Arches Part 1: Introduction to the Uintah Computational Framework. Charles Reid Scientific Computing Summer Workshop July 14, 2010
|
|
|
- Lenard Bishop
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Arches Part 1: Introduction to the Uintah Computational Framework Charles Reid Scientific Computing Summer Workshop July 14, 2010
2 Arches Uintah Computational Framework Cluster Node Node Node Node Node Node Node Node Node
3 Arches Uintah Computational Framework Cluster Node Node Node Node Node Node Node Node Node
4 What is a computational framework? Common code Generic functionality Reusable abstractions Wrapped through API (Application Programming Interface) Abstracts low-level coding details Similar to libraries
5 What is the UCF? Computational framework Designed for solving timedependent PDEs Object-oriented C++ Parallelizes to thousands of processors
6 UCF Design Common component architecture (CCA) Components have common features Components use common interface to framework Components solve time-dependent PDEs on a structured Cartesian mesh
7 Standalone Uintah Simulation (sus) Framework needs a driver - something with a main() function sus is the main executable Location: uintah/src/standalone/sus.cc
8 Standalone Uintah Simulation (sus) Framework needs a driver - Input File something with a main() function Format: XML sus is the main executable Extension:.ups Component e.g. Arches Driver Program "sus" Scheduler MPI Manager etc... Saved Simulation Data
9 What does the framework provide? (Cartesian) Grids, patches, cells Levels - for automatic mesh refinement (AMR) Variables (cell-centered, face-centered) & stencils Variable labels Data warehouse (abstraction for data storage and retrieval) Tasks (computations) Scheduler (organizes the tasks) MPI Manager
10 What does the framework provide? Domain/mesh abstractions (Cartesian) Grids, patches, cells Levels - for automatic mesh refinement (AMR) Variables (cell-centered, face-centered) & stencils Variable labels Data warehouse (abstraction for data storage and retrieval) Tasks (computations) Scheduler (organizes the tasks) MPI Manager
11 What does the framework provide? (Cartesian) Grids, patches, cells Levels - for automatic mesh refinement (AMR) Variables (cell-centered, face-centered) & stencils Variable labels Data warehouse (abstraction for data storage and retrieval) Tasks (computations) Data abstractions Scheduler (organizes the tasks) MPI Manager
12 What does the framework provide? (Cartesian) Grids, patches, cells Levels - for automatic mesh refinement (AMR) Variables (cell-centered, face-centered) & stencils Variable labels Data warehouse (abstraction for data storage and retrieval) Tasks (computations) Scheduler (organizes the tasks) MPI Manager Parallelization abstractions
13 Domain & Mesh Abstractions Input file: user specifies domain size and number of cells Patch - a chunk of the grid Each patch is owned by a processor # patches = # processors
14
15 Data Abstractions Data warehouse as a library Framework as librarian Simulation data as the books VarLabels as book call numbers: unique identifiers
16 Data Abstractions To get a book: Have to check out To return a book: Have to check in Can t check in books that aren t registered with library (no call number)
17 Parallelization Abstraction Each component is split into tasks Any given task will have: things it requires things it calculates If each task specifies what it requires and what it calculates, the workload can be balanced (BEFORE the work is done)
18 ρ i How does the framework t + (ρ iv) = j i parallelize? Each component is split into tasks j Any given task will have things it needs j j = ρd ω things it calculates ρ If each task specifies what it needs D ω and what it calculates, the workload can be balanced T ω (BEFORE the work is done)
19 Tasks and the Taskgraph Each task run on each processor But, each task run on different portions of the data (or grid) Each task has two data warehouses: OldDW and NewDW
20 Examples Located in: uintah/src/cca/components/examples Poisson example walkthrough uintah/src/cca/components/examples/ Poisson1.cc,Poisson1.h Important functions to focus on: Poisson1::scheduleTimeAdvance Poisson1::timeAdvance
21 Examples Poisson1::scheduleTimeAdvance() Specifies that task requires phi Specifies that task computes phi Located Specifies in: that task computes a residual uintah/src/cca/components/examples Poisson example walkthrough uintah/src/cca/components/examples/ Poisson1::timeAdvance() Poisson1.cc,Poisson1.h Call to GET phi from old data warehouse Call Important to ALLOCATE functions AND PUT to phi focus in new on: data warehouse Call to PUT residual in new data warehouse Poisson1::scheduleTimeAdvance Poisson1::timeAdvance
22 Examples Poisson1::scheduleTimeAdvance() Specifies that task requires phi Specifies that task computes phi Located Specifies in: that task computes a residual uintah/src/cca/components/examples Poisson example walkthrough uintah/src/cca/components/examples/ Poisson1::timeAdvance() Poisson1.cc,Poisson1.h Call to GET phi from old data warehouse Call Important to ALLOCATE functions AND PUT to phi focus in new on: data warehouse Call to PUT residual in new data warehouse Poisson1::scheduleTimeAdvance Poisson1::timeAdvance
23 Examples Poisson1::scheduleTimeAdvance() Specifies that task requires phi Specifies that task computes phi Located Specifies in: that task computes a residual uintah/src/cca/components/examples Poisson example walkthrough uintah/src/cca/components/examples/ Poisson1::timeAdvance() Poisson1.cc,Poisson1.h Call to GET phi from old data warehouse Call Important to ALLOCATE functions AND PUT to phi focus in new on: data warehouse Call to PUT residual in new data warehouse Poisson1::scheduleTimeAdvance Poisson1::timeAdvance
24 Examples Poisson1::scheduleTimeAdvance() Specifies that task requires phi Specifies that task computes phi Located Specifies in: that task computes a residual uintah/src/cca/components/examples Poisson example walkthrough uintah/src/cca/components/examples/ Poisson1::timeAdvance() Poisson1.cc,Poisson1.h Call to GET phi from old data warehouse Call Important to ALLOCATE functions AND PUT to phi focus in new on: data warehouse Call to PUT residual in new data warehouse Poisson1::scheduleTimeAdvance Poisson1::timeAdvance
25 Example Component: Poisson Solver Poisson example input file: uintah/src/standalone/inputs/examples/poisson1.ups To run the Poisson example: /path/to/sus /path/to/inputs/poisson1.ups
26 Other Examples Poisson2: Demonstrates use of sub-schedulers Non-linear solver iterations within timestep HeatEquation: Uses a Poisson solver to solve heat equation SolverTest1: Interfaces with generic SolverInterface This can then create linear solvers for stencil matrices
27 Other Examples 2 1 Poisson1: A = Demonstrates use of sub-schedulers Non-linear solver iterations within timestep HeatEquation: Poisson solver to solve heat equation SolverTest1: Interfaces with generic SolverInterface This can then create linear solvers for stencil matrices
28 Other Examples 2 1 Poisson1: A = Demonstrates use of sub-schedulers Non-linear solver iterations within timestep HeatEquation: Poisson solver to solve heat equation SolverTest1: Interfaces Interface: uintah/src/cca/ports/solverinterface.* with generic This can then create linear solvers for stencil Solvers: matrices uintah/src/cca/components/solvers/*
29 Other Examples Burgers: Solves the Burgers equation using Forward Euler u t = u u
30 Where to go for more info User s Guide/Installation Guide uintah/doc/ Contains general information applicable to all Uintah users Uintah Wiki: Contains non-general information Configure lines for specific clusters Machine-specific scripts/compiling info
31 Where to go for more info Uintah Doxygen: Homebrew list - Uintah developers csafe-homebrew@cs.utah.edu If you can t find what you re looking for in the documentation... Tell John Schmidt! John.Schmidt@utah.edu (He s the guy in charge of documentation)
32 A Final Word: How you can contribute
33 A Final Word: How you can contribute The Uintah documentation SUCKS Most developers don t care enough to contribute It s up to users to improve documentation and make it better Don t be afraid to contribute to the documentation! Add Doxygen comments to classes you figure out, add to the User Guide and Installation Guide, add to the wiki, etc... Don t be shy!
34 Arches Part 2: Introduction to Arches Charles Reid Scientific Computing Summer Workshop July 14, 2010
35 Where is Arches? From the Uintah tree: src/cca/components/arches/
36 What is Arches? Finite-volume LES code Explicit time integration Tabulated chemistry (i.e. table lookup) Pressure projection method
37 What is Arches? Finite-volume LES code Explicit time integration Tabulated chemistry (i.e. table lookup) Pressure projection method
38 Capabilities: Subgrid Models Smagorinsky (SmagorinskyModel.*) Incompressible dynamic model (IncDynamicProcedure.*) Variable density dynamc model (CompDynamicProcedure.*) Local dynamic model (CompLocalDynamicProcedure.*)
39 Capabilities: Subgrid Models Smagorinsky (SmagorinskyModel.*) All are child classes of Incompressible dynamic TurbulenceModel model class (IncDynamicProcedure.*) Variable density dynamc model (CompDynamicProcedure.*) Local dynamic model (CompLocalDynamicProcedure.*)
40 Capabilities: Combustion Chemistry Arches uses table lookups Tabulated combustion chemistry tables Reaction models vs. Mixing models:
41 Capabilities: Combustion Chemistry Arches uses table lookups Tabulated combustion chemistry tables Reaction models vs. Mixing models: Reaction Models: φ = φ (η) φ = Full thermochemical state η = Reduced set of parameters
42 Capabilities: Combustion Chemistry Arches uses table lookups Tabulated combustion chemistry tables Reaction models vs. Mixing models: Mixing Models: φ =... η φ (η ) P (η )dη
43 Capabilities: DQMOM Novel multiphase application of Arches Applying Arches to coal combustion and gasification Models for two-phase drag, heat transfer, reactions, &c.
44 Capabilities: Transport Equation Framework Handle arbitrary numbers of transport equations Simple to add via input file Flexible: much more flexible than existing Arches transport equations Can apply arbitrary discretization schemes (currently superbee and upwind), arbitrary time integrators (currently 1st/2nd/3rd order RK)
45 How it all fits together Remember the Poisson component? The most important method was timeadvance() Arches is very similar
46 Arches Component Arches.* How it all fits Arches::timeAdvance() together NonlinearSolver.* ExplicitSolver.* Nonlinear Solver Remember the PicardNonlinearSolver.* Poisson component? The most important NonlinearSolver::nonlinearSolve() method was timeadvance() Mixture Fraction Transport Equation ScalarSolver.* Arches is very similar Enthalpy Transport Equation EnthalpySolver.* Momentum Transport Equation MomentumSolver.* Pressure PressureSolver.* Radiation RadiationSolver.* DORadiationModel.* Radiation/ Chemistry Table Properties.* NewStaticMixingTable.* ColdFlowMixingModel.* TabPropsInterface.* Mixing/ ChemMix/ Boundary Conditions BoundaryCondition.* BoundaryCond_new.* Transport Equations ScalarEqn.* EqnFactory.* Discretization_new.* ExplicitTimeInt.* DQMOM DQMOM.* DQMOMEqn.* DQMOMEqnFactory.* CoalModelFactory.* CoalModels/
47 Questions so far about the code side of Arches?
48 Algorithm
49 Algorithm
50 Questions about the Arches algorithm?
51 Wrap-up
Earth System Modeling Domain decomposition
 Earth System Modeling Domain decomposition Graziano Giuliani International Centre for Theorethical Physics Earth System Physics Section Advanced School on Regional Climate Modeling over South America February
Earth System Modeling Domain decomposition Graziano Giuliani International Centre for Theorethical Physics Earth System Physics Section Advanced School on Regional Climate Modeling over South America February
Numerically Solving Partial Differential Equations
 Numerically Solving Partial Differential Equations Michael Lavell Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics Abstract The physics describing the fundamental principles of fluid dynamics can be written
Numerically Solving Partial Differential Equations Michael Lavell Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics Abstract The physics describing the fundamental principles of fluid dynamics can be written
Cluster Computing: Updraft. Charles Reid Scientific Computing Summer Workshop June 29, 2010
 Cluster Computing: Updraft Charles Reid Scientific Computing Summer Workshop June 29, 2010 Updraft Cluster: Hardware 256 Dual Quad-Core Nodes 2048 Cores 2.8 GHz Intel Xeon Processors 16 GB memory per
Cluster Computing: Updraft Charles Reid Scientific Computing Summer Workshop June 29, 2010 Updraft Cluster: Hardware 256 Dual Quad-Core Nodes 2048 Cores 2.8 GHz Intel Xeon Processors 16 GB memory per
Application of Chimera Grids in Rotational Flow
 CES Seminar Write-up Application of Chimera Grids in Rotational Flow Marc Schwalbach 292414 marc.schwalbach@rwth-aachen.de Supervisors: Dr. Anil Nemili & Emre Özkaya, M.Sc. MATHCCES RWTH Aachen University
CES Seminar Write-up Application of Chimera Grids in Rotational Flow Marc Schwalbach 292414 marc.schwalbach@rwth-aachen.de Supervisors: Dr. Anil Nemili & Emre Özkaya, M.Sc. MATHCCES RWTH Aachen University
Part 1. The diffusion equation
 Differential Equations FMNN10 Graded Project #3 c G Söderlind 2016 2017 Published 2017-11-27. Instruction in computer lab 2017-11-30/2017-12-06/07. Project due date: Monday 2017-12-11 at 12:00:00. Goals.
Differential Equations FMNN10 Graded Project #3 c G Söderlind 2016 2017 Published 2017-11-27. Instruction in computer lab 2017-11-30/2017-12-06/07. Project due date: Monday 2017-12-11 at 12:00:00. Goals.
Cactus Tools for Petascale Computing
 Cactus Tools for Petascale Computing Erik Schnetter Reno, November 2007 Gamma Ray Bursts ~10 7 km He Protoneutron Star Accretion Collapse to a Black Hole Jet Formation and Sustainment Fe-group nuclei Si
Cactus Tools for Petascale Computing Erik Schnetter Reno, November 2007 Gamma Ray Bursts ~10 7 km He Protoneutron Star Accretion Collapse to a Black Hole Jet Formation and Sustainment Fe-group nuclei Si
Basic Aspects of Discretization
 Basic Aspects of Discretization Solution Methods Singularity Methods Panel method and VLM Simple, very powerful, can be used on PC Nonlinear flow effects were excluded Direct numerical Methods (Field Methods)
Basic Aspects of Discretization Solution Methods Singularity Methods Panel method and VLM Simple, very powerful, can be used on PC Nonlinear flow effects were excluded Direct numerical Methods (Field Methods)
Introduction. J.M. Burgers Center Graduate Course CFD I January Least-Squares Spectral Element Methods
 Introduction In this workshop we will introduce you to the least-squares spectral element method. As you can see from the lecture notes, this method is a combination of the weak formulation derived from
Introduction In this workshop we will introduce you to the least-squares spectral element method. As you can see from the lecture notes, this method is a combination of the weak formulation derived from
Poisson Equation in 2D
 A Parallel Strategy Department of Mathematics and Statistics McMaster University March 31, 2010 Outline Introduction 1 Introduction Motivation Discretization Iterative Methods 2 Additive Schwarz Method
A Parallel Strategy Department of Mathematics and Statistics McMaster University March 31, 2010 Outline Introduction 1 Introduction Motivation Discretization Iterative Methods 2 Additive Schwarz Method
PDE Solvers for Fluid Flow
 PDE Solvers for Fluid Flow issues and algorithms for the Streaming Supercomputer Eran Guendelman February 5, 2002 Topics Equations for incompressible fluid flow 3 model PDEs: Hyperbolic, Elliptic, Parabolic
PDE Solvers for Fluid Flow issues and algorithms for the Streaming Supercomputer Eran Guendelman February 5, 2002 Topics Equations for incompressible fluid flow 3 model PDEs: Hyperbolic, Elliptic, Parabolic
ORBIT Code Review and Future Directions. S. Cousineau, A. Shishlo, J. Holmes ECloud07
 ORBIT Code Review and Future Directions S. Cousineau, A. Shishlo, J. Holmes ECloud07 ORBIT Code ORBIT (Objective Ring Beam Injection and Transport code) ORBIT is an object-oriented, open-source code started
ORBIT Code Review and Future Directions S. Cousineau, A. Shishlo, J. Holmes ECloud07 ORBIT Code ORBIT (Objective Ring Beam Injection and Transport code) ORBIT is an object-oriented, open-source code started
Towards a formal description of models and workflows
 Towards a formal description of models and workflows Heinz A Preisig Process Systems Engineering @ Chemical Engineering NTNU, Trondheim, Norway MoDeNa - FP7 ++ Computational engineering The vision that
Towards a formal description of models and workflows Heinz A Preisig Process Systems Engineering @ Chemical Engineering NTNU, Trondheim, Norway MoDeNa - FP7 ++ Computational engineering The vision that
Interfaces and simulations in SELALIB
 Interfaces and simulations in SELALIB M. Mehrenberger IRMA, Université de Strasbourg Garching, Selalib Day, November 2014 M. Mehrenberger (UDS) Interfaces and simulations in SELALIB Garching, November
Interfaces and simulations in SELALIB M. Mehrenberger IRMA, Université de Strasbourg Garching, Selalib Day, November 2014 M. Mehrenberger (UDS) Interfaces and simulations in SELALIB Garching, November
Mathematical Models with Maple
 Algebraic Biology 005 151 Mathematical Models with Maple Tetsu YAMAGUCHI Applied System nd Division, Cybernet Systems Co., Ltd., Otsuka -9-3, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 11-001, Japan tetsuy@cybernet.co.jp Abstract
Algebraic Biology 005 151 Mathematical Models with Maple Tetsu YAMAGUCHI Applied System nd Division, Cybernet Systems Co., Ltd., Otsuka -9-3, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 11-001, Japan tetsuy@cybernet.co.jp Abstract
Recent Developments in Overture
 Recent Developments in Overture Bill Henshaw Center for Applied Scientific Computing, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA, USA. 11th Symposium on Overset Grids and Solution Technology,
Recent Developments in Overture Bill Henshaw Center for Applied Scientific Computing, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA, USA. 11th Symposium on Overset Grids and Solution Technology,
Numerical modelling of phase change processes in clouds. Challenges and Approaches. Martin Reitzle Bernard Weigand
 Institute of Aerospace Thermodynamics Numerical modelling of phase change processes in clouds Challenges and Approaches Martin Reitzle Bernard Weigand Introduction Institute of Aerospace Thermodynamics
Institute of Aerospace Thermodynamics Numerical modelling of phase change processes in clouds Challenges and Approaches Martin Reitzle Bernard Weigand Introduction Institute of Aerospace Thermodynamics
5. FVM discretization and Solution Procedure
 5. FVM discretization and Solution Procedure 1. The fluid domain is divided into a finite number of control volumes (cells of a computational grid). 2. Integral form of the conservation equations are discretized
5. FVM discretization and Solution Procedure 1. The fluid domain is divided into a finite number of control volumes (cells of a computational grid). 2. Integral form of the conservation equations are discretized
Distributed Memory Parallelization in NGSolve
 Distributed Memory Parallelization in NGSolve Lukas Kogler June, 2017 Inst. for Analysis and Scientific Computing, TU Wien From Shared to Distributed Memory Shared Memory Parallelization via threads (
Distributed Memory Parallelization in NGSolve Lukas Kogler June, 2017 Inst. for Analysis and Scientific Computing, TU Wien From Shared to Distributed Memory Shared Memory Parallelization via threads (
LibMesh Experience and Usage
 LibMesh Experience and Usage John W. Peterson peterson@cfdlab.ae.utexas.edu and Roy H. Stogner roystgnr@cfdlab.ae.utexas.edu Univ. of Texas at Austin September 9, 2008 1 Introduction 2 Weighted Residuals
LibMesh Experience and Usage John W. Peterson peterson@cfdlab.ae.utexas.edu and Roy H. Stogner roystgnr@cfdlab.ae.utexas.edu Univ. of Texas at Austin September 9, 2008 1 Introduction 2 Weighted Residuals
DUE: WEDS MARCH 26TH 2018
 HOMEWORK # 2: FINITE DIFFERENCES MAPPING AND TWO DIMENSIONAL PROBLEMS DUE: WEDS MARCH 26TH 2018 NOTE: In this homework, you will choose ONE of the following three questions to perform and hand-in. Each
HOMEWORK # 2: FINITE DIFFERENCES MAPPING AND TWO DIMENSIONAL PROBLEMS DUE: WEDS MARCH 26TH 2018 NOTE: In this homework, you will choose ONE of the following three questions to perform and hand-in. Each
fluid mechanics as a prominent discipline of application for numerical
 1. fluid mechanics as a prominent discipline of application for numerical simulations: experimental fluid mechanics: wind tunnel studies, laser Doppler anemometry, hot wire techniques,... theoretical fluid
1. fluid mechanics as a prominent discipline of application for numerical simulations: experimental fluid mechanics: wind tunnel studies, laser Doppler anemometry, hot wire techniques,... theoretical fluid
Block-Structured Adaptive Mesh Refinement
 Block-Structured Adaptive Mesh Refinement Lecture 2 Incompressible Navier-Stokes Equations Fractional Step Scheme 1-D AMR for classical PDE s hyperbolic elliptic parabolic Accuracy considerations Bell
Block-Structured Adaptive Mesh Refinement Lecture 2 Incompressible Navier-Stokes Equations Fractional Step Scheme 1-D AMR for classical PDE s hyperbolic elliptic parabolic Accuracy considerations Bell
The Advanced Research WRF (ARW) Dynamics Solver
 Dynamics: Introduction The Advanced Research WRF (ARW) Dynamics Solver 1. What is a dynamics solver? 2. Variables and coordinates 3. Equations 4. Time integration scheme 5. Grid staggering 6. Advection
Dynamics: Introduction The Advanced Research WRF (ARW) Dynamics Solver 1. What is a dynamics solver? 2. Variables and coordinates 3. Equations 4. Time integration scheme 5. Grid staggering 6. Advection
"C:\Program Files\ANSYS Inc\v190\CFX\bin\perllib\cfx5solve.pl" -batch -ccl runinput.ccl -fullname "Fluid Flow CFX_002"
 This run of the CFX Release 19.0 Solver started at 19:06:17 on 05 Jun 2018 by user ltval on DESKTOP-JCG0747 (intel_xeon64.sse2_winnt) using the command: "C:\Program Files\ANSYS Inc\v190\CFX\bin\perllib\cfx5solve.pl"
This run of the CFX Release 19.0 Solver started at 19:06:17 on 05 Jun 2018 by user ltval on DESKTOP-JCG0747 (intel_xeon64.sse2_winnt) using the command: "C:\Program Files\ANSYS Inc\v190\CFX\bin\perllib\cfx5solve.pl"
Fluid-Structure Interaction Problems using SU2 and External Finite-Element Solvers
 Fluid-Structure Interaction Problems using SU2 and External Finite-Element Solvers R. Sanchez 1, D. Thomas 2, R. Palacios 1, V. Terrapon 2 1 Department of Aeronautics, Imperial College London 2 Department
Fluid-Structure Interaction Problems using SU2 and External Finite-Element Solvers R. Sanchez 1, D. Thomas 2, R. Palacios 1, V. Terrapon 2 1 Department of Aeronautics, Imperial College London 2 Department
J S Parker (QUB), Martin Plummer (STFC), H W van der Hart (QUB) Version 1.0, September 29, 2015
 Report on ecse project Performance enhancement in R-matrix with time-dependence (RMT) codes in preparation for application to circular polarised light fields J S Parker (QUB), Martin Plummer (STFC), H
Report on ecse project Performance enhancement in R-matrix with time-dependence (RMT) codes in preparation for application to circular polarised light fields J S Parker (QUB), Martin Plummer (STFC), H
1D-HAM. Coupled Heat, Air and Moisture Transport in Multi-layered Wall Structures. Manual with brief theory and an example. Version 2.
 1D-HAM Coupled Heat, Air and Moisture Transport in Multi-layered Wall Structures. Manual with brief theory and an example. Version 2.0 30 t=70 days (1680 h) 100 Temperatures ( C) v (g/m³) 25 20 15 10 5
1D-HAM Coupled Heat, Air and Moisture Transport in Multi-layered Wall Structures. Manual with brief theory and an example. Version 2.0 30 t=70 days (1680 h) 100 Temperatures ( C) v (g/m³) 25 20 15 10 5
Application of Maxwell Equations to Human Body Modelling
 Application of Maxwell Equations to Human Body Modelling Fumie Costen Room E3, E0c at Sackville Street Building, fc@cs.man.ac.uk November 6, 00 Fumie Costen Room E3, E0c at Sackville Street Building, Application
Application of Maxwell Equations to Human Body Modelling Fumie Costen Room E3, E0c at Sackville Street Building, fc@cs.man.ac.uk November 6, 00 Fumie Costen Room E3, E0c at Sackville Street Building, Application
SPARSE SOLVERS POISSON EQUATION. Margreet Nool. November 9, 2015 FOR THE. CWI, Multiscale Dynamics
 SPARSE SOLVERS FOR THE POISSON EQUATION Margreet Nool CWI, Multiscale Dynamics November 9, 2015 OUTLINE OF THIS TALK 1 FISHPACK, LAPACK, PARDISO 2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW OF CARTESIUS 3 POISSON EQUATION 4 SOLVERS
SPARSE SOLVERS FOR THE POISSON EQUATION Margreet Nool CWI, Multiscale Dynamics November 9, 2015 OUTLINE OF THIS TALK 1 FISHPACK, LAPACK, PARDISO 2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW OF CARTESIUS 3 POISSON EQUATION 4 SOLVERS
Parallel Iterative Methods for Sparse Linear Systems. H. Martin Bücker Lehrstuhl für Hochleistungsrechnen
 Parallel Iterative Methods for Sparse Linear Systems Lehrstuhl für Hochleistungsrechnen www.sc.rwth-aachen.de RWTH Aachen Large and Sparse Small and Dense Outline Problem with Direct Methods Iterative
Parallel Iterative Methods for Sparse Linear Systems Lehrstuhl für Hochleistungsrechnen www.sc.rwth-aachen.de RWTH Aachen Large and Sparse Small and Dense Outline Problem with Direct Methods Iterative
Supplementary Material: A Guide for Using the Coupled SWAT MODSIM (SM) Model
 Supplementary Material: A Guide for Using the Coupled SWAT MODSIM (SM) Model Saeid Ashraf Vaghefi (saeedashrafv@gmail.com) The coupled SWAT MODSIM (SM) is a tool that can be used in integrated watershed
Supplementary Material: A Guide for Using the Coupled SWAT MODSIM (SM) Model Saeid Ashraf Vaghefi (saeedashrafv@gmail.com) The coupled SWAT MODSIM (SM) is a tool that can be used in integrated watershed
Transient flow and heat equations - the Rayleigh-Benard instability
 Transient flow and heat equations - the Rayleigh-Benard instability Directory: RayleighBenard Solvers: HeatSolve, FlowSolve Tools: ElmerGUI Dimensions: 2D, Transient Case definition This tutorial is about
Transient flow and heat equations - the Rayleigh-Benard instability Directory: RayleighBenard Solvers: HeatSolve, FlowSolve Tools: ElmerGUI Dimensions: 2D, Transient Case definition This tutorial is about
Open-source finite element solver for domain decomposition problems
 1/29 Open-source finite element solver for domain decomposition problems C. Geuzaine 1, X. Antoine 2,3, D. Colignon 1, M. El Bouajaji 3,2 and B. Thierry 4 1 - University of Liège, Belgium 2 - University
1/29 Open-source finite element solver for domain decomposition problems C. Geuzaine 1, X. Antoine 2,3, D. Colignon 1, M. El Bouajaji 3,2 and B. Thierry 4 1 - University of Liège, Belgium 2 - University
Is My CFD Mesh Adequate? A Quantitative Answer
 Is My CFD Mesh Adequate? A Quantitative Answer Krzysztof J. Fidkowski Gas Dynamics Research Colloqium Aerospace Engineering Department University of Michigan January 26, 2011 K.J. Fidkowski (UM) GDRC 2011
Is My CFD Mesh Adequate? A Quantitative Answer Krzysztof J. Fidkowski Gas Dynamics Research Colloqium Aerospace Engineering Department University of Michigan January 26, 2011 K.J. Fidkowski (UM) GDRC 2011
Numerical Programming I (for CSE)
 Technische Universität München WT 1/13 Fakultät für Mathematik Prof. Dr. M. Mehl B. Gatzhammer January 1, 13 Numerical Programming I (for CSE) Tutorial 1: Iterative Methods 1) Relaxation Methods a) Let
Technische Universität München WT 1/13 Fakultät für Mathematik Prof. Dr. M. Mehl B. Gatzhammer January 1, 13 Numerical Programming I (for CSE) Tutorial 1: Iterative Methods 1) Relaxation Methods a) Let
High-resolution finite volume methods for hyperbolic PDEs on manifolds
 High-resolution finite volume methods for hyperbolic PDEs on manifolds Randall J. LeVeque Department of Applied Mathematics University of Washington Supported in part by NSF, DOE Overview High-resolution
High-resolution finite volume methods for hyperbolic PDEs on manifolds Randall J. LeVeque Department of Applied Mathematics University of Washington Supported in part by NSF, DOE Overview High-resolution
Introduction to FARGO3D
 Introduction to FARGO3D PABLO BENITEZ-LLAMBAY / PBLLAMBAY@NBI.KU.DK FARGO3D is a versatile HD/MHD code that runs on clusters of CPUs or GPUs, developed with special emphasis on protoplanetary disks. However,
Introduction to FARGO3D PABLO BENITEZ-LLAMBAY / PBLLAMBAY@NBI.KU.DK FARGO3D is a versatile HD/MHD code that runs on clusters of CPUs or GPUs, developed with special emphasis on protoplanetary disks. However,
FEAST eigenvalue algorithm and solver: review and perspectives
 FEAST eigenvalue algorithm and solver: review and perspectives Eric Polizzi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Masachusetts, Amherst, USA Sparse Days, CERFACS, June 25, 2012
FEAST eigenvalue algorithm and solver: review and perspectives Eric Polizzi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Masachusetts, Amherst, USA Sparse Days, CERFACS, June 25, 2012
1 Overview. 2 Adapting to computing system evolution. 11 th European LS-DYNA Conference 2017, Salzburg, Austria
 1 Overview Improving LSTC s Multifrontal Linear Solver Roger Grimes 3, Robert Lucas 3, Nick Meng 2, Francois-Henry Rouet 3, Clement Weisbecker 3, and Ting-Ting Zhu 1 1 Cray Incorporated 2 Intel Corporation
1 Overview Improving LSTC s Multifrontal Linear Solver Roger Grimes 3, Robert Lucas 3, Nick Meng 2, Francois-Henry Rouet 3, Clement Weisbecker 3, and Ting-Ting Zhu 1 1 Cray Incorporated 2 Intel Corporation
Elliptic Problems / Multigrid. PHY 604: Computational Methods for Physics and Astrophysics II
 Elliptic Problems / Multigrid Summary of Hyperbolic PDEs We looked at a simple linear and a nonlinear scalar hyperbolic PDE There is a speed associated with the change of the solution Explicit methods
Elliptic Problems / Multigrid Summary of Hyperbolic PDEs We looked at a simple linear and a nonlinear scalar hyperbolic PDE There is a speed associated with the change of the solution Explicit methods
The Conjugate Gradient Method
 The Conjugate Gradient Method Classical Iterations We have a problem, We assume that the matrix comes from a discretization of a PDE. The best and most popular model problem is, The matrix will be as large
The Conjugate Gradient Method Classical Iterations We have a problem, We assume that the matrix comes from a discretization of a PDE. The best and most popular model problem is, The matrix will be as large
FDM for parabolic equations
 FDM for parabolic equations Consider the heat equation where Well-posed problem Existence & Uniqueness Mass & Energy decreasing FDM for parabolic equations CNFD Crank-Nicolson + 2 nd order finite difference
FDM for parabolic equations Consider the heat equation where Well-posed problem Existence & Uniqueness Mass & Energy decreasing FDM for parabolic equations CNFD Crank-Nicolson + 2 nd order finite difference
A Finite-Element based Navier-Stokes Solver for LES
 A Finite-Element based Navier-Stokes Solver for LES W. Wienken a, J. Stiller b and U. Fladrich c. a Technische Universität Dresden, Institute of Fluid Mechanics (ISM) b Technische Universität Dresden,
A Finite-Element based Navier-Stokes Solver for LES W. Wienken a, J. Stiller b and U. Fladrich c. a Technische Universität Dresden, Institute of Fluid Mechanics (ISM) b Technische Universität Dresden,
Special Nodes for Interface
 fi fi Special Nodes for Interface SW on processors Chip-level HW Board-level HW fi fi C code VHDL VHDL code retargetable compilation high-level synthesis SW costs HW costs partitioning (solve ILP) cluster
fi fi Special Nodes for Interface SW on processors Chip-level HW Board-level HW fi fi C code VHDL VHDL code retargetable compilation high-level synthesis SW costs HW costs partitioning (solve ILP) cluster
Iterative Methods for Solving A x = b
 Iterative Methods for Solving A x = b A good (free) online source for iterative methods for solving A x = b is given in the description of a set of iterative solvers called templates found at netlib: http
Iterative Methods for Solving A x = b A good (free) online source for iterative methods for solving A x = b is given in the description of a set of iterative solvers called templates found at netlib: http
Performance of the fusion code GYRO on three four generations of Crays. Mark Fahey University of Tennessee, Knoxville
 Performance of the fusion code GYRO on three four generations of Crays Mark Fahey mfahey@utk.edu University of Tennessee, Knoxville Contents Introduction GYRO Overview Benchmark Problem Test Platforms
Performance of the fusion code GYRO on three four generations of Crays Mark Fahey mfahey@utk.edu University of Tennessee, Knoxville Contents Introduction GYRO Overview Benchmark Problem Test Platforms
Sunrise: Patrik Jonsson. Panchromatic SED Models of Simulated Galaxies. Lecture 2: Working with Sunrise. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
 Sunrise: Panchromatic SED Models of Simulated Galaxies Lecture 2: Working with Sunrise Patrik Jonsson Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Lecture outline Lecture 1: Why Sunrise? What does it do?
Sunrise: Panchromatic SED Models of Simulated Galaxies Lecture 2: Working with Sunrise Patrik Jonsson Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Lecture outline Lecture 1: Why Sunrise? What does it do?
The Lattice Boltzmann method for hyperbolic systems. Benjamin Graille. October 19, 2016
 The Lattice Boltzmann method for hyperbolic systems Benjamin Graille October 19, 2016 Framework The Lattice Boltzmann method 1 Description of the lattice Boltzmann method Link with the kinetic theory Classical
The Lattice Boltzmann method for hyperbolic systems Benjamin Graille October 19, 2016 Framework The Lattice Boltzmann method 1 Description of the lattice Boltzmann method Link with the kinetic theory Classical
Modeling Multiphase Flow in Porous Media with Complementary Constraints
 Background Modeling Multiphase Flow in Porous Media with Complementary Constraints Applied Math, Statistics, and Scientific Computation, University of Maryland - College Park October 07, 2014 Advisors
Background Modeling Multiphase Flow in Porous Media with Complementary Constraints Applied Math, Statistics, and Scientific Computation, University of Maryland - College Park October 07, 2014 Advisors
Calculation of Sound Fields in Flowing Media Using CAPA and Diffpack
 Calculation of Sound Fields in Flowing Media Using CAPA and Diffpack H. Landes 1, M. Kaltenbacher 2, W. Rathmann 3, F. Vogel 3 1 WisSoft, 2 Univ. Erlangen 3 inutech GmbH Outline Introduction Sound in Flowing
Calculation of Sound Fields in Flowing Media Using CAPA and Diffpack H. Landes 1, M. Kaltenbacher 2, W. Rathmann 3, F. Vogel 3 1 WisSoft, 2 Univ. Erlangen 3 inutech GmbH Outline Introduction Sound in Flowing
Improvements for Implicit Linear Equation Solvers
 Improvements for Implicit Linear Equation Solvers Roger Grimes, Bob Lucas, Clement Weisbecker Livermore Software Technology Corporation Abstract Solving large sparse linear systems of equations is often
Improvements for Implicit Linear Equation Solvers Roger Grimes, Bob Lucas, Clement Weisbecker Livermore Software Technology Corporation Abstract Solving large sparse linear systems of equations is often
Matrix Assembly in FEA
 Matrix Assembly in FEA 1 In Chapter 2, we spoke about how the global matrix equations are assembled in the finite element method. We now want to revisit that discussion and add some details. For example,
Matrix Assembly in FEA 1 In Chapter 2, we spoke about how the global matrix equations are assembled in the finite element method. We now want to revisit that discussion and add some details. For example,
Multipole-Based Preconditioners for Sparse Linear Systems.
 Multipole-Based Preconditioners for Sparse Linear Systems. Ananth Grama Purdue University. Supported by the National Science Foundation. Overview Summary of Contributions Generalized Stokes Problem Solenoidal
Multipole-Based Preconditioners for Sparse Linear Systems. Ananth Grama Purdue University. Supported by the National Science Foundation. Overview Summary of Contributions Generalized Stokes Problem Solenoidal
MATLAB Solution of Flow and Heat Transfer through a Porous Cooling Channel and the Conjugate Heat Transfer in the Surrounding Wall
 MATLAB Solution of Flow and Heat Transfer through a Porous Cooling Channel and the Conjugate Heat Transfer in the Surrounding Wall James Cherry, Mehmet Sözen Grand Valley State University, cherryj1@gmail.com,
MATLAB Solution of Flow and Heat Transfer through a Porous Cooling Channel and the Conjugate Heat Transfer in the Surrounding Wall James Cherry, Mehmet Sözen Grand Valley State University, cherryj1@gmail.com,
- Part 4 - Multicore and Manycore Technology: Chances and Challenges. Vincent Heuveline
 - Part 4 - Multicore and Manycore Technology: Chances and Challenges Vincent Heuveline 1 Numerical Simulation of Tropical Cyclones Goal oriented adaptivity for tropical cyclones ~10⁴km ~1500km ~100km 2
- Part 4 - Multicore and Manycore Technology: Chances and Challenges Vincent Heuveline 1 Numerical Simulation of Tropical Cyclones Goal oriented adaptivity for tropical cyclones ~10⁴km ~1500km ~100km 2
Physics-Based Animation
 CSCI 5980/8980: Special Topics in Computer Science Physics-Based Animation 13 Fluid simulation with grids October 20, 2015 Today Presentation schedule Fluid simulation with grids Course feedback survey
CSCI 5980/8980: Special Topics in Computer Science Physics-Based Animation 13 Fluid simulation with grids October 20, 2015 Today Presentation schedule Fluid simulation with grids Course feedback survey
The Chemical Kinetics Time Step a detailed lecture. Andrew Conley ACOM Division
 The Chemical Kinetics Time Step a detailed lecture Andrew Conley ACOM Division Simulation Time Step Deep convection Shallow convection Stratiform tend (sedimentation, detrain, cloud fraction, microphysics)
The Chemical Kinetics Time Step a detailed lecture Andrew Conley ACOM Division Simulation Time Step Deep convection Shallow convection Stratiform tend (sedimentation, detrain, cloud fraction, microphysics)
Building Blocks for Direct Sequential Simulation on Unstructured Grids
 Building Blocks for Direct Sequential Simulation on Unstructured Grids Abstract M. J. Pyrcz (mpyrcz@ualberta.ca) and C. V. Deutsch (cdeutsch@ualberta.ca) University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, CANADA
Building Blocks for Direct Sequential Simulation on Unstructured Grids Abstract M. J. Pyrcz (mpyrcz@ualberta.ca) and C. V. Deutsch (cdeutsch@ualberta.ca) University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, CANADA
A recovery-assisted DG code for the compressible Navier-Stokes equations
 A recovery-assisted DG code for the compressible Navier-Stokes equations January 6 th, 217 5 th International Workshop on High-Order CFD Methods Kissimmee, Florida Philip E. Johnson & Eric Johnsen Scientific
A recovery-assisted DG code for the compressible Navier-Stokes equations January 6 th, 217 5 th International Workshop on High-Order CFD Methods Kissimmee, Florida Philip E. Johnson & Eric Johnsen Scientific
Efficient FEM-multigrid solver for granular material
 Efficient FEM-multigrid solver for granular material S. Mandal, A. Ouazzi, S. Turek Chair for Applied Mathematics and Numerics (LSIII), TU Dortmund STW user committee meeting Enschede, 25th September,
Efficient FEM-multigrid solver for granular material S. Mandal, A. Ouazzi, S. Turek Chair for Applied Mathematics and Numerics (LSIII), TU Dortmund STW user committee meeting Enschede, 25th September,
Review for Exam 2 Ben Wang and Mark Styczynski
 Review for Exam Ben Wang and Mark Styczynski This is a rough approximation of what we went over in the review session. This is actually more detailed in portions than what we went over. Also, please note
Review for Exam Ben Wang and Mark Styczynski This is a rough approximation of what we went over in the review session. This is actually more detailed in portions than what we went over. Also, please note
Preface to the Second Edition. Preface to the First Edition
 n page v Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xiii xvii 1 Background in Linear Algebra 1 1.1 Matrices................................. 1 1.2 Square Matrices and Eigenvalues....................
n page v Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition xiii xvii 1 Background in Linear Algebra 1 1.1 Matrices................................. 1 1.2 Square Matrices and Eigenvalues....................
Large-scale Electronic Structure Simulations with MVAPICH2 on Intel Knights Landing Manycore Processors
 Large-scale Electronic Structure Simulations with MVAPICH2 on Intel Knights Landing Manycore Processors Hoon Ryu, Ph.D. (E: elec1020@kisti.re.kr) Principal Researcher / Korea Institute of Science and Technology
Large-scale Electronic Structure Simulations with MVAPICH2 on Intel Knights Landing Manycore Processors Hoon Ryu, Ph.D. (E: elec1020@kisti.re.kr) Principal Researcher / Korea Institute of Science and Technology
SOLVING ELLIPTIC PDES
 university-logo SOLVING ELLIPTIC PDES School of Mathematics Semester 1 2008 OUTLINE 1 REVIEW 2 POISSON S EQUATION Equation and Boundary Conditions Solving the Model Problem 3 THE LINEAR ALGEBRA PROBLEM
university-logo SOLVING ELLIPTIC PDES School of Mathematics Semester 1 2008 OUTLINE 1 REVIEW 2 POISSON S EQUATION Equation and Boundary Conditions Solving the Model Problem 3 THE LINEAR ALGEBRA PROBLEM
Algorithms for Scientific Computing
 Algorithms for Scientific Computing Finite Element Methods Michael Bader Technical University of Munich Summer 2016 Part I Looking Back: Discrete Models for Heat Transfer and the Poisson Equation Modelling
Algorithms for Scientific Computing Finite Element Methods Michael Bader Technical University of Munich Summer 2016 Part I Looking Back: Discrete Models for Heat Transfer and the Poisson Equation Modelling
Numerical Solutions for Hyperbolic Systems of Conservation Laws: from Godunov Method to Adaptive Mesh Refinement
 Numerical Solutions for Hyperbolic Systems of Conservation Laws: from Godunov Method to Adaptive Mesh Refinement Romain Teyssier CEA Saclay Romain Teyssier 1 Outline - Euler equations, MHD, waves, hyperbolic
Numerical Solutions for Hyperbolic Systems of Conservation Laws: from Godunov Method to Adaptive Mesh Refinement Romain Teyssier CEA Saclay Romain Teyssier 1 Outline - Euler equations, MHD, waves, hyperbolic
CAEFEM v9.5 Information
 CAEFEM v9.5 Information Concurrent Analysis Corporation, 50 Via Ricardo, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 USA Tel. (805) 375 1060, Fax (805) 375 1061 email: info@caefem.com or support@caefem.com Web: http://www.caefem.com
CAEFEM v9.5 Information Concurrent Analysis Corporation, 50 Via Ricardo, Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 USA Tel. (805) 375 1060, Fax (805) 375 1061 email: info@caefem.com or support@caefem.com Web: http://www.caefem.com
An Overview of Fluid Animation. Christopher Batty March 11, 2014
 An Overview of Fluid Animation Christopher Batty March 11, 2014 What distinguishes fluids? What distinguishes fluids? No preferred shape. Always flows when force is applied. Deforms to fit its container.
An Overview of Fluid Animation Christopher Batty March 11, 2014 What distinguishes fluids? What distinguishes fluids? No preferred shape. Always flows when force is applied. Deforms to fit its container.
Statistical Clustering of Vesicle Patterns Practical Aspects of the Analysis of Large Datasets with R
 Statistical Clustering of Vesicle Patterns Mirko Birbaumer Rmetrics Workshop 3th July 2008 1 / 23 Statistical Clustering of Vesicle Patterns Practical Aspects of the Analysis of Large Datasets with R Mirko
Statistical Clustering of Vesicle Patterns Mirko Birbaumer Rmetrics Workshop 3th July 2008 1 / 23 Statistical Clustering of Vesicle Patterns Practical Aspects of the Analysis of Large Datasets with R Mirko
Lecture 8: Fast Linear Solvers (Part 7)
 Lecture 8: Fast Linear Solvers (Part 7) 1 Modified Gram-Schmidt Process with Reorthogonalization Test Reorthogonalization If Av k 2 + δ v k+1 2 = Av k 2 to working precision. δ = 10 3 2 Householder Arnoldi
Lecture 8: Fast Linear Solvers (Part 7) 1 Modified Gram-Schmidt Process with Reorthogonalization Test Reorthogonalization If Av k 2 + δ v k+1 2 = Av k 2 to working precision. δ = 10 3 2 Householder Arnoldi
Description of. Jimy Dudhia Dave Gill. Bill Skamarock. WPS d1 output. WPS d2 output Real and WRF. real.exe General Functions.
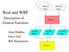 WPS d1 output WPS d2 output Real and WRF Description of real.exe General Functions Jimy Dudhia Dave Gill wrf d01 input wrf d01 bdy wrf d02 input Bill Skamarock wrf.exe Real program in a nutshell Function
WPS d1 output WPS d2 output Real and WRF Description of real.exe General Functions Jimy Dudhia Dave Gill wrf d01 input wrf d01 bdy wrf d02 input Bill Skamarock wrf.exe Real program in a nutshell Function
Part IV: Numerical schemes for the phase-filed model
 Part IV: Numerical schemes for the phase-filed model Jie Shen Department of Mathematics Purdue University IMS, Singapore July 29-3, 29 The complete set of governing equations Find u, p, (φ, ξ) such that
Part IV: Numerical schemes for the phase-filed model Jie Shen Department of Mathematics Purdue University IMS, Singapore July 29-3, 29 The complete set of governing equations Find u, p, (φ, ξ) such that
Assignment on iterative solution methods and preconditioning
 Division of Scientific Computing, Department of Information Technology, Uppsala University Numerical Linear Algebra October-November, 2018 Assignment on iterative solution methods and preconditioning 1.
Division of Scientific Computing, Department of Information Technology, Uppsala University Numerical Linear Algebra October-November, 2018 Assignment on iterative solution methods and preconditioning 1.
NIMROD Project Overview
 NIMROD Project Overview Christopher Carey - Univ. Wisconsin NIMROD Team www.nimrodteam.org CScADS Workshop July 23, 2007 Project Overview NIMROD models the macroscopic dynamics of magnetized plasmas by
NIMROD Project Overview Christopher Carey - Univ. Wisconsin NIMROD Team www.nimrodteam.org CScADS Workshop July 23, 2007 Project Overview NIMROD models the macroscopic dynamics of magnetized plasmas by
Code Verification of Multiphase Flow with MFIX
 Code Verification of Multiphase Flow with MFIX A N I R U D D H A C H O U D H A R Y ( A N I R U D D @ V T. E D U ), C H R I S T O P H E R J. ROY ( C J R O Y @ V T. E D U ), ( V I R G I N I A T E C H ) 23
Code Verification of Multiphase Flow with MFIX A N I R U D D H A C H O U D H A R Y ( A N I R U D D @ V T. E D U ), C H R I S T O P H E R J. ROY ( C J R O Y @ V T. E D U ), ( V I R G I N I A T E C H ) 23
2 CAI, KEYES AND MARCINKOWSKI proportional to the relative nonlinearity of the function; i.e., as the relative nonlinearity increases the domain of co
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL METHODS IN FLUIDS Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 2002; 00:1 6 [Version: 2000/07/27 v1.0] Nonlinear Additive Schwarz Preconditioners and Application in Computational Fluid
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR NUMERICAL METHODS IN FLUIDS Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 2002; 00:1 6 [Version: 2000/07/27 v1.0] Nonlinear Additive Schwarz Preconditioners and Application in Computational Fluid
Numerical Solution Techniques in Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
 Numerical Solution Techniques in Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Chunlei Liang LECTURE 9 Finite Volume method II 9.1. Outline of Lecture Conservation property of Finite Volume method Apply FVM to
Numerical Solution Techniques in Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Chunlei Liang LECTURE 9 Finite Volume method II 9.1. Outline of Lecture Conservation property of Finite Volume method Apply FVM to
Überblick von NX Nastran Multistep Nonlinear Solutions 401 und 402 Global Simcenter Portfolio Development Linz, 5.10.
 Überblick von NX Nastran Multistep Nonlinear Solutions 401 und 402 Martin.Kuessner@siemens.com Global Simcenter Portfolio Development Linz, 5.10.2018 Unrestricted Siemens AG 2018 Realize innovation. Simulation
Überblick von NX Nastran Multistep Nonlinear Solutions 401 und 402 Martin.Kuessner@siemens.com Global Simcenter Portfolio Development Linz, 5.10.2018 Unrestricted Siemens AG 2018 Realize innovation. Simulation
Large Scale Fluid-Structure Interaction by coupling OpenFOAM with external codes
 Large Scale Fluid-Structure Interaction by coupling OpenFOAM with external codes Thomas Gallinger * Alexander Kupzok Roland Wüchner Kai-Uwe Bletzinger Lehrstuhl für Statik Technische Universität München
Large Scale Fluid-Structure Interaction by coupling OpenFOAM with external codes Thomas Gallinger * Alexander Kupzok Roland Wüchner Kai-Uwe Bletzinger Lehrstuhl für Statik Technische Universität München
The Next Generation of Astrophysical Simulations of Compact Objects
 The Next Generation of Astrophysical Simulations of Compact Objects Christian Reisswig Caltech Einstein Symposium 2014 Motivation: Compact Objects Astrophysical phenomena with strong dynamical gravitational
The Next Generation of Astrophysical Simulations of Compact Objects Christian Reisswig Caltech Einstein Symposium 2014 Motivation: Compact Objects Astrophysical phenomena with strong dynamical gravitational
A Hybrid Method for the Wave Equation. beilina
 A Hybrid Method for the Wave Equation http://www.math.unibas.ch/ beilina 1 The mathematical model The model problem is the wave equation 2 u t 2 = (a 2 u) + f, x Ω R 3, t > 0, (1) u(x, 0) = 0, x Ω, (2)
A Hybrid Method for the Wave Equation http://www.math.unibas.ch/ beilina 1 The mathematical model The model problem is the wave equation 2 u t 2 = (a 2 u) + f, x Ω R 3, t > 0, (1) u(x, 0) = 0, x Ω, (2)
The RAMSES code and related techniques I. Hydro solvers
 The RAMSES code and related techniques I. Hydro solvers Outline - The Euler equations - Systems of conservation laws - The Riemann problem - The Godunov Method - Riemann solvers - 2D Godunov schemes -
The RAMSES code and related techniques I. Hydro solvers Outline - The Euler equations - Systems of conservation laws - The Riemann problem - The Godunov Method - Riemann solvers - 2D Godunov schemes -
Comprehensive support for quantitation
 Comprehensive support for quantitation One of the major new features in the current release of Mascot is support for quantitation. This is still work in progress. Our goal is to support all of the popular
Comprehensive support for quantitation One of the major new features in the current release of Mascot is support for quantitation. This is still work in progress. Our goal is to support all of the popular
Nonlinear Classification
 Nonlinear Classification INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder October 5-10, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Linear Classification Most classifiers we ve seen use linear functions
Nonlinear Classification INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder October 5-10, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Linear Classification Most classifiers we ve seen use linear functions
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Lecture 2 Boundary Conditions & Solver Settings
 Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Lecture 2 Boundary Conditions & Solver Settings Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Lecture 2 Boundary Conditions & Solver Settings Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry
Stellar Atmosphere Codes III. Mats Carlsson Rosseland Centre for Solar Physics, Univ Oslo La Laguna, November
 Stellar Atmosphere Codes III Mats Carlsson Rosseland Centre for Solar Physics, Univ Oslo La Laguna, November 14-15 2017 What physics need to be included when modeling the solar chromosphere? Boundaries
Stellar Atmosphere Codes III Mats Carlsson Rosseland Centre for Solar Physics, Univ Oslo La Laguna, November 14-15 2017 What physics need to be included when modeling the solar chromosphere? Boundaries
Computational Fluid Dynamics Prof. Dr. Suman Chakraborty Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Computational Fluid Dynamics Prof. Dr. Suman Chakraborty Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. #12 Fundamentals of Discretization: Finite Volume Method
Computational Fluid Dynamics Prof. Dr. Suman Chakraborty Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. #12 Fundamentals of Discretization: Finite Volume Method
Open boundary conditions in numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow
 Open boundary conditions in numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow M. P. Kirkpatrick S. W. Armfield Abstract In numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow, mass conservation can
Open boundary conditions in numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow M. P. Kirkpatrick S. W. Armfield Abstract In numerical simulations of unsteady incompressible flow, mass conservation can
Chapter 5 HIGH ACCURACY CUBIC SPLINE APPROXIMATION FOR TWO DIMENSIONAL QUASI-LINEAR ELLIPTIC BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS
 Chapter 5 HIGH ACCURACY CUBIC SPLINE APPROXIMATION FOR TWO DIMENSIONAL QUASI-LINEAR ELLIPTIC BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS 5.1 Introduction When a physical system depends on more than one variable a general
Chapter 5 HIGH ACCURACY CUBIC SPLINE APPROXIMATION FOR TWO DIMENSIONAL QUASI-LINEAR ELLIPTIC BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS 5.1 Introduction When a physical system depends on more than one variable a general
Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics. in Marine Engineering
 Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics in Marine Engineering Objectives Understand basic CFD theory Learn how to set up and run simulations in Star CCM+ and interpret results Learn about limitations and
Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics in Marine Engineering Objectives Understand basic CFD theory Learn how to set up and run simulations in Star CCM+ and interpret results Learn about limitations and
Chapter 6. Finite Element Method. Literature: (tiny selection from an enormous number of publications)
 Chapter 6 Finite Element Method Literature: (tiny selection from an enormous number of publications) K.J. Bathe, Finite Element procedures, 2nd edition, Pearson 2014 (1043 pages, comprehensive). Available
Chapter 6 Finite Element Method Literature: (tiny selection from an enormous number of publications) K.J. Bathe, Finite Element procedures, 2nd edition, Pearson 2014 (1043 pages, comprehensive). Available
Two-Dimensional Unsteady Flow in a Lid Driven Cavity with Constant Density and Viscosity ME 412 Project 5
 Two-Dimensional Unsteady Flow in a Lid Driven Cavity with Constant Density and Viscosity ME 412 Project 5 Jingwei Zhu May 14, 2014 Instructor: Surya Pratap Vanka 1 Project Description The objective of
Two-Dimensional Unsteady Flow in a Lid Driven Cavity with Constant Density and Viscosity ME 412 Project 5 Jingwei Zhu May 14, 2014 Instructor: Surya Pratap Vanka 1 Project Description The objective of
arxiv: v2 [physics.comp-ph] 4 Feb 2014
![arxiv: v2 [physics.comp-ph] 4 Feb 2014 arxiv: v2 [physics.comp-ph] 4 Feb 2014](/thumbs/87/95073421.jpg) Fast and accurate solution of the Poisson equation in an immersed setting arxiv:1401.8084v2 [physics.comp-ph] 4 Feb 2014 Alexandre Noll Marques a, Jean-Christophe Nave b, Rodolfo Ruben Rosales c Abstract
Fast and accurate solution of the Poisson equation in an immersed setting arxiv:1401.8084v2 [physics.comp-ph] 4 Feb 2014 Alexandre Noll Marques a, Jean-Christophe Nave b, Rodolfo Ruben Rosales c Abstract
Chapter 10 Exercises
 Chapter 10 Exercises From: Finite Difference Methods for Ordinary and Partial Differential Equations by R. J. LeVeque, SIAM, 2007. http://www.amath.washington.edu/ rl/fdmbook Exercise 10.1 (One-sided and
Chapter 10 Exercises From: Finite Difference Methods for Ordinary and Partial Differential Equations by R. J. LeVeque, SIAM, 2007. http://www.amath.washington.edu/ rl/fdmbook Exercise 10.1 (One-sided and
Numerik 2 Motivation
 Numerik 2 Motivation P. Bastian Universität Heidelberg Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für Wissenschaftliches Rechnen Im Neuenheimer Feld 368, D-69120 Heidelberg email: Peter.Bastian@iwr.uni-heidelberg.de April
Numerik 2 Motivation P. Bastian Universität Heidelberg Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für Wissenschaftliches Rechnen Im Neuenheimer Feld 368, D-69120 Heidelberg email: Peter.Bastian@iwr.uni-heidelberg.de April
11.3 MATLAB for Partial Differential Equations
 276 3. Generate the shape functions N (i) j = a (i) j where i =1, 2, 3,..., m and j =1, 2, 3,..., m. + b (i) j x + c(i) j y (11.2.17) 4. Compute the integrals for matrix elements α ij and vector elements
276 3. Generate the shape functions N (i) j = a (i) j where i =1, 2, 3,..., m and j =1, 2, 3,..., m. + b (i) j x + c(i) j y (11.2.17) 4. Compute the integrals for matrix elements α ij and vector elements
- Why aren t there more quantum algorithms? - Quantum Programming Languages. By : Amanda Cieslak and Ahmana Tarin
 - Why aren t there more quantum algorithms? - Quantum Programming Languages By : Amanda Cieslak and Ahmana Tarin Why aren t there more quantum algorithms? there are only a few problems for which quantum
- Why aren t there more quantum algorithms? - Quantum Programming Languages By : Amanda Cieslak and Ahmana Tarin Why aren t there more quantum algorithms? there are only a few problems for which quantum
Discretization of PDEs and Tools for the Parallel Solution of the Resulting Systems
 Discretization of PDEs and Tools for the Parallel Solution of the Resulting Systems Stan Tomov Innovative Computing Laboratory Computer Science Department The University of Tennessee Wednesday April 4,
Discretization of PDEs and Tools for the Parallel Solution of the Resulting Systems Stan Tomov Innovative Computing Laboratory Computer Science Department The University of Tennessee Wednesday April 4,
CS425: Algorithms for Web Scale Data
 CS425: Algorithms for Web Scale Data Most of the slides are from the Mining of Massive Datasets book. These slides have been modified for CS425. The original slides can be accessed at: www.mmds.org Challenges
CS425: Algorithms for Web Scale Data Most of the slides are from the Mining of Massive Datasets book. These slides have been modified for CS425. The original slides can be accessed at: www.mmds.org Challenges
Heat Transfer Modeling using ANSYS FLUENT
 Lecture 2 - Conduction Heat Transfer 14.5 Release Heat Transfer Modeling using ANSYS FLUENT 2013 ANSYS, Inc. March 28, 2013 1 Release 14.5 Agenda Introduction Energy equation in solids Equation solved
Lecture 2 - Conduction Heat Transfer 14.5 Release Heat Transfer Modeling using ANSYS FLUENT 2013 ANSYS, Inc. March 28, 2013 1 Release 14.5 Agenda Introduction Energy equation in solids Equation solved
