Plasma Modulation of Harmonic Emission Spectra from Laser-Dense Plasma Interactions
|
|
|
- Garry Morton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Plasa Modulation of Haronic Eission Spectra fro Laser-Dense Plasa Interactions R. Ondarza-Rovira and T.J.M. Boyd 2 ININ, A.P , México 80, Distrito Federal, Mexico; ondarza@nuclear.inin.x 2 Centre for Physics, University of Essex, Wivenhoe Park, Colchester CO4 3SQ, UK We report results fro PIC siulations of the interaction of intense laser light with overdense plasa designed to exaine the effects of plasa waves generated by pulses of fast electrons on high haronic eission fro the plasa. We show that the eission spectru is odulated at the plasa frequency and identify cobinations of paraeters and circustances favourable for odulation. In particular the observed odulation is shown to depend not only on the chosen plasa electron density and intensity of the incident light but on the density profile and pulse shape.. Introduction. The generation of ultiple haronics of the incident light in laser-plasa interactions is a topic that has proved to be of enduring interest, not only because of its intrinsic iportance but for its potential as a diagnostic of conditions at the target surface and as a eans of generating intense coherent pulses at short wavelengths. Distinct echaniss are responsible for haronic generation across different intensity ranges and target characteristics. For gas-jet targets haronics up to several hundred are generated through the nonlinear response of atoic electrons. However their intensities are liited by field ionization. No such constraint applies to haronic generation when intense laser pulses are focussed on the surface of solid targets. This was first observed in experients with nanosecond pulses [] and subsequently detected for picosecond pulse lengths [2]. Conditions in short-pulse experients ensured two prerequisites essential for high haronic generation, naely an electron density uch greater than the critical density, n c, cobined with high brightness of the source. Using light of intensity I and wavelength λ L, at values of I λ 2 L in the range W c 2 µ 2 Norreys et al. [2] detected haronics up to the 75th (with conversion efficiency of 0 6 ) for.053 µ wavelength light interacting with a solid target. Subsequently haronic generation using pulse lengths of 00 fs has been observed [3]. Such short pulses with no significant pre-pulse present, create plasa free fro extensive underdense coronal regions and with extreely steep density gradients at the plasa surface. In the absence of any convincing theoretical odel for high haronic generation in this paraeter regie, particle-in-cell (PIC) siulations have proved invaluable in understanding and characterizing the eission. Gibbon [4] used PIC siulations to identify the physical echanis underlying haronic generation, showing that the current sources generating the haronics are localized just
2 within the overdense plasa boundary. Gibbon found an epirical expression for the efficiency of high-order haronic generation η (I 8 λ 2 L) 2 (/0) 5 where I 8 denotes light intensity in units of 0 8 W c 2, with λ L in icrons and is the haronic nuber. Useful as this scaling is, it akes no allowance for any dependence of haronic power levels on the plasa electron density [5]. Alternative scaling laws have been proposed by Baeva et al. [6]. on the basis of ultrarelativistic siilarity theory, independent of details of the interaction. These authors report a scaling in which the spectru decays with haronic nuber as 8/3 with a cut-off at = 8 α γax 3 where α is of order and γ is the axiu value of the relativistic factor associated with the otion of the plasa surface. Boyd and Ondarza-Rovira [7] showed that the haronic spectru is affected by plasa line eission which has been seen in a nuber of experients [8]. Moreover they reported for the first tie an unexpected feature in the spectru which they attributed to the effect of the plasa wave on neighbouring haronic lines. This so-called cobination line is in effect a footprint of the odulation subsequently observed experientally [3,9]. In this Letter we investigate these odulation effects using a odel in which the source of the odulation is identified as plasa waves generated in the supra-dense target plasa by pulses of re-entrant electrons. 2. Nuerical siulations. It is iportant at the outset to underline a liitation of our, or for that atter ost other, PIC siulations. We do not attept to odel the ionization of target aterial but treat instead the interaction of a laser pulse of length τ p with a plasa slab of initially unifor density, apart fro an interface at the front end. This vacuu-plasa interface is characterised by a density profile with scale length that is soe prescribed fraction of a wavelength across the rap. The -/2D PIC code we use ebeds the Bourdier technique [0] to allow for oblique incidence. The siulation plasa can be up to ten wavelengths in extent. Vacuu gaps extend fro both the front of the rap and the planar rear surface of the plasa to the walls of the siulation box to allow for particle and wave propagation. The initial electron teperature was chosen to be 00 ev and we used gaussian pulses of variable length and profile. The noralized quiver oentu a (I 8 λ 2 L) /2 lay in the range with electron densities between 0 n c and 64 n c. The reflected eission spectra showing the relative strength of the different oscillation odes is deterined fro the haronic contents of the reflected electric field at the vacuu gap, noralised to the fundaental. Our earlier work [5,7] established that plasa line eission was present alongside the haronics of the incident light. The source of the plasa eission was identified as plasa waves excited in the supra-dense plasa by jets of Brunel-accelerated electrons fored when p-polarized light is obliquely incident on the plasa surface []. The re-entrant electrons bunch to generate plasa oscillations at the surface before penetrating the overdense plasa. Plasa oscillations at the target surface couple efficiently to the radiation field. In Fig. we reproduce the effect for a plasa with slab electron density n e = 20 n c. Fig. a plots electron density contours across a 0.λ L section of the plasa target (3λ L wide in this siulation). The striations correspond to the pulses of fast electrons that excite plasa oscillations. A coparable density bunching effect and corresponding excitation of plasa oscillations has been reported by Quéré et al. [2] but in this case for a foil only λ L /5 thick. 2
3 noralised Fourier density In Fig. b we present a Fourier analysis of the nubers of electrons at a point just inside the siulation plasa for the paraeters used in Fig. a. Envelopes are sketched over the Fourier coponents of the density showing approxiately 3 odulation cycles across a span of 4 haronics, suggestive of odulation at the plasa frequency ω p = 4.5 ω L where ω L is the frequency of the incident light. This odulation in turn is reflected in the power spectra. <5 5-7 e-0 e-02 n e/nc 8-20 >20 e-03 e ' Figure : Plasa electron density contours for a target plasa density n e /n c = 20, a 0 = 0.5, with angle of incidence θ = 23. The tie-scale corresponds to 3 laser periods and the section of plasa shown extends over 0. λ L. Fourier decoposition of the electron density at a point x = 0. λ L inside the plasa. To explore the odulation of the eission spectru we carried out PIC siulations across a wide paraeter range that included not only the intensity of the incident light and the density of the target plasa but both pulse shape and length and the steepness of the density gradient at the front edge of the plasa box. Insofar as the behaviour of the odulation as a function of laser intensity is concerned, our conclusions are broadly in line with those of Watts et al. [9], naely the higher the intensity, the ore pronounced the odulation, albeit for different reasons. In our case at values of a 0 significantly below the range of interest ( ), the nuber of haronics with intensities above threshold (in our case 0 6 ) is correspondingly reduced. This in turn is reflected in the nuber of odulation cycles observed, or indeed by their disappearance altogether. For the odel we have adopted there is a ore fundaental reason why odulation should disappear at lower laser intensity. Since the flux of electrons injected into the target plasa depends critically on intensity, a diinished flux in turn eans that the level of plasa waves excited in the overdense plasa is correspondingly weaker. A selection of spectra is shown in Fig. 2. Figs. 2a and 2b use a 0 = 0.5, n e = 0 n c and a 0 = 0.6, n e = 9 n c, respectively, where θ = 23 o is the angle between the wave propagation vector and the noral to the target surface. For Fig. 2c, a 0 =.0, n e = 40 n c and in the highest density run shown in Fig. 2d, a 0 = 0.5, n e = 64 n c. In all four cases the pulse length used was 7 fs, chosen to iniise noise fro plasa line eission. To highlight the effect we show envelopes across the bands of odulation for P /P > 0 6 and for values of >.5 (ω p /ω L ). For the paraeters used in Figs. 2a,b and c the PIC results show 3 or 4 clear odulation cycles with average odulation frequencies 3.3 ω L, 4.3 ω L and 6.3 ω L respectively, values that correspond 3
4 closely to the plasa frequencies for each of these densities. Fig. 2c shows soe fine structure in the odulation across the range = 0 to = 8. In this case there is soe contribution fro second haronic plasa eission which perturbs the eission spectra slightly in the neighbourhood of = 2. The choice of paraeters in Fig. 2d cobines relatively high density and oderate light intensity, ensuring that the plasa wave is not too strongly driven. For n e /n c = 64 the plasa line is centred at = 8 with the blue half of the odulation structure clearly defined (haronic lines 9 to 2). The red wing is cut off at = 6, asked by the relative strength of the fourth and fifth haronic lines. Higher laser intensities are needed to extend the range of odulation at higher densities. This in turn results in the Languir waves being ore strongly driven and, at the sae tie, significantly broadened. A siple linear estiate of the bandwidth of Languir waves excited by a bea of fast electrons is given by ω ( V b /v b ) (n e /n c ) /2 ω L for a bea velocity v b with velocity spread V b. Broadened plasa line eission in turn affects neighbouring haronic lines P/P e-05 P/P e-05 e-07 e-08 e-07 e e e-0 e-02 ( c ) e-0 e-02 (d) e-03 e-03 P/P e-04 e-05 P/P e-04 e-05 e-07 e-07 e-08 e-08 e e Figure 2: Haronic odulation for a laser pulse with τ p = 7 fs and λ L = µ: a 0 = 0.5, n e /n c = 0, a 0 = 0.6, n e /n c = 9, (c) a 0 =.0, n e /n c = 40 and (d) a 0 = 0.5, n e /n c = 64. Envelopes over the haronics have been added to indicate the respective odulation frequencies. Fig. 3 illustrates the susceptibility of odulation to pulse shape and steepness of the density gradient at the front edge of the plasa box. Essentially steepening the pulse over the sin 2 profile used to obtain the data in Fig. 2 iproves the definition of the odulation (Fig. 3a). Varying 4
5 the pulse length τ p on the other hand has relatively little effect on the odulation as such, always provided the pulse is sufficiently longer than the growth tie, t g of the electron-generated plasa waves. If we ake use of the estiate given by Boyd and Ondarza-Rovira [7], this eans τ p > 0 (n c /n b )(n e /n c ) /2 ( V b /v b ) 2 τ L where n b is the density of the electron pulse exciting the plasa waves. For the paraeters in these siulations this iplies τ p > 0fs. e-0 e-02 e-02 P/P e-03 e-04 e-05 P/P e-04 e-08 e-07 e e Figure 3: Haronic odulation for a laser pulse with a 0 =.0, τ p = 30 fs, and n e /n c = 30, for a steepened pulse envelope; effectiveness of a density rap in suppressing odulation for a siulation with a 0 = 0.6, τ p = 30 fs and n e /n c = 6 for a density rap of width = 0.6 λ L. As one ight expect relaxing the steepness of the density gradient has the effect of weakening the odulation. This supports the observation by Watts et al. that the introduction of a density rap suppressed the odulation in their spectra. With a density rap present, electrons injected into the plasa excite plasa oscillations across the rap. Thus, for exaple for the paraeters used in Fig. 3b, n e = 6 n c, a 0 = 0.6, the siulations now show an enhanced = 3 line consistent with additional plasa excitation at n e = 9 n c in contrast to the sharp boundary case where only plasa oscillations with ω p = 4 ω L are present. A further distinction to be drawn is that the coupling of plasa waves to the radiation field is proportionately weaker in the case of an extensive rap. Note that the disappearance of odulation is not the only difference between the two spectra. Whereas the axiu over threshold (P /P 0 6 ) in Fig. 2b is 24, the result in Fig. 3b for a rap 0.6 λ L in width shows a range alost twice this value. Precisely why a rap should have this effect is not clear. The odulation first reported by Watts et al. was recorded over a range of about 5 haronics. Their spectra showed a distinct if irregular odulation with a frequency of between 2 and 4 ties that of the incident light. A less pronounced effect was subsequently found by Teubner et al. in experients using shorter pulses (typically 00 fs) and reduced intensities. Over a haronic range of about 0 lines they noted anoalies in eission though it is not possible to identify a odulation frequency over such a liited range. PIC siulations were carried out by both groups with a view to interpreting their data. The siulated spectru in [9] showed an average odulation frequency of 5-6, as against the 2-4 observed. Both sets of authors interpreted the odulation in ters of the so-called oscillating irror odel proposed by Bulanov et al. [3]. The ain stubling block to a fuller understanding of these anoalies is the uncertainty over 5
6 the ionization state of the target and hence the electron density. We illustrate in Fig. 4 data points fro our siulated spectra alongside the haronic efficiency easured in [3] for carbon and glass targets using frequency-doubled light fro a Ti:sapphire laser (395 n) at an intensity W c 2. Though this generated a relatively restricted range of soe 4 haronics, these experients were characterised not only by clean experiental conditions but by the choice of target aterials, both dielectric and etallic. In Fig. 4a we show the results of a siulation in which n e /n c = 30 for which the plasa line appears at 5.5 ω L. Fro the pattern found in Fig. 2 we should expect to see the first iniu in the odulated spectru at = 9 and so it appears. We have added data points fro the haronic spectru easured by Teubner et al. for a carbon target for coparison. In Fig. 4b we show results across the sae spectral range for a siulation with n e /n c = 45 which is characterised by a iniu at = and, by way of coparison, the easured spectru in this range for a glass target. In each case the haronics, siulated and observed, show a broadly coparable dependence on haronic nuber. However, in aking these coparisons we stress that the electron densities corresponding to the easured spectra were not deterined experientally. e-04 e-03 e-05 e-04 P/P P/P e-05 e e Figure 4: Haronic reflected power fro PIC siulations and fro experient: solid circles ( ) correspond to: a 0 =.0, λ L = µ, and n e /n c = 30, open circles ( ) correspond to eission easured fro a carbon target [3], : a 0 =.0, λ L = µ, n e /n c = 45 and τ p = 7 fs; : correspond to eission found fro a glass target [3]. 3. Conclusions. Our siulations lead us to conclude that the odulations we see in the haronic spectru ste fro the effect of plasa waves excited in the plasa slab. We have shown that the odulation frequency varies with the plasa density as n e /2 over a wide range. The odulation is evident for choices of intensity and pulse length for which plasa line eission does not distort the spectru to any arked degree. On this interpretation the odulation frequency affords a easure of plasa density. The presence of a density rap a fraction of a wavelength thick appears to suppress the odulation in agreeent with the observation by Watts et al. This finding is consistent with our interpretation, in that, in the presence of a rap there is no longer a unique plasa density at 6
7 the surface. The question ay properly be asked as to whether results obtained fro a PIC code such as that used in this work, liited in its diensionality, can reliably describe the physics of this interaction. In particular, should one expect the odulation effect to persist in three diensions? While it would be incautious to press this clai too strongly, we are encouraged, not least by the coparisons drawn fro Fig. 4 to believe that it ight. Acknowledgents. One of us (ROR) acknowledges support fro CONACyT under Contract No F. T.J.M. Boyd is grateful to G.J. Tallents for a helpful discussion. [] R.L. Caran, D.W. Forslund and J.M. Kindel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 46 (), 29 (98). [2] P.A. Norreys et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 (), 832 (996). [3] U. Teubner et al., Phys. Rev. A 67, 0386 (2003). [4] P. Gibbon, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76 (), 50 (996). [5] T.J.M. Boyd and R. Ondarza-Rovira, in Proceedings of the International Conference on Plasa Physics, Nagoya, Septeber 996, edited by H. Sugai and T. Hayashi (Japan Society of Plasa Science, Nagoya, 997). Vol. 2, p. 78; T.J.M. Boyd and R. Ondarza-Rovira, Rev. Mex. Fís. 52 (2), 43 (2006). [6] T. Baeva, S. Gordienko, and A. Pukhov, Phys. Rev. E 74, (2006); S. Gordienko et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 (), 5002 (2004). [7] T.J.M. Boyd and R. Ondarza-Rovira, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85 (7), 440 (2000). [8] U. Teubner et al., Optics Co. 44, 27 (997); D. von der Linde, Appl. Phys. B 68, 35 (999). [9] I. Watts et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 (5), 5500 (2002). [0] A. Bourdier, Phys. Fluids 26, 804 (983). [] F. Brunel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 59 (), 52 (987). [2] F. Quéré et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, (2006). [3] S.V. Bulanov and N.M. Nauova, and F. Pegoraro, Phys. Plasas (3), 745 (994). 7
Modulation of Harmonic Emission Spectra from Intense Laser-Plasma Interactions
 Modulation of Haronic Eission Spectra fro Intense Laser-Plasa Interactions T.J.M. Boyd and R. Ondarza-Rovira 2 Centre for Physics, University of Essex, Wivenhoe Park, Colchester CO4 3SQ, U.K. 2 ININ, A.P.
Modulation of Haronic Eission Spectra fro Intense Laser-Plasa Interactions T.J.M. Boyd and R. Ondarza-Rovira 2 Centre for Physics, University of Essex, Wivenhoe Park, Colchester CO4 3SQ, U.K. 2 ININ, A.P.
2 Q 10. Likewise, in case of multiple particles, the corresponding density in 2 must be averaged over all
 Lecture 6 Introduction to kinetic theory of plasa waves Introduction to kinetic theory So far we have been odeling plasa dynaics using fluid equations. The assuption has been that the pressure can be either
Lecture 6 Introduction to kinetic theory of plasa waves Introduction to kinetic theory So far we have been odeling plasa dynaics using fluid equations. The assuption has been that the pressure can be either
The source of THz radiation based on dielectric waveguide excited by sequence of electron bunches
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The source of THz radiation based on dielectric waveguide excited by sequence of electron bunches To cite this article: A M Altark and A D Kanareykin
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The source of THz radiation based on dielectric waveguide excited by sequence of electron bunches To cite this article: A M Altark and A D Kanareykin
Measuring orbital angular momentum superpositions of light by mode transformation
 CHAPTER 7 Measuring orbital angular oentu superpositions of light by ode transforation In chapter 6 we reported on a ethod for easuring orbital angular oentu (OAM) states of light based on the transforation
CHAPTER 7 Measuring orbital angular oentu superpositions of light by ode transforation In chapter 6 we reported on a ethod for easuring orbital angular oentu (OAM) states of light based on the transforation
External Transverse Direct Current Magnetic Field Effect On Optical Emission Of a Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Argon Plasma Jet
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 014 Available online at www.irjabs.co ISSN 51-838X / Vol, 8 (7): 944-950 Science Explorer Publications External Transverse Direct Current Magnetic
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 014 Available online at www.irjabs.co ISSN 51-838X / Vol, 8 (7): 944-950 Science Explorer Publications External Transverse Direct Current Magnetic
Optical Properties of Plasmas of High-Z Elements
 Forschungszentru Karlsruhe Techni und Uwelt Wissenschaftlishe Berichte FZK Optical Properties of Plasas of High-Z Eleents V.Tolach 1, G.Miloshevsy 1, H.Würz Project Kernfusion 1 Heat and Mass Transfer
Forschungszentru Karlsruhe Techni und Uwelt Wissenschaftlishe Berichte FZK Optical Properties of Plasas of High-Z Eleents V.Tolach 1, G.Miloshevsy 1, H.Würz Project Kernfusion 1 Heat and Mass Transfer
THERMAL ENDURANCE OF UNREINFORCED UNSATURATED POLYESTERS AND VINYL ESTER RESINS = (1) ln = COMPOSITES & POLYCON 2009
 Aerican Coposites Manufacturers Association January 15-17, 29 Tapa, FL USA Abstract THERMAL ENDURANCE OF UNREINFORCED UNSATURATED POLYESTERS AND VINYL ESTER RESINS by Thore M. Klaveness, Reichhold AS In
Aerican Coposites Manufacturers Association January 15-17, 29 Tapa, FL USA Abstract THERMAL ENDURANCE OF UNREINFORCED UNSATURATED POLYESTERS AND VINYL ESTER RESINS by Thore M. Klaveness, Reichhold AS In
Chapter 2 General Properties of Radiation Detectors
 Med Phys 4RA3, 4RB3/6R3 Radioisotopes and Radiation Methodology -1 Chapter General Properties of Radiation Detectors Ionizing radiation is ost coonly detected by the charge created when radiation interacts
Med Phys 4RA3, 4RB3/6R3 Radioisotopes and Radiation Methodology -1 Chapter General Properties of Radiation Detectors Ionizing radiation is ost coonly detected by the charge created when radiation interacts
Figure 1: Equivalent electric (RC) circuit of a neurons membrane
 Exercise: Leaky integrate and fire odel of neural spike generation This exercise investigates a siplified odel of how neurons spike in response to current inputs, one of the ost fundaental properties of
Exercise: Leaky integrate and fire odel of neural spike generation This exercise investigates a siplified odel of how neurons spike in response to current inputs, one of the ost fundaental properties of
NEGATIVE-INDEX MEDIA FOR MATTER WAVES
 NEGATIVE-INDEX MEDIA FOR MATTER WAVES F. PERALES, V. BOCVARSKI, J. BAUDON *, M. HAMAMDA, J. GRUCKER, G. DUTIER, C. MAINOS, M. BOUSTIMI and M. DUCLOY Laboratoire de Physique des Lasers, CNRS UMR 7538, Université
NEGATIVE-INDEX MEDIA FOR MATTER WAVES F. PERALES, V. BOCVARSKI, J. BAUDON *, M. HAMAMDA, J. GRUCKER, G. DUTIER, C. MAINOS, M. BOUSTIMI and M. DUCLOY Laboratoire de Physique des Lasers, CNRS UMR 7538, Université
PHYS 102 Previous Exam Problems
 PHYS 102 Previous Exa Probles CHAPTER 16 Waves Transverse waves on a string Power Interference of waves Standing waves Resonance on a string 1. The displaceent of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal
PHYS 102 Previous Exa Probles CHAPTER 16 Waves Transverse waves on a string Power Interference of waves Standing waves Resonance on a string 1. The displaceent of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal
Easy Evaluation Method of Self-Compactability of Self-Compacting Concrete
 Easy Evaluation Method of Self-Copactability of Self-Copacting Concrete Masanori Maruoka 1 Hiroi Fujiwara 2 Erika Ogura 3 Nobu Watanabe 4 T 11 ABSTRACT The use of self-copacting concrete (SCC) in construction
Easy Evaluation Method of Self-Copactability of Self-Copacting Concrete Masanori Maruoka 1 Hiroi Fujiwara 2 Erika Ogura 3 Nobu Watanabe 4 T 11 ABSTRACT The use of self-copacting concrete (SCC) in construction
Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyramidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular Cross-Sectional Area
 Proceedings of the 006 WSEAS/IASME International Conference on Heat and Mass Transfer, Miai, Florida, USA, January 18-0, 006 (pp13-18) Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyraidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular
Proceedings of the 006 WSEAS/IASME International Conference on Heat and Mass Transfer, Miai, Florida, USA, January 18-0, 006 (pp13-18) Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyraidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular
Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measurement Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES
 Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measureent Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES Belinda Lipa Codar Ocean Sensors 15 La Sandra Way, Portola Valley, CA 98 blipa@pogo.co
Proc. of the IEEE/OES Seventh Working Conference on Current Measureent Technology UNCERTAINTIES IN SEASONDE CURRENT VELOCITIES Belinda Lipa Codar Ocean Sensors 15 La Sandra Way, Portola Valley, CA 98 blipa@pogo.co
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electroagnetic Waves Physics 4 Maxwell s Equations Maxwell s equations suarize the relationships between electric and agnetic fields. A ajor consequence of these equations is that an accelerating charge
Electroagnetic Waves Physics 4 Maxwell s Equations Maxwell s equations suarize the relationships between electric and agnetic fields. A ajor consequence of these equations is that an accelerating charge
MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on Deceber 15, 2014 Partners Naes: Grade: EXPERIMENT 8 Electron Beas 0. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. Nae the 2 forces that are equated in order to derive the charge to
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on Deceber 15, 2014 Partners Naes: Grade: EXPERIMENT 8 Electron Beas 0. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. Nae the 2 forces that are equated in order to derive the charge to
EVAPORATION EFFECT IN NONLINEAR PENETRATION OF HIGH ENERGY BEAM DRILLING
 1 Journal of Marine Science and echnology, Vol. 17, No., pp. 1-17 (9) EVAPORAION EFFEC IN NONLINEAR PENERAION OF HIGH ENERGY BEAM DRILLING Je-Ee Ho* and Chen-Lung Yen** Key words: enthalpy ethod. ABSRAC
1 Journal of Marine Science and echnology, Vol. 17, No., pp. 1-17 (9) EVAPORAION EFFEC IN NONLINEAR PENERAION OF HIGH ENERGY BEAM DRILLING Je-Ee Ho* and Chen-Lung Yen** Key words: enthalpy ethod. ABSRAC
LONGITUDINAL EFFECTS AND FOCUSING IN SPACE-CHARGE DOMINATED BEAMS. John Richardson Harris
 ONGITUDINA EFFECTS AND FOCUSING IN SPACE-CHARGE DOMINATED BEAMS by John Richardson Harris Thesis subitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of the University of Maryland, College Park in partial fulfillent
ONGITUDINA EFFECTS AND FOCUSING IN SPACE-CHARGE DOMINATED BEAMS by John Richardson Harris Thesis subitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of the University of Maryland, College Park in partial fulfillent
III.H Zeroth Order Hydrodynamics
 III.H Zeroth Order Hydrodynaics As a first approxiation, we shall assue that in local equilibriu, the density f 1 at each point in space can be represented as in eq.iii.56, i.e. f 0 1 p, q, t = n q, t
III.H Zeroth Order Hydrodynaics As a first approxiation, we shall assue that in local equilibriu, the density f 1 at each point in space can be represented as in eq.iii.56, i.e. f 0 1 p, q, t = n q, t
UNCERTAINTIES IN THE APPLICATION OF ATMOSPHERIC AND ALTITUDE CORRECTIONS AS RECOMMENDED IN IEC STANDARDS
 Paper Published on the16th International Syposiu on High Voltage Engineering, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009 UNCERTAINTIES IN THE APPLICATION OF ATMOSPHERIC AND ALTITUDE CORRECTIONS AS RECOMMENDED IN IEC
Paper Published on the16th International Syposiu on High Voltage Engineering, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009 UNCERTAINTIES IN THE APPLICATION OF ATMOSPHERIC AND ALTITUDE CORRECTIONS AS RECOMMENDED IN IEC
Chapter 4: Hypothesis of Diffusion-Limited Growth
 Suary This section derives a useful equation to predict quantu dot size evolution under typical organoetallic synthesis conditions that are used to achieve narrow size distributions. Assuing diffusion-controlled
Suary This section derives a useful equation to predict quantu dot size evolution under typical organoetallic synthesis conditions that are used to achieve narrow size distributions. Assuing diffusion-controlled
DETECTION OF NONLINEARITY IN VIBRATIONAL SYSTEMS USING THE SECOND TIME DERIVATIVE OF ABSOLUTE ACCELERATION
 DETECTION OF NONLINEARITY IN VIBRATIONAL SYSTEMS USING THE SECOND TIME DERIVATIVE OF ABSOLUTE ACCELERATION Masaki WAKUI 1 and Jun IYAMA and Tsuyoshi KOYAMA 3 ABSTRACT This paper shows a criteria to detect
DETECTION OF NONLINEARITY IN VIBRATIONAL SYSTEMS USING THE SECOND TIME DERIVATIVE OF ABSOLUTE ACCELERATION Masaki WAKUI 1 and Jun IYAMA and Tsuyoshi KOYAMA 3 ABSTRACT This paper shows a criteria to detect
13 Harmonic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization
 3 Haronic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization. Dirac cae up with a ore elegant way to solve the haronic oscillator proble. We will now study this approach. The
3 Haronic oscillator revisited: Dirac s approach and introduction to Second Quantization. Dirac cae up with a ore elegant way to solve the haronic oscillator proble. We will now study this approach. The
Title Surface Interaction under Oblique Intense. Author(s) Ruhl, H.; Sentoku, Y.; Mima, K.; Ta. Citation Physical Review Letters. 82(4) P.
 Title Collimated Electron Jets by Surface Interaction under Oblique Intense I Author(s) Ruhl, H.; Sentoku, Y.; Mima, K.; Ta Citation Physical Review Letters. 82(4) P.74 Issue 1999-01-25 Date Text Version
Title Collimated Electron Jets by Surface Interaction under Oblique Intense I Author(s) Ruhl, H.; Sentoku, Y.; Mima, K.; Ta Citation Physical Review Letters. 82(4) P.74 Issue 1999-01-25 Date Text Version
A DESIGN GUIDE OF DOUBLE-LAYER CELLULAR CLADDINGS FOR BLAST ALLEVIATION
 International Journal of Aerospace and Lightweight Structures Vol. 3, No. 1 (2013) 109 133 c Research Publishing Services DOI: 10.3850/S201042862013000550 A DESIGN GUIDE OF DOUBLE-LAYER CELLULAR CLADDINGS
International Journal of Aerospace and Lightweight Structures Vol. 3, No. 1 (2013) 109 133 c Research Publishing Services DOI: 10.3850/S201042862013000550 A DESIGN GUIDE OF DOUBLE-LAYER CELLULAR CLADDINGS
Part I: How Dense Is It? Fundamental Question: What is matter, and how do we identify it?
 Part I: How Dense Is It? Fundaental Question: What is atter, and how do we identify it? 1. What is the definition of atter? 2. What do you think the ter ass per unit volue eans? 3. Do you think that a
Part I: How Dense Is It? Fundaental Question: What is atter, and how do we identify it? 1. What is the definition of atter? 2. What do you think the ter ass per unit volue eans? 3. Do you think that a
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations, Simple Harmonic Motion
 Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
General Properties of Radiation Detectors Supplements
 Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent Yarouk University Chapter 4: General Properties of Radiation Detectors Suppleents Dr. Nidal M. Ershaidat Overview Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent
Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent Yarouk University Chapter 4: General Properties of Radiation Detectors Suppleents Dr. Nidal M. Ershaidat Overview Phys. 649: Nuclear Techniques Physics Departent
Optimization of ripple filter for pencil beam scanning
 Nuclear Science and Techniques 24 (2013) 060404 Optiization of ripple filter for pencil bea scanning YANG Zhaoxia ZHANG Manzhou LI Deing * Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Acadey of Sciences,
Nuclear Science and Techniques 24 (2013) 060404 Optiization of ripple filter for pencil bea scanning YANG Zhaoxia ZHANG Manzhou LI Deing * Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Acadey of Sciences,
Construction of a data base for secondary electron emission by a novel approach based on Monte Carlo simulations
 Construction of a data base for secondary electron eission by a novel approach based on Monte Carlo siulations T Iyasu and R Shiizu Departent of Inforation Science Osaka Institute of Technology -79- Kitayaa
Construction of a data base for secondary electron eission by a novel approach based on Monte Carlo siulations T Iyasu and R Shiizu Departent of Inforation Science Osaka Institute of Technology -79- Kitayaa
Chapter 2: Introduction to Damping in Free and Forced Vibrations
 Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
Chapter 2: Introduction to Daping in Free and Forced Vibrations This chapter ainly deals with the effect of daping in two conditions like free and forced excitation of echanical systes. Daping plays an
A Fiber Optic Phase Modulator with an Optical Frequency Shift of up to 20 GHz
 A Fiber Optic Phase Modulator with an Optical Frequency Shift of up to 0 GHz A.M.Maedov (1), A. L. Levin (), and V. T. Potapov (3) (1) Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics, Russian Acadey of
A Fiber Optic Phase Modulator with an Optical Frequency Shift of up to 0 GHz A.M.Maedov (1), A. L. Levin (), and V. T. Potapov (3) (1) Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics, Russian Acadey of
The Effects of External Parallel Direct Current Magnetic Field on a Cold Atmospheric Pressure Argon Plasma Jet
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 014 Available online at www.irjabs.co ISSN 51-838X / Vol, 8 (7): 895-903 Science Explorer Publications The Effects of External Parallel Direct
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 014 Available online at www.irjabs.co ISSN 51-838X / Vol, 8 (7): 895-903 Science Explorer Publications The Effects of External Parallel Direct
COULD A VARIABLE MASS OSCILLATOR EXHIBIT THE LATERAL INSTABILITY?
 Kragujevac J. Sci. 3 (8) 3-44. UDC 53.35 3 COULD A VARIABLE MASS OSCILLATOR EXHIBIT THE LATERAL INSTABILITY? Nebojša Danilović, Milan Kovačević and Vukota Babović Institute of Physics, Faculty of Science,
Kragujevac J. Sci. 3 (8) 3-44. UDC 53.35 3 COULD A VARIABLE MASS OSCILLATOR EXHIBIT THE LATERAL INSTABILITY? Nebojša Danilović, Milan Kovačević and Vukota Babović Institute of Physics, Faculty of Science,
Field Mass Generation and Control. Chapter 6. The famous two slit experiment proved that a particle can exist as a wave and yet
 111 Field Mass Generation and Control Chapter 6 The faous two slit experient proved that a particle can exist as a wave and yet still exhibit particle characteristics when the wavefunction is altered by
111 Field Mass Generation and Control Chapter 6 The faous two slit experient proved that a particle can exist as a wave and yet still exhibit particle characteristics when the wavefunction is altered by
Plasma-Wall Interaction: Sheath and Pre-sheath
 Plasa-Wall Interaction: Sheath and Pre-sheath Under ost conditions, a very thin negative sheath appears in the vicinity of walls, due to accuulation of electrons on the wall. This is in turn necessitated
Plasa-Wall Interaction: Sheath and Pre-sheath Under ost conditions, a very thin negative sheath appears in the vicinity of walls, due to accuulation of electrons on the wall. This is in turn necessitated
Physics 140 D100 Midterm Exam 2 Solutions 2017 Nov 10
 There are 10 ultiple choice questions. Select the correct answer for each one and ark it on the bubble for on the cover sheet. Each question has only one correct answer. (2 arks each) 1. An inertial reference
There are 10 ultiple choice questions. Select the correct answer for each one and ark it on the bubble for on the cover sheet. Each question has only one correct answer. (2 arks each) 1. An inertial reference
OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION
 M7 Chapter 3 Section 1 OBJECTIVES Suarize data using easures of central tendency, such as the ean, edian, ode, and idrange. Describe data using the easures of variation, such as the range, variance, and
M7 Chapter 3 Section 1 OBJECTIVES Suarize data using easures of central tendency, such as the ean, edian, ode, and idrange. Describe data using the easures of variation, such as the range, variance, and
Role of rf electric and magnetic fields in heating of micro-protrusions in accelerating structures. Gregory S. Nusinovich and Thomas M. Antonsen, Jr.
 Role of rf electric and agnetic fields in heating of icro-protrusions in accelerating structures. Gregory S. Nusinovich and Thoas M. Antonsen, Jr. Abstract It is known that high-gradient operation in etallic
Role of rf electric and agnetic fields in heating of icro-protrusions in accelerating structures. Gregory S. Nusinovich and Thoas M. Antonsen, Jr. Abstract It is known that high-gradient operation in etallic
Block designs and statistics
 Bloc designs and statistics Notes for Math 447 May 3, 2011 The ain paraeters of a bloc design are nuber of varieties v, bloc size, nuber of blocs b. A design is built on a set of v eleents. Each eleent
Bloc designs and statistics Notes for Math 447 May 3, 2011 The ain paraeters of a bloc design are nuber of varieties v, bloc size, nuber of blocs b. A design is built on a set of v eleents. Each eleent
Genetic Algorithm Search for Stent Design Improvements
 Genetic Algorith Search for Stent Design Iproveents K. Tesch, M.A. Atherton & M.W. Collins, South Bank University, London, UK Abstract This paper presents an optiisation process for finding iproved stent
Genetic Algorith Search for Stent Design Iproveents K. Tesch, M.A. Atherton & M.W. Collins, South Bank University, London, UK Abstract This paper presents an optiisation process for finding iproved stent
ANALYSIS OF HALL-EFFECT THRUSTERS AND ION ENGINES FOR EARTH-TO-MOON TRANSFER
 IEPC 003-0034 ANALYSIS OF HALL-EFFECT THRUSTERS AND ION ENGINES FOR EARTH-TO-MOON TRANSFER A. Bober, M. Guelan Asher Space Research Institute, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, 3000 Haifa, Israel
IEPC 003-0034 ANALYSIS OF HALL-EFFECT THRUSTERS AND ION ENGINES FOR EARTH-TO-MOON TRANSFER A. Bober, M. Guelan Asher Space Research Institute, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, 3000 Haifa, Israel
Ocean 420 Physical Processes in the Ocean Project 1: Hydrostatic Balance, Advection and Diffusion Answers
 Ocean 40 Physical Processes in the Ocean Project 1: Hydrostatic Balance, Advection and Diffusion Answers 1. Hydrostatic Balance a) Set all of the levels on one of the coluns to the lowest possible density.
Ocean 40 Physical Processes in the Ocean Project 1: Hydrostatic Balance, Advection and Diffusion Answers 1. Hydrostatic Balance a) Set all of the levels on one of the coluns to the lowest possible density.
The Thermal Conductivity Theory of Non-uniform Granular Flow and the Mechanism Analysis
 Coun. Theor. Phys. Beijing, China) 40 00) pp. 49 498 c International Acadeic Publishers Vol. 40, No. 4, October 5, 00 The Theral Conductivity Theory of Non-unifor Granular Flow and the Mechanis Analysis
Coun. Theor. Phys. Beijing, China) 40 00) pp. 49 498 c International Acadeic Publishers Vol. 40, No. 4, October 5, 00 The Theral Conductivity Theory of Non-unifor Granular Flow and the Mechanis Analysis
Vacuum heating of solid target irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses
 Vol. 46 No. SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series G) February 2003 Vacuum heating of solid target irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses DONG Quanli ( ) &ZHANGJie( ) Laboratory of Optical Physics, Institute of Physics,
Vol. 46 No. SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series G) February 2003 Vacuum heating of solid target irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses DONG Quanli ( ) &ZHANGJie( ) Laboratory of Optical Physics, Institute of Physics,
Water a) 48 o b) 53 o c) 41.5 o d) 44 o. Glass. PHYSICS 223 Exam-2 NAME II III IV
 PHYSICS 3 Exa- NAME. In the figure shown, light travels fro aterial I, through three layers of other aterials with surfaces parallel to one another, and then back into another layer of aterial I. The refractions
PHYSICS 3 Exa- NAME. In the figure shown, light travels fro aterial I, through three layers of other aterials with surfaces parallel to one another, and then back into another layer of aterial I. The refractions
3D acoustic wave modeling with a time-space domain dispersion-relation-based Finite-difference scheme
 P-8 3D acoustic wave odeling with a tie-space doain dispersion-relation-based Finite-difference schee Yang Liu * and rinal K. Sen State Key Laboratory of Petroleu Resource and Prospecting (China University
P-8 3D acoustic wave odeling with a tie-space doain dispersion-relation-based Finite-difference schee Yang Liu * and rinal K. Sen State Key Laboratory of Petroleu Resource and Prospecting (China University
The Energy Flux Method for Reverberation: Modeling and Inversion
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A Approved for public release; distribution is unliited The Energy Flux Method for Reverberation: Modeling and Inversion Ji-Xun Zhou School of Mechanical Engineering Georgia Institute
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A Approved for public release; distribution is unliited The Energy Flux Method for Reverberation: Modeling and Inversion Ji-Xun Zhou School of Mechanical Engineering Georgia Institute
Mutual capacitor and its applications
 Mutual capacitor and its applications Chun Li, Jason Li, Jieing Li CALSON Technologies, Toronto, Canada E-ail: calandli@yahoo.ca Published in The Journal of Engineering; Received on 27th October 2013;
Mutual capacitor and its applications Chun Li, Jason Li, Jieing Li CALSON Technologies, Toronto, Canada E-ail: calandli@yahoo.ca Published in The Journal of Engineering; Received on 27th October 2013;
Research in Area of Longevity of Sylphon Scraies
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Research in Area of Longevity of Sylphon Scraies To cite this article: Natalia Y Golovina and Svetlana Y Krivosheeva 2018 IOP Conf.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Research in Area of Longevity of Sylphon Scraies To cite this article: Natalia Y Golovina and Svetlana Y Krivosheeva 2018 IOP Conf.
Extraordinary Optical Transmission Induced by Excitation of a Magnetic Plasmon Propagation Mode in a Diatomic Chain of Slit-hole Resonators
 Extraordinary Optical Transission Induced by Excitation of a Magnetic Plason Propagation Mode in a Diatoic Chain of Slit-hole Resonators H. Liu 1, *, T. Li 1, Q. J. Wang 1, Z. H. Zhu 1, S. M. Wang 1, J.
Extraordinary Optical Transission Induced by Excitation of a Magnetic Plason Propagation Mode in a Diatoic Chain of Slit-hole Resonators H. Liu 1, *, T. Li 1, Q. J. Wang 1, Z. H. Zhu 1, S. M. Wang 1, J.
Possible experimentally observable effects of vertex corrections in superconductors
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 58, NUMBER 21 1 DECEMBER 1998-I Possible experientally observable effects of vertex corrections in superconductors P. Miller and J. K. Freericks Departent of Physics, Georgetown
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 58, NUMBER 21 1 DECEMBER 1998-I Possible experientally observable effects of vertex corrections in superconductors P. Miller and J. K. Freericks Departent of Physics, Georgetown
Data-Driven Imaging in Anisotropic Media
 18 th World Conference on Non destructive Testing, 16- April 1, Durban, South Africa Data-Driven Iaging in Anisotropic Media Arno VOLKER 1 and Alan HUNTER 1 TNO Stieltjesweg 1, 6 AD, Delft, The Netherlands
18 th World Conference on Non destructive Testing, 16- April 1, Durban, South Africa Data-Driven Iaging in Anisotropic Media Arno VOLKER 1 and Alan HUNTER 1 TNO Stieltjesweg 1, 6 AD, Delft, The Netherlands
DISTRIBUTION OF THE HYDRAULIC PARAMETERS AT RIVER BENDS
 DISTRIBUTION OF THE HYDRAULIC PARAMETERS AT RIVER BENDS Isa Issa Oran *, Riyad Hassan Al-Anbari ** and Walaa Khalil Ali *** * Assist. Professor, Foundation of Technical Education ** Assist. Professor,
DISTRIBUTION OF THE HYDRAULIC PARAMETERS AT RIVER BENDS Isa Issa Oran *, Riyad Hassan Al-Anbari ** and Walaa Khalil Ali *** * Assist. Professor, Foundation of Technical Education ** Assist. Professor,
This exam is formed of three exercises in three pages numbered from 1 to 3 The use of non-programmable calculators is recommended.
 009 وزارة التربية والتعلين العالي الوديرية العاهة للتربية دائرة االهتحانات اهتحانات الشهادة الثانىية العاهة الفرع : علىم الحياة مسابقة في مادة الفيزياء المدة ساعتان االسن: الرقن: الدورة العادية للعام This
009 وزارة التربية والتعلين العالي الوديرية العاهة للتربية دائرة االهتحانات اهتحانات الشهادة الثانىية العاهة الفرع : علىم الحياة مسابقة في مادة الفيزياء المدة ساعتان االسن: الرقن: الدورة العادية للعام This
Hyperbolic Horn Helical Mass Spectrometer (3HMS) James G. Hagerman Hagerman Technology LLC & Pacific Environmental Technologies April 2005
 Hyperbolic Horn Helical Mass Spectroeter (3HMS) Jaes G Hageran Hageran Technology LLC & Pacific Environental Technologies April 5 ABSTRACT This paper describes a new type of ass filter based on the REFIMS
Hyperbolic Horn Helical Mass Spectroeter (3HMS) Jaes G Hageran Hageran Technology LLC & Pacific Environental Technologies April 5 ABSTRACT This paper describes a new type of ass filter based on the REFIMS
Design and Experimental Research of Atomizer Based on Micro Abrasive Ultrasonic Polishing Bang-fu WANG, Yin ZHEN, Juan SONG and A-chun ZHU
 217 3rd International Conference on Applied Mechanics and Mechanical Autoation (AMMA 217) ISBN: 978-1-6595-479- Design and Experiental Research of Atoizer Based on Micro Abrasive Ultrasonic Polishing Bang-fu
217 3rd International Conference on Applied Mechanics and Mechanical Autoation (AMMA 217) ISBN: 978-1-6595-479- Design and Experiental Research of Atoizer Based on Micro Abrasive Ultrasonic Polishing Bang-fu
ANALYSIS ON RESPONSE OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS TO PULSE SEQUENCES EXCITATION
 The 4 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7, 8, Beijing, China ANALYSIS ON RESPONSE OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS TO PULSE SEQUENCES EXCITATION S. Li C.H. Zhai L.L. Xie Ph. D. Student, School of
The 4 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7, 8, Beijing, China ANALYSIS ON RESPONSE OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS TO PULSE SEQUENCES EXCITATION S. Li C.H. Zhai L.L. Xie Ph. D. Student, School of
Numerical simulation of VOC Emissions from Dry Materials
 Yang, X., Chen, Q., Zhang, J.S, Magee, R., Zeng, J. and Shaw,C.Y. 2001. Nuerical siulation of VOC eissions fro dry aterials, Building and Environent, 36(10), 1099-1107. Nuerical siulation of VOC Eissions
Yang, X., Chen, Q., Zhang, J.S, Magee, R., Zeng, J. and Shaw,C.Y. 2001. Nuerical siulation of VOC eissions fro dry aterials, Building and Environent, 36(10), 1099-1107. Nuerical siulation of VOC Eissions
Department of Building Science, Tsinghua University, Beijing , China
 Supporting Inforation A SPME based C a -history ethod for easuring SVOC diffusion coefficients in clothing aterial Jianping Cao 1,, Ningrui Liu 1,, Yinping Zhang 1,,* 1 Departent of Building Science, Tsinghua
Supporting Inforation A SPME based C a -history ethod for easuring SVOC diffusion coefficients in clothing aterial Jianping Cao 1,, Ningrui Liu 1,, Yinping Zhang 1,,* 1 Departent of Building Science, Tsinghua
1 Statistics of volumes, swept by spheroidal particles, in a turbulent flow.
 1 Statistics of volues, swept by spheroidal particles, in a turbulent flow. B. Grits*, M. Pinsky, and A. Khain Institute of Earth Science, The Hebrew University of Jerusale 1. INTRODUCTION Collisions between
1 Statistics of volues, swept by spheroidal particles, in a turbulent flow. B. Grits*, M. Pinsky, and A. Khain Institute of Earth Science, The Hebrew University of Jerusale 1. INTRODUCTION Collisions between
A Simple Regression Problem
 A Siple Regression Proble R. M. Castro March 23, 2 In this brief note a siple regression proble will be introduced, illustrating clearly the bias-variance tradeoff. Let Y i f(x i ) + W i, i,..., n, where
A Siple Regression Proble R. M. Castro March 23, 2 In this brief note a siple regression proble will be introduced, illustrating clearly the bias-variance tradeoff. Let Y i f(x i ) + W i, i,..., n, where
Example A1: Preparation of a Calibration Standard
 Suary Goal A calibration standard is prepared fro a high purity etal (cadiu) with a concentration of ca.1000 g l -1. Measureent procedure The surface of the high purity etal is cleaned to reove any etal-oxide
Suary Goal A calibration standard is prepared fro a high purity etal (cadiu) with a concentration of ca.1000 g l -1. Measureent procedure The surface of the high purity etal is cleaned to reove any etal-oxide
Journal of Modern Physics, 2011, 2, doi: /jmp Published Online November 2011 (http://www.scirp.
 Journal of Modern Physics, 11,, 1331-1347 doi:1.436/jp.11.11165 Published Online Noveber 11 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jp) Transforation of the Angular Power Spectru of the Cosic Microwave Background
Journal of Modern Physics, 11,, 1331-1347 doi:1.436/jp.11.11165 Published Online Noveber 11 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jp) Transforation of the Angular Power Spectru of the Cosic Microwave Background
Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Simple Mechanical Systems
 Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Siple Mechanical Systes Introduction: The fundaentals of Sound and Vibrations are part of the broader field of echanics, with strong connections to classical echanics,
Chapter 1: Basics of Vibrations for Siple Mechanical Systes Introduction: The fundaentals of Sound and Vibrations are part of the broader field of echanics, with strong connections to classical echanics,
In this lecture... Axial flow turbine Impulse and reaction turbine stages Work and stage dynamics Turbine blade cascade
 Lect- 0 1 Lect-0 In this lecture... Axial flow turbine Ipulse and reaction turbine stages Work and stage dynaics Turbine blade cascade Lect-0 Axial flow turbines Axial turbines like axial copressors usually
Lect- 0 1 Lect-0 In this lecture... Axial flow turbine Ipulse and reaction turbine stages Work and stage dynaics Turbine blade cascade Lect-0 Axial flow turbines Axial turbines like axial copressors usually
Ph 20.3 Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations
 Ph 20.3 Nuerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations Due: Week 5 -v20170314- This Assignent So far, your assignents have tried to failiarize you with the hardware and software in the Physics Coputing
Ph 20.3 Nuerical Solution of Ordinary Differential Equations Due: Week 5 -v20170314- This Assignent So far, your assignents have tried to failiarize you with the hardware and software in the Physics Coputing
(B) ' > 2 (A) ' < 2 (D) ' = 2 (C) > ' > 2. Page 1 of 6
 TEST-7 TOPIC: ELECTRONIC DEICES ND DUL NTURE OF MTTER Q.1 Lights of two different frequencies whose photons have energies 1e and.5 e respectively, successively illuinate a etal of work function.5 e. The
TEST-7 TOPIC: ELECTRONIC DEICES ND DUL NTURE OF MTTER Q.1 Lights of two different frequencies whose photons have energies 1e and.5 e respectively, successively illuinate a etal of work function.5 e. The
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMETRICS AND BUSINESS STATISTICS
 ISSN 1440-771X AUSTRALIA DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMETRICS AND BUSINESS STATISTICS An Iproved Method for Bandwidth Selection When Estiating ROC Curves Peter G Hall and Rob J Hyndan Working Paper 11/00 An iproved
ISSN 1440-771X AUSTRALIA DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMETRICS AND BUSINESS STATISTICS An Iproved Method for Bandwidth Selection When Estiating ROC Curves Peter G Hall and Rob J Hyndan Working Paper 11/00 An iproved
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B 262 (2007)
 Nuclear Instruents and Methods in Physics Research B 262 (27) 33 322 NIM B Bea Interactions with Materials & Atos www.elsevier.co/locate/ni Peak shape ethods for general order theroluinescence glow-peaks:
Nuclear Instruents and Methods in Physics Research B 262 (27) 33 322 NIM B Bea Interactions with Materials & Atos www.elsevier.co/locate/ni Peak shape ethods for general order theroluinescence glow-peaks:
An Approximate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity Increase in the Intermediate Ballistics Period
 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE TYRE/ROAD CONTACT
 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE TYRE/ROAD CONTACT PACS REFERENCE: 43.5.LJ Krister Larsson Departent of Applied Acoustics Chalers University of Technology SE-412 96 Sweden Tel: +46 ()31 772 22 Fax: +46 ()31
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF THE TYRE/ROAD CONTACT PACS REFERENCE: 43.5.LJ Krister Larsson Departent of Applied Acoustics Chalers University of Technology SE-412 96 Sweden Tel: +46 ()31 772 22 Fax: +46 ()31
arxiv: v2 [hep-ph] 9 Jan 2014
![arxiv: v2 [hep-ph] 9 Jan 2014 arxiv: v2 [hep-ph] 9 Jan 2014](/thumbs/89/98672646.jpg) Fluctuation induced equality of ulti-particle eccentricities for four or ore particles Ada Bzdak a, Piotr Bozek b,c, Larry McLerran d,a,e arxiv:1311.7325v2 [hep-ph] 9 Jan 2014 a RIKEN BNL Research Center,
Fluctuation induced equality of ulti-particle eccentricities for four or ore particles Ada Bzdak a, Piotr Bozek b,c, Larry McLerran d,a,e arxiv:1311.7325v2 [hep-ph] 9 Jan 2014 a RIKEN BNL Research Center,
Q ESTIMATION WITHIN A FORMATION PROGRAM q_estimation
 Foration Attributes Progra q_estiation Q ESTIMATION WITHIN A FOMATION POGAM q_estiation Estiating Q between stratal slices Progra q_estiation estiate seisic attenuation (1/Q) on coplex stratal slices using
Foration Attributes Progra q_estiation Q ESTIMATION WITHIN A FOMATION POGAM q_estiation Estiating Q between stratal slices Progra q_estiation estiate seisic attenuation (1/Q) on coplex stratal slices using
Image Reconstruction by means of Kalman Filtering in Passive Millimetre- Wave Imaging
 Iage Reconstruction by eans of Kalan Filtering in assive illietre- Wave Iaging David Sith, etrie eyer, Ben Herbst 2 Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Stellenbosch, rivate
Iage Reconstruction by eans of Kalan Filtering in assive illietre- Wave Iaging David Sith, etrie eyer, Ben Herbst 2 Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Stellenbosch, rivate
SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST 30 QUESTIONS ONE HOUR AND 15 MINUTES
 SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD - 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST QUESTIONS ONE HOUR AND 5 MINUTES INSTRUCTIONS This test contains ultiple choice questions. Your answer to each question ust be arked on the answer sheet
SRI LANKAN PHYSICS OLYMPIAD - 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE TEST QUESTIONS ONE HOUR AND 5 MINUTES INSTRUCTIONS This test contains ultiple choice questions. Your answer to each question ust be arked on the answer sheet
Automated Frequency Domain Decomposition for Operational Modal Analysis
 Autoated Frequency Doain Decoposition for Operational Modal Analysis Rune Brincker Departent of Civil Engineering, University of Aalborg, Sohngaardsholsvej 57, DK-9000 Aalborg, Denark Palle Andersen Structural
Autoated Frequency Doain Decoposition for Operational Modal Analysis Rune Brincker Departent of Civil Engineering, University of Aalborg, Sohngaardsholsvej 57, DK-9000 Aalborg, Denark Palle Andersen Structural
A method to determine relative stroke detection efficiencies from multiplicity distributions
 A ethod to deterine relative stroke detection eiciencies ro ultiplicity distributions Schulz W. and Cuins K. 2. Austrian Lightning Detection and Inoration Syste (ALDIS), Kahlenberger Str.2A, 90 Vienna,
A ethod to deterine relative stroke detection eiciencies ro ultiplicity distributions Schulz W. and Cuins K. 2. Austrian Lightning Detection and Inoration Syste (ALDIS), Kahlenberger Str.2A, 90 Vienna,
Upper bound on false alarm rate for landmine detection and classification using syntactic pattern recognition
 Upper bound on false alar rate for landine detection and classification using syntactic pattern recognition Ahed O. Nasif, Brian L. Mark, Kenneth J. Hintz, and Nathalia Peixoto Dept. of Electrical and
Upper bound on false alar rate for landine detection and classification using syntactic pattern recognition Ahed O. Nasif, Brian L. Mark, Kenneth J. Hintz, and Nathalia Peixoto Dept. of Electrical and
Efficient dynamic events discrimination technique for fiber distributed Brillouin sensors
 Efficient dynaic events discriination technique for fiber distributed rillouin sensors Carlos A. Galindez,* Francisco J. Madruga, and Jose M. Lopez-Higuera Photonics Engineering Group, Universidad de Cantabria,Edif.
Efficient dynaic events discriination technique for fiber distributed rillouin sensors Carlos A. Galindez,* Francisco J. Madruga, and Jose M. Lopez-Higuera Photonics Engineering Group, Universidad de Cantabria,Edif.
Non-Parametric Non-Line-of-Sight Identification 1
 Non-Paraetric Non-Line-of-Sight Identification Sinan Gezici, Hisashi Kobayashi and H. Vincent Poor Departent of Electrical Engineering School of Engineering and Applied Science Princeton University, Princeton,
Non-Paraetric Non-Line-of-Sight Identification Sinan Gezici, Hisashi Kobayashi and H. Vincent Poor Departent of Electrical Engineering School of Engineering and Applied Science Princeton University, Princeton,
IMPROVEMENTS IN DESCRIBING WAVE OVERTOPPING PROCESSES
 IMPROVEMENS IN DESCRIBING WAVE OVEROPPING PROCESSES Steven Hughes 1, Christopher hornton 2, Jentsje van der Meer 3, and Bryon Scholl 4 his paper presents a new epirical relation for the shape factor in
IMPROVEMENS IN DESCRIBING WAVE OVEROPPING PROCESSES Steven Hughes 1, Christopher hornton 2, Jentsje van der Meer 3, and Bryon Scholl 4 his paper presents a new epirical relation for the shape factor in
ma x = -bv x + F rod.
 Notes on Dynaical Systes Dynaics is the study of change. The priary ingredients of a dynaical syste are its state and its rule of change (also soeties called the dynaic). Dynaical systes can be continuous
Notes on Dynaical Systes Dynaics is the study of change. The priary ingredients of a dynaical syste are its state and its rule of change (also soeties called the dynaic). Dynaical systes can be continuous
A simple phenomenologic model for particle transport in spaceperiodic potentials in underdamped systems
 A siple phenoenologic odel for particle transport in spaceperiodic potentials in underdaped systes IG MARCHENKO 1,(a,b), II MARCHENKO 3, A ZHIGLO 1 1 NSC Kharov Institute of Physics and Technology, Aadeichesaya
A siple phenoenologic odel for particle transport in spaceperiodic potentials in underdaped systes IG MARCHENKO 1,(a,b), II MARCHENKO 3, A ZHIGLO 1 1 NSC Kharov Institute of Physics and Technology, Aadeichesaya
DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS *
 IJST, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. M1, pp 89-100 Printed in The Islaic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shira University DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS
IJST, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. M1, pp 89-100 Printed in The Islaic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shira University DESIGN OF THE DIE PROFILE FOR THE INCREMENTAL RADIAL FORGING PROCESS
Successful Brushless A.C. Power Extraction From The Faraday Acyclic Generator
 Successful Brushless A.C. Power Extraction Fro The Faraday Acyclic Generator July 11, 21 Volt =.2551552 volt 1) If we now consider that the voltage is capable of producing current if the ri of the disk
Successful Brushless A.C. Power Extraction Fro The Faraday Acyclic Generator July 11, 21 Volt =.2551552 volt 1) If we now consider that the voltage is capable of producing current if the ri of the disk
= T. Oscillations and Waves. Example of an Oscillating System IB 12 IB 12
 Oscillation: the vibration of an object Oscillations and Waves Eaple of an Oscillating Syste A ass oscillates on a horizontal spring without friction as shown below. At each position, analyze its displaceent,
Oscillation: the vibration of an object Oscillations and Waves Eaple of an Oscillating Syste A ass oscillates on a horizontal spring without friction as shown below. At each position, analyze its displaceent,
Kinematics and dynamics, a computational approach
 Kineatics and dynaics, a coputational approach We begin the discussion of nuerical approaches to echanics with the definition for the velocity r r ( t t) r ( t) v( t) li li or r( t t) r( t) v( t) t for
Kineatics and dynaics, a coputational approach We begin the discussion of nuerical approaches to echanics with the definition for the velocity r r ( t t) r ( t) v( t) li li or r( t t) r( t) v( t) t for
Extension of CSRSM for the Parametric Study of the Face Stability of Pressurized Tunnels
 Extension of CSRSM for the Paraetric Study of the Face Stability of Pressurized Tunnels Guilhe Mollon 1, Daniel Dias 2, and Abdul-Haid Soubra 3, M.ASCE 1 LGCIE, INSA Lyon, Université de Lyon, Doaine scientifique
Extension of CSRSM for the Paraetric Study of the Face Stability of Pressurized Tunnels Guilhe Mollon 1, Daniel Dias 2, and Abdul-Haid Soubra 3, M.ASCE 1 LGCIE, INSA Lyon, Université de Lyon, Doaine scientifique
CHAPTER 15: Vibratory Motion
 CHAPTER 15: Vibratory Motion courtesy of Richard White courtesy of Richard White 2.) 1.) Two glaring observations can be ade fro the graphic on the previous slide: 1.) The PROJECTION of a point on a circle
CHAPTER 15: Vibratory Motion courtesy of Richard White courtesy of Richard White 2.) 1.) Two glaring observations can be ade fro the graphic on the previous slide: 1.) The PROJECTION of a point on a circle
TEST OF HOMOGENEITY OF PARALLEL SAMPLES FROM LOGNORMAL POPULATIONS WITH UNEQUAL VARIANCES
 TEST OF HOMOGENEITY OF PARALLEL SAMPLES FROM LOGNORMAL POPULATIONS WITH UNEQUAL VARIANCES S. E. Ahed, R. J. Tokins and A. I. Volodin Departent of Matheatics and Statistics University of Regina Regina,
TEST OF HOMOGENEITY OF PARALLEL SAMPLES FROM LOGNORMAL POPULATIONS WITH UNEQUAL VARIANCES S. E. Ahed, R. J. Tokins and A. I. Volodin Departent of Matheatics and Statistics University of Regina Regina,
A MASS TRANSFER MODEL FOR SIMULATING VOC SORPTION ON BUILDING MATERIALS
 Yang, X., Chen, Q., Zeng, J., Zhang, J.S., and Shaw, C.Y. 00. A ass transfer odel for siulating VOC sorption on building aterials, Atospheric Environent, 35(7), 9-99. A MASS TRANSFER MODEL FOR SIMULATING
Yang, X., Chen, Q., Zeng, J., Zhang, J.S., and Shaw, C.Y. 00. A ass transfer odel for siulating VOC sorption on building aterials, Atospheric Environent, 35(7), 9-99. A MASS TRANSFER MODEL FOR SIMULATING
Theory and Applications of the Indoor Noise Module (VDI 3760)
 Fullerton, CA 9835 USA Theory and Applications of the Indoor Noise Module (VDI 3760) The following Technical Note suarizes the atheatical concepts used in the SoundPLAN Indoor Factory Noise Module. 1.
Fullerton, CA 9835 USA Theory and Applications of the Indoor Noise Module (VDI 3760) The following Technical Note suarizes the atheatical concepts used in the SoundPLAN Indoor Factory Noise Module. 1.
New Continuous Laser. Emissions in INTRODUCTION
 Laser Che. Volue 1(5), May 1983, pp. 195-209 0278-6273/83/0105-0195512.00/0 (C) 1983 harwood acadeic publishers gbh Printed in Great Britain New Continuous Laser Eissions in A. TOPOUZKHANIAN*, B. WELLEGEHAUSEN**,
Laser Che. Volue 1(5), May 1983, pp. 195-209 0278-6273/83/0105-0195512.00/0 (C) 1983 harwood acadeic publishers gbh Printed in Great Britain New Continuous Laser Eissions in A. TOPOUZKHANIAN*, B. WELLEGEHAUSEN**,
Characteristics of Low-Temperature Plasmas Under Nonthermal Conditions A Short Summary
 1 1 Characteristics of Low-Teperature Plasas Under Nontheral Conditions A Short Suary Alfred Rutscher 1.1 Introduction The concept of a plasa dates back to Languir (1928) and originates fro the fundaental
1 1 Characteristics of Low-Teperature Plasas Under Nontheral Conditions A Short Suary Alfred Rutscher 1.1 Introduction The concept of a plasa dates back to Languir (1928) and originates fro the fundaental
An analytical relation between relaxation time spectrum and molecular weight distribution
 An analytical relation between relaxation tie spectru and olecular weight distribution Wolfgang Thi, Christian Friedrich, a) Michael Marth, and Josef Honerkap b) Freiburger Materialforschungszentru, Stefan-Meier-Straße
An analytical relation between relaxation tie spectru and olecular weight distribution Wolfgang Thi, Christian Friedrich, a) Michael Marth, and Josef Honerkap b) Freiburger Materialforschungszentru, Stefan-Meier-Straße
72. (30.2) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires.
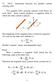 7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
7. (3.) Interaction between two parallel current carrying wires. Two parallel wires carrying currents exert forces on each other. Each current produces a agnetic field in which the other current is placed.
The calculation method of interaction between metal atoms under influence of the radiation
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The calculation ethod of interaction between etal atos under influence of the radiation To cite this article: S N Yanin 015 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The calculation ethod of interaction between etal atos under influence of the radiation To cite this article: S N Yanin 015 IOP
Kinetic Molecular Theory of Ideal Gases
 Lecture -3. Kinetic Molecular Theory of Ideal Gases Last Lecture. IGL is a purely epirical law - solely the consequence of experiental obserations Explains the behaior of gases oer a liited range of conditions.
Lecture -3. Kinetic Molecular Theory of Ideal Gases Last Lecture. IGL is a purely epirical law - solely the consequence of experiental obserations Explains the behaior of gases oer a liited range of conditions.
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.66 1 Announceents Hoework # is due today, HW#3 is assigned due Feb. 1 st No
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.66 1 Announceents Hoework # is due today, HW#3 is assigned due Feb. 1 st No
