FAU MATH DAY 2011 Math Trivia Challenge MATHEMATICAL DIVERSIONS 2011
|
|
|
- Allen Fleming
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FAU MATH DAY 2011 Math Trivia Challenge MATHEMATICAL DIVERSIONS 2011
2 Warm up Question The ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter A. is known to be infinite. B. is denoted by the Greek letter π (pi). C. depends on the particular circle. D. depends on the day of the week. E. is one of the seven wonders of the ancient world.
3 Warm up Question The ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter A. is known to be infinite. B. is denoted by the Greek letter π (pi). C. depends on the particular circle. D. depends on the day of the week. E. is one of the seven wonders of the ancient world.
4 Usually there will be a third slide with some explanation of the answer. Or I ll give one. I can t help myself from adding such a page! Format from now on: Math questions and so called trivia will alternate. You ll have one minute to answer trivia, one to three minutes for the math.
5 The Babylonians The Babylonians wrote numbers in base 60. One of their tablets states that the ratio of a regular hexagon to the circumference of the circumscribed circle is This means that for them π was equal to A B C D E
6 The Babylonians The Babylonians wrote numbers in base 60. One of their tablets states that the ratio of a regular hexagon to the circumference of the circumscribed circle is This means that for them π was equal to A B C D E
7 The Babylonians The Babylonians wrote numbers in base 60. One of their tablets states that the ratio of a regular hexagon to the circumference of the circumscribed circle is This means that for them π was equal to A B C D E
8 Irrational questions By definition, an irrational number is one that: A. Has a never ending decimal expansion, like for example B. Cannot be expressed as the quotient of two integers. C. Is the square root of an integer. D. Is a number smaller than all positive numbers. E. Is a number that doesn t make sense.
9 Irrational questions By definition, an irrational number is one that: A. Has a never ending decimal expansion, like for example B. Cannot be expressed as the quotient of two integers. C. Is the square root of an integer. D. Is a number smaller than all positive numbers. E. Is a number that doesn t make sense.
10 In the days of Archimedes Archimedes ( BCE) was one of the greatest mathematicians/physicists of all times. By a process similar to Calculus (2000 years before it was invented) he found that the volume of a sphere of radius r is given by V =(4/3)π r 3. Knowing this, which of the following could be a formula for a spherical segment of altitude h and base radii a, b.
11 In the days of Archimedes Archimedes ( BCE) was one of the greatest mathematicians/physicists of all times. By a process similar to Calculus (2000 years before it was invented) he found that the volume of a sphere of radius r is given by V =(4/3)π r 3. Knowing this, which of the following could be a formula for a spherical segment of altitude h and base radii a, b.
12 In the days of Archimedes The last formula is the only one giving the correct volume of the half-sphere, namely (4/6)πr 3 when a = h = r, b = 0.
13 The European Middle Ages His most famous book begins: These are the nine figures of the Indians: 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1. With these nine figures, and with the sign 0, which in Arabic is called zephirum, any number can be written He was Leonardo of Pisa, better known as A. Leonardo DaVinci B. Leonardo Montessori C. Leonardo Caprio D. Michelangelo E. Fibonacci
14 The European Middle Ages His most famous book begins: These are the nine figures of the Indians: 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1. With these nine figures, and with the sign 0, which in Arabic is called zephirum, any number can be written He was Leonardo of Pisa, better known as A. Leonardo DaVinci B. Leonardo Montessori C. Leonardo Caprio D. Michelangelo E. Fibonacci
15 The European Middle Ages His most famous book begins: These are the nine figures of the Indians: 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1. With these nine figures, and with the sign 0, which in Arabic is called zephirum, any number can be written He was Leonardo of Pisa, better known as Fibonacci. In Liber Abaci, Fibonacci introduced the Arabic numbering into Europe. It is also where his famous sequence first appears, as solution to a rabbit question.
16 A problem by Luca Pacioli The radius of the incircle of a triangle is 4; side BC is divided into segments 8 and 6 by the point of contact. How long is AB? A. 13 B. 14 C. 15 D. 16 E. Not enough information to tell.
17 A problem by Luca Pacioli The radius of the incircle of a triangle is 4; side BC is divided into segments 8 and 6 by the point of contact. How long is AB? A. 13 B. 14 C. 15 D. 16 E. Not enough information to tell.
18 A problem by Luca Pacioli The radius of the incircle of a triangle is 4; side BC is divided into segments 8 and 6 by the point of contact. How long is AB? A. 13 B. 14 C. 15 D. 16 E. Not enough information to tell.
19 Traveling with Gulliver On his third voyage, Gulliver visits a land of mathematicians and he is served a pudding in the shape of a: A.Cycloid. B.Paraboloid C.Ellipsoid. D.Perfect sphere. E. Cardioid.
20 Traveling with Gulliver On his third voyage, Gulliver visits a land of mathematicians and he is served a pudding in the shape of a: A.Cycloid. B.Paraboloid C.Ellipsoid. D.Perfect sphere. E. Cardioid.
21 Traveling with Gulliver On his third voyage, Gulliver visits a land of mathematicians and he is served a pudding in the shape of a: A.Cycloid. B.Paraboloid C.Ellipsoid. D.Perfect sphere. E. Cardioid. A cycloid is the curve described by a point on a circle that rolls without slipping. Cycloids were studied by Pascal, the Bernoullis, Huygens, among others.
22 Circle in the Triangle The radius of the incircle (inscribed circle) in the equilateral triangle ABC is r = 1. Find the area of the triangle. 3
23 Circle in the Triangle The radius of the incircle (inscribed circle) in the equilateral triangle ABC is r = 1. Find the area of the triangle. 3
24 Circle in the Triangle The radius of the incircle (inscribed circle) in the equilateral triangle ABC is r = 1. Find the area of the triangle. 3
25 MicroSoft Powerpoint meet Points P, A, Q are collinear (on the same line). The line PQ is tangent to the circle at Q. PA = 5 PQ = 7 What is the radius of the circle? A. 2 B. 2.2 C. 2.4 D. 2.5 E. 2.75
26 MicroSoft Powerpoint meet Points P, A, Q are collinear (on the same line). The line PQ is tangent to the circle at Q. PA = 5 PQ = 7 What is the radius of the circle? A. 2 B. 2.2 C. 2.4 D. 2.5 E. 2.75
27 MicroSoft Powerpoint meet Points P, A, Q are collinear (on the same line). The line PQ is tangent to the circle at Q. PA = 5 PQ = 7 What is the radius of the circle? A. 2 B. 2.2 C. 2.4 D. 2.5 E The so called power of a point with respect to a circle is constant, meaning PA PC = PQ 2. Now PC = PA + 2r, thus 5 (5+2r) = 49. Solving for r = 24/10 = 2.4
28 A Bologna sandwich Girolamo Cardano ( ) swore the following to Niccolo Tartaglia ( ): I swear to you, by God's holy Gospels, and as a true man of honour, not only never to publish your discoveries, if you teach me them, but I also promise you, and I pledge my faith as a true Christian, to note them down in code, so that after my death no one will be able to understand them. What was the discovery: A. A formula to solve cubic equations. B. How to trisect angles. C. Squaring the circle. D. Calculus. E. How to cure the common cold.
29 A Bologna sandwich Girolamo Cardano ( ) swore the following to Niccolo Tartaglia ( ): I swear to you, by God's holy Gospels, and as a true man of honour, not only never to publish your discoveries, if you teach me them, but I also promise you, and I pledge my faith as a true Christian, to note them down in code, so that after my death no one will be able to understand them. What was the discovery: A. A formula to solve cubic equations. B. How to trisect angles. C. Squaring the circle. D. Calculus. E. How to cure the common cold.
30 A Bologna sandwich The cubic formula was one the first discoveries by European mathematicians that went further than what the Greeks had done centuries before. Tartaglia claimed to have it (he did) and Cardano just needed to know. After he swore to never divulge it, Tartaglia revealed the secret. Soon afterwards, Cardano published the formula. Tartaglia spent the rest of his life trying to get revenge. But the truth is not so simple, Cardano actually had a good reason.
31 Augustus DeMorgan Augustus DeMorgan was a famous 19 th century mathematician. He once said: I was x years old in the year x 2. In what year was DeMorgan born? A B C D E. 1800
32 Augustus DeMorgan Augustus DeMorgan was a famous 19 th century mathematician. He once said: I was x years old in the year x 2. In what year was DeMorgan born? A B C D E. 1800
33 Augustus DeMorgan Augustus DeMorgan was a famous 19 th century mathematician. He once said: I was x years old in the year x 2. In what year was DeMorgan born? A B C D E. 1800
34 A Russian Childhood This Russian mathematician had to marry to be allowed to leave her home and study in Germany. It took a special request by university professors impressed by her ability to even let her study at Heidelberg, she was not allowed to attend classes later on at Berlin, being then privately tutored by a famous professor. At age 25 she published (among others) the paper containing the theorem that still bears her name. Even so, she was unable to get a university position. She finally found a haven in Sweden. She was: A. Sofia Kovaleskaya B. Olga Ladyzhenskaya C. Olga Oleinik D. Pelageia Kochina E. Anna Karenina
35 A Russian Childhood This Russian mathematician had to marry to be allowed to leave her home and study in Germany. It took a special request by university professors impressed by her ability to even let her study at Heidelberg, she was not allowed to attend classes later on at Berlin, being then privately tutored by a famous professor. At age 25 she published (among others) the paper containing the theorem that still bears her name. Even so, she was unable to get a university position. She finally found a haven in Sweden. She was: A. Sofia Kovaleskaya B. Olga Ladyzhenskaya C. Olga Oleinik D. Pelageia Kochina E. Anna Karenina
36 A Russian Childhood This Russian mathematician had to marry to be allowed to leave her home and study in Germany. It took a special request by university professors impressed by her ability to even let her study at Heidelberg, she was not allowed to attend classes later on at Berlin, being then privately tutored by a famous professor. At age 25 she published (among others) the paper containing the theorem that still bears her name. Even so, she was unable to get a university position. She finally found a haven in Sweden. She was: A. Sofia Kovaleskaya B. Olga Ladyzhenskaya C. Olga Oleinik D. Pelageia Kochina E. Anna Karenina Ladyzhenskaya, Oleinink, Kochina also were important mathematicians, especially Ladyzhenskaya. Anna Karenina was not.
37 Triangle and square ABCD is a square of center X and side length 8 ( AB = 8). XYZ is a right triangle with right angle at X and XY = 10, XZ = 24. If XY intersects BC at E such that CE = 2, and EB = 6, find the area of the region that is common to the triangle and the square. A. 16 B. 5 3 C. 6 2 D E. Not enough information to tell.
38 Triangle and square ABCD is a square of center X and side length 8 ( AB = 8). XYZ is a right triangle with right angle at X and XY = 10, XZ = 24. If XY intersects BC at E such that CE = 2, and EB = 6, find the area of the region that is common to the triangle and the square. A. 16 B. 5 3 C. 6 2 D E. Not enough information to tell.
39 Triangle and square ABCD is a square of center X and side length 8 ( AB = 8). XYZ is a right triangle with right angle at X and XY = 10, XZ = 24. If XY intersects BC at E such that CE = 2, and EB = 6, find the area of the region that is common to the triangle and the square. A. 16 B. 5 3 C. 6 2 D E. Not enough information to tell. This problem came with a lot of superfluous information. This is related to this year s T-shirt. With the added lines it should be clear that the common region has area one fourth that of the square.
40 From Sam Loyd s Cyclopedia The picture shows a blue triangle; with a square on each one of its sides. The areas of the squares are as given. What is the area in acres of the blue triangle? (You do not need to know what an acre is to solve the problem. You can replace acres by square feet, for example.) A B. 16 C D. 11 E. 10
41 From Sam Loyd s Cyclopedia The picture shows a blue triangle; with a square on each one of its sides. The areas of the squares are as given. What is the area in acres of the blue triangle? (You do not need to know what an acre is to solve the problem. You can replace acres by square feet, for example.) A B. 16 C D. 11 E. 10
42 From Sam Loyd s Cyclopedia The picture shows a blue triangle; with a square on each one of its sides. The areas of the squares are as given. What is the area in acres of the blue triangle? (You do not need to know what an acre is to solve the problem. You can replace acres by square feet, for example.) A B. 16 C D. 11 E. 10
43 From Sam Loyd s Cyclopedia A B. 16 C D. 11 E. 10
44 From a 1970 s Contest In the figure, AB is parallel to CD. The angle at D is twice the size of the angle at B. AD = a, CD = b Then AB is equal to A. ½ a + 2b B. 3 / 2 b + 3 / 4 a C. 2a b D. 4b ½ a E. a + b
45 From a 1970 s Contest In the figure, AB is parallel to CD. The angle at D is twice the size of the angle at B. AD = a, CD = b Then AB is equal to A. ½ a + 2b B. 3 / 2 b + 3 / 4 a C. 2a b D. 4b ½ a E. a + b
46 From a 1970 s Contest In the figure, AB is parallel to CD. The angle at D is twice the size of the angle at B. AD = a, CD = b Then AB is equal to A. ½ a + 2b B. 3 / 2 b + 3 / 4 a C. 2a b If we draw the line PD parallel to BC, we see that all the red angles are equal, so APD is isosceles. D. 4b ½ a E. a + b
47 Curiouser and curiouser Which of these mathematicians became convinced that someone was trying to poison him, so he stopped eating, and died from starvation. A. Leonhard Euler. B. Niels Henryk Abel. C. Carl Friedrich Gauss. D. Kurt Gödel. E. Bertrand Russell
48 Breaking Ties From now on, only the scores of the teams having the highest scores will be considered.
49 Curiouser and curiouser Which of these mathematicians became convinced that someone was trying to poison him, so he stopped eating, and died from starvation. A. Leonhard Euler. B. Niels Henryk Abel. C. Carl Friedrich Gauss. D. Kurt Gödel. E. Bertrand Russell
50 Curiouser and curiouser Which of these mathematicians became convinced that someone was trying to poison him, so he stopped eating, and died from starvation. Gödel s work was in mathematical logic. His 1930 s results caused a crisis and a revolution in mathematics. He came to the U.S. in 1940 and became a memberof the IAS in Princeton, and a close friend of Albert Einstein.
51 Friends of Diophantus If x and y are positive integers and xy + 5y + 7x = 168, then x + y equals A. 6 B. 12 C. 24 D. 48 E. 96
52 Friends of Diophantus If x and y are positive integers and xy + 5y + 7x = 168, then x + y equals A. 6 B. 12 C. 24 D. 48 E. 96
53 Friends of Diophantus If x and y are positive integers and xy + 5y + 7x = 168, then x + y equals A. 6 B. 12 C. 24 D. 48 E. 96
54 Q1. The sentence: Certainly one would wish for a stricter proof here; I have meanwhile temporarily put aside the search for this after some fleeting futile attempts, as it appears unnecessary for the next objective of my investigation initiates the search for the solution of a famous problem. Who wrote it, and what is the problem? A. Pierre Fermat; Fermat s last theorem. B. Christian Goldbach, The Goldbach conjecture. C. Carl Friedrich Gauss, The parallel postulate. D. Bernhard Riemann, The Riemann hypothesis. E. Bertrand Russell, The Russell paradox.
55 Q1. The sentence: Certainly one would wish for a stricter proof here; I have meanwhile temporarily put aside the search for this after some fleeting futile attempts, as it appears unnecessary for the next objective of my investigation initiates the search for the solution of a famous problem. Who wrote it, and what is the problem? A. Pierre Fermat; Fermat s last theorem. B. Christian Goldbach, The Goldbach conjecture. C. Carl Friedrich Gauss, The parallel postulate. D. Bernhard Riemann, The Riemann hypothesis. E. Bertrand Russell, The Russell paradox.
56 Q4. Which U.S president came up with a proof of the Theorem of Pythagoras, which was later published? A. Tomas Jefferson. B. Zachary Taylor. C. Abraham Lincoln. D. James Garfield. E. Grover Cleveland.
57 Q4. Which U.S president came up with a proof of the Theorem of Pythagoras, which was later published? A. Tomas Jefferson. B. Zachary Taylor. C. Abraham Lincoln. D. James Garfield. E. Grover Cleveland.
58 Q6. What French mathematician wrote under the pseudonym Lovis de Montalte? A. René Descartes. B. Pierre de Fermat. C. Blaise Pascal. D. Adrien-Marie Legendre. E. Simeon Poisson
59 Q6. What French mathematician wrote under the pseudonym Lovis de Montalte? A. René Descartes. B. Pierre de Fermat. C. Blaise Pascal. D. Adrien-Marie Legendre. E. Simeon Poisson
60 Q7. What mathematician used the pseudonym of M. Le Blanc? A. Sophie-Marie Germain. B. Emilie du Chatelet. C. Marie-Louise Dubreil Jacotin. D. Maria Agnesi. E. Emily Noether.
61 Q7. What mathematician used the pseudonym of M. Le Blanc? A. Sophie-Marie Germain. B. Emilie du Chatelet. C. Marie-Louise Dubreil Jacotin. D. Maria Agnesi. E. Emily Noether.
62 Q8. He spent 23 years to compute π to 35 decimal places: A. Leonardo of Pisa, Fibonacci. B. Johannes Müller, Regiomontanus. C. Ludolph van Ceulen. D. Jakob Bernoulli. E. Leonhard Euler.
63 Q8. He spent 23 years to compute π to 35 decimal places: A. Leonardo of Pisa, Fibonacci. B. Johannes Müller, Regiomontanus. C. Ludolph van Ceulen. D. Jakob Bernoulli. E. Leonhard Euler.
64 Q9. This mathematician defined π as being twice the first positive root of the cosine function. This definition was considered as ungermanic, Jewish, by a rabble of students already imbued with the poison of Nazism, resulting in the mathematician losing his post and being driven into exile. A. Edmund Landau. B. Hermann Minkowski. C. Felix Klein. D. Felix Hausdorff. E. Rudolph Lipschitz.
65 Q9. This mathematician defined π as being twice the first positive root of the cosine function. This definition was considered as ungermanic, Jewish, by a rabble of students already imbued with the poison of Nazism, resulting in the mathematician losing his post and being driven into exile. A. Edmund Landau. B. Hermann Minkowski. C. Felix Klein. D. Felix Hausdorff. E. Rudolph Lipschitz.
66 Q10. Which of these regular polygons is NOT constructible using only a compass and a straightedge? A. The regular polygon of 85 sides. B. The regular polygon of 119 sides. C. The regular polygon of 3855 sides. D. The regular polygon of 4369 sides. E. The regular polygon of 196,611 sides.
67 Q10. Which of these regular polygons is NOT constructible using only a compass and a straightedge? A. The regular polygon of 85 sides. 85 = 5 17 B. The regular polygon of 119 sides. 119 = 7 17 C. The regular polygon of 3855 sides = D. The regular polygon of 4369 sides = E. The regular polygon of 196,611 sides
68 Q12. Evariste Galois was born in 1811 and died in 1832, not quite 21 years old. In what year was his first paper published: A B C D E
69 Q12. Evariste Galois was born in 1811 and died in 1832, not quite 21 years old. In what year was his first paper published: A B C D E
70 The series for the inverse tangent, namely Is usually known as Gregory s series, as is arctan x x 3 5 the series you get setting x =1. But two centuries before Gregory (who lived ), and before Newton, an Indian mathematician already had discovered all this. The name of this Indian mathematician is A. Aryabhata. B. Brahmagupta C. Madhava. D. Mahavira. E. Ramanujan. x 3 x 5
71 The series for the inverse tangent, namely Is usually known as Gregory s series, as is arctan x x 3 5 the series you get setting x =1. But two centuries before Gregory (who lived ), and before Newton, an Indian mathematician already had discovered all this. The name of this Indian mathematician is A. Aryabhata. B. Brahmagupta C. Madhava. D. Mahavira. E. Ramanujan. x 3 x 5
MATH DAY 2017 TEAM COMPETITION
 An excursion through mathematics and its history (In no particular order)(and some trivia) MATH DAY 2017 TEAM COMPETITION Made possible by A quick review of the rules History (or trivia) questions alternate
An excursion through mathematics and its history (In no particular order)(and some trivia) MATH DAY 2017 TEAM COMPETITION Made possible by A quick review of the rules History (or trivia) questions alternate
An excursion through mathematics and its history MATH DAY 2013 TEAM COMPETITION
 An excursion through mathematics and its history MATH DAY 2013 TEAM COMPETITION A quick review of the rules History (or trivia) questions alternate with math questions Math questions are numbered by MQ1,
An excursion through mathematics and its history MATH DAY 2013 TEAM COMPETITION A quick review of the rules History (or trivia) questions alternate with math questions Math questions are numbered by MQ1,
MthEd/Math 300 Williams Fall 2011 Midterm Exam 2
 Name: MthEd/Math 300 Williams Fall 2011 Midterm Exam 2 Closed Book / Closed Note. Answer all problems. You may use a calculator for numerical computations. Section 1: For each event listed in the first
Name: MthEd/Math 300 Williams Fall 2011 Midterm Exam 2 Closed Book / Closed Note. Answer all problems. You may use a calculator for numerical computations. Section 1: For each event listed in the first
11 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament
 11 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 23 February 2008 Guts Round.. 1. [5] Determine all pairs (a, b) of real numbers such that 10, a, b, ab is an arithmetic progression. 2. [5] Given
11 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 23 February 2008 Guts Round.. 1. [5] Determine all pairs (a, b) of real numbers such that 10, a, b, ab is an arithmetic progression. 2. [5] Given
A Brief History of Algebra
 A Brief History of Algebra The Greeks: Euclid, Pythagora, Archimedes Indian and arab mathematicians Italian mathematics in the Renaissance The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Hilbert s problems 1 Pythagoras,
A Brief History of Algebra The Greeks: Euclid, Pythagora, Archimedes Indian and arab mathematicians Italian mathematics in the Renaissance The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Hilbert s problems 1 Pythagoras,
Syllabus for MTH U201: History of Mathematics
 Syllabus for MTH U201: History of Mathematics Instructor: Professor Mark Bridger Office: 527 Nightingale; ext. 2450 Hours: M,W,Th, 1:00-1:30, and by appointment e-mail: bridger@neu.edu Text: The History
Syllabus for MTH U201: History of Mathematics Instructor: Professor Mark Bridger Office: 527 Nightingale; ext. 2450 Hours: M,W,Th, 1:00-1:30, and by appointment e-mail: bridger@neu.edu Text: The History
THE INTRODUCTION OF COMPLEX NUMBERS*
 THE INTRODUCTION OF COMPLEX NUMBERS* John N. Crossley Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Any keen mathematics student will tell you that complex numbers come in when you want to solve a quadratic
THE INTRODUCTION OF COMPLEX NUMBERS* John N. Crossley Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Any keen mathematics student will tell you that complex numbers come in when you want to solve a quadratic
Chapter 12: Ruler and compass constructions
 Chapter 12: Ruler and compass constructions Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4120, Spring 2014 M. Macauley (Clemson) Chapter
Chapter 12: Ruler and compass constructions Matthew Macauley Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University http://www.math.clemson.edu/~macaule/ Math 4120, Spring 2014 M. Macauley (Clemson) Chapter
Euclidean Geometry. The Elements of Mathematics
 Euclidean Geometry The Elements of Mathematics Euclid, We Hardly Knew Ye Born around 300 BCE in Alexandria, Egypt We really know almost nothing else about his personal life Taught students in mathematics
Euclidean Geometry The Elements of Mathematics Euclid, We Hardly Knew Ye Born around 300 BCE in Alexandria, Egypt We really know almost nothing else about his personal life Taught students in mathematics
The Italian Connection THE CUBIC CHRONICLES
 The Italian Connection THE CUBIC CHRONICLES Cast of Characters Omar Khayyam (1048 1131). A great Persian mathematician working in the Seljuk (Turkish) empire. Solved cubic equations numerically by intersection
The Italian Connection THE CUBIC CHRONICLES Cast of Characters Omar Khayyam (1048 1131). A great Persian mathematician working in the Seljuk (Turkish) empire. Solved cubic equations numerically by intersection
Euclid Geometry And Non-Euclid Geometry. Have you ever asked yourself why is it that if you walk to a specific place from
 Hu1 Haotian Hu Dr. Boman Math 475W 9 November 2016 Euclid Geometry And Non-Euclid Geometry Have you ever asked yourself why is it that if you walk to a specific place from somewhere, you will always find
Hu1 Haotian Hu Dr. Boman Math 475W 9 November 2016 Euclid Geometry And Non-Euclid Geometry Have you ever asked yourself why is it that if you walk to a specific place from somewhere, you will always find
The Three Ancient Geometric Problems
 The Three Ancient Geometric Problems The Three Problems Constructions trisect the angle double the cube square the circle The Three Problems trisecting the angle Given an angle, The Three Problems trisecting
The Three Ancient Geometric Problems The Three Problems Constructions trisect the angle double the cube square the circle The Three Problems trisecting the angle Given an angle, The Three Problems trisecting
MAT 115H Mathematics: An Historical Perspective Fall 2015
 MAT 115H Mathematics: An Historical Perspective Fall 2015 Final Student Projects Below are listed 15 projects featuring a famous theorem prominent in the history of mathematics. These theorems, dating
MAT 115H Mathematics: An Historical Perspective Fall 2015 Final Student Projects Below are listed 15 projects featuring a famous theorem prominent in the history of mathematics. These theorems, dating
A proof has to be rigorously checked before it is published, after which other mathematicians can use it to further develop the subject.
 Proof in mathematics is crucial to its development. When an idea is formulated or an observation is noticed it becomes necessary to prove what has been discovered. Then again, the observation may prove
Proof in mathematics is crucial to its development. When an idea is formulated or an observation is noticed it becomes necessary to prove what has been discovered. Then again, the observation may prove
r=1 Our discussion will not apply to negative values of r, since we make frequent use of the fact that for all non-negative numbers x and t
 Chapter 2 Some Area Calculations 2.1 The Area Under a Power Function Let a be a positive number, let r be a positive number, and let S r a be the set of points (x, y) in R 2 such that 0 x a and 0 y x r.
Chapter 2 Some Area Calculations 2.1 The Area Under a Power Function Let a be a positive number, let r be a positive number, and let S r a be the set of points (x, y) in R 2 such that 0 x a and 0 y x r.
MthEd/Math 300 Williams Winter 2012 Review for Midterm Exam 2 PART 1
 MthEd/Math 300 Williams Winter 2012 Review for Midterm Exam 2 PART 1 1. In terms of the machine-scored sections of the test, you ll basically need to coordinate mathematical developments or events, people,
MthEd/Math 300 Williams Winter 2012 Review for Midterm Exam 2 PART 1 1. In terms of the machine-scored sections of the test, you ll basically need to coordinate mathematical developments or events, people,
than meets the eye. Without the concept of zero, math as we know it would be far less
 History of Math Essay 1 Kimberly Hannusch The Origin of Zero Many people don t think twice about the number zero. It s just nothing, after all. Isn t it? Though the simplest numerical value of zero may
History of Math Essay 1 Kimberly Hannusch The Origin of Zero Many people don t think twice about the number zero. It s just nothing, after all. Isn t it? Though the simplest numerical value of zero may
Geometry beyond Euclid
 Geometry beyond Euclid M.S. Narasimhan IISc & TIFR, Bangalore narasim@math.tifrbng.res.in 1 Outline: Aspects of Geometry which have gone beyond Euclid Two topics which have played important role in development
Geometry beyond Euclid M.S. Narasimhan IISc & TIFR, Bangalore narasim@math.tifrbng.res.in 1 Outline: Aspects of Geometry which have gone beyond Euclid Two topics which have played important role in development
Foundations of Basic Geometry
 GENERAL I ARTICLE Foundations of Basic Geometry Jasbir S Chahal Jasbir S Chahal is Professor of Mathematics at Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah, USA. His research interest is in number theory. The
GENERAL I ARTICLE Foundations of Basic Geometry Jasbir S Chahal Jasbir S Chahal is Professor of Mathematics at Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah, USA. His research interest is in number theory. The
5.2. Perfect Numbers Divisors of a natural number were covered in Section 5.1.
 5.2 Smith Numbers The mathematician Albert Wilansky, when phoning his brother-in-law, Mr. Smith, noticed an interesting property concerning Smith s phone number (493-7775). The number 4,937,775 is composite,
5.2 Smith Numbers The mathematician Albert Wilansky, when phoning his brother-in-law, Mr. Smith, noticed an interesting property concerning Smith s phone number (493-7775). The number 4,937,775 is composite,
Pascal s Triangle Introduction!
 Math 0 Section 2A! Page! 209 Eitel Section 2A Lecture Pascal s Triangle Introduction! A Rich Source of Number Patterns Many interesting number patterns can be found in Pascal's Triangle. This pattern was
Math 0 Section 2A! Page! 209 Eitel Section 2A Lecture Pascal s Triangle Introduction! A Rich Source of Number Patterns Many interesting number patterns can be found in Pascal's Triangle. This pattern was
History of Mathematics Workbook
 History of Mathematics Workbook Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Last Update: April 7, 2014 Student: Spring 2014 Problem A1. Given a square ABCD, equilateral triangles ABX
History of Mathematics Workbook Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Last Update: April 7, 2014 Student: Spring 2014 Problem A1. Given a square ABCD, equilateral triangles ABX
Complex Analysis: A Round-Up
 Complex Analysis: A Round-Up October 1, 2009 Sergey Lototsky, USC, Dept. of Math. *** 1 Prelude: Arnold s Principle Valdimir Igorevich Arnold (b. 1937): Russian The Arnold Principle. If a notion bears
Complex Analysis: A Round-Up October 1, 2009 Sergey Lototsky, USC, Dept. of Math. *** 1 Prelude: Arnold s Principle Valdimir Igorevich Arnold (b. 1937): Russian The Arnold Principle. If a notion bears
Index. Excerpt from "Art of Problem Solving Volume 1: the Basics" 2014 AoPS Inc. / 267. Copyrighted Material
 Index Ø, 247 n k, 229 AA similarity, 102 AAS congruence, 100 abscissa, 143 absolute value, 191 abstract algebra, 66, 210 altitude, 95 angle bisector, 94 Angle Bisector Theorem, 103 angle chasing, 133 angle
Index Ø, 247 n k, 229 AA similarity, 102 AAS congruence, 100 abscissa, 143 absolute value, 191 abstract algebra, 66, 210 altitude, 95 angle bisector, 94 Angle Bisector Theorem, 103 angle chasing, 133 angle
PHASE 9 Ali PERFECT ALI-PI.
 PHASE 9 PERFECT ALI-PI Pi as a Fraction pi is written and expressed as definite fraction and ratio of two numbers: pi = 19 /6 = 3.16666666. pi = 3 + 1/6 Any rational number which cannot be expressed as
PHASE 9 PERFECT ALI-PI Pi as a Fraction pi is written and expressed as definite fraction and ratio of two numbers: pi = 19 /6 = 3.16666666. pi = 3 + 1/6 Any rational number which cannot be expressed as
How to (Almost) Square a Circle
 How to (Almost) Square a Circle Moti Ben-Ari Department of Science Teaching Weizmann Institute of Science http://www.weizmann.ac.il/sci-tea/benari/ c 2017 by Moti Ben-Ari. This work is licensed under the
How to (Almost) Square a Circle Moti Ben-Ari Department of Science Teaching Weizmann Institute of Science http://www.weizmann.ac.il/sci-tea/benari/ c 2017 by Moti Ben-Ari. This work is licensed under the
Grade 8 Chapter 7: Rational and Irrational Numbers
 Grade 8 Chapter 7: Rational and Irrational Numbers In this chapter we first review the real line model for numbers, as discussed in Chapter 2 of seventh grade, by recalling how the integers and then the
Grade 8 Chapter 7: Rational and Irrational Numbers In this chapter we first review the real line model for numbers, as discussed in Chapter 2 of seventh grade, by recalling how the integers and then the
The mighty zero. Abstract
 The mighty zero Rintu Nath Scientist E Vigyan Prasar, Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India A 50, Sector 62, NOIDA 201 309 rnath@vigyanprasar.gov.in rnath07@gmail.com Abstract Zero is a
The mighty zero Rintu Nath Scientist E Vigyan Prasar, Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India A 50, Sector 62, NOIDA 201 309 rnath@vigyanprasar.gov.in rnath07@gmail.com Abstract Zero is a
Pell s Equation Claire Larkin
 Pell s Equation is a Diophantine equation in the form: Pell s Equation Claire Larkin The Equation x 2 dy 2 = where x and y are both integer solutions and n is a positive nonsquare integer. A diophantine
Pell s Equation is a Diophantine equation in the form: Pell s Equation Claire Larkin The Equation x 2 dy 2 = where x and y are both integer solutions and n is a positive nonsquare integer. A diophantine
THE END OF YEAR 2015 COMPETITION
 FAU Math Circle 12/5/2015 THE END OF YEAR 2015 COMPETITION SOLUTIONS 1. Erika promised to sell an average of 20 boxes of girl scout cookies per week over a period of six weeks. In the first five weeks
FAU Math Circle 12/5/2015 THE END OF YEAR 2015 COMPETITION SOLUTIONS 1. Erika promised to sell an average of 20 boxes of girl scout cookies per week over a period of six weeks. In the first five weeks
x = y +z +2, y = z +x+1, and z = x+y +4. C R
 1. [5] Solve for x in the equation 20 14+x = 20+14 x. 2. [5] Find the area of a triangle with side lengths 14, 48, and 50. 3. [5] Victoria wants to order at least 550 donuts from Dunkin Donuts for the
1. [5] Solve for x in the equation 20 14+x = 20+14 x. 2. [5] Find the area of a triangle with side lengths 14, 48, and 50. 3. [5] Victoria wants to order at least 550 donuts from Dunkin Donuts for the
MATH3560/GENS2005 HISTORY OF MATHEMATICS
 THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS OCTOBER/NOVEMBER 2008 MATH3560/GENS2005 HISTORY OF MATHEMATICS (1) TIME ALLOWED 2 Hours (2) TOTAL NUMBER OF QUESTIONS 19 (3) CANDIDATES SHOULD ATTEMPT
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS OCTOBER/NOVEMBER 2008 MATH3560/GENS2005 HISTORY OF MATHEMATICS (1) TIME ALLOWED 2 Hours (2) TOTAL NUMBER OF QUESTIONS 19 (3) CANDIDATES SHOULD ATTEMPT
Comprehensive Mathematics Contest
 Comprehensive Mathematics Contest Elon University Mathematics and Statistics Department Saturday, March 17, 2018 Multiple Choice 1. Let a and b be lengths of the major and minor axis of the ellipse given
Comprehensive Mathematics Contest Elon University Mathematics and Statistics Department Saturday, March 17, 2018 Multiple Choice 1. Let a and b be lengths of the major and minor axis of the ellipse given
Shi Feng Sheng Danny Wong
 Exhibit C A Proof of the Fermat s Last Theorem Shi Feng Sheng Danny Wong Abstract: Prior to the Diophantine geometry, number theory (or arithmetic) was to study the patterns of the numbers and elementary
Exhibit C A Proof of the Fermat s Last Theorem Shi Feng Sheng Danny Wong Abstract: Prior to the Diophantine geometry, number theory (or arithmetic) was to study the patterns of the numbers and elementary
~ 2. Who was Euclid? How might he have been influenced by the Library of Alexandria?
 CD Reading Guide Sections 5.1 and 5. 2 1. What was the Museum of Alexandria? ~ 2. Who was Euclid? How might he have been influenced by the Library of Alexandria? --)~ 3. What are the Elements of Euclid?
CD Reading Guide Sections 5.1 and 5. 2 1. What was the Museum of Alexandria? ~ 2. Who was Euclid? How might he have been influenced by the Library of Alexandria? --)~ 3. What are the Elements of Euclid?
Lecture 2: What is Proof?
 Lecture 2: What is Proof? Math 295 08/26/16 Webster Proof and Its History 8/2016 1 / 1 Evolution of Proof Proof, a relatively new idea Modern mathematics could not be supported at its foundation, nor construct
Lecture 2: What is Proof? Math 295 08/26/16 Webster Proof and Its History 8/2016 1 / 1 Evolution of Proof Proof, a relatively new idea Modern mathematics could not be supported at its foundation, nor construct
Solutions. End of Year Competition 12/10/2016
 12/10/2016 End of Year Competition Solutions 1. Sasheer has $93, Aidy has $5 more than Cecily, and Cecily has one third as much as Sasheer. How much money does Aidy have? Solution. $ 1 393 + 5 = $36. 2.
12/10/2016 End of Year Competition Solutions 1. Sasheer has $93, Aidy has $5 more than Cecily, and Cecily has one third as much as Sasheer. How much money does Aidy have? Solution. $ 1 393 + 5 = $36. 2.
Math 410, Spring 2013 Homework Problems (updated 5/1/13)
 Math 410, Spring 2013 Homework Problems (updated 5/1/13) In the 6th century, the Indian mathematician Aryabhata wrote that Half the circumference multiplied by half the diameter is the area of a circle.
Math 410, Spring 2013 Homework Problems (updated 5/1/13) In the 6th century, the Indian mathematician Aryabhata wrote that Half the circumference multiplied by half the diameter is the area of a circle.
Session # 1 SOLUTIONS
 09/23/2017 Session # 1 SOLUTIONS Problems marked with a star ( ) are from Lectures and Problems, A Gift to Young Mathematicians, by V.I. Arnold, c 2015 Mathematical Sciences Research Institute. 1. Mary
09/23/2017 Session # 1 SOLUTIONS Problems marked with a star ( ) are from Lectures and Problems, A Gift to Young Mathematicians, by V.I. Arnold, c 2015 Mathematical Sciences Research Institute. 1. Mary
Indian Mathematicians and Their Contributions
 Indian Mathematicians and Their Contributions By: G. Nagamani M.sc,M.Ed Teacher, Nalgonda-Telangana State ABSTRACT Indian mathematics has its roots in Vedic literature. Between 1000 B.C. and 1800 A.D.
Indian Mathematicians and Their Contributions By: G. Nagamani M.sc,M.Ed Teacher, Nalgonda-Telangana State ABSTRACT Indian mathematics has its roots in Vedic literature. Between 1000 B.C. and 1800 A.D.
PROJECTS. Project work in mathematics may be performed individually by a
 PROJECTS Project work in mathematics may be performed individually by a student or jointly by a group of students. These projects may be in the form of construction such as curve sketching or drawing of
PROJECTS Project work in mathematics may be performed individually by a student or jointly by a group of students. These projects may be in the form of construction such as curve sketching or drawing of
Course Competencies Template - Form 112
 Course Competencies Template - Form 112 GENERAL INFORMATION Name: Dr. Susan Neimand Phone #: (305) 237-6152 Course Prefix/Number: MHF4404 Course Title: History of Mathematics Number of Credits: 3 Degree
Course Competencies Template - Form 112 GENERAL INFORMATION Name: Dr. Susan Neimand Phone #: (305) 237-6152 Course Prefix/Number: MHF4404 Course Title: History of Mathematics Number of Credits: 3 Degree
Written test, 25 problems / 90 minutes
 Sponsored by: UGA Math Department and UGA Math Club Written test, 5 problems / 90 minutes October, 06 WITH SOLUTIONS Problem. Let a represent a digit from to 9. Which a gives a! aa + a = 06? Here aa indicates
Sponsored by: UGA Math Department and UGA Math Club Written test, 5 problems / 90 minutes October, 06 WITH SOLUTIONS Problem. Let a represent a digit from to 9. Which a gives a! aa + a = 06? Here aa indicates
Classwork 8.1. Perform the indicated operation and simplify each as much as possible. 1) 24 2) ) 54w y 11) wy 6) 5 9.
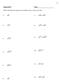 - 7 - Classwork 8.1 Name Perform the indicated operation and simplify each as much as possible. 1) 4 7) 16+ 5 49 ) 5 4 8) 11 6 81 ) 5 4x 9) 9 x + 49x 4) 75w 10) 6 5 54w y 5) 80wy 11) 15 6 6) 5 9 1) 15x
- 7 - Classwork 8.1 Name Perform the indicated operation and simplify each as much as possible. 1) 4 7) 16+ 5 49 ) 5 4 8) 11 6 81 ) 5 4x 9) 9 x + 49x 4) 75w 10) 6 5 54w y 5) 80wy 11) 15 6 6) 5 9 1) 15x
Math 312, Lecture 1. Zinovy Reichstein. September 9, 2015 Math 312
 Math 312, Lecture 1 Zinovy Reichstein September 9, 2015 Math 312 Number theory Number theory is a branch of mathematics Number theory Number theory is a branch of mathematics which studies the properties
Math 312, Lecture 1 Zinovy Reichstein September 9, 2015 Math 312 Number theory Number theory is a branch of mathematics Number theory Number theory is a branch of mathematics which studies the properties
Basic Ideas in Greek Mathematics
 previous index next Basic Ideas in Greek Mathematics Michael Fowler UVa Physics Department Closing in on the Square Root of 2 In our earlier discussion of the irrationality of the square root of 2, we
previous index next Basic Ideas in Greek Mathematics Michael Fowler UVa Physics Department Closing in on the Square Root of 2 In our earlier discussion of the irrationality of the square root of 2, we
1. Which German mathematician created a paradox involving a hotel with infinite rooms?
 1. Which German mathematician created a paradox involving a hotel with infinite rooms? A. David Hilbert B. Georg Cantor C. Carl Fredrich Gauss D. Felix Klein 2. Although more commonly known for his famous
1. Which German mathematician created a paradox involving a hotel with infinite rooms? A. David Hilbert B. Georg Cantor C. Carl Fredrich Gauss D. Felix Klein 2. Although more commonly known for his famous
Geometry Individual. AoPS Mu Alpha Theta. February 23 - March 9, 2019
 AoPS Mu Alpha Theta February 2 - March 9, 2019 1 The answer choice denotes that none of these answers are correct. Tests are scored such that each correct answer is worth 4 points, each question left blank
AoPS Mu Alpha Theta February 2 - March 9, 2019 1 The answer choice denotes that none of these answers are correct. Tests are scored such that each correct answer is worth 4 points, each question left blank
Math is Cool Masters
 Sponsored by: GENIE Industries 7 th Grade November 19, 2005 Individual Contest Express all answers as reduced fractions unless stated otherwise. Leave answers in terms of π where applicable. Do not round
Sponsored by: GENIE Industries 7 th Grade November 19, 2005 Individual Contest Express all answers as reduced fractions unless stated otherwise. Leave answers in terms of π where applicable. Do not round
Algebra and Geometry in the Sixteenth and Seventeenth Centuries
 Algebra and Geometry in the Sixteenth and Seventeenth Centuries Introduction After outlining the state of algebra and geometry at the beginning of the sixteenth century, we move to discuss the advances
Algebra and Geometry in the Sixteenth and Seventeenth Centuries Introduction After outlining the state of algebra and geometry at the beginning of the sixteenth century, we move to discuss the advances
Lecture 6. Three Famous Geometric Construction Problems
 Lecture 6. Three Famous Geometric Construction Problems The first Athenian school: the Sophist School After the final defeat of the Persians at Mycale in 479 B.C., Athens became a major city and commercial
Lecture 6. Three Famous Geometric Construction Problems The first Athenian school: the Sophist School After the final defeat of the Persians at Mycale in 479 B.C., Athens became a major city and commercial
What is proof? Lesson 1
 What is proof? Lesson The topic for this Math Explorer Club is mathematical proof. In this post we will go over what was covered in the first session. The word proof is a normal English word that you might
What is proof? Lesson The topic for this Math Explorer Club is mathematical proof. In this post we will go over what was covered in the first session. The word proof is a normal English word that you might
221 MATH REFRESHER session 3 SAT2015_P06.indd 221 4/23/14 11:39 AM
 Math Refresher Session 3 1 Area, Perimeter, and Volume Problems Area, Perimeter, and Volume 301. Formula Problems. Here, you are given certain data about one or more geometric figures, and you are asked
Math Refresher Session 3 1 Area, Perimeter, and Volume Problems Area, Perimeter, and Volume 301. Formula Problems. Here, you are given certain data about one or more geometric figures, and you are asked
π-day, 2013 Michael Kozdron
 π-day, 2013 Michael Kozdron What is π? In any circle, the ratio of the circumference to the diameter is constant. We are taught in high school that this number is called π. That is, for any circle. π =
π-day, 2013 Michael Kozdron What is π? In any circle, the ratio of the circumference to the diameter is constant. We are taught in high school that this number is called π. That is, for any circle. π =
Item 8. Constructing the Square Area of Two Proving No Irrationals. 6 Total Pages
 Item 8 Constructing the Square Area of Two Proving No Irrationals 6 Total Pages 1 2 We want to start with Pi. How Geometry Proves No Irrations They call Pi the ratio of the circumference of a circle to
Item 8 Constructing the Square Area of Two Proving No Irrationals 6 Total Pages 1 2 We want to start with Pi. How Geometry Proves No Irrations They call Pi the ratio of the circumference of a circle to
Figurate Numbers: presentation of a book
 Figurate Numbers: presentation of a book Elena DEZA and Michel DEZA Moscow State Pegagogical University, and Ecole Normale Superieure, Paris October 2011, Fields Institute Overview 1 Overview 2 Chapter
Figurate Numbers: presentation of a book Elena DEZA and Michel DEZA Moscow State Pegagogical University, and Ecole Normale Superieure, Paris October 2011, Fields Institute Overview 1 Overview 2 Chapter
Mathematics on Stamps. Robert McGee November 7, 2013 mathhappy.com
 Mathematics on Stamps Robert McGee November 7, 2013 mathhappy.com Tool Kit 1.Images of Mathematics on Postage Stamps http://jeff560.tripod.com/stamps.html Very large number of images of mathematics
Mathematics on Stamps Robert McGee November 7, 2013 mathhappy.com Tool Kit 1.Images of Mathematics on Postage Stamps http://jeff560.tripod.com/stamps.html Very large number of images of mathematics
CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction A typical Modern Geometry course will focus on some variation of a set of axioms for Euclidean geometry due to Hilbert. At the end of such a course, non-euclidean geometries (always
CHAPTER 1 Introduction A typical Modern Geometry course will focus on some variation of a set of axioms for Euclidean geometry due to Hilbert. At the end of such a course, non-euclidean geometries (always
MATH (43128): Topics in History of Mathematics JB-387, TuTh 6-7:50PM SYLLABUS Spring 2013
 MATH 480-01 (43128): Topics in History of Mathematics JB-387, TuTh 6-7:50PM SYLLABUS Spring 2013 John Sarli JB-326 (909)537-5374 jsarli@csusb.edu TuTh 11AM-1PM, or by appointment Text: V.S. Varadarajan,
MATH 480-01 (43128): Topics in History of Mathematics JB-387, TuTh 6-7:50PM SYLLABUS Spring 2013 John Sarli JB-326 (909)537-5374 jsarli@csusb.edu TuTh 11AM-1PM, or by appointment Text: V.S. Varadarajan,
Mathematicians in History Srinivasa Ramanujan
 Mathematicians in History Srinivasa Ramanujan Srinivasa Ramanujan was a self-taught Indian mathematician, viewed by many to be one of the greatest mathematical geniuses in history. As a student, he became
Mathematicians in History Srinivasa Ramanujan Srinivasa Ramanujan was a self-taught Indian mathematician, viewed by many to be one of the greatest mathematical geniuses in history. As a student, he became
There s a science to it!
 Page 1 There s a science to it REDESIGNED SAT Practice Material Written by Montclair High School Math Teacher Ryan Casazza Topic: Geometry and Statistics *All answers are at the end of this document. 1)
Page 1 There s a science to it REDESIGNED SAT Practice Material Written by Montclair High School Math Teacher Ryan Casazza Topic: Geometry and Statistics *All answers are at the end of this document. 1)
MATH DAY 2018 TEAM COMPETITION
 An excursion through mathematics and its history (the middle ages and beyond)(and some trivia) MATH DAY 2018 TEAM COMPETITION Made possible by A quick review of the rules History (or trivia) questions
An excursion through mathematics and its history (the middle ages and beyond)(and some trivia) MATH DAY 2018 TEAM COMPETITION Made possible by A quick review of the rules History (or trivia) questions
Solutions Math is Cool HS Championships Mental Math
 Mental Math 9/11 Answer Solution 1 30 There are 5 such even numbers and the formula is n(n+1)=5(6)=30. 2 3 [ways] HHT, HTH, THH. 3 6 1x60, 2x30, 3x20, 4x15, 5x12, 6x10. 4 9 37 = 3x + 10, 27 = 3x, x = 9.
Mental Math 9/11 Answer Solution 1 30 There are 5 such even numbers and the formula is n(n+1)=5(6)=30. 2 3 [ways] HHT, HTH, THH. 3 6 1x60, 2x30, 3x20, 4x15, 5x12, 6x10. 4 9 37 = 3x + 10, 27 = 3x, x = 9.
Screening Test Gauss Contest NMTC at PRIMARY LEVEL V & VI Standards Saturday, 27th August, 2016
 THE ASSOCIATION OF MATHEMATICS TEACHERS OF INDIA Screening Test Gauss Contest NMTC at PRIMARY LEVEL V & VI Standards Saturday, 7th August, 06 :. Fill in the response sheet with your Name, Class and the
THE ASSOCIATION OF MATHEMATICS TEACHERS OF INDIA Screening Test Gauss Contest NMTC at PRIMARY LEVEL V & VI Standards Saturday, 7th August, 06 :. Fill in the response sheet with your Name, Class and the
Introduction: Pythagorean Triplets
 Introduction: Pythagorean Triplets On this first day I want to give you an idea of what sorts of things we talk about in number theory. In number theory we want to study the natural numbers, and in particular
Introduction: Pythagorean Triplets On this first day I want to give you an idea of what sorts of things we talk about in number theory. In number theory we want to study the natural numbers, and in particular
1966 IMO Shortlist. IMO Shortlist 1966
 IMO Shortlist 1966 1 Given n > 3 points in the plane such that no three of the points are collinear. Does there exist a circle passing through (at least) 3 of the given points and not containing any other
IMO Shortlist 1966 1 Given n > 3 points in the plane such that no three of the points are collinear. Does there exist a circle passing through (at least) 3 of the given points and not containing any other
On the computational complexity of mathematical functions
 On the computational complexity of mathematical functions Jean-Pierre Demailly Institut Fourier, Université de Grenoble I & Académie des Sciences, Paris (France) November 26, 2011 KVPY conference at Vijyoshi
On the computational complexity of mathematical functions Jean-Pierre Demailly Institut Fourier, Université de Grenoble I & Académie des Sciences, Paris (France) November 26, 2011 KVPY conference at Vijyoshi
Cardano and the Solution of the Cubic. Bryan Dorsey, Kerry-Lyn Downie, and Marcus Huber
 Cardano and the Solution of the Cubic Bryan Dorsey, Kerry-Lyn Downie, and Marcus Huber Pacioli In 1494, the Italian Luca Pacioli produced his volume titled Summa de Arithmetica. In this a step was made
Cardano and the Solution of the Cubic Bryan Dorsey, Kerry-Lyn Downie, and Marcus Huber Pacioli In 1494, the Italian Luca Pacioli produced his volume titled Summa de Arithmetica. In this a step was made
The Cubic formula and beyond?"
 The Cubic formula and beyond?" Which polynomials can we solve using radicals? When was it figured out? Milan vs. Venice" (Cardano and Tartaglia)" 1500ʼs" Doubling the Cube (The Delian Problem)" To rid
The Cubic formula and beyond?" Which polynomials can we solve using radicals? When was it figured out? Milan vs. Venice" (Cardano and Tartaglia)" 1500ʼs" Doubling the Cube (The Delian Problem)" To rid
Infinity and Infinite Series
 Infinity and Infinite Series Numbers rule the Universe Pythagoras (-580-500 BC) God is a geometer Plato (-427-347 BC) God created everything by numbers Isaac Newton (1642-1727) The Great Architect of
Infinity and Infinite Series Numbers rule the Universe Pythagoras (-580-500 BC) God is a geometer Plato (-427-347 BC) God created everything by numbers Isaac Newton (1642-1727) The Great Architect of
CHAPTER 5 INTRODUCTION TO EUCLID S GEOMETRY. 5.1 Introduction
 78 MATHEMATICS INTRODUCTION TO EUCLID S GEOMETRY CHAPTER 5 5.1 Introduction The word geometry comes form the Greek words geo, meaning the earth, and metrein, meaning to measure. Geometry appears to have
78 MATHEMATICS INTRODUCTION TO EUCLID S GEOMETRY CHAPTER 5 5.1 Introduction The word geometry comes form the Greek words geo, meaning the earth, and metrein, meaning to measure. Geometry appears to have
Individual Round Arithmetic
 Individual Round Arithmetic (1) What is two-thirds times three-quarters? 1/2 (2) True or False: If the average of twenty exam scores is 75.65% (and no one actually had a score of 75.65%) there must be
Individual Round Arithmetic (1) What is two-thirds times three-quarters? 1/2 (2) True or False: If the average of twenty exam scores is 75.65% (and no one actually had a score of 75.65%) there must be
Jennifer Duong Daniel Szara October 9, 2009
 Jennifer Duong Daniel Szara October 9, 2009 By around 2000 BC, Geometry was developed further by the Babylonians who conquered the Sumerians. By around 2000 BC, Rational and Irrational numbers were used
Jennifer Duong Daniel Szara October 9, 2009 By around 2000 BC, Geometry was developed further by the Babylonians who conquered the Sumerians. By around 2000 BC, Rational and Irrational numbers were used
Take It To The Limit. Calculus H Mr. Russo Reaction to Take It To The Limit
 Calculus H Mr. Russo Reaction to Take It To The Limit For Tuesday, I am asking you to read the article below, Take It To The Limit by Steven Strogatz, and to write a brief reaction paper to this reading.
Calculus H Mr. Russo Reaction to Take It To The Limit For Tuesday, I am asking you to read the article below, Take It To The Limit by Steven Strogatz, and to write a brief reaction paper to this reading.
DISCOVERING GEOMETRY Over 6000 years ago, geometry consisted primarily of practical rules for measuring land and for
 Name Period GEOMETRY Chapter One BASICS OF GEOMETRY Geometry, like much of mathematics and science, developed when people began recognizing and describing patterns. In this course, you will study many
Name Period GEOMETRY Chapter One BASICS OF GEOMETRY Geometry, like much of mathematics and science, developed when people began recognizing and describing patterns. In this course, you will study many
7. Mathematical revival in Western Europe
 7. Mathematical revival in Western Europe (Burton, 6.2 6.4, 7.1) Mathematical studies and discoveries during the early Dark Ages in Europe were extremely limited. One illustration of this fact is the chronology
7. Mathematical revival in Western Europe (Burton, 6.2 6.4, 7.1) Mathematical studies and discoveries during the early Dark Ages in Europe were extremely limited. One illustration of this fact is the chronology
A plane in which each point is identified with a ordered pair of real numbers (x,y) is called a coordinate (or Cartesian) plane.
 Coordinate Geometry Rene Descartes, considered the father of modern philosophy (Cogito ergo sum), also had a great influence on mathematics. He and Fermat corresponded regularly and as a result of their
Coordinate Geometry Rene Descartes, considered the father of modern philosophy (Cogito ergo sum), also had a great influence on mathematics. He and Fermat corresponded regularly and as a result of their
Lecture 3: Geometry. Sadov s theorem. Morley s miracle. The butterfly theorem. E-320: Teaching Math with a Historical Perspective Oliver Knill, 2013
 E-320: Teaching Math with a Historical Perspective Oliver Knill, 2013 Lecture 3: Geometry Sadov s theorem Here is an example of a geometric theorem which has been found only 10 years ago: The quadrilateral
E-320: Teaching Math with a Historical Perspective Oliver Knill, 2013 Lecture 3: Geometry Sadov s theorem Here is an example of a geometric theorem which has been found only 10 years ago: The quadrilateral
MthEd/Math 300 Williams Fall 2011 Midterm Exam 3
 Name: MthEd/Math 300 Williams Fall 2011 Midterm Exam 3 Closed Book / Closed Note. Answer all problems. You may use a calculator for numerical computations. Section 1: For each event listed in the first
Name: MthEd/Math 300 Williams Fall 2011 Midterm Exam 3 Closed Book / Closed Note. Answer all problems. You may use a calculator for numerical computations. Section 1: For each event listed in the first
1. (A) Factor to get (2x+3)(2x 10) = 0, so the two roots are 3/2 and 5, which sum to 7/2.
 Solutions 00 53 rd AMC 1 A 1. (A) Factor to get (x+3)(x 10) = 0, so the two roots are 3/ and 5, which sum to 7/.. (A) Let x be the number she was given. Her calculations produce so x 9 3 = 43, x 9 = 19
Solutions 00 53 rd AMC 1 A 1. (A) Factor to get (x+3)(x 10) = 0, so the two roots are 3/ and 5, which sum to 7/.. (A) Let x be the number she was given. Her calculations produce so x 9 3 = 43, x 9 = 19
Introduction to Geometry
 Introduction to Geometry What is Geometry Why do we use Geometry What is Geometry? Geometry is a branch of mathematics that concerns itself with the questions of shape, size, position of figures, and the
Introduction to Geometry What is Geometry Why do we use Geometry What is Geometry? Geometry is a branch of mathematics that concerns itself with the questions of shape, size, position of figures, and the
2012 GCSE Maths Tutor All Rights Reserved
 2012 GCSE Maths Tutor All Rights Reserved www.gcsemathstutor.com This book is under copyright to GCSE Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents angles
2012 GCSE Maths Tutor All Rights Reserved www.gcsemathstutor.com This book is under copyright to GCSE Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents angles
State Math Contest Senior Exam SOLUTIONS
 State Math Contest Senior Exam SOLUTIONS 1. The following pictures show two views of a non standard die (however the numbers 1-6 are represented on the die). How many dots are on the bottom face of figure?
State Math Contest Senior Exam SOLUTIONS 1. The following pictures show two views of a non standard die (however the numbers 1-6 are represented on the die). How many dots are on the bottom face of figure?
 FROSH-SOPH 2 PERSON COMPETITION LARGE PRINT QUESTION 1 ICTM 2017 STATE DIVISION AA 1. Determine the sum of all distinct positive integers between 8 and 16 inclusive that can be expressed in one and only
FROSH-SOPH 2 PERSON COMPETITION LARGE PRINT QUESTION 1 ICTM 2017 STATE DIVISION AA 1. Determine the sum of all distinct positive integers between 8 and 16 inclusive that can be expressed in one and only
In today s world, people with basic calculus knowledge take the subject for granted. As
 Ziya Chen Math 4388 Shanyu Ji Calculus In today s world, people with basic calculus knowledge take the subject for granted. As long as they plug in numbers into the right formula and do the calculation
Ziya Chen Math 4388 Shanyu Ji Calculus In today s world, people with basic calculus knowledge take the subject for granted. As long as they plug in numbers into the right formula and do the calculation
A Lab Dethroned Ed s Chimera 1 Bobby Hanson October 17, 2007
 A Lab Dethroned Ed s Chimera 1 Bobby Hanson October 17, 2007 The mathematician s patterns, like the painter s or the poet s must be beautiful; the ideas like the colours or the words, must fit together
A Lab Dethroned Ed s Chimera 1 Bobby Hanson October 17, 2007 The mathematician s patterns, like the painter s or the poet s must be beautiful; the ideas like the colours or the words, must fit together
2017 Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament
 Team Round 1 Let P(x), Q(x) be nonconstant polynomials with real number coefficients. Prove that if P(y) = Q(y) for all real numbers y, then P(x) = Q(x) for all real numbers x. 2 Does there exist a two-variable
Team Round 1 Let P(x), Q(x) be nonconstant polynomials with real number coefficients. Prove that if P(y) = Q(y) for all real numbers y, then P(x) = Q(x) for all real numbers x. 2 Does there exist a two-variable
MEI Conference Squaring the Circle and Other Shapes
 MEI Conference 2017 Squaring the Circle and Other Shapes Kevin Lord kevin.lord@mei.org.uk Can you prove that the area of the square and the rectangle are equal? Use the triangle HPN to show that area of
MEI Conference 2017 Squaring the Circle and Other Shapes Kevin Lord kevin.lord@mei.org.uk Can you prove that the area of the square and the rectangle are equal? Use the triangle HPN to show that area of
11-6. Solving All Polynomial Equations. Vocabulary. What Types of Numbers Are Needed to Solve Polynomial Equations? Lesson
 Chapter 11 Lesson 11-6 Solving All Polynomial Equations Vocabulary double root, root of multiplicity 2 multiplicity BIG IDEA Every polynomial equation of degree n 1 has exactly n solutions, counting multiplicities.
Chapter 11 Lesson 11-6 Solving All Polynomial Equations Vocabulary double root, root of multiplicity 2 multiplicity BIG IDEA Every polynomial equation of degree n 1 has exactly n solutions, counting multiplicities.
Math 200 University of Connecticut
 IRRATIONALITY OF π AND e KEITH CONRAD Math 2 University of Connecticut Date: Aug. 3, 25. Contents. Introduction 2. Irrationality of π 2 3. Irrationality of e 3 4. General Ideas 4 5. Irrationality of rational
IRRATIONALITY OF π AND e KEITH CONRAD Math 2 University of Connecticut Date: Aug. 3, 25. Contents. Introduction 2. Irrationality of π 2 3. Irrationality of e 3 4. General Ideas 4 5. Irrationality of rational
TRIGONOMETRY RATIOS. LCOL and JCHL Revision
 TRIGONOMETRY RATIOS LCOL and JCHL Revision 2017 JCHL Paper 2 Question 8 (a) (i) The diagram below shows two right-angled triangles, ABC and ACD. They have right angles at B and D, respectively. AB = 10,
TRIGONOMETRY RATIOS LCOL and JCHL Revision 2017 JCHL Paper 2 Question 8 (a) (i) The diagram below shows two right-angled triangles, ABC and ACD. They have right angles at B and D, respectively. AB = 10,
Homework 2 from lecture 11 to lecture 20
 Homework 2 from lecture 11 to lecture 20 June 14, 2016 Lecture 11 1. Take a look at Apollonius Conics in the appendices. 2. UseCalculus toproveapropertyinapollonius book: LetC beapointonahyperbola. Let
Homework 2 from lecture 11 to lecture 20 June 14, 2016 Lecture 11 1. Take a look at Apollonius Conics in the appendices. 2. UseCalculus toproveapropertyinapollonius book: LetC beapointonahyperbola. Let
Chapter 1. Complex Numbers. 1.1 Complex Numbers. Did it come from the equation x = 0 (1.1)
 Chapter 1 Complex Numbers 1.1 Complex Numbers Origin of Complex Numbers Did it come from the equation Where did the notion of complex numbers came from? x 2 + 1 = 0 (1.1) as i is defined today? No. Very
Chapter 1 Complex Numbers 1.1 Complex Numbers Origin of Complex Numbers Did it come from the equation Where did the notion of complex numbers came from? x 2 + 1 = 0 (1.1) as i is defined today? No. Very
7 th Grade Algebra & Geometry Main Lesson Lesson Plan Outline
 Day #1 7 th Grade Algebra & Geometry Main Lesson Lesson Plan Outline Ask students: "What do you think algebra is?" The essence of algebra is: It is the universal language of mathematics. Everywhere in
Day #1 7 th Grade Algebra & Geometry Main Lesson Lesson Plan Outline Ask students: "What do you think algebra is?" The essence of algebra is: It is the universal language of mathematics. Everywhere in
History of π. Andrew Dolbee. November 7, 2012
 History of Andrew Dolbee November 7, 01 The search for the ratio between a circle's circumference and its diameter, known as PI(), has been a very long one; appearing in some of the oldest mathematical
History of Andrew Dolbee November 7, 01 The search for the ratio between a circle's circumference and its diameter, known as PI(), has been a very long one; appearing in some of the oldest mathematical
GROUP ROUND INSTRUCTIONS
 GROUP ROUND INSTRUCTIONS Your team will have 40 minutes to answer 10 questions. Each team will have the same questions. Each question is worth 6 points. However, some questions are easier than others!
GROUP ROUND INSTRUCTIONS Your team will have 40 minutes to answer 10 questions. Each team will have the same questions. Each question is worth 6 points. However, some questions are easier than others!
Grade 7/8 Math Circles Winter March 20/21/22 Types of Numbers
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Winter 2018 - March 20/21/22 Types of Numbers Introduction Today, we take our number
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Winter 2018 - March 20/21/22 Types of Numbers Introduction Today, we take our number
Preliminary Concepts. Relativity at 100 Years Old
 302685_ch_0P_01.QXP 11/3/06 7:11 AM Page 1 P Preliminary Concepts P.1 The Real Number System P.2 Integer and Rational Number Exponents P.3 Polynomials P.4 Factoring P.5 Rational Expressions P.6 Complex
302685_ch_0P_01.QXP 11/3/06 7:11 AM Page 1 P Preliminary Concepts P.1 The Real Number System P.2 Integer and Rational Number Exponents P.3 Polynomials P.4 Factoring P.5 Rational Expressions P.6 Complex
The Fibonacci Sequence
 Elvis Numbers Elvis the Elf skips up a flight of numbered stairs, starting at step 1 and going up one or two steps with each leap Along with an illustrious name, Elvis parents have endowed him with an
Elvis Numbers Elvis the Elf skips up a flight of numbered stairs, starting at step 1 and going up one or two steps with each leap Along with an illustrious name, Elvis parents have endowed him with an
Isaac Newton: Development of the Calculus and a Recalculation of π
 Isaac Newton: Development of the Calculus and a Recalculation of π Waseda University, SILS, History of Mathematics Outline Introduction Early modern Britain The early modern period in Britain The early
Isaac Newton: Development of the Calculus and a Recalculation of π Waseda University, SILS, History of Mathematics Outline Introduction Early modern Britain The early modern period in Britain The early
