QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING UNIT I - INTRODUCTION SYLLABUS
|
|
|
- Eleanor Davis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING YEAR/SEM NAME OF THE SUBJECT NAME OF THE FACULTY : II / IV : EE6404 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION : K.M.S.MUTHUKUMARA RAJAGURU, AP/EEE UNIT I - INTRODUCTION SYLLABUS X. Functional elements of an instrument Static and dynamic characteristics Errors in measurement. Y. Statistical evaluation of measurement data Standards and calibration. PART A I X 1 Define dynamic characteristics of an instrument? [AUC Nov/Dec 2008] I X 2 Differentiate Resolution from Threshold. [NOV/DEC 09] I X 3 How are the absolute and relative errors expressed mathematically? [NOV/DEC 09] I X 4 What are the static characteristics of measurement system? [APR/MAY 10] I X 5 Define static characteristics of an instrument. [NOV/DEC 10] I X 6 What is meant by absolute error of measurement? [NOV/DEC 10] I X 7 Define dynamic characteristics of an instrument. [APR/MAY 11] I X 8 List the functional elements of a measuring instrument.[ NOV/DEC 11] I X 9 What is drift? [NOV/DEC 11] I X 10 Define the term 'Sensitivity' of an instrument. [NOV/DEC 12] I X 11 I X 12 I X 13 The true value of a voltage is 100 V. The values indicated by a measuring instrument are 104, 103, 105, 103 and 105. Find the accuracy and precision of the instrument. [NOV/DEC 12] The expected value of the voltage across a resistor is 40V. However the measurement gives a value of 39V. Calculate the absolute error. [MAY/JUN 13] What are the various important functional elements of a typical measurement system? [MAY/JUN 13] I X 14 Define the terms precision and sensitivity. [NOV/DEC 13] I X 15 What is the significance of calibration? [NOV/DEC 13] I X 16 [MAY/ JUN 14] Define measuring lag and fidelity of dynamic characteristics of instrument.
2 I X 17 [NOV /DEC 14] I X 18 [NOV /DEC 14] I X 19 I X 20 I X 21 I X 22 I X 23 I X 24 Define limiting errors. Derive the expression for relative limiting error. Define linear time invariant and linear time variant systems. Give examples. What is meant by accuracy of an instrument? What is primary sensing element? What is calibration? When are static characteristics important? Define static error. Distinguish reproducibility and repeatability. Distinguish between direct and indirect methods of measurements. I Y 25. Write down the different Standards of an instrument. [APR/MAY 11] I Y 26. Give the international standards of instruments. [MAY/ JUN 14] I Y 27. What are primary standards? Where are they used? I Y 28. Define Gross and random errors [APR/MAY 2015] I Y 29. Illustrate the difference between Accuracy and Precision. [APR/MAY 2015] I Y 30. What is an error? How it is classified? I Y 31. How are static errors classified? I Y 32. How are systematic errors classified? I Y 33. Define static error and dynamic error. I Y 34. What are the sources of error? I Y 35. Define arithmetic mean and median. I Y 36. Define average deviation. I Y 37. Define standard deviation. I Y 38. What is the significance of calibration? [APR/MAY 10] I Y 39. Write down the different standards of an instrument? [Nov/Dec 2008] PART B 16 Marks I Y 1. A circuit was tuned for resonance by eight different students, and the value of resonant frequency in khz were recorded as 532, 548, 543, 535, 546, 531, 543 and 536. Calculate (i) the arithmetic mean, (ii) deviation from the mean, (iii) average deviation, and (iv) standard deviation. [APR/MAY 10, NOV/DEC 13] 10 Marks I X 1 Write a note on different types of errors. [NOV/DEC 09, NOV/DEC 10, NOV/DEC 11, I X 2 NOV/DEC 14] (10) Draw and explain the general block diagram and functional elements of measurement system. [NOV/DEC 09, APR/MAY 10, NOV/DEC 10, NOV/DEC 13, MAY/JUN 14, NOV/DEC 14] (10)
3 8 Marks I X 1 Define and explain the static and dynamic characteristics of an instrument. [NOV/DEC 09, APR/MAY 11, NOV/DEC 11, NOV/DEC 12, MAY/JUN 13, MAY/JUN 14, NOV/DEC 14] I X 2 What are the different types of error? Explain how to eliminate errors in instrument. [MAY/JUN 14] I Y 1 The probable values of two resistors and their S.D are specified as R1 = Ω, S.D = Ω, R2 = Ω, S.D. = 0.05 Ω. Find the probable value and S.D for the two resistors when they are connected in Series and Parallel. [NOV/DEC 10] I Y 2 Discuss the different types of standards of measurements. [NOV/DEC 10, NOV/DEC 11, MAY/JUN 14, NOV/DEC 14] I Y 3 Explain the concept of static evaluation of measurement data. [APR/MAY 11, MAY/JUN 13] I Y 4 Describe the different calibration procedures of measuring instrument. [APR/MAY 11] I Y 5 How are histogram and arithmetic mean helpful in the statistical analysis of data? [NOV/DEC 11] I Y 6 Describe the various modes of statistical evaluation of measurement data. I Y 7 Discuss in detail about calibration. [NOV/DEC 12] I Y 8 For the given data calculate any three statistically analyzed values X1 = 49.7; X2 = 50.1; X3 = 50.2; X4 = 49.6; X5 = [MAY/JUN 13] I Y 9 With a suitable illustration elaborate the significance of calibrations. [NOV/DEC 14] I Y 10 Describe the different types of calibration procedures. [NOV/DEC 2008] 6 Marks I X 1 Describe primary and secondary standards in instruments. [MAY/JUN 14] & [MAY/JUN 14] (6) I X 2 Define accuracy and reproducibility of an instrument and explain. [MAY/JUN 14] (6)
4 QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING YEAR/SEM NAME OF THE SUBJECT NAME OF THE FACULTY : II / IV : EE6404 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION : K.M.S.MUTHUKUMARA RAJAGURU, AP/EEE UNIT II - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS INSTRUMENTS SYLLABUS X. Principle and types of analog and digital voltmeters, ammeters, multimeters Single and three phase watt meters and energy meters. Y. Magnetic measurements Determination of B-H curve and measurements of iron loss Instrument transformers Instruments for measurement of frequency and phase. PART A II X 1 What is the essential torques required for operating an instrument? [NOV/DEC 09] II X 2 What is phase meter? Mention the types of phase meter. [NOV/DEC 09] II X 3 Write any four types of analog ammeter used for instrumentation. [APR/MAY 10] II X 4 Why are the ordinary watt meters not suitable for low power factor circuits? [NOV/DEC 10] II X 5 What is a phase sequence indicator? [NOV/DEC 10] II X 6 State the purpose of Shunts in the Voltmeter. [APR/MAY 11] II X 7 How does one extend the range of ammeter and voltmeter? [NOV/DEC 11] II X 8 A (0-25) A ammeter has a guaranteed accuracy of 1 percent of full scale reading. The current measured by this instrument is 10 A. Determine the limiting error in percentage. [NOV/DEC 12] II X 9 Draw the circuit of a basic DC voltmeter. [MAY/ JUNE 13] II X 10 Write any four types of analog ammeter used for instrumentation. [NOV/DEC 13] II X 11 How are basic instruments converted into higher range ammeter? [MAY/JUNE 14] II X 12 Define creeping in energy meter. [MAY/JUNE 14] II X 13 Why the PMMC ammeters are the most widely used instrument? [NOV/DEC 14] II X 14 An absolute electrometer has a movable circular plate 10 cm in diameter. Determine the potential difference across the plates if the plates during measurement are 6 mm
5 apart and the force of attraction is 4*10-13 N. [NOV/DEC 14] II Y 15. List out the methods used for measurement of iron loss in ferromagnetic materials. [APR/MAY 10] II Y 16. Classify different types of iron loss. [APR/MAY 11] II Y 17. Why do we do Ballistic tests? [NOV/DEC 11] II Y 18. Explain with example, the term 'Hysteresis'. [NOV/DEC 12] II Y 19. Discuss in brief about the hysteresis in B-H curve. [MAY/ JUNE 13] II Y 20. What are the different methods used for frequency measurement in power frequency range? [NOV/DEC 13] PART B 16 Marks II X 1 II Y 2 II X 1 II X 1 II X 2 II X 3 II X 4 II X 5 II X 6 Describe the construction and working of permanent magnet moving coil instrument. Also derive the expression for deflection. [NOV/DEC 13, NOV/DEC 14] Explain with neat sketch the classification of Instrument Transformers. Write a note on the errors affecting the characteristics of an Instrument Transformer. 12 Marks With a neat block diagram of a digital multimeter explain their working principle. [MAY/JUN 13] 8 Marks Describe the construction and working principle of single phase induction type energy meter. Write a short note on any two adjustments required in energy meters. [NOV/DEC 09, APR/MAY 11, MAY/JUN 14] With a neat diagram, explain the construction, working principle of single phase wattmeter. What is the importance of deflection torque in these instruments? [APR/MAY 10] What are the various types of digital voltmeters? With a neat sketch explain the working principle of any one type of a digital voltmeter. [NOV/DEC 10, APR/MAY 11] With a neat diagram explain the construction and its working principle of electrodynamometer type wattmeter. Also derive its torque equation. [NOV/DEC 10] Explain the working principle of operation of electrodynamometer type of instruments with its constructional diagram. [NOV/DEC 12, NOV/DEC 14] A PMMC ammeter gives reading of 40 ma when connected across two opposite corners of a bridge rectifier, the other two corners of which are connected in series with a capacitor to 100k, 50Hz supply. Determine the capacitance. [NOV/DEC 12]
6 II Y 7. Write short notes on: Use of current transformer for current and power measurement. II Y 8. Write short notes on: Working of Weston frequency meter. (8) [APR/MAY 10, II Y 9. NOV/DEC 13] Explain the method of measurements of B.H curve of a ring specimen with a neat diagram. [NOV/DEC 10, MAY/JUN 14] II Y 10. Describe the construction and working principle of digital frequency meter. [NOV/DEC 10] II Y 11. Describe the basic magnetic measurement using B-H curve. [APR/MAY 11] II Y 12. Explain the operating principle and characteristics of instrument transformer. [APR/MAY 11, NOV/DEC 14] II Y 13. How to measure the power using instrument transformers? Explain. II Y 14. How is multi-meter used to measure different parameters? Explain. [NOV/DEC 11] II Y 15. How do you determine the B-H curve using step by step method? II Y 16. What are the different methods used for the measurement of frequency? Explain any one method. [NOV/DEC 11] II Y 17. The coil of instrument has 42.5 turns. The mean width of the coil is 2.5 cm and the axial length of the coil is 2 cm. if the flux density is 0.1 Wb/m 2, calculate the torque on the moving coil in Nm. II Y 18. A 100/5A current transformer having a rated burden of 25 VA has an iron loss of 0.4W and a magnetizing current of 2 A. calculate its ratio error and phase angle error when supplying rated output current to a meter having a ratio of resistance to reactance 5. [NOV/DEC 12] 6 Marks II X 1 A PMMC ammeter gives reading of 40 ma when connected across two opposite corners of a bridge rectifier, the other two corners of which are connected in series with a capacitor to 100k, 50Hz supply. Determine the capacitance. [NOV/DEC 12] 4 Marks II Y 3 What are the main considerations in selecting a voltmeter? [MAY/JUN 13]
7 QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING YEAR/SEM NAME OF THE SUBJECT NAME OF THE FACULTY : II / IV : EE6404 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION : K.M.S.MUTHUKUMARA RAJAGURU, AP/EEE UNIT III - COMPARISON METHODS OF MEASUREMENTS SYLLABUS X. D.C & A.C potentiometers, D.C & A.C bridges, transformer ratio bridges, selfbalancing bridges. Y. Interference & screening Multiple earth and earth loops - Electrostatic and electromagnetic interference Grounding techniques. PART A III X 1 State the condition for balance in a Wheatstone bridge. (Nov/Dec 2013) III X 2 How does Hay s bridge differ from Maxwell s bridge? What is its uniqueness? (May/June 2013) III X 3 State the condition for balance in a Wheatstone bridge? (Nov/Dec 2009) III X 4 What are the applications of potentiometers? (Nov/Dec 2013) III X 5 List the application of AC Bridges. (April/May 2011) III X 6 III X 7 III X 8 III X 9 What are the types of DC potentiometer? What are the types of potentiometer? What are the features of transformer Ratio Bridge? What is Wien Bridge? III X 10 What are the advantages and disadvantages of Anderson Bridge? III X 11 What is Owen Bridge and also draw the circuit diagram? III X 12 Draw the circuit diagram of Maxwell Bridge? III X 13 What are the two conditions must be satisfied to make an AC bridge balance? III Y 14. Draw the equivalent circuit and phasor diagram of a potential transformer. (Nov/Dec 2014) III Y 15. Write the working principle of a digital plotter. (Nov/Dec 2014) III Y 16. What is an isolation amplifier? Where is it used? (Nov/Dec 2013) III Y 17. Which instrument is used for measuring very high resistances found in cable insulations? (May/June 2013) III Y 18. What is an isolation amplifier? Where is it used? (Nov/Dec 2009)
8 III Y 19. What are the sources of electromagnetic interference? (Nov/Dec 2013) III Y 20. What is the need for screening? (April/May 2010) III Y 21. What are the merits and demerits of digital storage oscilloscope? (April/May 2010) III Y 22. Enumerate the principle of grounding. (April/May 2011) III X 1 III X 2 III X 3 III X 4 III X 5 PART B 16 Marks With a neat sketch describe a bridge to determine the unknown inductance and a bridge to determine the unknown capacitance. (16) (Nov/Dec 2009) Consider an unbalanced Wheatstone bridge. Calculate the current through the galvanometer. R1 = 1kΩ, R2 = 2.5kΩ, R3 = 3.5kΩ, R4 = 10kΩ, Rg = 300Ω, E = 6V. (May/June 2013) Explain how the inductance is measured in terms of known capacitance using Maxwell s bridge. Derive the conditions for balance. (16) (Nov/Dec 2013) What are the difficulties associated with measurement of low resistance? Describe how low resistance is measured accurately by Kelvin s double bridge. (4+12) (April/May 2010), (April/May 2015) Explain the operation of Schering Bridge to determine the unknown capacitance. Derive the relevant equations andexplain the computation procedure using phasor diagram. (April/May 2011) III Y 1. Explain the grounding techniques in detail to reduce the ground loop interference signal. (16) (Nov/Dec 2009) 10 Marks III X 1 Give the construction of an Anderson s bridge and derive its balance conditions. (10) (May/June 2013) III X 1 8 Marks Explain the theory and working principle of Wheatstone s bridge. Derive the relation for finding unknown resistance. (8) (Nov/Dec 2014) (Nov/Dec 2012) III X 2 Describe any one method for the measurement of high resistance. (8) (Nov/Dec 2014) III X 3 Explain the comparison method of measurement of inductance by Maxwell s LC Bridge with its balance equations. (8) (Nov/Dec 2014) III X 4 Explain the measurement of frequency by Wien s bridge. (8) (Nov/Dec 2014) III X 5 III X 6 Describe the operation of A.C. potentiometer. With a neat bridge network, derive the equation for the general bridge balance with an a.c. bridge diagram. (April/May 2011) III Y 1. Describe in detail about: Interference and Screening. III Y 2. Describe in detail about: Multiple earth and earth loops. (April/May 2015) 6 Marks III X 1 Write a detailed technical note on grounding techniques. (6) (May/June 2013)
9 QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING YEAR/SEM NAME OF THE SUBJECT NAME OF THE FACULTY : II / IV : EE6404 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION : K.M.S.MUTHUKUMARA RAJAGURU, AP/EEE UNIT IV - STORAGE AND DISPLAY DEVICES SYLLABUS X. Magnetic disk and tape Recorders, digital plotters and printers, CRT display, Y. Digital CRO, LED, LCD & dot matrix display Data Loggers. PART A IV X 1 Write the working principle of digital plotters. (Nov/Dec 2014) IV X 2 What are the types of printers according to printing methodology? (Nov/Dec 2013) IV X 3 What are the various components of a recording instrument? (May/June 2013) IV X 4 List any two storage devices.(april/may 2011) IV X 5 Differentiate the functions of printer and plotter. (April/May 2011) IV X 6 Give the functional difference between strip chart recorder and X-Y recorder. (April/May 2015) IV X 7 What is isolation probe? IV X 8 Brief up the working of a digital encoder. (Nov/Dec 2012) IV X 9 What is the principle of operation of an ink-jet printer? (Nov/Dec 2012) IV X 10 State the features of ink-jet printers? IV X 11 What are the various methods of recording data? IV X 12 What is recorder? How are they classified? IV X 13 What is the digital principle of working of Dot Matrix display? (April/May 2014) IV Y 14 What are the main parts of the cathode ray tube? IV Y 15 Reason out why today s commercial LED monitor has become more popular than their LCD counterparts. (May/June 2013) IV Y 16 Distinguish between LED and LCD. (Nov/Dec 2013) IV Y 17 What are the functions of data logger? (Nov/Dec 2013) & (April/May 2015) IV Y 18 What are the different types of amplifiers used for CRO s? IV Y 19 Give the principle of LCD type display device. IV Y 20 Write two advantages of LED on electronic displays? IV Y 21 What is the power requirement of LCD? IV Y 22 What are data loggers?
10 IV Y 23 What are functions of data loggers? IV Y 24 List out the main parts of cathode ray tube. IV Y 25 What is LED? (April/May 2014) PART B 16 Marks IV X 1 Describe the direct and frequency modulation magnetic tape recording types. Give its merits and demerits. (16) (Nov/Dec 2013) IV X 2 What is the advantage of using a magnetic tape recorder? Explain how the tape recorder works with suitable diagrams.(16) (May/June 2013) (April/May 2015) IV X 3 With neat diagram, explain the basic components and working principle of magnetic tape recorder. (16) (Nov/Dec 2013) IV Y 4 Describe the LED and LCD display devices (16) (Nov/Dec 2013) (Nov/Dec 2012) IV Y 5 Bring out how data loggers measure and record data effortlessly, accurately and quickly explaining the working of them. (16) (May/June 2013) IV Y 6 With the help of functional block diagram, explain the working principle of digital storage oscilloscope, mention its advantages over analog CRO? (16) (Nov/Dec 2013), (Nov/Dec 2012) & (April/May 2015) IV Y 7 With a help of simplified block diagram, explain the construction and operating principle of general purpose Cathode Ray Oscilloscope. (April/May 2011) (16) 8 Marks IV X 4 Discuss the working principle of a magnetic tape recorder. (8) (Nov/Dec 2014) IV X 5 Explain the construction and functionalities of various components of a CRT display. (8) (Nov/Dec 2014) IV X 6 Discuss the working of digital CRO. (8) IV X 7 Write a detailed technical note on dot matrix display. (8) (Nov/Dec 2012) IV X 8 Draw a neat diagram of X-Y recorder and describe it s working. (8) IV X 9 Explain the principle and working of CRT display with a neat diagram. (8) (April/May 2014) IV X 10 Write brief notes on: Magnetic disk and tape. IV Y 1 Write brief notes on: Recorders and printers. (April/May 2011) IV Y 2 Compare and contrast the construction, working principle and applications of LED and LCDs (8) (Nov/Dec 2014) IV Y 3 Write a detailed technical note on data loggers. Explain how they differ from Data Acquisition systems. (8) (Nov/Dec 2014)
11 QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING YEAR/SEM NAME OF THE SUBJECT NAME OF THE FACULTY : II / IV : EE6404 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION : K.M.S.MUTHUKUMARA RAJAGURU, AP/EEE UNIT V - TRANSDUCERS AND DATA ACQUISITION SYSTEMS SYLLABUS X. Classification of transducers Selection of transducers Resistive, capacitive & inductive transducers - Piezoelectric, Hall effect, optical and digital transducers. Y. Elements of data acquisition system A/D, D/A converters Smart sensors. V X 1. PART A What is transducer? What is the difference between sensor and transducer? (Nov/Dec 2014), (Nov/Dec 2012) V X 2. Differentiate sensor from transducer. (Nov/Dec 2013) V X 3. What is known as thermocouple effect and how do you use it in a transducer? (May/June 2013) V X 4. What are the factors to be considered for selection of transducers? (Nov/Dec 2013) V X 5. Mention some examples of the active transducer which are used in the measurement of temperature. (Nov/Dec 2012) V X 6. Write the function of transducer. (April/May 2011) V X 7. V X 8. V X 9. Define Hall effect transducer. Write their uses. What is optical sensor? What are the major classes of fiber optics sensor and explain it. V X 10. Define inverse transducers with example. V X 11. How are the transducers classified? V X 12. What is an active transducer? V X 13. Mention some examples of active transducer. V X 14. Mention different types of strain gauges. V X 15. What is piezoelectric effect? V X 16. What are the applications of capacitive transducers? V X 17. How is the resistive transducer works? V X 18. How is a differential output taken from an inductive transducer? V X 19. Write the desired properties of thermocouple metals. (April/May 2015) V Y 20. Draw the block diagram for 4 bit ADC. (Nov/Dec 2013) V Y 21. When do you call an instrument to be intelligent? (May/June 2013)
12 V Y 22. Mention any four types of ADC? (Nov/Dec 2013) V Y 23. Give any two applications of Smart Sensors. (April/May 2011) V Y 24. What is smart sensor? V Y 25. Mention the importance of settling time in D/A converter? V Y 26. What are the advantages of successive approximation type ADC? (Nov/Dec 2014) V Y 27. What are the two ways that the DAS are used to measure and record analog signals? (April/May 2015) V X 1 PART B 16 Marks What are the selection criteria for the transducer? Explain the working principle of LVDT with neat sketch and characteristics. Give advantages, disadvantages and applications of LVDT. (16) (Nov/Dec 2013) & (Nov/Dec 2012) V X 2 Explain the following : strain gauges, piezoelectric transducers and smart sensors (16) V X 3 V Y 4 V Y 5 (May/June 2013) Explain the classification of transducers and discuss about the selection criteria for them. (16) (May/June 2013) What are the performance parameters of Analog to Digital converter? Explain any two basic A/D conversion techniques in detail. (16) (Nov/Dec 2013) Explain the following: grounding techniques causes of electromagnetic interferences in measurements. (16) (Nov/Dec 2013) 10 Marks V Y 7. (i) What is data acquisition system? With generalized block diagram, explain the functions of it. (10) 8 Marks V X 1 Explain the measurement of resistance using strain gauge. (8) V X 2 V X 3 Describe the various factors influencing the type of transducer for a particular application. (April/May 2011) Explain the principle of operation: Piezoelectric transducer. V X 4 Explain the principle of operation: A/D converter. (April/May 2011) V X 5 Write short notes on the following: Seeback effect. V X 6 Write short notes on the following: Piezoelectric transducer. V X 7 Write short notes on the following: Resistance thermometers. (April/May 2015) V Y 8. Describe in detail, the working principle of capacitive microphone (8)
13 V Y 9. Write in detailed technical note on smart sensors. Explain also the various built-in features of them compared to conventional sensors. (8) (Nov/Dec 2014) V Y 10. Explain the successive approximation type ADC with its characteristics. V Y 11. A 5-plate transducer has plates of dimensions 20mm*20mm and separated 0.25 mm apart. The arrangement is to be used for measuring displacement. Determine the sensitivity of the arrangement. Assume air medium. (Nov/Dec 2012) V Y 12. Explain the basic operation of A/D converter utilizing D/A converter. V Y 13. Explain the concept of Smart sensors. (April/May 2015) V Y 14. Explain in detail, the working principle of piezoelectric transducers. (8) V Y 15. Discuss any one method of D/A converter (8) (Nov/Dec 2014) 6 Marks V Y 1. Write short notes on smart sensors. (6) (Nov/Dec 2013)
PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6404-MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION
 PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6404-MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION ACADEMIC YEAR: 2015-2016 (EVEN SEMESTER) Branch: EEE QUESTION BANK
PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6404-MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION ACADEMIC YEAR: 2015-2016 (EVEN SEMESTER) Branch: EEE QUESTION BANK
coil of the circuit. [8+8]
![coil of the circuit. [8+8] coil of the circuit. [8+8]](/thumbs/80/81218867.jpg) Code No: R05310202 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS (Electrical & Electronic Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Code No: R05310202 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS (Electrical & Electronic Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad DEPARTMENT OF ECE QUESTION BANK. : G.Lakshminarayana, Asst.
 ` INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 DEPARTMENT OF ECE QUESTION BANK Name Code Class Branch P a g e : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation : A504 : III - B. Tech
` INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 DEPARTMENT OF ECE QUESTION BANK Name Code Class Branch P a g e : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation : A504 : III - B. Tech
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Name : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation Code : A50422 Class : III -
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Name : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation Code : A50422 Class : III -
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Course Name : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation Course Code : A50422
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Course Name : Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation Course Code : A50422
AE60 INSTRUMENTATION & MEASUREMENTS DEC 2013
 Q.2 a. Differentiate between the direct and indirect method of measurement. There are two methods of measurement: 1) direct comparison with the standard, and 2) indirect comparison with the standard. Both
Q.2 a. Differentiate between the direct and indirect method of measurement. There are two methods of measurement: 1) direct comparison with the standard, and 2) indirect comparison with the standard. Both
ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS
 EE 326 (RR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 02 III/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 2017 Second Semester ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS Time: Three Hours Answer
EE 326 (RR) Total No. of Questions :09] [Total No. of Pages : 02 III/IV B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY- 2017 Second Semester ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS Time: Three Hours Answer
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17322 21314 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
17322 21314 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
Bridge Measurement 2.1 INTRODUCTION Advantages of Bridge Circuit
 2 Bridge Measurement 2.1 INTRODUCTION Bridges are often used for the precision measurement of component values, like resistance, inductance, capacitance, etc. The simplest form of a bridge circuit consists
2 Bridge Measurement 2.1 INTRODUCTION Bridges are often used for the precision measurement of component values, like resistance, inductance, capacitance, etc. The simplest form of a bridge circuit consists
Conventional Paper-I-2011 PART-A
 Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
ANDERSON S BRIDGE & SCHERING S BRIDGE
 ANDERSON S BRIDGE & SCHERING S BRIDGE ANDERSON S BRIDGE AIM: A)To measure inductance of a given coil by Anderson s bridge. B) To determine the value of a given capacitor and to obtain for its dissipation
ANDERSON S BRIDGE & SCHERING S BRIDGE ANDERSON S BRIDGE AIM: A)To measure inductance of a given coil by Anderson s bridge. B) To determine the value of a given capacitor and to obtain for its dissipation
CHAPTER 5. BRIDGES AND THEIR APPLICATION Resistance Measurements. Dr. Wael Salah
 CHAPTER 5 BRIDGES AND THEIR APPLICATION Resistance Measurements 1 RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS Conventional Ways of Measuring Resistance:- 1) Using a Ohmmeter Convenient but inaccurate, requires calibration
CHAPTER 5 BRIDGES AND THEIR APPLICATION Resistance Measurements 1 RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS Conventional Ways of Measuring Resistance:- 1) Using a Ohmmeter Convenient but inaccurate, requires calibration
Unit 3 Transducers. Lecture_3.1 Introduction to Transducers
 Unit 3 Transducers Lecture_3.1 Introduction to Transducers Introduction to transducers A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy to other form. It converts the measurand to a usable electrical
Unit 3 Transducers Lecture_3.1 Introduction to Transducers Introduction to transducers A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy to other form. It converts the measurand to a usable electrical
OR Explain thermal breakdown in solid dielectrics. How this mechanism is
 Subject : High Voltage Engineering (2090) ITM Universe, Vadodara Electrical Engineering Department Class : Electrical Sem : th Long Questions Sr. No Question Unit No : 0 Explain Charge Simulation method
Subject : High Voltage Engineering (2090) ITM Universe, Vadodara Electrical Engineering Department Class : Electrical Sem : th Long Questions Sr. No Question Unit No : 0 Explain Charge Simulation method
Dept. of Electrical Engineering Final Exam, Summer Semester: 2014/2015
 de Form No. T611 Philadelphia University Faculty of Engineering Dept. of Electrical Engineering Final Exam, Summer Semester: 2014/2015 Student Name: Student Number: Course Title: nstrumentation and Measurement
de Form No. T611 Philadelphia University Faculty of Engineering Dept. of Electrical Engineering Final Exam, Summer Semester: 2014/2015 Student Name: Student Number: Course Title: nstrumentation and Measurement
Work, Energy and Power
 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16]
![1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16] 1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16]](/thumbs/96/127822274.jpg) Code No: RR320204 Set No. 1 1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16] 2. Distinguish between deterministic signals and
Code No: RR320204 Set No. 1 1. Distinguish the important characteristics of instrument that are totally electrical and totally electronic in nature. [16] 2. Distinguish between deterministic signals and
CHAPTER 5 DC AND AC BRIDGE
 5. Introduction HAPTE 5 D AND A BIDGE Bridge circuits, which are instruments for making comparison measurements, are widely used to measure resistance, inductance, capacitance, and impedance. Bridge circuits
5. Introduction HAPTE 5 D AND A BIDGE Bridge circuits, which are instruments for making comparison measurements, are widely used to measure resistance, inductance, capacitance, and impedance. Bridge circuits
 Set No. 1 1. (a) Differentiate among Desired, Modifying and Interfering inputs. (b) How do you eliminate the effects of interfering and modifying inputs? Explain 2. (a) Define the term Transducer and explain
Set No. 1 1. (a) Differentiate among Desired, Modifying and Interfering inputs. (b) How do you eliminate the effects of interfering and modifying inputs? Explain 2. (a) Define the term Transducer and explain
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING
 INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
INSTRUMENTAL ENGINEERING Subject Code: IN Course Structure Sections/Units Section A Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Section B Section C Section D Section E Section F Section G Section H Section
Code No: RR Set No. 1
 Code No: RR410209 Set No. 1 1. What are the gases mainly used in insulating medium at high pressures? Which is more suitable? Why? What about its dielectric strength? Explain. [16] 2. (a) Define time lags
Code No: RR410209 Set No. 1 1. What are the gases mainly used in insulating medium at high pressures? Which is more suitable? Why? What about its dielectric strength? Explain. [16] 2. (a) Define time lags
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER BE8255 BASIC ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONICS AND MEASUREMENT ENGINEERING
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK II SEMESTER BE8255 BASIC ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONICS AND MEASUREMENT ENGINEERING
Work, Energy and Power
 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is the capacity for doing work (Joules) Power is the rate of using energy (Watt) P = W / t,
SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL. EE-Measurement and Measuring Instruments
 S S C - J E Measurement and Measuring Instruments P a g e 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL EE-Measurement and Measuring Instruments EE-Measurement and Measuring
S S C - J E Measurement and Measuring Instruments P a g e 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL EE-Measurement and Measuring Instruments EE-Measurement and Measuring
COURSE OF Prepared By: MUHAMMAD MOEEN SULTAN Department of Mechanical Engineering UET Lahore, KSK Campus
 COURSE OF Active and passive instruments Null-type and deflection-type instruments Analogue and digital instruments In active instruments, the external power source is usually required to produce an output
COURSE OF Active and passive instruments Null-type and deflection-type instruments Analogue and digital instruments In active instruments, the external power source is usually required to produce an output
Transducers. EEE355 Industrial Electronics
 Transducers EEE355 Industrial Electronics 1 Terminology Transducers convert one form of energy into another Sensors/Actuators are input/output transducers Sensors can be passive (e.g. change in resistance)
Transducers EEE355 Industrial Electronics 1 Terminology Transducers convert one form of energy into another Sensors/Actuators are input/output transducers Sensors can be passive (e.g. change in resistance)
ADIKAVI NANNAYA UNIVERSITY::RAJAMAHENDRAVARAM II BTech (EIE) I Semester BTEIE301 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN MODEL QUESTION PAPER Time:3 hrs. Max.
 II BTech (EIE) I Semester BTEIE301 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN SECTION-A (4 X 15 = 60 M) 1. a) List out the Basic Theorems and Properties of Boolean Algebra. Justify with the Proof (15M) b) Explain how 1's complement
II BTech (EIE) I Semester BTEIE301 DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN SECTION-A (4 X 15 = 60 M) 1. a) List out the Basic Theorems and Properties of Boolean Algebra. Justify with the Proof (15M) b) Explain how 1's complement
Siddharth Institute of Engineering & Technology
 SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi & Affiliated to JNTUA, Anantapuramu) (Accredited by NBA & Accredited by NAAC with A Grade) (An ISO 9001:2008
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi & Affiliated to JNTUA, Anantapuramu) (Accredited by NBA & Accredited by NAAC with A Grade) (An ISO 9001:2008
Power and Energy Measurement
 Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
Power and Energy Measurement EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement April 24, 2015 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction of force (Joules) Energy is
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ
 BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ Year/Sem : III/V Sub.Code/Title: ME6504- METROLOGY & MEASUREMENTS UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT PART-A 1. Define
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ Year/Sem : III/V Sub.Code/Title: ME6504- METROLOGY & MEASUREMENTS UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT PART-A 1. Define
Part 2. Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour)
 Part 2 Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour) At the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the definition of sensor and transducer Determine the specification of control
Part 2 Sensor and Transducer Instrument Selection Criteria (3 Hour) At the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the definition of sensor and transducer Determine the specification of control
Outline of College Physics OpenStax Book
 Outline of College Physics OpenStax Book Taken from the online version of the book Dec. 27, 2017 18. Electric Charge and Electric Field 18.1. Static Electricity and Charge: Conservation of Charge Define
Outline of College Physics OpenStax Book Taken from the online version of the book Dec. 27, 2017 18. Electric Charge and Electric Field 18.1. Static Electricity and Charge: Conservation of Charge Define
PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION STD : XII MARKS : 150
 PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION STD : XII MARKS : 150 SUB : PHYSICS TIME : 3.00 Hrs I.Choose the correct answer: 30x1=30 1.Which of the following quantities not a scalar? a)electric flux b) electric potential c)
PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION STD : XII MARKS : 150 SUB : PHYSICS TIME : 3.00 Hrs I.Choose the correct answer: 30x1=30 1.Which of the following quantities not a scalar? a)electric flux b) electric potential c)
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS
 UNIT 2: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS MODULE 1: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand
UNIT 2: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM, A. C. THEORY AND ELECTRONICS, ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR PHYSICS MODULE 1: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand
+2 Physics Important FIVE marks Questions. English Medium : Volume I. (From - March: 2006 to Oct : 2015)
 +2 Physics Important FIVE marks Questions English Medium : Volume I (From - March: 2006 to Oct : 2015) +2 Physics Unit -1 Electrostatics - Five marks questions 1. Write the properties of electric lines
+2 Physics Important FIVE marks Questions English Medium : Volume I (From - March: 2006 to Oct : 2015) +2 Physics Unit -1 Electrostatics - Five marks questions 1. Write the properties of electric lines
III B.Tech. II Semester Regular Examinations, April/May INSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL SYSTEMS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 75
 R10 Set No: 1 1. (a) Distinguish between accuracy and Precision. Which of these is more desirable during the act of measurement and why? (b) Discuss the necessity and importance of dynamic performance
R10 Set No: 1 1. (a) Distinguish between accuracy and Precision. Which of these is more desirable during the act of measurement and why? (b) Discuss the necessity and importance of dynamic performance
SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS
 Electrical Measurements International Program Department of Electrical Engineering UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANDRITTO ABDUL GHAFFAR ANDHIKA ADIEL INSANI Lecturer : Ir. Chairul Hudaya, ST, M.Eng., Ph.D., IPM
Electrical Measurements International Program Department of Electrical Engineering UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANDRITTO ABDUL GHAFFAR ANDHIKA ADIEL INSANI Lecturer : Ir. Chairul Hudaya, ST, M.Eng., Ph.D., IPM
Q.1 Attempt any TEN of the following : A a) State the range for low and medium resistance.
 Subject Code: 17322 Model Answer Page 1 of 30 Important suggestions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17322 Model Answer Page 1 of 30 Important suggestions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
LOW & HIGH RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS and A.C. BRIDGES
 LOW & HIGH RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS and A.C. BRIDGES SECTION D LOW & HIGH RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS: LIMITATIONS OF WHEATSTONE BRIDGE; KELVIN S DOUBLE BRIDGE METHOD, DIFFICULTIES IN HIGH RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS.
LOW & HIGH RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS and A.C. BRIDGES SECTION D LOW & HIGH RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS: LIMITATIONS OF WHEATSTONE BRIDGE; KELVIN S DOUBLE BRIDGE METHOD, DIFFICULTIES IN HIGH RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS.
PHYSICS : CLASS XII ALL SUBJECTIVE ASSESSMENT TEST ASAT
 PHYSICS 202 203: CLASS XII ALL SUBJECTIVE ASSESSMENT TEST ASAT MM MARKS: 70] [TIME: 3 HOUR General Instructions: All the questions are compulsory Question no. to 8 consist of one marks questions, which
PHYSICS 202 203: CLASS XII ALL SUBJECTIVE ASSESSMENT TEST ASAT MM MARKS: 70] [TIME: 3 HOUR General Instructions: All the questions are compulsory Question no. to 8 consist of one marks questions, which
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 Subject Code: 17322 (EEM) Model Answers Page No: 1 of 19 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Subject Code: 17322 (EEM) Model Answers Page No: 1 of 19 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Sensors and Transducers. mywbut.com
 Sensors and Transducers 1 Objectives At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: describe the principle of operation of various sensors and transducers; namely.. Resistive Position Transducers.
Sensors and Transducers 1 Objectives At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: describe the principle of operation of various sensors and transducers; namely.. Resistive Position Transducers.
Alternating Current Circuits
 Alternating Current Circuits AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source. The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal and varies with time according
Alternating Current Circuits AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source. The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal and varies with time according
ELECTRONIC SENSORS PREAMBLE. This note gives a brief introduction to sensors. The focus is. on sensor mechanisms. It describes in general terms how
 ELECTRONIC SENSORS PREAMBLE This note gives a brief introduction to sensors. The focus is on sensor mechanisms. It describes in general terms how sensors work. It covers strain gage sensors in detail.
ELECTRONIC SENSORS PREAMBLE This note gives a brief introduction to sensors. The focus is on sensor mechanisms. It describes in general terms how sensors work. It covers strain gage sensors in detail.
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS LAB MANUAL
 ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS LAB MANUAL Prepared by B.SAIDAMMA R13 Regulation Any 10 of the following experiments are to be conducted 1. Calibration and Testing of single phase energy Meter 2. Calibration of
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS LAB MANUAL Prepared by B.SAIDAMMA R13 Regulation Any 10 of the following experiments are to be conducted 1. Calibration and Testing of single phase energy Meter 2. Calibration of
EE 441: Advanced computer programming & Data Structures. L T P ESE: 100 Sessional 50 Laboratory: 50
 EE 441: Advanced computer programming & Data Structures L T P 3-2 3 ESE: 100 Sessional 50 Laboratory: 50 1. Review of 1st semester IC course: Control structure, decision control structure, case control
EE 441: Advanced computer programming & Data Structures L T P 3-2 3 ESE: 100 Sessional 50 Laboratory: 50 1. Review of 1st semester IC course: Control structure, decision control structure, case control
PHYSICS Course Structure Units Topics Marks Electrostatics Current Electricity III Magnetic Effect of Current & Magnetism
 PHYSICS Course Structure Units Topics Marks I Chapter 1 Chapter 2 II Chapter 3 III Chapter 4 Chapter 5 IV Chapter 6 Chapter 7 V Chapter 8 VI Chapter 9 Electrostatics Electric Charges and Fields Electrostatic
PHYSICS Course Structure Units Topics Marks I Chapter 1 Chapter 2 II Chapter 3 III Chapter 4 Chapter 5 IV Chapter 6 Chapter 7 V Chapter 8 VI Chapter 9 Electrostatics Electric Charges and Fields Electrostatic
Module I Module I: traditional test instrumentation and acquisition systems. Prof. Ramat, Stefano
 Preparatory Course (task NA 3.6) Basics of experimental testing and theoretical background Module I Module I: traditional test instrumentation and acquisition systems Prof. Ramat, Stefano Transducers A
Preparatory Course (task NA 3.6) Basics of experimental testing and theoretical background Module I Module I: traditional test instrumentation and acquisition systems Prof. Ramat, Stefano Transducers A
e453.eps 1 Change (or the absolute value) in the measured physical variable 2 Change in the sensor property is translated into low-power-level
 3 Basic Phenomenon in Effect in Sensor Operation Sensors Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of
3 Basic Phenomenon in Effect in Sensor Operation Sensors Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of
2. (a) Differentiate between rare metal thermocouples and base metal thermocouples.
 Code No: R05410304 Set No. 1 1. (a) Distinguish between direct and indirect methods of measurement with suitable examples. (b) What are desired, modifying and interfering inputs for an instrumentation
Code No: R05410304 Set No. 1 1. (a) Distinguish between direct and indirect methods of measurement with suitable examples. (b) What are desired, modifying and interfering inputs for an instrumentation
Chapter wise Theoretical Important Questions in Physics for. Class-XII. Electrostatics
 Chapter wise Theoretical Important Questions in Physics for Class-XII Electrostatics 1. Derive an expression for the electric field at a point on the axial position of an electric dipole. 2. Derive an
Chapter wise Theoretical Important Questions in Physics for Class-XII Electrostatics 1. Derive an expression for the electric field at a point on the axial position of an electric dipole. 2. Derive an
Summary Notes ALTERNATING CURRENT AND VOLTAGE
 HIGHER CIRCUIT THEORY Wheatstone Bridge Circuit Any method of measuring resistance using an ammeter or voltmeter necessarily involves some error unless the resistances of the meters themselves are taken
HIGHER CIRCUIT THEORY Wheatstone Bridge Circuit Any method of measuring resistance using an ammeter or voltmeter necessarily involves some error unless the resistances of the meters themselves are taken
 Anna University B.E/B.Tech Degree Examination November/December 2010, Seventh Semester, Electrical and Electronics Engineering, EE1402-HIGH VOLTAGE ENGINEERING Answer all the questions. Part-A (10*2=20)
Anna University B.E/B.Tech Degree Examination November/December 2010, Seventh Semester, Electrical and Electronics Engineering, EE1402-HIGH VOLTAGE ENGINEERING Answer all the questions. Part-A (10*2=20)
1 Written and composed by: Prof. Muhammad Ali Malik (M. Phil. Physics), Govt. Degree College, Naushera
 ELECTROMAGNETISM Q # 1. Describe the properties of magnetic field due to current in a long straight conductor. Ans. When the heavy current is passed through a straight conductor: i. A magnetic field is
ELECTROMAGNETISM Q # 1. Describe the properties of magnetic field due to current in a long straight conductor. Ans. When the heavy current is passed through a straight conductor: i. A magnetic field is
Transducer. A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity. Transducer. (Input) Sensor.
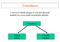 Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
Electrical Circuits Lab Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram
 Electrical Circuits Lab. 0903219 Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram - Simple steps to draw phasor diagram of a series RC circuit without memorizing: * Start with the quantity (voltage or current) that is
Electrical Circuits Lab. 0903219 Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram - Simple steps to draw phasor diagram of a series RC circuit without memorizing: * Start with the quantity (voltage or current) that is
Overview. Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples
 Intro to Sensors Overview Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples Sensors? American National Standards Institute A device
Intro to Sensors Overview Sensors? Commonly Detectable Phenomenon Physical Principles How Sensors Work? Need for Sensors Choosing a Sensor Examples Sensors? American National Standards Institute A device
BHARATHIAR UNIVERSITY, COIMBATORE B.Sc. PHYSICS DEGREE COURSE (Colleges) Course Title
 Part Ins. hrs / Week Dur.Hr CIA Marks Total Marks Credit Page 1 of 6 BHARATHIAR UNIVERSITY, COIMBATORE-641 046 B.Sc. PHYSICS DEGREE COURSE (Colleges) REVISED SCHEME OF EXAMINATIONS (CBCS PATTERN) (For
Part Ins. hrs / Week Dur.Hr CIA Marks Total Marks Credit Page 1 of 6 BHARATHIAR UNIVERSITY, COIMBATORE-641 046 B.Sc. PHYSICS DEGREE COURSE (Colleges) REVISED SCHEME OF EXAMINATIONS (CBCS PATTERN) (For
ME 515 Mechatronics. Overview of Computer based Control System
 ME 515 Mechatronics Introduction to Sensors I Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Faculty of Engineering University of Peradeniya Tel: 081239 (3627) Email: asangar@pdn.ac.lk Overview of Computer based Control
ME 515 Mechatronics Introduction to Sensors I Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Faculty of Engineering University of Peradeniya Tel: 081239 (3627) Email: asangar@pdn.ac.lk Overview of Computer based Control
SUGGESTED LESSON PLANS FOR PHY 097 SEMESTER NOV10 Text Book : PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS & ENGINEERS WITH MODERN PHYSICS BY GIANCOLI, FOURTH EDITION
 SUGGESTED LESSON PLANS FOR PHY 097 SEMESTER NOV0 Text Book : PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS & ENGINEERS WITH MODERN PHYSICS BY GIANCOLI, FOURTH EDITION Week Topics Section Page Hrs Sub-Topics WAVES AND OPTICS,.0
SUGGESTED LESSON PLANS FOR PHY 097 SEMESTER NOV0 Text Book : PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS & ENGINEERS WITH MODERN PHYSICS BY GIANCOLI, FOURTH EDITION Week Topics Section Page Hrs Sub-Topics WAVES AND OPTICS,.0
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL SYSTEMS Code : A70343 Class : IV B. Tech
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL SYSTEMS Code : A70343 Class : IV B. Tech
INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester. Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE
 INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE Detailed Contents Objectives Sensors and transducer Classification of transducers Temperature transducers Resistance
INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE Detailed Contents Objectives Sensors and transducer Classification of transducers Temperature transducers Resistance
Chapter wise Theoretical Important Questions in Physics for Class-XII
 Electrostatics- 1. Derive an expression for the electric field at a point on the axial position of an electric dipole. 2. Derive an expression for the electric field at a point on the equatorial position
Electrostatics- 1. Derive an expression for the electric field at a point on the axial position of an electric dipole. 2. Derive an expression for the electric field at a point on the equatorial position
e453.eps 1 Change (or the absolute value) in the measured physical variable 2 Change in the sensor property is translated into low-power-level
 3 Basic Phenomenon in Effect in Sensor Operation Measurement & Sensors Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering
3 Basic Phenomenon in Effect in Sensor Operation Measurement & Sensors Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering
ITL Public School First - Term( )
 Date: 9/09/6 ITL Public School First - Term(06-7) Class: XII Physics(04) Answer key Time: hrs M. M: 70 SECTION-A An ac source of voltage V =V 0 sin ωt is connected to an ideal capacitor. Draw graphs and
Date: 9/09/6 ITL Public School First - Term(06-7) Class: XII Physics(04) Answer key Time: hrs M. M: 70 SECTION-A An ac source of voltage V =V 0 sin ωt is connected to an ideal capacitor. Draw graphs and
Experimentation. Third Edition. Wheeler. Ahmad R. Ganji. School of Engineering. With Third Edition contributions by. V. V. Krishnan. Brian S.
 Introduction to Engineering Experimentation Third Edition Anthony J. Ahmad R. Wheeler Ganji School of Engineering San Francisco State University With Third Edition contributions by V. V. Krishnan San Francisco
Introduction to Engineering Experimentation Third Edition Anthony J. Ahmad R. Wheeler Ganji School of Engineering San Francisco State University With Third Edition contributions by V. V. Krishnan San Francisco
KCET PHYSICS 2014 Version Code: C-2
 KCET PHYSICS 04 Version Code: C-. A solenoid has length 0.4 cm, radius cm and 400 turns of wire. If a current of 5 A is passed through this solenoid, what is the magnetic field inside the solenoid? ().8
KCET PHYSICS 04 Version Code: C-. A solenoid has length 0.4 cm, radius cm and 400 turns of wire. If a current of 5 A is passed through this solenoid, what is the magnetic field inside the solenoid? ().8
Capacitor. Capacitor (Cont d)
 1 2 1 Capacitor Capacitor is a passive two-terminal component storing the energy in an electric field charged by the voltage across the dielectric. Fixed Polarized Variable Capacitance is the ratio of
1 2 1 Capacitor Capacitor is a passive two-terminal component storing the energy in an electric field charged by the voltage across the dielectric. Fixed Polarized Variable Capacitance is the ratio of
Measurements in Mechatronic design. Transducers
 Measurements in Mechatronic design Transducers Quantities Current Voltage Torque Force Magnetic flux Distance Temperature Measurement system Physical quanties Transducer Signal conditioning Measurement
Measurements in Mechatronic design Transducers Quantities Current Voltage Torque Force Magnetic flux Distance Temperature Measurement system Physical quanties Transducer Signal conditioning Measurement
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINERING DUNDIGAL ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINERING DUNDIGAL ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Course code : 067(07-08) Course title : High voltage engineering Course structure Lectures Tutorials Practical credits
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINERING DUNDIGAL ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Course code : 067(07-08) Course title : High voltage engineering Course structure Lectures Tutorials Practical credits
Force and Displacement Measurement
 Force and Displacement Measurement Prof. R.G. Longoria Updated Fall 20 Simple ways to measure a force http://scienceblogs.com/dotphysics/200/02/diy_force_probe.php Example: Key Force/Deflection measure
Force and Displacement Measurement Prof. R.G. Longoria Updated Fall 20 Simple ways to measure a force http://scienceblogs.com/dotphysics/200/02/diy_force_probe.php Example: Key Force/Deflection measure
MODEL QUESTION PAPER Higher Secondary Second Year Physics
 MODEL QUESTION PAPER Higher Secondary Second Year Physics Time : 3 hrs. Mark : 150 PART I Note : (i) Answer all the questions. 30 x 1 = 30 (ii) Choose and write the correct answer. (iii) Each question
MODEL QUESTION PAPER Higher Secondary Second Year Physics Time : 3 hrs. Mark : 150 PART I Note : (i) Answer all the questions. 30 x 1 = 30 (ii) Choose and write the correct answer. (iii) Each question
Module 3 Electrical Fundamentals
 3.1 Electron Theory Structure and distribution of electrical charges within: atoms, molecules, ions, compounds; Molecular structure of conductors, semiconductors and insulators. 3.2 Static Electricity
3.1 Electron Theory Structure and distribution of electrical charges within: atoms, molecules, ions, compounds; Molecular structure of conductors, semiconductors and insulators. 3.2 Static Electricity
Slide 1. Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic Fields Strain Pressure Displacement and Rotation Acceleration Electronic Sensors
 Slide 1 Electronic Sensors Electronic sensors can be designed to detect a variety of quantitative aspects of a given physical system. Such quantities include: Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic
Slide 1 Electronic Sensors Electronic sensors can be designed to detect a variety of quantitative aspects of a given physical system. Such quantities include: Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic
Lecture 19. Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity
 MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 19 Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity Measuring Accepleration and
MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 19 Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity Measuring Accepleration and
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE
 I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
Magnetic field outside a straight conductor (Item No.: P )
 Magnetic field outside a straight conductor (Item No.: P2430500) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Electricity and Magnetism Subtopic: Magnetic Field and
Magnetic field outside a straight conductor (Item No.: P2430500) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Electricity and Magnetism Subtopic: Magnetic Field and
Bridge Method. Bridge Method
 ridge Method EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement Class 7, March 13, 2015 1 ridge Method Diode bridge is an arrangement of four or more diodes for AC/DC full-wave rectifier. Component bridge methods
ridge Method EIE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement Class 7, March 13, 2015 1 ridge Method Diode bridge is an arrangement of four or more diodes for AC/DC full-wave rectifier. Component bridge methods
Course Name: Sensor and Transducer Course Code: EE 802B Credit: 3
 Course Name: Sensor and Transducer Course Code: EE 802B Credit: 3 Prerequisites: Sl. No. Subject Description Level of Study 01 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering 02 Electrical & Electronics Measurement
Course Name: Sensor and Transducer Course Code: EE 802B Credit: 3 Prerequisites: Sl. No. Subject Description Level of Study 01 Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering 02 Electrical & Electronics Measurement
DUBLIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Kevin Street, Dublin 8.
 Question Sheet Page 1 of 5 Instructions for the student: Question 1 is compulsory [40 marks] Attempt any two other questions [30 marks per question] The following must be made available during the examination:
Question Sheet Page 1 of 5 Instructions for the student: Question 1 is compulsory [40 marks] Attempt any two other questions [30 marks per question] The following must be made available during the examination:
10 Measurement of Acceleration, Vibration and Shock Transducers
 Chapter 10: Acceleration, Vibration and Shock Measurement Dr. Lufti Al-Sharif (Revision 1.0, 25/5/2008) 1. Introduction This chapter examines the measurement of acceleration, vibration and shock. It starts
Chapter 10: Acceleration, Vibration and Shock Measurement Dr. Lufti Al-Sharif (Revision 1.0, 25/5/2008) 1. Introduction This chapter examines the measurement of acceleration, vibration and shock. It starts
Conventional Paper-I Part A. 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy
 EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
Curriculum Interpretation Electricity and Magnetism. Lee Wai Kit
 Curriculum Interpretation Electricity and Magnetism Lee Wai Kit Electricity and Magnetism 4.1 Electrostatics 4.2 Circuits and domestic electricity 4.3 Electromagnetism 4.1 Electrostatics electric charges
Curriculum Interpretation Electricity and Magnetism Lee Wai Kit Electricity and Magnetism 4.1 Electrostatics 4.2 Circuits and domestic electricity 4.3 Electromagnetism 4.1 Electrostatics electric charges
Fatima Michael College of Engineering & Technology
 ANNA UNIVERSITY AFFILIATED COLLEGES BE EEE SEMESTER VI EE2353 - HIGH VOLTAGE ENGINEERING UNIT IOVER VOLTAGES IN ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEMS 1. What is surge arrester? 2. Name the sources of switching surges.
ANNA UNIVERSITY AFFILIATED COLLEGES BE EEE SEMESTER VI EE2353 - HIGH VOLTAGE ENGINEERING UNIT IOVER VOLTAGES IN ELECTRICAL POWER SYSTEMS 1. What is surge arrester? 2. Name the sources of switching surges.
EXEMPLAR NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE NQF LEVEL 3 ( ) (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00
 NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE NQF LEVEL 3 2008 (12041002) (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 EXEMPLAR This question paper consists of 7 pages. EXEMPLAR -2- NC(V) TIME: 3 HOURS
NATIONAL CERTIFICATE (VOCATIONAL) ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE NQF LEVEL 3 2008 (12041002) (X-Paper) 09:00 12:00 EXEMPLAR This question paper consists of 7 pages. EXEMPLAR -2- NC(V) TIME: 3 HOURS
The secondary winding have equal no. of turns. The secondary windings are placed identically on either side of the primary winding.
 UNIT 4 DISPLACEMENT MEASURMENT Electrical comparator Working principle of Electrical comparators: These instruments are based on the theory of Wheatstone A.C. Bridge. When the bridge is electrically balanced,
UNIT 4 DISPLACEMENT MEASURMENT Electrical comparator Working principle of Electrical comparators: These instruments are based on the theory of Wheatstone A.C. Bridge. When the bridge is electrically balanced,
Electromagnetism Notes 1 Magnetic Fields
 Electromagnetism Notes 1 Magnetic Fields Magnets can or other magnets. They are able to exert forces on each other without touching because they are surrounded by. Magnetic Flux refers to Areas with many
Electromagnetism Notes 1 Magnetic Fields Magnets can or other magnets. They are able to exert forces on each other without touching because they are surrounded by. Magnetic Flux refers to Areas with many
Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts. Measurement System Components. Sensor - Transducer. Signal-conditioning. Output. Feedback-control
 Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts Measurement System Components Sensor - Transducer Signal-conditioning Output Feedback-control MeasurementSystemConcepts.doc 8/27/2008 12:03 PM Page 1 Example: Sensor/ Transducer
Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts Measurement System Components Sensor - Transducer Signal-conditioning Output Feedback-control MeasurementSystemConcepts.doc 8/27/2008 12:03 PM Page 1 Example: Sensor/ Transducer
Lecture - 2A Instruments-I
 Engineering Metrology Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering & Design Programme Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Dr. Amandeep Singh Oberoi Department of Industrial & Production Engineering
Engineering Metrology Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering & Design Programme Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Dr. Amandeep Singh Oberoi Department of Industrial & Production Engineering
Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance
 Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance First Six-Weeks Second Six-Weeks Third Six-Weeks Lab safety Lab practices and ethical practices Math and Calculus
Mansfield Independent School District AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism Year at a Glance First Six-Weeks Second Six-Weeks Third Six-Weeks Lab safety Lab practices and ethical practices Math and Calculus
AP Physics C. Magnetism - Term 4
 AP Physics C Magnetism - Term 4 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the world
AP Physics C Magnetism - Term 4 Interest Packet Term Introduction: AP Physics has been specifically designed to build on physics knowledge previously acquired for a more in depth understanding of the world
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6502 -INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION I Regulation 2013
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK V SEMESTER EI6502 -INDUSTRIAL INSTRUMENTATION I Regulation 2013
Power and Energy Measurement
 Power and Energy Measurement ENE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement Class 11, February 4, 2009 werapon.chi@kmutt.ac.th 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction
Power and Energy Measurement ENE 240 Electrical and Electronic Measurement Class 11, February 4, 2009 werapon.chi@kmutt.ac.th 1 Work, Energy and Power Work is an activity of force and movement in the direction
Conventional Paper I-2010
 Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE
 Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Sol: Semiconductor diode.
 48 49 1. What is the resistance value of a resistor of colour code Brown, Black, Red and silver? Sol: Brown-1, Black-0, Red-2, Silver- 10%. Resistance, R = 10 X 10-2 ±10Ω. 2. Mention a non-ohmic device.
48 49 1. What is the resistance value of a resistor of colour code Brown, Black, Red and silver? Sol: Brown-1, Black-0, Red-2, Silver- 10%. Resistance, R = 10 X 10-2 ±10Ω. 2. Mention a non-ohmic device.
CBSE_2014_SET_3 Physics
 CBSE_2014_SET_3 Physics 1. A conducting loop is held below a current carrying wire PQ as shown. Predict the direction of the induced current in the loop when the current in the wire is constantly increasing.
CBSE_2014_SET_3 Physics 1. A conducting loop is held below a current carrying wire PQ as shown. Predict the direction of the induced current in the loop when the current in the wire is constantly increasing.
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : HIGH VOLTAGE ENGINEERING Course Code
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : HIGH VOLTAGE ENGINEERING Course Code
LABORATORY MANUAL MEASUREMENTS & INSTRUMENTATION (ME- 318-F)
 LABORATORY MANUAL MEASUREMENTS & INSTRUMENTATION (ME- 318-F) LIST OF THE EXPERIMENT S. NO. NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT PAGE NO FROM TO 1. To measure stress and strain using strain gauge mounted on a cantilever
LABORATORY MANUAL MEASUREMENTS & INSTRUMENTATION (ME- 318-F) LIST OF THE EXPERIMENT S. NO. NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT PAGE NO FROM TO 1. To measure stress and strain using strain gauge mounted on a cantilever
