RESEARCH MEMORANDUM NATIONAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS. -9:.f CANCELLED. . *..,t--:;.,q. By Edward C. Polhamus and Thomas J. Ring, Jr.
|
|
|
- Owen Charles
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RESEARCH MEMORANDUM AERODYNAMIC CIylRACTEmTICS WITH FEED AND FRcEE TRAN;SITION '",? f- I r\ t 7-1. *..,t--:;.,q OF A MODIFIED DELTA WINGIN COMBINATION WITH A FUSEIAGE AT EIGE SUBSONIC SPEEDS By Edward C. Polhamus and Thomas J. Ring, Jr. -9:.f CANCELLED Langley Aeronautical Laboratory Langley Air Force'Base, Va. NATIONAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS WASH I NGTON lvlag 2, 1950
2 NACA RM ~5~x21 G xmroma, ADVISORY CO-E.FOR AEXOWAUTICS AEZ0DY IC OF A CHARACTERISTICS WITH FMED AMD FREE TRANSITION MODIFIED DELTA WING IN CWINkTION WITH A FUSELAGE AT HIGH SUBSONIC SPEEDS By Edward C. Polhanrus and Thomas J. King, Jr. SUMMARY.- An investigation has been made in the Langley high-speed 7- by 10- foot tunnel to determine the aerodynamic characteristics with fixed asd free transition at high subsonic speeds a of modified delta wing combination with a fmelage, The wing had an aspect ratio of 3, a taper ratio of 0.313, a sweepback of 27.70, and an NACA 641~012 airfoil section. The results indicate that the lift-force-break Mach nmiber was about 0.84 for both the transition free and fixed conditiona; with however, fixed transition the lift was curve nonlinear in the high Mach nuder range and the slopes in the low-lift range were considerably lower than with free tramition, The drag force break occurred at a Mach nmber of about 0.84 for both the transition-free and transition-fixed conditions, but for the transition-fixed condition, the was drag considerably higher. Mach number had little effect on the aerodynamic-center location for the free-transition cabe up a Mach to number of about 0.80 above which there is a rearward movement of approximately 5 percent mean aerodynamic chord followed by a rapid forward movement at a Mach nder of about At the higher Mach nunbere with fixed transition the pitching-moment characteristics were nonlinear and the aerodynamic-center position was considerably forward of its positfon with free transition. INTRODUCTION An investigation of the high-speed aerodynamic characteristics of a modified delta wing combination with a fuselage was conducted in the
3 2 NACA RM L5oc21 Langley high-speed 7- by 10-foot tunnel. The model was tested on the sting support system through a Mach number range of 0.40 to 0.90 with both free and fixed transition. Because of the nature of the transition effect, the results seemed to be of general interest and are presented in the present paper. COEFFICmS AND SYMBOLS The system of axes used for the presentation of the data, together with an indication of the positive forces, moments, and angles, Is presented in figure 1. Pertinent symbols are defined a8 follows: CL CD lift coefficient (Lift/qS) pitching-moment coefficient measured about the 25-percent mean-aerodynamic-chord position (Pitching moment/qsc ') free-stream dynamic pressure, pounds.per square foot (P.'/.) S C' b wing area, square feet wing mean aerodynamic chord, feet wing span, feet V air velocity, feet per second a M R speed of sound, feet per Machnumber (V/a) Reynolds number ( pvc /p) second CI absolute viscosity, pound-seconds per square foot P a mss density air, of slugs cubic per foot angle of attack of the fuselage, measured from the X-axis to the fuselage center line, degrees c
4 3 Tunnel and Model The tests were conducted in the Langley high-speed 7- by 10-foot tunnel, which is a closed, rectangular tunnel of the return-flow type with a contraction ratio of 15.7 to 1. The wing of the model was constructed of steel and the fuselage of aluminum. Details of the model as tested are presented in figure 2. The wing was a modified delta wing having a quarter-chord mep angle of 27.7, an aspect ratio of 3, a taper ratio of 0.313, and an NACA 6%~012 airfoil section pmallel to the plane of symmetry. For the tests with transition fixed, the leading upper and lower 8 percent of the chord measured dong the surface was covered with nmiber 60, carborundum. Support System A sting support system was used to support the model in the tupnel and a photograph of the test setup is presented as figure 3. The sting extended from the rear of the fuselage to a vertical strut located behind the test section. Thia strut was mounted on the tunnel balance system and was shielded from the air stream by a streamline fairing. The tare forces and moments produced by the stfng were determined by mounting the model on two wing tare stings, whichwere also attached to the vertical strut, and by tegbing the model with and without the center sting. A photograph of the modelmounted on the tare stings is presented as figure 4. Anglesof attack werechanged by the use of interchangeable couplings in the stings rearward of the model.the deflections of the support aystem under load were determined from static loading tests.
5 4 NACA RM L5OC21 CORRECTIONS The test redts have been corrected for the tare forces andmomenta produced by the support system. The corrections due to the jet-boundary induced upwash were computed from the following equations, which were I determined by the method of reference 1: CD = ~l where the subscript m indicates measured value. The streamlinecurvature corrections to the pitching moment and angle of attack were negligible. The drag has been corrected for the buoyancy produced by the longitudinal atatic-pressure gradient in the tunnel, and the dynamic pressure and Machnumber have been corrected for blockage effects by the method of reference 2. TESTS Themodelwas tested through a Mach nmiber range of 0.40 to 0.90 at various angles of attack. The variation of test Reynolds nmiber with Machnumber for average test conditions is presented in figure 5. The degree of turbulence of the tunnel is not horn but is believed to be small because of the high contraction ratio. Experience has indicated that, for a model of this size, constriction effects should not invalidate the test results at corrected Mach nmibers below about RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Presentation of Results The results are presented in figwe 6 as plots of angle of attack, drag coefficient, and pitching-moment coefficient against lift coefficient for different Mach nurnbers ranging from 0.40 to 0.9. Results are presented for both the transition-free a d transition-fixed conditions. A summary of the data is presented in figure 7.
6 NACA RM ~ 5x Di scussion of Result 8 Lift.- The results indicate that the lift-curve slope, for both the transition-free and transition-fixed conditions, increases with Mach nuher up to a Mach nmiber of about 0.84 above which there is a rather rapid decrease. Fixing transition had a large effect on the lift characterietics of this wing in the high Mach nuiber range as can be seen from figures 6 and 7. With fixed transition the lift curve nonlinear in the high Mach nuniber range (fig. 6(a) ) and the slopes in the low-lift range were considerably lower than with free transition (figs. 6(a) and 7). Although the transition strip had am effect on the lift, it caused only a slight decrease in the lift-force-break Mach nurnber (fig. 7). Although no pressure distributions were obtained for this wing, some have been obtained on a 12-percent-thicb, two-dimensional airfoil with and without a transition strip and the results are presented in reference 3. The results indicated that when the transition strip was added to the airfoil the location of the shock was moved forward and in lfft resulted. Throughout the present paper it should be kept in mind that tranoition from a laminar to a turbulent boundary layer was effected artificially by the use of roughness and therefore this transition does not necessarily represent the natural transition process that would occur on a smooth surface. Draq.- For both the transition-f ree and transition-fixed cases the drag-rise Machnumber in the low-lift range is about 0.84 (fig. 7). Transition caused a rather large increase in the drag (fig. 7) but had little effect on the drag-riee Machn-er or the rate of the drag rise. The increase in drag is probably due to a longer run of turbulent boundary layer or an increased wake due to earlier separation caused by the forward movemnt of the shock mentioned earlier, or both. The transition strip had little effect on the drag due to lift below a lift coefficient of about 0.3, but above this lift coefficient the drag due to lift was generally higher for the transition-fixed case. Pitching moment.- For the transition-free case there is little effect of Mach number on the aemdyncamic center up to a Mach number of about 0.80 above which there is a rearward movement of about 5 percent man aerodynamic chord followed by a rapid forward movement at a Mach number of about With transition fixed there is a gradual forward movement of the aerodynamic center up to a Machnumber of about 0.85 followed by a very rapid forward shift. At the higher Mach numbers (above about 0.80) the transition strip had a very pronounced effect on the pitching-moment characteristics. For example, at a Machnumber of 0.90 * the aerodynamic center with transition fixed was approximately 60 percent mean aerodynamic chord forward of that with transition free (fig. 7).
7 6 NACA RM L5OC21 The pressure distributions of reference 3 indicate that the loss in lift mentioned previously occurs over the rearward of portion the wing and this fact accounts for the forward shift of the aerodynamic center. At the higher bbch numbers the pltching-moment curve8 for tramition the fixed case are very nonlinear (fig. 6(c)). 1. The lift-force-break Mach number was about 0.84 for both the transition-free and traneition-ffxed conditione. However, with fixed transition the lift curve was nonlinear In the high Mach number range and the elopes in the law lift range were conaiderably lower than with free transition. 2. The drag force break occurred a at Mach nmiber of about 0.84 for both the tranaition-free and transition-fixed conditione, but for the transition-fixed condition, drag the was conaiderably higher. 3. Mach number had little effect on the aerodynamic-center location for the free-transition case up to a Mach nunher of about 0.80, above which there is a rearward movement of approximately 5 percent mean aerodynamic chord follmd by a rapid forward movement a at Mach number of about At the higher Mach nunibera with fixed transition the pitching-moment characteristics were nonlinear and the aerodynamic-center position was considerably forward of ita position with free tramition. Langley Aeronautical Laboratory National Advisory Committee for Aer~n&UtiCs Langley Air Force Base, Va.
8 W A RM L5OC Gillis, Clarence L., Polhanrus, Edward C., and Gray, Joseph L., Jr.: Charts for Deterraining Jet-Boundary Corrections for Cmplete Models n 7- by 10-Foot Closed Rectmgulcc Wind Tunnels. NACA ARR L5G31, Herriot, John G.: Blockage Corrections for Three-Dfmensional-Flow Closed-Throat WFnd Tunnels, with Consideration of the Effect of Compressibility. maca RM ~7~28, Allen, H. Julia, Heaslet, Max A., and Nitzberg, Gerald E.: The Interaction of Boundary Layer and Compression Shock and Its Effect upon Airfoil Pressure Distributions. EACA RM A7A02,
9 8 NACA RM ~50~21 5 Figure 1.- Syetem of axes with positive values of forces, moments, and angles indicated by arrows.
10 .... I L C 1 Figure 2. - General arrangement of wing with u.7" sweepback, smect ratio 3.0, ana taper ratio
11
12 Figure 3. - Photograph of the model mounted on the center sting....
13
14 . I.. i Figure 4. - Photograph of the model munted on the tare stings......
15 1
16 Figure 5.- Variation of mean test Reynolds nlzniber wfth Mach number. c.
17 ... (a) Variation of lift coefficient with angle of attack. Figure 6.- k~oaynamic characteristics with free and fixed transition of a wing-fuselage combination with eweepback, aspect ratio 3.0, kper ratio 0.33, and NACA 64lA012 airfoil. I '! 1.
18 .... I I I Figure 6.- Continued...
19 ... Figure 6.- Concluded. * I
20 NACA RM ~5~x21.06 " " M Figure 7.- Summary of the effect of Machnuniber on the aerodynamic characteristics in the low-lift range of a wing-fuselage combination with meepback, aspect ratio 3.0, taper ratio 0.313, and NACA 641Ao12 airfoil.
MACH NUMBERS BETWEEN 0.8 AND 2.2 AS DETERMINED FROM THE
 NACA RM SL5kH2 NATIONAL ADVISORY COMMI'ITEE FOR AERONAUTICS RESEARCH MEMORANDUM for the Bureau of Aeronautics, Department of the Navy mo-lift DRAG OF THE CHANCE VOUGHT Rl3GULUS I1 MISSILE AT MACH NUMBERS
NACA RM SL5kH2 NATIONAL ADVISORY COMMI'ITEE FOR AERONAUTICS RESEARCH MEMORANDUM for the Bureau of Aeronautics, Department of the Navy mo-lift DRAG OF THE CHANCE VOUGHT Rl3GULUS I1 MISSILE AT MACH NUMBERS
Definitions. Temperature: Property of the atmosphere (τ). Function of altitude. Pressure: Property of the atmosphere (p). Function of altitude.
 Definitions Chapter 3 Standard atmosphere: A model of the atmosphere based on the aerostatic equation, the perfect gas law, an assumed temperature distribution, and standard sea level conditions. Temperature:
Definitions Chapter 3 Standard atmosphere: A model of the atmosphere based on the aerostatic equation, the perfect gas law, an assumed temperature distribution, and standard sea level conditions. Temperature:
RESEARCH MEMORANDUM. JUL3 1%-i NATIONAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE. 8 Langley Aeronautical Laboratory Langley Ffeld$XASSIFICATION CHANGED
 03 0 w r-l t- z JUL3 1%-i RESEARCH MEMORANDUM LFT AND DRAG COEFFCENTS FOR THE BELL X-1 ARPLANE (8-PEFCEN"TEUCK WNG) N POWER-OFF 3 TFUWSONC FLGHT By L. Robert Carman and John R. Carden B 8 Langley Aeronautical
03 0 w r-l t- z JUL3 1%-i RESEARCH MEMORANDUM LFT AND DRAG COEFFCENTS FOR THE BELL X-1 ARPLANE (8-PEFCEN"TEUCK WNG) N POWER-OFF 3 TFUWSONC FLGHT By L. Robert Carman and John R. Carden B 8 Langley Aeronautical
Stability and Control Some Characteristics of Lifting Surfaces, and Pitch-Moments
 Stability and Control Some Characteristics of Lifting Surfaces, and Pitch-Moments The lifting surfaces of a vehicle generally include the wings, the horizontal and vertical tail, and other surfaces such
Stability and Control Some Characteristics of Lifting Surfaces, and Pitch-Moments The lifting surfaces of a vehicle generally include the wings, the horizontal and vertical tail, and other surfaces such
Given a stream function for a cylinder in a uniform flow with circulation: a) Sketch the flow pattern in terms of streamlines.
 Question Given a stream function for a cylinder in a uniform flow with circulation: R Γ r ψ = U r sinθ + ln r π R a) Sketch the flow pattern in terms of streamlines. b) Derive an expression for the angular
Question Given a stream function for a cylinder in a uniform flow with circulation: R Γ r ψ = U r sinθ + ln r π R a) Sketch the flow pattern in terms of streamlines. b) Derive an expression for the angular
RESEARCH MEMORANDUM FUGHT CHARACTERSSTICS OF A WINGIZSS ROCKET-POWERED MODEL WITH FOUR EXTERNALLY MOUNTED AIR-TO-APR MISSILES,$ Langley.Field, Va.
 3 1176 6 693 i RESEARCH MEMORANDUM FUGHT CHARACTERSSTCS OF A WNGZSS ROCKET-POWERED MODEL 'r- WTH FOUR EXTERNALLY MOUNTED AR-TO-APR MSSLES,$ AT MACH NUMBERS FROM.7 TO 1.6 By Allen B. Henning and Clarence
3 1176 6 693 i RESEARCH MEMORANDUM FUGHT CHARACTERSSTCS OF A WNGZSS ROCKET-POWERED MODEL 'r- WTH FOUR EXTERNALLY MOUNTED AR-TO-APR MSSLES,$ AT MACH NUMBERS FROM.7 TO 1.6 By Allen B. Henning and Clarence
ROAD MAP... D-1: Aerodynamics of 3-D Wings D-2: Boundary Layer and Viscous Effects D-3: XFLR (Aerodynamics Analysis Tool)
 AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT D: Applied Aerodynamics ROAD MAP... D-1: Aerodynamics o 3-D Wings D-2: Boundary Layer and Viscous Eects D-3: XFLR (Aerodynamics Analysis Tool) AE301 Aerodynamics I : List o Subjects
AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT D: Applied Aerodynamics ROAD MAP... D-1: Aerodynamics o 3-D Wings D-2: Boundary Layer and Viscous Eects D-3: XFLR (Aerodynamics Analysis Tool) AE301 Aerodynamics I : List o Subjects
TECHNICAL NOTE 4006 INVESTIGATION AT TRANSONIC SPEEDS OF DEFLECTORS AND SPOILERS AS GUST ALLEVMTORS ON A 35 SWEPT WING TRANSOIWC -BUMP
 TECHNICAL NOTE 4006 INVESTIGATION AT TRANSONIC SPEEDS OF DEFLECTORS AND SPOILERS AS GUST ALLEVMTORS ON A 35 SWEPT WING TRANSOIWC -BUMP METHOD By Delwh R Croorn md Jarrett K Huffman Langley Aeronautical
TECHNICAL NOTE 4006 INVESTIGATION AT TRANSONIC SPEEDS OF DEFLECTORS AND SPOILERS AS GUST ALLEVMTORS ON A 35 SWEPT WING TRANSOIWC -BUMP METHOD By Delwh R Croorn md Jarrett K Huffman Langley Aeronautical
Analysis of the high Reynolds number 2D tests on a wind turbine airfoil performed at two different wind tunnels
 Analysis of the high Reynolds number 2D tests on a wind turbine airfoil performed at two different wind tunnels O.Pires 1, X.Munduate 2, O.Ceyhan 3, M.Jacobs 4, J.Madsen 5 1 National Renewable Energy Centre
Analysis of the high Reynolds number 2D tests on a wind turbine airfoil performed at two different wind tunnels O.Pires 1, X.Munduate 2, O.Ceyhan 3, M.Jacobs 4, J.Madsen 5 1 National Renewable Energy Centre
Transonic Aerodynamics Wind Tunnel Testing Considerations. W.H. Mason Configuration Aerodynamics Class
 Transonic Aerodynamics Wind Tunnel Testing Considerations W.H. Mason Configuration Aerodynamics Class Transonic Aerodynamics History Pre WWII propeller tip speeds limited airplane speed Props did encounter
Transonic Aerodynamics Wind Tunnel Testing Considerations W.H. Mason Configuration Aerodynamics Class Transonic Aerodynamics History Pre WWII propeller tip speeds limited airplane speed Props did encounter
RESEARCH MEMORANDUM NATIONAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS UNCLASSIFIED AND DIRECTIONAL AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF FOUR
 " I RESEARCH MEMORANDUM SOME EFFECTS OF AILERON DEFLECTION ON THE STATIC LATERAL AND DIRECTIONAL AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF FOUR CONTEMPORARY AIRPLANE MODELS By Willard G. Smith and Peter F. Intrieri
" I RESEARCH MEMORANDUM SOME EFFECTS OF AILERON DEFLECTION ON THE STATIC LATERAL AND DIRECTIONAL AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF FOUR CONTEMPORARY AIRPLANE MODELS By Willard G. Smith and Peter F. Intrieri
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Introduction to Aeronautics
 Introduction to Aeronautics ARO 101 Sections 03 & 04 Sep 30, 2015 thru Dec 9, 2015 Instructor: Raymond A. Hudson Week #8 Lecture Material 1 Topics For Week #8 Airfoil Geometry & Nomenclature Identify the
Introduction to Aeronautics ARO 101 Sections 03 & 04 Sep 30, 2015 thru Dec 9, 2015 Instructor: Raymond A. Hudson Week #8 Lecture Material 1 Topics For Week #8 Airfoil Geometry & Nomenclature Identify the
NATIONALADVISORY COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS TECHNICAL NOTE 2741 INVESTIGATION OF THE INFLUENCE OF FUSELAGE AND TAIL
 : I NATIONALADVISORY COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS TECHNICAL NOTE 2741 INVESTIGATION OF THE INFLUENCE OF FUSELAGE AND TAIL SURFACES ON LOW-SPEED STATIC STABILITY AND ROLLING CHARACTERISTICS, 1 OF A SWEPT-WING
: I NATIONALADVISORY COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS TECHNICAL NOTE 2741 INVESTIGATION OF THE INFLUENCE OF FUSELAGE AND TAIL SURFACES ON LOW-SPEED STATIC STABILITY AND ROLLING CHARACTERISTICS, 1 OF A SWEPT-WING
Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig L. Hilmes Boeing Commercial Airplane Group, Seattle, Washington, 98124
 AIAA--2007-0684 Pressures and Drag Characteristics of Bodies of Revolution at Near Sonic Speeds Including the Effects of Viscosity and Wind Tunnel Walls Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig
AIAA--2007-0684 Pressures and Drag Characteristics of Bodies of Revolution at Near Sonic Speeds Including the Effects of Viscosity and Wind Tunnel Walls Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig
NATIONAL ADVISORy COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS WARTIME REPORT. ORIGINALLY ISSUED October l$kk as Advance Restricted Report IAE31
 FILE COPY NO. I-W n NATIONAL ADVISORy COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS WARTIME REPORT ORIGINALLY ISSUED October l$kk as Advance Restricted Report IAE31 WIND-TUNNEL CALIBRATION AND CORRECTION PROCEDURES FOR THREE-DIMENSIONAL
FILE COPY NO. I-W n NATIONAL ADVISORy COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS WARTIME REPORT ORIGINALLY ISSUED October l$kk as Advance Restricted Report IAE31 WIND-TUNNEL CALIBRATION AND CORRECTION PROCEDURES FOR THREE-DIMENSIONAL
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF NACA 4 SERIES AIRFOILS
 54 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF NACA 4 SERIES AIRFOILS The baseline characteristics and analysis of NACA 4 series airfoils are presented in this chapter in detail. The correlations for coefficient of lift and
54 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF NACA 4 SERIES AIRFOILS The baseline characteristics and analysis of NACA 4 series airfoils are presented in this chapter in detail. The correlations for coefficient of lift and
Experimental Studies on Complex Swept Rotor Blades
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 974-3154 Volume 6, Number 1 (213), pp. 115-128 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental Studies on
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 974-3154 Volume 6, Number 1 (213), pp. 115-128 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Experimental Studies on
MDTS 5705 : Aerodynamics & Propulsion Lecture 2 : Missile lift and drag. G. Leng, MDTS, NUS
 MDTS 5705 : Aerodynamics & Propulsion Lecture 2 : Missile lift and drag 2.1. The design of supersonic airfoils For efficient lift generation at subsonic speeds, airfoils look like : So why can t a similar
MDTS 5705 : Aerodynamics & Propulsion Lecture 2 : Missile lift and drag 2.1. The design of supersonic airfoils For efficient lift generation at subsonic speeds, airfoils look like : So why can t a similar
APPENDIX C DRAG POLAR, STABILITY DERIVATIVES AND CHARACTERISTIC ROOTS OF A JET AIRPLANE (Lectures 37 to 40)
 APPENDIX C DRAG POLAR, STABILITY DERIVATIVES AND CHARACTERISTIC ROOTS OF A JET AIRPLANE (Lectures 37 to 40 E.G. TULAPURKARA YASHKUMAR A. VENKATTRAMAN REPORT NO: AE TR 2007-3 APRIL 2007 (REVISED NOVEMBER
APPENDIX C DRAG POLAR, STABILITY DERIVATIVES AND CHARACTERISTIC ROOTS OF A JET AIRPLANE (Lectures 37 to 40 E.G. TULAPURKARA YASHKUMAR A. VENKATTRAMAN REPORT NO: AE TR 2007-3 APRIL 2007 (REVISED NOVEMBER
Flight Dynamics and Control. Lecture 3: Longitudinal stability Derivatives G. Dimitriadis University of Liege
 Flight Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Longitudinal stability Derivatives G. Dimitriadis University of Liege Previously on AERO0003-1 We developed linearized equations of motion Longitudinal direction
Flight Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Longitudinal stability Derivatives G. Dimitriadis University of Liege Previously on AERO0003-1 We developed linearized equations of motion Longitudinal direction
for what specific application did Henri Pitot develop the Pitot tube? what was the name of NACA s (now NASA) first research laboratory?
 1. 5% short answers for what specific application did Henri Pitot develop the Pitot tube? what was the name of NACA s (now NASA) first research laboratory? in what country (per Anderson) was the first
1. 5% short answers for what specific application did Henri Pitot develop the Pitot tube? what was the name of NACA s (now NASA) first research laboratory? in what country (per Anderson) was the first
List of symbols. Latin symbols. Symbol Property Unit
 Abstract Aircraft icing continues to be a threat for modern day aircraft. Icing occurs when supercooled large droplets (SLD s) impinge on the body of the aircraft. These droplets can bounce off, freeze
Abstract Aircraft icing continues to be a threat for modern day aircraft. Icing occurs when supercooled large droplets (SLD s) impinge on the body of the aircraft. These droplets can bounce off, freeze
344 JAXA Special Publication JAXA-SP E 2. Prediction by the CFD Approach 2.1 Numerical Procedure The plane shape of the thin delta wing of the r
 5th Symposium on Integrating CFD and Experiments in Aerodynamics (Integration 2012) 343 Aerodynamic Characteristics of a Delta Wing with Arc Camber for Mars Exploration Takao Unoguchi,* 1 Shogo Aoyama,*
5th Symposium on Integrating CFD and Experiments in Aerodynamics (Integration 2012) 343 Aerodynamic Characteristics of a Delta Wing with Arc Camber for Mars Exploration Takao Unoguchi,* 1 Shogo Aoyama,*
Wind-Tunnel Investigation of Aerodynamic Efficiency of Three Planar Elliptical Wings With Curvature of Quarter-Chord Line
 NASA Technical Paper 3359 October 1993 Wind-Tunnel Investigation of Aerodynamic Efficiency of Three Planar Elliptical Wings With Curvature of Quarter-Chord Line Raymond E. Mineck and Paul M. H. W. Vijgen
NASA Technical Paper 3359 October 1993 Wind-Tunnel Investigation of Aerodynamic Efficiency of Three Planar Elliptical Wings With Curvature of Quarter-Chord Line Raymond E. Mineck and Paul M. H. W. Vijgen
Flight Vehicle Terminology
 Flight Vehicle Terminology 1.0 Axes Systems There are 3 axes systems which can be used in Aeronautics, Aerodynamics & Flight Mechanics: Ground Axes G(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) Body Axes G(x, y, z) Aerodynamic Axes
Flight Vehicle Terminology 1.0 Axes Systems There are 3 axes systems which can be used in Aeronautics, Aerodynamics & Flight Mechanics: Ground Axes G(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) Body Axes G(x, y, z) Aerodynamic Axes
Thin airfoil theory. Chapter Compressible potential flow The full potential equation
 hapter 4 Thin airfoil theory 4. ompressible potential flow 4.. The full potential equation In compressible flow, both the lift and drag of a thin airfoil can be determined to a reasonable level of accuracy
hapter 4 Thin airfoil theory 4. ompressible potential flow 4.. The full potential equation In compressible flow, both the lift and drag of a thin airfoil can be determined to a reasonable level of accuracy
AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION AT SUBSONIC AND SUPERSONIC. RATIO 2 TRIANGULAR WING,:% By David E. Reese, Jr. Ames Aeronautical Laboratory
 RESEARCH MEMORANDUM AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION AT SUBSONIC AND SUPERSONIC I SPEEDS OF THE TORSIONAL.DAMPING CHARACTERISTICS OF A CONSTANT-CHORD CONTR-OL SURFACE OF AN ASPECT RATIO 2 TRIANGULAR WING,:%
RESEARCH MEMORANDUM AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION AT SUBSONIC AND SUPERSONIC I SPEEDS OF THE TORSIONAL.DAMPING CHARACTERISTICS OF A CONSTANT-CHORD CONTR-OL SURFACE OF AN ASPECT RATIO 2 TRIANGULAR WING,:%
Test-to-Test Repeatability of Results From a Subsonic Wing-Body Configuration in the National Transonic Facility
 NASA/TM-2-21 Test-to-Test Repeatability of Results From a Subsonic Wing-Body Configuration in the National Transonic Facility Raymond E. Mineck and Odis C. Pendergraft, Jr. Langley Research Center, Hampton,
NASA/TM-2-21 Test-to-Test Repeatability of Results From a Subsonic Wing-Body Configuration in the National Transonic Facility Raymond E. Mineck and Odis C. Pendergraft, Jr. Langley Research Center, Hampton,
The E80 Wind Tunnel Experiment the experience will blow you away. by Professor Duron Spring 2012
 The E80 Wind Tunnel Experiment the experience will blow you away by Professor Duron Spring 2012 Objectives To familiarize the student with the basic operation and instrumentation of the HMC wind tunnel
The E80 Wind Tunnel Experiment the experience will blow you away by Professor Duron Spring 2012 Objectives To familiarize the student with the basic operation and instrumentation of the HMC wind tunnel
Drag (2) Induced Drag Friction Drag Form Drag Wave Drag
 Drag () Induced Drag Friction Drag Form Drag Wave Drag Outline Nomenclature and Concepts Farfield Drag Analysis Induced Drag Multiple Lifting Surfaces Zero Lift Drag :Friction and Form Drag Supersonic
Drag () Induced Drag Friction Drag Form Drag Wave Drag Outline Nomenclature and Concepts Farfield Drag Analysis Induced Drag Multiple Lifting Surfaces Zero Lift Drag :Friction and Form Drag Supersonic
Bluff Body, Viscous Flow Characteristics ( Immersed Bodies)
 Bluff Body, Viscous Flow Characteristics ( Immersed Bodies) In general, a body immersed in a flow will experience both externally applied forces and moments as a result of the flow about its external surfaces.
Bluff Body, Viscous Flow Characteristics ( Immersed Bodies) In general, a body immersed in a flow will experience both externally applied forces and moments as a result of the flow about its external surfaces.
Numerical study of battle damaged two-dimensional wings
 Advances in Fluid Mechanics IX 141 Numerical study of battle damaged two-dimensional wings S. Djellal, T. Azzam, M. Djellab & K. Lakkaichi Fluid Mechanics Laboratory Polytechnical School Bordj El Bahri,
Advances in Fluid Mechanics IX 141 Numerical study of battle damaged two-dimensional wings S. Djellal, T. Azzam, M. Djellab & K. Lakkaichi Fluid Mechanics Laboratory Polytechnical School Bordj El Bahri,
Module3: Waves in Supersonic Flow Lecture14: Waves in Supersonic Flow (Contd.)
 1 Module3: Waves in Supersonic Flow Lecture14: Waves in Supersonic Flow (Contd.) Mach Reflection: The appearance of subsonic regions in the flow complicates the problem. The complications are also encountered
1 Module3: Waves in Supersonic Flow Lecture14: Waves in Supersonic Flow (Contd.) Mach Reflection: The appearance of subsonic regions in the flow complicates the problem. The complications are also encountered
An Experimental Validation of Numerical Post-Stall Aerodynamic Characteristics of a Wing
 Proceedings of ICTACEM 2017 International Conference on Theoretical, Applied, Computational and Experimental Mechanics December 28-30, 2017, IIT Kharagpur, India ICTACEM-2017/XXXX(paper No.) An Experimental
Proceedings of ICTACEM 2017 International Conference on Theoretical, Applied, Computational and Experimental Mechanics December 28-30, 2017, IIT Kharagpur, India ICTACEM-2017/XXXX(paper No.) An Experimental
AIRFOIL DESIGN PROCEDURE A MODIFIED THEODORSEN E-FUNCTION. by Raymond L. Barger. Langley Research Center NASA TECHNICAL NOTE NASA TN D-7741
 NASA TECHNICAL NOTE NASA TN D-7741 AND 1- I- 6~7 (NASA-TN-D-7741) A MODIFIED THEODORSEN N74-33428 EPSILON-FUNCTION AIRFOIL DESIGN PROCEDURE (NASA) 19 p BC $3.00 CSCL 01A Unclas H1/01 48910 rr A MODIFIED
NASA TECHNICAL NOTE NASA TN D-7741 AND 1- I- 6~7 (NASA-TN-D-7741) A MODIFIED THEODORSEN N74-33428 EPSILON-FUNCTION AIRFOIL DESIGN PROCEDURE (NASA) 19 p BC $3.00 CSCL 01A Unclas H1/01 48910 rr A MODIFIED
DYNAMIC STALL ONSET VARIATION WITH REDUCED FREQUENCY FOR THREE STALL MECHANISMS
 International Forum on Aeroelasticity and Structural Dynamics IFASD 27 25-28 June 27 Como, Italy DYNAMIC STALL ONSET VARIATION WITH REDUCED FREQUENCY FOR THREE STALL MECHANISMS Boutet Johan, Dimitriadis
International Forum on Aeroelasticity and Structural Dynamics IFASD 27 25-28 June 27 Como, Italy DYNAMIC STALL ONSET VARIATION WITH REDUCED FREQUENCY FOR THREE STALL MECHANISMS Boutet Johan, Dimitriadis
High Reynolds Number Tests on an Unswept 11% Thick
 C. P. No. 531 \ : * 1, ~.. ++? C. P. No. 531 MNSTRY O F AVATON AERONAUTCAL RESEARCH COUNCL CURRENT PAPERS High Reynolds Number Tests on an Unswept 11% Thick RAE 101 Section Aerofoi by?. W. F. Gdd, BSc.,
C. P. No. 531 \ : * 1, ~.. ++? C. P. No. 531 MNSTRY O F AVATON AERONAUTCAL RESEARCH COUNCL CURRENT PAPERS High Reynolds Number Tests on an Unswept 11% Thick RAE 101 Section Aerofoi by?. W. F. Gdd, BSc.,
Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Department of Mechanical Engineering AMEE401 / AUTO400 Aerodynamics Instructor: Marios M. Fyrillas Email: eng.fm@fit.ac.cy HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #2 QUESTION 1 Clearly there are two mechanisms responsible
Department of Mechanical Engineering AMEE401 / AUTO400 Aerodynamics Instructor: Marios M. Fyrillas Email: eng.fm@fit.ac.cy HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #2 QUESTION 1 Clearly there are two mechanisms responsible
RECENT near-sonic and low-sonic boom transport aircraft
 JOURNAL OF AIRCRAFT Vol. 44, No. 6, November December 2007 Aerodynamic Characteristics of Bodies of Revolution at Near-Sonic Speeds Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig L. Hilmes The Boeing
JOURNAL OF AIRCRAFT Vol. 44, No. 6, November December 2007 Aerodynamic Characteristics of Bodies of Revolution at Near-Sonic Speeds Brenda M. Kulfan, John E. Bussoletti, and Craig L. Hilmes The Boeing
AIAA Sensing Aircraft Effects by Flap Hinge Moment Measurement
 AIAA 99-349 Sensing Aircraft Effects by Flap Hinge Moment Measurement Holly M. Gurbacki and Michael B. Bragg University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana, IL 7th Applied Aerodynamics Conference June
AIAA 99-349 Sensing Aircraft Effects by Flap Hinge Moment Measurement Holly M. Gurbacki and Michael B. Bragg University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana, IL 7th Applied Aerodynamics Conference June
Evaluation of Gritting Strategies for High Angle of Attack Using Wind Tunnel and Flight Test Data for the F/A-18
 NASA/TP-1998-2767 Evaluation of ting Strategies for High Angle of Attack Using Wind Tunnel and Flight Test Data for the F/A-18 Robert M. Hall, Gary E. Erickson, and Charles H. Fox, Jr. Langley Research
NASA/TP-1998-2767 Evaluation of ting Strategies for High Angle of Attack Using Wind Tunnel and Flight Test Data for the F/A-18 Robert M. Hall, Gary E. Erickson, and Charles H. Fox, Jr. Langley Research
Lecture-4. Flow Past Immersed Bodies
 Lecture-4 Flow Past Immersed Bodies Learning objectives After completing this lecture, you should be able to: Identify and discuss the features of external flow Explain the fundamental characteristics
Lecture-4 Flow Past Immersed Bodies Learning objectives After completing this lecture, you should be able to: Identify and discuss the features of external flow Explain the fundamental characteristics
ADVERSE REYNOLDS NUMBER EFFECT ON MAXIMUM LIFT OF TWO DIMENSIONAL AIRFOILS
 ICAS 2 CONGRESS ADVERSE REYNOLDS NUMBER EFFECT ON MAXIMUM LIFT OF TWO DIMENSIONAL AIRFOILS Kenji YOSHIDA, Masayoshi NOGUCHI Advanced Technology Aircraft Project Center NATIONAL AEROSPACE LABORATORY 6-
ICAS 2 CONGRESS ADVERSE REYNOLDS NUMBER EFFECT ON MAXIMUM LIFT OF TWO DIMENSIONAL AIRFOILS Kenji YOSHIDA, Masayoshi NOGUCHI Advanced Technology Aircraft Project Center NATIONAL AEROSPACE LABORATORY 6-
AIAA Investigation of Reynolds Number Effects on a Generic Fighter Configuration in the National Transonic Facility (Invited)
 Investigation of Reynolds Number Effects on a Generic Fighter Configuration in the National Transonic Facility (Invited) W. G. Tomek, R. M. Hall, R. A. Wahls, J. M. Luckring, and L. R. Owens NASA Langley
Investigation of Reynolds Number Effects on a Generic Fighter Configuration in the National Transonic Facility (Invited) W. G. Tomek, R. M. Hall, R. A. Wahls, J. M. Luckring, and L. R. Owens NASA Langley
NATIONAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS TECHNICAL NOTE. No INVESTIGATION OF EFFECTS OF GEOMETRIC DIHEDRAL ON LOW-SPEED
 f'00 O 5 NATIONAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS TECHNICAL NOTE No. 668 INVESTIGATION OF EFFECTS OF GEOMETRIC DIHEDRAL ON LOW-SPEED STATIC STABILITY AND YAWING CHARACTERISTICS OF AN UNTAPERED 45 SWEPT
f'00 O 5 NATIONAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS TECHNICAL NOTE No. 668 INVESTIGATION OF EFFECTS OF GEOMETRIC DIHEDRAL ON LOW-SPEED STATIC STABILITY AND YAWING CHARACTERISTICS OF AN UNTAPERED 45 SWEPT
A STUDENT'S INTRODUCTION TO THE WRIGHT BROTHERS WIND TUNNEL AT MIT. Eugene E. Covert T. Wilson Professor Emeritus INTRODUCTION
 A STUDENT'S INTRODUCTION TO THE WRIGHT BROTHERS WIND TUNNEL AT MIT Eugene E. Covert T. Wilson Professor Emeritus INTRODUCTION A wind tunnel is an instrument whose purpose is to measure some aerodynamic
A STUDENT'S INTRODUCTION TO THE WRIGHT BROTHERS WIND TUNNEL AT MIT Eugene E. Covert T. Wilson Professor Emeritus INTRODUCTION A wind tunnel is an instrument whose purpose is to measure some aerodynamic
Stability and Control
 Stability and Control Introduction An important concept that must be considered when designing an aircraft, missile, or other type of vehicle, is that of stability and control. The study of stability is
Stability and Control Introduction An important concept that must be considered when designing an aircraft, missile, or other type of vehicle, is that of stability and control. The study of stability is
Introduction to Aerospace Engineering
 4. Basic Fluid (Aero) Dynamics Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Here, we will try and look at a few basic ideas from the complicated field of fluid dynamics. The general area includes studies of incompressible,
4. Basic Fluid (Aero) Dynamics Introduction to Aerospace Engineering Here, we will try and look at a few basic ideas from the complicated field of fluid dynamics. The general area includes studies of incompressible,
Masters in Mechanical Engineering Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 2015/16
 Masters in Mechanical Engineering Aerodynamics st Semester 05/6 Exam st season, 8 January 06 Name : Time : 8:30 Number: Duration : 3 hours st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed nd Part : Textbooks allowed
Masters in Mechanical Engineering Aerodynamics st Semester 05/6 Exam st season, 8 January 06 Name : Time : 8:30 Number: Duration : 3 hours st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed nd Part : Textbooks allowed
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : LOW SPEED AERODYNAMICS Course Code : AAE004 Regulation : IARE
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : LOW SPEED AERODYNAMICS Course Code : AAE004 Regulation : IARE
SPC Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30
 SPC 307 - Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30 1. The maximum velocity at which an aircraft can cruise occurs when the thrust available with the engines operating with the
SPC 307 - Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30 1. The maximum velocity at which an aircraft can cruise occurs when the thrust available with the engines operating with the
Aerodynamic Measurement on the High Speed Test Track
 Trans. JSASS Aerospace Tech. Japan Vol. 12, No. ists29, pp. Tg_5-Tg_10, 2014 Topics Aerodynamic Measurement on the High Speed Test Track By Daisuke NAKATA 1), Kenji NISHINE 2), Kaoru TATEOKE 1), Nobuhiro
Trans. JSASS Aerospace Tech. Japan Vol. 12, No. ists29, pp. Tg_5-Tg_10, 2014 Topics Aerodynamic Measurement on the High Speed Test Track By Daisuke NAKATA 1), Kenji NISHINE 2), Kaoru TATEOKE 1), Nobuhiro
Active Control of Separated Cascade Flow
 Chapter 5 Active Control of Separated Cascade Flow In this chapter, the possibility of active control using a synthetic jet applied to an unconventional axial stator-rotor arrangement is investigated.
Chapter 5 Active Control of Separated Cascade Flow In this chapter, the possibility of active control using a synthetic jet applied to an unconventional axial stator-rotor arrangement is investigated.
Given the water behaves as shown above, which direction will the cylinder rotate?
 water stream fixed but free to rotate Given the water behaves as shown above, which direction will the cylinder rotate? ) Clockwise 2) Counter-clockwise 3) Not enough information F y U 0 U F x V=0 V=0
water stream fixed but free to rotate Given the water behaves as shown above, which direction will the cylinder rotate? ) Clockwise 2) Counter-clockwise 3) Not enough information F y U 0 U F x V=0 V=0
OpenFOAM Simulations for MAV Applications
 16 th Annual CFD Symposium 11th-12th August 2014, Bangalore 1 OpenFOAM Simulations for MAV Applications Syed Zahid*, A. Rajesh, M.B. Subrahmanya, B.N. Rajani *Student, Dept. of Mech. Engg, SDM, Dharwad,
16 th Annual CFD Symposium 11th-12th August 2014, Bangalore 1 OpenFOAM Simulations for MAV Applications Syed Zahid*, A. Rajesh, M.B. Subrahmanya, B.N. Rajani *Student, Dept. of Mech. Engg, SDM, Dharwad,
THE EFFECT OF LARGE EXTERNAL STORES ON THE LOW SPEED LONGITUDINAL AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS
 THE EFFECT OF LARGE EXTERNAL STORES ON THE LOW SPEED LONGITUDINAL AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A 60 DELTA WING AND FUSELAGE WITH STORES LOCATED ON THE LOWER SURFACE A Thesis Presented to the Faculty
THE EFFECT OF LARGE EXTERNAL STORES ON THE LOW SPEED LONGITUDINAL AERODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A 60 DELTA WING AND FUSELAGE WITH STORES LOCATED ON THE LOWER SURFACE A Thesis Presented to the Faculty
ν δ - 1 -
 ν δ - 1 - δ ν ν δ ν ν - 2 - ρ δ ρ θ θ θ δ τ ρ θ δ δ θ δ δ δ δ τ μ δ μ δ ν δ δ δ - 3 - τ ρ δ ρ δ ρ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ - 4 - ρ μ ρ μ ρ ρ μ μ ρ - 5 - ρ τ μ τ μ ρ δ δ δ - 6 - τ ρ μ τ ρ μ ρ δ θ θ δ θ - 7
ν δ - 1 - δ ν ν δ ν ν - 2 - ρ δ ρ θ θ θ δ τ ρ θ δ δ θ δ δ δ δ τ μ δ μ δ ν δ δ δ - 3 - τ ρ δ ρ δ ρ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ - 4 - ρ μ ρ μ ρ ρ μ μ ρ - 5 - ρ τ μ τ μ ρ δ δ δ - 6 - τ ρ μ τ ρ μ ρ δ θ θ δ θ - 7
Steady waves in compressible flow
 Chapter Steady waves in compressible flow. Oblique shock waves Figure. shows an oblique shock wave produced when a supersonic flow is deflected by an angle. Figure.: Flow geometry near a plane oblique
Chapter Steady waves in compressible flow. Oblique shock waves Figure. shows an oblique shock wave produced when a supersonic flow is deflected by an angle. Figure.: Flow geometry near a plane oblique
ME 425: Aerodynamics
 ME 45: Aerodynamics Dr. A.B.M. Toufique Hasan Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET), Dhaka Lecture-0 Introduction toufiquehasan.buet.ac.bd
ME 45: Aerodynamics Dr. A.B.M. Toufique Hasan Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET), Dhaka Lecture-0 Introduction toufiquehasan.buet.ac.bd
THE EFFECT OF WING GEOMETRY ON LIFT AT SUPERSONIC SPEEDS
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology EURECA 2013 Special Issue August (2014) 16-27 School of Engineering, Taylor s University THE EFFECT OF WING GEOMETRY ON LIFT AT SUPERSONIC SPEEDS ABDULKAREEM
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology EURECA 2013 Special Issue August (2014) 16-27 School of Engineering, Taylor s University THE EFFECT OF WING GEOMETRY ON LIFT AT SUPERSONIC SPEEDS ABDULKAREEM
Reynolds Number Effects on the Performance of Lateral Control Devices
 NASA/TM-2-21541 Reynolds Number Effects on the Performance of Lateral Control Devices Raymond E. Mineck Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia October 2 The NASA STI Program Office... in Profile Since
NASA/TM-2-21541 Reynolds Number Effects on the Performance of Lateral Control Devices Raymond E. Mineck Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia October 2 The NASA STI Program Office... in Profile Since
1. Fluid Dynamics Around Airfoils
 1. Fluid Dynamics Around Airfoils Two-dimensional flow around a streamlined shape Foces on an airfoil Distribution of pressue coefficient over an airfoil The variation of the lift coefficient with the
1. Fluid Dynamics Around Airfoils Two-dimensional flow around a streamlined shape Foces on an airfoil Distribution of pressue coefficient over an airfoil The variation of the lift coefficient with the
CFD COMPUTATION OF THE GROUND EFFECT ON AIRPLANE WITH HIGH ASPECT RATIO WING
 28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES CFD COMPUTATION OF THE GROUND EFFECT ON AIRPLANE WITH HIGH ASPECT RATIO WING Sun Tae Kim*, Youngtae Kim**, Tae Kyu Reu* *Agency for Defense Development,
28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES CFD COMPUTATION OF THE GROUND EFFECT ON AIRPLANE WITH HIGH ASPECT RATIO WING Sun Tae Kim*, Youngtae Kim**, Tae Kyu Reu* *Agency for Defense Development,
Improved Method for Prediction of Attainable Wing Leading-Edge Thrust
 NASA Technical Paper 3557 Improved Method for Prediction of Attainable Wing Leading-Edge Thrust Harry W. Carlson Lockheed Engineering & Sciences Company Hampton, Virginia Marcus O. McElroy and Wendy B.
NASA Technical Paper 3557 Improved Method for Prediction of Attainable Wing Leading-Edge Thrust Harry W. Carlson Lockheed Engineering & Sciences Company Hampton, Virginia Marcus O. McElroy and Wendy B.
Restriction/ Classification Cancelled
 Restriction/ Classification Cancelled NACA RM E55KOla SYMBOLS............................... 3 PRELIMINARY CONSIDERATIONS..................... 5 Description of Cascade...................... 5 Performance
Restriction/ Classification Cancelled NACA RM E55KOla SYMBOLS............................... 3 PRELIMINARY CONSIDERATIONS..................... 5 Description of Cascade...................... 5 Performance
Introduction to Flight
 l_ Introduction to Flight Fifth Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Curator for Aerodynamics, National Air and Space Museum Smithsonian Institution Professor Emeritus University of Maryland Me Graw Higher Education
l_ Introduction to Flight Fifth Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Curator for Aerodynamics, National Air and Space Museum Smithsonian Institution Professor Emeritus University of Maryland Me Graw Higher Education
Experimental Investigation to Study Flow Characteristics over a Naca0018 Aerofoil and an Automobile Dome-A Comparative Study
 Experimental Investigation to Study Flow Characteristics over a Naca0018 Aerofoil and an Automobile Dome-A Comparative Study M. Sri Rama Murthy 1, A. V. S. S. K. S. Gupta 2 1 Associate professor, Department
Experimental Investigation to Study Flow Characteristics over a Naca0018 Aerofoil and an Automobile Dome-A Comparative Study M. Sri Rama Murthy 1, A. V. S. S. K. S. Gupta 2 1 Associate professor, Department
Evaluation of Surface Finish Affect on Aerodynamic Coefficients Of Wind Tunnel Testing Models
 Evaluation of Finish Affect on Aerodynamic Coefficients Of Wind Tunnel Testing s R. ADELNIA 1, S. AGHANAJAFI 2, S. DANESHMAND 3 Department of Mechanical Engineering Islamic Azad University Majlesi Branch
Evaluation of Finish Affect on Aerodynamic Coefficients Of Wind Tunnel Testing s R. ADELNIA 1, S. AGHANAJAFI 2, S. DANESHMAND 3 Department of Mechanical Engineering Islamic Azad University Majlesi Branch
Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Mecânica Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 2012/13
 Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Mecânica Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 212/13 Exam 2ª época, 2 February 213 Name : Time : 8: Number: Duration : 3 hours 1 st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed 2 nd Part :
Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia Mecânica Aerodynamics 1 st Semester 212/13 Exam 2ª época, 2 February 213 Name : Time : 8: Number: Duration : 3 hours 1 st Part : No textbooks/notes allowed 2 nd Part :
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE DYNAMIC STABILITY DERIVATIVES FOR A FIGHTER MODEL
 24 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE DYNAMIC STABILITY DERIVATIVES FOR A FIGHTER MODEL MR Soltani*, Ali R Davari** *Associate Professor, **PhD Student
24 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE DYNAMIC STABILITY DERIVATIVES FOR A FIGHTER MODEL MR Soltani*, Ali R Davari** *Associate Professor, **PhD Student
An Investigation of the Attainable Efficiency of Flight at Mach One or Just Beyond
 45 th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, January 8 11, 2007, Reno, Nevada An Investigation of the Attainable Efficiency of Flight at Mach One or Just Beyond Antony Jameson Department of Aeronautics
45 th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, January 8 11, 2007, Reno, Nevada An Investigation of the Attainable Efficiency of Flight at Mach One or Just Beyond Antony Jameson Department of Aeronautics
Effect of Full-Chord Porosity on Aerodynamic Characteristics of the NACA 0012 Airfoil
 NASA Technical Paper 3591 Effect of Full-Chord Porosity on Aerodynamic Characteristics of the NACA 12 Airfoil Raymond E. Mineck Langley Research Center Hampton, Virginia Peter M. Hartwich ViGYAN Inc. Hampton,
NASA Technical Paper 3591 Effect of Full-Chord Porosity on Aerodynamic Characteristics of the NACA 12 Airfoil Raymond E. Mineck Langley Research Center Hampton, Virginia Peter M. Hartwich ViGYAN Inc. Hampton,
PRINCIPLES OF FLIGHT
 1 Considering a positive cambered aerofoil, the pitching moment when Cl=0 is: A infinite B positive (nose-up). C negative (nose-down). D equal to zero. 2 The angle between the aeroplane longitudinal axis
1 Considering a positive cambered aerofoil, the pitching moment when Cl=0 is: A infinite B positive (nose-up). C negative (nose-down). D equal to zero. 2 The angle between the aeroplane longitudinal axis
AEROSPACE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT. Second Year - Second Term ( ) Fluid Mechanics & Gas Dynamics
 AEROSPACE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Second Year - Second Term (2008-2009) Fluid Mechanics & Gas Dynamics Similitude,Dimensional Analysis &Modeling (1) [7.2R*] Some common variables in fluid mechanics include:
AEROSPACE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Second Year - Second Term (2008-2009) Fluid Mechanics & Gas Dynamics Similitude,Dimensional Analysis &Modeling (1) [7.2R*] Some common variables in fluid mechanics include:
Air Loads. Airfoil Geometry. Upper surface. Lower surface
 AE1 Jha Loads-1 Air Loads Airfoil Geometry z LE circle (radius) Chord line Upper surface thickness Zt camber Zc Zl Zu Lower surface TE thickness Camber line line joining the midpoints between upper and
AE1 Jha Loads-1 Air Loads Airfoil Geometry z LE circle (radius) Chord line Upper surface thickness Zt camber Zc Zl Zu Lower surface TE thickness Camber line line joining the midpoints between upper and
RESEARCH MEMORANDUM NATIONALADVISORY COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS. OF SONIC PROPpUMIVE JETS OF A FOUR-ENGINE. Langley Aeronautical Langley Field, Va.
 :. i COPY RM L57E31 RESEARCH MEMORANDUM.. -. OF SONIC PROPpUMIVE JETS OF A FOUR-ENGINE DELTA-WING CONFIGURATION By Joseph H. Judd and Ralph A. Falanga Langley Aeronautical Langley Field, Va. CLASSIFIED
:. i COPY RM L57E31 RESEARCH MEMORANDUM.. -. OF SONIC PROPpUMIVE JETS OF A FOUR-ENGINE DELTA-WING CONFIGURATION By Joseph H. Judd and Ralph A. Falanga Langley Aeronautical Langley Field, Va. CLASSIFIED
Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters 2 Lecture 20 Topics
 Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters Lecture 0 Topics 5..4 Effects of geometric parameters, Reynolds number and roughness on aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils 5..5 Choice of airfoil
Chapter 5 Wing design - selection of wing parameters Lecture 0 Topics 5..4 Effects of geometric parameters, Reynolds number and roughness on aerodynamic characteristics of airfoils 5..5 Choice of airfoil
A technique to predict the aerodynamic effects of battle damage on an aircraft's wing
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository A technique to predict the aerodynamic effects of battle damage on an aircraft's wing This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Loughborough University Institutional Repository A technique to predict the aerodynamic effects of battle damage on an aircraft's wing This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Syllabus for AE3610, Aerodynamics I
 Syllabus for AE3610, Aerodynamics I Current Catalog Data: AE 3610 Aerodynamics I Credit: 4 hours A study of incompressible aerodynamics of flight vehicles with emphasis on combined application of theory
Syllabus for AE3610, Aerodynamics I Current Catalog Data: AE 3610 Aerodynamics I Credit: 4 hours A study of incompressible aerodynamics of flight vehicles with emphasis on combined application of theory
Wings and Bodies in Compressible Flows
 Wings and Bodies in Compressible Flows Prandtl-Glauert-Goethert Transformation Potential equation: 1 If we choose and Laplace eqn. The transformation has stretched the x co-ordinate by 2 Values of at corresponding
Wings and Bodies in Compressible Flows Prandtl-Glauert-Goethert Transformation Potential equation: 1 If we choose and Laplace eqn. The transformation has stretched the x co-ordinate by 2 Values of at corresponding
Drag Analysis of a Supermarine. Spitfire Mk V at Cruise Conditions
 Introduction to Flight Aircraft Drag Project April 2016 2016 Drag Analysis of a Supermarine Spitfire Mk V at Cruise Conditions Nicholas Conde nicholasconde@gmail.com U66182304 Introduction to Flight Nicholas
Introduction to Flight Aircraft Drag Project April 2016 2016 Drag Analysis of a Supermarine Spitfire Mk V at Cruise Conditions Nicholas Conde nicholasconde@gmail.com U66182304 Introduction to Flight Nicholas
UNIT 4 FORCES ON IMMERSED BODIES. Lecture-01
 1 UNIT 4 FORCES ON IMMERSED BODIES Lecture-01 Forces on immersed bodies When a body is immersed in a real fluid, which is flowing at a uniform velocity U, the fluid will exert a force on the body. The
1 UNIT 4 FORCES ON IMMERSED BODIES Lecture-01 Forces on immersed bodies When a body is immersed in a real fluid, which is flowing at a uniform velocity U, the fluid will exert a force on the body. The
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research e-issn No.: , Date: 2-4 July, 2015
 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 2-4 July, 2015 CFD Analysis of Airfoil NACA0012 Pritesh S. Gugliya 1, Yogesh R. Jaiswal 2,
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 2-4 July, 2015 CFD Analysis of Airfoil NACA0012 Pritesh S. Gugliya 1, Yogesh R. Jaiswal 2,
TECHNICAL NOTE D ABLATING UNDER CONSTANT AERODYNAMIC CONDITIONS. By Robert R. Howell. Langley Research Center Langley Station, Hampton, Va.
 -. NASA TN D-1635 TECHNICAL NOTE 1 D- 1635 AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE BEHAVIOR OF SPHERES ABLATING UNDER CONSTANT AERODYNAMIC CONDITIONS By Robert R. Howell Langley Research Center Langley Station, Hampton,
-. NASA TN D-1635 TECHNICAL NOTE 1 D- 1635 AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE BEHAVIOR OF SPHERES ABLATING UNDER CONSTANT AERODYNAMIC CONDITIONS By Robert R. Howell Langley Research Center Langley Station, Hampton,
The polar for uncambered and cambered airfoils. The angel of attack α
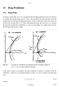 13-1 13 Drag Prediction 13.1 Drag Polar In Section under Step 14 it was a requirement that the flight performance has to be checked to complete the aircraft design process. This is only possible if the
13-1 13 Drag Prediction 13.1 Drag Polar In Section under Step 14 it was a requirement that the flight performance has to be checked to complete the aircraft design process. This is only possible if the
Computational Fluid Dynamics Study Of Fluid Flow And Aerodynamic Forces On An Airfoil S.Kandwal 1, Dr. S. Singh 2
 Computational Fluid Dynamics Study Of Fluid Flow And Aerodynamic Forces On An Airfoil S.Kandwal 1, Dr. S. Singh 2 1 M. Tech Scholar, 2 Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bipin Tripathi
Computational Fluid Dynamics Study Of Fluid Flow And Aerodynamic Forces On An Airfoil S.Kandwal 1, Dr. S. Singh 2 1 M. Tech Scholar, 2 Associate Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bipin Tripathi
1. Introduction Some Basic Concepts
 1. Introduction Some Basic Concepts 1.What is a fluid? A substance that will go on deforming in the presence of a deforming force, however small 2. What Properties Do Fluids Have? Density ( ) Pressure
1. Introduction Some Basic Concepts 1.What is a fluid? A substance that will go on deforming in the presence of a deforming force, however small 2. What Properties Do Fluids Have? Density ( ) Pressure
INFLUENCE OF ACOUSTIC EXCITATION ON AIRFOIL PERFORMANCE AT LOW REYNOLDS NUMBERS
 ICAS 2002 CONGRESS INFLUENCE OF ACOUSTIC EXCITATION ON AIRFOIL PERFORMANCE AT LOW REYNOLDS NUMBERS S. Yarusevych*, J.G. Kawall** and P. Sullivan* *Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, University
ICAS 2002 CONGRESS INFLUENCE OF ACOUSTIC EXCITATION ON AIRFOIL PERFORMANCE AT LOW REYNOLDS NUMBERS S. Yarusevych*, J.G. Kawall** and P. Sullivan* *Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, University
Coupled Fluid and Heat Flow Analysis Around NACA Aerofoil Profiles at Various Mach Numbers
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 2 (2013), pp. 249-258 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Coupled Fluid and Heat
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 2 (2013), pp. 249-258 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Coupled Fluid and Heat
Numerical Investigation of Wind Tunnel Wall Effects on a Supersonic Finned Missile
 16 th International Conference on AEROSPACE SCIENCES & AVIATION TECHNOLOGY, ASAT - 16 May 26-28, 2015, E-Mail: asat@mtc.edu.eg Military Technical College, Kobry Elkobbah, Cairo, Egypt Tel : +(202) 24025292
16 th International Conference on AEROSPACE SCIENCES & AVIATION TECHNOLOGY, ASAT - 16 May 26-28, 2015, E-Mail: asat@mtc.edu.eg Military Technical College, Kobry Elkobbah, Cairo, Egypt Tel : +(202) 24025292
RESEARCH MEMORANDUM NATIONAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS THE STATIC AND DYNAMIC-ROTARY STABILITY DERIVATIVES. Arnes Aeronautical Laboratory
 RESEARCH MEMORANDUM THE STATIC AND DYNAMIC-ROTARY STABILITY DERIVATIVES AT SUBSONIC SPEEDS OF A MODEL OF THE X-15 RESEARCH AIRPLANE By Armando E. Lopez and Bruce E. Tinling Arnes Aeronautical Laboratory
RESEARCH MEMORANDUM THE STATIC AND DYNAMIC-ROTARY STABILITY DERIVATIVES AT SUBSONIC SPEEDS OF A MODEL OF THE X-15 RESEARCH AIRPLANE By Armando E. Lopez and Bruce E. Tinling Arnes Aeronautical Laboratory
6.1 According to Handbook of Chemistry and Physics the composition of air is
 6. Compressible flow 6.1 According to Handbook of Chemistry and Physics the composition of air is From this, compute the gas constant R for air. 6. The figure shows a, Pitot-static tube used for velocity
6. Compressible flow 6.1 According to Handbook of Chemistry and Physics the composition of air is From this, compute the gas constant R for air. 6. The figure shows a, Pitot-static tube used for velocity
FUNDAMENTALS OF AERODYNAMICS
 *A \ FUNDAMENTALS OF AERODYNAMICS Second Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Professor of Aerospace Engineering University of Maryland H ' McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas
*A \ FUNDAMENTALS OF AERODYNAMICS Second Edition John D. Anderson, Jr. Professor of Aerospace Engineering University of Maryland H ' McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas
Nonlinear Aerodynamic Predictions Of Aircraft and Missiles Employing Trailing-Edge Flaps
 Nonlinear Aerodynamic Predictions Of Aircraft and Missiles Employing Trailing-Edge Flaps Daniel J. Lesieutre 1 Nielsen Engineering & Research, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, 95054 The nonlinear missile aerodynamic
Nonlinear Aerodynamic Predictions Of Aircraft and Missiles Employing Trailing-Edge Flaps Daniel J. Lesieutre 1 Nielsen Engineering & Research, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, 95054 The nonlinear missile aerodynamic
Aircraft Performance Sensitivity to Icing Cloud Conditions
 45 th Aerospace Sciences Meeting & Exhibit AIAA-2007-0086 January 8-11, 2007 Reno, NV Aircraft Performance Sensitivity to Icing Cloud Conditions Scot E. Campbell 1, Andy P. Broeren 2, and Michael B. Bragg
45 th Aerospace Sciences Meeting & Exhibit AIAA-2007-0086 January 8-11, 2007 Reno, NV Aircraft Performance Sensitivity to Icing Cloud Conditions Scot E. Campbell 1, Andy P. Broeren 2, and Michael B. Bragg
AE Stability and Control of Aerospace Vehicles
 AE 430 - Stability and ontrol of Aerospace Vehicles Static/Dynamic Stability Longitudinal Static Stability Static Stability We begin ith the concept of Equilibrium (Trim). Equilibrium is a state of an
AE 430 - Stability and ontrol of Aerospace Vehicles Static/Dynamic Stability Longitudinal Static Stability Static Stability We begin ith the concept of Equilibrium (Trim). Equilibrium is a state of an
Numerical Simulation of Unsteady Aerodynamic Coefficients for Wing Moving Near Ground
 ISSN -6 International Journal of Advances in Computer Science and Technology (IJACST), Vol., No., Pages : -7 Special Issue of ICCEeT - Held during -5 November, Dubai Numerical Simulation of Unsteady Aerodynamic
ISSN -6 International Journal of Advances in Computer Science and Technology (IJACST), Vol., No., Pages : -7 Special Issue of ICCEeT - Held during -5 November, Dubai Numerical Simulation of Unsteady Aerodynamic
NATIONALADVISORYCOMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS
 NATIONALADVISORYCOMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS TECHNICAIJ NOTE 4385 COMPARISON OF SHOCK-EXPANSION THEORY WITH EXPERIMENT FOR THE LIFT, DRAG, AND PITCHING-MOMENT CHARACTERISTICS. OF TWO WING-BODY COMBINATIONS
NATIONALADVISORYCOMMITTEE FOR AERONAUTICS TECHNICAIJ NOTE 4385 COMPARISON OF SHOCK-EXPANSION THEORY WITH EXPERIMENT FOR THE LIFT, DRAG, AND PITCHING-MOMENT CHARACTERISTICS. OF TWO WING-BODY COMBINATIONS

 RM -L7G02
RM -L7G02