Dispersion and how to control it
|
|
|
- Winifred Abigayle Atkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dispersion and how to control it Group velocity versus phase velocity Angular dispersion Prism sequences Grating pairs Chirped mirrors Intracavity and extra-cavity examples 1
2 Pulse propagation and broadening After propagating a distance z, an (initially) unchirped Gaussian of initial duration t G becomes: Etz (, ) exp tz/v g p t G ik" z exp 1 iz t z pulse duration increases with z G 1 tg pulse duration t G (z)/t G chirp parameter 3 1 k " propagation distance z
3 Chirped vs. transform-limited A transform-limited pulse: satisfies the equal sign in the relation C is as short as it could possibly be, given the spectral bandwidth has an envelope function which is REAL (phase = 0) has an electric field that can be computed directly from S exhibits zero chirp: the same period A chirped pulse: satisfies the greater than sign in the relation C is longer than it needs to be, given the spectral bandwidth has an envelope function which is COMPLEX (phase 0) requires knowledge of more than just S in order to determine E(t) exhibits non-zero chirp: not the same period 3
4 4 p p 0 ' 1 dk d k V g p p p k V where: " z ik t z t G G 0 V / V / exp 1 ), ( z t z t z t i z t E z t E G p g p p G pulse width increases with propagation phase velocity group velocity - speed of pulse envelope Group velocity dispersion (GVD) (different for each material) Propagation of Gaussian pulses 1 g dk d k d d V If (and only if) GVD = 0, then V = V g. For most transparent solids, V > V g
5 GVD yields group delay dispersion (GDD) The delay is just the medium length L divided by the velocity. The phase delay: k( ) 0 0 v( ) 0 so: t L v( ) k( 0) L 0 0 The group delay: k( ) 0 1 v ( ) d 1 k( ) d v g g 0 so: L t ( ) k( ) L g 0 0 v g ( 0) The group delay dispersion (GDD): GDD = GVD L so: d 1 GDD L k( ) L d v g Units: fs or fs/hz 5
6 Dispersion in a laser cavity n() At = 800 nm: GDD k " L = 10-3 fs sapphire, L ~ 1 cm There is a small positive GDD added to the pulse on each round trip. m 1-5e-5 dn/d 3e-7 Material: Al O 3 Pulse width: t p = 100 fsec -1e-4 5e-7 cm e-7 k" t G m 3e-7 d n/d 1e-7 1e (m) 6
7 So how can we generate negative GDD? This is a big issue because pulses spread further and further as they propagate through materials. We need a way of generating negative GDD to compensate for the positive GDD that comes from propagating through transparent materials. Negative GDD Device 7
8 Group and phase velocities - refraction sin i nsin i t d 1 index n() D' t Beam width: D' cost D cos time to propagate the distance d 1 : i D d T phase d1 D tan i c c must equal the time to propagate the distance d : n nd 'tan T d t c c phase propagation direction phase fronts: perpendicular to propagation pulse fronts: not necessarily! BUT: the pulse front travels at V g, so the travel distance is less by: d V V T g phase 8
9 Angular dispersion yields negative GDD. Suppose that an optical element introduces angular dispersion. Optical element Input beam Optic axis Here, there is negative GDD because the blue precedes the red. We ll need to compute the projection onto the optic axis (the propagation direction of the center frequency of the pulse). 9
10 Negative GDD Taking the projection of onto the optic axis, a given frequency sees a phase delay of z ( ) k( ) r optic axis k ( ) k( ) z cos[ ( )] ( / c) z cos[ ( )] Optic axis We re considering only the GDD due to dispersion and not that of the prism itself. So n = 1 (that of the air after the prism). d / d ( z/ c)cos( ) ( / c) zsin( ) d / d d z d z d z d z d sin( ) sin( ) cos( ) sin( ) d c d c d c d c d But << 1, so the sine terms can be neglected, and cos() ~ 1. 10
11 Angular dispersion yields negative GDD. d 0 z d d c d 0 0 The GDD due to angular dispersion is always negative! But recall: In most dielectric materials, k" is positive! (and k" L = ") We can use angular dispersion to compensate for material dispersion: k" total = k" material + k" angular These two terms have opposite sign. 11
12 Prisms In principle, we are free to specify: the apex angle 0 the angle of incidence 0 These are chosen using two conditions: Brewster condition for minimum reflection loss ( polarization) minimum deviation condition (symmetric propagation) 1 50 Reflectance n = 1.78 deviation angle n = 1.5 = 67.4º incidence angle incidence angle 1
13 A prism pair has negative GDD. Assume Brewster angle incidence and exit angles. How can we use dispersion to introduce negative chirp conveniently? Let L prism be the path through each prism and L sep be the prism separation. d 3 4L 0 d sep 0 c Always negative! dn d 0 This term accounts for the angular dispersion only. L prism 0 3 c d n d 0 This term accounts for the beam passing through a length, L prism, of prism material. Always positive (in visible and near-ir) Vary L sep or L prism to tune the GDD! 13
14 Adjusting the GDD maintains alignment. Any prism in the compressor can be translated perpendicular to the beam path to add glass and reduce the magnitude of negative GDD. Remarkably, this does not misalign the beam. The beam s output path is independent of prism displacement along the axis of the apex bisector. Input beam Output beam 14
15 Four-prism Pulse Compressor This device, which also puts the pulse back together, has negative group-delay dispersion and hence can compensate for propagation through materials (i.e., for positive chirp). Angular dispersion yields negative GDD. It s routine to stretch and then compress ultrashort pulses by factors of >
16 What does the pulse look like inside a pulse compressor? If we send an unchirped pulse into a pulse compressor, it emerges with negative chirp. Note all the spatio-temporal distortions. 16
17 Appl. Phys. Lett. 38, 671 (1981) 17
18 The required separation between prisms in a pulse compressor can be large. The GDD the prism separation and the square of the dispersion. Different prism materials Compression of a 1-ps, 600-nm pulse with 10 nm of bandwidth (to about 50 fs). Kafka and Baer, Opt. Lett., 1, 401 (1987) It s best to use highly dispersive glass, like SF10. But compressors can still be > 1 m long. 18
19 Four-prism pulse compressor Also, alignment is critical, and many knobs must be tuned. Prism Wavelength tuning Wavelength tuning Prism Wavelength tuning Prism Prism Fine GDD tuning Coarse GDD tuning (change distance between prisms) Wavelength tuning All prisms and their incidence angles must be identical. 19
20 Pulse-compressors have alignment issues. Pulse compressors are notorious for their large size, alignment complexity, and spatio-temporal distortions. Pulsefront tilt Spatial chirp Unless the compressor is aligned perfectly, the output pulse has significant: 1. 1D beam magnification. Angular dispersion 3. Spatial chirp 4. Pulse-front tilt 0
21 Why is it difficult to align a pulse compressor? The prisms are usually aligned using the minimum deviation condition. Deviation angle Prism angle Minimum deviation Angular dispersion The variation of the deviation angle is nd order in the prism angle. But what matters is the prism angular dispersion, which is 1 st order! Using a nd -order effect to align a 1 st -order effect is tricky. 1
22 Two-prism pulse compressor Coarse GDD tuning Periscope Wavelength tuning Roof mirror Prism Wavelength tuning Prism Fine GDD tuning This design cuts the size and alignment issues in half.
23 Single-prism pulse compressor Corner cube Periscope Prism Roof mirror Wavelength tuning GDD tuning 3
24 Angular dispersion from a sequence of prisms 800 " (fsec ) L p =14 cm L p =16 cm Example: 4 SF11 prisms L m =1 cm -800 L p =18 cm " depends on! Wavelength (m) For very short pulses, third order dispersion is important. 4 1L p n n n n nn L n n c 3 m 4
25 When prisms are not sufficient 3 " L " 4 ' mn Lpn c SF6 glass at 800 nm n = 1.78 n' = 59 m n" = 0. m L L 4n' n" m " = 0 if p But then "' L p fsec 3 /cm Minimum value of L p or L m determines size of "' It is not possible to ideally compensate both nd and 3rd order dispersion with prisms alone. Diffraction gratings! 5
26 B Double pass: Diffraction-grating pulse compressor ' A C P ABC grating equation: sin sin x cos( ' ) ' c d 1 cos( ' ) x = perpendicular grating separation d = grating constant (distance/groove) 3/ 3 3 x x 1 sin r cd d cd 3 r sin cr d d 3/ 6
27 nd- and 3rd-order phase terms for prism and grating pulse compressors Grating compressors offer more compression than prism compressors. '' ''' Piece of glass Note that the relative signs of the nd and 3rd-order terms are opposite for prism compressors and grating compressors. 7
28 Compensating nd and 3rd-order spectral phase Use both a prism and a grating compressor. Since they have 3rd-order terms with opposite signs, they can be used to achieve almost arbitrary amounts of both second- and third-order phase. Prism compressor Grating compressor Given the nd- and 3rd-order phases of the input pulse, input and input3, solve simultaneous equations: input prism grating 0 input 3 prism 3 grating 3 0 This design was used by Fork and Shank at Bell Labs in the mid 1980 s to achieve a 6-fs pulse, a record that stood for over a decade. 8
29 Pulse Compression Simulation Using prism and grating pulse compressors vs. only a grating compressor Resulting intensity vs. time with only a grating compressor: Note the cubic spectral phase! Resulting intensity vs. time with a grating compressor and a prism compressor: Brito Cruz, et al., Opt. Lett., 13, 13 (1988). 9
30 Chirped mirrors A mirror whose reflection coefficient is engineered so that it has the form: so that r 1 r e i and is chosen to cancel out the phase of the incident pulse. All 5 mirrors are chirped mirrors 8.5 fsec pulse from the laser 30
31 Chirped mirror coatings Longest wavelengths penetrate furthest. Doesn t work for < 600 nm 31
32 Theory: Experiment: 3
33 33
Swamp Optics Tutorial. Pulse Compression
 Swamp Optics, LLC. 6300 Powers Ferry Rd. Suite 600-345 Atlanta, GA 30339 +1.404.547.9267 www.swamoptics.com Swamp Optics Tutorial Pulse Compression Recall that different colors propagate at different velocities
Swamp Optics, LLC. 6300 Powers Ferry Rd. Suite 600-345 Atlanta, GA 30339 +1.404.547.9267 www.swamoptics.com Swamp Optics Tutorial Pulse Compression Recall that different colors propagate at different velocities
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE. Advanced laboratory exercise: studying the dispersion properties of a prism pair
 PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Advanced laboratory exercise: studying the dispersion properties of a prism pair T. Grósz, L. Gulyás, A. P. Kovács T. Grósz, L.
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Advanced laboratory exercise: studying the dispersion properties of a prism pair T. Grósz, L. Gulyás, A. P. Kovács T. Grósz, L.
Strongly enhanced negative dispersion from thermal lensing or other focusing effects in femtosecond laser cavities
 646 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 17, No. 4/ April 2000 Paschotta et al. Strongly enhanced negative dispersion from thermal lensing or other focusing effects in femtosecond laser cavities R. Paschotta, J. Aus
646 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 17, No. 4/ April 2000 Paschotta et al. Strongly enhanced negative dispersion from thermal lensing or other focusing effects in femtosecond laser cavities R. Paschotta, J. Aus
The spectrogram in acoustics
 Measuring the power spectrum at various delays gives the spectrogram 2 S ω, τ = dd E t g t τ e iii The spectrogram in acoustics E ssssss t, τ = E t g t τ where g t is a variable gating function Frequency
Measuring the power spectrum at various delays gives the spectrogram 2 S ω, τ = dd E t g t τ e iii The spectrogram in acoustics E ssssss t, τ = E t g t τ where g t is a variable gating function Frequency
No. 9 Experimental study on the chirped structure of the construct the early time spectra. [14;15] The prevailing account of the chirped struct
![No. 9 Experimental study on the chirped structure of the construct the early time spectra. [14;15] The prevailing account of the chirped struct No. 9 Experimental study on the chirped structure of the construct the early time spectra. [14;15] The prevailing account of the chirped struct](/thumbs/85/91339585.jpg) Vol 12 No 9, September 2003 cfl 2003 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2003/12(09)/0986-06 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Experimental study on the chirped structure of the white-light continuum generation
Vol 12 No 9, September 2003 cfl 2003 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2003/12(09)/0986-06 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd Experimental study on the chirped structure of the white-light continuum generation
Linear pulse propagation
 Ultrafast Laser Physics Ursula Keller / Lukas Gallmann ETH Zurich, Physics Department, Switzerland www.ulp.ethz.ch Linear pulse propagation Ultrafast Laser Physics ETH Zurich Superposition of many monochromatic
Ultrafast Laser Physics Ursula Keller / Lukas Gallmann ETH Zurich, Physics Department, Switzerland www.ulp.ethz.ch Linear pulse propagation Ultrafast Laser Physics ETH Zurich Superposition of many monochromatic
Compression and broadening of phase-conjugate pulses in photorefractive self-pumped phase conjugators
 1390 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 17, No. 8/ August 000 Yang et al. Compression and broadening of phase-conjugate pulses in photorefractive self-pumped phase conjugators Changxi Yang and Min Xiao Department
1390 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 17, No. 8/ August 000 Yang et al. Compression and broadening of phase-conjugate pulses in photorefractive self-pumped phase conjugators Changxi Yang and Min Xiao Department
ULTRAFAST COMPONENTS
 ULTRAFAST COMPONENTS Mirrors CVI Laser Optics offers both the PulseLine family of optical components and other existing product lines that are ideal for use with femtosecond lasers and associated applications.
ULTRAFAST COMPONENTS Mirrors CVI Laser Optics offers both the PulseLine family of optical components and other existing product lines that are ideal for use with femtosecond lasers and associated applications.
32. Interference and Coherence
 32. Interference and Coherence Interference Only parallel polarizations interfere Interference of a wave with itself The Michelson Interferometer Fringes in delay Measure of temporal coherence Interference
32. Interference and Coherence Interference Only parallel polarizations interfere Interference of a wave with itself The Michelson Interferometer Fringes in delay Measure of temporal coherence Interference
REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
 S-108-2110 OPTICS 1/6 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Student Labwork S-108-2110 OPTICS 2/6 Table of contents 1. Theory...3 2. Performing the measurements...4 2.1. Total internal reflection...4 2.2. Brewster
S-108-2110 OPTICS 1/6 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Student Labwork S-108-2110 OPTICS 2/6 Table of contents 1. Theory...3 2. Performing the measurements...4 2.1. Total internal reflection...4 2.2. Brewster
Lecture 4 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 4, Slide 1
 ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics. Final Exam. April 16, 2007.
 Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Final Exam April 16, 2007 Exam Type: D (Close-book + two double-sided aid sheets + a non-programmable
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Final Exam April 16, 2007 Exam Type: D (Close-book + two double-sided aid sheets + a non-programmable
LAB 10: OPTICAL MATERIALS AND DISPERSION I
 OPTI 202L - Geometrical and Instrumental Optics Lab LAB 10: OPTICAL MATERIALS AND DISPERSION I 10-1 Measuring the refractive index of a material is one of the most fundamental optical measurements, and
OPTI 202L - Geometrical and Instrumental Optics Lab LAB 10: OPTICAL MATERIALS AND DISPERSION I 10-1 Measuring the refractive index of a material is one of the most fundamental optical measurements, and
Dispersion Compensation with a Prism-pair
 arxiv:1411.0232v1 [physics.optics] 2 Nov 2014 Dispersion Compensation with a Prism-pair Yaakov Shaked, Shai Yefet and Avi Pe er Department of physics and BINA Center of nano-technology, Bar-Ilan university,
arxiv:1411.0232v1 [physics.optics] 2 Nov 2014 Dispersion Compensation with a Prism-pair Yaakov Shaked, Shai Yefet and Avi Pe er Department of physics and BINA Center of nano-technology, Bar-Ilan university,
The structure of laser pulses
 1 The structure of laser pulses 2 The structure of laser pulses Pulse characteristics Temporal and spectral representation Fourier transforms Temporal and spectral widths Instantaneous frequency Chirped
1 The structure of laser pulses 2 The structure of laser pulses Pulse characteristics Temporal and spectral representation Fourier transforms Temporal and spectral widths Instantaneous frequency Chirped
Speed of Light in Glass
 Experiment (1) Speed of Light in Glass Objective:- This experiment is used to determine the speed of propagation of light waves in glass. Apparatus:- Prism, spectrometer, Halogen lamp source. Theory:-
Experiment (1) Speed of Light in Glass Objective:- This experiment is used to determine the speed of propagation of light waves in glass. Apparatus:- Prism, spectrometer, Halogen lamp source. Theory:-
Multilayer Thin Films Dielectric Double Chirped Mirrors Design
 International Journal of Physics and Applications. ISSN 974-313 Volume 5, Number 1 (13), pp. 19-3 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Multilayer Thin Films Dielectric Double
International Journal of Physics and Applications. ISSN 974-313 Volume 5, Number 1 (13), pp. 19-3 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Multilayer Thin Films Dielectric Double
MEFT / Quantum Optics and Lasers. Suggested problems Set 4 Gonçalo Figueira, spring 2015
 MEFT / Quantum Optics and Lasers Suggested problems Set 4 Gonçalo Figueira, spring 05 Note: some problems are taken or adapted from Fundamentals of Photonics, in which case the corresponding number is
MEFT / Quantum Optics and Lasers Suggested problems Set 4 Gonçalo Figueira, spring 05 Note: some problems are taken or adapted from Fundamentals of Photonics, in which case the corresponding number is
Innovation and Development of Study Field. nano.tul.cz
 Innovation and Development of Study Field Nanomaterials at the Technical University of Liberec nano.tul.cz These materials have been developed within the ESF project: Innovation and development of study
Innovation and Development of Study Field Nanomaterials at the Technical University of Liberec nano.tul.cz These materials have been developed within the ESF project: Innovation and development of study
A novel scheme for measuring the relative phase difference between S and P polarization in optically denser medium
 A novel scheme for measuring the relative phase difference between S and P polarization in optically denser medium Abstract Yu Peng School of Physics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081,
A novel scheme for measuring the relative phase difference between S and P polarization in optically denser medium Abstract Yu Peng School of Physics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081,
Effects of resonator input power on Kerr lens mode-locked lasers
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 1 journal of July 2015 physics pp. 115 124 Effects of resonator input power on Kerr lens mode-locked lasers S KAZEMPOUR, A KESHAVARZ and G HONARASA Department
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 85, No. 1 journal of July 2015 physics pp. 115 124 Effects of resonator input power on Kerr lens mode-locked lasers S KAZEMPOUR, A KESHAVARZ and G HONARASA Department
Experiment O-2. The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Describing first-order spatio-temporal distortions in ultrashort pulses using normalized parameters
 Describing first-order spatio-temporal distortions in ultrashort pulses using normalized parameters Pablo Gabolde, Dongjoo Lee, Selcuk Akturk and Rick Trebino Georgia Institute of Technology, 837 State
Describing first-order spatio-temporal distortions in ultrashort pulses using normalized parameters Pablo Gabolde, Dongjoo Lee, Selcuk Akturk and Rick Trebino Georgia Institute of Technology, 837 State
Ultrafast Laser Physics
 Ultrafast Laser Physics Ursula Keller / Lukas Gallmann ETH Zurich, Physics Department, Switzerland www.ulp.ethz.ch Chapter 7: Active modelocking Ultrafast Laser Physics ETH Zurich Mode locking by forcing
Ultrafast Laser Physics Ursula Keller / Lukas Gallmann ETH Zurich, Physics Department, Switzerland www.ulp.ethz.ch Chapter 7: Active modelocking Ultrafast Laser Physics ETH Zurich Mode locking by forcing
18. Standing Waves, Beats, and Group Velocity
 18. Standing Waves, Beats, and Group Velocity Superposition again Standing waves: the sum of two oppositely traveling waves Beats: the sum of two different frequencies Group velocity: the speed of information
18. Standing Waves, Beats, and Group Velocity Superposition again Standing waves: the sum of two oppositely traveling waves Beats: the sum of two different frequencies Group velocity: the speed of information
Effects of self-steepening and self-frequency shifting on short-pulse splitting in dispersive nonlinear media
 PHYSICAL REVIEW A VOLUME 57, NUMBER 6 JUNE 1998 Effects of self-steepening and self-frequency shifting on short-pulse splitting in dispersive nonlinear media Marek Trippenbach and Y. B. Band Departments
PHYSICAL REVIEW A VOLUME 57, NUMBER 6 JUNE 1998 Effects of self-steepening and self-frequency shifting on short-pulse splitting in dispersive nonlinear media Marek Trippenbach and Y. B. Band Departments
37. 3rd order nonlinearities
 37. 3rd order nonlinearities Characterizing 3rd order effects The nonlinear refractive index Self-lensing Self-phase modulation Solitons When the whole idea of χ (n) fails Attosecond pulses! χ () : New
37. 3rd order nonlinearities Characterizing 3rd order effects The nonlinear refractive index Self-lensing Self-phase modulation Solitons When the whole idea of χ (n) fails Attosecond pulses! χ () : New
Optical Spectroscopy of Advanced Materials
 Phys 590B Condensed Matter Physics: Experimental Methods Optical Spectroscopy of Advanced Materials Basic optics, nonlinear and ultrafast optics Jigang Wang Department of Physics, Iowa State University
Phys 590B Condensed Matter Physics: Experimental Methods Optical Spectroscopy of Advanced Materials Basic optics, nonlinear and ultrafast optics Jigang Wang Department of Physics, Iowa State University
Evolution of the frequency chirp of Gaussian pulses and beams when passing through a pulse compressor
 Evolution of the frequency chirp of Gaussian pulses and beams when passing through a pulse compressor Derong Li, 3, Xiaohua Lv *, Pamela Bowlan, Rui Du, Shaoqun Zeng, Qingming Luo Britton Chance Center
Evolution of the frequency chirp of Gaussian pulses and beams when passing through a pulse compressor Derong Li, 3, Xiaohua Lv *, Pamela Bowlan, Rui Du, Shaoqun Zeng, Qingming Luo Britton Chance Center
UNIT-5 EM WAVES UNIT-6 RAY OPTICS
 UNIT-5 EM WAVES 2 Marks Question 1. To which regions of electromagnetic spectrum do the following wavelengths belong: (a) 250 nm (b) 1500 nm 2. State any one property which is common to all electromagnetic
UNIT-5 EM WAVES 2 Marks Question 1. To which regions of electromagnetic spectrum do the following wavelengths belong: (a) 250 nm (b) 1500 nm 2. State any one property which is common to all electromagnetic
Constructive vs. destructive interference; Coherent vs. incoherent interference
 Constructive vs. destructive interference; Coherent vs. incoherent interference Waves that combine in phase add up to relatively high irradiance. = Constructive interference (coherent) Waves that combine
Constructive vs. destructive interference; Coherent vs. incoherent interference Waves that combine in phase add up to relatively high irradiance. = Constructive interference (coherent) Waves that combine
Polarizers and Retarders
 Phys 531 Lecture 20 11 November 2004 Polarizers and Retarders Last time, discussed basics of polarization Linear, circular, elliptical states Describe by polarization vector ĵ Today: Describe elements
Phys 531 Lecture 20 11 November 2004 Polarizers and Retarders Last time, discussed basics of polarization Linear, circular, elliptical states Describe by polarization vector ĵ Today: Describe elements
What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light
 What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
37. 3rd order nonlinearities
 37. 3rd order nonlinearities Characterizing 3rd order effects The nonlinear refractive index Self-lensing Self-phase modulation Solitons When the whole idea of χ (n) fails Attosecond pulses! χ () : New
37. 3rd order nonlinearities Characterizing 3rd order effects The nonlinear refractive index Self-lensing Self-phase modulation Solitons When the whole idea of χ (n) fails Attosecond pulses! χ () : New
Femtosecond laser-tissue interactions. G. Fibich. University of California, Los Angeles, Department of Mathematics ABSTRACT
 Femtosecond laser-tissue interactions G. Fibich University of California, Los Angeles, Department of Mathematics Los-Angeles, CA 90095 ABSTRACT Time dispersion plays an important role in the propagation
Femtosecond laser-tissue interactions G. Fibich University of California, Los Angeles, Department of Mathematics Los-Angeles, CA 90095 ABSTRACT Time dispersion plays an important role in the propagation
The Generation of Ultrashort Laser Pulses
 The Generation of Ultrashort Laser Pulses The importance of bandwidth More than just a light bulb Two, three, and four levels rate equations Gain and saturation But first: the progress has been amazing!
The Generation of Ultrashort Laser Pulses The importance of bandwidth More than just a light bulb Two, three, and four levels rate equations Gain and saturation But first: the progress has been amazing!
Laser Types Two main types depending on time operation Continuous Wave (CW) Pulsed operation Pulsed is easier, CW more useful
 Main Requirements of the Laser Optical Resonator Cavity Laser Gain Medium of 2, 3 or 4 level types in the Cavity Sufficient means of Excitation (called pumping) eg. light, current, chemical reaction Population
Main Requirements of the Laser Optical Resonator Cavity Laser Gain Medium of 2, 3 or 4 level types in the Cavity Sufficient means of Excitation (called pumping) eg. light, current, chemical reaction Population
Laser Types Two main types depending on time operation Continuous Wave (CW) Pulsed operation Pulsed is easier, CW more useful
 What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
What Makes a Laser Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation Main Requirements of the Laser Laser Gain Medium (provides the light amplification) Optical Resonator Cavity (greatly increase
Assessment of Threshold for Nonlinear Effects in Ibsen Transmission Gratings
 Assessment of Threshold for Nonlinear Effects in Ibsen Transmission Gratings Temple University 13th & Norris Street Philadelphia, PA 19122 T: 1-215-204-1052 contact: johanan@temple.edu http://www.temple.edu/capr/
Assessment of Threshold for Nonlinear Effects in Ibsen Transmission Gratings Temple University 13th & Norris Street Philadelphia, PA 19122 T: 1-215-204-1052 contact: johanan@temple.edu http://www.temple.edu/capr/
Multilayer thin-film structures with high spatial dispersion
 Multilayer thin-film structures with high spatial dispersion Martina Gerken and David A. B. Miller We demonstrate how to design thin-film multilayer structures that separate multiple wavelength channels
Multilayer thin-film structures with high spatial dispersion Martina Gerken and David A. B. Miller We demonstrate how to design thin-film multilayer structures that separate multiple wavelength channels
Lab 10: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy208 Fall 2008
 Lab 10: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy208 Fall 2008 Name Section This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit
Lab 10: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy208 Fall 2008 Name Section This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit
16. More About Polarization
 16. More About Polarization Polarization control Wave plates Circular polarizers Reflection & polarization Scattering & polarization Birefringent materials have more than one refractive index A special
16. More About Polarization Polarization control Wave plates Circular polarizers Reflection & polarization Scattering & polarization Birefringent materials have more than one refractive index A special
28. Fourier transforms in optics, part 3
 28. Fourier transforms in optics, part 3 Magnitude and phase some examples amplitude and phase of light waves what is the spectral phase, anyway? The Scale Theorem Defining the duration of a pulse the
28. Fourier transforms in optics, part 3 Magnitude and phase some examples amplitude and phase of light waves what is the spectral phase, anyway? The Scale Theorem Defining the duration of a pulse the
Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra. Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016
 Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016 1 Increase number of slits: 2 Visual Comparisons 3 4 8 2 Diffraction Grating Note: despite the name, this
Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016 1 Increase number of slits: 2 Visual Comparisons 3 4 8 2 Diffraction Grating Note: despite the name, this
An electric field wave packet propagating in a laser beam along the z axis can be described as
 Electromagnetic pulses: propagation & properties Propagation equation, group velocity, group velocity dispersion An electric field wave packet propagating in a laser beam along the z axis can be described
Electromagnetic pulses: propagation & properties Propagation equation, group velocity, group velocity dispersion An electric field wave packet propagating in a laser beam along the z axis can be described
Step index planar waveguide
 N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
Control of the filamentation distance and pattern in long-range atmospheric propagation
 Control of the filamentation distance and pattern in long-range atmospheric propagation Shmuel Eisenmann, Einat Louzon, Yiftach Katzir, Tala Palchan, and Arie Zigler Racah Institute of Physics, Hebrew
Control of the filamentation distance and pattern in long-range atmospheric propagation Shmuel Eisenmann, Einat Louzon, Yiftach Katzir, Tala Palchan, and Arie Zigler Racah Institute of Physics, Hebrew
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2016 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
Fast Light, Slow Light
 Light pulses can be made to propagate with group velocities exceeding the speed of light in a vacuum or, at the opposite extreme, to come to a complete stop. Fast Light, Slow Light Raymond Y. Chiao and
Light pulses can be made to propagate with group velocities exceeding the speed of light in a vacuum or, at the opposite extreme, to come to a complete stop. Fast Light, Slow Light Raymond Y. Chiao and
Polarization properties of corner-cube retroreflectors: Theory and experiment
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 3--997 Polarization properties of corner-cube retroreflectors: Theory and experiment
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 3--997 Polarization properties of corner-cube retroreflectors: Theory and experiment
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224. Your name Lab section
 Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 THE DIFFRACTION GRATING AND THE OPTICAL SPECTRUM Your name Lab section 1. What are the goals of this experiment? 2. If the period of a diffraction grating is d = 1,000 nm, where the
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 THE DIFFRACTION GRATING AND THE OPTICAL SPECTRUM Your name Lab section 1. What are the goals of this experiment? 2. If the period of a diffraction grating is d = 1,000 nm, where the
10. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY
 1. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a label-free (intrinsic contrast) technique that enables 3D imaging of tissues. The principle of its operation relies on low-coherence
1. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a label-free (intrinsic contrast) technique that enables 3D imaging of tissues. The principle of its operation relies on low-coherence
PHYS 450 Fall semester Lecture 05: Dispersion and the Prism Spectrometer. Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University
 PHYS 450 Fall semester 06 Lecture 05: Dispersion and the Prism Spectrometer Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University Lecture 05 Prisms Dispersion of Light n n As early as the 3th
PHYS 450 Fall semester 06 Lecture 05: Dispersion and the Prism Spectrometer Ron Reifenberger Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University Lecture 05 Prisms Dispersion of Light n n As early as the 3th
Interference. Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website
 Chapter 9 Interference Phys 322 Lecture 25 Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website Interferometers Wavefront-splitting interferometers Amplitude-splitting interferometers ed
Chapter 9 Interference Phys 322 Lecture 25 Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website Interferometers Wavefront-splitting interferometers Amplitude-splitting interferometers ed
Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a).
 7.1. Low-Coherence Interferometry (LCI) Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a). The light is split by the beam splitter (BS) and
7.1. Low-Coherence Interferometry (LCI) Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a). The light is split by the beam splitter (BS) and
Astronomy 203 practice final examination
 Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Self-Phase Modulation in Optical Fiber Communications: Good or Bad?
 1/100 Self-Phase Modulation in Optical Fiber Communications: Good or Bad? Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Historical Introduction
1/100 Self-Phase Modulation in Optical Fiber Communications: Good or Bad? Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Historical Introduction
Extreme pulse-front tilt from an etalon
 2322 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 27, No. 11/ November 2010 P. Bowlan and R. Trebino Extreme pulse-front tilt from an etalon Pamela Bowlan 1,2, * and Rick Trebino 1,2 1 Swamp Optics, LLC, 6300 Powers Ferry
2322 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 27, No. 11/ November 2010 P. Bowlan and R. Trebino Extreme pulse-front tilt from an etalon Pamela Bowlan 1,2, * and Rick Trebino 1,2 1 Swamp Optics, LLC, 6300 Powers Ferry
Lukas Gallmann. ETH Zurich, Physics Department, Switzerland Chapter 4b: χ (2) -nonlinearities with ultrashort pulses.
 Ultrafast Laser Physics Lukas Gallmann ETH Zurich, Physics Department, Switzerland www.ulp.ethz.ch Chapter 4b: χ (2) -nonlinearities with ultrashort pulses Ultrafast Laser Physics ETH Zurich Contents Second
Ultrafast Laser Physics Lukas Gallmann ETH Zurich, Physics Department, Switzerland www.ulp.ethz.ch Chapter 4b: χ (2) -nonlinearities with ultrashort pulses Ultrafast Laser Physics ETH Zurich Contents Second
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide
 AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
STUDYING ULTRAFAST MOLECULAR DYNAMICS IN PUMP-PROBE EXPERIMENTS WITH FEMTOSECOND LASERS JOSEPH HARRINGTON, DR. ARTEM RUDENKO, AND DR.
 STUDYING ULTRAFAST MOLECULAR DYNAMICS IN PUMP-PROBE EXPERIMENTS WITH FEMTOSECOND LASERS JOSEPH HARRINGTON, DR. ARTEM RUDENKO, AND DR. DANIEL ROLLES PHYSICS DEPARTMENT 2018 REU KANSAS STATE UNIVERSITY MOTIVATION
STUDYING ULTRAFAST MOLECULAR DYNAMICS IN PUMP-PROBE EXPERIMENTS WITH FEMTOSECOND LASERS JOSEPH HARRINGTON, DR. ARTEM RUDENKO, AND DR. DANIEL ROLLES PHYSICS DEPARTMENT 2018 REU KANSAS STATE UNIVERSITY MOTIVATION
1 Mathematical description of ultrashort laser pulses
 1 Mathematical description of ultrashort laser pulses 1.1 We first perform the Fourier transform directly on the Gaussian electric field: E(ω) = F[E(t)] = A 0 e 4 ln ( t T FWHM ) e i(ω 0t+ϕ CE ) e iωt
1 Mathematical description of ultrashort laser pulses 1.1 We first perform the Fourier transform directly on the Gaussian electric field: E(ω) = F[E(t)] = A 0 e 4 ln ( t T FWHM ) e i(ω 0t+ϕ CE ) e iωt
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2016/17) Lecture 9: December 16, 2016 Continue 9 Optical Parametric Amplifiers and Oscillators
 Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2016/17) Lecture 9: December 16, 2016 Continue 9 Optical Parametric Amplifiers and Oscillators 9.10 Passive CEP-stabilization in parametric amplifiers 9.10.1 Active versus passive
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2016/17) Lecture 9: December 16, 2016 Continue 9 Optical Parametric Amplifiers and Oscillators 9.10 Passive CEP-stabilization in parametric amplifiers 9.10.1 Active versus passive
Protokoll. Grundpraktikum II - Optical Spectroscopy
 Protokoll Grundpraktikum II - Optical Spectroscopy 1 Elaboration 1.1 Optical Spectroscopy Student: Hauke Rasch, Martin Borchert Tutor: Madsen Date: 22.October2014 This experiment is about the fundamental
Protokoll Grundpraktikum II - Optical Spectroscopy 1 Elaboration 1.1 Optical Spectroscopy Student: Hauke Rasch, Martin Borchert Tutor: Madsen Date: 22.October2014 This experiment is about the fundamental
Downloaded from
 Question 10.1: Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. What are the wavelength, frequency and speed of (a) reflected, and (b) refracted light? Refractive index
Question 10.1: Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. What are the wavelength, frequency and speed of (a) reflected, and (b) refracted light? Refractive index
Some Topics in Optics
 Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
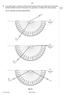 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
4. Dispersion. The index of refraction of the prism at the input wavelength can be calculated using
 4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
Molecular alignment, wavepacket interference and Isotope separation
 Molecular alignment, wavepacket interference and Isotope separation Sharly Fleischer, Ilya Averbukh and Yehiam Prior Chemical Physics, Weizmann Institute Yehiam.prior@weizmann.ac.il Frisno-8, Ein Bokek,
Molecular alignment, wavepacket interference and Isotope separation Sharly Fleischer, Ilya Averbukh and Yehiam Prior Chemical Physics, Weizmann Institute Yehiam.prior@weizmann.ac.il Frisno-8, Ein Bokek,
Grading. Class attendance: (1 point/class) x 9 classes = 9 points maximum Homework: (10 points/hw) x 3 HW = 30 points maximum
 Grading Class attendance: (1 point/class) x 9 classes = 9 points maximum Homework: (10 points/hw) x 3 HW = 30 points maximum Maximum total = 39 points Pass if total >= 20 points Fail if total
Grading Class attendance: (1 point/class) x 9 classes = 9 points maximum Homework: (10 points/hw) x 3 HW = 30 points maximum Maximum total = 39 points Pass if total >= 20 points Fail if total
Self-Phase-Modulation of Optical Pulses From Filaments to Solitons to Frequency Combs
 Self-Phase-Modulation of Optical Pulses From Filaments to Solitons to Frequency Combs P. L. Kelley Optical Society of America Washington, DC and T. K. Gustafson EECS University of California Berkeley,
Self-Phase-Modulation of Optical Pulses From Filaments to Solitons to Frequency Combs P. L. Kelley Optical Society of America Washington, DC and T. K. Gustafson EECS University of California Berkeley,
Richard Miles and Arthur Dogariu. Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08540, USA
 Richard Miles and Arthur Dogariu Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08540, USA Workshop on Oxygen Plasma Kinetics Sept 20, 2016 Financial support: ONR and MetroLaser
Richard Miles and Arthur Dogariu Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08540, USA Workshop on Oxygen Plasma Kinetics Sept 20, 2016 Financial support: ONR and MetroLaser
4. Dispersion. The index of refraction of the prism at the input wavelength can be calculated using
 4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
Speed of Light in Air
 Speed of Light in Air Electromagnetic waves represent energy in the form of oscillating electric and magnetic fields which propagate through vacuum with a speed c = 2.9979246x10 8 m/s. Electromagnetic
Speed of Light in Air Electromagnetic waves represent energy in the form of oscillating electric and magnetic fields which propagate through vacuum with a speed c = 2.9979246x10 8 m/s. Electromagnetic
Direct measurement of spectral phase for ultrashort laser pulses
 Direct measurement of spectral phase for ultrashort laser pulses Vadim V. Lozovoy, 1 Bingwei Xu, 1 Yves Coello, 1 and Marcos Dantus 1,2,* 1 Department of Chemistry, Michigan State University 2 Department
Direct measurement of spectral phase for ultrashort laser pulses Vadim V. Lozovoy, 1 Bingwei Xu, 1 Yves Coello, 1 and Marcos Dantus 1,2,* 1 Department of Chemistry, Michigan State University 2 Department
Lab 2: Mach Zender Interferometer Overview
 Lab : Mach Zender Interferometer Overview Goals:. Study factors that govern the interference between two light waves with identical amplitudes and frequencies. Relative phase. Relative polarization. Learn
Lab : Mach Zender Interferometer Overview Goals:. Study factors that govern the interference between two light waves with identical amplitudes and frequencies. Relative phase. Relative polarization. Learn
EE 119 Homework 2. 4 o
 EE 119 Homework 2 Professor: Jeff Bokor TA: Xi Luo Due Tuesday, Feb 9 th 2010 (Please submit your answers in EE119 homework box located in 240 Cory Hall) 1. (a) In class, the angle of deviation (δ) has
EE 119 Homework 2 Professor: Jeff Bokor TA: Xi Luo Due Tuesday, Feb 9 th 2010 (Please submit your answers in EE119 homework box located in 240 Cory Hall) 1. (a) In class, the angle of deviation (δ) has
Optical second harmonic generation properties of BiB 3 O 6
 Optical second harmonic generation properties of BiB 3 O 6 M. Ghotbi and M. Ebrahim-Zadeh ICFO-Institut de Ciencies Fotoniques, Jordi Girona 29, Nexus II, 834 Barcelona, Spain Abstract: We present studies
Optical second harmonic generation properties of BiB 3 O 6 M. Ghotbi and M. Ebrahim-Zadeh ICFO-Institut de Ciencies Fotoniques, Jordi Girona 29, Nexus II, 834 Barcelona, Spain Abstract: We present studies
Optical Solitons. Lisa Larrimore Physics 116
 Lisa Larrimore Physics 116 Optical Solitons An optical soliton is a pulse that travels without distortion due to dispersion or other effects. They are a nonlinear phenomenon caused by self-phase modulation
Lisa Larrimore Physics 116 Optical Solitons An optical soliton is a pulse that travels without distortion due to dispersion or other effects. They are a nonlinear phenomenon caused by self-phase modulation
Nonlinear effects and pulse propagation in PCFs
 Nonlinear effects and pulse propagation in PCFs --Examples of nonlinear effects in small glass core photonic crystal fibers --Physics of nonlinear effects in fibers --Theoretical framework --Solitons and
Nonlinear effects and pulse propagation in PCFs --Examples of nonlinear effects in small glass core photonic crystal fibers --Physics of nonlinear effects in fibers --Theoretical framework --Solitons and
Chapter 4. Dispersion of Glass. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 Apparatus
 Chapter 4 Dispersion of Glass 4.1 Introduction This experiment will develop skills in choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting curve. Curve fitting will count for a big chunk of the
Chapter 4 Dispersion of Glass 4.1 Introduction This experiment will develop skills in choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting curve. Curve fitting will count for a big chunk of the
EXPERIMENT 5:Determination of the refractive index (µ) of the material of a prism using sprectometer
 EXPERIMENT 5:Determination of the refractive index (µ) of the material of a prism using sprectometer Debangshu Mukherjee B.Sc Physics,1st year Chennai Mathematical Institute 17.10.008 1 Aim of Experiment
EXPERIMENT 5:Determination of the refractive index (µ) of the material of a prism using sprectometer Debangshu Mukherjee B.Sc Physics,1st year Chennai Mathematical Institute 17.10.008 1 Aim of Experiment
Third Harmonic Generator
 Third Harmonic Generator MODEL ATsG800-7 S/N 0003 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Del Mar Photonics, Inc 4119 Twilight Ridge San Diego, CA 9130 tel: (858) 876-3133 fax: (858) 630-376 support@dmphotonics.com http://www.dmphotonics.com/
Third Harmonic Generator MODEL ATsG800-7 S/N 0003 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Del Mar Photonics, Inc 4119 Twilight Ridge San Diego, CA 9130 tel: (858) 876-3133 fax: (858) 630-376 support@dmphotonics.com http://www.dmphotonics.com/
Laser Optics-II. ME 677: Laser Material Processing Instructor: Ramesh Singh 1
 Laser Optics-II 1 Outline Absorption Modes Irradiance Reflectivity/Absorption Absorption coefficient will vary with the same effects as the reflectivity For opaque materials: reflectivity = 1 - absorptivity
Laser Optics-II 1 Outline Absorption Modes Irradiance Reflectivity/Absorption Absorption coefficient will vary with the same effects as the reflectivity For opaque materials: reflectivity = 1 - absorptivity
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S
 OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S-108.3110 1 Course program 1. Introduction and Optical Fibers 2. Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fibers 3. Fiber-Optic Components I 4. Transmitters and Receivers 5. Fiber-Optic Measurements
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S-108.3110 1 Course program 1. Introduction and Optical Fibers 2. Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fibers 3. Fiber-Optic Components I 4. Transmitters and Receivers 5. Fiber-Optic Measurements
Coherent Cherenkov radiation from ultra-short electron bunch passing through vacuum channel in conical target
 Coherent Cherenkov radiation from ultra-short electron bunch passing through vacuum channel in conical target A.P. Potylitsyn, S.Yu. Gogolev RREPS_11, London, 2011, Sept.12-16 Motivation Existing experimental
Coherent Cherenkov radiation from ultra-short electron bunch passing through vacuum channel in conical target A.P. Potylitsyn, S.Yu. Gogolev RREPS_11, London, 2011, Sept.12-16 Motivation Existing experimental
Lab #13: Polarization
 Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Control of dispersion effects for resonant ultrashort pulses M. A. Bouchene, J. C. Delagnes
 Control of dispersion effects for resonant ultrashort pulses M. A. Bouchene, J. C. Delagnes Laboratoire «Collisions, Agrégats, Réactivité», Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France Context: - Dispersion
Control of dispersion effects for resonant ultrashort pulses M. A. Bouchene, J. C. Delagnes Laboratoire «Collisions, Agrégats, Réactivité», Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France Context: - Dispersion
Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 5
 Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the wavelength of the longest wavelength light visible to the human eye? a. 400 nm b. 4000 nm c. 7000 nm
Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the wavelength of the longest wavelength light visible to the human eye? a. 400 nm b. 4000 nm c. 7000 nm
Third harmonic generator
 Third harmonic generator MODEL ATsG800 S/N 0003 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Del Mar Photonics, Inc 49 Twilight Ridge San Diego, CA 930 tel: (858) 876-333 fax: (858) 630-376 support@dmphotonics.com http://www.dmphotonics.com/
Third harmonic generator MODEL ATsG800 S/N 0003 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Del Mar Photonics, Inc 49 Twilight Ridge San Diego, CA 930 tel: (858) 876-333 fax: (858) 630-376 support@dmphotonics.com http://www.dmphotonics.com/
3.5 Cavities Cavity modes and ABCD-matrix analysis 206 CHAPTER 3. ULTRASHORT SOURCES I - FUNDAMENTALS
 206 CHAPTER 3. ULTRASHORT SOURCES I - FUNDAMENTALS which is a special case of Eq. (3.30. Note that this treatment of dispersion is equivalent to solving the differential equation (1.94 for an incremental
206 CHAPTER 3. ULTRASHORT SOURCES I - FUNDAMENTALS which is a special case of Eq. (3.30. Note that this treatment of dispersion is equivalent to solving the differential equation (1.94 for an incremental
Physics 1252 Sec.A Exam #1A
 Physics 1252 Sec.A Exam #1A Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write
Physics 1252 Sec.A Exam #1A Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write
Commissioning of the new Injector Laser System for the Short Pulse Project at FLASH
 Commissioning of the new Injector Laser System for the Short Pulse Project at FLASH Uni Hamburg tim.plath@desy.de 05.11.2013 Supported by BMBF under contract 05K10GU2 & FS FLASH 301 Motivation short pulses
Commissioning of the new Injector Laser System for the Short Pulse Project at FLASH Uni Hamburg tim.plath@desy.de 05.11.2013 Supported by BMBF under contract 05K10GU2 & FS FLASH 301 Motivation short pulses
Chapter 1 - The Nature of Light
 David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
High-Harmonic Generation II
 Soft X-Rays and Extreme Ultraviolet Radiation High-Harmonic Generation II Phasematching techniques Attosecond pulse generation Applications Specialized optics for HHG sources Dr. Yanwei Liu, University
Soft X-Rays and Extreme Ultraviolet Radiation High-Harmonic Generation II Phasematching techniques Attosecond pulse generation Applications Specialized optics for HHG sources Dr. Yanwei Liu, University
Fizeau s Interference Experiment with Moving Water Contradicts the Special Theory of Relativity.
 Fizeau s Interference Experiment with Moving Water Contradicts the Special Theory of Relativity. Gennady Sokolov, Vitali Sokolov gennadiy@vtmedicalstaffing.com The interference experiment with moving water
Fizeau s Interference Experiment with Moving Water Contradicts the Special Theory of Relativity. Gennady Sokolov, Vitali Sokolov gennadiy@vtmedicalstaffing.com The interference experiment with moving water
sin constructive n same condition destructive 2 Interference Constructive - Destructive 2-slit single slit diff. grating
 Interference Constructive - Destructive 2-slit single slit diff. grating reflection Note: difference = 0 difference destructive 2 d sin reflection constructive d 2 sin tot. inter. = reflection + path length
Interference Constructive - Destructive 2-slit single slit diff. grating reflection Note: difference = 0 difference destructive 2 d sin reflection constructive d 2 sin tot. inter. = reflection + path length
Fresnel Equations cont.
 Lecture 11 Chapter 4 Fresnel quations cont. Total internal reflection and evanescent waves Optical properties of metals Familiar aspects of the interaction of light and matter Fresnel quations: phases
Lecture 11 Chapter 4 Fresnel quations cont. Total internal reflection and evanescent waves Optical properties of metals Familiar aspects of the interaction of light and matter Fresnel quations: phases
EXPERIMENT 12 THE WAVELENGTH OF LIGHT; THE DIFFRACTION GRATING
 EXPERIMENT 12 THE WAVELENGTH OF LIGHT; THE DIFFRACTION GRATING INTRODUCTION: One of the most fascinating chapters in the history of physics has been the search for an understanding of the true nature of
EXPERIMENT 12 THE WAVELENGTH OF LIGHT; THE DIFFRACTION GRATING INTRODUCTION: One of the most fascinating chapters in the history of physics has been the search for an understanding of the true nature of
Coherence and width of spectral lines with Michelson interferometer
 Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
