Performance Prediction of Multi-Phase Induction Motor
|
|
|
- Elfrieda Booker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology ISSN INPRESSCO. All Rights Resered. Aailable at Performance Prediction of Multi-Phase Induction Motor Prabhat Kumar Ȧ and K.B.Yada Ȧ Ȧ Department of Electrical Engineering, NIT Jamshedpur,India) Accepted 05 Noember 2013, Aailable online 01 December 2013, Vol.3, No.5 (December 2013) Abstract Performance prediction of an asymmetrically wound multi-phase (6-phase) induction motor under arious phase loss conditions on the basis of comparatie analysis is presented. The captured scopes are accompanied by a magnified (zoom) in order to obtain a better sense of the consequences on the torque-ripple content in the resulting time-domain torque profile. The phase loss scenarios analyzed in this paper are based on the simulated result of an AWSP-IM a modeled using MATLAB/SIMULINK platform. The analysis of ripple contents in the torque profiles under arious phase loss conditions reflects the deterioration of the torque-profile quality in each case. Further its comparison with result of three phase counterpart shows that AWSP-IM exhibits better performance than the Three Phase Induction Motor (TPIM) under the phase loss without any external control techniques. Moreoer, some of the cases gae results, which were ery close to the healthy operation of TPIM. Keywords: AWSP-IM, Comparatie analysis, Phase loss conditions, TPIM 1. Introduction 1 Very early Induction motors had two phases, but in all performance aspects three-phase ersion ery soon replaced these, and resulted in a motor that was generally better Increasing the number of phases beyond three, though may be costly, has the adantages which might be worth considering for certain special applications. Multiphase motors (more than three) find their application in areas which require high reliability, power density and high efficiency. Although multi-phase motor dries hae been around for more than 35 years, it is in the last fie years or so that one sees a substantial increase in the olume of research related to these motor drie systems. For multiphase induction machines, as in three phase induction machines, the constant olts/hertz (V/f) control was extensiely studied in the 1970 s and 1980 s, whereas in recent times the emphasis has shifted to ector (field-oriented) control and direct torque control of induction motors. A most important area of research is the deelopment of fault-tolerant control techniques for multiphase motors. Control algorithms used for continuous disturbance free operation of multi-phase induction and permanent magnet machines can be found in the literature in references. For a three-phase motor to continue operating under loss of one phase, a diided dc bus and neutral connection are required. In other words, a zero sequence component is necessary to proide an undisturbed rotating MMF after a phase is lost. Due to their additional degrees of freedom, multi-phase (more than three) motors are potentially more fault tolerant than their three-phase counterparts. This also eliminates the need for accessibility to the neutral line. If one phase of a multi-phase machine is open circuited, the combination of phase currents required to generate an undisturbed forward rotating MMF is no longer unique. The most important consideration then is to establish on optimum set of currents which would produce the same alue of MMF as under the healthy conditions. Therefore, with proper current control, an undisturbed forward rotating MMF can be maintained, which can be used to control the electromagnetic torque. Similar control algorithms can be worked out for any other multi-phase machine, in the case of an open-circuit. Due to additional degrees of freedom, the current in the remaining phases can be used to control the torque of the machine without the presence of negatie-sequence or zero-sequence current. Some of the other areas of research include modeling of multi-phase induction machine with structural unbalance, influence of the loss of a stator phase /phases on the stator current spectrum. This is done through studying the behaior of some of the frequency components which depend on the speed/slip of the motor. The fluctuation of these frequencies was examined to ealuate the effect of torque ripples generated by the negatie sequence component in the stator current which is associated with loss of phase/phases. One of their main adantages is an inherent higher reliability at a system leel and this is because, a multiphase machine can operate with an asymmetrical winding *Corresponding author: Prabhat Kumar 1756
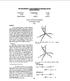
2 configuration in the case of loss of more than one inerter leg/a machine phase. Thus, on the basis of literature surey it has been found that the conentional three-phase induction motors hae an inherent drawback in so far as performance under loss of phase conditions. The two-phase operation of a threephase induction motor doesn t proide the necessary performance such as torque and output power under applications which require high reliability such as in electric traction applications, electric ship propulsion, etc. Therefore one of the means to oercome this drawback is by the addition of more phases. The detailed inestigation particularly in suriability aspects of machine under faulty conditions is quite essential from design points of iew and hence the work is on improing reliability of operation of induction motors in case of phase-loss scenarios by incorporating the multi-phase (more than three) design concept. 0 r i ( ) p The torque and rotor dynamics equations can be expressed as: T 3/ 2)( P/ 2)[( i i ) ( i i ) ] (7) em ( q1 q2 md d1 d 2 mq i m is gien by 2 2 i [( i i i ) ( i i i ) ] (8) m r k r dr q1 q2 d1 d 2 dr where, = the speed of the reference frame, P = differentiation w.r.t. time, = the rotor speed, k r All other symbols hae their usual meaning rotor quantities are referred to stator. (6) 2. Mathematical model A schematic representation of the stator and rotor windings for a two pole, six phase induction machine is gien in figure 1. Fig.2 The q-and d-axis equialent circuit of a six- phase induction m/c in arbitrary reference frame Fig.1 A two-pole six-phase induction machine with displacement between two stator winding set 3. Simulation of the 6-phase induction motor under arious phase loss scenarios 6-phase stator are diided into two Y connected three phase sets, abc and xyz, whose magnetic axes are displaced by an arbitrary angle α. The windings of each 3 - phase set are uniformly distributed and hae axes that are displaced apart. 3-ph rotor windings ar, br, cr are also sinusoidal distributed and hae axes that are displaced by apart. Equations are deeloped, which describe the behaior of a multi-phase machine. The following oltage equations of a multi-phase induction machine in arbitrary reference frame are: ri p q1 1 q1 k d1 q1 d1 1 d1 k q1 d1 r i p q2 2 q2 k d 2 q2 ri r i p d 2 2 d 2 k q2 d 2 0 r i ( ) p r dr p k r dr (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) Fig.3 Flow-Chart of types of phase-loss scenarios As depicted in Fig 3, the phase loss scenarios studied in this work are, 5-phase operation where there is a loss of 1757
3 one phase, 4-phase operation where there is a loss of two phases and 3-phase operation where there is a loss of three phases. Furthermore, the 4-phase and 3-phase operations, in which two or three phases hae been taken out of serice, were studied under conditions where there is a loss of adjacent phases that is a loss of phases which are located adjacent to each other or alternately a loss of two or more phases which are non-adjacent to each other, that is the loss of phases separated by one or two other healthy phases were also studied in this work healthy phase conditions Fig.4 shows the phasor representation of oltages in the 6- phase healthy case. In Fig 5 the torque profiles of the 6- phase healthy is shown. Fig.7 Torque profile of the 5-healthy phase case with loss of phase A (Ripple content: 18.33%) These figures show magnified (zoom), portion of the steady-state torque profiles, in order to obtain a better sense of the consequences of the loss of one phase on the torque-ripple content in the resulting time-domain torque profile. From these analysis, the torque ripple content in the resulting torque is 18.33% with the 5-healthy phases and one faulty phase case, in comparison with 6.67% torque ripple content in the healthy six-phase case. 3.3 The four healthy phases two faulty phase operation Fig.4 Voltage phasors in healthy six-phase operation Fig.5 show magnified (zoom), portion of the steady-state torque profiles, in order to obtain a better sense of the torque-ripple content in the time-domain torque profile. Here two cases are considered, one case is the loss of two adjacent phases and the other case is the loss of two nonadjacent phases. Fig.5Torque profile of the healthy 6-phase case under full- load (Ripple content: 6.67 %) healthy phase conditions and one faulty phase operation Fig.6 shows oltage phasors the fie-phase healthy and one faulty phase case, under the loss of phase A. In Fig 7 and Fig 5, the torque profiles of the faulty case with 5 healthy phases are compared with the 6-phase healthy. Fig.8 Flow chart of 4-phase operations Fig 8 summarizes the four-healthy phase and two faulty phase operations Loss of two adjacent phases Fig.6 Voltage phasors in the fie-phase operation with loss of phase A In this case, the 6-phase motor is simulated under loss of two adjacent phases namely Phase A and Phase B. Fig 9 shows the phasor representation of oltages in the fourhealthy phase faulty two-phase case under loss of phase A and phase B. In Fig 10 and Fig 5, the torque profiles of the 4-healthy phase and two faulty phases case are compared 1758
4 with the 6-healthy phase case. These figures show magnified (zoom) portion of the steady-state torque profiles. Fig.12 Torque profile of the 4-healthy phase case with loss of non- adjacent phases A and C (Ripple content: %) Fig.9 Phasor representation of the oltages in the fourhealthy phase operation with loss of adjacent phases A and B In the second case, the six-phase motor is simulated under loss of two non-adjacent Phases separated by e, i.e., the loss of phase A and phase D are considered. Fig 13 show the phasor representation of oltages in the four phase healthy case with two non-adjacent faulty phases separated by e under loss of phase A and phase D. In Fig 14 and Fig 5, the torque profile of the four-phase healthy case with two non-adjacent faulty phases separated by e is compared with the 6-phase healthy case. Fig.10 Torque profile of the 4-healthy phase case with loss of two adjacent phases A and B (Ripple content: %) From the aboe analysis, the torque ripple content in the resulting torque is % with the 4-healthy phases and two faulty phase adjacent to each other, in comparison with 6.67% torque ripple content in the healthy six-phase case. This is significant, and some applications may constitute an unacceptable performance. Fig.13 Phasor representation of the oltages in the 4- healthy phase with two non-adjacent faulty phase with loss of phases A and D Loss of two non-adjacent phases Here, the two non-adjacent faulty phase cases are considered, In the first case, the 6-phase motor is simulated under loss of two non-adjacent phases separated by e i.e., loss of phase A and phase C are considered. Fig 11 shows the phasor representation of the oltages in the four-healthy phase faulty two-phase case such as under loss of phase A and phase C. In Fig 12 and Fig 5, the torque profile of the 4-healthy phase with two faulty phases separated by e is compared with the 6-phase healthy case. These figures show magnified (zoom) portion of the steady-state torque profiles Fig.11Phasor representation of the oltages in the fourhealthy phases with two non-adjacent faulty phase with loss of phases A and C Fig.14 Torque profile of the4-healthy phase case with loss of two non-adjacent phases A and D (Ripple content: 111%) The torque ripple content in the resulting torque is % with the 4-healthy phases and two non-adjacent faulty phase separated by e, in comparison with 6.67% torque ripple content in the healthy 6-phase case whereas, the torque ripple content in the 4-healthy phases and two non-adjacent faulty phase separated by e is 111% in comparison with 6.67% torque ripple content in the healthy 6-phase case. It should be obsered that for the two non-adjacent faulty phase cases there is a marked difference between the e separation and the e separation cases in so far as the aderse effect on the 1759
5 ripple content in the time-domain torque profile. The e separation is far less seere. 4. The 3-healthy phase and 3-faulty phase operation When there is loss of three adjacent phases each separated by 60 e and when there is loss of three non-adjacent phases each separated by 120 e. Fig.17 Torque profile of healthy phase case with loss of three adjacent phases A, B and C (Ripple content: 178%) From the aboe analysis, the torque ripple content in the resulting torque is 178 % with the 3-healthy phases and three adjacent faulty phases, in comparison with 6.67% torque ripple content in the healthy six-phase case. This is a ery significant amount of torque ripple and is not suitable. 4.2 Loss of three non adjacent phases Fig.15.Flow chart summarizing the arious cases of 3- phase operations. Here, the two non-adjacent faulty phase cases shown in Fig 18 are considered, In the first case, the six-phase motor is simulated under loss of three non-adjacent phases each separated by e, such as the loss of phase A and phase C and phase E. Fig 18 show the phasor representation of the oltages in the three-healthy phase and three non-adjacent faulty phase separated by e case such as under loss of phase A, phase C and phase E. In Fig 19 and Fig 5, the torque profile of the 3-healthy phase with three faulty phases each separated by e is compared with the 6-phase healthy case. Fig.15 summarizes the phase loss scenarios of the threehealthy phase and three faulty phase operations. 4.1 Loss of three adjacent phases Fig.18 Voltage phasor operation of three healthy phase with three non-adjacent phase loss operation with loss of phases A, C and E Fig.16 Voltage phasors in the 3- healthy phase operation with 3-adjacent faulty phase loss operation with loss of phases A, B The six-phase motor is simulated under loss of three phases adjacent to each other such as when phases A, B and C become faulty and are taken out of operation. Fig 16 show the phasor representation of oltages in the threehealthy phase and three adjacent faulty phase case under loss of phases A, B and C. In Fig 17 and 5, the torque profile of the three-healthy phase and three adjacent faulty phase case is compared with the 6-phase healthy case Fig.19Torque profile of the 3-healthy phase case with loss of three non- adjacent phases phases A, C and E (Ripple content: 7.13 %) In the second case, the six-phase motor is simulated under loss of three non-adjacent phases, two of which are separated by e and the other is separated by e, i.e. the loss of phase A, phase B and phase D are considered. 1760
6 Fig 20 shows the phasor representation of oltages in the three-phase healthy case with three non-adjacent faulty phases separated by e and e under loss of phase A, phase B and phase D. In Fig 21 and Fig 5, the torque profile of the three-phase healthy case with three nonadjacent faulty phases separated by e and e is compared with the 6-phase healthy case. healthy case and the two-phase healthy and one-phase faulty case under the loss of phase A. In Fig 24 the torque profiles of the two-phase faulty operation is shown. Fig.22 Voltages phasor of the 3-healthy phase case Fig.20 Voltage in phasor in the three healthy phases with three non-adjacent faulty phase los operation with loss of phases A, B and D Fig.23 Voltages phasor of the 2-healthy phase case with loss of phase A Fig.21 Torque profile of the 3-healthyphase case with loss of three non- adjacent phases phases A, B and D (Ripple content: 83.6 %) From the aboe analysis, the torque ripple content in the resulting torque is 7.13 % with the 3-healthy phases and three non-adjacent faulty phases each separated by e, in comparison with 6.67% torque ripple content in the healthy six-phase case whereas, the torque ripple content in the 3-healthy phases and three non-adjacent faulty phase separated by e and e is 83.6 % in comparison with 6.67% torque ripple content in the healthy six-phase case. It should be obsered that for the three non-adjacent faulty phase cases there is a marked difference between the e separation and the phases separated by e and e cases in so far as the aderse effect on the ripple content in the time-domain torque profile. The e separation is far less seere. It should also be obsered that the ripple content in the three healthy phase and three non-adjacent faulty phase separated by e and e is far less when compared to the three phase healthy and three adjacent faulty phase operation. This would be acceptable in certain applications. 5. Simulation of the two-phase healthy operation with one faulty phase in a 3-phase motor Here, the case-study 5HP, 3-phase induction motor was simulated with the loss of one phase. Fig.22 and Fig.23 show the phasor representation of oltages in the 3-phase Fig.24 Torque profile of the 2-healthy phase case with loss of phase A (Ripple content: 213%) From the aboe analysis, the torque ripple content in the resulting torque is 213 % with the 2- healthy phase operation, in comparison with 6.67% torque ripple content in the healthy 3-phase case. This case yields the highest and has the most aderse effect on the torque ripple content when compared to any of the cases discussed earlier. Table-1: Showing the torque ripple content different phase loss cases Phases Condition % age Torque Cases Phases Condition Ripple Content 1 Healthy Healthy Phase with loss of Phase(A) Healthy Phase with loss of Adj phases (A,B) 4 Healthy Phase with loss of Non Adj phases ( A and C) 4 Healthy Phase with loss of Non Adj phases ( A and D) 3 Healthy Phase with loss of Adj phases ( A,B, C) 3 Healthy Phase with loss of Non Adj phases ( A,C,E ) 3 Healthy Phase with loss of Non Adj phases ( A,B,D ) 2-healthy phases and one faulty phase of a 3- phase motor under 1761
7 A summary representing by a table and the chart percentage torque ripple content for arious faults considered in percent of the deeloped aerage torque is shown in Table-1 and Fig 25 Conclusion A comparatie analysis of the arious phase-loss conditions with respect to the healthy case was presented. The analysis of the ripple content in the torque under arious loss of phase / phases conditions were presented. These analyses effectiely reflect the deterioration of the quality of the torque-profile under the different cases. Oerall, it is shown that the six-phase motor exhibits better performance under the loss of phases than the threephase motor without any external control techniques. Moreoer, some of the cases gae results which were ery close to the healthy operation. Fig.25 Summarized chart showing the torque ripple content under different cases. Table-1 clearly indicates that the 5-healthy phase operation with one faulty phase, 3-healthy phase and three non-adjacent faulty phase operation and 4-healthy phase and two nonadjacent faulty phase operation considering loss of phases separated by e yields the least amount of torque ripple and are almost equal in ripple content, to the healthy case. The current space ector locus diagrams affirm these results in being closest in shape to a circle. Een the 4-healthy phase non-adjacent operation considering loss of phases separated by 180 O e, the 4- healthy phase adjacent phase-loss operation and the 3- healthy phase non-adjacent phase-loss operation exhibit relatiely lower amount of torque ripple content when compared to the standard two-phase operation of a threephase motor. References T.M. Jahns (May/June 1980), Improed Reliability in Solid-State AC Dries by Means of Multiple Independent Phase-Drie Units. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, Vol. IA-16, pp E. A. Klingshirn (Jan 1983), High phase order induction motors - Part I Description and theoretical consideration, IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, ol. PAS-102, no. 1, pp G.K. Singh (2002), Multi-phase induction machine drie research a surey, Electric Power Systems Research, ol. 61, no. 2, pp H. A. Toliyat and H. Xu (2000), DSP-based direct torque control (DTC) for fie-phase induction machines, Proc. Int. Power Electronics Conf. IPEC, Tokyo, Japan, pp E. Lei, S.N. Vukosaic and M. Jones (2005), Vector control schemes for series-connected six-phase two-motor drie systems, IEE Proc. Electric Power Applications, ol. 152, no. 2, pp R. Bojoi, F. Farina, G. Gria, F. Profumo and A. Tenconi (2005), Direct torque control for dual three-phase induction motor dries, IEEE Trans. on Industry Applications, ol. 41, no. 6,pp Peter Vas (1998), Sensorless Vector and Direct Torque Control, Oxford Uniersity Press B. K. Bose (1986), Power Electronics and AC Dries, Prentice- Hall,Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey. J.B. Wang, K. Atallah and D. Howe (2003), Optimal torque control of fault-tolerant permanentmagnet brushless machines, IEEE Trans. on Magnetics, ol. 39, no. 5, pp B.C. Mecrow, A. G. Jack, D.J. Atkinson, S.R. Green, G.J.Atkinson, A. King and B. Green (2004), Design and testing of a Four phase faulttolerant permanent magnet machine for an engine fuel pump, IEEE Trans. on Energy Conersion, ol.19, no. 3, pp G.J. Atkinson, B.C. Mecrow, A.G. Jack, D.J. Atkinson, P. Sangha and M. Benarous (2005), The design of fault tolerant machines for aerospace applications, Proc. IEEE Int. Electric Machines and Dries Conf. IEMDC, San Antonio, TX, pp A.J. Mitcham, G. Antonopoulos and J.J.A. Cullen (2004), Faourable slot and pole number combinations for fault-tolerant PM machines, IEE Proc. - Electrical Power Applications,ol.151, no. 5, pp J. R. Fu and T.A. Lipo (Sept 1994), Disturbance free operation of a multiphase current regulatedmotor drie with an open phase, IEEE Trans on.ind Applications,Vol. 30, Issue.5,pp Leila Parsa, Hamid A. Toliyat (July 2007), Fault-Tolerant Interior- Permanent-magnet Machines forhybrid Electric Vehicle Applications, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, Vol.56, No.4, pp, T. H. Liu, J. R. Fu, and T. A. Lipo (1991), A strategy for improing reliability of field orientedcontrolled induction motor dries, 1991 IEEE U S Annu. Meet. Conf. Rec., ol. 1, pp C. B. Jacobina, R. S. Miranda, M. B. de R. Corrêa, A. M. N. Lima (2004), Disturbance-Free operation of a six-phase AC motor drie system, IEEE Power Electronics Specialist Conference, Aachen Germany. H. A. Toliyat (March 1996), Analysis and simulation of multi-phase ariable speed induction motordries under asymmetrical connections, APEC '96, Volume 2, 3-7, pp Yifan Zhao, Thomas A. Lipo (Sept 1996), Modeling and control of a multi-phase induction machinewith structural unbalance, IEEE Transactions on Energy Conersion, ol.11,no.3, pp Gerard Aroquiadassou, Humberto Henao (Sept 2007), Experimental Analysis of the dqo stator current component spectra of a 42V faulttolerant six-phase induction machine drie with opened stator phases, Diagnostics for Electric Machines, Power Electronics and Dries, pp J. P. Martin and F. Meibody-Tabar (Oct 2000), Multi - phase permanent magnet synchronous machine supplied by VSIs, working under fault conditions, IEEE Industry Applications Conference, Volume 3, 8-12, pp N.A.O. Demerdash (2007), Design and Analysis of Electric Motors in Adjustable SpeedDries Class Notes for EECE 185, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Marquette Uniersity, Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Miranda R. S., Jacobina C. B., Lima A. M. N (2009), Modeling and analysis of six phase induction machine under fault condition, Power Electronics Conference. P M. A. Fnaiech, F. Betin, G. A. Capolino, and F. Fnaiech (Jan 2010), Fuzzy Logic and Sliding-Mode Controls Applied to Six-Phase Induction Machine With Open Phase, IEEE Trans on Industrial Electronics, ol. 57, no. 1, pp B. Kundrotas, S. Lisauskas, R. Rinkeiciene (2011) Model of Multiphase Induction Motor / Electronics and electrical Engineering. Kaunas: Technologija, No. 5(111). P
Generalized d-q Model of n-phase Induction Motor Drive
 Generalized d-q Model of n-phase Induction Motor Drie G. Renukadei, K. Rajambal Abstract This paper presents a generalized d-q model of n- phase induction motor drie. Multi -phase (n-phase) induction motor
Generalized d-q Model of n-phase Induction Motor Drie G. Renukadei, K. Rajambal Abstract This paper presents a generalized d-q model of n- phase induction motor drie. Multi -phase (n-phase) induction motor
PERFORMANCE OF SENSORLESS CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR IN WIND TURBINE SYSTEM*
 Vol. 1(6), No. 2, 2016 POWER ELECTRONICS AND DRIVES DOI: 10.5277/PED160210 PERFORMANCE OF SENSORLESS CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR IN WIND TURBINE SYSTEM OTR GAJEWSKI, KRZYSZTOF EŃKOWSKI
Vol. 1(6), No. 2, 2016 POWER ELECTRONICS AND DRIVES DOI: 10.5277/PED160210 PERFORMANCE OF SENSORLESS CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR IN WIND TURBINE SYSTEM OTR GAJEWSKI, KRZYSZTOF EŃKOWSKI
Performance Analysis of Six-Phase Induction Motor
 Performance Analysis of Six-Phase Induction Motor Mr. Sumit Mandal 1 Electrical Engineering Department JIS college of Engineering Kalyani, India Abstract This paper presents a mathematical d-q model of
Performance Analysis of Six-Phase Induction Motor Mr. Sumit Mandal 1 Electrical Engineering Department JIS college of Engineering Kalyani, India Abstract This paper presents a mathematical d-q model of
Conditions for Capacitor Voltage Regulation in a Five-Level Cascade Multilevel Inverter: Application to Voltage-Boost in a PM Drive
 Conditions for Capacitor oltage Regulation in a FieLeel Cascade Multileel Inerter: Application to oltageboost in a PM Drie John Chiasson, Burak Özpineci, Zhong Du 3 and Leon M. Tolbert 4 Abstract A cascade
Conditions for Capacitor oltage Regulation in a FieLeel Cascade Multileel Inerter: Application to oltageboost in a PM Drie John Chiasson, Burak Özpineci, Zhong Du 3 and Leon M. Tolbert 4 Abstract A cascade
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR 1 A.PANDIAN, 2 Dr.R.DHANASEKARAN 1 Associate Professor., Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Angel College of
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR 1 A.PANDIAN, 2 Dr.R.DHANASEKARAN 1 Associate Professor., Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Angel College of
CONTROL STRATEGY OF DUAL FED OPEN- END WINDING PMSM DRIVE WITH FLOATING BRIDGE CAPACITOR
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 10, Issue 04, April 2019, pp. 580 587, Article ID: IJMET_10_04_057 Aailable online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=10&itype=4
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 10, Issue 04, April 2019, pp. 580 587, Article ID: IJMET_10_04_057 Aailable online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=10&itype=4
SIMULATION OF STEADY-STATE PERFORMANCE OF THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR BY MATLAB
 olume No.0, Issue No. 08, August 014 ISSN (online): 48 7550 SIMULATION OF STEADY-STATE PERFORMANCE OF THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR BY MATLAB Harish Kumar Mishra 1, Dr.Anurag Tripathi 1 Research Scholar,
olume No.0, Issue No. 08, August 014 ISSN (online): 48 7550 SIMULATION OF STEADY-STATE PERFORMANCE OF THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR BY MATLAB Harish Kumar Mishra 1, Dr.Anurag Tripathi 1 Research Scholar,
Comparative Analysis of Speed Control of Induction Motor by DTC over Scalar Control Technique
 Comparative Analysis of Speed Control of Induction Motor by DTC over Scalar Control Technique S.Anuradha 1, N.Amarnadh Reddy 2 M.Tech (PE), Dept. of EEE, VNRVJIET, T.S, India 1 Assistant Professor, Dept.
Comparative Analysis of Speed Control of Induction Motor by DTC over Scalar Control Technique S.Anuradha 1, N.Amarnadh Reddy 2 M.Tech (PE), Dept. of EEE, VNRVJIET, T.S, India 1 Assistant Professor, Dept.
POSITION CONTROL OF AN INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR BY USING ADAPTIVE BACK STEPPING ALGORITHM
 Research and Applications (IJERA) ISSN: 2248-9622 www.ijera.com Vol. 2, Issue 3, May-Jun 212, pp.27-276 POSITION CONTROL OF AN INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR BY USING ADAPTIVE BACK STEPPING
Research and Applications (IJERA) ISSN: 2248-9622 www.ijera.com Vol. 2, Issue 3, May-Jun 212, pp.27-276 POSITION CONTROL OF AN INTERIOR PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR BY USING ADAPTIVE BACK STEPPING
Transient Analysis of Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Machine using Matlab
 Transient Analysis of Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Machine using Matlab Mukesh Kumar Arya*, Dr.Sulochana Wadhwani** *( Department of Electrical Engineering, Madhav Institute of Technology & Science,
Transient Analysis of Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Machine using Matlab Mukesh Kumar Arya*, Dr.Sulochana Wadhwani** *( Department of Electrical Engineering, Madhav Institute of Technology & Science,
Vector control of asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor
 Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: 11344 ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING RESEARCH ARTICLE Vector control of asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor Arif Iqbal 1 *, G.K. Singh 1 and Vinay Pant
Iqbal et al., Cogent Engineering (216, 3: 11344 ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING RESEARCH ARTICLE Vector control of asymmetrical six-phase synchronous motor Arif Iqbal 1 *, G.K. Singh 1 and Vinay Pant
CHAPTER 5 SIMULATION AND TEST SETUP FOR FAULT ANALYSIS
 47 CHAPTER 5 SIMULATION AND TEST SETUP FOR FAULT ANALYSIS 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the simulation model and experimental set up used for the fault analysis. For the simulation set up, the
47 CHAPTER 5 SIMULATION AND TEST SETUP FOR FAULT ANALYSIS 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the simulation model and experimental set up used for the fault analysis. For the simulation set up, the
Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS/IASME Int. Conf. on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Tenerife, Spain, December 16-18,
 Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS/IASME Int. Conf. on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Tenerife, Spain, December 16-18, 2006 196 A Method for the Modeling and Analysis of Permanent
Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS/IASME Int. Conf. on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Tenerife, Spain, December 16-18, 2006 196 A Method for the Modeling and Analysis of Permanent
Accurate Joule Loss Estimation for Rotating Machines: An Engineering Approach
 Accurate Joule Loss Estimation for Rotating Machines: An Engineering Approach Adeeb Ahmed Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC, USA aahmed4@ncsu.edu
Accurate Joule Loss Estimation for Rotating Machines: An Engineering Approach Adeeb Ahmed Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC, USA aahmed4@ncsu.edu
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development SIMULATION OF FIELD ORIENTED CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 4, April -2015 SIMULATION
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 4, April -2015 SIMULATION
Four-Switch Inverter-Fed Direct Torque control of Three Phase Induction Motor
 Four-Switch Inverter-Fed Direct Torque control of Three Phase Induction Motor R.Dharmaprakash 1, Joseph Henry 2, P.Gowtham 3 Research Scholar, Department of EEE, JNT University, Hyderabad, India 1 Professor,
Four-Switch Inverter-Fed Direct Torque control of Three Phase Induction Motor R.Dharmaprakash 1, Joseph Henry 2, P.Gowtham 3 Research Scholar, Department of EEE, JNT University, Hyderabad, India 1 Professor,
Optimisation of Inner Diameter to Outer Diameter Ratio of Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Generator
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 220-1, Volume 9, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov Dec. 2014), PP 4-47 Optimisation of Inner Diameter to Outer Diameter
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 220-1, Volume 9, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov Dec. 2014), PP 4-47 Optimisation of Inner Diameter to Outer Diameter
Direct Torque Control of Three Phase Induction Motor FED with Three Leg Inverter Using Proportional Controller
 Direct Torque Control of Three Phase Induction Motor FED with Three Leg Inverter Using Proportional Controller Bijay Kumar Mudi 1, Sk. Rabiul Hossain 2,Sibdas Mondal 3, Prof. Gautam Kumar Panda 4, Prof.
Direct Torque Control of Three Phase Induction Motor FED with Three Leg Inverter Using Proportional Controller Bijay Kumar Mudi 1, Sk. Rabiul Hossain 2,Sibdas Mondal 3, Prof. Gautam Kumar Panda 4, Prof.
Modeling of Direct Torque Control (DTC) of BLDC Motor Drive
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 3 Issue 09 March 2017 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Modeling of Direct Torque Control (DTC) of BLDC Motor Drive Addagatla Nagaraju Lecturer
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 3 Issue 09 March 2017 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Modeling of Direct Torque Control (DTC) of BLDC Motor Drive Addagatla Nagaraju Lecturer
Implementation of Twelve-Sector based Direct Torque Control for Induction motor
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 4 ǁ April. 2013 ǁ PP.32-37 Implementation of Twelve-Sector based Direct Torque Control
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 4 ǁ April. 2013 ǁ PP.32-37 Implementation of Twelve-Sector based Direct Torque Control
Torque Performance and Permanent Magnet Arrangement for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
 Extended Summary pp.954 960 Torque Performance and Permanent Magnet Arrangement for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Naohisa Matsumoto Student Member (Osaka Prefecture University, matumoto@eis.osakafu-u.ac.jp)
Extended Summary pp.954 960 Torque Performance and Permanent Magnet Arrangement for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Naohisa Matsumoto Student Member (Osaka Prefecture University, matumoto@eis.osakafu-u.ac.jp)
Mathematical Modelling of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Rotor Frame of Reference
 Mathematical Modelling of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Rotor Frame of Reference Mukesh C Chauhan 1, Hitesh R Khunt 2 1 P.G Student (Electrical),2 Electrical Department, AITS, rajkot 1 mcchauhan1@aits.edu.in
Mathematical Modelling of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Rotor Frame of Reference Mukesh C Chauhan 1, Hitesh R Khunt 2 1 P.G Student (Electrical),2 Electrical Department, AITS, rajkot 1 mcchauhan1@aits.edu.in
Keywords: Electric Machines, Rotating Machinery, Stator faults, Fault tolerant control, Field Weakening, Anisotropy, Dual rotor, 3D modeling
 Analysis of Electromagnetic Behavior of Permanent Magnetized Electrical Machines in Fault Modes M. U. Hassan 1, R. Nilssen 1, A. Røkke 2 1. Department of Electrical Power Engineering, Norwegian University
Analysis of Electromagnetic Behavior of Permanent Magnetized Electrical Machines in Fault Modes M. U. Hassan 1, R. Nilssen 1, A. Røkke 2 1. Department of Electrical Power Engineering, Norwegian University
Three phase induction motor using direct torque control by Matlab Simulink
 Three phase induction motor using direct torque control by Matlab Simulink Arun Kumar Yadav 1, Dr. Vinod Kumar Singh 2 1 Reaserch Scholor SVU Gajraula Amroha, U.P. 2 Assistant professor ABSTRACT Induction
Three phase induction motor using direct torque control by Matlab Simulink Arun Kumar Yadav 1, Dr. Vinod Kumar Singh 2 1 Reaserch Scholor SVU Gajraula Amroha, U.P. 2 Assistant professor ABSTRACT Induction
DTC Based Induction Motor Speed Control Using 10-Sector Methodology For Torque Ripple Reduction
 DTC Based Induction Motor Speed Control Using 10-Sector Methodology For Torque Ripple Reduction S. Pavithra, Dinesh Krishna. A. S & Shridharan. S Netaji Subhas Institute of Technology, Delhi University
DTC Based Induction Motor Speed Control Using 10-Sector Methodology For Torque Ripple Reduction S. Pavithra, Dinesh Krishna. A. S & Shridharan. S Netaji Subhas Institute of Technology, Delhi University
ISSN: (Online) Volume 2, Issue 2, February 2014 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies
 ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 2, Issue 2, February 2014 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Paper / Case Study Available online at:
ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 2, Issue 2, February 2014 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Article / Paper / Case Study Available online at:
Sensorless Field Oriented Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Sensorless
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2015 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Sensorless
A New Model Reference Adaptive Formulation to Estimate Stator Resistance in Field Oriented Induction Motor Drive
 A New Model Reference Adaptive Formulation to Estimate Stator Resistance in Field Oriented Induction Motor Drive Saptarshi Basak 1, Chandan Chakraborty 1, Senior Member IEEE and Yoichi Hori 2, Fellow IEEE
A New Model Reference Adaptive Formulation to Estimate Stator Resistance in Field Oriented Induction Motor Drive Saptarshi Basak 1, Chandan Chakraborty 1, Senior Member IEEE and Yoichi Hori 2, Fellow IEEE
MATLAB SIMULINK Based DQ Modeling and Dynamic Characteristics of Three Phase Self Excited Induction Generator
 628 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 MATLAB SIMULINK Based DQ Modeling and Dynamic Characteristics of Three Phase Self Excited Induction Generator A. Kishore,
628 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 MATLAB SIMULINK Based DQ Modeling and Dynamic Characteristics of Three Phase Self Excited Induction Generator A. Kishore,
Model of the Induction Machine including Saturation
 Model of the Induction Machine including Saturation José M. Aller, Daniel Delgado, Alexander Bueno, Julio C. Viola and José A. Restrepo UNIVERSIDAD SIMÓN BOLÍVAR Valle de Sartenejas, Baruta, Edo. Miranda
Model of the Induction Machine including Saturation José M. Aller, Daniel Delgado, Alexander Bueno, Julio C. Viola and José A. Restrepo UNIVERSIDAD SIMÓN BOLÍVAR Valle de Sartenejas, Baruta, Edo. Miranda
970 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS, VOL. 48, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2012
 970 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS, VOL. 48, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2012 Control Method Suitable for Direct-Torque-Control-Based Motor Drive System Satisfying Voltage and Current Limitations Yukinori
970 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS, VOL. 48, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2012 Control Method Suitable for Direct-Torque-Control-Based Motor Drive System Satisfying Voltage and Current Limitations Yukinori
1. Introduction. (Received 21 December 2012; accepted 28 February 2013)
 940. Magnetic equivalent circuit model of surface type fractional-slot permanent magnet synchronous generator Y. Oner, I. enol,. Bekiroglu, E. Aycicek Y. Oner 1, I. enol 2,. Bekiroglu 3, E. Aycicek 4 Yıldız
940. Magnetic equivalent circuit model of surface type fractional-slot permanent magnet synchronous generator Y. Oner, I. enol,. Bekiroglu, E. Aycicek Y. Oner 1, I. enol 2,. Bekiroglu 3, E. Aycicek 4 Yıldız
Tools for Investigation of Dynamics of DC-DC Converters within Matlab/Simulink
 Tools for Inestigation of Dynamics of DD onerters within Matlab/Simulink Riga Technical Uniersity, Riga, Latia Email: pikulin03@inbox.l Dmitry Pikulin Abstract: In this paper the study of complex phenomenon
Tools for Inestigation of Dynamics of DD onerters within Matlab/Simulink Riga Technical Uniersity, Riga, Latia Email: pikulin03@inbox.l Dmitry Pikulin Abstract: In this paper the study of complex phenomenon
Sensorless Control for High-Speed BLDC Motors With Low Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF
 Sensorless Control for High-Speed BLDC Motors With Low Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF P.Suganya Assistant Professor, Department of EEE, Bharathiyar Institute of Engineering for Women Salem (DT). Abstract
Sensorless Control for High-Speed BLDC Motors With Low Inductance and Nonideal Back EMF P.Suganya Assistant Professor, Department of EEE, Bharathiyar Institute of Engineering for Women Salem (DT). Abstract
Modelling short- and open-circuit faults in permanent magnet synchronous machines using Modelica
 Modelling short- and open-circuit faults in permanent magnet synchronous machines using Modelica Paolo Giangrande, Luca Papini, Chris Gerada Power Electronics Machines and Control Research Group, Faculty
Modelling short- and open-circuit faults in permanent magnet synchronous machines using Modelica Paolo Giangrande, Luca Papini, Chris Gerada Power Electronics Machines and Control Research Group, Faculty
PARAMETER SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR
 HUNGARIAN JOURNAL OF INDUSTRIAL CHEMISTRY VESZPRÉM Vol. 39(1) pp. 157-161 (2011) PARAMETER SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR P. HATOS, A. FODOR, A. MAGYAR University of Pannonia, Department of
HUNGARIAN JOURNAL OF INDUSTRIAL CHEMISTRY VESZPRÉM Vol. 39(1) pp. 157-161 (2011) PARAMETER SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR P. HATOS, A. FODOR, A. MAGYAR University of Pannonia, Department of
Research on Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Control System Simulation *
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com AASRI Procedia 3 (2012 ) 262 269 2012 AASRI Conference on Modeling, Identification and Control Research on Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Control System
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com AASRI Procedia 3 (2012 ) 262 269 2012 AASRI Conference on Modeling, Identification and Control Research on Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Control System
DEVELOPMENT OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL MODELWITH USING SVI FOR THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR
 DEVELOPMENT OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL MODELWITH USING SVI FOR THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR MUKESH KUMAR ARYA * Electrical Engg. Department, Madhav Institute of Technology & Science, Gwalior, Gwalior, 474005,
DEVELOPMENT OF DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL MODELWITH USING SVI FOR THREE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR MUKESH KUMAR ARYA * Electrical Engg. Department, Madhav Institute of Technology & Science, Gwalior, Gwalior, 474005,
MODELING surface-mounted permanent-magnet (PM)
 Modeling of Axial Flux Permanent-Magnet Machines Asko Parviainen, Markku Niemelä, and Juha Pyrhönen Abstract In modeling axial field machines, three dimensional (3-D) finite-element method (FEM) models
Modeling of Axial Flux Permanent-Magnet Machines Asko Parviainen, Markku Niemelä, and Juha Pyrhönen Abstract In modeling axial field machines, three dimensional (3-D) finite-element method (FEM) models
A High Performance DTC Strategy for Torque Ripple Minimization Using duty ratio control for SRM Drive
 A High Performance DTC Strategy for Torque Ripple Minimization Using duty ratio control for SRM Drive Veena P & Jeyabharath R 1, Rajaram M 2, S.N.Sivanandam 3 K.S.Rangasamy College of Technology, Tiruchengode-637
A High Performance DTC Strategy for Torque Ripple Minimization Using duty ratio control for SRM Drive Veena P & Jeyabharath R 1, Rajaram M 2, S.N.Sivanandam 3 K.S.Rangasamy College of Technology, Tiruchengode-637
CPPM Mahine: A Synchronous Permanent Magnet Machine with Field Weakening
 CPPM Mahine: A Synchronous Permanent Magnet Machine with Field Weakening Juan A. Tapia, Thomas A. Lipo, Fellow, IEEE Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison 45 Engineering
CPPM Mahine: A Synchronous Permanent Magnet Machine with Field Weakening Juan A. Tapia, Thomas A. Lipo, Fellow, IEEE Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison 45 Engineering
STEADY STATE AND TRANSIENT ANALYSIS OF INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVING A PUMP LOAD
 Nigerian Journal of Technology, Vol. 22, No. 1, March 2003, Okoro 46 STEADY STATE AND TRANSIENT ANALYSIS OF INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVING A PUMP LOAD O. I. Okoro Department of Electrical Engineering, University
Nigerian Journal of Technology, Vol. 22, No. 1, March 2003, Okoro 46 STEADY STATE AND TRANSIENT ANALYSIS OF INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVING A PUMP LOAD O. I. Okoro Department of Electrical Engineering, University
Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
DESIGN AND MODELLING OF SENSORLESS VECTOR CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR USING MODEL REFERENCE ADAPTIVE SYSTEMS
 DESIGN AND MODELLING OF SENSORLESS VECTOR CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR USING MODEL REFERENCE ADAPTIVE SYSTEMS Janaki Pakalapati 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE, Avanthi Institute of Engineering and Technology,
DESIGN AND MODELLING OF SENSORLESS VECTOR CONTROLLED INDUCTION MOTOR USING MODEL REFERENCE ADAPTIVE SYSTEMS Janaki Pakalapati 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE, Avanthi Institute of Engineering and Technology,
Sensorless Torque and Speed Control of Traction Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Railway Applications based on Model Reference Adaptive System
 5 th SASTech 211, Khavaran Higher-education Institute, Mashhad, Iran. May 12-14. 1 Sensorless Torue and Speed Control of Traction Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Railway Applications based on Model
5 th SASTech 211, Khavaran Higher-education Institute, Mashhad, Iran. May 12-14. 1 Sensorless Torue and Speed Control of Traction Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Railway Applications based on Model
Chapter 5 Three phase induction machine (1) Shengnan Li
 Chapter 5 Three phase induction machine (1) Shengnan Li Main content Structure of three phase induction motor Operating principle of three phase induction motor Rotating magnetic field Graphical representation
Chapter 5 Three phase induction machine (1) Shengnan Li Main content Structure of three phase induction motor Operating principle of three phase induction motor Rotating magnetic field Graphical representation
Hybrid Excited Vernier Machines with All Excitation Sources on the Stator for Electric Vehicles
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 6, 113 123, 16 Hybrid Excited Vernier Machines with All Excitation Sources on the Stator for Electric Vehicles Liang Xu, Guohai Liu, Wenxiang Zhao *, and Jinghua
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 6, 113 123, 16 Hybrid Excited Vernier Machines with All Excitation Sources on the Stator for Electric Vehicles Liang Xu, Guohai Liu, Wenxiang Zhao *, and Jinghua
Modelling of Closed Loop Speed Control for Pmsm Drive
 Modelling of Closed Loop Speed Control for Pmsm Drive Vikram S. Sathe, Shankar S. Vanamane M. Tech Student, Department of Electrical Engg, Walchand College of Engineering, Sangli. Associate Prof, Department
Modelling of Closed Loop Speed Control for Pmsm Drive Vikram S. Sathe, Shankar S. Vanamane M. Tech Student, Department of Electrical Engg, Walchand College of Engineering, Sangli. Associate Prof, Department
A new FOC technique based on predictive current control for PMSM drive
 ISSN 1 746-7, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (009) No. 4, pp. 87-94 A new FOC technique based on predictive current control for PMSM drive F. Heydari, A. Sheikholeslami, K.
ISSN 1 746-7, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 5 (009) No. 4, pp. 87-94 A new FOC technique based on predictive current control for PMSM drive F. Heydari, A. Sheikholeslami, K.
Improved efficiency of a fan drive system without using an encoder or current sensors
 Improved efficiency of a fan drive system without using an encoder or current sensors Tian-Hua Liu, Jyun-Jie Huang Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University of Science Technology,
Improved efficiency of a fan drive system without using an encoder or current sensors Tian-Hua Liu, Jyun-Jie Huang Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taiwan University of Science Technology,
Unified Theory of Electrical Machines and A philosophical explanation to how a Universe can be created just from nothing
 June 18, 212 Unified Theory of Electrical achines and A philosophical explanation to how a Unierse can be created just from nothing ourici hachter Holon, Israel mourici@walla.co.il Introduction It is well
June 18, 212 Unified Theory of Electrical achines and A philosophical explanation to how a Unierse can be created just from nothing ourici hachter Holon, Israel mourici@walla.co.il Introduction It is well
Saliency torque and V -curve of permanent-magnet-excited
 No. 6] Proc. Japan Acad., 76, Ser. B (2000) 77 Saliency torque and V -curve of permanent-magnet-excited synchronous motor (Contributed By Sakae YAMAMURA, M. J. A. by Sakae YAMAMURA, M.J.A., June 13, 2000)
No. 6] Proc. Japan Acad., 76, Ser. B (2000) 77 Saliency torque and V -curve of permanent-magnet-excited synchronous motor (Contributed By Sakae YAMAMURA, M. J. A. by Sakae YAMAMURA, M.J.A., June 13, 2000)
Modeling and Simulation of Indirect Field Oriented Control of Three Phase Induction Motor using Fuzzy Logic Controller
 Modeling and Simulation of Indirect Field Oriented Control of Three Phase Induction Motor using Fuzzy Logic Controller Gurmeet Singh Electrical Engineering Dept. DIT University Dehradun, India Gagan Singh
Modeling and Simulation of Indirect Field Oriented Control of Three Phase Induction Motor using Fuzzy Logic Controller Gurmeet Singh Electrical Engineering Dept. DIT University Dehradun, India Gagan Singh
Dynamic Modeling of Surface Mounted Permanent Synchronous Motor for Servo motor application
 797 Dynamic Modeling of Surface Mounted Permanent Synchronous Motor for Servo motor application Ritu Tak 1, Sudhir Y Kumar 2, B.S.Rajpurohit 3 1,2 Electrical Engineering, Mody University of Science & Technology,
797 Dynamic Modeling of Surface Mounted Permanent Synchronous Motor for Servo motor application Ritu Tak 1, Sudhir Y Kumar 2, B.S.Rajpurohit 3 1,2 Electrical Engineering, Mody University of Science & Technology,
TRANSIENT ANALYSIS OF SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATOR UNDER BALANCED AND UNBALANCED OPERATING CONDITIONS
 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS OF SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATOR UNDER BALANCED AND UNBALANCED OPERATING CONDITIONS G. HARI BABU Assistant Professor Department of EEE Gitam(Deemed to be University), Visakhapatnam
TRANSIENT ANALYSIS OF SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATOR UNDER BALANCED AND UNBALANCED OPERATING CONDITIONS G. HARI BABU Assistant Professor Department of EEE Gitam(Deemed to be University), Visakhapatnam
Control of Wind Turbine Generators. James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University
 Control of Wind Turbine Generators James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University Review from Day 1 Review Last time, we started with basic concepts from physics such as
Control of Wind Turbine Generators James Cale Guest Lecturer EE 566, Fall Semester 2014 Colorado State University Review from Day 1 Review Last time, we started with basic concepts from physics such as
Modelling and Parameter Determination of an Induction Servo-Motor
 British Journal of Applied Science & Technology 13(2): 1-11, 2016, Article no.bjast.21969 ISSN: 2231-0843, NLM ID: 101664541 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Modelling and Parameter Determination
British Journal of Applied Science & Technology 13(2): 1-11, 2016, Article no.bjast.21969 ISSN: 2231-0843, NLM ID: 101664541 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Modelling and Parameter Determination
Comparison Between Direct and Indirect Field Oriented Control of Induction Motor
 Comparison Between Direct and Indirect Field Oriented Control of Induction Motor Venu Gopal B T Research Scholar, Department of Electrical Engineering UVCE, Bangalore University, Bengaluru ABSTRACT - Vector
Comparison Between Direct and Indirect Field Oriented Control of Induction Motor Venu Gopal B T Research Scholar, Department of Electrical Engineering UVCE, Bangalore University, Bengaluru ABSTRACT - Vector
Lecture 7: Synchronous Motor Drives
 1 / 46 Lecture 7: Synchronous Motor Drives ELEC-E8402 Control of Electric Drives and Power Converters (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Spring 2017 2 / 46 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises you
1 / 46 Lecture 7: Synchronous Motor Drives ELEC-E8402 Control of Electric Drives and Power Converters (5 ECTS) Marko Hinkkanen Spring 2017 2 / 46 Learning Outcomes After this lecture and exercises you
High Performance and Reliable Torque Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors in Electric Vehicle Applications
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5755/j01.eee.19.7.159 ELEKTRONIKA IR ELEKTROTECHNIKA, ISSN 139-115, VOL. 19, NO. 7, 013 High Performance and Reliable Torque Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors in Electric
http://dx.doi.org/10.5755/j01.eee.19.7.159 ELEKTRONIKA IR ELEKTROTECHNIKA, ISSN 139-115, VOL. 19, NO. 7, 013 High Performance and Reliable Torque Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors in Electric
Mathematical Modelling of an 3 Phase Induction Motor Using MATLAB/Simulink
 2016 IJSRSET Volume 2 Issue 3 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology Mathematical Modelling of an 3 Phase Induction Motor Using MATLAB/Simulink ABSTRACT
2016 IJSRSET Volume 2 Issue 3 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology Mathematical Modelling of an 3 Phase Induction Motor Using MATLAB/Simulink ABSTRACT
Characteristics Analysis of Claw-Pole Alternator for Automobiles by Nonlinear Magnetic Field Decomposition for Armature Reaction
 IEEJ Journal of Industry Applications Vol.6 No.6 pp.362 369 DOI: 10.1541/ieejjia.6.362 Paper Characteristics Analysis of Claw-Pole Alternator for Automobiles by Nonlinear Magnetic Field Decomposition for
IEEJ Journal of Industry Applications Vol.6 No.6 pp.362 369 DOI: 10.1541/ieejjia.6.362 Paper Characteristics Analysis of Claw-Pole Alternator for Automobiles by Nonlinear Magnetic Field Decomposition for
Modeling of Symmetrical Squirrel Cage Induction Machine with MatLab Simulink
 Modeling of Symmetrical Squirrel Cage Induction Machine with MatLab Simulink Marcus Svoboda *, Lucian Tutelea *, Gheorghe Madescu **, Marius Biriescu *, Martian Mot ** * University POLITEHNICA Timisoara/Electrical
Modeling of Symmetrical Squirrel Cage Induction Machine with MatLab Simulink Marcus Svoboda *, Lucian Tutelea *, Gheorghe Madescu **, Marius Biriescu *, Martian Mot ** * University POLITEHNICA Timisoara/Electrical
DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR USING TWO LEVEL INVERTER- SURVEY PAPER
 DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR USING TWO LEVEL INVERTER- SURVEY PAPER 1 PREETI SINGH, BHUPAL SINGH 1 M.Tech (scholar) Electrical Power & Energy System, lecturer Ajay Kumar
DIRECT TORQUE CONTROL OF PERMANENT MAGNET SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR USING TWO LEVEL INVERTER- SURVEY PAPER 1 PREETI SINGH, BHUPAL SINGH 1 M.Tech (scholar) Electrical Power & Energy System, lecturer Ajay Kumar
EFFECTS OF LOAD AND SPEED VARIATIONS IN A MODIFIED CLOSED LOOP V/F INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE
 Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol. 31, No. 3, November, 2012, pp. 365 369. Copyright 2012 Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria. ISSN 1115-8443 EFFECTS OF LOAD AND SPEED VARIATIONS
Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol. 31, No. 3, November, 2012, pp. 365 369. Copyright 2012 Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria. ISSN 1115-8443 EFFECTS OF LOAD AND SPEED VARIATIONS
Wide-Speed Operation of Direct Torque-Controlled Interior Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors
 Wide-Speed Operation of Direct Torque-Controlled Interior Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors Adina Muntean, M.M. Radulescu Small Electric Motors and Electric Traction (SEMET) Group, Technical University
Wide-Speed Operation of Direct Torque-Controlled Interior Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors Adina Muntean, M.M. Radulescu Small Electric Motors and Electric Traction (SEMET) Group, Technical University
Anakapalli Andhra Pradesh, India I. INTRODUCTION
 Robust MRAS Based Sensorless Rotor Speed Measurement of Induction Motor against Variations in Stator Resistance Using Combination of Back Emf and Reactive Power Methods Srikanth Mandarapu Pydah College
Robust MRAS Based Sensorless Rotor Speed Measurement of Induction Motor against Variations in Stator Resistance Using Combination of Back Emf and Reactive Power Methods Srikanth Mandarapu Pydah College
ANALYTICAL COMPUTATION OF RELUCTANCE SYN- CHRONOUS MACHINE INDUCTANCES UNDER DIF- FERENT ECCENTRICITY FAULTS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 24, 29 44, 2012 ANALYTICAL COMPUTATION OF RELUCTANCE SYN- CHRONOUS MACHINE INDUCTANCES UNDER DIF- FERENT ECCENTRICITY FAULTS H. Akbari * Department of Electrical
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 24, 29 44, 2012 ANALYTICAL COMPUTATION OF RELUCTANCE SYN- CHRONOUS MACHINE INDUCTANCES UNDER DIF- FERENT ECCENTRICITY FAULTS H. Akbari * Department of Electrical
Simulation of Direct Torque Control of Induction motor using Space Vector Modulation Methodology
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Simulation of Direct Torque Control of Induction motor using Space Vector Modulation Methodology Arpit S. Bhugul 1, Dr. Archana
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Simulation of Direct Torque Control of Induction motor using Space Vector Modulation Methodology Arpit S. Bhugul 1, Dr. Archana
1439. Numerical simulation of the magnetic field and electromagnetic vibration analysis of the AC permanent-magnet synchronous motor
 1439. Numerical simulation of the magnetic field and electromagnetic vibration analysis of the AC permanent-magnet synchronous motor Bai-zhou Li 1, Yu Wang 2, Qi-chang Zhang 3 1, 2, 3 School of Mechanical
1439. Numerical simulation of the magnetic field and electromagnetic vibration analysis of the AC permanent-magnet synchronous motor Bai-zhou Li 1, Yu Wang 2, Qi-chang Zhang 3 1, 2, 3 School of Mechanical
VECTOR CONTROL OF INDUCTION MOTOR WITH SPLIT PHASE STATOR WINDINGS. K T. Ranganathan E. E. Professor
 VECTOR CONTROL OF INDUCTION MOTOR WITH SPLIT PHASE STATOR WINDINGS K Gopakumar CEDT Research stadent K T. Ranganathan E. E Professor S. R. Bhat CEDT Professor ABSTRACT A vector controlled scheme is described
VECTOR CONTROL OF INDUCTION MOTOR WITH SPLIT PHASE STATOR WINDINGS K Gopakumar CEDT Research stadent K T. Ranganathan E. E Professor S. R. Bhat CEDT Professor ABSTRACT A vector controlled scheme is described
Implementation of Induction Machine VBR Model with Optional Zero-Sequence in SimPowerSystems, ASMG, and PLECS Toolboxes
 Implementation of Induction Machine VBR Model with Optional Zero-Sequence in SimPowerSystems, ASMG, and PECS oolboxes M. Chapariha, F. herrien, J. Jatskeich, H. W. ommel Abstract-- In distributed generation
Implementation of Induction Machine VBR Model with Optional Zero-Sequence in SimPowerSystems, ASMG, and PECS oolboxes M. Chapariha, F. herrien, J. Jatskeich, H. W. ommel Abstract-- In distributed generation
On-line Parameter Estimation Method for IPMSM Based on Decoupling Control
 World Electric Vehicle Journal Vol. 4 - ISSN 232-6653 - 21 WEVA Page61 EVS25 Shenzhen, China, Nov 5-9, 21 On-line Parameter Estimation Method for IPMSM Based on Decoupling Control Aimeng Wang,Xingwang
World Electric Vehicle Journal Vol. 4 - ISSN 232-6653 - 21 WEVA Page61 EVS25 Shenzhen, China, Nov 5-9, 21 On-line Parameter Estimation Method for IPMSM Based on Decoupling Control Aimeng Wang,Xingwang
Cogging Torque Reduction in Surface-mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Axial Pole Pairing
 EVS28 KINTEX, Korea, May 3-6, 215 Cogging Torque Reduction in Surface-mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Axial Pole Pairing Soo-Gyung Lee 1, Kyung-Tae Jung 1, Seung-Hee Chai 1, and Jung-Pyo
EVS28 KINTEX, Korea, May 3-6, 215 Cogging Torque Reduction in Surface-mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Axial Pole Pairing Soo-Gyung Lee 1, Kyung-Tae Jung 1, Seung-Hee Chai 1, and Jung-Pyo
A Direct Torque Controlled Induction Motor with Variable Hysteresis Band
 UKSim 2009: th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation A Direct Torque Controlled Induction Motor with Variable Hysteresis Band Kanungo Barada Mohanty Electrical Engineering Department,
UKSim 2009: th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation A Direct Torque Controlled Induction Motor with Variable Hysteresis Band Kanungo Barada Mohanty Electrical Engineering Department,
Mathematical MATLAB Model and Performance Analysis of Asynchronous Machine
 Mathematical MATLAB Model and Performance Analysis of Asynchronous Machine Bikram Dutta 1, Suman Ghosh 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of EE, Guru Nanak Institute of Technology, Kolkata, West Bengal, India
Mathematical MATLAB Model and Performance Analysis of Asynchronous Machine Bikram Dutta 1, Suman Ghosh 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of EE, Guru Nanak Institute of Technology, Kolkata, West Bengal, India
Parameter Estimation of Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor
 International Conference On Emerging Trends in Mechanical and Electrical Engineering RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Parameter Estimation of Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Sonakshi Gupta Department
International Conference On Emerging Trends in Mechanical and Electrical Engineering RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Parameter Estimation of Three Phase Squirrel Cage Induction Motor Sonakshi Gupta Department
Modeling and Analysis of Six-phase Self-excited Induction Generators for Wind Energy Conversion
 Modeling and Analysis of Six-phase Self-excited Induction Generators for Wind Energy Conversion S.SASIKUMAR AND S.SINGARAVELU Department of Electrical Engineering, Annamalai University, Chidambaram, India
Modeling and Analysis of Six-phase Self-excited Induction Generators for Wind Energy Conversion S.SASIKUMAR AND S.SINGARAVELU Department of Electrical Engineering, Annamalai University, Chidambaram, India
White Rose Research Online URL for this paper:
 This is a repository copy of Eddy-current loss in the rotor magnets of permanent-magnet brushless machines having a fractional number of slots per pole. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/861/
This is a repository copy of Eddy-current loss in the rotor magnets of permanent-magnet brushless machines having a fractional number of slots per pole. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/861/
CHAPTER 2 CAPACITANCE REQUIREMENTS OF SIX-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS
 9 CHAPTER 2 CAPACITANCE REQUIREMENTS OF SIX-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 2.. INTRODUCTION Rapidly depleting rate of conventional energy sources, has led the scientists to explore the possibility
9 CHAPTER 2 CAPACITANCE REQUIREMENTS OF SIX-PHASE SELF-EXCITED INDUCTION GENERATORS 2.. INTRODUCTION Rapidly depleting rate of conventional energy sources, has led the scientists to explore the possibility
Analytical Calculation of Air Gap Magnetic Field Distribution in Vernier Motor
 IEEE PEDS 017, Honolulu, USA 1-15 June 015 Analytical Calculation of Air Gap Magnetic Field Distribution in Vernier Motor Hyoseok Shi, Noboru Niguchi, and Katsuhiro Hirata Department of Adaptive Machine
IEEE PEDS 017, Honolulu, USA 1-15 June 015 Analytical Calculation of Air Gap Magnetic Field Distribution in Vernier Motor Hyoseok Shi, Noboru Niguchi, and Katsuhiro Hirata Department of Adaptive Machine
Simplified EKF Based Sensorless Direct Torque Control of Permanent Magnet Brushless AC Drives
 International Journal of Automation and Computing (24) 35-4 Simplified EKF Based Sensorless Direct Torque Control of Permanent Magnet Brushless AC Drives Yong Liu, Ziqiang Zhu, David Howe Department of
International Journal of Automation and Computing (24) 35-4 Simplified EKF Based Sensorless Direct Torque Control of Permanent Magnet Brushless AC Drives Yong Liu, Ziqiang Zhu, David Howe Department of
A GENERALISED OPERATIONAL EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT OF INDUCTION MACHINES FOR TRANSIENT/DYNAMIC STUDIES UNDER DIFFERENT OPERATING CONDITIONS
 A GENERALISED OPERATIONAL EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT OF INDUCTION MACHINES FOR TRANSIENT/DYNAMIC STUDIES UNDER DIFFERENT OPERATING CONDITIONS S. S. Murthy Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute
A GENERALISED OPERATIONAL EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT OF INDUCTION MACHINES FOR TRANSIENT/DYNAMIC STUDIES UNDER DIFFERENT OPERATING CONDITIONS S. S. Murthy Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute
Novel DTC-SVM for an Adjustable Speed Sensorless Induction Motor Drive
 Novel DTC-SVM for an Adjustable Speed Sensorless Induction Motor Drive Nazeer Ahammad S1, Sadik Ahamad Khan2, Ravi Kumar Reddy P3, Prasanthi M4 1*Pursuing M.Tech in the field of Power Electronics 2*Working
Novel DTC-SVM for an Adjustable Speed Sensorless Induction Motor Drive Nazeer Ahammad S1, Sadik Ahamad Khan2, Ravi Kumar Reddy P3, Prasanthi M4 1*Pursuing M.Tech in the field of Power Electronics 2*Working
The Effects of Mutual Coupling and Transformer Connection Type on Frequency Response of Unbalanced Three Phases Electrical Distribution System
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 9, 2013 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 The Effects of Mutual Coupling and Transformer Connection Type on Frequency Response of
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 1, Issue 9, 2013 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 The Effects of Mutual Coupling and Transformer Connection Type on Frequency Response of
AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm
 7th WSEAS International Conference on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Venice, Italy, November 21-23, 27 86 AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm PETR BLAHA
7th WSEAS International Conference on Electric Power Systems, High Voltages, Electric Machines, Venice, Italy, November 21-23, 27 86 AC Induction Motor Stator Resistance Estimation Algorithm PETR BLAHA
Realization of Hull Stability Control System for Continuous Track Vehicle with the Robot Arm
 Adanced Science and Technology Letters Vol.86 (Ubiquitous Science and Engineering 05), pp.96-0 http://dx.doi.org/0.457/astl.05.86.0 Realization of Hull Stability Control System for Continuous Track Vehicle
Adanced Science and Technology Letters Vol.86 (Ubiquitous Science and Engineering 05), pp.96-0 http://dx.doi.org/0.457/astl.05.86.0 Realization of Hull Stability Control System for Continuous Track Vehicle
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Technology 25 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Technology 25 (2016 ) 801 807 Global Colloquium in Recent Advancement and Effectual Researches in Engineering, Science and Technology (RAEREST
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Technology 25 (2016 ) 801 807 Global Colloquium in Recent Advancement and Effectual Researches in Engineering, Science and Technology (RAEREST
Zero speed sensorless drive capability of fractional slot inset PM machine
 Zero speed sensorless drive capability of fractional slot inset PM Adriano Faggion Nicola Bianchi Silverio Bolognani Emanuele Fornasiero Electric Drives Laboratory Department of Industrial Engineering
Zero speed sensorless drive capability of fractional slot inset PM Adriano Faggion Nicola Bianchi Silverio Bolognani Emanuele Fornasiero Electric Drives Laboratory Department of Industrial Engineering
TRACING OF MAXIMUM POWER DENSITY POINT FOR AXIAL FLUX TORUS TYPE MACHINES USING GENERAL PURPOSE SIZING EQUATIONS
 TRACING OF MAXIMUM POWER DENSITY POINT FOR AXIAL FLUX TORUS TYPE MACHINES USING GENERAL PURPOSE SIZING EQUATIONS M. Ramanjaneyulu Chowdary Dr.G.S Raju Mr.V.Rameshbabu M.Tech power electronics Former BHU
TRACING OF MAXIMUM POWER DENSITY POINT FOR AXIAL FLUX TORUS TYPE MACHINES USING GENERAL PURPOSE SIZING EQUATIONS M. Ramanjaneyulu Chowdary Dr.G.S Raju Mr.V.Rameshbabu M.Tech power electronics Former BHU
Nonlinear Electrical FEA Simulation of 1MW High Power. Synchronous Generator System
 Nonlinear Electrical FEA Simulation of 1MW High Power Synchronous Generator System Jie Chen Jay G Vaidya Electrodynamics Associates, Inc. 409 Eastbridge Drive, Oviedo, FL 32765 Shaohua Lin Thomas Wu ABSTRACT
Nonlinear Electrical FEA Simulation of 1MW High Power Synchronous Generator System Jie Chen Jay G Vaidya Electrodynamics Associates, Inc. 409 Eastbridge Drive, Oviedo, FL 32765 Shaohua Lin Thomas Wu ABSTRACT
EFFECT OF NUMBER OF ROTOR POLES ON AC LOSSES OF PERMANENT MAGNET MACHINES HAVING TWO SEPARATE STATORS
 Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol. 36, No. 4, October 217, pp. 1145 1149 Copyright Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Print ISSN: 331-8443, Electronic ISSN: 2467-8821 www.nijotech.com
Nigerian Journal of Technology (NIJOTECH) Vol. 36, No. 4, October 217, pp. 1145 1149 Copyright Faculty of Engineering, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Print ISSN: 331-8443, Electronic ISSN: 2467-8821 www.nijotech.com
LINEAR MOTORS produce a direct thrust force without
 5436 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 60, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2013 Investigation and General Design Principle of a New Series of Complementary and Modular Linear FSPM Motors Ruiwu Cao, Student
5436 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 60, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2013 Investigation and General Design Principle of a New Series of Complementary and Modular Linear FSPM Motors Ruiwu Cao, Student
Inductance Testing According to the New IEEE Std 1812 Application and Possible Extensions for IPM Machines
 Inductance Testing According to the New IEEE Std 1812 Application and Possible Extensions for IPM Machines Vandana Rallabandi Narges Taran Dan M. Ionel Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Inductance Testing According to the New IEEE Std 1812 Application and Possible Extensions for IPM Machines Vandana Rallabandi Narges Taran Dan M. Ionel Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Analytical Method for Predicting the Air-Gap Flux Density of Dual-Rotor Permanent- Magnet (DRPM) Machine
 Analytical Method for Predicting the Air-Gap Flux Density of Dual-Rotor Permanent- Magnet (DRPM) Machine W.Xie, G.Dajaku*, D.Gerling Institute for Electrical Drives and Actuators, University of Federal
Analytical Method for Predicting the Air-Gap Flux Density of Dual-Rotor Permanent- Magnet (DRPM) Machine W.Xie, G.Dajaku*, D.Gerling Institute for Electrical Drives and Actuators, University of Federal
4. A Physical Model for an Electron with Angular Momentum. An Electron in a Bohr Orbit. The Quantum Magnet Resulting from Orbital Motion.
 4. A Physical Model for an Electron with Angular Momentum. An Electron in a Bohr Orbit. The Quantum Magnet Resulting from Orbital Motion. We now hae deeloped a ector model that allows the ready isualization
4. A Physical Model for an Electron with Angular Momentum. An Electron in a Bohr Orbit. The Quantum Magnet Resulting from Orbital Motion. We now hae deeloped a ector model that allows the ready isualization
Chapter 6: Operational Amplifiers
 Chapter 6: Operational Amplifiers Circuit symbol and nomenclature: An op amp is a circuit element that behaes as a VCVS: The controlling oltage is in = and the controlled oltage is such that 5 5 A where
Chapter 6: Operational Amplifiers Circuit symbol and nomenclature: An op amp is a circuit element that behaes as a VCVS: The controlling oltage is in = and the controlled oltage is such that 5 5 A where
Space and time harmonics related problems and their mitigation for position and speed sensorless slip-ring induction motor drives applications
 Sādhanā Vol. 33, Part 5, October 2008, pp. 565 580. Printed in India Space and time harmonics related problems and their mitigation for position and speed sensorless slip-ring induction motor drives applications
Sādhanā Vol. 33, Part 5, October 2008, pp. 565 580. Printed in India Space and time harmonics related problems and their mitigation for position and speed sensorless slip-ring induction motor drives applications
MODELLING ANALYSIS & DESIGN OF DSP BASED NOVEL SPEED SENSORLESS VECTOR CONTROLLER FOR INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 6, Issue 3, March, 2015, pp. 70-81, Article ID: IJARET_06_03_008 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtypeijaret&vtype=6&itype=3
International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 6, Issue 3, March, 2015, pp. 70-81, Article ID: IJARET_06_03_008 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtypeijaret&vtype=6&itype=3
Direct Flux Vector Control Of Induction Motor Drives With Maximum Efficiency Per Torque
 Direct Flux Vector Control Of Induction Motor Drives With Maximum Efficiency Per Torque S. Rajesh Babu 1, S. Sridhar 2 1 PG Scholar, Dept. Of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, JNTUACEA, Anantapuramu,
Direct Flux Vector Control Of Induction Motor Drives With Maximum Efficiency Per Torque S. Rajesh Babu 1, S. Sridhar 2 1 PG Scholar, Dept. Of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, JNTUACEA, Anantapuramu,
