Math 362, Problem set 1
|
|
|
- Denis Reed
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 6, roblem set Due //. (4..8) Determine the mean variance of the mean X of a rom sample of size 9 from a distribution having pdf f(x) = 4x, < x <, zero elsewhere. We have that: Using the pdf, so E[ X] = E[ n Xi ] = n ne[x i] = E[X i ] var( X) = var( X i ) n = var(x i). n E[X] = E[X ] = var(x i ) = ( 4 5 4x 4 dx = x 5 dx =, var( X) = 675. ) = 75,. (4..5) Let S = n (Xi X) d denote the sample variance of a rom sample from a distribution with variance σ >. Since E[S ] = σ, why isn t E[S] = σ? Note: There is a hint in the book that gives it away, but maybe think about it for a second before looking there. This follows from the fact that f(x) = x is strictly convex (that is f (x) = >, from Jensen s inequality: σ = E[S ] > (E[S] ),
2 so E[S] < σ. Note: some of you also (cleverly) noticed this follows from the fact that var(s) >.. (5..4) Let X,..., X n be a rom sample from the Γ(, θ) distribution, where θ is unknown. (Recall, look back in chapter if you forget the specifics of the Γ distribution). Let Y = n i= X i. (a) Find the distribution of Y determine c so that cy is anunbiased estimator of θ. (b) If n = 5 show that (9.59 < Yθ ) < 4. =.95 (c) Using (b), show that if y is the value of Y once the sample is drawn then the interval ( ) y 4., y 9.59 is a 95% confidence interval for Θ. (d) Suppose the sample results in the values, Based on these data, obtain the point estimate of θ as described in art (a) the computed 95% confidence interval in art (c). What does the confidence interval mean? For (a), Y Γ(n, θ) by the additive property of the Gamma distribution. Thus E[Y ] = nθ we should take c = n. For (b), we will simply set up the integral. (9.59 < Yθ ) < 4. = (4.795θ < Y < 7.θ) = = 7.θ 4.795θ !θ x9 e x/θ dx u 9 9! e u du = Note: The important part here is that this does not depend on θ.
3 For (c), note that: (9.59 < Yθ ) < 4. = ( y 4. < θ < y 9.59 ) =.95 so the given interval is a 95% confidence interval. For (d), θ y n =.8654, we have a confidence interval of (6.685,.84), meaning that the true value of θ has a 95% chance of ling between these values. 4. (5..5) Suppose the number of customers X that enter a store between the hours of 9AM AM follows a oisson distribution with parameter θ. Suppose a rom sample of the number of customers for days results in the values Based on these data obtain an unbiased point estimate of θ. Explain the meaning of this estimate in terms of the number of customers. Since E[X] = θ for a oisson θ rom variable, we have a point estimate of 9.5 customers per day. (Of course while it is impossible to actually obtain this on any given day, but it s a fine estimate of the average - it s even perfectly fine if it is the true mean of the distribution. 5. (5..) Obtain the probability that an observationis a potential outlier for the following distributions (a) The underlying distribution is normal (b) The underlying distribution is logistic, in other words it has pdf: f(x) = e x ( + e x ), < x < (c) The underlying distribution is Laplace, the pdf given by: f(x) = e x, < x <. For (a), we find (from the back of the book) that Q =.675 Q =.675.
4 Thus h =.5, UF =.7 LF =.7. We have (Z > UF ) =.46697, so (LF < Z < UF ) =.9966, so the probability of a potential outlier is.7 For (b), we have that Q e x ( + e x ) dx = 4, similar for Q. We thus get Q = ln() Q = ln(). Thus h = ln(), UF = 4 ln() LF = 4 ln(). We have then, that the (LF < X < UF ) = 4 ln() 4 ln() e x 4 ( + e x dx = ) 4, so the probability of a potential outlier is For (c) we have that Q e x = 4. Solving, we find Q = ln() likewise Q = ln(). Thus h = ln(), we have UF = 4 ln() LF = 4 ln(). Since 4 ln() 4 ln() e x dx = 5 6. Thus the probability of a potential outlier is 6 = (5..5) Let Y < Y < Y < Y 4 be the order statistics of a rom sample of size 4 from the distribution having pdf f(x) = e x, < x <, zero elsewhere. Find ( Y 4 ). We have that F (x) = x e t dx = e t. Using the formula we derived in class: (Y 4 ) = 4( e t ) e t dt = ( e ) (5..) Let Y < Y < Y be the order statistics of a rom sample of size from a distribution having the pdf f(x) = x, < x <, zero elsewhere. Show that Z = Y /Y, Z = Y /Y Z = Y are mutually independent. 4
5 We have that Y = Z, Y = Z Z Y = Z Z Z. Thus, z z z z z z J = z z = z z. We have f Z,Z,Z (z, z, z ) = f Y,Y,Y (z z z, z z, z )z z =!(z z z )(z z )(z )(z z) = (z )(4z )(6z 5 ), where < z i <. This is the product of the marginal pdfs of Z, Z Z which shows that the variables are mutually independent. 8. (5..) Let X, X,..., X n be a rom sample. A measure of spread is Gini s mean difference n j ( ) n G = X i X j / j= i= (a) If n =, find a,..., a so that G = i= a iy i, where Y, Y,..., Y are the order statistics of the sample. (b) Show that E[G] = σ/ π if the sample arises from the normal distribution N(µ, σ ). Hint: This looks worse than it is: Think about the fact that X i X j is either X i X j or X j X i depending on which is larger. The Y i appear in the sum G, as they are some X j. The key observation is that Y i Y j = Y i Y j if i > j Y i Y j = Y j Y i, if i < j. Thus Y i appears with a positive sign i times, with a negative sign n i times. In all, Y i has coefficient: (i ) (n i) a i = ( n. ) Since n = 9, we have that for i =,..., 9.. a i = i 45 For (b), note that E[G] = E[ X i X j ]. Since X i X j N(, σ ) we have that E[ X i X j ] = = x x (π)(σ ) exp( σ )dx σ e u du = σ. π π 5
Two hours. Statistical Tables to be provided THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER. 14 January :45 11:45
 Two hours Statistical Tables to be provided THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER PROBABILITY 2 14 January 2015 09:45 11:45 Answer ALL four questions in Section A (40 marks in total) and TWO of the THREE questions
Two hours Statistical Tables to be provided THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER PROBABILITY 2 14 January 2015 09:45 11:45 Answer ALL four questions in Section A (40 marks in total) and TWO of the THREE questions
STA 2201/442 Assignment 2
 STA 2201/442 Assignment 2 1. This is about how to simulate from a continuous univariate distribution. Let the random variable X have a continuous distribution with density f X (x) and cumulative distribution
STA 2201/442 Assignment 2 1. This is about how to simulate from a continuous univariate distribution. Let the random variable X have a continuous distribution with density f X (x) and cumulative distribution
Statistics STAT:5100 (22S:193), Fall Sample Final Exam B
 Statistics STAT:5 (22S:93), Fall 25 Sample Final Exam B Please write your answers in the exam books provided.. Let X, Y, and Y 2 be independent random variables with X N(µ X, σ 2 X ) and Y i N(µ Y, σ 2
Statistics STAT:5 (22S:93), Fall 25 Sample Final Exam B Please write your answers in the exam books provided.. Let X, Y, and Y 2 be independent random variables with X N(µ X, σ 2 X ) and Y i N(µ Y, σ 2
Stat410 Probability and Statistics II (F16)
 Stat4 Probability and Statistics II (F6 Exponential, Poisson and Gamma Suppose on average every /λ hours, a Stochastic train arrives at the Random station. Further we assume the waiting time between two
Stat4 Probability and Statistics II (F6 Exponential, Poisson and Gamma Suppose on average every /λ hours, a Stochastic train arrives at the Random station. Further we assume the waiting time between two
Space Telescope Science Institute statistics mini-course. October Inference I: Estimation, Confidence Intervals, and Tests of Hypotheses
 Space Telescope Science Institute statistics mini-course October 2011 Inference I: Estimation, Confidence Intervals, and Tests of Hypotheses James L Rosenberger Acknowledgements: Donald Richards, William
Space Telescope Science Institute statistics mini-course October 2011 Inference I: Estimation, Confidence Intervals, and Tests of Hypotheses James L Rosenberger Acknowledgements: Donald Richards, William
Probability and Distributions
 Probability and Distributions What is a statistical model? A statistical model is a set of assumptions by which the hypothetical population distribution of data is inferred. It is typically postulated
Probability and Distributions What is a statistical model? A statistical model is a set of assumptions by which the hypothetical population distribution of data is inferred. It is typically postulated
6 The normal distribution, the central limit theorem and random samples
 6 The normal distribution, the central limit theorem and random samples 6.1 The normal distribution We mentioned the normal (or Gaussian) distribution in Chapter 4. It has density f X (x) = 1 σ 1 2π e
6 The normal distribution, the central limit theorem and random samples 6.1 The normal distribution We mentioned the normal (or Gaussian) distribution in Chapter 4. It has density f X (x) = 1 σ 1 2π e
Mathematical Statistics
 Mathematical Statistics Chapter Three. Point Estimation 3.4 Uniformly Minimum Variance Unbiased Estimator(UMVUE) Criteria for Best Estimators MSE Criterion Let F = {p(x; θ) : θ Θ} be a parametric distribution
Mathematical Statistics Chapter Three. Point Estimation 3.4 Uniformly Minimum Variance Unbiased Estimator(UMVUE) Criteria for Best Estimators MSE Criterion Let F = {p(x; θ) : θ Θ} be a parametric distribution
Distributions of Functions of Random Variables. 5.1 Functions of One Random Variable
 Distributions of Functions of Random Variables 5.1 Functions of One Random Variable 5.2 Transformations of Two Random Variables 5.3 Several Random Variables 5.4 The Moment-Generating Function Technique
Distributions of Functions of Random Variables 5.1 Functions of One Random Variable 5.2 Transformations of Two Random Variables 5.3 Several Random Variables 5.4 The Moment-Generating Function Technique
Statistics & Data Sciences: First Year Prelim Exam May 2018
 Statistics & Data Sciences: First Year Prelim Exam May 2018 Instructions: 1. Do not turn this page until instructed to do so. 2. Start each new question on a new sheet of paper. 3. This is a closed book
Statistics & Data Sciences: First Year Prelim Exam May 2018 Instructions: 1. Do not turn this page until instructed to do so. 2. Start each new question on a new sheet of paper. 3. This is a closed book
4. Distributions of Functions of Random Variables
 4. Distributions of Functions of Random Variables Setup: Consider as given the joint distribution of X 1,..., X n (i.e. consider as given f X1,...,X n and F X1,...,X n ) Consider k functions g 1 : R n
4. Distributions of Functions of Random Variables Setup: Consider as given the joint distribution of X 1,..., X n (i.e. consider as given f X1,...,X n and F X1,...,X n ) Consider k functions g 1 : R n
EXAMINATIONS OF THE HONG KONG STATISTICAL SOCIETY
 EXAMINATIONS OF THE HONG KONG STATISTICAL SOCIETY HIGHER CERTIFICATE IN STATISTICS, 2013 MODULE 5 : Further probability and inference Time allowed: One and a half hours Candidates should answer THREE questions.
EXAMINATIONS OF THE HONG KONG STATISTICAL SOCIETY HIGHER CERTIFICATE IN STATISTICS, 2013 MODULE 5 : Further probability and inference Time allowed: One and a half hours Candidates should answer THREE questions.
Spring 2012 Math 541B Exam 1
 Spring 2012 Math 541B Exam 1 1. A sample of size n is drawn without replacement from an urn containing N balls, m of which are red and N m are black; the balls are otherwise indistinguishable. Let X denote
Spring 2012 Math 541B Exam 1 1. A sample of size n is drawn without replacement from an urn containing N balls, m of which are red and N m are black; the balls are otherwise indistinguishable. Let X denote
SOLUTION FOR HOMEWORK 7, STAT p(x σ) = (1/[2πσ 2 ] 1/2 )e (x µ)2 /2σ 2.
![SOLUTION FOR HOMEWORK 7, STAT p(x σ) = (1/[2πσ 2 ] 1/2 )e (x µ)2 /2σ 2. SOLUTION FOR HOMEWORK 7, STAT p(x σ) = (1/[2πσ 2 ] 1/2 )e (x µ)2 /2σ 2.](/thumbs/88/116543015.jpg) SOLUTION FOR HOMEWORK 7, STAT 6332 1. We have (for a general case) Denote p (x) p(x σ)/ σ. Then p(x σ) (1/[2πσ 2 ] 1/2 )e (x µ)2 /2σ 2. p (x σ) p(x σ) 1 (x µ)2 +. σ σ 3 Then E{ p (x σ) p(x σ) } σ 2 2σ
SOLUTION FOR HOMEWORK 7, STAT 6332 1. We have (for a general case) Denote p (x) p(x σ)/ σ. Then p(x σ) (1/[2πσ 2 ] 1/2 )e (x µ)2 /2σ 2. p (x σ) p(x σ) 1 (x µ)2 +. σ σ 3 Then E{ p (x σ) p(x σ) } σ 2 2σ
THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY GRADUATE DIPLOMA
 THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY 4 EXAINATIONS SOLUTIONS GRADUATE DIPLOA PAPER I STATISTICAL THEORY & ETHODS The Societ provides these solutions to assist candidates preparing for the examinations in future
THE ROYAL STATISTICAL SOCIETY 4 EXAINATIONS SOLUTIONS GRADUATE DIPLOA PAPER I STATISTICAL THEORY & ETHODS The Societ provides these solutions to assist candidates preparing for the examinations in future
M(t) = 1 t. (1 t), 6 M (0) = 20 P (95. X i 110) i=1
 Math 66/566 - Midterm Solutions NOTE: These solutions are for both the 66 and 566 exam. The problems are the same until questions and 5. 1. The moment generating function of a random variable X is M(t)
Math 66/566 - Midterm Solutions NOTE: These solutions are for both the 66 and 566 exam. The problems are the same until questions and 5. 1. The moment generating function of a random variable X is M(t)
T has many other desirable properties, and we will return to this example
 2. Introduction to statistics: first examples 2.1. Introduction. The basic problem of statistics is to draw conclusions about unknown distributions of random variables from observed values. These conclusions
2. Introduction to statistics: first examples 2.1. Introduction. The basic problem of statistics is to draw conclusions about unknown distributions of random variables from observed values. These conclusions
Continuous Random Variables
 MATH 38 Continuous Random Variables Dr. Neal, WKU Throughout, let Ω be a sample space with a defined probability measure P. Definition. A continuous random variable is a real-valued function X defined
MATH 38 Continuous Random Variables Dr. Neal, WKU Throughout, let Ω be a sample space with a defined probability measure P. Definition. A continuous random variable is a real-valued function X defined
ECE534, Spring 2018: Solutions for Problem Set #3
 ECE534, Spring 08: Solutions for Problem Set #3 Jointly Gaussian Random Variables and MMSE Estimation Suppose that X, Y are jointly Gaussian random variables with µ X = µ Y = 0 and σ X = σ Y = Let their
ECE534, Spring 08: Solutions for Problem Set #3 Jointly Gaussian Random Variables and MMSE Estimation Suppose that X, Y are jointly Gaussian random variables with µ X = µ Y = 0 and σ X = σ Y = Let their
Stat 426 : Homework 1.
 Stat 426 : Homework 1. Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan Announcement: The homework carries 120 points and contributes 10 points to the total grade. (1) A geometric random variable W takes values
Stat 426 : Homework 1. Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan Announcement: The homework carries 120 points and contributes 10 points to the total grade. (1) A geometric random variable W takes values
MATH 151, FINAL EXAM Winter Quarter, 21 March, 2014
 Time: 3 hours, 8:3-11:3 Instructions: MATH 151, FINAL EXAM Winter Quarter, 21 March, 214 (1) Write your name in blue-book provided and sign that you agree to abide by the honor code. (2) The exam consists
Time: 3 hours, 8:3-11:3 Instructions: MATH 151, FINAL EXAM Winter Quarter, 21 March, 214 (1) Write your name in blue-book provided and sign that you agree to abide by the honor code. (2) The exam consists
Partial Solutions for h4/2014s: Sampling Distributions
 27 Partial Solutions for h4/24s: Sampling Distributions ( Let X and X 2 be two independent random variables, each with the same probability distribution given as follows. f(x 2 e x/2, x (a Compute the
27 Partial Solutions for h4/24s: Sampling Distributions ( Let X and X 2 be two independent random variables, each with the same probability distribution given as follows. f(x 2 e x/2, x (a Compute the
Final Exam. 1. (6 points) True/False. Please read the statements carefully, as no partial credit will be given.
 1. (6 points) True/False. Please read the statements carefully, as no partial credit will be given. (a) If X and Y are independent, Corr(X, Y ) = 0. (b) (c) (d) (e) A consistent estimator must be asymptotically
1. (6 points) True/False. Please read the statements carefully, as no partial credit will be given. (a) If X and Y are independent, Corr(X, Y ) = 0. (b) (c) (d) (e) A consistent estimator must be asymptotically
Part IA Probability. Theorems. Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua. Lent 2015
 Part IA Probability Theorems Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Part IA Probability Theorems Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
This exam is closed book and closed notes. (You will have access to a copy of the Table of Common Distributions given in the back of the text.
 TEST #3 STA 5326 December 4, 214 Name: Please read the following directions. DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO Directions This exam is closed book and closed notes. (You will have access to
TEST #3 STA 5326 December 4, 214 Name: Please read the following directions. DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO Directions This exam is closed book and closed notes. (You will have access to
Joint Probability Distributions and Random Samples (Devore Chapter Five)
 Joint Probability Distributions and Random Samples (Devore Chapter Five) 1016-345-01: Probability and Statistics for Engineers Spring 2013 Contents 1 Joint Probability Distributions 2 1.1 Two Discrete
Joint Probability Distributions and Random Samples (Devore Chapter Five) 1016-345-01: Probability and Statistics for Engineers Spring 2013 Contents 1 Joint Probability Distributions 2 1.1 Two Discrete
Part IA Probability. Definitions. Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua. Lent 2015
 Part IA Probability Definitions Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Part IA Probability Definitions Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
IIT JAM : MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS (MS) 2013
 IIT JAM : MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS (MS 2013 Question Paper with Answer Keys Ctanujit Classes Of Mathematics, Statistics & Economics Visit our website for more: www.ctanujit.in IMPORTANT NOTE FOR CANDIDATES
IIT JAM : MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS (MS 2013 Question Paper with Answer Keys Ctanujit Classes Of Mathematics, Statistics & Economics Visit our website for more: www.ctanujit.in IMPORTANT NOTE FOR CANDIDATES
MATH Solutions to Probability Exercises
 MATH 5 9 MATH 5 9 Problem. Suppose we flip a fair coin once and observe either T for tails or H for heads. Let X denote the random variable that equals when we observe tails and equals when we observe
MATH 5 9 MATH 5 9 Problem. Suppose we flip a fair coin once and observe either T for tails or H for heads. Let X denote the random variable that equals when we observe tails and equals when we observe
SOLUTIONS TO MATH68181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO MATH68181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question A1 a) The marginal cdfs of F X,Y (x, y) = [1 + exp( x) + exp( y) + (1 α) exp( x y)] 1 are F X (x) = F X,Y (x, ) = [1
SOLUTIONS TO MATH68181 EXTREME VALUES AND FINANCIAL RISK EXAM Solutions to Question A1 a) The marginal cdfs of F X,Y (x, y) = [1 + exp( x) + exp( y) + (1 α) exp( x y)] 1 are F X (x) = F X,Y (x, ) = [1
Definition 1.1 (Parametric family of distributions) A parametric distribution is a set of distribution functions, each of which is determined by speci
 Definition 1.1 (Parametric family of distributions) A parametric distribution is a set of distribution functions, each of which is determined by specifying one or more values called parameters. The number
Definition 1.1 (Parametric family of distributions) A parametric distribution is a set of distribution functions, each of which is determined by specifying one or more values called parameters. The number
Problem 1 (20) Log-normal. f(x) Cauchy
 ORF 245. Rigollet Date: 11/21/2008 Problem 1 (20) f(x) f(x) 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 4 2 0 2 4 Normal (with mean -1) 4 2 0 2 4 Negative-exponential x x f(x) f(x) 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
ORF 245. Rigollet Date: 11/21/2008 Problem 1 (20) f(x) f(x) 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 4 2 0 2 4 Normal (with mean -1) 4 2 0 2 4 Negative-exponential x x f(x) f(x) 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
Exercises and Answers to Chapter 1
 Exercises and Answers to Chapter The continuous type of random variable X has the following density function: a x, if < x < a, f (x), otherwise. Answer the following questions. () Find a. () Obtain mean
Exercises and Answers to Chapter The continuous type of random variable X has the following density function: a x, if < x < a, f (x), otherwise. Answer the following questions. () Find a. () Obtain mean
Problem Solving. Correlation and Covariance. Yi Lu. Problem Solving. Yi Lu ECE 313 2/51
 Yi Lu Correlation and Covariance Yi Lu ECE 313 2/51 Definition Let X and Y be random variables with finite second moments. the correlation: E[XY ] Yi Lu ECE 313 3/51 Definition Let X and Y be random variables
Yi Lu Correlation and Covariance Yi Lu ECE 313 2/51 Definition Let X and Y be random variables with finite second moments. the correlation: E[XY ] Yi Lu ECE 313 3/51 Definition Let X and Y be random variables
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences FINAL EXAMINATION, APRIL 2013
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences FINAL EXAMINATION, APRIL 2013 STAB57H3 Introduction to Statistics Duration: 3 hours Last Name: First Name: Student number:
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences FINAL EXAMINATION, APRIL 2013 STAB57H3 Introduction to Statistics Duration: 3 hours Last Name: First Name: Student number:
18 Bivariate normal distribution I
 8 Bivariate normal distribution I 8 Example Imagine firing arrows at a target Hopefully they will fall close to the target centre As we fire more arrows we find a high density near the centre and fewer
8 Bivariate normal distribution I 8 Example Imagine firing arrows at a target Hopefully they will fall close to the target centre As we fire more arrows we find a high density near the centre and fewer
If g is also continuous and strictly increasing on J, we may apply the strictly increasing inverse function g 1 to this inequality to get
 18:2 1/24/2 TOPIC. Inequalities; measures of spread. This lecture explores the implications of Jensen s inequality for g-means in general, and for harmonic, geometric, arithmetic, and related means in
18:2 1/24/2 TOPIC. Inequalities; measures of spread. This lecture explores the implications of Jensen s inequality for g-means in general, and for harmonic, geometric, arithmetic, and related means in
Homework 10 (due December 2, 2009)
 Homework (due December, 9) Problem. Let X and Y be independent binomial random variables with parameters (n, p) and (n, p) respectively. Prove that X + Y is a binomial random variable with parameters (n
Homework (due December, 9) Problem. Let X and Y be independent binomial random variables with parameters (n, p) and (n, p) respectively. Prove that X + Y is a binomial random variable with parameters (n
f (1 0.5)/n Z =
 Math 466/566 - Homework 4. We want to test a hypothesis involving a population proportion. The unknown population proportion is p. The null hypothesis is p = / and the alternative hypothesis is p > /.
Math 466/566 - Homework 4. We want to test a hypothesis involving a population proportion. The unknown population proportion is p. The null hypothesis is p = / and the alternative hypothesis is p > /.
Lecture 1: August 28
 36-705: Intermediate Statistics Fall 2017 Lecturer: Siva Balakrishnan Lecture 1: August 28 Our broad goal for the first few lectures is to try to understand the behaviour of sums of independent random
36-705: Intermediate Statistics Fall 2017 Lecturer: Siva Balakrishnan Lecture 1: August 28 Our broad goal for the first few lectures is to try to understand the behaviour of sums of independent random
Chapter 1: Revie of Calculus and Probability
 Chapter 1: Revie of Calculus and Probability Refer to Text Book: Operations Research: Applications and Algorithms By Wayne L. Winston,Ch. 12 Operations Research: An Introduction By Hamdi Taha, Ch. 12 OR441-Dr.Khalid
Chapter 1: Revie of Calculus and Probability Refer to Text Book: Operations Research: Applications and Algorithms By Wayne L. Winston,Ch. 12 Operations Research: An Introduction By Hamdi Taha, Ch. 12 OR441-Dr.Khalid
f(x θ)dx with respect to θ. Assuming certain smoothness conditions concern differentiating under the integral the integral sign, we first obtain
 0.1. INTRODUCTION 1 0.1 Introduction R. A. Fisher, a pioneer in the development of mathematical statistics, introduced a measure of the amount of information contained in an observaton from f(x θ). Fisher
0.1. INTRODUCTION 1 0.1 Introduction R. A. Fisher, a pioneer in the development of mathematical statistics, introduced a measure of the amount of information contained in an observaton from f(x θ). Fisher
Economics 520. Lecture Note 19: Hypothesis Testing via the Neyman-Pearson Lemma CB 8.1,
 Economics 520 Lecture Note 9: Hypothesis Testing via the Neyman-Pearson Lemma CB 8., 8.3.-8.3.3 Uniformly Most Powerful Tests and the Neyman-Pearson Lemma Let s return to the hypothesis testing problem
Economics 520 Lecture Note 9: Hypothesis Testing via the Neyman-Pearson Lemma CB 8., 8.3.-8.3.3 Uniformly Most Powerful Tests and the Neyman-Pearson Lemma Let s return to the hypothesis testing problem
15 Discrete Distributions
 Lecture Note 6 Special Distributions (Discrete and Continuous) MIT 4.30 Spring 006 Herman Bennett 5 Discrete Distributions We have already seen the binomial distribution and the uniform distribution. 5.
Lecture Note 6 Special Distributions (Discrete and Continuous) MIT 4.30 Spring 006 Herman Bennett 5 Discrete Distributions We have already seen the binomial distribution and the uniform distribution. 5.
MATH c UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS Examination for the Module MATH2715 (January 2015) STATISTICAL METHODS. Time allowed: 2 hours
 MATH2750 This question paper consists of 8 printed pages, each of which is identified by the reference MATH275. All calculators must carry an approval sticker issued by the School of Mathematics. c UNIVERSITY
MATH2750 This question paper consists of 8 printed pages, each of which is identified by the reference MATH275. All calculators must carry an approval sticker issued by the School of Mathematics. c UNIVERSITY
STA 4321/5325 Solution to Homework 5 March 3, 2017
 STA 4/55 Solution to Homework 5 March, 7. Suppose X is a RV with E(X and V (X 4. Find E(X +. By the formula, V (X E(X E (X E(X V (X + E (X. Therefore, in the current setting, E(X V (X + E (X 4 + 4 8. Therefore,
STA 4/55 Solution to Homework 5 March, 7. Suppose X is a RV with E(X and V (X 4. Find E(X +. By the formula, V (X E(X E (X E(X V (X + E (X. Therefore, in the current setting, E(X V (X + E (X 4 + 4 8. Therefore,
Recitation 2: Probability
 Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
Proving the central limit theorem
 SOR3012: Stochastic Processes Proving the central limit theorem Gareth Tribello March 3, 2019 1 Purpose In the lectures and exercises we have learnt about the law of large numbers and the central limit
SOR3012: Stochastic Processes Proving the central limit theorem Gareth Tribello March 3, 2019 1 Purpose In the lectures and exercises we have learnt about the law of large numbers and the central limit
Sampling Distributions
 In statistics, a random sample is a collection of independent and identically distributed (iid) random variables, and a sampling distribution is the distribution of a function of random sample. For example,
In statistics, a random sample is a collection of independent and identically distributed (iid) random variables, and a sampling distribution is the distribution of a function of random sample. For example,
MAS223 Statistical Inference and Modelling Exercises
 MAS223 Statistical Inference and Modelling Exercises The exercises are grouped into sections, corresponding to chapters of the lecture notes Within each section exercises are divided into warm-up questions,
MAS223 Statistical Inference and Modelling Exercises The exercises are grouped into sections, corresponding to chapters of the lecture notes Within each section exercises are divided into warm-up questions,
Continuous Random Variables
 1 / 24 Continuous Random Variables Saravanan Vijayakumaran sarva@ee.iitb.ac.in Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay February 27, 2013 2 / 24 Continuous Random Variables
1 / 24 Continuous Random Variables Saravanan Vijayakumaran sarva@ee.iitb.ac.in Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay February 27, 2013 2 / 24 Continuous Random Variables
5.2 Continuous random variables
 5.2 Continuous random variables It is often convenient to think of a random variable as having a whole (continuous) interval for its set of possible values. The devices used to describe continuous probability
5.2 Continuous random variables It is often convenient to think of a random variable as having a whole (continuous) interval for its set of possible values. The devices used to describe continuous probability
Solution. (i) Find a minimal sufficient statistic for (θ, β) and give your justification. X i=1. By the factorization theorem, ( n
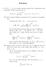 Solution 1. Let (X 1,..., X n ) be a simple random sample from a distribution with probability density function given by f(x;, β) = 1 ( ) 1 β x β, 0 x, > 0, β < 1. β (i) Find a minimal sufficient statistic
Solution 1. Let (X 1,..., X n ) be a simple random sample from a distribution with probability density function given by f(x;, β) = 1 ( ) 1 β x β, 0 x, > 0, β < 1. β (i) Find a minimal sufficient statistic
EXAM. Exam #1. Math 3342 Summer II, July 21, 2000 ANSWERS
 EXAM Exam # Math 3342 Summer II, 2 July 2, 2 ANSWERS i pts. Problem. Consider the following data: 7, 8, 9, 2,, 7, 2, 3. Find the first quartile, the median, and the third quartile. Make a box and whisker
EXAM Exam # Math 3342 Summer II, 2 July 2, 2 ANSWERS i pts. Problem. Consider the following data: 7, 8, 9, 2,, 7, 2, 3. Find the first quartile, the median, and the third quartile. Make a box and whisker
This exam contains 6 questions. The questions are of equal weight. Print your name at the top of this page in the upper right hand corner.
 GROUND RULES: This exam contains 6 questions. The questions are of equal weight. Print your name at the top of this page in the upper right hand corner. This exam is closed book and closed notes. Show
GROUND RULES: This exam contains 6 questions. The questions are of equal weight. Print your name at the top of this page in the upper right hand corner. This exam is closed book and closed notes. Show
S n = x + X 1 + X X n.
 0 Lecture 0 0. Gambler Ruin Problem Let X be a payoff if a coin toss game such that P(X = ) = P(X = ) = /2. Suppose you start with x dollars and play the game n times. Let X,X 2,...,X n be payoffs in each
0 Lecture 0 0. Gambler Ruin Problem Let X be a payoff if a coin toss game such that P(X = ) = P(X = ) = /2. Suppose you start with x dollars and play the game n times. Let X,X 2,...,X n be payoffs in each
3 Modeling Process Quality
 3 Modeling Process Quality 3.1 Introduction Section 3.1 contains basic numerical and graphical methods. familiar with these methods. It is assumed the student is Goal: Review several discrete and continuous
3 Modeling Process Quality 3.1 Introduction Section 3.1 contains basic numerical and graphical methods. familiar with these methods. It is assumed the student is Goal: Review several discrete and continuous
2. Suppose (X, Y ) is a pair of random variables uniformly distributed over the triangle with vertices (0, 0), (2, 0), (2, 1).
 Name M362K Final Exam Instructions: Show all of your work. You do not have to simplify your answers. No calculators allowed. There is a table of formulae on the last page. 1. Suppose X 1,..., X 1 are independent
Name M362K Final Exam Instructions: Show all of your work. You do not have to simplify your answers. No calculators allowed. There is a table of formulae on the last page. 1. Suppose X 1,..., X 1 are independent
Lecture 7: Chapter 7. Sums of Random Variables and Long-Term Averages
 Lecture 7: Chapter 7. Sums of Random Variables and Long-Term Averages ELEC206 Probability and Random Processes, Fall 2014 Gil-Jin Jang gjang@knu.ac.kr School of EE, KNU page 1 / 15 Chapter 7. Sums of Random
Lecture 7: Chapter 7. Sums of Random Variables and Long-Term Averages ELEC206 Probability and Random Processes, Fall 2014 Gil-Jin Jang gjang@knu.ac.kr School of EE, KNU page 1 / 15 Chapter 7. Sums of Random
Math Spring Practice for the final Exam.
 Math 4 - Spring 8 - Practice for the final Exam.. Let X, Y, Z be three independnet random variables uniformly distributed on [, ]. Let W := X + Y. Compute P(W t) for t. Honors: Compute the CDF function
Math 4 - Spring 8 - Practice for the final Exam.. Let X, Y, Z be three independnet random variables uniformly distributed on [, ]. Let W := X + Y. Compute P(W t) for t. Honors: Compute the CDF function
Mathematical statistics
 October 4 th, 2018 Lecture 12: Information Where are we? Week 1 Week 2 Week 4 Week 7 Week 10 Week 14 Probability reviews Chapter 6: Statistics and Sampling Distributions Chapter 7: Point Estimation Chapter
October 4 th, 2018 Lecture 12: Information Where are we? Week 1 Week 2 Week 4 Week 7 Week 10 Week 14 Probability reviews Chapter 6: Statistics and Sampling Distributions Chapter 7: Point Estimation Chapter
Spring 2012 Math 541A Exam 1. X i, S 2 = 1 n. n 1. X i I(X i < c), T n =
 Spring 2012 Math 541A Exam 1 1. (a) Let Z i be independent N(0, 1), i = 1, 2,, n. Are Z = 1 n n Z i and S 2 Z = 1 n 1 n (Z i Z) 2 independent? Prove your claim. (b) Let X 1, X 2,, X n be independent identically
Spring 2012 Math 541A Exam 1 1. (a) Let Z i be independent N(0, 1), i = 1, 2,, n. Are Z = 1 n n Z i and S 2 Z = 1 n 1 n (Z i Z) 2 independent? Prove your claim. (b) Let X 1, X 2,, X n be independent identically
0, otherwise. U = Y 1 Y 2 Hint: Use either the method of distribution functions or a bivariate transformation. (b) Find E(U).
 1. Suppose Y U(0, 2) so that the probability density function (pdf) of Y is 1 2, 0 < y < 2 (a) Find the pdf of U = Y 4 + 1. Make sure to note the support. (c) Suppose Y 1, Y 2,..., Y n is an iid sample
1. Suppose Y U(0, 2) so that the probability density function (pdf) of Y is 1 2, 0 < y < 2 (a) Find the pdf of U = Y 4 + 1. Make sure to note the support. (c) Suppose Y 1, Y 2,..., Y n is an iid sample
Chapter 5 continued. Chapter 5 sections
 Chapter 5 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
Chapter 5 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
Bell-shaped curves, variance
 November 7, 2017 Pop-in lunch on Wednesday Pop-in lunch tomorrow, November 8, at high noon. Please join our group at the Faculty Club for lunch. Means If X is a random variable with PDF equal to f (x),
November 7, 2017 Pop-in lunch on Wednesday Pop-in lunch tomorrow, November 8, at high noon. Please join our group at the Faculty Club for lunch. Means If X is a random variable with PDF equal to f (x),
MATH2715: Statistical Methods
 MATH2715: Statistical Methods Exercises V (based on lectures 9-10, work week 6, hand in lecture Mon 7 Nov) ALL questions count towards the continuous assessment for this module. Q1. If X gamma(α,λ), write
MATH2715: Statistical Methods Exercises V (based on lectures 9-10, work week 6, hand in lecture Mon 7 Nov) ALL questions count towards the continuous assessment for this module. Q1. If X gamma(α,λ), write
Evaluating the Performance of Estimators (Section 7.3)
 Evaluating the Performance of Estimators (Section 7.3) Example: Suppose we observe X 1,..., X n iid N(θ, σ 2 0 ), with σ2 0 known, and wish to estimate θ. Two possible estimators are: ˆθ = X sample mean
Evaluating the Performance of Estimators (Section 7.3) Example: Suppose we observe X 1,..., X n iid N(θ, σ 2 0 ), with σ2 0 known, and wish to estimate θ. Two possible estimators are: ˆθ = X sample mean
First Year Examination Department of Statistics, University of Florida
 First Year Examination Department of Statistics, University of Florida August 19, 010, 8:00 am - 1:00 noon Instructions: 1. You have four hours to answer questions in this examination.. You must show your
First Year Examination Department of Statistics, University of Florida August 19, 010, 8:00 am - 1:00 noon Instructions: 1. You have four hours to answer questions in this examination.. You must show your
Sampling Distributions
 Sampling Distributions In statistics, a random sample is a collection of independent and identically distributed (iid) random variables, and a sampling distribution is the distribution of a function of
Sampling Distributions In statistics, a random sample is a collection of independent and identically distributed (iid) random variables, and a sampling distribution is the distribution of a function of
Analysis of Experimental Designs
 Analysis of Experimental Designs p. 1/? Analysis of Experimental Designs Gilles Lamothe Mathematics and Statistics University of Ottawa Analysis of Experimental Designs p. 2/? Review of Probability A short
Analysis of Experimental Designs p. 1/? Analysis of Experimental Designs Gilles Lamothe Mathematics and Statistics University of Ottawa Analysis of Experimental Designs p. 2/? Review of Probability A short
Fall 2017 STAT 532 Homework Peter Hoff. 1. Let P be a probability measure on a collection of sets A.
 1. Let P be a probability measure on a collection of sets A. (a) For each n N, let H n be a set in A such that H n H n+1. Show that P (H n ) monotonically converges to P ( k=1 H k) as n. (b) For each n
1. Let P be a probability measure on a collection of sets A. (a) For each n N, let H n be a set in A such that H n H n+1. Show that P (H n ) monotonically converges to P ( k=1 H k) as n. (b) For each n
5 Operations on Multiple Random Variables
 EE360 Random Signal analysis Chapter 5: Operations on Multiple Random Variables 5 Operations on Multiple Random Variables Expected value of a function of r.v. s Two r.v. s: ḡ = E[g(X, Y )] = g(x, y)f X,Y
EE360 Random Signal analysis Chapter 5: Operations on Multiple Random Variables 5 Operations on Multiple Random Variables Expected value of a function of r.v. s Two r.v. s: ḡ = E[g(X, Y )] = g(x, y)f X,Y
Math 341: Probability Seventeenth Lecture (11/10/09)
 Math 341: Probability Seventeenth Lecture (11/10/09) Steven J Miller Williams College Steven.J.Miller@williams.edu http://www.williams.edu/go/math/sjmiller/ public html/341/ Bronfman Science Center Williams
Math 341: Probability Seventeenth Lecture (11/10/09) Steven J Miller Williams College Steven.J.Miller@williams.edu http://www.williams.edu/go/math/sjmiller/ public html/341/ Bronfman Science Center Williams
1 Review of Probability and Distributions
 Random variables. A numerically valued function X of an outcome ω from a sample space Ω X : Ω R : ω X(ω) is called a random variable (r.v.), and usually determined by an experiment. We conventionally denote
Random variables. A numerically valued function X of an outcome ω from a sample space Ω X : Ω R : ω X(ω) is called a random variable (r.v.), and usually determined by an experiment. We conventionally denote
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2015 Note 20. A Brief Introduction to Continuous Probability
 CS 7 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 215 Note 2 A Brief Introduction to Continuous Probability Up to now we have focused exclusively on discrete probability spaces Ω, where the number
CS 7 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 215 Note 2 A Brief Introduction to Continuous Probability Up to now we have focused exclusively on discrete probability spaces Ω, where the number
E X A M. Probability Theory and Stochastic Processes Date: December 13, 2016 Duration: 4 hours. Number of pages incl.
 E X A M Course code: Course name: Number of pages incl. front page: 6 MA430-G Probability Theory and Stochastic Processes Date: December 13, 2016 Duration: 4 hours Resources allowed: Notes: Pocket calculator,
E X A M Course code: Course name: Number of pages incl. front page: 6 MA430-G Probability Theory and Stochastic Processes Date: December 13, 2016 Duration: 4 hours Resources allowed: Notes: Pocket calculator,
Question Points Score Total: 76
 Math 447 Test 2 March 17, Spring 216 No books, no notes, only SOA-approved calculators. true/false or fill-in-the-blank question. You must show work, unless the question is a Name: Question Points Score
Math 447 Test 2 March 17, Spring 216 No books, no notes, only SOA-approved calculators. true/false or fill-in-the-blank question. You must show work, unless the question is a Name: Question Points Score
Math 180A. Lecture 16 Friday May 7 th. Expectation. Recall the three main probability density functions so far (1) Uniform (2) Exponential.
 Math 8A Lecture 6 Friday May 7 th Epectation Recall the three main probability density functions so far () Uniform () Eponential (3) Power Law e, ( ), Math 8A Lecture 6 Friday May 7 th Epectation Eample
Math 8A Lecture 6 Friday May 7 th Epectation Recall the three main probability density functions so far () Uniform () Eponential (3) Power Law e, ( ), Math 8A Lecture 6 Friday May 7 th Epectation Eample
This does not cover everything on the final. Look at the posted practice problems for other topics.
 Class 7: Review Problems for Final Exam 8.5 Spring 7 This does not cover everything on the final. Look at the posted practice problems for other topics. To save time in class: set up, but do not carry
Class 7: Review Problems for Final Exam 8.5 Spring 7 This does not cover everything on the final. Look at the posted practice problems for other topics. To save time in class: set up, but do not carry
Lecture 4. Continuous Random Variables and Transformations of Random Variables
 Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 4. Continuous Random Variables and Transformations of Random Variables January 25, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 4 January 25, 2013 1 / 13 Agenda
Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 4. Continuous Random Variables and Transformations of Random Variables January 25, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 4 January 25, 2013 1 / 13 Agenda
Statistics Ph.D. Qualifying Exam: Part I October 18, 2003
 Statistics Ph.D. Qualifying Exam: Part I October 18, 2003 Student Name: 1. Answer 8 out of 12 problems. Mark the problems you selected in the following table. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Write your answer
Statistics Ph.D. Qualifying Exam: Part I October 18, 2003 Student Name: 1. Answer 8 out of 12 problems. Mark the problems you selected in the following table. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Write your answer
ST5215: Advanced Statistical Theory
 Department of Statistics & Applied Probability Wednesday, October 19, 2011 Lecture 17: UMVUE and the first method of derivation Estimable parameters Let ϑ be a parameter in the family P. If there exists
Department of Statistics & Applied Probability Wednesday, October 19, 2011 Lecture 17: UMVUE and the first method of derivation Estimable parameters Let ϑ be a parameter in the family P. If there exists
Math 447. Introduction to Probability and Statistics I. Fall 1998.
 Math 447. Introduction to Probability and Statistics I. Fall 1998. Schedule: M. W. F.: 08:00-09:30 am. SW 323 Textbook: Introduction to Mathematical Statistics by R. V. Hogg and A. T. Craig, 1995, Fifth
Math 447. Introduction to Probability and Statistics I. Fall 1998. Schedule: M. W. F.: 08:00-09:30 am. SW 323 Textbook: Introduction to Mathematical Statistics by R. V. Hogg and A. T. Craig, 1995, Fifth
YORK UNIVERSITY. Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH A Test #2 June 11, Solutions
 YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 2. A Test #2 June, 2 Solutions. (5 + 5 + 5 pts) The probability of a student in MATH 4 passing a test is.82. Suppose students
YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 2. A Test #2 June, 2 Solutions. (5 + 5 + 5 pts) The probability of a student in MATH 4 passing a test is.82. Suppose students
Course: ESO-209 Home Work: 1 Instructor: Debasis Kundu
 Home Work: 1 1. Describe the sample space when a coin is tossed (a) once, (b) three times, (c) n times, (d) an infinite number of times. 2. A coin is tossed until for the first time the same result appear
Home Work: 1 1. Describe the sample space when a coin is tossed (a) once, (b) three times, (c) n times, (d) an infinite number of times. 2. A coin is tossed until for the first time the same result appear
Statistics 427: Sample Final Exam
 Statistics 427: Sample Final Exam Instructions: The following sample exam was given several quarters ago in Stat 427. The same topics were covered in the class that year. This sample exam is meant to be
Statistics 427: Sample Final Exam Instructions: The following sample exam was given several quarters ago in Stat 427. The same topics were covered in the class that year. This sample exam is meant to be
APPM/MATH 4/5520 Solutions to Exam I Review Problems. f X 1,X 2. 2e x 1 x 2. = x 2
 APPM/MATH 4/5520 Solutions to Exam I Review Problems. (a) f X (x ) f X,X 2 (x,x 2 )dx 2 x 2e x x 2 dx 2 2e 2x x was below x 2, but when marginalizing out x 2, we ran it over all values from 0 to and so
APPM/MATH 4/5520 Solutions to Exam I Review Problems. (a) f X (x ) f X,X 2 (x,x 2 )dx 2 x 2e x x 2 dx 2 2e 2x x was below x 2, but when marginalizing out x 2, we ran it over all values from 0 to and so
Chapter 3: Unbiased Estimation Lecture 22: UMVUE and the method of using a sufficient and complete statistic
 Chapter 3: Unbiased Estimation Lecture 22: UMVUE and the method of using a sufficient and complete statistic Unbiased estimation Unbiased or asymptotically unbiased estimation plays an important role in
Chapter 3: Unbiased Estimation Lecture 22: UMVUE and the method of using a sufficient and complete statistic Unbiased estimation Unbiased or asymptotically unbiased estimation plays an important role in
Math 562 Homework 1 August 29, 2006 Dr. Ron Sahoo
 Math 56 Homework August 9, 006 Dr. Ron Sahoo He who labors diligently need never despair; for all things are accomplished by diligence and labor. Menander of Athens Direction: This homework worths 60 points
Math 56 Homework August 9, 006 Dr. Ron Sahoo He who labors diligently need never despair; for all things are accomplished by diligence and labor. Menander of Athens Direction: This homework worths 60 points
Notes, March 4, 2013, R. Dudley Maximum likelihood estimation: actual or supposed
 18.466 Notes, March 4, 2013, R. Dudley Maximum likelihood estimation: actual or supposed 1. MLEs in exponential families Let f(x,θ) for x X and θ Θ be a likelihood function, that is, for present purposes,
18.466 Notes, March 4, 2013, R. Dudley Maximum likelihood estimation: actual or supposed 1. MLEs in exponential families Let f(x,θ) for x X and θ Θ be a likelihood function, that is, for present purposes,
February 26, 2017 COMPLETENESS AND THE LEHMANN-SCHEFFE THEOREM
 February 26, 2017 COMPLETENESS AND THE LEHMANN-SCHEFFE THEOREM Abstract. The Rao-Blacwell theorem told us how to improve an estimator. We will discuss conditions on when the Rao-Blacwellization of an estimator
February 26, 2017 COMPLETENESS AND THE LEHMANN-SCHEFFE THEOREM Abstract. The Rao-Blacwell theorem told us how to improve an estimator. We will discuss conditions on when the Rao-Blacwellization of an estimator
MATH 4426 HW7 solutions. April 15, Recall, Z is said to have a standard normal distribution (denoted Z N(0, 1)) if its pdf is
 MATH 446 HW7 solutions April 5, 5 Recall, Z is said to have a standard normal distribution (denoted Z N(, )) if its pdf is f Z (z) = p e z /,z (, ). Table A. (pp.697-698) tabulates values of its cdf (denoted.)
MATH 446 HW7 solutions April 5, 5 Recall, Z is said to have a standard normal distribution (denoted Z N(, )) if its pdf is f Z (z) = p e z /,z (, ). Table A. (pp.697-698) tabulates values of its cdf (denoted.)
Statistics GIDP Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Theory Jan 11, 2016, 9:00am-1:00pm
 Statistics GIDP Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Theory Jan, 06, 9:00am-:00pm Instructions: Provide answers on the supplied pads of paper; write on only one side of each sheet. Complete exactly 5 of the 6 problems.
Statistics GIDP Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Theory Jan, 06, 9:00am-:00pm Instructions: Provide answers on the supplied pads of paper; write on only one side of each sheet. Complete exactly 5 of the 6 problems.
Probability Background
 Probability Background Namrata Vaswani, Iowa State University August 24, 2015 Probability recap 1: EE 322 notes Quick test of concepts: Given random variables X 1, X 2,... X n. Compute the PDF of the second
Probability Background Namrata Vaswani, Iowa State University August 24, 2015 Probability recap 1: EE 322 notes Quick test of concepts: Given random variables X 1, X 2,... X n. Compute the PDF of the second
Review of Maximum Likelihood Estimators
 Libby MacKinnon CSE 527 notes Lecture 7, October 7, 2007 MLE and EM Review of Maximum Likelihood Estimators MLE is one of many approaches to parameter estimation. The likelihood of independent observations
Libby MacKinnon CSE 527 notes Lecture 7, October 7, 2007 MLE and EM Review of Maximum Likelihood Estimators MLE is one of many approaches to parameter estimation. The likelihood of independent observations
STATISTICS 1 REVISION NOTES
 STATISTICS 1 REVISION NOTES Statistical Model Representing and summarising Sample Data Key words: Quantitative Data This is data in NUMERICAL FORM such as shoe size, height etc. Qualitative Data This is
STATISTICS 1 REVISION NOTES Statistical Model Representing and summarising Sample Data Key words: Quantitative Data This is data in NUMERICAL FORM such as shoe size, height etc. Qualitative Data This is
Continuous Distributions
 A normal distribution and other density functions involving exponential forms play the most important role in probability and statistics. They are related in a certain way, as summarized in a diagram later
A normal distribution and other density functions involving exponential forms play the most important role in probability and statistics. They are related in a certain way, as summarized in a diagram later
Institute of Actuaries of India
 Institute of Actuaries of India Subject CT3 Probability & Mathematical Statistics May 2011 Examinations INDICATIVE SOLUTION Introduction The indicative solution has been written by the Examiners with the
Institute of Actuaries of India Subject CT3 Probability & Mathematical Statistics May 2011 Examinations INDICATIVE SOLUTION Introduction The indicative solution has been written by the Examiners with the
Expectation, Variance and Standard Deviation for Continuous Random Variables Class 6, Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom
 Expectation, Variance and Standard Deviation for Continuous Random Variables Class 6, 8.5 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom Learning Goals. Be able to compute and interpret expectation, variance, and standard
Expectation, Variance and Standard Deviation for Continuous Random Variables Class 6, 8.5 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom Learning Goals. Be able to compute and interpret expectation, variance, and standard
Lecture The Sample Mean and the Sample Variance Under Assumption of Normality
 Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 13-14. The Sample Mean and the Sample Variance Under Assumption of Normality February 20, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 13-14 February 20, 2013
Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 13-14. The Sample Mean and the Sample Variance Under Assumption of Normality February 20, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 13-14 February 20, 2013
