10. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY
|
|
|
- Christal Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a label-free (intrinsic contrast) technique that enables 3D imaging of tissues. The principle of its operation relies on low-coherence interferometry, i.e. interferometry with broadband light.
2 1.1. Low-coherence Interferometry (LCI). Consider a Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1). Such sources include light emitting diodes (LEDs) superluminescent diodes (SLD), Ti:Saph lasers, and white light lamps.
3 Figure 1-1. LCI using a Michelson interferometer. Mirror M adjust the path-length delay between the two arms. A qualitative comparison between the optical spectrum of a broadband source and that of a laser is shown in Fig.. We found previously that the coherence time is of the order of is the central wavelength and the bandwidth. c, where
4 The total instantaneous field at the detector is the sum of the two fields. U t U t U t (1.1) 1 is the delay introduced by the mobile mirror ( M ). The intensity at the detector is the modulus-squared average of the field, I U t * * I I U t U t U t U t I1I Re 1, Angular brackets denote temporal averaging. (1.) In Eq. we recognize the temporal cross-correlation function 1, defined as * U t U t * U t U t dt (1.3)
5 From Eq. 3, we see that the cross-correlation function can be measured experimentally by simply scanning the position of M. Using the Wiener- Kintchin theorem, 1 can be expressed as a Fourier transform i 1 W1 e d. (1.4) W 1 is known as cross-spectral density, defined as * W U U (1.5) 1 1 We assume that the fields on the two arms are identical. Thus, if U U 1 reduces to the spectrum of light, S, and 1 reduces to the autocorrelation function,, i S e d (1.6)
6 The intensity measured by the detector has the form shown in Fig. 3a. Subtracting the signal at large (the c component), which equals I 1 for perfectly balanced interferometers, the real part of is obtained as shown in Fig. 3b.
7 Using a Hilbert transform, the imaginary part of can be obtained, Im 1 Re ' P d ', (1.7) ' P indicates a principal value integral. The complex analytic signal associated with Re function, characterized by an amplitude and phase (Fig. 3c). is the (complex)
8 For a symmetric spectrum centered at, S S', it can be easily shown (via the shift theorem) that the autocorrelation function has the form ' i S e d i i e S' e d e i (1.8) Equation 8 establishes that the envelope of equals the Fourier transform of the spectrum. Since we assumed a symmetric spectrum, the envelope is a real function. Further, the phase (modulation) of is linear with, where the shape is given by the mean frequency,.
9 1.. Effects of unbalanced dispersion. The fields on the two arms of the interferometer are rarely identical. While the amplitude of the two fields can be easily matched via attenuators, making the optical pattern identical is more difficult. Here, we will study the effect of dispersion due to the beams passing through different lengths of dispersion media, such as glass. This is always the case when using a thick beam splitter in the Michelson interferometer (Fig. 4). Typically, the beam splitter is made of a piece of glass half-silvered on one side.
10 Figure 1-4. Transmission of the two beams through a thick beam splitter. It can be seen in Fig. 4 that field U 1 passes through the glass 3 times, while field U passes through only once. Therefore the phase difference between U 1 and U has the frequency dependence k L (1.9)
11 where L is the thickness of the beam splitter. This spectral phase can be expanded in Taylor series around the central frequency, dk L L dk (1.1) d d In Eq. 1, we define the following quantities: Phase shift of mean frequency: L, c (1.11) Group velocity: v g d, (1.1) dk
12 Group velocity dispersion (GVD) dk d 1 v g (1.13) GVD has units of s m s Hz m and defines how a phase spreads in the material due to dispersion effects. GVD is sometimes defined as a derivative with respect to wavelength. We can now express the cross-spectral density as * i Se W U U e i L i i v g il S' e e e (1.14)
13 In Eq. 14 we assumed that the two fields are of equal amplitude, and differ only through the phase shift due to the unbalanced dispersion. The temporal crosscorrelation function is obtained by taking the Fourier transform of Eq. 14. Consider first the case of negligible GVD, : L i v i g i e S' e e d 1 i i vg e e S' e d L i (1.15) The integral in Eq. 15 amounts to the shifted autocorrelation envelope, such that Eq. 15 becomes 1 e v g L i (1.16) Equation 16 establishes that, in the absence of GVD, there is no shape change in either the amplitude or the phase of the original correlation function.
14 The phase shift,, is due to the zeroth order (phase velocity) term in the expansion of Eq. 1, while the envelope shift, or group delay, is caused by the first (group velocity) term (Fig. 4).
15 The envelope shift, L vg, can be conveniently compensated by adjusting the mobile mirror of the interferometer. If the beam splitter material has no GVD, the interferometer operates as if it is perfectly balanced. Let us investigate separately the effect of the GVD itself. The cross-correlation has the form il i S' e e d.(1.17) 1 The Fourier transform in Eq. 17 yields a convolution between the Fourier transform of S and that of il e, i.e. i 4 L (1.18) 1 e L Equation 18 establishes that the cross-correlation function 1 is broader than due to the convolution operation. This effect is to ultimately degrade the axial resolution of OCT images.
16 In practice, great effort is devoted towards compensating for unbalanced dispersion in the interferometer.
17 1.3. Optical coherence tomography. OCT is typically implemented in fiber optics, where one of the mirrors in the interferometer is replaced by a 3D specimen. Thus, the depth-information is provided by virtue of the LCI discussed above. In order to obtain x-y resolution, the sample arm must be equipped with a D scanning system, typically comprised of galvo-mirrors (Fig. 5).
18 At each point xy,, the OCT signal consists of the cross-correlation 1 between the reference field U R and specimen field as the Fourier transform of the cross-correlation density * W1 USUR S h, S U U (1.19) is the spectrum of the source. R R In Eq. 19, we introduced the spectral modifier h function characterizing the spectral response of the specimen, S. U U h (1.) R U S, which can be expressed, which is a complex The two fields are initially identical, i.e. the interferometer is balanced, and the specimen is modifying the incident field via h.
19 The resulting cross-correlation obtained by measurement is a convolution operation h (1.1) 1, h is the time response function of the sample, the Fourier transform of h, i. h h e d (1.)
20 Depth-resolution in OCT. The LCI configuration depicted in Fig. 1 is recovered by introducing a response function, h. In this case the cross-correlation reduces to (1.3) 1, z is the time delay due to the depth location of the reflector (Fig. 6) c
21 OCT images are obtained by retaining the modulus of 1, which is a complex function 1 1 i e. i The high frequency component (carrier), e, is filtered via demodulation (lowpass filtering). Equation 3 gives access to the impulse response function of OCT,. As in Fig. 6b the width of the envelope of establishes the ultimate resolution in locating the reflector s position. This resolution in time is nothing more that the coherence time of the source, C. In terms of depth, this resolution limit is the coherence length, l C v, with v the speed of light in the medium. This result establishes the need for broadband sources in OCT, as C 1. C
22 The coherence length is the absolute best resolution that OCT can deliver. The performance can be drastically reduced by dispersion effects. The specimen itself can unbalance the interferometer. Consider a reflective surface buried in a medium characterized by dispersion (e.g. a tumor located at a certain depth in the tissue), as illustrated in Fig. 7. Figure 1-8. Depth-dependent resolution in OCT.
23 Even when the attenuation due to depth propagation is negligible (weakly scattering medium), the spectral phase accumulate differs for the two depths (see Eq. 18), L 1,,, (1.4) 1 1, e i 4 L L 1, is the GVD of the medium above the reflector. The signal is broader from the reflector that is placed deeper ( L L 1 ) in the medium, i.e. the axial resolution degrades with depth.
24 1.3.. Contrast in OCT. Contrast in OCT is given by differences in reflectivity between different structures. Contrast in a transverse (x-y, en face) OCT image depends on depth.
25 Figure 8 illustrates the change in SNR with depth. The scattering properties of the surrounding medium is an important variable that affects depth-dependent SNR. Thus, the backscattering limits the contrast to noise ratio in an x-y image. The signal and noise must be defined locally, i.e. at each depth, for which the signal to noise has the form
26 SNR N N, (1.5) is the standard deviation of the noise around the time delay. This noise component is due to mechanical vibrations, source noise, detection/electronic noise, and most importantly, due to the scattering from the medium that surrounds the structure of interest. In an en face image, we can define the contrast to noise ratio as CNR A B, (1.6) N where A and B are two structures of interest.
Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a).
 7.1. Low-Coherence Interferometry (LCI) Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a). The light is split by the beam splitter (BS) and
7.1. Low-Coherence Interferometry (LCI) Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a). The light is split by the beam splitter (BS) and
Lecture 4 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 4, Slide 1
 ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
Light Propagation in Free Space
 Intro Light Propagation in Free Space Helmholtz Equation 1-D Propagation Plane waves Plane wave propagation Light Propagation in Free Space 3-D Propagation Spherical Waves Huygen s Principle Each point
Intro Light Propagation in Free Space Helmholtz Equation 1-D Propagation Plane waves Plane wave propagation Light Propagation in Free Space 3-D Propagation Spherical Waves Huygen s Principle Each point
High-Resolution Imagers
 40 Telescopes and Imagers High-Resolution Imagers High-resolution imagers look at very small fields of view with diffraction-limited angular resolution. As the field is small, intrinsic aberrations are
40 Telescopes and Imagers High-Resolution Imagers High-resolution imagers look at very small fields of view with diffraction-limited angular resolution. As the field is small, intrinsic aberrations are
Physical Optics. Lecture 7: Coherence Herbert Gross.
 Physical Optics Lecture 7: Coherence 07-05-7 Herbert Gross www.iap.uni-jena.de Physical Optics: Content No Date Subject Ref Detailed Content 05.04. Wave optics G Complex fields, wave equation, k-vectors,
Physical Optics Lecture 7: Coherence 07-05-7 Herbert Gross www.iap.uni-jena.de Physical Optics: Content No Date Subject Ref Detailed Content 05.04. Wave optics G Complex fields, wave equation, k-vectors,
Analysis of the signal fall-off in spectral domain optical coherence tomography systems
 Analysis of the signal fall-off in spectral domain optical coherence tomography systems M. Hagen-Eggert 1,2,P.Koch 3, G.Hüttmann 2 1 Medical Laser Center Lübeck, Germany 2 Institute of Biomedical Optics
Analysis of the signal fall-off in spectral domain optical coherence tomography systems M. Hagen-Eggert 1,2,P.Koch 3, G.Hüttmann 2 1 Medical Laser Center Lübeck, Germany 2 Institute of Biomedical Optics
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 15. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 15 IR Instruments Types of Instrumentation Dispersive Spectrophotometers (gratings) Fourier transform spectrometers (interferometer) Single beam Double beam
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 15 IR Instruments Types of Instrumentation Dispersive Spectrophotometers (gratings) Fourier transform spectrometers (interferometer) Single beam Double beam
Interferometric. Gravitational Wav. Detectors. \p World Scientific. Fundamentals of. Peter R. Sawlson. Syracuse University, USA.
 SINGAPORE HONGKONG Fundamentals of Interferometric Gravitational Wav Detectors Second Edition Peter R. Sawlson Martin A. Pomerantz '37 Professor of Physics Syracuse University, USA \p World Scientific
SINGAPORE HONGKONG Fundamentals of Interferometric Gravitational Wav Detectors Second Edition Peter R. Sawlson Martin A. Pomerantz '37 Professor of Physics Syracuse University, USA \p World Scientific
Michelson Interferometer. crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity.
 Michelson Interferometer The interferometer Michelson experiment Interferometer of Michelson and Morley played 0 a crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity. Michelson
Michelson Interferometer The interferometer Michelson experiment Interferometer of Michelson and Morley played 0 a crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity. Michelson
Engineering Note. Measuring the Polarization Rotation Angle of a Faraday Rotator Mirror with the Optical Vector Analyzer
 Engineering Note Revision 4 April, 014 Measuring the Polarization Rotation Angle of a Faraday Rotator Mirror with the Optical Vector Analyzer Contents Introduction... 1 Measurement Set-Up... 1 ones Matrix
Engineering Note Revision 4 April, 014 Measuring the Polarization Rotation Angle of a Faraday Rotator Mirror with the Optical Vector Analyzer Contents Introduction... 1 Measurement Set-Up... 1 ones Matrix
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Important announcements Homework #1 is due. Homework #2 is assigned, due
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Important announcements Homework #1 is due. Homework #2 is assigned, due
Interference. Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website
 Chapter 9 Interference Phys 322 Lecture 25 Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website Interferometers Wavefront-splitting interferometers Amplitude-splitting interferometers ed
Chapter 9 Interference Phys 322 Lecture 25 Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website Interferometers Wavefront-splitting interferometers Amplitude-splitting interferometers ed
Where are the Fringes? (in a real system) Div. of Amplitude - Wedged Plates. Fringe Localisation Double Slit. Fringe Localisation Grating
 Where are the Fringes? (in a real system) Fringe Localisation Double Slit spatial modulation transverse fringes? everywhere or well localised? affected by source properties: coherence, extension Plane
Where are the Fringes? (in a real system) Fringe Localisation Double Slit spatial modulation transverse fringes? everywhere or well localised? affected by source properties: coherence, extension Plane
Quantum Optical Coherence Tomography
 Quantum Optical Coherence Tomography Bahaa Saleh Alexander Sergienko Malvin Teich Quantum Imaging Lab Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering & Photonics Center QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed)
Quantum Optical Coherence Tomography Bahaa Saleh Alexander Sergienko Malvin Teich Quantum Imaging Lab Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering & Photonics Center QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed)
Metrology and Sensing
 Metrology and Sensing Lecture 5: Interferometry I 06--09 Herbert Gross Winter term 06 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 8.0. Introduction Introduction, optical measurements,
Metrology and Sensing Lecture 5: Interferometry I 06--09 Herbert Gross Winter term 06 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 8.0. Introduction Introduction, optical measurements,
Effect of source spectral shape on task-based assessment of detection and resolution in optical coherence tomography
 Effect of source spectral shape on task-based assessment of detection and resolution in optical coherence tomography A. Ceyhun Akcay, Eric Clarkson, and Jannick P. Rolland We demonstrate the effect of
Effect of source spectral shape on task-based assessment of detection and resolution in optical coherence tomography A. Ceyhun Akcay, Eric Clarkson, and Jannick P. Rolland We demonstrate the effect of
THE MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER Intermediate ( first part) to Advanced (latter parts)
 THE MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER Intermediate ( first part) to Advanced (latter parts) Goal: There is a progression of goals for this experiment but you do not have to do the last goal. The first goal is to
THE MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER Intermediate ( first part) to Advanced (latter parts) Goal: There is a progression of goals for this experiment but you do not have to do the last goal. The first goal is to
COMPUTER GENERATED HOLOGRAMS Optical Sciences 627 W.J. Dallas (Monday, August 23, 2004, 12:14 PM)
 COMPUTER GENERATED HOLOGRAMS Optical Sciences 67 W.J. Dallas (Monday, August 3, 4, 1:14 PM) PART IV: CHAPTER FOUR OPTICAL TESTING Part IV: Chapter Four Page 1 of 1 Introduction In optical testing an element
COMPUTER GENERATED HOLOGRAMS Optical Sciences 67 W.J. Dallas (Monday, August 3, 4, 1:14 PM) PART IV: CHAPTER FOUR OPTICAL TESTING Part IV: Chapter Four Page 1 of 1 Introduction In optical testing an element
Linear pulse propagation
 Ultrafast Laser Physics Ursula Keller / Lukas Gallmann ETH Zurich, Physics Department, Switzerland www.ulp.ethz.ch Linear pulse propagation Ultrafast Laser Physics ETH Zurich Superposition of many monochromatic
Ultrafast Laser Physics Ursula Keller / Lukas Gallmann ETH Zurich, Physics Department, Switzerland www.ulp.ethz.ch Linear pulse propagation Ultrafast Laser Physics ETH Zurich Superposition of many monochromatic
Step index planar waveguide
 N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
Richard Miles and Arthur Dogariu. Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08540, USA
 Richard Miles and Arthur Dogariu Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08540, USA Workshop on Oxygen Plasma Kinetics Sept 20, 2016 Financial support: ONR and MetroLaser
Richard Miles and Arthur Dogariu Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08540, USA Workshop on Oxygen Plasma Kinetics Sept 20, 2016 Financial support: ONR and MetroLaser
4 Classical Coherence Theory
 This chapter is based largely on Wolf, Introduction to the theory of coherence and polarization of light [? ]. Until now, we have not been concerned with the nature of the light field itself. Instead,
This chapter is based largely on Wolf, Introduction to the theory of coherence and polarization of light [? ]. Until now, we have not been concerned with the nature of the light field itself. Instead,
Contents Preface iii 1 Origins and Manifestations of Speckle 2 Random Phasor Sums 3 First-Order Statistical Properties
 Contents Preface iii 1 Origins and Manifestations of Speckle 1 1.1 General Background............................. 1 1.2 Intuitive Explanation of the Cause of Speckle................ 2 1.3 Some Mathematical
Contents Preface iii 1 Origins and Manifestations of Speckle 1 1.1 General Background............................. 1 1.2 Intuitive Explanation of the Cause of Speckle................ 2 1.3 Some Mathematical
Phase-Referencing and the Atmosphere
 Phase-Referencing and the Atmosphere Francoise Delplancke Outline: Basic principle of phase-referencing Atmospheric / astrophysical limitations Phase-referencing requirements: Practical problems: dispersion
Phase-Referencing and the Atmosphere Francoise Delplancke Outline: Basic principle of phase-referencing Atmospheric / astrophysical limitations Phase-referencing requirements: Practical problems: dispersion
Transform Representation of Signals
 C H A P T E R 3 Transform Representation of Signals and LTI Systems As you have seen in your prior studies of signals and systems, and as emphasized in the review in Chapter 2, transforms play a central
C H A P T E R 3 Transform Representation of Signals and LTI Systems As you have seen in your prior studies of signals and systems, and as emphasized in the review in Chapter 2, transforms play a central
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 15. Optical Sources-LASER
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 15 Optical Sources-LASER Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 15 Optical Sources-LASER Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 07
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 07 Analysis of Wave-Model of Light Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 07 Analysis of Wave-Model of Light Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of
Course Syllabus. OSE6211 Imaging & Optical Systems, 3 Cr. Instructor: Bahaa Saleh Term: Fall 2017
 Course Syllabus OSE6211 Imaging & Optical Systems, 3 Cr Instructor: Bahaa Saleh Term: Fall 2017 Email: besaleh@creol.ucf.edu Class Meeting Days: Tuesday, Thursday Phone: 407 882-3326 Class Meeting Time:
Course Syllabus OSE6211 Imaging & Optical Systems, 3 Cr Instructor: Bahaa Saleh Term: Fall 2017 Email: besaleh@creol.ucf.edu Class Meeting Days: Tuesday, Thursday Phone: 407 882-3326 Class Meeting Time:
Main Notation Used in This Book
 Main Notation Used in This Book z Direction normal to the surface x,y Directions in the plane of the surface Used to describe a component parallel to the interface plane xoz Plane of incidence j Label
Main Notation Used in This Book z Direction normal to the surface x,y Directions in the plane of the surface Used to describe a component parallel to the interface plane xoz Plane of incidence j Label
CHIRP OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY
 JOURNAL OF BIOMEDICAL OPTICS 3(3), 259 266 (JULY 1998) CHIRP OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY OF LAYERED SCATTERING MEDIA U. H. P. Haberland, V. Blazek, and H. J. Schmitt Institute of High Frequency Technology,
JOURNAL OF BIOMEDICAL OPTICS 3(3), 259 266 (JULY 1998) CHIRP OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY OF LAYERED SCATTERING MEDIA U. H. P. Haberland, V. Blazek, and H. J. Schmitt Institute of High Frequency Technology,
5. LIGHT MICROSCOPY Abbe s theory of imaging
 5. LIGHT MICROSCOPY. We use Fourier optics to describe coherent image formation, imaging obtained by illuminating the specimen with spatially coherent light. We define resolution, contrast, and phase-sensitive
5. LIGHT MICROSCOPY. We use Fourier optics to describe coherent image formation, imaging obtained by illuminating the specimen with spatially coherent light. We define resolution, contrast, and phase-sensitive
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematics of an optical pulse in a nonlinear medium. A Gaussian optical pulse propagates along z-axis in a nonlinear medium
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematics of an optical pulse in a nonlinear medium. A Gaussian optical pulse propagates along z-axis in a nonlinear medium with thickness L. Supplementary Figure Measurement of
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematics of an optical pulse in a nonlinear medium. A Gaussian optical pulse propagates along z-axis in a nonlinear medium with thickness L. Supplementary Figure Measurement of
and the radiation from source 2 has the form. The vector r points from the origin to the point P. What will the net electric field be at point P?
 Physics 3 Interference and Interferometry Page 1 of 6 Interference Imagine that we have two or more waves that interact at a single point. At that point, we are concerned with the interaction of those
Physics 3 Interference and Interferometry Page 1 of 6 Interference Imagine that we have two or more waves that interact at a single point. At that point, we are concerned with the interaction of those
Dispersion and how to control it
 Dispersion and how to control it Group velocity versus phase velocity Angular dispersion Prism sequences Grating pairs Chirped mirrors Intracavity and extra-cavity examples 1 Pulse propagation and broadening
Dispersion and how to control it Group velocity versus phase velocity Angular dispersion Prism sequences Grating pairs Chirped mirrors Intracavity and extra-cavity examples 1 Pulse propagation and broadening
2.71. Final examination. 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET
 2.71 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
2.71 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS
 PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
Metrology and Sensing
 Metrology and Sensing Lecture 5: Interferometry I 017-11-16 Herbert Gross Winter term 017 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 1 19.10. Introduction Introduction, optical
Metrology and Sensing Lecture 5: Interferometry I 017-11-16 Herbert Gross Winter term 017 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 1 19.10. Introduction Introduction, optical
Metrology and Sensing
 Metrology and Sensing Lecture 5: Interferometry I 08--6 Herbert Gross Winter term 08 www.iap.uni-jena.de Schedule Optical Metrology and Sensing 08 No Date Subject Detailed Content 6.0. Introduction Introduction,
Metrology and Sensing Lecture 5: Interferometry I 08--6 Herbert Gross Winter term 08 www.iap.uni-jena.de Schedule Optical Metrology and Sensing 08 No Date Subject Detailed Content 6.0. Introduction Introduction,
Single-Mode Propagation ofmutual Temporal Coherence: Equivalence of Time and Frequency Measurements of Polarization Mode Dispersion
 r~3 HEWLETT ~~ PACKARD Single-Mode Propagation ofmutual Temporal Coherence: Equivalence of Time and Frequency Measurements of Polarization Mode Dispersion Brian Heffner Instruments and Photonics Laboratory
r~3 HEWLETT ~~ PACKARD Single-Mode Propagation ofmutual Temporal Coherence: Equivalence of Time and Frequency Measurements of Polarization Mode Dispersion Brian Heffner Instruments and Photonics Laboratory
3.1 The Plane Mirror Resonator 3.2 The Spherical Mirror Resonator 3.3 Gaussian modes and resonance frequencies 3.4 The Unstable Resonator
 Quantum Electronics Laser Physics Chapter 3 The Optical Resonator 3.1 The Plane Mirror Resonator 3. The Spherical Mirror Resonator 3.3 Gaussian modes and resonance frequencies 3.4 The Unstable Resonator
Quantum Electronics Laser Physics Chapter 3 The Optical Resonator 3.1 The Plane Mirror Resonator 3. The Spherical Mirror Resonator 3.3 Gaussian modes and resonance frequencies 3.4 The Unstable Resonator
Optimisation using measured Green s function for improving spatial coherence in acoustic measurements
 Ultrasonics 42 (2004) 205 212 www.elsevier.com/locate/ultras Optimisation using measured Green s function for improving spatial coherence in acoustic measurements Matthew Clark *, Steve D. Sharples, Mike
Ultrasonics 42 (2004) 205 212 www.elsevier.com/locate/ultras Optimisation using measured Green s function for improving spatial coherence in acoustic measurements Matthew Clark *, Steve D. Sharples, Mike
Introducing speckle noise maps for laser vibrometry
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Introducing speckle noise maps for laser vibrometry This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Introducing speckle noise maps for laser vibrometry This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory. ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy
 Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy The three major branches of optics Geometrical Optics Light travels as straight rays Physical Optics Light can be
Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy The three major branches of optics Geometrical Optics Light travels as straight rays Physical Optics Light can be
EUV Reflectivity measurements on Acktar Sample Magic Black
 Report EUV Reflectivity measurements on Acktar Sample Magic Black S. Döring, Dr. K. Mann Laser-Laboratorium Göttingen e.v. October 28, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Setup 3 3 Measurements 4 4 Conclusion
Report EUV Reflectivity measurements on Acktar Sample Magic Black S. Döring, Dr. K. Mann Laser-Laboratorium Göttingen e.v. October 28, 2011 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Setup 3 3 Measurements 4 4 Conclusion
Optical Interferometry
 Optical Interferometry MIT Department of Physics The objective of this experiment is to observe the interference of light by combining coherent monochromatic light beams using a Michelson interferometer.
Optical Interferometry MIT Department of Physics The objective of this experiment is to observe the interference of light by combining coherent monochromatic light beams using a Michelson interferometer.
Highly Efficient and Anomalous Charge Transfer in van der Waals Trilayer Semiconductors
 Highly Efficient and Anomalous Charge Transfer in van der Waals Trilayer Semiconductors Frank Ceballos 1, Ming-Gang Ju 2 Samuel D. Lane 1, Xiao Cheng Zeng 2 & Hui Zhao 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Highly Efficient and Anomalous Charge Transfer in van der Waals Trilayer Semiconductors Frank Ceballos 1, Ming-Gang Ju 2 Samuel D. Lane 1, Xiao Cheng Zeng 2 & Hui Zhao 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Optical Component Characterization: A Linear Systems Approach
 Optical Component Characterization: A Linear Systems Approach Authors: Mark Froggatt, Brian Soller, Eric Moore, Matthew Wolfe Email: froggattm@lunatechnologies.com Luna Technologies, 2020 Kraft Drive,
Optical Component Characterization: A Linear Systems Approach Authors: Mark Froggatt, Brian Soller, Eric Moore, Matthew Wolfe Email: froggattm@lunatechnologies.com Luna Technologies, 2020 Kraft Drive,
Optics.
 Optics www.optics.rochester.edu/classes/opt100/opt100page.html Course outline Light is a Ray (Geometrical Optics) 1. Nature of light 2. Production and measurement of light 3. Geometrical optics 4. Matrix
Optics www.optics.rochester.edu/classes/opt100/opt100page.html Course outline Light is a Ray (Geometrical Optics) 1. Nature of light 2. Production and measurement of light 3. Geometrical optics 4. Matrix
Propagation losses in optical fibers
 Chapter Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers 1-Fev-017 Propagation losses in optical fibers Charles Kao, Nobel Laureate (009) Courtesy of the Chinese University of Hong Kong S.O. Kasap, Optoelectronics
Chapter Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers 1-Fev-017 Propagation losses in optical fibers Charles Kao, Nobel Laureate (009) Courtesy of the Chinese University of Hong Kong S.O. Kasap, Optoelectronics
Advanced Optical Coherence Tomography techniques: novel and fast imaging tools for non-destructive testing
 17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China Advanced Optical Coherence Tomography techniques: novel and fast imaging tools for non-destructive testing David STIFTER
17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China Advanced Optical Coherence Tomography techniques: novel and fast imaging tools for non-destructive testing David STIFTER
Interferometer for Squareness measurement
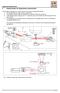 F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 15 Laser - I In the last lecture, we discussed various
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 15 Laser - I In the last lecture, we discussed various
Scattering properties of the retina and the choroids determined from OCT-A-scans
 International Ophthalmology 23: 291 295, 2001. J.R. Sampaolesi (ed.), Laser Scanning: Update 1, 109 113. 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 291 Scattering properties of the retina
International Ophthalmology 23: 291 295, 2001. J.R. Sampaolesi (ed.), Laser Scanning: Update 1, 109 113. 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 291 Scattering properties of the retina
Lecture 7: Optical Spectroscopy. Astrophysical Spectroscopy. Broadband Filters. Fabry-Perot Filters. Interference Filters. Prism Spectrograph
 Lecture 7: Optical Spectroscopy Outline 1 Astrophysical Spectroscopy 2 Broadband Filters 3 Fabry-Perot Filters 4 Interference Filters 5 Prism Spectrograph 6 Grating Spectrograph 7 Fourier Transform Spectrometer
Lecture 7: Optical Spectroscopy Outline 1 Astrophysical Spectroscopy 2 Broadband Filters 3 Fabry-Perot Filters 4 Interference Filters 5 Prism Spectrograph 6 Grating Spectrograph 7 Fourier Transform Spectrometer
1. Consider the biconvex thick lens shown in the figure below, made from transparent material with index n and thickness L.
 Optical Science and Engineering 2013 Advanced Optics Exam Answer all questions. Begin each question on a new blank page. Put your banner ID at the top of each page. Please staple all pages for each individual
Optical Science and Engineering 2013 Advanced Optics Exam Answer all questions. Begin each question on a new blank page. Put your banner ID at the top of each page. Please staple all pages for each individual
34. Even more Interference Effects
 34. Even more Interference Effects The Fabry-Perot interferometer Thin-film interference Anti-reflection coatings Single- and multi-layer Advanced topic: Photonic crystals Natural and artificial periodic
34. Even more Interference Effects The Fabry-Perot interferometer Thin-film interference Anti-reflection coatings Single- and multi-layer Advanced topic: Photonic crystals Natural and artificial periodic
Chapter 2. Optical FMCW Reflectometry. 2.1 Introduction
 6 Chapter Optical FMCW Reflectometry.1 Introduction The centerpiece and workhorse of the research described in this thesis is the optoelectronic swept-frequency laser (SFL) a feedback system designed around
6 Chapter Optical FMCW Reflectometry.1 Introduction The centerpiece and workhorse of the research described in this thesis is the optoelectronic swept-frequency laser (SFL) a feedback system designed around
Electron-Acoustic Wave in a Plasma
 Electron-Acoustic Wave in a Plasma 0 (uniform ion distribution) For small fluctuations, n ~ e /n 0
Electron-Acoustic Wave in a Plasma 0 (uniform ion distribution) For small fluctuations, n ~ e /n 0
Spatial phase-shifting moiré tomography
 Spatial phase-shifting moiré tomography Song Yang,, Zhao Zhimin, Chen YunYun, He Anzhi College of Natural Science Nanking University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, Nanking, 006 P. R. China Department of
Spatial phase-shifting moiré tomography Song Yang,, Zhao Zhimin, Chen YunYun, He Anzhi College of Natural Science Nanking University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, Nanking, 006 P. R. China Department of
Revision of Lecture 4
 Revision of Lecture 4 We have discussed all basic components of MODEM Pulse shaping Tx/Rx filter pair Modulator/demodulator Bits map symbols Discussions assume ideal channel, and for dispersive channel
Revision of Lecture 4 We have discussed all basic components of MODEM Pulse shaping Tx/Rx filter pair Modulator/demodulator Bits map symbols Discussions assume ideal channel, and for dispersive channel
The structure of laser pulses
 1 The structure of laser pulses 2 The structure of laser pulses Pulse characteristics Temporal and spectral representation Fourier transforms Temporal and spectral widths Instantaneous frequency Chirped
1 The structure of laser pulses 2 The structure of laser pulses Pulse characteristics Temporal and spectral representation Fourier transforms Temporal and spectral widths Instantaneous frequency Chirped
Ambiguity of optical coherence tomography measurements due to rough surface scattering
 Ambiguity of optical coherence tomography measurements due to rough surface scattering Y. Ashtamker, 1 V Freilikher, 1,* and J C Dainty 2 1 Department of Physics, Bar-Ilan University, Ramat Gan 52900,
Ambiguity of optical coherence tomography measurements due to rough surface scattering Y. Ashtamker, 1 V Freilikher, 1,* and J C Dainty 2 1 Department of Physics, Bar-Ilan University, Ramat Gan 52900,
Fresnel Equations cont.
 Lecture 11 Chapter 4 Fresnel quations cont. Total internal reflection and evanescent waves Optical properties of metals Familiar aspects of the interaction of light and matter Fresnel quations: phases
Lecture 11 Chapter 4 Fresnel quations cont. Total internal reflection and evanescent waves Optical properties of metals Familiar aspects of the interaction of light and matter Fresnel quations: phases
Constructive vs. destructive interference; Coherent vs. incoherent interference
 Constructive vs. destructive interference; Coherent vs. incoherent interference Waves that combine in phase add up to relatively high irradiance. = Constructive interference (coherent) Waves that combine
Constructive vs. destructive interference; Coherent vs. incoherent interference Waves that combine in phase add up to relatively high irradiance. = Constructive interference (coherent) Waves that combine
Experiment O-2. The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
6. LIGHT SCATTERING 6.1 The first Born approximation
 6. LIGHT SCATTERING 6.1 The first Born approximation In many situations, light interacts with inhomogeneous systems, in which case the generic light-matter interaction process is referred to as scattering
6. LIGHT SCATTERING 6.1 The first Born approximation In many situations, light interacts with inhomogeneous systems, in which case the generic light-matter interaction process is referred to as scattering
Optics and Optical Design. Chapter 5: Electromagnetic Optics. Lectures 9 & 10
 Optics and Optical Design Chapter 5: Electromagnetic Optics Lectures 9 & 1 Cord Arnold / Anne L Huillier Electromagnetic waves in dielectric media EM optics compared to simpler theories Electromagnetic
Optics and Optical Design Chapter 5: Electromagnetic Optics Lectures 9 & 1 Cord Arnold / Anne L Huillier Electromagnetic waves in dielectric media EM optics compared to simpler theories Electromagnetic
Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan
 Biomedical Optics Hsiao-Lung Chan, Ph.D. Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan chanhl@mail.cgu.edu.tw Outline Essential optical principle Light propagation in biological tissue Blood
Biomedical Optics Hsiao-Lung Chan, Ph.D. Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan chanhl@mail.cgu.edu.tw Outline Essential optical principle Light propagation in biological tissue Blood
Scattering of low coherence radiation and applications
 Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 73 93 (2005) DOI: 10.1051/epjap:2005082 THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL APPLIED PHYSICS Scattering of low coherence radiation and applications G. Popescu 1 and A. Dogariu 2,a
Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 73 93 (2005) DOI: 10.1051/epjap:2005082 THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL APPLIED PHYSICS Scattering of low coherence radiation and applications G. Popescu 1 and A. Dogariu 2,a
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics. Final Exam. April 16, 2007.
 Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Final Exam April 16, 2007 Exam Type: D (Close-book + two double-sided aid sheets + a non-programmable
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Final Exam April 16, 2007 Exam Type: D (Close-book + two double-sided aid sheets + a non-programmable
Fast Light, Slow Light
 Light pulses can be made to propagate with group velocities exceeding the speed of light in a vacuum or, at the opposite extreme, to come to a complete stop. Fast Light, Slow Light Raymond Y. Chiao and
Light pulses can be made to propagate with group velocities exceeding the speed of light in a vacuum or, at the opposite extreme, to come to a complete stop. Fast Light, Slow Light Raymond Y. Chiao and
MODERN INTERFEROMETRY
 MODERN INTERFEROMETRY * No actual laser photons were harmed during the filming of this cover. Build Michelson, Sagnac, and Mach-Zehnder Interferometers Generate and Count Interference Fringes Manually
MODERN INTERFEROMETRY * No actual laser photons were harmed during the filming of this cover. Build Michelson, Sagnac, and Mach-Zehnder Interferometers Generate and Count Interference Fringes Manually
Physics 20 Work Plan
 Units/Topics Time Frame Major Learning Outcomes Unit Major Resource(s) Assessment methods Unit 2 Wave Motion A. Properties of waves 1. Wave terminology 2. Universal wave equation 3. Principle of Superposition
Units/Topics Time Frame Major Learning Outcomes Unit Major Resource(s) Assessment methods Unit 2 Wave Motion A. Properties of waves 1. Wave terminology 2. Universal wave equation 3. Principle of Superposition
Nonlinear effects in optical fibers - v1. Miguel A. Muriel UPM-ETSIT-MUIT-CFOP
 Nonlinear effects in optical fibers - v1 Miguel A. Muriel UPM-ETSIT-MUIT-CFOP Miguel A. Muriel-015/10-1 Nonlinear effects in optical fibers 1) Introduction ) Causes 3) Parameters 4) Fundamental processes
Nonlinear effects in optical fibers - v1 Miguel A. Muriel UPM-ETSIT-MUIT-CFOP Miguel A. Muriel-015/10-1 Nonlinear effects in optical fibers 1) Introduction ) Causes 3) Parameters 4) Fundamental processes
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S
 OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S-108.3110 1 Course program 1. Introduction and Optical Fibers 2. Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fibers 3. Fiber-Optic Components I 4. Transmitters and Receivers 5. Fiber-Optic Measurements
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S-108.3110 1 Course program 1. Introduction and Optical Fibers 2. Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fibers 3. Fiber-Optic Components I 4. Transmitters and Receivers 5. Fiber-Optic Measurements
Lecture 9. PMTs and Laser Noise. Lecture 9. Photon Counting. Photomultiplier Tubes (PMTs) Laser Phase Noise. Relative Intensity
 s and Laser Phase Phase Density ECE 185 Lasers and Modulators Lab - Spring 2018 1 Detectors Continuous Output Internal Photoelectron Flux Thermal Filtered External Current w(t) Sensor i(t) External System
s and Laser Phase Phase Density ECE 185 Lasers and Modulators Lab - Spring 2018 1 Detectors Continuous Output Internal Photoelectron Flux Thermal Filtered External Current w(t) Sensor i(t) External System
Optical solitons and its applications
 Physics 568 (Nonlinear optics) 04/30/007 Final report Optical solitons and its applications 04/30/007 1 1 Introduction to optical soliton. (temporal soliton) The optical pulses which propagate in the lossless
Physics 568 (Nonlinear optics) 04/30/007 Final report Optical solitons and its applications 04/30/007 1 1 Introduction to optical soliton. (temporal soliton) The optical pulses which propagate in the lossless
Probing the orbital angular momentum of light with a multipoint interferometer
 CHAPTER 2 Probing the orbital angular momentum of light with a multipoint interferometer We present an efficient method for probing the orbital angular momentum of optical vortices of arbitrary sizes.
CHAPTER 2 Probing the orbital angular momentum of light with a multipoint interferometer We present an efficient method for probing the orbital angular momentum of optical vortices of arbitrary sizes.
Metrology and Sensing
 Metrology and Sensing Lecture 5: Interferometry I 07--6 Herbert Gross Winter term 07 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 9.0. Introduction Introduction, optical measurements,
Metrology and Sensing Lecture 5: Interferometry I 07--6 Herbert Gross Winter term 07 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 9.0. Introduction Introduction, optical measurements,
United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization and International Atomic Energy Agency
 IC/99/48 United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization and International Atomic Energy Agency THE ABDUS SALAM INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS SPATIAL COHERENCE AND YOUNG
IC/99/48 United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization and International Atomic Energy Agency THE ABDUS SALAM INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL PHYSICS SPATIAL COHERENCE AND YOUNG
Recent progress in SR interferometer
 Recent progress in SR interferometer -for small beam size measurement- T. Mitsuhashi, KEK Agenda 1. Brief introduction of beam size measurement through SR interferometry. 2. Theoretical resolution of interferometry
Recent progress in SR interferometer -for small beam size measurement- T. Mitsuhashi, KEK Agenda 1. Brief introduction of beam size measurement through SR interferometry. 2. Theoretical resolution of interferometry
Phononic Crystals. J.H. Page
 Phononic Crystals J.H. Page University of Manitoba with Suxia Yang and M.L. Cowan at U of M, Ping Sheng and C.T. Chan at HKUST, & Zhengyou Liu at Wuhan University. We study ultrasonic waves in complex
Phononic Crystals J.H. Page University of Manitoba with Suxia Yang and M.L. Cowan at U of M, Ping Sheng and C.T. Chan at HKUST, & Zhengyou Liu at Wuhan University. We study ultrasonic waves in complex
Spectrally controlled source for interferometric measurements of multiple surface cavities Jan Posthumus 1,2
 Spectrally controlled source for interferometric measurements of multiple surface cavities Jan Posthumus 1,2 Chase Salsbury 1,3, Artur Olszak 1 [1] Äpre Instruments, LLC [2] Laser Peak, GmbH [3] College
Spectrally controlled source for interferometric measurements of multiple surface cavities Jan Posthumus 1,2 Chase Salsbury 1,3, Artur Olszak 1 [1] Äpre Instruments, LLC [2] Laser Peak, GmbH [3] College
Chapter 16 Holography
 Chapter 16 Holography Virtually all recording devices for light respond to light intensity. Problem: How to record, and then later reconstruct both the amplitude and phase of an optical wave. [This question
Chapter 16 Holography Virtually all recording devices for light respond to light intensity. Problem: How to record, and then later reconstruct both the amplitude and phase of an optical wave. [This question
Introduction to FT-IR Spectroscopy
 Introduction to FT-IR Spectroscopy An FT-IR Spectrometer is an instrument which acquires broadband NIR to FIR spectra. Unlike a dispersive instrument, i.e. grating monochromator or spectrograph, an FT-IR
Introduction to FT-IR Spectroscopy An FT-IR Spectrometer is an instrument which acquires broadband NIR to FIR spectra. Unlike a dispersive instrument, i.e. grating monochromator or spectrograph, an FT-IR
Supplementary Figure 1: Example non-overlapping, binary probe functions P1 (~q) and P2 (~q), that add to form a top hat function A(~q).
 Supplementary Figures P(q) A(q) + Function Value P(q) qmax = Supplementary Figure : Example non-overlapping, binary probe functions P (~q) and P (~q), that add to form a top hat function A(~q). qprobe
Supplementary Figures P(q) A(q) + Function Value P(q) qmax = Supplementary Figure : Example non-overlapping, binary probe functions P (~q) and P (~q), that add to form a top hat function A(~q). qprobe
Resolution improvement in optical coherence tomography with segmented spectrum management
 Optical and Quantum Electronics (2005) 37:1165 1173 Springer 2006 DOI 10.1007/s11082-005-4188-3 Resolution improvement in optical coherence tomography with segmented spectrum management chih-wei lu, meng-tsan
Optical and Quantum Electronics (2005) 37:1165 1173 Springer 2006 DOI 10.1007/s11082-005-4188-3 Resolution improvement in optical coherence tomography with segmented spectrum management chih-wei lu, meng-tsan
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
Using dispersion-induced group delay to solve the integer ambiguity problem: a theoretical analysis
 J. Eur. Opt. Soc.-Rapid 10, 15035 (2015) www.jeos.org Using dispersion-induced group delay to solve the integer ambiguity problem: a theoretical analysis D. Wei weidong@mech.nagaokaut.ac.jp Department
J. Eur. Opt. Soc.-Rapid 10, 15035 (2015) www.jeos.org Using dispersion-induced group delay to solve the integer ambiguity problem: a theoretical analysis D. Wei weidong@mech.nagaokaut.ac.jp Department
Low-coherence heterodyne photon correlation spectroscopy
 Low-coherence heterodyne photon correlation spectroscopy J.H. Johnson, S.L. Siefken, A. Schmidt, R. Corey, and P. Saulnier Department of Physics, Gustavus Adolphus College Saint Peter, MN 56082 ABSTRACT
Low-coherence heterodyne photon correlation spectroscopy J.H. Johnson, S.L. Siefken, A. Schmidt, R. Corey, and P. Saulnier Department of Physics, Gustavus Adolphus College Saint Peter, MN 56082 ABSTRACT
Low Coherence Optic Source Characterization
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Low Coherence Optic Source Characterization To cite this article: C E Flores-Domínguez et al 15 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 58 143 View the article online for
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Low Coherence Optic Source Characterization To cite this article: C E Flores-Domínguez et al 15 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 58 143 View the article online for
WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
 WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Optical Metrology and NDT ME-593L, C 018 Introduction: Wave Optics January 018 Wave optics: light waves Wave equation An optical wave --
WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Optical Metrology and NDT ME-593L, C 018 Introduction: Wave Optics January 018 Wave optics: light waves Wave equation An optical wave --
Interference- Michelson Interferometer. Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam
 Interference- Michelson Interferometer Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam * Measurement of the coherence length of a spectral line * Measurement of thickness of thin transparent flakes * Measurement
Interference- Michelson Interferometer Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam * Measurement of the coherence length of a spectral line * Measurement of thickness of thin transparent flakes * Measurement
FT-IR Spectroscopy. An introduction in measurement techniques and interpretation
 FT-IR Spectroscopy An introduction in measurement techniques and interpretation History Albert Abraham Michelson (1852-1931) Devised Michelson Interferometer with Edward Morley in 1880 (Michelson-Morley
FT-IR Spectroscopy An introduction in measurement techniques and interpretation History Albert Abraham Michelson (1852-1931) Devised Michelson Interferometer with Edward Morley in 1880 (Michelson-Morley
HYDROBETA: A NEW INSTRUMENT FOR MEASURING IN-SITU PROFILES OF THE VOLUME SCATTERING FUNCTION FROM 10 TO 170 DEGREES
 HYDROBETA: A NEW INSTRUMENT FOR MEASURING IN-SITU PROFILES OF THE VOLUME SCATTERING FUNCTION FROM 10 TO 170 DEGREES David R. Dana, Robert A. Maffione Hydro-Optics, Biology and Instrumentation Laboratories,
HYDROBETA: A NEW INSTRUMENT FOR MEASURING IN-SITU PROFILES OF THE VOLUME SCATTERING FUNCTION FROM 10 TO 170 DEGREES David R. Dana, Robert A. Maffione Hydro-Optics, Biology and Instrumentation Laboratories,
TA/TI survey. Phy Phy
 TA/TI survey https://webapps.pas.rochester.edu/secure/phpq/ Phy121 7 60 73 Phy123 1 6 11 Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference Units of Chapter 34 34-5 Interference in Thin Films 34-6 Michelson
TA/TI survey https://webapps.pas.rochester.edu/secure/phpq/ Phy121 7 60 73 Phy123 1 6 11 Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference Units of Chapter 34 34-5 Interference in Thin Films 34-6 Michelson
Restoring dispersion cancellation for entangled photons produced by ultrashort pulses
 Restoring dispersion cancellation for entangled photons produced by ultrashort pulses Reinhard Erdmann* Air Force Research Laboratory, SNDP, Rome, New York 13441 David Branning NIST, 1 Bureau Drive, Stop
Restoring dispersion cancellation for entangled photons produced by ultrashort pulses Reinhard Erdmann* Air Force Research Laboratory, SNDP, Rome, New York 13441 David Branning NIST, 1 Bureau Drive, Stop
A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging. Outline
 A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging Outline General Goals Linear Imaging Systems An Example, The Pin Hole Camera Radiations and Their Interactions with Matter Coherent vs. Incoherent Imaging Length
A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging Outline General Goals Linear Imaging Systems An Example, The Pin Hole Camera Radiations and Their Interactions with Matter Coherent vs. Incoherent Imaging Length
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Time: March 10, 006, -3:30pm MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.097 (UG) Fundamentals of Photonics 6.974 (G) Quantum Electronics Spring 006
Time: March 10, 006, -3:30pm MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.097 (UG) Fundamentals of Photonics 6.974 (G) Quantum Electronics Spring 006
