: 60 km/h to the North Constant velocity or constant speed -- equal distances are covered for equal intervals of time. Constant velocity means constant speed with no change in the direction of motion. Velocity vector -- a pictorial way to represent velocity -- an arrow drawn to scale that represents the magnitude and direction of a given velocity Any quantity that is described by magnitude and direction Velocity vector: magnitude=speed, direction= N, S, E, W, etc Vectors can be added and subtracted - new vector - resultant Vectors that act along a parallel directions Vectors not parallel to each other - parallelogram rule: parallelogram with the two vectors as adjacent sides, with tails together - the diagonal is the resultant Steady motion -- velocity does not undergo changes Accelerated motion -- velocity undergoes changes We change the velocity if we change the speed and/or the direction Acceleration is the rate of change in velocity: Acceleration = change of velocity / time interval Acceleration can increase or decrease the velocity: positive or negative acceleration
3 Car moving with a constant velocity of +10 m/s for 5 seconds. Motion in a curved path -- we accelerate even when we move with constant speed Stand up during a buss ride -- difference between velocity and acceleration Motion along a straight line -- speed = velocity: acceleration = change is speed / time interval Speed increases -- acceleration is in direction of velocity Speed decreases -- acceleration is opposite to velocity the slope of the line (10 m/s) is the same as the velocity of the car 2004 The Physics Classroom and Mathsoft Engineering & Education, Inc. The Meaning of Slope for a p-t Graph a small slope means a small velocity a negative slope means a negative velocity a constant slope (straight line) means a constant velocity a changing slope (curved line) means a changing velocity
4 Slow, leftward (-) Fast, leftward (-) car moving with a changing, rightward (+) velocity: that is, a car that is moving rightward and speeding up or accelerating. Slow, Rightward (+) Fast, Rightward (+) Positive Velocity Positive Velocity Changing Velocity (acceleration) If an object is slowing down, then its acceleration is in the opposite direction of its motion. If an object is speeding up, then its acceleration is in the same direction as its motion. a<0 a>0 Leftward ( ) Velocity Slow to Fast Acceleration same direction as the motion Leftward ( ) Velocity Fast to Slow Acceleration opposite to motion
5 Object, free of all restraints, falls under the influence of gravity alone during each second of free fall an object gains a speed of 10 m/s free fall acceleration is about 10 m/s 2 For an object falling from rest the instantaneous velocity is All objects fall equally fast!!! If there is no air resistance For uniform acceleration Distance traveled = 1/2 acceleration x time x time For free-fall d=1/2 gt 2 Distance Fallen in Free-Fall Time of Inst. Speed Distance of Fall (s) (m/s) Fall (m) at at at at at t 10 t t 2 During time interval 0 to1 s: Average speed =(0+10)/2 = 5 m/s At the end of the first second the distance fallen is 5 m
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line
 Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s
Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line. We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics.
 Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s
Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s
Speed how fast an object is moving (also, the magnitude of the velocity) scalar
 Mechanics Recall Mechanics Kinematics Dynamics Kinematics The description of motion without reference to forces. Terminology Distance total length of a journey scalar Time instant when an event occurs
Mechanics Recall Mechanics Kinematics Dynamics Kinematics The description of motion without reference to forces. Terminology Distance total length of a journey scalar Time instant when an event occurs
UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion
 IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
Acceleration. 3. Changing Direction occurs when the velocity and acceleration are neither parallel nor anti-parallel
 Acceleration When the velocity of an object changes, we say that the object is accelerating. This acceleration can take one of three forms: 1. Speeding Up occurs when the object s velocity and acceleration
Acceleration When the velocity of an object changes, we say that the object is accelerating. This acceleration can take one of three forms: 1. Speeding Up occurs when the object s velocity and acceleration
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration?
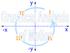 Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line
 Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s
Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s
11.3 Acceleration The basketball constantly changes velocity as it rises and falls.
 The basketball constantly changes velocity as it rises and falls. Describing changes in velocity, and how fast they occur, is a part of describing motion. What Is Acceleration? How are changes in velocity
The basketball constantly changes velocity as it rises and falls. Describing changes in velocity, and how fast they occur, is a part of describing motion. What Is Acceleration? How are changes in velocity
Physics. Chapter 3 Linear Motion
 Physics Chapter 3 Linear Motion Motion is Relative How fast are you moving? We can only speak of how fast in relation to some other thing. Unless otherwise specified, we will assume motion relative to
Physics Chapter 3 Linear Motion Motion is Relative How fast are you moving? We can only speak of how fast in relation to some other thing. Unless otherwise specified, we will assume motion relative to
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line
 Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Specifically, the description of motion. Examples: The Earth orbits around
Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Specifically, the description of motion. Examples: The Earth orbits around
average speed instantaneous origin resultant average velocity position particle model scalar
 REPRESENTING MOTION Vocabulary Review Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. average speed instantaneous origin resultant average velocity position particle model scalar
REPRESENTING MOTION Vocabulary Review Write the term that correctly completes the statement. Use each term once. average speed instantaneous origin resultant average velocity position particle model scalar
Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ]
![Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ]](/thumbs/77/76428187.jpg) Chapter 8 : Motion KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] 1 Motion **** 2 Graphical Representation of Motion *** & Graphs 3 Equation of motion **** 4 Uniform Circular Motion ** 1 Motion
Chapter 8 : Motion KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] 1 Motion **** 2 Graphical Representation of Motion *** & Graphs 3 Equation of motion **** 4 Uniform Circular Motion ** 1 Motion
Chapter 4 Linear Motion
 Chapter 4 Linear Motion You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. I. Motion Is Relative A. Everything moves. Even things that appear to be at rest move.
Chapter 4 Linear Motion You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. I. Motion Is Relative A. Everything moves. Even things that appear to be at rest move.
Chapter 2 Mechanical Equilibrium
 Chapter 2 Mechanical Equilibrium I. Force (2.1) A. force is a push or pull 1. A force is needed to change an object s state of motion 2. State of motion may be one of two things a. At rest b. Moving uniformly
Chapter 2 Mechanical Equilibrium I. Force (2.1) A. force is a push or pull 1. A force is needed to change an object s state of motion 2. State of motion may be one of two things a. At rest b. Moving uniformly
Unit 1 Parent Guide: Kinematics
 Unit 1 Parent Guide: Kinematics Kinematics is the study of the motion of objects. Scientists can represent this information in the following ways: written and verbal descriptions, mathematically (with
Unit 1 Parent Guide: Kinematics Kinematics is the study of the motion of objects. Scientists can represent this information in the following ways: written and verbal descriptions, mathematically (with
A B C D. Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment
 Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Physics Review. Do: Page # Which of the following is an appropriate unit for velocity? A. s B. m C. m/s 2 D. km/h
 Physics Review Do: Page 413 417 #1 51 1. Which of the following is an appropriate unit for velocity? A. s B. m C. m/s 2 D. km/h Use the following information to answer Question 2. The following distance
Physics Review Do: Page 413 417 #1 51 1. Which of the following is an appropriate unit for velocity? A. s B. m C. m/s 2 D. km/h Use the following information to answer Question 2. The following distance
Motion Chapter 3, Section 1: Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity
 3 Motion Chapter 3, Section 1: Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object is to describe how far it has moved, which is distance. The SI unit
3 Motion Chapter 3, Section 1: Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object is to describe how far it has moved, which is distance. The SI unit
Section 11.1 Distance and Displacement (pages )
 Name Class Date Section 11.1 Distance and Displacement (pages 328 331) This section defines distance and displacement. Methods of describing motion are presented. Vector addition and subtraction are introduced.
Name Class Date Section 11.1 Distance and Displacement (pages 328 331) This section defines distance and displacement. Methods of describing motion are presented. Vector addition and subtraction are introduced.
Representing Motion Chapter 2
 Phenomena Representing Motion Chapter 2 Pop Quiz! How fast are you moving at this moment? o A.) 0m/s o B.) 783 mi/h o C.) 350m/s o D.) 30 km/s Pop Quiz! How fast are you moving? oa.) 0m/s ob.) 783 mi/h
Phenomena Representing Motion Chapter 2 Pop Quiz! How fast are you moving at this moment? o A.) 0m/s o B.) 783 mi/h o C.) 350m/s o D.) 30 km/s Pop Quiz! How fast are you moving? oa.) 0m/s ob.) 783 mi/h
11.3 Acceleration. What Is Acceleration? How are changes in velocity described?
 What Is Acceleration? How are changes in velocity described? What Is Acceleration? Changes in Speed In science, acceleration applies to Acceleration can be caused by Deceleration is DOK question Predict
What Is Acceleration? How are changes in velocity described? What Is Acceleration? Changes in Speed In science, acceleration applies to Acceleration can be caused by Deceleration is DOK question Predict
Mathematical review trigonometry vectors Motion in one dimension
 Mathematical review trigonometry vectors Motion in one dimension Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate system (frame) consists of a fixed reference point called the origin specific
Mathematical review trigonometry vectors Motion in one dimension Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate system (frame) consists of a fixed reference point called the origin specific
AP Physics C Mechanics Vectors
 1 AP Physics C Mechanics Vectors 2015 12 03 www.njctl.org 2 Scalar Versus Vector A scalar has only a physical quantity such as mass, speed, and time. A vector has both a magnitude and a direction associated
1 AP Physics C Mechanics Vectors 2015 12 03 www.njctl.org 2 Scalar Versus Vector A scalar has only a physical quantity such as mass, speed, and time. A vector has both a magnitude and a direction associated
2- Scalars and Vectors
 2- Scalars and Vectors Scalars : have magnitude only : Length, time, mass, speed and volume is example of scalar. v Vectors : have magnitude and direction. v The magnitude of is written v v Position, displacement,
2- Scalars and Vectors Scalars : have magnitude only : Length, time, mass, speed and volume is example of scalar. v Vectors : have magnitude and direction. v The magnitude of is written v v Position, displacement,
Position-Time Graphs
 Position-Time Graphs Suppose that a man is jogging at a constant velocity of 5.0 m / s. A data table representing the man s motion is shown below: If we plot this data on a graph, we get: 0 0 1.0 5.0 2.0
Position-Time Graphs Suppose that a man is jogging at a constant velocity of 5.0 m / s. A data table representing the man s motion is shown below: If we plot this data on a graph, we get: 0 0 1.0 5.0 2.0
CHAPTER 3 ACCELERATED MOTION
 Physics Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 3 ACCELERATED MOTION Day Plans for the day Assignments for the day 1 3.1 Acceleration o Changing Velocity
Physics Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 3 ACCELERATED MOTION Day Plans for the day Assignments for the day 1 3.1 Acceleration o Changing Velocity
AP Physics C: Mechanics Ch. 2 Motion. SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: AP Physics C: Mechanics Ch. Motion SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. ) Car A is traveling at twice the speed of car
Name: Period: Date: AP Physics C: Mechanics Ch. Motion SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. ) Car A is traveling at twice the speed of car
Summary of motion graphs Object is moving to the right (in positive direction) v = 0 a = 0
 Summary of motion graphs Object is moving to the right (in positive direction) Object at rest (not moving) Position is constant v (m/s) a (m/s 2 ) v = 0 a = 0 Constant velocity Position increases at constant
Summary of motion graphs Object is moving to the right (in positive direction) Object at rest (not moving) Position is constant v (m/s) a (m/s 2 ) v = 0 a = 0 Constant velocity Position increases at constant
Calculating Acceleration
 Calculating Acceleration Textbook pages 392 405 Before You Read Section 9. 2 Summary How do you think a velocity-time graph might differ from the position-time graph you learned about in the previous chapter?
Calculating Acceleration Textbook pages 392 405 Before You Read Section 9. 2 Summary How do you think a velocity-time graph might differ from the position-time graph you learned about in the previous chapter?
Parametric Equations, Vectors, and Vector Valued Functions. Different parametric equations can yield the same curve:
 Parametric Equations, Vectors, and Vector Valued Functions Different parametric equations can yield the same curve: x=t, y=t 2 for t in [ 1,1] and x=t 3, y=t 6 for t in [ 1,1] give the same parabolic arc,
Parametric Equations, Vectors, and Vector Valued Functions Different parametric equations can yield the same curve: x=t, y=t 2 for t in [ 1,1] and x=t 3, y=t 6 for t in [ 1,1] give the same parabolic arc,
Section 1.1 Distance, Position and Displacement
 Unit 1 Motion Section 1.1 Distance, Position and Displacement Kinematics is the study of MOTION. Motion is the CHANGE in an object's location as measured by a particular observer. Why is the OBSERVER important
Unit 1 Motion Section 1.1 Distance, Position and Displacement Kinematics is the study of MOTION. Motion is the CHANGE in an object's location as measured by a particular observer. Why is the OBSERVER important
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition
 Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 3: LINEAR MOTION This lecture will help you understand: Motion Is Relative Speed : Average and Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Free Fall Motion Is Relative
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 3: LINEAR MOTION This lecture will help you understand: Motion Is Relative Speed : Average and Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Free Fall Motion Is Relative
If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph.
 Physics Lecture #2: Position Time Graphs If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph. Suppose a
Physics Lecture #2: Position Time Graphs If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph. Suppose a
3.3 Acceleration An example of acceleration Definition of acceleration Acceleration Figure 3.16: Steeper hills
 3.3 Acceleration Constant speed is easy to understand. However, almost nothing moves with constant speed for long. When the driver steps on the gas pedal, the speed of the car increases. When the driver
3.3 Acceleration Constant speed is easy to understand. However, almost nothing moves with constant speed for long. When the driver steps on the gas pedal, the speed of the car increases. When the driver
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs,
 Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
Chapter 4: Accelera.on
 Chapter 4: Accelera.on Accelera.on the rate at which velocity changes (increases or decreases). changing velocity = accelera6on constant velocity = zero accelera6on a = v t = v f - v i t a = average accelera6on
Chapter 4: Accelera.on Accelera.on the rate at which velocity changes (increases or decreases). changing velocity = accelera6on constant velocity = zero accelera6on a = v t = v f - v i t a = average accelera6on
Motion Point object Motion in one, two and three dimensions one dimensional motion. two dimensional Motion. three dimensional motion.
 Motion An object is said to be in motion, if its position changes with respect to time. This is related to the observer. If its position is not changing, the object is said to be at rest. Point object
Motion An object is said to be in motion, if its position changes with respect to time. This is related to the observer. If its position is not changing, the object is said to be at rest. Point object
Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars.
 1 Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars. Scalars: have magnitude (magnitude means size) only Examples of scalar quantities include time, mass, volume, area,
1 Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars. Scalars: have magnitude (magnitude means size) only Examples of scalar quantities include time, mass, volume, area,
Lecture 2. 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion.
 Lecture 2 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion. Types of motion Trajectory is the line drawn to track the position of an abject in coordinates space (no time axis). y 1D motion: Trajectory
Lecture 2 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion. Types of motion Trajectory is the line drawn to track the position of an abject in coordinates space (no time axis). y 1D motion: Trajectory
1. Joseph runs along a long straight track. The variation of his speed v with time t is shown below.
 Kinematics 1. Joseph runs along a long straight track. The variation of his speed v with time t is shown below. After 25 seconds Joseph has run 200 m. Which of the following is correct at 25 seconds? Instantaneous
Kinematics 1. Joseph runs along a long straight track. The variation of his speed v with time t is shown below. After 25 seconds Joseph has run 200 m. Which of the following is correct at 25 seconds? Instantaneous
2/18/2019. Position-versus-Time Graphs. Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school.
 Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Chapter 3. Motion in One Dimension
 Chapter 3 Motion in One Dimension Outline 3.1 Position, Velocity and Speed 3.2 Instantaneous Velocity and Speed 3.3 Acceleration 3.4 Motion Diagrams 3.5 One-Dimensional Motion with Constant Acceleration
Chapter 3 Motion in One Dimension Outline 3.1 Position, Velocity and Speed 3.2 Instantaneous Velocity and Speed 3.3 Acceleration 3.4 Motion Diagrams 3.5 One-Dimensional Motion with Constant Acceleration
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors & Scalars!! Scalars They are specified only by a number and units and have no direction associated with them, such as time, mass, and temperature.!! Vectors
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors & Scalars!! Scalars They are specified only by a number and units and have no direction associated with them, such as time, mass, and temperature.!! Vectors
QuickCheck. A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65
 QuickCheck A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65 QuickCheck A cart speeds up toward the origin. What do the position and velocity
QuickCheck A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65 QuickCheck A cart speeds up toward the origin. What do the position and velocity
HRW 7e Chapter 2 Page 1 of 13
 HRW 7e Chapter Page of 3 Halliday/Resnick/Walker 7e Chapter. Huber s speed is v 0 =(00 m)/(6.509 s)=30.7 m/s = 0.6 km/h, where we have used the conversion factor m/s = 3.6 km/h. Since Whittingham beat
HRW 7e Chapter Page of 3 Halliday/Resnick/Walker 7e Chapter. Huber s speed is v 0 =(00 m)/(6.509 s)=30.7 m/s = 0.6 km/h, where we have used the conversion factor m/s = 3.6 km/h. Since Whittingham beat
Section Distance and displacment
 Chapter 11 Motion Section 11.1 Distance and displacment Choosing a Frame of Reference What is needed to describe motion completely? A frame of reference is a system of objects that are not moving with
Chapter 11 Motion Section 11.1 Distance and displacment Choosing a Frame of Reference What is needed to describe motion completely? A frame of reference is a system of objects that are not moving with
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0.
 Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
Veronika Kollár PreMed course
 Veronika Kollár PreMed course 30.07.013. The slope of a line y y y b y 1 x x 1 x The general equation of the line: f (x) = y = m x + b Where: b: intersection on the y axis m: the slope of the line x Intersection
Veronika Kollár PreMed course 30.07.013. The slope of a line y y y b y 1 x x 1 x The general equation of the line: f (x) = y = m x + b Where: b: intersection on the y axis m: the slope of the line x Intersection
A scalar quantity has just magnitude A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction
 Name Date Mods REVIEW FOR MIDYEAR ASSESSMENT 1. Physics is the most basic science because Physics supports chemistry, chemistry supports biology. The ideas of physics are fundamental to these more complicated
Name Date Mods REVIEW FOR MIDYEAR ASSESSMENT 1. Physics is the most basic science because Physics supports chemistry, chemistry supports biology. The ideas of physics are fundamental to these more complicated
Motion in One Dimension
 Motion in One Dimension Chapter 2 Physics Table of Contents Position and Displacement Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Falling Objects The Big Idea Displacement is a change of position
Motion in One Dimension Chapter 2 Physics Table of Contents Position and Displacement Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Falling Objects The Big Idea Displacement is a change of position
Chapter 3. Accelerated Motion
 Chapter 3 Accelerated Motion Chapter 3 Accelerated Motion In this chapter you will: Develop descriptions of accelerated motions. Use graphs and equations to solve problems involving moving objects. Describe
Chapter 3 Accelerated Motion Chapter 3 Accelerated Motion In this chapter you will: Develop descriptions of accelerated motions. Use graphs and equations to solve problems involving moving objects. Describe
Clayton State University Department of Natural Sciences. Physics 1111 Quiz 2
 Clayton State University September 8, 2005 Name SOLUTION 1. A new car manufacturer advertises that their car can go "from zero to sixty in 8 s". This is a description of a. Average speed. b. Instantaneous
Clayton State University September 8, 2005 Name SOLUTION 1. A new car manufacturer advertises that their car can go "from zero to sixty in 8 s". This is a description of a. Average speed. b. Instantaneous
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line
 Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s rotation
Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Examples: The Earth orbits around the Sun A roadway moves with Earth s rotation
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without
 MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
Page 1 / 15. Motion Unit Test. Name: Motion ONLY, no forces. Question 1 (1 point) Examine the graphs below:
 Motion Unit Test Motion ONLY, no forces Name: Question 1 (1 point) Examine the graphs below: Which of the four graphs shows the runner with the fastest speed? A. Graph A B. Graph B C. Graph C D. Graph
Motion Unit Test Motion ONLY, no forces Name: Question 1 (1 point) Examine the graphs below: Which of the four graphs shows the runner with the fastest speed? A. Graph A B. Graph B C. Graph C D. Graph
4.1 Motion Is Relative. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. You can describe the motion of an object by its
 4.1 Motion Is Relative You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. 4.1 Motion
4.1 Motion Is Relative You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. 4.1 Motion
SPH 4C Unit 1 Motion and its Applications
 SPH 4C Unit 1 Motion and its Applications Review of Trigonometry and Pythagorean Theorem Learning Goal: I can use SOH CAH TOA and Pythagorean Theorem in real world applications. Your Calculator You will
SPH 4C Unit 1 Motion and its Applications Review of Trigonometry and Pythagorean Theorem Learning Goal: I can use SOH CAH TOA and Pythagorean Theorem in real world applications. Your Calculator You will
Motion Along a Straight Line
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER Motion Along a Straight Line Position & displacement Average & instantaneous velocity Average & instantaneous acceleration Constant acceleration Free fall Graphical
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER Motion Along a Straight Line Position & displacement Average & instantaneous velocity Average & instantaneous acceleration Constant acceleration Free fall Graphical
Position time graph Type of motion Example
 Acceleration Some theme parks have rides in which you are slowly carried up in a seat to the top of a tower, and then suddenly released (Figure 1). On the way down, your arms and hair may fly upward as
Acceleration Some theme parks have rides in which you are slowly carried up in a seat to the top of a tower, and then suddenly released (Figure 1). On the way down, your arms and hair may fly upward as
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line
 Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line Introduction: Study of the motion of objects Physics studies: Properties of matter and energy: solid state physics, thermal physics/ thermodynamics, atomic physics,
Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line Introduction: Study of the motion of objects Physics studies: Properties of matter and energy: solid state physics, thermal physics/ thermodynamics, atomic physics,
A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once.
 PART III. KINEMATICS A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once. 1. rise (Δy) The vertical separation of any two points on a curve is
PART III. KINEMATICS A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once. 1. rise (Δy) The vertical separation of any two points on a curve is
Position-versus-Time Graphs
 Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Lecture 2. 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion.
 Lecture 2 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion. Types of motion Trajectory is the line drawn to track the position of an abject in coordinates space (no time axis). y 1D motion: Trajectory
Lecture 2 1D motion with Constant Acceleration. Vertical Motion. Types of motion Trajectory is the line drawn to track the position of an abject in coordinates space (no time axis). y 1D motion: Trajectory
Physics of Everyday Phenomena. Chapter 2
 Physics of Everyday Phenomena W. Thomas Griffith Juliet W. Brosing Chapter 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Question 2.1 Ben leaves his home
Physics of Everyday Phenomena W. Thomas Griffith Juliet W. Brosing Chapter 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Question 2.1 Ben leaves his home
Vectors in Physics. Topics to review:
 Vectors in Physics Topics to review: Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors Relative Motion
Vectors in Physics Topics to review: Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors Relative Motion
Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension. Professor Wa el Salah
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Kinematics Describes motion while ignoring the external agents that might have caused or modified the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Kinematics Describes motion while ignoring the external agents that might have caused or modified the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight
Created by T. Madas CALCULUS KINEMATICS. Created by T. Madas
 CALCULUS KINEMATICS CALCULUS KINEMATICS IN SCALAR FORM Question (**) A particle P is moving on the x axis and its acceleration a ms, t seconds after a given instant, is given by a = 6t 8, t 0. The particle
CALCULUS KINEMATICS CALCULUS KINEMATICS IN SCALAR FORM Question (**) A particle P is moving on the x axis and its acceleration a ms, t seconds after a given instant, is given by a = 6t 8, t 0. The particle
Kinematics. Chapter 2. Position-Time Graph. Position
 Kinematics Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Describes motion while ignoring the agents that caused the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight line Will use the particle
Kinematics Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Describes motion while ignoring the agents that caused the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight line Will use the particle
UAM Paradigm Lab. Uniform Acceleration Background. X-t graph. V-t graph now. What about displacement? *Displacement method 2 9/18/2017
 9/8/07 UAM Paradigm Lab Uniform Acceleration Background Wheel down a rail Observations Dots got further apart as the wheel rolled down rail This means the change in position increased over time X-t graph
9/8/07 UAM Paradigm Lab Uniform Acceleration Background Wheel down a rail Observations Dots got further apart as the wheel rolled down rail This means the change in position increased over time X-t graph
1.1 Graphing Motion. IB Physics 11 Kinematics
 IB Physics 11 Kinematics 1.1 Graphing Motion Kinematics is the study of motion without reference to forces and masses. We will need to learn some definitions: A Scalar quantity is a measurement that has
IB Physics 11 Kinematics 1.1 Graphing Motion Kinematics is the study of motion without reference to forces and masses. We will need to learn some definitions: A Scalar quantity is a measurement that has
( ) 4 and 20, find the value. v c is equal to this average CALCULUS WORKSHEET 1 ON PARTICLE MOTION
 CALCULUS WORKSHEET 1 ON PARTICLE MOTION Work these on notebook paper. Use your calculator only on part (f) of problems 1. Do not use your calculator on the other problems. Write your justifications in
CALCULUS WORKSHEET 1 ON PARTICLE MOTION Work these on notebook paper. Use your calculator only on part (f) of problems 1. Do not use your calculator on the other problems. Write your justifications in
Motion Graphs Refer to the following information for the next four questions.
 Motion Graphs Refer to the following information for the next four questions. 1. Match the description provided about the behavior of a cart along a linear track to its best graphical representation. Remember
Motion Graphs Refer to the following information for the next four questions. 1. Match the description provided about the behavior of a cart along a linear track to its best graphical representation. Remember
Kinematics. 1. Introduction to Kinematics. 2. Position and displacement
 Kinematics 1. Introduction to Kinematics. Scalars & vectors 2. Position & displacement 3. Velocity 4. Acceleration 5. Uniform linear motion 6. Uniformly accelerated motion 7. Uniform circular motion 1.
Kinematics 1. Introduction to Kinematics. Scalars & vectors 2. Position & displacement 3. Velocity 4. Acceleration 5. Uniform linear motion 6. Uniformly accelerated motion 7. Uniform circular motion 1.
Chapter 1 Problem 28: Agenda. Quantities in Motion. Displacement Isn t Distance. Velocity. Speed 1/23/14
 Agenda We need a note-taker! If you re interested, see me after class. Today: HW Quiz #1, 1D Motion Lecture for this week: Chapter 2 (finish reading Chapter 2 by Thursday) Homework #2: continue to check
Agenda We need a note-taker! If you re interested, see me after class. Today: HW Quiz #1, 1D Motion Lecture for this week: Chapter 2 (finish reading Chapter 2 by Thursday) Homework #2: continue to check
Vectors. Slide 2 / 36. Slide 1 / 36. Slide 3 / 36. Slide 4 / 36. Slide 5 / 36. Slide 6 / 36. Scalar versus Vector. Determining magnitude and direction
 Slide 1 / 3 Slide 2 / 3 Scalar versus Vector Vectors scalar has only a physical quantity such as mass, speed, and time. vector has both a magnitude and a direction associated with it, such as velocity
Slide 1 / 3 Slide 2 / 3 Scalar versus Vector Vectors scalar has only a physical quantity such as mass, speed, and time. vector has both a magnitude and a direction associated with it, such as velocity
MOTION. Chapter 2: Sections 1 and 2
 MOTION Chapter 2: Sections 1 and 2 Vocab: Ch 2.1-2.2 Distance Displacement Speed Average speed Instantaneous speed Velocity Acceleration Describing Motion Motion is an object s change in position relative
MOTION Chapter 2: Sections 1 and 2 Vocab: Ch 2.1-2.2 Distance Displacement Speed Average speed Instantaneous speed Velocity Acceleration Describing Motion Motion is an object s change in position relative
What does the lab partner observe during the instant the student pushes off?
 Motion Unit Review State Test Questions 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer.
Motion Unit Review State Test Questions 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer.
MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE
 MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE 2 21 IDENTIFY: The average velocity is Let be upward EXECUTE: (a) EVALUATE: For the first 115 s of the flight, When the velocity isn t constant the average velocity depends
MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE 2 21 IDENTIFY: The average velocity is Let be upward EXECUTE: (a) EVALUATE: For the first 115 s of the flight, When the velocity isn t constant the average velocity depends
Chapter Four: Motion
 Chapter Four: Motion 4.1 Speed and Velocity 4.2 Graphs of Motion 4.3 Acceleration Section 4.3 Learning Goals Define acceleration. Determine acceleration by mathematical and graphical means. Explain the
Chapter Four: Motion 4.1 Speed and Velocity 4.2 Graphs of Motion 4.3 Acceleration Section 4.3 Learning Goals Define acceleration. Determine acceleration by mathematical and graphical means. Explain the
Quiz No. 1: Tuesday Jan. 31. Assignment No. 2, due Thursday Feb 2: Problems 8.4, 8.13, 3.10, 3.28 Conceptual questions: 8.1, 3.6, 3.12, 3.
 Quiz No. 1: Tuesday Jan. 31 Assignment No. 2, due Thursday Feb 2: Problems 8.4, 8.13, 3.10, 3.28 Conceptual questions: 8.1, 3.6, 3.12, 3.20 Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Kinematics Properties of
Quiz No. 1: Tuesday Jan. 31 Assignment No. 2, due Thursday Feb 2: Problems 8.4, 8.13, 3.10, 3.28 Conceptual questions: 8.1, 3.6, 3.12, 3.20 Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Kinematics Properties of
DOWNLOAD PDF KINEMATICS NOTES PHYSICS 11
 Chapter 1 : Kinematics Grade 11 Physics Notes Khullakitab Physics 11 à Kinematics 1 Physics 11 à Kinematics à Graphing Motion Kinematics is the study of motion without reference to forces and masses. Note
Chapter 1 : Kinematics Grade 11 Physics Notes Khullakitab Physics 11 à Kinematics 1 Physics 11 à Kinematics à Graphing Motion Kinematics is the study of motion without reference to forces and masses. Note
Theme 1: On the Move
 Theme 1: On the Move Kinematics is the science of describing the motion of objects using words, diagrams, numbers, graphs, and equations. Vectors, Scalars, Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity, Acceleration
Theme 1: On the Move Kinematics is the science of describing the motion of objects using words, diagrams, numbers, graphs, and equations. Vectors, Scalars, Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity, Acceleration
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
Physics 12. Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions
 Physics 12 Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions 1. Definitions When studying mechanics in Physics 11, we have realized that there are two major types of quantities that we can measure for the systems
Physics 12 Chapter 1: Vector Analysis in Two Dimensions 1. Definitions When studying mechanics in Physics 11, we have realized that there are two major types of quantities that we can measure for the systems
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
What You Will Learn In This Chapter. Displacement Vector Distance Velocity Vectors Acceleration Vectors Motion with constant Acceleration
 Chapter 2 What You Will Learn In This Chapter Displacement Vector Distance Velocity Vectors Acceleration Vectors Motion with constant Acceleration 2.1 Introduction to kinematics Kinematics is the study
Chapter 2 What You Will Learn In This Chapter Displacement Vector Distance Velocity Vectors Acceleration Vectors Motion with constant Acceleration 2.1 Introduction to kinematics Kinematics is the study
3.1 Using Vectors 3.3 Coordinate Systems and Vector Components.notebook September 19, 2017
 Using Vectors A vector is a quantity with both a size (magnitude) and a direction. Figure 3.1 shows how to represent a particle s velocity as a vector. Section 3.1 Using Vectors The particle s speed at
Using Vectors A vector is a quantity with both a size (magnitude) and a direction. Figure 3.1 shows how to represent a particle s velocity as a vector. Section 3.1 Using Vectors The particle s speed at
Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension. AIT AP Physics C
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Kinematics Describes motion while ignoring the agents that caused the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight line Will use the particle
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Kinematics Describes motion while ignoring the agents that caused the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight line Will use the particle
Chapter 3: Introduction to Kinematics
 Chapter 3: Introduction to Kinematics Kari Eloranta 2018 Jyväskylän Lyseon lukio Pre Diploma Program Year October 11, 2017 1 / 17 3.1 Displacement Definition of Displacement Displacement is the change
Chapter 3: Introduction to Kinematics Kari Eloranta 2018 Jyväskylän Lyseon lukio Pre Diploma Program Year October 11, 2017 1 / 17 3.1 Displacement Definition of Displacement Displacement is the change
Physics Revision Guide Volume 1
 Physics Revision Guide Volume 1 "Many people do not plan to fail, they just fail to plan!" Develop a customized success plan Create necessity in you to take action now Boost your confidence in your revision
Physics Revision Guide Volume 1 "Many people do not plan to fail, they just fail to plan!" Develop a customized success plan Create necessity in you to take action now Boost your confidence in your revision
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Example problem: Free Fall
 Example problem: Free Fall A ball is thrown from the top of a building with an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s straight upward, at an initial height of 50.0 m above the ground. The ball just misses the edge
Example problem: Free Fall A ball is thrown from the top of a building with an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s straight upward, at an initial height of 50.0 m above the ground. The ball just misses the edge
Chapter 2: Representing Motion. Click the mouse or press the spacebar to continue.
 Chapter 2: Representing Motion Click the mouse or press the spacebar to continue. Chapter 2 Representing Motion In this chapter you will: Represent motion through the use of words, motion diagrams, and
Chapter 2: Representing Motion Click the mouse or press the spacebar to continue. Chapter 2 Representing Motion In this chapter you will: Represent motion through the use of words, motion diagrams, and
Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Types of Motion Translational An example is a car traveling on a highway. Rotational An example is the Earth s spin on its axis. Vibrational An example is the back-and-forth
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Types of Motion Translational An example is a car traveling on a highway. Rotational An example is the Earth s spin on its axis. Vibrational An example is the back-and-forth
Formative Assessment: Uniform Acceleration
 Formative Assessment: Uniform Acceleration Name 1) A truck on a straight road starts from rest and accelerates at 3.0 m/s 2 until it reaches a speed of 24 m/s. Then the truck travels for 20 s at constant
Formative Assessment: Uniform Acceleration Name 1) A truck on a straight road starts from rest and accelerates at 3.0 m/s 2 until it reaches a speed of 24 m/s. Then the truck travels for 20 s at constant
Linear Motion. By Jack, Cole, Kate and Linus
 Linear Motion By Jack, Cole, Kate and Linus What is it? -Linear Motion is the study of motion, Kinematics, and Dynamics Motion Motion is dependent on the reference frame in which you are observing. If
Linear Motion By Jack, Cole, Kate and Linus What is it? -Linear Motion is the study of motion, Kinematics, and Dynamics Motion Motion is dependent on the reference frame in which you are observing. If
Total Distance traveled (d) S.I. Unit: meters Vector? No
 Total Distance traveled (d) S.I. Unit: meters Vector? No What does Total Distance traveled mean? Total Distance traveled d is the total length of the path traveled (i.e. the path length). d = Σ l d is
Total Distance traveled (d) S.I. Unit: meters Vector? No What does Total Distance traveled mean? Total Distance traveled d is the total length of the path traveled (i.e. the path length). d = Σ l d is
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension. Slide 2-1
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Slide 2-1 MasteringPhysics, PackBack Answers You should be on both by now. MasteringPhysics first reading quiz Wednesday PackBack should have email & be signed up 2014
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Slide 2-1 MasteringPhysics, PackBack Answers You should be on both by now. MasteringPhysics first reading quiz Wednesday PackBack should have email & be signed up 2014
Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107. Note - 3 : Motion in One Dimension
 Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107 Note - 3 : Motion in One Dimension Abu Mohammad Khan Department of Mathematics and Physics North South University https://abukhan.weebly.com Copyright: It is unlawful
Course Name : Physics I Course # PHY 107 Note - 3 : Motion in One Dimension Abu Mohammad Khan Department of Mathematics and Physics North South University https://abukhan.weebly.com Copyright: It is unlawful
