Lecture 9 Overview (Ch. 1-3)
|
|
|
- Gerald Ferguson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 9 Overview (Ch. -) Format of the first midterm: four problems with multiple questions. he Ideal Gas Law, calculation of δw, δq and ds for various ideal gas processes. Einstein solid and two-state paramagnet, multiplicity and entropy, the stat. phys. definition of, how to get from the multiplicity to the equation of state. he test is an open textbook exam (but no open HW solutions!). I recommend to list all essential equations you won t have time to read the textbook!
2 (a) roblem One mole of a monatomic ideal gas goes through a quasistatic three-stage cycle (-, -, -) shown in the Figure. and are given. (a) () Calculate the work done by the gas. Is it positive or negative? (b) () sing two methods (Sackur-etrode eq. and dq/), calculate the entropy change for each stage and for the whole cycle, ΔS total. Did you get the expected result for ΔS total? Explain. (c) () What is the heat capacity (in units ) for each stage? const (isobaric process) δw ( ) ( ) > const (isochoric process) δw W d const (isothermal process) δ < δ W total δw d ( ) + + δw >
3 roblem (cont.) (b) Sackur-etrode equation: S, f f f f ΔS + + i i i i (,, ) + + k f ( m) const (isobaric process) ΔS const (isochoric process) const (isothermal process) ΔS ΔS Δ S cycle as it should be for a quasistatic cyclic process (quasistatic reversible), because S is a state function.
4 roblem (cont.) (b) δ Q d S - for quasi-static processes const (isobaric process) δ Q C d ΔS Cd const (isochoric process) d δ Q δ Q C d C d ΔS const (isothermal process) d d d δq δwo ΔS Δ S cycle
5 roblem (cont) (c) δqcd Let s express both δq and d in terms of d : const (isobaric process) C C C + + const (isochoric process) C C const (isothermal process), d while δq C t home: recall how these results would be modified for diatomic and polyatomic gases.
6 roblem One mole of a monatomic ideal gas goes through a quasistatic three-stage cycle (-, -, -) shown in the Figure. rocess - is adiabatic;,, and are given. (a) () For each stage and for the whole cycle, express the work δw done on the gas in terms of,, and. Comment on the sign of δw. (b) () What is the heat capacity (in units ) for each stage? (c) () Calculate δq transferred to the gas in the cycle; the same for the reverse cycle; what would be the result if δq were an exact differential? (d) () sing the Sackur-etrode equation, calculate the entropy change for each stage and for the whole cycle, ΔS total. Did you get the expected result for ΔS total? Explain. (a) const (isobaric process) δ W ( ) < const (isochoric process) δw adiabatic process δ W γ γ ( ) d d γ γ γ γ γ / >
7 roblem (cont.) adiabatic process δ Q (c) const (isobaric process) const (isochoric process) ( ) ( ) > C δ Q ( ) ( ) [ ] < γ γ γ δ C Q ( ) + + γ δ δ δ Q Q Q For the reverse cycle: Q Q reverse δ δ If δq were an exact differential, for a cycle δq should be zero.
8 roblem (cont.) const (isobaric process) ( ) ( ) f k S,, Δ i f i f i f i f S ΔS const (isochoric process) S Δ γ γ ΔS Δ S cycle as it should be for a quasistatic cyclic process (quasistatic reversible), because S is a state function. Sackur-etrode equation: δq (quasistatic adiabatic isentropic process) (d)
9 roblem Calculate the heat capacity of one mole of an ideal monatomic gas C() in the quasistatic process shown in the Figure. and are given. Start with the definition: C δ Q d δq d δw d + ( )d we need to find the equation of Q d this process C ( ) δ + ( ) d d () 4 d d d + d C( ) + ( ) + / d d d d C( ) 4
10 roblem (cont.) Does it make sense? Sconst adiabat C/ C( ) 4 C ( ) at / the line touches an isotherm const isotherm.. / /8 / /8 / C ( ) at /8 the line touches an adiabat
11 roblem 4 You are in possession of an Einstein solid with three oscillators and a two-state paramagnet with four spins. he magnetic field in the region of the paramagnet points up and is carefully tuned so that µ ε, where µ is the energy of a spin pointing down, -µ is the energy of a spin pointing up, and ε is the energy level separation of the oscillators. t the beginning of the experiment the energy in the Einstein solid S is 4 ε and the energy in the paramagnet is -4 ε. (a) (4) sing a schematic drawing of the Einstein solid, give an example of a microstate which corresponds to the macrostate S 4 ε. (b) (4) sing a schematic drawing of the paramagnet, give an example of a microstate which corresponds to the macrostate -4 ε. (c) (8) Considering that the system comprises the solid and the paramagnet, calculate the multiplicity of the system assuming that the solid and paramagnet cannot exchange energy. (d) (4) ow let the solid and paramagnet exchange energy until they come to thermal equilibrium. ote that because this system is small, there will be large fluctuations around thermal equilibrium, but let s assume that the system is not fluctuating at the moment. What is the value of S now? Draw an example of a microstate in which you might find the solid. What is the value of now? Draw an example of a microstate in which you might find the paramagnet.
12 roblem 4 (cont.) wo-state paramagnet Einstein solid E + μ E - μ ε ε (a) S 4 ε (b) -4 ε E + μ E - μ (c) ( 4 + ) Ω S Ω S Ω! 4!! Most of the confusion came from the fact that we usually measure the energy of an oscillator in the Einstein solid from its ground state (which is / ε above the bottom of the potential well), whereas for the two-state paramagnet we ve chosen the zero energy in the middle of the energy gap between spinup and spin-down levels. he avoid confusion, consider the number of energy quanta ε available for the system.
13 (d) roblem 4 (cont.) S 4ε const In equilibrium, the multiplicity is maximum. he two-state paramagnet can absorb only multiples of ε. wo options: ε is transferred from S to, and 4ε is transferred from S to. ε transfer S, q, 4, 4ε transfer S, q, 4, 4!!! Example of one of the equilibrium microstates: Ω Ω S Ω Ω S Ω 4!!! 4!!! hus, the equilibrium situation corresponds to the transfer of ε from the Einstein solid to the two-state paramagnet S S Ω 6 4 E + μ E - μ ε ε ote that the equilibrium condition / / holds if both systems have only quadratic degrees of freedom.
14 roblem Consider a system whose multiplicity / Ω,, f f is described by the equation: where is the internal energy, is the volume, is the number of particles in the system, f is the total number of degrees of freedom, f() is some function of. (a) () Find the system s entropy and temperature as functions of. re these results in agreement with the equipartition theorem? Does the expression for the entropy makes sense when? (b) () Find the heat capacity of the system at fixed volume. (c) () ssume that the system is divided into two sub-systems, and ; subsystem holds energy and volume, while the sub-system holds - and -. Show that for an equilibrium macropartition, the energy per molecule is the same for both sub-systems. (a) S k f ( ) + k k Ω k f + f k S k f, - in agreement with the equipartition theorem f k ( ) ( ) When,, and S - - doesn t make sense. his means that the expression for Ω holds in the classical limit of high temperatures, it should be modified at low.
15 roblem (cont.) ( ) ( ) /,, f Ω ( ) ( ) ( ) / /,, Ω ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) / / / / Ω ( ) (b) [ ] k f f k S d ds d Q C,,, δ (c)
16 roblem 6 () he ES (electron spin resonance) set-up can detect the minimum difference in the number of spin-up and spin-down electrons in a two-state paramagnet -. he paramagnetic sample is placed at K in an external magnetic field. he component of the electron s magnetic moment along is ± μ ± 9.x -4 J/. Find the minimum total number of electrons in the sample that is required to make this detection possible. E E exp E E k μ μ exp k + + exp μ μ + exp k μ k exp k 4 μ 9. exp exp.8 k.99 - the high- limit +.4 4,4
Results of. Midterm 1. Points < Grade C D,F C B points.
 esults of Midterm 0 0 0 0 40 50 60 70 80 90 points Grade C D,F oints A 80-95 + 70-79 55-69 C + 45-54 0-44
esults of Midterm 0 0 0 0 40 50 60 70 80 90 points Grade C D,F oints A 80-95 + 70-79 55-69 C + 45-54 0-44
Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics
 hysics GRE: hermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics G. J. Loges University of Rochester Dept. of hysics & Astronomy xkcd.com/66/ c Gregory Loges, 206 Contents Ensembles 2 Laws of hermodynamics 3 hermodynamic
hysics GRE: hermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics G. J. Loges University of Rochester Dept. of hysics & Astronomy xkcd.com/66/ c Gregory Loges, 206 Contents Ensembles 2 Laws of hermodynamics 3 hermodynamic
Lecture 5. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 5 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Ch. 19 First Law of Thermodynamics In a thermodynamic process, changes occur in the state of the system. Careful of signs! Q is positive when heat flows into a system. W is
Lecture 5 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Ch. 19 First Law of Thermodynamics In a thermodynamic process, changes occur in the state of the system. Careful of signs! Q is positive when heat flows into a system. W is
Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is an extension of the principle of conservation of energy. It includes the transfer of both mechanical and thermal energy. First
Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is an extension of the principle of conservation of energy. It includes the transfer of both mechanical and thermal energy. First
Lecture 2 The First Law of Thermodynamics (Ch.1)
 Lecture he First Law o hermodynamics (h.) Lecture - we introduced macroscopic parameters that describe the state o a thermodynamic system (including temperature), the equation o state (,,) 0, and linked
Lecture he First Law o hermodynamics (h.) Lecture - we introduced macroscopic parameters that describe the state o a thermodynamic system (including temperature), the equation o state (,,) 0, and linked
The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 19 To represent
Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 19 To represent
Lecture 8. The Second Law of Thermodynamics; Energy Exchange
 Lecture 8 The Second Law of Thermodynamics; Energy Exchange The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of energy exchange General definition of temperature Why heat flows from hot to cold Reading for
Lecture 8 The Second Law of Thermodynamics; Energy Exchange The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of energy exchange General definition of temperature Why heat flows from hot to cold Reading for
(prev) (top) (next) (Throughout, we will assume the processes involve an ideal gas with constant n.)
 1 of 9 8/22/12 9:51 PM (prev) (top) (next) Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamic processes can be: 2 isothermal processes, ΔT = 0 (so P ~ 1 / V); isobaric processes, ΔP = 0 (so T ~ V); isovolumetric or isochoric
1 of 9 8/22/12 9:51 PM (prev) (top) (next) Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamic processes can be: 2 isothermal processes, ΔT = 0 (so P ~ 1 / V); isobaric processes, ΔP = 0 (so T ~ V); isovolumetric or isochoric
Part II: Statistical Physics
 Chapter 6: Boltzmann Statistics SDSMT, Physics Fall Semester: Oct. - Dec., 2013 1 Introduction: Very brief 2 Boltzmann Factor Isolated System and System of Interest Boltzmann Factor The Partition Function
Chapter 6: Boltzmann Statistics SDSMT, Physics Fall Semester: Oct. - Dec., 2013 1 Introduction: Very brief 2 Boltzmann Factor Isolated System and System of Interest Boltzmann Factor The Partition Function
PHYSICS 214A Midterm Exam February 10, 2009
 Clearly Print LAS NAME: FIRS NAME: SIGNAURE: I.D. # PHYSICS 2A Midterm Exam February 0, 2009. Do not open the exam until instructed to do so. 2. Write your answers in the spaces provided for each part
Clearly Print LAS NAME: FIRS NAME: SIGNAURE: I.D. # PHYSICS 2A Midterm Exam February 0, 2009. Do not open the exam until instructed to do so. 2. Write your answers in the spaces provided for each part
PHY214 Thermal & Kinetic Physics Duration: 2 hours 30 minutes
 BSc Examination by course unit. Friday 5th May 01 10:00 1:30 PHY14 Thermal & Kinetic Physics Duration: hours 30 minutes YOU ARE NOT PERMITTED TO READ THE CONTENTS OF THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL INSTRUCTED
BSc Examination by course unit. Friday 5th May 01 10:00 1:30 PHY14 Thermal & Kinetic Physics Duration: hours 30 minutes YOU ARE NOT PERMITTED TO READ THE CONTENTS OF THIS QUESTION PAPER UNTIL INSTRUCTED
(# = %(& )(* +,(- Closed system, well-defined energy (or e.g. E± E/2): Microcanonical ensemble
 Recall from before: Internal energy (or Entropy): &, *, - (# = %(& )(* +,(- Closed system, well-defined energy (or e.g. E± E/2): Microcanonical ensemble & = /01Ω maximized Ω: fundamental statistical quantity
Recall from before: Internal energy (or Entropy): &, *, - (# = %(& )(* +,(- Closed system, well-defined energy (or e.g. E± E/2): Microcanonical ensemble & = /01Ω maximized Ω: fundamental statistical quantity
Part II: Statistical Physics
 Chapter 6: Boltzmann Statistics SDSMT, Physics Fall Semester: Oct. - Dec., 2014 1 Introduction: Very brief 2 Boltzmann Factor Isolated System and System of Interest Boltzmann Factor The Partition Function
Chapter 6: Boltzmann Statistics SDSMT, Physics Fall Semester: Oct. - Dec., 2014 1 Introduction: Very brief 2 Boltzmann Factor Isolated System and System of Interest Boltzmann Factor The Partition Function
Chapter 20. Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Lecture 8. The Second Law of Thermodynamics; Energy Exchange
 Lecture 8 The Second Law of Thermodynamics; Energy Exchange The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of energy exchange General definition of temperature Why heat flows from hot to cold Reading for
Lecture 8 The Second Law of Thermodynamics; Energy Exchange The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of energy exchange General definition of temperature Why heat flows from hot to cold Reading for
More Thermodynamics. Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes
 More Thermodynamics Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes Carnot Cycle Efficiency of Engines Entropy More Thermodynamics 1 Specific Heat of Gases
More Thermodynamics Specific Specific Heats of a Gas Equipartition of Energy Reversible and Irreversible Processes Carnot Cycle Efficiency of Engines Entropy More Thermodynamics 1 Specific Heat of Gases
Physics Nov Cooling by Expansion
 Physics 301 19-Nov-2004 25-1 Cooling by Expansion Now we re going to change the subject and consider the techniques used to get really cold temperatures. Of course, the best way to learn about these techniques
Physics 301 19-Nov-2004 25-1 Cooling by Expansion Now we re going to change the subject and consider the techniques used to get really cold temperatures. Of course, the best way to learn about these techniques
Exam 2, Chemistry 481, 4 November 2016
 1 Exam, Chemistry 481, 4 November 016 Show all work for full credit Useful constants: h = 6.66 10 34 J s; c (speed of light) =.998 10 8 m s 1 k B = 1.3807 10 3 J K 1 ; R (molar gas constant) = 8.314 J
1 Exam, Chemistry 481, 4 November 016 Show all work for full credit Useful constants: h = 6.66 10 34 J s; c (speed of light) =.998 10 8 m s 1 k B = 1.3807 10 3 J K 1 ; R (molar gas constant) = 8.314 J
Physics 172H Modern Mechanics
 Physics 172H Modern Mechanics Instructor: Dr. Mark Haugan Office: PHYS 282 haugan@purdue.edu TAs: Alex Kryzwda John Lorenz akryzwda@purdue.edu jdlorenz@purdue.edu Lecture 22: Matter & Interactions, Ch.
Physics 172H Modern Mechanics Instructor: Dr. Mark Haugan Office: PHYS 282 haugan@purdue.edu TAs: Alex Kryzwda John Lorenz akryzwda@purdue.edu jdlorenz@purdue.edu Lecture 22: Matter & Interactions, Ch.
Heat Capacities, Absolute Zero, and the Third Law
 Heat Capacities, Absolute Zero, and the hird Law We have already noted that heat capacity and entropy have the same units. We will explore further the relationship between heat capacity and entropy. We
Heat Capacities, Absolute Zero, and the hird Law We have already noted that heat capacity and entropy have the same units. We will explore further the relationship between heat capacity and entropy. We
Lecture 9 Examples and Problems
 Lecture 9 Examples and Problems Counting microstates of combined systems Volume exchange between systems Definition of Entropy and its role in equilibrium The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of
Lecture 9 Examples and Problems Counting microstates of combined systems Volume exchange between systems Definition of Entropy and its role in equilibrium The second law of thermodynamics Statistics of
Physics 4311 ANSWERS: Sample Problems for Exam #2. (1)Short answer questions:
 (1)Short answer questions: Physics 4311 ANSWERS: Sample Problems for Exam #2 (a) Consider an isolated system that consists of several subsystems interacting thermally and mechanically with each other.
(1)Short answer questions: Physics 4311 ANSWERS: Sample Problems for Exam #2 (a) Consider an isolated system that consists of several subsystems interacting thermally and mechanically with each other.
(a) How much work is done by the gas? (b) Assuming the gas behaves as an ideal gas, what is the final temperature? V γ+1 2 V γ+1 ) pdv = K 1 γ + 1
 P340: hermodynamics and Statistical Physics, Exam#, Solution. (0 point) When gasoline explodes in an automobile cylinder, the temperature is about 2000 K, the pressure is is 8.0 0 5 Pa, and the volume
P340: hermodynamics and Statistical Physics, Exam#, Solution. (0 point) When gasoline explodes in an automobile cylinder, the temperature is about 2000 K, the pressure is is 8.0 0 5 Pa, and the volume
If the dividing wall were allowed to move, which of the following statements would not be true about its equilibrium position?
 PHYS 213 Exams Database Midterm (A) A block slides across a rough surface, eventually coming to a stop. 1) What happens to the block's internal thermal energy and entropy? a. and both stay the same b.
PHYS 213 Exams Database Midterm (A) A block slides across a rough surface, eventually coming to a stop. 1) What happens to the block's internal thermal energy and entropy? a. and both stay the same b.
Physics Fall Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Fluids. Lecture 32: Heat and Work II. Slide 32-1
 Physics 1501 Fall 2008 Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Fluids Lecture 32: Heat and Work II Slide 32-1 Recap: the first law of thermodynamics Two ways to raise temperature: Thermally: flow of heat Energy
Physics 1501 Fall 2008 Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Fluids Lecture 32: Heat and Work II Slide 32-1 Recap: the first law of thermodynamics Two ways to raise temperature: Thermally: flow of heat Energy
Physics 213 Spring 2009 Midterm exam. Review Lecture
 Physics 213 Spring 2009 Midterm exam Review Lecture The next two questions pertain to the following situation. A container of air (primarily nitrogen and oxygen molecules) is initially at 300 K and atmospheric
Physics 213 Spring 2009 Midterm exam Review Lecture The next two questions pertain to the following situation. A container of air (primarily nitrogen and oxygen molecules) is initially at 300 K and atmospheric
Work, heat and the first law of thermodynamics
 Chapter 3 Work, heat and the first law of thermodynamics 3.1 Mechanical work Mechanical work is defined as an energy transfer to the system through the change of an external parameter. Work is the only
Chapter 3 Work, heat and the first law of thermodynamics 3.1 Mechanical work Mechanical work is defined as an energy transfer to the system through the change of an external parameter. Work is the only
Physics 111. Thursday, Dec. 9, 3-5pm and 7-9pm. Announcements. Thursday, December 9, 2004
 ics day, ember 9, 2004 Ch 18: diagrams isobaric process isochoric process isothermal process adiabatic process 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Class Reviews/Evaluations For the rest of the semester day,. 9,
ics day, ember 9, 2004 Ch 18: diagrams isobaric process isochoric process isothermal process adiabatic process 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Class Reviews/Evaluations For the rest of the semester day,. 9,
CH 15. Zeroth and First Law of Thermodynamics
 CH 15 Zeroth and First Law of Thermodynamics THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics Branch of Physics that is built upon the fundamental laws that heat and work obey. Central Heating Objectives: After finishing
CH 15 Zeroth and First Law of Thermodynamics THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics Branch of Physics that is built upon the fundamental laws that heat and work obey. Central Heating Objectives: After finishing
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
Lecture 5: Temperature, Adiabatic Processes
 Lecture 5: Temperature, Adiabatic Processes Chapter II. Thermodynamic Quantities A.G. Petukhov, PHYS 743 September 20, 2017 Chapter II. Thermodynamic Quantities Lecture 5: Temperature, Adiabatic Processes
Lecture 5: Temperature, Adiabatic Processes Chapter II. Thermodynamic Quantities A.G. Petukhov, PHYS 743 September 20, 2017 Chapter II. Thermodynamic Quantities Lecture 5: Temperature, Adiabatic Processes
Phys Midterm. March 17
 Phys 7230 Midterm March 17 Consider a spin 1/2 particle fixed in space in the presence of magnetic field H he energy E of such a system can take one of the two values given by E s = µhs, where µ is the
Phys 7230 Midterm March 17 Consider a spin 1/2 particle fixed in space in the presence of magnetic field H he energy E of such a system can take one of the two values given by E s = µhs, where µ is the
International Physics Course Entrance Examination Questions
 International Physics Course Entrance Examination Questions (May 2010) Please answer the four questions from Problem 1 to Problem 4. You can use as many answer sheets you need. Your name, question numbers
International Physics Course Entrance Examination Questions (May 2010) Please answer the four questions from Problem 1 to Problem 4. You can use as many answer sheets you need. Your name, question numbers
Exam 2 Solutions. for a gas obeying the equation of state. Z = PV m RT = 1 + BP + CP 2,
 Chemistry 360 Dr. Jean M. Standard Fall 016 Name KEY 1.) (14 points) Determine # H & % ( $ ' Exam Solutions for a gas obeying the equation of state Z = V m R = 1 + B + C, where B and C are constants. Since
Chemistry 360 Dr. Jean M. Standard Fall 016 Name KEY 1.) (14 points) Determine # H & % ( $ ' Exam Solutions for a gas obeying the equation of state Z = V m R = 1 + B + C, where B and C are constants. Since
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
Thermal and Statistical Physics Department Exam Last updated November 4, L π
 Thermal and Statistical Physics Department Exam Last updated November 4, 013 1. a. Define the chemical potential µ. Show that two systems are in diffusive equilibrium if µ 1 =µ. You may start with F =
Thermal and Statistical Physics Department Exam Last updated November 4, 013 1. a. Define the chemical potential µ. Show that two systems are in diffusive equilibrium if µ 1 =µ. You may start with F =
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
du = δq + δw = δq rev + δw rev = δq rev + 0
 Chem 4501 Introduction to hermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics Module Number 6 Active Learning Answers and Optional Problems/Solutions 1. McQuarrie and Simon, 6-6. Paraphrase: Compute
Chem 4501 Introduction to hermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics Module Number 6 Active Learning Answers and Optional Problems/Solutions 1. McQuarrie and Simon, 6-6. Paraphrase: Compute
Chapter 19 Entropy Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 20-1
 Chapter 19 Entropy Slide 20-1 Ch 19 & 20 material What to focus on? Just put out some practice problems for Ch. 19/20 Ideal gas how to find P/V/T changes. How to calculate energy required for a given T
Chapter 19 Entropy Slide 20-1 Ch 19 & 20 material What to focus on? Just put out some practice problems for Ch. 19/20 Ideal gas how to find P/V/T changes. How to calculate energy required for a given T
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 19 The Kinetic Theory of Gases Ideal gas RMS speed Internal energy Isothermal process Isobaric process Isochoric process Adiabatic process General process 1. Figure
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 19 The Kinetic Theory of Gases Ideal gas RMS speed Internal energy Isothermal process Isobaric process Isochoric process Adiabatic process General process 1. Figure
Speed Distribution at CONSTANT Temperature is given by the Maxwell Boltzmann Speed Distribution
 Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2014-2015 ENERGY AND MATTER Duration: 120 MINS (2 hours) This paper contains 8 questions. Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate
213 Midterm coming up
 213 Midterm coming up Monday April 8 @ 7 pm (conflict exam @ 5:15pm) Covers: Lectures 1-12 (not including thermal radiation) HW 1-4 Discussion 1-4 Labs 1-2 Review Session Sunday April 7, 3-5 PM, 141 Loomis
213 Midterm coming up Monday April 8 @ 7 pm (conflict exam @ 5:15pm) Covers: Lectures 1-12 (not including thermal radiation) HW 1-4 Discussion 1-4 Labs 1-2 Review Session Sunday April 7, 3-5 PM, 141 Loomis
1. Thermodynamics 1.1. A macroscopic view of matter
 1. Thermodynamics 1.1. A macroscopic view of matter Intensive: independent of the amount of substance, e.g. temperature,pressure. Extensive: depends on the amount of substance, e.g. internal energy, enthalpy.
1. Thermodynamics 1.1. A macroscopic view of matter Intensive: independent of the amount of substance, e.g. temperature,pressure. Extensive: depends on the amount of substance, e.g. internal energy, enthalpy.
Internal Energy (example)
 Internal Energy (example) A bucket of water KEs: translational: rotational: vibrational: PEs: within molecules: between molecules: @ rest on the table molecular bonds dipole-dipole interactions Internal
Internal Energy (example) A bucket of water KEs: translational: rotational: vibrational: PEs: within molecules: between molecules: @ rest on the table molecular bonds dipole-dipole interactions Internal
Irreversible Processes
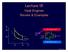 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
4.1 LAWS OF MECHANICS - Review
 4.1 LAWS OF MECHANICS - Review Ch4 9 SYSTEM System: Moving Fluid Definitions: System is defined as an arbitrary quantity of mass of fixed identity. Surrounding is everything external to this system. Boundary
4.1 LAWS OF MECHANICS - Review Ch4 9 SYSTEM System: Moving Fluid Definitions: System is defined as an arbitrary quantity of mass of fixed identity. Surrounding is everything external to this system. Boundary
Heat Machines (Chapters 18.6, 19)
 eat Machines (hapters 8.6, 9) eat machines eat engines eat pumps The Second Law of thermodynamics Entropy Ideal heat engines arnot cycle Other cycles: Brayton, Otto, Diesel eat Machines Description The
eat Machines (hapters 8.6, 9) eat machines eat engines eat pumps The Second Law of thermodynamics Entropy Ideal heat engines arnot cycle Other cycles: Brayton, Otto, Diesel eat Machines Description The
Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases Unit Concepts: A) A bit more about temperature B) Ideal Gas Law C) Molar specific heats D) Using them all Unit 05 Kinetic Theory, Slide 1 Temperature and Velocity Recall:
Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases Unit Concepts: A) A bit more about temperature B) Ideal Gas Law C) Molar specific heats D) Using them all Unit 05 Kinetic Theory, Slide 1 Temperature and Velocity Recall:
Molar Specific Heat of Ideal Gases
 Molar Specific Heat of Ideal Gases Since Q depends on process, C dq/dt also depends on process. Define a) molar specific heat at constant volume: C V (1/n) dq/dt for constant V process. b) molar specific
Molar Specific Heat of Ideal Gases Since Q depends on process, C dq/dt also depends on process. Define a) molar specific heat at constant volume: C V (1/n) dq/dt for constant V process. b) molar specific
Specific Heat of Diatomic Gases and. The Adiabatic Process
 Specific Heat of Diatomic Gases and Solids The Adiabatic Process Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University February 22, 2012 Lecture 7 1 Specific Heat for Solids and Diatomic i Gasses
Specific Heat of Diatomic Gases and Solids The Adiabatic Process Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University February 22, 2012 Lecture 7 1 Specific Heat for Solids and Diatomic i Gasses
 第 1 頁, 共 6 頁 Chap20 1. Test Bank, Question 5 Which of the following is NOT a state variable? Work Internal energy Entropy Temperature Pressure 2. Test Bank, Question 18 Let denote the change in entropy
第 1 頁, 共 6 頁 Chap20 1. Test Bank, Question 5 Which of the following is NOT a state variable? Work Internal energy Entropy Temperature Pressure 2. Test Bank, Question 18 Let denote the change in entropy
Solutions to Problem Set 4
 Cornell University, Physics Department Fall 2014 PHYS-3341 Statistical Physics Prof. Itai Cohen Solutions to Problem Set 4 David C. sang, Woosong Choi 4.1 Equilibrium Fluctuations (a From lecture we had
Cornell University, Physics Department Fall 2014 PHYS-3341 Statistical Physics Prof. Itai Cohen Solutions to Problem Set 4 David C. sang, Woosong Choi 4.1 Equilibrium Fluctuations (a From lecture we had
Lecture 13 Heat Engines
 Lecture 3 Heat Engines hermodynamic rocesses and entroy hermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat - How do we define engine efficiency? - Carnot cycle: the best ossible efficiency Reading for this
Lecture 3 Heat Engines hermodynamic rocesses and entroy hermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat - How do we define engine efficiency? - Carnot cycle: the best ossible efficiency Reading for this
Thermodynamic system is classified into the following three systems. (ii) Closed System It exchanges only energy (not matter) with surroundings.
 1 P a g e The branch of physics which deals with the study of transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa. A thermodynamical system is said to be in thermal equilibrium when
1 P a g e The branch of physics which deals with the study of transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa. A thermodynamical system is said to be in thermal equilibrium when
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_21 Monday, November 26, 2007 Page 1
 University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_21 Monday, November 26, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. Let k be the Boltzmann constant. If the configuration of the molecules in a gas changes so that the multiplicity
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_21 Monday, November 26, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. Let k be the Boltzmann constant. If the configuration of the molecules in a gas changes so that the multiplicity
Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law
 Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law Etymology: Entropy, entropie in German. En from energy and trope turning toward Turning to energy Zeroth law temperature First law energy Second law - entropy CY1001 2010
Lecture 2 Entropy and Second Law Etymology: Entropy, entropie in German. En from energy and trope turning toward Turning to energy Zeroth law temperature First law energy Second law - entropy CY1001 2010
The first law of thermodynamics continued
 Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Outline Review Example Problem 1. Thermodynamics. Review and Example Problems: Part-2. X Bai. SDSMT, Physics. Fall 2014
 Review and Example Problems: Part- SDSMT, Physics Fall 014 1 Review Example Problem 1 Exponents of phase transformation : contents 1 Basic Concepts: Temperature, Work, Energy, Thermal systems, Ideal Gas,
Review and Example Problems: Part- SDSMT, Physics Fall 014 1 Review Example Problem 1 Exponents of phase transformation : contents 1 Basic Concepts: Temperature, Work, Energy, Thermal systems, Ideal Gas,
Problem: Calculate the entropy change that results from mixing 54.0 g of water at 280 K with 27.0 g of water at 360 K in a vessel whose walls are
 Problem: Calculate the entropy change that results from mixing 54.0 g of water at 280 K with 27.0 g of water at 360 K in a vessel whose walls are perfectly insulated from the surroundings. Is this a spontaneous
Problem: Calculate the entropy change that results from mixing 54.0 g of water at 280 K with 27.0 g of water at 360 K in a vessel whose walls are perfectly insulated from the surroundings. Is this a spontaneous
Classical Physics I. PHY131 Lecture 36 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Lecture 36 1
 Classical Physics I PHY131 Lecture 36 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Lecture 36 1 Recap: (Ir)reversible( Processes Reversible processes are processes that occur under quasi-equilibrium conditions:
Classical Physics I PHY131 Lecture 36 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Lecture 36 1 Recap: (Ir)reversible( Processes Reversible processes are processes that occur under quasi-equilibrium conditions:
Lecture 12. Refrigerators. Toward Absolute Zero (Ch. 4)
 0 9 0 7 Center of hottest stars Center of Sun, nuclear reactions Lecture. Refrigerators. oward Absolute Zero (Ch. ) emperature, K 0 5 0 0 0-0 - 0-5 Electronic/chemical energy Surface of Sun, hottest boiling
0 9 0 7 Center of hottest stars Center of Sun, nuclear reactions Lecture. Refrigerators. oward Absolute Zero (Ch. ) emperature, K 0 5 0 0 0-0 - 0-5 Electronic/chemical energy Surface of Sun, hottest boiling
Classical thermodynamics
 Classical thermodynamics More about irreversibility chap. 6 Isentropic expansion of an ideal gas Sudden expansion of a gas into vacuum cf Kittel and Kroemer end of Cyclic engines cf Kittel and Kroemer
Classical thermodynamics More about irreversibility chap. 6 Isentropic expansion of an ideal gas Sudden expansion of a gas into vacuum cf Kittel and Kroemer end of Cyclic engines cf Kittel and Kroemer
Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Assignment Due at 11:59pm on Sunday, December 7 HW set on Masteringphysics.com Final exam: Time: 2:15pm~4:15pm, Monday, December 8. Location:
Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Assignment Due at 11:59pm on Sunday, December 7 HW set on Masteringphysics.com Final exam: Time: 2:15pm~4:15pm, Monday, December 8. Location:
Ch. 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Ch. 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases In this chapter we consider the physics of gases. If the atoms or molecules that make up a gas collide with the walls of their container, they exert a pressure p on
Ch. 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases In this chapter we consider the physics of gases. If the atoms or molecules that make up a gas collide with the walls of their container, they exert a pressure p on
Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics SCQF Level 9, U03272, PHY-3-ThermStat. Thursday 24th April, a.m p.m.
 College of Science and Engineering School of Physics H T O F E E U D N I I N V E B R U S I R T Y H G Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics SCQF Level 9, U03272, PHY-3-ThermStat Thursday 24th April, 2008
College of Science and Engineering School of Physics H T O F E E U D N I I N V E B R U S I R T Y H G Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics SCQF Level 9, U03272, PHY-3-ThermStat Thursday 24th April, 2008
Chapter 2 Carnot Principle
 Chapter 2 Carnot Principle 2.1 Temperature 2.1.1 Isothermal Process When two bodies are placed in thermal contact, the hotter body gives off heat to the colder body. As long as the temperatures are different,
Chapter 2 Carnot Principle 2.1 Temperature 2.1.1 Isothermal Process When two bodies are placed in thermal contact, the hotter body gives off heat to the colder body. As long as the temperatures are different,
Lecture 7: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Part 2. ! = mn v x
 Lecture 7: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Part 2 Last lecture, we began to explore the behavior of an ideal gas in terms of the molecules in it We found that the pressure of the gas was: P = N 2 mv x,i! = mn
Lecture 7: Kinetic Theory of Gases, Part 2 Last lecture, we began to explore the behavior of an ideal gas in terms of the molecules in it We found that the pressure of the gas was: P = N 2 mv x,i! = mn
Physics 119A Final Examination
 First letter of last name Name: Perm #: Email: Physics 119A Final Examination Thursday 10 December, 2009 Question 1 / 25 Question 2 / 25 Question 3 / 15 Question 4 / 20 Question 5 / 15 BONUS Total / 100
First letter of last name Name: Perm #: Email: Physics 119A Final Examination Thursday 10 December, 2009 Question 1 / 25 Question 2 / 25 Question 3 / 15 Question 4 / 20 Question 5 / 15 BONUS Total / 100
18.13 Review & Summary
 5/2/10 10:04 PM Print this page 18.13 Review & Summary Temperature; Thermometers Temperature is an SI base quantity related to our sense of hot and cold. It is measured with a thermometer, which contains
5/2/10 10:04 PM Print this page 18.13 Review & Summary Temperature; Thermometers Temperature is an SI base quantity related to our sense of hot and cold. It is measured with a thermometer, which contains
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS. Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5
 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5 Chemical Equilibrium N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3 Chemical reactions go in both directions Systems started from any initial state
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5 Chemical Equilibrium N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3 Chemical reactions go in both directions Systems started from any initial state
Lecture 13. Heat Engines. Thermodynamic processes and entropy Thermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat
 Lecture 3 Heat Engines hermodynamic rocesses and entroy hermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat - How do we define engine efficiency? - Carnot cycle: the best ossible efficiency Reading for this
Lecture 3 Heat Engines hermodynamic rocesses and entroy hermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat - How do we define engine efficiency? - Carnot cycle: the best ossible efficiency Reading for this
Last Name: First Name ID
 Last Name: First Name ID This is a set of practice problems for the final exam. It is not meant to represent every topic and is not meant to be equivalent to a 2-hour exam. These problems have not been
Last Name: First Name ID This is a set of practice problems for the final exam. It is not meant to represent every topic and is not meant to be equivalent to a 2-hour exam. These problems have not been
Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws
 Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws Please select only one of the five choices, (a)-(e) for each of the 33 questions. All temperatures T are absolute temperatures. All experiments
Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws Please select only one of the five choices, (a)-(e) for each of the 33 questions. All temperatures T are absolute temperatures. All experiments
Reversibility. Processes in nature are always irreversible: far from equilibrium
 Reversibility Processes in nature are always irreversible: far from equilibrium Reversible process: idealized process infinitely close to thermodynamic equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) Necessary conditions
Reversibility Processes in nature are always irreversible: far from equilibrium Reversible process: idealized process infinitely close to thermodynamic equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) Necessary conditions
01. Equilibrium Thermodynamics I: Introduction
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Equilibrium Statistical Physics Physics Course Materials 2015 01. Equilibrium Thermodynamics I: Introduction Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Equilibrium Statistical Physics Physics Course Materials 2015 01. Equilibrium Thermodynamics I: Introduction Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 he Second Law of hermodynamics So far We have studied the second law by looking at its results We don t have a thermodynamic property that can describe it In this chapter we will develop a mathematical
he Second Law of hermodynamics So far We have studied the second law by looking at its results We don t have a thermodynamic property that can describe it In this chapter we will develop a mathematical
Review of classical thermodynamics
 Review of classical thermodynamics Fundamental Laws, Properties and Processes (2) Entropy and the Second Law Concepts of equilibrium Reversible and irreversible processes he direction of spontaneous change
Review of classical thermodynamics Fundamental Laws, Properties and Processes (2) Entropy and the Second Law Concepts of equilibrium Reversible and irreversible processes he direction of spontaneous change
ABCD42BEF F2 F8 5 4D65F8 CC8 9
 ABCD BEF F F D F CC Physics 7B Fall 2015 Midterm 1 Solutions Problem 1 Let R h be the radius of the hole. R h = 2 3 Rα R h = 2 3 R+ R h = 2 3 R(1+α ) (4 points) In order for the marble to fit through the
ABCD BEF F F D F CC Physics 7B Fall 2015 Midterm 1 Solutions Problem 1 Let R h be the radius of the hole. R h = 2 3 Rα R h = 2 3 R+ R h = 2 3 R(1+α ) (4 points) In order for the marble to fit through the
Outline Review Example Problem 1 Example Problem 2. Thermodynamics. Review and Example Problems. X Bai. SDSMT, Physics. Fall 2013
 Review and Example Problems SDSMT, Physics Fall 013 1 Review Example Problem 1 Exponents of phase transformation 3 Example Problem Application of Thermodynamic Identity : contents 1 Basic Concepts: Temperature,
Review and Example Problems SDSMT, Physics Fall 013 1 Review Example Problem 1 Exponents of phase transformation 3 Example Problem Application of Thermodynamic Identity : contents 1 Basic Concepts: Temperature,
Chapter 16 Thermodynamics
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 16 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Introduction Another area of physics is thermodynamics Continues with the principle of conservation of energy
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 16 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Introduction Another area of physics is thermodynamics Continues with the principle of conservation of energy
Chapter 18 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 18 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics Heat is the transfer of energy due to the difference in temperature. The internal energy is the total energy of the object in its centerofmass reference
Chapter 18 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics Heat is the transfer of energy due to the difference in temperature. The internal energy is the total energy of the object in its centerofmass reference
CH352 Assignment 3: Due Thursday, 27 April 2017
 CH352 Assignment 3: Due Thursday, 27 April 2017 Prof. David Coker Thursday, 20 April 2017 Q1 Adiabatic quasi-static volume and temperature changes in ideal gases In the last assignment you showed that
CH352 Assignment 3: Due Thursday, 27 April 2017 Prof. David Coker Thursday, 20 April 2017 Q1 Adiabatic quasi-static volume and temperature changes in ideal gases In the last assignment you showed that
HEAT, WORK, AND THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 HET, WORK, ND THE FIRST LW OF THERMODYNMICS 8 EXERCISES Section 8. The First Law of Thermodynamics 5. INTERPRET We identify the system as the water in the insulated container. The problem involves calculating
HET, WORK, ND THE FIRST LW OF THERMODYNMICS 8 EXERCISES Section 8. The First Law of Thermodynamics 5. INTERPRET We identify the system as the water in the insulated container. The problem involves calculating
Statistical Physics. The Second Law. Most macroscopic processes are irreversible in everyday life.
 Statistical Physics he Second Law ime s Arrow Most macroscopic processes are irreversible in everyday life. Glass breaks but does not reform. Coffee cools to room temperature but does not spontaneously
Statistical Physics he Second Law ime s Arrow Most macroscopic processes are irreversible in everyday life. Glass breaks but does not reform. Coffee cools to room temperature but does not spontaneously
X α = E x α = E. Ω Y (E,x)
 LCTUR 4 Reversible and Irreversible Processes Consider an isolated system in equilibrium (i.e., all microstates are equally probable), with some number of microstates Ω i that are accessible to the system.
LCTUR 4 Reversible and Irreversible Processes Consider an isolated system in equilibrium (i.e., all microstates are equally probable), with some number of microstates Ω i that are accessible to the system.
4. Systems in contact with a thermal bath
 4. Systems in contact with a thermal bath So far, isolated systems microcanonical methods 4.1 Constant number of particles:kittelkroemer Chap. 3 Boltzmann factor Partition function canonical methods Ideal
4. Systems in contact with a thermal bath So far, isolated systems microcanonical methods 4.1 Constant number of particles:kittelkroemer Chap. 3 Boltzmann factor Partition function canonical methods Ideal
dv = adx, where a is the active area of the piston. In equilibrium, the external force F is related to pressure P as
 Chapter 3 Work, heat and the first law of thermodynamics 3.1 Mechanical work Mechanical work is defined as an energy transfer to the system through the change of an external parameter. Work is the only
Chapter 3 Work, heat and the first law of thermodynamics 3.1 Mechanical work Mechanical work is defined as an energy transfer to the system through the change of an external parameter. Work is the only
Physics 115. Specific heats revisited Entropy. General Physics II. Session 13
 Physics 115 General Physics II Session 13 Specific heats revisited Entropy R. J. Wilkes Email: phy115a@u.washington.edu Home page: http://courses.washington.edu/phy115a/ 4/22/14 Physics 115 1 Lecture Schedule
Physics 115 General Physics II Session 13 Specific heats revisited Entropy R. J. Wilkes Email: phy115a@u.washington.edu Home page: http://courses.washington.edu/phy115a/ 4/22/14 Physics 115 1 Lecture Schedule
First Law CML 100, IIT Delhi SS. The total energy of the system. Contribution from translation + rotation + vibrations.
 Internal Energy he total energy of the system. Contribution from translation + rotation + vibrations. Equipartition theorem for the translation and rotational degrees of freedom. 1/ k B Work Path function,
Internal Energy he total energy of the system. Contribution from translation + rotation + vibrations. Equipartition theorem for the translation and rotational degrees of freedom. 1/ k B Work Path function,
PY2005: Thermodynamics
 ome Multivariate Calculus Y2005: hermodynamics Notes by Chris Blair hese notes cover the enior Freshman course given by Dr. Graham Cross in Michaelmas erm 2007, except for lecture 12 on phase changes.
ome Multivariate Calculus Y2005: hermodynamics Notes by Chris Blair hese notes cover the enior Freshman course given by Dr. Graham Cross in Michaelmas erm 2007, except for lecture 12 on phase changes.
Entropy. Entropy Changes for an Ideal Gas
 Entropy and Entropy Changes for an Ideal Gas Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University March 28, 2012 Lecture 10 1 Recall that we discussed an idealized process called reversible A
Entropy and Entropy Changes for an Ideal Gas Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University March 28, 2012 Lecture 10 1 Recall that we discussed an idealized process called reversible A
Lecture Notes Set 3a: Probabilities, Microstates and Entropy
 Lecture Notes Set 3a: Probabilities, Microstates and Entropy Thus far.. In Sections 1 and 2 of the module we ve covered a broad variety of topics at the heart of the thermal and statistical behaviour of
Lecture Notes Set 3a: Probabilities, Microstates and Entropy Thus far.. In Sections 1 and 2 of the module we ve covered a broad variety of topics at the heart of the thermal and statistical behaviour of
Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name:
 Physics 213 Final Exam Spring 2014 Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. This is a closed book exam. You have 2 hours
Physics 213 Final Exam Spring 2014 Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. This is a closed book exam. You have 2 hours
ATMOS Lecture 7. The First Law and Its Consequences Pressure-Volume Work Internal Energy Heat Capacity Special Cases of the First Law
 TMOS 5130 Lecture 7 The First Law and Its Consequences Pressure-Volume Work Internal Energy Heat Caacity Secial Cases of the First Law Pressure-Volume Work Exanding Volume Pressure δw = f & dx δw = F ds
TMOS 5130 Lecture 7 The First Law and Its Consequences Pressure-Volume Work Internal Energy Heat Caacity Secial Cases of the First Law Pressure-Volume Work Exanding Volume Pressure δw = f & dx δw = F ds
THERMODYNAMICS. Chapter Twelve MCQ I
 Chapter welve HERMODYNAMICS MCQ I. An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (Fig..). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of,, and 4
Chapter welve HERMODYNAMICS MCQ I. An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (Fig..). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of,, and 4
Thermodynamics 1 Lecture Note 2
 Thermodynamics 1 Lecture Note 2 March 20, 2015 Kwang Kim Yonsei University kbkim@yonsei.ac.kr 39 8 7 34 53 Y O N Se I 88.91 16.00 14.01 78.96 126.9 Physical Chemistry Chemistry is the study of Matter and
Thermodynamics 1 Lecture Note 2 March 20, 2015 Kwang Kim Yonsei University kbkim@yonsei.ac.kr 39 8 7 34 53 Y O N Se I 88.91 16.00 14.01 78.96 126.9 Physical Chemistry Chemistry is the study of Matter and
I.D The Second Law Q C
 I.D he Second Law he historical development of thermodynamics follows the industrial revolution in the 19 th century, and the advent of heat engines. It is interesting to see how such practical considerations
I.D he Second Law he historical development of thermodynamics follows the industrial revolution in the 19 th century, and the advent of heat engines. It is interesting to see how such practical considerations
5. Systems in contact with a thermal bath
 5. Systems in contact with a thermal bath So far, isolated systems (micro-canonical methods) 5.1 Constant number of particles:kittel&kroemer Chap. 3 Boltzmann factor Partition function (canonical methods)
5. Systems in contact with a thermal bath So far, isolated systems (micro-canonical methods) 5.1 Constant number of particles:kittel&kroemer Chap. 3 Boltzmann factor Partition function (canonical methods)
a. 4.2x10-4 m 3 b. 5.5x10-4 m 3 c. 1.2x10-4 m 3 d. 1.4x10-5 m 3 e. 8.8x10-5 m 3
 The following two problems refer to this situation: #1 A cylindrical chamber containing an ideal diatomic gas is sealed by a movable piston with cross-sectional area A = 0.0015 m 2. The volume of the chamber
The following two problems refer to this situation: #1 A cylindrical chamber containing an ideal diatomic gas is sealed by a movable piston with cross-sectional area A = 0.0015 m 2. The volume of the chamber
