This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS
|
|
|
- Bernard Gardner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp:// ETOOS Comprehensive Study Material For NEET & AMS
2 CHAPTER 11 WAVES Life is a wave, which in no two consecutive moments of its existence is composed of the same particles. "JOHN TYNDALL" NTRODUCTON Wave motion is the phenomenon that can be observed almost everywhere around us, as well it appears in almost every branch of physics. Surface waves on bodies of matter are commonly observed. Sound waves and light waves are essential to our perception of the environment. All waves have a similar mathematical description, which makes the study of one kind of wave useful for the study of other kinds of waves. n this chapter, we will concentrate on string waves, which are type of a mechanical waves. Mechanical waves require a medium to travel through. Sound waves, water waves are other examples of mechanical waves. Light waves are not mechanical waves, these are electromagnetic waves which do not require medium to propagate. Mechanical waves originate from a disturbance in the medium (such as a stone dropping in a pond) and the disturbance propagates through the medium. The forces between the atoms in the medium are responsible for the propagation of mechanical waves. Each atom exerts a force on the atoms near it, and through this force the motion of the atom is transmitted to the others. The atoms in the medium do not, however, experience any net displacement. As the wave passes, the atoms simply move back and forth. Again for simplicity, we concentrate on the study of harmonic waves (that is those that can be represented by sine and cosine functions).
3 PHYSCS FOR NEET & AMS Also, tan = A sin A A cos 1 ( is phase difference of the resultant wave with the first wave) Since intensity is proportional to the square of the amplitude, therefore 1 1 cos Constructive nterference : when cos = + 1 i.e. when = n (n = 0,1,,...) i.e. when position of crests and through of one wave coincide with the positions of crests and thorough respectively of another wave then A = A 1 + A i.e. maximum Also is maximum and max 1 This is called constructive interference. Destructive interference : When cos = 1 i.e. when = (n 1) (n = 1,,...) i.e. when positive crests of one wave matches with troughs of another wave. A is minimum and A min = A 1 A and min 1 E T TS OO N S KEY PO (i) Maximum and minimum intensities in any interference wave form. Max Min = 1 1 = A 1 A A1 A (ii) Average intensity of interference wave form %& < >or av = max min if A = A 1 = A and 1 = = then max = 4, min = 0 and AV = = 1 + (iii) Degree of interference Pattern (f) : Degree of hearing (Sound Wave) or Degree of visibility (Light Wave) f = max max min min 100 n condition of perfect interference degree of interference pattern is maximum f max = 1 or 100% (iv) Condition of maximum contrast in interference wave form a 1 =a and 1 = then max = 4 and min = 0 For perfect destructive interference we have a maximum contrast in interference wave form. 11 etoosindia.com ndia s No. 1 Online Coaching nstitute
4 The resultant displacements of the particles of the string are given by the principle of superposition as y = y 1 + y = A [sin (t kx) + sin(t + kx)] = A sin t cos kx or, y = (A cos kx) sin t. we may write, y = A 0 sin (t) [where A 0 = A cos kx] The result obtained from the above equation are : 1. As this equation satisfies the wave equation, y 1 y x v t WAVES it represents a wave. However, as it is not of the form f(ax ± bt), the wave is not travelling and so is called standing or stationary wave.. The amplitude of the wave A c = A cos kx is not same for all prints of the medium but varies periodically with position (and not with time as in beats). 3. The points for which amplitude is minimum are called nodes. For nodes cos kx = 0, i.e., kx = 3,, 3 i.e., x =,,,... as k n a stationary wave, consecutive nodes are equally spaced and their separation is. 4. The points for which amplitude is maximum are called antinodes For antinodes, cos kx = ± 1, i.e., kx = 0,,, 3,... 3 i.e., x = 0,,,,... as k i.e., like nodes, antinodes are also equally spaced with spacing (/) and A max = ± A. Furthermore, nodes and antinodes are alternate with spacing (/4).. The nodes divide the medium into segments (or loops). All the particles in a segment vibrate in same phase, but in opposite phase with the particles in the adjacent segment. Twice in one period all the particles pass through their mean position simultaneously with maximum velocity (A), the direction of motion being reversed after each half cycle. 116 etoosindia.com Study with Best Etoos Faculties of Kota
5 PHYSCS FOR NEET & AMS A wave is a disturbance that propagates in space, transports energy and momentum from one point to another without the transport of matter. 1. Classification of Waves (a) A mechanical wave will be transverse or longitudinal depending on the nature of medium and mode of excita tion. (b) n strings, mechanical waves are always transverse. (c) n gases and liquids, mechanical waves are always longitudinal because fluids cannot sustain shear. (d) Partially transverse waves are possible on a liquid surface because surface tension provide some rigidity on a liquid surface. The waves are called as ripples as they are combination of transverse & longitudinal. (e) n solids mechanical waves (may be sound) can be either transverse or longitudinal depending on the mode of excitation. (f) n longitudinal wave motion, oscillatory motion of the medium particles produce regions of compression (high pressure) and rarefaction (low pressure).. Plane Progressive Waves (a) Wave equation : y = A sin(t kx) where k = wave propagation constant. 1 y y (b) Differential equation : = x vp t dx ω Wave velocity (phase velocity) v = = t kx = constant dx dt k dt dy dy (c) Particle Velocity vp A cos( t kx) vp v slope = v dt dx y (d) Particle acceleration : ap Asin( t kx) y t For particle 1 : v p and a p For particle : vp and a p For particle 3 : v p and a p For particle 4 : v p and a p k 10 etoosindia.com ndia s No. 1 Online Coaching nstitute
6 WAVES SOLVED EXAMPLE Ex.1 Sol. A sonometer wire resonates with a given tuning fork forming a standing wave with five antinodes between the two bridges when a mass of 9 kg is suspended from the wire. When this mass is replaced by a mass M kg, the wire resonates with the same tuning fork forming three antinodes for the same positions of the bridges. Find the value of M. (A) (B) 0 (C) 1 (D) 10 Sol. having a uniform cross-sectional area of 10 6 m is rigidly fixed at both ends. The temperature of the wire is lowered by 0 C. f the wire is vibrating in fundamental mode, find the frequency (in Hz).(Y steel = N/m, steel = / C) (A) 11 (B) 0 (C) 1 (D) 10 T A Y T YA T YA 48.4N ; f 9 g T 48.4 v m / s for fundamental note m Ex. f Mg f 3 9g Mg M 3 A particle of mass 0 g participates in two simple harmonic oscillations, simultaneously as given by x 1 = 10(cm) cos[80(s 1 ) t] and x = (cm) sin[(80(s 1 ) t + /6]. The amplitude of particle's oscillations is given by A. Find the value of A (in cm ). (A) 17 (B) 16 (C) 7 (D) 37 Sol. A A A A A cos Ex A = 17 1 A steel wire of length 1 m and mass 0.1 kg and Ex.4 Sol. v f 11Hz Two tuning forks A and B lying on opposite sides of observer O and of natural frequency 8 Hz move with velocity 10 m/s relative to stationary observer O. Fork A moves away from the observer while the fork B moves towards him. A wind with a speed 10 m/s is blowing in the direction of motion of fork A. Find the beat frequency measured by the observer in Hz. [Take speed of sound in air as 340 m/s] (A) (B) 6 (C) 7 (D) 8 vsound vmedium 33 fobserver for source 'A' f0 f0 ; vsound vmedium vsource 34 vsound vmedium 3 fobserver for source 'B' f0 f0 vsound vmedium vsource Beat frequency = f f f etoosindia.com Study with Best Etoos Faculties of Kota
7 PHYSCS FOR NEET & AMS Exercise # 1 SNGLE OBJECTVE NEET LEVEL 1. The speed of sound in oxygen (O ) at a certain temperature is 460 ms 1. The speed of sound in helium (He) at the same temperature will be (assume both gases to be ideal) (A) 00 ms 1 (B) 60 ms 1 (C) 330 ms 1 (D) 140 ms 1. A wavelength 0.60 cm is produced in air and it travels at a speed of 330 ms 1. t will be an (A) Audible wave (B) nfrasonic wave (C) Ultrasonic wave (D) None of the above 3. The speed of sound in air is 33 m/s. The speed of sound in air in units of km per hour will be (A) 1.19 km/h (B) 11.9 km/h (C) 119. km/h (D) 119. km/h 4. The speed of sound in a gas of density at a pressure P is p (A) (C) P (E) P p (B) (D). The intensity of sound increases at night due to (A) ncrease in density of air (B) Decreases in density of air (C) Low temperature (D) None of these 6. Sound waves travel at 30 m/s through a warm air and at 300 m/s through brass. The wavelength of a 700 Hz acoustic wave ass it enters brass from warm air (A) Decreases by a factor 0 (B) Decreases by a factor 10 (C) ncreases by a factor 0 (D) ncreases by a factor When a sound wave of frequency 300 Hz passes through a medium the maximum displacement of a particle of the medium is 0.1 cm. The maximum velocity of the particle is equal to (A) 60 cm/sec (B) 30 cm/sec (C) 30 cm/sec (D) 60 cm/sec P 3/ 8. Speed of sound in mercury at a certain temperature is 140 m/s. Given the density of mercury as kg/m 3, the bulk modulus for mercury is (A) N/m 3 (B) N/m 3 (C) N/m 3 (D) N/m 3 9. Consider the following. Waves created on the surfaces of a water pond by a vibrating sources.. Wave created by an oscillating electric field in air.. Sound waves travelling under water. Which of these can be polarized (A) and (B) only (C) and (D), and 10. f the frequency of human heart beat is 1. Hz, the number of heart beats in 1 minute is (A) 80 (B) 6 (C) 90 (D) 7 (E) A progressive wave y = Asin(kx t) is reflected by a rigid wall at x = 0. Then the reflected wave can br represented by (A) y = Asin(kx + t) (B) y = Acos(kx + t) (C) y = Asin(kx t) (D) y = Asin(kx + t) (E) y = acos (kx t) 1. Two waves represented by the following equations are travelling in the same medium y1 sin (7t 0.x), y = 10 sin (10 t 0.0x) (A) 1 : (B) 1 : 4 (C) 1 : 8 (D) 1 : A sound wave y = A 0 sin(t kx) is reflected from a rigid wall with 64% of its amplitude. The equation of the reflected wave is 64 (A) y A0 sin( t kx) (B) y A0 sin( t kx) (C) y A0 sin( t kx) (D) y A0 cos( t kx) 100 etoosindia.com 16 ndia s No. 1 Online Coaching nstitute
8 WAVES Exercise # SNGLE OBJECTVE AMS LEVEL 1. A boat at anchor is rocked by waves whose crests are 100m apart and velocity is m/s. The boat bounces up once in every : (A) 00 s (B) 7 s (C) 4 s (D) 0 s. The waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are: (A) Transverse (B) Longitudinal (C) Longitudinal and transverse (D) Stationary 3. A wave of frequency 00 Hz travels between X and Y, a distance of 600 m in sec. How many wavelength are there in distance XY: (A) 1000 (B) 300 (C) 180 (D) Two wave are represented by equation y 1 = a sin t and y = a cos t the first wave: (A) leads the second by (B) lags the second by (C) leads the second by (D) lags the second by. The distance between two consecutive crests in a wave train produced in string is m. f two complete waves pass through any point per second, the velocity of wave is: (A). m/s (B) m/s (C) 10 m/s (D) 1 m/s 6. The displacement y of a particle executing periodic motion is given by : y = 4cos 1 t sin (1000t). This expression may be considered to be a result of the superposition of... independent, simple harmonic motions. (A) two (B) three (C) four (D) five 7. The displacement of particles in a string stretched in the x direction is represented by y. Among the following expressions for y, those describing wave motion are: (A) cos kx sint (B) k x t (C) cos (kx + t) (D) cos(k x t ) 8. Two waves traveling in a medium in the x direction are represented by y 1 = A sin(t x) and y A cos x t 4, where y and y are 1 the displacements of the particles of the medium, t is time, and and are constants. The two waves have different: (A) speeds (B) directions of propagation (C) wavelengths (D) frequencies 9. A transverse wave is described by the equation x y = y 0 sin(ƒt ). The maximum particle velocity is equal to four times the wave velocity if: (A) = y0 (B) = y0 4 (C) = y 0 (D) = y Dependence of disturbances due to two waves on time is shown in the figure. The ratio of their intensities 1 / will be: (A) 1 : 1 (B) 1 : (C) 4 : 1 (D) 16 : The equation of displacement of two waves are given as y 1 = 10 sin (3t + /3) and y sin 3 t 3 cos3 t, then what is the ratio of their amplitude: (A) 1 : (B) : 1 (C) 1 : 1 (D) None of these 1. A plane progressive wave is represented by the equation y = 0. cos (t x). The equation of a wave is with double the amplitude and half frequency but travelling in the opposite direction will be: (A) y = 0. cos (t x) (B) y = 0. cos (t + x) (C) y = 0. cos (t + x) (D) y = 0. cos (t + x) 170 etoosindia.com Study with Best Etoos Faculties of Kota
9 PHYSCS FOR NEET & AMS Exercise # 3 PART - 1 MATRX MATCH COLUMN 1. Column Column (A) y = 4sin(x 4t)+3cos(4t x+/6) (P) Particles at every position are performing SHM (B) x y = 10cos t 330 sin(100) x t 330 (Q) Equation of travelling wave (C) y=10sin(x 10t)+10cos(10t+x) (R) Equation of standing wave (D) y=10sin(x 10t)+8cos(118t 9/30x) (S) Equation of Beats. From a single source, two wave trains are sent in two different strings. Strings is 4 times heavy than string 1. The two wave equations are : (area of cross section and tension of both strings is same) y 1 = A sin ( 1 t k 1 x) and y = A sin ( t k x). Suppose u= energy density, P=power transmitted and =intensity of the wave. Column (A) u 1 /u is equal to (P) 1/8 (B) P 1 /P is equal to (Q) 1/16 (C) 1 / is equal to (R) 1/4 Column 3. Column Column (A) nterference (P) ntensity varies periodically with time (B) Beats (Q) ntensity varies periodically with position (C) Echo (R) Reflection of waves (S) Refraction of waves 4. Column Column (A) nfrasonic (P) Speed is greater than speed of sound (B) Ultrasonic (Q) Frequency < 0 Hz (C) Audible (sonic) (R) Frequency > 0 khz (D) Supersonic (S) 0 Hz < frequency < 0 khz. Column Column (A) Pitch (P) Number of overtones (B) Quality (Q) ntensity (C) Loudness (R) Frequency (D) Musical interval (S) Difference of the frequencies of two notes (T) Ratio of the frequencies of two notes etoosindia.com 17 ndia s No. 1 Online Coaching nstitute
10 Exercise # 4 PART - 1 PREVOUS YEAR (NEET/APMT) WAVES 1. Two sources are at a finite distacne apart. They emit sounds of wavelength. An observer situated between them on line joining approaches one source with speed u. Then, the number of beat heart/second by observer will be [CBSE APMT 000] (A) u (C) u (B) u (D) u. A sonometer wire when vibrated in full length has frequency n. Now, it is divided by the help of bridges into a number of segments of lengths l 1, l, l 3,... When vibrated these segments have frequencies n 1, n, n 3,... The, the correct, relation is [CBSE APMT 000] (A) n = n 1 + n + n (B) n = n 1 + n + n (C)... n n n n (D) n n n n Two strings A and B have lengths l A and l B and carry masses M A and M B at their lower ends, the upper ends being supported by rigid supports. f n A and n B are the frequencies of their vibrations and n A = n B, then [CBSE APMT 000] (A) l A = 4l B, regardless of masses (B) l B = 4l A, regardless of masses (C) M A = M B, l A = l B (D) M B = M A, l B = l A 4. Equations of two progressive waves are given by y 1 = a sin (t + 1 ) and y = a sin (t + ). f amplitude and time period of resultant wave are same as that of both the waves, then ( 1 ) is [CBSE APMT 001] (A) 3 (C) 6 (B) 3 (D) 4. A wave enters to water from air. n air frequency, wavelength, intensity and velocity are n 1, 1 and v 1 respectively. n water the corresponding quantities are n, l, and v respectively, then [CBSE APMT 001] (A) l 1 = l (B) n 1 = n (C) v 1 = v (D) 1 = 6. The equation of a wave is given by x y a sin 100t 10, where x and y are in metre and t in second, then velocity of wave is [CBSE APMT 001] (A) 0.1 m/s (C) 100 m/s (B) 10 m/s (D) 1000 m/s 7. A wave of amplitude a = 0. m, velocity v = 360 m/s and wavelength 60 m is travelling along positive x- axis, then the correct expression for the wave is [CBSE APMT 00] (A) y 0.sin 6t 60 x (B) y 0.sin 6t 60 x (C) y 0.sin 6t 60 x (D) y 0.sin 6t A whistle revolves in a circle with angular velocity = 0 rad/s using a string of length 0 cm.f the actual frequency of sound from the whistle is 38 Hz, then the minimum frequency heard by the observer far away from the centre is (velocity of sound v = 340 m/s) [CBSE APMT 00] (A) 38 Hz (C) 394 Hz (B) 374 Hz (D) 333 Hz 178 etoosindia.com Study with Best Etoos Faculties of Kota
11 PHYSCS FOR NEET & AMS MOCK TEST STRAGHT OBJECTVE TYPE 1. A travelling wave y = A sin (k x t + ) passes from a heavier string to a lighter string. The reflected wave has amplitude 0. A. The junction of the strings is at x = 0. The equation of the reflected wave is: (A) y = 0. A sin (k x + t + ) (B) y = 0. A sin (k x + t + ) (C) y = 0. A sin ( t k x ) (D) y = 0. A sin (k x + t ). Which of the following travelling wave will produce standing wave, with node at x = 0, when superimposed on y = A sin ( t k x) (A) A sin ( t + k x) (B) A sin ( t + k x + ) (C) A cos ( t + k x) (D) A cos ( t + k x + ) 3. A wire of length having tension T and radius r vibrates with fundamental frequency f. Another wire of the same metal with length having tension T and radius r will vibrate with fundamental frequency: (A) f (B) f (C) 4. A string of length 1. m with its two ends clamped is vibrating in fundamental mode. Amplitude at the centre of the string is 4 mm. Distances between the two points having amplitude mm is: (A) 1 m (B) 7 cm (C) 60 cm (D) 0 cm. Two particles of medium disturbed by the wave propagation are at x 1 = 0 and x = 1cm. The respective displacements (in cm) of the particles can be given by the equations : y 1 = sin3t y = sin(3t /8) The wave velocity is : (A) 16 cm/sec (B) 4 cm/sec (C) 1 cm/sec (D) 8 cm/sec. 6. The displacement Vs time graph for two waves A and B which travel along the same string are shown in the figure. Their intensity ratio A / B is f (D) f (A) (B) 1 (C) 16 (D) etoosindia.com ndia s No. 1 Online Coaching nstitute
12 11 th Class Modules Chapter Details Physics Modules Chemistry Modules Mathematics Modules Module-1 PHYSCS 1. Physical World & Measurements. Basic Maths & Vector 3. Kinematics Module- 1. Law of Motion & Friction. Work, Energy & Power Module-3 1. Motion of system of particles & Rigid Body. Gravitation Module-4 1. Mechanical Properties of Matter. Thermal Properties of Matter Module- 1. Oscillations. Waves Module-1(PC) CHEMSTRY 1. Some Basic Conceps of Chemistry. Atomic Structure 3. Chemical Equilibrium 4. onic Equilibrium Module-(PC) 1. Thermodynamics & Thermochemistry. Redox Reaction 3. States Of Matter (Gaseous & Liquid) Module-3(C) 1. Periodic Table. Chemical Bonding 3. Hydrogen & ts Compounds 4. S-Block Module-4(OC) 1. Nomenclature of Organic Compounds. somerism 3. General Organic Chemistry Module-(OC) 1. Reaction Mechanism. Hydrocarbon 3. Aromatic Hydrocarbon 4. Environmental Chemistry & Analysis Of Organic Compounds Module-1 BOLOGY 1. Diversity in the Living World. Plant Kingdom 3. Animal Kingdom Module- 1. Morphology in Flowering Plants. Anatomy of Flowering Plants 3. Structural Organization in Animals Module-3 1. Cell: The Unit of Life. Biomolecules 3. Cell Cycle & Cell Division 4. Transport in Plants. Mineral Nutrition Module-4 1. Photosynthesis in Higher Plants. Respiration in Plants 3. Plant Growth and Development 4. Digestion & Absorption. Breathing & Exchange of Gases Module- 1. Body Fluids & ts Circulation. Excretory Products & Their Elimination 3. Locomotion & ts Movement 4. Neural Control & Coordination. Chemical Coordination and ntegration To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://
13 1 th Class Modules Chapter Details Physics Modules Chemistry Modules Mathematics Modules Module-1 PHYSCS 1. Electrostatics. Capacitance Module- 1. Current Electricity. Magnetic Effect of Current and Magnetism Module-3 1. Electromagnetic nduction. Alternating Current Module-4 1. Geometrical Optics. Wave Optics Module- 1. Modern Physics. Nuclear Physics 3. Solids & Semiconductor Devices 4. Electromagnetic Waves Module-1(PC) CHEMSTRY 1. Solid State. Chemical Kinetics 3. Solutions and Colligative Properties Module-(PC) 1. Electrochemistry. Surface Chemistry Module-3(C) 1. P-Block Elements. Transition Elements (d & f block) 3. Co-ordination Compound 4. Metallurgy Module-4(OC) 1. HaloAlkanes & HaloArenes. Alcohol, Phenol & Ether 3. Aldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic Acid Module-(OC) 1. Nitrogen & ts Derivatives. Biomolecules & Polymers 3. Chemistry in Everyday Life Module-1 BOLOGY 1. Reproduction in Organisms. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants 3. Human Reproduction 4. Reproductive Health Module- 1. Principles of nheritance and Variation. Molecular Basis of nheritance 3. Evolution Module-3 1. Human Health and Disease. Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production 3. Microbes in Human Welfare Module-4 1. Biotechnology: Principles and Processes. Biotechnology and ts Applications 3. Organisms and Populations Module- 1. Ecosystem. Biodiversity and Conservation 3. Environmental ssues To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://
Downloaded from
 Chapter 15 (Waves) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Water waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are (a) neither longitudinal nor transverse (b) both longitudinal and transverse
Chapter 15 (Waves) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Water waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are (a) neither longitudinal nor transverse (b) both longitudinal and transverse
Re AIPMT 2015 Paper Analysis
 Re AIPMT 2015 Paper Analysis Biology The Biology section of the paper was slightly easier than the previous paper and the distribution pattern of the paper shows that there are 49 questions from 11 th
Re AIPMT 2015 Paper Analysis Biology The Biology section of the paper was slightly easier than the previous paper and the distribution pattern of the paper shows that there are 49 questions from 11 th
Class Biology
 Class - 10+1 Biology April & May Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 The Living World Biological Classification Plant Kingdom July Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Animal kingdom Morphology of flowering plants August Chapter
Class - 10+1 Biology April & May Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 The Living World Biological Classification Plant Kingdom July Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Animal kingdom Morphology of flowering plants August Chapter
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS
 This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www.etoosindia.com/smartmall/booklist.do ETOOS Comprehensive
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www.etoosindia.com/smartmall/booklist.do ETOOS Comprehensive
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar
 Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 PW W A V E S PW CONCEPTS C C Equation of a Travelling Wave The equation of a wave traveling along the positive x-ax given by y = f(x vt) If the wave travelling along the negative x-ax, the wave funcion
PW W A V E S PW CONCEPTS C C Equation of a Travelling Wave The equation of a wave traveling along the positive x-ax given by y = f(x vt) If the wave travelling along the negative x-ax, the wave funcion
The velocity (v) of the transverse wave in the string is given by the relation: Time taken by the disturbance to reach the other end, t =
 Question 15.1: A string of mass 2.50 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance
Question 15.1: A string of mass 2.50 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance
JEE MEDICAL-UG BOARDS KVPY NTSE OLYMPIADS
 7TH - STANDARD SCIENCE 1. Measurement 2. Motion 3. Force and Friction 4. Fluids 5. Heat 6. Light 7. Sound 8. Electricity 9. Universe 10. Symbol & Chemical Formulae 11. Air and Water 12. Physical & Chemical
7TH - STANDARD SCIENCE 1. Measurement 2. Motion 3. Force and Friction 4. Fluids 5. Heat 6. Light 7. Sound 8. Electricity 9. Universe 10. Symbol & Chemical Formulae 11. Air and Water 12. Physical & Chemical
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 PW W A V E S Syllabus : Wave motion. Longitudinal and transverse waves, speed of wave. Dplacement relation for a progressive wave. Principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, Standing waves
PW W A V E S Syllabus : Wave motion. Longitudinal and transverse waves, speed of wave. Dplacement relation for a progressive wave. Principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, Standing waves
WAVES( SUB) 2. What is the property of the medium that is essential for the propagation of mechanical wave? Ans: Elasticity and inertia
 WAES( SUB). What is meant by a wave? Ans: The disturbance set up in a medium is known as a wave. What is the property of the medium that is essential for the propagation of mechanical wave? Ans: Elasticity
WAES( SUB). What is meant by a wave? Ans: The disturbance set up in a medium is known as a wave. What is the property of the medium that is essential for the propagation of mechanical wave? Ans: Elasticity
NARAYANA JUNIOR COLLEGE
 SR IIT ALL STREAMS ADV MODEL DPT-6 Date: 18/04/2016 One (or) More Than One Answer Type: PHYSICS 31. A particle is executing SHM between points -X m and X m, as shown in figure-i. The velocity V(t) of the
SR IIT ALL STREAMS ADV MODEL DPT-6 Date: 18/04/2016 One (or) More Than One Answer Type: PHYSICS 31. A particle is executing SHM between points -X m and X m, as shown in figure-i. The velocity V(t) of the
1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is:
 1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is: 2) The bob of simple Pendulum is a spherical hallow ball filled with water. A plugged hole near
1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is: 2) The bob of simple Pendulum is a spherical hallow ball filled with water. A plugged hole near
SOUND. Representative Sample Physics: Sound. 1. Periodic Motion of Particles PLANCESS CONCEPTS
 Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
 Wave Motion Wave and Wave motion Wave is a carrier of energy Wave is a form of disturbance which travels through a material medium due to the repeated periodic motion of the particles of the medium about
Wave Motion Wave and Wave motion Wave is a carrier of energy Wave is a form of disturbance which travels through a material medium due to the repeated periodic motion of the particles of the medium about
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS
 This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www.etoosindia.com/smartmall/booklist.do ETOOS Comprehensive
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www.etoosindia.com/smartmall/booklist.do ETOOS Comprehensive
JEE MEDICAL-UG BOARDS KVPY NTSE OLYMPIADS
 7TH - STANDARD SCIENCE MATHS 1. Measurement 2. Motion 3. Force and Friction 4. Fluids 5. Heat 6. Light 7. Sound 8. Electricity 9. Universe 10. Symbol & Chemical Formulae 11. Air and Water 12. Physical
7TH - STANDARD SCIENCE MATHS 1. Measurement 2. Motion 3. Force and Friction 4. Fluids 5. Heat 6. Light 7. Sound 8. Electricity 9. Universe 10. Symbol & Chemical Formulae 11. Air and Water 12. Physical
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. The student is expected to:
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Transverse Wave - Only in solids (having rigidity), in liquids possible only on the surface. Longitudinal Wave
 Wave is when one particle passes its motion to its neighbour. The Elasticity and Inertia of the medium play important role in the propagation of wave. The elasticity brings the particle momentarily at
Wave is when one particle passes its motion to its neighbour. The Elasticity and Inertia of the medium play important role in the propagation of wave. The elasticity brings the particle momentarily at
Marketed and Distributed By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 WAVES GUPTA CLASSES For any help contact: 995368795, 968789880 Nishant Gupta, D-, Prashant vihar, Rohini, Delhi-85 Waves Wave motion A wave motion is a kind of disturbance which is transferred from one
WAVES GUPTA CLASSES For any help contact: 995368795, 968789880 Nishant Gupta, D-, Prashant vihar, Rohini, Delhi-85 Waves Wave motion A wave motion is a kind of disturbance which is transferred from one
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES
 CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984
 Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. Chapter 11. Preview. Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Chapter 15. Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension
 Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Reading Quiz 16.05 f = c Slide 16-2 Reading Quiz 16.06 Slide 16-3 Reading Quiz 16.07 Heavier portion looks like a fixed end, pulse is inverted on reflection.
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Reading Quiz 16.05 f = c Slide 16-2 Reading Quiz 16.06 Slide 16-3 Reading Quiz 16.07 Heavier portion looks like a fixed end, pulse is inverted on reflection.
Unit Title Marks HOURS Starting Date I Basic Concepts of Chemistry April-2019 II Structure of Atom
 Class 11+12, Classes Schedule & Syllabus [ CBSE ] Chemistry Class 11 Unit Title Marks HOURS Starting Date I Basic Concepts of Chemistry 11 18 1-April- II Structure of Atom III Classification of Elements
Class 11+12, Classes Schedule & Syllabus [ CBSE ] Chemistry Class 11 Unit Title Marks HOURS Starting Date I Basic Concepts of Chemistry 11 18 1-April- II Structure of Atom III Classification of Elements
Oscillation the vibration of an object. Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter
 Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
2016 AP Physics Unit 6 Oscillations and Waves.notebook December 09, 2016
 AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AIPMT (NEET) A Detailed Analysis by Resonance
 AIPMT (NEET) - 2016 AIPMT (NEET) 2016 A Detailed by Resonance As per the directions of honorable Supreme Court, NEET 2016 was conducted as per the schedule (01 st May 2016) decided for AIPMT 2016. This
AIPMT (NEET) - 2016 AIPMT (NEET) 2016 A Detailed by Resonance As per the directions of honorable Supreme Court, NEET 2016 was conducted as per the schedule (01 st May 2016) decided for AIPMT 2016. This
1 f. result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by
 result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by amplitude (how far do the bits move from their equilibrium positions? Amplitude of MEDIUM)
result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by amplitude (how far do the bits move from their equilibrium positions? Amplitude of MEDIUM)
CHAPTERS WAVES SOUND STATIONARY WAVES ACOUSTICSOF BUILDINGS
 CET -IPUC: PHYSICS Unit VI : WAVES and SOUND CHAPTERS OSCILLATIONS WAVES SOUND STATIONARY WAVES ACOUSTICSOF BUILDINGS Particle acceleration: a = Aω 2 sinωt= ω 2 y Maximum acceleration: a max = A ω 2 The
CET -IPUC: PHYSICS Unit VI : WAVES and SOUND CHAPTERS OSCILLATIONS WAVES SOUND STATIONARY WAVES ACOUSTICSOF BUILDINGS Particle acceleration: a = Aω 2 sinωt= ω 2 y Maximum acceleration: a max = A ω 2 The
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves 1 Types of Mechanical Waves This chapter and the next are about mechanical waves waves that travel within some material called a medium. Waves play an important role in how
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves 1 Types of Mechanical Waves This chapter and the next are about mechanical waves waves that travel within some material called a medium. Waves play an important role in how
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects.
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
42 TRAVELING WAVES (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G)
 42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
Standing waves [49 marks]
![Standing waves [49 marks] Standing waves [49 marks]](/thumbs/92/110837906.jpg) Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
Theory 70 Marks + Practical 30 marks= maximum Marks 100 for both ISC and CBSE
 Theory 70 Marks + Practical 30 marks= maximum Marks 100 for both ISC and CBSE ISC CHEMISTRY XI CBSE CHEMISTRY XI Units Mark Units Mark 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry 2 Structure of Atom 3 Classification
Theory 70 Marks + Practical 30 marks= maximum Marks 100 for both ISC and CBSE ISC CHEMISTRY XI CBSE CHEMISTRY XI Units Mark Units Mark 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry 2 Structure of Atom 3 Classification
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
Producing a Sound Wave. Chapter 14. Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a Sound Wave. Using a Tuning Fork, cont.
 Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Wave Motions and Sound
 EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves. The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position.
 Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
Chapter 2 SOUND WAVES
 Chapter SOUND WAVES Introduction: A sound wave (or pressure or compression wave) results when a surface (layer of molecules) moves back and forth in a medium producing a sequence of compressions C and
Chapter SOUND WAVES Introduction: A sound wave (or pressure or compression wave) results when a surface (layer of molecules) moves back and forth in a medium producing a sequence of compressions C and
1. The waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are: (A) Transverse (B) Longitudinal (C) Longitudinal and transverse(d) Stationary
 J-Physics XRCIS 01 CHCK YOUR GRASP MCQs wi th one correct answer 1. The waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are: (A) Transverse (B) Longitudinal (C) Longitudinal and transverse(d) Stationary.
J-Physics XRCIS 01 CHCK YOUR GRASP MCQs wi th one correct answer 1. The waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are: (A) Transverse (B) Longitudinal (C) Longitudinal and transverse(d) Stationary.
Work. Work and Energy Examples. Energy. To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or:
 Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS
 This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www./smartmall/booklist.do ETOOS Comprehensive Study Material
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www./smartmall/booklist.do ETOOS Comprehensive Study Material
1. Types of Waves. There are three main types of waves:
 Chapter 16 WAVES I 1. Types of Waves There are three main types of waves: https://youtu.be/kvc7obkzq9u?t=3m49s 1. Mechanical waves: These are the most familiar waves. Examples include water waves, sound
Chapter 16 WAVES I 1. Types of Waves There are three main types of waves: https://youtu.be/kvc7obkzq9u?t=3m49s 1. Mechanical waves: These are the most familiar waves. Examples include water waves, sound
Exam 3 Review. Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations A stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations.
 Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
Unit 4 Waves and Sound Waves and Their Properties
 Lesson35.notebook May 27, 2013 Unit 4 Waves and Sound Waves and Their Properties Today's goal: I can explain the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves and their properties. Waves are a disturbances
Lesson35.notebook May 27, 2013 Unit 4 Waves and Sound Waves and Their Properties Today's goal: I can explain the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves and their properties. Waves are a disturbances
7 th May Only few Days are remaining
 in 30 Days 7 th May 2017 - Only few Days are remaining Confusion: How to start revision? What should I study first? What should be my target of study to secure good rank? Board Exam is also approaching
in 30 Days 7 th May 2017 - Only few Days are remaining Confusion: How to start revision? What should I study first? What should be my target of study to secure good rank? Board Exam is also approaching
16 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES
 Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam
 G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Exam Instructions The final exam will be weighted as follows: Modules 1 6 15 20% Modules
G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Exam Instructions The final exam will be weighted as follows: Modules 1 6 15 20% Modules
Old Exams - Questions Ch-16
 Old Exams - Questions Ch-16 T081 : Q1. The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by: y( x, t) = y sin( kx ω t + ϕ). At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 m has a displacement
Old Exams - Questions Ch-16 T081 : Q1. The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by: y( x, t) = y sin( kx ω t + ϕ). At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 m has a displacement
General Physics I. Lecture 14: Sinusoidal Waves. Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 )
 General Physics I Lecture 14: Sinusoidal Waves Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Motivation When analyzing a linear medium that is, one in which the restoring force
General Physics I Lecture 14: Sinusoidal Waves Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Motivation When analyzing a linear medium that is, one in which the restoring force
Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string)
 1 Part 5: Waves 5.1: Harmonic Waves Wave a disturbance in a medium that propagates Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string) Longitudinal
1 Part 5: Waves 5.1: Harmonic Waves Wave a disturbance in a medium that propagates Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string) Longitudinal
A.M Wake up, Have Breakfast & Get ready for School. In free time during school- revise formulae/reactions in chemistry
 NEET Study Plan 2018 PDF Below we have provided the NEET Study Plan 2018 with the proper time table for 3 Months. Get the 3 Months-Week Wise Study Plan with time slot details. The below study plan for
NEET Study Plan 2018 PDF Below we have provided the NEET Study Plan 2018 with the proper time table for 3 Months. Get the 3 Months-Week Wise Study Plan with time slot details. The below study plan for
Baccalieu Collegiate. Physics Course Outline
 Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
f 1/ T T 1/ f Formulas Fs kx m T s 2 k l T p 2 g v f
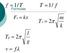 f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
Homework Book. Wave Properties. Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2. Name: Homeroom: Physics Class:
 Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension
 Lecture Outline Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Chapter 16: Waves in One Dimension Chapter Goal: To study the kinematic and dynamics of wave motion, i.e., the transport of energy through a
Lecture Outline Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Chapter 16: Waves in One Dimension Chapter Goal: To study the kinematic and dynamics of wave motion, i.e., the transport of energy through a
Chapter 16: Oscillatory Motion and Waves. Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
 Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
JEE MEDICAL-UG BOARDS KVPY NTSE OLYMPIADS
 5TH - STANDARD SCIENCE 1. Simple machine 2. State of matter 3. Rock and minerals 4. Air & water 5. Our environment 6. Living and non-living things 7. Plants animal life 8. The human body 9. Food 10. Health
5TH - STANDARD SCIENCE 1. Simple machine 2. State of matter 3. Rock and minerals 4. Air & water 5. Our environment 6. Living and non-living things 7. Plants animal life 8. The human body 9. Food 10. Health
Superposition and Standing Waves
 Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
(d) None 11. The unit for moment of inertia is (a) kg m 2 (b) kg m (c) kg m 2 (d) kg m The unit for pressure is
 1. A man is standing between two parallel cliffs and fires a gun. If he hears first and second echos after 1.5s and 3.5s respectively, the distance between the cliffs is (velocity of sound in air = 340ms
1. A man is standing between two parallel cliffs and fires a gun. If he hears first and second echos after 1.5s and 3.5s respectively, the distance between the cliffs is (velocity of sound in air = 340ms
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Physics in Faculty of
 Why we study Physics in Faculty of Engineering? Dimensional analysis Scalars and vector analysis Rotational of a rigid body about a fixed axis Rotational kinematics 1. Dimensional analysis The ward dimension
Why we study Physics in Faculty of Engineering? Dimensional analysis Scalars and vector analysis Rotational of a rigid body about a fixed axis Rotational kinematics 1. Dimensional analysis The ward dimension
jfpr% ekuo /kez iz.ksrk ln~xq# Jh j.knksm+nklth egkjkt
 Phone : 93 93 7779, 9893 58881 Sount & Waves Page: 9 fo/u fopkjr Hkh# tu] ugha vkjehks dke] foifr ns[k NksM+s rqjar e/;e eu dj ';kea iq#"k flag ladyi dj] lgrs foifr vusd] ^cuk^ u NksM+s /;s; dks] j?kqcj
Phone : 93 93 7779, 9893 58881 Sount & Waves Page: 9 fo/u fopkjr Hkh# tu] ugha vkjehks dke] foifr ns[k NksM+s rqjar e/;e eu dj ';kea iq#"k flag ladyi dj] lgrs foifr vusd] ^cuk^ u NksM+s /;s; dks] j?kqcj
Simple Harmonic Motion and Waves
 Simple Harmonic Motion and Waves Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) periodic motion that occurs whenever the restoring force is proportional to the displacement and in the opposite direction. Give some example
Simple Harmonic Motion and Waves Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) periodic motion that occurs whenever the restoring force is proportional to the displacement and in the opposite direction. Give some example
Question 01. A. Incorrect! The speed of sound is not the same in all medium; it is dependent on the properties of the material.
 High School Physics - Problem Drill 15: Sound 1. Which of these is not a true statement about sound waves? Question 01 (A) Sound waves are travel at different speeds in different mediums. (B) Sound waves
High School Physics - Problem Drill 15: Sound 1. Which of these is not a true statement about sound waves? Question 01 (A) Sound waves are travel at different speeds in different mediums. (B) Sound waves
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
4. What is the speed (in cm s - 1 ) of the tip of the minute hand?
 Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
(Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Physics 1
 1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
MCAT Physics Problem Solving Drill 13: Sound
 MCAT Physics Problem Solving Drill 13: Sound Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The wave lengths of audible sounds are 17 m to 0.017 m. Find the range of audible frequencies assuming velocity of sound in
MCAT Physics Problem Solving Drill 13: Sound Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The wave lengths of audible sounds are 17 m to 0.017 m. Find the range of audible frequencies assuming velocity of sound in
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test
 AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
Class Average = 71. Counts Scores
 30 Class Average = 71 25 20 Counts 15 10 5 0 0 20 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Scores Chapter 12 Mechanical Waves and Sound To describe mechanical waves. To study superposition, standing waves, and interference.
30 Class Average = 71 25 20 Counts 15 10 5 0 0 20 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Scores Chapter 12 Mechanical Waves and Sound To describe mechanical waves. To study superposition, standing waves, and interference.
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Phys101 Lectures 28, 29. Wave Motion
 Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220. Final Exam. Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total)
 Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
Content of the course 3NAB0 (see study guide)
 Content of the course 3NAB0 (see study guide) 17 November diagnostic test! Week 1 : 14 November Week 2 : 21 November Introduction, units (Ch1), Circuits (Ch25,26) Heat (Ch17), Kinematics (Ch2 3) Week 3:
Content of the course 3NAB0 (see study guide) 17 November diagnostic test! Week 1 : 14 November Week 2 : 21 November Introduction, units (Ch1), Circuits (Ch25,26) Heat (Ch17), Kinematics (Ch2 3) Week 3:
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
CHAPTER 11 TEST REVIEW
 AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
CLASS 2 CLASS 2. Section 13.5
 CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
Chapter 16 Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 6 Mechanical Waves A wave is a disturbance that travels, or propagates, without the transport of matter. Examples: sound/ultrasonic wave, EM waves, and earthquake wave. Mechanical waves, such as
Chapter 6 Mechanical Waves A wave is a disturbance that travels, or propagates, without the transport of matter. Examples: sound/ultrasonic wave, EM waves, and earthquake wave. Mechanical waves, such as
Outline. Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves
 Outline Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves Hooke s Law Force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from the equilibrium
Outline Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves Hooke s Law Force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from the equilibrium
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES KINEMATICS 3.A.1.1: The student is able to express the motion of an object using narrative, mathematical, and graphical representations. [SP 1.5, 2.1, 2.2]
AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES KINEMATICS 3.A.1.1: The student is able to express the motion of an object using narrative, mathematical, and graphical representations. [SP 1.5, 2.1, 2.2]
Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations
 Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
University Physics Volume I Unit 2: Waves and Acoustics Chapter 16: Waves Conceptual Questions
 Unit : Waves and Acoustics University Physics Volume I Unit : Waves and Acoustics Conceptual Questions. Give one example of a transverse wave and one example of a longitudinal wave, being careful to note
Unit : Waves and Acoustics University Physics Volume I Unit : Waves and Acoustics Conceptual Questions. Give one example of a transverse wave and one example of a longitudinal wave, being careful to note
AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to
Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to
Chapter 16 Waves. Types of waves Mechanical waves. Electromagnetic waves. Matter waves
 Chapter 16 Waves Types of waves Mechanical waves exist only within a material medium. e.g. water waves, sound waves, etc. Electromagnetic waves require no material medium to exist. e.g. light, radio, microwaves,
Chapter 16 Waves Types of waves Mechanical waves exist only within a material medium. e.g. water waves, sound waves, etc. Electromagnetic waves require no material medium to exist. e.g. light, radio, microwaves,
Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2)
 Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2) What to study: Quiz 6 Homework problems for Chapters 15 & 16 Material indicated in the following review slides Other Specific things:
Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2) What to study: Quiz 6 Homework problems for Chapters 15 & 16 Material indicated in the following review slides Other Specific things:
Solution The light plates are at the same heights. In balance, the pressure at both plates has to be the same. m g A A A F A = F B.
 43. A piece of metal rests in a toy wood boat floating in water in a bathtub. If the metal is removed from the boat, and kept out of the water, what happens to the water level in the tub? A) It does not
43. A piece of metal rests in a toy wood boat floating in water in a bathtub. If the metal is removed from the boat, and kept out of the water, what happens to the water level in the tub? A) It does not
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #3 January 25, 2007 Time: 90 minutes NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #3 January 25, 2007 Time: 90 minutes NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please
Chapter 16: Oscillations
 Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 PW WAVES C C Wave A wave is a disturbance that travels or propagates and transports energy and momentum without the transport of matter. The ripples on a pond, the sound we hear, visible light, radio and
PW WAVES C C Wave A wave is a disturbance that travels or propagates and transports energy and momentum without the transport of matter. The ripples on a pond, the sound we hear, visible light, radio and
NEET A Detailed Analysis by Resonance
 NEET 2017 A Detailed by Resonance As per the directions of honorable Supreme Court, NEET 2017 was conducted as per the schedule (7 th May 2017). This exam is conducted for entrance into state and national
NEET 2017 A Detailed by Resonance As per the directions of honorable Supreme Court, NEET 2017 was conducted as per the schedule (7 th May 2017). This exam is conducted for entrance into state and national
NEET A Detailed Analysis by Resonance
 NEET 2018 A Detailed Analysis by Resonance NEET 2018 was conducted as per the schedule (6 th May 2018). This exam is conducted for entrance into state and national level medical colleges for MBBS, BDS
NEET 2018 A Detailed Analysis by Resonance NEET 2018 was conducted as per the schedule (6 th May 2018). This exam is conducted for entrance into state and national level medical colleges for MBBS, BDS
XI PHYSICS [WAVES AND SOUND] CHAPTER NO. 8. M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K. https://promotephysics.wordpress.
![XI PHYSICS [WAVES AND SOUND] CHAPTER NO. 8. M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K. https://promotephysics.wordpress. XI PHYSICS [WAVES AND SOUND] CHAPTER NO. 8. M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K. https://promotephysics.wordpress.](/thumbs/72/67254202.jpg) XI PHYSICS M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [WAVES AND SOUND] CHAPTER NO. 8 OSCILLATORY MOTION A motion in which an object moves to and fro
XI PHYSICS M. Affan Khan LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [WAVES AND SOUND] CHAPTER NO. 8 OSCILLATORY MOTION A motion in which an object moves to and fro
SCIENCEBEAM SYLLABUS CLASS VI MATHEMATICS CLASS VI - SCIENCE
 SCIENCEBEAM SYLLABUS CLASS VI MATHEMATICS Number system HCF, LCM, Prime factorisation Whole numbers Negative numbers and Integers Fractions Algebra Ratio and Proportion Geometry Mensuration- area and perimeter
SCIENCEBEAM SYLLABUS CLASS VI MATHEMATICS Number system HCF, LCM, Prime factorisation Whole numbers Negative numbers and Integers Fractions Algebra Ratio and Proportion Geometry Mensuration- area and perimeter
Welcome to: Physics I. I m Dr Alex Pettitt, and I ll be your guide!
 Welcome to: Physics I I m Dr Alex Pettitt, and I ll be your guide! Interference superposition principal: most waves can be added y(x, t) =y 1 (x vt)+y 2 (x + vt) wave 1 + wave 2 = resulting wave y 1 +
Welcome to: Physics I I m Dr Alex Pettitt, and I ll be your guide! Interference superposition principal: most waves can be added y(x, t) =y 1 (x vt)+y 2 (x + vt) wave 1 + wave 2 = resulting wave y 1 +
Physics 106 Group Problems Summer 2015 Oscillations and Waves
 Physics 106 Group Problems Summer 2015 Oscillations and Waves Name: 1. (5 points) The tension in a string with a linear mass density of 0.0010 kg/m is 0.40 N. What is the frequency of a sinusoidal wave
Physics 106 Group Problems Summer 2015 Oscillations and Waves Name: 1. (5 points) The tension in a string with a linear mass density of 0.0010 kg/m is 0.40 N. What is the frequency of a sinusoidal wave
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES
 Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
