Range Expansions & Spatial Population Genetics
|
|
|
- Kathryn Summers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Range Expansions & Spatial Population Genetics Oskar Hallatschek & drn, (E. coli) In 500 generations. Large mammals expand over ~10 4 km Bacteria (in a Petri dish) expand ~ 1 cm K. Korolev et al., Reviews of Modern Physics 82, 1691 (2010) K. Foster, J. Xavier, K. Korolev, drn (genetic demixing in P. Aeruginosa)
2 Gene Surfing and Survival of the Luckiest The fate of mutations in a spreading population Oskar Hallatschek Kirill Korolev Severine Atis, Bryan Weinstein, Andrew Murray vs.
3 Fisher Waves and Population Dynamics ct () population of species at time t in region dc() t dt births - deaths + saturation + migration 1798 T.R. Matthus dc() t dt ac(), t a P.F. Verhulst dc() t dt 2 ac() t bc () t c* stable population size: c a/ b biomass of yeast you are here J. Maynard Smith, Evolutionary Genetics B B B B B B B B time (hours) B 1937 R.A. Fisher c c( r, t) crt (, ) t 2 2 D crt (, ) acrt (, ) bc( rt, )
4 Population Waves In One Dimension (R. A. Fisher, Kolmogorov-Petrovsky-Piscounov, 1937) t 2 cxt (, ) D cxt (, ) acxt (, )[1 ( b/ a)( cxt (, )]; letcxt (, ) f( x vt) 2 x c(x,t) c(x,t) c(x,t) a/ b a/ b a/ b at e v 2Dt Schematic time development of a wavefront solution of Fisher s equation on the infinite line. (J.D. Murray, Mathematical Biology) Interface velocity v = 2 Da Interface width = D / a
5 Genetic drift for a neutral mutation, (M. Kimura) Populus 5.3 N = 20 u(p,t)= probability allele A has frequency p at time t. Finite populations go to fixation for long times(using, e.g., Fisher- Wright population sampling) u( p, t) t 2 [ DG u( p, t)] 2 p D ( p) p(1 p)/(4 N) G pt () pt ()(1 pt ())/2 N () t t ( t) ( t') ( t t') (Ito calculus)
6 Genetic drift for a neutral mutation, (M. Kimura) Populus 5.3 N = 20 u(p,t)= probability allele A has frequency p at time t. Finite populations go to fixation for long times(using, e.g., Fisher- Wright population sampling) 2 u( p, t) [ DG u( p, t)] 2 t p D ( p) p(1 p)/(4 N) G Finite populations go to fixation for long times Probability of fixation of a single neutral mutation in a population of size N is just 1/N But N is small in the vicinity of an expanding population front!
7 Successful Surfing (1d) c s (x), steady state population density (O. Hallatschek) c x, comoving frame
8 c s Successful Surfing (1d) (x), steady state population density c x, comoving frame
9 c s Successful Surfing (1d) (x), steady state population density c x, comoving frame
10 c s Successful Surfing (1d) (x), steady state population density c x, comoving frame
11 c s Successful Surfing (1d) (x), steady state population density c x, comoving frame
12 Often however c s (x), steady state population density (O. Hallatschek) c x, comoving frame
13 c s Often however (x), steady state population density c x, comoving frame
14 c s Often however (x), steady state population density c x, comoving frame
15 c s Often however (x), steady state population density c x, comoving frame
16 c s Often however (x), steady state population density surfing is not achieved! c x, comoving frame
17 Gene Surfing in nonmotile E. coli (thanks to Tom Shimizu, Berg Lab, for strains) HCB1553/pVS133 Background DH5 Amp(R) Ori pbr HCB1550/pVS130 Background DH5 Amp(R) Ori pbr PTrc99A: yfp A206K Ptrc PTrc99A: ecfp A206K Ptrc mixture, 1550/1553
18 Gene Surfing in nonmotile E. coli (thanks to Tom Shimizu, Berg Lab, for strains) HCB1553/pVS133 Background DH5 Amp(R) Ori pbr HCB1550/pVS130 Background DH5 Amp(R) Ori pbr PTrc99A: yfp A206K Ptrc PTrc99A: ecfp A206K Ptrc mixture, 1550/1553 Cyan Red 1mm
19 Genetic demixing in non-motile E. coli (thanks to Tom Shimizu, Berg Lab, for strains) HCB1553/pVS133 Background DH5 Amp(R) Ori pbr HCB1550/pVS130 Background DH5 Amp(R) Ori pbr PTrc99A: yfp A206K Ptrc PTrc99A: ecfp A206K Ptrc a r = doubling time of red cells a g = doubling time of green cells = (1+s)a r s = selective advantage (s=0) mixture, 1550/1553 Cyan Red
20 Genetic demixing time effective population size for range expansions ΔR fix = 1mm t ( p) 2 N [(1 p)ln(1 p) pln p] fix eff g (2ln 2) N 2.83N eff g eff g v Da g cm / sec; 1560sec (2.83 N ) v R N 22 eff g fix eff
21 What would happen if we could replay the tape of life? R 0 R 0 R 0 Ecoli. range expansions: can infer the radius R of the homeland from data at the boundary: Nsec R0v/2D W Chiral range expansion (Kirill Korolev) 0
22 Gene surfing in the dilute limit: survival of the luckiest 95%-5% mixture, founder population ~ %-2% mixture, founder population ~ 5000
23 Gene surfing and simple models of tumor growth Exponential phase succeeded by linear growth 1 : Growth confined to tumor edge 1,2 Rt () vt Growth may stop (due to mechanical stress 3 or nutrient shielding 4 ), creating a "treadmilling" effect Prevascular tumors can grow to radius R 0 ~ mm. R 0 /a ~ 20, a = cell diameter necrotic core (volume loss) quiescent region (cells not dividing) thin growing region cells Hemispherical yeast colonies 1 A Bru et al. Biophys. J (2003) 2 T Roose et al. SIAM Rev. 49(2) 179 (2007) 3 F Montel et al. PRL (2011) Confocal images of nutrient shielding in S. cerevisiae RED: protein with growth-independent expression GREEN: ribosomal protein indicating growth 4 Lavrentovich, Koschwanez,drn, PRE 87, (2013)
24 Selection and driver mutations driver mutations form logarithmic spirals: Mean field theory () r s(2 s)ln( r/ r0 ) s selective advantage Max Lavrentovich, ( Domany-Kinzel models Friday talk) *Cancer often results from mutations in normal cells, leading to abnormal growth. or they die out! *A series of driver mutations (in oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes, etc.) can lead to benign or malignant cell clusters. What is the survival probability of a single frontier cell with a driver mutation?
25 Exact asymptotics in two dimensions (cell size a is important ) Successful escape from genetic drift to a deterministic logarithmic spiral determined by dimensionless radial selective advantage s R / a ( a cell size) 0 R0 initial radius of tumor 1, strong selection 1, weak selection () t noisy logarithmic spiral described by a stochastic differential equation d () t sa 2 () t (), t R() t R0 vt dt R() t g 2 2 () t a / g R (), t () t (') t 2 ( t t')
26 lim P ( s, R, a,,, v, t) ( R / a, s R / a ) t Survival probability of a driver mutation in two dimensions: surv 0 g 0 t surv ( x R / a, ) 0 0 s R / a 0 LARGE survival probability at s =0 Much larger than a/2πr 0 (treadmilling circle result) inflation at frontier helps neutral passenger mutations
27 We obtain similar results for driver mutations on spherical colonies Surface of an inflating sphere P fix (s) vs. Large survival probability at s =0! compare a treadmilling sphere... lim P ( s) a / 4 R 8 10 s 0 fix when R 10 a, inflation amplifies 27 fixation prob. by a factor of
28 Spatial population genetics and fluid flow Life first evolved in a liquid environment! Cyanobacterium Synechococcus Effect of compressible fluid flow on the Fisher Equation What is the effect on fluid motion on spatial population genetics? R. Benzi, M. Jensen P. Perlecar, S. Pigolotti F. Toschi Severine Atis, Bryan Weinstein & Andrew Murray
29 Buoyant population dyanamics in Silico (P. Perlekar and F. Toschi) Reynolds number Schmidt number Doubling time/eddy turnover time τ 2 /τ eddy / TN & WI 11/04/11
30 Compressible population genetics with two interacting species Compressible turbulent flow (Re ~10 5) 2 2 ( u) / ( u ) 0.17 i j time Survival of the luckiest Wanted: simple repeatable experiments that explore how fluid flows affect spatial population genetics. High Reynolds numbers might be hard to achieve in the laboratory, but low Reynolds numbers can also be biologically relevant Can we impose a flow with pumps and syringes, such that the doubling time τ 2 << τ eddy, where τ eddy is a eddy turnover time?
31 Actually, microorganisms grown on a liquid but highly viscous substrates create their own flows (without pumps and syringes!) Hard Agar Epoch of genetic demixing stretched out. Liquid Media Yeast on a 1% hard agar YPD plate (viscosity η = ) Yeast on a liquid but highly viscous YPD media with 3% cellulose (η 600 Pa-s) (the viscosity of water is η 10-3 Pa-s; our viscosities are times larger) The colony metabolism (after only two generation times) generates fluid flows that dilate the colony radially.
32 Deformations of features inside colony in liquid regimes are consistent with flow-induced dilation!
33 PIV (particle imaging velocimetry) measurements quantify the self-induced flow under the colony Air Liquid Like an anti-helmholtz coil!
34 What is the origin of the flow beneath colonies growing on liquid substrates? = dextrose wikipedia
35 Flow simulations Isobars and isoclines in the absence of flow (η = ) A thresholdless baroclinic instability generates a ring of vorticity beneath the colony.
36 Liquid-like fingering instabilities (moderate substrate viscosity η 450 Pa-s) Happy 4 th of July (and Bastille Day!) Dynamics of a finger: Rayleigh-Plateau type instability with growth?
37 Solid-like colony fragmentation (low substrate viscosity η 85 Pa-s) Colony takes over plate in one day!
38 Microbes on highly viscous liquids generate buoyant flows that alter colony morphology and evolutionary dynamics
Population Genetics on Land
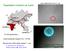 Population Genetics on Land Oskar Hallatschek & drn, (E. coli) In 500 generations. Large mammals expand over ~10 4 km Bacteria (in a Petri dish) expand ~ 1 cm K. Korolev et al., Reviews of Modern Physics
Population Genetics on Land Oskar Hallatschek & drn, (E. coli) In 500 generations. Large mammals expand over ~10 4 km Bacteria (in a Petri dish) expand ~ 1 cm K. Korolev et al., Reviews of Modern Physics
The fate of beneficial mutations in a range expansion
 The fate of beneficial mutations in a range expansion R. Lehe (Paris) O. Hallatschek (Göttingen) L. Peliti (Naples) February 19, 2015 / Rutgers Outline Introduction The model Results Analysis Range expansion
The fate of beneficial mutations in a range expansion R. Lehe (Paris) O. Hallatschek (Göttingen) L. Peliti (Naples) February 19, 2015 / Rutgers Outline Introduction The model Results Analysis Range expansion
Eindhoven University of Technology MASTER. Population dynamics and genetics in inhomogeneous media. Alards, K.M.J.
 Eindhoven University of Technology MASTER Population dynamics and genetics in inhomogeneous media Alards, K.M.J. Award date: 214 Disclaimer This document contains a student thesis (bachelor's or master's),
Eindhoven University of Technology MASTER Population dynamics and genetics in inhomogeneous media Alards, K.M.J. Award date: 214 Disclaimer This document contains a student thesis (bachelor's or master's),
Surfing genes. On the fate of neutral mutations in a spreading population
 Surfing genes On the fate of neutral mutations in a spreading population Oskar Hallatschek David Nelson Harvard University ohallats@physics.harvard.edu Genetic impact of range expansions Population expansions
Surfing genes On the fate of neutral mutations in a spreading population Oskar Hallatschek David Nelson Harvard University ohallats@physics.harvard.edu Genetic impact of range expansions Population expansions
1 (t + 4)(t 1) dt. Solution: The denominator of the integrand is already factored with the factors being distinct, so 1 (t + 4)(t 1) = A
 Calculus Topic: Integration of Rational Functions Section 8. # 0: Evaluate the integral (t + )(t ) Solution: The denominator of the integrand is already factored with the factors being distinct, so (t
Calculus Topic: Integration of Rational Functions Section 8. # 0: Evaluate the integral (t + )(t ) Solution: The denominator of the integrand is already factored with the factors being distinct, so (t
Figure 1: Ca2+ wave in a Xenopus oocyte following fertilization. Time goes from top left to bottom right. From Fall et al., 2002.
 1 Traveling Fronts Richard Bertram Department of Mathematics and Programs in Neuroscience and Molecular Biophysics Florida State University Tallahassee, Florida 32306 2 When mature Xenopus oocytes (frog
1 Traveling Fronts Richard Bertram Department of Mathematics and Programs in Neuroscience and Molecular Biophysics Florida State University Tallahassee, Florida 32306 2 When mature Xenopus oocytes (frog
AGITATION AND AERATION
 AGITATION AND AERATION Although in many aerobic cultures, gas sparging provides the method for both mixing and aeration - it is important that these two aspects of fermenter design be considered separately.
AGITATION AND AERATION Although in many aerobic cultures, gas sparging provides the method for both mixing and aeration - it is important that these two aspects of fermenter design be considered separately.
Selective Sweeps in Growing Microbial Colonies
 Selective Sweeps in Growing Microbial Colonies The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Korolev, Kirill S, Melanie
Selective Sweeps in Growing Microbial Colonies The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Korolev, Kirill S, Melanie
arxiv: v2 [q-bio.pe] 13 Apr 2011
![arxiv: v2 [q-bio.pe] 13 Apr 2011 arxiv: v2 [q-bio.pe] 13 Apr 2011](/thumbs/77/75601557.jpg) Genetic Demixing and Evolutionary Forces in the One-Dimensional Stepping Stone Model arxiv:94.465v [q-bio.pe] 13 Apr 11 K.S. Korolev Department of Physics and FAS Center for Systems Biology, Harvard University,
Genetic Demixing and Evolutionary Forces in the One-Dimensional Stepping Stone Model arxiv:94.465v [q-bio.pe] 13 Apr 11 K.S. Korolev Department of Physics and FAS Center for Systems Biology, Harvard University,
Evolution & Natural Selection
 Evolution & Natural Selection Learning Objectives Know what biological evolution is and understand the driving force behind biological evolution. know the major mechanisms that change allele frequencies
Evolution & Natural Selection Learning Objectives Know what biological evolution is and understand the driving force behind biological evolution. know the major mechanisms that change allele frequencies
V (r,t) = i ˆ u( x, y,z,t) + ˆ j v( x, y,z,t) + k ˆ w( x, y, z,t)
 IV. DIFFERENTIAL RELATIONS FOR A FLUID PARTICLE This chapter presents the development and application of the basic differential equations of fluid motion. Simplifications in the general equations and common
IV. DIFFERENTIAL RELATIONS FOR A FLUID PARTICLE This chapter presents the development and application of the basic differential equations of fluid motion. Simplifications in the general equations and common
Intermediate Differential Equations. John A. Burns
 Intermediate Differential Equations Delay Differential Equations John A. Burns jaburns@vt.edu Interdisciplinary Center for Applied Mathematics Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University Blacksburg,
Intermediate Differential Equations Delay Differential Equations John A. Burns jaburns@vt.edu Interdisciplinary Center for Applied Mathematics Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University Blacksburg,
Problems on Evolutionary dynamics
 Problems on Evolutionary dynamics Doctoral Programme in Physics José A. Cuesta Lausanne, June 10 13, 2014 Replication 1. Consider the Galton-Watson process defined by the offspring distribution p 0 =
Problems on Evolutionary dynamics Doctoral Programme in Physics José A. Cuesta Lausanne, June 10 13, 2014 Replication 1. Consider the Galton-Watson process defined by the offspring distribution p 0 =
Turbulence Laboratory
 Objective: CE 319F Elementary Mechanics of Fluids Department of Civil, Architectural and Environmental Engineering The University of Texas at Austin Turbulence Laboratory The objective of this laboratory
Objective: CE 319F Elementary Mechanics of Fluids Department of Civil, Architectural and Environmental Engineering The University of Texas at Austin Turbulence Laboratory The objective of this laboratory
1.1. Bacteria Reproduce like Rabbits. (a) A differential equation is an equation. a function, and both the function and its
 G NAGY ODE January 7, 2018 1 11 Bacteria Reproduce like Rabbits Section Objective(s): Overview of Differential Equations The Discrete Equation The Continuum Equation Summary and Consistency 111 Overview
G NAGY ODE January 7, 2018 1 11 Bacteria Reproduce like Rabbits Section Objective(s): Overview of Differential Equations The Discrete Equation The Continuum Equation Summary and Consistency 111 Overview
Genetic drift at expanding frontiers promotes gene segregation (Preprint; look up PNAS website for published version)
 1 Genetic drift at expanding frontiers promotes gene segregation (Preprint; look up PNAS website for published version) Oskar Hallatschek 1, 2, Pascal Hersen 2, 3, Sharad Ramanathan 2, 4 and David R. Nelson
1 Genetic drift at expanding frontiers promotes gene segregation (Preprint; look up PNAS website for published version) Oskar Hallatschek 1, 2, Pascal Hersen 2, 3, Sharad Ramanathan 2, 4 and David R. Nelson
The Polymers Tug Back
 Tugging at Polymers in Turbulent Flow The Polymers Tug Back Jean-Luc Thiffeault http://plasma.ap.columbia.edu/ jeanluc Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics Columbia University Tugging
Tugging at Polymers in Turbulent Flow The Polymers Tug Back Jean-Luc Thiffeault http://plasma.ap.columbia.edu/ jeanluc Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics Columbia University Tugging
Spatial Moran model. Rick Durrett... A report on joint work with Jasmine Foo, Kevin Leder (Minnesota), and Marc Ryser (postdoc at Duke)
 Spatial Moran model Rick Durrett... A report on joint work with Jasmine Foo, Kevin Leder (Minnesota), and Marc Ryser (postdoc at Duke) Rick Durrett (Duke) ASU 1 / 27 Stan Ulam once said: I have sunk so
Spatial Moran model Rick Durrett... A report on joint work with Jasmine Foo, Kevin Leder (Minnesota), and Marc Ryser (postdoc at Duke) Rick Durrett (Duke) ASU 1 / 27 Stan Ulam once said: I have sunk so
Chapter 6 Microbial Growth With a focus on Bacteria
 Chapter 6 Microbial Growth With a focus on Bacteria Temperature Minimum growth temperature Optimum growth temperature Maximum growth temperature Usually within a 30-40 degree range Microbial growth = increase
Chapter 6 Microbial Growth With a focus on Bacteria Temperature Minimum growth temperature Optimum growth temperature Maximum growth temperature Usually within a 30-40 degree range Microbial growth = increase
Evolutionary dynamics on graphs
 Evolutionary dynamics on graphs Laura Hindersin May 4th 2015 Max-Planck-Institut für Evolutionsbiologie, Plön Evolutionary dynamics Main ingredients: Fitness: The ability to survive and reproduce. Selection
Evolutionary dynamics on graphs Laura Hindersin May 4th 2015 Max-Planck-Institut für Evolutionsbiologie, Plön Evolutionary dynamics Main ingredients: Fitness: The ability to survive and reproduce. Selection
Convective Mass Transfer
 Convective Mass Transfer Definition of convective mass transfer: The transport of material between a boundary surface and a moving fluid or between two immiscible moving fluids separated by a mobile interface
Convective Mass Transfer Definition of convective mass transfer: The transport of material between a boundary surface and a moving fluid or between two immiscible moving fluids separated by a mobile interface
Multi-Scale Modeling and Simulation of the Growth of Bacterial Colony with Cell-Cell Mechanical Interactions
 Multi-Scale Modeling and Simulation of the Growth of Bacterial Colony with Cell-Cell Mechanical Interactions Hui Sun Department of Mathematics and Statistics California State University Long Beach SIAM
Multi-Scale Modeling and Simulation of the Growth of Bacterial Colony with Cell-Cell Mechanical Interactions Hui Sun Department of Mathematics and Statistics California State University Long Beach SIAM
Role of polymers in the mixing of Rayleigh-Taylor turbulence
 Physics Department University of Genova Italy Role of polymers in the mixing of Rayleigh-Taylor turbulence Andrea Mazzino andrea.mazzino@unige.it Guido Boffetta: University of Torino (Italy) Stefano Musacchio:
Physics Department University of Genova Italy Role of polymers in the mixing of Rayleigh-Taylor turbulence Andrea Mazzino andrea.mazzino@unige.it Guido Boffetta: University of Torino (Italy) Stefano Musacchio:
Rise and Fall of Mutator Bacteria
 Rise and Fall of Mutator Bacteria The Evolution of Mutation Rates in Bacteria Yoav Ram Hadany Evolutionary Theory Lab 29 May 2011 Bacteria Bacteria are unicellular, haploid and asexual Reproduce by binary
Rise and Fall of Mutator Bacteria The Evolution of Mutation Rates in Bacteria Yoav Ram Hadany Evolutionary Theory Lab 29 May 2011 Bacteria Bacteria are unicellular, haploid and asexual Reproduce by binary
Introduction to population genetics & evolution
 Introduction to population genetics & evolution Course Organization Exam dates: Feb 19 March 1st Has everybody registered? Did you get the email with the exam schedule Summer seminar: Hot topics in Bioinformatics
Introduction to population genetics & evolution Course Organization Exam dates: Feb 19 March 1st Has everybody registered? Did you get the email with the exam schedule Summer seminar: Hot topics in Bioinformatics
CPGAN # 006. The Basics of Filament Stretching Rheometry
 Introduction Measurement of the elongational behavior of fluids is important both for basic research purposes and in industrial applications, since many complex flows contain strong extensional components,
Introduction Measurement of the elongational behavior of fluids is important both for basic research purposes and in industrial applications, since many complex flows contain strong extensional components,
Lecture 2. Turbulent Flow
 Lecture 2. Turbulent Flow Note the diverse scales of eddy motion and self-similar appearance at different lengthscales of this turbulent water jet. If L is the size of the largest eddies, only very small
Lecture 2. Turbulent Flow Note the diverse scales of eddy motion and self-similar appearance at different lengthscales of this turbulent water jet. If L is the size of the largest eddies, only very small
Project Topic. Simulation of turbulent flow laden with finite-size particles using LBM. Leila Jahanshaloo
 Project Topic Simulation of turbulent flow laden with finite-size particles using LBM Leila Jahanshaloo Project Details Turbulent flow modeling Lattice Boltzmann Method All I know about my project Solid-liquid
Project Topic Simulation of turbulent flow laden with finite-size particles using LBM Leila Jahanshaloo Project Details Turbulent flow modeling Lattice Boltzmann Method All I know about my project Solid-liquid
6.2 Governing Equations for Natural Convection
 6. Governing Equations for Natural Convection 6..1 Generalized Governing Equations The governing equations for natural convection are special cases of the generalized governing equations that were discussed
6. Governing Equations for Natural Convection 6..1 Generalized Governing Equations The governing equations for natural convection are special cases of the generalized governing equations that were discussed
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer
 CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
Gene regulation: From biophysics to evolutionary genetics
 Gene regulation: From biophysics to evolutionary genetics Michael Lässig Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Cologne Thanks Ville Mustonen Johannes Berg Stana Willmann Curt Callan (Princeton)
Gene regulation: From biophysics to evolutionary genetics Michael Lässig Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Cologne Thanks Ville Mustonen Johannes Berg Stana Willmann Curt Callan (Princeton)
What s important: viscosity Poiseuille's law Stokes' law Demo: dissipation in flow through a tube
 PHYS 101 Lecture 29x - Viscosity 29x - 1 Lecture 29x Viscosity (extended version) What s important: viscosity Poiseuille's law Stokes' law Demo: dissipation in flow through a tube Viscosity We introduced
PHYS 101 Lecture 29x - Viscosity 29x - 1 Lecture 29x Viscosity (extended version) What s important: viscosity Poiseuille's law Stokes' law Demo: dissipation in flow through a tube Viscosity We introduced
Evolution in a spatial continuum
 Evolution in a spatial continuum Drift, draft and structure Alison Etheridge University of Oxford Joint work with Nick Barton (Edinburgh) and Tom Kurtz (Wisconsin) New York, Sept. 2007 p.1 Kingman s Coalescent
Evolution in a spatial continuum Drift, draft and structure Alison Etheridge University of Oxford Joint work with Nick Barton (Edinburgh) and Tom Kurtz (Wisconsin) New York, Sept. 2007 p.1 Kingman s Coalescent
The Wright-Fisher Model and Genetic Drift
 The Wright-Fisher Model and Genetic Drift January 22, 2015 1 1 Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Our goal is to understand the dynamics of allele and genotype frequencies in an infinite, randomlymating population
The Wright-Fisher Model and Genetic Drift January 22, 2015 1 1 Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Our goal is to understand the dynamics of allele and genotype frequencies in an infinite, randomlymating population
Evolutionary dynamics of cancer: A spatial model of cancer initiation
 Evolutionary dynamics of cancer: A spatial model of cancer initiation Jasmine Foo University of Minnesota School of Mathematics May 8, 2014 Collaborators Rick Durrett Kevin Leder Marc Ryser Next talk by
Evolutionary dynamics of cancer: A spatial model of cancer initiation Jasmine Foo University of Minnesota School of Mathematics May 8, 2014 Collaborators Rick Durrett Kevin Leder Marc Ryser Next talk by
Silver Nanoparticles Microbial Assessment by Adam Yang
 Silver Nanoparticles Microbial Assessment by Adam Yang Research Silver is considered to be a very toxic and lethal element to many microbes and bacteria. In the last decade, scientist believed that the
Silver Nanoparticles Microbial Assessment by Adam Yang Research Silver is considered to be a very toxic and lethal element to many microbes and bacteria. In the last decade, scientist believed that the
Competition and cooperation in onedimensional
 Competition and cooperation in onedimensional stepping-stone models The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation
Competition and cooperation in onedimensional stepping-stone models The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation
EVOLUTIONARY DYNAMICS AND THE EVOLUTION OF MULTIPLAYER COOPERATION IN A SUBDIVIDED POPULATION
 Friday, July 27th, 11:00 EVOLUTIONARY DYNAMICS AND THE EVOLUTION OF MULTIPLAYER COOPERATION IN A SUBDIVIDED POPULATION Karan Pattni karanp@liverpool.ac.uk University of Liverpool Joint work with Prof.
Friday, July 27th, 11:00 EVOLUTIONARY DYNAMICS AND THE EVOLUTION OF MULTIPLAYER COOPERATION IN A SUBDIVIDED POPULATION Karan Pattni karanp@liverpool.ac.uk University of Liverpool Joint work with Prof.
Figure 1.1: Flaccid (a) and swollen (b) red blood cells being drawn into a micropipette. The scale bars represent 5 µm. Figure adapted from [2].
![Figure 1.1: Flaccid (a) and swollen (b) red blood cells being drawn into a micropipette. The scale bars represent 5 µm. Figure adapted from [2]. Figure 1.1: Flaccid (a) and swollen (b) red blood cells being drawn into a micropipette. The scale bars represent 5 µm. Figure adapted from [2].](/thumbs/77/75728743.jpg) 1 Biomembranes 1.1 Micropipette aspiration 1.1.1 Experimental setup Figure 1.1: Flaccid (a) and swollen (b) red blood cells being drawn into a micropipette. The scale bars represent 5 µm. Figure adapted
1 Biomembranes 1.1 Micropipette aspiration 1.1.1 Experimental setup Figure 1.1: Flaccid (a) and swollen (b) red blood cells being drawn into a micropipette. The scale bars represent 5 µm. Figure adapted
Evolutionary dynamics of populations with genotype-phenotype map
 Evolutionary dynamics of populations with genotype-phenotype map Esther Ibáñez Marcelo, Tomas Alarcon Cor Biomat 2013: Mathematics of Planet Earth CENTRE DE RECERCA MATEMÀTICA 17-21 June 2013 Esther Ibáñez
Evolutionary dynamics of populations with genotype-phenotype map Esther Ibáñez Marcelo, Tomas Alarcon Cor Biomat 2013: Mathematics of Planet Earth CENTRE DE RECERCA MATEMÀTICA 17-21 June 2013 Esther Ibáñez
A Quantitative Test of Population Genetics Using Spatio-Genetic Patterns in Bacterial Colonies
 A Quantitative Test of Population Genetics Using Spatio-Genetic Patterns in Bacterial Colonies The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
A Quantitative Test of Population Genetics Using Spatio-Genetic Patterns in Bacterial Colonies The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Exercises in Combustion Technology
 Exercises in Combustion Technology Exercise 4: Turbulent Premixed Flames Turbulent Flow: Task 1: Estimation of Turbulence Quantities Borghi-Peters diagram for premixed combustion Task 2: Derivation of
Exercises in Combustion Technology Exercise 4: Turbulent Premixed Flames Turbulent Flow: Task 1: Estimation of Turbulence Quantities Borghi-Peters diagram for premixed combustion Task 2: Derivation of
Frequency Spectra and Inference in Population Genetics
 Frequency Spectra and Inference in Population Genetics Although coalescent models have come to play a central role in population genetics, there are some situations where genealogies may not lead to efficient
Frequency Spectra and Inference in Population Genetics Although coalescent models have come to play a central role in population genetics, there are some situations where genealogies may not lead to efficient
Origin and Evolution of Life
 Origin and Evolution of Life OCN 201 Science of the Sea Biology Lecture 2 The Handfish -BBC Blue Planet!1!1 Evolution Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution I am a creationist
Origin and Evolution of Life OCN 201 Science of the Sea Biology Lecture 2 The Handfish -BBC Blue Planet!1!1 Evolution Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution I am a creationist
Simulation of mixing of heterogeneous HE components
 Chapter Simulation of mixing of heterogeneous HE components The majority on high explosives (HEs) used are blend ones. Properties of components differ that produces interaction on the grain scale (mesoprocesses).
Chapter Simulation of mixing of heterogeneous HE components The majority on high explosives (HEs) used are blend ones. Properties of components differ that produces interaction on the grain scale (mesoprocesses).
Population Genetics: a tutorial
 : a tutorial Institute for Science and Technology Austria ThRaSh 2014 provides the basic mathematical foundation of evolutionary theory allows a better understanding of experiments allows the development
: a tutorial Institute for Science and Technology Austria ThRaSh 2014 provides the basic mathematical foundation of evolutionary theory allows a better understanding of experiments allows the development
Optimization of Immunoblot Protocol for Use with a Yeast Strain Containing the CDC7 Gene Tagged with myc
 OPTIMIZATION OF IMMUNOBLOT PROTOCOL 121 Optimization of Immunoblot Protocol for Use with a Yeast Strain Containing the CDC7 Gene Tagged with myc Jacqueline Bjornton and John Wheeler Faculty Sponsor: Anne
OPTIMIZATION OF IMMUNOBLOT PROTOCOL 121 Optimization of Immunoblot Protocol for Use with a Yeast Strain Containing the CDC7 Gene Tagged with myc Jacqueline Bjornton and John Wheeler Faculty Sponsor: Anne
Microfluidics 1 Basics, Laminar flow, shear and flow profiles
 MT-0.6081 Microfluidics and BioMEMS Microfluidics 1 Basics, Laminar flow, shear and flow profiles 11.1.2017 Ville Jokinen Outline of the next 3 weeks: Today: Microfluidics 1: Laminar flow, flow profiles,
MT-0.6081 Microfluidics and BioMEMS Microfluidics 1 Basics, Laminar flow, shear and flow profiles 11.1.2017 Ville Jokinen Outline of the next 3 weeks: Today: Microfluidics 1: Laminar flow, flow profiles,
Lecture 4: viscoelasticity and cell mechanics
 Teaser movie: flexible robots! R. Shepherd, Whitesides group, Harvard 1 Lecture 4: viscoelasticity and cell mechanics S-RSI Physics Lectures: Soft Condensed Matter Physics Jacinta C. Conrad University
Teaser movie: flexible robots! R. Shepherd, Whitesides group, Harvard 1 Lecture 4: viscoelasticity and cell mechanics S-RSI Physics Lectures: Soft Condensed Matter Physics Jacinta C. Conrad University
THE EVOLUTION OF POPULATIONS THE EVOLUTION OF POPULATIONS
 WHAT IS LIFE? A GUIDE TO BIOLOGY, ART NOTEBOOK, PAGE 8 THE OF POPULATIONS Figure 8-10, part 1 Evolution defined. THE OF POPULATIONS TIGER POPULATION Allele frequencies: Proportion of orange fur-pigment
WHAT IS LIFE? A GUIDE TO BIOLOGY, ART NOTEBOOK, PAGE 8 THE OF POPULATIONS Figure 8-10, part 1 Evolution defined. THE OF POPULATIONS TIGER POPULATION Allele frequencies: Proportion of orange fur-pigment
Liquids and solids are essentially incompressible substances and the variation of their density with pressure is usually negligible.
 Properties of Fluids Intensive properties are those that are independent of the mass of a system i.e. temperature, pressure and density. Extensive properties are those whose values depend on the size of
Properties of Fluids Intensive properties are those that are independent of the mass of a system i.e. temperature, pressure and density. Extensive properties are those whose values depend on the size of
Fluid Mechanics Prof. T.I. Eldho Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture - 17 Laminar and Turbulent flows
 Fluid Mechanics Prof. T.I. Eldho Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 17 Laminar and Turbulent flows Welcome back to the video course on fluid mechanics. In
Fluid Mechanics Prof. T.I. Eldho Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 17 Laminar and Turbulent flows Welcome back to the video course on fluid mechanics. In
Note the diverse scales of eddy motion and self-similar appearance at different lengthscales of the turbulence in this water jet. Only eddies of size
 L Note the diverse scales of eddy motion and self-similar appearance at different lengthscales of the turbulence in this water jet. Only eddies of size 0.01L or smaller are subject to substantial viscous
L Note the diverse scales of eddy motion and self-similar appearance at different lengthscales of the turbulence in this water jet. Only eddies of size 0.01L or smaller are subject to substantial viscous
Population Genetics I. Bio
 Population Genetics I. Bio5488-2018 Don Conrad dconrad@genetics.wustl.edu Why study population genetics? Functional Inference Demographic inference: History of mankind is written in our DNA. We can learn
Population Genetics I. Bio5488-2018 Don Conrad dconrad@genetics.wustl.edu Why study population genetics? Functional Inference Demographic inference: History of mankind is written in our DNA. We can learn
Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology
 CEA-Saclay/SPEC; Group Instabilities and Turbulence Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology Olivier Dauchot together with many contributors: D. Bonamy, E. Bertin, S. Deboeuf, B. Andreotti,
CEA-Saclay/SPEC; Group Instabilities and Turbulence Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology Olivier Dauchot together with many contributors: D. Bonamy, E. Bertin, S. Deboeuf, B. Andreotti,
Wright-Fisher Models, Approximations, and Minimum Increments of Evolution
 Wright-Fisher Models, Approximations, and Minimum Increments of Evolution William H. Press The University of Texas at Austin January 10, 2011 1 Introduction Wright-Fisher models [1] are idealized models
Wright-Fisher Models, Approximations, and Minimum Increments of Evolution William H. Press The University of Texas at Austin January 10, 2011 1 Introduction Wright-Fisher models [1] are idealized models
Gene Surfing in Expanding Populations
 Gene Surfing in Expanding Populations The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed Citable
Gene Surfing in Expanding Populations The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed Citable
Supplementary Information. Text S1:
 Supplementary Information Text S1: In order to characterize the change in visco-elastic response in the course of a shear thickening transition in a controlled shear stress flow, on a fresh sample of for
Supplementary Information Text S1: In order to characterize the change in visco-elastic response in the course of a shear thickening transition in a controlled shear stress flow, on a fresh sample of for
Random Walks and Diffusion. APC 514 December 5, 2002 Cox&Shvartsman
 Random Walks and Diffusion APC 514 December 5, 2002 Cox&Shvartsman Cell motility over adhesive substrates: a periodic phenomenon Simple model for linear motion: DIMILLA PA, BARBEE K, LAUFFENBURGER DA MATHEMATICAL-MODEL
Random Walks and Diffusion APC 514 December 5, 2002 Cox&Shvartsman Cell motility over adhesive substrates: a periodic phenomenon Simple model for linear motion: DIMILLA PA, BARBEE K, LAUFFENBURGER DA MATHEMATICAL-MODEL
MULTIPLE-CHOICE PROBLEMS :(Two marks per answer) (Circle the Letter Beside the Most Correct Answer in the Questions Below.)
 Test Midterm 1 F2013 MULTIPLE-CHOICE PROBLEMS :(Two marks per answer) (Circle the Letter Beside the Most Correct nswer in the Questions Below.) 1. The absolute viscosity µ of a fluid is primarily a function
Test Midterm 1 F2013 MULTIPLE-CHOICE PROBLEMS :(Two marks per answer) (Circle the Letter Beside the Most Correct nswer in the Questions Below.) 1. The absolute viscosity µ of a fluid is primarily a function
Evolution 1 Star. 6. The different tools used during the beaks of finches lab represented. A. feeding adaptations in finches
 Name: Date: 1. ccording to modern evolutionary theory, genes responsible for new traits that help a species survive in a particular environment will usually. not change in frequency. decrease gradually
Name: Date: 1. ccording to modern evolutionary theory, genes responsible for new traits that help a species survive in a particular environment will usually. not change in frequency. decrease gradually
The role of micro-scale inertia in transport processes. - Ganesh Subramanian (JNCASR, Bangalore)
 The role of micro-scale inertia in transport processes - Ganesh Subramanian (JNCASR, Bangalore) Micro-scale inertia (suspensions and emulsions) Navier-Stokes equations : Re u t + Re u u = Inertial acceleration
The role of micro-scale inertia in transport processes - Ganesh Subramanian (JNCASR, Bangalore) Micro-scale inertia (suspensions and emulsions) Navier-Stokes equations : Re u t + Re u u = Inertial acceleration
Derivation of Itô SDE and Relationship to ODE and CTMC Models
 Derivation of Itô SDE and Relationship to ODE and CTMC Models Biomathematics II April 23, 2015 Linda J. S. Allen Texas Tech University TTU 1 Euler-Maruyama Method for Numerical Solution of an Itô SDE dx(t)
Derivation of Itô SDE and Relationship to ODE and CTMC Models Biomathematics II April 23, 2015 Linda J. S. Allen Texas Tech University TTU 1 Euler-Maruyama Method for Numerical Solution of an Itô SDE dx(t)
MULTIPLE-CHOICE PROBLEMS:(Two marks per answer) (Circle the Letter Beside the Most Correct Answer in the Questions Below.)
 MULTIPLE-CHOICE PROLEMS:(Two marks per answer) (Circle the Letter eside the Most Correct Answer in the Questions elow.) 1. The absolute viscosity µ of a fluid is primarily a function of: a. Density. b.
MULTIPLE-CHOICE PROLEMS:(Two marks per answer) (Circle the Letter eside the Most Correct Answer in the Questions elow.) 1. The absolute viscosity µ of a fluid is primarily a function of: a. Density. b.
Module BIO- M1- S06 Evolu-onary ecology. Adaptive dynamics. David Claessen Ins-tut de Biologie de l ENS Equipe Eco- Evolu-on Mathéma-que
 Module BIO- M1- S06 Evolu-onary ecology Adaptive dynamics David Claessen Ins-tut de Biologie de l ENS Equipe Eco- Evolu-on Mathéma-que OBJECTIF Une théorie quantitative pour prédire la tendence evolutive
Module BIO- M1- S06 Evolu-onary ecology Adaptive dynamics David Claessen Ins-tut de Biologie de l ENS Equipe Eco- Evolu-on Mathéma-que OBJECTIF Une théorie quantitative pour prédire la tendence evolutive
Principles of Convection
 Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
An-Najah National University Civil Engineering Department. Fluid Mechanics. Chapter 1. General Introduction
 1 An-Najah National University Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics Chapter 1 General Introduction 2 What is Fluid Mechanics? Mechanics deals with the behavior of both stationary and moving bodies
1 An-Najah National University Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics Chapter 1 General Introduction 2 What is Fluid Mechanics? Mechanics deals with the behavior of both stationary and moving bodies
So in terms of conditional probability densities, we have by differentiating this relationship:
 Modeling with Finite State Markov Chains Tuesday, September 27, 2011 1:54 PM Homework 1 due Friday, September 30 at 2 PM. Office hours on 09/28: Only 11 AM-12 PM (not at 3 PM) Important side remark about
Modeling with Finite State Markov Chains Tuesday, September 27, 2011 1:54 PM Homework 1 due Friday, September 30 at 2 PM. Office hours on 09/28: Only 11 AM-12 PM (not at 3 PM) Important side remark about
Convection. forced convection when the flow is caused by external means, such as by a fan, a pump, or atmospheric winds.
 Convection The convection heat transfer mode is comprised of two mechanisms. In addition to energy transfer due to random molecular motion (diffusion), energy is also transferred by the bulk, or macroscopic,
Convection The convection heat transfer mode is comprised of two mechanisms. In addition to energy transfer due to random molecular motion (diffusion), energy is also transferred by the bulk, or macroscopic,
Mathematical models in population genetics II
 Mathematical models in population genetics II Anand Bhaskar Evolutionary Biology and Theory of Computing Bootcamp January 1, 014 Quick recap Large discrete-time randomly mating Wright-Fisher population
Mathematical models in population genetics II Anand Bhaskar Evolutionary Biology and Theory of Computing Bootcamp January 1, 014 Quick recap Large discrete-time randomly mating Wright-Fisher population
Mixing at the External Boundary of a Submerged Turbulent Jet
 Mixing at the External Boundary of a Submerged Turbulent Jet A. Eidelman, T. Elperin, N. Kleeorin, I. Rogachevskii, I. Sapir-Katiraie The Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel G. Hazak
Mixing at the External Boundary of a Submerged Turbulent Jet A. Eidelman, T. Elperin, N. Kleeorin, I. Rogachevskii, I. Sapir-Katiraie The Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel G. Hazak
Interfacial dynamics
 Interfacial dynamics Interfacial dynamics = dynamic processes at fluid interfaces upon their deformation Interfacial rheological properties: elasticity, viscosity, yield stress, Relation between macroscopic
Interfacial dynamics Interfacial dynamics = dynamic processes at fluid interfaces upon their deformation Interfacial rheological properties: elasticity, viscosity, yield stress, Relation between macroscopic
Biology 11 UNIT 1: EVOLUTION LESSON 2: HOW EVOLUTION?? (MICRO-EVOLUTION AND POPULATIONS)
 Biology 11 UNIT 1: EVOLUTION LESSON 2: HOW EVOLUTION?? (MICRO-EVOLUTION AND POPULATIONS) Objectives: By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the 2 types of evolution Describe the 5 ways
Biology 11 UNIT 1: EVOLUTION LESSON 2: HOW EVOLUTION?? (MICRO-EVOLUTION AND POPULATIONS) Objectives: By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the 2 types of evolution Describe the 5 ways
Hydrodynamics. l. mahadevan harvard university
 Thermodynamics / statistical mechanics : Hydrodynamics N>>1; large number of interacting particles! Hydrodynamics : L >> l; T >> t; long wavelength, slow time - average over (some) microscopic length and
Thermodynamics / statistical mechanics : Hydrodynamics N>>1; large number of interacting particles! Hydrodynamics : L >> l; T >> t; long wavelength, slow time - average over (some) microscopic length and
ANALYSIS OF MICROBIAL COMPETITION
 ANALYSIS OF MICROBIAL COMPETITION Eric Pomper Microbiology 9 Pittsburgh Central Catholic High School Grade 9 Introduction Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast) were grown together
ANALYSIS OF MICROBIAL COMPETITION Eric Pomper Microbiology 9 Pittsburgh Central Catholic High School Grade 9 Introduction Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Yeast) were grown together
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields
 Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Evolution and Impact of Cosmic Magnetic Fields Robi Banerjee University of Hamburg Collaborators: Dominik Schleicher (Göttingen), C. Federrath (Lyon, HD), Karsten Jedamzik (Montpellier), R. Klessen (Heidelberg),
Major questions of evolutionary genetics. Experimental tools of evolutionary genetics. Theoretical population genetics.
 Evolutionary Genetics (for Encyclopedia of Biodiversity) Sergey Gavrilets Departments of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and Mathematics, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996-6 USA Evolutionary
Evolutionary Genetics (for Encyclopedia of Biodiversity) Sergey Gavrilets Departments of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and Mathematics, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996-6 USA Evolutionary
Fluctuation dynamo amplified by intermittent shear bursts
 by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
by intermittent Thanks to my collaborators: A. Busse (U. Glasgow), W.-C. Müller (TU Berlin) Dynamics Days Europe 8-12 September 2014 Mini-symposium on Nonlinear Problems in Plasma Astrophysics Introduction
Fluid Mechanics II Viscosity and shear stresses
 Fluid Mechanics II Viscosity and shear stresses Shear stresses in a Newtonian fluid A fluid at rest can not resist shearing forces. Under the action of such forces it deforms continuously, however small
Fluid Mechanics II Viscosity and shear stresses Shear stresses in a Newtonian fluid A fluid at rest can not resist shearing forces. Under the action of such forces it deforms continuously, however small
Basic modeling approaches for biological systems. Mahesh Bule
 Basic modeling approaches for biological systems Mahesh Bule The hierarchy of life from atoms to living organisms Modeling biological processes often requires accounting for action and feedback involving
Basic modeling approaches for biological systems Mahesh Bule The hierarchy of life from atoms to living organisms Modeling biological processes often requires accounting for action and feedback involving
Wave-like phenomena are ubiquitous in nature and have. Fluctuations uncover a distinct class of traveling waves
 Fluctuations uncover a distinct class of traveling waves Gabriel Birzu a, Oskar Hallatschek b,c, and Kirill S. Korolev a,d,1 a Department of Physics, Boston University, Boston, MA 015; b Department of
Fluctuations uncover a distinct class of traveling waves Gabriel Birzu a, Oskar Hallatschek b,c, and Kirill S. Korolev a,d,1 a Department of Physics, Boston University, Boston, MA 015; b Department of
Outline. Definition and mechanism Theory of diffusion Molecular diffusion in gases Molecular diffusion in liquid Mass transfer
 Diffusion 051333 Unit operation in gro-industry III Department of Biotechnology, Faculty of gro-industry Kasetsart University Lecturer: Kittipong Rattanaporn 1 Outline Definition and mechanism Theory of
Diffusion 051333 Unit operation in gro-industry III Department of Biotechnology, Faculty of gro-industry Kasetsart University Lecturer: Kittipong Rattanaporn 1 Outline Definition and mechanism Theory of
Experiments at the University of Minnesota (draft 2)
 Experiments at the University of Minnesota (draft 2) September 17, 2001 Studies of migration and lift and of the orientation of particles in shear flows Experiments to determine positions of spherical
Experiments at the University of Minnesota (draft 2) September 17, 2001 Studies of migration and lift and of the orientation of particles in shear flows Experiments to determine positions of spherical
Types of biological networks. I. Intra-cellurar networks
 Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
Eddy viscosity. AdOc 4060/5060 Spring 2013 Chris Jenkins. Turbulence (video 1hr):
 AdOc 4060/5060 Spring 2013 Chris Jenkins Eddy viscosity Turbulence (video 1hr): http://cosee.umaine.edu/programs/webinars/turbulence/?cfid=8452711&cftoken=36780601 Part B Surface wind stress Wind stress
AdOc 4060/5060 Spring 2013 Chris Jenkins Eddy viscosity Turbulence (video 1hr): http://cosee.umaine.edu/programs/webinars/turbulence/?cfid=8452711&cftoken=36780601 Part B Surface wind stress Wind stress
Citation PHYSICS OF FLUIDS (2005), 17(5)
 Title Energy dissipation in spiral vortex straight vortex tube Author(s) Kawahara, G Citation PHYSICS OF FLUIDS (005), 17(5) Issue Date 005-05 URL http://hdl.handle.net/433/50071 Copyright 005 American
Title Energy dissipation in spiral vortex straight vortex tube Author(s) Kawahara, G Citation PHYSICS OF FLUIDS (005), 17(5) Issue Date 005-05 URL http://hdl.handle.net/433/50071 Copyright 005 American
On the physics of shear flows in 3D geometry
 On the physics of shear flows in 3D geometry C. Hidalgo and M.A. Pedrosa Laboratorio Nacional de Fusión, EURATOM-CIEMAT, Madrid, Spain Recent experiments have shown the importance of multi-scale (long-range)
On the physics of shear flows in 3D geometry C. Hidalgo and M.A. Pedrosa Laboratorio Nacional de Fusión, EURATOM-CIEMAT, Madrid, Spain Recent experiments have shown the importance of multi-scale (long-range)
Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
Perplexing Observations. Today: Thinking About Darwinian Evolution. We owe much of our understanding of EVOLUTION to CHARLES DARWIN.
 Today: Thinking About Darwinian Evolution Part 1: Darwin s Theory Perplexing Observations Mystery of the Black Death?? What is evolution?? And what is this finch doing?!? We owe much of our understanding
Today: Thinking About Darwinian Evolution Part 1: Darwin s Theory Perplexing Observations Mystery of the Black Death?? What is evolution?? And what is this finch doing?!? We owe much of our understanding
Turbulence Instability
 Turbulence Instability 1) All flows become unstable above a certain Reynolds number. 2) At low Reynolds numbers flows are laminar. 3) For high Reynolds numbers flows are turbulent. 4) The transition occurs
Turbulence Instability 1) All flows become unstable above a certain Reynolds number. 2) At low Reynolds numbers flows are laminar. 3) For high Reynolds numbers flows are turbulent. 4) The transition occurs
Using Evolutionary Approaches To Study Biological Pathways. Pathways Have Evolved
 Pathways Have Evolved Using Evolutionary Approaches To Study Biological Pathways Orkun S. Soyer The Microsoft Research - University of Trento Centre for Computational and Systems Biology Protein-protein
Pathways Have Evolved Using Evolutionary Approaches To Study Biological Pathways Orkun S. Soyer The Microsoft Research - University of Trento Centre for Computational and Systems Biology Protein-protein
Turbulent Rankine Vortices
 Turbulent Rankine Vortices Roger Kingdon April 2008 Turbulent Rankine Vortices Overview of key results in the theory of turbulence Motivation for a fresh perspective on turbulence The Rankine vortex CFD
Turbulent Rankine Vortices Roger Kingdon April 2008 Turbulent Rankine Vortices Overview of key results in the theory of turbulence Motivation for a fresh perspective on turbulence The Rankine vortex CFD
- point mutations in most non-coding DNA sites likely are likely neutral in their phenotypic effects.
 January 29 th, 2010 Bioe 109 Winter 2010 Lecture 10 Microevolution 3 - random genetic drift - one of the most important shifts in evolutionary thinking over the past 30 years has been an appreciation of
January 29 th, 2010 Bioe 109 Winter 2010 Lecture 10 Microevolution 3 - random genetic drift - one of the most important shifts in evolutionary thinking over the past 30 years has been an appreciation of
Non-equilibrium phenomena and fluctuation relations
 Non-equilibrium phenomena and fluctuation relations Lamberto Rondoni Politecnico di Torino Beijing 16 March 2012 http://www.rarenoise.lnl.infn.it/ Outline 1 Background: Local Thermodyamic Equilibrium 2
Non-equilibrium phenomena and fluctuation relations Lamberto Rondoni Politecnico di Torino Beijing 16 March 2012 http://www.rarenoise.lnl.infn.it/ Outline 1 Background: Local Thermodyamic Equilibrium 2
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Photographs of the 3D-MTC device and the confocal fluorescence microscopy. I: The system consists of a Leica SP8-Confocal microscope (with an option of STED), a confocal PC, a 3D-MTC
Supplementary Figure 1 Photographs of the 3D-MTC device and the confocal fluorescence microscopy. I: The system consists of a Leica SP8-Confocal microscope (with an option of STED), a confocal PC, a 3D-MTC
Transient Heat Transfer Experiment. ME 331 Introduction to Heat Transfer. June 1 st, 2017
 Transient Heat Transfer Experiment ME 331 Introduction to Heat Transfer June 1 st, 2017 Abstract The lumped capacitance assumption for transient conduction was tested for three heated spheres; a gold plated
Transient Heat Transfer Experiment ME 331 Introduction to Heat Transfer June 1 st, 2017 Abstract The lumped capacitance assumption for transient conduction was tested for three heated spheres; a gold plated
SC/BIOL Current Topics in Biophysics TERM TEST ONE
 Page 1 of 1 SC/BIOL 2090.02 Current Topics in Biophysics TERM TEST ONE Name: KEY Student ID: There are three questions. You must complete all three. Ensure that you show your work (that is, equations,
Page 1 of 1 SC/BIOL 2090.02 Current Topics in Biophysics TERM TEST ONE Name: KEY Student ID: There are three questions. You must complete all three. Ensure that you show your work (that is, equations,
Analysis of Turbulent Free Convection in a Rectangular Rayleigh-Bénard Cell
 Proceedings of the 8 th International Symposium on Experimental and Computational Aerothermodynamics of Internal Flows Lyon, July 2007 Paper reference : ISAIF8-00130 Analysis of Turbulent Free Convection
Proceedings of the 8 th International Symposium on Experimental and Computational Aerothermodynamics of Internal Flows Lyon, July 2007 Paper reference : ISAIF8-00130 Analysis of Turbulent Free Convection
2. Modeling of shrinkage during first drying period
 2. Modeling of shrinkage during first drying period In this chapter we propose and develop a mathematical model of to describe nonuniform shrinkage of porous medium during drying starting with several
2. Modeling of shrinkage during first drying period In this chapter we propose and develop a mathematical model of to describe nonuniform shrinkage of porous medium during drying starting with several
