E 600 Chapter 3: Multivariate Calculus
|
|
|
- Brianna May Craig
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 E 600 Chapter 3: Multivariate Calculus Simona Helmsmueller August 21, 2017
2 Goals of this lecture: Know when an inverse to a function exists, be able to graphically and analytically determine whether a function is convex, concave or quasiconcave. Have an intuition about the meaning of derivatives as measures of small change, be able to calculate the Gradient, Jacobian and Hessian of a function Know all the calculation rules for derivatives (sum, quotient, product, chain rule) Know the difference between partial and total derivatives Be able to write down the Taylor approximation of a function Know what a function s differentials tell us about its continuity and convexity Know and be able to apply the calculation rules of integral theory; know and be able to apply Fubini s theorem
3 Contents Multivariate functions Invertibility Convexity, Concavity, and Multivariate Real-Valued Functions Multivariate differential calculus Introduction Revision: single-variable differential calculus Partial Derivatives and the Gradient Differentiability of real-valued functions Differentiability of vector-valued functions Higher Order Partial Derivatives and the Taylor Approximation Theorems Characterization of convex functions Integral theory Univariate integral calculus The definite integral and the fundamental theorem of calculus Multivariate extension
4 Definition (Surjective functions) A function f : X Y is said to be surjective or onto, if for every y Y there exists at least one x X with f (x) = y.
5 Definition (Injective functions) A function f : X Y is said to be injective or one-to-one, if the following property holds for all x 1, x 2 X : f (x 1 ) = f (x 2 ) x 1 = x 2.
6 Theorem ( Existence and definition of the inverse function) Let f : X Y be onto and one-to-one (i.e. bijective). Then there exists a unique bijective function f 1 : Y X with f 1 (f (x)) = x. Conversely, if such a function exists, then f is bijective.
7 Definition (Convex Real Valued Function) Let X R n. A function f : X R is convex if and only if X is a convex set and for any two x, y X and λ [0, 1] we have f (λx + (1 λ)y) λf (x) + (1 λ)f (y) Moreover, if this statement holds strictly whenever y x and λ (0, 1), we say that f is strictly convex.
8 Definition (Concave Real-Valued Function) Let X R n. A function f : X R is concave if and only if f is convex. Similarly f is strictly concave if and only if f is strictly convex.
9
10
11 Definition (Multivariate Convexity) Let X be a convex subset of R n. A real-valued function f : X R n is (strictly) convex if and only if, for every x X and every z {z R n {0} z = 1}, the function g(t) = f (x + tz) is (strictly) convex on {t R x + tz X }.
12 Definition (Quasiconvexity, Quasiconcavity) Let X be a convex subset of R n. A real-valued function f : X R is quasiconvex if and only if for any c R the set L c := {x x X, f (x) c}, also referred to as f lower-level set, is convex. Iff f is such that L + c := {x x X, f (x) c}, also referred to as f upper-level set, is convex for any c R, then f is said to be quasiconcave.
13 Theorem ( Quasiconvexity, Quasiconcavity) Let X be a convex subset of R n. A real-valued function f : X R is quasiconvex if and only if x, y X λ [0, 1] f (λx + (1 λ)y) max{f (x), f (y)} Iff f is such that x, y X λ [0, 1] f (λx + (1 λ)y) min{f (x), f (y)} then f is said to be quasiconcave.
14 Contents Multivariate functions Invertibility Convexity, Concavity, and Multivariate Real-Valued Functions Multivariate differential calculus Introduction Revision: single-variable differential calculus Partial Derivatives and the Gradient Differentiability of real-valued functions Differentiability of vector-valued functions Higher Order Partial Derivatives and the Taylor Approximation Theorems Characterization of convex functions Integral theory Univariate integral calculus The definite integral and the fundamental theorem of calculus Multivariate extension
15 Calculus is the mathematical study of change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape and algebra is the study of operations and their application to solving equations. It has two major branches, differential calculus (concerning rates of change and slopes of curves), and integral calculus (concerning accumulation of quantities and the areas under and between curves); these two branches are related to each other by the fundamental theorem of calculus, [...] [which] states that differentiation and integration are inverse operations.
16 Theorem Let f, g : R R differentiable at x 0 with derivatives f (x 0 ), g (x 0 ), and λ, µ R. Then 1. λf + µg is differentiable in x 0 with (λf + µg) (x 0 ) = λf (x 0 ) + µg (x 0 ), 2. fg is differentiable in x 0 with (fg) (x 0 ) = (f g + fg )(x 0 ) 3. if g(x) 0 in a neighborhood of x 0, then f /g is differentiable with ( ) f (x 0 ) = f g fg g g 2 (x 0 ), 4. if all the following expressions are well-defined, then g f is differentiable in x 0 with (g f ) (x 0 ) = g (f (x 0 ))f (x 0 ).
17 Let f be differentiable at x, then f is continuous at x. Let f be differentiable at x, then there exists a good linear approximation of f in a neighborhood Let a and b be real numbers such that a < b. If f is continuous and differentiable on (a, b), then: (i) f (x) = 0 for all x (a, b) iff f is constant on (a, b). (ii) f (x) < 0 for all x (a, b) iff f is decreasing on (a, b). (iii) f (x) > 0 for all x (a, b) iff f is increasing on (a, b).
18 Convince yourself of these geometric properties by looking at the following four functions: 1. f 1 (x) = x 2 2. f 2 (x) = x 3. f 3 (x) = max{k Z : k x} 4. f 4 (x) = 1 if x Q and f 4 (x) = 0 if x R Q
19 Definition (Partial Derivative) Let X R n and suppose f : X R. If x is an interior point of X, then, the partial derivative of f with respect to x i at x is defined as f ( x) x i := lim h 0 f ( x 1,..., x i 1, x i + h, x i+1,..., x n ) f ( x 1,..., x i,..., x n ) h with h R, whenever the limit exists. Another common notation for the partial derivative of f with respect to x i at x is f i ( x).
20
21 Definition (Gradient) Let f : R n R a function which is partially differentiable with respect ot all x i, i = 1,..., n. Then the row vector ( ) f ( x) := f 1 ( x) f 2 ( x) f n ( x) is called the gradient of f at x.
22
23 Definition (Jacobian matrix) Let f : R n R m with partially differentiable component functions f 1,..., f m : R n R, and let x R n. Then the Jacobian matrix of f at x is defined as f 1 f 1 f 1 J f ( x) = ( x) x 1 f 2 ( x) x 1. f m ( x) x 1 ( x) ( x) x 2 x n f 2 f 2 ( x) ( x) x 2 x n..... f m f m ( x) ( x) x 2 x n.
24
25 Definition (Multivariate Derivative) Let X R n and suppose f : X R. If x is an interior point of X, then f is differentiable at x if and only if there exists a row vector Df ( x) such that f ( x + h) f ( x) Df ( x) h lim = 0 h 0 h where h is a vector in R n. If such a vector Df ( x) exists, we interpret it as the derivative of f at x.
26 Theorem ( Total Differential, Partial Derivative, and Gradient) Let X R n and suppose f : X R. If x is an interior point of X, and if f is differentiable at x, then: (i) all partial derivatives 1 of f exist at x and, (ii) z in X, z = 1: df ( x, z) := Df ( x) z = f ( x) z
27 Theorem ( Partial Differentiablility and Differentiability) Let X R n, suppose f : X R, and let x be an interior point of X. If all the partial derivatives of f at x exist and are continuous, then f is differentiable.
28 Definition (Multivariate Derivative of Vector-Valued Functions) Let X R n and suppose f : X R m. If x is an interior point of X, then f is differentiable at x if and only if there exists a matrix Df ( x) such that f ( x + h) f ( x) Df ( x) h lim = 0 h 0 h where h is a vector in R n. If such a matrix Df ( x) exists, we interpret it as the derivative of f at x.
29 Theorem ( Multivariate Derivative and Jacobian Matrix) Let X R n, suppose f : X R m, and let x be an interior point of X. Then, f is differentiable at x if and only if each of its component functions is differentiable at x. Moreover, if f is differentiable at x, then: (i) all partial derivatives of the component functions exist at x, and (ii) the derivative of f at x is the matrix of partial derivatives of the component functions at x:
30 J f ( x) := D f ( x) = f 1( x). f m( x) = R m n f 1 x 1 ( x). f m ( x) x 1 f 1 ( x) x n. f m ( x) x n
31 Theorem ( Multivariate Chain Rule) Let X R n suppose g : X Y, where Y R m. Further, suppose f : Y Z, where Z R p. If x is an interior point of X, g( x) an interior point of Y, and g and f are differentiable at x and g( x), respectively, then f g is differentiable at x and: D[f g](x) = Df (g( x))dg( x)
32 Definition (Hessian matrix) Let X R n be open, suppose f : X R, and let x be an element of X. If all second order partial derivatives of f are defined at x, then, in the same way as the first order partial derivatives could be gathered in a vector the gradient, all the second order partial derivatives can be gathered in a matrix. Such a matrix, denoted H f ( x), is called the Hessian of f at x, is square, and should be thought of as a generalized second order derivative for multivariate real valued functions. f1 ( x) f 1,1 ( x) f 1,2 ( x) f 1,n ( x) H f ( x) = f2 ( x). = f 2,1 ( x) f 2,2 ( x) f 2,n ( x) fn ( x) f n,1 ( x) f n,2 ( x) f n,n ( x)
33 Definition (Function of class C k ) Let X R n be an open set, Y R, and suppose f : X Y. f is said to be of class C k on X, denoted f C k (X, Y ) 2, if all partial derivatives of order less or equal to k exist and are continuous on X.
34 Theorem ( Schwarz s Theorem / Young s Theorem) If f C k (X ), then the order in which the derivatives up to order k are taken can be permuted.
35 Theorem ( nth Order Univariate Taylor Approximation) Let X R be an open set and consider f C n+1 (X ). Then f can be best nth order approximated around x by the nth order Taylor expansion: f ( x + h) f ( x) + n f (k) ( x)h k k=1 where h R is such that x + h X and f (k) (x) denotes f s derivative of order k at x. The error of approximation, also known as the remainder of the Taylor approximation, is given by the following formula: k! R n (h x) := f ( x +h) f ( x) n f (k) ( x)h k k! = f (n+1) (x + λh) h n+1 (n + 1)!
36 Theorem ( Second Order Multivariate Taylor Approximation) Let X R n be an open set, f C 3 (X ). Then f can be best 2nd order approximated around x by the second order Taylor expansion: f ( x + h) f ( x) + f ( x) h h H f ( x)h where h R n is such that x + h X. As h approaches zero, the remainder approaches zero at a faster rate than h itself. R 2 (h x) := f ( x + h) f ( x) f ( x) h h H f ( x)h = for some λ (0, 1). f (n) (x + λh) h n+1 (n + 1)!
37 Theorem ( Multivariate Convexity ) Let X be a convex subset of R n. A real-valued function f : X R that is also an element of C 2 (X ) is convex if and only if, H f (x) is positive semidefinite for all x Int(X ). Further, if H f (x) is positive definite for all x Int(X ), then f is strictly convex.
38 Contents Multivariate functions Invertibility Convexity, Concavity, and Multivariate Real-Valued Functions Multivariate differential calculus Introduction Revision: single-variable differential calculus Partial Derivatives and the Gradient Differentiability of real-valued functions Differentiability of vector-valued functions Higher Order Partial Derivatives and the Taylor Approximation Theorems Characterization of convex functions Integral theory Univariate integral calculus The definite integral and the fundamental theorem of calculus Multivariate extension
39 Theorem ( Calculation rules for indefinite integrals) Let f, g be two integrable functions 3 and let a, C be constants, n N. Then (af (x) + g(x))dx = a f (x)dx + g(x)dx x n dx = x n C if n 1 and dx = lnx + C n + 1 x e x dx = e x + C and e f (x) f (x)dx = e f (x) + C (f (x)) n f (x)dx = 1 n + 1 (f (x))n+1 + C if n f (x) 1 and f dx = lnf (x) + C (x)
40 Theorem ( Integration by parts) Let u, v be two differentiable functions. Then, u(x)v (x)dx = u(x)v(x) u (x)v(x)dx.
41 Theorem Let f : [a, b] R be continuous and define F (x) = all x [a, b]. Then, F is differentiable on (a, b) with F (x) = f (x) for all x (a, b). x a f (t)dt for
42 Theorem ( Fubini s theorem) Let I x = [a, b] and I y = [c, d] be two intervals in R n and define I := I x I y. Let f : I R continuous. Then ( ) f (x, y)d(x, y) = f (x, y)dy dx, I I y and all the integrals on the right-hand side are well-defined. I x
43 Theorem Let A, B R two closed intervals, f : A R, g : B R continuous functions. Then A B ( f (x)g(y)d(x, y) = f (x)dx A )( B ) g(y)dy.
Chapter 3 - Multivariate Calculus
 Chapter 3 - Multivariate Calculus Justin Leduc These lecture notes are meant to be used by students entering the University of Mannheim Master program in Economics. They constitute the base for a pre-course
Chapter 3 - Multivariate Calculus Justin Leduc These lecture notes are meant to be used by students entering the University of Mannheim Master program in Economics. They constitute the base for a pre-course
Week 3: Sets and Mappings/Calculus and Optimization (Jehle September and Reny, 20, 2015 Chapter A1/A2)
 Week 3: Sets and Mappings/Calculus and Optimization (Jehle and Reny, Chapter A1/A2) Tsun-Feng Chiang *School of Economics, Henan University, Kaifeng, China September 20, 2015 Week 3: Sets and Mappings/Calculus
Week 3: Sets and Mappings/Calculus and Optimization (Jehle and Reny, Chapter A1/A2) Tsun-Feng Chiang *School of Economics, Henan University, Kaifeng, China September 20, 2015 Week 3: Sets and Mappings/Calculus
ARE211, Fall 2005 CONTENTS. 5. Characteristics of Functions Surjective, Injective and Bijective functions. 5.2.
 ARE211, Fall 2005 LECTURE #18: THU, NOV 3, 2005 PRINT DATE: NOVEMBER 22, 2005 (COMPSTAT2) CONTENTS 5. Characteristics of Functions. 1 5.1. Surjective, Injective and Bijective functions 1 5.2. Homotheticity
ARE211, Fall 2005 LECTURE #18: THU, NOV 3, 2005 PRINT DATE: NOVEMBER 22, 2005 (COMPSTAT2) CONTENTS 5. Characteristics of Functions. 1 5.1. Surjective, Injective and Bijective functions 1 5.2. Homotheticity
1 Overview. 2 A Characterization of Convex Functions. 2.1 First-order Taylor approximation. AM 221: Advanced Optimization Spring 2016
 AM 221: Advanced Optimization Spring 2016 Prof. Yaron Singer Lecture 8 February 22nd 1 Overview In the previous lecture we saw characterizations of optimality in linear optimization, and we reviewed the
AM 221: Advanced Optimization Spring 2016 Prof. Yaron Singer Lecture 8 February 22nd 1 Overview In the previous lecture we saw characterizations of optimality in linear optimization, and we reviewed the
Mathematical Economics (ECON 471) Lecture 3 Calculus of Several Variables & Implicit Functions
 Mathematical Economics (ECON 471) Lecture 3 Calculus of Several Variables & Implicit Functions Teng Wah Leo 1 Calculus of Several Variables 11 Functions Mapping between Euclidean Spaces Where as in univariate
Mathematical Economics (ECON 471) Lecture 3 Calculus of Several Variables & Implicit Functions Teng Wah Leo 1 Calculus of Several Variables 11 Functions Mapping between Euclidean Spaces Where as in univariate
Preliminary draft only: please check for final version
 ARE211, Fall2012 CALCULUS4: THU, OCT 11, 2012 PRINTED: AUGUST 22, 2012 (LEC# 15) Contents 3. Univariate and Multivariate Differentiation (cont) 1 3.6. Taylor s Theorem (cont) 2 3.7. Applying Taylor theory:
ARE211, Fall2012 CALCULUS4: THU, OCT 11, 2012 PRINTED: AUGUST 22, 2012 (LEC# 15) Contents 3. Univariate and Multivariate Differentiation (cont) 1 3.6. Taylor s Theorem (cont) 2 3.7. Applying Taylor theory:
Math Camp II. Calculus. Yiqing Xu. August 27, 2014 MIT
 Math Camp II Calculus Yiqing Xu MIT August 27, 2014 1 Sequence and Limit 2 Derivatives 3 OLS Asymptotics 4 Integrals Sequence Definition A sequence {y n } = {y 1, y 2, y 3,..., y n } is an ordered set
Math Camp II Calculus Yiqing Xu MIT August 27, 2014 1 Sequence and Limit 2 Derivatives 3 OLS Asymptotics 4 Integrals Sequence Definition A sequence {y n } = {y 1, y 2, y 3,..., y n } is an ordered set
CHAPTER 1. LINEAR ALGEBRA Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices
 CHAPTER 1. LINEAR ALGEBRA 3 Chapter 1 LINEAR ALGEBRA 1.1 Introduction [To be written.] 1.2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Why are we interested in solving simultaneous equations? We often have
CHAPTER 1. LINEAR ALGEBRA 3 Chapter 1 LINEAR ALGEBRA 1.1 Introduction [To be written.] 1.2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices Why are we interested in solving simultaneous equations? We often have
Chapter 13. Convex and Concave. Josef Leydold Mathematical Methods WS 2018/19 13 Convex and Concave 1 / 44
 Chapter 13 Convex and Concave Josef Leydold Mathematical Methods WS 2018/19 13 Convex and Concave 1 / 44 Monotone Function Function f is called monotonically increasing, if x 1 x 2 f (x 1 ) f (x 2 ) It
Chapter 13 Convex and Concave Josef Leydold Mathematical Methods WS 2018/19 13 Convex and Concave 1 / 44 Monotone Function Function f is called monotonically increasing, if x 1 x 2 f (x 1 ) f (x 2 ) It
Multivariate calculus
 Multivariate calculus Lecture note 5 Outline 1. Multivariate functions in Euclidean space 2. Continuity 3. Multivariate differentiation 4. Differentiability 5. Higher order derivatives 6. Implicit functions
Multivariate calculus Lecture note 5 Outline 1. Multivariate functions in Euclidean space 2. Continuity 3. Multivariate differentiation 4. Differentiability 5. Higher order derivatives 6. Implicit functions
Math 104: l Hospital s rule, Differential Equations and Integration
 Math 104: l Hospital s rule, and Integration Ryan Blair University of Pennsylvania Tuesday January 22, 2013 Math 104:l Hospital s rule, andtuesday Integration January 22, 2013 1 / 8 Outline 1 l Hospital
Math 104: l Hospital s rule, and Integration Ryan Blair University of Pennsylvania Tuesday January 22, 2013 Math 104:l Hospital s rule, andtuesday Integration January 22, 2013 1 / 8 Outline 1 l Hospital
Unconstrained Optimization
 1 / 36 Unconstrained Optimization ME598/494 Lecture Max Yi Ren Department of Mechanical Engineering, Arizona State University February 2, 2015 2 / 36 3 / 36 4 / 36 5 / 36 1. preliminaries 1.1 local approximation
1 / 36 Unconstrained Optimization ME598/494 Lecture Max Yi Ren Department of Mechanical Engineering, Arizona State University February 2, 2015 2 / 36 3 / 36 4 / 36 5 / 36 1. preliminaries 1.1 local approximation
ARE211, Fall2015. Contents. 2. Univariate and Multivariate Differentiation (cont) Taylor s Theorem (cont) 2
 ARE211, Fall2015 CALCULUS4: THU, SEP 17, 2015 PRINTED: SEPTEMBER 22, 2015 (LEC# 7) Contents 2. Univariate and Multivariate Differentiation (cont) 1 2.4. Taylor s Theorem (cont) 2 2.5. Applying Taylor theory:
ARE211, Fall2015 CALCULUS4: THU, SEP 17, 2015 PRINTED: SEPTEMBER 22, 2015 (LEC# 7) Contents 2. Univariate and Multivariate Differentiation (cont) 1 2.4. Taylor s Theorem (cont) 2 2.5. Applying Taylor theory:
OR MSc Maths Revision Course
 OR MSc Maths Revision Course Tom Byrne School of Mathematics University of Edinburgh t.m.byrne@sms.ed.ac.uk 15 September 2017 General Information Today JCMB Lecture Theatre A, 09:30-12:30 Mathematics revision
OR MSc Maths Revision Course Tom Byrne School of Mathematics University of Edinburgh t.m.byrne@sms.ed.ac.uk 15 September 2017 General Information Today JCMB Lecture Theatre A, 09:30-12:30 Mathematics revision
Chapter 2: Unconstrained Extrema
 Chapter 2: Unconstrained Extrema Math 368 c Copyright 2012, 2013 R Clark Robinson May 22, 2013 Chapter 2: Unconstrained Extrema 1 Types of Sets Definition For p R n and r > 0, the open ball about p of
Chapter 2: Unconstrained Extrema Math 368 c Copyright 2012, 2013 R Clark Robinson May 22, 2013 Chapter 2: Unconstrained Extrema 1 Types of Sets Definition For p R n and r > 0, the open ball about p of
Review of Multi-Calculus (Study Guide for Spivak s CHAPTER ONE TO THREE)
 Review of Multi-Calculus (Study Guide for Spivak s CHPTER ONE TO THREE) This material is for June 9 to 16 (Monday to Monday) Chapter I: Functions on R n Dot product and norm for vectors in R n : Let X
Review of Multi-Calculus (Study Guide for Spivak s CHPTER ONE TO THREE) This material is for June 9 to 16 (Monday to Monday) Chapter I: Functions on R n Dot product and norm for vectors in R n : Let X
Microeconomics I. September, c Leopold Sögner
 Microeconomics I c Leopold Sögner Department of Economics and Finance Institute for Advanced Studies Stumpergasse 56 1060 Wien Tel: +43-1-59991 182 soegner@ihs.ac.at http://www.ihs.ac.at/ soegner September,
Microeconomics I c Leopold Sögner Department of Economics and Finance Institute for Advanced Studies Stumpergasse 56 1060 Wien Tel: +43-1-59991 182 soegner@ihs.ac.at http://www.ihs.ac.at/ soegner September,
Selçuk Demir WS 2017 Functional Analysis Homework Sheet
 Selçuk Demir WS 2017 Functional Analysis Homework Sheet 1. Let M be a metric space. If A M is non-empty, we say that A is bounded iff diam(a) = sup{d(x, y) : x.y A} exists. Show that A is bounded iff there
Selçuk Demir WS 2017 Functional Analysis Homework Sheet 1. Let M be a metric space. If A M is non-empty, we say that A is bounded iff diam(a) = sup{d(x, y) : x.y A} exists. Show that A is bounded iff there
EC /11. Math for Microeconomics September Course, Part II Lecture Notes. Course Outline
 LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS Professor Leonardo Felli Department of Economics S.478; x7525 EC400 20010/11 Math for Microeconomics September Course, Part II Lecture Notes Course Outline Lecture 1: Tools for
LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS Professor Leonardo Felli Department of Economics S.478; x7525 EC400 20010/11 Math for Microeconomics September Course, Part II Lecture Notes Course Outline Lecture 1: Tools for
Monotone Function. Function f is called monotonically increasing, if. x 1 x 2 f (x 1 ) f (x 2 ) x 1 < x 2 f (x 1 ) < f (x 2 ) x 1 x 2
 Monotone Function Function f is called monotonically increasing, if Chapter 3 x x 2 f (x ) f (x 2 ) It is called strictly monotonically increasing, if f (x 2) f (x ) Convex and Concave x < x 2 f (x )
Monotone Function Function f is called monotonically increasing, if Chapter 3 x x 2 f (x ) f (x 2 ) It is called strictly monotonically increasing, if f (x 2) f (x ) Convex and Concave x < x 2 f (x )
Week 4: Calculus and Optimization (Jehle and Reny, Chapter A2)
 Week 4: Calculus and Optimization (Jehle and Reny, Chapter A2) Tsun-Feng Chiang *School of Economics, Henan University, Kaifeng, China September 27, 2015 Microeconomic Theory Week 4: Calculus and Optimization
Week 4: Calculus and Optimization (Jehle and Reny, Chapter A2) Tsun-Feng Chiang *School of Economics, Henan University, Kaifeng, China September 27, 2015 Microeconomic Theory Week 4: Calculus and Optimization
QF101: Quantitative Finance August 22, Week 1: Functions. Facilitator: Christopher Ting AY 2017/2018
 QF101: Quantitative Finance August 22, 2017 Week 1: Functions Facilitator: Christopher Ting AY 2017/2018 The chief function of the body is to carry the brain around. Thomas A. Edison 1.1 What is a function?
QF101: Quantitative Finance August 22, 2017 Week 1: Functions Facilitator: Christopher Ting AY 2017/2018 The chief function of the body is to carry the brain around. Thomas A. Edison 1.1 What is a function?
Economics 205 Exercises
 Economics 05 Eercises Prof. Watson, Fall 006 (Includes eaminations through Fall 003) Part 1: Basic Analysis 1. Using ε and δ, write in formal terms the meaning of lim a f() = c, where f : R R.. Write the
Economics 05 Eercises Prof. Watson, Fall 006 (Includes eaminations through Fall 003) Part 1: Basic Analysis 1. Using ε and δ, write in formal terms the meaning of lim a f() = c, where f : R R.. Write the
Real Analysis. Joe Patten August 12, 2018
 Real Analysis Joe Patten August 12, 2018 1 Relations and Functions 1.1 Relations A (binary) relation, R, from set A to set B is a subset of A B. Since R is a subset of A B, it is a set of ordered pairs.
Real Analysis Joe Patten August 12, 2018 1 Relations and Functions 1.1 Relations A (binary) relation, R, from set A to set B is a subset of A B. Since R is a subset of A B, it is a set of ordered pairs.
Mathematical Economics: Lecture 16
 Mathematical Economics: Lecture 16 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University November 26, 2012 Outline 1 Chapter 21: Concave and Quasiconcave Functions New Section Chapter 21: Concave and Quasiconcave Functions Concave
Mathematical Economics: Lecture 16 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University November 26, 2012 Outline 1 Chapter 21: Concave and Quasiconcave Functions New Section Chapter 21: Concave and Quasiconcave Functions Concave
September Math Course: First Order Derivative
 September Math Course: First Order Derivative Arina Nikandrova Functions Function y = f (x), where x is either be a scalar or a vector of several variables (x,..., x n ), can be thought of as a rule which
September Math Course: First Order Derivative Arina Nikandrova Functions Function y = f (x), where x is either be a scalar or a vector of several variables (x,..., x n ), can be thought of as a rule which
2.1 Sets. Definition 1 A set is an unordered collection of objects. Important sets: N, Z, Z +, Q, R.
 2. Basic Structures 2.1 Sets Definition 1 A set is an unordered collection of objects. Important sets: N, Z, Z +, Q, R. Definition 2 Objects in a set are called elements or members of the set. A set is
2. Basic Structures 2.1 Sets Definition 1 A set is an unordered collection of objects. Important sets: N, Z, Z +, Q, R. Definition 2 Objects in a set are called elements or members of the set. A set is
Chapter 8: Taylor s theorem and L Hospital s rule
 Chapter 8: Taylor s theorem and L Hospital s rule Theorem: [Inverse Mapping Theorem] Suppose that a < b and f : [a, b] R. Given that f (x) > 0 for all x (a, b) then f 1 is differentiable on (f(a), f(b))
Chapter 8: Taylor s theorem and L Hospital s rule Theorem: [Inverse Mapping Theorem] Suppose that a < b and f : [a, b] R. Given that f (x) > 0 for all x (a, b) then f 1 is differentiable on (f(a), f(b))
ARE211, Fall 2004 CONTENTS. 4. Univariate and Multivariate Differentiation (cont) Four graphical examples Taylor s Theorem 9
 ARE211, Fall 24 LECTURE #18: TUE, NOV 9, 24 PRINT DATE: DECEMBER 17, 24 (CALCULUS3) CONTENTS 4. Univariate and Multivariate Differentiation (cont) 1 4.4. Multivariate Calculus: functions from R n to R
ARE211, Fall 24 LECTURE #18: TUE, NOV 9, 24 PRINT DATE: DECEMBER 17, 24 (CALCULUS3) CONTENTS 4. Univariate and Multivariate Differentiation (cont) 1 4.4. Multivariate Calculus: functions from R n to R
The general programming problem is the nonlinear programming problem where a given function is maximized subject to a set of inequality constraints.
 1 Optimization Mathematical programming refers to the basic mathematical problem of finding a maximum to a function, f, subject to some constraints. 1 In other words, the objective is to find a point,
1 Optimization Mathematical programming refers to the basic mathematical problem of finding a maximum to a function, f, subject to some constraints. 1 In other words, the objective is to find a point,
Math 141: Lecture 11
 Math 141: Lecture 11 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and integration methods Bob Hough October 12, 2016 Bob Hough Math 141: Lecture 11 October 12, 2016 1 / 36 First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Math 141: Lecture 11 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and integration methods Bob Hough October 12, 2016 Bob Hough Math 141: Lecture 11 October 12, 2016 1 / 36 First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
3 FUNCTIONS. 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties. c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall
 c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2014 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from A to B is a rule that assigns to each element in the set
c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2014 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from A to B is a rule that assigns to each element in the set
3 FUNCTIONS. 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties. c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall
 c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2016 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from the set A to the set B is a correspondence that assigns to
c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2016 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from the set A to the set B is a correspondence that assigns to
MA102: Multivariable Calculus
 MA102: Multivariable Calculus Rupam Barman and Shreemayee Bora Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Differentiability of f : U R n R m Definition: Let U R n be open. Then f : U R n R m is differentiable
MA102: Multivariable Calculus Rupam Barman and Shreemayee Bora Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Differentiability of f : U R n R m Definition: Let U R n be open. Then f : U R n R m is differentiable
Math Refresher - Calculus
 Math Refresher - Calculus David Sovich Washington University in St. Louis TODAY S AGENDA Today we will refresh Calculus for FIN 451 I will focus less on rigor and more on application We will cover both
Math Refresher - Calculus David Sovich Washington University in St. Louis TODAY S AGENDA Today we will refresh Calculus for FIN 451 I will focus less on rigor and more on application We will cover both
MATHEMATICS FOR ECONOMISTS. Course Convener. Contact: Office-Hours: X and Y. Teaching Assistant ATIYEH YEGANLOO
 INTRODUCTION TO QUANTITATIVE METHODS IN ECONOMICS MATHEMATICS FOR ECONOMISTS Course Convener DR. ALESSIA ISOPI Contact: alessia.isopi@manchester.ac.uk Office-Hours: X and Y Teaching Assistant ATIYEH YEGANLOO
INTRODUCTION TO QUANTITATIVE METHODS IN ECONOMICS MATHEMATICS FOR ECONOMISTS Course Convener DR. ALESSIA ISOPI Contact: alessia.isopi@manchester.ac.uk Office-Hours: X and Y Teaching Assistant ATIYEH YEGANLOO
Mathematical Preliminaries for Microeconomics: Exercises
 Mathematical Preliminaries for Microeconomics: Exercises Igor Letina 1 Universität Zürich Fall 2013 1 Based on exercises by Dennis Gärtner, Andreas Hefti and Nick Netzer. How to prove A B Direct proof
Mathematical Preliminaries for Microeconomics: Exercises Igor Letina 1 Universität Zürich Fall 2013 1 Based on exercises by Dennis Gärtner, Andreas Hefti and Nick Netzer. How to prove A B Direct proof
Lecture 32: Taylor Series and McLaurin series We saw last day that some functions are equal to a power series on part of their domain.
 Lecture 32: Taylor Series and McLaurin series We saw last day that some functions are equal to a power series on part of their domain. For example f(x) = 1 1 x = 1 + x + x2 + x 3 + = ln(1 + x) = x x2 2
Lecture 32: Taylor Series and McLaurin series We saw last day that some functions are equal to a power series on part of their domain. For example f(x) = 1 1 x = 1 + x + x2 + x 3 + = ln(1 + x) = x x2 2
Lecture 10. Econ August 21
 Lecture 10 Econ 2001 2015 August 21 Lecture 10 Outline 1 Derivatives and Partial Derivatives 2 Differentiability 3 Tangents to Level Sets Calculus! This material will not be included in today s exam. Announcement:
Lecture 10 Econ 2001 2015 August 21 Lecture 10 Outline 1 Derivatives and Partial Derivatives 2 Differentiability 3 Tangents to Level Sets Calculus! This material will not be included in today s exam. Announcement:
MATH. 4548, Autumn 15, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 September 4, 2015 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points.
 MATH. 4548, Autumn 15, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 September 4, 2015 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points. 1. Let f : (, 0) IR be given by f(x) = 1/x 2. Prove
MATH. 4548, Autumn 15, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 September 4, 2015 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points. 1. Let f : (, 0) IR be given by f(x) = 1/x 2. Prove
Comparative Statics. Autumn 2018
 Comparative Statics Autumn 2018 What is comparative statics? Contents 1 What is comparative statics? 2 One variable functions Multiple variable functions Vector valued functions Differential and total
Comparative Statics Autumn 2018 What is comparative statics? Contents 1 What is comparative statics? 2 One variable functions Multiple variable functions Vector valued functions Differential and total
Functions of Several Variables
 Jim Lambers MAT 419/519 Summer Session 2011-12 Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Section 1.2 in the text. Functions of Several Variables We now generalize the results from the previous section,
Jim Lambers MAT 419/519 Summer Session 2011-12 Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Section 1.2 in the text. Functions of Several Variables We now generalize the results from the previous section,
Multi Variable Calculus
 Multi Variable Calculus Joshua Wilde, revised by Isabel Tecu, Takeshi Suzuki and María José Boccardi August 3, 03 Functions from R n to R m So far we have looked at functions that map one number to another
Multi Variable Calculus Joshua Wilde, revised by Isabel Tecu, Takeshi Suzuki and María José Boccardi August 3, 03 Functions from R n to R m So far we have looked at functions that map one number to another
AP Calculus BC Scope & Sequence
 AP Calculus BC Scope & Sequence Grading Period Unit Title Learning Targets Throughout the School Year First Grading Period *Apply mathematics to problems in everyday life *Use a problem-solving model that
AP Calculus BC Scope & Sequence Grading Period Unit Title Learning Targets Throughout the School Year First Grading Period *Apply mathematics to problems in everyday life *Use a problem-solving model that
MTAEA Differentiation
 School of Economics, Australian National University February 5, 2010 Basic Properties of the Derivative. Secant Tangent Applet l 3 l 2 l 1 a a 3 a 2 a 1 Figure: The derivative of f at a is the limiting
School of Economics, Australian National University February 5, 2010 Basic Properties of the Derivative. Secant Tangent Applet l 3 l 2 l 1 a a 3 a 2 a 1 Figure: The derivative of f at a is the limiting
EC /11. Math for Microeconomics September Course, Part II Problem Set 1 with Solutions. a11 a 12. x 2
 LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS Professor Leonardo Felli Department of Economics S.478; x7525 EC400 2010/11 Math for Microeconomics September Course, Part II Problem Set 1 with Solutions 1. Show that the general
LONDON SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS Professor Leonardo Felli Department of Economics S.478; x7525 EC400 2010/11 Math for Microeconomics September Course, Part II Problem Set 1 with Solutions 1. Show that the general
Greenwich Public Schools Mathematics Curriculum Objectives. Calculus
 Mathematics Curriculum Objectives Calculus June 30, 2006 NUMERICAL AND PROPORTIONAL REASONING Quantitative relationships can be expressed numerically in multiple ways in order to make connections and simplify
Mathematics Curriculum Objectives Calculus June 30, 2006 NUMERICAL AND PROPORTIONAL REASONING Quantitative relationships can be expressed numerically in multiple ways in order to make connections and simplify
14 Lecture 14 Local Extrema of Function
 14 Lecture 14 Local Extrema of Function 14.1 Taylor s Formula with Lagrangian Remainder Term Theorem 14.1. Let n N {0} and f : (a,b) R. We assume that there exists f (n+1) (x) for all x (a,b). Then for
14 Lecture 14 Local Extrema of Function 14.1 Taylor s Formula with Lagrangian Remainder Term Theorem 14.1. Let n N {0} and f : (a,b) R. We assume that there exists f (n+1) (x) for all x (a,b). Then for
Topics Covered in Calculus BC
 Topics Covered in Calculus BC Calculus BC Correlation 5 A Functions, Graphs, and Limits 1. Analysis of graphs 2. Limits or functions (including one sides limits) a. An intuitive understanding of the limiting
Topics Covered in Calculus BC Calculus BC Correlation 5 A Functions, Graphs, and Limits 1. Analysis of graphs 2. Limits or functions (including one sides limits) a. An intuitive understanding of the limiting
3 FUNCTIONS. 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties. c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Spring
 c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Spring 2016 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from A to B is a rule that assigns to each element in the set
c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Spring 2016 1 3 FUNCTIONS 3.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from A to B is a rule that assigns to each element in the set
Economics 204 Summer/Fall 2011 Lecture 11 Monday August 8, f(x + h) (f(x) + ah) = a = 0 = 0. f(x + h) (f(x) + T x (h))
 Economics 204 Summer/Fall 2011 Lecture 11 Monday August 8, 2011 Sections 41-43 (Unified) Definition 1 Let f : I R, where I R is an open interval f is differentiable at x I if for some a R f(x + h) f lim
Economics 204 Summer/Fall 2011 Lecture 11 Monday August 8, 2011 Sections 41-43 (Unified) Definition 1 Let f : I R, where I R is an open interval f is differentiable at x I if for some a R f(x + h) f lim
Session: 09 Aug 2016 (Tue), 10:00am 1:00pm; 10 Aug 2016 (Wed), 10:00am 1:00pm &3:00pm 5:00pm (Revision)
 Seminars on Mathematics for Economics and Finance Topic 2: Topics in multivariate calculus, concavity and convexity 1 Session: 09 Aug 2016 (Tue), 10:00am 1:00pm; 10 Aug 2016 (Wed), 10:00am 1:00pm &3:00pm
Seminars on Mathematics for Economics and Finance Topic 2: Topics in multivariate calculus, concavity and convexity 1 Session: 09 Aug 2016 (Tue), 10:00am 1:00pm; 10 Aug 2016 (Wed), 10:00am 1:00pm &3:00pm
Math 5052 Measure Theory and Functional Analysis II Homework Assignment 7
 Math 5052 Measure Theory and Functional Analysis II Homework Assignment 7 Prof. Wickerhauser Due Friday, February 5th, 2016 Please do Exercises 3, 6, 14, 16*, 17, 18, 21*, 23*, 24, 27*. Exercises marked
Math 5052 Measure Theory and Functional Analysis II Homework Assignment 7 Prof. Wickerhauser Due Friday, February 5th, 2016 Please do Exercises 3, 6, 14, 16*, 17, 18, 21*, 23*, 24, 27*. Exercises marked
The Derivative. Appendix B. B.1 The Derivative of f. Mappings from IR to IR
 Appendix B The Derivative B.1 The Derivative of f In this chapter, we give a short summary of the derivative. Specifically, we want to compare/contrast how the derivative appears for functions whose domain
Appendix B The Derivative B.1 The Derivative of f In this chapter, we give a short summary of the derivative. Specifically, we want to compare/contrast how the derivative appears for functions whose domain
HOMEWORK 7 SOLUTIONS
 HOMEWORK 7 SOLUTIONS MA11: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 17 (1) Using the method of Lagrange multipliers, find the largest and smallest values of the function f(x, y) xy on the ellipse x + y 1. Solution: The
HOMEWORK 7 SOLUTIONS MA11: ADVANCED CALCULUS, HILARY 17 (1) Using the method of Lagrange multipliers, find the largest and smallest values of the function f(x, y) xy on the ellipse x + y 1. Solution: The
Functions. Given a function f: A B:
 Functions Given a function f: A B: We say f maps A to B or f is a mapping from A to B. A is called the domain of f. B is called the codomain of f. If f(a) = b, then b is called the image of a under f.
Functions Given a function f: A B: We say f maps A to B or f is a mapping from A to B. A is called the domain of f. B is called the codomain of f. If f(a) = b, then b is called the image of a under f.
MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 45
 official website http://uoft.me/mat137 MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 45 Today: Taylor Polynomials Taylor Series Next: Taylor Series Power Series Definition (Power Series) A power series is a series of the form
official website http://uoft.me/mat137 MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 45 Today: Taylor Polynomials Taylor Series Next: Taylor Series Power Series Definition (Power Series) A power series is a series of the form
1.2 Functions What is a Function? 1.2. FUNCTIONS 11
 1.2. FUNCTIONS 11 1.2 Functions 1.2.1 What is a Function? In this section, we only consider functions of one variable. Loosely speaking, a function is a special relation which exists between two variables.
1.2. FUNCTIONS 11 1.2 Functions 1.2.1 What is a Function? In this section, we only consider functions of one variable. Loosely speaking, a function is a special relation which exists between two variables.
Optimization, for QEM-IMAEF-MMEF, this is the First Part (september-november). For MAEF, it corresponds to the whole course of the semester.
 Paris. Optimization, for QEM-IMAEF-MMEF, this is the First Part (september-november). For MAEF, it corresponds to the whole course of the semester. (Paris 1 Panthéon-Sorbonne and PSE) Paris, 2016. Why
Paris. Optimization, for QEM-IMAEF-MMEF, this is the First Part (september-november). For MAEF, it corresponds to the whole course of the semester. (Paris 1 Panthéon-Sorbonne and PSE) Paris, 2016. Why
INDEX. Bolzano-Weierstrass theorem, for sequences, boundary points, bounded functions, 142 bounded sets, 42 43
 INDEX Abel s identity, 131 Abel s test, 131 132 Abel s theorem, 463 464 absolute convergence, 113 114 implication of conditional convergence, 114 absolute value, 7 reverse triangle inequality, 9 triangle
INDEX Abel s identity, 131 Abel s test, 131 132 Abel s theorem, 463 464 absolute convergence, 113 114 implication of conditional convergence, 114 absolute value, 7 reverse triangle inequality, 9 triangle
3 Applications of partial differentiation
 Advanced Calculus Chapter 3 Applications of partial differentiation 37 3 Applications of partial differentiation 3.1 Stationary points Higher derivatives Let U R 2 and f : U R. The partial derivatives
Advanced Calculus Chapter 3 Applications of partial differentiation 37 3 Applications of partial differentiation 3.1 Stationary points Higher derivatives Let U R 2 and f : U R. The partial derivatives
Recitation 1. Gradients and Directional Derivatives. Brett Bernstein. CDS at NYU. January 21, 2018
 Gradients and Directional Derivatives Brett Bernstein CDS at NYU January 21, 2018 Brett Bernstein (CDS at NYU) Recitation 1 January 21, 2018 1 / 23 Initial Question Intro Question Question We are given
Gradients and Directional Derivatives Brett Bernstein CDS at NYU January 21, 2018 Brett Bernstein (CDS at NYU) Recitation 1 January 21, 2018 1 / 23 Initial Question Intro Question Question We are given
EC400 Math for Microeconomics Syllabus The course is based on 6 sixty minutes lectures and on 6 ninety minutes classes.
 London School of Economics Department of Economics Dr Francesco Nava Offi ce: 32L.3.20 EC400 Math for Microeconomics Syllabus 2016 The course is based on 6 sixty minutes lectures and on 6 ninety minutes
London School of Economics Department of Economics Dr Francesco Nava Offi ce: 32L.3.20 EC400 Math for Microeconomics Syllabus 2016 The course is based on 6 sixty minutes lectures and on 6 ninety minutes
Taylor and Maclaurin Series. Approximating functions using Polynomials.
 Taylor and Maclaurin Series Approximating functions using Polynomials. Approximating f x = e x near x = 0 In order to approximate the function f x = e x near x = 0, we can use the tangent line (The Linear
Taylor and Maclaurin Series Approximating functions using Polynomials. Approximating f x = e x near x = 0 In order to approximate the function f x = e x near x = 0, we can use the tangent line (The Linear
7) Important properties of functions: homogeneity, homotheticity, convexity and quasi-convexity
 30C00300 Mathematical Methods for Economists (6 cr) 7) Important properties of functions: homogeneity, homotheticity, convexity and quasi-convexity Abolfazl Keshvari Ph.D. Aalto University School of Business
30C00300 Mathematical Methods for Economists (6 cr) 7) Important properties of functions: homogeneity, homotheticity, convexity and quasi-convexity Abolfazl Keshvari Ph.D. Aalto University School of Business
Logical Connectives and Quantifiers
 Chapter 1 Logical Connectives and Quantifiers 1.1 Logical Connectives 1.2 Quantifiers 1.3 Techniques of Proof: I 1.4 Techniques of Proof: II Theorem 1. Let f be a continuous function. If 1 f(x)dx 0, then
Chapter 1 Logical Connectives and Quantifiers 1.1 Logical Connectives 1.2 Quantifiers 1.3 Techniques of Proof: I 1.4 Techniques of Proof: II Theorem 1. Let f be a continuous function. If 1 f(x)dx 0, then
7: FOURIER SERIES STEVEN HEILMAN
 7: FOURIER SERIES STEVE HEILMA Contents 1. Review 1 2. Introduction 1 3. Periodic Functions 2 4. Inner Products on Periodic Functions 3 5. Trigonometric Polynomials 5 6. Periodic Convolutions 7 7. Fourier
7: FOURIER SERIES STEVE HEILMA Contents 1. Review 1 2. Introduction 1 3. Periodic Functions 2 4. Inner Products on Periodic Functions 3 5. Trigonometric Polynomials 5 6. Periodic Convolutions 7 7. Fourier
Homework for MATH 4603 (Advanced Calculus I) Fall Homework 13: Due on Tuesday 15 December. Homework 12: Due on Tuesday 8 December
 Homework for MATH 4603 (Advanced Calculus I) Fall 2015 Homework 13: Due on Tuesday 15 December 49. Let D R, f : D R and S D. Let a S (acc S). Assume that f is differentiable at a. Let g := f S. Show that
Homework for MATH 4603 (Advanced Calculus I) Fall 2015 Homework 13: Due on Tuesday 15 December 49. Let D R, f : D R and S D. Let a S (acc S). Assume that f is differentiable at a. Let g := f S. Show that
Implicit Functions, Curves and Surfaces
 Chapter 11 Implicit Functions, Curves and Surfaces 11.1 Implicit Function Theorem Motivation. In many problems, objects or quantities of interest can only be described indirectly or implicitly. It is then
Chapter 11 Implicit Functions, Curves and Surfaces 11.1 Implicit Function Theorem Motivation. In many problems, objects or quantities of interest can only be described indirectly or implicitly. It is then
CHAPTER 2: CONVEX SETS AND CONCAVE FUNCTIONS. W. Erwin Diewert January 31, 2008.
 1 ECONOMICS 594: LECTURE NOTES CHAPTER 2: CONVEX SETS AND CONCAVE FUNCTIONS W. Erwin Diewert January 31, 2008. 1. Introduction Many economic problems have the following structure: (i) a linear function
1 ECONOMICS 594: LECTURE NOTES CHAPTER 2: CONVEX SETS AND CONCAVE FUNCTIONS W. Erwin Diewert January 31, 2008. 1. Introduction Many economic problems have the following structure: (i) a linear function
Math 273a: Optimization Basic concepts
 Math 273a: Optimization Basic concepts Instructor: Wotao Yin Department of Mathematics, UCLA Spring 2015 slides based on Chong-Zak, 4th Ed. Goals of this lecture The general form of optimization: minimize
Math 273a: Optimization Basic concepts Instructor: Wotao Yin Department of Mathematics, UCLA Spring 2015 slides based on Chong-Zak, 4th Ed. Goals of this lecture The general form of optimization: minimize
9 FUNCTIONS. 9.1 The Definition of Function. c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall
 c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2018 1 9 FUNCTIONS 9.1 The Definition of Function DEFINITION 1. Let X and Y be nonempty sets. A function f from the set X to the set Y is a correspondence that assigns to each
c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2018 1 9 FUNCTIONS 9.1 The Definition of Function DEFINITION 1. Let X and Y be nonempty sets. A function f from the set X to the set Y is a correspondence that assigns to each
5 FUNCTIONS. 5.1 Definition and Basic Properties. c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall
 c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2017 1 5 FUNCTIONS 5.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from the set A to the set B is a correspondence that assigns to
c Dr Oksana Shatalov, Fall 2017 1 5 FUNCTIONS 5.1 Definition and Basic Properties DEFINITION 1. Let A and B be nonempty sets. A function f from the set A to the set B is a correspondence that assigns to
Part II Probability and Measure
 Part II Probability and Measure Theorems Based on lectures by J. Miller Notes taken by Dexter Chua Michaelmas 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
Part II Probability and Measure Theorems Based on lectures by J. Miller Notes taken by Dexter Chua Michaelmas 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
MATHEMATICAL ECONOMICS: OPTIMIZATION. Contents
 MATHEMATICAL ECONOMICS: OPTIMIZATION JOÃO LOPES DIAS Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1. Preliminaries 2 1.2. Optimal points and values 2 1.3. The optimization problems 3 1.4. Existence of optimal points 4
MATHEMATICAL ECONOMICS: OPTIMIZATION JOÃO LOPES DIAS Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1. Preliminaries 2 1.2. Optimal points and values 2 1.3. The optimization problems 3 1.4. Existence of optimal points 4
Lecture 5: Rules of Differentiation. First Order Derivatives
 Lecture 5: Rules of Differentiation First order derivatives Higher order derivatives Partial differentiation Higher order partials Differentials Derivatives of implicit functions Generalized implicit function
Lecture 5: Rules of Differentiation First order derivatives Higher order derivatives Partial differentiation Higher order partials Differentials Derivatives of implicit functions Generalized implicit function
Multivariate Differentiation 1
 John Nachbar Washington University February 23, 2017 1 Preliminaries. Multivariate Differentiation 1 I assume that you are already familiar with standard concepts and results from univariate calculus;
John Nachbar Washington University February 23, 2017 1 Preliminaries. Multivariate Differentiation 1 I assume that you are already familiar with standard concepts and results from univariate calculus;
Caculus 221. Possible questions for Exam II. March 19, 2002
 Caculus 221 Possible questions for Exam II March 19, 2002 These notes cover the recent material in a style more like the lecture than the book. The proofs in the book are in section 1-11. At the end there
Caculus 221 Possible questions for Exam II March 19, 2002 These notes cover the recent material in a style more like the lecture than the book. The proofs in the book are in section 1-11. At the end there
ECM Calculus and Geometry. Revision Notes
 ECM1702 - Calculus and Geometry Revision Notes Joshua Byrne Autumn 2011 Contents 1 The Real Numbers 1 1.1 Notation.................................................. 1 1.2 Set Notation...............................................
ECM1702 - Calculus and Geometry Revision Notes Joshua Byrne Autumn 2011 Contents 1 The Real Numbers 1 1.1 Notation.................................................. 1 1.2 Set Notation...............................................
Chapter 12: Differentiation. SSMth2: Basic Calculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Strands Mr. Migo M.
 Chapter 12: Differentiation SSMth2: Basic Calculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Strands Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 12: Differentiation Lecture 12.1: The Derivative Lecture
Chapter 12: Differentiation SSMth2: Basic Calculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Strands Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 12: Differentiation Lecture 12.1: The Derivative Lecture
Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 6
 Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 6 Andrew Nobel September 21, 2017 Functions Functions Given: Sets A and B, possibly different Definition: A function f : A B is a rule that assigns every element
Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 6 Andrew Nobel September 21, 2017 Functions Functions Given: Sets A and B, possibly different Definition: A function f : A B is a rule that assigns every element
MATHEMATICS AP Calculus (BC) Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations
 Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations Computation and A. Develop an understanding of limits and continuity. 1. Recognize the types of nonexistence of limits and why they Estimation are nonexistent.
Standard: Number, Number Sense and Operations Computation and A. Develop an understanding of limits and continuity. 1. Recognize the types of nonexistence of limits and why they Estimation are nonexistent.
f(x, y) = 1 2 x y2 xy 3
 Problem. Find the critical points of the function and determine their nature. We have We find the critical points We calculate f(x, y) = 2 x2 + 3 2 y2 xy 3 f x = x y 3 = 0 = x = y 3 f y = 3y 3xy 2 = 0
Problem. Find the critical points of the function and determine their nature. We have We find the critical points We calculate f(x, y) = 2 x2 + 3 2 y2 xy 3 f x = x y 3 = 0 = x = y 3 f y = 3y 3xy 2 = 0
Economics 101A (Lecture 3) Stefano DellaVigna
 Economics 101A (Lecture 3) Stefano DellaVigna January 24, 2017 Outline 1. Implicit Function Theorem 2. Envelope Theorem 3. Convexity and concavity 4. Constrained Maximization 1 Implicit function theorem
Economics 101A (Lecture 3) Stefano DellaVigna January 24, 2017 Outline 1. Implicit Function Theorem 2. Envelope Theorem 3. Convexity and concavity 4. Constrained Maximization 1 Implicit function theorem
MA 137 Calculus 1 with Life Science Applications Monotonicity and Concavity (Section 5.2) Extrema, Inflection Points, and Graphing (Section 5.
 MA 137 Calculus 1 with Life Science Applications Monotonicity and Concavity (Section 52) Extrema, Inflection Points, and Graphing (Section 53) Alberto Corso albertocorso@ukyedu Department of Mathematics
MA 137 Calculus 1 with Life Science Applications Monotonicity and Concavity (Section 52) Extrema, Inflection Points, and Graphing (Section 53) Alberto Corso albertocorso@ukyedu Department of Mathematics
REVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS
 REVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS DONU ARAPURA 1. Limits and continuity To simplify the statements, we will often stick to two variables, but everything holds with any number of variables. Let f(x, y) be
REVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS DONU ARAPURA 1. Limits and continuity To simplify the statements, we will often stick to two variables, but everything holds with any number of variables. Let f(x, y) be
Calculus Overview. f(x) f (x) is slope. I. Single Variable. A. First Order Derivative : Concept : measures slope of curve at a point.
 Calculus Overview I. Single Variable A. First Order Derivative : Concept : measures slope of curve at a point. Notation : Let y = f (x). First derivative denoted f ʹ (x), df dx, dy dx, f, etc. Example
Calculus Overview I. Single Variable A. First Order Derivative : Concept : measures slope of curve at a point. Notation : Let y = f (x). First derivative denoted f ʹ (x), df dx, dy dx, f, etc. Example
MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES. 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) ax 2 + bx + c = 0. x = b ± b 2 4ac 2a. i = 1.
 MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) 1.1 Introduction Types of numbers (natural, integers, rationals, reals) The need to solve quadratic equations:
MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) 1.1 Introduction Types of numbers (natural, integers, rationals, reals) The need to solve quadratic equations:
8.5 Taylor Polynomials and Taylor Series
 8.5. TAYLOR POLYNOMIALS AND TAYLOR SERIES 50 8.5 Taylor Polynomials and Taylor Series Motivating Questions In this section, we strive to understand the ideas generated by the following important questions:
8.5. TAYLOR POLYNOMIALS AND TAYLOR SERIES 50 8.5 Taylor Polynomials and Taylor Series Motivating Questions In this section, we strive to understand the ideas generated by the following important questions:
Convex Functions and Optimization
 Chapter 5 Convex Functions and Optimization 5.1 Convex Functions Our next topic is that of convex functions. Again, we will concentrate on the context of a map f : R n R although the situation can be generalized
Chapter 5 Convex Functions and Optimization 5.1 Convex Functions Our next topic is that of convex functions. Again, we will concentrate on the context of a map f : R n R although the situation can be generalized
Section 3.1. Best Affine Approximations. Difference Equations to Differential Equations
 Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 3.1 Best Affine Approximations We are now in a position to discuss the two central problems of calculus as mentioned in Section 1.1. In this chapter
Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 3.1 Best Affine Approximations We are now in a position to discuss the two central problems of calculus as mentioned in Section 1.1. In this chapter
1/37. Convexity theory. Victor Kitov
 1/37 Convexity theory Victor Kitov 2/37 Table of Contents 1 2 Strictly convex functions 3 Concave & strictly concave functions 4 Kullback-Leibler divergence 3/37 Convex sets Denition 1 Set X is convex
1/37 Convexity theory Victor Kitov 2/37 Table of Contents 1 2 Strictly convex functions 3 Concave & strictly concave functions 4 Kullback-Leibler divergence 3/37 Convex sets Denition 1 Set X is convex
TEST CODE: PMB SYLLABUS
 TEST CODE: PMB SYLLABUS Convergence and divergence of sequence and series; Cauchy sequence and completeness; Bolzano-Weierstrass theorem; continuity, uniform continuity, differentiability; directional
TEST CODE: PMB SYLLABUS Convergence and divergence of sequence and series; Cauchy sequence and completeness; Bolzano-Weierstrass theorem; continuity, uniform continuity, differentiability; directional
B553 Lecture 1: Calculus Review
 B553 Lecture 1: Calculus Review Kris Hauser January 10, 2012 This course requires a familiarity with basic calculus, some multivariate calculus, linear algebra, and some basic notions of metric topology.
B553 Lecture 1: Calculus Review Kris Hauser January 10, 2012 This course requires a familiarity with basic calculus, some multivariate calculus, linear algebra, and some basic notions of metric topology.
Math (P)refresher Lecture 8: Unconstrained Optimization
 Math (P)refresher Lecture 8: Unconstrained Optimization September 2006 Today s Topics : Quadratic Forms Definiteness of Quadratic Forms Maxima and Minima in R n First Order Conditions Second Order Conditions
Math (P)refresher Lecture 8: Unconstrained Optimization September 2006 Today s Topics : Quadratic Forms Definiteness of Quadratic Forms Maxima and Minima in R n First Order Conditions Second Order Conditions
Academic Content Standard MATHEMATICS. MA 51 Advanced Placement Calculus BC
 Academic Content Standard MATHEMATICS MA 51 Advanced Placement Calculus BC Course #: MA 51 Grade Level: High School Course Name: Advanced Placement Calculus BC Level of Difficulty: High Prerequisites:
Academic Content Standard MATHEMATICS MA 51 Advanced Placement Calculus BC Course #: MA 51 Grade Level: High School Course Name: Advanced Placement Calculus BC Level of Difficulty: High Prerequisites:
Mathematical Foundations -1- Convexity and quasi-convexity. Convex set Convex function Concave function Quasi-concave function Supporting hyperplane
 Mathematical Foundations -1- Convexity and quasi-convexity Convex set Convex function Concave function Quasi-concave function Supporting hyperplane Mathematical Foundations -2- Convexity and quasi-convexity
Mathematical Foundations -1- Convexity and quasi-convexity Convex set Convex function Concave function Quasi-concave function Supporting hyperplane Mathematical Foundations -2- Convexity and quasi-convexity
CHAPTER 4: HIGHER ORDER DERIVATIVES. Likewise, we may define the higher order derivatives. f(x, y, z) = xy 2 + e zx. y = 2xy.
 April 15, 2009 CHAPTER 4: HIGHER ORDER DERIVATIVES In this chapter D denotes an open subset of R n. 1. Introduction Definition 1.1. Given a function f : D R we define the second partial derivatives as
April 15, 2009 CHAPTER 4: HIGHER ORDER DERIVATIVES In this chapter D denotes an open subset of R n. 1. Introduction Definition 1.1. Given a function f : D R we define the second partial derivatives as
Computational Optimization. Mathematical Programming Fundamentals 1/25 (revised)
 Computational Optimization Mathematical Programming Fundamentals 1/5 (revised) If you don t know where you are going, you probably won t get there. -from some book I read in eight grade If you do get there,
Computational Optimization Mathematical Programming Fundamentals 1/5 (revised) If you don t know where you are going, you probably won t get there. -from some book I read in eight grade If you do get there,
Calculus Example Exam Solutions
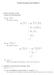 Calculus Example Exam Solutions. Limits (8 points, 6 each) Evaluate the following limits: p x 2 (a) lim x 4 We compute as follows: lim p x 2 x 4 p p x 2 x +2 x 4 p x +2 x 4 (x 4)( p x + 2) p x +2 = p 4+2
Calculus Example Exam Solutions. Limits (8 points, 6 each) Evaluate the following limits: p x 2 (a) lim x 4 We compute as follows: lim p x 2 x 4 p p x 2 x +2 x 4 p x +2 x 4 (x 4)( p x + 2) p x +2 = p 4+2
