PROJECT COLLECT INFORMATION ABOUT THE APPLICATIONS OF NEWTON S THIRD LAW
|
|
|
- Barnard Cain
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROJECT COLLECT INFORMATION ABOUT THE APPLICATIONS OF NEWTON S THIRD LAW Title of the project : Applications of Newton s third law in our daily life. Purpose of the project : To Know about the applications of Newton s third law in our daily life. Hypothesis : The three laws of motion were first compiled by Isaac Newton in his Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in Newton used them to explain and investigate the motion of many physical objects and systems. The third law states that For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction Material : Internet, 9th class physical science text book, balloon, straw, tread and spring balances. Proceedure : We collect information from different sources about the applications of Newton s Third law. We collect some pictures about the applications of newton s third law. An experiment was conducted by me about the Newton s third law. According to gathered information we have prepaed a project report. Introduction : Newton s laws of motion: The three laws of motion were first compiled by Isaac Newton in his Philosophiae Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), first published in The first law states that an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. An object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This law is often called "the law of inertia". Second law states that the Acceleration is produced when a force acts on a mass. The greater the mass (of the object being accelerated) the greater the amount of force needed (to accelerate the object). The third law states that every action there is an equal and opposite re-action. Newton s third Law: The third law states that every action there is an equal and opposite re-action. This means that for every force there is a reaction force that is equal in size, but opposite in direction. That is to say that whenever an object pushes another object it gets pushed back in the opposite direction equally hard. The third law states that all forces between two objects exist in equal magnitude and opposite direction: if one object A exerts a force F A on a second object B, then B simultaneously exerts a force F B on A, and the two forces are equal and opposite: F A = F B. The third law means that all forces are interactions between different bodies, and thus that there is no such thing as a unidirectional force or a force that acts on only one body. This law is sometimes referred to as the action-reaction law., with F A called the "action" and F B the "reaction". The action and the reaction are simultaneous, and it does not matter which is called the action and which is called reaction; both forces are part of a single interaction, and neither force exists without the other.
2 Process: To know the opposite forces: Hook two spring balances as shown in the diagram and pull from either side. You will notice that the pointers on the spring balances read equally (say 100 N). This shows that both the spring balances are registering equal force. Observations: 1) The readings on the two spring balances are equal. 2) If we pulled the spring balance more, then the reading are Result : changes but they are same. When one object exerts a force upon a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force upon the first object. Balloon Straw Experiment: Materials: balloon drinking straw string tape printout of worksheet. Procedure: Slide the drinking straw onto a piece of string. Place two loops of masking tape onto the straw. Blow up the balloon to its maximum capacity (greatest volume). Hold tightly onto the neck of the balloon so that no air escapes, and attach the balloon to the two pieces of tape. The neck of the balloon should be parallel to the string. Release the neck to let the air rush out of the balloon. Observations: 1) When the air rush out to the balloon, the balloon with straw travelled opposite side. 2) Air rush out to the balloown is an acton and the balloon travelled with straw is a reaction. Result: The third law states that every action there is an equal and opposite re-action.
3 Applications: 1) When you walk forward you push your foot back wards on the ground. The earth pushes your shoe forward. 2) As birds push down on the air with their wings the air pushes their wings up and gives them lift. 3) The fish uses its fins to push water backwards. In turn the water reacts by pushing the fish forward, moving fish through the water. 4) if someone pushes horizontally against a wall with a force of 100 N, then the wall will push horizontally against the person with a force of 100N. 5) In Rocket, Various fuels are burnt in the engine produces hot hases. The hot gases push against the inside tube of rocket and escape out the bottom of the tube. As the gases move down ward, the rocket moves in opposite direction. 6) Arms push against the water, water pushes swimmer ahead. 7) When bullet is fired from a gun the force sending the bullet forward is equal is equal to the force sending the gun backward. But due to the high mass of the gun, it moves a little distance backward and gives a backward jerk or a kick to shoulder of the gunman. Gun is said to be recoiled. 8) When a swimmer turns, the pool wall pushes against the swimmer with the same force as the swimmer pushes against the pool wall.
4 Precautions: 1) The spring balance should be brought in elastic mode before doing the experiment. 2) The second spring balance should not be pulled beyond its elastic limit. 3) The reading of the spring balance should be taken without any parallax error. 4) We should blow the balloon in its volume limit. Interpretation of the student: We collect the information of daily life applications of Newton s third law from Internet. We have done an experement to prove the newton s third law. We have done an experiment of spring balances to show that action and reaction forces are same. Conclusion: After completion of the project we conclude that For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. To prove the law we have done some experiment with the help of our teachers. We collect information about the applications of Newtons s third law from internet. We know the various daily life examples of Newton s third law. Analysis: In the above collection of the applications of Newton s third law. We observed that For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
5 Title of the Project Class Subject School Time frame PROJECT REPORT : Applications of Newton s third law in our daily life. : 9 th : Physics : Z,P.High School, Lolugu, Ponduru Mandal, Srikakulam district : 7 ర జ ల Material/Sources used tools: Internet, News paper clippings, Science books, laboratory equipment. Details of procedure follwoed: We collect data about the applications of Newton s third law from Internet and various Science books. We understand the Newton s third law by the balloon-straw experiment. We understand the use of the Newton s third law in our daily life. And we also know that the various equipment prepared by the Newton s third law. Ex: Rocket. Finding Observations: Newton s third law used in our walking. This law is applicable when a swimmer jumped in the swimming pool. This law helps to flying the birds and swimming the fishes. Experiences faced: when we collect information about newton s law from internet we know the process to search the results from internet. We use balloons and tread experiment to prove the Newton s third law. Project outcome : After completion of the project we conclude that For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. To prove the law we have done some experiment with the help of our teachers. We collect information about the applications of Newtons s third law from internet. We know the various daily life examples of Newton s third law. Name of the group members and work allotment: Sl.No Name of the team member Work allotment Date of Submission : Signatures
Newton s Laws of Motion. Chapter 3, Section 2
 Newton s Laws of Motion Chapter 3, Section 2 3 Motion and Forces Inertia and Mass Inertia (ih NUR shuh) is the tendency of an object to resist any change in its motion. If an object is moving, it will
Newton s Laws of Motion Chapter 3, Section 2 3 Motion and Forces Inertia and Mass Inertia (ih NUR shuh) is the tendency of an object to resist any change in its motion. If an object is moving, it will
Newton s Laws of Motion. I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction
 Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction While most people know what Newton's laws say, many people do not know what they mean (or simply do not believe what they mean).
Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction While most people know what Newton's laws say, many people do not know what they mean (or simply do not believe what they mean).
CHAPTER 9 FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION
 CHAPTER 9 FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION Q 1. What is a force? Ans: Force is a push or pull which tries to bring the change in the state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line. Unit of force: force
CHAPTER 9 FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION Q 1. What is a force? Ans: Force is a push or pull which tries to bring the change in the state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line. Unit of force: force
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action Reaction Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at constant velocity,
Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action Reaction Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at constant velocity,
Newton s Laws of Motion. I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction
 Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction While most people know what Newton's laws say, many people do not know what they mean (or simply do not believe what they mean).
Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction While most people know what Newton's laws say, many people do not know what they mean (or simply do not believe what they mean).
Newton s Laws of Motion. I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction
 Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction While most people know what Newton's laws say, many people do not know what they mean (or simply do not believe what they mean).
Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction While most people know what Newton's laws say, many people do not know what they mean (or simply do not believe what they mean).
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton s Laws of Motion While most people know what Newton's Laws are, many people do not understand what they mean. Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object
Newton s Laws of Motion While most people know what Newton's Laws are, many people do not understand what they mean. Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object
FORCE, WORK, ENERGY & POWER
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) PHYS 101 - LECTURE 5 FORCE, WORK, ENERGY & POWER DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM 1 What change the state of object is called force. We mean by saying state, shape or position of the
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) PHYS 101 - LECTURE 5 FORCE, WORK, ENERGY & POWER DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM 1 What change the state of object is called force. We mean by saying state, shape or position of the
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at a constant velocity,
Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at a constant velocity,
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion 4-1 Force A force is a push or pull. An object at rest needs a force to get it moving; a moving object needs a force to change its velocity. The magnitude of
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion 4-1 Force A force is a push or pull. An object at rest needs a force to get it moving; a moving object needs a force to change its velocity. The magnitude of
If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not move. If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not stop. The List:
 If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not move. If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not stop. The List: No Push No Go No Push No Stop No Push No Speed Up No Push No Slow Down
If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not move. If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not stop. The List: No Push No Go No Push No Stop No Push No Speed Up No Push No Slow Down
Forces. A force is a push or a pull on an object
 Forces Forces A force is a push or a pull on an object Arrows are used to represent forces. The direction of the arrow represent the direction the force that exist or being applied. Forces A net force
Forces Forces A force is a push or a pull on an object Arrows are used to represent forces. The direction of the arrow represent the direction the force that exist or being applied. Forces A net force
Newton's Third Law. Examples of Interaction Force Pairs
 Newton's Third Law A force is a push or a pull that acts upon an object as a results of its interaction with another object. Forces result from interactions! Some forces result from contact interactions
Newton's Third Law A force is a push or a pull that acts upon an object as a results of its interaction with another object. Forces result from interactions! Some forces result from contact interactions
NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION. Review
 NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION Review BACKGROUND Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician famous for his discovery of the law of gravity also discovered the three laws of motion. He
NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION Review BACKGROUND Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician famous for his discovery of the law of gravity also discovered the three laws of motion. He
Name: Block: Date: / / Engineering Design Challenge: Balloon Rocket Race!
 Name: Block: Date: / / Engineering Design Challenge: Balloon Rocket Race! Introduction: In 1919 Robert Goddard, a professor at Clark University in Worcester, Massachusetts, claimed that a multistage rocket
Name: Block: Date: / / Engineering Design Challenge: Balloon Rocket Race! Introduction: In 1919 Robert Goddard, a professor at Clark University in Worcester, Massachusetts, claimed that a multistage rocket
LAWS OF MOTION Newtons laws of motion. (i) First law: Law of inertia. Every body continues to be in its state of rest or of uniform motion in a
 LAWS OF MOTION Newtons laws of motion. (i) First law: Law of inertia. Every body continues to be in its state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless compelled to change that state by an
LAWS OF MOTION Newtons laws of motion. (i) First law: Law of inertia. Every body continues to be in its state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless compelled to change that state by an
Chapter 2. Force and Newton s Laws
 Chapter 2 Force and Newton s Laws 2 1 Newton s First Law Force Force A push or pull that one body exerts on another body. Examples : 2 Categories of Forces Forces Balanced Forces Unbalanced Forces Balanced
Chapter 2 Force and Newton s Laws 2 1 Newton s First Law Force Force A push or pull that one body exerts on another body. Examples : 2 Categories of Forces Forces Balanced Forces Unbalanced Forces Balanced
12.1 Forces and Motion Notes
 12.1 Forces and Motion Notes What Is a Force? A is a push or a pull that acts on an object. A force can cause a object to, or it can a object by changing the object s speed or direction. Force can be measured
12.1 Forces and Motion Notes What Is a Force? A is a push or a pull that acts on an object. A force can cause a object to, or it can a object by changing the object s speed or direction. Force can be measured
Newton s Laws of Motion. Steve Case NMGK-8 University of Mississippi October 2005
 Newton s Laws of Motion Steve Case NMGK-8 University of Mississippi October 2005 Background Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician famous for his discovery of the law of gravity
Newton s Laws of Motion Steve Case NMGK-8 University of Mississippi October 2005 Background Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician famous for his discovery of the law of gravity
NEWTON S THIRD LAW OF MOTION ACTION AND REACTION. For Every Force There Is An Equal and Opposite Force
 NEWTON S THIRD LAW OF MOTION ACTION AND REACTION For Every Force There Is An Equal and Opposite Force Forces and Interactions n A force is always part of a mutual action that involves another force. n
NEWTON S THIRD LAW OF MOTION ACTION AND REACTION For Every Force There Is An Equal and Opposite Force Forces and Interactions n A force is always part of a mutual action that involves another force. n
Redhound Day 2 Assignment (continued)
 Redhound Day 2 Assignment (continued) Directions: Watch the power point and answer the questions on the last slide Which Law is It? on your own paper. You will turn this in for a grade. Background Sir
Redhound Day 2 Assignment (continued) Directions: Watch the power point and answer the questions on the last slide Which Law is It? on your own paper. You will turn this in for a grade. Background Sir
Page 1/6
 FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION Force An agent that change or try to change the state of an object is called force.the force applied on a body can bring about the following changes: It can change the state of
FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION Force An agent that change or try to change the state of an object is called force.the force applied on a body can bring about the following changes: It can change the state of
A N D. c h a p t e r 1 2 M O T I O N F O R C E S
 F O R C E S A N D c h a p t e r 1 2 M O T I O N What is a FORCE? A FORCE is a push or pull that acts on an object. A force can cause a resting object to move OR Accelerate a moving object by: changing
F O R C E S A N D c h a p t e r 1 2 M O T I O N What is a FORCE? A FORCE is a push or pull that acts on an object. A force can cause a resting object to move OR Accelerate a moving object by: changing
*ANSWER KEY * ANSWER KEY* ANSWER KEY* Newton's First Law of Motion Study Guide
 *ANSWER KEY * ANSWER KEY* ANSWER KEY* Newton's First Law of Motion Study Guide Newton's First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia) An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force.
*ANSWER KEY * ANSWER KEY* ANSWER KEY* Newton's First Law of Motion Study Guide Newton's First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia) An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force.
Newton s Wagon. Materials. friends rocks wagon balloon fishing line tape stopwatch measuring tape. Lab Time Part 1
 Newton s Wagon Overview: The natural state of objects is to follow a straight line. In fact, Newton s First Law of Motion states that objects in motion will tend to stay in motion unless they are acted
Newton s Wagon Overview: The natural state of objects is to follow a straight line. In fact, Newton s First Law of Motion states that objects in motion will tend to stay in motion unless they are acted
UC Irvine FOCUS! 5 E Lesson Plan
 UC Irvine FOCUS! 5 E Lesson Plan Title: Stomp Rockets Grade Level and Course: Pre-Algebra, Geometry, Grade 8 Physical Science, Grades 9-12 Physics (extension) - Trigonometry Materials: 1 stomp rocket per
UC Irvine FOCUS! 5 E Lesson Plan Title: Stomp Rockets Grade Level and Course: Pre-Algebra, Geometry, Grade 8 Physical Science, Grades 9-12 Physics (extension) - Trigonometry Materials: 1 stomp rocket per
Newton s second law of motion states:
 Newton s second law of motion states: The acceleration produced by a force on an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the force, is in the same direction as the force, and is inversely proportional
Newton s second law of motion states: The acceleration produced by a force on an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the force, is in the same direction as the force, and is inversely proportional
Directed Reading B. Section: Newton s Laws of Motion NEWTON S FIRST LAW OF MOTION
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Newton s Laws of Motion NEWTON S FIRST LAW OF MOTION Part 1: Objects at Rest 1. Which is NOT an example of an object at rest? a. a golf ball on a tee b. a jet
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: Newton s Laws of Motion NEWTON S FIRST LAW OF MOTION Part 1: Objects at Rest 1. Which is NOT an example of an object at rest? a. a golf ball on a tee b. a jet
Newton s 3 rd Law. 3rd Six Weeks
 Newton s 3 rd Law 3rd Six Weeks Golf and Newton s 3 rd Law Newton s 3 rd Law of Motion The Law states: Whenever one object exerts a force upon a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite
Newton s 3 rd Law 3rd Six Weeks Golf and Newton s 3 rd Law Newton s 3 rd Law of Motion The Law states: Whenever one object exerts a force upon a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite
NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION. Chapter 2: pages Review questions 1, 5-10, 14, 17, 21-24, 30
 NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION Chapter 2: pages 37-53 Review questions 1, 5-10, 14, 17, 21-24, 30 Sir Isaac Newton Born 1642 1665 began individual studies Proved universal gravitation Invented the Calculus Reflector
NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION Chapter 2: pages 37-53 Review questions 1, 5-10, 14, 17, 21-24, 30 Sir Isaac Newton Born 1642 1665 began individual studies Proved universal gravitation Invented the Calculus Reflector
Engage 1. When you exert a force on a balloon, what does the balloon exert on you?
 Unit 1 Forces and Motion Lesson 2.c Newton s Third Law of Motion Student Performance Outcomes Students know that when one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object always exerts a force
Unit 1 Forces and Motion Lesson 2.c Newton s Third Law of Motion Student Performance Outcomes Students know that when one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object always exerts a force
4 Newton s Third Law of Motion Action and Reaction. For every force, there is an equal and opposite force.
 For every force, there is an equal and opposite force. Forces and Interactions A force is always part of a mutual action that involves another force. Forces and Interactions In the simplest sense, a force
For every force, there is an equal and opposite force. Forces and Interactions A force is always part of a mutual action that involves another force. Forces and Interactions In the simplest sense, a force
7.1 Forces and Interactions. A force is always part of a mutual action that involves another force. For every force, there. opposite force.
 For every force, there is an equal and opposite force. A force is always part of a mutual action that involves another force. In the simplest sense, a force is a push or a pull. A mutual action is an interaction
For every force, there is an equal and opposite force. A force is always part of a mutual action that involves another force. In the simplest sense, a force is a push or a pull. A mutual action is an interaction
Isaac Newton ( ) 1687 Published Principia Invented Calculus 3 Laws of Motion Universal Law of Gravity
 Isaac Newton (1642-1727) 1687 Published Principia Invented Calculus 3 Laws of Motion Universal Law of Gravity Newton s First Law (Law of Inertia) An object will remain at rest or in a constant state of
Isaac Newton (1642-1727) 1687 Published Principia Invented Calculus 3 Laws of Motion Universal Law of Gravity Newton s First Law (Law of Inertia) An object will remain at rest or in a constant state of
Balanced forces do not cause an object to change its motion Moving objects will keep moving and stationary objects will stay stationary
 Newton s Laws Test 8.PS2.3) Create a demonstration of an object in motion and describe the position, force, and direction of the object. 8.PS2.4) Plan and conduct an investigation to provide evidence that
Newton s Laws Test 8.PS2.3) Create a demonstration of an object in motion and describe the position, force, and direction of the object. 8.PS2.4) Plan and conduct an investigation to provide evidence that
Forces. Unit 2. Why are forces important? In this Unit, you will learn: Key words. Previously PHYSICS 219
 Previously Remember From Page 218 Forces are pushes and pulls that can move or squash objects. An object s speed is the distance it travels every second; if its speed increases, it is accelerating. Unit
Previously Remember From Page 218 Forces are pushes and pulls that can move or squash objects. An object s speed is the distance it travels every second; if its speed increases, it is accelerating. Unit
CHAPTER 7 NEWTON'S THIRD LAW OF MOTION MOMENTUM & CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION POINTS
 1 Name Period CHAPTER 7 NEWTON'S THIRD LAW OF MOTION MOMENTUM & CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION POINTS 1. NT OVERHEAD NOTES WITH WORKSHEET GUIDE /30 2. WS MOMENTUM WORKSHEET /17 3.
1 Name Period CHAPTER 7 NEWTON'S THIRD LAW OF MOTION MOMENTUM & CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION POINTS 1. NT OVERHEAD NOTES WITH WORKSHEET GUIDE /30 2. WS MOMENTUM WORKSHEET /17 3.
Newton s Laws. 8 th Science. Image:
 Newton s Laws 8 th Science Image: http://literaturequeen.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/09/isaac_newton_gravity_panana_627535.jpg Part A: EDPuzzle - Watch the Newton's Laws video on EDPuzzle to help you complete
Newton s Laws 8 th Science Image: http://literaturequeen.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/09/isaac_newton_gravity_panana_627535.jpg Part A: EDPuzzle - Watch the Newton's Laws video on EDPuzzle to help you complete
ROCKET LABTM. Up and Down and All Around with Newton
 Science 1. LEARN (15 minutes) STEP Up and Down and All Around with Newton Objectives Students will gain knowledge of Newton s Three Laws of Motion. Students will demonstrate how all Three Laws of Motion
Science 1. LEARN (15 minutes) STEP Up and Down and All Around with Newton Objectives Students will gain knowledge of Newton s Three Laws of Motion. Students will demonstrate how all Three Laws of Motion
Forces I. Newtons Laws
 Forces I Newtons Laws Kinematics The study of how objects move Dynamics The study of why objects move Newton s Laws and Forces What is force? What are they? Force A push or a pull Symbol is F Unit is N
Forces I Newtons Laws Kinematics The study of how objects move Dynamics The study of why objects move Newton s Laws and Forces What is force? What are they? Force A push or a pull Symbol is F Unit is N
NEWTON S FIRST LAW OF MOTION. Law of Inertia
 NEWTON S FIRST LAW OF MOTION Law of Inertia An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. An object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction
NEWTON S FIRST LAW OF MOTION Law of Inertia An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force. An object in motion continues in motion with the same speed and in the same direction
Engage 1. When you exert a force on a balloon, what does the balloon exert on you?
 Unit 1: Phenomenon The Physics of Skydiving Lesson 3c Newton s Third Law of Motion California Standard Addressed PH1. Newton s laws predict the motion of most objects. As a basis for understanding this
Unit 1: Phenomenon The Physics of Skydiving Lesson 3c Newton s Third Law of Motion California Standard Addressed PH1. Newton s laws predict the motion of most objects. As a basis for understanding this
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 3
 Chapter 2 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 3 2.1 Forces 2.2 Net Force 2.3 Newton s first law Lecture 3 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 Forces Forces are interactions between objects Different type of forces: Contact
Chapter 2 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 3 2.1 Forces 2.2 Net Force 2.3 Newton s first law Lecture 3 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 Forces Forces are interactions between objects Different type of forces: Contact
ConcepTest 3.7a Punts I
 ConcepTest 3.7a Punts I Which of the 3 punts has the longest hang time? 1 2 3 4) all have the same hang time h ConcepTest 3.7a Punts I Which of the 3 punts has the longest hang time? 1 2 3 4) all have
ConcepTest 3.7a Punts I Which of the 3 punts has the longest hang time? 1 2 3 4) all have the same hang time h ConcepTest 3.7a Punts I Which of the 3 punts has the longest hang time? 1 2 3 4) all have
SCIENCE CIRCUS Lesson Plan
 Edna Patricia Martinez epmartinez145@gmail.com Samantha Flores sflores22@miners.utep.edu SCIENCE CIRCUS Lesson Plan Title: Acting and Reacting Objectives: The students will be able to. observe and experiment
Edna Patricia Martinez epmartinez145@gmail.com Samantha Flores sflores22@miners.utep.edu SCIENCE CIRCUS Lesson Plan Title: Acting and Reacting Objectives: The students will be able to. observe and experiment
NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION
 Name Period Date NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION If I am anything, which I highly doubt, I have made myself so by hard work. Isaac Newton Goals: 1. Students will use conceptual and mathematical models to predict
Name Period Date NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION If I am anything, which I highly doubt, I have made myself so by hard work. Isaac Newton Goals: 1. Students will use conceptual and mathematical models to predict
Chapter: The Laws of Motion
 Table of Contents Chapter: The Laws of Motion Section 1: Newton s Second Law Section 2: Gravity Section 3: The Third Law of Motion 1 Newton s Second Law Force, Mass, and Acceleration Newton s first law
Table of Contents Chapter: The Laws of Motion Section 1: Newton s Second Law Section 2: Gravity Section 3: The Third Law of Motion 1 Newton s Second Law Force, Mass, and Acceleration Newton s first law
Exercises. 7.1 Forces and Interactions (page 107) 7.2 Newton s Third Law (page 108)
 Exercises 71 Forces and Interactions (page 107) 1 A force is always part of a(n) that involves another force 2 Define interaction 3 Describe the interaction forces between a nail and a hammer that hits
Exercises 71 Forces and Interactions (page 107) 1 A force is always part of a(n) that involves another force 2 Define interaction 3 Describe the interaction forces between a nail and a hammer that hits
Station 1 Block, spring scale
 Station 1 Block, spring scale Place the wooden block on Surface A with the metal loop facing you. Hook the green force gauge to the metal loop on the block. With the force gauge held horizontal, pull it
Station 1 Block, spring scale Place the wooden block on Surface A with the metal loop facing you. Hook the green force gauge to the metal loop on the block. With the force gauge held horizontal, pull it
Newton s 2 nd Law If an unbalanced (net) force acts on an object, that object will accelerate (or decelerate) in the direction of the force.
 Bottle Rocket Lab Physics Concepts: Newton s 1 st Law - Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an external force is applied to it. This we recognize as
Bottle Rocket Lab Physics Concepts: Newton s 1 st Law - Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an external force is applied to it. This we recognize as
Newton s 3 rd Law of Motion. Action and Reaction
 Newton s 3 rd Law of Motion Action and Reaction A Force is Part of an Interaction Up till now, a force has been a single and simple push or pull From now on, a force is part of a mutual action between
Newton s 3 rd Law of Motion Action and Reaction A Force is Part of an Interaction Up till now, a force has been a single and simple push or pull From now on, a force is part of a mutual action between
Physics 20 Lesson 14 Forces & Dynamics Conceptual Change
 Physics 20 Lesson 14 Forces & Dynamics Conceptual Change t this point in the course you have learned about Kinematics (the description of motion) and you have learned about vectors (addition, components).
Physics 20 Lesson 14 Forces & Dynamics Conceptual Change t this point in the course you have learned about Kinematics (the description of motion) and you have learned about vectors (addition, components).
LAB National Science Teachers Association. Lab Handout. Introduction
 Lab Handout Lab 5. Force, Mass, and Acceleration: What Is the Mathematical Relationship Among the Net Force Exerted on an Object, the Object s Inertial Mass, and Its Acceleration? Introduction Western
Lab Handout Lab 5. Force, Mass, and Acceleration: What Is the Mathematical Relationship Among the Net Force Exerted on an Object, the Object s Inertial Mass, and Its Acceleration? Introduction Western
Newton s Laws of Motion. Supplemental Text Material Pages
 Newton s Laws of Motion Supplemental Text Material Pages 300-320 Sir Isaac Newton Born 1642 1665 began individual studies Proved universal gravitation Invented the Calculus Reflector telescope 1672 First
Newton s Laws of Motion Supplemental Text Material Pages 300-320 Sir Isaac Newton Born 1642 1665 began individual studies Proved universal gravitation Invented the Calculus Reflector telescope 1672 First
Physics-MC Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1.
 Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
Let's See What we can Remember?
 Let's See What we can Remember? * What is Acceleration? A change in velocity * How do you determine an objects velocity? Speed & Direction * What is speed? How fast an objects position is changing *What
Let's See What we can Remember? * What is Acceleration? A change in velocity * How do you determine an objects velocity? Speed & Direction * What is speed? How fast an objects position is changing *What
Model Rocketry. The Science Behind the Fun
 Model Rocketry The Science Behind the Fun Topics History of Rockets Sir Isaac Newton Laws of Motion Rocket Principles Flight of a Model Rocket Rocket Propulsion Forces at Work History Rockets and rocket
Model Rocketry The Science Behind the Fun Topics History of Rockets Sir Isaac Newton Laws of Motion Rocket Principles Flight of a Model Rocket Rocket Propulsion Forces at Work History Rockets and rocket
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Motion & Forces Newton s Laws of Motion If I have seen far, it is because I have stood on the shoulders of giants. - Sir Isaac Newton (referring to Galileo) A. Newton s First Law Newton s First Law of
Motion & Forces Newton s Laws of Motion If I have seen far, it is because I have stood on the shoulders of giants. - Sir Isaac Newton (referring to Galileo) A. Newton s First Law Newton s First Law of
Chapter: The Laws of Motion
 Chapter 4 Table of Contents Chapter: The Laws of Motion Section 1: Newton s Second Law Section 2: Gravity Section 3: The Third Law of Motion 3 Motion and Forces Newton s Laws of Motion The British scientist
Chapter 4 Table of Contents Chapter: The Laws of Motion Section 1: Newton s Second Law Section 2: Gravity Section 3: The Third Law of Motion 3 Motion and Forces Newton s Laws of Motion The British scientist
Laws of Motion. What is force? What happens when you push or pull objects? Some examples of pushing and pulling. Definition Force:
 1 Laws of Motion What is force? What happens when you push or pull objects? Some examples of pushing and pulling Kicking Pushing Lifting Squeezing Definition Force: Activity: Tug of war In a tug of war,
1 Laws of Motion What is force? What happens when you push or pull objects? Some examples of pushing and pulling Kicking Pushing Lifting Squeezing Definition Force: Activity: Tug of war In a tug of war,
Can anyone think of an example of an action-reaction pair? [jumping, rowing...]
![Can anyone think of an example of an action-reaction pair? [jumping, rowing...] Can anyone think of an example of an action-reaction pair? [jumping, rowing...]](/thumbs/81/83715485.jpg) Newton s Laws of Motion (cont d) Astronomy Lesson 17 Newton proposed that whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force back on the first. The force exerted by
Newton s Laws of Motion (cont d) Astronomy Lesson 17 Newton proposed that whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force back on the first. The force exerted by
Unit 4 Forces (Newton s Laws)
 Name: Pd: Date: Unit Forces (Newton s Laws) The Nature of Forces force A push or pull exerted on an object. newton A unit of measure that equals the force required to accelerate kilogram of mass at meter
Name: Pd: Date: Unit Forces (Newton s Laws) The Nature of Forces force A push or pull exerted on an object. newton A unit of measure that equals the force required to accelerate kilogram of mass at meter
Overview The Laws of Motion
 Directed Reading for Content Mastery Overview The Laws of Motion Directions: Fill in the blanks using the terms listed below. force inertia momentum sliding conservation of momentum gravitational ma mv
Directed Reading for Content Mastery Overview The Laws of Motion Directions: Fill in the blanks using the terms listed below. force inertia momentum sliding conservation of momentum gravitational ma mv
CHAPTER 6 TEST. Directions: Show work on problems. Choose correct answer when available and place next to the question number.
 CHAPTER 6 TEST Directions: Show work on problems. Choose correct answer when available and place next to the question number. 1. What is inertia? A. the amount of matter in an object B. the force of gravity
CHAPTER 6 TEST Directions: Show work on problems. Choose correct answer when available and place next to the question number. 1. What is inertia? A. the amount of matter in an object B. the force of gravity
Physical Science Unit Exam Review. Date Period
 1. Give an example of gravitational potential energy. Frog at the top of its jump Rock at the edge of a hill Skateboarder at the top of the ramp Pendulum at the top of its swing 2. Use Newton s 2 nd law
1. Give an example of gravitational potential energy. Frog at the top of its jump Rock at the edge of a hill Skateboarder at the top of the ramp Pendulum at the top of its swing 2. Use Newton s 2 nd law
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton's Laws of Motion The British scientist Sir Isaac Newton (164 177) was able to state rules that describe the effects of forces on the motion of objects. These rules are known as Newton's law's of
Newton's Laws of Motion The British scientist Sir Isaac Newton (164 177) was able to state rules that describe the effects of forces on the motion of objects. These rules are known as Newton's law's of
Name Period CHAPTER 7 NEWTON'S THIRD LAW OF MOTION MOMENTUM & CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION POINTS
 Name Period CHAPTER 7 NEWTON'S THIRD LAW OF MOTION MOMENTUM & CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION POINTS 1. NT OVERHEAD NOTES WITH WORKSHEET GUIDE /30 2. WS MOMENTUM WORKSHEET /17 3. WS
Name Period CHAPTER 7 NEWTON'S THIRD LAW OF MOTION MOMENTUM & CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION POINTS 1. NT OVERHEAD NOTES WITH WORKSHEET GUIDE /30 2. WS MOMENTUM WORKSHEET /17 3. WS
Science Teaching Junkie Science Teaching Junkie
 Science Teaching Junkie Thank you for your purchase. I hope you enjoy the Force and Motion for Interactive Science Notebooks! It includes 30 pages of foldables and flippables for student notebooks. Many
Science Teaching Junkie Thank you for your purchase. I hope you enjoy the Force and Motion for Interactive Science Notebooks! It includes 30 pages of foldables and flippables for student notebooks. Many
Newton s 3 Laws of Motion
 Newton s 3 Laws of Motion 1. If F = 0 No change in motion 2. = ma Change in motion Fnet 3. F = F 1 on 2 2 on 1 Newton s First Law (Law of Inertia) An object will remain at rest or in a constant state of
Newton s 3 Laws of Motion 1. If F = 0 No change in motion 2. = ma Change in motion Fnet 3. F = F 1 on 2 2 on 1 Newton s First Law (Law of Inertia) An object will remain at rest or in a constant state of
Matter, Atoms & Molecules
 Matter, Atoms & Molecules Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms, which are too small to see with the naked eye. Matter Matter is anything
Matter, Atoms & Molecules Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms, which are too small to see with the naked eye. Matter Matter is anything
TEK 8.6C: Newton s Laws
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: TEK 8.6C: Newton s Laws TEK 8.6C: Investigate and describe applications of Newton's law of inertia, law of force and acceleration, and law of action-reaction such as in vehicle
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: TEK 8.6C: Newton s Laws TEK 8.6C: Investigate and describe applications of Newton's law of inertia, law of force and acceleration, and law of action-reaction such as in vehicle
Hands-On Science. Force & Motion. Karen Kwitter and Steven Souza illustrated by Lloyd Birmingham
 Hands-On Science Force & Motion Karen Kwitter and Steven Souza illustrated by Lloyd Birmingham WALCH EDUCATION Contents To the Teacher... v National Science Education Standards Correlations...vi General
Hands-On Science Force & Motion Karen Kwitter and Steven Souza illustrated by Lloyd Birmingham WALCH EDUCATION Contents To the Teacher... v National Science Education Standards Correlations...vi General
Physics 100. Today. Finish Chapter 4: Newton s Second Law. Start Chapter 5: Newton s Third Law
 Physics 100 Today Finish Chapter 4: Newton s Second Law Start Chapter 5: Newton s Third Law First, let s clarify notion of a force: Previously defined force as a push or pull. Better to think of force
Physics 100 Today Finish Chapter 4: Newton s Second Law Start Chapter 5: Newton s Third Law First, let s clarify notion of a force: Previously defined force as a push or pull. Better to think of force
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
Work. explode. Through centuries of trial and error, rockets became more reliable. However, real advancements in rocketry depended upon a
 Work launching a giant cargo rocket to Mars, the principles of how rockets work are exactly the same. Understanding and applying these principles means mission success. explode. Through centuries of trial
Work launching a giant cargo rocket to Mars, the principles of how rockets work are exactly the same. Understanding and applying these principles means mission success. explode. Through centuries of trial
Physics 101. Today Chapter 5: Newton s Third Law
 Physics 101 Today Chapter 5: Newton s Third Law First, let s clarify notion of a force: Previously defined force as a push or pull. Better to think of force as an interaction between two objects. Eg. I
Physics 101 Today Chapter 5: Newton s Third Law First, let s clarify notion of a force: Previously defined force as a push or pull. Better to think of force as an interaction between two objects. Eg. I
Chapter 06 Test A. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Chapter 06 Test A Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The property of matter that resists changes in motion is: a. acceleration.
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 06 Test A Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The property of matter that resists changes in motion is: a. acceleration.
that when friction is present, a is needed to keep an object moving. 21. State Newton s first law of motion.
 Chapter 3 Newton s First Law of Motion Inertia Exercises 31 Aristotle on Motion (pages 29 30) Fill in the blanks with the correct terms 1 Aristotle divided motion into two types: and 2 Natural motion on
Chapter 3 Newton s First Law of Motion Inertia Exercises 31 Aristotle on Motion (pages 29 30) Fill in the blanks with the correct terms 1 Aristotle divided motion into two types: and 2 Natural motion on
Isaac Newton. What is the acceleration of the car? "If I have seen further it is by standing on the shoulders of giants" Isaac Newton to Robert Hooke
 Aim: What did Isaac Newton teach us about motion? Do Now: 1. A 2009 Ford Mustang convertible is travelling at constant velocity on Interstate 95 south from Philadelphia to Wilmington Delaware. It passes
Aim: What did Isaac Newton teach us about motion? Do Now: 1. A 2009 Ford Mustang convertible is travelling at constant velocity on Interstate 95 south from Philadelphia to Wilmington Delaware. It passes
The diagram below shows a block on a horizontal frictionless surface. A 100.-newton force acts on the block at an angle of 30. above the horizontal.
 Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
P11 Dynamics 1 Forces and Laws of Motion Bundle.notebook October 14, 2013
 Dynamics 1 Definition of Dynamics Dynamics is the study of why an object moves. In order to understand why objects move, we must first study forces. Forces A force is defined as a push or a pull. Forces
Dynamics 1 Definition of Dynamics Dynamics is the study of why an object moves. In order to understand why objects move, we must first study forces. Forces A force is defined as a push or a pull. Forces
This week's Vocabulary Words focus: Inertia Unbalanced Force Force Balanced Force Mass Gravity Net Force Weight
 Warm up 1.) What is the formula for finding speed or velocity? 2.) Mia ran 11 km around the track in 2 hours. What was Mia's average speed in km/h? What was her average speed in m/s This week's Vocabulary
Warm up 1.) What is the formula for finding speed or velocity? 2.) Mia ran 11 km around the track in 2 hours. What was Mia's average speed in km/h? What was her average speed in m/s This week's Vocabulary
MOTION & FORCES. Observing Motion. Speed and Velocity. Distance vs. Displacement CHAPTERS 11 & 12
 Observing Motion CHAPTERS 11 & 12 MOTION & FORCES Everything surrounding us is in motion, but it is relative to other object that remain in place. Motion is observed using a frame of reference. Motion
Observing Motion CHAPTERS 11 & 12 MOTION & FORCES Everything surrounding us is in motion, but it is relative to other object that remain in place. Motion is observed using a frame of reference. Motion
Laws of Motion 1. (a) (b) Ans. (a) Force : (b) (1) Examples : (i) (ii) (2) Examples : (i) (ii) (3) Examples : (i) (ii) (4) Examples : (i) (ii)
 Laws of Motion 1. (a) Define force. (b) State four effects, which a force can bring about, giving two examples in each case. Ans. (a) Force : An external cause, which changes or tends to changes the state
Laws of Motion 1. (a) Define force. (b) State four effects, which a force can bring about, giving two examples in each case. Ans. (a) Force : An external cause, which changes or tends to changes the state
Exercise 7: Thrust and the Rocket Equation
 Astronomy 102 Name: Exercise 7: Thrust and the Rocket Equation Parts of this exercise were taken from NASA s Beginner s Guide to Rockets: Rocket Propulsion Activity, edited by Tom Benson. Objective: To
Astronomy 102 Name: Exercise 7: Thrust and the Rocket Equation Parts of this exercise were taken from NASA s Beginner s Guide to Rockets: Rocket Propulsion Activity, edited by Tom Benson. Objective: To
Chapter 2. Forces & Newton s Laws
 Chapter 2 Forces & Newton s Laws 1st thing you need to know Everything from chapter 1 Speed formula Acceleration formula All their units There is only 1 main formula, but some equations will utilize previous
Chapter 2 Forces & Newton s Laws 1st thing you need to know Everything from chapter 1 Speed formula Acceleration formula All their units There is only 1 main formula, but some equations will utilize previous
Newton s Laws of Motion
 DUY TAN UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCE Newton s Laws of Motion Lecturer: HO VAN TUYEN Da Nang, 2017 Motions Newton s Contributions Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician.
DUY TAN UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCE Newton s Laws of Motion Lecturer: HO VAN TUYEN Da Nang, 2017 Motions Newton s Contributions Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician.
Determine the resultant for each group of vectors below: b) c)
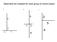 Determine the resultant for each group of vectors below: a) b) c) 8 8 2 5-3 3 7-3 2-8 -8 a) 11 8 3 4 Magnitude 11.7 Direction: 70 degrees North of East -3 7 b) 8-3 2-8 1 Magnitude: 1 Direction: West c)
Determine the resultant for each group of vectors below: a) b) c) 8 8 2 5-3 3 7-3 2-8 -8 a) 11 8 3 4 Magnitude 11.7 Direction: 70 degrees North of East -3 7 b) 8-3 2-8 1 Magnitude: 1 Direction: West c)
Force Test Review. 1. Give two ways to increase acceleration. You can increase acceleration by decreasing mass or increasing force.
 Force Test Review 1. Give two ways to increase acceleration. You can increase acceleration by decreasing mass or increasing force. 2. Define weight. The force of gravity on an object at the surface of
Force Test Review 1. Give two ways to increase acceleration. You can increase acceleration by decreasing mass or increasing force. 2. Define weight. The force of gravity on an object at the surface of
Chapter 4. Answer Key. Physics Lab Sample Data. Mini Lab Worksheet. Tug-of-War Challenge. b. Since the rocket takes off from the ground, d i
 Chapter 3 continued b. Since the rocket takes off from the ground, d i 0.0 m, and at its highest point, v f 0.0 m/s. v f v i a t f (d f d i ) 0 v i a t f d f v i d f a t f (450 m/s) ( 9.80 m/s )(4.6 s)
Chapter 3 continued b. Since the rocket takes off from the ground, d i 0.0 m, and at its highest point, v f 0.0 m/s. v f v i a t f (d f d i ) 0 v i a t f d f v i d f a t f (450 m/s) ( 9.80 m/s )(4.6 s)
How Do Objects Move? Describing Motion. Different Kinds of Motion
 How Do Objects Move? Describing Motion Different Kinds of Motion Motion is everywhere. The planets are in motion around the Sun. Cars are in motion as they are driven down the street. There s even motion
How Do Objects Move? Describing Motion Different Kinds of Motion Motion is everywhere. The planets are in motion around the Sun. Cars are in motion as they are driven down the street. There s even motion
Lecture Notes (Momentum & Impulse)
 Lecture Notes (Momentum & Impulse) Intro: - earlier in the year, we introduced Galileo's Principle of Inertia and we talked how Newton used this idea to formulate his first law of motion - Newton discussed
Lecture Notes (Momentum & Impulse) Intro: - earlier in the year, we introduced Galileo's Principle of Inertia and we talked how Newton used this idea to formulate his first law of motion - Newton discussed
A. true. 6. An object is in motion when
 1. The SI unit for speed is A. Miles per hour B. meters per second 5. Frictional forces are greatest when both surfaces are rough. A. true B. false 2. The combination of all of the forces acting on an
1. The SI unit for speed is A. Miles per hour B. meters per second 5. Frictional forces are greatest when both surfaces are rough. A. true B. false 2. The combination of all of the forces acting on an
Make sure you know the three laws inside and out! You must know the vocabulary too!
 Newton's Laws Study Guide Test March 9 th The best plan is to study every night for 15 to 20 minutes. Make sure you know the three laws inside and out! You must know the vocabulary too! Newton s First
Newton's Laws Study Guide Test March 9 th The best plan is to study every night for 15 to 20 minutes. Make sure you know the three laws inside and out! You must know the vocabulary too! Newton s First
Unit 2: Newton s Laws Note 1 : Forces
 Unit 2: Newton s Laws Note 1 : Forces Force: The units of force are: There are four fundamental forces that make up all of the forces in the universe: 1) 2) 3) 4) Force of Gravity Force of Gravity: The
Unit 2: Newton s Laws Note 1 : Forces Force: The units of force are: There are four fundamental forces that make up all of the forces in the universe: 1) 2) 3) 4) Force of Gravity Force of Gravity: The
Chapter: Newton s Laws of Motion
 Table of Contents Chapter: Newton s Laws of Motion Section 1: Motion Section 2: Newton s First Law Section 3: Newton s Second Law Section 4: Newton s Third Law 1 Motion What is motion? Distance and Displacement
Table of Contents Chapter: Newton s Laws of Motion Section 1: Motion Section 2: Newton s First Law Section 3: Newton s Second Law Section 4: Newton s Third Law 1 Motion What is motion? Distance and Displacement
Newton s Laws of Motion
 3 Newton s Laws of Motion Key Concept Newton s laws of motion describe the relationship between forces and the motion of an object. What You Will Learn Newton s first law of motion states that the motion
3 Newton s Laws of Motion Key Concept Newton s laws of motion describe the relationship between forces and the motion of an object. What You Will Learn Newton s first law of motion states that the motion
Laws of Force and Motion
 Does anything happen without a cause? Many people would say yes, because that often seems to be our experience. A cup near the edge of a table suddenly crashes to the floor. An apple falls from a tree
Does anything happen without a cause? Many people would say yes, because that often seems to be our experience. A cup near the edge of a table suddenly crashes to the floor. An apple falls from a tree
FORCES AND THE LAWS OF MOTION
 FORCES AND THE LAWS OF MOTION FORCE A force is the cause of an acceleration, or the change in an object s velocity (speed or direction). Forces are usually thought of as a push or a pull. The SI unit of
FORCES AND THE LAWS OF MOTION FORCE A force is the cause of an acceleration, or the change in an object s velocity (speed or direction). Forces are usually thought of as a push or a pull. The SI unit of
AP Physics Momentum Practice Test. Answers: A,E,E,A,E,B,D,C,B,A,B,E,D,C 16.(a)5450,5650 (b)2.25e7 (c)3 (d)1.5e7 17.(a)9 (b)2 (c)1.5 (d) (e).
 AP Physics Momentum Practice Test Answers: A,E,E,A,E,B,D,C,B,A,B,E,D,C 16.(a)5450,5650 (b).5e7 (c)3 (d)1.5e7 17.(a)9 (b) (c)1.5 (d)-4.75 (e).65 For multiple choice ( points) write the CAPITAL letter of
AP Physics Momentum Practice Test Answers: A,E,E,A,E,B,D,C,B,A,B,E,D,C 16.(a)5450,5650 (b).5e7 (c)3 (d)1.5e7 17.(a)9 (b) (c)1.5 (d)-4.75 (e).65 For multiple choice ( points) write the CAPITAL letter of
