20th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad
|
|
|
- Derrick Robinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 0th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Mathematical Society of the Philippines Department of Science and Technology - Science Education Institute PMO Director: Ma. Nerissa Abara Test Development Committee: Christian Paul Chan Shio, Richard Eden, Louie John Vallejo Carlo Francisco Adajar, David Martin Cuajunco, Russelle Guadalupe, Job Nable, Lu Christian Ong, Lu Kevin Ong, Timothy Robin Teng
2 0th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad National Stage, Written Phase 0 January 018 Time: 4.5 hours Each item is worth 7 points. 1. In triangle ABC with ABC = 60 and 5AB = 4BC, points D and E are the feet of the altitudes from B and C, respectively. M is the midpoint of BD and the circumcircle of triangle BMC meets line AC again at N. Lines BN and CM meet at P. Prove that EDP = 90. Solution: From the given, AB = 4l and BC = 5l for some constant l > 0. Since ABC = 60, BE = 5l and CE = 5 l. Also, by the cosine law, AC = 1l. Since BEDC is cyclic, EDA = ABC = 60. Consequently, EDB = 0 and AED ACB. From the latter, AD = 4k, DE = 5k, and AE = 1k for some constant k > 0. Since 4l = AB = BE + AE = 5l + 1k, then l k = 1. The area of ABC equals 1 sin 60 4l 5l = 1 1l BM which gives BM = 5l 7. Observe that l/ CE DE = 5 5k = l k = 1 = 7 = 5l 5l/ 7 = CB MB. This, along with MBC = DBC = DEC, implies that DEC MBC, so ECD = BCM and thus, MCD = BCE = 0. As BMNC is cyclic, MBN = 0 so that lines ED and BN are parallel. We have DMC = 60 so that BP M = 0. Thus, BMP is isosceles with BM = MP and it follows that M is the circumcenter of BP D. Therefore, BP D = 90. It follows that EDP = 90.
3 . Suppose a 1, a,... is a sequence of integers, and d is some integer. For all natural numbers n, (i) a n is prime; (ii) a n+ = a n+1 + a n + d. Show that the sequence is constant. Solution: Consider the sequence {b n } defined by b n = a n + d for all n, so that b n+ = b n+1 + b n for all n. This sequence is determined by its first two terms b 1 and b, and the same holds true if we reduce the sequence mod a 1. Taking remainders mod a 1, pairs of consecutive terms will repeat themselves, and so the sequence {b n } is periodic mod a 1, i.e., there exists a positive integer l for which b k+l b l (mod a 1 ) for all k, and so a l+1 a 1 (mod a 1 ). Thus, a 1 a l+1. From (i), we must have a 1 = a l+1, and in fact, a 1 = a kl+1 for all k. In particular, a kl+1, and thus b kl+1, assumes at most two distinct values. It suffices to show that {b n } is constant. Consider the characteristic polynomial of the recurrence defining {b n }, P (x) = x x 1. Let ϕ and ψ be the distinct roots of P, with ϕ > ψ. Note that in fact ϕ > 1 while 0 > ψ > 1. There exists a unique pair of constants c 1, c, dependent on the values of b 1 and b, satisfying the system b 1 = c 1 + c b = c 1 ϕ + c ψ. It can be proved easily by induction that b n = c 1 ϕ n 1 + c ψ n 1 for all n 1. From this, we get that b n c 1 ϕ n 1 c. If c 1 0, then b n eventually grows without bound, which contradicts our previous assertion that b kl+1 assumes at most two values. Thus, c 1 = 0, and consequently, b n+1 = ψb n. However, b n+1 and b n are integers while ψ is irrational. This forces us to conclude that b n+1 = b n = 0, and so c = 0 as well. Thus, b n = 0 for all n, and a n = a 1 (with d = a 1 ).. Let n be a positive integer. An n n matrix (a rectangular array of numbers with n rows and n columns) is said to be a platinum 1 matrix if (i) the n entries are integers from 1 to n; (ii) each row, each column, and the main diagonal (from the upper left corner to the lower right corner) contains each integer from 1 to n exactly once; and 1 Platinum is the modern gift for the 0th wedding anniversary.
4 (iii) there exists a collection of n entries containing each of the numbers from 1 to n, such that no two entries lie on the same row or column, and none of which lie on the main diagonal of the matrix. Determine all values of n for which there exists an n n platinum matrix. This is based on the paper A Simple Method for Constructing Doubly Diagonalized Latin Squares by Ervin Gergely, Journal of Combinatorial Theory (A) 16, 66-7 (1974). Solution: There is no platinum matrix for n = 1 and for n =. We claim that a platinum matrix exists for all integers n. Define a transversal as a collection of n matrix entries which are taken from distinct rows and columns, and which contains each of the numbers 1 to n. When n is odd, we can construct an n n platinum matrix in the following manner: First, fill up the first row with 1, n, n 1,...,, from left to right. Then fill up each diagonal (which goes up to down, left to right and wraps back to the 1st column after the nth column) by starting with its first row entry and incrementing by 1 as we go down to the last row. From this point onwards, entries are reduced mod n, but with n written instead of 0. For example, for n =, we have the following platinum matrix = From the construction described, the entry in row i, column j (1 i, j n) is a ij = i j (again, reduced mod n as mentioned above). For a fixed row i, the entries for different columns j and j are distinct. For a fixed column j, the entries for different rows i and i are distinct since n is odd. The diagonal whose first row entry is is a transversal; in fact, each diagonal is a transversal. Thus, the matrix is platinum. Let n 8 be even, so n 5 is odd. Consider the (n ) (n ) platinum matrix, denoted by C n, following the construction above. We start constructing our n n platinum matrix as follows: ( ) n n n 1 Cn where C C = n n 1 n. n 1 n n We then need to fill in the (n ) matrix and the (n ) matrix adjacent to C n. To do this, from the (n ) 1 = n 4 4 diagonals of 4
5 C n other than its main diagonal, choose. For one of these transversals, project its entries vertically into an empty row and horizontally into an empty column, then replace all of the entries of this chosen transversal by n. Then repeat this procedure using the symbols n 1 and n using the two other transversals. The resulting matrix is then a platinum matrix. Of the n 4 4 transversals described above for C n, at least one has not been used yet. This, along with a transversal of C other than its main diagonal, then form a transversal of the formed n n matrix; none of the entries of this transversal are in the main diagonal. The matrix formed is thus platinum. The following illustrates the construction for the case n = 8. The final matrix is platinum, with the boxed entries all off-diagonal and forming a transversal Lastly, consider the following matrices It is straightforward to verify that these are platinum matrices for n = 4 and n = 6. 5
6 4. Determine all ordered pairs (x, y) of nonnegative integers that satisfy the equation x + 9 y = x(4 y+1 1). This is a modified version of Problem N from the 010 IMO shortlist. Solution: The equation is equivalent to (x) + y+1 = x Letting a = x and b = y + 1, we have [ ] (y+1)+1 1. a + b = a( b+1 1). (1) Case 1: b = 1 We have a a + 6 = 0 which has no integer solution for a. Thus, there is no solution in this case. Case : b = We have a 15a + 54 = 0, whose roots are 6 and 9, both divisible by. This case then has the solutions (, 1) and (, 1) for the original equation. Case : b = 5 We have a 6a = 0, whose roots are 9 and 54, both divisible by. We get as additional solutions (, ) and (18, ). Case 4: b 7, b odd It follows from (1) that a b. Since a is divisible by, either a = p for some 1 p b or a = q for some 1 q b. For the first case a = p, let q = b p. Then we have b+1 1 = a + b a = p + q. For the second case a = q, let p = b q. Then we have b+1 1 = a + b a = q + p. In either case, b+1 1 = p + q () where p + q = b. Consequently, b+1 > p and b+1 > q. Thus, p < b+1 = 8 b+1 < 9 b+1 = (b+1) q < b+1 = 8 b b b (b+1) < 9 = < 6
7 Thus, p, q < (b+1). Since p = b q and q = b p, we get p, q > b (b+1) b. Therefore, b < p, q < (b + 1). = Let r = min{p, q}. Since r > b 5, then r. Consequently, the right hand side of () is divisible by 9. Thus, 9 divides b+1 1. This is true only if 6 b + 1. Since b 7, then b 11. Thus, we can let b + 1 = 6s for some positive integer s, and we can write b+1 1 = 6s 1 = 4 s 1 = ( s 1)( s + 1)(4 s + 4 s + 1). Since 4 s 1 mod, then 4 s +4 s +1 = (4 s 1) + 4 s is always divisible by but never by 9. Furthermore, at most one of s 1 and s + 1 is divisible by, being consecutive odd numbers. Since r b+1 1, then either r 1 s 1 or r 1 s + 1. From both cases, we have r 1 s + 1. Thus, r 1 s + 1 s = b+1 6. Therefore, b 1 < r 1 b which implies b < 11. However, there is no odd integer b between 7 (included) and 11 (excluded) such that 6 b+1. There are then no solutions for this last case. Therefore, the solutions (x, y) of the given equation are (, 1), (, 1), (, ), and (18, ). 7
8 . The PHILIPPINE TEAM to the 59th International Mathematical Olympiad Cluj-Napoca, Romania July to 14, 018 Left to Right 1. Shaquille Wyan Que, Grace Christian College. Sean Anderson Ty, Zamboanga Chong Hua High School. Albert John Patupat, De La Salle University Integrated School 4. Kyle Patrick Dulay, Philippine Science High School - Main Campus 5. Andres Rico Gonzales III, Colegio de San Juan de Letran 6. Emmanuel Osbert Cajayon, Emilio Aguinaldo College Team Leader: Richard Eden, Ateneo de Manila University Deputy Team Leader: Christian Paul Chan Shio, Ateneo de Manila University Observer B: Carlo Francisco Adajar, University of the Philippines - Diliman 8
XX Asian Pacific Mathematics Olympiad
 XX Asian Pacific Mathematics Olympiad March, 008 Problem 1. Let ABC be a triangle with A < 60. Let X and Y be the points on the sides AB and AC, respectively, such that CA + AX = CB + BX and BA + AY =
XX Asian Pacific Mathematics Olympiad March, 008 Problem 1. Let ABC be a triangle with A < 60. Let X and Y be the points on the sides AB and AC, respectively, such that CA + AX = CB + BX and BA + AY =
Problems and Solutions
 46 th Canadian Mathematical Olympiad Wednesday, April 2, 204 Problems and Solutions. Let a, a 2,..., a n be positive real numbers whose product is. Show that the sum a a 2 + + a ( + a )( + a 2 ) + a 3
46 th Canadian Mathematical Olympiad Wednesday, April 2, 204 Problems and Solutions. Let a, a 2,..., a n be positive real numbers whose product is. Show that the sum a a 2 + + a ( + a )( + a 2 ) + a 3
11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers, and Hints
 view.php3 (JPEG Image, 840x888 pixels) - Scaled (71%) https://mail.ateneo.net/horde/imp/view.php3?mailbox=inbox&inde... 1 of 1 11/5/2008 5:02 PM 11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers,
view.php3 (JPEG Image, 840x888 pixels) - Scaled (71%) https://mail.ateneo.net/horde/imp/view.php3?mailbox=inbox&inde... 1 of 1 11/5/2008 5:02 PM 11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers,
1998 IMO Shortlist BM BN BA BC AB BC CD DE EF BC CA AE EF FD
 IMO Shortlist 1998 Geometry 1 A convex quadrilateral ABCD has perpendicular diagonals. The perpendicular bisectors of the sides AB and CD meet at a unique point P inside ABCD. the quadrilateral ABCD is
IMO Shortlist 1998 Geometry 1 A convex quadrilateral ABCD has perpendicular diagonals. The perpendicular bisectors of the sides AB and CD meet at a unique point P inside ABCD. the quadrilateral ABCD is
This class will demonstrate the use of bijections to solve certain combinatorial problems simply and effectively.
 . Induction This class will demonstrate the fundamental problem solving technique of mathematical induction. Example Problem: Prove that for every positive integer n there exists an n-digit number divisible
. Induction This class will demonstrate the fundamental problem solving technique of mathematical induction. Example Problem: Prove that for every positive integer n there exists an n-digit number divisible
IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2
 IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2 July 3, 2008 1. Given an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC. The midpoint of side BC is denoted by M. Let X be a variable point on the shorter arc MA of the circumcircle
IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2 July 3, 2008 1. Given an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC. The midpoint of side BC is denoted by M. Let X be a variable point on the shorter arc MA of the circumcircle
37th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad
 37th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad 1. Prove that for each positive integer n, there are pairwise relatively prime integers k 0, k 1,..., k n, all strictly greater than 1, such that k 0
37th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad 1. Prove that for each positive integer n, there are pairwise relatively prime integers k 0, k 1,..., k n, all strictly greater than 1, such that k 0
IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2 Solutions
 IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2 Solutions July 3, 2008 1. Given an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC. The midpoint of side BC is denoted by M. Let X be a variable point on the shorter arc MA of the
IMO Training Camp Mock Olympiad #2 Solutions July 3, 2008 1. Given an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC. The midpoint of side BC is denoted by M. Let X be a variable point on the shorter arc MA of the
1. Prove that for every positive integer n there exists an n-digit number divisible by 5 n all of whose digits are odd.
 32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Proposed Solutions May, 23 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of IMO 22. This scheme encourages complete solutions.
32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Proposed Solutions May, 23 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of IMO 22. This scheme encourages complete solutions.
Gordon solutions. n=1 1. p n
 Gordon solutions 1. A positive integer is called a palindrome if its base-10 expansion is unchanged when it is reversed. For example, 121 and 7447 are palindromes. Show that if we denote by p n the nth
Gordon solutions 1. A positive integer is called a palindrome if its base-10 expansion is unchanged when it is reversed. For example, 121 and 7447 are palindromes. Show that if we denote by p n the nth
32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Recommended Marking Scheme May 1, 2003
 32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Recommended Marking Scheme May 1, 23 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of IMO 22. This scheme encourages complete solutions.
32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Recommended Marking Scheme May 1, 23 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of IMO 22. This scheme encourages complete solutions.
15th Bay Area Mathematical Olympiad. BAMO Exam. February 26, Solutions to BAMO-8 and BAMO-12 Problems
 15th Bay Area Mathematical Olympiad BAMO Exam February 26, 2013 Solutions to BAMO-8 and BAMO-12 Problems 1 How many different sets of three points in this equilateral triangular grid are the vertices of
15th Bay Area Mathematical Olympiad BAMO Exam February 26, 2013 Solutions to BAMO-8 and BAMO-12 Problems 1 How many different sets of three points in this equilateral triangular grid are the vertices of
13 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 20 February 2010
 13 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 0 February 010 1. [3] Suppose that x and y are positive reals such that Find x. x y = 3, x + y = 13. 3+ Answer: 17 Squaring both sides of x y =
13 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 0 February 010 1. [3] Suppose that x and y are positive reals such that Find x. x y = 3, x + y = 13. 3+ Answer: 17 Squaring both sides of x y =
2003 AIME Given that ((3!)!)! = k n!, where k and n are positive integers and n is as large as possible, find k + n.
 003 AIME 1 Given that ((3!)!)! = k n!, where k and n are positive integers and n is as large 3! as possible, find k + n One hundred concentric circles with radii 1,, 3,, 100 are drawn in a plane The interior
003 AIME 1 Given that ((3!)!)! = k n!, where k and n are positive integers and n is as large 3! as possible, find k + n One hundred concentric circles with radii 1,, 3,, 100 are drawn in a plane The interior
NEW YORK CITY INTERSCHOLASTIC MATHEMATICS LEAGUE Senior A Division CONTEST NUMBER 1
 Senior A Division CONTEST NUMBER 1 PART I FALL 2011 CONTEST 1 TIME: 10 MINUTES F11A1 Larry selects a 13-digit number while David selects a 10-digit number. Let be the number of digits in the product of
Senior A Division CONTEST NUMBER 1 PART I FALL 2011 CONTEST 1 TIME: 10 MINUTES F11A1 Larry selects a 13-digit number while David selects a 10-digit number. Let be the number of digits in the product of
The sum x 1 + x 2 + x 3 is (A): 4 (B): 6 (C): 8 (D): 14 (E): None of the above. How many pairs of positive integers (x, y) are there, those satisfy
 Important: Answer to all 15 questions. Write your answers on the answer sheets provided. For the multiple choice questions, stick only the letters (A, B, C, D or E) of your choice. No calculator is allowed.
Important: Answer to all 15 questions. Write your answers on the answer sheets provided. For the multiple choice questions, stick only the letters (A, B, C, D or E) of your choice. No calculator is allowed.
Syllabus. + + x + n 1 n. + x + 2
 1. Special Functions This class will cover problems involving algebraic functions other than polynomials, such as square roots, the floor function, and logarithms. Example Problem: Let n be a positive
1. Special Functions This class will cover problems involving algebraic functions other than polynomials, such as square roots, the floor function, and logarithms. Example Problem: Let n be a positive
1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2017
 1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 017 1.1 Junior Section Question 1. Suppose x 1, x, x 3 are the roots of polynomial P (x) = x 3 6x + 5x + 1. The sum x 1 + x + x 3 is (A): 4 (B): 6 (C): 8 (D): 14 (E):
1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 017 1.1 Junior Section Question 1. Suppose x 1, x, x 3 are the roots of polynomial P (x) = x 3 6x + 5x + 1. The sum x 1 + x + x 3 is (A): 4 (B): 6 (C): 8 (D): 14 (E):
HMMT November 2012 Saturday 10 November 2012
 HMMT November 01 Saturday 10 November 01 1. [5] 10 total. The prime numbers under 0 are:,, 5, 7, 11, 1, 17, 19,, 9. There are 10 in. [5] 180 Albert s choice of burgers, sides, and drinks are independent
HMMT November 01 Saturday 10 November 01 1. [5] 10 total. The prime numbers under 0 are:,, 5, 7, 11, 1, 17, 19,, 9. There are 10 in. [5] 180 Albert s choice of burgers, sides, and drinks are independent
1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why. (a b)(a c)(a d)(b c)(b d)(c d) a 2 + ab b = 2018.
 New Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Committee Camp Selection Problems 2018 Solutions Due: 28th September 2018 1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why must be a multiple of
New Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Committee Camp Selection Problems 2018 Solutions Due: 28th September 2018 1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why must be a multiple of
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K R MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND First Printing, 99 Chapter LINEAR EQUATIONS Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x,
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K R MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND First Printing, 99 Chapter LINEAR EQUATIONS Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x,
Solutions, 2004 NCS/MAA TEAM COMPETITION
 Solutions, 004 NCS/MAA TEAM COMPETITION Each problem number is followed by an 11-tuple (a 10, a 9, a 8, a 7, a 6, a 5, a 4, a 3, a, a 1, a 0 ), where a k is the number of teams that scored k points on
Solutions, 004 NCS/MAA TEAM COMPETITION Each problem number is followed by an 11-tuple (a 10, a 9, a 8, a 7, a 6, a 5, a 4, a 3, a, a 1, a 0 ), where a k is the number of teams that scored k points on
20th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Qualifying Stage, 28 October 2017
 0th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Qualifying Stage, 8 October 017 A project of the Mathematical Society of the Philippines (MSP) and the Department of Science and Technology - Science Education Institute
0th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Qualifying Stage, 8 October 017 A project of the Mathematical Society of the Philippines (MSP) and the Department of Science and Technology - Science Education Institute
Non-standard MMC problems
 Non-standard MMC problems Carl Joshua Quines 1 Algebra 1. (15S/9B/E6) A quadratic function f(x) satisfies f(0) = 30 and f(2) = 0. Determine all the zeros of f(x). [2 and 15] 2. (15S/IVB/E6) What is the
Non-standard MMC problems Carl Joshua Quines 1 Algebra 1. (15S/9B/E6) A quadratic function f(x) satisfies f(0) = 30 and f(2) = 0. Determine all the zeros of f(x). [2 and 15] 2. (15S/IVB/E6) What is the
1 2n. i=1. 2m+1 i = m, while. 2m + 1 = 1. is the best possible for any odd n.
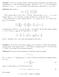 Problem 1. Let n be a positive integer. Find the largest nonnegative real number f(n) (depending on n) with the following property: whenever a 1, a,..., a n are real numbers such that a 1 + a + + a n is
Problem 1. Let n be a positive integer. Find the largest nonnegative real number f(n) (depending on n) with the following property: whenever a 1, a,..., a n are real numbers such that a 1 + a + + a n is
Solutions I.N. Herstein- Second Edition
 Solutions I.N. Herstein- Second Edition Sadiah Zahoor 25, July 2016 Please email me if any corrections at sadiahzahoor@cantab.net. Problem 0.1. In the following determine whether the systems described
Solutions I.N. Herstein- Second Edition Sadiah Zahoor 25, July 2016 Please email me if any corrections at sadiahzahoor@cantab.net. Problem 0.1. In the following determine whether the systems described
a 11 x 1 + a 12 x a 1n x n = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x a 2n x n = b 2.
 Chapter 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS 11 Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x 1, x,, x n is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a x + + a n x n = b, where a 1, a,, a n, b are given real
Chapter 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS 11 Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x 1, x,, x n is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a x + + a n x n = b, where a 1, a,, a n, b are given real
2015 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 205 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest April 205 Solutions 205 University of Waterloo 205 CTMC Solutions Page 2 Individual Problems.
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 205 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest April 205 Solutions 205 University of Waterloo 205 CTMC Solutions Page 2 Individual Problems.
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K. R. MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 1998 Comments to the author at krm@maths.uq.edu.au Contents 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K. R. MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 1998 Comments to the author at krm@maths.uq.edu.au Contents 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS
International Mathematical Olympiad. Preliminary Selection Contest 2011 Hong Kong. Outline of Solutions
 International Mathematical Olympiad Preliminary Selection Contest Hong Kong Outline of Solutions Answers:.. 76... 6. 7.. 6.. 6. 6.... 6. 7.. 76. 6. 7 Solutions:. Such fractions include. They can be grouped
International Mathematical Olympiad Preliminary Selection Contest Hong Kong Outline of Solutions Answers:.. 76... 6. 7.. 6.. 6. 6.... 6. 7.. 76. 6. 7 Solutions:. Such fractions include. They can be grouped
Solutions of APMO 2017
 Solutions of APMO 2017 Problem 1. We call a 5-tuple of integers arrangeable if its elements can be labeled a, b, c, d, e in some order so that a b + c d + e = 29. Determine all 2017-tuples of integers
Solutions of APMO 2017 Problem 1. We call a 5-tuple of integers arrangeable if its elements can be labeled a, b, c, d, e in some order so that a b + c d + e = 29. Determine all 2017-tuples of integers
34 th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad
 34 th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad 1. Determine all composite positive integers n for which it is possible to arrange all divisors of n that are greater than 1 in a circle so that no
34 th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad 1. Determine all composite positive integers n for which it is possible to arrange all divisors of n that are greater than 1 in a circle so that no
International Mathematical Olympiad. Preliminary Selection Contest 2017 Hong Kong. Outline of Solutions 5. 3*
 International Mathematical Olympiad Preliminary Selection Contest Hong Kong Outline of Solutions Answers: 06 0000 * 6 97 7 6 8 7007 9 6 0 6 8 77 66 7 7 0 6 7 7 6 8 9 8 0 0 8 *See the remar after the solution
International Mathematical Olympiad Preliminary Selection Contest Hong Kong Outline of Solutions Answers: 06 0000 * 6 97 7 6 8 7007 9 6 0 6 8 77 66 7 7 0 6 7 7 6 8 9 8 0 0 8 *See the remar after the solution
2011 Olympiad Solutions
 011 Olympiad Problem 1 Let A 0, A 1, A,..., A n be nonnegative numbers such that Prove that A 0 A 1 A A n. A i 1 n A n. Note: x means the greatest integer that is less than or equal to x.) Solution: We
011 Olympiad Problem 1 Let A 0, A 1, A,..., A n be nonnegative numbers such that Prove that A 0 A 1 A A n. A i 1 n A n. Note: x means the greatest integer that is less than or equal to x.) Solution: We
40th International Mathematical Olympiad
 40th International Mathematical Olympiad Bucharest, Romania, July 999 Determine all finite sets S of at least three points in the plane which satisfy the following condition: for any two distinct points
40th International Mathematical Olympiad Bucharest, Romania, July 999 Determine all finite sets S of at least three points in the plane which satisfy the following condition: for any two distinct points
The 33 rd Balkan Mathematical Olympiad Tirana, May 7, 2016
 Language: English The 33 rd Balkan Mathematical Olympiad Tirana, May 7, 2016 Problem 1. Find all injective functions f : R R such that for every real number x and every positive integer n, n i f(x + i
Language: English The 33 rd Balkan Mathematical Olympiad Tirana, May 7, 2016 Problem 1. Find all injective functions f : R R such that for every real number x and every positive integer n, n i f(x + i
40th Canadian Mathematical Olympiad
 40th Canadian Mathematical Olympiad Wednesday, March 26, 2008 Solutions - CMO 2008 1. ABCD is a convex quadrilateral in which AB is the longest side. Points M and N are located on sides AB and BC respectively,
40th Canadian Mathematical Olympiad Wednesday, March 26, 2008 Solutions - CMO 2008 1. ABCD is a convex quadrilateral in which AB is the longest side. Points M and N are located on sides AB and BC respectively,
The PMO Problems and Solutions of the Tenth Philippine Mathematical Olympiad
 J.M. Basilla E.P. Bautista I.J.L. Garces J.A. Marasigan A.R.L. Valdez The PMO 007-008 Problems and Solutions of the Tenth Philippine Mathematical Olympiad DOST-SEI MSP HSBC VPHI Preface and Introduction
J.M. Basilla E.P. Bautista I.J.L. Garces J.A. Marasigan A.R.L. Valdez The PMO 007-008 Problems and Solutions of the Tenth Philippine Mathematical Olympiad DOST-SEI MSP HSBC VPHI Preface and Introduction
Classical Theorems in Plane Geometry 1
 BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE 1999 2000 Classical Theorems in Plane Geometry 1 Zvezdelina Stankova-Frenkel UC Berkeley and Mills College Note: All objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual
BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE 1999 2000 Classical Theorems in Plane Geometry 1 Zvezdelina Stankova-Frenkel UC Berkeley and Mills College Note: All objects in this handout are planar - i.e. they lie in the usual
OLYMON. Produced by the Canadian Mathematical Society and the Department of Mathematics of the University of Toronto. Issue 10:3.
 OLYMON Produced by the Canadian Mathematical Society and the Department of Mathematics of the University of Toronto. Please send your solutions to Rosu Mihai 54 Judith Crescent Brampton, ON L6S 3J4 Issue
OLYMON Produced by the Canadian Mathematical Society and the Department of Mathematics of the University of Toronto. Please send your solutions to Rosu Mihai 54 Judith Crescent Brampton, ON L6S 3J4 Issue
HANOI OPEN MATHEMATICAL COMPETITON PROBLEMS
 HANOI MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY NGUYEN VAN MAU HANOI OPEN MATHEMATICAL COMPETITON PROBLEMS HANOI - 2013 Contents 1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 3 1.1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2006... 3 1.1.1
HANOI MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY NGUYEN VAN MAU HANOI OPEN MATHEMATICAL COMPETITON PROBLEMS HANOI - 2013 Contents 1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 3 1.1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2006... 3 1.1.1
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K R MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 998 Comments to the author at krm@mathsuqeduau All contents copyright c 99 Keith
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K R MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 998 Comments to the author at krm@mathsuqeduau All contents copyright c 99 Keith
2007 Shortlist JBMO - Problems
 Chapter 1 007 Shortlist JBMO - Problems 1.1 Algebra A1 Let a be a real positive number such that a 3 = 6(a + 1). Prove that the equation x + ax + a 6 = 0 has no solution in the set of the real number.
Chapter 1 007 Shortlist JBMO - Problems 1.1 Algebra A1 Let a be a real positive number such that a 3 = 6(a + 1). Prove that the equation x + ax + a 6 = 0 has no solution in the set of the real number.
The Pigeonhole Principle
 The Pigeonhole Principle 2 2.1 The Pigeonhole Principle The pigeonhole principle is one of the most used tools in combinatorics, and one of the simplest ones. It is applied frequently in graph theory,
The Pigeonhole Principle 2 2.1 The Pigeonhole Principle The pigeonhole principle is one of the most used tools in combinatorics, and one of the simplest ones. It is applied frequently in graph theory,
Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road Branch
 Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. in the parallelogram, each two opposite
Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. in the parallelogram, each two opposite
T-2 In the equation A B C + D E F = G H I, each letter denotes a distinct non-zero digit. Compute the greatest possible value of G H I.
 2016 ARML Local Problems and Solutions Team Round Solutions T-1 All the shelves in a library are the same length. When filled, two shelves side-by-side can hold exactly 12 algebra books and 10 geometry
2016 ARML Local Problems and Solutions Team Round Solutions T-1 All the shelves in a library are the same length. When filled, two shelves side-by-side can hold exactly 12 algebra books and 10 geometry
41st International Mathematical Olympiad
 41st International Mathematical Olympiad Taejon, Korea July 13 25, 2001 Problems Problem 1 A B is tangent to the circles C A M N and N M B D. M lies between C and D on the line C D, and C D is parallel
41st International Mathematical Olympiad Taejon, Korea July 13 25, 2001 Problems Problem 1 A B is tangent to the circles C A M N and N M B D. M lies between C and D on the line C D, and C D is parallel
Some Basic Logic. Henry Liu, 25 October 2010
 Some Basic Logic Henry Liu, 25 October 2010 In the solution to almost every olympiad style mathematical problem, a very important part is existence of accurate proofs. Therefore, the student should be
Some Basic Logic Henry Liu, 25 October 2010 In the solution to almost every olympiad style mathematical problem, a very important part is existence of accurate proofs. Therefore, the student should be
A matrix over a field F is a rectangular array of elements from F. The symbol
 Chapter MATRICES Matrix arithmetic A matrix over a field F is a rectangular array of elements from F The symbol M m n (F ) denotes the collection of all m n matrices over F Matrices will usually be denoted
Chapter MATRICES Matrix arithmetic A matrix over a field F is a rectangular array of elements from F The symbol M m n (F ) denotes the collection of all m n matrices over F Matrices will usually be denoted
SOLUTIONS FOR 2012 APMO PROBLEMS
 Problem. SOLUTIONS FOR 0 APMO PROBLEMS Solution: Let us denote by XY Z the area of the triangle XY Z. Let x = P AB, y = P BC and z = P CA. From y : z = BCP : ACP = BF : AF = BP F : AP F = x : follows that
Problem. SOLUTIONS FOR 0 APMO PROBLEMS Solution: Let us denote by XY Z the area of the triangle XY Z. Let x = P AB, y = P BC and z = P CA. From y : z = BCP : ACP = BF : AF = BP F : AP F = x : follows that
THE UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO UNDERGRADUATE MATHEMATICS COMPETITION. Sunday, March 14, 2004 Time: hours No aids or calculators permitted.
 THE UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO UNDERGRADUATE MATHEMATICS COMPETITION Sunday, March 1, Time: 3 1 hours No aids or calculators permitted. 1. Prove that, for any complex numbers z and w, ( z + w z z + w w z +
THE UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO UNDERGRADUATE MATHEMATICS COMPETITION Sunday, March 1, Time: 3 1 hours No aids or calculators permitted. 1. Prove that, for any complex numbers z and w, ( z + w z z + w w z +
USAMO - USAJMO 1
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Proposed Solutions May 1, 2003 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 32 nd United States of America Mathematical Olympiad Proposed Solutions May 1, 2003 Remark: The general philosophy of this marking scheme follows that of
Figure 1: Problem 1 diagram. Figure 2: Problem 2 diagram
 Geometry A Solutions 1. Note that the solid formed is a generalized cylinder. It is clear from the diagram that the area of the base of this cylinder (i.e., a vertical cross-section of the log) is composed
Geometry A Solutions 1. Note that the solid formed is a generalized cylinder. It is clear from the diagram that the area of the base of this cylinder (i.e., a vertical cross-section of the log) is composed
Math Contest, Fall 2017 BC EXAM , z =
 Math Contest, Fall 017 BC EXAM 1. List x, y, z in order from smallest to largest fraction: x = 111110 111111, y = 1 3, z = 333331 333334 Consider 1 x = 1 111111, 1 y = thus 1 x > 1 z > 1 y, and so x
Math Contest, Fall 017 BC EXAM 1. List x, y, z in order from smallest to largest fraction: x = 111110 111111, y = 1 3, z = 333331 333334 Consider 1 x = 1 111111, 1 y = thus 1 x > 1 z > 1 y, and so x
Baltic Way 2008 Gdańsk, November 8, 2008
 Baltic Way 008 Gdańsk, November 8, 008 Problems and solutions Problem 1. Determine all polynomials p(x) with real coefficients such that p((x + 1) ) = (p(x) + 1) and p(0) = 0. Answer: p(x) = x. Solution:
Baltic Way 008 Gdańsk, November 8, 008 Problems and solutions Problem 1. Determine all polynomials p(x) with real coefficients such that p((x + 1) ) = (p(x) + 1) and p(0) = 0. Answer: p(x) = x. Solution:
SOUTH AFRICAN TERTIARY MATHEMATICS OLYMPIAD
 SOUTH AFRICAN TERTIARY MATHEMATICS OLYMPIAD. Determine the following value: 7 August 6 Solutions π + π. Solution: Since π
SOUTH AFRICAN TERTIARY MATHEMATICS OLYMPIAD. Determine the following value: 7 August 6 Solutions π + π. Solution: Since π
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K. R. MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Corrected Version, 7th April 013 Comments to the author at keithmatt@gmail.com Chapter 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS 1.1
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K. R. MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Corrected Version, 7th April 013 Comments to the author at keithmatt@gmail.com Chapter 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS 1.1
International Mathematics TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS
 International Mathematics TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS Senior A-Level Paper Fall 2008. 1. A standard 8 8 chessboard is modified by varying the distances between parallel grid lines, so that the cells are rectangles
International Mathematics TOURNAMENT OF THE TOWNS Senior A-Level Paper Fall 2008. 1. A standard 8 8 chessboard is modified by varying the distances between parallel grid lines, so that the cells are rectangles
HANOI OPEN MATHEMATICS COMPETITON PROBLEMS
 HANOI MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY NGUYEN VAN MAU HANOI OPEN MATHEMATICS COMPETITON PROBLEMS 2006-2013 HANOI - 2013 Contents 1 Hanoi Open Mathematics Competition 3 1.1 Hanoi Open Mathematics Competition 2006...
HANOI MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY NGUYEN VAN MAU HANOI OPEN MATHEMATICS COMPETITON PROBLEMS 2006-2013 HANOI - 2013 Contents 1 Hanoi Open Mathematics Competition 3 1.1 Hanoi Open Mathematics Competition 2006...
2003 AIME2 SOLUTIONS (Answer: 336)
 1 (Answer: 336) 2003 AIME2 SOLUTIONS 2 Call the three integers a, b, and c, and, without loss of generality, assume a b c Then abc = 6(a + b + c), and c = a + b Thus abc = 12c, and ab = 12, so (a, b, c)
1 (Answer: 336) 2003 AIME2 SOLUTIONS 2 Call the three integers a, b, and c, and, without loss of generality, assume a b c Then abc = 6(a + b + c), and c = a + b Thus abc = 12c, and ab = 12, so (a, b, c)
USA Mathematical Talent Search Round 2 Solutions Year 20 Academic Year
 //0. Sarah and Joe play a standard 3-by-3 game of tic-tac-toe. Sarah goes first and plays X, and Joe goes second and plays O. They alternate turns placing their letter in an empty space, and the first
//0. Sarah and Joe play a standard 3-by-3 game of tic-tac-toe. Sarah goes first and plays X, and Joe goes second and plays O. They alternate turns placing their letter in an empty space, and the first
Olympiad Correspondence Problems. Set 3
 (solutions follow) 1998-1999 Olympiad Correspondence Problems Set 3 13. The following construction and proof was proposed for trisecting a given angle with ruler and Criticizecompasses the arguments. Construction.
(solutions follow) 1998-1999 Olympiad Correspondence Problems Set 3 13. The following construction and proof was proposed for trisecting a given angle with ruler and Criticizecompasses the arguments. Construction.
46th ANNUAL MASSACHUSETTS MATHEMATICS OLYMPIAD. A High School Competition Conducted by. And Sponsored by FIRST-LEVEL EXAMINATION SOLUTIONS
 46th ANNUAL MASSACHUSETTS MATHEMATICS OLYMPIAD 009 00 A High School Competition Conducted by THE MASSACHUSETTS ASSOCIATION OF MATHEMATICS LEAGUES (MAML) And Sponsored by THE ACTUARIES CLUB OF BOSTON FIRST-LEVEL
46th ANNUAL MASSACHUSETTS MATHEMATICS OLYMPIAD 009 00 A High School Competition Conducted by THE MASSACHUSETTS ASSOCIATION OF MATHEMATICS LEAGUES (MAML) And Sponsored by THE ACTUARIES CLUB OF BOSTON FIRST-LEVEL
SMT 2011 General Test and Solutions February 19, F (x) + F = 1 + x. 2 = 3. Now take x = 2 2 F ( 1) = F ( 1) = 3 2 F (2)
 SMT 0 General Test and Solutions February 9, 0 Let F () be a real-valued function defined for all real 0, such that ( ) F () + F = + Find F () Answer: Setting =, we find that F () + F ( ) = Now take =,
SMT 0 General Test and Solutions February 9, 0 Let F () be a real-valued function defined for all real 0, such that ( ) F () + F = + Find F () Answer: Setting =, we find that F () + F ( ) = Now take =,
2008 Euclid Contest. Solutions. Canadian Mathematics Competition. Tuesday, April 15, c 2008 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 5, 008 Solutions c 008
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 5, 008 Solutions c 008
INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL OLYMPIADS. Hojoo Lee, Version 1.0. Contents 1. Problems 1 2. Answers and Hints References
 INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL OLYMPIADS 1990 2002 Hojoo Lee, Version 1.0 Contents 1. Problems 1 2. Answers and Hints 15 3. References 16 1. Problems 021 Let n be a positive integer. Let T be the set of points
INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL OLYMPIADS 1990 2002 Hojoo Lee, Version 1.0 Contents 1. Problems 1 2. Answers and Hints 15 3. References 16 1. Problems 021 Let n be a positive integer. Let T be the set of points
Calculus II - Basic Matrix Operations
 Calculus II - Basic Matrix Operations Ryan C Daileda Terminology A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, for example 7,, 7 7 9, or / / /4 / / /4 / / /4 / /6 The numbers in any matrix are called its
Calculus II - Basic Matrix Operations Ryan C Daileda Terminology A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, for example 7,, 7 7 9, or / / /4 / / /4 / / /4 / /6 The numbers in any matrix are called its
First selection test
 First selection test Problem 1. Let ABC be a triangle right at C and consider points D, E on the sides BC, CA, respectively such that BD = AE = k. Lines BE and AC CD AD intersect at point O. Show that
First selection test Problem 1. Let ABC be a triangle right at C and consider points D, E on the sides BC, CA, respectively such that BD = AE = k. Lines BE and AC CD AD intersect at point O. Show that
OLYMON. Produced by the Canadian Mathematical Society and the Department of Mathematics of the University of Toronto. Issue 9:4.
 OLYMON Produced by the Canadian Mathematical Society and the Department of Mathematics of the University of Toronto. Please send your solution to Ms. Valeria Pandelieva 64 Kirkwood Avenue Ottawa, ON KZ
OLYMON Produced by the Canadian Mathematical Society and the Department of Mathematics of the University of Toronto. Please send your solution to Ms. Valeria Pandelieva 64 Kirkwood Avenue Ottawa, ON KZ
XIX Asian Pacific Mathematics Olympiad
 XIX Asian Pacific Mathematics Olympiad Problem 1. Let S be a set of 9 distinct integers all of whose prime factors are at most 3. Prove that S contains 3 distinct integers such that their product is a
XIX Asian Pacific Mathematics Olympiad Problem 1. Let S be a set of 9 distinct integers all of whose prime factors are at most 3. Prove that S contains 3 distinct integers such that their product is a
Unofficial Solutions
 Canadian Open Mathematics Challenge 2016 Unofficial Solutions COMC exams from other years, with or without the solutions included, are free to download online. Please visit http://comc.math.ca/2016/practice.html
Canadian Open Mathematics Challenge 2016 Unofficial Solutions COMC exams from other years, with or without the solutions included, are free to download online. Please visit http://comc.math.ca/2016/practice.html
3. A square has 4 sides, so S = 4. A pentagon has 5 vertices, so P = 5. Hence, S + P = 9. = = 5 3.
 JHMMC 01 Grade Solutions October 1, 01 1. By counting, there are 7 words in this question.. (, 1, ) = 1 + 1 + = 9 + 1 + =.. A square has sides, so S =. A pentagon has vertices, so P =. Hence, S + P = 9..
JHMMC 01 Grade Solutions October 1, 01 1. By counting, there are 7 words in this question.. (, 1, ) = 1 + 1 + = 9 + 1 + =.. A square has sides, so S =. A pentagon has vertices, so P =. Hence, S + P = 9..
41st International Mathematical Olympiad
 41st International Mathematical Olympiad Taejon, Korea, July 2000 1 Two circles Γ 1 and Γ 2 intersect at M and N Let l be the common tangent to Γ 1 and Γ 2 so that M is closer to l than N is Let l touch
41st International Mathematical Olympiad Taejon, Korea, July 2000 1 Two circles Γ 1 and Γ 2 intersect at M and N Let l be the common tangent to Γ 1 and Γ 2 so that M is closer to l than N is Let l touch
45-th Moldova Mathematical Olympiad 2001
 45-th Moldova Mathematical Olympiad 200 Final Round Chişinǎu, March 2 Grade 7. Prove that y 3 2x+ x 3 2y x 2 + y 2 for any numbers x,y [, 2 3 ]. When does equality occur? 2. Let S(n) denote the sum of
45-th Moldova Mathematical Olympiad 200 Final Round Chişinǎu, March 2 Grade 7. Prove that y 3 2x+ x 3 2y x 2 + y 2 for any numbers x,y [, 2 3 ]. When does equality occur? 2. Let S(n) denote the sum of
Canadian Open Mathematics Challenge
 The Canadian Mathematical Society in collaboration with The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING presents the Canadian Open Mathematics Challenge Wednesday, November, 006 Supported by: Solutions
The Canadian Mathematical Society in collaboration with The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING presents the Canadian Open Mathematics Challenge Wednesday, November, 006 Supported by: Solutions
Collinearity/Concurrence
 Collinearity/Concurrence Ray Li (rayyli@stanford.edu) June 29, 2017 1 Introduction/Facts you should know 1. (Cevian Triangle) Let ABC be a triangle and P be a point. Let lines AP, BP, CP meet lines BC,
Collinearity/Concurrence Ray Li (rayyli@stanford.edu) June 29, 2017 1 Introduction/Facts you should know 1. (Cevian Triangle) Let ABC be a triangle and P be a point. Let lines AP, BP, CP meet lines BC,
4 a b 1 1 c 1 d 3 e 2 f g 6 h i j k 7 l m n o 3 p q 5 r 2 s 4 t 3 3 u v 2
 Round Solutions Year 25 Academic Year 201 201 1//25. In the hexagonal grid shown, fill in each space with a number. After the grid is completely filled in, the number in each space must be equal to the
Round Solutions Year 25 Academic Year 201 201 1//25. In the hexagonal grid shown, fill in each space with a number. After the grid is completely filled in, the number in each space must be equal to the
Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep
 Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep Nozha Language Schools Geometry Revision Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. In the parallelogram, each
Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep Nozha Language Schools Geometry Revision Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. In the parallelogram, each
Objective Type Questions
 DISTANCE EDUCATION, UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT NUMBER THEORY AND LINEARALGEBRA Objective Type Questions Shyama M.P. Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics Malabar Christian College, Calicut 7/3/2014
DISTANCE EDUCATION, UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT NUMBER THEORY AND LINEARALGEBRA Objective Type Questions Shyama M.P. Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics Malabar Christian College, Calicut 7/3/2014
2010 Shortlist JBMO - Problems
 Chapter 1 2010 Shortlist JBMO - Problems 1.1 Algebra A1 The real numbers a, b, c, d satisfy simultaneously the equations abc d = 1, bcd a = 2, cda b = 3, dab c = 6. Prove that a + b + c + d 0. A2 Determine
Chapter 1 2010 Shortlist JBMO - Problems 1.1 Algebra A1 The real numbers a, b, c, d satisfy simultaneously the equations abc d = 1, bcd a = 2, cda b = 3, dab c = 6. Prove that a + b + c + d 0. A2 Determine
2013 Sharygin Geometry Olympiad
 Sharygin Geometry Olympiad 2013 First Round 1 Let ABC be an isosceles triangle with AB = BC. Point E lies on the side AB, and ED is the perpendicular from E to BC. It is known that AE = DE. Find DAC. 2
Sharygin Geometry Olympiad 2013 First Round 1 Let ABC be an isosceles triangle with AB = BC. Point E lies on the side AB, and ED is the perpendicular from E to BC. It is known that AE = DE. Find DAC. 2
Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 2007
 Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 007 Questions will be set on the following and related topics. Algebra: Sets, operations on sets. Prime numbers, factorisation of integers
Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 007 Questions will be set on the following and related topics. Algebra: Sets, operations on sets. Prime numbers, factorisation of integers
Lagrange s polynomial
 Lagrange s polynomial Nguyen Trung Tuan November 16, 2016 Abstract In this article, I will use Lagrange polynomial to solve some problems from Mathematical Olympiads. Contents 1 Lagrange s interpolation
Lagrange s polynomial Nguyen Trung Tuan November 16, 2016 Abstract In this article, I will use Lagrange polynomial to solve some problems from Mathematical Olympiads. Contents 1 Lagrange s interpolation
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, IX / Class IX
 I, 0 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, 0 0 MATHEMATICS / MATHEMATICS MATHEMATICS CLASS CLASS - IX - IX IX / Class IX MA-0 90 Time allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 90 (i) (ii) 8 6 0 0 (iii) 8 (iv) (v) General Instructions:
I, 0 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, 0 0 MATHEMATICS / MATHEMATICS MATHEMATICS CLASS CLASS - IX - IX IX / Class IX MA-0 90 Time allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 90 (i) (ii) 8 6 0 0 (iii) 8 (iv) (v) General Instructions:
SOLUTION. Taken together, the preceding equations imply that ABC DEF by the SSS criterion for triangle congruence.
 1. [20 points] Suppose that we have ABC and DEF in the Euclidean plane and points G and H on (BC) and (EF) respectively such that ABG DEH and AGC DHF. Prove that ABC DEF. The first congruence assumption
1. [20 points] Suppose that we have ABC and DEF in the Euclidean plane and points G and H on (BC) and (EF) respectively such that ABG DEH and AGC DHF. Prove that ABC DEF. The first congruence assumption
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Euclid Contest. Wednesday, April 15, 2015
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Euclid Contest Wednesday, April 15, 015 (in North America and South America) Thursday, April 16, 015 (outside of North America
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 015 Euclid Contest Wednesday, April 15, 015 (in North America and South America) Thursday, April 16, 015 (outside of North America
**** NO CALCULATORS IN THIS ROUND ****
 A) Evaluate 8 8. CONTEST NOVEMBER 0 ROUN COMLEX NUMBERS (No Trig) ANSWERS A) B) I II III IV C) **** NO CALCULATORS IN THIS ROUN **** B) Let z = x + yi be represented by the point (x, y). In what quadrant
A) Evaluate 8 8. CONTEST NOVEMBER 0 ROUN COMLEX NUMBERS (No Trig) ANSWERS A) B) I II III IV C) **** NO CALCULATORS IN THIS ROUN **** B) Let z = x + yi be represented by the point (x, y). In what quadrant
How to prove it (or not) Gerry Leversha MA Conference, Royal Holloway April 2017
 How to prove it (or not) Gerry Leversha MA Conference, Royal Holloway April 2017 My favourite maxim It is better to solve one problem in five different ways than to solve five problems using the same method
How to prove it (or not) Gerry Leversha MA Conference, Royal Holloway April 2017 My favourite maxim It is better to solve one problem in five different ways than to solve five problems using the same method
Written test, 25 problems / 90 minutes
 Sponsored by: UGA Math Department and UGA Math Club Written test, 25 problems / 90 minutes October 24, 2015 Problem 1. How many prime numbers can be written both as a sum and as a difference of two prime
Sponsored by: UGA Math Department and UGA Math Club Written test, 25 problems / 90 minutes October 24, 2015 Problem 1. How many prime numbers can be written both as a sum and as a difference of two prime
Winter Mathematical Competition Varna, February, 9-11, 2007
 Winter Mathematical Competition Varna, February, 9-11, 007 Problem 91 (Peter Boyvalenkov) Find all values of the real parameter p such that the equation x + (p + 1)x + p = has two real distinct roots x
Winter Mathematical Competition Varna, February, 9-11, 007 Problem 91 (Peter Boyvalenkov) Find all values of the real parameter p such that the equation x + (p + 1)x + p = has two real distinct roots x
 FROSH-SOPH 2 PERSON COMPETITION LARGE PRINT QUESTION 1 ICTM 2017 STATE DIVISION AA 1. Determine the sum of all distinct positive integers between 8 and 16 inclusive that can be expressed in one and only
FROSH-SOPH 2 PERSON COMPETITION LARGE PRINT QUESTION 1 ICTM 2017 STATE DIVISION AA 1. Determine the sum of all distinct positive integers between 8 and 16 inclusive that can be expressed in one and only
The Advantage Testing Foundation Olympiad Solutions
 The Advantage Testing Foundation 014 Olympiad Problem 1 Say that a convex quadrilateral is tasty if its two diagonals divide the quadrilateral into four nonoverlapping similar triangles. Find all tasty
The Advantage Testing Foundation 014 Olympiad Problem 1 Say that a convex quadrilateral is tasty if its two diagonals divide the quadrilateral into four nonoverlapping similar triangles. Find all tasty
Singapore International Mathematical Olympiad 2008 Senior Team Training. Take Home Test Solutions. 15x 2 7y 2 = 9 y 2 0 (mod 3) x 0 (mod 3).
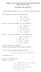 Singapore International Mathematical Olympiad 2008 Senior Team Training Take Home Test Solutions. Show that the equation 5x 2 7y 2 = 9 has no solution in integers. If the equation has a solution in integer,
Singapore International Mathematical Olympiad 2008 Senior Team Training Take Home Test Solutions. Show that the equation 5x 2 7y 2 = 9 has no solution in integers. If the equation has a solution in integer,
THE OLYMPIAD CORNER No. 305
 THE OLYMPIAD CORNER / 67 THE OLYMPIAD CORNER No. 305 Nicolae Strungaru The solutions to the problems are due to the editor by 1 January 014. Each problem is given in English and French, the official languages
THE OLYMPIAD CORNER / 67 THE OLYMPIAD CORNER No. 305 Nicolae Strungaru The solutions to the problems are due to the editor by 1 January 014. Each problem is given in English and French, the official languages
36th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad
 36th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad 1. Let n be a positive integer. Define a sequence by setting a 1 = n and, for each k > 1, letting a k be the unique integer in the range 0 a k k 1 for
36th United States of America Mathematical Olympiad 1. Let n be a positive integer. Define a sequence by setting a 1 = n and, for each k > 1, letting a k be the unique integer in the range 0 a k k 1 for
21. Prove that If one side of the cyclic quadrilateral is produced then the exterior angle is equal to the interior opposite angle.
 21. Prove that If one side of the cyclic quadrilateral is produced then the exterior angle is equal to the interior opposite angle. 22. Prove that If two sides of a cyclic quadrilateral are parallel, then
21. Prove that If one side of the cyclic quadrilateral is produced then the exterior angle is equal to the interior opposite angle. 22. Prove that If two sides of a cyclic quadrilateral are parallel, then
Write down all the 3-digit positive integers that are squares and whose individual digits are non-zero squares. Answer: Relay
 A Write down all the 3-digit positive integers that are squares and whose individual digits are non-zero squares. A2 What is the sum of all positive fractions that are less than and have denominator 73?
A Write down all the 3-digit positive integers that are squares and whose individual digits are non-zero squares. A2 What is the sum of all positive fractions that are less than and have denominator 73?
Solutions to CRMO-2003
 Solutions to CRMO-003 1. Let ABC be a triangle in which AB AC and CAB 90. Suppose M and N are points on the hypotenuse BC such that BM + CN MN. Prove that MAN 45. Solution: Draw CP perpendicular to CB
Solutions to CRMO-003 1. Let ABC be a triangle in which AB AC and CAB 90. Suppose M and N are points on the hypotenuse BC such that BM + CN MN. Prove that MAN 45. Solution: Draw CP perpendicular to CB
1987 IMO Shortlist. IMO Shortlist 1987
 IMO Shortlist 1987 1 Let f be a function that satisfies the following conditions: (i) If x > y and f(y) y v f(x) x, then f(z) = v + z, for some number z between x and y. (ii) The equation f(x) = 0 has
IMO Shortlist 1987 1 Let f be a function that satisfies the following conditions: (i) If x > y and f(y) y v f(x) x, then f(z) = v + z, for some number z between x and y. (ii) The equation f(x) = 0 has
14 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 12 February 2011
 14 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 1 February 011 1. Let a, b, and c be positive real numbers. etermine the largest total number of real roots that the following three polynomials
14 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 1 February 011 1. Let a, b, and c be positive real numbers. etermine the largest total number of real roots that the following three polynomials
