Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition
|
|
|
- Letitia Walsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Powerpoint slides copied from or based upon: Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition Connally, Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, Et Al. Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
2 Chapter 4: Logarithmic Functions Section 4.1 Logarithms and Their Properties
3 Suppose that a population grows according to the formula P = 10 t, where P is the colony size at time t, in hours. When will the population be 2500? We want to solve which equation for t? Page 152 3
4 Suppose that a population grows according to the formula P = 10 t, where P is the colony size at time t, in hours. When will the population be 2500? We want to solve which equation for t? 10 t 2500 Page 152 4
5 Let's solve graphically via our calculator. 10 t 2500 Page 152 5
6 Let's solve graphically via our calculator. y 10 x Window Value Xmin -1 Xmax 4 Xscl 1 Ymin 0 Ymax 3000 Yscl 300 Page 152 6
7 Let's solve graphically via our calculator. y 10 x 3,000 2,000 1,000 Page x 7
8 But we really want What is the next step? 3,000 t ,000 1,000 Page x 8
9 But we really want What is the next step? 3,000 2,000 t Add y 2 = ,000 Page x 9
10 But we really want t ,000 2,000 1,000 Page x 10
11 But we really want t ,000 Next? 2,000 1,000 Page x 11
12 But we really want t ,000 2nd Trace Intersect 2,000 1,000 Page x 12
13 But we really want t ,000 x= , y=2500 2,000 1,000 Page x 13
14 The central question is: Is there another way to solve this problem without graphics on our calculator? 3, t ,000 1,000 Page x 14
15 To answer this question, we define the common logarithm function, or simply the log function, written: log 10 x, or log x, as follows: Page
16 If x is a positive number, log x is the exponent of 10 that gives x. In other words, if y log x then 10 y x Page 152 Blue Box 16
17 To what power must 10 be raised to = 100? Page
18 To what power must 10 be raised to = 100? 2 "Log100 is the exponent of 10 that gives 100." 2 log100 2 means: if y log x then 10 x y if 2 log100 then Page
19 To what power must 10 be raised to = 10? Page
20 To what power must 10 be raised to = 10? 1 "Log10 is the exponent of 10 that gives 10." 1 log10 1 means: if y log x then 10 x y if 1 log10 then Page
21 To what power must 10 be raised to = 1? Page
22 To what power must 10 be raised to = 1? 0 "Log1 is the exponent of 10 that gives 1." 0 log1 0 means: 10 1 if y log x then 10 x y if 0 log1 then Page
23 To what power must 10 be raised to =.1? Page
24 To what power must 10 be raised to =.1? -1 "Log.1 is the exponent of 10 that gives.1." 1 log.1 1 means: 10.1 if y log x then 10 x y if 1 log.1 then Page
25 To what power must 10 be raised to =.01? Page
26 To what power must 10 be raised to =.01? -2 "Log.01 is the exponent of 10 that gives.01." 2 log.01 2 means: if y log x then 10 x y if -2 log.01 then Page
27 Back to our problem: 10 t 2500 How can we use logarithms to solve? Page
28 To what power must 10 be raised to = 2500? Page
29 To what power must 10 be raised to = 2500?? "Log2500 is the exponent of 10 that gives?" Page
30 To what power must 10 be raised to = 2500? "Log2500 is the exponent of 10 that gives " log means: y if y log x then 10 x if log 2500 then Page
31 Rewrite the following statements using exponents instead of logs. (a) log 100 = 2 (b) log 0.01 = 2 (c) log 30 = Page 152 Example #1 31
32 Rewrite the following statements using exponents instead of logs. (a) log 100 = 2 (b) log 0.01 = 2 (c) log 30 = if y log x then 10 y x Page 152 Example #1 32
33 Rewrite the following statements using exponents instead of logs. (a) log 100 = 2 (b) log 0.01 = 2 (c) log 30 = (a) 2 = log = 100. Page 152 Example #1 33
34 Rewrite the following statements using exponents instead of logs. (a) log 100 = 2 (b) log 0.01 = 2 (c) log 30 = (a) 2 = log = 100. (b) 2 = log = Page 152 Example #1 34
35 Rewrite the following statements using exponents instead of logs. (a) log 100 = 2 (b) log 0.01 = 2 (c) log 30 = (a) 2 = log = 100. (b) 2 = log = (c) = log = 30. Page 152 Example #1 35
36 Rewrite the following statements using logs instead of exponents. (a) 10 5 = 100,000 (b) 10 4 = (c) = if 10 y x then y log x Page 152 Example #2 36
37 Rewrite the following statements using logs instead of exponents. (a) 10 5 = 100,000 (b) 10 4 = (c) = (a) 10 5 = 100,000 log 100,000 = 5. Page 152 Example #2 37
38 Rewrite the following statements using logs instead of exponents. (a) 10 5 = 100,000 (b) 10 4 = (c) = (a) 10 5 = 100,000 log 100,000 = 5. (b) 10 4 = log = 4. Page 152 Example #2 38
39 Rewrite the following statements using logs instead of exponents. (a) 10 5 = 100,000 (b) 10 4 = (c) = (a) 10 5 = 100,000 log 100,000 = 5. (b) 10 4 = log = 4. (c) = log = 0.8. Page 152 Example #2 39
40 Logarithms are just exponents!!! Page
41 Without a calculator, evaluate the following, if possible: (a) log 1 (b) log 10 (c) log 1,000,000 (d) log (e) log 10 (f) log( 100) Page 153 Example #3 41
42 (a) log 1 = 0, since 10 0 = 1.? 10 1 Page 153 Example #3 42
43 (b) log 10 = 1, since 10 1 = 10.? Page 153 Example #3 43
44 (c) Since 1,000,000 = 10 6, the exponent of 10 that gives 1,000,000 is 6. Thus, log 1,000,000 = 6.? 10 1,000,000 Page 153 Example #3 44
45 (d) = 10 3, the exponent of 10 that gives is 3. Thus, log = 3.? Page 153 Example #3 45
46 (e) Since , the exponent of 10 that gives is -1/2. Thus log( ) = -1/2.? Page 153 Example #3 46
47 (f) Since 10 to any power is positive, 100 cannot be written as a power of 10.? Page 153 Example #3 47
48 (f) Since 10 to any power is positive, 100 cannot be written as a power of 10. Thus, log( 100) is undefined.? Page 153 Example #3 48
49 Logarithmic and Exponential Functions are Inverses For any N, log 10 N N and for N > 0, 10 log N N Page 153 Blue Box 49
50 Evaluate without a calculator: (a) log ( ) (b) 10log 2.7 (c) 10log(x + 3) Page 153 Example #4 50
51 Using log(10 N ) = N and 10 logn = N, we have: (a) log ( ) = 8.5 (b) 10 log 2.7 = 2.7 (c) 10 log(x + 3) = x + 3 A calculator will confirm (a) & (b). Page 153 Example #4 51
52 Properties of the Common Logarithm By definition, y = logx means 10 y = x. In particular, log 1 = 0 & log 10 = 1. The functions 10 x and logx are inverses, so x they undo each other: log 10 x for all x, log x 10 x for x 0 Page 154 Blue Box 52
53 Properties of the Common Logarithm For a and b both positive and any value of t, log ab log a logb a log log a log b b log t b t logb Page 154 Blue Box 53
54 Properties of the Common Logarithm log ab log a log b, note: log( a b) log a log b a log log a log b, note: log( a b) log a log b b a log a and note: log b logb t log b t log b Page 154 Blue Box 54
55 Solve (100)(2 t )=337,000,000 for t Page 154 Example #5 55
56 Solve (100)(2 t )=337,000,000 for t t (100)(2 ) t t log 2 log Page 154 Example #5 t log 2 log t log log
57 The Natural Logarithm When e is used as the base for exponential functions, computations are easier with the use of another logarithm function, called log base e. The log base e is used so frequently that it has its own notation: ln x, read as the natural log of x. Page
58 The Natural Logarithm Definition: ln x is the power of e that gives x or ln x = y means e y = x y is called the natural logarithm of x Page
59 The Natural Logarithm Just as the functions 10 x and logx are inverses, so are e x and ln x. The function ln x has similar properties to the common log function: Page
60 Properties of the Natural Logarithm By definition, y = ln x means x = e y. In particular, ln 1 = 0 & ln e = 1. The functions e x and ln x are inverses, so they x undo each other: ln e x for all x, ln x e x x for 0 Page 155 Blue Box 60
61 Properties of the Natural Logarithm For a and b both positive and any value of t, ln ab ln a ln b a ln ln a ln b b ln t b t ln b Page 155 Blue Box 61
62 Properties of the Natural Logarithm ln ab ln a ln b, note: ln( a b) ln a ln b a ln ln a ln b, note: ln( a b) ln a ln b b a ln a and note: ln b ln b t ln b t ln b Page 155 Blue Box 62
63 Solve for x: (a) 5e 2x = 50 (b) 3 x = 100. Page
64 Solve for x: (a) 5e 2x = 50 Page
65 Page 155 Solve for x: (a) 5e 2x = 50 ln 2x 5e 50 e e 2x 2x 10 ln(10) 2x ln 10 x ln
66 Solve for x: (b) 3 x = 100. Page
67 Solve for x: (b) 3 x = 100. ln 3 x xln 3 x x x ln(100) ln(100) ln(100) ln(3) Page
68 Note: log( a b) log a logb log( a b) log a logb log( ab) (log a)(log b) log a b log a logb log 1 1 a log a Page 156 Blue Box 68
69 Note: 2 log5x 2log(5 x) (since exponent only applies to the x) 2 2 log5x log(5) log( x ) log(5) 2log( x) Page 156 Blue Box 69
70 Note: ln( a b) ln a ln b ln( a b) ln a ln b ln( ab) (ln a)(ln b) ln a b ln ln a b ln 1 1 a ln a Page 156 Blue Box 70
71 End of Section
Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition
 Powerpoint slides copied from or based upon: Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition Connally, Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, Et Al. Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 CHAPTER
Powerpoint slides copied from or based upon: Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition Connally, Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, Et Al. Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 CHAPTER
Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition
 Powerpoint slides copied from or based upon: Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition Connally, Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, Et Al. Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Section
Powerpoint slides copied from or based upon: Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition Connally, Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, Et Al. Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Section
At right: Closeups of the graphs of. with WINDOW settings Xmin=-1, Xmax=1, Xscl=0.1, Ymin=-1, Ymax=1, Yscl=0.1
 Know the graphs of f(x) = x n for n = odd, positive: 1, 3, 5, The Domain is All Real Numbers, (, ), or R. The Range is All Real Numbers, (, ), or R. It is an Odd function because f( x) = f(x). It is symmetric
Know the graphs of f(x) = x n for n = odd, positive: 1, 3, 5, The Domain is All Real Numbers, (, ), or R. The Range is All Real Numbers, (, ), or R. It is an Odd function because f( x) = f(x). It is symmetric
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment. Due Date: First day of school.
 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: Due Date: First day of school. The purpose of this assignment is to have you practice the mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Calculus AB. All of the
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: Due Date: First day of school. The purpose of this assignment is to have you practice the mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Calculus AB. All of the
Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition
 Powerpoint slides copied from or based upon: Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition Connally, Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, Et Al. Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter
Powerpoint slides copied from or based upon: Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition Connally, Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, Et Al. Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter
Week #1 The Exponential and Logarithm Functions Section 1.2
 Week #1 The Exponential and Logarithm Functions Section 1.2 From Calculus, Single Variable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is used by
Week #1 The Exponential and Logarithm Functions Section 1.2 From Calculus, Single Variable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is used by
Week #1 The Exponential and Logarithm Functions Section 1.4
 Week #1 The Exponential and Logarithm Functions Section 1.4 From Calculus, Single Variable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is used by
Week #1 The Exponential and Logarithm Functions Section 1.4 From Calculus, Single Variable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is used by
If a function has an inverse then we can determine the input if we know the output. For example if the function
 1 Inverse Functions We know what it means for a relation to be a function. Every input maps to only one output, it passes the vertical line test. But not every function has an inverse. A function has no
1 Inverse Functions We know what it means for a relation to be a function. Every input maps to only one output, it passes the vertical line test. But not every function has an inverse. A function has no
Section 4.4 Z-Scores and the Empirical Rule
 Section 4.4 Z-Scores and the Empirical Rule 1 GPA Example A sample of GPAs of 40 freshman college students appear below (sorted in increasing order) 1.40 1.90 1.90 2.00 2.10 2.10 2.20 2.30 2.30 2.40 2.50
Section 4.4 Z-Scores and the Empirical Rule 1 GPA Example A sample of GPAs of 40 freshman college students appear below (sorted in increasing order) 1.40 1.90 1.90 2.00 2.10 2.10 2.20 2.30 2.30 2.40 2.50
A repeated root is a root that occurs more than once in a polynomial function.
 Unit 2A, Lesson 3.3 Finding Zeros Synthetic division, along with your knowledge of end behavior and turning points, can be used to identify the x-intercepts of a polynomial function. This information allows
Unit 2A, Lesson 3.3 Finding Zeros Synthetic division, along with your knowledge of end behavior and turning points, can be used to identify the x-intercepts of a polynomial function. This information allows
( ) ( ) SECTION 1.1, Page ( x 3) 5 = 4( x 5) = 7. x = = = x x+ 0.12(4000 x) = 432
 CHAPTER Functions and Graphs SECTION., Page. x + x + x x x. x + x x x x x. ( x ) ( x ) x 6 x x x x x + x x 7. x + x + x + 6 8 x 8 6 x x. x x 6 x 6 x x x 8 x x 8 + x..x +..6.x. x 6 ( n + ) ( n ) n + n.
CHAPTER Functions and Graphs SECTION., Page. x + x + x x x. x + x x x x x. ( x ) ( x ) x 6 x x x x x + x x 7. x + x + x + 6 8 x 8 6 x x. x x 6 x 6 x x x 8 x x 8 + x..x +..6.x. x 6 ( n + ) ( n ) n + n.
Section 4.4 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations
 Section 4.4 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations Exponential Equations An exponential equation is one in which the variable occurs in the exponent. EXAMPLE: Solve the equation 2 x = 7. Solution 1: We
Section 4.4 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations Exponential Equations An exponential equation is one in which the variable occurs in the exponent. EXAMPLE: Solve the equation 2 x = 7. Solution 1: We
Logarithms Dr. Laura J. Pyzdrowski
 1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory An exponential function of the form f(x) = a x, where a is a positive real number not equal to 1, is an example of a one-to-one function. This means
1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory An exponential function of the form f(x) = a x, where a is a positive real number not equal to 1, is an example of a one-to-one function. This means
( ) a (graphical) transformation of y = f ( x )? x 0,2π. f ( 1 b) = a if and only if f ( a ) = b. f 1 1 f
 Warm-Up: Solve sinx = 2 for x 0,2π 5 (a) graphically (approximate to three decimal places) y (b) algebraically BY HAND EXACTLY (do NOT approximate except to verify your solutions) x x 0,2π, xscl = π 6,y,,
Warm-Up: Solve sinx = 2 for x 0,2π 5 (a) graphically (approximate to three decimal places) y (b) algebraically BY HAND EXACTLY (do NOT approximate except to verify your solutions) x x 0,2π, xscl = π 6,y,,
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt McDougal Algebra 2
 4-5 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Solve. 1. log 16 x = 3 2 64 2. log x 1.331 = 3 1.1 3. log10,000 = x 4 Objectives Solve exponential and logarithmic equations and equalities.
4-5 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Solve. 1. log 16 x = 3 2 64 2. log x 1.331 = 3 1.1 3. log10,000 = x 4 Objectives Solve exponential and logarithmic equations and equalities.
Unit #1 - Transformation of Functions; Exponential and Logarithms Section 1.4
 Unit #1 - Transformation of Functions; Exponential and Logarithms Section 1.4 Some material from Calculus, Single and MultiVariable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 005 by John Wiley
Unit #1 - Transformation of Functions; Exponential and Logarithms Section 1.4 Some material from Calculus, Single and MultiVariable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 005 by John Wiley
Moving Straight Ahead Practice Answers
 Copright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. Investigation Additional Practice. a. Francine:. mph; Geraldo: mph; Jennifer: 7. mph; Divide the number of miles traveled in hours
Copright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. Investigation Additional Practice. a. Francine:. mph; Geraldo: mph; Jennifer: 7. mph; Divide the number of miles traveled in hours
Linear Equations and Inequalities
 Unit 2 Linear Equations and Inequalities 9/26/2016 10/21/2016 Name: By the end of this unit, you will be able to Use rate of change to solve problems Find the slope of a line Model real-world data with
Unit 2 Linear Equations and Inequalities 9/26/2016 10/21/2016 Name: By the end of this unit, you will be able to Use rate of change to solve problems Find the slope of a line Model real-world data with
FLEX Mathematics Introduction to Trigonometry. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 FLEX Mathematics Introduction to Trigonometry Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the expression. 1) 8 tan 0 + 3 csc 20
FLEX Mathematics Introduction to Trigonometry Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Evaluate the expression. 1) 8 tan 0 + 3 csc 20
Lesson 6 Practice Problems
 Name: Date: Lesson 6 Section 6.1: Writing Exponential Models 1. Complete the following table. Growth Rate as a % Growth Rate as a decimal Growth Factor 13% 0.13 1.13 21% 7% 0.20 0.05 1.25 1.075 2.03 2.
Name: Date: Lesson 6 Section 6.1: Writing Exponential Models 1. Complete the following table. Growth Rate as a % Growth Rate as a decimal Growth Factor 13% 0.13 1.13 21% 7% 0.20 0.05 1.25 1.075 2.03 2.
Chapter 1: January 26 January 30
 Chapter : January 26 January 30 Section.7: Inequalities As a diagnostic quiz, I want you to go through the first ten problems of the Chapter Test on page 32. These will test your knowledge of Sections.
Chapter : January 26 January 30 Section.7: Inequalities As a diagnostic quiz, I want you to go through the first ten problems of the Chapter Test on page 32. These will test your knowledge of Sections.
AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT. Dear future Calculus AB student
 AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Dear future Calculus AB student We are ecited to work with you net year in Calculus AB. In order to help you be prepared for this class, please complete the summer assignment.
AP Calculus AB SUMMER ASSIGNMENT Dear future Calculus AB student We are ecited to work with you net year in Calculus AB. In order to help you be prepared for this class, please complete the summer assignment.
Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Skill 6a: Graphs of Exponential Functions Skill 6b: Solving Exponential Equations (not requiring logarithms) Skill 6c: Definition of Logarithms Skill 6d: Graphs
Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Skill 6a: Graphs of Exponential Functions Skill 6b: Solving Exponential Equations (not requiring logarithms) Skill 6c: Definition of Logarithms Skill 6d: Graphs
POD. A) Graph: y = 2e x +2 B) Evaluate: (e 2x e x ) 2 2e -x. e 7x 2
 POD A) Graph: y = 2e x +2 B) Evaluate: (e 2x e x ) 2 2e -x e 7x 2 4.4 Evaluate Logarithms & Graph Logarithmic Functions What is a logarithm? How do you read it? What relationship exists between logs and
POD A) Graph: y = 2e x +2 B) Evaluate: (e 2x e x ) 2 2e -x e 7x 2 4.4 Evaluate Logarithms & Graph Logarithmic Functions What is a logarithm? How do you read it? What relationship exists between logs and
3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations
 3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Pre-Calculus Mr. Niedert Pre-Calculus 3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Mr. Niedert 1 / 18 3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations 1 Solving Simple Equations
3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Pre-Calculus Mr. Niedert Pre-Calculus 3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Mr. Niedert 1 / 18 3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations 1 Solving Simple Equations
Lesson 5 Practice Problems
 Name: Date: Lesson 5 Section 5.1: Linear Functions vs. Exponential Functions 1. Complete the table below. Function Linear or Exponential? Linear: Increasing or Decreasing? Exponential: Growth or Decay?
Name: Date: Lesson 5 Section 5.1: Linear Functions vs. Exponential Functions 1. Complete the table below. Function Linear or Exponential? Linear: Increasing or Decreasing? Exponential: Growth or Decay?
The Mathematics of a Football Kick (Parametric Equations) (Adapted from an article in COMAP)
 The Mathematics of a Football Kick (Parametric Equations) (Adapted from an article in COMAP) I. Problem The punter on the 1994 Handley State Championship Football team, Michael Partlow, was also a calculus
The Mathematics of a Football Kick (Parametric Equations) (Adapted from an article in COMAP) I. Problem The punter on the 1994 Handley State Championship Football team, Michael Partlow, was also a calculus
Lesson 4b More on LOGARITHMS
 Lesson 4b More on LOGARITHMS Learning Packet Student Name Due Date Class Time/Day Submission Date THIS BOX FOR INSTRUCTOR GRADING USE ONLY Mini-Lesson is complete and information presented is as found
Lesson 4b More on LOGARITHMS Learning Packet Student Name Due Date Class Time/Day Submission Date THIS BOX FOR INSTRUCTOR GRADING USE ONLY Mini-Lesson is complete and information presented is as found
A factor times a logarithm can be re-written as the argument of the logarithm raised to the power of that factor
 In this section we will be working with Properties of Logarithms in an attempt to take equations with more than one logarithm and condense them down into just a single logarithm. Properties of Logarithms:
In this section we will be working with Properties of Logarithms in an attempt to take equations with more than one logarithm and condense them down into just a single logarithm. Properties of Logarithms:
Unit 2 Linear Equations and Inequalities
 Unit 2 Linear Equations and Inequalities Test Date: Name: By the end of this unit, you will be able to Use rate of change to solve problems Find the slope of a line Model real-world data with linear equations
Unit 2 Linear Equations and Inequalities Test Date: Name: By the end of this unit, you will be able to Use rate of change to solve problems Find the slope of a line Model real-world data with linear equations
Before we do that, I need to show you another way of writing an exponential. We all know 5² = 25. Another way of writing that is: log
 Chapter 13 Logarithms Sec. 1 Definition of a Logarithm In the last chapter we solved and graphed exponential equations. The strategy we used to solve those was to make the bases the same, set the exponents
Chapter 13 Logarithms Sec. 1 Definition of a Logarithm In the last chapter we solved and graphed exponential equations. The strategy we used to solve those was to make the bases the same, set the exponents
Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Skill 6a: Graphs of Exponential Functions Skill 6b: Solving Exponential Equations (not requiring logarithms) Skill 6c: Definition of Logarithms Skill 6d: Graphs
Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Skill 6a: Graphs of Exponential Functions Skill 6b: Solving Exponential Equations (not requiring logarithms) Skill 6c: Definition of Logarithms Skill 6d: Graphs
Composition of Functions
 Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Composite and Inverse Functions Composition of Functions The composite function f g, the composition of f and g, is defined as (f g)(x) = f(g(x)). Recall that a function
Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Composite and Inverse Functions Composition of Functions The composite function f g, the composition of f and g, is defined as (f g)(x) = f(g(x)). Recall that a function
Unit #17 - Differential Equations Section 11.6
 Unit #7 - Differential Equations Section.6 Some material from Calculus, Single and MultiVariable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is used
Unit #7 - Differential Equations Section.6 Some material from Calculus, Single and MultiVariable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is used
25 = 2. Remember to put the base lower than the g of log so you don t get confused 2. Write the log equation in exponential form 2.
 LOGARITHMS The logarithm of a number to a given base is the exponent to which that base must be raised in order to produce the number. For example: What is the exponent that must be raised to in order
LOGARITHMS The logarithm of a number to a given base is the exponent to which that base must be raised in order to produce the number. For example: What is the exponent that must be raised to in order
ASTROMATH 101: BEGINNING MATHEMATICS IN ASTRONOMY
 Name Partner(s) Section Date ASTROMATH 101: BEGINNING MATHEMATICS IN ASTRONOMY Astronomers deal with very, very large distances, some incredible temperatures, and even really, really small wavelengths.
Name Partner(s) Section Date ASTROMATH 101: BEGINNING MATHEMATICS IN ASTRONOMY Astronomers deal with very, very large distances, some incredible temperatures, and even really, really small wavelengths.
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School
 Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
Final Exam logistics. Here is what I've found out about the final exam in MyMathLab (running from a week ago to 11:59pm five days after class tonight.
 MTH 209 Week 5 Final Exam logistics Here is what I've found out about the final exam in MyMathLab (running from a week ago to 11:59pm five days after class tonight.. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
MTH 209 Week 5 Final Exam logistics Here is what I've found out about the final exam in MyMathLab (running from a week ago to 11:59pm five days after class tonight.. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
6.4 Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities
 6.4 Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities 459 6.4 Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities In Section 6.3 we solved equations and inequalities involving exponential functions using one of two basic strategies.
6.4 Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities 459 6.4 Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities In Section 6.3 we solved equations and inequalities involving exponential functions using one of two basic strategies.
Week #16 - Differential Equations (Euler s Method) Section 11.3
 Week #16 - Differential Equations (Euler s Method) Section 11.3 From Calculus, Single Variable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is used
Week #16 - Differential Equations (Euler s Method) Section 11.3 From Calculus, Single Variable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is used
MATH 099 Name (please print) FINAL EXAM - FORM A Winter 2015 Instructor Score
 MATH 099 Name (please print) Winter 2015 Instructor Score Point-values for each problem are shown at the right in parentheses. PART I: SIMPLIFY AS MUCH AS POSSIBLE: 1. ( 16 c 12 ) 3 4 1. (2) 2. 52 m "7
MATH 099 Name (please print) Winter 2015 Instructor Score Point-values for each problem are shown at the right in parentheses. PART I: SIMPLIFY AS MUCH AS POSSIBLE: 1. ( 16 c 12 ) 3 4 1. (2) 2. 52 m "7
Section 3.3: Laws of Logarithms
 CHAPTER Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Section.: Laws of Logarithms Laws of Logarithms Laws of Logarithms Three Laws of Logarithms: Verifying Laws of Logarithms: 00 SECTION. Laws of Logarithms Example:
CHAPTER Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Section.: Laws of Logarithms Laws of Logarithms Laws of Logarithms Three Laws of Logarithms: Verifying Laws of Logarithms: 00 SECTION. Laws of Logarithms Example:
Pure Math 30: Explained!
 Pure Math 30: Eplained! www.puremath30.com 9 Logarithms Lesson PART I: Eponential Functions Eponential functions: These are functions where the variable is an eponent. The first type of eponential graph
Pure Math 30: Eplained! www.puremath30.com 9 Logarithms Lesson PART I: Eponential Functions Eponential functions: These are functions where the variable is an eponent. The first type of eponential graph
The SIR Disease Model Trajectories and MatLab
 The SIR Disease Model Trajectories and MatLab James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 17, 2013 Outline Reviewing the SIR
The SIR Disease Model Trajectories and MatLab James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 17, 2013 Outline Reviewing the SIR
PART 1 - CALCULATOR ACTIVE QUESTIONS
 Name: Date : IM 3 UNIT TEST Linear Functions Teacher: Mr. Santowski and Mr. Smith Score: PART 1 - CALCULATOR ACTIVE QUESTIONS SHOW ALL WORK AND WRITE ALL ANSWERS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED. Maximum marks will
Name: Date : IM 3 UNIT TEST Linear Functions Teacher: Mr. Santowski and Mr. Smith Score: PART 1 - CALCULATOR ACTIVE QUESTIONS SHOW ALL WORK AND WRITE ALL ANSWERS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED. Maximum marks will
5.6 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations
 SECTION 5.6 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations 305 5.6 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations PREPARING FOR THIS SECTION Before getting started, review the following: Solving Equations Using a Graphing
SECTION 5.6 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations 305 5.6 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations PREPARING FOR THIS SECTION Before getting started, review the following: Solving Equations Using a Graphing
Since the logs have the same base, I can set the arguments equal and solve: x 2 30 = x x 2 x 30 = 0
 LOGARITHMIC EQUATIONS (LOGS) 1 Type 1: The first type of logarithmic equation has two logs, each having the same base, set equal to each other, and you solve by setting the insides (the "arguments") equal
LOGARITHMIC EQUATIONS (LOGS) 1 Type 1: The first type of logarithmic equation has two logs, each having the same base, set equal to each other, and you solve by setting the insides (the "arguments") equal
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School
 Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
3.4 Properties of Logarithmic Functions
 SECTION 3.4 Properties of Logarithmic Functions 283 What you ll learn about Properties of Logarithms Change of Base Graphs of Logarithmic Functions with Base b Re-expressing Data... and why The applications
SECTION 3.4 Properties of Logarithmic Functions 283 What you ll learn about Properties of Logarithms Change of Base Graphs of Logarithmic Functions with Base b Re-expressing Data... and why The applications
Week #6 - Taylor Series, Derivatives and Graphs Section 10.1
 Week #6 - Taylor Series, Derivatives and Graphs Section 10.1 From Calculus, Single Variable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is used by
Week #6 - Taylor Series, Derivatives and Graphs Section 10.1 From Calculus, Single Variable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is used by
MAC Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I. Rev.S08
 MAC 1105 Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between linear and exponential growth. 2. Model data with
MAC 1105 Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between linear and exponential growth. 2. Model data with
MAC Module 8. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I. Learning Objectives. - Exponential Functions - Logarithmic Functions
 MAC 1105 Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between linear and exponential growth. 2. Model data with
MAC 1105 Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between linear and exponential growth. 2. Model data with
Definition of a Logarithm
 Chapter 17 Logarithms Sec. 1 Definition of a Logarithm In the last chapter we solved and graphed exponential equations. The strategy we used to solve those was to make the bases the same, set the exponents
Chapter 17 Logarithms Sec. 1 Definition of a Logarithm In the last chapter we solved and graphed exponential equations. The strategy we used to solve those was to make the bases the same, set the exponents
Section 5.1 Logarithms and Their Properties
 Section 5.1 Logarithms and Their Properties Definition. If x is a positive number, then 1. logx is the power of 10 that gives x. 2. lnx is the power of e that gives x. In other words, y = logx means that
Section 5.1 Logarithms and Their Properties Definition. If x is a positive number, then 1. logx is the power of 10 that gives x. 2. lnx is the power of e that gives x. In other words, y = logx means that
Objectives. Materials
 . Objectives Activity 6 To investigate the relationship between mass and volume To find the x value of a function, given the y value To find the y value of a function, given the x value To use technology
. Objectives Activity 6 To investigate the relationship between mass and volume To find the x value of a function, given the y value To find the y value of a function, given the x value To use technology
Topics from Algebra and Pre-Calculus. (Key contains solved problems)
 Topics from Algebra and Pre-Calculus (Key contains solved problems) Note: The purpose of this packet is to give you a review of basic skills. You are asked not to use the calculator, except on p. (8) and
Topics from Algebra and Pre-Calculus (Key contains solved problems) Note: The purpose of this packet is to give you a review of basic skills. You are asked not to use the calculator, except on p. (8) and
Unit #17 - Differential Equations Section 11.5
 Unit #17 - Differential Equations Section 11.5 Some material from Calculus, Single and MultiVariable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material
Unit #17 - Differential Equations Section 11.5 Some material from Calculus, Single and MultiVariable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material
Section 3.1 Exercises
 Section Exponential and Logistic Functions Chapter Exponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions Section Exponential and Logistic Functions Exploration The point (0, ) is common to all four graphs,
Section Exponential and Logistic Functions Chapter Exponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions Section Exponential and Logistic Functions Exploration The point (0, ) is common to all four graphs,
Chapter 3 Exponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter Exponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions Section. Exponential and Logistic Functions 75 Section. Exponential and Logistic Functions Exploration. The point (0, ) is common to all four graphs,
Chapter Exponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions Section. Exponential and Logistic Functions 75 Section. Exponential and Logistic Functions Exploration. The point (0, ) is common to all four graphs,
Week #5 - Related Rates, Linear Approximation, and Taylor Polynomials Section 4.6
 Week #5 - Related Rates, Linear Approximation, and Taylor Polynomials Section 4.6 From Calculus, Single Variable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This
Week #5 - Related Rates, Linear Approximation, and Taylor Polynomials Section 4.6 From Calculus, Single Variable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This
YOU CAN BACK SUBSTITUTE TO ANY OF THE PREVIOUS EQUATIONS
 The two methods we will use to solve systems are substitution and elimination. Substitution was covered in the last lesson and elimination is covered in this lesson. Method of Elimination: 1. multiply
The two methods we will use to solve systems are substitution and elimination. Substitution was covered in the last lesson and elimination is covered in this lesson. Method of Elimination: 1. multiply
Chapter 3 Exponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions
 ch0_p_6qxd /8/0 :5 PM Page Section Exponential and Logistic Functions Chapter Exponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions Section Exponential and Logistic Functions Exploration The point (0, ) is
ch0_p_6qxd /8/0 :5 PM Page Section Exponential and Logistic Functions Chapter Exponential, Logistic, and Logarithmic Functions Section Exponential and Logistic Functions Exploration The point (0, ) is
1 Wyner PreCalculus Fall 2013
 1 Wyner PreCalculus Fall 2013 CHAPTER ONE: FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Summary, Terms, and Objectives Most of calculus and precalculus is based on functions. A function is a process that takes one or more
1 Wyner PreCalculus Fall 2013 CHAPTER ONE: FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS Summary, Terms, and Objectives Most of calculus and precalculus is based on functions. A function is a process that takes one or more
4. Find x, log 4 32 = x. 5. ln e ln ln e. 8. log log log 3 243
 Session #5 Logarithms What is a log? it is the inverse of an exponential equation. When you take the inverse of an exponential equation with a base of e, you have a natural logarithm, written as ln. 1.
Session #5 Logarithms What is a log? it is the inverse of an exponential equation. When you take the inverse of an exponential equation with a base of e, you have a natural logarithm, written as ln. 1.
Sec. 4.2 Logarithmic Functions
 Sec. 4.2 Logarithmic Functions The Logarithmic Function with Base a has domain all positive real numbers and is defined by Where and is the inverse function of So and Logarithms are inverses of Exponential
Sec. 4.2 Logarithmic Functions The Logarithmic Function with Base a has domain all positive real numbers and is defined by Where and is the inverse function of So and Logarithms are inverses of Exponential
Practice Calculus Test without Trig
 Practice Calculus Test without Trig The problems here are similar to those on the practice test Slight changes have been made 1 What is the domain of the function f (x) = 3x 1? Express the answer in interval
Practice Calculus Test without Trig The problems here are similar to those on the practice test Slight changes have been made 1 What is the domain of the function f (x) = 3x 1? Express the answer in interval
Week #1 The Exponential and Logarithm Functions Section 1.3
 Week #1 The Exponential and Logarithm Functions Section 1.3 From Calculus, Single Variable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is used by
Week #1 The Exponential and Logarithm Functions Section 1.3 From Calculus, Single Variable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is used by
2.6 Logarithmic Functions. Inverse Functions. Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x?
 Inverse Functions Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 3 and g(x) = 3 x? Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x? Definition (One-to-One Function) A function f
Inverse Functions Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 3 and g(x) = 3 x? Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x? Definition (One-to-One Function) A function f
Chapter 3. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. 3.2 Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 Logarithmic Functions 1/23 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 4, 8, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 39, 42, 54, 56, 62, 68,
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 Logarithmic Functions 1/23 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 4, 8, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 39, 42, 54, 56, 62, 68,
Lesson 6b Rational Exponents & Radical Functions
 Lesson 6b Rational Exponents & Radical Functions In this lesson, we will continue our review of Properties of Exponents and will learn some new properties including those dealing with Rational and Radical
Lesson 6b Rational Exponents & Radical Functions In this lesson, we will continue our review of Properties of Exponents and will learn some new properties including those dealing with Rational and Radical
2. Laws of Exponents (1) b 0 1 (2) b x b y b x y (3) bx b y. b x y (4) b n (5) b r s b rs (6) n b b 1/n Example: Solve the equations (a) e 2x
 7.1 Derivative of Exponential Function 1. Exponential Functions Let b 0 and b 1. f x b x is called an exponential function. Domain of f x :, Range of f x : 0, Example: lim x e x x2 2. Laws of Exponents
7.1 Derivative of Exponential Function 1. Exponential Functions Let b 0 and b 1. f x b x is called an exponential function. Domain of f x :, Range of f x : 0, Example: lim x e x x2 2. Laws of Exponents
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.5 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Exponential
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4.5 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Exponential
Solutions to MAT 117 Test #3
 Solutions to MAT 7 Test #3 Because there are two versions of the test, solutions will only be given for Form C. Differences from the Form D version will be given. (The values for Form C appear above those
Solutions to MAT 7 Test #3 Because there are two versions of the test, solutions will only be given for Form C. Differences from the Form D version will be given. (The values for Form C appear above those
CHAPTER 1. Functions and Linear Models
 CHAPTER 1 Functions and Linear Models 1. Functions Definition. A function is a rule that associates each input with exactly one output. Example. (1) Millions of cameras made Cost in million $ 1 175 5 260
CHAPTER 1 Functions and Linear Models 1. Functions Definition. A function is a rule that associates each input with exactly one output. Example. (1) Millions of cameras made Cost in million $ 1 175 5 260
1.) Suppose the graph of f(x) looks like this (each tick mark denotes 1 unit). x y
 College Algebra Summer 2014 Exam File Exam #1 1.) Suppose the graph of f(x) looks like this (each tick mark denotes 1 unit). Graph g(x) = -0.5 f(x + 1) - 3 2.) Consider the following table of values. x
College Algebra Summer 2014 Exam File Exam #1 1.) Suppose the graph of f(x) looks like this (each tick mark denotes 1 unit). Graph g(x) = -0.5 f(x + 1) - 3 2.) Consider the following table of values. x
Logarithms Tutorial for Chemistry Students
 1 Logarithms 1.1 What is a logarithm? Logarithms Tutorial for Chemistry Students Logarithms are the mathematical function that is used to represent the number (y) to which a base integer (a) is raised
1 Logarithms 1.1 What is a logarithm? Logarithms Tutorial for Chemistry Students Logarithms are the mathematical function that is used to represent the number (y) to which a base integer (a) is raised
IM3 Unit 1 TEST - Working with Linear Relations SEP 2015
 Name: Date : IM 3 UNIT TEST Linear Functions Teacher: Mr. Santowski and Ms. Aschenbrenner Score: PART 1 - CALCULATOR ACTIVE QUESTIONS Maximum marks will be given for correct answers. Where an answer is
Name: Date : IM 3 UNIT TEST Linear Functions Teacher: Mr. Santowski and Ms. Aschenbrenner Score: PART 1 - CALCULATOR ACTIVE QUESTIONS Maximum marks will be given for correct answers. Where an answer is
Pre-Calculus Notes from Week 6
 1-105 Pre-Calculus Notes from Week 6 Logarithmic Functions: Let a > 0, a 1 be a given base (as in, base of an exponential function), and let x be any positive number. By our properties of exponential functions,
1-105 Pre-Calculus Notes from Week 6 Logarithmic Functions: Let a > 0, a 1 be a given base (as in, base of an exponential function), and let x be any positive number. By our properties of exponential functions,
y z ). Write all solutions using only positive
 1. a) Graph the equation x y =. b) What is the x-intercept? What is the y-intercept? d) What is the slope of this line?. a) Find the slope of the line joining the points and ( b) Find the equation of this
1. a) Graph the equation x y =. b) What is the x-intercept? What is the y-intercept? d) What is the slope of this line?. a) Find the slope of the line joining the points and ( b) Find the equation of this
3.5. Equation Solving and Modeling. Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc.
 3.5 Equation Solving and Modeling Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc. What you ll learn about Solving Exponential Equations Solving Logarithmic Equations Orders of Magnitude and Logarithmic Models Newton s Law
3.5 Equation Solving and Modeling Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc. What you ll learn about Solving Exponential Equations Solving Logarithmic Equations Orders of Magnitude and Logarithmic Models Newton s Law
Definition of a Logarithm
 Chapter 17 Logarithms Sec. 1 Definition of a Logarithm In the last chapter we solved and graphed exponential equations. The strategy we used to solve those was to make the bases the same, set the exponents
Chapter 17 Logarithms Sec. 1 Definition of a Logarithm In the last chapter we solved and graphed exponential equations. The strategy we used to solve those was to make the bases the same, set the exponents
Solve by equating exponents
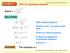 EXAMPLE 1 x Solve 4 = 1 Solve by equating exponents x 3 SOLUTION x 1 4 = x x 3 1 ( ) = ( ) x x + 3 = x = x + 3 x = 1 x 3 Write original equation. Rewrite 4 and base. 1 as powers with Power of a power property
EXAMPLE 1 x Solve 4 = 1 Solve by equating exponents x 3 SOLUTION x 1 4 = x x 3 1 ( ) = ( ) x x + 3 = x = x + 3 x = 1 x 3 Write original equation. Rewrite 4 and base. 1 as powers with Power of a power property
Logarithmic and Exponential Equations and Change-of-Base
 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations and Change-of-Base MATH 101 College Algebra J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2012 Objectives In this lesson we will learn to solve exponential equations
Logarithmic and Exponential Equations and Change-of-Base MATH 101 College Algebra J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2012 Objectives In this lesson we will learn to solve exponential equations
Algebra II. Slide 1 / 261. Slide 2 / 261. Slide 3 / 261. Linear, Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 261 Algebra II Slide 2 / 261 Linear, Exponential and 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 261 Linear Functions Exponential Functions Properties
Slide 1 / 261 Algebra II Slide 2 / 261 Linear, Exponential and 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 261 Linear Functions Exponential Functions Properties
AP Calculus Summer Prep
 AP Calculus Summer Prep Topics from Algebra and Pre-Calculus (Solutions are on the Answer Key on the Last Pages) The purpose of this packet is to give you a review of basic skills. You are asked to have
AP Calculus Summer Prep Topics from Algebra and Pre-Calculus (Solutions are on the Answer Key on the Last Pages) The purpose of this packet is to give you a review of basic skills. You are asked to have
6.3 logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
 SECTION 6.3 logarithmic functions 4 9 1 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, you will: Convert from logarithmic to exponential form. Convert from exponential to logarithmic form. Evaluate logarithms. Use
SECTION 6.3 logarithmic functions 4 9 1 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, you will: Convert from logarithmic to exponential form. Convert from exponential to logarithmic form. Evaluate logarithms. Use
Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections
 Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections 4.1 4.5 Due Dates for Reading Assignments Note: There will be a very short online reading quiz (WebWork) on each reading assignment due one hour before class on
Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections 4.1 4.5 Due Dates for Reading Assignments Note: There will be a very short online reading quiz (WebWork) on each reading assignment due one hour before class on
Objectives. Materials
 . Objectives Activity 13 To graphically represent and analyze climate data To use linear regressions to understand the relationship between temperatures as measured in the Fahrenheit and Celsius scale
. Objectives Activity 13 To graphically represent and analyze climate data To use linear regressions to understand the relationship between temperatures as measured in the Fahrenheit and Celsius scale
Section 4.2 Logarithmic Functions & Applications
 34 Section 4.2 Logarithmic Functions & Applications Recall that exponential functions are one-to-one since every horizontal line passes through at most one point on the graph of y = b x. So, an exponential
34 Section 4.2 Logarithmic Functions & Applications Recall that exponential functions are one-to-one since every horizontal line passes through at most one point on the graph of y = b x. So, an exponential
Logarithmic Functions
 Name Student ID Number Group Name Group Members Logarithmic Functions 1. Solve the equations below. xx = xx = 5. Were you able solve both equations above? If so, was one of the equations easier to solve
Name Student ID Number Group Name Group Members Logarithmic Functions 1. Solve the equations below. xx = xx = 5. Were you able solve both equations above? If so, was one of the equations easier to solve
Math 148. Polynomial Graphs
 Math 148 Lab 1 Polynomial Graphs Due: Monday Wednesday, April April 10 5 Directions: Work out each problem on a separate sheet of paper, and write your answers on the answer sheet provided. Submit the
Math 148 Lab 1 Polynomial Graphs Due: Monday Wednesday, April April 10 5 Directions: Work out each problem on a separate sheet of paper, and write your answers on the answer sheet provided. Submit the
Using a graphic display calculator
 12 Using a graphic display calculator CHAPTER OBJECTIVES: This chapter shows you how to use your graphic display calculator (GDC) to solve the different types of problems that you will meet in your course.
12 Using a graphic display calculator CHAPTER OBJECTIVES: This chapter shows you how to use your graphic display calculator (GDC) to solve the different types of problems that you will meet in your course.
1.1 Checkpoint GCF Checkpoint GCF 2 1. Circle the smaller number in each pair. Name the GCF of the following:
 39 0 . Checkpoint GCF Name the GCF of the following:.. 3.. + 9 + 0 + 0 6 y + 5ab + 8 5. 3 3 y 5y + 7 y 6. 3 3 y 8 y + y.. Checkpoint GCF. Circle the smaller number in each pair. 5, 0 8, 0,,,, 3 0 3 5,,,
39 0 . Checkpoint GCF Name the GCF of the following:.. 3.. + 9 + 0 + 0 6 y + 5ab + 8 5. 3 3 y 5y + 7 y 6. 3 3 y 8 y + y.. Checkpoint GCF. Circle the smaller number in each pair. 5, 0 8, 0,,,, 3 0 3 5,,,
Logarithmic Properties
 Logarithmic Properties By: OpenStaxCollege The ph of hydrochloric acid is tested with litmus paper. (credit: David Berardan) In chemistry, ph is used as a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance.
Logarithmic Properties By: OpenStaxCollege The ph of hydrochloric acid is tested with litmus paper. (credit: David Berardan) In chemistry, ph is used as a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance.
Regressions of Olympic Proportions
 About the Lesson In this activity, students use the Manual-Fit and Linear Regression commands to find lines of best fit to model data from the Olympic Games. As a result, students will: Develop and evaluate
About the Lesson In this activity, students use the Manual-Fit and Linear Regression commands to find lines of best fit to model data from the Olympic Games. As a result, students will: Develop and evaluate
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 1.4. ALGEBRA 4 (Logarithms) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 1.4 ALGEBRA 4 (Logarithms) by A.J.Hobson 1.4.1 Common logarithms 1.4.2 Logarithms in general 1.4.3 Useful Results 1.4.4 Properties of logarithms 1.4.5 Natural logarithms 1.4.6
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 1.4 ALGEBRA 4 (Logarithms) by A.J.Hobson 1.4.1 Common logarithms 1.4.2 Logarithms in general 1.4.3 Useful Results 1.4.4 Properties of logarithms 1.4.5 Natural logarithms 1.4.6
1. Algebra and Functions
 1. Algebra and Functions 1.1.1 Equations and Inequalities 1.1.2 The Quadratic Formula 1.1.3 Exponentials and Logarithms 1.2 Introduction to Functions 1.3 Domain and Range 1.4.1 Graphing Functions 1.4.2
1. Algebra and Functions 1.1.1 Equations and Inequalities 1.1.2 The Quadratic Formula 1.1.3 Exponentials and Logarithms 1.2 Introduction to Functions 1.3 Domain and Range 1.4.1 Graphing Functions 1.4.2
Using Exploration and Technology to Teach Graph Translations
 Using Eploration and Technology to Teach Graph Translations Rutgers Precalculus Conference March 16, 2018 Frank Forte Raritan Valley Community College Opening Introduction Motivation learning the alphabet
Using Eploration and Technology to Teach Graph Translations Rutgers Precalculus Conference March 16, 2018 Frank Forte Raritan Valley Community College Opening Introduction Motivation learning the alphabet
AdvAlg9.7LogarithmsToBasesOtherThan10.notebook. March 08, 2018
 AdvAlg9.7LogarithmsToBasesOtherThan10.notebook In order to isolate a variable within a logarithm of an equation, you need to re write the equation as the equivalent exponential equation. In order to isolate
AdvAlg9.7LogarithmsToBasesOtherThan10.notebook In order to isolate a variable within a logarithm of an equation, you need to re write the equation as the equivalent exponential equation. In order to isolate
Pre-Calculus Module 4
 Pre-Calculus Module 4 4 th Nine Weeks Table of Contents Precalculus Module 4 Unit 9 Rational Functions Rational Functions with Removable Discontinuities (1 5) End Behavior of Rational Functions (6) Rational
Pre-Calculus Module 4 4 th Nine Weeks Table of Contents Precalculus Module 4 Unit 9 Rational Functions Rational Functions with Removable Discontinuities (1 5) End Behavior of Rational Functions (6) Rational
