New Family of the t Distributions for Modeling Semicircular Data
|
|
|
- Luke Turner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Communications of the Korean Statistical Society Vol. 15, No. 5, 008, pp New Family of the t Distributions for Modeling Semicircular Data Hyoung-Moon Kim 1) Abstract We develop new family of the t distributions for modeling semicircular data. It has convenient mathematical features. It is extended to the l-axial t distribution and a generalized semicircular t distribution. Keywords: Projection; axial data; heavy tail; transformation. 1. Introduction Angular data are very common in the areas of geology, meteorology, biology, etc. Sometimes it is not necessary to model angular data on a full circle. However most of works devoted to the modeling of circular data (Fisher, 1993; Jammalamadaka and SenGupta, 001; Mardia and Jupp, 000). This fact is emphasized on Guardiola (004) and Jones (1968). Guardiola (004) obtained a semicircular normal distribution using a simple projection. Similarly we project a t distribution over a semicircular segment and obtain the semicircular t(sct) distribution. Often a t distribution is an alternative to a normal distribution if the errors are heavier than those of a normal distribution in linear statistics. Similarly a SCT distribution has more heavier tail than a semicircular normal distribution. So a SCT distribution is an alternative to a semicircular normal distribution for the heavy tail semicircular data. This paper is organized as follows. Section defines the distribution and lists some of its basic properties. We estimate parameters of the SCT distribution by a maximum likelihood method in Section 3. We concludes in Section 4 with two extensions of the SCT distribution: the l-axial distribution for modeling any arc of arbitrary length, say π/l, l = 1,, and a generalized SCT distribution. Corresponding author s work was supported by the faculty research fund of Konkuk University in ) Associate Professor, Department of Applied Statistics, Konkuk University, 1 Hwayang-Dong, Gwangjin-Gu, Seoul , Korea. hmkim@konkuk.ac.kr
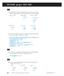
2 668 Hyoung-Moon Kim. New Family of the t Distributions.1. Definition and some basic properties The SCT distribution is obtained by projecting a t distribution over a semicircular segment. Let X have a t distribution with a df ν, i.e., the density of X is Γ ((ν + 1)/) Γ (ν/) ( x νπ ν, < x <, ν = 1,,. (.1) For brevity, we shall also say that X is t(ν). For a positive real number r, define the angle θ by θ = tan 1 (x/r). Hence, x = r tan. Obviously, the pdf of θ is given by Γ ((ν + 1)/) sec ( 1 + tan, ϕ = ν Γ (ν/) ϕπ ϕ r, π < θ < π. (.) More generally, we introduce the parameter µ as the location parameter for the SCT distribution and write the pdf as Γ(()/) sec ( (θ µ) 1+ tan (θ µ), π Γ(ν/) ϕπ ϕ +µ<θ < π +µ, π <µ<π. (.3) Then, we say that θ is an SCT random variable with parameters µ, ν and ϕ; for brevity, we shall also say that θ is SCT(µ, ν, ϕ). Figure.1 shows the shape of (.3) for four values of ν with µ = 0 and r = 10. Geometrically r is the distance between the radius and the support of the t density. The closer the support is to the radius, the larger ϕ. One special case of (.3) is the semicircular Uniform distribution over ( π/, π/) when ν = r = 1. To compare the tail behavior of a semicircular normal distribution and a SCT distribution, Figure. shows two pdfs. SCT distribution is the pdf of Figure.1 with ν = 1. And a semicircular normal distribution is obtained from transforming the standard normal distribution with r = 10. From the Figure., we denote that a SCT distribution has more heavier tail than a semicircular normal distribution. Similar relationship also appears at linear statistics, i.e. a relationship between a normal distribution and a t distribution. It is straightforward to generate samples from an SCT distribution using the transformation. First, generate samples from a t distribution, and then use the inverse transformation, θ = µ + tan 1 (x/r), r = ν/ϕ. Similarly, the cdf of an SCT distribution is F (θ; µ, ν, ϕ) = T (r tan(θ µ)), where the function T ( ) is a cdf of a t distribution. We consider the behavior of the SCT distribution when the degree of freedom ν goes to. Suppose θ follows SCT(µ, ν, ϕ). W.L.O.G., we assume that µ = 0, r = 1, then the pdf is as follows: [ ] ( Γ ((ν + 1)/) Γ (ν/) sec 1 + tan, π νπ ν < θ < π. (.4)
3 New Family of the t Distributions for Modeling Semicircular Data 669 f(theta) nu=1 nu=10 nu=50 nu= theta Figure.1: The density functions SCT(0, ν, ϕ) f(theta) SCN SCT theta Figure.: A SCT pdf and a semicircular normal(scn) pdf
4 670 Hyoung-Moon Kim Denote the quantity in square brackets by C ν. From an extension of Stirling s formula and an application of the following Lemma (Casella and Berger, 00), we have lim C ν = 1. (.5) ν π Lemma.1 Let a 1, a, be a sequence of numbers converging to a, that is, lim n a n = a. Then lim n (1 + a n /n) n = e a. Furthermore ( lim ν sec 1 + tan = sec e tan (.6) ν using the above Lemma again. So the SCT distribution converges to the semicircular normal distribution as ν goes to. Similar phenomenon also occurs in linear statistics, i.e. the t distribution converges to the standard normal distribution as the degree of freedom goes to... Trigonometric moments Similar to those of any circular density, trigonometric moments of the SCT distribution are defined as follows: φ p = Ee ipθ = α p + iβ p = E cos(pθ) + ie sin(pθ), p = 0, ±1, ±,. We assumed that the location parameter µ = 0 without loss of generality. The first and the second α p, p = 1, are given as follows: α 1 = νϕ ( ν ν + 1 π F 1, ν + 1 α = ϕ ν (ν + 1)Γ ((ν + 1)/) νπγ (ν/) ; ν + ) ; 1 ϕ, F 1 ( ν + 1, ν + ) ; ν + 3 ; 1 ϕ, (.7) where F 1 is the hypergeometric function (Abramowitz and Stegun, 197). For example, α 1 = /π when ν = 1 and r = 1. The hypergeometric function has a series expansion F 1 (a, b; c; z) = k=0 (a) k (b) k (c) k where (a) k is the Pochhammer symbol or rising factorial (a) k = Γ(a + k) Γ(a) z k k!, (.8) = a(a + 1) (a + k 1). (.9) The function is a solution of the hypergeometric differential equation z(1 z)y + [c (a + b + 1)z]y aby = 0.
5 New Family of the t Distributions for Modeling Semicircular Data 671 The proof is the process of using some transformations. For the first cosine moment, use the transformation x = tan and use a property of even function. So Γ((ν + 1)/) α 1 = 0 Γ(ν/) ϕπ (1 + x 1 Finally a transformation y = x is applied. Then α 1 = Γ((ν + 1)/)ϕ ν Γ(ν/) π 0 (1 + x dx. (.10) ϕ y 1 (1 + y) 1 (ϕ + y) dy. (.11) The result α 1 follows by the integral formula (Gradshteyn and Ryzhik, 1994). To obtain α, we use the transformation x = tan and a property of a generalized t (Arellano-Valle and Bolfarine, 1995) pdf is used. So α = Γ((ν + 1)/)ϕ ν Γ(ν/) π (1 + x 1 (ϕ + x dx. (.1) After using a property of even function followed by y = x and the result is immediate by the same integral formula of α 1. Like any other symmetric circular density, β p = E sin(pθ), are 0 as the density is symmetric about Parameter Estimation and Example The minus log-likelihood for a random sample of size n, θ = (θ 1,..., θ n ), from the SCT distribution is given by ( ) ν + 1 ( ν ) l(µ, ν, ϕ; θ) = n log Γ + n log Γ + n log(ϕπ) n + log cos (θ i µ) + ν + 1 n ( ) log 1 + tan (θ i µ). (3.1) ϕ i=1 For the following example, the corresponding estimates have been computed by direct minimization of the minus log-likelihood itself. Example 3.1 We simulated a dataset of size 5,000 from an SCT distribution with µ = 0, ϕ = 5 and ν = 50. For this dataset, the corresponding maximum likelihood estimates are given by ˆµ = 0.007, ˆϕ = 4.97 and ˆν = 51. Histogram with pdfs and Healy s plot (Healy, 1968) are shown in Figure 3.1. A visual inspection of Figure 3.1 indicates a satisfactory fit of the density to the data. Healy s plot is based on i=1 d i = r tan(θ i µ), (i = 1,..., n) (3.) and is sampled from t(ν) distribution if the fitted model is appropriate. In practice, estimates must replace the exact parameter values in equation (3.). d i above must
6 67 Hyoung-Moon Kim f(theta) theta nominal values fitted cumulative probability Figure 3.1: Histogram with pdfs(the solid line represents the original pdf and the dashed line corresponds to the fitted pdf) and Healy s plot be sorted and plotted against the t(ν) percentage points. Equivalently, the cumulative t(ν) probabilities can be plotted against their nominal values 1/n, /n,..., 1; the points should lie on the bisection line of the quadrant. This diagnostic method is a natural analogue of a well-known diagnostic used in the normal theory context (Healy, 1968).
7 New Family of the t Distributions for Modeling Semicircular Data Extensions We extend the suggested model to the l-axial distribution, which is applicable to any arc of arbitrary length say π/l for l = 1,,.... Occasionally, measurements result in any arc of arbitrary length, say π/l, l = 1,,..., so it is desirable to extend the SCT distribution. To construct the l-axial t distribution, we consider the pdf (.) and use the transformation θ = θ/l, l = 1,,.... The pdf of θ is given by Γ ((ν + 1)/) sec (lθ ( /) 1 + tan (lθ /), ϕ = ν Γ (ν/) ϕπ ϕ r, π l < θ < π l. (4.1) Please note that when l =, the pdf (4.1) is the same as the pdf (.), the SCT pdf. When l = 1, it becomes the pdf of a circular t distribution. Arellano-Valle and Bolfarine (1995) extended a t distribution to a generalized t distribution since the usual t distribution does not retain its conditional distributions. Let X have a generalized t distribution with dfs λ and ν, i.e., the density of X is Γ ((ν + 1)/) Γ (ν/) ( x λπ λ, < x <, ν & λ = 1,,. (4.) For brevity, we shall also say that X is gt(λ, ν). When λ = ν, it is a usual t distribution. Similarly we use the same transformation of an SCT distribution, then obtained a generalized SCT distribution as follows: Γ ((ν + 1)/) sec ( 1 + tan, ϕ = λ Γ (ν/) ϕπ ϕ r, π < θ < π. (4.3) Please note that ϕ = λ/r instead of ϕ = ν/r since it has two degree of freedom parameters. References Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, I. A. (197). Handbook of Mathematical Functions: With Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, Dover Publications, New York. Arellano-Valle, R. B. and Bolfarine, H. (1995). On some characterizations of the t-distribution, Statistics & Probability Letters, 5, Casella, G. and Berger, R. L. (00). Statistical Inference, Duxbury Press, California. Fisher, N. I. (1993). Statistical Analysis of Circular Data, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. Gradshteyn, I. S. and Ryzhik, I. M. (1994). Table of Integrals, Series and Products, (5th ed.) Ed. A. Jeffrey, Academic Press, San Diego. Guardiola, J. H. (004). The Semicircular Normal Distribution, Ph. D. Dissertation. Baylor University, Institute of Statistics.
8 674 Hyoung-Moon Kim Healy, M. J. R. (1968). Multivariate normal plotting, Applied Statistics, 17, Jammalamadaka, S. R. and SenGupta, A. (001). Topics in Circular Statistics, World Scientific Publishing, Singapore. Jones, T. A. (1968). Statistical analysis of orientation data, Journal of Sedimentary Research, 38, Mardia, K. V. and Jupp, P. (000). Directional Statistics, John Wiley & Sons, New York. [Received June 008, Accepted July 008]
( ) g θ denote the Cumulative. G θ and. g ( θ ) can be written in terms of F( x ) and f ( ) x using. tan 2
 IRACST Engineering Science and Technology: An International Journal (ESTIJ), ISSN: 50-3498, Vol., No. 5, October 0 Circular Model Induced by Inverse Stereographic Projection On Extreme-Value Distribution
IRACST Engineering Science and Technology: An International Journal (ESTIJ), ISSN: 50-3498, Vol., No. 5, October 0 Circular Model Induced by Inverse Stereographic Projection On Extreme-Value Distribution
Notes on a skew-symmetric inverse double Weibull distribution
 Journal of the Korean Data & Information Science Society 2009, 20(2), 459 465 한국데이터정보과학회지 Notes on a skew-symmetric inverse double Weibull distribution Jungsoo Woo 1 Department of Statistics, Yeungnam
Journal of the Korean Data & Information Science Society 2009, 20(2), 459 465 한국데이터정보과학회지 Notes on a skew-symmetric inverse double Weibull distribution Jungsoo Woo 1 Department of Statistics, Yeungnam
On the Ratio of Rice Random Variables
 JIRSS 9 Vol. 8, Nos. 1-, pp 61-71 On the Ratio of Rice Random Variables N. B. Khoolenjani 1, K. Khorshidian 1, 1 Departments of Statistics, Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran. n.b.khoolenjani@gmail.com Departments
JIRSS 9 Vol. 8, Nos. 1-, pp 61-71 On the Ratio of Rice Random Variables N. B. Khoolenjani 1, K. Khorshidian 1, 1 Departments of Statistics, Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran. n.b.khoolenjani@gmail.com Departments
SYMMETRIC UNIMODAL MODELS FOR DIRECTIONAL DATA MOTIVATED BY INVERSE STEREOGRAPHIC PROJECTION
 J. Japan Statist. Soc. Vol. 40 No. 1 010 45 61 SYMMETRIC UNIMODAL MODELS FOR DIRECTIONAL DATA MOTIVATED BY INVERSE STEREOGRAPHIC PROJECTION Toshihiro Abe*, Kunio Shimizu** and Arthur Pewsey*** In this
J. Japan Statist. Soc. Vol. 40 No. 1 010 45 61 SYMMETRIC UNIMODAL MODELS FOR DIRECTIONAL DATA MOTIVATED BY INVERSE STEREOGRAPHIC PROJECTION Toshihiro Abe*, Kunio Shimizu** and Arthur Pewsey*** In this
AN EFFICIENT INTEGRAL TRANSFORM TECHNIQUE OF A SINGULAR WIRE ANTENNA KERNEL. S.-O. Park
 AN EFFICIENT INTEGRAL TRANSFORM TECHNIQUE OF A SINGULAR WIRE ANTENNA KERNEL S.-O. Park Department of Electronics Engineering Information and Communications University 58-4 Hwaam-dong, Yusung-gu Taejon,
AN EFFICIENT INTEGRAL TRANSFORM TECHNIQUE OF A SINGULAR WIRE ANTENNA KERNEL S.-O. Park Department of Electronics Engineering Information and Communications University 58-4 Hwaam-dong, Yusung-gu Taejon,
Candidates are expected to have available a calculator. Only division by (x + a) or (x a) will be required.
 Revision Checklist Unit C2: Core Mathematics 2 Unit description Algebra and functions; coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane; sequences and series; trigonometry; exponentials and logarithms; differentiation;
Revision Checklist Unit C2: Core Mathematics 2 Unit description Algebra and functions; coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane; sequences and series; trigonometry; exponentials and logarithms; differentiation;
Given an arc of length s on a circle of radius r, the radian measure of the central angle subtended by the arc is given by θ = s r :
 Given an arc of length s on a circle of radius r, the radian measure of the central angle subtended by the arc is given by θ = s r : To convert from radians (rad) to degrees ( ) and vice versa, use the
Given an arc of length s on a circle of radius r, the radian measure of the central angle subtended by the arc is given by θ = s r : To convert from radians (rad) to degrees ( ) and vice versa, use the
Given an arc of length s on a circle of radius r, the radian measure of the central angle subtended by the arc is given by θ = s r :
 Given an arc of length s on a circle of radius r, the radian measure of the central angle subtended by the arc is given by θ = s r : To convert from radians (rad) to degrees ( ) and vice versa, use the
Given an arc of length s on a circle of radius r, the radian measure of the central angle subtended by the arc is given by θ = s r : To convert from radians (rad) to degrees ( ) and vice versa, use the
Physics 6303 Lecture 22 November 7, There are numerous methods of calculating these residues, and I list them below. lim
 Physics 6303 Lecture 22 November 7, 208 LAST TIME:, 2 2 2, There are numerous methods of calculating these residues, I list them below.. We may calculate the Laurent series pick out the coefficient. 2.
Physics 6303 Lecture 22 November 7, 208 LAST TIME:, 2 2 2, There are numerous methods of calculating these residues, I list them below.. We may calculate the Laurent series pick out the coefficient. 2.
Generalised definitions of certain functions and their uses
 arxiv:math-ph/0307065v2 6 Aug 2003 Generalised definitions of certain functions and their uses Debasis Biswas 1 and Asoke P. Chattopadhyay 2 1 Department of Physics and 2 Department of Chemistry University
arxiv:math-ph/0307065v2 6 Aug 2003 Generalised definitions of certain functions and their uses Debasis Biswas 1 and Asoke P. Chattopadhyay 2 1 Department of Physics and 2 Department of Chemistry University
Circular Distributions Arising from the Möbius Transformation of Wrapped Distributions
 isid/ms/05/09 August, 05 http://www.isid.ac.in/ statmath/index.php?module=preprint Circular Distributions Arising from the Möbius Transformation of Wrapped Distributions Yogendra P. Chaubey and N.N. Midhu
isid/ms/05/09 August, 05 http://www.isid.ac.in/ statmath/index.php?module=preprint Circular Distributions Arising from the Möbius Transformation of Wrapped Distributions Yogendra P. Chaubey and N.N. Midhu
HANDBOOK OF APPLICABLE MATHEMATICS
 HANDBOOK OF APPLICABLE MATHEMATICS Chief Editor: Walter Ledermann Volume VI: Statistics PART A Edited by Emlyn Lloyd University of Lancaster A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester
HANDBOOK OF APPLICABLE MATHEMATICS Chief Editor: Walter Ledermann Volume VI: Statistics PART A Edited by Emlyn Lloyd University of Lancaster A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester
Speed and change of direction in larvae of Drosophila melanogaster
 CHAPTER Speed and change of direction in larvae of Drosophila melanogaster. Introduction Holzmann et al. (6) have described, inter alia, the application of HMMs with circular state-dependent distributions
CHAPTER Speed and change of direction in larvae of Drosophila melanogaster. Introduction Holzmann et al. (6) have described, inter alia, the application of HMMs with circular state-dependent distributions
40.2. Interval Estimation for the Variance. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Interval Estimation for the Variance 40.2 Introduction In Section 40.1 we have seen that the sampling distribution of the sample mean, when the data come from a normal distribution (and even, in large
Interval Estimation for the Variance 40.2 Introduction In Section 40.1 we have seen that the sampling distribution of the sample mean, when the data come from a normal distribution (and even, in large
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS GCE NORMAL ACADEMIC LEVEL (016) (Syllabus 4044) CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION AIMS ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES SCHEME OF ASSESSMENT 3 USE OF CALCULATORS 3 SUBJECT CONTENT 4 MATHEMATICAL FORMULAE
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS GCE NORMAL ACADEMIC LEVEL (016) (Syllabus 4044) CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION AIMS ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES SCHEME OF ASSESSMENT 3 USE OF CALCULATORS 3 SUBJECT CONTENT 4 MATHEMATICAL FORMULAE
Understand the difference between truncating and rounding. Calculate with roots, and with integer and fractional indices.
 The assessments will cover the following content headings: 1. Number 2. Algebra 3. Ratio, and rates of change 4. Geometry and measures 5. Probability 6. Statistics Higher Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Year 10 Year
The assessments will cover the following content headings: 1. Number 2. Algebra 3. Ratio, and rates of change 4. Geometry and measures 5. Probability 6. Statistics Higher Year 7 Year 8 Year 9 Year 10 Year
By Bhattacharjee, Das. Published: 26 April 2018
 Electronic Journal of Applied Statistical Analysis EJASA, Electron. J. App. Stat. Anal. http://siba-ese.unisalento.it/index.php/ejasa/index e-issn: 2070-5948 DOI: 10.1285/i20705948v11n1p155 Estimation
Electronic Journal of Applied Statistical Analysis EJASA, Electron. J. App. Stat. Anal. http://siba-ese.unisalento.it/index.php/ejasa/index e-issn: 2070-5948 DOI: 10.1285/i20705948v11n1p155 Estimation
4.3 TRIGONOMETRY EXTENDED: THE CIRCULAR FUNCTIONS
 4.3 TRIGONOMETRY EXTENDED: THE CIRCULAR FUNCTIONS MR. FORTIER 1. Trig Functions of Any Angle We now extend the definitions of the six basic trig functions beyond triangles so that we do not have to restrict
4.3 TRIGONOMETRY EXTENDED: THE CIRCULAR FUNCTIONS MR. FORTIER 1. Trig Functions of Any Angle We now extend the definitions of the six basic trig functions beyond triangles so that we do not have to restrict
1 Isotropic Covariance Functions
 1 Isotropic Covariance Functions Let {Z(s)} be a Gaussian process on, ie, a collection of jointly normal random variables Z(s) associated with n-dimensional locations s The joint distribution of {Z(s)}
1 Isotropic Covariance Functions Let {Z(s)} be a Gaussian process on, ie, a collection of jointly normal random variables Z(s) associated with n-dimensional locations s The joint distribution of {Z(s)}
University of Lisbon, Portugal
 Development and comparative study of two near-exact approximations to the distribution of the product of an odd number of independent Beta random variables Luís M. Grilo a,, Carlos A. Coelho b, a Dep.
Development and comparative study of two near-exact approximations to the distribution of the product of an odd number of independent Beta random variables Luís M. Grilo a,, Carlos A. Coelho b, a Dep.
Exponential, Logarithmic &Trigonometric Derivatives
 1 U n i t 9 12CV Date: Name: Exponential, Logarithmic &Trigonometric Derivatives Tentative TEST date Big idea/learning Goals The world s population experiences exponential growth the rate of growth becomes
1 U n i t 9 12CV Date: Name: Exponential, Logarithmic &Trigonometric Derivatives Tentative TEST date Big idea/learning Goals The world s population experiences exponential growth the rate of growth becomes
Asymptotic distribution of the sample average value-at-risk in the case of heavy-tailed returns
 Asymptotic distribution of the sample average value-at-risk in the case of heavy-tailed returns Stoyan V. Stoyanov Chief Financial Researcher, FinAnalytica Inc., Seattle, USA e-mail: stoyan.stoyanov@finanalytica.com
Asymptotic distribution of the sample average value-at-risk in the case of heavy-tailed returns Stoyan V. Stoyanov Chief Financial Researcher, FinAnalytica Inc., Seattle, USA e-mail: stoyan.stoyanov@finanalytica.com
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
A NEW CLASS OF SKEW-NORMAL DISTRIBUTIONS
 A NEW CLASS OF SKEW-NORMAL DISTRIBUTIONS Reinaldo B. Arellano-Valle Héctor W. Gómez Fernando A. Quintana November, 2003 Abstract We introduce a new family of asymmetric normal distributions that contains
A NEW CLASS OF SKEW-NORMAL DISTRIBUTIONS Reinaldo B. Arellano-Valle Héctor W. Gómez Fernando A. Quintana November, 2003 Abstract We introduce a new family of asymmetric normal distributions that contains
PARAMETER ESTIMATION FOR THE LOG-LOGISTIC DISTRIBUTION BASED ON ORDER STATISTICS
 PARAMETER ESTIMATION FOR THE LOG-LOGISTIC DISTRIBUTION BASED ON ORDER STATISTICS Authors: Mohammad Ahsanullah Department of Management Sciences, Rider University, New Jersey, USA ahsan@rider.edu) Ayman
PARAMETER ESTIMATION FOR THE LOG-LOGISTIC DISTRIBUTION BASED ON ORDER STATISTICS Authors: Mohammad Ahsanullah Department of Management Sciences, Rider University, New Jersey, USA ahsan@rider.edu) Ayman
CAMI Education linked to CAPS: Mathematics
 - 1 - The main topics in the Curriculum: NUMBER TOPIC 1 Functions 2 Number patterns, sequences and series 3 Finance, growth and decay 4 Algebra 5 Differential Calculus 6 Probability 7 Euclidian geometry
- 1 - The main topics in the Curriculum: NUMBER TOPIC 1 Functions 2 Number patterns, sequences and series 3 Finance, growth and decay 4 Algebra 5 Differential Calculus 6 Probability 7 Euclidian geometry
Mathematics Trigonometry: Unit Circle
 a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
Hypothesis Testing. Robert L. Wolpert Department of Statistical Science Duke University, Durham, NC, USA
 Hypothesis Testing Robert L. Wolpert Department of Statistical Science Duke University, Durham, NC, USA An Example Mardia et al. (979, p. ) reprint data from Frets (9) giving the length and breadth (in
Hypothesis Testing Robert L. Wolpert Department of Statistical Science Duke University, Durham, NC, USA An Example Mardia et al. (979, p. ) reprint data from Frets (9) giving the length and breadth (in
Practice Test - Chapter 4
 Find the value of x. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. 1. An acute angle measure and the length of the hypotenuse are given, so the sine function can be used to find the length of the side opposite.
Find the value of x. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. 1. An acute angle measure and the length of the hypotenuse are given, so the sine function can be used to find the length of the side opposite.
WKB solution of the wave equation for a plane angular sector
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER JULY 998 WKB solution of the wave equation for a plane angular sector Ahmad T. Abawi* Roger F. Dashen Physics Department, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER JULY 998 WKB solution of the wave equation for a plane angular sector Ahmad T. Abawi* Roger F. Dashen Physics Department, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla,
On Development of Spoke Plot for Circular Variables
 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2010; 37(3) 369 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2010; 37(3) : 369-376 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper On Development of Spoke Plot for Circular Variables Fakhrulrozi
Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2010; 37(3) 369 Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2010; 37(3) : 369-376 www.science.cmu.ac.th/journal-science/josci.html Contributed Paper On Development of Spoke Plot for Circular Variables Fakhrulrozi
An angle in the Cartesian plane is in standard position if its vertex lies at the origin and its initial arm lies on the positive x-axis.
 Learning Goals 1. To understand what standard position represents. 2. To understand what a principal and related acute angle are. 3. To understand that positive angles are measured by a counter-clockwise
Learning Goals 1. To understand what standard position represents. 2. To understand what a principal and related acute angle are. 3. To understand that positive angles are measured by a counter-clockwise
Comparing measures of fit for circular distributions
 Comparing measures of fit for circular distributions by Zheng Sun B.Sc., Simon Fraser University, 2006 A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE
Comparing measures of fit for circular distributions by Zheng Sun B.Sc., Simon Fraser University, 2006 A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE
Outline schemes of work A-level Mathematics 6360
 Outline schemes of work A-level Mathematics 6360 Version.0, Autumn 013 Introduction These outline schemes of work are intended to help teachers plan and implement the teaching of the AQA A-level Mathematics
Outline schemes of work A-level Mathematics 6360 Version.0, Autumn 013 Introduction These outline schemes of work are intended to help teachers plan and implement the teaching of the AQA A-level Mathematics
A Correlation of. Pearson Integrated CME Project. to the. Common Core State Standards for Mathematics - High School PARRC Model Content Frameworks
 A Correlation of Pearson 2013 to the Common Core State Standards for A Correlation of Pearson Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson 2013 meets the standards of the Mathematics, PAARC Model
A Correlation of Pearson 2013 to the Common Core State Standards for A Correlation of Pearson Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson 2013 meets the standards of the Mathematics, PAARC Model
Interpolation. Create a program for linear interpolation of a three axis manufacturing machine with a constant
 QUESTION 1 Create a program for linear interpolation of a three axis manufacturing machine with a constant velocity profile. The inputs are the initial and final positions, feed rate, and sample period.
QUESTION 1 Create a program for linear interpolation of a three axis manufacturing machine with a constant velocity profile. The inputs are the initial and final positions, feed rate, and sample period.
Fundamentals of Applied Probability and Random Processes
 Fundamentals of Applied Probability and Random Processes,nd 2 na Edition Oliver C. Ibe University of Massachusetts, LoweLL, Massachusetts ip^ W >!^ AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS
Fundamentals of Applied Probability and Random Processes,nd 2 na Edition Oliver C. Ibe University of Massachusetts, LoweLL, Massachusetts ip^ W >!^ AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS
The choice of origin, axes, and length is completely arbitrary.
 Polar Coordinates There are many ways to mark points in the plane or in 3-dim space for purposes of navigation. In the familiar rectangular coordinate system, a point is chosen as the origin and a perpendicular
Polar Coordinates There are many ways to mark points in the plane or in 3-dim space for purposes of navigation. In the familiar rectangular coordinate system, a point is chosen as the origin and a perpendicular
Notes on multivariable calculus
 Notes on multivariable calculus Jonathan Wise February 2, 2010 1 Review of trigonometry Trigonometry is essentially the study of the relationship between polar coordinates and Cartesian coordinates in
Notes on multivariable calculus Jonathan Wise February 2, 2010 1 Review of trigonometry Trigonometry is essentially the study of the relationship between polar coordinates and Cartesian coordinates in
18.02SC Multivariable Calculus, Fall 2010 Transcript Recitation 34, Integration in Polar Coordinates
 18.02SC Multivariable Calculus, Fall 2010 Transcript Recitation 34, Integration in Polar Coordinates DAVID JORDAN: Hello, and welcome back to recitation. So today I want to practice doing some computings
18.02SC Multivariable Calculus, Fall 2010 Transcript Recitation 34, Integration in Polar Coordinates DAVID JORDAN: Hello, and welcome back to recitation. So today I want to practice doing some computings
Lesson 28 Working with Special Triangles
 Lesson 28 Working with Special Triangles Pre-Calculus 3/3/14 Pre-Calculus 1 Review Where We ve Been We have a new understanding of angles as we have now placed angles in a circle on a coordinate plane
Lesson 28 Working with Special Triangles Pre-Calculus 3/3/14 Pre-Calculus 1 Review Where We ve Been We have a new understanding of angles as we have now placed angles in a circle on a coordinate plane
Multivariate Distribution Models
 Multivariate Distribution Models Model Description While the probability distribution for an individual random variable is called marginal, the probability distribution for multiple random variables is
Multivariate Distribution Models Model Description While the probability distribution for an individual random variable is called marginal, the probability distribution for multiple random variables is
Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
 Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Parametrizations of Plane Curves In previous chapters, we have studied curves as the graphs of functions or equations involving the two variables x and y. Another
Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Parametrizations of Plane Curves In previous chapters, we have studied curves as the graphs of functions or equations involving the two variables x and y. Another
 1 Solving equations 1.1 Kick off with CAS 1. Polynomials 1. Trigonometric symmetry properties 1.4 Trigonometric equations and general solutions 1.5 Literal and simultaneous equations 1.6 Review 1.1 Kick
1 Solving equations 1.1 Kick off with CAS 1. Polynomials 1. Trigonometric symmetry properties 1.4 Trigonometric equations and general solutions 1.5 Literal and simultaneous equations 1.6 Review 1.1 Kick
Given one trigonometric ratio and quadrant, determining the remaining function values
 MATH 2412 Precalculus Sections 4.1-4.5 Trigonometry (quick review) Below is a list of topics you should be familiar with if you have completed a course recently in Trigonometry. I am going to assume knowledge
MATH 2412 Precalculus Sections 4.1-4.5 Trigonometry (quick review) Below is a list of topics you should be familiar with if you have completed a course recently in Trigonometry. I am going to assume knowledge
On the discrepancy of circular sequences of reals
 On the discrepancy of circular sequences of reals Fan Chung Ron Graham Abstract In this paper we study a refined measure of the discrepancy of sequences of real numbers in [0, ] on a circle C of circumference.
On the discrepancy of circular sequences of reals Fan Chung Ron Graham Abstract In this paper we study a refined measure of the discrepancy of sequences of real numbers in [0, ] on a circle C of circumference.
More with Angles Reference Angles
 More with Angles Reference Angles A reference angle is the angle formed by the terminal side of an angle θ, and the (closest) x axis. A reference angle, θ', is always 0 o
More with Angles Reference Angles A reference angle is the angle formed by the terminal side of an angle θ, and the (closest) x axis. A reference angle, θ', is always 0 o
COMPUTATION OF BESSEL AND AIRY FUNCTIONS AND OF RELATED GAUSSIAN QUADRATURE FORMULAE
 BIT 6-85//41-11 $16., Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 11 118 c Swets & Zeitlinger COMPUTATION OF BESSEL AND AIRY FUNCTIONS AND OF RELATED GAUSSIAN QUADRATURE FORMULAE WALTER GAUTSCHI Department of Computer Sciences,
BIT 6-85//41-11 $16., Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 11 118 c Swets & Zeitlinger COMPUTATION OF BESSEL AND AIRY FUNCTIONS AND OF RELATED GAUSSIAN QUADRATURE FORMULAE WALTER GAUTSCHI Department of Computer Sciences,
FOR beamforming and emitter localization applications in
 IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 17, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1999 1829 Angle and Time of Arrival Statistics for Circular and Elliptical Scattering Models Richard B. Ertel and Jeffrey H.
IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 17, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1999 1829 Angle and Time of Arrival Statistics for Circular and Elliptical Scattering Models Richard B. Ertel and Jeffrey H.
The Generating Functions for Pochhammer
 The Generating Functions for Pochhammer Symbol { }, n N Aleksandar Petoević University of Novi Sad Teacher Training Faculty, Department of Mathematics Podgorička 4, 25000 Sombor SERBIA and MONTENEGRO Email
The Generating Functions for Pochhammer Symbol { }, n N Aleksandar Petoević University of Novi Sad Teacher Training Faculty, Department of Mathematics Podgorička 4, 25000 Sombor SERBIA and MONTENEGRO Email
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Stat 704 Data Analysis I Probability Review
 1 / 39 Stat 704 Data Analysis I Probability Review Dr. Yen-Yi Ho Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina A.3 Random Variables 2 / 39 def n: A random variable is defined as a function that
1 / 39 Stat 704 Data Analysis I Probability Review Dr. Yen-Yi Ho Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina A.3 Random Variables 2 / 39 def n: A random variable is defined as a function that
STAT 3610: Review of Probability Distributions
 STAT 3610: Review of Probability Distributions Mark Carpenter Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics and Statistics August 25, 2015 Support of a Random Variable Definition The support of a random
STAT 3610: Review of Probability Distributions Mark Carpenter Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics and Statistics August 25, 2015 Support of a Random Variable Definition The support of a random
Approximating the Conway-Maxwell-Poisson normalizing constant
 Filomat 30:4 016, 953 960 DOI 10.98/FIL1604953S Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Approximating the Conway-Maxwell-Poisson
Filomat 30:4 016, 953 960 DOI 10.98/FIL1604953S Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Approximating the Conway-Maxwell-Poisson
The Distributions of Sums, Products and Ratios of Inverted Bivariate Beta Distribution 1
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 2, 28, no. 48, 2377-2391 The Distributions of Sums, Products and Ratios of Inverted Bivariate Beta Distribution 1 A. S. Al-Ruzaiza and Awad El-Gohary 2 Department of
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 2, 28, no. 48, 2377-2391 The Distributions of Sums, Products and Ratios of Inverted Bivariate Beta Distribution 1 A. S. Al-Ruzaiza and Awad El-Gohary 2 Department of
INFERENCE FOR MULTIPLE LINEAR REGRESSION MODEL WITH EXTENDED SKEW NORMAL ERRORS
 Pak. J. Statist. 2016 Vol. 32(2), 81-96 INFERENCE FOR MULTIPLE LINEAR REGRESSION MODEL WITH EXTENDED SKEW NORMAL ERRORS A.A. Alhamide 1, K. Ibrahim 1 M.T. Alodat 2 1 Statistics Program, School of Mathematical
Pak. J. Statist. 2016 Vol. 32(2), 81-96 INFERENCE FOR MULTIPLE LINEAR REGRESSION MODEL WITH EXTENDED SKEW NORMAL ERRORS A.A. Alhamide 1, K. Ibrahim 1 M.T. Alodat 2 1 Statistics Program, School of Mathematical
The closed-form resolution of integrals is one of the
 Construction of Generalized Integral Formulas By Means of Laplace Transformations Adam C. Buss, Department of Physics, Indiana University - Northwest Faculty Mentor: Dr. Axel Schulze-Halberg ABSTRACT We
Construction of Generalized Integral Formulas By Means of Laplace Transformations Adam C. Buss, Department of Physics, Indiana University - Northwest Faculty Mentor: Dr. Axel Schulze-Halberg ABSTRACT We
Bessel function - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Bessel function - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Bessel function Page 1 of 9 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In mathematics, Bessel functions, first defined by the mathematician Daniel Bernoulli
Bessel function - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Bessel function Page 1 of 9 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In mathematics, Bessel functions, first defined by the mathematician Daniel Bernoulli
2.2 The derivative as a Function
 2.2 The derivative as a Function Recall: The derivative of a function f at a fixed number a: f a f a+h f(a) = lim h 0 h Definition (Derivative of f) For any number x, the derivative of f is f x f x+h f(x)
2.2 The derivative as a Function Recall: The derivative of a function f at a fixed number a: f a f a+h f(a) = lim h 0 h Definition (Derivative of f) For any number x, the derivative of f is f x f x+h f(x)
Mth 133 Trigonometry Review Problems for the Final Examination
 Mth 1 Trigonometry Review Problems for the Final Examination Thomas W. Judson Stephen F. Austin State University Fall 017 Final Exam Details The final exam for MTH 1 will is comprehensive and will cover
Mth 1 Trigonometry Review Problems for the Final Examination Thomas W. Judson Stephen F. Austin State University Fall 017 Final Exam Details The final exam for MTH 1 will is comprehensive and will cover
arxiv:math/ v1 [math.st] 9 Nov 2005
![arxiv:math/ v1 [math.st] 9 Nov 2005 arxiv:math/ v1 [math.st] 9 Nov 2005](/thumbs/89/100784007.jpg) arxiv:math/511226v1 [math.st] 9 Nov 25 ASYMPTOTIC EXPANSION FOR INVERSE MOMENTS OF BINOMIAL AND POISSON DISTRIBUTIONS MARKO ŽNIDARIČ Abstract. An asymptotic expansion for inverse moments of positive binomial
arxiv:math/511226v1 [math.st] 9 Nov 25 ASYMPTOTIC EXPANSION FOR INVERSE MOMENTS OF BINOMIAL AND POISSON DISTRIBUTIONS MARKO ŽNIDARIČ Abstract. An asymptotic expansion for inverse moments of positive binomial
Math III Curriculum Map
 6 weeks Unit Unit Focus Common Core Math Standards 1 Rational and Irrational Numbers N-RN.3. Explain why the sum or product of two rational numbers is rational; that the sum of a rational number and an
6 weeks Unit Unit Focus Common Core Math Standards 1 Rational and Irrational Numbers N-RN.3. Explain why the sum or product of two rational numbers is rational; that the sum of a rational number and an
Nonlinear Autonomous Systems of Differential
 Chapter 4 Nonlinear Autonomous Systems of Differential Equations 4.0 The Phase Plane: Linear Systems 4.0.1 Introduction Consider a system of the form x = A(x), (4.0.1) where A is independent of t. Such
Chapter 4 Nonlinear Autonomous Systems of Differential Equations 4.0 The Phase Plane: Linear Systems 4.0.1 Introduction Consider a system of the form x = A(x), (4.0.1) where A is independent of t. Such
On the Ratio of two Independent Exponentiated Pareto Variables
 AUSTRIAN JOURNAL OF STATISTICS Volume 39 21), Number 4, 329 34 On the Ratio of two Independent Exponentiated Pareto Variables M. Masoom Ali 1, Manisha Pal 2 and Jungsoo Woo 3 1 Dept. of Mathematical Sciences,
AUSTRIAN JOURNAL OF STATISTICS Volume 39 21), Number 4, 329 34 On the Ratio of two Independent Exponentiated Pareto Variables M. Masoom Ali 1, Manisha Pal 2 and Jungsoo Woo 3 1 Dept. of Mathematical Sciences,
Math 113/113H Winter 2006 Departmental Final Exam
 Name KEY Instructor Section No. Student Number Math 3/3H Winter 26 Departmental Final Exam Instructions: The time limit is 3 hours. Problems -6 short-answer questions, each worth 2 points. Problems 7 through
Name KEY Instructor Section No. Student Number Math 3/3H Winter 26 Departmental Final Exam Instructions: The time limit is 3 hours. Problems -6 short-answer questions, each worth 2 points. Problems 7 through
Universal, non-asymptotic confidence sets for circular means
 Universal, non-asymptotic confidence sets for circular means Institut für Mathematik Technische Universität Ilmenau 2nd Conference on Geometric Science of Information 28 30 October 2015 École polytechnique,
Universal, non-asymptotic confidence sets for circular means Institut für Mathematik Technische Universität Ilmenau 2nd Conference on Geometric Science of Information 28 30 October 2015 École polytechnique,
( ) ( ) ( ) 2 6A: Special Trig Limits! Math 400
 2 6A: Special Trig Limits Math 400 This section focuses entirely on the its of 2 specific trigonometric functions. The use of Theorem and the indeterminate cases of Theorem are all considered. a The it
2 6A: Special Trig Limits Math 400 This section focuses entirely on the its of 2 specific trigonometric functions. The use of Theorem and the indeterminate cases of Theorem are all considered. a The it
MAT1035 Analytic Geometry
 MAT1035 Analytic Geometry Lecture Notes R.A. Sabri Kaan Gürbüzer Dokuz Eylül University 2016 2 Contents 1 Review of Trigonometry 5 2 Polar Coordinates 7 3 Vectors in R n 9 3.1 Located Vectors..............................................
MAT1035 Analytic Geometry Lecture Notes R.A. Sabri Kaan Gürbüzer Dokuz Eylül University 2016 2 Contents 1 Review of Trigonometry 5 2 Polar Coordinates 7 3 Vectors in R n 9 3.1 Located Vectors..............................................
Section 5.4 The Other Trigonometric Functions
 Section 5.4 The Other Trigonometric Functions Section 5.4 The Other Trigonometric Functions In the previous section, we defined the e and coe functions as ratios of the sides of a right triangle in a circle.
Section 5.4 The Other Trigonometric Functions Section 5.4 The Other Trigonometric Functions In the previous section, we defined the e and coe functions as ratios of the sides of a right triangle in a circle.
Bayesian inference for the location parameter of a Student-t density
 Bayesian inference for the location parameter of a Student-t density Jean-François Angers CRM-2642 February 2000 Dép. de mathématiques et de statistique; Université de Montréal; C.P. 628, Succ. Centre-ville
Bayesian inference for the location parameter of a Student-t density Jean-François Angers CRM-2642 February 2000 Dép. de mathématiques et de statistique; Université de Montréal; C.P. 628, Succ. Centre-ville
1.3 Distance and Midpoint Formulas
 Graduate Teacher Department of Mathematics San Diego State University Dynamical Systems Program August 29, 2011 In mathematics, a theorem is a statement that has been proven on the basis of previously
Graduate Teacher Department of Mathematics San Diego State University Dynamical Systems Program August 29, 2011 In mathematics, a theorem is a statement that has been proven on the basis of previously
Year 12 Maths C1-C2-S1 2016/2017
 Half Term 1 5 th September 12 th September 19 th September 26 th September 3 rd October 10 th October 17 th October Basic algebra and Laws of indices Factorising expressions Manipulating surds and rationalising
Half Term 1 5 th September 12 th September 19 th September 26 th September 3 rd October 10 th October 17 th October Basic algebra and Laws of indices Factorising expressions Manipulating surds and rationalising
CHAPTER 11 RADIATION 4/13/2017. Outlines. 1. Electric Dipole radiation. 2. Magnetic Dipole Radiation. 3. Point Charge. 4. Synchrotron Radiation
 CHAPTER 11 RADIATION Outlines 1. Electric Dipole radiation 2. Magnetic Dipole Radiation 3. Point Charge Lee Chow Department of Physics University of Central Florida Orlando, FL 32816 4. Synchrotron Radiation
CHAPTER 11 RADIATION Outlines 1. Electric Dipole radiation 2. Magnetic Dipole Radiation 3. Point Charge Lee Chow Department of Physics University of Central Florida Orlando, FL 32816 4. Synchrotron Radiation
Midterm Examination. STA 215: Statistical Inference. Due Wednesday, 2006 Mar 8, 1:15 pm
 Midterm Examination STA 215: Statistical Inference Due Wednesday, 2006 Mar 8, 1:15 pm This is an open-book take-home examination. You may work on it during any consecutive 24-hour period you like; please
Midterm Examination STA 215: Statistical Inference Due Wednesday, 2006 Mar 8, 1:15 pm This is an open-book take-home examination. You may work on it during any consecutive 24-hour period you like; please
REVIEW, pages
 REVIEW, pages 5 5.. Determine the value of each trigonometric ratio. Use eact values where possible; otherwise write the value to the nearest thousandth. a) tan (5 ) b) cos c) sec ( ) cos º cos ( ) cos
REVIEW, pages 5 5.. Determine the value of each trigonometric ratio. Use eact values where possible; otherwise write the value to the nearest thousandth. a) tan (5 ) b) cos c) sec ( ) cos º cos ( ) cos
Approximation of Circular Arcs by Parametric Polynomial Curves
 Approximation of Circular Arcs by Parametric Polynomial Curves Gašper Jaklič Jernej Kozak Marjeta Krajnc Emil Žagar September 19, 005 Abstract In this paper the approximation of circular arcs by parametric
Approximation of Circular Arcs by Parametric Polynomial Curves Gašper Jaklič Jernej Kozak Marjeta Krajnc Emil Žagar September 19, 005 Abstract In this paper the approximation of circular arcs by parametric
Year 12 Maths C1-C2-S1 2017/2018
 Half Term 1 5 th September 12 th September 19 th September 26 th September 3 rd October 10 th October 17 th October Basic algebra and Laws of indices Factorising expressions Manipulating surds and rationalising
Half Term 1 5 th September 12 th September 19 th September 26 th September 3 rd October 10 th October 17 th October Basic algebra and Laws of indices Factorising expressions Manipulating surds and rationalising
Likelihood Ratio tests
 Likelihood Ratio tests For general composite hypotheses optimality theory is not usually successful in producing an optimal test. instead we look for heuristics to guide our choices. The simplest approach
Likelihood Ratio tests For general composite hypotheses optimality theory is not usually successful in producing an optimal test. instead we look for heuristics to guide our choices. The simplest approach
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS GCE Ordinary Level (Syllabus 4018) CONTENTS Page NOTES 1 GCE ORDINARY LEVEL ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 4018 2 MATHEMATICAL NOTATION 7 4018 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS O LEVEL (2009) NOTES
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS GCE Ordinary Level (Syllabus 4018) CONTENTS Page NOTES 1 GCE ORDINARY LEVEL ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 4018 2 MATHEMATICAL NOTATION 7 4018 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS O LEVEL (2009) NOTES
Practice Final Exam Solutions
 Important Notice: To prepare for the final exam, study past exams and practice exams, and homeworks, quizzes, and worksheets, not just this practice final. A topic not being on the practice final does
Important Notice: To prepare for the final exam, study past exams and practice exams, and homeworks, quizzes, and worksheets, not just this practice final. A topic not being on the practice final does
I.e., the range of f(x) = arctan(x) is all real numbers y such that π 2 < y < π 2
 Inverse Trigonometric Functions: The inverse sine function, denoted by fx = arcsinx or fx = sin 1 x is defined by: y = sin 1 x if and only if siny = x and π y π I.e., the range of fx = arcsinx is all real
Inverse Trigonometric Functions: The inverse sine function, denoted by fx = arcsinx or fx = sin 1 x is defined by: y = sin 1 x if and only if siny = x and π y π I.e., the range of fx = arcsinx is all real
1. Compute the derivatives of the following functions, by any means necessary. f (x) = (1 x3 )(1/2)(x 2 1) 1/2 (2x) x 2 1( 3x 2 ) (1 x 3 ) 2
 Math 51 Exam Nov. 4, 009 SOLUTIONS Directions 1. SHOW YOUR WORK and be thorough in your solutions. Partial credit will only be given for work shown.. Any numerical answers should be left in exact form,
Math 51 Exam Nov. 4, 009 SOLUTIONS Directions 1. SHOW YOUR WORK and be thorough in your solutions. Partial credit will only be given for work shown.. Any numerical answers should be left in exact form,
) # ( 281). Give units with your answer.
 Math 120 Winter 2009 Handout 17: In-Class Review for Exam 2 The topics covered by Exam 2 in the course include the following: Implicit differentiation. Finding formulas for tangent lines using implicit
Math 120 Winter 2009 Handout 17: In-Class Review for Exam 2 The topics covered by Exam 2 in the course include the following: Implicit differentiation. Finding formulas for tangent lines using implicit
MODULE 1 PAPER 1 (3472/1)
 MODULE 1 PAPER 1 (347/1) FUNCTIONS 1. Given that h(x) =, x 0 and v(x) = 3x +, find hv 1 ) x ( x. p : t t + qp : t t + 4t + 1. Based on the above information, find the function of q. QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS
MODULE 1 PAPER 1 (347/1) FUNCTIONS 1. Given that h(x) =, x 0 and v(x) = 3x +, find hv 1 ) x ( x. p : t t + qp : t t + 4t + 1. Based on the above information, find the function of q. QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS
Elements of Vector Calculus : Line and Surface Integrals
 Elements of Vector Calculus : Line and Surface Integrals Lecture 2: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay In this lecture we will talk about special functions
Elements of Vector Calculus : Line and Surface Integrals Lecture 2: Electromagnetic Theory Professor D. K. Ghosh, Physics Department, I.I.T., Bombay In this lecture we will talk about special functions
Learning Objectives for Math 166
 Learning Objectives for Math 166 Chapter 6 Applications of Definite Integrals Section 6.1: Volumes Using Cross-Sections Draw and label both 2-dimensional perspectives and 3-dimensional sketches of the
Learning Objectives for Math 166 Chapter 6 Applications of Definite Integrals Section 6.1: Volumes Using Cross-Sections Draw and label both 2-dimensional perspectives and 3-dimensional sketches of the
Math 1310 Final Exam
 Math 1310 Final Exam December 11, 2014 NAME: INSTRUCTOR: Write neatly and show all your work in the space provided below each question. You may use the back of the exam pages if you need additional space
Math 1310 Final Exam December 11, 2014 NAME: INSTRUCTOR: Write neatly and show all your work in the space provided below each question. You may use the back of the exam pages if you need additional space
We saw in Section 5.1 that a limit of the form. arises when we compute an area.
 INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS Equation 1 We saw in Section 5.1 that a limit of the form n lim f ( x *) x n i 1 i lim[ f ( x *) x f ( x *) x... f ( x *) x] n 1 2 arises when we compute an area. n We also saw that
INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS Equation 1 We saw in Section 5.1 that a limit of the form n lim f ( x *) x n i 1 i lim[ f ( x *) x f ( x *) x... f ( x *) x] n 1 2 arises when we compute an area. n We also saw that
Near-exact approximations for the likelihood ratio test statistic for testing equality of several variance-covariance matrices
 Near-exact approximations for the likelihood ratio test statistic for testing euality of several variance-covariance matrices Carlos A. Coelho 1 Filipe J. Marues 1 Mathematics Department, Faculty of Sciences
Near-exact approximations for the likelihood ratio test statistic for testing euality of several variance-covariance matrices Carlos A. Coelho 1 Filipe J. Marues 1 Mathematics Department, Faculty of Sciences
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER INTEGRATION APPLICATIONS 13 (Second moments of a volume (A)) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 13.13 INTEGRATION APPLICATIONS 13 (Second moments of a volume (A)) by A.J.Hobson 13.13.1 Introduction 13.13. The second moment of a volume of revolution about the y-axis 13.13.3
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 13.13 INTEGRATION APPLICATIONS 13 (Second moments of a volume (A)) by A.J.Hobson 13.13.1 Introduction 13.13. The second moment of a volume of revolution about the y-axis 13.13.3
True or False. Circle T if the statement is always true; otherwise circle F. for all angles θ. T F. 1 sin θ
 Math 90 Practice Midterm III Solutions Ch. 8-0 (Ebersole), 3.3-3.8 (Stewart) DISCLAIMER. This collection of practice problems is not guaranteed to be identical, in length or content, to the actual exam.
Math 90 Practice Midterm III Solutions Ch. 8-0 (Ebersole), 3.3-3.8 (Stewart) DISCLAIMER. This collection of practice problems is not guaranteed to be identical, in length or content, to the actual exam.
Some Expectations of a Non-Central Chi-Square Distribution With an Even Number of Degrees of Freedom
 Some Expectations of a Non-Central Chi-Square Distribution With an Even Number of Degrees of Freedom Stefan M. Moser April 7, 007 Abstract The non-central chi-square distribution plays an important role
Some Expectations of a Non-Central Chi-Square Distribution With an Even Number of Degrees of Freedom Stefan M. Moser April 7, 007 Abstract The non-central chi-square distribution plays an important role
2.8 Linear Approximation and Differentials
 2.8 Linear Approximation Contemporary Calculus 1 2.8 Linear Approximation and Differentials Newton's method used tangent lines to "point toward" a root of the function. In this section we examine and use
2.8 Linear Approximation Contemporary Calculus 1 2.8 Linear Approximation and Differentials Newton's method used tangent lines to "point toward" a root of the function. In this section we examine and use
Transformation formulas for the generalized hypergeometric function with integral parameter differences
 Transformation formulas for the generalized hypergeometric function with integral parameter differences A. R. Miller Formerly Professor of Mathematics at George Washington University, 66 8th Street NW,
Transformation formulas for the generalized hypergeometric function with integral parameter differences A. R. Miller Formerly Professor of Mathematics at George Washington University, 66 8th Street NW,
Directional Statistics
 Directional Statistics Kanti V. Mardia University of Leeds, UK Peter E. Jupp University of St Andrews, UK I JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD Chichester New York Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto Contents Preface
Directional Statistics Kanti V. Mardia University of Leeds, UK Peter E. Jupp University of St Andrews, UK I JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD Chichester New York Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto Contents Preface
This is the number of cycles per unit time, and its units are, for example,
 16 4. Sinusoidal solutions Many things in nature are periodic, even sinusoidal. We will begin by reviewing terms surrounding periodic functions. If an LTI system is fed a periodic input signal, we have
16 4. Sinusoidal solutions Many things in nature are periodic, even sinusoidal. We will begin by reviewing terms surrounding periodic functions. If an LTI system is fed a periodic input signal, we have
Asymptotics of Integrals of. Hermite Polynomials
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 4, 010, no. 61, 04-056 Asymptotics of Integrals of Hermite Polynomials R. B. Paris Division of Complex Systems University of Abertay Dundee Dundee DD1 1HG, UK R.Paris@abertay.ac.uk
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 4, 010, no. 61, 04-056 Asymptotics of Integrals of Hermite Polynomials R. B. Paris Division of Complex Systems University of Abertay Dundee Dundee DD1 1HG, UK R.Paris@abertay.ac.uk
The effect of wind direction on ozone levels - a case study
 The effect of wind direction on ozone levels - a case study S. Rao Jammalamadaka and Ulric J. Lund University of California, Santa Barbara and California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo Abstract
The effect of wind direction on ozone levels - a case study S. Rao Jammalamadaka and Ulric J. Lund University of California, Santa Barbara and California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo Abstract
Eco517 Fall 2004 C. Sims MIDTERM EXAM
 Eco517 Fall 2004 C. Sims MIDTERM EXAM Answer all four questions. Each is worth 23 points. Do not devote disproportionate time to any one question unless you have answered all the others. (1) We are considering
Eco517 Fall 2004 C. Sims MIDTERM EXAM Answer all four questions. Each is worth 23 points. Do not devote disproportionate time to any one question unless you have answered all the others. (1) We are considering

 Inference for P(Y
Inference for P(Y