STELLAR MAGNETISM: ORIGINS, EFFECTS, ENIGMAS
|
|
|
- Mervyn Hines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STELLAR MAGNETISM: ORIGINS, EFFECTS, ENIGMAS MATTHEW BROWNING, LAURA CURRIE, LUCIA DUARTE, MARIA WEBER, FELIX SAINSBURY-MARTINEZ, LEWIS IRELAND + FRIENDS ELSEWHERE (NICK FEATHERSTONE, MARK MIESCH, SACHA BRUN )
2 SOME MOTIVATING QUESTIONS FOR TODAY Some stars have strong B fields; others don t. Why? Donati et al. (2006) Schmidt et al. (2015) Some stars have clear cycles; others seem not to. Why? Baliunas et al. (1995) How is a star s life shaped by magnetism?
3 YOU CAN DETECT MAGNETISM IN A VARIETY OF WAYS Astro 101: measure flux as function of wavelength as function of time as function of position Basri et `al. (2011) Johns-Krull & Valenti (1996) (plus polarisation state, maybe) Roettenbacher et al. (2016)
4 THE SUN: ORDER AMIDST CHAOS Solar interior is turbulent (anything/diffusivity = big) How do you build ordered fields? Full disk: SOHO/MDI. Close-up: Hinode (SOT)
5 MAGNETIC FIELDS CONTRIBUTE TO HEATING OF STELLAR ATMOSPHERES High-energy emission magnetogram (Solar Dynamics Observatory: AIA 171, HMI, Sept 8-10, 2017) Physical picture: fields linked to heating
6 SURFACE CONVECTION AND MAGNETISM ARE LINKED Convection in envelopes, cores, or full interiors Convective cores Convective envelopes Magnetism often found where you have surface convection (exceptions: Ap/Bp) Fully convective ESA/Gaia/DPAC
7 SURFACE MAGNETISM IS RELATED TO STELLAR ROTATION RATE Activity (here, coronal) See et al. (2015) Observed in many stars Pizzolato et al. (2003) More rapid rotation= more activity (to a point) Rotational influence
8 SOME STARS EXHIBIT MAGNETIC CYCLES, WITH (ROTATION- DEPENDENT) PERIODS Long-term monitoring needed! Mt Wilson Observatory HK project Lowell Observatory SSS project see, e.g., review in Hall (2008) See et al. (2016) Baliunas et al. (1995) Relation between cycle period and rotation rate: it s complicated (see Egeland talk) see, e.g., Saar & Brandenburg (1999); Bohm-Vitense (2007); Reinhold et al. (2017); Egeland (2017)
9 wind magnetization MAGNETISM FEEDS BACK ON A STAR S ROTATIONAL EVOLUTION Stars lose mass and angular momentum over time Magnetic field strength and morphology both affect this ~Normalised torque dipole octupole Finley & Matt (2018) Skumanich (1972) see also, e.g., Garraffo et al. 2015
10 COULD B (OR ROTATION) AFFECT STELLAR RADII? Eclipsing binary measurements of stellar radii Radii inflated w/r/t models (by 3-15 percent) (Teff lower, L~const) Ribas et al. (2006) Convective inefficiency and/or spots frequently invoked see, e.g., Feiden & Chaboyer (2014), Feiden (2016) MacDonald & Mullan (2013, 2015, 2017, ) Chabrier et al. (2007)
11 THE RADIUS OF A STELLAR MODEL IS PROPORTIONAL TO ITS ENTROPY Standard MLT: S~const in interior R increases with S see, e.g., Stahler (1988) Ireland & Browning 2018, using MESA If B is big enough, will affect P/T/S in interior, and hence R Extreme case: stably stratified (Mullan & MacDonald 2001)
12 BUT THERMALLY RELEVANT FIELDS ARE PROBABLY UNREALISTICALLY STRONG Strong, small-scale B: Ohmic dissipation>> L Strong, large-scale B: Rise faster than can be regenerated* Browning et al. (2016). See also Feiden & Chaboyer (2014) Beyond a certain (really high!) strength, no* field can satisfy both constraints
13 WHAT DO WEAKER FIELDS DO? (DEPENDS A BIT ON MODEL) No universally-agreed way of incorporating B in 1-D But various models try to do so in plausible ways, e.g.: a) model mag. pressure Feiden (2016) b) model ds/dr as f(b) If you affect layers near surface -> overall structure adjusts See also MacDonald & Mullan ( ), Ireland & Browning (2018) May lead to inflation, (particularly on pre-ms)
14 HELIOSEISMOLOGY REVEALS SUN HAS TWO SHEARING BOUNDARY LAYERS Howe (2009), LRSP Using ~12 years of MDI data In classic interface Solar dynamo models, tachocline long thought to play a crucial role shear stratification helicity
15 FULLY CONVECTIVE STARS ALSO SHOW ROTATION-ACTIVITY CORRELATION Activity Newton et al. (2016) Pizzolato et al. (2003) Wright et al. (2018) Rotation
16 WHAT ARE BUILDING BLOCKS OF DYNAMO ACTION? For small-scale fields: complex flow, high conductivity For ordered fields: need more (symmetry-breaking) Alpha effect: helical convection Olson et al. (1999) + potentially many other effects Omega effect: shear (meridional circulation, Babcock-Leighton, ) Bennett et al. (2003)
17 HIERARCHY OF APPROACHES (EACH WITH PROS/CONS) Global models: Resolve largest scales, ignore (or parameterise) smallest More local 2D/3D models: higher local resolution, (but boundaries, geometry) 1D-like: evolution models, MFT, Cheaper to compute, can build intuition
18 ASIDE: YOU CAN DO THIS, TOO Many of these codes are publicly available, e.g. Rayleigh: geodynamics.org/cig/software/rayleigh/ Magic: magic-sph.github.io Dedalus: dedalus-project.org (+ many others: MESA, Pencil, )
19 FLOWS THAT FEEL ROTATION, STRATIFICATION, MAGNETISM 3D deep-shell simulation by Lucia Duarte (Duarte et al. 2016) Radial velocity on a particular shell near the upper surface Upflows are red; down flows are blue
20 ROTATION MATTERS FOR CONVECTIVE FLOWS No rotation Visualisations and simulations by Nick Featherstone with Rayleigh Rapid rotation Rotation shapes the convective flows
21 R O TAT I O N S TA B I L I S E S CONVECTION IN THE LAB, TOO If you spin rapidly enough, eventually convection stops Cheng et al (for fixed driving/flux/ dt/etc)
22 ROTATION MATTERS FOR HEAT TRANSPORT Barker et al. (2014) Simulations by Laura Currie, Adrian Barker, et al., using Dedalus Need stronger dt/dz at higher rotation rates (for given flux) Theory and simulations give similar scalings e.g., Stevenson (1979), Julien et al. (2012),
23 ROTATION MATTERS FOR DIFFERENTIAL ROTATION Solar-like (fast EQ) Anti-solar (slow EQ) Featherstone & Miesch (2015) Rotation rate (+ many prior papers: e.g., Gilman ( ); Gastine et al. 2014) + eventually, banded zonal flows (Jupiter) Brun et al. 2017
24 ROTATION MATTERS FOR FIELD GENERATION Rotation typically favours the generation of more ordered fields Here ( planetary simulations), more rapid rotation-> more dipolar Many outcomes possible: Steady dipoles, wreaths, cycles Christensen & Aubert (2006)
25 ORDERED AND CYCLICAL FIELDS CAN BE GENERATED WITHOUT A TACHOCLINE Azimuthal field Yadav et al. (2015) Kapyla et al. (2012) + many other examples! e.g., Brown et al. (2011), Augustson et al. (2015) Duarte et al. (2016) (this does not necessarily mean tachocline plays no role in Sun)
26 RELATIONS BETWEEN CYCLE PERIOD AND ROTATION IN SIMULATIONS Here, more rapid rotation yields longer cycles Strugarek et al. (2017) More on this in later talks + splinters Warnecke (2018)
27 THE INTERACTION BETWEEN CONVECTION, MAGNETISM, AND SHEAR CAN BE COMPLEX In some regimes, B may increase convective heat transport Convective heat flux No shear Shear reduces convective F With shear Goluskin et al. (2014), JFM Magnetism reduces shear Browning (2008) Net effect of B can be increased F see, e.g., Yadav et al. (2016), GJI
28 IN SEARCH OF A PRIVATE ISLAND Where we d like to go vs. What we can afford Necker Island, BVI Images: Rebecca Anthony (DevonLive); Luca Galuzzi
29 SUMMARY: THE MAGNETIC LIVES OF ROTATING STARS Magnetism shapes the lives of stars in a variety of ways The magnetism is built by dynamo action, usually involving convection. The character of the fields is influenced by rotation. We still don t have a comprehensive theory of how this all works (or what the fields do), but lots of clues!
Magnetometry of M dwarfs: methodology & results
 Magnetometry of M dwarfs: methodology & results Julien Morin Laboratoire Univers et Particules de Montpellier First MaTYSSE meeting - Toulouse 2nd November 2015 Outline 1 Magnetic fields: a crucial ingredient
Magnetometry of M dwarfs: methodology & results Julien Morin Laboratoire Univers et Particules de Montpellier First MaTYSSE meeting - Toulouse 2nd November 2015 Outline 1 Magnetic fields: a crucial ingredient
Large-scale Flows and Dynamo In Solar-Like Stars
 Large-scale Flows and Dynamo In Solar-Like Stars Gustavo Guerrero Physics Department Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais Brazil P. Smolarkiewicz (ECMWF) A. Kosovichev (NJIT), Elisabete M. de G. Dal Pino
Large-scale Flows and Dynamo In Solar-Like Stars Gustavo Guerrero Physics Department Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais Brazil P. Smolarkiewicz (ECMWF) A. Kosovichev (NJIT), Elisabete M. de G. Dal Pino
Stratified Convection Driven by Internal Heating
 Stratified Convection Driven by Internal Heating (a convective amplitudes talk) Nick Featherstone Collaborators: Brad Hindman Mark Miesch Juri Toomre The Rossby Number typical velocity v Rotational Timescale
Stratified Convection Driven by Internal Heating (a convective amplitudes talk) Nick Featherstone Collaborators: Brad Hindman Mark Miesch Juri Toomre The Rossby Number typical velocity v Rotational Timescale
Surface magnetic fields across the HR Diagram
 Surface magnetic fields across the HR Diagram John Landstreet University of Western Ontario London, Upper Canada & Armagh Observatory Armagh, Northern Ireland Objective of this talk... This meeting combines
Surface magnetic fields across the HR Diagram John Landstreet University of Western Ontario London, Upper Canada & Armagh Observatory Armagh, Northern Ireland Objective of this talk... This meeting combines
Logistics 2/14/17. Topics for Today and Thur. Helioseismology: Millions of sound waves available to probe solar interior. ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Pleiades Star Cluster Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 9 Tues 14 Feb 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Topics for Today and Thur Helioseismology:
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Pleiades Star Cluster Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 9 Tues 14 Feb 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Topics for Today and Thur Helioseismology:
Rotation and activity in low-mass stars
 Rotation and activity in low-mass stars ät öttingen Outline I. Introduction: Magnetic activity and why we care about it II. III. Spin-up and spin-down: Rotational evolution of sun-like stars Magnetic field
Rotation and activity in low-mass stars ät öttingen Outline I. Introduction: Magnetic activity and why we care about it II. III. Spin-up and spin-down: Rotational evolution of sun-like stars Magnetic field
"Heinrich Schwabe's holistic detective agency
 "Heinrich Schwabe's holistic detective agency, Ricky Egeland* High Altitude Observatory, NCAR 1. Sun alone is a complex system, emergence, total is > Σ of parts=> holistic 2. The Sun alone has provided
"Heinrich Schwabe's holistic detective agency, Ricky Egeland* High Altitude Observatory, NCAR 1. Sun alone is a complex system, emergence, total is > Σ of parts=> holistic 2. The Sun alone has provided
Logistics 2/13/18. Topics for Today and Thur+ Helioseismology: Millions of sound waves available to probe solar interior. ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Pleiades Star Cluster Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 9 Tues 13 Feb 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Topics for Today and Thur+ Helioseismology:
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Pleiades Star Cluster Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 9 Tues 13 Feb 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Topics for Today and Thur+ Helioseismology:
Dynamo Simulations in Solar Convection Zone
 Dynamo Simulations in Solar Convection Zone Bidya Binay Karak (Nordita fellow & Visitor at MPS) Collaborators: Axel Brandenburg (Nordita), Petri Käpylä and Maarit Käpylä (Aalto University) Thanks to organisers
Dynamo Simulations in Solar Convection Zone Bidya Binay Karak (Nordita fellow & Visitor at MPS) Collaborators: Axel Brandenburg (Nordita), Petri Käpylä and Maarit Käpylä (Aalto University) Thanks to organisers
Meridional Flow, Differential Rotation, and the Solar Dynamo
 Meridional Flow, Differential Rotation, and the Solar Dynamo Manfred Küker 1 1 Leibniz Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, 14482 Potsdam, Germany Abstract. Mean field models of rotating
Meridional Flow, Differential Rotation, and the Solar Dynamo Manfred Küker 1 1 Leibniz Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, 14482 Potsdam, Germany Abstract. Mean field models of rotating
Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul]
![Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul] Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul]](/thumbs/82/84973983.jpg) Dynamo tutorial Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul] ISSI Dynamo tutorial 1 1 Dynamo tutorial
Dynamo tutorial Part 1 : solar dynamo models [Paul] Part 2 : Fluctuations and intermittency [Dario] Part 3 : From dynamo to interplanetary magnetic field [Paul] ISSI Dynamo tutorial 1 1 Dynamo tutorial
Supercomputers simulation of solar granulation
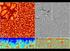 Supercomputers simulation of solar granulation simulation by Stein et al (2006), visualization by Henze (2008) Beyond Solar Dermatology But still stops at 0.97R! what lies deeper still? Supercomputers
Supercomputers simulation of solar granulation simulation by Stein et al (2006), visualization by Henze (2008) Beyond Solar Dermatology But still stops at 0.97R! what lies deeper still? Supercomputers
Stellar magnetic fields of young sun-like stars. Aline Vidotto Swiss National Science Foundation Ambizione Fellow University of Geneva
 Swiss National Science Foundation Ambizione Fellow University of Geneva Age-rotation-activity relation Skumanich 72 rotation velocity (km/s) chromospheric activity Young stars = fast rotation & high activity
Swiss National Science Foundation Ambizione Fellow University of Geneva Age-rotation-activity relation Skumanich 72 rotation velocity (km/s) chromospheric activity Young stars = fast rotation & high activity
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 8 Aug 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 8 Aug 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 8 Aug 2014](/thumbs/90/103247377.jpg) Magnetic Modulation of Stellar Angular Momentum Loss Cecilia Garraffo 1, Jeremy J. Drake 1, and Ofer Cohen 1 ABSTRACT arxiv:1408.1965v1 [astro-ph.sr] 8 Aug 2014 Angular Momentum Loss is important for understanding
Magnetic Modulation of Stellar Angular Momentum Loss Cecilia Garraffo 1, Jeremy J. Drake 1, and Ofer Cohen 1 ABSTRACT arxiv:1408.1965v1 [astro-ph.sr] 8 Aug 2014 Angular Momentum Loss is important for understanding
Paul Charbonneau, Université de Montréal
 Stellar dynamos Paul Charbonneau, Université de Montréal Magnetohydrodynamics (ch. I.3) Simulations of solar/stellar dynamos (ch. III.5, +) Mean-field electrodynamics (ch. I.3, III.6) From MHD to simpler
Stellar dynamos Paul Charbonneau, Université de Montréal Magnetohydrodynamics (ch. I.3) Simulations of solar/stellar dynamos (ch. III.5, +) Mean-field electrodynamics (ch. I.3, III.6) From MHD to simpler
Solar Structure. Connections between the solar interior and solar activity. Deep roots of solar activity
 Deep roots of solar activity Michael Thompson University of Sheffield Sheffield, U.K. michael.thompson@sheffield.ac.uk With thanks to: Alexander Kosovichev, Rudi Komm, Steve Tobias Connections between
Deep roots of solar activity Michael Thompson University of Sheffield Sheffield, U.K. michael.thompson@sheffield.ac.uk With thanks to: Alexander Kosovichev, Rudi Komm, Steve Tobias Connections between
Magnetic Modulation of Stellar Angular Momentum Loss
 Magnetic Modulation of Stellar Angular Momentum Loss Cecilia Garraffo 1, Jeremy J. Drake 1, Ofer Cohen 1 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St. Cambridge, MA 02138 Abstract. Angular
Magnetic Modulation of Stellar Angular Momentum Loss Cecilia Garraffo 1, Jeremy J. Drake 1, Ofer Cohen 1 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St. Cambridge, MA 02138 Abstract. Angular
Magnetic instabilities in stellar interiors
 Magnetic instabilities in stellar interiors Laurène Jouve Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie Toulouse Journées Equip@Meso, 26/27 Novembre 2015 Stellar magnetism Our Sun Stellar magnetism
Magnetic instabilities in stellar interiors Laurène Jouve Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie Toulouse Journées Equip@Meso, 26/27 Novembre 2015 Stellar magnetism Our Sun Stellar magnetism
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Jun 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Jun 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Jun 2018](/thumbs/88/116029012.jpg) Breaking Taylor-Proudman balance by magnetic field in stellar convection zone H. Hotta arxiv:1806.01452v1 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Jun 2018 Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, Chiba university, 1-33
Breaking Taylor-Proudman balance by magnetic field in stellar convection zone H. Hotta arxiv:1806.01452v1 [astro-ph.sr] 5 Jun 2018 Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, Chiba university, 1-33
Stellar magnetic activity: Is Rossby number really the key?
 Solar Group Seminar June 24, 2014 Stellar magnetic activity: Is Rossby number really the key? or Rossby or not Rossby (Gibor Basri, 1986) Ansgar Reiners (IAG), Vera Maria Passeger (IAG) Manfred Schüssler
Solar Group Seminar June 24, 2014 Stellar magnetic activity: Is Rossby number really the key? or Rossby or not Rossby (Gibor Basri, 1986) Ansgar Reiners (IAG), Vera Maria Passeger (IAG) Manfred Schüssler
The solar dynamo (critical comments on) SPD Hale talk 14 June 2011
 The solar dynamo (critical comments on) The solar dynamo (critical comments on) - what observations show - what they show is not the case - what is known from theory - interesting open questions quantitative
The solar dynamo (critical comments on) The solar dynamo (critical comments on) - what observations show - what they show is not the case - what is known from theory - interesting open questions quantitative
Extrapolating Solar Dynamo Models throughout the Heliosphere
 Extrapolating Solar Dynamo Models throughout the Heliosphere Taylor Cox Bridgewater College Mentors: Mark Miesch, Kyle Augustson, Nick Featherstone Solar Convection Convection arises from heat in the Sun
Extrapolating Solar Dynamo Models throughout the Heliosphere Taylor Cox Bridgewater College Mentors: Mark Miesch, Kyle Augustson, Nick Featherstone Solar Convection Convection arises from heat in the Sun
Does inertia determine the magnetic topology of low-mass stars?
 Does inertia determine the magnetic topology of low-mass stars? Julien Morin Institut für Astrophysik Göttingen T. Gastine Max Planck Institut für Sonnensystemforschung A. Reiners Institut für Astrophysik
Does inertia determine the magnetic topology of low-mass stars? Julien Morin Institut für Astrophysik Göttingen T. Gastine Max Planck Institut für Sonnensystemforschung A. Reiners Institut für Astrophysik
Solar and stellar dynamo models
 Solar and stellar dynamo models Paul Charbonneau, Université de Montréal From MHD to simple dynamo models Mean-field models Babcock-Leighton models Stochastic forcing Cycle forecasting Stellar dynamos
Solar and stellar dynamo models Paul Charbonneau, Université de Montréal From MHD to simple dynamo models Mean-field models Babcock-Leighton models Stochastic forcing Cycle forecasting Stellar dynamos
1. Solar Atmosphere Surface Features and Magnetic Fields
 1. Solar Atmosphere Surface Features and Magnetic Fields Sunspots, Granulation, Filaments and Prominences, Coronal Loops 2. Solar Cycle: Observations The Sun: applying black-body radiation laws Radius
1. Solar Atmosphere Surface Features and Magnetic Fields Sunspots, Granulation, Filaments and Prominences, Coronal Loops 2. Solar Cycle: Observations The Sun: applying black-body radiation laws Radius
Solar Cycle Prediction and Reconstruction. Dr. David H. Hathaway NASA/Ames Research Center
 Solar Cycle Prediction and Reconstruction Dr. David H. Hathaway NASA/Ames Research Center Outline Solar cycle characteristics Producing the solar cycle the solar dynamo Polar magnetic fields producing
Solar Cycle Prediction and Reconstruction Dr. David H. Hathaway NASA/Ames Research Center Outline Solar cycle characteristics Producing the solar cycle the solar dynamo Polar magnetic fields producing
The Origin of the Solar Cycle & Helioseismology
 The Origin of the Solar Cycle & Helioseismology What is the solar cycle? Simple concept of cycle mechanism, dynamo What is helioseismology? Global properties of the solar interior Local properties of the
The Origin of the Solar Cycle & Helioseismology What is the solar cycle? Simple concept of cycle mechanism, dynamo What is helioseismology? Global properties of the solar interior Local properties of the
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015
 Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015 Today: Continue Ch. 13: Star Stuff Reading in Bennett: For Monday: Finish Chapter 13 Star Stuff Reminders: Ch. 12 HW now on Mastering Astronomy, due Monday. Ch. 13 will be
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015 Today: Continue Ch. 13: Star Stuff Reading in Bennett: For Monday: Finish Chapter 13 Star Stuff Reminders: Ch. 12 HW now on Mastering Astronomy, due Monday. Ch. 13 will be
Dynamics of Giant Planet Atmospheres. Tapio Schneider (with Junjun Liu) California Institute of Technology
 Dynamics of Giant Planet Atmospheres Tapio Schneider (with Junjun Liu) California Institute of Technology Jupiter from Cassini (Cassini Imaging Team 2000) Jupiter from Cassini (Cassini Imaging Team 2000)
Dynamics of Giant Planet Atmospheres Tapio Schneider (with Junjun Liu) California Institute of Technology Jupiter from Cassini (Cassini Imaging Team 2000) Jupiter from Cassini (Cassini Imaging Team 2000)
Magnetic field topologies of M dwarfs
 LATT CNRS / Université de Toulouse J. F. Donati, P. Petit, B. Dintrans LATT CNRS / Université de Toulouse X. Delfosse, T. Forveille LAOG CNRS / Université de Grenoble M. M. Jardine University of St Andrews
LATT CNRS / Université de Toulouse J. F. Donati, P. Petit, B. Dintrans LATT CNRS / Université de Toulouse X. Delfosse, T. Forveille LAOG CNRS / Université de Grenoble M. M. Jardine University of St Andrews
Magnetic mapping of solar-type stars
 Magnetic mapping of solar-type stars Pascal Petit figure: M. Jardine Magnetic mapping of solar-type stars introduction: scientific context tomographic tools magnetic maps of active stars stellar differential
Magnetic mapping of solar-type stars Pascal Petit figure: M. Jardine Magnetic mapping of solar-type stars introduction: scientific context tomographic tools magnetic maps of active stars stellar differential
The Solar Interior. Paul Bushby (Newcastle University) STFC Introductory Course in Solar System Physics Leeds, 06 Sept 2010
 The Solar Interior Paul Bushby (Newcastle University) STFC Introductory Course in Solar System Physics Leeds, 06 Sept 2010 General Outline 1. Basic properties of the Sun 2. Solar rotation and large-scale
The Solar Interior Paul Bushby (Newcastle University) STFC Introductory Course in Solar System Physics Leeds, 06 Sept 2010 General Outline 1. Basic properties of the Sun 2. Solar rotation and large-scale
Meridional Flow, Torsional Oscillations, and the Solar Magnetic Cycle
 Meridional Flow, Torsional Oscillations, and the Solar Magnetic Cycle David H. Hathaway NASA/MSFC National Space Science and Technology Center Outline 1. Key observational components of the solar magnetic
Meridional Flow, Torsional Oscillations, and the Solar Magnetic Cycle David H. Hathaway NASA/MSFC National Space Science and Technology Center Outline 1. Key observational components of the solar magnetic
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Nov 2013 Accepted for publication in MNRAS, 8 November 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Nov 2013 Accepted for publication in MNRAS, 8 November 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 13 Nov 2013 Accepted for publication in MNRAS, 8 November 2013](/thumbs/72/67736402.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 5 (2013) Printed 14 November 2013 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) From solar-like to anti-solar differential rotation in cool stars T. Gastine 1, R. K. Yadav 1,2, J. Morin 2,3,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 5 (2013) Printed 14 November 2013 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) From solar-like to anti-solar differential rotation in cool stars T. Gastine 1, R. K. Yadav 1,2, J. Morin 2,3,
THE DYNAMO EFFECT IN STARS
 THE DYNAMO EFFECT IN STARS Axel Brandenburg NORDITA, Blegdamsvej 17, DK-2100 Copenhagen 0, Denmark; and Department of Mathematics, University of Newcastle upon Tyne, NEl 7RU, UK brandenb@nordita.dk Abstract
THE DYNAMO EFFECT IN STARS Axel Brandenburg NORDITA, Blegdamsvej 17, DK-2100 Copenhagen 0, Denmark; and Department of Mathematics, University of Newcastle upon Tyne, NEl 7RU, UK brandenb@nordita.dk Abstract
Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars
 Doppler Shift At each point the emitter is at the center of a circular wavefront extending out from its present location. Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html
Doppler Shift At each point the emitter is at the center of a circular wavefront extending out from its present location. Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html
From solar-like to antisolar differential rotation in cool stars
 MNRASL 438, L76 L80 (2014) Advance Access publication 2013 December 9 doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slt162 From solar-like to antisolar differential rotation in cool stars T. Gastine, 1 R. K. Yadav, 1,2 J. Morin,
MNRASL 438, L76 L80 (2014) Advance Access publication 2013 December 9 doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slt162 From solar-like to antisolar differential rotation in cool stars T. Gastine, 1 R. K. Yadav, 1,2 J. Morin,
Tests of stellar physics with high-precision data from eclipsing binary stars
 Tests of stellar physics with high-precision data from eclipsing binary stars Ignasi Ribas Institut de Ciències de l Espai (CSIC-IEEC, Barcelona) Barcelona, April 2013 Eclipsing binary systems Eclipsing
Tests of stellar physics with high-precision data from eclipsing binary stars Ignasi Ribas Institut de Ciències de l Espai (CSIC-IEEC, Barcelona) Barcelona, April 2013 Eclipsing binary systems Eclipsing
Recent developments on the formation and evolution of young low-mass stars
 Recent developments on the formation and evolution of young low-mass stars Rob Jeffries Keele University, UK Observations of young clusters that probe: The influence of magnetic activity and rotation on
Recent developments on the formation and evolution of young low-mass stars Rob Jeffries Keele University, UK Observations of young clusters that probe: The influence of magnetic activity and rotation on
Problem set: solar irradiance and solar wind
 Problem set: solar irradiance and solar wind Karel Schrijver July 3, 203 Stratification of a static atmosphere within a force-free magnetic field Problem: Write down the general MHD force-balance equation
Problem set: solar irradiance and solar wind Karel Schrijver July 3, 203 Stratification of a static atmosphere within a force-free magnetic field Problem: Write down the general MHD force-balance equation
The Interior Structure of the Sun
 The Interior Structure of the Sun Data for one of many model calculations of the Sun center Temperature 1.57 10 7 K Pressure 2.34 10 16 N m -2 Density 1.53 10 5 kg m -3 Hydrogen 0.3397 Helium 0.6405 The
The Interior Structure of the Sun Data for one of many model calculations of the Sun center Temperature 1.57 10 7 K Pressure 2.34 10 16 N m -2 Density 1.53 10 5 kg m -3 Hydrogen 0.3397 Helium 0.6405 The
On the role of tachoclines in solar and stellar dynamos
 Not to appear in Nonlearned J., 45. On the role of tachoclines in solar and stellar dynamos G. Guerrero Physics Department, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Av. Antonio Carlos, 6627, Belo Horizonte,
Not to appear in Nonlearned J., 45. On the role of tachoclines in solar and stellar dynamos G. Guerrero Physics Department, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Av. Antonio Carlos, 6627, Belo Horizonte,
Magnetic Induction in Hot Jupiter Atmospheres
 Magnetic Induction in Hot Jupiter Atmospheres University of Toronto May 12 th, 2010 Outline An Overview of Extra solar Giant Planets Hot Jupiter General Circulation in the Atmosphere Preliminaries: Ionization,
Magnetic Induction in Hot Jupiter Atmospheres University of Toronto May 12 th, 2010 Outline An Overview of Extra solar Giant Planets Hot Jupiter General Circulation in the Atmosphere Preliminaries: Ionization,
where G is Newton s gravitational constant, M is the mass internal to radius r, and Ω 0 is the
 Homework Exercise Solar Convection and the Solar Dynamo Mark Miesch (HAO/NCAR) NASA Heliophysics Summer School Boulder, Colorado, July 27 - August 3, 2011 PROBLEM 1: THERMAL WIND BALANCE We begin with
Homework Exercise Solar Convection and the Solar Dynamo Mark Miesch (HAO/NCAR) NASA Heliophysics Summer School Boulder, Colorado, July 27 - August 3, 2011 PROBLEM 1: THERMAL WIND BALANCE We begin with
The Sun. The Sun. Bhishek Manek UM-DAE Centre for Excellence in Basic Sciences. May 7, 2016
 The Sun Bhishek Manek UM-DAE Centre for Excellence in Basic Sciences May 7, 2016 Outline 1 Motivation 2 Resume of the Sun 3 Structure of the Sun - Solar Interior and Atmosphere 4 Standard Solar Model -
The Sun Bhishek Manek UM-DAE Centre for Excellence in Basic Sciences May 7, 2016 Outline 1 Motivation 2 Resume of the Sun 3 Structure of the Sun - Solar Interior and Atmosphere 4 Standard Solar Model -
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Oct 2011
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Oct 2011 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Oct 2011](/thumbs/74/70649382.jpg) 1 st Asia - Pacific Solar Physics Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 00, pp 1 10 Editors: A. R. Choudhuri, S. P. Rajaguru, D. Banerjee arxiv:1108.1604v2 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Oct 2011 Solar differential
1 st Asia - Pacific Solar Physics Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 00, pp 1 10 Editors: A. R. Choudhuri, S. P. Rajaguru, D. Banerjee arxiv:1108.1604v2 [astro-ph.sr] 11 Oct 2011 Solar differential
Solar surface rotation
 Stellar rotation Solar surface rotation Solar nearsurface rotation Surface Doppler Schou et al. (1998; ApJ 505, 390) Rotational splitting Inferred solar internal rotation Near solidbody rotation of interior
Stellar rotation Solar surface rotation Solar nearsurface rotation Surface Doppler Schou et al. (1998; ApJ 505, 390) Rotational splitting Inferred solar internal rotation Near solidbody rotation of interior
Simulations of the solar magnetic cycle with EULAG-MHD Paul Charbonneau Département de Physique, Université de Montréal
 Simulations of the solar magnetic cycle with EULAG-MHD Paul Charbonneau Département de Physique, Université de Montréal 1. The solar magnetic field and its cycle 2. Magnetic cycles with EULAG-MHD 3. Why
Simulations of the solar magnetic cycle with EULAG-MHD Paul Charbonneau Département de Physique, Université de Montréal 1. The solar magnetic field and its cycle 2. Magnetic cycles with EULAG-MHD 3. Why
Solar cycle & Dynamo Modeling
 Solar cycle & Dynamo Modeling Andrés Muñoz-Jaramillo www.solardynamo.org Georgia State University University of California - Berkeley Stanford University THE SOLAR CYCLE: A MAGNETIC PHENOMENON Sunspots
Solar cycle & Dynamo Modeling Andrés Muñoz-Jaramillo www.solardynamo.org Georgia State University University of California - Berkeley Stanford University THE SOLAR CYCLE: A MAGNETIC PHENOMENON Sunspots
Large scale magnetic fields and Dynamo theory. Roman Shcherbakov, Turbulence Discussion Group 14 Apr 2008
 Large scale magnetic fields and Dynamo theory Roman Shcherbakov, Turbulence Discussion Group 14 Apr 2008 The Earth Mainly dipolar magnetic field Would decay in 20kyr if not regenerated Declination of the
Large scale magnetic fields and Dynamo theory Roman Shcherbakov, Turbulence Discussion Group 14 Apr 2008 The Earth Mainly dipolar magnetic field Would decay in 20kyr if not regenerated Declination of the
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
Differential rotation in solar-like stars from global simulations
 Differential rotation in solar-like stars from global simulations G. Guerrero Solar Physics, HEPL, Stanford University, 452 Lomita mall, Stanford, CA, 94305-4085 gag@stanford.edu P. K. Smolarkiewicz European
Differential rotation in solar-like stars from global simulations G. Guerrero Solar Physics, HEPL, Stanford University, 452 Lomita mall, Stanford, CA, 94305-4085 gag@stanford.edu P. K. Smolarkiewicz European
22. Kinematic Dynamo Theory; Mean Field Theory. We seek solutions to the Induction (dynamo) equation
 238 22. Kinematic Dynamo Theory; Mean Field Theory Dynamo Solutions We seek solutions to the Induction (dynamo) equation B/ t = λ 2B + x (u x B) (22.1) that do not decay with time and have no external
238 22. Kinematic Dynamo Theory; Mean Field Theory Dynamo Solutions We seek solutions to the Induction (dynamo) equation B/ t = λ 2B + x (u x B) (22.1) that do not decay with time and have no external
Pulsations and Magnetic Fields in Massive Stars. Matteo Cantiello KITP Fellow Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics, UCSB
 Pulsations and Magnetic Fields in Massive Stars Matteo Cantiello KITP Fellow Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics, UCSB Massive stars Energy / Momentum in ISM Stellar Winds, SNe Nucleosynthesis Remnants:
Pulsations and Magnetic Fields in Massive Stars Matteo Cantiello KITP Fellow Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics, UCSB Massive stars Energy / Momentum in ISM Stellar Winds, SNe Nucleosynthesis Remnants:
Parity of solar global magnetic field determined by turbulent diffusivity
 First Asia-Pacific Solar Physics Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 1, pp 117 122 Edited by Arnab Rai Choudhuri & Dipankar Banerjee Parity of solar global magnetic field determined by turbulent
First Asia-Pacific Solar Physics Meeting ASI Conference Series, 2011, Vol. 1, pp 117 122 Edited by Arnab Rai Choudhuri & Dipankar Banerjee Parity of solar global magnetic field determined by turbulent
Turbulent three-dimensional MHD dynamo model in spherical shells: Regular oscillations of the dipolar field
 Center for Turbulence Research Proceedings of the Summer Program 2010 475 Turbulent three-dimensional MHD dynamo model in spherical shells: Regular oscillations of the dipolar field By R. D. Simitev, F.
Center for Turbulence Research Proceedings of the Summer Program 2010 475 Turbulent three-dimensional MHD dynamo model in spherical shells: Regular oscillations of the dipolar field By R. D. Simitev, F.
The Sun as Our Star. Properties of the Sun. Solar Composition. Last class we talked about how the Sun compares to other stars in the sky
 The Sun as Our Star Last class we talked about how the Sun compares to other stars in the sky Today's lecture will concentrate on the different layers of the Sun's interior and its atmosphere We will also
The Sun as Our Star Last class we talked about how the Sun compares to other stars in the sky Today's lecture will concentrate on the different layers of the Sun's interior and its atmosphere We will also
We just finished talking about the classical, spherically symmetric, (quasi) time-steady solar interior.
 We just finished talking about the classical, spherically symmetric, (quasi) time-steady solar interior. In reality, it s not any of those things: Helioseismology: the Sun pulsates & jiggles like a big
We just finished talking about the classical, spherically symmetric, (quasi) time-steady solar interior. In reality, it s not any of those things: Helioseismology: the Sun pulsates & jiggles like a big
Lecture 14: Solar Cycle. Observations of the Solar Cycle. Babcock-Leighton Model. Outline
 Lecture 14: Solar Cycle Outline 1 Observations of the Solar Cycle 2 Babcock-Leighton Model Observations of the Solar Cycle Sunspot Number 11-year (average) cycle period as short as 8 years as long as 15
Lecture 14: Solar Cycle Outline 1 Observations of the Solar Cycle 2 Babcock-Leighton Model Observations of the Solar Cycle Sunspot Number 11-year (average) cycle period as short as 8 years as long as 15
IS THE SMALL-SCALE MAGNETIC FIELD CORRELATED WITH THE DYNAMO CYCLE? ApJ press (arxiv: ) Bidya Binay Karak & Axel Brandenburg (Nordita)
 IS THE SMALL-SCALE MAGNETIC FIELD CORRELATED WITH THE DYNAMO CYCLE? ApJ press (arxiv:1505.06632) Bidya Binay Karak & Axel Brandenburg (Nordita) Solar Seminar at MPS Oct 25, 2015 Large-scale magnetic field
IS THE SMALL-SCALE MAGNETIC FIELD CORRELATED WITH THE DYNAMO CYCLE? ApJ press (arxiv:1505.06632) Bidya Binay Karak & Axel Brandenburg (Nordita) Solar Seminar at MPS Oct 25, 2015 Large-scale magnetic field
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 10 Sep 2004
 Differential rotation of main sequence F stars M. Küker and G. Rüdiger Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, D-14482 Potsdam, Germany Received / Accepted arxiv:astro-ph/49246v1 1
Differential rotation of main sequence F stars M. Küker and G. Rüdiger Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, D-14482 Potsdam, Germany Received / Accepted arxiv:astro-ph/49246v1 1
The solar dynamo and its influence on the earth climate. Gustavo A. Guerrero Departamento de Física (UFMG) IAG-USP Palio-climate Workshop
 The solar dynamo and its influence on the earth climate Gustavo A. Guerrero Departamento de Física (UFMG) IAG-USP Palio-climate Workshop - 2016 3 Bsp 10 G Maunder (1904) Besides the 11 yr cycle ~80 yr
The solar dynamo and its influence on the earth climate Gustavo A. Guerrero Departamento de Física (UFMG) IAG-USP Palio-climate Workshop - 2016 3 Bsp 10 G Maunder (1904) Besides the 11 yr cycle ~80 yr
! The Sun as a star! Structure of the Sun! The Solar Cycle! Solar Activity! Solar Wind! Observing the Sun. The Sun & Solar Activity
 ! The Sun as a star! Structure of the Sun! The Solar Cycle! Solar Activity! Solar Wind! Observing the Sun The Sun & Solar Activity The Sun in Perspective Planck s Law for Black Body Radiation ν = c / λ
! The Sun as a star! Structure of the Sun! The Solar Cycle! Solar Activity! Solar Wind! Observing the Sun The Sun & Solar Activity The Sun in Perspective Planck s Law for Black Body Radiation ν = c / λ
The Sun s Internal Magnetic Field
 The Sun s Internal Magnetic Field... and Rotation and Stratification Toby Wood & Michael McIntyre DAMTP, University of Cambridge Toby Wood & Michael McIntyre (DAMTP) The Sun s Internal Magnetic Field 1
The Sun s Internal Magnetic Field... and Rotation and Stratification Toby Wood & Michael McIntyre DAMTP, University of Cambridge Toby Wood & Michael McIntyre (DAMTP) The Sun s Internal Magnetic Field 1
9/13/18. ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies. Topics for Today and Tues. Nonvisible Light X-ray, UV, IR, Radio. SPITZER Infrared Telescope
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Solar Prominence from SOHO EIT Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Ryan Horton, Loren Matilsky Lecture 6 Thur 13 Sept 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Topics for Today and Tues Next
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Solar Prominence from SOHO EIT Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Ryan Horton, Loren Matilsky Lecture 6 Thur 13 Sept 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Topics for Today and Tues Next
Things to do 2/28/17. Topics for Today. C-N-O Fusion Cycle. Main sequence (MS) stars. ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies
 Topics for Today ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Winds from Massive Star Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 13 Tues 28 Feb 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Briefly look at life
Topics for Today ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Winds from Massive Star Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 13 Tues 28 Feb 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Briefly look at life
The Solar Interior and Helioseismology
 The Solar Interior and Helioseismology Bill Chaplin, School of Physics & Astronomy University of Birmingham, UK STFC Advanced Summer School, 2016 Sep 6 University of Sheffield http://solarscience.msfc.nasa.gov/predict.shtml
The Solar Interior and Helioseismology Bill Chaplin, School of Physics & Astronomy University of Birmingham, UK STFC Advanced Summer School, 2016 Sep 6 University of Sheffield http://solarscience.msfc.nasa.gov/predict.shtml
L. A. Upton. Heliophysics Summer School. July 27 th 2016
 L. A. Upton Heliophysics Summer School July 27 th 2016 Sunspots, cool dark regions appearing on the surface of the Sun, are formed when the magnetic field lines pass through the photosphere. (6000 times
L. A. Upton Heliophysics Summer School July 27 th 2016 Sunspots, cool dark regions appearing on the surface of the Sun, are formed when the magnetic field lines pass through the photosphere. (6000 times
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Magnetic field generation in weak-line T Tauri stars: an α 2 -dynamo
 Astron. Astrophys. 346, 922 928 (1999) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Magnetic field generation in weak-line T Tauri stars: an α 2 -dynamo M. Küker and G. Rüdiger Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam, An der
Astron. Astrophys. 346, 922 928 (1999) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Magnetic field generation in weak-line T Tauri stars: an α 2 -dynamo M. Küker and G. Rüdiger Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam, An der
The Long and the Short of it: Timescales for Stellar Activity
 The Long and the Short of it: Timescales for Stellar Activity M. Jardine 1, A. Vidotto 2, J. Llama 1, V. See 1, G. Gibb 3 1 SUPA, School of Physics and Astronomy, North Haugh, St Andrews, Fife, KY16 9SS,
The Long and the Short of it: Timescales for Stellar Activity M. Jardine 1, A. Vidotto 2, J. Llama 1, V. See 1, G. Gibb 3 1 SUPA, School of Physics and Astronomy, North Haugh, St Andrews, Fife, KY16 9SS,
Simulations and understanding large-scale dynamos
 Simulations and understanding large-scale dynamos Issues with global models Possibility of smaller scales Consequences of this Magnetic flux concentrations Unusual dynamo effects Axel randenburg (Nordita,
Simulations and understanding large-scale dynamos Issues with global models Possibility of smaller scales Consequences of this Magnetic flux concentrations Unusual dynamo effects Axel randenburg (Nordita,
Modeling intrinsic luminosity variations induced by internal magnetic field in the Sun and solar-like stars
 Modeling intrinsic luminosity variations induced by internal magnetic field in the Sun and solar-like stars Federico Spada Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung, Göttingen Collaborators: Sabatino
Modeling intrinsic luminosity variations induced by internal magnetic field in the Sun and solar-like stars Federico Spada Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung, Göttingen Collaborators: Sabatino
The Sun: A Star of Our Own ASTR 2110 Sarazin
 The Sun: A Star of Our Own ASTR 2110 Sarazin Sarazin Travel Wednesday, September 19 afternoon Friday, September 21 Will miss class Friday, September 21 TA Molly Finn will be guest lecturer Cancel Office
The Sun: A Star of Our Own ASTR 2110 Sarazin Sarazin Travel Wednesday, September 19 afternoon Friday, September 21 Will miss class Friday, September 21 TA Molly Finn will be guest lecturer Cancel Office
Solar Cycle Propagation, Memory, and Prediction Insights from a Century of Magnetic Proxies
 Solar Cycle Propagation, Memory, and Prediction Insights from a Century of Magnetic Proxies Neil R. Sheeley Jr. Jie Zhang Andrés Muñoz-Jaramillo Edward E. DeLuca Work performed in collaboration with: Maria
Solar Cycle Propagation, Memory, and Prediction Insights from a Century of Magnetic Proxies Neil R. Sheeley Jr. Jie Zhang Andrés Muñoz-Jaramillo Edward E. DeLuca Work performed in collaboration with: Maria
SEARCHING FOR MAGNETIC ACTIVITY IN SOLAR-LIKE STARS OBSERVED BY KEPLER
 SEARCHING FOR MAGNETIC ACTIVITY IN SOLAR-LIKE STARS OBSERVED BY KEPLER Lauren Balliet Clarion University of Pennsylvania Space Science Institute : Savita Mathur LASP National Science Foundation IMPORTANCE
SEARCHING FOR MAGNETIC ACTIVITY IN SOLAR-LIKE STARS OBSERVED BY KEPLER Lauren Balliet Clarion University of Pennsylvania Space Science Institute : Savita Mathur LASP National Science Foundation IMPORTANCE
Differential Rotation and Emerging Flux in Solar Convective Dynamo Simulations
 Differential Rotation and Emerging Flux in Solar Convective Dynamo Simulations Yuhong Fan (HAO/NCAR), Fang Fang (LASP/CU) GTP workshop August 17, 2016 The High Altitude Observatory (HAO) at the National
Differential Rotation and Emerging Flux in Solar Convective Dynamo Simulations Yuhong Fan (HAO/NCAR), Fang Fang (LASP/CU) GTP workshop August 17, 2016 The High Altitude Observatory (HAO) at the National
The Magnetic Sun. CESAR s Booklet
 The Magnetic Sun CESAR s Booklet 1 Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium Most of the planets in our Solar system are enclosed by huge magnetic structures, named magnetospheres
The Magnetic Sun CESAR s Booklet 1 Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium Most of the planets in our Solar system are enclosed by huge magnetic structures, named magnetospheres
The effect of stellar activity on radial velocities. Raphaëlle D. Haywood Sagan Fellow, Harvard College Observatory
 The effect of stellar activity on radial velocities Raphaëlle D. Haywood Sagan Fellow, Harvard College Observatory Mass and radius are the most fundamental parameters of a planet Main inputs for models
The effect of stellar activity on radial velocities Raphaëlle D. Haywood Sagan Fellow, Harvard College Observatory Mass and radius are the most fundamental parameters of a planet Main inputs for models
2/6/18. Topics for Today and Thur. ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies. EUV and Visible Images
 2/6/18 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Topics for Today and Thur Consider Sun s energy source (fusion H--He) Solar granulation Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 7 Tues 6 Feb 2018 What
2/6/18 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Topics for Today and Thur Consider Sun s energy source (fusion H--He) Solar granulation Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 7 Tues 6 Feb 2018 What
Answer Key for Exam C
 Answer Key for Exam C 2 points each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam C 2 points each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam B
 Answer Key for Exam B 2 points each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam B 2 points each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Chapter 16 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Birth Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Chapter 13 Notes The Deaths of Stars Astronomy Name: Date:
 Chapter 13 Notes The Deaths of Stars Astronomy Name: Date: I. The End of a Star s Life When all the fuel in a star is used up, will win over pressure and the star will die nuclear fuel; gravity High-mass
Chapter 13 Notes The Deaths of Stars Astronomy Name: Date: I. The End of a Star s Life When all the fuel in a star is used up, will win over pressure and the star will die nuclear fuel; gravity High-mass
Scaling laws for dynamos in rotating spheres: from planets to stars
 Scaling laws for dynamos in rotating spheres: from planets to stars Ulrich Christensen Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research, Katlenburg- Lindau, Germany In collaboration with: Julien Aubert,
Scaling laws for dynamos in rotating spheres: from planets to stars Ulrich Christensen Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research, Katlenburg- Lindau, Germany In collaboration with: Julien Aubert,
Joy s Law: A Space-Age Update Aimee Norton, Stanford University, SDO/HMI
 Joy s Law: A Space-Age Update Aimee Norton, Stanford University, SDO/HMI Bipolar magnetic regions exhibit a tilt with respect to E-W direction Follower (f) is farther from Equator than preceding (p) spot
Joy s Law: A Space-Age Update Aimee Norton, Stanford University, SDO/HMI Bipolar magnetic regions exhibit a tilt with respect to E-W direction Follower (f) is farther from Equator than preceding (p) spot
Answer Key for Exam D
 Answer Key for Exam D 2 points each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Answer Key for Exam D 2 points each Choose the answer that best completes the question. Read each problem carefully and read through all the answers. Take your time. If a question is unclear, ask for clarification
Tilts and Obliquities!
 Fran Bagenal! University of Colorado! Tilts and Obliquities! Offset Tilted Dipole Approximation Earth Stanley & Bloxham 2006 Jupiter Saturn B radial @ surface Uranus Neptune Magnetic Potential 3-D harmonics
Fran Bagenal! University of Colorado! Tilts and Obliquities! Offset Tilted Dipole Approximation Earth Stanley & Bloxham 2006 Jupiter Saturn B radial @ surface Uranus Neptune Magnetic Potential 3-D harmonics
THE AGE OF THE KIC SYSTEM. James MacDonald and D. J. Mullan Department of Physics and Astronomy, DE 19716, USA
 THE AGE OF THE KIC 7177553 SYSTEM James MacDonald and D. J. Mullan Department of Physics and Astronomy, DE 19716, USA ABSTRACT KIC 7177553 is a quadruple system containing two binaries of orbital periods
THE AGE OF THE KIC 7177553 SYSTEM James MacDonald and D. J. Mullan Department of Physics and Astronomy, DE 19716, USA ABSTRACT KIC 7177553 is a quadruple system containing two binaries of orbital periods
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields
 Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
Turbulent Magnetic Helicity Transport and the Rapid Growth of Large Scale Magnetic Fields Jungyeon Cho Dmitry Shapovalov MWMF Madison, Wisconsin April 2012 The Large Scale Dynamo The accumulation of magnetic
The Sun. Nearest Star Contains most of the mass of the solar system Source of heat and illumination
 The Sun Nearest Star Contains most of the mass of the solar system Source of heat and illumination Outline Properties Structure Solar Cycle Energetics Equation of Stellar Structure TBC Properties of Sun
The Sun Nearest Star Contains most of the mass of the solar system Source of heat and illumination Outline Properties Structure Solar Cycle Energetics Equation of Stellar Structure TBC Properties of Sun
Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics
 Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics Tapio Schneider ETH Zurich, Caltech (Source: CLAUS, http://badc.nerc.ac.uk/data/claus/) Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics Tapio Schneider ETH
Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics Tapio Schneider ETH Zurich, Caltech (Source: CLAUS, http://badc.nerc.ac.uk/data/claus/) Grand Challenges in Global Circulation Dynamics Tapio Schneider ETH
Helioseismology. Bill Chaplin, School of Physics & Astronomy University of Birmingham, UK
 Helioseismology Bill Chaplin, School of Physics & Astronomy University of Birmingham, UK STFC Advanced Summer School, 2014 Sep 1 University of Dundee http://solarscience.msfc.nasa.gov/predict.shtml http://solarscience.msfc.nasa.gov/predict.shtml
Helioseismology Bill Chaplin, School of Physics & Astronomy University of Birmingham, UK STFC Advanced Summer School, 2014 Sep 1 University of Dundee http://solarscience.msfc.nasa.gov/predict.shtml http://solarscience.msfc.nasa.gov/predict.shtml
Physical Parameters of KID , a Low-Mass, Double- Lined Eclipsing Binary
 Physical Parameters of KID 6131659, a Low-Mass, Double- Lined Eclipsing Binary Gideon Bass Jerome Orosz, William Welsh, Gur Windmiller, Trevor Gregg, Tara Fetherolf, Richard Wade, Samuel Quinn Paper available
Physical Parameters of KID 6131659, a Low-Mass, Double- Lined Eclipsing Binary Gideon Bass Jerome Orosz, William Welsh, Gur Windmiller, Trevor Gregg, Tara Fetherolf, Richard Wade, Samuel Quinn Paper available
Helioseismology. Jesper Schou Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research
 Helioseismology Jesper Schou Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research schou@mps.mpg.de Page 1 of 60 Helioseismology The study of the Sun using waves Similar to Earth seismology Sounds waves are trapped
Helioseismology Jesper Schou Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research schou@mps.mpg.de Page 1 of 60 Helioseismology The study of the Sun using waves Similar to Earth seismology Sounds waves are trapped
Astro 1050 Wed. Apr. 5, 2017
 Astro 1050 Wed. Apr. 5, 2017 Today: Ch. 17, Star Stuff Reading in Horizons: For Mon.: Finish Ch. 17 Star Stuff Reminders: Rooftop Nighttime Observing Mon, Tues, Wed. 1 Ch.9: Interstellar Medium Since stars
Astro 1050 Wed. Apr. 5, 2017 Today: Ch. 17, Star Stuff Reading in Horizons: For Mon.: Finish Ch. 17 Star Stuff Reminders: Rooftop Nighttime Observing Mon, Tues, Wed. 1 Ch.9: Interstellar Medium Since stars
Lecture 21. Stellar Size
 Lecture 21 Stellar Mass; The Main Sequence Visual and Spectroscopic Binaries Mass and the Main Sequence Explaining the Main Sequence Mar 8, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 21 1 Stellar Size Taking ratios to the
Lecture 21 Stellar Mass; The Main Sequence Visual and Spectroscopic Binaries Mass and the Main Sequence Explaining the Main Sequence Mar 8, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 21 1 Stellar Size Taking ratios to the
Prediction of Solar Cycles
 Prediction of Solar Cycles Leif Svalgaard Stanford University 26 Aug. 2016 On occasion of Phil Scherrer s 70 th birthday Chaminade, Santa Cruz, CA 1 The Origin of the Polar Field Precursor Method 2 The
Prediction of Solar Cycles Leif Svalgaard Stanford University 26 Aug. 2016 On occasion of Phil Scherrer s 70 th birthday Chaminade, Santa Cruz, CA 1 The Origin of the Polar Field Precursor Method 2 The
Magnetohydrodynamics and the magnetic fields of white dwarfs
 Magnetohydrodynamics and the magnetic fields of white dwarfs JDL Decay of large scale magnetic fields We have seen that some upper main sequence stars host magnetic fields of global scale and dipolar topology
Magnetohydrodynamics and the magnetic fields of white dwarfs JDL Decay of large scale magnetic fields We have seen that some upper main sequence stars host magnetic fields of global scale and dipolar topology
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Dec 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Dec 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 30 Dec 2010](/thumbs/87/97110704.jpg) A Science White Paper in response to the 2012 Heliophysics Decadal Survey Solar & Heliospheric Physics and Solar Wind-Magnetospheric Interactions An Experimental Plasma Dynamo Program for Investigations
A Science White Paper in response to the 2012 Heliophysics Decadal Survey Solar & Heliospheric Physics and Solar Wind-Magnetospheric Interactions An Experimental Plasma Dynamo Program for Investigations
Outline. What is overshoot? Why is overshoot interesting? Overshoot at the base of the solar convection zone. What is overshoot?
 Overshoot at the base of the solar convection zone What can we learn from numerical simulations? Matthias Rempel HAO / NCAR Outline What is overshoot? Why is overshoot interesting? Overshoot modeling different
Overshoot at the base of the solar convection zone What can we learn from numerical simulations? Matthias Rempel HAO / NCAR Outline What is overshoot? Why is overshoot interesting? Overshoot modeling different
