Math 520a - Final take home exam - solutions
|
|
|
- Bennett Warren
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 52a - Final take home exam - solutions 1. Let f(z) be entire. Prove that f has finite order if and only if f has finite order and that when they have finite order their orders are the same. Solution: Suppose that f satisfies f(z) A exp(b z σ ) By the Cauchy integral formula, f (z) = 1 2πi f(w) w 2, dw where we take to be a circle of radius 1 centered at z. On this contour, f(w) A exp(b( z + 1) σ ) and w z 1. So f (z) A exp(b( z + 1)σ ) ( z 1) 2 A exp(b z σ ) for some constants A, B, with the same σ as in the bound on f. It follows that if f has order ρ, then f has order less than or equal to ρ. Now suppose f satisfies We have f (z) A exp(b z σ ) So f(z) = f() + z f (w) dw f(z) f() + z A exp(b z σ ) For any ǫ > there are constants A, B such that the above is A exp(b z σ+ǫ ) It follows that if f has order ρ, then f has order less than or equal to ρ. 2. Consider the entire function 1/Γ(z). 1
2 (a) Show it does not satisfy 1 Γ(z) A exp(b z ) for any constants A, B. Hint: look at the points n 1/2 where n is a positive integer. Solution: We showed in class that Γ(z)Γ(1 z) = π sin(πz) Take z = n 1/2. Then sin(π( n 1/2)) = ±1. So 1 Γ( n 1/2) = 1 π Γ(1 ( n 1/2)) = 1 Γ(n + 3/2)) π = 1 n! n! (n + 1/2)(n 1/2) 3/2 Γ(1/2)) Γ(1/2)) = π π π We have z = n + 1/2, and for any constants A, B, n! is eventually greater than A exp(b(n + 1/2)). (b) Show there is no entire function satisfying a bound of the above form with simple zeros at, 1, 2, 3, and no other zeroes. Solution: Let f(z) be such a function. Then it has order less than or equal to 1. By the Hadamard factorization theorem, f(z) = exp(az + b) E 1 ( z/n) Recall that 1/Γ(z) is also of this form with a = and b =. So 1/Γ(z) = exp(z az b)f(z). This implies 1/Γ(z) satisfies a bound of the form A exp(b z ) and we know from part (a) that it does not. 3. Suppose there is an entire function f(z) and a polynomial p(z) such that p(f(z)) = e z for all z. Prove that p(z) can only have one root. Solution: Since e z is never zero, f(z) cannot equal a root of p(z). So f(c) cannot contain any of the roots. By the little Picard theorem, f(c) is either C or C minus a single point. So there can only be one root. n=1 2
3 4. Prove that for all z C cos( πz 2 ) = n= [ 1 ] z 2 (2n + 1) 2 Solution: cos( πz ) is an entire function and since cos(πz) exp(π z /2), 2 2 it has finite order with order 1. It has zeroes at 2n + 1 where n is an integer. We can also label the zeroes as ±(2n + 1) with n =, 1, 2,. So the Hadamard factorization theorem says cos( πz 2 ) = eaz+b z [E 1 ( (2n + 1) )E z 1( (2n + 1) )] n= (The product converges absolutely, so we can order it any way we want.) Since z [E 1 ( (2n + 1) )E z 1( (2n + 1) )] = (1 z 2n + 1 ) exp( z 2n + 1 )(1 + z (2n + 1) ) exp( z 2n + 1 ) = (1 z 2 (2n + 1) 2) to finish the proof we need to show a =, b =. Evaluating at z = shows e b = 1. The evenness of cos and of the infinite product shows a =. 5. (a) Prove that for R < 1 there is a constant c(r) such for all complex a with a < 1 R and all f which are analytic on the unit disc D, we have R f(a) c(r) f(a + re iθ ) rdrdθ So Solution: Since a + R < 1, if r R, then the circle of radius r centered at a is contained in D. By Cauchy s integral formula f(a) = 1 2πi = 1 2π f(z) z dz f(a + re iθ )dθ 3
4 So f(a) 1 f(a + re iθ ) dθ 2π Multiply both sides by r and integrate from to R. f(a) R r dr 1 2π This proves (a) with c(r) = 2 R 2 π. R f(a + re iθ ) r dθdr (b) Let f n be analytic on D and f continuous on D. Suppose that f n converges to f in L 1 (D) meaning that 1 f n (re iθ ) f(re iθ ) 2 rdrdθ Prove that f is analytic. Solution: It suffice to show that f n converges to f uniformly on the disc z < 1 δ for all δ >. (Uniform limits of analytic functions are analytic.) Fix such an δ >. For any constant c, f n (z) c is an analytic function of z and so part (a) implies that for any for a D 1 δ () and any r such that r < δ/2, r f n (a) c c(r) f n (a + re iθ ) c rdrdθ Take c = f(a) and we have f n (a) f(a) c(r) By triangle inequality this is c(r) + c(r) r r r f n (a + re iθ ) f(a) rdrdθ f n (a + re iθ ) f(a + re iθ ) rdrdθ f(a + re iθ ) f(a) rdrdθ The first term may be bounded by c(r) f n f 1 since the region of integration is contained inside the unit disc. The second term may be bounded by c(r)πr 2 sup z: z a r 4 f(z) f(a) (1)
5 Note that c(r)πr 2 = 2. And the requirement that r δ/2 means that z in the above sup lies in D 1 δ/2 (). Since f is uniformly continuous on the compact set D 1 δ/2 (), the above sup goes to as r. We have to be a bit careful with the order in which we choose things. Let ǫ >. Pick r so that (1) is < ǫ/2. Then pick N so that c(r) f n f 1 < ǫ/2. Then putting this all together gives f n (a) f(a) < ǫ for z < R and n > N. This shows f n converges to f uniformly on D r (). 6. Prove the following theorem. We have proved most of the various implications needed in class. For many implications you can just cite a theorem we have proved. For example, to prove (a) implies (e) you can just cite the Riemann mapping theorem. Hint: just what property of Ω did we need in the proof of the Riemann mapping theorem? Theorem: The following are equivalent for a connected open set Ω C. (a) Ω is simply connected, i.e., every closed curve is homotopic to a point. (b) For every analytic function f on Ω and every closed contour in Ω, we have f(z) dz = (c) For every analytic function f on Ω there is an analytic function F on Ω such that F = f. (d) For every analytic function f on Ω which does not vanish on Ω there is an analytic function g on Ω such that e g = f. (e) Either Ω = C or there is a conformal map from Ω onto the unit disc. Solution: (a) (b) : This is Cauchy s theorem. (b) (c) : We proved this in class. The idea is that you fix a point z in Ω and define F(z) = f(w) dw where is any contour from z to z. Property (b) implies that the integral does not depend on the choice of contour. It is then routine to show F = f. (c) (d) : We proved this in class. Since f is never zero, f /f is analytic on Ω. So there is an F with F = f /f. The the derivative of e F f is zero. So e F = c. Let g(z) = F(z) + ln(c). 5
6 (d) (e) : Riemann s theorem says that (a) (e). But if you look at the proof you see that the only property we needed for Ω was (d) and the existence of square roots of functions on Ω which never vanish which follows immediately from (d). (e) (a) : A conformal map is a homeomorphism. So Ω has whatever topological properties the unit disc does. In particular, Ω is simply connected. We have proved (a) (b) (c) (d) (e), which proves the five properties are equivalent. 6
FINAL EXAM MATH 220A, UCSD, AUTUMN 14. You have three hours.
 FINAL EXAM MATH 220A, UCSD, AUTUMN 4 You have three hours. Problem Points Score There are 6 problems, and the total number of points is 00. Show all your work. Please make your work as clear and easy to
FINAL EXAM MATH 220A, UCSD, AUTUMN 4 You have three hours. Problem Points Score There are 6 problems, and the total number of points is 00. Show all your work. Please make your work as clear and easy to
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser
 Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
CONSEQUENCES OF POWER SERIES REPRESENTATION
 CONSEQUENCES OF POWER SERIES REPRESENTATION 1. The Uniqueness Theorem Theorem 1.1 (Uniqueness). Let Ω C be a region, and consider two analytic functions f, g : Ω C. Suppose that S is a subset of Ω that
CONSEQUENCES OF POWER SERIES REPRESENTATION 1. The Uniqueness Theorem Theorem 1.1 (Uniqueness). Let Ω C be a region, and consider two analytic functions f, g : Ω C. Suppose that S is a subset of Ω that
Part IB. Further Analysis. Year
 Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 530) January 2019
 Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
MATH5685 Assignment 3
 MATH5685 Assignment 3 Due: Wednesday 3 October 1. The open unit disk is denoted D. Q1. Suppose that a n for all n. Show that (1 + a n) converges if and only if a n converges. [Hint: prove that ( N (1 +
MATH5685 Assignment 3 Due: Wednesday 3 October 1. The open unit disk is denoted D. Q1. Suppose that a n for all n. Show that (1 + a n) converges if and only if a n converges. [Hint: prove that ( N (1 +
Math Homework 2
 Math 73 Homework Due: September 8, 6 Suppose that f is holomorphic in a region Ω, ie an open connected set Prove that in any of the following cases (a) R(f) is constant; (b) I(f) is constant; (c) f is
Math 73 Homework Due: September 8, 6 Suppose that f is holomorphic in a region Ω, ie an open connected set Prove that in any of the following cases (a) R(f) is constant; (b) I(f) is constant; (c) f is
Solutions to practice problems for the final
 Solutions to practice problems for the final Holomorphicity, Cauchy-Riemann equations, and Cauchy-Goursat theorem 1. (a) Show that there is a holomorphic function on Ω = {z z > 2} whose derivative is z
Solutions to practice problems for the final Holomorphicity, Cauchy-Riemann equations, and Cauchy-Goursat theorem 1. (a) Show that there is a holomorphic function on Ω = {z z > 2} whose derivative is z
Math 220A - Fall Final Exam Solutions
 Math 22A - Fall 216 - Final Exam Solutions Problem 1. Let f be an entire function and let n 2. Show that there exists an entire function g with g n = f if and only if the orders of all zeroes of f are
Math 22A - Fall 216 - Final Exam Solutions Problem 1. Let f be an entire function and let n 2. Show that there exists an entire function g with g n = f if and only if the orders of all zeroes of f are
11 COMPLEX ANALYSIS IN C. 1.1 Holomorphic Functions
 11 COMPLEX ANALYSIS IN C 1.1 Holomorphic Functions A domain Ω in the complex plane C is a connected, open subset of C. Let z o Ω and f a map f : Ω C. We say that f is real differentiable at z o if there
11 COMPLEX ANALYSIS IN C 1.1 Holomorphic Functions A domain Ω in the complex plane C is a connected, open subset of C. Let z o Ω and f a map f : Ω C. We say that f is real differentiable at z o if there
Part IB Complex Analysis
 Part IB Complex Analysis Theorems Based on lectures by I. Smith Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after
Part IB Complex Analysis Theorems Based on lectures by I. Smith Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after
Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both
 Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both real and complex analysis. You have 3 hours. Real
Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both real and complex analysis. You have 3 hours. Real
f(w) f(a) = 1 2πi w a Proof. There exists a number r such that the disc D(a,r) is contained in I(γ). For any ǫ < r, w a dw
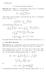 Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
Part IB. Complex Analysis. Year
 Part IB Complex Analysis Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 Paper 1, Section I 2A Complex Analysis or Complex Methods 7 (a) Show that w = log(z) is a conformal
Part IB Complex Analysis Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 Paper 1, Section I 2A Complex Analysis or Complex Methods 7 (a) Show that w = log(z) is a conformal
Math Final Exam.
 Math 106 - Final Exam. This is a closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. The exam consists of 8 questions worth 100 points. Good luck! Name: Acknowledgment and acceptance of honor code: Signature:
Math 106 - Final Exam. This is a closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. The exam consists of 8 questions worth 100 points. Good luck! Name: Acknowledgment and acceptance of honor code: Signature:
Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r
![Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r](/thumbs/77/75527144.jpg) 2. A harmonic conjugate always exists locally: if u is a harmonic function in an open set U, then for any disk D(z 0, r) U, there is f, which is analytic in D(z 0, r) and satisfies that Re f u. Since such
2. A harmonic conjugate always exists locally: if u is a harmonic function in an open set U, then for any disk D(z 0, r) U, there is f, which is analytic in D(z 0, r) and satisfies that Re f u. Since such
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 2014
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
Complex Analysis Qual Sheet
 Complex Analysis Qual Sheet Robert Won Tricks and traps. traps. Basically all complex analysis qualifying exams are collections of tricks and - Jim Agler Useful facts. e z = 2. sin z = n=0 3. cos z = z
Complex Analysis Qual Sheet Robert Won Tricks and traps. traps. Basically all complex analysis qualifying exams are collections of tricks and - Jim Agler Useful facts. e z = 2. sin z = n=0 3. cos z = z
NOTES ON RIEMANN S ZETA FUNCTION. Γ(z) = t z 1 e t dt
 NOTES ON RIEMANN S ZETA FUNCTION DRAGAN MILIČIĆ. Gamma function.. Definition of the Gamma function. The integral Γz = t z e t dt is well-defined and defines a holomorphic function in the right half-plane
NOTES ON RIEMANN S ZETA FUNCTION DRAGAN MILIČIĆ. Gamma function.. Definition of the Gamma function. The integral Γz = t z e t dt is well-defined and defines a holomorphic function in the right half-plane
Complex Analysis Problems
 Complex Analysis Problems transcribed from the originals by William J. DeMeo October 2, 2008 Contents 99 November 2 2 2 200 November 26 4 3 2006 November 3 6 4 2007 April 6 7 5 2007 November 6 8 99 NOVEMBER
Complex Analysis Problems transcribed from the originals by William J. DeMeo October 2, 2008 Contents 99 November 2 2 2 200 November 26 4 3 2006 November 3 6 4 2007 April 6 7 5 2007 November 6 8 99 NOVEMBER
f (n) (z 0 ) Theorem [Morera s Theorem] Suppose f is continuous on a domain U, and satisfies that for any closed curve γ in U, γ
![f (n) (z 0 ) Theorem [Morera s Theorem] Suppose f is continuous on a domain U, and satisfies that for any closed curve γ in U, γ f (n) (z 0 ) Theorem [Morera s Theorem] Suppose f is continuous on a domain U, and satisfies that for any closed curve γ in U, γ](/thumbs/87/95570641.jpg) Remarks. 1. So far we have seen that holomorphic is equivalent to analytic. Thus, if f is complex differentiable in an open set, then it is infinitely many times complex differentiable in that set. This
Remarks. 1. So far we have seen that holomorphic is equivalent to analytic. Thus, if f is complex differentiable in an open set, then it is infinitely many times complex differentiable in that set. This
Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014
 Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014 1. Determine whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answer (i.e., prove the claim, derive a contradiction or give a counter-example). (a) (10
Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014 1. Determine whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answer (i.e., prove the claim, derive a contradiction or give a counter-example). (a) (10
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5
 MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010
 An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONTOUR INTEGRALS LECTURE
 MATH 3: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONTOUR INTEGRALS LECTURE Recall the Residue Theorem: Let be a simple closed loop, traversed counterclockwise. Let f be a function that is analytic on and meromorphic inside. Then
MATH 3: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONTOUR INTEGRALS LECTURE Recall the Residue Theorem: Let be a simple closed loop, traversed counterclockwise. Let f be a function that is analytic on and meromorphic inside. Then
Complex Analysis Math 185A, Winter 2010 Final: Solutions
 Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
= 2 x y 2. (1)
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 5: HARMONIC FUNCTIONS A Let me start by asking you a question. Suppose that f is an analytic function so that the CR-equation f/ z = 0 is satisfied. Let us write u and v for the real
COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 5: HARMONIC FUNCTIONS A Let me start by asking you a question. Suppose that f is an analytic function so that the CR-equation f/ z = 0 is satisfied. Let us write u and v for the real
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm
 Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions
 Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions May, 04 Part.. Let log z be the principal branch of the logarithm defined on G = {z C z (, 0]}. Show that if t > 0, then the equation log z = t has exactly one
Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions May, 04 Part.. Let log z be the principal branch of the logarithm defined on G = {z C z (, 0]}. Show that if t > 0, then the equation log z = t has exactly one
MATH FINAL SOLUTION
 MATH 185-4 FINAL SOLUTION 1. (8 points) Determine whether the following statements are true of false, no justification is required. (1) (1 point) Let D be a domain and let u,v : D R be two harmonic functions,
MATH 185-4 FINAL SOLUTION 1. (8 points) Determine whether the following statements are true of false, no justification is required. (1) (1 point) Let D be a domain and let u,v : D R be two harmonic functions,
Complex Analysis Slide 9: Power Series
 Complex Analysis Slide 9: Power Series MA201 Mathematics III Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati August 2015 Complex Analysis Slide 9: Power Series 1 / 37 Learning Outcome of this Lecture We learn Sequence
Complex Analysis Slide 9: Power Series MA201 Mathematics III Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati August 2015 Complex Analysis Slide 9: Power Series 1 / 37 Learning Outcome of this Lecture We learn Sequence
1. The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions.
 Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
z b k P k p k (z), (z a) f (n 1) (a) 2 (n 1)! (z a)n 1 +f n (z)(z a) n, where f n (z) = 1 C
 . Representations of Meromorphic Functions There are two natural ways to represent a rational function. One is to express it as a quotient of two polynomials, the other is to use partial fractions. The
. Representations of Meromorphic Functions There are two natural ways to represent a rational function. One is to express it as a quotient of two polynomials, the other is to use partial fractions. The
Properties of Analytic Functions
 Properties of Analytic Functions Generalizing Results to Analytic Functions In the last few sections, we completely described entire functions through the use of everywhere convergent power series. Our
Properties of Analytic Functions Generalizing Results to Analytic Functions In the last few sections, we completely described entire functions through the use of everywhere convergent power series. Our
13 Maximum Modulus Principle
 3 Maximum Modulus Principle Theorem 3. (maximum modulus principle). If f is non-constant and analytic on an open connected set Ω, then there is no point z 0 Ω such that f(z) f(z 0 ) for all z Ω. Remark
3 Maximum Modulus Principle Theorem 3. (maximum modulus principle). If f is non-constant and analytic on an open connected set Ω, then there is no point z 0 Ω such that f(z) f(z 0 ) for all z Ω. Remark
Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions
 Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions Jim Agler 26. (# pg. 73 Conway). Prove the assertion made in Proposition 2. (pg. 68) that g is continuous. Solution. We wish to show that if g : [a, b] [c, d] C is a continuous
Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions Jim Agler 26. (# pg. 73 Conway). Prove the assertion made in Proposition 2. (pg. 68) that g is continuous. Solution. We wish to show that if g : [a, b] [c, d] C is a continuous
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative
 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
The result above is known as the Riemann mapping theorem. We will prove it using basic theory of normal families. We start this lecture with that.
 Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 6: NORMAL FAMILIES AND THE THEOREMS OF PICARD
 MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 6: NORMAL FAMILIES AND THE THEOREMS OF PICARD TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR 1. Introduction Suppose that we want to solve the equation f(z) = β where f is a nonconstant entire function and
MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 6: NORMAL FAMILIES AND THE THEOREMS OF PICARD TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR 1. Introduction Suppose that we want to solve the equation f(z) = β where f is a nonconstant entire function and
MA30056: Complex Analysis. Revision: Checklist & Previous Exam Questions I
 MA30056: Complex Analysis Revision: Checklist & Previous Exam Questions I Given z C and r > 0, define B r (z) and B r (z). Define what it means for a subset A C to be open/closed. If M A C, when is M said
MA30056: Complex Analysis Revision: Checklist & Previous Exam Questions I Given z C and r > 0, define B r (z) and B r (z). Define what it means for a subset A C to be open/closed. If M A C, when is M said
MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I
 MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I 1. The Algebra of Complex Numbers A complex number is an expression of the form a + ib, where a and b are real numbers. a is called the real part of a + ib and b the imaginary
MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I 1. The Algebra of Complex Numbers A complex number is an expression of the form a + ib, where a and b are real numbers. a is called the real part of a + ib and b the imaginary
III. Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem
 MTH6 Complex Analysis 2009-0 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 III. Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem. Cauchy s formulae. Cauchy s Integral Formula Let f be holomorphic on and everywhere inside a simple
MTH6 Complex Analysis 2009-0 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 III. Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem. Cauchy s formulae. Cauchy s Integral Formula Let f be holomorphic on and everywhere inside a simple
Complex Analysis Math 205A, Winter 2014 Final: Solutions
 Part I: Short Questions Complex Analysis Math 205A, Winter 2014 Final: Solutions I.1 [5%] State the Cauchy-Riemann equations for a holomorphic function f(z) = u(x,y)+iv(x,y). The Cauchy-Riemann equations
Part I: Short Questions Complex Analysis Math 205A, Winter 2014 Final: Solutions I.1 [5%] State the Cauchy-Riemann equations for a holomorphic function f(z) = u(x,y)+iv(x,y). The Cauchy-Riemann equations
Synopsis of Complex Analysis. Ryan D. Reece
 Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Notes Lent 2006
 Department of Pure Mathematics and Mathematical Statistics University of Cambridge COMPLEX ANALYSIS Notes Lent 2006 T. K. Carne. t.k.carne@dpmms.cam.ac.uk c Copyright. Not for distribution outside Cambridge
Department of Pure Mathematics and Mathematical Statistics University of Cambridge COMPLEX ANALYSIS Notes Lent 2006 T. K. Carne. t.k.carne@dpmms.cam.ac.uk c Copyright. Not for distribution outside Cambridge
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative
 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY
 INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
Conformal maps. Lent 2019 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor. A star means optional and not necessarily harder.
 Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
Accumulation constants of iterated function systems with Bloch target domains
 Accumulation constants of iterated function systems with Bloch target domains September 29, 2005 1 Introduction Linda Keen and Nikola Lakic 1 Suppose that we are given a random sequence of holomorphic
Accumulation constants of iterated function systems with Bloch target domains September 29, 2005 1 Introduction Linda Keen and Nikola Lakic 1 Suppose that we are given a random sequence of holomorphic
Problems for MATH-6300 Complex Analysis
 Problems for MATH-63 Complex Analysis Gregor Kovačič December, 7 This list will change as the semester goes on. Please make sure you always have the newest version of it.. Prove the following Theorem For
Problems for MATH-63 Complex Analysis Gregor Kovačič December, 7 This list will change as the semester goes on. Please make sure you always have the newest version of it.. Prove the following Theorem For
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BOMBAY MA205 Complex Analysis Autumn 2012 September 5, 2012 Mapping Properties Lecture 13 We shall once again return to the study of general behaviour of holomorphic functions
NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis. A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India. and. V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India
 NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India and V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India A.Swaminathan and V.K.Katiyar (NPTEL) Complex Analysis 1 / 17 Complex Analysis Module: 5:
NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India and V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India A.Swaminathan and V.K.Katiyar (NPTEL) Complex Analysis 1 / 17 Complex Analysis Module: 5:
Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15)
 Math 752 Spring 2015 Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15) Definition 1. A class F of continuous functions defined on an open set G is called a normal family if every sequence of elements in F contains a
Math 752 Spring 2015 Riemann Mapping Theorem (4/10-4/15) Definition 1. A class F of continuous functions defined on an open set G is called a normal family if every sequence of elements in F contains a
7.2 Conformal mappings
 7.2 Conformal mappings Let f be an analytic function. At points where f (z) 0 such a map has the remarkable property that it is conformal. This means that angle is preserved (in the sense that any 2 smooth
7.2 Conformal mappings Let f be an analytic function. At points where f (z) 0 such a map has the remarkable property that it is conformal. This means that angle is preserved (in the sense that any 2 smooth
From the definition of a surface, each point has a neighbourhood U and a homeomorphism. U : ϕ U(U U ) ϕ U (U U )
 3 Riemann surfaces 3.1 Definitions and examples From the definition of a surface, each point has a neighbourhood U and a homeomorphism ϕ U from U to an open set V in R 2. If two such neighbourhoods U,
3 Riemann surfaces 3.1 Definitions and examples From the definition of a surface, each point has a neighbourhood U and a homeomorphism ϕ U from U to an open set V in R 2. If two such neighbourhoods U,
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
Complex Variables...Review Problems (Residue Calculus Comments)...Fall Initial Draft
 Complex Variables........Review Problems Residue Calculus Comments)........Fall 22 Initial Draft ) Show that the singular point of fz) is a pole; determine its order m and its residue B: a) e 2z )/z 4,
Complex Variables........Review Problems Residue Calculus Comments)........Fall 22 Initial Draft ) Show that the singular point of fz) is a pole; determine its order m and its residue B: a) e 2z )/z 4,
PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL
 PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL Abstract. We give a summary for the proof of Picard s Theorem. The proof is for the most part an excerpt of [F]. 1. Introduction Definition. Let U C be an open subset. A
PICARD S THEOREM STEFAN FRIEDL Abstract. We give a summary for the proof of Picard s Theorem. The proof is for the most part an excerpt of [F]. 1. Introduction Definition. Let U C be an open subset. A
Exercises for Part 1
 MATH200 Complex Analysis. Exercises for Part Exercises for Part The following exercises are provided for you to revise complex numbers. Exercise. Write the following expressions in the form x + iy, x,y
MATH200 Complex Analysis. Exercises for Part Exercises for Part The following exercises are provided for you to revise complex numbers. Exercise. Write the following expressions in the form x + iy, x,y
MATH COMPLEX ANALYSIS. Contents
 MATH 3964 - OMPLEX ANALYSIS ANDREW TULLOH AND GILES GARDAM ontents 1. ontour Integration and auchy s Theorem 2 1.1. Analytic functions 2 1.2. ontour integration 3 1.3. auchy s theorem and extensions 3
MATH 3964 - OMPLEX ANALYSIS ANDREW TULLOH AND GILES GARDAM ontents 1. ontour Integration and auchy s Theorem 2 1.1. Analytic functions 2 1.2. ontour integration 3 1.3. auchy s theorem and extensions 3
carries the circle w 1 onto the circle z R and sends w = 0 to z = a. The function u(s(w)) is harmonic in the unit circle w 1 and we obtain
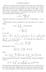 4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
4. Poisson formula In fact we can write down a formula for the values of u in the interior using only the values on the boundary, in the case when E is a closed disk. First note that (3.5) determines the
F (z) =f(z). f(z) = a n (z z 0 ) n. F (z) = a n (z z 0 ) n
 6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
4 Uniform convergence
 4 Uniform convergence In the last few sections we have seen several functions which have been defined via series or integrals. We now want to develop tools that will allow us to show that these functions
4 Uniform convergence In the last few sections we have seen several functions which have been defined via series or integrals. We now want to develop tools that will allow us to show that these functions
1 Assignment 1: Nonlinear dynamics (due September
 Assignment : Nonlinear dynamics (due September 4, 28). Consider the ordinary differential equation du/dt = cos(u). Sketch the equilibria and indicate by arrows the increase or decrease of the solutions.
Assignment : Nonlinear dynamics (due September 4, 28). Consider the ordinary differential equation du/dt = cos(u). Sketch the equilibria and indicate by arrows the increase or decrease of the solutions.
MATH 185: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 2009/10 PROBLEM SET 9 SOLUTIONS. and g b (z) = eπz/2 1
 MATH 85: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 2009/0 PROBLEM SET 9 SOLUTIONS. Consider the functions defined y g a (z) = eiπz/2 e iπz/2 + Show that g a maps the set to D(0, ) while g maps the set and g (z) = eπz/2 e
MATH 85: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 2009/0 PROBLEM SET 9 SOLUTIONS. Consider the functions defined y g a (z) = eiπz/2 e iπz/2 + Show that g a maps the set to D(0, ) while g maps the set and g (z) = eπz/2 e
Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014
 Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014 1. (a) (10 points) State the formal definition of a Cauchy sequence of real numbers. A sequence, {a n } n N, of real numbers, is Cauchy if and only if for every ɛ > 0,
Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014 1. (a) (10 points) State the formal definition of a Cauchy sequence of real numbers. A sequence, {a n } n N, of real numbers, is Cauchy if and only if for every ɛ > 0,
Let X be a topological space. We want it to look locally like C. So we make the following definition.
 February 17, 2010 1 Riemann surfaces 1.1 Definitions and examples Let X be a topological space. We want it to look locally like C. So we make the following definition. Definition 1. A complex chart on
February 17, 2010 1 Riemann surfaces 1.1 Definitions and examples Let X be a topological space. We want it to look locally like C. So we make the following definition. Definition 1. A complex chart on
Part IB Complex Analysis
 Part IB Complex Analysis Theorems with proof Based on lectures by I. Smith Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 206 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
Part IB Complex Analysis Theorems with proof Based on lectures by I. Smith Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 206 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall Anton R. Schep
 Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall 20 Anton R. Schep CHAPTER Holomorphic (or Analytic) Functions. Definitions and elementary properties In complex analysis we study functions f : S C,
Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall 20 Anton R. Schep CHAPTER Holomorphic (or Analytic) Functions. Definitions and elementary properties In complex analysis we study functions f : S C,
Homework 27. Homework 28. Homework 29. Homework 30. Prof. Girardi, Math 703, Fall 2012 Homework: Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by
 Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
Conformal Mappings. Chapter Schwarz Lemma
 Chapter 5 Conformal Mappings In this chapter we study analytic isomorphisms. An analytic isomorphism is also called a conformal map. We say that f is an analytic isomorphism of U with V if f is an analytic
Chapter 5 Conformal Mappings In this chapter we study analytic isomorphisms. An analytic isomorphism is also called a conformal map. We say that f is an analytic isomorphism of U with V if f is an analytic
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley. GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2016
 Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2016 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2016 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION
 POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION 1. Analytic functions Definition 1.1. A function f : Ω C C is complex-analytic if for each z 0 Ω there exists a power series f z0 (z) := a n (z z 0 ) n which converges
POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION 1. Analytic functions Definition 1.1. A function f : Ω C C is complex-analytic if for each z 0 Ω there exists a power series f z0 (z) := a n (z z 0 ) n which converges
Functions of a Complex Variable and Integral Transforms
 Functions of a Complex Variable and Integral Transforms Department of Mathematics Zhou Lingjun Textbook Functions of Complex Analysis with Applications to Engineering and Science, 3rd Edition. A. D. Snider
Functions of a Complex Variable and Integral Transforms Department of Mathematics Zhou Lingjun Textbook Functions of Complex Analysis with Applications to Engineering and Science, 3rd Edition. A. D. Snider
Math 411, Complex Analysis Definitions, Formulas and Theorems Winter y = sinα
 Math 411, Complex Analysis Definitions, Formulas and Theorems Winter 014 Trigonometric Functions of Special Angles α, degrees α, radians sin α cos α tan α 0 0 0 1 0 30 π 6 45 π 4 1 3 1 3 1 y = sinα π 90,
Math 411, Complex Analysis Definitions, Formulas and Theorems Winter 014 Trigonometric Functions of Special Angles α, degrees α, radians sin α cos α tan α 0 0 0 1 0 30 π 6 45 π 4 1 3 1 3 1 y = sinα π 90,
Complex Analysis review notes for weeks 1-6
 Complex Analysis review notes for weeks -6 Peter Milley Semester 2, 2007 In what follows, unless stated otherwise a domain is a connected open set. Generally we do not include the boundary of the set,
Complex Analysis review notes for weeks -6 Peter Milley Semester 2, 2007 In what follows, unless stated otherwise a domain is a connected open set. Generally we do not include the boundary of the set,
Definition We say that a topological manifold X is C p if there is an atlas such that the transition functions are C p.
 13. Riemann surfaces Definition 13.1. Let X be a topological space. We say that X is a topological manifold, if (1) X is Hausdorff, (2) X is 2nd countable (that is, there is a base for the topology which
13. Riemann surfaces Definition 13.1. Let X be a topological space. We say that X is a topological manifold, if (1) X is Hausdorff, (2) X is 2nd countable (that is, there is a base for the topology which
Fourth Week: Lectures 10-12
 Fourth Week: Lectures 10-12 Lecture 10 The fact that a power series p of positive radius of convergence defines a function inside its disc of convergence via substitution is something that we cannot ignore
Fourth Week: Lectures 10-12 Lecture 10 The fact that a power series p of positive radius of convergence defines a function inside its disc of convergence via substitution is something that we cannot ignore
5.3 The Upper Half Plane
 Remark. Combining Schwarz Lemma with the map g α, we can obtain some inequalities of analytic maps f : D D. For example, if z D and w = f(z) D, then the composition h := g w f g z satisfies the condition
Remark. Combining Schwarz Lemma with the map g α, we can obtain some inequalities of analytic maps f : D D. For example, if z D and w = f(z) D, then the composition h := g w f g z satisfies the condition
ζ(u) z du du Since γ does not pass through z, f is defined and continuous on [a, b]. Furthermore, for all t such that dζ
![ζ(u) z du du Since γ does not pass through z, f is defined and continuous on [a, b]. Furthermore, for all t such that dζ ζ(u) z du du Since γ does not pass through z, f is defined and continuous on [a, b]. Furthermore, for all t such that dζ](/thumbs/92/109116539.jpg) Lecture 6 Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem MATH-GA 45.00 Complex Variables Cauchy s Integral Formula. Index of a point with respect to a closed curve Let z C, and a piecewise differentiable closed curve
Lecture 6 Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem MATH-GA 45.00 Complex Variables Cauchy s Integral Formula. Index of a point with respect to a closed curve Let z C, and a piecewise differentiable closed curve
7 Asymptotics for Meromorphic Functions
 Lecture G jacques@ucsd.edu 7 Asymptotics for Meromorphic Functions Hadamard s Theorem gives a broad description of the exponential growth of coefficients in power series, but the notion of exponential
Lecture G jacques@ucsd.edu 7 Asymptotics for Meromorphic Functions Hadamard s Theorem gives a broad description of the exponential growth of coefficients in power series, but the notion of exponential
Hadamard s Theorem and Entire Functions of Finite Order For Math 331
 Hadamard s Theorem and Entire Functions of Finite Order For Math 33 Taylor Dupuy Entire functions of finite order Definition.. An entire function f is finite order if and only if ρ, R such that f(z)
Hadamard s Theorem and Entire Functions of Finite Order For Math 33 Taylor Dupuy Entire functions of finite order Definition.. An entire function f is finite order if and only if ρ, R such that f(z)
MA 412 Complex Analysis Final Exam
 MA 4 Complex Analysis Final Exam Summer II Session, August 9, 00.. Find all the values of ( 8i) /3. Sketch the solutions. Answer: We start by writing 8i in polar form and then we ll compute the cubic root:
MA 4 Complex Analysis Final Exam Summer II Session, August 9, 00.. Find all the values of ( 8i) /3. Sketch the solutions. Answer: We start by writing 8i in polar form and then we ll compute the cubic root:
III.2. Analytic Functions
 III.2. Analytic Functions 1 III.2. Analytic Functions Recall. When you hear analytic function, think power series representation! Definition. If G is an open set in C and f : G C, then f is differentiable
III.2. Analytic Functions 1 III.2. Analytic Functions Recall. When you hear analytic function, think power series representation! Definition. If G is an open set in C and f : G C, then f is differentiable
10 Cauchy s integral theorem
 10 Cauchy s integral theorem Here is the general version of the theorem I plan to discuss. Theorem 10.1 (Cauchy s integral theorem). Let G be a simply connected domain, and let f be a single-valued holomorphic
10 Cauchy s integral theorem Here is the general version of the theorem I plan to discuss. Theorem 10.1 (Cauchy s integral theorem). Let G be a simply connected domain, and let f be a single-valued holomorphic
Math 185 Homework Problems IV Solutions
 Math 185 Homework Problems IV Solutions Instructor: Andrés Caicedo July 31, 22 12 Suppose that Ω is a domain which is not simply connected Show that the polynomials are not dense in H(Ω) PROOF As mentioned
Math 185 Homework Problems IV Solutions Instructor: Andrés Caicedo July 31, 22 12 Suppose that Ω is a domain which is not simply connected Show that the polynomials are not dense in H(Ω) PROOF As mentioned
Complex Analysis for F2
 Institutionen för Matematik KTH Stanislav Smirnov stas@math.kth.se Complex Analysis for F2 Projects September 2002 Suggested projects ask you to prove a few important and difficult theorems in complex
Institutionen för Matematik KTH Stanislav Smirnov stas@math.kth.se Complex Analysis for F2 Projects September 2002 Suggested projects ask you to prove a few important and difficult theorems in complex
Complex Analysis Homework 9: Solutions
 Complex Analysis Fall 2007 Homework 9: Solutions 3..4 (a) Let z C \ {ni : n Z}. Then /(n 2 + z 2 ) n /n 2 n 2 n n 2 + z 2. According to the it comparison test from calculus, the series n 2 + z 2 converges
Complex Analysis Fall 2007 Homework 9: Solutions 3..4 (a) Let z C \ {ni : n Z}. Then /(n 2 + z 2 ) n /n 2 n 2 n n 2 + z 2. According to the it comparison test from calculus, the series n 2 + z 2 converges
Chapter 11. Cauchy s Integral Formula
 hapter 11 auchy s Integral Formula If I were founding a university I would begin with a smoking room; next a dormitory; and then a decent reading room and a library. After that, if I still had more money
hapter 11 auchy s Integral Formula If I were founding a university I would begin with a smoking room; next a dormitory; and then a decent reading room and a library. After that, if I still had more money
MATH 215A NOTES MOOR XU NOTES FROM A COURSE BY KANNAN SOUNDARARAJAN
 MATH 25A NOTES MOOR XU NOTES FROM A COURSE BY KANNAN SOUNDARARAJAN Abstract. These notes were taken during Math 25A (Complex Analysis) taught by Kannan Soundararajan in Fall 2 at Stanford University. They
MATH 25A NOTES MOOR XU NOTES FROM A COURSE BY KANNAN SOUNDARARAJAN Abstract. These notes were taken during Math 25A (Complex Analysis) taught by Kannan Soundararajan in Fall 2 at Stanford University. They
Properties of Entire Functions
 Properties of Entire Functions Generalizing Results to Entire Functions Our main goal is still to show that every entire function can be represented as an everywhere convergent power series in z. So far
Properties of Entire Functions Generalizing Results to Entire Functions Our main goal is still to show that every entire function can be represented as an everywhere convergent power series in z. So far
Part II. Riemann Surfaces. Year
 Part II Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 96 Paper 2, Section II 23F State the uniformisation theorem. List without proof the Riemann surfaces which are uniformised
Part II Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 96 Paper 2, Section II 23F State the uniformisation theorem. List without proof the Riemann surfaces which are uniformised
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 2003 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES
 INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 23 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES DOUGLAS ULMER 1. Meromorphic functions on the Riemann sphere It s often useful to allow functions to take the value. This exercise outlines one way to
INTEGRATION WORKSHOP 23 COMPLEX ANALYSIS EXERCISES DOUGLAS ULMER 1. Meromorphic functions on the Riemann sphere It s often useful to allow functions to take the value. This exercise outlines one way to
8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM. 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces
 8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces Our aim is to prove the Riemann Mapping Theorem which states that every simply connected Riemann surface R is conformally equivalent to D,
8 8 THE RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM 8.1 Simply Connected Surfaces Our aim is to prove the Riemann Mapping Theorem which states that every simply connected Riemann surface R is conformally equivalent to D,
Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4
 Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4 Due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM Note that to get full credit on any problem in this class, you must solve the problems in an efficient and elegant manner,
Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4 Due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM Note that to get full credit on any problem in this class, you must solve the problems in an efficient and elegant manner,
LECTURE-15 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS
 LECTURE-5 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS VED V. DATAR The purpose of this lecture is twofold - first, to characterize domains on which a holomorphic logarithm can be defined, and second, to show that
LECTURE-5 : LOGARITHMS AND COMPLEX POWERS VED V. DATAR The purpose of this lecture is twofold - first, to characterize domains on which a holomorphic logarithm can be defined, and second, to show that
Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions
 Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions Nikhil Srivastava December 12, 2015 1. True or false: (a) If f is analytic in the annulus A = {z : 1 < z < 2} then there exist functions g and h such that
Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions Nikhil Srivastava December 12, 2015 1. True or false: (a) If f is analytic in the annulus A = {z : 1 < z < 2} then there exist functions g and h such that
WEIERSTRASS THEOREMS AND RINGS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS
 WEIERSTRASS THEOREMS AND RINGS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS YIFEI ZHAO Contents. The Weierstrass factorization theorem 2. The Weierstrass preparation theorem 6 3. The Weierstrass division theorem 8 References
WEIERSTRASS THEOREMS AND RINGS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS YIFEI ZHAO Contents. The Weierstrass factorization theorem 2. The Weierstrass preparation theorem 6 3. The Weierstrass division theorem 8 References
Complex Analysis Math 147 Winter 2008
 Complex Analysis Math 147 Winter 2008 Bernard Russo March 14, 2008 Contents 1 Monday January 7 Course information; complex numbers; Assignment 1 1 1.1 Course information................................
Complex Analysis Math 147 Winter 2008 Bernard Russo March 14, 2008 Contents 1 Monday January 7 Course information; complex numbers; Assignment 1 1 1.1 Course information................................
Homework in Topology, Spring 2009.
 Homework in Topology, Spring 2009. Björn Gustafsson April 29, 2009 1 Generalities To pass the course you should hand in correct and well-written solutions of approximately 10-15 of the problems. For higher
Homework in Topology, Spring 2009. Björn Gustafsson April 29, 2009 1 Generalities To pass the course you should hand in correct and well-written solutions of approximately 10-15 of the problems. For higher
