Complex Analysis Homework 9: Solutions
|
|
|
- Abigayle Lamb
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Complex Analysis Fall 2007 Homework 9: Solutions 3..4 (a) Let z C \ {ni : n Z}. Then /(n 2 + z 2 ) n /n 2 n 2 n n 2 + z 2. According to the it comparison test from calculus, the series n 2 + z 2 converges if and only if converges. Since the latter series is known to converge, the former must as well. That is, n 2 + z 2 n 2 converges absolutely for z C \ {ni : n Z}. (b) Let D be any bounded subset of C \ {ni : n Z}. Then there is an C > 0 so that z < C for all z D. For z D we then have n 2 + z 2 n 2 z 2 n 2 z 2 > n 2 C 2. If n > C then the above implies that n 2 + z 2 n 2 C M 2 n for all z D. Appealing to the it comparison test as above, we conclude that n>c M n converges. Hence, the Weierstrass M-test implies that n 2 + z 2 n>c converges uniformly and absolutely on D. Since neither of these modes of convergence is altered by adding finitely many terms (Why? Convince yourself of this.) we conclude that n 2 + z 2
2 converges uniformly and absolutely on D. Since the functions /(n 2 z 2 ) are all analytic on D, we conclude that the series is an analytic function on D. Finally, since every point z C \ {ni : n Z} belongs to some bounded subset, we see that the series represents an analytic function on z C \ {ni : n Z} Let ɛ > 0 and A ɛ {z C : z ɛ}. I will prove that n!z n converges uniformly on A ɛ. Let z A ɛ. Then z ɛ so that n!z n n!ɛ M n. n Since /(n + )!ɛ n+ n /n!ɛ n n nɛ 0 the ratio test implies that M n converges. Since /n!z n is analytic on A ɛ for each n, the Weierstrass M-test implies that the series in question converges uniformly and absolutely to an analytic function on A ɛ. Since every point z C \ {0} is contained in some A ɛ, this proves that the series gives us a function that is analytic on all of z C \ {0}. As to the integral, since the series converges uniformly on A /2 and the unit circle γ is contained in this set, we have n!z dz dz 2πi n n! γ zn since γ γ z n dz is zero unless n, in which case we know it s 2πi Let ɛ > 0. Since {f n } converge uniformly on the boundary of A, they are uniformly Cauchy there, and so there is an N Z + so that f n (z) f m (z) < ɛ for all m, n > N and all z bd(a). Since the functions f n f m are analytic on A, and A is bounded, the maximum modulus principle then implies that f n (z) f m (z) < ɛ for all m, n > N and all z A. Since ɛ > 0 was arbitrary this proves that the sequence {f n } is uniformly Cauchy on A and hence converges uniformly to a function f on A. Since the convergence is uniform on all of A the Analytic Convergence Theorem applies and we conclude that f is analytic on A. 2
3 3.2.2 (a) We apply the ratio test: (n + ) 2 z n+ n n 2 z n (n + ) 2 z z. n n 2 It follows that the series in question converges (absolutely) when z < and diverges when z >. Hence, the radius of convergence is. (b) Again, we apply the ratio test: z 2(n+) /4 n+ n z 2n /4 n n 4 z 2 z 2 4. Hence the power series in question will converge (absolutely) for z < 2 and will diverge for z > 2. That is, its radius of convergence is 2. (c) Once more, its the ratio test to the rescue: (n + )!z n+ n n!z n n z. n This it is infinite if z 0 and is 0 when z 0. Hence, the series converges only when z 0 and so its radius of convergence is 0. (d) Ratio test, last time: z n+ /( + 2 n+ ) n z n /( + 2 n ) n + 2 n z + 2n+ n 2 n + z z 2 n As above, this implies the series converges (absolutely) for z < 2 and diverges for z > 2, i.e. the radius of convergence is Let f(z) sin z. Since f (z) cos z, f (z) sin z, f (z) cos z and f (4) (z) sin z f(z), it is easy to verify inductively that f (4k) (0) sin 0 0 f (4k+) (0) cos 0 ( ) 2k f (4k+2) (0) sin 0 0 f (4k+3) (0) cos 0 ( ) 2k+ for k 0. Hence, all of the even power terms in the Taylor series at z 0 0 vanish while the odd power terms are given by ( ) n z 2n+ /(2n + )!. Since sin z is entire, its Taylor series at z 0 0 converges everywhere and we have sin z 3 ( ) n z 2n+ (2n + )!
4 for all z C. Because the Taylor series for sin z has an infinite radius of convergence, it may be differentiated termwise: cos z d dz sin z d ( ) n z 2n+ ( ) n z 2n dz (2n + )! (2n)! for all z C. Uniqueness of power series guarantees that this is the Taylor series for cos z at z 0 0. If g(z) ( + z) α (α 0), another easy induction can be used to verify that g (n) (z) α(α )(α 2) (α n + )( + z) α n for n. We note that when α is a positive integer this formula is still valid for n > α, since then one of the terms in the product is zero. If we use the principal branch of the logarithm to compute the power function, we obtain g (n) (0) α(α )(α 2) (α n + ) for n and so the Taylor series for ( + z) α about z 0 0 is + α(α )(α 2) (α n + ) z n n! ( ) α z n. n If α is not a positive integer, then ( + z) α fails to be analytic at z (because the logarithm does) and so the Taylor series has radius of convergence. However, when α Z + the function ( + z) α is entire and so the Taylor series (really just a polynomial in this case) has infinite radius of convergence It is straightforward to verify that if then: f (z) f(z) + e z e z ( + e z ) 2 f (z) e2z e z ( + e z ) 3 f (z) e3z + 4e 2z e z ( + e z ) 4. 4
5 Hence f(0) 2 f (0) 4 f (0) 0 f (0) 8 and so the first four terms of the Taylor expansion of f(z) at z 0 0 are 2 4 z + 48 z3. The radius of convergence of this Taylor series is the distance from 0 to the nearest point at which f(z) fails to be analytic. Since z ±πi are equidistant from 0, the radius of convergence is π (a) Since sin z is entire, we can use the Taylor series for sin z to compute its value at any point. In particular, we have sin z 2 ( ) n (z 2 ) 2n+ (2n + )! ( ) n z 4n+2. (2n + )! By uniqueness of power series expansions, this must be the Taylor series for sin z at z 0 0. (b) As above, since e z is entire, we have e 2z (2z) n n! 2 n z n and uniqueness again guarantees this is the Taylor series for e 2z at z 0 0. n! Let g(z) b n (z z 0 ) n denote the Taylor series of f around z 0. If z z 0 < R z 0 then the triangle inequality gives z z z 0 + z 0 < R z 0 + z 0 R. 5
6 Therefore z A (the disk of convergence of f). It follows that D(z 0, R z 0 ) A and since f is analytic on A, Taylor s theorem implies that g converges to f on D(z 0, R z 0 ), i.e. the radius of convergence of g is at least R z 0. In other words (or other symbols?) R R z 0. The other inequality is somewhat more difficult to establish. Assume, for the sake of contradiction, that R > R + z 0. Let B {z C : z z 0 < R} (i.e. B is the disk of convergence of g) and let ɛ R (R + z 0 ) > 0. I first claim that D(0, R + ɛ/2) B. To prove this, let z D(0, R + ɛ/2). Then z z 0 z + z 0 < R + ɛ 2 + z 0 R + R 2 R 2 z z 0 R 2 + R + z 0 < R R 2 R which proves that z B and, since z D(0, R + ɛ/2) was arbitrary, establishes the claim. We will use the claim to arrive at a contradiction. The function g is analytic on B which, as we have just seen, contains D(0, R + ɛ/2). In particular, if F (z) denotes the Taylor series for g(z) centered at 0, then the radius of convergence of F (z) is at least R + ɛ/2. However, since A D(0, R + ɛ/2), for z A we have f(z) g(z) and therefore the Taylor series for g at zero is exactly the same as the Taylor series for f at zero. That is, F (z) and f(z) are the same series. Since F converges on D(0, R + ɛ/2), so too then does f. But this contradicts the fact that the radius of convergence of f is exactly R. Hence, or original assumption (that R > R + z 0 ) must be false and we conclude that R R + z Let a n (z z 0 ) n have radius or convergence R <. Let z, w C be on circle of convergence, i.e. let w z 0 z z 0 R. Then we have a n (w z 0 ) n a n w z 0 n a n R n a n z z 0 n a n (z z 0 ) n. Therefore, if the series converges absolutely at z it converges absolutely at w as well. It follows that if the power series converges absolutely at a single point on the circle of convergence then it converges absolutely at all such points. Hence, the series converges absolutely nowhere or everywhere on the circle of convergence. and As examples of each situation, consider the two power series z n n 6 z n n 2.
7 Both series have radius of convergence, as is readily verified using the ratio test, but the former does not converge absolutely when z (it becomes the harmonic series in that case) and the latter does converge absolutely when z (it becomes a p-series in that case with p 2) Since the series for ζ(z) converges uniformly on closed disks in the half plane {Re z > }, we can differentiate the series term-wise to compute the derivatives necessary for the Taylor expansion. Indeed, we have: d k dk ζ(z) n z dzk dz k d k dz k n z d k log n e z dzk ( log n) k z log n e ( log n) k n z for Re z >. Therefore and the Taylor series is ζ (k) (2) ( log n) k n 2 k0 ( ) ( log n) k n 2 (z 2) k. k! 7
Considering our result for the sum and product of analytic functions, this means that for (a 0, a 1,..., a N ) C N+1, the polynomial.
 Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
MORE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOREM
 MOE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOEM Contents. The Mean Value Property and the Maximum-Modulus Principle 2. Morera s Theorem and some applications 3 3. The Schwarz eflection Principle 6 We have stated Cauchy
MOE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOEM Contents. The Mean Value Property and the Maximum-Modulus Principle 2. Morera s Theorem and some applications 3 3. The Schwarz eflection Principle 6 We have stated Cauchy
13 Maximum Modulus Principle
 3 Maximum Modulus Principle Theorem 3. (maximum modulus principle). If f is non-constant and analytic on an open connected set Ω, then there is no point z 0 Ω such that f(z) f(z 0 ) for all z Ω. Remark
3 Maximum Modulus Principle Theorem 3. (maximum modulus principle). If f is non-constant and analytic on an open connected set Ω, then there is no point z 0 Ω such that f(z) f(z 0 ) for all z Ω. Remark
Complex Analysis Slide 9: Power Series
 Complex Analysis Slide 9: Power Series MA201 Mathematics III Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati August 2015 Complex Analysis Slide 9: Power Series 1 / 37 Learning Outcome of this Lecture We learn Sequence
Complex Analysis Slide 9: Power Series MA201 Mathematics III Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati August 2015 Complex Analysis Slide 9: Power Series 1 / 37 Learning Outcome of this Lecture We learn Sequence
MA30056: Complex Analysis. Revision: Checklist & Previous Exam Questions I
 MA30056: Complex Analysis Revision: Checklist & Previous Exam Questions I Given z C and r > 0, define B r (z) and B r (z). Define what it means for a subset A C to be open/closed. If M A C, when is M said
MA30056: Complex Analysis Revision: Checklist & Previous Exam Questions I Given z C and r > 0, define B r (z) and B r (z). Define what it means for a subset A C to be open/closed. If M A C, when is M said
Part IB Complex Analysis
 Part IB Complex Analysis Theorems Based on lectures by I. Smith Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after
Part IB Complex Analysis Theorems Based on lectures by I. Smith Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after
CONSEQUENCES OF POWER SERIES REPRESENTATION
 CONSEQUENCES OF POWER SERIES REPRESENTATION 1. The Uniqueness Theorem Theorem 1.1 (Uniqueness). Let Ω C be a region, and consider two analytic functions f, g : Ω C. Suppose that S is a subset of Ω that
CONSEQUENCES OF POWER SERIES REPRESENTATION 1. The Uniqueness Theorem Theorem 1.1 (Uniqueness). Let Ω C be a region, and consider two analytic functions f, g : Ω C. Suppose that S is a subset of Ω that
POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION
 POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION 1. Analytic functions Definition 1.1. A function f : Ω C C is complex-analytic if for each z 0 Ω there exists a power series f z0 (z) := a n (z z 0 ) n which converges
POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION 1. Analytic functions Definition 1.1. A function f : Ω C C is complex-analytic if for each z 0 Ω there exists a power series f z0 (z) := a n (z z 0 ) n which converges
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 2014
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions
 Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions May, 04 Part.. Let log z be the principal branch of the logarithm defined on G = {z C z (, 0]}. Show that if t > 0, then the equation log z = t has exactly one
Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions May, 04 Part.. Let log z be the principal branch of the logarithm defined on G = {z C z (, 0]}. Show that if t > 0, then the equation log z = t has exactly one
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010
 An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
An Introduction to Complex Analysis and Geometry John P. D Angelo, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts Volume 12, American Mathematical Society, 2010 John P. D Angelo, Univ. of Illinois, Urbana IL 61801.
NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis. A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India. and. V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India
 NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India and V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India A.Swaminathan and V.K.Katiyar (NPTEL) Complex Analysis 1 / 17 Complex Analysis Module: 5:
NPTEL web course on Complex Analysis A. Swaminathan I.I.T. Roorkee, India and V.K. Katiyar I.I.T. Roorkee, India A.Swaminathan and V.K.Katiyar (NPTEL) Complex Analysis 1 / 17 Complex Analysis Module: 5:
Course 214 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions Second Semester 2008
 Course 214 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions Second Semester 2008 David R. Wilkins Copyright c David R. Wilkins 1989 2008 Contents 7 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions 72 7.1 Taylor s Theorem
Course 214 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions Second Semester 2008 David R. Wilkins Copyright c David R. Wilkins 1989 2008 Contents 7 Basic Properties of Holomorphic Functions 72 7.1 Taylor s Theorem
Paul-Eugène Parent. March 12th, Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Ottawa. MAT 3121: Complex Analysis I
 Paul-Eugène Parent Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Ottawa March 12th, 2014 Outline 1 Holomorphic power Series Proposition Let f (z) = a n (z z o ) n be the holomorphic function defined
Paul-Eugène Parent Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Ottawa March 12th, 2014 Outline 1 Holomorphic power Series Proposition Let f (z) = a n (z z o ) n be the holomorphic function defined
9. Series representation for analytic functions
 9. Series representation for analytic functions 9.. Power series. Definition: A power series is the formal expression S(z) := c n (z a) n, a, c i, i =,,, fixed, z C. () The n.th partial sum S n (z) is
9. Series representation for analytic functions 9.. Power series. Definition: A power series is the formal expression S(z) := c n (z a) n, a, c i, i =,,, fixed, z C. () The n.th partial sum S n (z) is
Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r
![Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r](/thumbs/77/75527144.jpg) 2. A harmonic conjugate always exists locally: if u is a harmonic function in an open set U, then for any disk D(z 0, r) U, there is f, which is analytic in D(z 0, r) and satisfies that Re f u. Since such
2. A harmonic conjugate always exists locally: if u is a harmonic function in an open set U, then for any disk D(z 0, r) U, there is f, which is analytic in D(z 0, r) and satisfies that Re f u. Since such
Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett/
 (February 9, 25) Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ (The present proof of this old result roughly follows the proof
(February 9, 25) Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ (The present proof of this old result roughly follows the proof
MATH 31BH Homework 1 Solutions
 MATH 3BH Homework Solutions January 0, 04 Problem.5. (a) (x, y)-plane in R 3 is closed and not open. To see that this plane is not open, notice that any ball around the origin (0, 0, 0) will contain points
MATH 3BH Homework Solutions January 0, 04 Problem.5. (a) (x, y)-plane in R 3 is closed and not open. To see that this plane is not open, notice that any ball around the origin (0, 0, 0) will contain points
f (n) (z 0 ) Theorem [Morera s Theorem] Suppose f is continuous on a domain U, and satisfies that for any closed curve γ in U, γ
![f (n) (z 0 ) Theorem [Morera s Theorem] Suppose f is continuous on a domain U, and satisfies that for any closed curve γ in U, γ f (n) (z 0 ) Theorem [Morera s Theorem] Suppose f is continuous on a domain U, and satisfies that for any closed curve γ in U, γ](/thumbs/87/95570641.jpg) Remarks. 1. So far we have seen that holomorphic is equivalent to analytic. Thus, if f is complex differentiable in an open set, then it is infinitely many times complex differentiable in that set. This
Remarks. 1. So far we have seen that holomorphic is equivalent to analytic. Thus, if f is complex differentiable in an open set, then it is infinitely many times complex differentiable in that set. This
= 2 x y 2. (1)
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 5: HARMONIC FUNCTIONS A Let me start by asking you a question. Suppose that f is an analytic function so that the CR-equation f/ z = 0 is satisfied. Let us write u and v for the real
COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 5: HARMONIC FUNCTIONS A Let me start by asking you a question. Suppose that f is an analytic function so that the CR-equation f/ z = 0 is satisfied. Let us write u and v for the real
Solutions to practice problems for the final
 Solutions to practice problems for the final Holomorphicity, Cauchy-Riemann equations, and Cauchy-Goursat theorem 1. (a) Show that there is a holomorphic function on Ω = {z z > 2} whose derivative is z
Solutions to practice problems for the final Holomorphicity, Cauchy-Riemann equations, and Cauchy-Goursat theorem 1. (a) Show that there is a holomorphic function on Ω = {z z > 2} whose derivative is z
Cauchy Integral Formula Consequences
 Cauchy Integral Formula Consequences Monday, October 28, 2013 1:59 PM Homework 3 due November 15, 2013 at 5 PM. Last time we derived Cauchy's Integral Formula, which we will present in somewhat generalized
Cauchy Integral Formula Consequences Monday, October 28, 2013 1:59 PM Homework 3 due November 15, 2013 at 5 PM. Last time we derived Cauchy's Integral Formula, which we will present in somewhat generalized
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser
 Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Course 214 Section 2: Infinite Series Second Semester 2008
 Course 214 Section 2: Infinite Series Second Semester 2008 David R. Wilkins Copyright c David R. Wilkins 1989 2008 Contents 2 Infinite Series 25 2.1 The Comparison Test and Ratio Test.............. 26
Course 214 Section 2: Infinite Series Second Semester 2008 David R. Wilkins Copyright c David R. Wilkins 1989 2008 Contents 2 Infinite Series 25 2.1 The Comparison Test and Ratio Test.............. 26
Part IB. Further Analysis. Year
 Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Math Final Exam.
 Math 106 - Final Exam. This is a closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. The exam consists of 8 questions worth 100 points. Good luck! Name: Acknowledgment and acceptance of honor code: Signature:
Math 106 - Final Exam. This is a closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. The exam consists of 8 questions worth 100 points. Good luck! Name: Acknowledgment and acceptance of honor code: Signature:
Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions
 Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions Nikhil Srivastava December 12, 2015 1. True or false: (a) If f is analytic in the annulus A = {z : 1 < z < 2} then there exist functions g and h such that
Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions Nikhil Srivastava December 12, 2015 1. True or false: (a) If f is analytic in the annulus A = {z : 1 < z < 2} then there exist functions g and h such that
Complex variables lecture 6: Taylor and Laurent series
 Complex variables lecture 6: Taylor and Laurent series Hyo-Sung Ahn School of Mechatronics Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) 1 Oryong-dong, Buk-gu, Gwangju, Korea Advanced Engineering
Complex variables lecture 6: Taylor and Laurent series Hyo-Sung Ahn School of Mechatronics Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) 1 Oryong-dong, Buk-gu, Gwangju, Korea Advanced Engineering
Notes on Complex Analysis
 Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
Math 220A - Fall Final Exam Solutions
 Math 22A - Fall 216 - Final Exam Solutions Problem 1. Let f be an entire function and let n 2. Show that there exists an entire function g with g n = f if and only if the orders of all zeroes of f are
Math 22A - Fall 216 - Final Exam Solutions Problem 1. Let f be an entire function and let n 2. Show that there exists an entire function g with g n = f if and only if the orders of all zeroes of f are
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 530) January 2019
 Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall Anton R. Schep
 Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall 20 Anton R. Schep CHAPTER Holomorphic (or Analytic) Functions. Definitions and elementary properties In complex analysis we study functions f : S C,
Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall 20 Anton R. Schep CHAPTER Holomorphic (or Analytic) Functions. Definitions and elementary properties In complex analysis we study functions f : S C,
Complex Analysis. Travis Dirle. December 4, 2016
 Complex Analysis 2 Complex Analysis Travis Dirle December 4, 2016 2 Contents 1 Complex Numbers and Functions 1 2 Power Series 3 3 Analytic Functions 7 4 Logarithms and Branches 13 5 Complex Integration
Complex Analysis 2 Complex Analysis Travis Dirle December 4, 2016 2 Contents 1 Complex Numbers and Functions 1 2 Power Series 3 3 Analytic Functions 7 4 Logarithms and Branches 13 5 Complex Integration
z b k P k p k (z), (z a) f (n 1) (a) 2 (n 1)! (z a)n 1 +f n (z)(z a) n, where f n (z) = 1 C
 . Representations of Meromorphic Functions There are two natural ways to represent a rational function. One is to express it as a quotient of two polynomials, the other is to use partial fractions. The
. Representations of Meromorphic Functions There are two natural ways to represent a rational function. One is to express it as a quotient of two polynomials, the other is to use partial fractions. The
Properties of Analytic Functions
 Properties of Analytic Functions Generalizing Results to Analytic Functions In the last few sections, we completely described entire functions through the use of everywhere convergent power series. Our
Properties of Analytic Functions Generalizing Results to Analytic Functions In the last few sections, we completely described entire functions through the use of everywhere convergent power series. Our
4 Uniform convergence
 4 Uniform convergence In the last few sections we have seen several functions which have been defined via series or integrals. We now want to develop tools that will allow us to show that these functions
4 Uniform convergence In the last few sections we have seen several functions which have been defined via series or integrals. We now want to develop tools that will allow us to show that these functions
CAUCHY INTEGRAL FORMULA AND POWER SERIES
 AUHY INTEGRAL FORMULA AND POWER SERIES L. MARIZZA A. BAILEY. auchy s Integral Formula The auchy Integral Formula is one of the most powerful theorems in complex analysis. With it we can prove many interesting
AUHY INTEGRAL FORMULA AND POWER SERIES L. MARIZZA A. BAILEY. auchy s Integral Formula The auchy Integral Formula is one of the most powerful theorems in complex analysis. With it we can prove many interesting
Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4
 Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4 Due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM Note that to get full credit on any problem in this class, you must solve the problems in an efficient and elegant manner,
Complex Analysis MATH 6300 Fall 2013 Homework 4 Due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM Note that to get full credit on any problem in this class, you must solve the problems in an efficient and elegant manner,
1 Introduction. or equivalently f(z) =
 Introduction In this unit on elliptic functions, we ll see how two very natural lines of questions interact. The first, as we have met several times in Berndt s book, involves elliptic integrals. In particular,
Introduction In this unit on elliptic functions, we ll see how two very natural lines of questions interact. The first, as we have met several times in Berndt s book, involves elliptic integrals. In particular,
f(w) f(a) = 1 2πi w a Proof. There exists a number r such that the disc D(a,r) is contained in I(γ). For any ǫ < r, w a dw
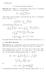 Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
FINAL EXAM MATH 220A, UCSD, AUTUMN 14. You have three hours.
 FINAL EXAM MATH 220A, UCSD, AUTUMN 4 You have three hours. Problem Points Score There are 6 problems, and the total number of points is 00. Show all your work. Please make your work as clear and easy to
FINAL EXAM MATH 220A, UCSD, AUTUMN 4 You have three hours. Problem Points Score There are 6 problems, and the total number of points is 00. Show all your work. Please make your work as clear and easy to
1. Theorem. (Archimedean Property) Let x be any real number. There exists a positive integer n greater than x.
 Advanced Calculus I, Dr. Block, Chapter 2 notes. Theorem. (Archimedean Property) Let x be any real number. There exists a positive integer n greater than x. 2. Definition. A sequence is a real-valued function
Advanced Calculus I, Dr. Block, Chapter 2 notes. Theorem. (Archimedean Property) Let x be any real number. There exists a positive integer n greater than x. 2. Definition. A sequence is a real-valued function
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley. GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2016
 Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2016 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2016 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
Math 425 Fall All About Zero
 Math 425 Fall 2005 All About Zero These notes supplement the discussion of zeros of analytic functions presented in 2.4 of our text, pp. 127 128. Throughout: Unless stated otherwise, f is a function analytic
Math 425 Fall 2005 All About Zero These notes supplement the discussion of zeros of analytic functions presented in 2.4 of our text, pp. 127 128. Throughout: Unless stated otherwise, f is a function analytic
Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014
 Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014 1. Determine whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answer (i.e., prove the claim, derive a contradiction or give a counter-example). (a) (10
Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014 1. Determine whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answer (i.e., prove the claim, derive a contradiction or give a counter-example). (a) (10
Complex Analysis Math 185A, Winter 2010 Final: Solutions
 Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
1. If 1, ω, ω 2, -----, ω 9 are the 10 th roots of unity, then (1 + ω) (1 + ω 2 ) (1 + ω 9 ) is A) 1 B) 1 C) 10 D) 0
 4 INUTES. If, ω, ω, -----, ω 9 are the th roots of unity, then ( + ω) ( + ω ) ----- ( + ω 9 ) is B) D) 5. i If - i = a + ib, then a =, b = B) a =, b = a =, b = D) a =, b= 3. Find the integral values for
4 INUTES. If, ω, ω, -----, ω 9 are the th roots of unity, then ( + ω) ( + ω ) ----- ( + ω 9 ) is B) D) 5. i If - i = a + ib, then a =, b = B) a =, b = a =, b = D) a =, b= 3. Find the integral values for
MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I
 MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I 1. The Algebra of Complex Numbers A complex number is an expression of the form a + ib, where a and b are real numbers. a is called the real part of a + ib and b the imaginary
MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I 1. The Algebra of Complex Numbers A complex number is an expression of the form a + ib, where a and b are real numbers. a is called the real part of a + ib and b the imaginary
Mittag-Leffler and Principle of the Argument
 Mittag-Leffler and Principle of the Argument Thursday, November 21, 2013 1:54 PM Homework 3 due Friday, November 22 at 5 PM. Homework 4 will be posted tonight, due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM. We'll
Mittag-Leffler and Principle of the Argument Thursday, November 21, 2013 1:54 PM Homework 3 due Friday, November 22 at 5 PM. Homework 4 will be posted tonight, due Wednesday, December 11 at 5 PM. We'll
Math Homework 2
 Math 73 Homework Due: September 8, 6 Suppose that f is holomorphic in a region Ω, ie an open connected set Prove that in any of the following cases (a) R(f) is constant; (b) I(f) is constant; (c) f is
Math 73 Homework Due: September 8, 6 Suppose that f is holomorphic in a region Ω, ie an open connected set Prove that in any of the following cases (a) R(f) is constant; (b) I(f) is constant; (c) f is
Complex Analysis Important Concepts
 Complex Analysis Important Concepts Travis Askham April 1, 2012 Contents 1 Complex Differentiation 2 1.1 Definition and Characterization.............................. 2 1.2 Examples..........................................
Complex Analysis Important Concepts Travis Askham April 1, 2012 Contents 1 Complex Differentiation 2 1.1 Definition and Characterization.............................. 2 1.2 Examples..........................................
III.2. Analytic Functions
 III.2. Analytic Functions 1 III.2. Analytic Functions Recall. When you hear analytic function, think power series representation! Definition. If G is an open set in C and f : G C, then f is differentiable
III.2. Analytic Functions 1 III.2. Analytic Functions Recall. When you hear analytic function, think power series representation! Definition. If G is an open set in C and f : G C, then f is differentiable
Synopsis of Complex Analysis. Ryan D. Reece
 Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley. GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Spring Semester 2015
 Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Spring Semester 205. Please write your - or 2-digit exam number on this
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Spring Semester 205. Please write your - or 2-digit exam number on this
MATH 452. SAMPLE 3 SOLUTIONS May 3, (10 pts) Let f(x + iy) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) be an analytic function. Show that u(x, y) is harmonic.
 MATH 45 SAMPLE 3 SOLUTIONS May 3, 06. (0 pts) Let f(x + iy) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) be an analytic function. Show that u(x, y) is harmonic. Because f is holomorphic, u and v satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations:
MATH 45 SAMPLE 3 SOLUTIONS May 3, 06. (0 pts) Let f(x + iy) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) be an analytic function. Show that u(x, y) is harmonic. Because f is holomorphic, u and v satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations:
NOTES ON RIEMANN S ZETA FUNCTION. Γ(z) = t z 1 e t dt
 NOTES ON RIEMANN S ZETA FUNCTION DRAGAN MILIČIĆ. Gamma function.. Definition of the Gamma function. The integral Γz = t z e t dt is well-defined and defines a holomorphic function in the right half-plane
NOTES ON RIEMANN S ZETA FUNCTION DRAGAN MILIČIĆ. Gamma function.. Definition of the Gamma function. The integral Γz = t z e t dt is well-defined and defines a holomorphic function in the right half-plane
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley. GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2014
 Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2014 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2014 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
Problem Set 5 Solution Set
 Problem Set 5 Solution Set Anthony Varilly Math 113: Complex Analysis, Fall 2002 1. (a) Let g(z) be a holomorphic function in a neighbourhood of z = a. Suppose that g(a) = 0. Prove that g(z)/(z a) extends
Problem Set 5 Solution Set Anthony Varilly Math 113: Complex Analysis, Fall 2002 1. (a) Let g(z) be a holomorphic function in a neighbourhood of z = a. Suppose that g(a) = 0. Prove that g(z)/(z a) extends
(x 1, y 1 ) = (x 2, y 2 ) if and only if x 1 = x 2 and y 1 = y 2.
 1. Complex numbers A complex number z is defined as an ordered pair z = (x, y), where x and y are a pair of real numbers. In usual notation, we write z = x + iy, where i is a symbol. The operations of
1. Complex numbers A complex number z is defined as an ordered pair z = (x, y), where x and y are a pair of real numbers. In usual notation, we write z = x + iy, where i is a symbol. The operations of
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm
 Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
(1) Let f(z) be the principal branch of z 4i. (a) Find f(i). Solution. f(i) = exp(4i Log(i)) = exp(4i(π/2)) = e 2π. (b) Show that
 Let fz be the principal branch of z 4i. a Find fi. Solution. fi = exp4i Logi = exp4iπ/2 = e 2π. b Show that fz fz 2 fz z 2 fz fz 2 = λfz z 2 for all z, z 2 0, where λ =, e 8π or e 8π. Proof. We have =
Let fz be the principal branch of z 4i. a Find fi. Solution. fi = exp4i Logi = exp4iπ/2 = e 2π. b Show that fz fz 2 fz z 2 fz fz 2 = λfz z 2 for all z, z 2 0, where λ =, e 8π or e 8π. Proof. We have =
2 Write down the range of values of α (real) or β (complex) for which the following integrals converge. (i) e z2 dz where {γ : z = se iα, < s < }
 Mathematical Tripos Part II Michaelmas term 2007 Further Complex Methods, Examples sheet Dr S.T.C. Siklos Comments and corrections: e-mail to stcs@cam. Sheet with commentary available for supervisors.
Mathematical Tripos Part II Michaelmas term 2007 Further Complex Methods, Examples sheet Dr S.T.C. Siklos Comments and corrections: e-mail to stcs@cam. Sheet with commentary available for supervisors.
Homework 27. Homework 28. Homework 29. Homework 30. Prof. Girardi, Math 703, Fall 2012 Homework: Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by
 Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
Some Fun with Divergent Series
 Some Fun with Divergent Series 1. Preliminary Results We begin by examining the (divergent) infinite series S 1 = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + = k=1 k S 2 = 1 2 + 2 2 + 3 2 + 4 2 + 5 2 + 6 2 + = k=1 k 2 (i)
Some Fun with Divergent Series 1. Preliminary Results We begin by examining the (divergent) infinite series S 1 = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + = k=1 k S 2 = 1 2 + 2 2 + 3 2 + 4 2 + 5 2 + 6 2 + = k=1 k 2 (i)
Exercises for Part 1
 MATH200 Complex Analysis. Exercises for Part Exercises for Part The following exercises are provided for you to revise complex numbers. Exercise. Write the following expressions in the form x + iy, x,y
MATH200 Complex Analysis. Exercises for Part Exercises for Part The following exercises are provided for you to revise complex numbers. Exercise. Write the following expressions in the form x + iy, x,y
Math 460: Complex Analysis MWF 11am, Fulton Hall 425 Homework 8 Solutions Please write neatly, and in complete sentences when possible.
 Math 460: Complex Analysis MWF am, Fulton Hall 45 Homework 8 Solutions Please write neatly, and in complete sentences when possible. Do the following problems from the book:.4.,.4.0,.4.-.4.6, 4.., 4..,
Math 460: Complex Analysis MWF am, Fulton Hall 45 Homework 8 Solutions Please write neatly, and in complete sentences when possible. Do the following problems from the book:.4.,.4.0,.4.-.4.6, 4.., 4..,
Math 421 Midterm 2 review questions
 Math 42 Midterm 2 review questions Paul Hacking November 7, 205 () Let U be an open set and f : U a continuous function. Let be a smooth curve contained in U, with endpoints α and β, oriented from α to
Math 42 Midterm 2 review questions Paul Hacking November 7, 205 () Let U be an open set and f : U a continuous function. Let be a smooth curve contained in U, with endpoints α and β, oriented from α to
Lecture 7 Local properties of analytic functions Part 1 MATH-GA Complex Variables
 Lecture 7 Local properties of analytic functions Part 1 MATH-GA 2451.001 omplex Variables 1 Removable singularities 1.1 Riemann s removable singularity theorem We have said that auchy s integral formula
Lecture 7 Local properties of analytic functions Part 1 MATH-GA 2451.001 omplex Variables 1 Removable singularities 1.1 Riemann s removable singularity theorem We have said that auchy s integral formula
MA30056: Complex Analysis. Exercise Sheet 7: Applications and Sequences of Complex Functions
 MA30056: Complex Analysis Exercise Sheet 7: Applications and Sequences of Complex Functions Please hand solutions in at the lecture on Monday 6th March..) Prove Gauss Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Hint:
MA30056: Complex Analysis Exercise Sheet 7: Applications and Sequences of Complex Functions Please hand solutions in at the lecture on Monday 6th March..) Prove Gauss Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Hint:
MASTERS EXAMINATION IN MATHEMATICS SOLUTIONS
 MASTERS EXAMINATION IN MATHEMATICS PURE MATHEMATICS OPTION SPRING 010 SOLUTIONS Algebra A1. Let F be a finite field. Prove that F [x] contains infinitely many prime ideals. Solution: The ring F [x] of
MASTERS EXAMINATION IN MATHEMATICS PURE MATHEMATICS OPTION SPRING 010 SOLUTIONS Algebra A1. Let F be a finite field. Prove that F [x] contains infinitely many prime ideals. Solution: The ring F [x] of
Homework 4, 5, 6 Solutions. > 0, and so a n 0 = n + 1 n = ( n+1 n)( n+1+ n) 1 if n is odd 1/n if n is even diverges.
 2..2(a) lim a n = 0. Homework 4, 5, 6 Solutions Proof. Let ɛ > 0. Then for n n = 2+ 2ɛ we have 2n 3 4+ ɛ 3 > ɛ > 0, so 0 < 2n 3 < ɛ, and thus a n 0 = 2n 3 < ɛ. 2..2(g) lim ( n + n) = 0. Proof. Let ɛ >
2..2(a) lim a n = 0. Homework 4, 5, 6 Solutions Proof. Let ɛ > 0. Then for n n = 2+ 2ɛ we have 2n 3 4+ ɛ 3 > ɛ > 0, so 0 < 2n 3 < ɛ, and thus a n 0 = 2n 3 < ɛ. 2..2(g) lim ( n + n) = 0. Proof. Let ɛ >
We have been going places in the car of calculus for years, but this analysis course is about how the car actually works.
 Analysis I We have been going places in the car of calculus for years, but this analysis course is about how the car actually works. Copier s Message These notes may contain errors. In fact, they almost
Analysis I We have been going places in the car of calculus for years, but this analysis course is about how the car actually works. Copier s Message These notes may contain errors. In fact, they almost
Chapter 11. Cauchy s Integral Formula
 hapter 11 auchy s Integral Formula If I were founding a university I would begin with a smoking room; next a dormitory; and then a decent reading room and a library. After that, if I still had more money
hapter 11 auchy s Integral Formula If I were founding a university I would begin with a smoking room; next a dormitory; and then a decent reading room and a library. After that, if I still had more money
Fundamental Properties of Holomorphic Functions
 Complex Analysis Contents Chapter 1. Fundamental Properties of Holomorphic Functions 5 1. Basic definitions 5 2. Integration and Integral formulas 6 3. Some consequences of the integral formulas 8 Chapter
Complex Analysis Contents Chapter 1. Fundamental Properties of Holomorphic Functions 5 1. Basic definitions 5 2. Integration and Integral formulas 6 3. Some consequences of the integral formulas 8 Chapter
THE RESIDUE THEOREM. f(z) dz = 2πi res z=z0 f(z). C
 THE RESIDUE THEOREM ontents 1. The Residue Formula 1 2. Applications and corollaries of the residue formula 2 3. ontour integration over more general curves 5 4. Defining the logarithm 7 Now that we have
THE RESIDUE THEOREM ontents 1. The Residue Formula 1 2. Applications and corollaries of the residue formula 2 3. ontour integration over more general curves 5 4. Defining the logarithm 7 Now that we have
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY
 INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
Complex Variables. Cathal Ormond
 Complex Variables Cathal Ormond Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Definition: Polar Form.............................. 3 1.2 Definition: Length................................ 3 1.3 Definitions.....................................
Complex Variables Cathal Ormond Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Definition: Polar Form.............................. 3 1.2 Definition: Length................................ 3 1.3 Definitions.....................................
Part IB. Complex Analysis. Year
 Part IB Complex Analysis Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 Paper 1, Section I 2A Complex Analysis or Complex Methods 7 (a) Show that w = log(z) is a conformal
Part IB Complex Analysis Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 Paper 1, Section I 2A Complex Analysis or Complex Methods 7 (a) Show that w = log(z) is a conformal
IV.3. Zeros of an Analytic Function
 IV.3. Zeros of an Analytic Function 1 IV.3. Zeros of an Analytic Function Note. We now explore factoring series in a way analogous to factoring a polynomial. Recall that if p is a polynomial with a zero
IV.3. Zeros of an Analytic Function 1 IV.3. Zeros of an Analytic Function Note. We now explore factoring series in a way analogous to factoring a polynomial. Recall that if p is a polynomial with a zero
Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions
 Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions Jim Agler 26. (# pg. 73 Conway). Prove the assertion made in Proposition 2. (pg. 68) that g is continuous. Solution. We wish to show that if g : [a, b] [c, d] C is a continuous
Math 220A Homework 4 Solutions Jim Agler 26. (# pg. 73 Conway). Prove the assertion made in Proposition 2. (pg. 68) that g is continuous. Solution. We wish to show that if g : [a, b] [c, d] C is a continuous
ANALYSIS QUALIFYING EXAM FALL 2017: SOLUTIONS. 1 cos(nx) lim. n 2 x 2. g n (x) = 1 cos(nx) n 2 x 2. x 2.
 ANALYSIS QUALIFYING EXAM FALL 27: SOLUTIONS Problem. Determine, with justification, the it cos(nx) n 2 x 2 dx. Solution. For an integer n >, define g n : (, ) R by Also define g : (, ) R by g(x) = g n
ANALYSIS QUALIFYING EXAM FALL 27: SOLUTIONS Problem. Determine, with justification, the it cos(nx) n 2 x 2 dx. Solution. For an integer n >, define g n : (, ) R by Also define g : (, ) R by g(x) = g n
18.03 LECTURE NOTES, SPRING 2014
 18.03 LECTURE NOTES, SPRING 2014 BJORN POONEN 7. Complex numbers Complex numbers are expressions of the form x + yi, where x and y are real numbers, and i is a new symbol. Multiplication of complex numbers
18.03 LECTURE NOTES, SPRING 2014 BJORN POONEN 7. Complex numbers Complex numbers are expressions of the form x + yi, where x and y are real numbers, and i is a new symbol. Multiplication of complex numbers
Complex Analysis review notes for weeks 1-6
 Complex Analysis review notes for weeks -6 Peter Milley Semester 2, 2007 In what follows, unless stated otherwise a domain is a connected open set. Generally we do not include the boundary of the set,
Complex Analysis review notes for weeks -6 Peter Milley Semester 2, 2007 In what follows, unless stated otherwise a domain is a connected open set. Generally we do not include the boundary of the set,
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5
 MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
Fourth Week: Lectures 10-12
 Fourth Week: Lectures 10-12 Lecture 10 The fact that a power series p of positive radius of convergence defines a function inside its disc of convergence via substitution is something that we cannot ignore
Fourth Week: Lectures 10-12 Lecture 10 The fact that a power series p of positive radius of convergence defines a function inside its disc of convergence via substitution is something that we cannot ignore
Mid Term-1 : Solutions to practice problems
 Mid Term- : Solutions to practice problems 0 October, 06. Is the function fz = e z x iy holomorphic at z = 0? Give proper justification. Here we are using the notation z = x + iy. Solution: Method-. Use
Mid Term- : Solutions to practice problems 0 October, 06. Is the function fz = e z x iy holomorphic at z = 0? Give proper justification. Here we are using the notation z = x + iy. Solution: Method-. Use
MATH 117 LECTURE NOTES
 MATH 117 LECTURE NOTES XIN ZHOU Abstract. This is the set of lecture notes for Math 117 during Fall quarter of 2017 at UC Santa Barbara. The lectures follow closely the textbook [1]. Contents 1. The set
MATH 117 LECTURE NOTES XIN ZHOU Abstract. This is the set of lecture notes for Math 117 during Fall quarter of 2017 at UC Santa Barbara. The lectures follow closely the textbook [1]. Contents 1. The set
Notes on uniform convergence
 Notes on uniform convergence Erik Wahlén erik.wahlen@math.lu.se January 17, 2012 1 Numerical sequences We begin by recalling some properties of numerical sequences. By a numerical sequence we simply mean
Notes on uniform convergence Erik Wahlén erik.wahlen@math.lu.se January 17, 2012 1 Numerical sequences We begin by recalling some properties of numerical sequences. By a numerical sequence we simply mean
Math 411, Complex Analysis Definitions, Formulas and Theorems Winter y = sinα
 Math 411, Complex Analysis Definitions, Formulas and Theorems Winter 014 Trigonometric Functions of Special Angles α, degrees α, radians sin α cos α tan α 0 0 0 1 0 30 π 6 45 π 4 1 3 1 3 1 y = sinα π 90,
Math 411, Complex Analysis Definitions, Formulas and Theorems Winter 014 Trigonometric Functions of Special Angles α, degrees α, radians sin α cos α tan α 0 0 0 1 0 30 π 6 45 π 4 1 3 1 3 1 y = sinα π 90,
CHAPTER 6. Limits of Functions. 1. Basic Definitions
 CHAPTER 6 Limits of Functions 1. Basic Definitions DEFINITION 6.1. Let D Ω R, x 0 be a limit point of D and f : D! R. The limit of f (x) at x 0 is L, if for each " > 0 there is a ± > 0 such that when x
CHAPTER 6 Limits of Functions 1. Basic Definitions DEFINITION 6.1. Let D Ω R, x 0 be a limit point of D and f : D! R. The limit of f (x) at x 0 is L, if for each " > 0 there is a ± > 0 such that when x
Q You mentioned that in complex analysis we study analytic functions, or, in another name, holomorphic functions. Pray tell me, what are they?
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 2: ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS Q You mentioned that in complex analysis we study analytic functions, or, in another name, holomorphic functions. Pray tell me, what are they? A There are many
COMPLEX ANALYSIS PART 2: ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS Q You mentioned that in complex analysis we study analytic functions, or, in another name, holomorphic functions. Pray tell me, what are they? A There are many
The result above is known as the Riemann mapping theorem. We will prove it using basic theory of normal families. We start this lecture with that.
 Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
Lecture 15 The Riemann mapping theorem Variables MATH-GA 2451.1 Complex The point of this lecture is to prove that the unit disk can be mapped conformally onto any simply connected open set in the plane,
THE RADIUS OF CONVERGENCE FORMULA. a n (z c) n, f(z) =
 THE RADIUS OF CONVERGENCE FORMULA Every complex power series, f(z) = (z c) n, n=0 has a radius of convergence, nonnegative-real or infinite, R = R(f) [0, + ], that describes the convergence of the series,
THE RADIUS OF CONVERGENCE FORMULA Every complex power series, f(z) = (z c) n, n=0 has a radius of convergence, nonnegative-real or infinite, R = R(f) [0, + ], that describes the convergence of the series,
Exercises for Part 1
 MATH200 Complex Analysis. Exercises for Part Exercises for Part The following exercises are provided for you to revise complex numbers. Exercise. Write the following expressions in the form x+iy, x,y R:
MATH200 Complex Analysis. Exercises for Part Exercises for Part The following exercises are provided for you to revise complex numbers. Exercise. Write the following expressions in the form x+iy, x,y R:
Supplementary Notes for W. Rudin: Principles of Mathematical Analysis
 Supplementary Notes for W. Rudin: Principles of Mathematical Analysis SIGURDUR HELGASON In 8.00B it is customary to cover Chapters 7 in Rudin s book. Experience shows that this requires careful planning
Supplementary Notes for W. Rudin: Principles of Mathematical Analysis SIGURDUR HELGASON In 8.00B it is customary to cover Chapters 7 in Rudin s book. Experience shows that this requires careful planning
LAURENT SERIES AND SINGULARITIES
 LAURENT SERIES AND SINGULARITIES Introduction So far we have studied analytic functions Locally, such functions are represented by power series Globally, the bounded ones are constant, the ones that get
LAURENT SERIES AND SINGULARITIES Introduction So far we have studied analytic functions Locally, such functions are represented by power series Globally, the bounded ones are constant, the ones that get
Spring 2010 Exam 2. You may not use your books, notes, or any calculator on this exam.
 MTH 282 final Spring 2010 Exam 2 Time Limit: 110 Minutes Name (Print): Instructor: Prof. Houhong Fan This exam contains 6 pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if any pages are
MTH 282 final Spring 2010 Exam 2 Time Limit: 110 Minutes Name (Print): Instructor: Prof. Houhong Fan This exam contains 6 pages (including this cover page) and 5 problems. Check to see if any pages are
Immerse Metric Space Homework
 Immerse Metric Space Homework (Exercises -2). In R n, define d(x, y) = x y +... + x n y n. Show that d is a metric that induces the usual topology. Sketch the basis elements when n = 2. Solution: Steps
Immerse Metric Space Homework (Exercises -2). In R n, define d(x, y) = x y +... + x n y n. Show that d is a metric that induces the usual topology. Sketch the basis elements when n = 2. Solution: Steps
Complex Analysis Math 147 Winter 2008
 Complex Analysis Math 147 Winter 2008 Bernard Russo March 14, 2008 Contents 1 Monday January 7 Course information; complex numbers; Assignment 1 1 1.1 Course information................................
Complex Analysis Math 147 Winter 2008 Bernard Russo March 14, 2008 Contents 1 Monday January 7 Course information; complex numbers; Assignment 1 1 1.1 Course information................................
