Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 1. Introductory Concepts and Definition
|
|
|
- Pauline Johnston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1.1 Introduction Chapter 1 Introductory Concepts and Definition Thermodynamics may be defined as follows : Thermodynamics is an axiomatic science which deals with the relations among heat, work and properties of system which are in equilibrium. It describes state and changes in state of physical systems. Thermodynamics is the science of the regularities governing processes of energy conversion. Thermodynamics is the science that deals with the interaction between energy and material systems. Thermodynamics can be defined as the science of energy. Although everybody has a feeling of what energy is, it is difficult to give a precise definition for it. Energy can be viewed as the ability to cause changes. The name thermodynamics stems from the Greek words therme (heat) and dynamis (power), which is most descriptive of the early efforts to convert heat into power. Today the same name is broadly interpreted to include all aspects of energy and energy transformations, including power generation, refrigeration, and relationships among the properties of matter. Some Energy Conversion application 1 Steam Power Plant Nuclear Power Plant Internal Combustion Engines Gas Turbines Refrigeration Systems 1 Read the additional hand out. Compiled by Yidnekachew M. Page 1 of 12
2 Area of Application Selected Areas of Application of Engineering Thermodynamics Aircraft and rocket propulsion Alternative energy systems o Fuel cells o Geothermal systems o Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) converters o Ocean thermal, wave, and tidal power generation o Solar-activated heating, cooling, and power generation o Thermoelectric and thermionic devices o Wind turbines Automobile engines Bioengineering applications Biomedical applications Combustion systems Compressors, pumps Cooling of electronic equipment Cryogenic systems, gas separation, and liquefaction Fossil and nuclear-fueled power stations Heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning systems o Absorption refrigeration and heat pumps o Vapor-compression refrigeration and heat pumps Steam and gas turbines o Power production o Propulsion Compiled by Yidnekachew M. Page 2 of 12
3 1.2 Closed, Open, and Isolated System A thermodynamic system, or simply system, is defined as a quantity of matter or a region in space chosen for study (A system is a finite quantity of matter or a prescribed region of space). The region outside the system is called the surroundings. The real or imaginary surface that separates the system from its surroundings is called the boundary. The boundary of a system may be fixed or movable. Surroundings are physical space outside the system boundary. Figure 1.1 The system. It is not difficult to visualize a real boundary but an example of imaginary boundary would be one drawn around a system consisting of the fresh mixture about to enter the cylinder of an I.C. engine together with the remnants of the last cylinder charge after the exhaust process. Figure 1.2 The real and imaginary boundaries Compiled by Yidnekachew M. Page 3 of 12
4 Systems may be considered to be closed or open, depending on whether a fixed mass or a fixed volume in space is chosen for study. Closed system A closed system consists of a fixed amount of mass and no mass may cross the system boundary. The closed system boundary may move. Examples of closed systems are sealed tanks and piston cylinder devices note the volume does not have to be fixed). However, energy in the form of heat and work may cross the boundaries of a closed system. Figure 1.3 Closed system. Figure 1.4 Closed system with movable boundary. Open system An open system, or control volume, has mass as well as energy crossing the boundary, called a control surface. Examples of open systems are pumps, compressors, turbines, valves, and heat exchangers. Figure 1.5 Open system Compiled by Yidnekachew M. Page 4 of 12
5 Isolated system An isolated system is a general system of fixed mass where no heat or work may cross the boundaries. An isolated system is a closed system with no energy crossing the boundaries and is normally a collection of a main system and its surroundings that are exchanging mass and energy among themselves and no other system. Figure 1.6 Isolated system Since some of the thermodynamic relations that are applicable to closed and open systems are different, it is extremely important that we recognize the type of system we have before we start analyzing it. 1.3 State, Equilibrium, Process and Properties State Consider a system that is not undergoing any change. The properties can be measured or calculated throughout the entire system. This gives us a set of properties that completely describe the condition or state of the system. At a given state all of the properties are known; changing one property changes the state. Equilibrium A system is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium if it maintains thermal (uniform temperature), mechanical (uniform pressure), phase (the mass of two phases, e.g., ice and liquid water, in equilibrium) and chemical equilibrium. Compiled by Yidnekachew M. Page 5 of 12
6 Figure 1.7 Thermal Equilibrium Process Any change from one state to another is called a process. During a quasi-equilibrium or quasistatic process the system remains practically in equilibrium at all times. We study quasiequilibrium processes because they are easy to analyze (equations of state apply) and workproducing devices deliver the most work when they operate on the quasi-equilibrium process. Figure 1.8 A process between states 1 and 2 and the process path. In most of the processes that we will study, one thermodynamic property is held constant. Some of these processes are Process Isobaric Isothermal Isochoric Isentropic Property held constant Pressure Temperature Volume Entropy Compiled by Yidnekachew M. Page 6 of 12
7 Process diagrams plotted by employing thermodynamic properties as coordinates are very useful in visualizing the processes. Some common properties that are used as coordinates are temperature T, pressure P, and volume V (or specific volume v). Cycle Figure 1.9 The P-V diagram of a compression process. A process (or a series of connected processes) with identical end states is called a cycle. Below is a cycle composed of two processes, A and B. Along process A, the pressure and volume change from state 1 to state 2. Then to complete the cycle, the pressure and volume change from state 2 back to the initial state 1 along process B. Keep in mind that all other thermodynamic properties must also change so that the pressure is a function of volume as described by these two processes. Figure 1.10 Cyclic Process Compiled by Yidnekachew M. Page 7 of 12
8 Property Any characteristic of a system is called a property. Some familiar properties are pressure P, temperature T, volume V, and mass m. The list can be extended to include less familiar ones such as viscosity, thermal conductivity, modulus of elasticity, thermal expansion coefficient, electric resistivity, and even velocity and elevation. Properties are considered to be either intensive or extensive. Intensive properties are those that are independent of the mass of a system, such as temperature, pressure, and density. Extensive properties are those whose values depend on the size or extent of the system. Total mass, total volume and total momentum are some examples of extensive properties. An easy way to determine whether a property is intensive or extensive is to divide the system into two equal parts with an imaginary partition, as shown in the figure below. Steady-Flow Process Figure 1.11 Intensive and Extensive Properties Consider a fluid flowing through an open system or control volume such as a water heater. The flow is often defined by the terms steady and uniform. The term steady implies that there are no changes with time. The term uniform implies no change with location over a specified region. Engineering flow devices that operate for long periods of time under the same conditions are classified as steady-flow devices. The processes for these devices is called the steady-flow process. The fluid properties can change from point to point with in the control volume, but at any fixed point the properties remain the same during the entire process. State Postulate As noted earlier, the state of a system is described by its properties. But by experience not all properties must be known before the state is specified. Once a sufficient number of properties are Compiled by Yidnekachew M. Page 8 of 12
9 known, the state is specified and all other properties are known. The number of properties required to fix the state of a simple, homogeneous system is given by the state postulate: The thermodynamic state of a simple compressible system is completely specified by two independent, intensive properties. 1.4 Dimension and Units Any physical quantity can be characterized by dimensions. The magnitudes assigned to the dimensions are called units. Some basic dimensions such as mass m, length L, time t, and temperature T are selected as primary or fundamental dimensions, while others such as velocity V, energy E, and volume V are expressed in terms of the primary dimensions and are called secondary dimensions, or derived dimensions. Quantity Dimension Units Mass M Kg Length L m Time T s 1.5 Specific volume, Pressure and Temperature Specific Volume It is the volume occupied by a unit mass of a substance (the reciprocal of density), and it is designated by the letter. Volume V mass m (1.1) v m 3 / kg Sometimes the density of a substance is given relative to the density of a well-known substance. Then it is called specific gravity, or relative density, and is defined as the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of some standard substance at a specified temperature (usually water at 4 C, for which rh2o =1000 kg/m 3 ). That is Specific gravity: SG( s ) (1.2) HO 2 Compiled by Yidnekachew M. Page 9 of 12
10 Pressure Pressure is defined as a normal force exerted by a fluid per unit area. We speak of pressure only when we deal with a gas or a liquid. Since pressure is defined as force per unit area, it has the unit of newtons per square meter (N/m 2 ), which is called a pascal (Pa). Force F N P Pascal Pa (1.3) 2 Area A m The pressure unit pascal is too small for pressures encountered in practice. Therefore, its multiples kilopascal (1 kpa= 10 3 Pa) and megapascal (1 MPa= 10 6 Pa) are commonly used. Three other pressure units commonly used in practice, especially in Europe, are bar, standard atmosphere, and kilogram-force per square centimeter: 5 1bar= Pa MPa kpa 1 atm = 101,325 Pa = kpa = bars The actual pressure at a given position is called the absolute pressure, and it is measured relative to absolute vacuum (i.e., absolute zero pressure). Most pressure-measuring devices, however, are calibrated to read zero in the atmosphere and so they indicate the difference between the absolute pressure and the local atmospheric pressure. This difference is called the gage pressure. Pressures below atmospheric pressure are called vacuum pressures and are measured by vacuum gages that indicate the difference between the atmospheric pressure and the absolute pressure. Absolute, gage, and vacuum pressures are all positive quantities and are related to each other by Pgage Pabs Patm (1.4) Pvac Patm Pabs (1.5) Compiled by Yidnekachew M. Page 10 of 12
11 Figure 1.12 Absolute, gage, and vacuum pressures. A device called manometer, it is commonly used to measure small and moderate pressure differences. A manometer mainly consists of a glass or plastic U-tube containing one or more fluids such as mercury, water, alcohol, or oil. To keep the size of the manometer to a manageable level, heavy fluids such as mercury are used if large pressure differences are anticipated. Consider the manometer shown in Fig that is used to measure the pressure in the tank. Since the gravitational effects of gases are negligible, the pressure anywhere in the tank and at position 1 has the same value. Furthermore, since pressure in a fluid does not vary in the horizontal direction within a fluid, the pressure at point 2 is the same as the pressure at point 1, P2 = P1. The differential fluid column of height h is in static equilibrium, and it is open to the atmosphere. Then the pressure at point 2 is determined directly from Eq. 1.6 to be P P gh(1.6) 2 atm W W mg Vg Ahg P2 Patm, hg P A A A A A P P hg 2 atm PP P gh 2 atm This pressure difference is determined from the manometer fluid displaced height as P gh Compiled by Yidnekachew M. Page 11 of 12
12 Temperature Although we are familiar with temperature as a measure of hotness or coldness, it is not easy to give an exact definition of it. However, temperature is considered as a thermodynamic property that is the measure of the energy content of a mass. When heat energy is transferred to a body, the body's energy content increases and so does its temperature. In fact it is the difference in temperature that causes energy, called heat transfer, to flow from a hot body to a cold body. Two bodies are in thermal equilibrium when they have reached the same temperature. If two bodies are in thermal equilibrium with a third body, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. This simple fact is known as the zeroth law of thermodynamics. Compiled by Yidnekachew M. Page 12 of 12
Course: TDEC202 (Energy II) dflwww.ece.drexel.edu/tdec
 Course: TDEC202 (Energy II) Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Course Director/Lecturer: Dr. Michael Carchidi Course Website URL dflwww.ece.drexel.edu/tdec 1 Course Textbook Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael
Course: TDEC202 (Energy II) Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Course Director/Lecturer: Dr. Michael Carchidi Course Website URL dflwww.ece.drexel.edu/tdec 1 Course Textbook Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael
The word thermodynamics is derived from two Greek words Therm which means heat Dynamis which means power
 THERMODYNAMICS INTRODUCTION The word thermodynamics is derived from two Greek words Therm which means heat Dynamis which means power Together the spell heat power which fits the time when the forefathers
THERMODYNAMICS INTRODUCTION The word thermodynamics is derived from two Greek words Therm which means heat Dynamis which means power Together the spell heat power which fits the time when the forefathers
Energy: The ability to cause changes. thermodynamics stems from therme (heat) and dynamis (power).
 Energy: The ability to cause changes. thermodynamics stems from therme (heat) and dynamis (power). Thermodynamics: The science of energy. Conservation of energy principle: During an interaction, energy
Energy: The ability to cause changes. thermodynamics stems from therme (heat) and dynamis (power). Thermodynamics: The science of energy. Conservation of energy principle: During an interaction, energy
Thermodynamics INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Thermodynamics INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. THERMODYNAMICS AND ENERGY Thermodynamics: The science of energy.
Thermodynamics INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. THERMODYNAMICS AND ENERGY Thermodynamics: The science of energy.
ME2320 Thermodynamics I. Summer I Instructor: Dr. William W. Liou
 ME2320 Thermodynamics I Summer I 2016 Instructor: Dr. William W. Liou Syllabus http://homepages.wmich.edu/~liou/wp_course.htm Homework Solutions Format 3 How to get, and stay, ahead in this class? Preview
ME2320 Thermodynamics I Summer I 2016 Instructor: Dr. William W. Liou Syllabus http://homepages.wmich.edu/~liou/wp_course.htm Homework Solutions Format 3 How to get, and stay, ahead in this class? Preview
CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Science that involves design and analysis of devices and systems for energy conversion Deals with heat and work and
CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Science that involves design and analysis of devices and systems for energy conversion Deals with heat and work and
Thermodynamic Systems
 Thermodynamic Systems For purposes of analysis we consider two types of Thermodynamic Systems: Closed System - usually referred to as a System or a Control Mass. This type of system is separated from its
Thermodynamic Systems For purposes of analysis we consider two types of Thermodynamic Systems: Closed System - usually referred to as a System or a Control Mass. This type of system is separated from its
! =!"#$% exerted by a fluid (liquid or gas) !"#$ =!"# FUNDAMENTAL AND MEASURABLE INTENSIVE PROPERTIES PRESSURE, TEMPERATURE AND SPECIFIC VOLUME
 FUNDAMENTAL AND MEASURABLE INTENSIVE PROPERTIES PRESSURE, TEMPERATURE AND SPECIFIC VOLUME PRESSURE, P! =!"#$%!"#! exerted by a fluid (liquid or gas) Thermodynamic importance of pressure One of two independent
FUNDAMENTAL AND MEASURABLE INTENSIVE PROPERTIES PRESSURE, TEMPERATURE AND SPECIFIC VOLUME PRESSURE, P! =!"#$%!"#! exerted by a fluid (liquid or gas) Thermodynamic importance of pressure One of two independent
INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS. Chapter 1. Mehmet Kanoglu. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition. Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A.
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Applied Thermodynamics (Lecture#01)
 Applied Thermodynamics (Lecture#0) Course Outline: Basic Concepts, the system, Open and close system, properties of a system, control volume, working substance, heat and work, state and properties, thermodynamic
Applied Thermodynamics (Lecture#0) Course Outline: Basic Concepts, the system, Open and close system, properties of a system, control volume, working substance, heat and work, state and properties, thermodynamic
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep
T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M E
 T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M E THERMODYNAMICS CONTENTS 1 BASIC CONCEPTS IN THERMODYNAMICS 2 TEMPERATURE 3 WORK AND HEAT TRANSFER Thermodynamic system, surroundings, universe, system boundary Types of
T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M E THERMODYNAMICS CONTENTS 1 BASIC CONCEPTS IN THERMODYNAMICS 2 TEMPERATURE 3 WORK AND HEAT TRANSFER Thermodynamic system, surroundings, universe, system boundary Types of
SKMM 2413 Thermodynamics
 SKMM 2413 Thermodynamics Md. Mizanur Rahman, PhD Department of Thermo-Fluids Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia UTM Office: C23-228 mizanur@fkm.utm.my Semester I, 2016-2017
SKMM 2413 Thermodynamics Md. Mizanur Rahman, PhD Department of Thermo-Fluids Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia UTM Office: C23-228 mizanur@fkm.utm.my Semester I, 2016-2017
GATE & PSUs CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
 Postal Correspondence GATE & PSUs CHEMICAL ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS 1 T A B L E O F C O N T E N T S. No. Title Page no. 1. Introduction 3 2. Work and Heat Transfer 9 3. Second Law of Thermodynamics 27
Postal Correspondence GATE & PSUs CHEMICAL ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS 1 T A B L E O F C O N T E N T S. No. Title Page no. 1. Introduction 3 2. Work and Heat Transfer 9 3. Second Law of Thermodynamics 27
Why do we need to study thermodynamics? Examples of practical thermodynamic devices:
 Why do we need to study thermodynamics? Knowledge of thermodynamics is required to design any device involving the interchange between heat and work, or the conversion of material to produce heat (combustion).
Why do we need to study thermodynamics? Knowledge of thermodynamics is required to design any device involving the interchange between heat and work, or the conversion of material to produce heat (combustion).
Spring_#1. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam.
 Spring_#1 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr Chapter 1: Objectives Understand the importance of thermodynamics Identify the unique vocabulary associated with thermodynamics through the precise
Spring_#1 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr Chapter 1: Objectives Understand the importance of thermodynamics Identify the unique vocabulary associated with thermodynamics through the precise
T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M T
 T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M T THERMODYNAMICS AND RATE PROCESSES CONTENTS CHAPTER DESCRIPTION PAGE NO 1 Thermodynamics NOTES 1.1. Definitions 1 1.2. Laws of Thermodynamics 3 1.2.1. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M T THERMODYNAMICS AND RATE PROCESSES CONTENTS CHAPTER DESCRIPTION PAGE NO 1 Thermodynamics NOTES 1.1. Definitions 1 1.2. Laws of Thermodynamics 3 1.2.1. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
Non-Newtonian fluids is the fluids in which shear stress is not directly proportional to deformation rate, such as toothpaste,
 CHAPTER1: Basic Definitions, Zeroth, First, and Second Laws of Thermodynamics 1.1. Definitions What does thermodynamic mean? It is a Greeks word which means a motion of the heat. Water is a liquid substance
CHAPTER1: Basic Definitions, Zeroth, First, and Second Laws of Thermodynamics 1.1. Definitions What does thermodynamic mean? It is a Greeks word which means a motion of the heat. Water is a liquid substance
Lecture 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
 Lecture 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS Objectives Identify the unique vocabulary associated with thermodynamics through the precise definition of basic concepts to form a sound foundation for the development
Lecture 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS Objectives Identify the unique vocabulary associated with thermodynamics through the precise definition of basic concepts to form a sound foundation for the development
Thermodynamic System. A thermodynamic system is a volume in space containing a quantity of matter that is being studied for thermodynamic analysis.
 Thermodynamic System A thermodynamic system is a volume in space containing a quantity of matter that is being studied for thermodynamic analysis. The system is bounded by an arbitrary surface called the
Thermodynamic System A thermodynamic system is a volume in space containing a quantity of matter that is being studied for thermodynamic analysis. The system is bounded by an arbitrary surface called the
Thermodynamics-1. S. M. Hosseini Sarvari Chapter 1 Introduction & Basic Concepts
 Mechanical Engineering Dept. Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman Thermodynamics-1 S. M. Hosseini Sarvari Chapter 1 Introduction & Basic Concepts Mechanical Engineering Dept. Shahid Bahonar University of
Mechanical Engineering Dept. Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman Thermodynamics-1 S. M. Hosseini Sarvari Chapter 1 Introduction & Basic Concepts Mechanical Engineering Dept. Shahid Bahonar University of
Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics. Thermodynamics and Energy. Dimensions and Units
 Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics Every science has its own unique vocabulary associated with it. recise definition of basic concepts forms a sound foundation for development of a science and
Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics Every science has its own unique vocabulary associated with it. recise definition of basic concepts forms a sound foundation for development of a science and
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW SVCET
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Chapter 1 Introduction Prof. Siyoung Jeong Thermodynamics I MEE2022-01 Thermodynamics : Science of energy and entropy - Science of heat and work and properties related to
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Chapter 1 Introduction Prof. Siyoung Jeong Thermodynamics I MEE2022-01 Thermodynamics : Science of energy and entropy - Science of heat and work and properties related to
IE 211 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
 IE 211 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Chapter1 Introduction and Basic Concepts INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION A period in 18th and early 19th centuries Major changes in agriculture, mining, manufacturing,
IE 211 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Chapter1 Introduction and Basic Concepts INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION A period in 18th and early 19th centuries Major changes in agriculture, mining, manufacturing,
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES
 Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Eric G. Paterson. Spring 2005
 Eric G. Paterson Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering Pennsylvania State University Spring 2005 Reading and Homework Read Chapter 3. Homework Set #2 has been posted. Due date: Friday 21 January.
Eric G. Paterson Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering Pennsylvania State University Spring 2005 Reading and Homework Read Chapter 3. Homework Set #2 has been posted. Due date: Friday 21 January.
Thermodynamics of Fluid Phase Equilibria Dr. Jayant K. Singh Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Thermodynamics of Fluid Phase Equilibria Dr. Jayant K. Singh Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 01 Review of basic concepts of thermodynamics Welcome to
Thermodynamics of Fluid Phase Equilibria Dr. Jayant K. Singh Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 01 Review of basic concepts of thermodynamics Welcome to
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
ENGG 3260: Thermodynamics. Home Assignment 1 (Chapter 1) (Answer)
 ENGG 360: Thermodynamics Home Assignment 1 (Chapter 1) (Answer) 1. Why does a bicyclist pick up speed on a downhill road even when he is not pedaling? Does this violate the conservation of energy principle?
ENGG 360: Thermodynamics Home Assignment 1 (Chapter 1) (Answer) 1. Why does a bicyclist pick up speed on a downhill road even when he is not pedaling? Does this violate the conservation of energy principle?
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES
 Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines
 Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third
FUNDAMENTALS OF CLASSICAL AND STATISTICAL THERMODYNAMICS SPRING 2005
 FUNDAMENTALS OF CLASSICAL AND STATISTICAL THERMODYNAMICS SPRING 2005 1 1. Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics The basic concepts of thermodynamics such as system, energy, property, state, process, cycle,
FUNDAMENTALS OF CLASSICAL AND STATISTICAL THERMODYNAMICS SPRING 2005 1 1. Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics The basic concepts of thermodynamics such as system, energy, property, state, process, cycle,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 5. The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
Chapter 1: Introduction and basic concepts 1. Chapter 2: Properties of pure substances 26. Chapter 3: Energy transfer by heat and work 49
 Contents Chapter 1: Introduction and basic concepts 1 Chapter : Properties of pure substances 6 Chapter 3: Energy transfer by heat and work 49 Chapter 4: First law of thermodynamics 56 Chapter 5: Second
Contents Chapter 1: Introduction and basic concepts 1 Chapter : Properties of pure substances 6 Chapter 3: Energy transfer by heat and work 49 Chapter 4: First law of thermodynamics 56 Chapter 5: Second
1.4 Perform the following unit conversions: (b) (c) s. g s. lb min. (d) (e) in. ft s. m 55 h. (f) ft s. km h. (g)
 1.4 Perform the following unit conversions: 0.05 ft 1 in. (a) 1L 61in. 1L 1ft (b) 1kJ 650 J 10 J 1Btu 1.0551kJ 0.616 Btu (c) 41 Btu/h 0.15 kw 1kW 1h 600 s 778.17 ft lbf 1Btu ft lbf 99.596 s (d) g 78 s
1.4 Perform the following unit conversions: 0.05 ft 1 in. (a) 1L 61in. 1L 1ft (b) 1kJ 650 J 10 J 1Btu 1.0551kJ 0.616 Btu (c) 41 Btu/h 0.15 kw 1kW 1h 600 s 778.17 ft lbf 1Btu ft lbf 99.596 s (d) g 78 s
Introduction CHAPTER Prime Movers. 1.2 Sources of Energy
 Introduction CHAPTER 1 1.1 Prime Movers Prime mover is a device which converts natural source of energy into mechanical work to drive machines for various applications. In olden days, man had to depend
Introduction CHAPTER 1 1.1 Prime Movers Prime mover is a device which converts natural source of energy into mechanical work to drive machines for various applications. In olden days, man had to depend
Properties of Gases. The perfect gas. States of gases Gas laws Kinetic model of gases (Ch th ed, th ed.) Real gases
 Properties of Gases Chapter 1 of Physical Chemistry - 6th Edition P.W. Atkins. Chapter 1 and a little bit of Chapter 24 of 7th Edition. Chapter 1 and a little bit of Chapter 21 of 8th edition. The perfect
Properties of Gases Chapter 1 of Physical Chemistry - 6th Edition P.W. Atkins. Chapter 1 and a little bit of Chapter 24 of 7th Edition. Chapter 1 and a little bit of Chapter 21 of 8th edition. The perfect
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
Boundary. Surroundings
 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics describes the physics of matter using the concept of the thermodynamic system, a region of the universe that is under study. All quantities, such as pressure or mechanical
Thermodynamics Thermodynamics describes the physics of matter using the concept of the thermodynamic system, a region of the universe that is under study. All quantities, such as pressure or mechanical
Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13
 Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13 (1.1). Thermodynamic system An isolated system is a system that exchanges neither mass nor energy with its environment. An insulated rigid tank
Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13 (1.1). Thermodynamic system An isolated system is a system that exchanges neither mass nor energy with its environment. An insulated rigid tank
Thermodynamics. Mechanical Engineering. For
 Thermodynamics For Mechanical Engineering By www.thegateacademy.com Syllabus Syllabus for Thermodynamics Zeroth, First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics, Thermodynamic System and rocesses, Carnot Cycle.
Thermodynamics For Mechanical Engineering By www.thegateacademy.com Syllabus Syllabus for Thermodynamics Zeroth, First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics, Thermodynamic System and rocesses, Carnot Cycle.
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1
 Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 1: Introduction Introduction The most of general sense of thermodynamics is the study of energy and its relationship to the properties of matter. All activities in
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 1: Introduction Introduction The most of general sense of thermodynamics is the study of energy and its relationship to the properties of matter. All activities in
The first law of thermodynamics. U = internal energy. Q = amount of heat energy transfer
 Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
The First Law of Thermodynamics. By: Yidnekachew Messele
 The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
TOPICS. Density. Pressure. Variation of Pressure with Depth. Pressure Measurements. Buoyant Forces-Archimedes Principle
 Lecture 6 Fluids TOPICS Density Pressure Variation of Pressure with Depth Pressure Measurements Buoyant Forces-Archimedes Principle Surface Tension ( External source ) Viscosity ( External source ) Equation
Lecture 6 Fluids TOPICS Density Pressure Variation of Pressure with Depth Pressure Measurements Buoyant Forces-Archimedes Principle Surface Tension ( External source ) Viscosity ( External source ) Equation
ENGR 292 Fluids and Thermodynamics
 ENGR 292 Fluids and Thermodynamics Scott Li, Ph.D., P.Eng. Mechanical Engineering Technology Camosun College Timeline Last week, Reading Break Feb.21: Thermodynamics 1 Feb.24: Midterm Review (Fluid Statics
ENGR 292 Fluids and Thermodynamics Scott Li, Ph.D., P.Eng. Mechanical Engineering Technology Camosun College Timeline Last week, Reading Break Feb.21: Thermodynamics 1 Feb.24: Midterm Review (Fluid Statics
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems
 First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 10 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
Thermodynamics I. Properties of Pure Substances
 Thermodynamics I Properties of Pure Substances Dr.-Eng. Zayed Al-Hamamre 1 Content Pure substance Phases of a pure substance Phase-change processes of pure substances o Compressed liquid, Saturated liquid,
Thermodynamics I Properties of Pure Substances Dr.-Eng. Zayed Al-Hamamre 1 Content Pure substance Phases of a pure substance Phase-change processes of pure substances o Compressed liquid, Saturated liquid,
(Refer Slide Time: 0:28)
 Engineering Thermodynamics Professor Jayant K Singh Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 08 Examples on basic concept & energy balance Welcome back! Myself Parul
Engineering Thermodynamics Professor Jayant K Singh Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 08 Examples on basic concept & energy balance Welcome back! Myself Parul
Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
Content. Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas.
 Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
THERMODYNAMICS SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL THERMODYNAMICS THERMODYNAMICS THERMODYNAMICS
 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL 2 Syllabus: Thermal Engineering (Thermodynamics) Properties of Pure Substances : p-v & P-T diagrams of pure substance like H 2
1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL 2 Syllabus: Thermal Engineering (Thermodynamics) Properties of Pure Substances : p-v & P-T diagrams of pure substance like H 2
열과유체, 에너지와친해지기 KAIST 기계공학과정상권
 열과유체, 에너지와친해지기 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 이번시간에는! 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 물과공기로움직이는기계 사라지지않는에너지 / 증가하는엔트로피 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 [ 학습목차 ] Thermofluids Energy conservation principle Energy Work (boundary work)
열과유체, 에너지와친해지기 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 이번시간에는! 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 물과공기로움직이는기계 사라지지않는에너지 / 증가하는엔트로피 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 [ 학습목차 ] Thermofluids Energy conservation principle Energy Work (boundary work)
CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1
 Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013
 Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
Lecture 2: Zero law of thermodynamics
 Lecture 2: Zero law of thermodynamics 1. Thermometers and temperature scales 2. Thermal contact and thermal equilibrium 3. Zeroth law of thermodynamics 1. Thermometers and Temperature scales We often associate
Lecture 2: Zero law of thermodynamics 1. Thermometers and temperature scales 2. Thermal contact and thermal equilibrium 3. Zeroth law of thermodynamics 1. Thermometers and Temperature scales We often associate
AME230 Thermodynamics. McGrath
 AME230 Thermodynamics McGrath Review Website and Syllabus Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics Using thermodynamics Analyze and design systems and processes for human needs Examples: Increase in
AME230 Thermodynamics McGrath Review Website and Syllabus Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics Using thermodynamics Analyze and design systems and processes for human needs Examples: Increase in
First Law of Thermodynamics
 CH2303 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Unit II First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. M. Subramanian 07-July-2011 Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College
CH2303 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Unit II First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. M. Subramanian 07-July-2011 Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College
S6. (a) State what is meant by an ideal gas...
 IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS TSOKOS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW S1. Thermal energy is transferred through the glass windows of a house mainly by A. conduction. B. radiation.
IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS TSOKOS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW S1. Thermal energy is transferred through the glass windows of a house mainly by A. conduction. B. radiation.
CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 CHAPTER 6 -- The Second Law of Thermodynamics OUTCOME: Identify Valid (possible) Processes as those that satisfy both the first and
CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 CHAPTER 6 -- The Second Law of Thermodynamics OUTCOME: Identify Valid (possible) Processes as those that satisfy both the first and
CHAPTER - 12 THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPER - HERMODYNAMICS ONE MARK QUESIONS. What is hermodynamics?. Mention the Macroscopic variables to specify the thermodynamics. 3. How does thermodynamics differ from Mechanics? 4. What is thermodynamic
CHAPER - HERMODYNAMICS ONE MARK QUESIONS. What is hermodynamics?. Mention the Macroscopic variables to specify the thermodynamics. 3. How does thermodynamics differ from Mechanics? 4. What is thermodynamic
This follows from the Clausius inequality as a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. Therefore. (for reversible process only) (22.
 Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Introduction to Aerospace Propulsion. Prof. Bhaskar Roy. Prof. A. M. Pradeep. Department of Aerospace Engineering
 Introduction to Aerospace Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A. M. Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 11 Reversible and irreversible
Introduction to Aerospace Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A. M. Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 11 Reversible and irreversible
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) PART- A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
Chapter 1: INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS. Thermodynamics = Greek words : therme(heat) + dynamis(force or power)
 Chapter 1: INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS 1.1 Basic concepts and definitions Thermodynamics = Greek words : therme(heat) + dynamis(force or power) Note that, force x displacement = work; power = work/time
Chapter 1: INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS 1.1 Basic concepts and definitions Thermodynamics = Greek words : therme(heat) + dynamis(force or power) Note that, force x displacement = work; power = work/time
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION. 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance in thermodynamics.
 QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
THERMODYNAMICS. Zeroth law of thermodynamics. Isotherm
 12 THERMODYNAMICS Zeroth law of thermodynamics Two systems separately in thermal equilibrium with a third system are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Isotherm It is the graph connecting pressure
12 THERMODYNAMICS Zeroth law of thermodynamics Two systems separately in thermal equilibrium with a third system are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Isotherm It is the graph connecting pressure
Chapter 10, Thermal Physics
 CHAPTER 10 1. If it is given that 546 K equals 273 C, then it follows that 400 K equals: a. 127 C b. 150 C c. 473 C d. 1 200 C 2. A steel wire, 150 m long at 10 C, has a coefficient of linear expansion
CHAPTER 10 1. If it is given that 546 K equals 273 C, then it follows that 400 K equals: a. 127 C b. 150 C c. 473 C d. 1 200 C 2. A steel wire, 150 m long at 10 C, has a coefficient of linear expansion
Thermodynamics Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Thermodynamics Introduction and Basic Concepts by Asst. Prof. Channarong Asavatesanupap Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering Thammasat University 2 What is Thermodynamics? Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics Introduction and Basic Concepts by Asst. Prof. Channarong Asavatesanupap Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering Thammasat University 2 What is Thermodynamics? Thermodynamics
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Physics 153 Introductory Physics II. Week One: FLUIDS. Dr. Joseph J. Trout
 Physics 153 Introductory Physics II Week One: FLUIDS Dr. Joseph J. Trout joseph.trout@drexel.edu 610-348-6495 States (Phases) of Matter: Solid: Fixed shape. Fixed size. Even a large force will not readily
Physics 153 Introductory Physics II Week One: FLUIDS Dr. Joseph J. Trout joseph.trout@drexel.edu 610-348-6495 States (Phases) of Matter: Solid: Fixed shape. Fixed size. Even a large force will not readily
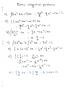 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper II. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
CHAPTER 2 Pressure and Head
 FLUID MECHANICS Gaza, Sep. 2012 CHAPTER 2 Pressure and Head Dr. Khalil Mahmoud ALASTAL Objectives of this Chapter: Introduce the concept of pressure. Prove it has a unique value at any particular elevation.
FLUID MECHANICS Gaza, Sep. 2012 CHAPTER 2 Pressure and Head Dr. Khalil Mahmoud ALASTAL Objectives of this Chapter: Introduce the concept of pressure. Prove it has a unique value at any particular elevation.
Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas (2)
 1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
Where F1 is the force and dl1 is the infinitesimal displacement, but F1 = p1a1
 In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
Heat & Mass Flow Processes (Lecture#01) Introduction & Basic Concepts of Heat & Mass Flow Processes
 Heat & Mass Flow Processes (Lecture#01) MT-364 Heat and Mass flow Applications Basic Concepts; Fourier s law; heat conduction equation; conduction through geometrical configurations, variable thermal conductivity,
Heat & Mass Flow Processes (Lecture#01) MT-364 Heat and Mass flow Applications Basic Concepts; Fourier s law; heat conduction equation; conduction through geometrical configurations, variable thermal conductivity,
Properties of Gases. Molecular interactions van der Waals equation Principle of corresponding states
 Properties of Gases Chapter 1 of Atkins and de Paula The Perfect Gas States of gases Gas laws Real Gases Molecular interactions van der Waals equation Principle of corresponding states Kinetic Model of
Properties of Gases Chapter 1 of Atkins and de Paula The Perfect Gas States of gases Gas laws Real Gases Molecular interactions van der Waals equation Principle of corresponding states Kinetic Model of
Petroleum Engineering Dept. Fluid Mechanics Second Stage Dr. Ahmed K. Alshara
 Continents Chapter 1. Fluid Mechanics -Properties of fluids -Density, specific gravity, specific volume and Viscosity -Newtonian and non Newtonian fluids -Surface tension Compressibility -Pressure -Cavitations
Continents Chapter 1. Fluid Mechanics -Properties of fluids -Density, specific gravity, specific volume and Viscosity -Newtonian and non Newtonian fluids -Surface tension Compressibility -Pressure -Cavitations
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT ON BERNOULLI S EQUATION
 AMEE 0 Introduction to Fluid Mechanics Instructor: Marios M. Fyrillas Email: m.fyrillas@frederick.ac.cy HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT ON BERNOULLI S EQUATION. Conventional spray-guns operate by achieving a low pressure
AMEE 0 Introduction to Fluid Mechanics Instructor: Marios M. Fyrillas Email: m.fyrillas@frederick.ac.cy HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT ON BERNOULLI S EQUATION. Conventional spray-guns operate by achieving a low pressure
THE FIRST LAW APPLIED TO STEADY FLOW PROCESSES
 Chapter 10 THE FIRST LAW APPLIED TO STEADY FLOW PROCESSES It is not the sun to overtake the moon, nor doth the night outstrip theday.theyfloateachinanorbit. The Holy Qur-ān In many engineering applications,
Chapter 10 THE FIRST LAW APPLIED TO STEADY FLOW PROCESSES It is not the sun to overtake the moon, nor doth the night outstrip theday.theyfloateachinanorbit. The Holy Qur-ān In many engineering applications,
1985B4. A kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100
 1985B4. A 0.020-kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100 joules per second until the temperature increases to 60
1985B4. A 0.020-kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100 joules per second until the temperature increases to 60
Chapter 1: Basic Definitions, Terminologies and Concepts
 Chapter : Basic Definitions, Terminologies and Concepts ---------------------------------------. UThermodynamics:U It is a basic science that deals with: -. Energy transformation from one form to another..
Chapter : Basic Definitions, Terminologies and Concepts ---------------------------------------. UThermodynamics:U It is a basic science that deals with: -. Energy transformation from one form to another..
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics 8e
 Fundamentals of Thermodynamics 8e Authors Borgnakke Copyright 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics 8e Authors Borgnakke Copyright 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted
20 m neon m propane. g 20. Problems with solutions:
 Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
(1)5. Which of the following equations is always valid for a fixed mass system undergoing an irreversible or reversible process:
 Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
