Fresnel s law, theory of reflection
|
|
|
- Robert Day
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
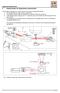
1 Fresnel s law, theory of reflection LP Used concepts Electromagnetic theory of light, reflection coefficient, reflection factor, Brewster s law, law of refraction, polarisation, degree of polarisation. Equipment Base plate with rubber feet HeNe laser Adjusting support 35 x 35 mm Surface mirror 30 x 30 mm Magnet foot Polarisation filter Prism table with support Prism, 60 o, flint glass Rotating guide rail with angular scale and magnet foot Photocell, silicone Measurement amplifier, universal Voltmeter V/ V~ Connecting cable, red, l = 500 mm Problem 1. The reflection coefficient of light, which is polarised either perpendicularly or parallel to the plane of incidence, is to be determined as a function of the angle of incidence and plotted graphically. Fig. 1: Experimental set up for the verification of the rotation of the plane of polarisation due to reflection (* only required for 5 mw laser) PHYWE Series of publication Handbook LASER PHYSICS I PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH D Göttingen, Germany
2 LP Fresnel s law, theory of reflection 2. The refraction index of the flint glass prism is to be determined. 3. The refraction coefficient is to be calculated by means of Fresnel s formula and compared to the measured curve. 4. The reflection factor for flint glass is calculated. 5. The rotation of the plane of polarisation for linearly polarised light after reflection is determined as a function of the angle of incidence and plotted graphically. This is compared to the values calculated by means of Fresnel s formula. Set-up and performance The experimental set up is shown in fig. 1. The recommended set up height (height of beam path) should be 130 mm. Set up of the rotating unit: To start with, the stopping screw of a magnet foot is removed. The circular orifice of the rotating guide rail is set under the foot. The angular scale is set onto the magnet foot and also on top of the rotating guide rail. The magnet foot is fixed to the optical base plate, and the rotating guide rail can be shifted sufficiently. Photocell LD can be fixed to one end and polarisation filter P 2 to the middle of the rotating guide rail, both by means of a magnet foot. During the set up of the optical base plate, the angular distribution should be reasonable, that is, the 0 o scale mark should be directed towards the incident laser beam. Prism Pr should be placed with the forward surface edge exactly on the central point of the table. The laser beam is then adjusted onto the central axis of the prism and of the table by means of adjusting screws M 1 and M 2. Concerning measurement: after letting the laser warm up for about 15 minutes, experimental set up is carried out without polarisation filter P 2 to start with. To determine the incident intensityi 0 of the light polarised parallel to the plane of incidence (pointer of polarizer P 1 set to 90), the prism is removed and the rotating guide rail is rotated so that the laser beam falls directly onto the photocell (amplification of the universal measurement amplifier must be adjusted in such a way that voltage does not increase above the maximum output voltage of 10 V). After the prism has been replaced onto the prism table, the rotating guide rail with detector LD is set to an angle ϕ of about 10 o. The prism table carrying the prism is now turned so that the reflected beam is directed towards detector LD. According to Snellius s law, the angle of incidence is equal to the exiting angle, that is, angle of incidence α is half the angle ϕ formed by the incident laser beam and the rotating guide rail. The angle of the rotating guide rail is now modified in steps of 5 o (steps of about 2.5 o in the area of Brewster s angle). The prism is turned every time in such a way that the laser beam falls on the detector, in order to determine light intensity I r. Angle ϕ should be varied up to about 160 o. This experiment is repeated with light polarised perpendicularly to the plane of incidence of the prism (pointer of polarizer P 1 set to 0 o ). For this, the intensity of the incident laser beam without prism, I 0 must be determined to start with. Concerning the 2 nd part of measurements: polarising filter P 2 is brought into the beam path between prism and photocell on the rotating guide rail. Polarizer P 1 is set to an angle of 45 o (pointer set to 45). Without prism, detector LD would indicate an intensity minimum if the polarising directions of the two polarising filters P 1 and P 2 were crossed (P 2 pointer at -45 o ). One makes use of the fact that the intensity minimum can be determined more precisely than the peak, so that during reflection at the prism, on looks for the intensity minimum through rotation of polarising filter P 2. The rotation supplementary to - 45 o is the rotation of the plane of polarisation Ψ due to reflection at the prism. This is carried out for different angles of incidence α of the laser beam on the surface of the prism. Variation of the angle of incidence is carried out as in the first part. Theory and evaluation In a light wave, the electric field vector E and the magnetic vector B oscillate perpendicularly and in phase to each other. Intensity is given by Maxwell s equation: B = n E (1) PHYWE Series of publication Handbook LASER PHYSICS I PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH D Göttingen, Germany
3 Fresnel s law, theory of reflection LP where n is the refraction index of the medium through which the light beam travels. The energy of the wave transported in the direction of propagation is given by Poynting s vector, according to the following relation: S E x B und S E 2 (2) If light falls onto a boundary surface of an isotropic medium of refraction index n with an angle of incidence α, part of the intensity is reflected and the rest goes through the medium under an angle of refraction β. The following indexes are used in the theory mentioned below: x, x direction of oscillation of the electric and magnetic filed vectors, which are directed either parallel or perpendicularly to the angle of incidence. x 0, x r, x t Incident, reflected and refracted vector components. In fig. 2A), the electric field vector E 0 of the incident light wave oscillates perpendicularly to the plane of incidence; according to (2), magnetic vector B 0 oscillates parallel to the latter. Related to the law of continuity of the tangential components (that is, the components which oscillate parallel to Fig. 2: A) direction of oscillation of the electric field vector perpendicularly and B) parallel to the direction of incidence the surface of the object) and to the direction of the beam, the following relation holds: E 0 + E r = E t ; (B 0 - Br ) cos α = B t cos β (3) With (1) and (3) one obtains: (E 0 E r ) cos α = n (E 0 + E r )cos β (4) Taking into account the law of refraction, the relation of field intensities is: ζ = E r I E 0 I cos α n cos β sin (α β) = = cos α + n cos β sin (α + β) (5) where ζ is defined as reflection coefficient. Fig. 2B) shows an incident light wave, whose vector E 0 oscillates perpendicularly to the plane of incidence. The following is obtained, similar to (3): B 0 + B r + B t ; (E 0 E r ) cos α = E t cos β (6) With (1) and (6) one obtains: (E 0 E r ) cos α = 1 n (E o + E r ) cos β (7) In a similar way to (5), one obtains the following reflection coefficients: ζ = E r E 0 = n cos α cos β n cos α + cos β = tan (α β) tan (α + β) (8) Fresnel s formulae (5) and (8) can be written in a different form, eliminating refraction angle β by means of Snellius law of refraction: ζ = E I r E I 0 = ( n 2 sin 2 α cos α) 2 n 2 1 ζ = E r E = n 2 cos α n 2 sin 2 α 0 n 2 cos α + n 2 sin 2 α (9a) (9b) ζ ζ is valid for all angles of incidence α between zero and π/2. PHYWE Series of publication Handbook LASER PHYSICS I PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH D Göttingen, Germany
4 LP Fresnel s law, theory of reflection Special cases A: the following relation is valid for perpendicular incidence (α = β = 0): ζ = ζ = n 1 n + 1 (10) B: for a grazing angle (α = π/2), the following holds: ζ = ζ = 1 (11) C: if the reflected and the refracted beams are perpendicular to each other (α + β = π/2), as shown in fig. 3, there follows from (8): ζ = 0 (12) that is, reflected light is completely polarised. In this case, the electric vector oscillates only perpendicularly to the plane of incidence. Related to Snellius law of refraction, the following is valid: Table 1 contains the voltages U r measured with the photocell for the reflected light intensity under an angle α. The voltages are directly proportional to light intensity, which itself is proportional to the square of field intensity according to (2). Fig. 4 shows the curves determined experimentally for ζ and ζ as a function of angle of incidence α. The curve for ζ displays a significant minimum for α p = 58.5 o. With this value and the point of intersection of the ζ curves with the ordinate axis, which can be obtained through extrapolation, applying (13) and (10), one obtains a value of n = 1.63 for the refraction index. The curve calculated theoretically according to (9), with n = 1.63, shows good agreement with experiment. The flatter curve of ζ at α p is caused by the laser light which has a degree of polarisation <1. If the reflection components from (9a) Fig. 4: Measured and calculated curves for ζ r and ζ r as a function of the angle of incidence sin α = n sin β = n sin ( π α) = n cos α 2 so that for this special case one obtains an angle of incidence from tan α p = n (13) (α p = polarisation or Brewster s angle). Fig. 3: Brewster s law PHYWE Series of publication Handbook LASER PHYSICS I PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH D Göttingen, Germany
5 Fresnel s law, theory of reflection LP and (9b) are squared and added, one obtains for the reflection factor R for perpendicular incidence: R = (E I r ) 2 + (E r ) 2 (E I 0 ) 2 + (E 0 ) = n 1 2 n (14) The reflection factor R for the flint glass prism (n = 1.63) s is thus approximately Another possibility to verify Fresnel s formulae is based on the following method: Linearly polarised light, with an electric field vector rotated by an azimuth angle δ against the plane of incidence, impinges on a glass reflector. The rotation of the plane of polarisation of the reflected beam is recorded as a function of the angle of incidence. In fig. 5, the plane of the paper represents the reflection surface. If the electric vector oscillates under an angle ω after reflection, the rotation of the plane of polarisation is given by the angle ψ = δ ω. The following relation is true for the field components parallel and perpendicular to the plane of incidence: E r = E r cos ω; E r = E r I sin ω (15) For the special case with δ = π/4, the following holds: tan ψ = tan ( π 4 ω) = 1 tanω 1+tanω (18) If tan ω from (17) is inserted into (18), one obtains after transformation: tan ψ = = cos (α + β) + cos (α β) cos (α + β) cos (α β) cos α 1 sin2 β sin α sin β (19) The definitive formula is obtained through elimination of refraction angle β through the law of refraction: ψ = arctan cos α n 2 sin 2 α sin 2 (20) α or tan ω = E I r E r = E I r E 0 E I 0 E I 0 E r E 0 (16) Fig. 6: Measured and calculated curves for the rotation of the direction of oscillation as a function of the angle of incidence (the azimuth of the incident beam is 45 o ) Using (5) and (8), one obtains from (16): tan ω = sin (α β) tan (α + β) sin (α + β) tan (α β) tan δ (17) Fig. 5: Rotation of the direction of oscillation through reflection PHYWE Series of publication Handbook LASER PHYSICS I PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH D Göttingen, Germany
6 LP Fresnel s law, theory of reflection If the plane of polarisation is turned by ψ = π/4, Brewster s law results: tan α ρ = n (21) Fig. 6 shows the measured rotation of the plane of polarisation as a function of the angle of incidence with good agreement with the values calculated by means of equation (20). Tabelle 1: Voltages U r and reflection coefficients as a function of angle α (U 0 = 3.0 V). α U r ζ U r ζ degrees Volt volt ~ PHYWE Series of publication Handbook LASER PHYSICS I PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH D Göttingen, Germany
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
Polarized Light. Nikki Truss. Abstract:
 Polarized Light Nikki Truss 9369481 Abstract: In this experiment, the properties of linearly polarised light were examined. Malus Law was verified using the apparatus shown in Fig. 1. Reflectance of s-polarised
Polarized Light Nikki Truss 9369481 Abstract: In this experiment, the properties of linearly polarised light were examined. Malus Law was verified using the apparatus shown in Fig. 1. Reflectance of s-polarised
LEP Faraday effect
 Related topics Electromagnetic field interaction, electron oscillation, electromagnetism, polarisation, Verdet s constant, Hall effect. Principle and task The angle of rotation of the polarisation-plane
Related topics Electromagnetic field interaction, electron oscillation, electromagnetism, polarisation, Verdet s constant, Hall effect. Principle and task The angle of rotation of the polarisation-plane
REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
 S-108-2110 OPTICS 1/6 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Student Labwork S-108-2110 OPTICS 2/6 Table of contents 1. Theory...3 2. Performing the measurements...4 2.1. Total internal reflection...4 2.2. Brewster
S-108-2110 OPTICS 1/6 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Student Labwork S-108-2110 OPTICS 2/6 Table of contents 1. Theory...3 2. Performing the measurements...4 2.1. Total internal reflection...4 2.2. Brewster
Coherence and width of spectral lines with Michelson interferometer
 Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
Polarised Light. Evan Sheridan, Chris Kervick, Tom Power October
 Polarised Light Evan Sheridan, Chris Kervick, Tom Power 11367741 October 22 2012 Abstract Properties of linear polarised light are investigated using Helium/Neon gas laser, polaroid,a silicon photodiode,a
Polarised Light Evan Sheridan, Chris Kervick, Tom Power 11367741 October 22 2012 Abstract Properties of linear polarised light are investigated using Helium/Neon gas laser, polaroid,a silicon photodiode,a
Polarization of light
 Laboratory#8 Phys4480/5480 Dr. Cristian Bahrim Polarization of light Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave (EM) which travels due to an electric field and a magnetic field oscillating in phase and
Laboratory#8 Phys4480/5480 Dr. Cristian Bahrim Polarization of light Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave (EM) which travels due to an electric field and a magnetic field oscillating in phase and
: Imaging Systems Laboratory II. Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 2002
 151-232: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 22 Abstract. In this lab, we will investigate linear and circular polarization of light. Linearly polarized
151-232: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 22 Abstract. In this lab, we will investigate linear and circular polarization of light. Linearly polarized
Wave Propagation in Uniaxial Media. Reflection and Transmission at Interfaces
 Lecture 5: Crystal Optics Outline 1 Homogeneous, Anisotropic Media 2 Crystals 3 Plane Waves in Anisotropic Media 4 Wave Propagation in Uniaxial Media 5 Reflection and Transmission at Interfaces Christoph
Lecture 5: Crystal Optics Outline 1 Homogeneous, Anisotropic Media 2 Crystals 3 Plane Waves in Anisotropic Media 4 Wave Propagation in Uniaxial Media 5 Reflection and Transmission at Interfaces Christoph
Chapter 1 - The Nature of Light
 David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
KERR EFFECT. Monochromatic, vertically polarized light impinges on a PLZT element (leadlanthanum-zirconium-titanium
 KERR EFFECT OBJECTVE 1. The phase-shift between the normal and the extra-ordinary light beam is to be recorded for different voltages applied to the PLZT-element respectively for different electric field
KERR EFFECT OBJECTVE 1. The phase-shift between the normal and the extra-ordinary light beam is to be recorded for different voltages applied to the PLZT-element respectively for different electric field
PH 222-2C Fall Electromagnetic Waves Lectures Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-2C Fall 2012 Electromagnetic Waves Lectures 21-22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
PH 222-2C Fall 2012 Electromagnetic Waves Lectures 21-22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
16. More About Polarization
 16. More About Polarization Polarization control Wave plates Circular polarizers Reflection & polarization Scattering & polarization Birefringent materials have more than one refractive index A special
16. More About Polarization Polarization control Wave plates Circular polarizers Reflection & polarization Scattering & polarization Birefringent materials have more than one refractive index A special
Lecture 5: Polarization. Polarized Light in the Universe. Descriptions of Polarized Light. Polarizers. Retarders. Outline
 Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Polarizers 4 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl ATI 2016,
Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Polarizers 4 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl ATI 2016,
Electromagnetic Waves. Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-3A Spring 2007 Electromagnetic Waves Lecture 22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
PH 222-3A Spring 2007 Electromagnetic Waves Lecture 22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
Chapter 33. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost entirely on the physics of electromagnetic waves. The connection between electric and magnetic fields to produce light is own of
Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost entirely on the physics of electromagnetic waves. The connection between electric and magnetic fields to produce light is own of
Learn how reflection at interfaces with different indices of refraction works and how interfaces can change the polarization states of light.
 Slide 1 Goals of the Lab: Learn how reflection at interfaces with different indices of refraction works and how interfaces can change the polarization states of light. Learn how to measure the influence
Slide 1 Goals of the Lab: Learn how reflection at interfaces with different indices of refraction works and how interfaces can change the polarization states of light. Learn how to measure the influence
Interferometer for Squareness measurement
 F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT
 POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics 8.03SC Fall 2016 Homework 9
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics 8.03SC Fall 016 Homework 9 Problems Problem 9.1 (0 pts) The ionosphere can be viewed as a dielectric medium of refractive index ωp n = 1 ω Where ω is the frequency
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics 8.03SC Fall 016 Homework 9 Problems Problem 9.1 (0 pts) The ionosphere can be viewed as a dielectric medium of refractive index ωp n = 1 ω Where ω is the frequency
Lecture 9. Transmission and Reflection. Reflection at a Boundary. Specific Boundary. Reflection at a Boundary
 Lecture 9 Reflection at a Boundary Transmission and Reflection A boundary is defined as a place where something is discontinuous Half the work is sorting out what is continuous and what is discontinuous
Lecture 9 Reflection at a Boundary Transmission and Reflection A boundary is defined as a place where something is discontinuous Half the work is sorting out what is continuous and what is discontinuous
Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials
 Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials Ajit Balagopal (Team Members Karunanand Ogirala, Hui Shen) ECE 614- PHOTONIC INFORMATION PROCESSING LABORATORY Abstract-- In this project, we study
Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials Ajit Balagopal (Team Members Karunanand Ogirala, Hui Shen) ECE 614- PHOTONIC INFORMATION PROCESSING LABORATORY Abstract-- In this project, we study
Experiment 8. Fresnel Coefficients. 8.1 Introduction. References
 Experiment 8 Fresnel Coefficients References Optics by Eugene Hecht, Chapter 4 Introduction to Modern Optics by Grant Fowles, Chapter 2 Principles of Optics by Max Born and Emil Wolf, Chapter 1 Optical
Experiment 8 Fresnel Coefficients References Optics by Eugene Hecht, Chapter 4 Introduction to Modern Optics by Grant Fowles, Chapter 2 Principles of Optics by Max Born and Emil Wolf, Chapter 1 Optical
Summary of Beam Optics
 Summary of Beam Optics Gaussian beams, waves with limited spatial extension perpendicular to propagation direction, Gaussian beam is solution of paraxial Helmholtz equation, Gaussian beam has parabolic
Summary of Beam Optics Gaussian beams, waves with limited spatial extension perpendicular to propagation direction, Gaussian beam is solution of paraxial Helmholtz equation, Gaussian beam has parabolic
Chiroptical Spectroscopy
 Chiroptical Spectroscopy Theory and Applications in Organic Chemistry Lecture 2: Polarized light Masters Level Class (181 041) Mondays, 8.15-9.45 am, NC 02/99 Wednesdays, 10.15-11.45 am, NC 02/99 28 Electromagnetic
Chiroptical Spectroscopy Theory and Applications in Organic Chemistry Lecture 2: Polarized light Masters Level Class (181 041) Mondays, 8.15-9.45 am, NC 02/99 Wednesdays, 10.15-11.45 am, NC 02/99 28 Electromagnetic
Electromagnetic Waves Across Interfaces
 Lecture 1: Foundations of Optics Outline 1 Electromagnetic Waves 2 Material Properties 3 Electromagnetic Waves Across Interfaces 4 Fresnel Equations 5 Brewster Angle 6 Total Internal Reflection Christoph
Lecture 1: Foundations of Optics Outline 1 Electromagnetic Waves 2 Material Properties 3 Electromagnetic Waves Across Interfaces 4 Fresnel Equations 5 Brewster Angle 6 Total Internal Reflection Christoph
Physics 214 Course Overview
 Physics 214 Course Overview Lecturer: Mike Kagan Course topics Electromagnetic waves Optics Thin lenses Interference Diffraction Relativity Photons Matter waves Black Holes EM waves Intensity Polarization
Physics 214 Course Overview Lecturer: Mike Kagan Course topics Electromagnetic waves Optics Thin lenses Interference Diffraction Relativity Photons Matter waves Black Holes EM waves Intensity Polarization
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 25 Propagation of Light Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Midterm Exam: Date: Wednesday, March 6 th Time: 8:00 10:00 pm Room: PHYS 203 Material: French, chapters
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 25 Propagation of Light Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Midterm Exam: Date: Wednesday, March 6 th Time: 8:00 10:00 pm Room: PHYS 203 Material: French, chapters
Homework 1. Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2017 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich
 Homework 1 Contact: mfrimmer@ethz.ch Due date: Friday 13.10.2017; 10:00 a.m. Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2017 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich www.photonics.ethz.ch The goal of this homework is to establish
Homework 1 Contact: mfrimmer@ethz.ch Due date: Friday 13.10.2017; 10:00 a.m. Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2017 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich www.photonics.ethz.ch The goal of this homework is to establish
Brewster's angle (3)
 Aim: Subjects: Diagram: To investigate the reflection and transmission of p- and s-polarized light at different angles of incidence at the surface of an acrylic block. Also the critical angle is shown.
Aim: Subjects: Diagram: To investigate the reflection and transmission of p- and s-polarized light at different angles of incidence at the surface of an acrylic block. Also the critical angle is shown.
Lab 11 - Polarization
 181 Name Date Partners Lab 11 - Polarization OBJECTIVES To study the general phenomena of electromagnetic wave polarization To investigate linearly polarized microwaves To investigate linearly polarized
181 Name Date Partners Lab 11 - Polarization OBJECTIVES To study the general phenomena of electromagnetic wave polarization To investigate linearly polarized microwaves To investigate linearly polarized
Lab #13: Polarization
 Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection
 Lecture 4: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light 4 Polarizers 5 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Utrecht
Lecture 4: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light 4 Polarizers 5 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Utrecht
Electromagnetic fields and waves
 Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c. Lecture 15 Reflection and Refraction
 Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 15 Reflection and Refraction What We (OK, Brian) Did Last Time Discussed EM waves in vacuum and in matter Maxwell s equations Wave equation Plane waves E t = c E B t
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 15 Reflection and Refraction What We (OK, Brian) Did Last Time Discussed EM waves in vacuum and in matter Maxwell s equations Wave equation Plane waves E t = c E B t
Sample Question Paper. Class XII -Physics. (Applicable for March 2016 Examination) Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70
 Sample Question Paper Class XII -Physics (Applicable for March 2016 Examination) Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions 1. All questions are compulsory. There are 26 questions in
Sample Question Paper Class XII -Physics (Applicable for March 2016 Examination) Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions 1. All questions are compulsory. There are 26 questions in
Physics 3312 Lecture 9 February 13, LAST TIME: Finished mirrors and aberrations, more on plane waves
 Physics 331 Lecture 9 February 13, 019 LAST TIME: Finished mirrors and aberrations, more on plane waves Recall, Represents a plane wave having a propagation vector k that propagates in any direction with
Physics 331 Lecture 9 February 13, 019 LAST TIME: Finished mirrors and aberrations, more on plane waves Recall, Represents a plane wave having a propagation vector k that propagates in any direction with
1. Consider the biconvex thick lens shown in the figure below, made from transparent material with index n and thickness L.
 Optical Science and Engineering 2013 Advanced Optics Exam Answer all questions. Begin each question on a new blank page. Put your banner ID at the top of each page. Please staple all pages for each individual
Optical Science and Engineering 2013 Advanced Optics Exam Answer all questions. Begin each question on a new blank page. Put your banner ID at the top of each page. Please staple all pages for each individual
Polarization properties of corner-cube retroreflectors: Theory and experiment
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 3--997 Polarization properties of corner-cube retroreflectors: Theory and experiment
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 3--997 Polarization properties of corner-cube retroreflectors: Theory and experiment
Lecture 36 Date:
 Lecture 36 Date: 5.04.04 Reflection of Plane Wave at Oblique Incidence (Snells Law, Brewster s Angle, Parallel Polarization, Perpendicular Polarization etc.) Introduction to RF/Microwave Introduction One
Lecture 36 Date: 5.04.04 Reflection of Plane Wave at Oblique Incidence (Snells Law, Brewster s Angle, Parallel Polarization, Perpendicular Polarization etc.) Introduction to RF/Microwave Introduction One
Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection
 Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light 4 Polarizers 5 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University,
Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light 4 Polarizers 5 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University,
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules: Waves and Optics. Hilary Term Dr Grant Ritchie
 The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules: Waves and Optics Hilary Term 008 Dr Grant Ritchie Wave motion - travelling waves Waves are collective bulk disturbances, whereby the motion at one position is
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules: Waves and Optics Hilary Term 008 Dr Grant Ritchie Wave motion - travelling waves Waves are collective bulk disturbances, whereby the motion at one position is
MIDSUMMER EXAMINATIONS 2001
 No. of Pages: 7 No. of Questions: 10 MIDSUMMER EXAMINATIONS 2001 Subject PHYSICS, PHYSICS WITH ASTROPHYSICS, PHYSICS WITH SPACE SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY, PHYSICS WITH MEDICAL PHYSICS Title of Paper MODULE
No. of Pages: 7 No. of Questions: 10 MIDSUMMER EXAMINATIONS 2001 Subject PHYSICS, PHYSICS WITH ASTROPHYSICS, PHYSICS WITH SPACE SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY, PHYSICS WITH MEDICAL PHYSICS Title of Paper MODULE
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2016 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
Homework 1. Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2018 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich
 Homework 1 Contact: mfrimmer@ethz.ch Due date: Friday 12 October 2018; 10:00 a.m. Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2018 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich www.photonics.ethz.ch The goal of this homework is to
Homework 1 Contact: mfrimmer@ethz.ch Due date: Friday 12 October 2018; 10:00 a.m. Nano Optics, Fall Semester 2018 Photonics Laboratory, ETH Zürich www.photonics.ethz.ch The goal of this homework is to
Experiment 5 Polarization and Modulation of Light
 1. Objective Experiment 5 Polarization and Modulation of Light Understanding the definition of polarized and un-polarized light. Understanding polarizer and analzer definition, Maluse s law. Retarding
1. Objective Experiment 5 Polarization and Modulation of Light Understanding the definition of polarized and un-polarized light. Understanding polarizer and analzer definition, Maluse s law. Retarding
Innovation and Development of Study Field. nano.tul.cz
 Innovation and Development of Study Field Nanomaterials at the Technical University of Liberec nano.tul.cz These materials have been developed within the ESF project: Innovation and development of study
Innovation and Development of Study Field Nanomaterials at the Technical University of Liberec nano.tul.cz These materials have been developed within the ESF project: Innovation and development of study
Light as a Transverse Wave.
 Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
Chapter 9. Reflection, Refraction and Polarization
 Reflection, Refraction and Polarization Introduction When you solved Problem 5.2 using the standing-wave approach, you found a rather curious behavior as the wave propagates and meets the boundary. A new
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization Introduction When you solved Problem 5.2 using the standing-wave approach, you found a rather curious behavior as the wave propagates and meets the boundary. A new
Sample Question Paper 3 Class XII Physics
 Sample Question Paper 3 Class XII Physics Time allowed: 3hrs Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. There are 26 questions in all. 2. This question paper has five sections:
Sample Question Paper 3 Class XII Physics Time allowed: 3hrs Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. There are 26 questions in all. 2. This question paper has five sections:
UNIT 102-6: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND POLARIZATION Approximate Time Three 100-minute Sessions
 Name St.No. - Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section UNIT 102-6: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND POLARIZATION Approximate Time Three 100-minute Sessions Hey diddle diddle, what kind of riddle Is this nature of light? Sometimes
Name St.No. - Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section UNIT 102-6: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND POLARIZATION Approximate Time Three 100-minute Sessions Hey diddle diddle, what kind of riddle Is this nature of light? Sometimes
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F)
 B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F) Note : Attempt FIVE questions in all taking least two questions from each Part. All questions carry equal marks Part-A Q. 1. (a) What are Newton's
B.Tech. First Semester Examination Physics-1 (PHY-101F) Note : Attempt FIVE questions in all taking least two questions from each Part. All questions carry equal marks Part-A Q. 1. (a) What are Newton's
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
Electromagnetic Waves Maxwell s equations predict the propagation of electromagnetic energy away from time-varying sources (current and charge) in the form of waves. Consider a linear, homogeneous, isotropic
Introduction to Polarization
 Phone: Ext 659, E-mail: hcchui@mail.ncku.edu.tw Fall/007 Introduction to Polarization Text Book: A Yariv and P Yeh, Photonics, Oxford (007) 1.6 Polarization States and Representations (Stokes Parameters
Phone: Ext 659, E-mail: hcchui@mail.ncku.edu.tw Fall/007 Introduction to Polarization Text Book: A Yariv and P Yeh, Photonics, Oxford (007) 1.6 Polarization States and Representations (Stokes Parameters
A COMMENTED EXAMPLE OF A GOOD LAB WORK REPORT. Why this document?
 A COMMENED EXAMPLE OF A GOOD LA WORK REPOR Why this document? his document summarizes with the help of an example how a good lab-work report should be written and formatted. n black on white the actual
A COMMENED EXAMPLE OF A GOOD LA WORK REPOR Why this document? his document summarizes with the help of an example how a good lab-work report should be written and formatted. n black on white the actual
Ref: J. D. Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics; A. Sommerfeld: Electrodynamics.
 2 Fresnel Equations Contents 2. Laws of reflection and refraction 2.2 Electric field parallel to the plane of incidence 2.3 Electric field perpendicular to the plane of incidence Keywords: Snell s law,
2 Fresnel Equations Contents 2. Laws of reflection and refraction 2.2 Electric field parallel to the plane of incidence 2.3 Electric field perpendicular to the plane of incidence Keywords: Snell s law,
Electromagnetic Waves
 Lecture 20 Chapter 34 Physics II Electromagnetic Waves Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Let s finish climbing our EM mountain. Maxwell s equations Let s revisit
Lecture 20 Chapter 34 Physics II Electromagnetic Waves Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Let s finish climbing our EM mountain. Maxwell s equations Let s revisit
Plane Waves Part II. 1. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when
 Plane Waves Part II. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when (a) The angle of incidence is equal to the Brewster angle with E field perpendicular
Plane Waves Part II. For an electromagnetic wave incident from one medium to a second medium, total reflection takes place when (a) The angle of incidence is equal to the Brewster angle with E field perpendicular
Atomic and nuclear physics
 Atomic and nuclear physics Atomic shell Normal Zeeman effect LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Observing the normal Zeeman effect in transverse and longitudinal Objects of the experiment Observing the line triplet
Atomic and nuclear physics Atomic shell Normal Zeeman effect LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Observing the normal Zeeman effect in transverse and longitudinal Objects of the experiment Observing the line triplet
Shear waves in solid-state materials
 Shear waves in solid-state materials TEAS Related topics Ultrasonic transmission measurement, propagation of ultrasound waves, ultrasound wave modes, shear waves, longitudinal and transverse waves, modulus
Shear waves in solid-state materials TEAS Related topics Ultrasonic transmission measurement, propagation of ultrasound waves, ultrasound wave modes, shear waves, longitudinal and transverse waves, modulus
Lab 11 - Polarization
 177 Name Date Partners OBJECTIVES Lab 11 - Polarization To study the general phenomena of electromagnetic polarization To see that microwaves are polarized To observe how light waves are linearly polarized
177 Name Date Partners OBJECTIVES Lab 11 - Polarization To study the general phenomena of electromagnetic polarization To see that microwaves are polarized To observe how light waves are linearly polarized
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
Surface Plasmon Wave
 Surface Plasmon Wave In this experiment you will learn about a surface plasmon wave. Certain metals (Au, Ag, Co, etc) exhibit a negative dielectric constant at certain regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Surface Plasmon Wave In this experiment you will learn about a surface plasmon wave. Certain metals (Au, Ag, Co, etc) exhibit a negative dielectric constant at certain regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Polarization of Light Spring 2015 Semester Matthew Jones Types of Polarization Light propagating through different materials: One polarization component can
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Polarization of Light Spring 2015 Semester Matthew Jones Types of Polarization Light propagating through different materials: One polarization component can
Poynting Theory & Wave Polarization
 Poynting Theory & Wave Polarization Prepared By Dr. Eng. Sherif Hekal Assistant Professor Electronics and Communications Engineering 10/31/2017 1 Agenda Poynting Theory o Poynting Vector o Time average
Poynting Theory & Wave Polarization Prepared By Dr. Eng. Sherif Hekal Assistant Professor Electronics and Communications Engineering 10/31/2017 1 Agenda Poynting Theory o Poynting Vector o Time average
Lab 8 - POLARIZATION
 137 Name Date Partners Lab 8 - POLARIZATION OBJECTIVES To study the general phenomena of electromagnetic wave polarization To investigate linearly polarized microwaves To investigate linearly polarized
137 Name Date Partners Lab 8 - POLARIZATION OBJECTIVES To study the general phenomena of electromagnetic wave polarization To investigate linearly polarized microwaves To investigate linearly polarized
Optics and Optical Design. Chapter 6: Polarization Optics. Lectures 11 13
 Optics and Optical Design Chapter 6: Polarization Optics Lectures 11 13 Cord Arnold / Anne L Huillier Polarization of Light Arbitrary wave vs. paraxial wave One component in x direction y x z Components
Optics and Optical Design Chapter 6: Polarization Optics Lectures 11 13 Cord Arnold / Anne L Huillier Polarization of Light Arbitrary wave vs. paraxial wave One component in x direction y x z Components
Lab 8 - Polarization
 Lab 8 Polarization L8-1 Name Date Partners Lab 8 - Polarization OBJECTIVES To study the general phenomena of electromagnetic wave polarization To investigate linearly polarized microwaves To investigate
Lab 8 Polarization L8-1 Name Date Partners Lab 8 - Polarization OBJECTIVES To study the general phenomena of electromagnetic wave polarization To investigate linearly polarized microwaves To investigate
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS
 PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Fundamentals of Optics. Midterm II. Mar. 21, :30 20:00.
 Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Midterm II Mar. 21, 217 18:3 2: Exam Type: C (A doublesided aid sheet and a nonprogrammable calculator
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Midterm II Mar. 21, 217 18:3 2: Exam Type: C (A doublesided aid sheet and a nonprogrammable calculator
III. Spherical Waves and Radiation
 III. Spherical Waves and Radiation Antennas radiate spherical waves into free space Receiving antennas, reciprocity, path gain and path loss Noise as a limit to reception Ray model for antennas above a
III. Spherical Waves and Radiation Antennas radiate spherical waves into free space Receiving antennas, reciprocity, path gain and path loss Noise as a limit to reception Ray model for antennas above a
Objectives. Faraday Rotation. Introduction. component. polarizers are at 0 with respect to. reduced to
 Faraday Rotation Objectives o To verify Malus law for two polarizers o To study the effect known as Faraday Rotation Introduction Light consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Light is polarized
Faraday Rotation Objectives o To verify Malus law for two polarizers o To study the effect known as Faraday Rotation Introduction Light consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Light is polarized
Reflection/Refraction
 Reflection/Refraction Page Reflection/Refraction Boundary Conditions Interfaces between different media imposed special boundary conditions on Maxwell s equations. It is important to understand what restrictions
Reflection/Refraction Page Reflection/Refraction Boundary Conditions Interfaces between different media imposed special boundary conditions on Maxwell s equations. It is important to understand what restrictions
PHYSICS 126, MESA COLLEGE Laboratory Manual
 PHYSICS 126, MESA COLLEGE Laboratory Manual Table of Content 1. Scotch Tape Electricity 2. Charging Processes 3. Equipotential Surfaces 4. Simple Circuits 5. Measurement of e/m 6. Magnetic Fields of Current
PHYSICS 126, MESA COLLEGE Laboratory Manual Table of Content 1. Scotch Tape Electricity 2. Charging Processes 3. Equipotential Surfaces 4. Simple Circuits 5. Measurement of e/m 6. Magnetic Fields of Current
Solutions: Homework 7
 Solutions: Homework 7 Ex. 7.1: Frustrated Total Internal Reflection a) Consider light propagating from a prism, with refraction index n, into air, with refraction index 1. We fix the angle of incidence
Solutions: Homework 7 Ex. 7.1: Frustrated Total Internal Reflection a) Consider light propagating from a prism, with refraction index n, into air, with refraction index 1. We fix the angle of incidence
EM waves: energy, resonators. Scalar wave equation Maxwell equations to the EM wave equation A simple linear resonator Energy in EM waves 3D waves
 EM waves: energy, resonators Scalar wave equation Maxwell equations to the EM wave equation A simple linear resonator Energy in EM waves 3D waves Simple scalar wave equation 2 nd order PDE 2 z 2 ψ (z,t)
EM waves: energy, resonators Scalar wave equation Maxwell equations to the EM wave equation A simple linear resonator Energy in EM waves 3D waves Simple scalar wave equation 2 nd order PDE 2 z 2 ψ (z,t)
444 Index Boundary condition at transmission line short circuit, 234 for normal component of B, 170, 180 for normal component of D, 169, 180 for tange
 Index A. see Magnetic vector potential. Acceptor, 193 Addition of complex numbers, 19 of vectors, 3, 4 Admittance characteristic, 251 input, 211 line, 251 Ampere, definition of, 427 Ampere s circuital
Index A. see Magnetic vector potential. Acceptor, 193 Addition of complex numbers, 19 of vectors, 3, 4 Admittance characteristic, 251 input, 211 line, 251 Ampere, definition of, 427 Ampere s circuital
Physics 313: Laboratory 8 - Polarization of Light Electric Fields
 Physics 313: Laboratory 8 - Polarization of Light Electric Fields Introduction: The electric fields that compose light have a magnitude, phase, and direction. The oscillating phase of the field and the
Physics 313: Laboratory 8 - Polarization of Light Electric Fields Introduction: The electric fields that compose light have a magnitude, phase, and direction. The oscillating phase of the field and the
Electromagnetic waves in free space
 Waveguide notes 018 Electromagnetic waves in free space We start with Maxwell s equations for an LIH medum in the case that the source terms are both zero. = =0 =0 = = Take the curl of Faraday s law, then
Waveguide notes 018 Electromagnetic waves in free space We start with Maxwell s equations for an LIH medum in the case that the source terms are both zero. = =0 =0 = = Take the curl of Faraday s law, then
Light propagation. Ken Intriligator s week 7 lectures, Nov.12, 2013
 Light propagation Ken Intriligator s week 7 lectures, Nov.12, 2013 What is light? Old question: is it a wave or a particle? Quantum mechanics: it is both! 1600-1900: it is a wave. ~1905: photons Wave:
Light propagation Ken Intriligator s week 7 lectures, Nov.12, 2013 What is light? Old question: is it a wave or a particle? Quantum mechanics: it is both! 1600-1900: it is a wave. ~1905: photons Wave:
Electromagnetic Theory: PHAS3201, Winter Maxwell s Equations and EM Waves
 Electromagnetic Theory: PHA3201, Winter 2008 5. Maxwell s Equations and EM Waves 1 Displacement Current We already have most of the pieces that we require for a full statement of Maxwell s Equations; however,
Electromagnetic Theory: PHA3201, Winter 2008 5. Maxwell s Equations and EM Waves 1 Displacement Current We already have most of the pieces that we require for a full statement of Maxwell s Equations; however,
REFLECTION AND REFRACTION OF PLANE EM WAVES
 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION OF PLANE EM WAVES When an electromagnetic wave hits a boundary between different materials, some of the wave s energy is reflected back while the rest continues on through the
REFLECTION AND REFRACTION OF PLANE EM WAVES When an electromagnetic wave hits a boundary between different materials, some of the wave s energy is reflected back while the rest continues on through the
1. In Young s double slit experiment, when the illumination is white light, the higherorder fringes are in color.
 TRUE-FALSE STATEMENTS: ELECTRICITY: 1. Electric field lines originate on negative charges. 2. The flux of the electric field over a closed surface is proportional to the net charge enclosed by the surface.
TRUE-FALSE STATEMENTS: ELECTRICITY: 1. Electric field lines originate on negative charges. 2. The flux of the electric field over a closed surface is proportional to the net charge enclosed by the surface.
Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Units of Chapter 31 Changing Electric Fields Produce Magnetic Fields; Ampère s Law and Displacement Current Gauss s Law for Magnetism Maxwell s
Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Units of Chapter 31 Changing Electric Fields Produce Magnetic Fields; Ampère s Law and Displacement Current Gauss s Law for Magnetism Maxwell s
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c
 Wave Phenomena Physics 5c Lecture 6 eflection and efraction (&L Sections. 3) Administravia! Laser safety video at the end of this lecture! Because you ll be doing take-home lab using a laser pointer! Lecture
Wave Phenomena Physics 5c Lecture 6 eflection and efraction (&L Sections. 3) Administravia! Laser safety video at the end of this lecture! Because you ll be doing take-home lab using a laser pointer! Lecture
PH 102 Exam II. 1. Solve 8 problems out of the 12 below. All problems have equal weight.
 PH 02 Exam II 20Mar07 LeClair INSTRUCTIONS. Solve 8 problems out of the 2 below. All problems have equal weight. 2. Clearly mark the problems you choose by filling in the adjacent circle. 3. Show as much
PH 02 Exam II 20Mar07 LeClair INSTRUCTIONS. Solve 8 problems out of the 2 below. All problems have equal weight. 2. Clearly mark the problems you choose by filling in the adjacent circle. 3. Show as much
4. Integrated Photonics. (or optoelectronics on a flatland)
 4. Integrated Photonics (or optoelectronics on a flatland) 1 x Benefits of integration in Electronics: Are we experiencing a similar transformation in Photonics? Mach-Zehnder modulator made from Indium
4. Integrated Photonics (or optoelectronics on a flatland) 1 x Benefits of integration in Electronics: Are we experiencing a similar transformation in Photonics? Mach-Zehnder modulator made from Indium
5. You may use the following values of physical constants wherever necessary. Class XII Physics (042) Sample Question Paper
 Class XII Physics (04) Sample Question Paper 018-19 Time allowed: hours. Max. Marks: 70 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. There are 7 questions in all.. This question paper has four
Class XII Physics (04) Sample Question Paper 018-19 Time allowed: hours. Max. Marks: 70 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. There are 7 questions in all.. This question paper has four
Maxwell s Equations & Hertz Waves
 Maxwell s Equations & Hertz Waves XI. Maxwell & Electromagnetic Waves A. Maxwell s Equations Dr. Bill Pezzaglia B. Hertz Waves & Poynting C. Polarization Updated: 3Aug5 A. Maxwell s Equations 3. Hints
Maxwell s Equations & Hertz Waves XI. Maxwell & Electromagnetic Waves A. Maxwell s Equations Dr. Bill Pezzaglia B. Hertz Waves & Poynting C. Polarization Updated: 3Aug5 A. Maxwell s Equations 3. Hints
EUV Reflectivity measurements on Acktar Sample Magic Black
 Report EUV Reflectivity measurements on Acktar Sample Magic Black S. Döring, Dr. K. Mann Laser-Laboratorium Göttingen e.v. October 28, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Setup 3 3 Measurements 4 4 Conclusion
Report EUV Reflectivity measurements on Acktar Sample Magic Black S. Döring, Dr. K. Mann Laser-Laboratorium Göttingen e.v. October 28, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Setup 3 3 Measurements 4 4 Conclusion
Optics. Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer. LD Physics Leaflets P
 Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light
 Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
Lecture 20 Optical Characterization 2
 Lecture 20 Optical Characterization 2 Schroder: Chapters 2, 7, 10 1/68 Announcements Homework 5/6: Is online now. Due Wednesday May 30th at 10:00am. I will return it the following Wednesday (6 th June).
Lecture 20 Optical Characterization 2 Schroder: Chapters 2, 7, 10 1/68 Announcements Homework 5/6: Is online now. Due Wednesday May 30th at 10:00am. I will return it the following Wednesday (6 th June).
X-ray absorption. 4. Prove that / = f(z 3.12 ) applies.
 Related topics Bremsstrahlung, characteristic radiation, Bragg scattering, law of absorption, mass absorption coefficient, absorption edge, half-value thickness, photoelectric effect, Compton scattering,
Related topics Bremsstrahlung, characteristic radiation, Bragg scattering, law of absorption, mass absorption coefficient, absorption edge, half-value thickness, photoelectric effect, Compton scattering,
PH2200 Practice Final Exam Summer 2003
 INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name and student identification number on the answer sheet. 2. Please cover your answer sheet at all times. 3. This is a closed book exam. You may use the PH2200 formula sheet
INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your name and student identification number on the answer sheet. 2. Please cover your answer sheet at all times. 3. This is a closed book exam. You may use the PH2200 formula sheet
9 Wave solution of Maxwells equations.
 9 Wave solution of Maxwells equations. Contents 9.1 Wave solution: Plane waves 9.2 Scalar Spherical waves 9.3 Cylindrical waves 9.4 Momentum and energy of the electromagnetic field Keywords: Plane, cylindrical
9 Wave solution of Maxwells equations. Contents 9.1 Wave solution: Plane waves 9.2 Scalar Spherical waves 9.3 Cylindrical waves 9.4 Momentum and energy of the electromagnetic field Keywords: Plane, cylindrical
Some Topics in Optics
 Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
