Math 220A - Fall Final Exam Solutions
|
|
|
- Abraham Young
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 22A - Fall Final Exam Solutions Problem 1. Let f be an entire function and let n 2. Show that there exists an entire function g with g n = f if and only if the orders of all zeroes of f are divisible by n. Answer: If f = g n, then for any zero a of g we have ord(f, a) = ord(g n, a) = n ord(g, a) is divisible by n. Conversely, assume ord (f, a) is divisible by n for any zero a of f. By Weierstraβ, we can construct an entire function h with zeros exactly at the zeros of f and of order 1 n ord(f, a). Clearly f and h n have exactly the same zeros with the same multiplicity, hence H = f/h n is entire and zero free. In particular, by Homework 2, Problem 4 (see solution there), we can write H = G n for some entire function G. Then f = h n H = (hg) n = g n for g = hg.
2 Problem 2. Calculate the integral x, for n Answer: We consider γ R the curve consisting of the segment [ R, R] and the half disc S R. We assume R > 1. By the residue theorem, we have z + 1 = 2πi γ R The possible values for the poles are a = ζ k = exp a +1= ( ) 1 Res z + 1, a. ( (2k + 1) πi ), k n 1. The last inequality k n 1 comes from the fact that the poles must be contained in the upper half plane. Using the method of computing residues in class, we have ( ) 1 Res z + 1, ζ 1 k = (z + 1) 1 z=ζ k = ζ 1 k using that ζ k As a result, We show = 1. Thus γ R n 1 z + 1 = 2πi = 2πi exp ( πi = 2πi n R R = ζ k, ( ζ k exp πi ) n 1 ( ) kπi = 2πi exp n k= k= ) 1 exp (πi) 1 exp ( ) = 2πi πi n exp ( ) πi n 1 exp ( ) πi n 1 exp ( πi ) ( exp πi ) = π n 1 ). x S R lim R S R z + 1 = π n z + 1 =. 1 ). Indeed, z + 1 R 1, and by the basic estimate z + 1 2πR 1 R 1. In consequence, R lim R R x + 1 = π n 1 S R ) = 2 x + 1 = π n 1 ) = x + 1 = π 1 ).
3 Problem 3. Consider f(z) = z n + a 1 z n a n. Show that there exists c with c = 1 such that f(c) 1. Answer: By Cauchy s estimates, we have f (n) () n! r n M(r) for M(r) = sup z =r f(z). Making r = 1 and noting f (n) () = n! we obtain Alternate Answer: Let 1 M(1) = sup f(z) = f(c) 1 for some c 1. z =1 g(z) = z n f(1/z) = a n z n a 1 z + 1. Note that g() = 1. By the maximum modulus principle, there exists z = 1, with g(z ) 1. We have Setting c = 1/z, we obtain and c = 1. g(z ) = z n f(1/z ) = f(1/z ) 1. f(c) 1 Alternate Answer: Assume that for all z = 1 we have f(z) < 1. Let G(z) = z n, F (z) = f(z) + g(z). Then for z = 1 we have F (z) G(z) = f(z) < 1 = z n = G(z). By Rouché s theorem, F and G have the same number of zeros inside the unit disc counted with multiplicity. Clearly, G has exactly one zero with multiplicity n. However, F (z) = f(z) + g(z) = a 1 z n a n is either identically equal to or it has at most n 1 zeros. The latter case contradicts Rouché. The former case shows f(z) = g(z) and the assertion of the problem is trivial since f(c) = g(c) = c n = 1 for c = 1.
4 Problem 4. Suppose f : { < z < 1} C is holomorphic and satisfies Show that f =. note f(z) log z. Answer: We first claim the origin is a removable singularity for f. Indeed, let g(z) = zf(z) and g(z) z log z = lim g(z) = since lim z log z =. z z Thus is a removable singularity for g. Extending g holomorphically across the origin, we have by continuity g() =. Since f(z) = g(z)/z and g() =, it follows that f is holomorphic at. Fix a (, 1) \ {}. Let r be so that a < r < 1. By Cauchy s formula f(a) = 1 f(z) 2π z a 1 log r 2π r a 2πr. z =r Here, we used the basic estimate, the fact that f(z) log z and z a r a. Making r 1 in the above estimate, we conclude conclude f(a) = for all a. Thus f =.
5 Problem 5. Let f(z) = P (z) Q(z) be a rational function with deg P deg Q 2 such that Q has no zeros along the non-negative real axis. Show that f(x) = Res z=a (f(z) log z) a C\R where for z C \ R we set log z = log r + iθ and θ (, 2π). Answer: We consider the keyhole contour consisting of a portion of a circle C r of radius r, a portion of a circle C R of radius R > r, and two line segments L + and L at distance δ and δ away from the positive x-axis, going from [r, R]. We let By the residue theorem γ γ = L + C R ( L ) ( S r ). f(z) log z = 2πi a Res z=a (f(z) log z). This gives R(z) log z R(z) log z + R(z) log z R(z) log z = 2πi C R C r L + L a Res z=a (R(z) log z). We first make δ, and then we make r, R. We claim the limits of the integrals over C R and C r equal. We first consider C R. Indeed, since Hence deg P deg Q 2 = f(z) M z 2, lim z z2 f(z) <. for z sufficiently large. If z = R, then log z = log R+iθ log R +2π. By the basic estimate, we have f(z) log z 2πR M (log R + 2π). C R R2 The estimates for C r are similar, but using that f(z) is bounded near the origin by continuity. Then, f(z) log z 2πr M ( log r + 2π) asr. C r Here, we used r log r which can be seen using the change of variables r = 1/y with y. By continuity arguments (f is continuous, and log is continuous provided we stay in compact regions either above or below the non-negative real axis), we have R lim f(z) log z = f(x) log x δ L + r
6 R R R lim f(z) log z = f(x)(log x + 2πi) = f(x) log x + 2πi f(x). δ L r r r Substituting in the residue theorem, after taking limits, first for δ, and then r, R, we obtain This completes the proof. 2πi f(x) = 2πi a C\R Res z=a (f(z) log z).
7 Problem 6. Let f : C C be entire, and assume that (Re f) (Im f) 216 = 1. Show that f is constant. Answer: We present first a solution that works for functions f : U C and can be generalized to polynomial identities P (Re f, Im f) =, for any polynomial P. If f is not constant, the image of f must be an open set in C so it must contain a disc. By assumption, the image is contained in the set u v 216 = 1. However, for each fixed value of u, there are at most 216 possible values of v, so (u, v) for finitely many v s. The contradiction comes because if (u, v), then (u, v ) for all v close to v. This shows f must be constant. Alternate Answer: For the problem at hand, a simpler second solution is as follows. We note (Re f) (Im f) 216 = 1 = Re f 1, Im f 1 = f 2. By Liouville s theorem, f is bounded, hence constant.
8 Problem 7. Let f : U \ {a} C be a holomorphic function with an isolated singularity at a. Let P be a non-constant polynomial. Show that f has a removable singularity, or a pole, or an essential singularity at a respectively if and only if P f has a removable singularity, or a pole, or an essential singularity at a. Answer: Write P (w) = a w n a n. (i) Assume first that a is a removable singularity for f. Then f is bounded in a neighborhood of a, say for z (a, ɛ) \ {a}. In this case f(z) M P (f(z)) = a f(z) n a n a M n a n is also bounded so the singularity of P f is also removable at a. (ii) Assume a is a pole for f. We show a is a pole for P f by proving lim P (f(z)) =. z a To this end, let R >. We seek to show P (f(z)) > R for all z (a, ɛ) \ {a} for a suitable ɛ. Note that for w real, we have lim a w n a 1 w n 1... a n =, w we can find r > such that if w > r, we have a w n a 1 w n 1... a n > R. Since a is a pole, we have lim z a f(z) =, so we can find ɛ > such that Thus f(z) > r for all z (a, ɛ) \ {a}. P (f(z)) = a f(z) n a n a f(z) n... a n > R where we used the triangle inequality, and the fact that w = f(z) > r. This shows that a is a pole for P f. (iii) Assume a is an essential singularity for f. Fix α and β two complex numbers such that We claim that we can find a sequence P (α) P (β). x n a such that f(x n ) α.
9 Indeed, by Casoratti-Weierstrass, for n sufficiently large so that ( a, n) 1 U, we have f ( ( a, n) 1 ) \ {a} is dense, hence we can find xn ( a, n) 1 \ {a} such that f(x n ) α < 1 n. In a similar fashion we can find y n a such that f(y n ) β. Thus P (f(x n )) P (α), P (f(y n )) P (β). If a were removable for P f, then P (α) = P (β) by continuity. This is however a contradiction. If a were a pole for P f, then the two limits would have to be infinite. Thus the only option is that a is an essential singularity. The reverse implication follows by putting (i)-(iii) together.
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser
 Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Solutions to Complex Analysis Prelims Ben Strasser In preparation for the complex analysis prelim, I typed up solutions to some old exams. This document includes complete solutions to both exams in 23,
Part IB Complex Analysis
 Part IB Complex Analysis Theorems Based on lectures by I. Smith Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after
Part IB Complex Analysis Theorems Based on lectures by I. Smith Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2016 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 2014
 COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
COMPLEX ANALYSIS Spring 24 Homework 4 Solutions Exercise Do and hand in exercise, Chapter 3, p. 4. Solution. The exercise states: Show that if a
Solutions to practice problems for the final
 Solutions to practice problems for the final Holomorphicity, Cauchy-Riemann equations, and Cauchy-Goursat theorem 1. (a) Show that there is a holomorphic function on Ω = {z z > 2} whose derivative is z
Solutions to practice problems for the final Holomorphicity, Cauchy-Riemann equations, and Cauchy-Goursat theorem 1. (a) Show that there is a holomorphic function on Ω = {z z > 2} whose derivative is z
Complex Analysis Problems
 Complex Analysis Problems transcribed from the originals by William J. DeMeo October 2, 2008 Contents 99 November 2 2 2 200 November 26 4 3 2006 November 3 6 4 2007 April 6 7 5 2007 November 6 8 99 NOVEMBER
Complex Analysis Problems transcribed from the originals by William J. DeMeo October 2, 2008 Contents 99 November 2 2 2 200 November 26 4 3 2006 November 3 6 4 2007 April 6 7 5 2007 November 6 8 99 NOVEMBER
Part IB. Further Analysis. Year
 Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Year 2004 2003 2002 2001 10 2004 2/I/4E Let τ be the topology on N consisting of the empty set and all sets X N such that N \ X is finite. Let σ be the usual topology on R, and let ρ be the topology on
Problem Set 5 Solution Set
 Problem Set 5 Solution Set Anthony Varilly Math 113: Complex Analysis, Fall 2002 1. (a) Let g(z) be a holomorphic function in a neighbourhood of z = a. Suppose that g(a) = 0. Prove that g(z)/(z a) extends
Problem Set 5 Solution Set Anthony Varilly Math 113: Complex Analysis, Fall 2002 1. (a) Let g(z) be a holomorphic function in a neighbourhood of z = a. Suppose that g(a) = 0. Prove that g(z)/(z a) extends
MATH 452. SAMPLE 3 SOLUTIONS May 3, (10 pts) Let f(x + iy) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) be an analytic function. Show that u(x, y) is harmonic.
 MATH 45 SAMPLE 3 SOLUTIONS May 3, 06. (0 pts) Let f(x + iy) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) be an analytic function. Show that u(x, y) is harmonic. Because f is holomorphic, u and v satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations:
MATH 45 SAMPLE 3 SOLUTIONS May 3, 06. (0 pts) Let f(x + iy) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) be an analytic function. Show that u(x, y) is harmonic. Because f is holomorphic, u and v satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations:
Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions
 Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions May, 04 Part.. Let log z be the principal branch of the logarithm defined on G = {z C z (, 0]}. Show that if t > 0, then the equation log z = t has exactly one
Complex Analysis Qualifying Exam Solutions May, 04 Part.. Let log z be the principal branch of the logarithm defined on G = {z C z (, 0]}. Show that if t > 0, then the equation log z = t has exactly one
Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014
 Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014 1. Determine whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answer (i.e., prove the claim, derive a contradiction or give a counter-example). (a) (10
Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014 1. Determine whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answer (i.e., prove the claim, derive a contradiction or give a counter-example). (a) (10
. Then g is holomorphic and bounded in U. So z 0 is a removable singularity of g. Since f(z) = w 0 + 1
 Now we describe the behavior of f near an isolated singularity of each kind. We will always assume that z 0 is a singularity of f, and f is holomorphic on D(z 0, r) \ {z 0 }. Theorem 4.2.. z 0 is a removable
Now we describe the behavior of f near an isolated singularity of each kind. We will always assume that z 0 is a singularity of f, and f is holomorphic on D(z 0, r) \ {z 0 }. Theorem 4.2.. z 0 is a removable
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5
 MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
MATH 722, COMPLEX ANALYSIS, SPRING 2009 PART 5.. The Arzela-Ascoli Theorem.. The Riemann mapping theorem Let X be a metric space, and let F be a family of continuous complex-valued functions on X. We have
Chapter 4: Open mapping theorem, removable singularities
 Chapter 4: Open mapping theorem, removable singularities Course 44, 2003 04 February 9, 2004 Theorem 4. (Laurent expansion) Let f : G C be analytic on an open G C be open that contains a nonempty annulus
Chapter 4: Open mapping theorem, removable singularities Course 44, 2003 04 February 9, 2004 Theorem 4. (Laurent expansion) Let f : G C be analytic on an open G C be open that contains a nonempty annulus
MORE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOREM
 MOE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOEM Contents. The Mean Value Property and the Maximum-Modulus Principle 2. Morera s Theorem and some applications 3 3. The Schwarz eflection Principle 6 We have stated Cauchy
MOE CONSEQUENCES OF CAUCHY S THEOEM Contents. The Mean Value Property and the Maximum-Modulus Principle 2. Morera s Theorem and some applications 3 3. The Schwarz eflection Principle 6 We have stated Cauchy
Solutions for Math 411 Assignment #10 1
 Solutions for Math 4 Assignment # AA. Compute the following integrals: a) + sin θ dθ cos x b) + x dx 4 Solution of a). Let z = e iθ. By the substitution = z + z ), sin θ = i z z ) and dθ = iz dz and Residue
Solutions for Math 4 Assignment # AA. Compute the following integrals: a) + sin θ dθ cos x b) + x dx 4 Solution of a). Let z = e iθ. By the substitution = z + z ), sin θ = i z z ) and dθ = iz dz and Residue
Complex Analysis Important Concepts
 Complex Analysis Important Concepts Travis Askham April 1, 2012 Contents 1 Complex Differentiation 2 1.1 Definition and Characterization.............................. 2 1.2 Examples..........................................
Complex Analysis Important Concepts Travis Askham April 1, 2012 Contents 1 Complex Differentiation 2 1.1 Definition and Characterization.............................. 2 1.2 Examples..........................................
Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r
![Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r](/thumbs/77/75527144.jpg) 2. A harmonic conjugate always exists locally: if u is a harmonic function in an open set U, then for any disk D(z 0, r) U, there is f, which is analytic in D(z 0, r) and satisfies that Re f u. Since such
2. A harmonic conjugate always exists locally: if u is a harmonic function in an open set U, then for any disk D(z 0, r) U, there is f, which is analytic in D(z 0, r) and satisfies that Re f u. Since such
Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall Anton R. Schep
 Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall 20 Anton R. Schep CHAPTER Holomorphic (or Analytic) Functions. Definitions and elementary properties In complex analysis we study functions f : S C,
Complex Variables Notes for Math 703. Updated Fall 20 Anton R. Schep CHAPTER Holomorphic (or Analytic) Functions. Definitions and elementary properties In complex analysis we study functions f : S C,
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm
 Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 3 Meromorphic Functions and the Logarithm Yung-Hsiang Huang 217.11.5 Exercises 1. From the identity sin πz = eiπz e iπz 2i, it s easy to show its zeros are
Final Exam - MATH 630: Solutions
 Final Exam - MATH 630: Solutions Problem. Find all x R satisfying e xeix e ix. Solution. Comparing the moduli of both parts, we obtain e x cos x, and therefore, x cos x 0, which is possible only if x 0
Final Exam - MATH 630: Solutions Problem. Find all x R satisfying e xeix e ix. Solution. Comparing the moduli of both parts, we obtain e x cos x, and therefore, x cos x 0, which is possible only if x 0
Complex Analysis Math 185A, Winter 2010 Final: Solutions
 Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Complex Analysis Math 85A, Winter 200 Final: Solutions. [25 pts] The Jacobian of two real-valued functions u(x, y), v(x, y) of (x, y) is defined by the determinant (u, v) J = (x, y) = u x u y v x v y.
Chapter 11. Cauchy s Integral Formula
 hapter 11 auchy s Integral Formula If I were founding a university I would begin with a smoking room; next a dormitory; and then a decent reading room and a library. After that, if I still had more money
hapter 11 auchy s Integral Formula If I were founding a university I would begin with a smoking room; next a dormitory; and then a decent reading room and a library. After that, if I still had more money
Complex Analysis Topic: Singularities
 Complex Analysis Topic: Singularities MA201 Mathematics III Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati August 2015 Complex Analysis Topic: Singularities 1 / 15 Zeroes of Analytic Functions A point z 0 C is
Complex Analysis Topic: Singularities MA201 Mathematics III Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati August 2015 Complex Analysis Topic: Singularities 1 / 15 Zeroes of Analytic Functions A point z 0 C is
MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 4: ISOLATED SINGULARITIES AND THE RESIDUE THEOREM
 MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 4: ISOLATED SINGULARITIES AND THE RESIDUE THEOREM TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR 1. Functions holomorphic on an annulus Let A = D R \D r be an annulus centered at 0 with 0 < r < R
MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 4: ISOLATED SINGULARITIES AND THE RESIDUE THEOREM TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR 1. Functions holomorphic on an annulus Let A = D R \D r be an annulus centered at 0 with 0 < r < R
Math Final Exam.
 Math 106 - Final Exam. This is a closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. The exam consists of 8 questions worth 100 points. Good luck! Name: Acknowledgment and acceptance of honor code: Signature:
Math 106 - Final Exam. This is a closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. The exam consists of 8 questions worth 100 points. Good luck! Name: Acknowledgment and acceptance of honor code: Signature:
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 530) January 2019
 Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Qualifying Exam Complex Analysis (Math 53) January 219 1. Let D be a domain. A function f : D C is antiholomorphic if for every z D the limit f(z + h) f(z) lim h h exists. Write f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,
Complex Analysis for F2
 Institutionen för Matematik KTH Stanislav Smirnov stas@math.kth.se Complex Analysis for F2 Projects September 2002 Suggested projects ask you to prove a few important and difficult theorems in complex
Institutionen för Matematik KTH Stanislav Smirnov stas@math.kth.se Complex Analysis for F2 Projects September 2002 Suggested projects ask you to prove a few important and difficult theorems in complex
Math 520a - Final take home exam - solutions
 Math 52a - Final take home exam - solutions 1. Let f(z) be entire. Prove that f has finite order if and only if f has finite order and that when they have finite order their orders are the same. Solution:
Math 52a - Final take home exam - solutions 1. Let f(z) be entire. Prove that f has finite order if and only if f has finite order and that when they have finite order their orders are the same. Solution:
RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM
 RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM VED V. DATAR Recall that two domains are called conformally equivalent if there exists a holomorphic bijection from one to the other. This automatically implies that there is an
RIEMANN MAPPING THEOREM VED V. DATAR Recall that two domains are called conformally equivalent if there exists a holomorphic bijection from one to the other. This automatically implies that there is an
Considering our result for the sum and product of analytic functions, this means that for (a 0, a 1,..., a N ) C N+1, the polynomial.
 Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
Lecture 3 Usual complex functions MATH-GA 245.00 Complex Variables Polynomials. Construction f : z z is analytic on all of C since its real and imaginary parts satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann relations and
FINAL EXAM MATH 220A, UCSD, AUTUMN 14. You have three hours.
 FINAL EXAM MATH 220A, UCSD, AUTUMN 4 You have three hours. Problem Points Score There are 6 problems, and the total number of points is 00. Show all your work. Please make your work as clear and easy to
FINAL EXAM MATH 220A, UCSD, AUTUMN 4 You have three hours. Problem Points Score There are 6 problems, and the total number of points is 00. Show all your work. Please make your work as clear and easy to
z b k P k p k (z), (z a) f (n 1) (a) 2 (n 1)! (z a)n 1 +f n (z)(z a) n, where f n (z) = 1 C
 . Representations of Meromorphic Functions There are two natural ways to represent a rational function. One is to express it as a quotient of two polynomials, the other is to use partial fractions. The
. Representations of Meromorphic Functions There are two natural ways to represent a rational function. One is to express it as a quotient of two polynomials, the other is to use partial fractions. The
POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION
 POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION 1. Analytic functions Definition 1.1. A function f : Ω C C is complex-analytic if for each z 0 Ω there exists a power series f z0 (z) := a n (z z 0 ) n which converges
POWER SERIES AND ANALYTIC CONTINUATION 1. Analytic functions Definition 1.1. A function f : Ω C C is complex-analytic if for each z 0 Ω there exists a power series f z0 (z) := a n (z z 0 ) n which converges
Notes on Complex Analysis
 Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
MATH 215A NOTES MOOR XU NOTES FROM A COURSE BY KANNAN SOUNDARARAJAN
 MATH 25A NOTES MOOR XU NOTES FROM A COURSE BY KANNAN SOUNDARARAJAN Abstract. These notes were taken during Math 25A (Complex Analysis) taught by Kannan Soundararajan in Fall 2 at Stanford University. They
MATH 25A NOTES MOOR XU NOTES FROM A COURSE BY KANNAN SOUNDARARAJAN Abstract. These notes were taken during Math 25A (Complex Analysis) taught by Kannan Soundararajan in Fall 2 at Stanford University. They
Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett/
 (February 9, 25) Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ (The present proof of this old result roughly follows the proof
(February 9, 25) Hartogs Theorem: separate analyticity implies joint Paul Garrett garrett@math.umn.edu http://www.math.umn.edu/ garrett/ (The present proof of this old result roughly follows the proof
Complex Analysis Homework 9: Solutions
 Complex Analysis Fall 2007 Homework 9: Solutions 3..4 (a) Let z C \ {ni : n Z}. Then /(n 2 + z 2 ) n /n 2 n 2 n n 2 + z 2. According to the it comparison test from calculus, the series n 2 + z 2 converges
Complex Analysis Fall 2007 Homework 9: Solutions 3..4 (a) Let z C \ {ni : n Z}. Then /(n 2 + z 2 ) n /n 2 n 2 n n 2 + z 2. According to the it comparison test from calculus, the series n 2 + z 2 converges
Complex Analysis Qual Sheet
 Complex Analysis Qual Sheet Robert Won Tricks and traps. traps. Basically all complex analysis qualifying exams are collections of tricks and - Jim Agler Useful facts. e z = 2. sin z = n=0 3. cos z = z
Complex Analysis Qual Sheet Robert Won Tricks and traps. traps. Basically all complex analysis qualifying exams are collections of tricks and - Jim Agler Useful facts. e z = 2. sin z = n=0 3. cos z = z
Math 341 Summer 2016 Midterm Exam 2 Solutions. 1. Complete the definitions of the following words or phrases:
 Math 34 Summer 06 Midterm Exam Solutions. Complete the definitions of the following words or phrases: (a) A sequence (a n ) is called a Cauchy sequence if and only if for every ɛ > 0, there exists and
Math 34 Summer 06 Midterm Exam Solutions. Complete the definitions of the following words or phrases: (a) A sequence (a n ) is called a Cauchy sequence if and only if for every ɛ > 0, there exists and
MATH 185: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 2009/10 PROBLEM SET 9 SOLUTIONS. and g b (z) = eπz/2 1
 MATH 85: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 2009/0 PROBLEM SET 9 SOLUTIONS. Consider the functions defined y g a (z) = eiπz/2 e iπz/2 + Show that g a maps the set to D(0, ) while g maps the set and g (z) = eπz/2 e
MATH 85: COMPLEX ANALYSIS FALL 2009/0 PROBLEM SET 9 SOLUTIONS. Consider the functions defined y g a (z) = eiπz/2 e iπz/2 + Show that g a maps the set to D(0, ) while g maps the set and g (z) = eπz/2 e
Complex Analysis. Travis Dirle. December 4, 2016
 Complex Analysis 2 Complex Analysis Travis Dirle December 4, 2016 2 Contents 1 Complex Numbers and Functions 1 2 Power Series 3 3 Analytic Functions 7 4 Logarithms and Branches 13 5 Complex Integration
Complex Analysis 2 Complex Analysis Travis Dirle December 4, 2016 2 Contents 1 Complex Numbers and Functions 1 2 Power Series 3 3 Analytic Functions 7 4 Logarithms and Branches 13 5 Complex Integration
LECTURE-20 : ISOLATED SINGULARITIES. A punctured domain is an open set with a point removed. For p Ω, we use the notation
 LECTURE-20 : ISOLATED SINGULARITIES VED V. DATAR A punctured domain is an open set with a point removed. For p Ω, we use the notation Ω p = Ω \ {p}, or simply Ω when there is no confusion about the point
LECTURE-20 : ISOLATED SINGULARITIES VED V. DATAR A punctured domain is an open set with a point removed. For p Ω, we use the notation Ω p = Ω \ {p}, or simply Ω when there is no confusion about the point
The Residue Theorem. Integration Methods over Closed Curves for Functions with Singularities
 The Residue Theorem Integration Methods over losed urves for Functions with Singularities We have shown that if f(z) is analytic inside and on a closed curve, then f(z)dz = 0. We have also seen examples
The Residue Theorem Integration Methods over losed urves for Functions with Singularities We have shown that if f(z) is analytic inside and on a closed curve, then f(z)dz = 0. We have also seen examples
MATH 6322, COMPLEX ANALYSIS
 Complex numbers: MATH 6322, COMPLEX ANALYSIS Motivating problem: you can write down equations which don t have solutions, like x 2 + = 0. Introduce a (formal) solution i, where i 2 =. Define the set C
Complex numbers: MATH 6322, COMPLEX ANALYSIS Motivating problem: you can write down equations which don t have solutions, like x 2 + = 0. Introduce a (formal) solution i, where i 2 =. Define the set C
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley. GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2016
 Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2016 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
Department of Mathematics, University of California, Berkeley YOUR 1 OR 2 DIGIT EXAM NUMBER GRADUATE PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION, Part A Fall Semester 2016 1. Please write your 1- or 2-digit exam number on
Complex Variables...Review Problems (Residue Calculus Comments)...Fall Initial Draft
 Complex Variables........Review Problems Residue Calculus Comments)........Fall 22 Initial Draft ) Show that the singular point of fz) is a pole; determine its order m and its residue B: a) e 2z )/z 4,
Complex Variables........Review Problems Residue Calculus Comments)........Fall 22 Initial Draft ) Show that the singular point of fz) is a pole; determine its order m and its residue B: a) e 2z )/z 4,
f (n) (z 0 ) Theorem [Morera s Theorem] Suppose f is continuous on a domain U, and satisfies that for any closed curve γ in U, γ
![f (n) (z 0 ) Theorem [Morera s Theorem] Suppose f is continuous on a domain U, and satisfies that for any closed curve γ in U, γ f (n) (z 0 ) Theorem [Morera s Theorem] Suppose f is continuous on a domain U, and satisfies that for any closed curve γ in U, γ](/thumbs/87/95570641.jpg) Remarks. 1. So far we have seen that holomorphic is equivalent to analytic. Thus, if f is complex differentiable in an open set, then it is infinitely many times complex differentiable in that set. This
Remarks. 1. So far we have seen that holomorphic is equivalent to analytic. Thus, if f is complex differentiable in an open set, then it is infinitely many times complex differentiable in that set. This
MTH 3102 Complex Variables Final Exam May 1, :30pm-5:30pm, Skurla Hall, Room 106
 Name (Last name, First name): MTH 32 Complex Variables Final Exam May, 27 3:3pm-5:3pm, Skurla Hall, Room 6 Exam Instructions: You have hour & 5 minutes to complete the exam. There are a total of problems.
Name (Last name, First name): MTH 32 Complex Variables Final Exam May, 27 3:3pm-5:3pm, Skurla Hall, Room 6 Exam Instructions: You have hour & 5 minutes to complete the exam. There are a total of problems.
Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions
 Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions Nikhil Srivastava December 12, 2015 1. True or false: (a) If f is analytic in the annulus A = {z : 1 < z < 2} then there exist functions g and h such that
Math 185 Fall 2015, Sample Final Exam Solutions Nikhil Srivastava December 12, 2015 1. True or false: (a) If f is analytic in the annulus A = {z : 1 < z < 2} then there exist functions g and h such that
III. Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem
 MTH6 Complex Analysis 2009-0 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 III. Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem. Cauchy s formulae. Cauchy s Integral Formula Let f be holomorphic on and everywhere inside a simple
MTH6 Complex Analysis 2009-0 Lecture Notes c Shaun Bullett 2009 III. Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem. Cauchy s formulae. Cauchy s Integral Formula Let f be holomorphic on and everywhere inside a simple
Complex Variables. Cathal Ormond
 Complex Variables Cathal Ormond Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Definition: Polar Form.............................. 3 1.2 Definition: Length................................ 3 1.3 Definitions.....................................
Complex Variables Cathal Ormond Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Definition: Polar Form.............................. 3 1.2 Definition: Length................................ 3 1.3 Definitions.....................................
1. Let A R be a nonempty set that is bounded from above, and let a be the least upper bound of A. Show that there exists a sequence {a n } n N
 Applied Analysis prelim July 15, 216, with solutions Solve 4 of the problems 1-5 and 2 of the problems 6-8. We will only grade the first 4 problems attempted from1-5 and the first 2 attempted from problems
Applied Analysis prelim July 15, 216, with solutions Solve 4 of the problems 1-5 and 2 of the problems 6-8. We will only grade the first 4 problems attempted from1-5 and the first 2 attempted from problems
13 Maximum Modulus Principle
 3 Maximum Modulus Principle Theorem 3. (maximum modulus principle). If f is non-constant and analytic on an open connected set Ω, then there is no point z 0 Ω such that f(z) f(z 0 ) for all z Ω. Remark
3 Maximum Modulus Principle Theorem 3. (maximum modulus principle). If f is non-constant and analytic on an open connected set Ω, then there is no point z 0 Ω such that f(z) f(z 0 ) for all z Ω. Remark
f(w) f(a) = 1 2πi w a Proof. There exists a number r such that the disc D(a,r) is contained in I(γ). For any ǫ < r, w a dw
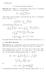 Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
Proof[section] 5. Cauchy integral formula Theorem 5.. Suppose f is holomorphic inside and on a positively oriented curve. Then if a is a point inside, f(a) = w a dw. Proof. There exists a number r such
Problem Set 5. 2 n k. Then a nk (x) = 1+( 1)k
 Problem Set 5 1. (Folland 2.43) For x [, 1), let 1 a n (x)2 n (a n (x) = or 1) be the base-2 expansion of x. (If x is a dyadic rational, choose the expansion such that a n (x) = for large n.) Then the
Problem Set 5 1. (Folland 2.43) For x [, 1), let 1 a n (x)2 n (a n (x) = or 1) be the base-2 expansion of x. (If x is a dyadic rational, choose the expansion such that a n (x) = for large n.) Then the
Problem 1A. Calculus. Problem 3A. Real analysis. f(x) = 0 x = 0.
 Problem A. Calculus Find the length of the spiral given in polar coordinates by r = e θ, < θ 0. Solution: The length is 0 θ= ds where by Pythagoras ds = dr 2 + (rdθ) 2 = dθ 2e θ, so the length is 0 2e
Problem A. Calculus Find the length of the spiral given in polar coordinates by r = e θ, < θ 0. Solution: The length is 0 θ= ds where by Pythagoras ds = dr 2 + (rdθ) 2 = dθ 2e θ, so the length is 0 2e
Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both
 Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both real and complex analysis. You have 3 hours. Real
Analysis Comprehensive Exam, January 2011 Instructions: Do as many problems as you can. You should attempt to answer completely some questions in both real and complex analysis. You have 3 hours. Real
Complex Analysis Math 205A, Winter 2014 Final: Solutions
 Part I: Short Questions Complex Analysis Math 205A, Winter 2014 Final: Solutions I.1 [5%] State the Cauchy-Riemann equations for a holomorphic function f(z) = u(x,y)+iv(x,y). The Cauchy-Riemann equations
Part I: Short Questions Complex Analysis Math 205A, Winter 2014 Final: Solutions I.1 [5%] State the Cauchy-Riemann equations for a holomorphic function f(z) = u(x,y)+iv(x,y). The Cauchy-Riemann equations
MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I
 MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I 1. The Algebra of Complex Numbers A complex number is an expression of the form a + ib, where a and b are real numbers. a is called the real part of a + ib and b the imaginary
MA3111S COMPLEX ANALYSIS I 1. The Algebra of Complex Numbers A complex number is an expression of the form a + ib, where a and b are real numbers. a is called the real part of a + ib and b the imaginary
Riemann sphere and rational maps
 Chapter 3 Riemann sphere and rational maps 3.1 Riemann sphere It is sometimes convenient, and fruitful, to work with holomorphic (or in general continuous) functions on a compact space. However, we wish
Chapter 3 Riemann sphere and rational maps 3.1 Riemann sphere It is sometimes convenient, and fruitful, to work with holomorphic (or in general continuous) functions on a compact space. However, we wish
4.6 Montel's Theorem. Robert Oeckl CA NOTES 7 17/11/2009 1
 Robert Oeckl CA NOTES 7 17/11/2009 1 4.6 Montel's Theorem Let X be a topological space. We denote by C(X) the set of complex valued continuous functions on X. Denition 4.26. A topological space is called
Robert Oeckl CA NOTES 7 17/11/2009 1 4.6 Montel's Theorem Let X be a topological space. We denote by C(X) the set of complex valued continuous functions on X. Denition 4.26. A topological space is called
MTH 3102 Complex Variables Final Exam May 1, :30pm-5:30pm, Skurla Hall, Room 106
 Name (Last name, First name): MTH 02 omplex Variables Final Exam May, 207 :0pm-5:0pm, Skurla Hall, Room 06 Exam Instructions: You have hour & 50 minutes to complete the exam. There are a total of problems.
Name (Last name, First name): MTH 02 omplex Variables Final Exam May, 207 :0pm-5:0pm, Skurla Hall, Room 06 Exam Instructions: You have hour & 50 minutes to complete the exam. There are a total of problems.
Chapter 30 MSMYP1 Further Complex Variable Theory
 Chapter 30 MSMYP Further Complex Variable Theory (30.) Multifunctions A multifunction is a function that may take many values at the same point. Clearly such functions are problematic for an analytic study,
Chapter 30 MSMYP Further Complex Variable Theory (30.) Multifunctions A multifunction is a function that may take many values at the same point. Clearly such functions are problematic for an analytic study,
Part IB. Complex Analysis. Year
 Part IB Complex Analysis Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 Paper 1, Section I 2A Complex Analysis or Complex Methods 7 (a) Show that w = log(z) is a conformal
Part IB Complex Analysis Year 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2018 Paper 1, Section I 2A Complex Analysis or Complex Methods 7 (a) Show that w = log(z) is a conformal
APPROXIMATING CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS: WEIERSTRASS, BERNSTEIN, AND RUNGE
 APPROXIMATING CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS: WEIERSTRASS, BERNSTEIN, AND RUNGE WILLIE WAI-YEUNG WONG. Introduction This set of notes is meant to describe some aspects of polynomial approximations to continuous
APPROXIMATING CONTINUOUS FUNCTIONS: WEIERSTRASS, BERNSTEIN, AND RUNGE WILLIE WAI-YEUNG WONG. Introduction This set of notes is meant to describe some aspects of polynomial approximations to continuous
IV.3. Zeros of an Analytic Function
 IV.3. Zeros of an Analytic Function 1 IV.3. Zeros of an Analytic Function Note. We now explore factoring series in a way analogous to factoring a polynomial. Recall that if p is a polynomial with a zero
IV.3. Zeros of an Analytic Function 1 IV.3. Zeros of an Analytic Function Note. We now explore factoring series in a way analogous to factoring a polynomial. Recall that if p is a polynomial with a zero
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi The Fourier Transform
 Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 4 The Fourier Transform Yung-Hsiang Huang 2017.11.05 1 Exercises 1. Suppose f L 1 (), and f 0. Show that f 0. emark 1. This proof is observed by Newmann (published
Complex Analysis, Stein and Shakarchi Chapter 4 The Fourier Transform Yung-Hsiang Huang 2017.11.05 1 Exercises 1. Suppose f L 1 (), and f 0. Show that f 0. emark 1. This proof is observed by Newmann (published
Homework 27. Homework 28. Homework 29. Homework 30. Prof. Girardi, Math 703, Fall 2012 Homework: Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by
 Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
Homework 27 Define f : C C and u, v : R 2 R by f(z) := xy where x := Re z, y := Im z u(x, y) = Re f(x + iy) v(x, y) = Im f(x + iy). Show that 1. u and v satisfies the Cauchy Riemann equations at (x, y)
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY
 INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYTIC GEOMETRY KRZYSZTOF KURDYKA 1. Analytic functions in several variables 1.1. Summable families. Let (E, ) be a normed space over the field R or C, dim E
WEIERSTRASS THEOREMS AND RINGS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS
 WEIERSTRASS THEOREMS AND RINGS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS YIFEI ZHAO Contents. The Weierstrass factorization theorem 2. The Weierstrass preparation theorem 6 3. The Weierstrass division theorem 8 References
WEIERSTRASS THEOREMS AND RINGS OF HOLOMORPHIC FUNCTIONS YIFEI ZHAO Contents. The Weierstrass factorization theorem 2. The Weierstrass preparation theorem 6 3. The Weierstrass division theorem 8 References
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative
 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative
 Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Math 259: Introduction to Analytic Number Theory Functions of finite order: product formula and logarithmic derivative This chapter is another review of standard material in complex analysis. See for instance
Introductory Complex Analysis
 Introductory Complex Analysis Course No. 100 312 Spring 2007 Michael Stoll Contents Acknowledgments 2 1. Basics 2 2. Complex Differentiability and Holomorphic Functions 3 3. Power Series and the Abel Limit
Introductory Complex Analysis Course No. 100 312 Spring 2007 Michael Stoll Contents Acknowledgments 2 1. Basics 2 2. Complex Differentiability and Holomorphic Functions 3 3. Power Series and the Abel Limit
Solutions for Problem Set #5 due October 17, 2003 Dustin Cartwright and Dylan Thurston
 Solutions for Problem Set #5 due October 17, 23 Dustin Cartwright and Dylan Thurston 1 (B&N 6.5) Suppose an analytic function f agrees with tan x, x 1. Show that f(z) = i has no solution. Could f be entire?
Solutions for Problem Set #5 due October 17, 23 Dustin Cartwright and Dylan Thurston 1 (B&N 6.5) Suppose an analytic function f agrees with tan x, x 1. Show that f(z) = i has no solution. Could f be entire?
4.5 The Open and Inverse Mapping Theorem
 4.5 The Open and Inverse Mapping Theorem Theorem 4.5.1. [Open Mapping Theorem] Let f be analytic in an open set U such that f is not constant in any open disc. Then f(u) = {f() : U} is open. Lemma 4.5.1.
4.5 The Open and Inverse Mapping Theorem Theorem 4.5.1. [Open Mapping Theorem] Let f be analytic in an open set U such that f is not constant in any open disc. Then f(u) = {f() : U} is open. Lemma 4.5.1.
1 Res z k+1 (z c), 0 =
 32. COMPLEX ANALYSIS FOR APPLICATIONS Mock Final examination. (Monday June 7..am 2.pm) You may consult your handwritten notes, the book by Gamelin, and the solutions and handouts provided during the Quarter.
32. COMPLEX ANALYSIS FOR APPLICATIONS Mock Final examination. (Monday June 7..am 2.pm) You may consult your handwritten notes, the book by Gamelin, and the solutions and handouts provided during the Quarter.
Complex Analysis Math 147 Winter 2008
 Complex Analysis Math 147 Winter 2008 Bernard Russo March 14, 2008 Contents 1 Monday January 7 Course information; complex numbers; Assignment 1 1 1.1 Course information................................
Complex Analysis Math 147 Winter 2008 Bernard Russo March 14, 2008 Contents 1 Monday January 7 Course information; complex numbers; Assignment 1 1 1.1 Course information................................
X.9 Revisited, Cauchy s Formula for Contours
 X.9 Revisited, Cauchy s Formula for Contours Let G C, G open. Let f be holomorphic on G. Let Γ be a simple contour with range(γ) G and int(γ) G. Then, for all z 0 int(γ), f (z 0 ) = 1 f (z) dz 2πi Γ z
X.9 Revisited, Cauchy s Formula for Contours Let G C, G open. Let f be holomorphic on G. Let Γ be a simple contour with range(γ) G and int(γ) G. Then, for all z 0 int(γ), f (z 0 ) = 1 f (z) dz 2πi Γ z
Lecture 16 and 17 Application to Evaluation of Real Integrals. R a (f)η(γ; a)
 Lecture 16 and 17 Application to Evaluation of Real Integrals Theorem 1 Residue theorem: Let Ω be a simply connected domain and A be an isolated subset of Ω. Suppose f : Ω\A C is a holomorphic function.
Lecture 16 and 17 Application to Evaluation of Real Integrals Theorem 1 Residue theorem: Let Ω be a simply connected domain and A be an isolated subset of Ω. Suppose f : Ω\A C is a holomorphic function.
Complex Variables. Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit.
 Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit. 1. The TI-89 calculator says, reasonably enough, that x 1) 1/3 1 ) 3 = 8. lim
Instructions Solve any eight of the following ten problems. Explain your reasoning in complete sentences to maximize credit. 1. The TI-89 calculator says, reasonably enough, that x 1) 1/3 1 ) 3 = 8. lim
MASTERS EXAMINATION IN MATHEMATICS
 MASTERS EXAMINATION IN MATHEMATICS PURE MATHEMATICS OPTION FALL 2007 Full points can be obtained for correct answers to 8 questions. Each numbered question (which may have several parts) is worth the same
MASTERS EXAMINATION IN MATHEMATICS PURE MATHEMATICS OPTION FALL 2007 Full points can be obtained for correct answers to 8 questions. Each numbered question (which may have several parts) is worth the same
Mid Term-1 : Solutions to practice problems
 Mid Term- : Solutions to practice problems 0 October, 06. Is the function fz = e z x iy holomorphic at z = 0? Give proper justification. Here we are using the notation z = x + iy. Solution: Method-. Use
Mid Term- : Solutions to practice problems 0 October, 06. Is the function fz = e z x iy holomorphic at z = 0? Give proper justification. Here we are using the notation z = x + iy. Solution: Method-. Use
1. Partial Fraction Expansion All the polynomials in this note are assumed to be complex polynomials.
 Partial Fraction Expansion All the polynomials in this note are assumed to be complex polynomials A rational function / is a quotient of two polynomials P, Q with 0 By Fundamental Theorem of algebra, =
Partial Fraction Expansion All the polynomials in this note are assumed to be complex polynomials A rational function / is a quotient of two polynomials P, Q with 0 By Fundamental Theorem of algebra, =
Complex Analysis Math 220C Spring 2008
 Complex Analysis Math 220C Spring 2008 Bernard Russo June 2, 2008 Contents 1 Monday March 31, 2008 class cancelled due to the Master s travel plans 1 2 Wednesday April 2, 2008 Course information; Riemann
Complex Analysis Math 220C Spring 2008 Bernard Russo June 2, 2008 Contents 1 Monday March 31, 2008 class cancelled due to the Master s travel plans 1 2 Wednesday April 2, 2008 Course information; Riemann
MATH COMPLEX ANALYSIS. Contents
 MATH 3964 - OMPLEX ANALYSIS ANDREW TULLOH AND GILES GARDAM ontents 1. ontour Integration and auchy s Theorem 2 1.1. Analytic functions 2 1.2. ontour integration 3 1.3. auchy s theorem and extensions 3
MATH 3964 - OMPLEX ANALYSIS ANDREW TULLOH AND GILES GARDAM ontents 1. ontour Integration and auchy s Theorem 2 1.1. Analytic functions 2 1.2. ontour integration 3 1.3. auchy s theorem and extensions 3
MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 6: NORMAL FAMILIES AND THE THEOREMS OF PICARD
 MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 6: NORMAL FAMILIES AND THE THEOREMS OF PICARD TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR 1. Introduction Suppose that we want to solve the equation f(z) = β where f is a nonconstant entire function and
MATH 566 LECTURE NOTES 6: NORMAL FAMILIES AND THE THEOREMS OF PICARD TSOGTGEREL GANTUMUR 1. Introduction Suppose that we want to solve the equation f(z) = β where f is a nonconstant entire function and
F (z) =f(z). f(z) = a n (z z 0 ) n. F (z) = a n (z z 0 ) n
 6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
6 Chapter 2. CAUCHY S THEOREM AND ITS APPLICATIONS Theorem 5.6 (Schwarz reflection principle) Suppose that f is a holomorphic function in Ω + that extends continuously to I and such that f is real-valued
Types of Real Integrals
 Math B: Complex Variables Types of Real Integrals p(x) I. Integrals of the form P.V. dx where p(x) and q(x) are polynomials and q(x) q(x) has no eros (for < x < ) and evaluate its integral along the fol-
Math B: Complex Variables Types of Real Integrals p(x) I. Integrals of the form P.V. dx where p(x) and q(x) are polynomials and q(x) q(x) has no eros (for < x < ) and evaluate its integral along the fol-
MATH 311: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONTOUR INTEGRALS LECTURE
 MATH 3: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONTOUR INTEGRALS LECTURE Recall the Residue Theorem: Let be a simple closed loop, traversed counterclockwise. Let f be a function that is analytic on and meromorphic inside. Then
MATH 3: COMPLEX ANALYSIS CONTOUR INTEGRALS LECTURE Recall the Residue Theorem: Let be a simple closed loop, traversed counterclockwise. Let f be a function that is analytic on and meromorphic inside. Then
Second Midterm Exam Name: Practice Problems March 10, 2015
 Math 160 1. Treibergs Second Midterm Exam Name: Practice Problems March 10, 015 1. Determine the singular points of the function and state why the function is analytic everywhere else: z 1 fz) = z + 1)z
Math 160 1. Treibergs Second Midterm Exam Name: Practice Problems March 10, 015 1. Determine the singular points of the function and state why the function is analytic everywhere else: z 1 fz) = z + 1)z
MA30056: Complex Analysis. Revision: Checklist & Previous Exam Questions I
 MA30056: Complex Analysis Revision: Checklist & Previous Exam Questions I Given z C and r > 0, define B r (z) and B r (z). Define what it means for a subset A C to be open/closed. If M A C, when is M said
MA30056: Complex Analysis Revision: Checklist & Previous Exam Questions I Given z C and r > 0, define B r (z) and B r (z). Define what it means for a subset A C to be open/closed. If M A C, when is M said
1. The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions.
 Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
Complex Analysis Qualifying Examination 1 The COMPLEX PLANE AND ELEMENTARY FUNCTIONS: Complex numbers; stereographic projection; simple and multiple connectivity, elementary functions 2 ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS:
MATH SPRING UC BERKELEY
 MATH 85 - SPRING 205 - UC BERKELEY JASON MURPHY Abstract. These are notes for Math 85 taught in the Spring of 205 at UC Berkeley. c 205 Jason Murphy - All Rights Reserved Contents. Course outline 2 2.
MATH 85 - SPRING 205 - UC BERKELEY JASON MURPHY Abstract. These are notes for Math 85 taught in the Spring of 205 at UC Berkeley. c 205 Jason Murphy - All Rights Reserved Contents. Course outline 2 2.
Synopsis of Complex Analysis. Ryan D. Reece
 Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
Synopsis of Complex Analysis Ryan D. Reece December 7, 2006 Chapter Complex Numbers. The Parts of a Complex Number A complex number, z, is an ordered pair of real numbers similar to the points in the real
Immerse Metric Space Homework
 Immerse Metric Space Homework (Exercises -2). In R n, define d(x, y) = x y +... + x n y n. Show that d is a metric that induces the usual topology. Sketch the basis elements when n = 2. Solution: Steps
Immerse Metric Space Homework (Exercises -2). In R n, define d(x, y) = x y +... + x n y n. Show that d is a metric that induces the usual topology. Sketch the basis elements when n = 2. Solution: Steps
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part I
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Comple Analsis II Lecture Notes Part I Chapter 1 Preliminar results/review of Comple Analsis I These are more detailed notes for the results
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Comple Analsis II Lecture Notes Part I Chapter 1 Preliminar results/review of Comple Analsis I These are more detailed notes for the results
From the definition of a surface, each point has a neighbourhood U and a homeomorphism. U : ϕ U(U U ) ϕ U (U U )
 3 Riemann surfaces 3.1 Definitions and examples From the definition of a surface, each point has a neighbourhood U and a homeomorphism ϕ U from U to an open set V in R 2. If two such neighbourhoods U,
3 Riemann surfaces 3.1 Definitions and examples From the definition of a surface, each point has a neighbourhood U and a homeomorphism ϕ U from U to an open set V in R 2. If two such neighbourhoods U,
Math Homework 2
 Math 73 Homework Due: September 8, 6 Suppose that f is holomorphic in a region Ω, ie an open connected set Prove that in any of the following cases (a) R(f) is constant; (b) I(f) is constant; (c) f is
Math 73 Homework Due: September 8, 6 Suppose that f is holomorphic in a region Ω, ie an open connected set Prove that in any of the following cases (a) R(f) is constant; (b) I(f) is constant; (c) f is
ζ(u) z du du Since γ does not pass through z, f is defined and continuous on [a, b]. Furthermore, for all t such that dζ
![ζ(u) z du du Since γ does not pass through z, f is defined and continuous on [a, b]. Furthermore, for all t such that dζ ζ(u) z du du Since γ does not pass through z, f is defined and continuous on [a, b]. Furthermore, for all t such that dζ](/thumbs/92/109116539.jpg) Lecture 6 Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem MATH-GA 45.00 Complex Variables Cauchy s Integral Formula. Index of a point with respect to a closed curve Let z C, and a piecewise differentiable closed curve
Lecture 6 Consequences of Cauchy s Theorem MATH-GA 45.00 Complex Variables Cauchy s Integral Formula. Index of a point with respect to a closed curve Let z C, and a piecewise differentiable closed curve
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics MA4247 Complex Analysis II Lecture Notes Part II Chapter 2 Further properties of analytic functions 21 Local/Global behavior of analytic functions;
