5.6 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations
|
|
|
- Elisabeth Wade
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SECTION 5.6 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations Logarithmic and Exponential Equations PREPARING FOR THIS SECTION Before getting started, review the following: Solving Equations Using a Graphing Utility (Appendix B, Section B.4, pp. B6 B7) Now Work the Are You Prepared? problems on page 309. OBJECTIVES 1 Solve Logarithmic Equations (p. 305) Solve Exponential Equations (p. 307) Solving Quadratic Equations (Appendix A, Section A.6, pp. A47 A51) 3 Solve Logarithmic and Exponential Equations Using a Graphing Utility (p. 308) 1 Solve Logarithmic Equations In Section 5.4 we solved logarithmic equations by changing a logarithmic expression to an exponential expression. That is, we used the definition of a logarithm: y = log a x is equivalent to x = a y a 7 0, a Z 1 For example, to solve the equation log 11 - x = 3, we write the logarithmic equation as an equivalent exponential equation 1 - x = 3 and solve for x. log 11 - x = x = 3 - x = 7 x =- 7 Change to an exponential statement. Simplify. Solve. You should check this solution for yourself. For most logarithmic equations, some manipulation of the equation (usually using properties of logarithms) is required to obtain a solution. Also, to avoid extraneous solutions with logarithmic equations, we determine the domain of the variable first. We begin with an example of a logarithmic equation that requires using the fact that a logarithmic function is a one-to-one function: If log a M = log a N, then M = N M, N, and a are positive and a Z 1. EXAMPLE 1 Solving a Logarithmic Equation Solve: log 5 x = log 5 9 The domain of the variable in this equation is x 7 0. Because each logarithm is to the same base, 5, we can obtain an exact solution as follows: log 5 x = log 5 9 log r log a M = log a M r 5 x = log 5 9 x = 9 If log a M = log a N, then M = N. x = 3 or x = - 3 Recall that the domain of the variable is x 7 0. Therefore, - 3 is extraneous and we discard it.
2 306 CHAPTER 5 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Check: log 5 3 log 5 9 log r log a M = log a M r 5 3 log 5 9 log 5 9 = log 5 9 The solution set is 536. Now Work PROBLEM 13 Often we need to use one or more properties of logarithms to rewrite the equation as a single logarithm. In the next example we employ the log of a product property to solve a logarithmic equation. EXAMPLE WARNING A negative solution is not automatically extraneous. You must determine whether the potential solution causes the argument of any logarithmic expression in the equation to be negative. Solving a Logarithmic Equation Solve: log 5 1x log 5 1x + = 1 The domain of the variable requires that x and x + 7 0, so x 7-6 and x 7 -. This means any solution must satisfy x 7 -. To obtain an exact solution, we need to express the left side as a single logarithm. Then we will change the equation to an equivalent exponential equation. log 5 1x log 5 1x + = 1 log 5 31x + 61x + 4 = 1 1x + 61x + = 5 1 = 5 x + 8x + 1 = 5 x + 8x + 7 = 0 1x + 71x + 1 = 0 x = - 7 or x = - 1 Change to an exponential statement. Simplify. Place the quadratic equation in standard form. Factor. Zero-Product Property Only x = - 1 satisfies the restriction that x 7 -, so x = - 7 is extraneous. The solution set is 5-16, which you should check. Now Work PROBLEM 1 log a M + log a N = log a (MN) EXAMPLE 3 Solving a Logarithmic Equation Solve: ln x = ln1x ln1x - 4 The domain of the variable requires that x 7 0, x , and x As a result, the domain of the variable here is x 7 4. We begin the solution using the log of a difference property. ln x = ln1x ln1x - 4 x + 6 ln x = lna x - 4 b In M - ln N = lna M N b x = x + 6 x - 4 If ln M = ln N, then M = N. x1x - 4 = x + 6 Multiply both sides by x 4. x - 4x = x + 6 Simplify. x - 5x - 6 = 0 Place the quadratic equation in standard form. 1x - 61x + 1 = 0 Factor. x = 6 or x = - 1 Zero-Product Property Since the domain of the variable is x 7 4, we discard - 1 as extraneous. The solution set is {6}, which you should check.
3 SECTION 5.6 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations 307 WARNING In using properties of logarithms to solve logarithmic equations, avoid using the property log a x r = r log a x, when r is even. The reason can be seen in this example: Solve: log 3 x = 4 : The domain of the variable x is all real numbers except 0. (a) log 3 x = 4 (b) log 3 x = 4 log a x r = r log a x x = 3 4 = 81 Change to exponential form. log 3 x = 4 Domain of variable is x 7 0. x =- 9 or x = 9 log 3 x = x = 9 Both 9 and 9 are solutions of log 3 x 4 (as you can verify). The solution in part (b) does not find the solution 9 because the domain of the variable was further restricted due to the application of the property log a x r = r log a x. Now Work PROBLEM 31 Solve Exponential Equations In Sections 5.3 and 5.4, we solved exponential equations algebraically by expressing each side of the equation using the same base. That is, we used the one-to-one property of the exponential function: If a u = a v, then u = v a 7 0, a Z 1 For example, to solve the exponential equation 4 x + 1 = 16, notice that 16 = 4 and apply the property above to obtain x + 1 =, from which we find x = 1. For most exponential equations, we cannot express each side of the equation using the same base. In such cases, algebraic techniques can sometimes be used to obtain exact solutions. EXAMPLE 4 Solving Exponential Equations Solve: (a) x = 5 (b) 8 # 3 x = 5 (a) Since 5 cannot be written as an integer power of ( = 4 and 3 = 8), write the exponential equation as the equivalent logarithmic equation. Alternatively, we can solve the equation x = 5 by taking the natural logarithm (or common logarithm) of each side. Taking the natural logarithm, The solution set is e ln 5. ln f x = 5 x = log 5 = ln 5 ln c Change-of-Base Formula (10), Section 5.5 x = 5 ln x = ln 5 x ln = ln 5 x = ln 5 ln L.3 If M = N, then ln M = ln N. In M r = r ln M Exact solution Approximate solution (b) 8 # 3 x = 5 3 x = 5 8 Solve for 3 x.
4 308 CHAPTER 5 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 5 x = log 3 a 5 lna 8 b = 8 b ln 3 L Exact solution Approximate solution lna 5 8 b The solution set is L ln 3 M. Now Work PROBLEM 35 EXAMPLE 5 EXAMPLE 6 Solving an Exponential Equation Solve: 5 x - = 3 3x + Because the bases are different, we first apply property (7), Section 5.5 (take the natural logarithm of each side), and then use a property of logarithms. The result is an equation in x that we can solve. 5 x - = 3 3x + ln 5 x - = ln 3 3x + 1x - ln 5 = 13x + ln 3 1ln 5x - ln 5 = 13 ln 3x + ln 3 1ln 5x - 13 ln 3x = ln 3 + ln 5 1ln 5-3 ln 3x = 1ln 3 + ln 5 1ln 3 + ln 5 x = ln 5-3 ln 3 L The solution set is 1ln 3 + ln 5 e ln 5-3 ln 3 f. Now Work PROBLEM 45 If M = N, ln M = ln N. ln M r = r ln M Distribute. Place terms involving x on the left. Factor. Exact solution Approximate solution Solving an Exponential Equation That Is Quadratic in Form Solve: 4 x - x - 1 = 0 We note that 4 x = 1 x = (x) = 1 x, so the equation is quadratic in form, and we can rewrite it as 1 x - x - 1 = 0 Now we can factor as usual. 1 x - 41 x + 3 = 0 x - 4 = 0 or x + 3 = 0 x = 4 x = - 3 Let u = x ; then u - u - 1 = 0. (u - 4)(u + 3) = 0 u - 4 = 0 or u + 3 = 0 u = x = 4 u = x = - 3 The equation on the left has the solution x =, since x = 4 = ; the equation on the right has no solution, since x 7 0 for all x.the only solution is.the solution set is 56. Now Work PROBLEM 53 3 Solve Logarithmic and Exponential Equations Using a Graphing Utility The algebraic techniques introduced in this section to obtain exact solutions apply only to certain types of logarithmic and exponential equations. s for other types are usually studied in calculus, using numerical methods. For such types, we can use a graphing utility to approximate the solution.
5 SECTION 5.6 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations 309 Figure 40 4 EXAMPLE 7 Y 1 x e x Y Solving Equations Using a Graphing Utility Solve: x + e x = Express the solution(s) rounded to two decimal places. The solution is found by graphing Y 1 = x + and Y =. Since Y 1 is an increasing function (do you know why?), there is only one point of intersection for Y 1 and Y. Figure 40 shows the graphs of Y 1 and Y. Using the INTERSECT command, the solution is 0.44 rounded to two decimal places. e x Now Work PROBLEM Assess Your Understanding Are You Prepared? Answers are given at the end of these exercises. If you get a wrong answer, read the pages listed in red. 1. Solve x - 7x - 30 = 0. (pp. A47 A51) 3. Approximate the solution(s) to x 3 = x - 5 using a graphing. Solve 1x x = 0. (pp. A47 A51) utility. (pp. B6 B7) 4. Approximate the solution(s) to x 3 - x + = 0 using a graphing utility. (pp. B6 B7) Skill Building In Problems 5 3, solve each logarithmic equation. Express irrational solutions in exact form and as a decimal rounded to three decimal places. 5. log 4 x = 6. log 1x + 6 = 1 7. log 15x = 4 8. log 3 13x - 1 = 9. log 4 1x + = log log 5 1x + 3 = log log 4 x = log log x = - log 7 log 3 x = log log 5 x = 3 log log 1x log 4 = log 3 1x log 3 9 = 17. log x + log1x + 15 = 18. log x + log 1x - 1 = 19. log1x + 1 = 1 + log1x - 0. log1x - log1x - 3 = 1 1. log 1x log 1x + 8 = 1. log 6 1x log 6 1x + 3 = 1 3. log 8 1x + 6 = 1 - log 8 1x log 5 1x + 3 = 1 - log 5 1x ln x + ln1x + = 4 6. ln1x ln x = 7. log 3 1x log 3 1x + 4 = 8. log 1x log 1x + 7 = 3 9. log 30. log 4 1x 1>3 1x + x - log 1>3 1x - x = log 4 1x + 3 = log a 1x log a 1x + 6 = log a 1x - - log a 1x log a x + log a 1x - = log a 1x + 4 In Problems 33 60, solve each exponential equation. Express irrational solutions in exact form and as a decimal rounded to three decimal places. 33. x - 5 = x = x = x = x = x = x = x = a x a 3 x x = 4 x x + 1 = x 3 b = 5 x 5 b = x x = x x = 1.7 x p 1 - x = e x 48. e x + 3 = p x
6 310 CHAPTER 5 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 49. x + x - 1 = x + 3 x - = x + 3 x = 0 5. x + x = x - 8 # x - 6 # x + 4 x = 0 9 x - 3 x = 0 5 x = x = x - 14 # 3-4 x - 10 # 4-3 # 4 x + 4 # x + 8 = 0 # 49 x + 11 # 7 x + 5 = 0 x = 3 x = 5 In Problems 61 74, use a graphing utility to solve each equation. Express your answer rounded to two decimal places. 61. log 5 1x log 4 1x - = 1 6. log 1x log 6 1x + = 63. e x = - x 64. e x = x e x = x 66. e x = x ln x = - x 68. ln1x = - x ln x = x ln x = - x 71. e x + ln x = 4 7. e x - ln x = e - x = ln x 74. e - x = - ln x Mixed Practice In Problems 75 86, solve each equation. Express irrational solutions in exact form and as a decimal rounded to three decimal places. 75. log 1x log 4 x = 1 [Hint: Change log 4 x to base.] 76. log 13x + - log 4 x = log 16 x + log 4 x + log x = log log x log x 9 x + 3 log 3 x = 14 A 3 B - x = x = e - x e x + = 1 [Hint: Multiply each side by e x.] e x + 8. = e - x e x - e - x = e x = log 5 x + log 3 x = 1 [Hint: Use the Change-of-Base Formula.] e - x 86. log x + log 6 x = f1x = log 1x + 3 and g1x = log 13x + 1. (a) Solve f1x = 3. What point is on the graph of f? (b) Solve g1x = 4. What point is on the graph of g? (c) Solve f1x = g1x. Do the graphs of f and g intersect? If so, where? (d) Solve 1f + (e) Solve 1f - g1x = 7. g1x =. 88. f1x = log 3 1x + 5 and g1x = log 3 1x - 1. (a) Solve f1x =. What point is on the graph of f? (b) Solve g1x = 3. What point is on the graph of g? (c) Solve f1x = g1x. Do the graphs of f and g intersect? If so, where? (d) Solve 1f + (e) Solve 1f - g1x = 3. g1x =. 89. (a) If f1x = 3 x + 1 and g1x = x +, graph f and g on the same (b) Find the point(s) of intersection of the graphs of f and g by solving f1x = g1x. Round answers to three decimal places. Label any intersection points on the graph drawn in part (a). (c) Based on the graph, solve f1x 7 g1x. 90. (a) If f1x = 5 x - 1 and g1x = x + 1, graph f and g on the same (b) Find the point(s) of intersection of the graphs of f and g by solving f1x = g1x. Label any intersection points (c) Based on the graph, solve f1x 7 g1x. 91. (a) Graph f1x = 3 x and g1x = 10 on the same (b) Shade the region bounded by the y-axis, f1x = 3 x, and g1x = 10 (c) Solve f1x = g1x and label the point of intersection 9. (a) Graph f1x = x and g1x = 1 on the same (b) Shade the region bounded by the y-axis, f1x = x, and g1x = 1 (c) Solve f1x = g1x and label the point of intersection 93. (a) Graph f1x = x + 1 and g1x = - x + on the same (b) Shade the region bounded by the y-axis, f1x = x + 1, and g1x = - x + on the graph draw in part (a). (c) Solve f1x = g1x and label the point of intersection 94. (a) Graph f1x = 3 - x + 1 and g1x = 3 x - on the same (b) Shade the region bounded by the y-axis, f1x = 3 - x + 1, and g1x = 3 x - on the graph draw in part (a). (c) Solve f1x = g1x and label the point of intersection 95. (a) Graph f1x = x - 4. (b) Find the zero of f. (c) Based on the graph, solve f1x (a) Graph g1x = 3 x - 9. (b) Find the zero of g. (c) Based on the graph, solve g1x 7 0.
Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Skill 6a: Graphs of Exponential Functions Skill 6b: Solving Exponential Equations (not requiring logarithms) Skill 6c: Definition of Logarithms Skill 6d: Graphs
Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Skill 6a: Graphs of Exponential Functions Skill 6b: Solving Exponential Equations (not requiring logarithms) Skill 6c: Definition of Logarithms Skill 6d: Graphs
Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Skill 6a: Graphs of Exponential Functions Skill 6b: Solving Exponential Equations (not requiring logarithms) Skill 6c: Definition of Logarithms Skill 6d: Graphs
Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Skill 6a: Graphs of Exponential Functions Skill 6b: Solving Exponential Equations (not requiring logarithms) Skill 6c: Definition of Logarithms Skill 6d: Graphs
Intermediate Algebra Chapter 12 Review
 Intermediate Algebra Chapter 1 Review Set up a Table of Coordinates and graph the given functions. Find the y-intercept. Label at least three points on the graph. Your graph must have the correct shape.
Intermediate Algebra Chapter 1 Review Set up a Table of Coordinates and graph the given functions. Find the y-intercept. Label at least three points on the graph. Your graph must have the correct shape.
Example. Determine the inverse of the given function (if it exists). f(x) = 3
 Example. Determine the inverse of the given function (if it exists). f(x) = g(x) = p x + x We know want to look at two di erent types of functions, called logarithmic functions and exponential functions.
Example. Determine the inverse of the given function (if it exists). f(x) = g(x) = p x + x We know want to look at two di erent types of functions, called logarithmic functions and exponential functions.
6.4 Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities
 6.4 Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities 459 6.4 Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities In Section 6.3 we solved equations and inequalities involving exponential functions using one of two basic strategies.
6.4 Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities 459 6.4 Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities In Section 6.3 we solved equations and inequalities involving exponential functions using one of two basic strategies.
f(x) = 2x + 5 3x 1. f 1 (x) = x + 5 3x 2. f(x) = 102x x
 1. Let f(x) = x 3 + 7x 2 x 2. Use the fact that f( 1) = 0 to factor f completely. (2x-1)(3x+2)(x+1). 2. Find x if log 2 x = 5. x = 1/32 3. Find the vertex of the parabola given by f(x) = 2x 2 + 3x 4. (Give
1. Let f(x) = x 3 + 7x 2 x 2. Use the fact that f( 1) = 0 to factor f completely. (2x-1)(3x+2)(x+1). 2. Find x if log 2 x = 5. x = 1/32 3. Find the vertex of the parabola given by f(x) = 2x 2 + 3x 4. (Give
ln(9 4x 5 = ln(75) (4x 5) ln(9) = ln(75) 4x 5 = ln(75) ln(9) ln(75) ln(9) = 1. You don t have to simplify the exact e x + 4e x
 Math 11. Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Fall 016 Instructions. Work in groups of 3 to solve the following problems. Turn them in at the end of class for credit. Names. 1. Find the (a) exact solution
Math 11. Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Fall 016 Instructions. Work in groups of 3 to solve the following problems. Turn them in at the end of class for credit. Names. 1. Find the (a) exact solution
Composition of Functions
 Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Composite and Inverse Functions Composition of Functions The composite function f g, the composition of f and g, is defined as (f g)(x) = f(g(x)). Recall that a function
Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Composite and Inverse Functions Composition of Functions The composite function f g, the composition of f and g, is defined as (f g)(x) = f(g(x)). Recall that a function
A factor times a logarithm can be re-written as the argument of the logarithm raised to the power of that factor
 In this section we will be working with Properties of Logarithms in an attempt to take equations with more than one logarithm and condense them down into just a single logarithm. Properties of Logarithms:
In this section we will be working with Properties of Logarithms in an attempt to take equations with more than one logarithm and condense them down into just a single logarithm. Properties of Logarithms:
Since the logs have the same base, I can set the arguments equal and solve: x 2 30 = x x 2 x 30 = 0
 LOGARITHMIC EQUATIONS (LOGS) 1 Type 1: The first type of logarithmic equation has two logs, each having the same base, set equal to each other, and you solve by setting the insides (the "arguments") equal
LOGARITHMIC EQUATIONS (LOGS) 1 Type 1: The first type of logarithmic equation has two logs, each having the same base, set equal to each other, and you solve by setting the insides (the "arguments") equal
Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections
 Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections 4.1 4.5 Due Dates for Reading Assignments Note: There will be a very short online reading quiz (WebWork) on each reading assignment due one hour before class on
Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections 4.1 4.5 Due Dates for Reading Assignments Note: There will be a very short online reading quiz (WebWork) on each reading assignment due one hour before class on
4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
 590 Chapter 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions In this section, you will: Learning Objectives 4.4.1 Identify the domain of a logarithmic function. 4.4.2 Graph logarithmic
590 Chapter 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions In this section, you will: Learning Objectives 4.4.1 Identify the domain of a logarithmic function. 4.4.2 Graph logarithmic
Section 6.1: Composite Functions
 Section 6.1: Composite Functions Def: Given two function f and g, the composite function, which we denote by f g and read as f composed with g, is defined by (f g)(x) = f(g(x)). In other words, the function
Section 6.1: Composite Functions Def: Given two function f and g, the composite function, which we denote by f g and read as f composed with g, is defined by (f g)(x) = f(g(x)). In other words, the function
Day 6: 6.4 Solving Polynomial Equations Warm Up: Factor. 1. x 2-2x x 2-9x x 2 + 6x + 5
 Day 6: 6.4 Solving Polynomial Equations Warm Up: Factor. 1. x 2-2x - 15 2. x 2-9x + 14 3. x 2 + 6x + 5 Solving Equations by Factoring Recall the factoring pattern: Difference of Squares:...... Note: There
Day 6: 6.4 Solving Polynomial Equations Warm Up: Factor. 1. x 2-2x - 15 2. x 2-9x + 14 3. x 2 + 6x + 5 Solving Equations by Factoring Recall the factoring pattern: Difference of Squares:...... Note: There
Exponential and. Logarithmic Functions. Exponential Functions. Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter Five Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Exponential Functions Logarithmic Functions Properties of Logarithms Exponential Equations Exponential Situations Logarithmic Equations Exponential Functions
Chapter Five Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Exponential Functions Logarithmic Functions Properties of Logarithms Exponential Equations Exponential Situations Logarithmic Equations Exponential Functions
Use a graphing utility to approximate the real solutions, if any, of the equation rounded to two decimal places. 4) x3-6x + 3 = 0 (-5,5) 4)
 Advanced College Prep Pre-Calculus Midyear Exam Review Name Date Per List the intercepts for the graph of the equation. 1) x2 + y - 81 = 0 1) Graph the equation by plotting points. 2) y = -x2 + 9 2) List
Advanced College Prep Pre-Calculus Midyear Exam Review Name Date Per List the intercepts for the graph of the equation. 1) x2 + y - 81 = 0 1) Graph the equation by plotting points. 2) y = -x2 + 9 2) List
Systems of Nonlinear Equations and Inequalities: Two Variables
 Systems of Nonlinear Equations and Inequalities: Two Variables By: OpenStaxCollege Halley s Comet ([link]) orbits the sun about once every 75 years. Its path can be considered to be a very elongated ellipse.
Systems of Nonlinear Equations and Inequalities: Two Variables By: OpenStaxCollege Halley s Comet ([link]) orbits the sun about once every 75 years. Its path can be considered to be a very elongated ellipse.
Objectives. Use the number e to write and graph exponential functions representing realworld
 Objectives Use the number e to write and graph exponential functions representing realworld situations. Solve equations and problems involving e or natural logarithms. natural logarithm Vocabulary natural
Objectives Use the number e to write and graph exponential functions representing realworld situations. Solve equations and problems involving e or natural logarithms. natural logarithm Vocabulary natural
Exponential and Logarithmic Equations and Models. College Algebra
 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations and Models College Algebra Product Rule for Logarithms The product rule for logarithms can be used to simplify a logarithm of a product by rewriting it as a sum of
Exponential and Logarithmic Equations and Models College Algebra Product Rule for Logarithms The product rule for logarithms can be used to simplify a logarithm of a product by rewriting it as a sum of
d. What are the steps for finding the y intercepts algebraically?(hint: what is equal to 0?)
 st Semester Pre Calculus Exam Review You will not receive hints on your exam. Make certain you know how to answer each of the following questions. This is a test grade. Your WORK and EXPLANATIONS are graded
st Semester Pre Calculus Exam Review You will not receive hints on your exam. Make certain you know how to answer each of the following questions. This is a test grade. Your WORK and EXPLANATIONS are graded
Reference Material /Formulas for Pre-Calculus CP/ H Summer Packet
 Reference Material /Formulas for Pre-Calculus CP/ H Summer Packet Week # 1 Order of Operations Step 1 Evaluate expressions inside grouping symbols. Order of Step 2 Evaluate all powers. Operations Step
Reference Material /Formulas for Pre-Calculus CP/ H Summer Packet Week # 1 Order of Operations Step 1 Evaluate expressions inside grouping symbols. Order of Step 2 Evaluate all powers. Operations Step
The final is cumulative, but with more emphasis on chapters 3 and 4. There will be two parts.
 Math 141 Review for Final The final is cumulative, but with more emphasis on chapters 3 and 4. There will be two parts. Part 1 (no calculator) graphing (polynomial, rational, linear, exponential, and logarithmic
Math 141 Review for Final The final is cumulative, but with more emphasis on chapters 3 and 4. There will be two parts. Part 1 (no calculator) graphing (polynomial, rational, linear, exponential, and logarithmic
Homework 3. (33-40) The graph of an exponential function is given. Match each graph to one of the following functions.
 Homework Section 4. (-40) The graph of an exponential function is given. Match each graph to one of the following functions. (a)y = x (b)y = x (c)y = x (d)y = x (e)y = x (f)y = x (g)y = x (h)y = x (46,
Homework Section 4. (-40) The graph of an exponential function is given. Match each graph to one of the following functions. (a)y = x (b)y = x (c)y = x (d)y = x (e)y = x (f)y = x (g)y = x (h)y = x (46,
INTERNET MAT 117. Solution for the Review Problems. (1) Let us consider the circle with equation. x 2 + 2x + y 2 + 3y = 3 4. (x + 1) 2 + (y + 3 2
 INTERNET MAT 117 Solution for the Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (i) Group
INTERNET MAT 117 Solution for the Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (i) Group
4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.1 Exponential Functions Definition 4.1 If a > 0 and a 1, then the exponential function with base a is given by fx) = a x. Examples: fx) = x, gx) = 10 x, hx) =
4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.1 Exponential Functions Definition 4.1 If a > 0 and a 1, then the exponential function with base a is given by fx) = a x. Examples: fx) = x, gx) = 10 x, hx) =
PLC Papers. Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: Algebra and proof 2 Grade 8 Objective: Use algebra to construct proofs Question 1 a) If n is a positive integer explain why the expression 2n + 1 is always an odd number. b) Use
PLC Papers Created For: Algebra and proof 2 Grade 8 Objective: Use algebra to construct proofs Question 1 a) If n is a positive integer explain why the expression 2n + 1 is always an odd number. b) Use
Spring 06/MAT 140/Worksheet 1 Name: Show all your work.
 Spring 06/MAT 140/Worksheet 1 Name: Show all your work. 1. (4pts) Write two examples of each kind of number: natural integer rational irrational 2. (12pts) Simplify: ( a) 3 4 2 + 4 2 ) = 3 b) 3 20 7 15
Spring 06/MAT 140/Worksheet 1 Name: Show all your work. 1. (4pts) Write two examples of each kind of number: natural integer rational irrational 2. (12pts) Simplify: ( a) 3 4 2 + 4 2 ) = 3 b) 3 20 7 15
INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems. (1) Let us consider the circle with equation. (b) Find the center and the radius of the circle given above.
 INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (b) Find the center and
INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (b) Find the center and
DISCUSS DISCOVER PROVE WRITE. (a) log a x y b log x log y (b) log 2 1x y2 log 2 x log 2 y. (c) log 5 a a b 2 b log 5 a 2 log 5 b
 360 CHAPTER 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 74. Biodiversity Some biologists model the number of species S in a fixed area A (such as an island) by the species-area relationship log S log c k log
360 CHAPTER 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 74. Biodiversity Some biologists model the number of species S in a fixed area A (such as an island) by the species-area relationship log S log c k log
z = log loglog
 Name: Units do not have to be included. 2016 2017 Log1 Contest Round 2 Theta Logs and Exponents points each 1 Write in logarithmic form: 2 = 1 8 2 Evaluate: log 5 0 log 5 8 (log 2 log 6) Simplify the expression
Name: Units do not have to be included. 2016 2017 Log1 Contest Round 2 Theta Logs and Exponents points each 1 Write in logarithmic form: 2 = 1 8 2 Evaluate: log 5 0 log 5 8 (log 2 log 6) Simplify the expression
2.6 Logarithmic Functions. Inverse Functions. Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x?
 Inverse Functions Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 3 and g(x) = 3 x? Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x? Definition (One-to-One Function) A function f
Inverse Functions Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 3 and g(x) = 3 x? Question: What is the relationship between f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x? Definition (One-to-One Function) A function f
Physical Chemistry - Problem Drill 02: Math Review for Physical Chemistry
 Physical Chemistry - Problem Drill 02: Math Review for Physical Chemistry No. 1 of 10 1. The Common Logarithm is based on the powers of 10. Solve the logarithmic equation: log(x+2) log(x-1) = 1 (A) 1 (B)
Physical Chemistry - Problem Drill 02: Math Review for Physical Chemistry No. 1 of 10 1. The Common Logarithm is based on the powers of 10. Solve the logarithmic equation: log(x+2) log(x-1) = 1 (A) 1 (B)
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt McDougal Algebra 2
 4-5 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Solve. 1. log 16 x = 3 2 64 2. log x 1.331 = 3 1.1 3. log10,000 = x 4 Objectives Solve exponential and logarithmic equations and equalities.
4-5 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Solve. 1. log 16 x = 3 2 64 2. log x 1.331 = 3 1.1 3. log10,000 = x 4 Objectives Solve exponential and logarithmic equations and equalities.
Module 6 Lecture Notes
 Module 6 Lecture Notes Contents 6. An Introduction to Logarithms....................... 6. Evaluating Logarithmic Expressions.................... 4 6.3 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions......................
Module 6 Lecture Notes Contents 6. An Introduction to Logarithms....................... 6. Evaluating Logarithmic Expressions.................... 4 6.3 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions......................
Algebra III: Blizzard Bag #1 Exponential and Logarithm Functions
 NAME : DATE: PERIOD: Algebra III: Blizzard Bag #1 Exponential and Logarithm Functions Students need to complete the following assignment, which will aid in review for the end of course exam. Look back
NAME : DATE: PERIOD: Algebra III: Blizzard Bag #1 Exponential and Logarithm Functions Students need to complete the following assignment, which will aid in review for the end of course exam. Look back
124b End of Semester Practice Problems. Simplify the radical. 1) ) ) ) 4) ) 5) 5 (-3)5 5)
 124b End of Semester Practice Problems Name Simplify the radical. 1) 3 1 27 1) 2) 4 256 2) 3) 4-16 3) 4) 3 83 4) 5) 5 (-3)5 5) 1 6) 3 (x + 2)3 6) Evaluate the expression, if possible. 7) 641/2 7) 8) 27
124b End of Semester Practice Problems Name Simplify the radical. 1) 3 1 27 1) 2) 4 256 2) 3) 4-16 3) 4) 3 83 4) 5) 5 (-3)5 5) 1 6) 3 (x + 2)3 6) Evaluate the expression, if possible. 7) 641/2 7) 8) 27
Math 121, Practice Questions for Final (Hints/Answers)
 Math 11, Practice Questions for Final Hints/Answers) 1. The graphs of the inverse functions are obtained by reflecting the graph of the original function over the line y = x. In each graph, the original
Math 11, Practice Questions for Final Hints/Answers) 1. The graphs of the inverse functions are obtained by reflecting the graph of the original function over the line y = x. In each graph, the original
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 1.4. ALGEBRA 4 (Logarithms) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 1.4 ALGEBRA 4 (Logarithms) by A.J.Hobson 1.4.1 Common logarithms 1.4.2 Logarithms in general 1.4.3 Useful Results 1.4.4 Properties of logarithms 1.4.5 Natural logarithms 1.4.6
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 1.4 ALGEBRA 4 (Logarithms) by A.J.Hobson 1.4.1 Common logarithms 1.4.2 Logarithms in general 1.4.3 Useful Results 1.4.4 Properties of logarithms 1.4.5 Natural logarithms 1.4.6
Teacher: Mr. Chafayay. Name: Class & Block : Date: ID: A. 3 Which function is represented by the graph?
 Teacher: Mr hafayay Name: lass & lock : ate: I: Midterm Exam Math III H Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question Which function is represented by the
Teacher: Mr hafayay Name: lass & lock : ate: I: Midterm Exam Math III H Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question Which function is represented by the
6.3 logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
 SECTION 6.3 logarithmic functions 4 9 1 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, you will: Convert from logarithmic to exponential form. Convert from exponential to logarithmic form. Evaluate logarithms. Use
SECTION 6.3 logarithmic functions 4 9 1 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, you will: Convert from logarithmic to exponential form. Convert from exponential to logarithmic form. Evaluate logarithms. Use
Assignment 5 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Assignment 5 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. For the given functions f and g, find the requested composite function. 1) f(x)
Assignment 5 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. For the given functions f and g, find the requested composite function. 1) f(x)
Pre-Calculus Notes from Week 6
 1-105 Pre-Calculus Notes from Week 6 Logarithmic Functions: Let a > 0, a 1 be a given base (as in, base of an exponential function), and let x be any positive number. By our properties of exponential functions,
1-105 Pre-Calculus Notes from Week 6 Logarithmic Functions: Let a > 0, a 1 be a given base (as in, base of an exponential function), and let x be any positive number. By our properties of exponential functions,
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 4 MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1
 Learning outcomes EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 4 MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 TUTORIAL 3 - FACTORISATION AND QUADRATICS On completion of this unit a learner should: 1 Know how to use algebraic
Learning outcomes EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 4 MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 TUTORIAL 3 - FACTORISATION AND QUADRATICS On completion of this unit a learner should: 1 Know how to use algebraic
Algebra Performance Level Descriptors
 Limited A student performing at the Limited Level demonstrates a minimal command of Ohio s Learning Standards for Algebra. A student at this level has an emerging ability to A student whose performance
Limited A student performing at the Limited Level demonstrates a minimal command of Ohio s Learning Standards for Algebra. A student at this level has an emerging ability to A student whose performance
Foundations of Math II Unit 5: Solving Equations
 Foundations of Math II Unit 5: Solving Equations Academics High School Mathematics 5.1 Warm Up Solving Linear Equations Using Graphing, Tables, and Algebraic Properties On the graph below, graph the following
Foundations of Math II Unit 5: Solving Equations Academics High School Mathematics 5.1 Warm Up Solving Linear Equations Using Graphing, Tables, and Algebraic Properties On the graph below, graph the following
44 Wyner PreCalculus Spring 2017
 44 Wyner PreCalculus Spring 207 CHAPTER FIVE: EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS Review January 30 Test February 7 An exponential function is one with the independent variable in the exponent, such
44 Wyner PreCalculus Spring 207 CHAPTER FIVE: EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS Review January 30 Test February 7 An exponential function is one with the independent variable in the exponent, such
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 6 Figure 1 Electron micrograph of E. Coli bacteria (credit: Mattosaurus, Wikimedia Commons) CHAPTER OUTLINE 6.1 Exponential Functions 6.5 Logarithmic Properties 6.2
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 6 Figure 1 Electron micrograph of E. Coli bacteria (credit: Mattosaurus, Wikimedia Commons) CHAPTER OUTLINE 6.1 Exponential Functions 6.5 Logarithmic Properties 6.2
Exploring and Generalizing Transformations of Functions
 Exploring and Generalizing Transformations of Functions In Algebra 1 and Algebra 2, you have studied transformations of functions. Today, you will revisit and generalize that knowledge. Goals: The goals
Exploring and Generalizing Transformations of Functions In Algebra 1 and Algebra 2, you have studied transformations of functions. Today, you will revisit and generalize that knowledge. Goals: The goals
Logarithms Dr. Laura J. Pyzdrowski
 1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory An exponential function of the form f(x) = a x, where a is a positive real number not equal to 1, is an example of a one-to-one function. This means
1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory An exponential function of the form f(x) = a x, where a is a positive real number not equal to 1, is an example of a one-to-one function. This means
Logarithms Tutorial for Chemistry Students
 1 Logarithms 1.1 What is a logarithm? Logarithms Tutorial for Chemistry Students Logarithms are the mathematical function that is used to represent the number (y) to which a base integer (a) is raised
1 Logarithms 1.1 What is a logarithm? Logarithms Tutorial for Chemistry Students Logarithms are the mathematical function that is used to represent the number (y) to which a base integer (a) is raised
Logarithmic Properties
 Logarithmic Properties By: OpenStaxCollege The ph of hydrochloric acid is tested with litmus paper. (credit: David Berardan) In chemistry, ph is used as a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance.
Logarithmic Properties By: OpenStaxCollege The ph of hydrochloric acid is tested with litmus paper. (credit: David Berardan) In chemistry, ph is used as a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance.
Hello Future Calculus Level One Student,
 Hello Future Calculus Level One Student, This assignment must be completed and handed in on the first day of class. This assignment will serve as the main review for a test on this material. The test will
Hello Future Calculus Level One Student, This assignment must be completed and handed in on the first day of class. This assignment will serve as the main review for a test on this material. The test will
4A: #1e-l,2-5,6g-l (Base 10 logs) 4B: #1-3last col,4,5,6 last col (Base a logs)
 1. Understand the meaning of and use logs of base 10 and base a 4A: #1e-l,2-5,6g-l (Base 10 logs) 4B: #1-3last col,4,5,6 last col (Base a logs) We have been looking at exponential functions of the form
1. Understand the meaning of and use logs of base 10 and base a 4A: #1e-l,2-5,6g-l (Base 10 logs) 4B: #1-3last col,4,5,6 last col (Base a logs) We have been looking at exponential functions of the form
Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review
 Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review c Trinity College 1 A note to the students from the lecturer: This course will be moving rather quickly, and it will be in your own best interests to
Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review c Trinity College 1 A note to the students from the lecturer: This course will be moving rather quickly, and it will be in your own best interests to
Chapter 3. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. 3.2 Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 Logarithmic Functions 1/23 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 4, 8, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 39, 42, 54, 56, 62, 68,
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 Logarithmic Functions 1/23 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 4, 8, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 39, 42, 54, 56, 62, 68,
Chapter 7: Exponents
 Chapter : Exponents Algebra Chapter Notes Name: Notes #: Sections.. Section.: Review Simplify; leave all answers in positive exponents:.) m -.) y -.) m 0.) -.) -.) - -.) (m ) 0.) 0 x y Evaluate if a =
Chapter : Exponents Algebra Chapter Notes Name: Notes #: Sections.. Section.: Review Simplify; leave all answers in positive exponents:.) m -.) y -.) m 0.) -.) -.) - -.) (m ) 0.) 0 x y Evaluate if a =
2(x 4 7x 2 18) 2(x 2 9)(x 2 + 2) 2(x 3)(x + 3)(x 2 + 2)
 Completely factor 2x 4 14x 2 36 2(x 4 7x 2 18) 2(x 2 9)(x 2 + 2) 2(x 3)(x + 3)(x 2 + 2) Add and simplify Simplify as much as possible Subtract and simplify Determine the inverse of Multiply and simplify
Completely factor 2x 4 14x 2 36 2(x 4 7x 2 18) 2(x 2 9)(x 2 + 2) 2(x 3)(x + 3)(x 2 + 2) Add and simplify Simplify as much as possible Subtract and simplify Determine the inverse of Multiply and simplify
A2 HW Imaginary Numbers
 Name: A2 HW Imaginary Numbers Rewrite the following in terms of i and in simplest form: 1) 100 2) 289 3) 15 4) 4 81 5) 5 12 6) -8 72 Rewrite the following as a radical: 7) 12i 8) 20i Solve for x in simplest
Name: A2 HW Imaginary Numbers Rewrite the following in terms of i and in simplest form: 1) 100 2) 289 3) 15 4) 4 81 5) 5 12 6) -8 72 Rewrite the following as a radical: 7) 12i 8) 20i Solve for x in simplest
3.4 Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations
 214 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.4 Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Introduction So far in this chapter, you have studied the definitions, graphs, and properties of exponential
214 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.4 Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Introduction So far in this chapter, you have studied the definitions, graphs, and properties of exponential
Appendix A. Common Mathematical Operations in Chemistry
 Appendix A Common Mathematical Operations in Chemistry In addition to basic arithmetic and algebra, four mathematical operations are used frequently in general chemistry: manipulating logarithms, using
Appendix A Common Mathematical Operations in Chemistry In addition to basic arithmetic and algebra, four mathematical operations are used frequently in general chemistry: manipulating logarithms, using
SET 1. (1) Solve for x: (a) e 2x = 5 3x
 () Solve for x: (a) e x = 5 3x SET We take natural log on both sides: ln(e x ) = ln(5 3x ) x = 3 x ln(5) Now we take log base on both sides: log ( x ) = log (3 x ln 5) x = log (3 x ) + log (ln(5)) x x
() Solve for x: (a) e x = 5 3x SET We take natural log on both sides: ln(e x ) = ln(5 3x ) x = 3 x ln(5) Now we take log base on both sides: log ( x ) = log (3 x ln 5) x = log (3 x ) + log (ln(5)) x x
8 + 6) x 2 ) y = h(x)
 . a. Horizontal shift 6 left and vertical shift up. Notice B' is ( 6, ) and B is (0, 0). b. h(x) = 0.5(x + 6) + (Enter in a grapher to check.) c. Use the graph. Notice A' to see h(x) crosses the x-axis
. a. Horizontal shift 6 left and vertical shift up. Notice B' is ( 6, ) and B is (0, 0). b. h(x) = 0.5(x + 6) + (Enter in a grapher to check.) c. Use the graph. Notice A' to see h(x) crosses the x-axis
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Learning Targets 1. I can evaluate, analyze, and graph exponential functions. 2. I can solve problems involving exponential growth & decay. 3. I can evaluate expressions
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Learning Targets 1. I can evaluate, analyze, and graph exponential functions. 2. I can solve problems involving exponential growth & decay. 3. I can evaluate expressions
Math 137 Exam #3 Review Guide
 Math 7 Exam # Review Guide The third exam will cover Sections.-.6, 4.-4.7. The problems on this review guide are representative of the type of problems worked on homework and during class time. Do not
Math 7 Exam # Review Guide The third exam will cover Sections.-.6, 4.-4.7. The problems on this review guide are representative of the type of problems worked on homework and during class time. Do not
Stephen F Austin. Exponents and Logarithms. chapter 3
 chapter 3 Starry Night was painted by Vincent Van Gogh in 1889. The brightness of a star as seen from Earth is measured using a logarithmic scale. Exponents and Logarithms This chapter focuses on understanding
chapter 3 Starry Night was painted by Vincent Van Gogh in 1889. The brightness of a star as seen from Earth is measured using a logarithmic scale. Exponents and Logarithms This chapter focuses on understanding
Logarithmic Functions
 Logarithmic Functions Definition 1. For x > 0, a > 0, and a 1, y = log a x if and only if x = a y. The function f(x) = log a x is called the logarithmic function with base a. Example 1. Evaluate the following
Logarithmic Functions Definition 1. For x > 0, a > 0, and a 1, y = log a x if and only if x = a y. The function f(x) = log a x is called the logarithmic function with base a. Example 1. Evaluate the following
If a function has an inverse then we can determine the input if we know the output. For example if the function
 1 Inverse Functions We know what it means for a relation to be a function. Every input maps to only one output, it passes the vertical line test. But not every function has an inverse. A function has no
1 Inverse Functions We know what it means for a relation to be a function. Every input maps to only one output, it passes the vertical line test. But not every function has an inverse. A function has no
7.4* General logarithmic and exponential functions
 7.4* General logarithmic and exponential functions Mark Woodard Furman U Fall 2010 Mark Woodard (Furman U) 7.4* General logarithmic and exponential functions Fall 2010 1 / 9 Outline 1 General exponential
7.4* General logarithmic and exponential functions Mark Woodard Furman U Fall 2010 Mark Woodard (Furman U) 7.4* General logarithmic and exponential functions Fall 2010 1 / 9 Outline 1 General exponential
Find: sinθ. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. Find the exact value of the given trigonometric function of the angle θ shown in the figure. (Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the third side of the triangle.) Find: sinθ c a θ a a =
Name: Date: 1. Find the exact value of the given trigonometric function of the angle θ shown in the figure. (Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the third side of the triangle.) Find: sinθ c a θ a a =
EXAM 3 Tuesday, March 18, 2003
 MATH 12001 Precalculus: Algebra & Trigonometry Spring 2003 Sections 2 & 3 Darci L. Kracht Name: Score: /100. 115 pts available EXAM 3 Tuesday, March 18, 2003 Part I: NO CALCULATORS. (You must turn this
MATH 12001 Precalculus: Algebra & Trigonometry Spring 2003 Sections 2 & 3 Darci L. Kracht Name: Score: /100. 115 pts available EXAM 3 Tuesday, March 18, 2003 Part I: NO CALCULATORS. (You must turn this
3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations
 3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Pre-Calculus Mr. Niedert Pre-Calculus 3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Mr. Niedert 1 / 18 3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations 1 Solving Simple Equations
3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Pre-Calculus Mr. Niedert Pre-Calculus 3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations Mr. Niedert 1 / 18 3.4 Exponential and Logarithmic Equations 1 Solving Simple Equations
Solve by equating exponents
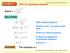 EXAMPLE 1 x Solve 4 = 1 Solve by equating exponents x 3 SOLUTION x 1 4 = x x 3 1 ( ) = ( ) x x + 3 = x = x + 3 x = 1 x 3 Write original equation. Rewrite 4 and base. 1 as powers with Power of a power property
EXAMPLE 1 x Solve 4 = 1 Solve by equating exponents x 3 SOLUTION x 1 4 = x x 3 1 ( ) = ( ) x x + 3 = x = x + 3 x = 1 x 3 Write original equation. Rewrite 4 and base. 1 as powers with Power of a power property
Math M110: Lecture Notes For Chapter 12 Section 12.1: Inverse and Composite Functions
 Math M110: Lecture Notes For Chapter 12 Section 12.1: Inverse and Composite Functions Inverse function (interchange x and y): Find the equation of the inverses for: y = 2x + 5 ; y = x 2 + 4 Function: (Vertical
Math M110: Lecture Notes For Chapter 12 Section 12.1: Inverse and Composite Functions Inverse function (interchange x and y): Find the equation of the inverses for: y = 2x + 5 ; y = x 2 + 4 Function: (Vertical
Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities
 Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities 1 MATH 1 REVIEW SOLVING AN ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATION Absolute value is a measure of distance; how far a number is from zero. In practice,
Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities 1 MATH 1 REVIEW SOLVING AN ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATION Absolute value is a measure of distance; how far a number is from zero. In practice,
Algebra II with Trig 3 rd Nine Weeks Pacing Guide Grade 11
 2017-2018 Grade 11 Week 1 (1/8-1/12) 6-1, 6-2, 6-3 First Semester Report Cards go home January 10 th Week 2 (1/15-1/19) 6-4, 6-5 24. [A-REI.12T] Solve simple rational and radical equations in one variable,
2017-2018 Grade 11 Week 1 (1/8-1/12) 6-1, 6-2, 6-3 First Semester Report Cards go home January 10 th Week 2 (1/15-1/19) 6-4, 6-5 24. [A-REI.12T] Solve simple rational and radical equations in one variable,
INSPECT Algebra I Summative Assessment Summary
 and Quantity The Real System Quantities Seeing Structure in Use properties of rational and irrational numbers. Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems. Interpret the structure of expressions.
and Quantity The Real System Quantities Seeing Structure in Use properties of rational and irrational numbers. Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems. Interpret the structure of expressions.
10/22/16. 1 Math HL - Santowski SKILLS REVIEW. Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions. Lesson Objectives. (A) Rational Functions
 Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions SKILLS REVIEW! Use function composition to prove that the following two funtions are inverses of each other. 2x 3 f(x) = g(x) = 5 2 x 1 1 2 Lesson Objectives! The
Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions SKILLS REVIEW! Use function composition to prove that the following two funtions are inverses of each other. 2x 3 f(x) = g(x) = 5 2 x 1 1 2 Lesson Objectives! The
NAME: DATE: CLASS: AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER MATH 2018
 NAME: DATE: CLASS: AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER MATH 2018 A] Refer to your pre-calculus notebook, the internet, or the sheets/links provided for assistance. B] Do not wait until the last minute to complete this
NAME: DATE: CLASS: AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER MATH 2018 A] Refer to your pre-calculus notebook, the internet, or the sheets/links provided for assistance. B] Do not wait until the last minute to complete this
Solving Equations by Factoring. Solve the quadratic equation x 2 16 by factoring. We write the equation in standard form: x
 11.1 E x a m p l e 1 714SECTION 11.1 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve quadratic equations by using the square root method 2. Solve quadratic equations by completing the square Here, we factor the quadratic member of
11.1 E x a m p l e 1 714SECTION 11.1 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve quadratic equations by using the square root method 2. Solve quadratic equations by completing the square Here, we factor the quadratic member of
Algebra II CP Final Exam Review Packet. Calculator Questions
 Name: Algebra II CP Final Exam Review Packet Calculator Questions 1. Solve the equation. Check for extraneous solutions. (Sec. 1.6) 2 8 37 2. Graph the inequality 31. (Sec. 2.8) 3. If y varies directly
Name: Algebra II CP Final Exam Review Packet Calculator Questions 1. Solve the equation. Check for extraneous solutions. (Sec. 1.6) 2 8 37 2. Graph the inequality 31. (Sec. 2.8) 3. If y varies directly
Topics from Algebra and Pre-Calculus. (Key contains solved problems)
 Topics from Algebra and Pre-Calculus (Key contains solved problems) Note: The purpose of this packet is to give you a review of basic skills. You are asked not to use the calculator, except on p. (8) and
Topics from Algebra and Pre-Calculus (Key contains solved problems) Note: The purpose of this packet is to give you a review of basic skills. You are asked not to use the calculator, except on p. (8) and
Controlling the Population
 Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Controlling the Population Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Vocabulary Match each definition with its corresponding term. 1. polynomial a. a polynomial with only 1
Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Controlling the Population Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Vocabulary Match each definition with its corresponding term. 1. polynomial a. a polynomial with only 1
Part I: Multiple Choice Questions
 Name: Part I: Multiple Choice Questions. What is the slope of the line y=3 A) 0 B) -3 ) C) 3 D) Undefined. What is the slope of the line perpendicular to the line x + 4y = 3 A) -/ B) / ) C) - D) 3. Find
Name: Part I: Multiple Choice Questions. What is the slope of the line y=3 A) 0 B) -3 ) C) 3 D) Undefined. What is the slope of the line perpendicular to the line x + 4y = 3 A) -/ B) / ) C) - D) 3. Find
Lesson 4b More on LOGARITHMS
 Lesson 4b More on LOGARITHMS Learning Packet Student Name Due Date Class Time/Day Submission Date THIS BOX FOR INSTRUCTOR GRADING USE ONLY Mini-Lesson is complete and information presented is as found
Lesson 4b More on LOGARITHMS Learning Packet Student Name Due Date Class Time/Day Submission Date THIS BOX FOR INSTRUCTOR GRADING USE ONLY Mini-Lesson is complete and information presented is as found
Mathematics: Algebra II Honors Unit 6: Radical Functions
 Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Radical functions can be used to model real-life situations. What are the properties of Algebra and how are these used to solve radical equations? How
Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Radical functions can be used to model real-life situations. What are the properties of Algebra and how are these used to solve radical equations? How
Algebra 2 Honors: Final Exam Review
 Name: Class: Date: Algebra 2 Honors: Final Exam Review Directions: You may write on this review packet. Remember that this packet is similar to the questions that you will have on your final exam. Attempt
Name: Class: Date: Algebra 2 Honors: Final Exam Review Directions: You may write on this review packet. Remember that this packet is similar to the questions that you will have on your final exam. Attempt
APPENDIX : PARTIAL FRACTIONS
 APPENDIX : PARTIAL FRACTIONS Appendix : Partial Fractions Given the expression x 2 and asked to find its integral, x + you can use work from Section. to give x 2 =ln( x 2) ln( x + )+c x + = ln k x 2 x+
APPENDIX : PARTIAL FRACTIONS Appendix : Partial Fractions Given the expression x 2 and asked to find its integral, x + you can use work from Section. to give x 2 =ln( x 2) ln( x + )+c x + = ln k x 2 x+
Domain and range of exponential and logarithmic function *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m15461 1 Domain and range of exponential and logarithmic function * Sunil Kumar Singh This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
OpenStax-CNX module: m15461 1 Domain and range of exponential and logarithmic function * Sunil Kumar Singh This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Solutions to MAT 117 Test #3
 Solutions to MAT 7 Test #3 Because there are two versions of the test, solutions will only be given for Form C. Differences from the Form D version will be given. (The values for Form C appear above those
Solutions to MAT 7 Test #3 Because there are two versions of the test, solutions will only be given for Form C. Differences from the Form D version will be given. (The values for Form C appear above those
Section 6.3: Exponential Equations and Inequalities, from College Algebra: Corrected Edition by Carl Stitz, Ph.D. and Jeff Zeager, Ph.D.
 Section 6.3: Exponential Equations and Inequalities, from College Algebra: Corrected Edition by Carl Stitz, Ph.D. and Jeff Zeager, Ph.D. is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-
Section 6.3: Exponential Equations and Inequalities, from College Algebra: Corrected Edition by Carl Stitz, Ph.D. and Jeff Zeager, Ph.D. is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-
CHAPTER FIVE. Solutions for Section 5.1. Skill Refresher. Exercises
 CHAPTER FIVE 5.1 SOLUTIONS 265 Solutions for Section 5.1 Skill Refresher S1. Since 1,000,000 = 10 6, we have x = 6. S2. Since 0.01 = 10 2, we have t = 2. S3. Since e 3 = ( e 3) 1/2 = e 3/2, we have z =
CHAPTER FIVE 5.1 SOLUTIONS 265 Solutions for Section 5.1 Skill Refresher S1. Since 1,000,000 = 10 6, we have x = 6. S2. Since 0.01 = 10 2, we have t = 2. S3. Since e 3 = ( e 3) 1/2 = e 3/2, we have z =
Course: Algebra MP: Reason abstractively and quantitatively MP: Model with mathematics MP: Look for and make use of structure
 Algebra Cluster: Interpret the structure of expressions. A.SSE.1: Interpret expressions that represent a quantity in terms of its context (Modeling standard). a. Interpret parts of an expression, such
Algebra Cluster: Interpret the structure of expressions. A.SSE.1: Interpret expressions that represent a quantity in terms of its context (Modeling standard). a. Interpret parts of an expression, such
2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Algebra II in Pearson Texas Algebra II
 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Algebra II in Pearson Texas Algebra II The following table shows where each of the from the 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra II
2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Algebra II in Pearson Texas Algebra II The following table shows where each of the from the 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra II
Chapter 2 Functions and Graphs
 Chapter 2 Functions and Graphs Section 6 Logarithmic Functions Learning Objectives for Section 2.6 Logarithmic Functions The student will be able to use and apply inverse functions. The student will be
Chapter 2 Functions and Graphs Section 6 Logarithmic Functions Learning Objectives for Section 2.6 Logarithmic Functions The student will be able to use and apply inverse functions. The student will be
1. Algebra and Functions
 1. Algebra and Functions 1.1.1 Equations and Inequalities 1.1.2 The Quadratic Formula 1.1.3 Exponentials and Logarithms 1.2 Introduction to Functions 1.3 Domain and Range 1.4.1 Graphing Functions 1.4.2
1. Algebra and Functions 1.1.1 Equations and Inequalities 1.1.2 The Quadratic Formula 1.1.3 Exponentials and Logarithms 1.2 Introduction to Functions 1.3 Domain and Range 1.4.1 Graphing Functions 1.4.2
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Calculus I - Homework Chapter 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether the graph is the graph of a function. 1) 1)
Calculus I - Homework Chapter 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether the graph is the graph of a function. 1) 1)
Intermediate Algebra Summary - Part II
 Intermediate Algebra Summary - Part II This is an overview of the key ideas we have discussed during the middle part of this course. You may find this summary useful as a study aid, but remember that the
Intermediate Algebra Summary - Part II This is an overview of the key ideas we have discussed during the middle part of this course. You may find this summary useful as a study aid, but remember that the
Parent Guide. Number System. Diocese of Cleveland
 Parent Guide Grade Eight Algebra Curriculum Diocese of Cleveland Below is a list of skills your child will be taught in Grade Eight Algebra. As parents, you are encouraged to support the work of your child
Parent Guide Grade Eight Algebra Curriculum Diocese of Cleveland Below is a list of skills your child will be taught in Grade Eight Algebra. As parents, you are encouraged to support the work of your child
9.7 Common Logarithms, Natural Logarithms, and Change of Base
 580 CHAPTER 9 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Graph each function. 6. y = a x 2 b 7. y = 2 x + 8. y = log x 9. y = log / x Solve. 20. 2 x = 8 2. 9 = x -5 22. 4 x - = 8 x +2 2. 25 x = 25 x - 24. log
580 CHAPTER 9 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Graph each function. 6. y = a x 2 b 7. y = 2 x + 8. y = log x 9. y = log / x Solve. 20. 2 x = 8 2. 9 = x -5 22. 4 x - = 8 x +2 2. 25 x = 25 x - 24. log
POD. A) Graph: y = 2e x +2 B) Evaluate: (e 2x e x ) 2 2e -x. e 7x 2
 POD A) Graph: y = 2e x +2 B) Evaluate: (e 2x e x ) 2 2e -x e 7x 2 4.4 Evaluate Logarithms & Graph Logarithmic Functions What is a logarithm? How do you read it? What relationship exists between logs and
POD A) Graph: y = 2e x +2 B) Evaluate: (e 2x e x ) 2 2e -x e 7x 2 4.4 Evaluate Logarithms & Graph Logarithmic Functions What is a logarithm? How do you read it? What relationship exists between logs and
