Throwing Light on Reaction Dynamics: H + HBr
|
|
|
- Damian Dorsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Throwing Light on Reaction Dynamics: H + HBr
2 The thermal reaction of hydrogen gas (H 2 ) and bromine gas (Br 2 ) to form hydrogen bromide vapor (HBr) is a classic reaction: 22+2rHBrHBææÆ Energetics (thermodynamics) tells does us NOT that the tell equilibrium us how this constant reaction is occurs large, or that howis, favors rapidly the equilibrium formation is of established. products because the Br-Br bond is so weak in comparison to For answers to those questions, we need the others. kinetics and dynamics.
3 Kinetic Studies of H 2 + Br 2 M. Bodenstein and S. Lind, Z. physikal. Chem. 57, 168 (1906). Rate of reaction: 12221d[]=k[][BrdtrHB]H2 Great surprise and mystery
4 Reaction Mechanism Initiation: æææ12k+m2+rbrbm(1) ææææææ232k2khhh++(br Propagation: Termination: æææ-1k2b2+mbrr+m(4)
5 Kinetic Studies of H 2 + Br 2 M. Bodenstein and S. Lind, Z. physikal. Chem. 57, 168 (1906). Rate of reaction: 22212k[][]1d[]=2dt1+HBrHBk
6 Reaction Mechanism Christiansen, Dansk. V. d. Math. Phys. Medd. 1, 14 (1919) Herzfeld, Ann. Phys. 59, 635 (1919) M. Polanyi, Z. El. Ch. 26, 10 (1920)
7 Reaction Mechanism Initiation: æææ12k+m2+rbrbm(1) ææææææ232k2khhh++(br Propagation: ææææææ-2-3kk22brbhbr Inhibition: Termination: æææ-1k2b2+mbrr+m(6)
8 H + HBr Æ H 2 + Br + + How does such a simple reaction occur? Try to make a movie in your mind of how the reaction takes place.
9 H + HBr Æ H 2 + Br + + How much does the H 2 product vibrate and rotate? Can a measurement of the rotation and vibration tell us about the mechanism of a chemical reaction?
10 The Transition State DistanceTimeRate 11310m10fs10m/s Reagents Products
11 The Born-Oppenheimer Approximation V (kcal/mol) H-H separation (Å) H-Br separation (Å) Separate wave equation; calculate the electronic energy as a function of nuclear geometry (PES). Calculate motion along that PES (using classical or quantum mechanics).
12 Asymptotic Approach The product vibrational energy can be related to the location of the transition state. A + BC _ AB + C r B-C r B-C r A-B r A-B
13 H + HBr Æ H 2 + Br H 2 is described by two quantum numbers: v', j'. Those quantum numbers describe the asymptotic state. We measure partial cross sections for forming individual quantum states: _(v', j'). v : Classical Barrier Height: 1.7 kcal/mol Reaction Exoergicity: 19.1 kcal/mol Total Reactive Cross Section: 1.2 Å 2 j :
14 Experimental Protocol
15 Experimental Results H + HBr Æ H 2 (v'=2, j') + Br
16 Possible State Distributions Purely Statistical ()(),,vibrottranspopvjdegeneracyvjdegendegen 121vibrottranstransDegenD
17 Different Approach Geometries Perpendicular Collinear
18 Kinematically Constrained State Distribution Valentini and co-workers: translational energy is needed to surmount the reaction barrier Perpendicular Collinear
19 Video of PES Video - Low >> Video - High >>
20 Kinematically Constrained State Distribution mass-weighted collinear PES TQQʈÁ Á Ë =+&& Min. E trans Max. E int Q 1 1ACABBCmmcos(mm)(mm)forthereactionABCABC-b E total ß(masses) The internal energy is kinematically constrained Q 2
21 C. A. Picconatto, A. Srivastava, and J. J. Valentini, J. Chem. Phys. 114, (2001). The minimum translational energy of the products is 2transtransEcosE =b
22 Reaction (E trans ) j' max,meas j' max,model j' max (Eavail) H+HCl (37 kcal/mol) H 2 (v'=0) H 2 (v'=1) P. M. Aker, G. J. Germann, and J. J. Valentini, J. Chem. Phys. 90, 4795 (1989).
23 Reaction (E trans ) j' max,meas j' max,model j' max (Eavail) H+HBr (37 kcal/mol) H 2 (v'=0) H 2 (v'=1) H 2 (v'=2) P. M. Aker, G. J. Germann, and J. J. Valentini, J. Chem. Phys. 90, 4795 (1989).
24 Reaction (E trans ) j' max,meas j' max,model j' max (Eavail) H+HI (37 kcal/mol) H 2 (v'=0) H 2 (v'=1) H 2 (v'=2) H 2 (v'=3) H 2 (v =4) P. M. Aker, G. J. Germann, and J. J. Valentini, J. Chem. Phys. 96, 2756 (1992).
25 H + HBr Æ H 2 (v'=2, j') + Br E coll = 53.0 kcal/mol Statistical Kinematic Limit
26 Quasiclassical Trajectory Method (QCT) V (kcal/mol) H-H separation (Å) H-Br separation (Å) Find potential quantum mechanically Take derivative to yield forces Solve Newton s equations of motion Find position of each atom at all times Bin into quantum states
27 Experimental and Theory H + HBr Æ H 2 (v'=2, j') + Br E coll = 53.0 kcal/mol
28 H + HBr Æ H 2 (v'=2, j') + Br E coll = 53.0 kcal/mol
29 Kinematically Forbidden Quantum States E coll = 53 kcal/mol
30 Kinematically Forbidden Quantum States Collinear Perpendicular H Br separation H Br separation H H separation H H separation
31 Transition State Geometry _ The transition state is the configuration for which potential energy reaches a maximum in a reactive trajectory. _ is the angle between the H Br bond axis and line connecting the attacking H-atom with the HBr center of mass.
32 Quasiclassical Trajectory Calculations Kinematically Allowed Kinematically Excluded Cos (_ ts ) Number H 2 Internal Energy (kcal/mol)
33 Spectroscopy of the Transition State Collinear: Perpendicular Cos (_ ts ) Kinematically Allowed Kinematically Excluded H 2 Internal Energy (kcal/mol)
34 Mechanism for Forming Internally Cold H 2
35 Mechanism for Forming Internally Cold H 2 _ = 15 v = 1, j = 3 E int = 16.7 Transition State
36 Mechanism for Forming Internally Hot H 2
37 Mechanism for Forming Internally Hot H 2 _ = 70 v = 4, j = 13 E int = 70.3 Transition State
38 Direct Trajectory
39 Direct Trajectory _ = 19 v = 0, j = 2 E int = 11.6 Transition State
40 Direct Trajectory
41 Direct Trajectory _ = 25 v = 0, j = 14 E int = 38.2 Transition State
42 Direct Trajectory
43 Direct Trajectory _ = 37 v = 3, j = 5 E int = 47.0 Transition State
44 Medium-Lifetime State Transition
45 Medium-Lifetime State Transition _ = 86 v = 0, j = 1 E int = 8.2 Transition State
46 Medium-Lifetime State Transition
47 Medium-Lifetime State Transition _ = 80 v = 3, j = 9 E int = 56.1 Transition State
48 Long-Lifetime Transition State
49 Long-Lifetime Transition State _ = 22 v = 7, j = 3 E int = 73.8 Transition State
50 Long-Lifetime Transition State
51 Long-Lifetime Transition State _ = 113 v = 0, j = 19 E int = 56.1 Transition State
52 What Did We Learn? Using this principle, we have identified two simple pathways for the reaction H + HBr Æ H 2 (v, j ) + Br: Cos (_ ts ) Kinematically Allowed Kinematically Excluded H 2 Internal Energy (kcal/mol) Internally cold H 2 results from collinear transition states Internally hot H 2 results from bent transition states.
53 Overarching Conclusion At sufficiently high energies some significant fraction of reactions do not proceed along or close to the minimum energy path. Prediction This behavior is general and more common than realized before.
54 Acknowledgments Drew Pomerantz, Jon Camden, Albert Chiou, Florian Ausfelder Navdeep Chawla William Hase National Science Foundation
55 H 2 CO + h Æ H 2 + CO: Production of Cold H 2 D. Townsend, S. A. Lahankar, S. K. Lee, S. D. Chambreau, A. G. Suits, X. Zhang, J. Rheinecker, L. B. Harding, and J. M. Bowman, Science 306, (2004).
56 H 2 CO + h Æ H 2 + CO: Production of Hot H 2 D. Townsend, S. A. Lahankar, S. K. Lee, S. D. Chambreau, A. G. Suits, X. Zhang, J. Rheinecker, L. B. Harding, and J. M. Bowman, Science 306, (2004).
57 O + CH 3 Six possible sets of exothermic products: CH 3 + O Æ H + H 2 CO H 2 + HCO H + HCOH H 2 + COH H + H 2 + CO CH + H 2 O _H=-70 kcal/mol _H=-84 _H=-13 _H=-44 _H=-70 _H=-10 Seakins and Leone (1992) reported the detection of CO (v) from this reaction using FTIR emission spectroscopy. They estimated the CO branching fraction to be 0.40 ± 0.10.
58 O + CH 3 Both experimental and theoretical studies confirm the existence of a CO producing channel in the reaction of CH 3 with O atoms [T. P. Marcy, R. R. Diaz, D. Heard, S. R. Leone, L. B. Harding, and S. J. Klippenstein, J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, ]. The mechanism involves the elimination of H 2 from an energy-rich CH 3 O radical forming HCO, followed by the decomposition of HCO to form the observed CO (v) product. The most unusual feature of this mechanism is that there appears to be no saddle point for the direct elimination of H 2 from CH 3 O.
59 O + CH 3 The methoxy radical is formed with 90 kcal/mol of excess energy, or 60 kcal/mol above its lowest barrier for decomposition (CH bond cleavage).
60 At these high energies, trajectories are found to stray far from the minimum-energy path, resulting in the production of unexpected products. Two-dimensional projections of each of the three selected H 2 -producing trajectories. The black contours correspond to the saddle point for the reaction H + H 2 CO Æ H 2 + HCO. Blue contours are lower in energy and red contours are higher in energy.
61 Kinematic Limit Model System H + HCl H + D 2 O H + D 2 O E coll kcal/mol v j max expt j max model j max energy H + HCl H + D H + D H + D 2 O Cl + CH
62 Jet Cooling Construct high vacuum chamber: 10-6 Torr Single collision conditions: (mean free path = 50 m) Expand HBr/Ar into vacuum Translational and internal cooling occurs Rotational Temperature = 25 K
63 Experimental Protocol
64 Generating Laser Light Nd:YAG laser: 1064 nm, 8 ns pulse, cm -1 bandwidth, 1 J/pulse, 10 Hz rep rate. Dye laser: pumped by Nd:YAG laser, tunable nm, 0.1 cm -1 bandwidth, same temporal width as Nd:YAG, 25% efficiency. Non-linear optical crystals: _ 3 = _ 1 + _ 2, 10 50% efficiency.
65 Generating Laser Light 660 nm 60 mj 330 nm 10 mj Nd:YAG 2x Dye laser 2x 3x 1064 nm 1.5 J 532 nm 250 mj 220 nm 1 mj
66 Generating Laser Light Nd:YAG 532 nm 200 mj 2x 3x Dye laser 580 nm 50 mj 1064 nm 1.5 J 355 nm 80 mj 220 nm 10 mj
67 HBr Photolysis ()BrHBrHBrmThEmnʈ=-DÁ hn Generate collisions energies ~ 50 kcal/mol
68 Experimental Protocol
69 (2+1) Resonance-Enhanced Multiphoton Ionization Two-photon transition to a bound state. One-photon transition to the continuum. Transition line strengths may depend on quantum numbers. These transitions require light in the nm range: nonlinear optical mixing
70 Measuring Line Strengths Source of excited H 2 /HD/D 2 1) Populate many states 2) Known relative concentrations of each state Measure the relative concentrations in each quantum state. Any differences between known and measured concentrations result from differences in line strengths. Hot filament H 2 / HD / D 2 2,000 K ( )) (( ) ( )) (( ) Rinnen et al., Israel Journal of Chemistry 29, 369 (1989). Collision cell ( )) (( ) Pomerantz et al., Canadian Journal of Chemistry 82, 723 (2004).
71 (2+1) REMPI Line Strengths Line strengths depend strongly on v, weakly on j. In agreement with calculations and earlier experiments In all, 142 quantum states calibrated.
72 Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry +50 V -50 V -400 V -2,400 V -200 V 15.5
73 Ortho/Para H 2 Pauli Principle: When the labels on two identical particles are exchanged, the wave function must change signs (fermions) or retain its sign (bosons). Rotating a homonuclear diatomic molecule interchanges two identical particles, so symmetry must be considered. J = even: symmetric totelecvrtcoibnuyyyyy= J = odd: anti-symmetric SSSASAAA Symmetric state: triply degenerate Anti-symmetric state: singly degenerate
74 Experimental Results H + HBr Æ H 2 (v'=2, j') + Br Collision Energy = 53.0 kcal/mol
75 Surprisal Analysis R. D. Levine and R. B. Bernstein, Accounts of Chemical Research 7, 393 (1974). If conservation of energy is the only constraint, the partial cross sections for forming each state are equal to the degeneracy of that state. ()()()0,;21,;transPvjEjEvjE =+ Use information theoretical techniques to compare the actual distribution to this prior distribution. ()()0,;ln,;jvEPvjEbPvjEEE È -=Q + _>0: cold _=0: statistical _<0: hot
76 Surprisal Analysis
77 Br- H = 1.5 angstrom H-H = 1.0 angstrom Br-H-H = 180 degrees Density = 0.1e - /au 3 Red = +232 kcal/mol of positive electron charge Blue = +497 Energy = au Br- H = 1.5 angstrom H-H = 1.0 angstrom Br-H-H = 90 degrees Density = 0.1e - /au 3 Red = +232 kcal/mol of positive electron charge Blue = +497 Energy = au
78
79 Experimental Results H + HBr Æ H 2 (v'=2, j') + Br
80 Is This The Movie You First Imagined?
81 Mass-Weighted PES Collinear reactive collision A + BC Æ AB + C Two bond distances: R AB =R A -R B and R BC =R B -R C PROBLEM: The kinetic energy in the center of mass system is not a simple function of R AB and R BC.
82 Solution to Problem Introduce New Coordinates cossincos/[()()]1()2ABBCBCBCABCABCC
83 Interpretation T represents the kinetic energy of a mass point (unit mass) whose position is specified by the the two cartesian coordinates Q 1 and Q 2. If we regard the potential energy as a function of Q 1 and Q 2, the entrance and exit valleys will be an an angle _ to one another.
Roaming and Spectroscopy
 Roaming and Spectroscopy D. Townsend, S. A. Lahankar, S. K. Lee, S. D. Chambreau, A. G. Suits, X. Zhang, and J. Rheinecker, L. B. Harding, J. M. Bowman, Science. 306, 1158 (2004). J. M. Bowman, X. Zhang,
Roaming and Spectroscopy D. Townsend, S. A. Lahankar, S. K. Lee, S. D. Chambreau, A. G. Suits, X. Zhang, and J. Rheinecker, L. B. Harding, J. M. Bowman, Science. 306, 1158 (2004). J. M. Bowman, X. Zhang,
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
The Potential Energy Surface (PES) Preamble to the Basic Force Field Chem 4021/8021 Video II.i
 The Potential Energy Surface (PES) Preamble to the Basic Force Field Chem 4021/8021 Video II.i The Potential Energy Surface Captures the idea that each structure that is, geometry has associated with it
The Potential Energy Surface (PES) Preamble to the Basic Force Field Chem 4021/8021 Video II.i The Potential Energy Surface Captures the idea that each structure that is, geometry has associated with it
Assignment: Read Atkins, Chapter 27 sections 7 and 8 or McQuarrie and Simon, Chapter 30 sections 7 and 10, before coming to lab on Monday
 Classical Trajectory 1 Classical Trajectory Calculations H + H-F H-H + F Assignment: Read Atkins, Chapter 27 sections 7 and 8 or McQuarrie and Simon, Chapter 30 sections 7 and 10, before coming to lab
Classical Trajectory 1 Classical Trajectory Calculations H + H-F H-H + F Assignment: Read Atkins, Chapter 27 sections 7 and 8 or McQuarrie and Simon, Chapter 30 sections 7 and 10, before coming to lab
c re l 4. Controlling reagents and characterizing products Control of reagent orientation
 4. Controlling reagents and characterizing products Reagent state selection in molecular beams Selection of velocity in a molecular beam. Achieved through the use of choppers, control of source pressure,
4. Controlling reagents and characterizing products Reagent state selection in molecular beams Selection of velocity in a molecular beam. Achieved through the use of choppers, control of source pressure,
Photodissociation of 1-bromo-2-butene, 4-bromo-1-butene, and cyclopropylmethyl bromide at 234 nm studied using velocity map imaging
 THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 125, 144312 2006 Photodissociation of 1-bromo-2-butene, 4-bromo-1-butene, and cyclopropylmethyl bromide at 234 nm studied using velocity map imaging Kai-Chung Lau, Yi Liu,
THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 125, 144312 2006 Photodissociation of 1-bromo-2-butene, 4-bromo-1-butene, and cyclopropylmethyl bromide at 234 nm studied using velocity map imaging Kai-Chung Lau, Yi Liu,
Richard Miles and Arthur Dogariu. Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08540, USA
 Richard Miles and Arthur Dogariu Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08540, USA Workshop on Oxygen Plasma Kinetics Sept 20, 2016 Financial support: ONR and MetroLaser
Richard Miles and Arthur Dogariu Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08540, USA Workshop on Oxygen Plasma Kinetics Sept 20, 2016 Financial support: ONR and MetroLaser
Chem 442 Review of Spectroscopy
 Chem 44 Review of Spectroscopy General spectroscopy Wavelength (nm), frequency (s -1 ), wavenumber (cm -1 ) Frequency (s -1 ): n= c l Wavenumbers (cm -1 ): n =1 l Chart of photon energies and spectroscopies
Chem 44 Review of Spectroscopy General spectroscopy Wavelength (nm), frequency (s -1 ), wavenumber (cm -1 ) Frequency (s -1 ): n= c l Wavenumbers (cm -1 ): n =1 l Chart of photon energies and spectroscopies
1 Molecular collisions
 1 Molecular collisions The present exercise starts with the basics of molecular collisions as presented in Chapter 4 of the lecture notes. After that, particular attention is devoted to several specific
1 Molecular collisions The present exercise starts with the basics of molecular collisions as presented in Chapter 4 of the lecture notes. After that, particular attention is devoted to several specific
CHEM3023: Spins, Atoms and Molecules
 CHEM3023: Spins, Atoms and Molecules Lecture 3 The Born-Oppenheimer approximation C.-K. Skylaris Learning outcomes Separate molecular Hamiltonians to electronic and nuclear parts according to the Born-Oppenheimer
CHEM3023: Spins, Atoms and Molecules Lecture 3 The Born-Oppenheimer approximation C.-K. Skylaris Learning outcomes Separate molecular Hamiltonians to electronic and nuclear parts according to the Born-Oppenheimer
Raman and stimulated Raman spectroscopy of chlorinated hydrocarbons
 Department of Chemistry Physical Chemistry Göteborg University KEN140 Spektroskopi Raman and stimulated Raman spectroscopy of chlorinated hydrocarbons WARNING! The laser gives a pulsed very energetic and
Department of Chemistry Physical Chemistry Göteborg University KEN140 Spektroskopi Raman and stimulated Raman spectroscopy of chlorinated hydrocarbons WARNING! The laser gives a pulsed very energetic and
Laser Dissociation of Protonated PAHs
 100 Chapter 5 Laser Dissociation of Protonated PAHs 5.1 Experiments The photodissociation experiments were performed with protonated PAHs using different laser sources. The calculations from Chapter 3
100 Chapter 5 Laser Dissociation of Protonated PAHs 5.1 Experiments The photodissociation experiments were performed with protonated PAHs using different laser sources. The calculations from Chapter 3
Vibrational Autoionization in Polyatomic molecules
 Vibrational Autoionization in Polyatomic molecules S.T. Pratt Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2005. 56:281-308 2006. 12. 4. Choi, Sunyoung 1 Schedule 12/4 (Mon) - Introduction - Theoretical background 12/6 (Wed)
Vibrational Autoionization in Polyatomic molecules S.T. Pratt Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2005. 56:281-308 2006. 12. 4. Choi, Sunyoung 1 Schedule 12/4 (Mon) - Introduction - Theoretical background 12/6 (Wed)
Crossed-beams and Theoretical Studies of Hyperthermal Reactions of O(3P) with HCl
 University of South Carolina Scholar Commons Faculty Publications Chemistry and Biochemistry, Department of 2010 Crossed-beams and Theoretical Studies of Hyperthermal Reactions of O(3P) with HCl Jianming
University of South Carolina Scholar Commons Faculty Publications Chemistry and Biochemistry, Department of 2010 Crossed-beams and Theoretical Studies of Hyperthermal Reactions of O(3P) with HCl Jianming
Resonances in Chemical Reactions : Theory and Experiment. Toshiyuki Takayanagi Saitama University Department of Chemistry
 Resonances in Chemical Reactions : Theory and Experiment Toshiyuki Takayanagi Saitama University Department of Chemistry What is Chemical Reaction? Collision process between molecules (atoms) containing
Resonances in Chemical Reactions : Theory and Experiment Toshiyuki Takayanagi Saitama University Department of Chemistry What is Chemical Reaction? Collision process between molecules (atoms) containing
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions"
 Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
CHAPTER 13 Molecular Spectroscopy 2: Electronic Transitions
 CHAPTER 13 Molecular Spectroscopy 2: Electronic Transitions I. General Features of Electronic spectroscopy. A. Visible and ultraviolet photons excite electronic state transitions. ε photon = 120 to 1200
CHAPTER 13 Molecular Spectroscopy 2: Electronic Transitions I. General Features of Electronic spectroscopy. A. Visible and ultraviolet photons excite electronic state transitions. ε photon = 120 to 1200
Density Functional Theory Study on Mechanism of Forming Spiro-Geheterocyclic Ring Compound from Me 2 Ge=Ge: and Acetaldehyde
 CHINESE JURNAL F CHEMICAL PHYSICS VLUME 26, NUMBER 1 FEBRUARY 27, 2013 ARTICLE Density Functional Theory Study on Mechanism of Forming Spiro-Geheterocyclic Ring Compound from Me 2 Ge=Ge: and Acetaldehyde
CHINESE JURNAL F CHEMICAL PHYSICS VLUME 26, NUMBER 1 FEBRUARY 27, 2013 ARTICLE Density Functional Theory Study on Mechanism of Forming Spiro-Geheterocyclic Ring Compound from Me 2 Ge=Ge: and Acetaldehyde
l ; Y l,l-1, Y l,-1+1; etc., plus a single non-degenerate function Y l,0, in axial symmetry.
 Chapter 6 Along "Reaction Paths", Orbitals Can be Connected One-to-One According to Their Symmetries and Energies. This is the Origin of the Woodward-offmann Rules I. Reduction in Symmetry As fragments
Chapter 6 Along "Reaction Paths", Orbitals Can be Connected One-to-One According to Their Symmetries and Energies. This is the Origin of the Woodward-offmann Rules I. Reduction in Symmetry As fragments
ATOMS. Central field model (4 quantum numbers + Pauli exclusion) n = 1, 2, 3,... 0 l n 1 (0, 1, 2, 3 s, p, d, f) m l l, m s = ±1/2
 ATOMS Central field model (4 quantum numbers + Pauli exclusion) n = 1, 2, 3,... 0 l n 1 (0, 1, 2, 3 s, p, d, f) m l l, m s = ±1/2 Spectroscopic notation: 2S+1 L J (Z 40) L is total orbital angular momentum
ATOMS Central field model (4 quantum numbers + Pauli exclusion) n = 1, 2, 3,... 0 l n 1 (0, 1, 2, 3 s, p, d, f) m l l, m s = ±1/2 Spectroscopic notation: 2S+1 L J (Z 40) L is total orbital angular momentum
The Study of Chemical Reactions. Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order.
 The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
Studies on the photodissociation and symmetry of SO 2 D
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 118, NUMBER 20 22 MAY 2003 Studies on the photodissociation and symmetry of SO 2 D Limin Zhang, a) Zhong Wang, Jiang Li, Feng Wang, Shilin Liu, Shuqin Yu, and Xingxiao
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 118, NUMBER 20 22 MAY 2003 Studies on the photodissociation and symmetry of SO 2 D Limin Zhang, a) Zhong Wang, Jiang Li, Feng Wang, Shilin Liu, Shuqin Yu, and Xingxiao
The dynamics of the Cl n-c 4 H 10 \HCl v,j C 4 H 9 reaction at 0.32 ev
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 121, NUMBER 15 15 OCTOBER 2004 The dynamics of the Cl n-c 4 H 10 \HCl v,j C 4 H 9 reaction at 0.32 ev M. J. Bass, M. Brouard, and C. Vallance The Physical and Theoretical
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 121, NUMBER 15 15 OCTOBER 2004 The dynamics of the Cl n-c 4 H 10 \HCl v,j C 4 H 9 reaction at 0.32 ev M. J. Bass, M. Brouard, and C. Vallance The Physical and Theoretical
Modeling the Rovibrationally Excited C 2 H 4 OH Radicals from the Photodissociation of 2-Bromoethanol at 193 nm
 4934 J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 4934 4945 Modeling the Rovibrationally Excited C 2 H 4 OH Radicals from the Photodissociation of 2-Bromoethanol at 193 nm B. J. Ratliff, C. C. Womack, X. N. Tang, W. M.
4934 J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 4934 4945 Modeling the Rovibrationally Excited C 2 H 4 OH Radicals from the Photodissociation of 2-Bromoethanol at 193 nm B. J. Ratliff, C. C. Womack, X. N. Tang, W. M.
PHOTOELECTRON SPECTROSCOPY OF RADICALS
 PHOTOELECTRON SPECTROSCOPY OF RADICALS Shibu E S (CY07D011) Uday Baskar Rao (CY06D028) Jasmine Maria Joseph (CY07D010) Goutam Kumar Kole (CY05C008) Puran Kumar De (CY05C013) 1 PHOTOELECTRON SPECTROSCOPY
PHOTOELECTRON SPECTROSCOPY OF RADICALS Shibu E S (CY07D011) Uday Baskar Rao (CY06D028) Jasmine Maria Joseph (CY07D010) Goutam Kumar Kole (CY05C008) Puran Kumar De (CY05C013) 1 PHOTOELECTRON SPECTROSCOPY
Spectroscopy in Inorganic Chemistry. Vibration and Rotation Spectroscopy
 Spectroscopy in Inorganic Chemistry Vibrational energy levels in a diatomic molecule f = k r r V = ½kX 2 Force constant r Displacement from equilibrium point 2 X= r=r-r eq V = ½kX 2 Fundamental Vibrational
Spectroscopy in Inorganic Chemistry Vibrational energy levels in a diatomic molecule f = k r r V = ½kX 2 Force constant r Displacement from equilibrium point 2 X= r=r-r eq V = ½kX 2 Fundamental Vibrational
Determination of Absolute Product Branching Ratios in Mass Spectrometric Experiments: Detecting Acetyl Radicals at CH 2 CO +
 5200 J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 5200-5204 Determination of Absolute Product Branching Ratios in Mass Spectrometric Experiments: Detecting Acetyl Radicals at CH 2 C + D. C. Kitchen, T. L. Myers, and L. J.
5200 J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 5200-5204 Determination of Absolute Product Branching Ratios in Mass Spectrometric Experiments: Detecting Acetyl Radicals at CH 2 C + D. C. Kitchen, T. L. Myers, and L. J.
UV-vis (Electronic) Spectra Ch.13 Atkins, Ch.19 Engel
 XV 74 UV-vis (Electronic) Spectra-2014 -Ch.13 Atkins, Ch.19 Engel Most broadly used analytical tech / especially bio-applic. inexpensive optics / solvent & cell usually not problem intense transitions
XV 74 UV-vis (Electronic) Spectra-2014 -Ch.13 Atkins, Ch.19 Engel Most broadly used analytical tech / especially bio-applic. inexpensive optics / solvent & cell usually not problem intense transitions
Disagreement between theory and experiment in the simplest chemical reaction: Collision energy dependent rotational distributions for H D 2 \HD Ä3,j D
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 120, NUMBER 7 15 FEBRUARY 2004 Disagreement between theory and experiment in the simplest chemical reaction: Collision energy dependent rotational distributions for H
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 120, NUMBER 7 15 FEBRUARY 2004 Disagreement between theory and experiment in the simplest chemical reaction: Collision energy dependent rotational distributions for H
High-resolution slice imaging of quantum state-to-state photodissociation of methyl bromide
 High-resolution slice imaging of quantum state-to-state photodissociation of methyl bromide M. Laura Lipciuc and Maurice H. M. Janssen Citation: The Journal of Chemical Physics 127, 224310 (2007); doi:
High-resolution slice imaging of quantum state-to-state photodissociation of methyl bromide M. Laura Lipciuc and Maurice H. M. Janssen Citation: The Journal of Chemical Physics 127, 224310 (2007); doi:
Vibrational Spectra of Chloroform, Freon-11 and Selected Isotopomers in the THz Frequency Region
 Vibrational Spectra of Chloroform, Freon-11 and Selected Isotopomers in the THz Frequency Region Christa Haase, Jinjun Liu, Frédéric Merkt, Laboratorium für physikalische Chemie, ETH Zürich current address:
Vibrational Spectra of Chloroform, Freon-11 and Selected Isotopomers in the THz Frequency Region Christa Haase, Jinjun Liu, Frédéric Merkt, Laboratorium für physikalische Chemie, ETH Zürich current address:
Photodissociative spectroscopy of the hydroxymethyl radical CH 2 OH in the 3s and 3p x states
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 117, NUMBER 10 8 SEPTEMBER 2002 Photodissociative spectroscopy of the hydroxymethyl radical CH 2 OH in the 3s and 3p x states Lin Feng, Xin Huang, and Hanna Reisler Department
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 117, NUMBER 10 8 SEPTEMBER 2002 Photodissociative spectroscopy of the hydroxymethyl radical CH 2 OH in the 3s and 3p x states Lin Feng, Xin Huang, and Hanna Reisler Department
3. A forward reaction has an activation energy of 50 kj and a H of 100 kj. The PE. diagram, which describes this reaction, is
 Kinetics Quiz 4 Potential Energy Diagrams 1. A catalyst increases the rate of a reaction by A. Increasing the concentration of the reactant(s) B. Decreasing the concentration of the reactant(s) C. Increasing
Kinetics Quiz 4 Potential Energy Diagrams 1. A catalyst increases the rate of a reaction by A. Increasing the concentration of the reactant(s) B. Decreasing the concentration of the reactant(s) C. Increasing
Lecture 18 Chain reactions Nikolai Nikolaevic Semenov , Nobel 1956
 Lecture 18 Chain reactions Nikolai Nikolaevic Semenov 1896-1986, Nobel 1956 Chain reactions are examples of complex reactions, with complex rate expressions. In a chain reaction, the intermediate produced
Lecture 18 Chain reactions Nikolai Nikolaevic Semenov 1896-1986, Nobel 1956 Chain reactions are examples of complex reactions, with complex rate expressions. In a chain reaction, the intermediate produced
Rotational Raman Spectroscopy
 Rotational Raman Spectroscopy If EM radiation falls upon an atom or molecule, it may be absorbed if the energy of the radiation corresponds to the separation of two energy levels of the atoms or molecules.
Rotational Raman Spectroscopy If EM radiation falls upon an atom or molecule, it may be absorbed if the energy of the radiation corresponds to the separation of two energy levels of the atoms or molecules.
Comparison of near-threshold reactivity of ground-state and spin-orbit excited chlorine atoms with methane
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 115, NUMBER 1 1 JULY 2001 Comparison of near-threshold reactivity of ground-state and spin-orbit excited chlorine atoms with methane Zee Hwan Kim, Andrew J. Alexander,
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 115, NUMBER 1 1 JULY 2001 Comparison of near-threshold reactivity of ground-state and spin-orbit excited chlorine atoms with methane Zee Hwan Kim, Andrew J. Alexander,
Effect of bending and torsional mode excitation on the reaction Cl+CH 4 \HCl+CH 3
 THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 122, 084303 2005 Effect of bending and torsional mode excitation on the reaction Cl+CH 4 \HCl+CH 3 Zee Hwan Kim, a Hans A. Bechtel, Jon P. Camden, and Richard N. Zare b
THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 122, 084303 2005 Effect of bending and torsional mode excitation on the reaction Cl+CH 4 \HCl+CH 3 Zee Hwan Kim, a Hans A. Bechtel, Jon P. Camden, and Richard N. Zare b
Velocity Mapping Studies of Molecular Photodissociation and... 25
 Velocity Mapping Studies of Molecular Photodissociation and... 25 Other capabilities of velocity imaging have been described in previous articles. 20,21 An interesting demonstration is the imaging of D
Velocity Mapping Studies of Molecular Photodissociation and... 25 Other capabilities of velocity imaging have been described in previous articles. 20,21 An interesting demonstration is the imaging of D
1 Molecular collisions
 Advanced Kinetics Solution 9 April 29, 216 1 Molecular collisions 1.1 The bimolecular rate constant for the reaction is defined as: dc A dt = k(t )C A C B. (1) The attenuation of the intensity of the beam
Advanced Kinetics Solution 9 April 29, 216 1 Molecular collisions 1.1 The bimolecular rate constant for the reaction is defined as: dc A dt = k(t )C A C B. (1) The attenuation of the intensity of the beam
5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.80 Lecture
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.80 Lecture
CHM Physical Chemistry II Chapter 12 - Supplementary Material. 1. Einstein A and B coefficients
 CHM 3411 - Physical Chemistry II Chapter 12 - Supplementary Material 1. Einstein A and B coefficients Consider two singly degenerate states in an atom, molecule, or ion, with wavefunctions 1 (for the lower
CHM 3411 - Physical Chemistry II Chapter 12 - Supplementary Material 1. Einstein A and B coefficients Consider two singly degenerate states in an atom, molecule, or ion, with wavefunctions 1 (for the lower
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 1: Introduction to the molecular orbital theory
 Chemistry 2000 Lecture 1: Introduction to the molecular orbital theory Marc R. Roussel January 5, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Introduction to molecular orbitals January 5, 2018 1 / 24 Review: quantum mechanics
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 1: Introduction to the molecular orbital theory Marc R. Roussel January 5, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Introduction to molecular orbitals January 5, 2018 1 / 24 Review: quantum mechanics
Conjugated Systems. With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn
 Conjugated Systems Double bonds in conjugation behave differently than isolated double bonds With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn With isolated double bonds cannot draw resonance
Conjugated Systems Double bonds in conjugation behave differently than isolated double bonds With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn With isolated double bonds cannot draw resonance
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 34. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 34 From molecular to elemental analysis there are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry Mass spectrometry X-ray spectrometry
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 34 From molecular to elemental analysis there are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry Mass spectrometry X-ray spectrometry
Figure 1: Transition State, Saddle Point, Reaction Pathway
 Computational Chemistry Workshops West Ridge Research Building-UAF Campus 9:00am-4:00pm, Room 009 Electronic Structure - July 19-21, 2016 Molecular Dynamics - July 26-28, 2016 Potential Energy Surfaces
Computational Chemistry Workshops West Ridge Research Building-UAF Campus 9:00am-4:00pm, Room 009 Electronic Structure - July 19-21, 2016 Molecular Dynamics - July 26-28, 2016 Potential Energy Surfaces
WELCOME TO MODERN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 WELCOME TO MODERN ORGANIC CEMISTRY Organic Chemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 4 The Study of Chemical Reactions WAT IS A REACTION MECANISM A DESCRIPTION OF STRUCTURES AN ENERGIES OF STARTING
WELCOME TO MODERN ORGANIC CEMISTRY Organic Chemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 4 The Study of Chemical Reactions WAT IS A REACTION MECANISM A DESCRIPTION OF STRUCTURES AN ENERGIES OF STARTING
Pulsed lasers. To induce new chemistry, different from that initiated by conventional sources
 Pulsed lasers As part of a method to study photoinitiated chemical reactions To induce new chemistry, different from that initiated by conventional sources As a light source, to initiate the same chemistry
Pulsed lasers As part of a method to study photoinitiated chemical reactions To induce new chemistry, different from that initiated by conventional sources As a light source, to initiate the same chemistry
Abstract... I. Acknowledgements... III. Table of Content... V. List of Tables... VIII. List of Figures... IX
 Abstract... I Acknowledgements... III Table of Content... V List of Tables... VIII List of Figures... IX Chapter One IR-VUV Photoionization Spectroscopy 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Vacuum-Ultraviolet-Ionization
Abstract... I Acknowledgements... III Table of Content... V List of Tables... VIII List of Figures... IX Chapter One IR-VUV Photoionization Spectroscopy 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Vacuum-Ultraviolet-Ionization
5.3 Rotational Raman Spectroscopy General Introduction
 5.3 Rotational Raman Spectroscopy 5.3.1 General Introduction When EM radiation falls on atoms or molecules, it may be absorbed or scattered. If λis unchanged, the process is referred as Rayleigh scattering.
5.3 Rotational Raman Spectroscopy 5.3.1 General Introduction When EM radiation falls on atoms or molecules, it may be absorbed or scattered. If λis unchanged, the process is referred as Rayleigh scattering.
Molecular Beam Studies of Energy Transfer in Molecule Surface Interactions
 Molecular Beam Studies of Energy Transfer in Molecule Surface Interactions Dissertation for the award of the degree Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) Division of Mathematics and Natural Sciences of the Georg-August-Universität
Molecular Beam Studies of Energy Transfer in Molecule Surface Interactions Dissertation for the award of the degree Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) Division of Mathematics and Natural Sciences of the Georg-August-Universität
Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3
 Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3 1. Carbon-carbon bonds are not easily broken. Which bond in the following compound would be the least difficult to break homolytically? 2. Which of the following molecules
Organic Chemistry(I) Chapter 3 1. Carbon-carbon bonds are not easily broken. Which bond in the following compound would be the least difficult to break homolytically? 2. Which of the following molecules
Photoelectron spectroscopy via the 1 1 u state of diacetylene
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 116, NUMBER 10 8 MARCH 2002 Photoelectron spectroscopy via the 1 1 u state of diacetylene C. Ramos, P. R. Winter, and T. S. Zwier Department of Chemistry, Purdue University,
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 116, NUMBER 10 8 MARCH 2002 Photoelectron spectroscopy via the 1 1 u state of diacetylene C. Ramos, P. R. Winter, and T. S. Zwier Department of Chemistry, Purdue University,
Progress of the interaction between e - and molecule in Fudan University
 Progress of the interaction between e - and molecule in Fudan University B. Wei, Z. Chen, X. Wang, R. Hutton, Y. Zou Fudan University, Shanghai The 2nd Research Coordination Meeting (RCM) of the CRP, 23-25
Progress of the interaction between e - and molecule in Fudan University B. Wei, Z. Chen, X. Wang, R. Hutton, Y. Zou Fudan University, Shanghai The 2nd Research Coordination Meeting (RCM) of the CRP, 23-25
Theoretical Studies of Reaction Mechanisms Relevant to Hydrocarbon Growth in Titan s Atmosphere
 Theoretical Studies of Reaction Mechanisms Relevant to Hydrocarbon Growth in Titan s Atmosphere Alexander M. Mebel, Adeel Jamal, Alexander Landera, and Ralf I. Kaiser Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
Theoretical Studies of Reaction Mechanisms Relevant to Hydrocarbon Growth in Titan s Atmosphere Alexander M. Mebel, Adeel Jamal, Alexander Landera, and Ralf I. Kaiser Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
Chem 442 Review for Exam 2. Exact separation of the Hamiltonian of a hydrogenic atom into center-of-mass (3D) and relative (3D) components.
 Chem 44 Review for Exam Hydrogenic atoms: The Coulomb energy between two point charges Ze and e: V r Ze r Exact separation of the Hamiltonian of a hydrogenic atom into center-of-mass (3D) and relative
Chem 44 Review for Exam Hydrogenic atoms: The Coulomb energy between two point charges Ze and e: V r Ze r Exact separation of the Hamiltonian of a hydrogenic atom into center-of-mass (3D) and relative
GAS PHASE CHEMICAL KINETICS : EXPERIMENTAL ADVANCES AND PROSPECTS
 GAS PHASE CHEMICAL KINETICS : EXPERIMENTAL ADVANCES AND PROSPECTS Sébastien Le Picard France Astrophysique de Laboratoire Institut de Physique de Rennes Université de Rennes 1 Gas phase chemistry in the
GAS PHASE CHEMICAL KINETICS : EXPERIMENTAL ADVANCES AND PROSPECTS Sébastien Le Picard France Astrophysique de Laboratoire Institut de Physique de Rennes Université de Rennes 1 Gas phase chemistry in the
Lecture 9. Detailed Balance, and Nonreactive Scattering of Molecules
 Lecture 9 Detailed Balance, and Nonreactive Scattering of Molecules 2014 D.J. Auerbach All rights reserved Reading List 1. Cardillo, M.J., M. Balooch, and R.E. Stickney, Detailed Balancing and Quasi- Equilibrium
Lecture 9 Detailed Balance, and Nonreactive Scattering of Molecules 2014 D.J. Auerbach All rights reserved Reading List 1. Cardillo, M.J., M. Balooch, and R.E. Stickney, Detailed Balancing and Quasi- Equilibrium
Figure 1 Relaxation processes within an excited state or the ground state.
 Excited State Processes and Application to Lasers The technology of the laser (Light Amplified by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) was developed in the early 1960s. The technology is based on an understanding
Excited State Processes and Application to Lasers The technology of the laser (Light Amplified by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) was developed in the early 1960s. The technology is based on an understanding
Reactions of Atomic Hydrogen with Isotopes of Nitric Oxide in Solid Parahydrogen
 University of Wyoming Wyoming Scholars Repository Honors Theses AY 15/16 Undergraduate Honors Theses Spring 5-12-2016 Reactions of Atomic Hydrogen with Isotopes of Nitric Oxide in Solid Parahydrogen Manford
University of Wyoming Wyoming Scholars Repository Honors Theses AY 15/16 Undergraduate Honors Theses Spring 5-12-2016 Reactions of Atomic Hydrogen with Isotopes of Nitric Oxide in Solid Parahydrogen Manford
MOLECULAR BEAM STUDIES OF ELEMENTARY CHEMICAL PROCESSES
 MOLECULAR BEAM STUDIES OF ELEMENTARY CHEMICAL PROCESSES Nobel lecture, 8 December, 1986 by YUAN TSEH LEE Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory and Department of Chemistry, University of California, Berkeley, CA
MOLECULAR BEAM STUDIES OF ELEMENTARY CHEMICAL PROCESSES Nobel lecture, 8 December, 1986 by YUAN TSEH LEE Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory and Department of Chemistry, University of California, Berkeley, CA
Module 4 : Third order nonlinear optical processes. Lecture 28 : Inelastic Scattering Processes. Objectives
 Module 4 : Third order nonlinear optical processes Lecture 28 : Inelastic Scattering Processes Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Light scattering- elastic and inelastic-processes,
Module 4 : Third order nonlinear optical processes Lecture 28 : Inelastic Scattering Processes Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Light scattering- elastic and inelastic-processes,
Critical Exponents. From P. Chaikin and T Lubensky Principles of Condensed Matter Physics
 Critical Exponents From P. Chaikin and T Lubensky Principles of Condensed Matter Physics Notice that convention allows for different exponents on either side of the transition, but often these are found
Critical Exponents From P. Chaikin and T Lubensky Principles of Condensed Matter Physics Notice that convention allows for different exponents on either side of the transition, but often these are found
Study of Chemical Reactions
 Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Non-Equilibrium Reaction Rates in Hydrogen Combustion
 25 th ICDERS August 2 7, 25 Leeds, UK Non-Equilibrium Reaction Rates in Hydrogen Combustion Stephen J. Voelkel, Venkat Raman 2, Philip Varghese The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX 7872, USA 2
25 th ICDERS August 2 7, 25 Leeds, UK Non-Equilibrium Reaction Rates in Hydrogen Combustion Stephen J. Voelkel, Venkat Raman 2, Philip Varghese The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX 7872, USA 2
Nuclear spin temperatures of hydrogen and water molecules formed and trapped on ice. Naoki Watanabe
 9 Jun 2014, Nuclear Spin Effects in Astrochemistry 2014, Göteborg Nuclear spin temperatures of hydrogen and water molecules formed and trapped on ice Naoki Watanabe Institute of Low Temperature Science,
9 Jun 2014, Nuclear Spin Effects in Astrochemistry 2014, Göteborg Nuclear spin temperatures of hydrogen and water molecules formed and trapped on ice Naoki Watanabe Institute of Low Temperature Science,
Thomas A. A. Oliver, Graeme A. King, Michael N. R. Ashfold
 Electronic Supplementary Information for: Position Matters: Competing O H and N H Photodissociation Pathways in Hydroxy- and Methoxy- substituted Indoles Thomas A. A. Oliver, Graeme A. King, Michael N.
Electronic Supplementary Information for: Position Matters: Competing O H and N H Photodissociation Pathways in Hydroxy- and Methoxy- substituted Indoles Thomas A. A. Oliver, Graeme A. King, Michael N.
2D Methyl Radical Measurement in a Methane/Air Flame at Atmospheric. Pressure. Abstract
 2D Methyl Radical Measurement in a Methane/Air Flame at Atmospheric Pressure Yue Wu, Zhili Zhang Mechanical, Aerospace and Biomedical Engineering Department, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996,
2D Methyl Radical Measurement in a Methane/Air Flame at Atmospheric Pressure Yue Wu, Zhili Zhang Mechanical, Aerospace and Biomedical Engineering Department, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996,
Spectroscopy, Energetics,, and Reaction Dynamics of Neutrals and Ions by High-Resolution. Photoionization and Photoelectron Methods
 Spectroscopy, Energetics,, and Reaction Dynamics of Neutrals and Ions by High-Resolution Photoionization and Photoelectron Methods Cheuk-Yiu Ng Department of Chemistry University of California, Davis Davis,
Spectroscopy, Energetics,, and Reaction Dynamics of Neutrals and Ions by High-Resolution Photoionization and Photoelectron Methods Cheuk-Yiu Ng Department of Chemistry University of California, Davis Davis,
Introduction to laser-based combustion diagnostics
 Introduction to laser-based combustion diagnostics (Lecture 1b) Lecture prepared for course in laser-based combustion diagnostics by Per-Erik Bengtsson and Joakim Bood Division of Combustion Physics at
Introduction to laser-based combustion diagnostics (Lecture 1b) Lecture prepared for course in laser-based combustion diagnostics by Per-Erik Bengtsson and Joakim Bood Division of Combustion Physics at
MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY
 MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY First Edition Jeanne L. McHale University of Idaho PRENTICE HALL, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 CONTENTS PREFACE xiii 1 INTRODUCTION AND REVIEW 1 1.1 Historical Perspective
MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY First Edition Jeanne L. McHale University of Idaho PRENTICE HALL, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 CONTENTS PREFACE xiii 1 INTRODUCTION AND REVIEW 1 1.1 Historical Perspective
Chapter 7: Optical Properties of Solids. Interaction of light with atoms. Insert Fig Allowed and forbidden electronic transitions
 Chapter 7: Optical Properties of Solids Interaction of light with atoms Insert Fig. 8.1 Allowed and forbidden electronic transitions 1 Insert Fig. 8.3 or equivalent Ti 3+ absorption: e g t 2g 2 Ruby Laser
Chapter 7: Optical Properties of Solids Interaction of light with atoms Insert Fig. 8.1 Allowed and forbidden electronic transitions 1 Insert Fig. 8.3 or equivalent Ti 3+ absorption: e g t 2g 2 Ruby Laser
An axis-specific rotational rainbow in the direct scatter of formaldehyde from Au(111) and its influence on trapping probability
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Supplementary Information An axis-specific rotational rainbow in the direct scatter
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Supplementary Information An axis-specific rotational rainbow in the direct scatter
Be H. Delocalized Bonding. Localized Bonding. σ 2. σ 1. Two (sp-1s) Be-H σ bonds. The two σ bonding MO s in BeH 2. MO diagram for BeH 2
 The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
CHM 5423 Atmospheric Chemistry Notes on kinetics (Chapter 4)
 CHM 5423 Atmospheric Chemistry Notes on kinetics (Chapter 4) Introduction A mechanism is one or a series of elementary reactions that convert reactants into products or otherwise model the chemistry of
CHM 5423 Atmospheric Chemistry Notes on kinetics (Chapter 4) Introduction A mechanism is one or a series of elementary reactions that convert reactants into products or otherwise model the chemistry of
Photodissociation spectroscopy and dynamics of CH 3 O and CD 3 O
 J. Phys. Chem. A 1997, 101, 6583-6592 6583 Photodissociation spectroscopy and dynamics of CH 3 O and CD 3 O David L. Osborn, David J. Leahy, and Daniel M. Neumark* Department of Chemistry, UniVersity of
J. Phys. Chem. A 1997, 101, 6583-6592 6583 Photodissociation spectroscopy and dynamics of CH 3 O and CD 3 O David L. Osborn, David J. Leahy, and Daniel M. Neumark* Department of Chemistry, UniVersity of
Dissociation Channels of the 1-Propenyl Radical and Its Photolytic Precursor cis-1-bromopropene
 J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 10831-10842 10831 Dissociation Channels of the 1-Propenyl Radical and Its Photolytic Precursor cis-1-bromopropene Melita L. Morton, Johanna L. Miller, and Laurie J. Butler*
J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 10831-10842 10831 Dissociation Channels of the 1-Propenyl Radical and Its Photolytic Precursor cis-1-bromopropene Melita L. Morton, Johanna L. Miller, and Laurie J. Butler*
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy
 Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
I. INTRODUCTION JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 110, NUMBER 21 1 JUNE 1999
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 110, NUMBER 21 1 JUNE 1999 Crossed-beam reaction of carbon atoms with hydrocarbon molecules. V. Chemical dynamics of n-c 4 H 3 formation from reaction of C 3 P j with
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 110, NUMBER 21 1 JUNE 1999 Crossed-beam reaction of carbon atoms with hydrocarbon molecules. V. Chemical dynamics of n-c 4 H 3 formation from reaction of C 3 P j with
Introduction to Theories of Chemical Reactions. Graduate Course Seminar Beate Flemmig FHI
 Introduction to Theories of Chemical Reactions Graduate Course Seminar Beate Flemmig FHI I. Overview What kind of reactions? gas phase / surface unimolecular / bimolecular thermal / photochemical What
Introduction to Theories of Chemical Reactions Graduate Course Seminar Beate Flemmig FHI I. Overview What kind of reactions? gas phase / surface unimolecular / bimolecular thermal / photochemical What
Symmetry: Translation and Rotation
 Symmetry: Translation and Rotation The sixth column of the C 2v character table indicates the symmetry species for translation along (T) and rotation about (R) the Cartesian axes. y y y C 2 F v (x) T x
Symmetry: Translation and Rotation The sixth column of the C 2v character table indicates the symmetry species for translation along (T) and rotation about (R) the Cartesian axes. y y y C 2 F v (x) T x
CHEMICAL REACTION DYNAMICS BEYOND THE BORN-OPPENHEIMER APPROXIMATION
 Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1998. 49:125 71 Copyright c 1998 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved CHEMICAL REACTION DYNAMICS BEYOND THE BORN-OPPENHEIMER APPROXIMATION Laurie J. Butler Department of Chemistry
Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1998. 49:125 71 Copyright c 1998 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved CHEMICAL REACTION DYNAMICS BEYOND THE BORN-OPPENHEIMER APPROXIMATION Laurie J. Butler Department of Chemistry
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 36, no. 3A, September,
 Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 36, no. 3A, September, 2006 725 Effects of Molecular Rovibrational States and Surface Topologies for Molecule-Surface Interaction: Chemisorption Dynamics of D 2 Collision
Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 36, no. 3A, September, 2006 725 Effects of Molecular Rovibrational States and Surface Topologies for Molecule-Surface Interaction: Chemisorption Dynamics of D 2 Collision
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Rethinking Hybridization
 Rethinking Hybridization For more than 60 years, one of the most used concepts to come out of the valence bond model developed by Pauling was that of hybrid orbitals. The ideas of hybridization seemed
Rethinking Hybridization For more than 60 years, one of the most used concepts to come out of the valence bond model developed by Pauling was that of hybrid orbitals. The ideas of hybridization seemed
An Overview of Organic Reactions. Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants:
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
 Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules +e r n = 3 n = 2 n = 1 +e +e r ψ even Lecture 19, p 1 Today Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Using RF photons to drive transitions between nuclear spin orientations in
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules +e r n = 3 n = 2 n = 1 +e +e r ψ even Lecture 19, p 1 Today Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Using RF photons to drive transitions between nuclear spin orientations in
Title. Author(s)Tachikawa, Hiroto. CitationThe Journal of Chemical Physics, 125(133119) Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type.
 Title Direct ab initio molecular dynamics study on a micro Author(s)Tachikawa, Hiroto CitationThe Journal of Chemical Physics, 125(133119) Issue Date 2006-10-07 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/14882
Title Direct ab initio molecular dynamics study on a micro Author(s)Tachikawa, Hiroto CitationThe Journal of Chemical Physics, 125(133119) Issue Date 2006-10-07 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/14882
Chem ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I CHEM 221 /4 02 Final Examination April 20, 2005 0900-1200 Dr. Cerrie ROGERS x x periodic table & pk a data table provided non-programmable calculators allowed molecular model kits allowed
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I CHEM 221 /4 02 Final Examination April 20, 2005 0900-1200 Dr. Cerrie ROGERS x x periodic table & pk a data table provided non-programmable calculators allowed molecular model kits allowed
Ho:YLF pumped HBr laser
 Ho:YLF pumped HBr laser L R Botha, 1,2,* C Bollig, 1 M J D Esser, 1 R N Campbell 4, C Jacobs 1,3 and D R Preussler 1 1 National Laser Centre, CSIR, Pretoria, South Africa 2 Laser Research Institute, Department
Ho:YLF pumped HBr laser L R Botha, 1,2,* C Bollig, 1 M J D Esser, 1 R N Campbell 4, C Jacobs 1,3 and D R Preussler 1 1 National Laser Centre, CSIR, Pretoria, South Africa 2 Laser Research Institute, Department
What is the major product of the following reaction?
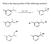 What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
QUANTUM MECHANICS AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
 6 QUANTUM MECHANICS AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 6.1 Quantum Picture of the Chemical Bond 6.2 Exact Molecular Orbital for the Simplest Molecule: H + 2 6.3 Molecular Orbital Theory and the Linear Combination
6 QUANTUM MECHANICS AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 6.1 Quantum Picture of the Chemical Bond 6.2 Exact Molecular Orbital for the Simplest Molecule: H + 2 6.3 Molecular Orbital Theory and the Linear Combination
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS)
 CHEM53200: Lecture 10 Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Major reference: Surface Analysis Edited by J. C. Vickerman (1997). 1 Primary particles may be: Secondary particles can be e s, neutral species
CHEM53200: Lecture 10 Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Major reference: Surface Analysis Edited by J. C. Vickerman (1997). 1 Primary particles may be: Secondary particles can be e s, neutral species
D. De Fazio, T. V. Tscherbul 2, S. Cavalli 3, and V. Aquilanti 3
 D. De Fazio, T. V. Tscherbul, S. Cavalli 3, and V. Aquilanti 3 1 Istituto di Struttura della Materia C.N.R., 00016 Roma, Italy Department of Chemistry, University of Toronto, M5S 3H6, Canada 3 Dipartimento
D. De Fazio, T. V. Tscherbul, S. Cavalli 3, and V. Aquilanti 3 1 Istituto di Struttura della Materia C.N.R., 00016 Roma, Italy Department of Chemistry, University of Toronto, M5S 3H6, Canada 3 Dipartimento
Resonant enhanced electron impact dissociation of molecules
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Resonant enhanced electron impact dissociation of molecules Recent citations - An R-matrix study of singlet and triplet continuum states of N 2 Duncan A Little and
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Resonant enhanced electron impact dissociation of molecules Recent citations - An R-matrix study of singlet and triplet continuum states of N 2 Duncan A Little and
Chemistry 543--Final Exam--Keiderling May 5, pm SES
 Chemistry 543--Final Exam--Keiderling May 5,1992 -- 1-5pm -- 174 SES Please answer all questions in the answer book provided. Make sure your name is clearly indicated and that the answers are clearly numbered,
Chemistry 543--Final Exam--Keiderling May 5,1992 -- 1-5pm -- 174 SES Please answer all questions in the answer book provided. Make sure your name is clearly indicated and that the answers are clearly numbered,
Mass Spectrometry. Introduction EI-MS and CI-MS Molecular mass & formulas Principles of fragmentation Fragmentation patterns Isotopic effects
 Mass Spectrometry Introduction EI-MS and CI-MS Molecular mass & formulas Principles of fragmentation Fragmentation patterns Isotopic effects 1 Introduction to MS Mass spectrometry is the method of analysis
Mass Spectrometry Introduction EI-MS and CI-MS Molecular mass & formulas Principles of fragmentation Fragmentation patterns Isotopic effects 1 Introduction to MS Mass spectrometry is the method of analysis
Exam 4 Review. Exam Review: A exam review sheet for exam 4 will be posted on the course webpage. Additionally, a practice exam will also be posted.
 Chem 4502 Quantum Mechanics & Spectroscopy (Jason Goodpaster) Exam 4 Review Exam Review: A exam review sheet for exam 4 will be posted on the course webpage. Additionally, a practice exam will also be
Chem 4502 Quantum Mechanics & Spectroscopy (Jason Goodpaster) Exam 4 Review Exam Review: A exam review sheet for exam 4 will be posted on the course webpage. Additionally, a practice exam will also be
Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy
 Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy Jim Cao Frontier of ultrafast science MeV UED Transition pathways Rate and time scale Elementary steps Probe dynamics on the atomic
Scientific opportunities with ultrafast electron diffraction & microscopy Jim Cao Frontier of ultrafast science MeV UED Transition pathways Rate and time scale Elementary steps Probe dynamics on the atomic
Study of the total and partial fragmentation dynamics of Ar HCl after uv photodissociation
 Study of the total and partial fragmentation dynamics of Ar HCl after uv photodissociation A. Garca-Vela Citation: The Journal of Chemical Physics 108, 5755 (1998); doi: 10.1063/1.475986 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.475986
Study of the total and partial fragmentation dynamics of Ar HCl after uv photodissociation A. Garca-Vela Citation: The Journal of Chemical Physics 108, 5755 (1998); doi: 10.1063/1.475986 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.475986
Lecture 4: Polyatomic Spectra
 Lecture 4: Polyatomic Spectra 1. From diatomic to polyatomic Ammonia molecule A-axis. Classification of polyatomic molecules 3. Rotational spectra of polyatomic molecules N 4. Vibrational bands, vibrational
Lecture 4: Polyatomic Spectra 1. From diatomic to polyatomic Ammonia molecule A-axis. Classification of polyatomic molecules 3. Rotational spectra of polyatomic molecules N 4. Vibrational bands, vibrational
