PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT OF A VALVELESS PUMP DRIVEN BY A NOBLE PIEZOELECTRIC COMPOSITE ACTUATOR
|
|
|
- Justina Brooks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Y. Uetsuji et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 4 (2014) PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT OF A VALVELESS PUMP DRIVEN BY A NOBLE PIEZOELECTRIC COMPOSITE ACTUATOR Y. UETSUJI 1, T. HIRAMORI 2, N. NISHIGUCHI 1, H. KURAMAE 3 & K. TSUCHIYA 4 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Osaka Institute of Technology, Japan. 2 Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka Institute of Technology, Japan. 3 Department of Technology Management, Osaka Institute of Technology, Japan. 4 Department of Precision Engineering, Tokai University, Japan. ABSTRACT This paper presents a computational and experimental study of a valveless pump driven by a noble piezoelectric composite actuator consisting of a bimorph piezoelectric plate and a metal cap. The superiority of deformation performance of the proposed composite actuator was demonstrated computationally through finite element simulation and was then verified experimentally by deflection measurements of a disc-shaped prototype under an alternating electric field. The proposed composite actuator was applied to a valveless pump in a Y-shaped fluid channel. The pump s performance was estimated using a piezoelectric-fluid interaction finite element simulation. The effect of the fluid channel configuration was investigated, and the liquid feed volume is discussed and compared with that of conventional actuators. Keywords: Deflection measurement, finite element simulation, m-tas, piezoelectric actuator, piezoelectric fluid interaction, valveless pump. 1 INTRODUCTION Micropumps, which were initially developed in 1980, have received considerable attention and played an important role in the development of microfluidics systems [1]. Micropumps are extensively used in inkjet printers, but their application is expanding into chemical, medical, and biological devices. These devices handle microliquids and are integrated into chemical analysis and microdosage systems, which are called micro-tas or BioMEMS. Hitherto, micropumps have been developed with various working principles, such as electroelasticity, shape memory, electromagneticity, and piezoelectricity [2]. Piezoelectric actuation has advantages such as low-power consumption, reliability, and energy efficiency. The first piezoelectric valveless pump was developed in 1993 [3]. Since then, many valveless pumps driven by piezoelectric actuators have been studied [3 13] because they can be easily incorporated into microfluidics systems. Their pumping performance depends on the flow channel topology design and on the piezoelectric actuator. Based on the flow channel, most valveless pumps can be classified into one of two types. The first has vertical flow channels with respect to a plate-shaped piezoelectric actuator and chamber [3 6]. In this type of valveless pump, two flow-directing valves are replaced by two diffuser/ nozzle channels. A diffuser is an expanding duct, and a nozzle is a converging duct. The diffuser/nozzle channel is geometrically designed to have a lower pressure loss in the diffuser direction than in the nozzle direction. As the chamber volume increases, the inlet acts as a diffuser with a lower flow restriction than the outlet, which acts as a nozzle. On the other hand, as the chamber volume decreases, the outlet acts as a diffuser with a lower flow restriction than the inlet, which acts as a nozzle. The second type of valveless pump has horizontal flow channels connected to a plate-shaped chamber with a piezoelectric actuator [7 11] WIT Press, ISSN: (paper format), ISSN: (online), DOI: /CMEM-V2-N
2 Y. Uetsuji et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 4 (2014) 393 A diffuser is defined as a channel with an expanding cross-sectional area in the flow direction, and a nozzle is a channel with a decreasing cross-sectional area in the flow direction. Although the pump operation is same as with the former type, the latter has a thin structure, which is advantageous for miniaturization. To improve the pumping performance of a valveless pump, the geometry of the diffuser/nozzle channels has been improved [12,13]. Furthermore, several piezoelectric-actuated chambers can be connected in series and/or parallel for enhanced performance [14,15]. Piezoelectric actuators can also be classified into two types. The first is the monomorph actuator, which has been used in various valveless pumps [3 11]. The monomorph actuator consists of a piezoelectric ceramic plate and a thin metal plate, and is deflected by the difference in in-plane strain between these two plates. The other type of actuator is the bimorph actuator, which is composed of two thin piezoelectric ceramic plates bonded together. The bimorph actuator, which has also been used in many valveless pumps [16 18], reverses the deformation of two piezoelectric plates by opposite electric field or opposite remanent polarization. Namely, the opposite sign of in-plane strain between the two piezoelectric plates can generate a large deflection in out-of-plane direction. To amplify the displacement of piezoelectric actuators, a composite actuator called the Moonie was designed and fabricated [19 21]. This was a piezoelectric actuator bonded to a metal cap. The Moonie actuator deforms the metal cap by utilizing the in-plane displacement generated by the piezoelectric actuator. Moonie actuators were followed by many advanced topology designs and improvements in the geometry and configuration of the metal cap [22,23]. Hitherto, only simple piezoelectric structures have been employed in Moonie actuators, even though the bimorph structure would enable the generation of larger in-plane displacements. The potentially superior bimorph Moonie actuator has not been investigated, and composite actuators have not yet been utilized in micropumps. Consequently, the objective of this work was the examination of a noble composite actuator consisting of a piezoelectric bimorph actuator and a metal cap, and its application to the valveless pump. We call this new actuator design the new Moonie actuator. In our previous work [24], the superiority of the proposed composite actuator to conventional ones at the view point of static deflection was verified through finite element simulations. In the present work, the dynamic deflection of the proposed composite actuator was examined experimentally. The proposed actuator was applied to a valveless pump with a Y-shaped fluid channel [18], and the pumping performance was investigated through piezoelectric fluid interaction finite element simulation. 2 PERFORMANCE VERIFICATION OF THE NEW MOONIE ACTUATOR Table 1 compares the configuration and deformation behavior of four piezoelectric actuators. If the x 1 x 2 x 3 orthogonal coordinate system in Table 1 is employed, x 1 and x 2 indicate the inplane direction and x 3 is the thickness direction of piezoelectric plate. The first is a simple piezoelectric plate, which is called a simple actuator in this paper. When a positive electric field (E 3 ) is applied in the thickness direction of the simple actuator, it extends in the thickness direction and contracts in the in-plane directions. Based on the piezoelectric strain constant d mij, the mechanical strains e 33 and e 11 (= e 22 ) can be expressed as d 333 E 3 and d 311 E 3, respectively. In a negative electric field, the deformation is reversed. To obtain the volume change in the piezoelectric pump, the out-of-plane strain e 33 caused by piezoelectric strain constant d 333 is utilized. The second actuator was a bimorph actuator consisting of two piezoelectric plates. This actuator generates a large deflection because of the difference between
3 394 Y. Uetsuji et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 4 (2014) Table 1: Comparison of piezoelectric actuator deformation mechanisms. in-plane strains e 11 and e 22 caused by d 311 and d 322 between the upper and lower piezoelectric plates. The out-of-plane and in-plane displacements of the bimorph actuator are larger than those of the simple actuator, and deflection angle occurs at the edge of the bimorph actuator. The third and fourth actuators were the Moonie and the proposed new Moonie. Both are composite actuators consisting of a piezoelectric element and a metal cap. In the conventional Moonie actuator, the metal cap is bent by the in-plane strains caused by a simple actuator. The deflection of the metal cap can be amplified if the in-plane strains of the piezoelectric element are increased. In the proposed new Moonie actuator, a bimorph actuator, which has in-plane strains larger than those of the simple actuator, is applied to the piezoelectric element of a Moonie actuator. The new Moonie actuator can amplify the overall deflection not only because of larger in-plane strains but also by the deflection angle of its edges. With the new Moonie actuator, the metal cap is deflected on the upper side if the piezoelectric element is deflected on the lower side. By contrast, the metal cap is deflected on the lower side if the piezoelectric element is deflected on the upper side. Consequently, it is important to provide sufficient clearance for the metal cap to prevent physical interference with the piezoelectric element. To verify the superior performance of the proposed new Moonie actuator, four prototype piezoelectric actuators were fabricated, as shown in Table 1. Figure 1 shows the dimensions of these prototypes. The piezoelectric disc was 1.8-mm thick and 10 mm in diameter. The metal cap was 0.2-mm thick and had a clearance of 0.2 mm. Before discussing the experimental results, let us review the computational results for static deformation, which we published in a previous report [24]. Figure 2 shows finite element models for the four piezoelectric actuators. Linear solid elements with eight nodes were employed. The material properties of the piezoelectric element and the metal cap were set to those of PZT ceramic and brass, respectively. In case of the simple actuator, the electric potential of the upper surface was set to 0.0 V, while +1.0 V was applied to the lower surface. In case of the bimorph actuator, the electric potential of the upper and lower surfaces was set to 0.0 V, while +1.0 V was applied to the middle bonded surface. The nodes at the outer edge of the bottom of the disk were fixed along the vertical direction. Figure 3 compares the deflection curves of the four actuators. The vertical axis represents deflection of the bottom surface, and the horizontal axis represents the radial distance from the center of the disc. Figure 4 compares the maximum deflections of the disc centers of the four actuators. The computational results
4 Y. Uetsuji et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 4 (2014) 395 Figure 1: Piezoelectric actuator dimensions. Figure 2: Finite element models and boundary conditions of four piezoelectric actuators. (a) Simple actuator, (b) biomorph actuator, (c) Moonie actuator, and (d) new Monnie actuator. Figure 3: Comparison of deflection curves for four piezoelectric actuators.
5 396 Y. Uetsuji et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 4 (2014) Figure 4: Comparison of the maximum deflections of four piezoelectric actuators under an applied DC voltage. Figure 5: Overview of the dynamic deflection measurement of a piezoelectric actuator. indicated that the proposed new Moonie actuator can generate the largest deflection, and its maximum deflection was more than double that of the conventional Moonie actuator. Figure 5 shows an overview of the dynamic deflection measurement of a piezoelectric actuator. The piezoelectric actuator was minimally fixed to an acrylic plate with scotch tape so as not to detract from its actuation performance. AC 30 V was applied, and frequency was swept from 20 Hz to 10 khz. The maximum deflection at the center was measured using a laser Doppler vibrometer. The experimentally observed frequency response curves are shown in Fig. 6. The primary resonance peak was below 2 khz for every actuator. Figure 7 compares
6 Y. Uetsuji et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 4 (2014) 397 Figure 6: Comparison of amplitude frequency response of the four piezoelectric actuators. Figure 7: Comparison of the maximum deflection of the primary resonance peaks of the four piezoelectric actuators. the maximum deflection of the primary resonance peaks of all four piezoelectric actuators. The maximum deflections of the actuators can be arranged in the following order: simple < Moonie < bimorph < new Moonie. The maximum deflection of the new Moonie actuator was more than triple that of the conventional Moonie actuator. 3.1 Evaluation of pumping performance 3 APPLICATION TO VALVELESS PUMP The proposed new Moonie actuator was applied to a Y-shaped fluid channel [18], and the pumping performance was evaluated using a piezoelectric fluid interaction finite element simulation. The configuration of the Y-shaped fluid channel driven by the piezoelectric actuator is shown in Fig. 8. The main and subfluid channels were 30- and 10-mm long, respectively. Both channels were 0.1-mm deep. The channel width w was 0.3 mm. The subfluid channel was connected to the center of the main fluid channel. The angle between the main and subfluid channels q was 30. Atmospheric pressure was applied to both edges of the straight
7 398 Y. Uetsuji et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 4 (2014) Piezoelectric actuator q =30,45,60,75 w = 0.5 mm, 0.3 mm, 0.1 mm 0.1 mm w P =1 atm Outlet A A cross section A A 30 mm q 10 mm Atmosphere pressure Flow channel P =1 atm Inlet Figure 8: Configuration of a Y-shaped fluid channel driven by a piezoelectric actuator. Flow rate [μl/s] A Time [s] Figure 9: Time history of flow rate at the outlet using a new Moonie actuator. B main fluid channel. There was a 10-mm-diameter chamber at the other end of the subfluid channel. The top surface of the chamber was hermetically sealed by the piezoelectric actuator. An AC voltage was applied to the piezoelectric actuator. This voltage had a peak value of 100 V at 50 Hz. The fluid was assumed to be water, which has a density of 998 kg/m 3 and a viscosity of 0.89 mpa.s. All of the channels and the chamber were filled with water. Although the water-level difference between the reservoir tanks at each end of the main channel was estimated in the previous study, the objective of this research was to examine the liquid feed rate for a given length of time. Figure 9 shows a time history of the flow rate at the outlet with a new Moonie actuator connected to the chamber. The flow rate changed regularly according to the piezoelectric actuation. The positive direction of flow was defined as left to right. The flow rate at the outlet was positive while the chamber volume increased, and negative while the chamber volume decreased. Figure 10 compares the flow velocity distributions of the supply and pump modes, which indicates the state at the peaks in regions A and B of Fig. 9. It is noteworthy that a large vortex appears at the right side of the interfluent point. This vortex caused the observed difference between the positive and negative flow rates, and determined the pumping performance. To
8 Y. Uetsuji et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 4 (2014) 399 Velocity [ m/s ] (a) Velocity [ m/s ] (b) Figure 10: Comparison of the flow velocity distributions of supply mode and pump mode using a new Moonie actuator: (a) supply mode and (b) pump mode. Liquid feed volume [nl/cycle] Simple Bimorph Moonie New Moonie Figure 11: Comparison of liquid feed volume per cycle for four piezoelectric actuators. estimate the pumping performance quantitatively, the difference in time integration within regions A and B shown in Fig. 9 was calculated for every piezoelectric actuator. Figure 11 summarizes the liquid feed volume per cycle of piezoelectric actuation, as estimated from the difference in time integration. The liquid feed volume of the new Moonie actuator was the highest of the four and was more than double that of the conventional Moonie actuator.
9 400 Y. Uetsuji et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 4 (2014) 3.2 Parametric investigation of the Y-shaped fluid channel Parametric investigation of the Y-shaped fluid channel geometry of the new Moonie actuator was carried out using response surface methodology [25] to improve the pumping performance. The channel width w and the angle between the main and sub fluid channels q were used as design variables. w was set to 0.1, 0.3, or 0.5 mm, and q was swept from 30 to 75 at intervals of 15. Figure 12(a) shows finite element solutions of the liquid feed volume per cycle of piezoelectric actuation. The first and second horizontal axes represent the width and angle of the channels, respectively. The vertical axis indicates the liquid feed volume, which was obtained through piezoelectric fluid interaction finite element simulations using the same process used for Fig. 11. To find the optimum geometry for maximum pumping performance, Fig. 12(b) presents computational results smoothed using a second-degree polynomial Maximum = ml ( w=0.10 mm, q =30 ) Liqiud feed volume [nl] q [deg] (a) w [mm] Maximum = ml ( w=0.15 mm, q =30 ) 1.8 Liqiud feed volume [nl] q [deg] w [mm] (b) Figure 12: Liquid feed volume per cycle for various fluid channel geometries in a new Moonie actuator: (a) finite element solutions and (b) response surface approximation.
10 Y. Uetsuji et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 4 (2014) 401 model based on response surface methodology. These computations indicated that the liquid feed volume increases when both the width and angle of the channel are decreased. A maximum liquid feed volume of nl was obtained at a channel width of 0.15 mm and a channel angle of CONCLUSIONS A new composite actuator called the new Moonie, which consists of a bimorph piezoelectric actuator and a metal cap, was examined experimentally and computationally. We obtained two remarkable results: First, dynamic deflection measurements of four different actuators indicated that the new Moonie actuator created the largest actuation, which was more than triple that of a conventional Moonie actuator. Second, when the proposed new Moonie actuator was applied to a Y-shaped fluid channel, piezoelectric fluid interaction finite element simulations indicated that the liquid feed volume of the new Moonie actuator was the largest of those examined and was more than double that of a conventional Moonie actuator. REFERENCES [1] Gravesen, P., Brandebjerg, J. & Jensen, O.S., Microfluidics a review. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 4, pp , doi: org/ / /3/4/002 [2] Laser, D.J. & Santiago, J.G., A review of micropumps. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 14, pp. R35 R64, doi: [3] Stemme, E. & Stemme, G., A valveless diffuser/nozzle-based fluid pump. Sensors and Actuators A, 39, pp , doi: [4] Koch, M., Evans, A.G.R. & Brunnschweiler, A., The dynamic micropump driven with a screen printed PZT actuator. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 8, pp , doi: [5] Li, S. & Chen, S., Analytical analysis of a circular PZT actuator for valveless micropumps. Sensors and Actuators A, 104, pp , doi: s (03) [6] Bu, M., Melvin, T., Ensell, G., Wilkinson, J.S. & Evans, A.G.R., Design and theoretical evaluation of a novel microfluidic device to be used for PCR. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 13, pp. S125 S130, doi: org/ / /13/4/321 [7] Olsson, A., Stemme, G. & Stemme, E., A valve-less planar fluid pump with two pump chambers. Sensors and Actuators A, 46 47, pp , doi: org/ / (94)00960-p [8] Olsson, A., Stemme, G. & Stemme, E., Diffuser-element design investigation for valve-less pumps. Sensors and Actuators A, 57, pp , doi: org/ /s (97) [9] Bardell, R., Sharma, N.R., Forester, F.K., Afromowitz, M.A. & Penney, R.J., Designing high-performance micro-pumps based on no-moving parts valves. Microelectromechanical Systems, 62, pp , [10] Ulhmann, A. & Fono, I., The piezoelectric valveless pump-improved dynamic model. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 11, pp , doi: org/ /jmems
11 402 Y. Uetsuji et al., Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas., Vol. 2, No. 4 (2014) [11] Zhang, T. & Wang, Q.M., Performance evaluation of a valveless micropump driven by a ring-type piezoelectric actuator. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 53, pp , doi: [12] Olsson, A., Stemme, G. & Stemme, E., Numerical and experimental studies of flatwalled diffuser elements for valveless micropump. Sensors and Actuators A, 84, pp , doi: [13] Gerlach, T., Schuenemann, M. & Wurmus, H., A new micropump principle of the reciprocationg type using pyramidic micro flow channels as passive valves. Numerical and experimental studies of flat-walled diffuser elements for valveless micropump. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 5, pp , doi: org/ / /5/2/039 [14] Ulhmann, A., The piezoelectric valveless pump-performance enhancement analysis. Sensors and Actuators A, 69, pp , doi: [15] Nguyen, N.-T. & Huang, X., Miniature valveless pumps based on printed circuit board technique. Sensors and Actuators A, 88, pp , doi: org/ /s (00) [16] Kojima, Y., Okusawa, T., Tsubouchi, K., Takagi, Y. & Hamano, N., Fundamental investigation of piezo-element-driven pump feeding a trace of liquid. Transactions of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers C, 58, pp , doi: org/ /kikaic [17] Morris, C.J. & Forster, F.K., Optimization of a circular piezoelectric bimorph for a micropump driver. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 10, pp , doi: [18] Kidera, M., Tsukamoto, H. & Miyazaki, K., A valve-less micro pump driven by a piezoelectric device. Turbomachinery, 31, pp , [19] Xu, Q.C., Yoshikawa, S., Belsick, J. & Newnham, R.E., Piezoelectric composites with high sensitivity and capacitance for use at high pressures. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics and Frequency Control, 38, pp , doi: org/ / [20] Sugawara, Y., Onitsuka, K., Yoshikawa, S., Xu, Q., Newnham, R.E. & Uchino, K., Metal-ceramic composite actuators. Journal of American Ceramic Society, 75, pp , doi: [21] Onitsuka, K., Dogan, A., Tressler, J.F., Xu, Q., Yoshikawa, S. & Newnham, R.E., Metalceramic composite transducer, the Moonie. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 6, pp , doi: [22] MeyerJr, R.J., Dogan, A., Yoon, C., Pilgrim, S.M. & Newnham, R.E., Displacement amplification of electroactive materials using the cymbal flextensional transducer. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 87, pp , doi: s (00) [23] Nelli Silva, E.C., Nader, G., Shirahige, A.B. & Adamowski, J.C., Characterization of novel flextensional actuators designed by using topology optimization method. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 14, pp , doi: dx.doi.org/ / x [24] Uetsuji, Y., Kuramae, H. & Tsuchiya, K., Piezoelectric fluid interaction finite element analysis of a valve-less piezoelectric pump. WIT Transactions on Modelling and Simulation, 55, pp , doi: [25] Box, G.E.P. & Wilson, K.B., On the experimental attainment of optimum conditions. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, B-13, pp. 1 45, 1951.
The research on micropumps initially emerged at Stanford
 ieee transactions on ultrasonics, ferroelectrics, and frequency control, vol. 53, no., february 006 463 Performance Evaluation of a Valveless Micropump Driven by a Ring-Type Piezoelectric Actuator Tao
ieee transactions on ultrasonics, ferroelectrics, and frequency control, vol. 53, no., february 006 463 Performance Evaluation of a Valveless Micropump Driven by a Ring-Type Piezoelectric Actuator Tao
Presented. Nayana.L MTech, CAID
 Presented by Nayana.L MTech, CAID AGENDA INTRODUCTION DESCRIPTION OF WORK SIMULATION RESULTS PROPOSED WORK CONCLUSIONS AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE WORK ACKNOWLEDGMENT REFERENCES INTRODUCTION Micro pump is a miniaturized
Presented by Nayana.L MTech, CAID AGENDA INTRODUCTION DESCRIPTION OF WORK SIMULATION RESULTS PROPOSED WORK CONCLUSIONS AND SCOPE FOR FUTURE WORK ACKNOWLEDGMENT REFERENCES INTRODUCTION Micro pump is a miniaturized
Low Reynolds Number Flow Through Nozzle- Diffuser Elements in Valveless Micropumps
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs CTRC Research Publications Cooling Technologies Research Center 4-26-2004 Low Reynolds Number Flow Through Nozzle- Diffuser Elements in Valveless Micropumps Vishal Singhal
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs CTRC Research Publications Cooling Technologies Research Center 4-26-2004 Low Reynolds Number Flow Through Nozzle- Diffuser Elements in Valveless Micropumps Vishal Singhal
DESIGNING HIGH-PERFORMANCE MICRO-PUMPS BASED ON NO-MOVING-PARTS VALVES
 DSC-Vol. 62/HTD-Vol. 354, Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) ASME 1997 DESIGNING HIGH-PERFORMANCE MICRO-PUMPS BASED ON NO-MOVING-PARTS VALVES Ron L. Bardell Nigel R. Sharma Fred K. Forster Martin A.
DSC-Vol. 62/HTD-Vol. 354, Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS) ASME 1997 DESIGNING HIGH-PERFORMANCE MICRO-PUMPS BASED ON NO-MOVING-PARTS VALVES Ron L. Bardell Nigel R. Sharma Fred K. Forster Martin A.
Single-phase driven ultrasonic motor using two orthogonal bending modes of sandwiching. piezo-ceramic plates
 Single-phase driven ultrasonic motor using two orthogonal bending modes of sandwiching piezo-ceramic plates Yuting Ma 1,2, Minkyu Choi 2 and Kenji Uchino 2 1 CAS Key Lab of Bio-Medical Diagnostics, Suzhou
Single-phase driven ultrasonic motor using two orthogonal bending modes of sandwiching piezo-ceramic plates Yuting Ma 1,2, Minkyu Choi 2 and Kenji Uchino 2 1 CAS Key Lab of Bio-Medical Diagnostics, Suzhou
Piezoelectric Resonators ME 2082
 Piezoelectric Resonators ME 2082 Introduction K T : relative dielectric constant of the material ε o : relative permittivity of free space (8.854*10-12 F/m) h: distance between electrodes (m - material
Piezoelectric Resonators ME 2082 Introduction K T : relative dielectric constant of the material ε o : relative permittivity of free space (8.854*10-12 F/m) h: distance between electrodes (m - material
Design and Simulation of Valve Less PZT Micropump for Drug Delivery System
 Design and Simulation of Valve Less PZT Micropump for Drug Delivery System Manoj Pandey 1,* and P.C. Upadhyay 1, 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering B K Birla Institute of Engineering
Design and Simulation of Valve Less PZT Micropump for Drug Delivery System Manoj Pandey 1,* and P.C. Upadhyay 1, 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering B K Birla Institute of Engineering
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 12 Sep 2013
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 12 Sep 2013 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 12 Sep 2013](/thumbs/82/86241511.jpg) FAST TRACK COMMUNICATION A new dimension for piezo actuators: Free-form out-of-plane displacement of single piezo layers arxiv:.v [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] Sep Matthias C Wapler, Jens Brunne and Ulrike Wallrabe
FAST TRACK COMMUNICATION A new dimension for piezo actuators: Free-form out-of-plane displacement of single piezo layers arxiv:.v [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] Sep Matthias C Wapler, Jens Brunne and Ulrike Wallrabe
Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever
 Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever Nitin N More Department of Mechanical Engineering K.L.E S College of Engineering and Technology, Belgaum, Karnataka, India. Abstract- Energy (or power)
Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever Nitin N More Department of Mechanical Engineering K.L.E S College of Engineering and Technology, Belgaum, Karnataka, India. Abstract- Energy (or power)
PARAMETRIC DESIGN OF FIXED-GEOMETRY MICROVALVES THE TESSER VALVE
 Proceedings of IMECE2002 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition November 7 22, 2002, New Orleans, Louisiana IMECE2002-33628 This CD version appears at pgs. 43-437 in the bound
Proceedings of IMECE2002 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition November 7 22, 2002, New Orleans, Louisiana IMECE2002-33628 This CD version appears at pgs. 43-437 in the bound
Using Finite Element Analysis and Experimental Analysis on Vibration of a Piezoelectric
 Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 2014, *, ** Published Online **** 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2014.***** Using Finite Element Analysis and
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 2014, *, ** Published Online **** 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2014.***** Using Finite Element Analysis and
SUBSTITUTING particle-sensitive check-valves in micropumps
 JOURNAL OF MICROELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEMS, VOL. 6, NO. 1, MARCH 1997 41 Fabrication and Characterization of Truly 3-D Diffuser/Nozzle Microstructures in Silicon M. Heschel, M. Müllenborn, and S. Bouwstra
JOURNAL OF MICROELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEMS, VOL. 6, NO. 1, MARCH 1997 41 Fabrication and Characterization of Truly 3-D Diffuser/Nozzle Microstructures in Silicon M. Heschel, M. Müllenborn, and S. Bouwstra
DESIGN, FABRICATION AND TESTING OF FIXED-VALVE MICRO-PUMPS
 FED-Vol. 234, 1995 IMECE Proceedings of the ASME Fluids Engineering Division ASME 1995 DESIGN, FABRICATION AND TESTING OF FIXED-VALVE MICRO-PUMPS Fred K. Forster 1 and Ronald L. Bardell Department of Mechanical
FED-Vol. 234, 1995 IMECE Proceedings of the ASME Fluids Engineering Division ASME 1995 DESIGN, FABRICATION AND TESTING OF FIXED-VALVE MICRO-PUMPS Fred K. Forster 1 and Ronald L. Bardell Department of Mechanical
PERFORMANCE OF HYDROTHERMAL PZT FILM ON HIGH INTENSITY OPERATION
 PERFORMANCE OF HYDROTHERMAL PZT FILM ON HIGH INTENSITY OPERATION Minoru Kuribayashi Kurosawa*, Hidehiko Yasui**, Takefumi Kanda** and Toshiro Higuchi** *Tokyo Institute of Technology, Dept. of Advanced
PERFORMANCE OF HYDROTHERMAL PZT FILM ON HIGH INTENSITY OPERATION Minoru Kuribayashi Kurosawa*, Hidehiko Yasui**, Takefumi Kanda** and Toshiro Higuchi** *Tokyo Institute of Technology, Dept. of Advanced
The dynamic characteristics of a valve-less micropump
 The dynamic characteristics of a valve-less micropump Jiang Dan( 蒋丹 ) a) and Li Song-Jing( 李松晶 ) b) a) School of Mechatronics Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu
The dynamic characteristics of a valve-less micropump Jiang Dan( 蒋丹 ) a) and Li Song-Jing( 李松晶 ) b) a) School of Mechatronics Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu
Design and Analysis of a Practical Large-Force Piezoelectric Inchworm Motor with a Novel Force Duplicator
 Design and Analysis of a Practical Large-Force Piezoelectric Inchworm Motor with a Novel Force Duplicator M.Eng Dissertation EF Williams Submitted to University of Pretoria Department of Mechanical and
Design and Analysis of a Practical Large-Force Piezoelectric Inchworm Motor with a Novel Force Duplicator M.Eng Dissertation EF Williams Submitted to University of Pretoria Department of Mechanical and
Optimization of a circular piezoelectric bimorph for a micropump driver
 J. Micromech. Microeng. 10 (2000) 459 465. Printed in the UK PII: S0960-1317(00)11502-5 Optimization of a circular piezoelectric bimorph for a micropump driver Christopher J Morris and Fred K Forster Mechanical
J. Micromech. Microeng. 10 (2000) 459 465. Printed in the UK PII: S0960-1317(00)11502-5 Optimization of a circular piezoelectric bimorph for a micropump driver Christopher J Morris and Fred K Forster Mechanical
Study on a PZT-actuated diaphragm pump for air supply for micro fuel cells
 Sensors and Actuators A 130 131 (2006) 531 536 Study on a PZT-actuated diaphragm pump for air supply for micro fuel cells Xing Yang a,b,c,, Zhaoying Zhou a,b,c, Hyejung Cho d, Xiaobing Luo d a MEMS Lab,
Sensors and Actuators A 130 131 (2006) 531 536 Study on a PZT-actuated diaphragm pump for air supply for micro fuel cells Xing Yang a,b,c,, Zhaoying Zhou a,b,c, Hyejung Cho d, Xiaobing Luo d a MEMS Lab,
DEVELOPMENT OF A BAR-SHAPED ULTRASONIC MOTOR FOR MULTI-DEGREES OF FREEDOM MOTION
 DEVELOPMENT OF A BAR-SHAPED ULTRASONIC MOTOR FOR MULTI-DEGREES OF FREEDOM MOTION Kenjiro Takemura KEIO University, Yokohama, Kanagawa, JAPAN, m982468@msr.st.keio.ac.jp Nobuyuki Kojima Canon Inc., Ohta-ku,
DEVELOPMENT OF A BAR-SHAPED ULTRASONIC MOTOR FOR MULTI-DEGREES OF FREEDOM MOTION Kenjiro Takemura KEIO University, Yokohama, Kanagawa, JAPAN, m982468@msr.st.keio.ac.jp Nobuyuki Kojima Canon Inc., Ohta-ku,
Development of the Screw-driven Motors by Stacked Piezoelectric Actuators
 Proceedings of the 4th IIAE International Conference on Industrial Application Engineering 2016 Development of the Screw-driven Motors by Stacked Piezoelectric Actuators Shine-Tzong Ho a,*, Hao-Wei Chen
Proceedings of the 4th IIAE International Conference on Industrial Application Engineering 2016 Development of the Screw-driven Motors by Stacked Piezoelectric Actuators Shine-Tzong Ho a,*, Hao-Wei Chen
Automated Microdosing System for Integration With a Miniaturized High-pressure Reactor System
 Journal of Automated Methods & Management in Chemistry, 5 (5), no., 3 3 c 5 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Automated Microdosing System for Integration With a Miniaturized High-pressure Reactor System
Journal of Automated Methods & Management in Chemistry, 5 (5), no., 3 3 c 5 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Automated Microdosing System for Integration With a Miniaturized High-pressure Reactor System
Analysis of flow characteristics of a cam rotor pump
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Analysis of flow characteristics of a cam rotor pump To cite this article: Y Y Liu et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 032023
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Analysis of flow characteristics of a cam rotor pump To cite this article: Y Y Liu et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 032023
Degradation of Piezoelectric Materials for Energy Harvesting Applications
 Degradation of Piezoelectric Materials for Energy Harvesting Applications P Pillatsch 1, N Shashoua 1,ASHolmes 2, E M Yeatman 2,PKWright 1 1 University of California Berkeley, Advanced Manufacturing for
Degradation of Piezoelectric Materials for Energy Harvesting Applications P Pillatsch 1, N Shashoua 1,ASHolmes 2, E M Yeatman 2,PKWright 1 1 University of California Berkeley, Advanced Manufacturing for
Laser Interferometric Displacement Measurements of Multi-Layer Actuators and PZT Ceramics
 Ferroelectrics, 320:161 169, 2005 Copyright Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 0015-0193 print / 1563-5112 online DOI: 10.1080/00150190590967026 Laser Interferometric Displacement Measurements of Multi-Layer
Ferroelectrics, 320:161 169, 2005 Copyright Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 0015-0193 print / 1563-5112 online DOI: 10.1080/00150190590967026 Laser Interferometric Displacement Measurements of Multi-Layer
Theory and Experimental Verification on Cymbal shaped Slotted Valve Piezoelectric Pump
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s10033-018-0217-6 Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Theory and Experimental Verification on Cymbal shaped Slotted Valve Piezoelectric Pump Jun
https://doi.org/10.1186/s10033-018-0217-6 Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Theory and Experimental Verification on Cymbal shaped Slotted Valve Piezoelectric Pump Jun
Module 6: Smart Materials & Smart Structural Control Lecture 33: Piezoelectric & Magnetostrictive Sensors and Actuators. The Lecture Contains:
 The Lecture Contains: Piezoelectric Sensors and Actuators Magnetostrictive Sensors and Actuators file:///d /chitra/vibration_upload/lecture33/33_1.htm[6/25/2012 12:42:09 PM] Piezoelectric Sensors and Actuators
The Lecture Contains: Piezoelectric Sensors and Actuators Magnetostrictive Sensors and Actuators file:///d /chitra/vibration_upload/lecture33/33_1.htm[6/25/2012 12:42:09 PM] Piezoelectric Sensors and Actuators
Surface Acoustic Wave Atomizer with Pumping Effect
 Surface Acoustic Wave Atomizer with Pumping Effect Minoru KUROSAWA, Takayuki WATANABE and Toshiro HIGUCHI Dept. of Precision Machinery Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo,
Surface Acoustic Wave Atomizer with Pumping Effect Minoru KUROSAWA, Takayuki WATANABE and Toshiro HIGUCHI Dept. of Precision Machinery Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo,
Testing and analysis of high frequency electroelastic characteristics of piezoelectric transformers
 Arch. Mech., 59, 2, pp. 119 131, Warszawa 2007 Testing and analysis of high frequency electroelastic characteristics of piezoelectric transformers F. NARITA, Y. SHINDO, F. SAITO, M. MIKAMI Department of
Arch. Mech., 59, 2, pp. 119 131, Warszawa 2007 Testing and analysis of high frequency electroelastic characteristics of piezoelectric transformers F. NARITA, Y. SHINDO, F. SAITO, M. MIKAMI Department of
Experimental Study of the Response of Transonic Diffuser Flow to a Piezoceramic Actuator at Diffuser Throat
 Open Journal of Fluid Dynamics, 213, 3, 14-21 http://dx.doi.org/236/ojfd.213.32a3 Published Online July 213 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojfd) Experimental Study of the Response of Transonic Diffuser
Open Journal of Fluid Dynamics, 213, 3, 14-21 http://dx.doi.org/236/ojfd.213.32a3 Published Online July 213 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojfd) Experimental Study of the Response of Transonic Diffuser
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING UNIT I - INTRODUCTION SYLLABUS
 QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING YEAR/SEM NAME OF THE SUBJECT NAME OF THE FACULTY : II / IV : EE6404 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION : K.M.S.MUTHUKUMARA RAJAGURU, AP/EEE
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING YEAR/SEM NAME OF THE SUBJECT NAME OF THE FACULTY : II / IV : EE6404 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION : K.M.S.MUTHUKUMARA RAJAGURU, AP/EEE
Piezoelectric Actuator for Micro Robot Used in Nanosatellite
 Piezoelectric Actuator for Micro Robot Used in Nanosatellite R Bansevicius, S Navickaite, V Jurenas and A Bubulis PIEZOELECTRIC ACTUATOR FOR MICRO ROBOT USED IN NANOSATELLITE. R Bansevicius 1, S Navickaite,
Piezoelectric Actuator for Micro Robot Used in Nanosatellite R Bansevicius, S Navickaite, V Jurenas and A Bubulis PIEZOELECTRIC ACTUATOR FOR MICRO ROBOT USED IN NANOSATELLITE. R Bansevicius 1, S Navickaite,
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 213 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 213 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 213 Engineering Acoustics Session 3aEA: Computational Methods in Transducer
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 213 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 213 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 213 Engineering Acoustics Session 3aEA: Computational Methods in Transducer
19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER Methodology for electro mechanical simulation of piezoelectric ceramics
 19 th INTRNATIONAL CONR ON ACOUTIC MADRID, 2-7 PTMBR 2007 Methodology for electro mechanical simulation of piezoelectric ceramics PAC: 43.38.Fx Morcillo López, Miguel Ángel 1 ; Cesteros Morante, Beatriz
19 th INTRNATIONAL CONR ON ACOUTIC MADRID, 2-7 PTMBR 2007 Methodology for electro mechanical simulation of piezoelectric ceramics PAC: 43.38.Fx Morcillo López, Miguel Ángel 1 ; Cesteros Morante, Beatriz
DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF THE MICRO- ACCELEROMETER USING PIEZOELECTRIC THIN FILMS
 DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF THE MICRO- ACCELEROMETER USING PIEZOELECTRIC THIN FILMS JYH-CHENG YU and FU-HSIN LAI Department of Mechanical Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology
DESIGN AND FABRICATION OF THE MICRO- ACCELEROMETER USING PIEZOELECTRIC THIN FILMS JYH-CHENG YU and FU-HSIN LAI Department of Mechanical Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology
Design of a MEMS Capacitive Comb-drive Accelerometer
 Design of a MEMS Capacitive Comb-drive Accelerometer Tolga Kaya* 1, Behrouz Shiari 2, Kevin Petsch 1 and David Yates 2 1 Central Michigan University, 2 University of Michigan * kaya2t@cmich.edu Abstract:
Design of a MEMS Capacitive Comb-drive Accelerometer Tolga Kaya* 1, Behrouz Shiari 2, Kevin Petsch 1 and David Yates 2 1 Central Michigan University, 2 University of Michigan * kaya2t@cmich.edu Abstract:
10 Measurement of Acceleration, Vibration and Shock Transducers
 Chapter 10: Acceleration, Vibration and Shock Measurement Dr. Lufti Al-Sharif (Revision 1.0, 25/5/2008) 1. Introduction This chapter examines the measurement of acceleration, vibration and shock. It starts
Chapter 10: Acceleration, Vibration and Shock Measurement Dr. Lufti Al-Sharif (Revision 1.0, 25/5/2008) 1. Introduction This chapter examines the measurement of acceleration, vibration and shock. It starts
Magneto-Mechanical Modeling and Simulation of MEMS Sensors Based on Electroactive Polymers
 Magneto-Mechanical Modeling and Simulation of MEMS Sensors Based on Electroactive Polymers F.J.O. RODRIGUES, L.M. GONÇALVES, J.H. CORREIA, P.M. MENDES University of Minho, Dept. Industrial Electronics,
Magneto-Mechanical Modeling and Simulation of MEMS Sensors Based on Electroactive Polymers F.J.O. RODRIGUES, L.M. GONÇALVES, J.H. CORREIA, P.M. MENDES University of Minho, Dept. Industrial Electronics,
Sensors and Actuators A: Physical
 Sensors and Actuators A 161 (2010) 266 270 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Sensors and Actuators A: Physical journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/sna Magnetic force memory effect using a
Sensors and Actuators A 161 (2010) 266 270 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Sensors and Actuators A: Physical journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/sna Magnetic force memory effect using a
Experimental Study on Electromechanical Performances of Two Kinds of the Integral Arrayed Cymbal Harvesters
 Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, Vol. 18, No. 4, pp. 339 344 (2015) DOI: 10.6180/jase.2015.18.4.04 Experimental Study on Electromechanical Performances of Two Kinds of the Integral Arrayed Cymbal
Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, Vol. 18, No. 4, pp. 339 344 (2015) DOI: 10.6180/jase.2015.18.4.04 Experimental Study on Electromechanical Performances of Two Kinds of the Integral Arrayed Cymbal
MCE603: Interfacing and Control of Mechatronic Systems
 MCE603: Interfacing and Control of Mechatronic Systems Chapter 7: Actuators and Sensors Topic 7d: Piezoelectric Actuators. Reference: Various articles. Cleveland State University Mechanical Engineering
MCE603: Interfacing and Control of Mechatronic Systems Chapter 7: Actuators and Sensors Topic 7d: Piezoelectric Actuators. Reference: Various articles. Cleveland State University Mechanical Engineering
Applicability of Self-Powered Synchronized Electric Charge Extraction (SECE) Circuit for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting
 International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 4 No. 11, November, 214 Applicability of Self-Powered Synchronized Electric Charge Extraction (SECE) Circuit for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting
International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 4 No. 11, November, 214 Applicability of Self-Powered Synchronized Electric Charge Extraction (SECE) Circuit for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting
Available online at ScienceDirect. Physics Procedia 70 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 70 (2015 ) 896 900 Application of PMN-32PT piezoelectric crystals for novel aircoupled ultrasonic transducers Rymantas Jonas Kazys
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 70 (2015 ) 896 900 Application of PMN-32PT piezoelectric crystals for novel aircoupled ultrasonic transducers Rymantas Jonas Kazys
AUTOMATIC CALIBRATION SYSTEM FOR MICRO-DISPLACEMENT DEVICES. Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Central University 2
 59 th ILMENAU SCIENTIFIC COLLOQUIUM Technische Universität Ilmenau, 11 15 September 2017 URN: urn:nbn:de:gbv:ilm1-2017iwk-103:8 AUTOMATIC CALIBRATION SYSTEM FOR MICRO-DISPLACEMENT DEVICES Hung-Ta Shih
59 th ILMENAU SCIENTIFIC COLLOQUIUM Technische Universität Ilmenau, 11 15 September 2017 URN: urn:nbn:de:gbv:ilm1-2017iwk-103:8 AUTOMATIC CALIBRATION SYSTEM FOR MICRO-DISPLACEMENT DEVICES Hung-Ta Shih
643. Rod-shaped piezoelectric actuator with radial polarization
 643. Rod-shaped piezoelectric actuator with radial polarization R. Lučinskis a, D. Mažeika b, R. Daukševičius c Vilnius Gediminas Technical University, Saul tekio al. 11, LT-10223 Vilnius, Lithuania E-mail:
643. Rod-shaped piezoelectric actuator with radial polarization R. Lučinskis a, D. Mažeika b, R. Daukševičius c Vilnius Gediminas Technical University, Saul tekio al. 11, LT-10223 Vilnius, Lithuania E-mail:
Impacts of Electroosmosis Forces on Surface-Tension- Driven Micro-Pumps
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 20-21, 2015 Paper No. 290 Impacts of Electroosmosis Forces on Surface-Tension- Driven
Proceedings of the World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 20-21, 2015 Paper No. 290 Impacts of Electroosmosis Forces on Surface-Tension- Driven
An Energy Circulation Driving Surface Acoustic Wave Motor
 An Energy Circulation Driving Surface Acoustic Wave Motor Minoru K. Kurosawa Tokyo Institute of Technology Yokohama, Japan mkur@ae.titech.ac.jp Purevdagva Nayanbuu Tokyo Institute of Technology Yokohama,
An Energy Circulation Driving Surface Acoustic Wave Motor Minoru K. Kurosawa Tokyo Institute of Technology Yokohama, Japan mkur@ae.titech.ac.jp Purevdagva Nayanbuu Tokyo Institute of Technology Yokohama,
INVESTIGATION OF ELECTRO-MECHANICAL FACTORS EFFECTING PIEZOELECTRIC ACTUATOR FOR VALVELESS MICROPUMP CHARACTERISTICS
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 13, No. 9 (2018) 2843-2856 School of Engineering, Taylor s University INVESTIGATION OF ELECTRO-MECHANICAL FACTORS EFFECTING PIEZOELECTRIC ACTUATOR FOR
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 13, No. 9 (2018) 2843-2856 School of Engineering, Taylor s University INVESTIGATION OF ELECTRO-MECHANICAL FACTORS EFFECTING PIEZOELECTRIC ACTUATOR FOR
Modelling of Different MEMS Pressure Sensors using COMSOL Multiphysics
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2017 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Modelling
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2017 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Modelling
Electrohydrodynamic Micropumps
 Electrohydrodynamic Micropumps Antonio Ramos Dept. Electrónica y Electromagnetismo Universidad de Sevilla Avda. Reina Mercedes s/n 41012 Sevilla. Spain 1. Introduction Microfluidics deals with the pumping,
Electrohydrodynamic Micropumps Antonio Ramos Dept. Electrónica y Electromagnetismo Universidad de Sevilla Avda. Reina Mercedes s/n 41012 Sevilla. Spain 1. Introduction Microfluidics deals with the pumping,
Conditions. 5 Page ,China. Cymbal transducer can. order to. applications. ELEMENT METHOD. boundary [1].
![Conditions. 5 Page ,China. Cymbal transducer can. order to. applications. ELEMENT METHOD. boundary [1]. Conditions. 5 Page ,China. Cymbal transducer can. order to. applications. ELEMENT METHOD. boundary [1].](/thumbs/87/95053700.jpg) International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES)( ISSN (Online): 232-9364, ISSN (Print): 232-9356 Volume 3 Issue 6 ǁ June 215 ǁ PP.5-12 Model Analysis of Cymbal Generator Under Different
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES)( ISSN (Online): 232-9364, ISSN (Print): 232-9356 Volume 3 Issue 6 ǁ June 215 ǁ PP.5-12 Model Analysis of Cymbal Generator Under Different
Research Article Design and Fabrication of the Large Thrust Force Piezoelectric Actuator
 Advances in Materials Science and Engineering Volume 2013, Article ID 912587, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/912587 Research Article Design and Fabrication of the Large Thrust Force Piezoelectric
Advances in Materials Science and Engineering Volume 2013, Article ID 912587, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/912587 Research Article Design and Fabrication of the Large Thrust Force Piezoelectric
Lecture 20. Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature MECH 373. Instrumentation and Measurements
 MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 20 Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature 1 Measuring Acceleration and Vibration Accelerometers using
MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 20 Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature 1 Measuring Acceleration and Vibration Accelerometers using
INTRODUCTION TO PIEZO TRANSDUCERS
 PIEZO SYSTEMS, INC. 65 Tower Office Park Woburn, MA 01801 USA Tel: 781 933 4850 Fax: 781 933 4743 email: sales@piezo.com Find Search for a product or category HOME PRODUCTS CUSTOM OEM CATALOG TECHNICAL
PIEZO SYSTEMS, INC. 65 Tower Office Park Woburn, MA 01801 USA Tel: 781 933 4850 Fax: 781 933 4743 email: sales@piezo.com Find Search for a product or category HOME PRODUCTS CUSTOM OEM CATALOG TECHNICAL
2044. Dynamics analysis for the clamping mechanisms of a rotary inchworm piezoelectric motor
 2044. Dynamics analysis for the clamping mechanisms of a rotary inchworm piezoelectric motor Yongfei Gu 1, Jichun Xing 2 1, 2 School of Mechanical Engineering, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao, China 1
2044. Dynamics analysis for the clamping mechanisms of a rotary inchworm piezoelectric motor Yongfei Gu 1, Jichun Xing 2 1, 2 School of Mechanical Engineering, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao, China 1
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) have become an increasingly important area of
 1 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Background Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) have become an increasingly important area of technology. This is due to the premise that the efficiencies of high volume production
1 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Background Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) have become an increasingly important area of technology. This is due to the premise that the efficiencies of high volume production
1106. Numerical investigation of dynamical properties of vibroactive pad during hot imprint process
 1106. Numerical investigation of dynamical properties of vibroactive pad during hot imprint process B. Narijauskaitė 1, A. Palevičius 2, G. Janušas 3, R. Šakalys 4 International Studies Centre, Kaunas
1106. Numerical investigation of dynamical properties of vibroactive pad during hot imprint process B. Narijauskaitė 1, A. Palevičius 2, G. Janušas 3, R. Šakalys 4 International Studies Centre, Kaunas
7.Piezoelectric, Accelerometer and Laser Sensors
 7.Piezoelectric, Accelerometer and Laser Sensors 7.1 Piezoelectric sensors: (Silva p.253) Piezoelectric materials such as lead-zirconate-titanate (PZT) can generate electrical charge and potential difference
7.Piezoelectric, Accelerometer and Laser Sensors 7.1 Piezoelectric sensors: (Silva p.253) Piezoelectric materials such as lead-zirconate-titanate (PZT) can generate electrical charge and potential difference
Sensors & Transducers 2016 by IFSA Publishing, S. L.
 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 96, Issue, January 206, pp. 52-56 Sensors & Transducers 206 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Collapse Mode Characteristics of Parallel Plate Ultrasonic
Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 96, Issue, January 206, pp. 52-56 Sensors & Transducers 206 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Collapse Mode Characteristics of Parallel Plate Ultrasonic
ACOUSTIC EMISSION MEASUREMENTS ON PIEZOELECTRIC/ FERROELECTRIC MATERIALS
 ACOUSTIC EMISSION MEASUREMENTS ON PIEZOELECTRIC/ FERROELECTRIC MATERIALS HIDEAKI ABURATANI Kitakyushu National College of Technology, Kokura-minami, Kitakyushu, Fukuoka, Japan Abstract Ferroelectric materials
ACOUSTIC EMISSION MEASUREMENTS ON PIEZOELECTRIC/ FERROELECTRIC MATERIALS HIDEAKI ABURATANI Kitakyushu National College of Technology, Kokura-minami, Kitakyushu, Fukuoka, Japan Abstract Ferroelectric materials
Foundations of MEMS. Chang Liu. McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science Northwestern University. International Edition Contributions by
 Foundations of MEMS Second Edition Chang Liu McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science Northwestern University International Edition Contributions by Vaishali B. Mungurwadi B. V. Bhoomaraddi
Foundations of MEMS Second Edition Chang Liu McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science Northwestern University International Edition Contributions by Vaishali B. Mungurwadi B. V. Bhoomaraddi
A Microfluidic Electroosmotic Mixer and the Effect of Potential and Frequency on its Mixing Efficiency
 Proceedings of the 009 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics San Antonio, TX, USA - October 009 A Microfluidic Electroosmotic Mixer and the Effect of Potential and Frequency on
Proceedings of the 009 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics San Antonio, TX, USA - October 009 A Microfluidic Electroosmotic Mixer and the Effect of Potential and Frequency on
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
DEVELOPMENT OF HIGH-STRAIN LOW-HYSTERESIS ACTUATORS USING ELECTROSTRICTIVE LEAD MAGNESIUM NIOBATE (PMN)
 Proc. 3 rd CanSmart Workshop on Smart Materials and Structures, 28-29 Sep. (2) p.31 DEVELOPMENT OF HIGH-STRAIN LOW-HYSTERESIS ACTUATORS USING ELECTROSTRICTIVE LEAD MAGNESIUM NIOBATE (PMN) D.F. Waechter,
Proc. 3 rd CanSmart Workshop on Smart Materials and Structures, 28-29 Sep. (2) p.31 DEVELOPMENT OF HIGH-STRAIN LOW-HYSTERESIS ACTUATORS USING ELECTROSTRICTIVE LEAD MAGNESIUM NIOBATE (PMN) D.F. Waechter,
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
BENCHMARKING OF PIEZOCERAMIC MATERIALS FOR GENERATOR APPLICATION
 BENCHMARKING OF PIEZOCERAMIC MATERIALS FOR GENERATOR APPLICATION Thomas Rödig www.ikts.fraunhofer.de OUTLINE Introduction Benchmarking of piezoelectric materials Energy output Degradation Proof of concept
BENCHMARKING OF PIEZOCERAMIC MATERIALS FOR GENERATOR APPLICATION Thomas Rödig www.ikts.fraunhofer.de OUTLINE Introduction Benchmarking of piezoelectric materials Energy output Degradation Proof of concept
Lecture 18: Microfluidic MEMS, Applications
 MECH 466 Microelectromechanical Systems University of Victoria Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Lecture 18: Microfluidic MEMS, Applications 1 Overview Microfluidic Electrokinetic Flow Basic Microfluidic
MECH 466 Microelectromechanical Systems University of Victoria Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Lecture 18: Microfluidic MEMS, Applications 1 Overview Microfluidic Electrokinetic Flow Basic Microfluidic
Acoustic Streaming Driven Mixing
 Acoustic Streaming Driven Mixing Nitesh Nama, Po-Hsun Huang, Francesco Costanzo, and Tony Jun Huang Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics The Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA,
Acoustic Streaming Driven Mixing Nitesh Nama, Po-Hsun Huang, Francesco Costanzo, and Tony Jun Huang Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics The Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA,
Research Article A New Type of Magnetic Actuator Capable of Wall-Climbing Movement Using Inertia Force
 Engineering Volume 14, Article ID 93178, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/14/93178 Research Article A New Type of Magnetic Actuator Capable of Wall-Climbing Movement Using Inertia Force H. Yaguchi, S.
Engineering Volume 14, Article ID 93178, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/14/93178 Research Article A New Type of Magnetic Actuator Capable of Wall-Climbing Movement Using Inertia Force H. Yaguchi, S.
COURSE OUTLINE. Introduction Signals and Noise Filtering Sensors: Piezoelectric Force Sensors. Sensors, Signals and Noise 1
 Sensors, Signals and Noise 1 COURSE OUTLINE Introduction Signals and Noise Filtering Sensors: Piezoelectric Force Sensors Piezoelectric Force Sensors 2 Piezoelectric Effect and Materials Piezoelectric
Sensors, Signals and Noise 1 COURSE OUTLINE Introduction Signals and Noise Filtering Sensors: Piezoelectric Force Sensors Piezoelectric Force Sensors 2 Piezoelectric Effect and Materials Piezoelectric
Analytical Design of Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS) based Piezoelectric Accelerometer for high g acceleration
 Analytical Design of Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS) based Piezoelectric Accelerometer for high g acceleration Arti Arora 1, Himanshu Monga 2, Anil Arora 3 Baddi University of Emerging Science
Analytical Design of Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS) based Piezoelectric Accelerometer for high g acceleration Arti Arora 1, Himanshu Monga 2, Anil Arora 3 Baddi University of Emerging Science
DAMPING CONTROL OF A PZT MULTILAYER VIBRATION USING NEGATIVE IMPEDANCE CIRCUIT
 International Workshop SMART MATERIALS, STRUCTURES & NDT in AEROSPACE Conference NDT in Canada 2011 2-4 November 2011, Montreal, Quebec, Canada DAMPING CONTROL OF A PZT MULTILAYER VIBRATION USING NEGATIVE
International Workshop SMART MATERIALS, STRUCTURES & NDT in AEROSPACE Conference NDT in Canada 2011 2-4 November 2011, Montreal, Quebec, Canada DAMPING CONTROL OF A PZT MULTILAYER VIBRATION USING NEGATIVE
Thickness Optimization of a Piezoelectric Converter for Energy Harvesting
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 29 Milan Thickness Optimization of a Piezoelectric Converter for Energy Harvesting M. Guizzetti* 1, V. Ferrari 1, D. Marioli 1 and T. Zawada 2 1 Dept.
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 29 Milan Thickness Optimization of a Piezoelectric Converter for Energy Harvesting M. Guizzetti* 1, V. Ferrari 1, D. Marioli 1 and T. Zawada 2 1 Dept.
Electric-Energy Generation Using Variable-Capacitive Resonator for Power-Free LSI: Efficiency Analysis and Fundamental Experiment
 Electric-Energy Generation Using Variable-Capacitive Resonator for Power-Free SI: Efficiency Analysis and Fundamental Experiment Masayuki Miyazaki, Hidetoshi Tanaka, Goichi Ono, Tomohiro Nagano*, Norio
Electric-Energy Generation Using Variable-Capacitive Resonator for Power-Free SI: Efficiency Analysis and Fundamental Experiment Masayuki Miyazaki, Hidetoshi Tanaka, Goichi Ono, Tomohiro Nagano*, Norio
Introduction to Micro/Nanofluidics. Date: 2015/03/13. Dr. Yi-Chung Tung. Outline
 Introduction to Micro/Nanofluidics Date: 2015/03/13 Dr. Yi-Chung Tung Outline Introduction to Microfluidics Basic Fluid Mechanics Concepts Equivalent Fluidic Circuit Model Conclusion What is Microfluidics
Introduction to Micro/Nanofluidics Date: 2015/03/13 Dr. Yi-Chung Tung Outline Introduction to Microfluidics Basic Fluid Mechanics Concepts Equivalent Fluidic Circuit Model Conclusion What is Microfluidics
Transducer. A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity. Transducer. (Input) Sensor.
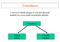 Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
UNIMORPH DEFORMABLE MIRROR FOR TELESCOPES AND LASER APPLICATIONS IN SPACE
 UNIMORPH DEFORMABLE MIRROR FOR TELESCOPES AND LASER APPLICATIONS IN SPACE S. Verpoort and U. Wittrock Photonics Laboratory, Münster University of Applied Sciences, Stegerwaldstrasse 39, 48565 Steinfurt,
UNIMORPH DEFORMABLE MIRROR FOR TELESCOPES AND LASER APPLICATIONS IN SPACE S. Verpoort and U. Wittrock Photonics Laboratory, Münster University of Applied Sciences, Stegerwaldstrasse 39, 48565 Steinfurt,
Drug Delivery Systems
 Introduction to BioMEMS & Medical Microdevices Drug Delivery Systems Companion lecture to the textbook: Fundamentals of BioMEMS and Medical Microdevices, by Prof., http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Star Tribune
Introduction to BioMEMS & Medical Microdevices Drug Delivery Systems Companion lecture to the textbook: Fundamentals of BioMEMS and Medical Microdevices, by Prof., http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Star Tribune
433. New linear piezoelectric actuator based on traveling wave
 433. New linear piezoelectric actuator based on traveling wave D. Mažeika 1, P. Vasiljev 2, G. Kulvietis 3, S. Vaičiulien 4 1,3 Vilnius Gediminas Technical University, Saul tekio al. 11, Vilnius, LT-10223,
433. New linear piezoelectric actuator based on traveling wave D. Mažeika 1, P. Vasiljev 2, G. Kulvietis 3, S. Vaičiulien 4 1,3 Vilnius Gediminas Technical University, Saul tekio al. 11, Vilnius, LT-10223,
ANALYSIS AND NUMERICAL MODELLING OF CERAMIC PIEZOELECTRIC BEAM BEHAVIOR UNDER THE EFFECT OF EXTERNAL SOLICITATIONS
 Third International Conference on Energy, Materials, Applied Energetics and Pollution. ICEMAEP016, October 30-31, 016, Constantine,Algeria. ANALYSIS AND NUMERICAL MODELLING OF CERAMIC PIEZOELECTRIC BEAM
Third International Conference on Energy, Materials, Applied Energetics and Pollution. ICEMAEP016, October 30-31, 016, Constantine,Algeria. ANALYSIS AND NUMERICAL MODELLING OF CERAMIC PIEZOELECTRIC BEAM
Validation of High Displacement Piezoelectric Actuator Finite Element Models
 Validation of High Displacement Piezoelectric Actuator Finite Element Models Barmac Taleghani * Army Research Laboratory Vehicle Technology Directorate NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA ABSTRACT
Validation of High Displacement Piezoelectric Actuator Finite Element Models Barmac Taleghani * Army Research Laboratory Vehicle Technology Directorate NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA ABSTRACT
Sensors and Transducers. mywbut.com
 Sensors and Transducers 1 Objectives At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: describe the principle of operation of various sensors and transducers; namely.. Resistive Position Transducers.
Sensors and Transducers 1 Objectives At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: describe the principle of operation of various sensors and transducers; namely.. Resistive Position Transducers.
PIEZOELECTRIC TECHNOLOGY PRIMER
 PIEZOELECTRIC TECHNOLOGY PRIMER James R. Phillips Sr. Member of Technical Staff CTS Wireless Components 4800 Alameda Blvd. N.E. Albuquerque, New Mexico 87113 Piezoelectricity The piezoelectric effect is
PIEZOELECTRIC TECHNOLOGY PRIMER James R. Phillips Sr. Member of Technical Staff CTS Wireless Components 4800 Alameda Blvd. N.E. Albuquerque, New Mexico 87113 Piezoelectricity The piezoelectric effect is
A flexoelectric microelectromechanical system on silicon
 A flexoelectric microelectromechanical system on silicon Umesh Kumar Bhaskar, Nirupam Banerjee, Amir Abdollahi, Zhe Wang, Darrell G. Schlom, Guus Rijnders, and Gustau Catalan Supporting Information Figure
A flexoelectric microelectromechanical system on silicon Umesh Kumar Bhaskar, Nirupam Banerjee, Amir Abdollahi, Zhe Wang, Darrell G. Schlom, Guus Rijnders, and Gustau Catalan Supporting Information Figure
Micro-Flow in a bundle of micro-pillars. A. Keißner, Ch. Brücker
 Micro-Flow in a bundle of micro-pillars A. Keißner, Ch. Brücker Institute of Mechanics and Fluid Dynamics, University of Freiberg, TU Freiberg, Germany, Email: armin.keissner@imfd.tu-freiberg.de Abstract
Micro-Flow in a bundle of micro-pillars A. Keißner, Ch. Brücker Institute of Mechanics and Fluid Dynamics, University of Freiberg, TU Freiberg, Germany, Email: armin.keissner@imfd.tu-freiberg.de Abstract
Influence of Ultraviolet Radiation on Surface Electric Potential of P(VDF-TrFE) Films
 Ferroelectrics, 446:102 106, 2013 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0015-0193 print / 1563-5112 online DOI: 10.1080/00150193.2013.821017 Influence of Ultraviolet Radiation on Surface Electric
Ferroelectrics, 446:102 106, 2013 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0015-0193 print / 1563-5112 online DOI: 10.1080/00150193.2013.821017 Influence of Ultraviolet Radiation on Surface Electric
Piezo Theory: Chapter 1 - Physics & Design
 Piezoelectric effect inverse piezoelectric effect The result of external forces to a piezoelectric material is positive and negative electrical charges at the surface of the material. If electrodes are
Piezoelectric effect inverse piezoelectric effect The result of external forces to a piezoelectric material is positive and negative electrical charges at the surface of the material. If electrodes are
Piezo materials. Actuators Sensors Generators Transducers. Piezoelectric materials may be used to produce e.g.: Piezo materials Ver1404
 Noliac Group develops and manufactures piezoelectric materials based on modified lead zirconate titanate (PZT) of high quality and tailored for custom specifications. Piezoelectric materials may be used
Noliac Group develops and manufactures piezoelectric materials based on modified lead zirconate titanate (PZT) of high quality and tailored for custom specifications. Piezoelectric materials may be used
An investigation on the behaviour of PDMS as a membrane material for underwater acoustic sensing
 Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 41(6), December 2012, pp. 557-562 An investigation on the behaviour of PDMS as a membrane material for underwater acoustic sensing M. F. A. Rahman, M. R. Arshad,
Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 41(6), December 2012, pp. 557-562 An investigation on the behaviour of PDMS as a membrane material for underwater acoustic sensing M. F. A. Rahman, M. R. Arshad,
Electric Rocket Engine System R&D
 Electric Rocket Engine System R&D In PROITERES, a powered flight by an electric rocket engine is planed; that is, orbital transfer will be carried out with a pulsed plasma thruster (PPT). We introduce
Electric Rocket Engine System R&D In PROITERES, a powered flight by an electric rocket engine is planed; that is, orbital transfer will be carried out with a pulsed plasma thruster (PPT). We introduce
Thermal deformation compensation of a composite beam using piezoelectric actuators
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Smart Mater. Struct. 13 (24) 3 37 SMART MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES PII: S964-1726(4)7973-8 Thermal deformation compensation of a composite beam using piezoelectric actuators
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Smart Mater. Struct. 13 (24) 3 37 SMART MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES PII: S964-1726(4)7973-8 Thermal deformation compensation of a composite beam using piezoelectric actuators
An Approach to Designing a Dual Frequency Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Transducer
 Journal of Stress Analysis Vol. 1, No. 2, Autumn Winter 2016-17 An Approach to Designing a Dual Frequency Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Transducer A. Pak a,, A. Abdullah b a Mechanical Engineering Department,
Journal of Stress Analysis Vol. 1, No. 2, Autumn Winter 2016-17 An Approach to Designing a Dual Frequency Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Transducer A. Pak a,, A. Abdullah b a Mechanical Engineering Department,
BaTiO 3 and TeO 2 based gyroscopes for guidance systems: FEM analysis
 Ferroelectrics ISSN: 0015-0193 (Print) 1563-5112 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/gfer20 BaTiO 3 and TeO 2 based gyroscopes for guidance systems: FEM analysis Zafer Ozer, Amirullah
Ferroelectrics ISSN: 0015-0193 (Print) 1563-5112 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/gfer20 BaTiO 3 and TeO 2 based gyroscopes for guidance systems: FEM analysis Zafer Ozer, Amirullah
Advances in Valveless Piezoelectric Pump with Cone-shaped Tubes
 Chin. J. Mech. Eng. (2017) 30:766 781 DOI 10.1007/s10033-017-0151-z REVIEW Advances in Valveless Piezoelectric Pump with Cone-shaped Tubes Jian-Hui Zhang 1 Ying Wang 2 Jun Huang 3 Received: 17 December
Chin. J. Mech. Eng. (2017) 30:766 781 DOI 10.1007/s10033-017-0151-z REVIEW Advances in Valveless Piezoelectric Pump with Cone-shaped Tubes Jian-Hui Zhang 1 Ying Wang 2 Jun Huang 3 Received: 17 December
Effect ofpiezoelectric fan height on flow and heat transfer for electronics cooling applications
 Effect ofpiezoelectric fan height on flow and heat transfer for electronics cooling applications 1M. K. Abdullah, 1M. Z. Abdullah, 2S. F. Wong, IC. Y. Khor, Iy. Ooi, IK. A. Ahmad, IZ. Mohd Ripin and 1M.
Effect ofpiezoelectric fan height on flow and heat transfer for electronics cooling applications 1M. K. Abdullah, 1M. Z. Abdullah, 2S. F. Wong, IC. Y. Khor, Iy. Ooi, IK. A. Ahmad, IZ. Mohd Ripin and 1M.
Advanced Piezoelectric Single Crystal Based Actuators
 Advanced Piezoelectric Single Crystal Based Actuators Xiaoning Jiang, 1* Paul W. Rehrig, 1 Wesley S. Hackenberger, 1 Edward Smith, 2 Shuxiang Dong, 3 Dwight Viehland 3 Jim Moore, 4 Brian Patrick 4 1 TRS
Advanced Piezoelectric Single Crystal Based Actuators Xiaoning Jiang, 1* Paul W. Rehrig, 1 Wesley S. Hackenberger, 1 Edward Smith, 2 Shuxiang Dong, 3 Dwight Viehland 3 Jim Moore, 4 Brian Patrick 4 1 TRS
MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF STARCH BASED ELECTRORHEOLOGICAL FLUIDS
 8 th International Machine Design and Production Conference 427 September 9-11, 1998 Ankara TURKEY ABSTRACT MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF STARCH BASED ELECTRORHEOLOGICAL FLUIDS E. R. TOPCU * and S. KAPUCU
8 th International Machine Design and Production Conference 427 September 9-11, 1998 Ankara TURKEY ABSTRACT MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF STARCH BASED ELECTRORHEOLOGICAL FLUIDS E. R. TOPCU * and S. KAPUCU
Design and analysis of a piezoelectric film embedded smart cutting tool
 Design and analysis of a piezoelectric film embedded smart cutting tool C Wang*, R Rakowski and K Cheng Advanced Manufacturing and Enterprise Engineering, School of Engineering and Design, Brunel University,
Design and analysis of a piezoelectric film embedded smart cutting tool C Wang*, R Rakowski and K Cheng Advanced Manufacturing and Enterprise Engineering, School of Engineering and Design, Brunel University,
Design and Test of a PZT Wind Generator Excited by Rotary Magnet
 5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 05) Design and Test of a PZT Wind Generator Excited by Rotary Magnet M.J. YAN, S.Y. WANG, C.T. FAN, W.J. WU & J.W.
5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 05) Design and Test of a PZT Wind Generator Excited by Rotary Magnet M.J. YAN, S.Y. WANG, C.T. FAN, W.J. WU & J.W.
Finite Element Modeling of Ultrasonic Transducers for Polymer Characterization
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Finite Element Modeling of Ultrasonic Transducers for Polymer Characterization Serena De Paolis *, Francesca Lionetto and Alfonso Maffezzoli
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Finite Element Modeling of Ultrasonic Transducers for Polymer Characterization Serena De Paolis *, Francesca Lionetto and Alfonso Maffezzoli
Measuring vibration characteristics at large amplitude region of materials for high power ultrasonic vibration system
 Ultrasonics 38 (2000) 122 126 www.elsevier.nl/locate/ultras Measuring vibration characteristics at large amplitude region of materials for high power ultrasonic vibration system Kentaro Nakamura *, Kiyotsugu
Ultrasonics 38 (2000) 122 126 www.elsevier.nl/locate/ultras Measuring vibration characteristics at large amplitude region of materials for high power ultrasonic vibration system Kentaro Nakamura *, Kiyotsugu
