Multivariate Gaussian Analysis
|
|
|
- Beverly Ramsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BS2 Statistical Inference, Lecture 7, Hilary Term 2009 February 13, 2009
2 Marginal and conditional distributions For a positive definite covariance matrix Σ, the multivariate Gaussian distribution has density on R d f (x ξ, Σ) = (2π) d/2 (det K) 1/2 e (x ξ) K(x ξ)/2, (1) where K = Σ 1 is the concentration matrix of the distribution. If X 1 N d (ξ 1, Σ 1 ) and X 2 N d (ξ 2, Σ 2 ) and X 1 X 2 X 1 + X 2 N d (ξ 1 + ξ 2, Σ 1 + Σ 2 ). If A is an r d matrix, b R r and X N d (ξ, Σ), then Y = AX + b N r (Aξ + b, AΣA ).
3 Marginal and conditional distributions Partition X into X 1 and X 2, where X 1 R r and X 2 R s with r + s = d and partition mean vector, concentration and covariance matrix accordingly. Then, if X N d (ξ, Σ) X 2 N s (ξ 2, Σ 22 ). If Σ 22 is regular, it further holds that where X 1 X 2 = x 2 N r (ξ 1 2, Σ 1 2 ), ξ 1 2 = ξ 1 + Σ 12 Σ 1 22 (x 2 ξ 2 ) and Σ 1 2 = Σ 11 Σ 12 Σ 1 22 Σ 21. In particular, if Σ 12 = 0 if and only if X 1 and X 2 are independent.
4 Marginal and conditional distributions From the matrix identities and K 1 11 = Σ 11 Σ 12 Σ 1 22 Σ 21 = Σ 1 2 (2) K 1 11 K 12 = Σ 12 Σ 1 22, (3) it follows that then the conditional expectation and concentrations also can be calculated as ξ 1 2 = ξ 1 K 1 11 K 12(x 2 ξ 2 ) and K 1 2 = K 11. Note that the marginal covariance is simply expressed in terms of Σ where as the conditional concentration is simply expressed in terms of K.
5 Trace of matrix Sample with known mean Maximizing the likelihood A square matrix A has trace tr(a) = i a ii. The trace has a number of properties: 1. tr(γa + µb) = γ tr(a) + µ tr(b) for γ, µ being scalars; 2. tr(a) = tr(a ); 3. tr(ab) = tr(ba) 4. tr(a) = i λ i where λ i are the eigenvalues of A.
6 Trace of matrix Sample with known mean Maximizing the likelihood For symmetric matrices the last statement follows from taking an orthogonal matrix O so that OAO = diag(λ 1,..., λ d ) and using tr(oao ) = tr(ao O) = tr(a). The trace is thus orthogonally invariant, as is the determinant: det(oao ) = det(o) det(a) det(o ) = 1 det(a)1 = det(a). There is an important trick that we shall use again and again: For λ R d λ Aλ = tr(λ Aλ) = tr(aλλ ) since λ Aλ is a scalar.
7 Trace of matrix Sample with known mean Maximizing the likelihood Consider first the case where ξ = 0 and a sample X 1 = x 1,..., X n = x n from a multivariate Gaussian distribution N d (0, Σ) with Σ regular. Using (1), we get the likelihood function where L(K) = (2π) nd/2 (det K) n/2 e n ν=1 x ν Kxν /2 (det K) n/2 e n ν=1 tr{kxνx ν }/2 = (det K) n/2 e tr{k n ν=1 xνx ν }/2 = (det K) n/2 e tr(kw)/2. (4) W = n X ν Xν = X X, ν=1 is the matrix of sums of squares and products. Here we have let X be the n d matrix with rows equal to X ν.
8 Trace of matrix Sample with known mean Maximizing the likelihood Writing the trace out tr(kw ) = i k ij W ji j emphasizes that it is linear in both K and W and we can recognize this as a linear and canonical exponential family with K as the canonical parameter and W /2 as the canonical sufficient statistic. Thus, the likelihood equation becomes E( W /2) == nσ/2 = W /2 since E(W ) = nσ. Solving, we get ˆK 1 = ˆΣ = W /n in analogy with the univariate case.
9 Trace of matrix Sample with known mean Maximizing the likelihood Rewriting the likelihood function as log L(K) = n log(det K) tr(kw )/2 2 we can of course also differentiate to find the maximum, leading to k ij log(det K) = w ij /n, which in combination with the previous result yields K log(det K) = K 1. The latter can also be derived directly by writing out the determinant, and it holds for any non-singular square matrix, i.e. one which is not necessarily positive definite.
10 Definition Wishart density Partioning the Wishart distribution is the sampling distribution of the matrix of sums of squares and products. More precisely: A random d d matrix W has a d-dimensional Wishart distribution with parameter Σ and n degrees of freedom if W D = n X ν Xν i=1 where X ν N d (0, Σ). We then write W W d (n, Σ). The Wishart is the multivariate analogue to the χ 2 : W 1 (n, σ 2 ) = σ 2 χ 2 (n). If W W d (n, Σ) its mean is E(W ) = nσ.
11 Definition Wishart density Partioning the Wishart distribution If W 1 and W 2 are independent with W i W d (n i, Σ), then W 1 + W 2 W d (n 1 + n 2, Σ). If A is an r d matrix and W W d (n, Σ), then AWA W r (n, AΣA ). For r = 1 we get that when W W d (n, Σ) and λ R d, λ W λ σλ 2 χ2 (n), where σλ 2 = λ Σλ.
12 Definition Wishart density Partioning the Wishart distribution If W W d (n, Σ), where Σ is regular, then W is regular with probability one if and only if n d. When n d the Wishart distribution has density f d (w n, Σ) = c(d, n) 1 (det Σ) n/2 (det w) (n d 1)/2 e tr(σ 1 w)/2 for w positive definite, and 0 otherwise. The Wishart constant c(d, n) is c(d, n) = 2 nd/2 (2π) d(d 1)/4 d Γ{(n + 1 i)/2}. i=1
13 Definition Wishart density Partioning the Wishart distribution Let X 1,..., X n be independent and identically distributed as N d (ξ, Σ). Let X be the n d matrix with rows equal to Xi assume that Π 1,..., Π k are n n matrices for orthogonal projections onto subspaces L 1,..., L k of R n, that is, and Then, if Π i ξ = 0 we have Π u Π v = δ uv Π u and Π u = Π u. W u = X Π u X W d (f i, Σ), where f u = dim L u = rank Π u = tr Π u. Further, W 1,..., W k are independent.
14 Definition Wishart density Partioning the Wishart distribution Let W W d (n, Σ) with Σ regular and n > d. Then W 22 is regular with probability one and (i) W 1 2 is independent of (W 12, W 22 );
15 Definition Wishart density Partioning the Wishart distribution Let W W d (n, Σ) with Σ regular and n > d. Then W 22 is regular with probability one and (i) W 1 2 is independent of (W 12, W 22 ); (ii) W 1 2 W r (n s, Σ 1 2 );
16 Definition Wishart density Partioning the Wishart distribution Let W W d (n, Σ) with Σ regular and n > d. Then W 22 is regular with probability one and (i) W 1 2 is independent of (W 12, W 22 ); (ii) W 1 2 W r (n s, Σ 1 2 ); (iii) W 22 W s (n, Σ 22 );
17 Definition Wishart density Partioning the Wishart distribution Let W W d (n, Σ) with Σ regular and n > d. Then W 22 is regular with probability one and (i) W 1 2 is independent of (W 12, W 22 ); (ii) W 1 2 W r (n s, Σ 1 2 ); (iii) W 22 W s (n, Σ 22 ); (iv) The conditional distribution of W 12 given W 22 = w 22 is multivariate Gaussian N r s (Σ 12 Σ 1 22 w 22, Λ) where Λ ij,kl = Cov(W ij, W kl W 22 = w 22 ) = w jl σ 1 2 ik w jl.
18 Definition Wishart density Partioning the Wishart distribution In the special case with Σ 12 = 0 this can be simplified to W 1 2 W r (n s, Σ 11 ) and with Λ ij,kl = σ ik w jl. W 12 W 22 = w 22 N r s (0, Λ) It follows that in this case, i.e. when Σ 12 = 0, it holds that cf. Problem sheet 4. W 12 W 1 22 W 21 W r (s, Σ 11 ),
Decomposable and Directed Graphical Gaussian Models
 Decomposable Decomposable and Directed Graphical Gaussian Models Graphical Models and Inference, Lecture 13, Michaelmas Term 2009 November 26, 2009 Decomposable Definition Basic properties Wishart density
Decomposable Decomposable and Directed Graphical Gaussian Models Graphical Models and Inference, Lecture 13, Michaelmas Term 2009 November 26, 2009 Decomposable Definition Basic properties Wishart density
Wilks Λ and Hotelling s T 2.
 Wilks Λ and. Steffen Lauritzen, University of Oxford BS2 Statistical Inference, Lecture 13, Hilary Term 2008 March 2, 2008 If X and Y are independent, X Γ(α x, γ), and Y Γ(α y, γ), then the ratio X /(X
Wilks Λ and. Steffen Lauritzen, University of Oxford BS2 Statistical Inference, Lecture 13, Hilary Term 2008 March 2, 2008 If X and Y are independent, X Γ(α x, γ), and Y Γ(α y, γ), then the ratio X /(X
Inverse Wishart Distribution and Conjugate Bayesian Analysis
 Inverse Wishart Distribution and Conjugate Bayesian Analysis BS2 Statistical Inference, Lecture 14, Hilary Term 2008 March 2, 2008 Definition Testing for independence Hotelling s T 2 If W 1 W d (f 1, Σ)
Inverse Wishart Distribution and Conjugate Bayesian Analysis BS2 Statistical Inference, Lecture 14, Hilary Term 2008 March 2, 2008 Definition Testing for independence Hotelling s T 2 If W 1 W d (f 1, Σ)
MA 1B ANALYTIC - HOMEWORK SET 7 SOLUTIONS
 MA 1B ANALYTIC - HOMEWORK SET 7 SOLUTIONS 1. (7 pts)[apostol IV.8., 13, 14] (.) Let A be an n n matrix with characteristic polynomial f(λ). Prove (by induction) that the coefficient of λ n 1 in f(λ) is
MA 1B ANALYTIC - HOMEWORK SET 7 SOLUTIONS 1. (7 pts)[apostol IV.8., 13, 14] (.) Let A be an n n matrix with characteristic polynomial f(λ). Prove (by induction) that the coefficient of λ n 1 in f(λ) is
Linear Algebra Formulas. Ben Lee
 Linear Algebra Formulas Ben Lee January 27, 2016 Definitions and Terms Diagonal: Diagonal of matrix A is a collection of entries A ij where i = j. Diagonal Matrix: A matrix (usually square), where entries
Linear Algebra Formulas Ben Lee January 27, 2016 Definitions and Terms Diagonal: Diagonal of matrix A is a collection of entries A ij where i = j. Diagonal Matrix: A matrix (usually square), where entries
Gaussian Models (9/9/13)
 STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Gaussian Models (9/9/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: Xi He, Jiangwei Pan, Ali Razeen, Animesh Srivastava 1 Multivariate Normal Distribution The multivariate
STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Gaussian Models (9/9/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: Xi He, Jiangwei Pan, Ali Razeen, Animesh Srivastava 1 Multivariate Normal Distribution The multivariate
ANOVA: Analysis of Variance - Part I
 ANOVA: Analysis of Variance - Part I The purpose of these notes is to discuss the theory behind the analysis of variance. It is a summary of the definitions and results presented in class with a few exercises.
ANOVA: Analysis of Variance - Part I The purpose of these notes is to discuss the theory behind the analysis of variance. It is a summary of the definitions and results presented in class with a few exercises.
Math 489AB Exercises for Chapter 1 Fall Section 1.0
 Math 489AB Exercises for Chapter 1 Fall 2008 Section 1.0 1.0.2 We want to maximize x T Ax subject to the condition x T x = 1. We use the method of Lagrange multipliers. Let f(x) = x T Ax and g(x) = x T
Math 489AB Exercises for Chapter 1 Fall 2008 Section 1.0 1.0.2 We want to maximize x T Ax subject to the condition x T x = 1. We use the method of Lagrange multipliers. Let f(x) = x T Ax and g(x) = x T
1 Data Arrays and Decompositions
 1 Data Arrays and Decompositions 1.1 Variance Matrices and Eigenstructure Consider a p p positive definite and symmetric matrix V - a model parameter or a sample variance matrix. The eigenstructure is
1 Data Arrays and Decompositions 1.1 Variance Matrices and Eigenstructure Consider a p p positive definite and symmetric matrix V - a model parameter or a sample variance matrix. The eigenstructure is
Common-Knowledge / Cheat Sheet
 CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Fall 2018 Common-Knowledge / Cheat Sheet 1 Randomized Algorithm Expectation: For a random variable X with domain, the discrete set S, E [X] = s S P [X = s]
CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Fall 2018 Common-Knowledge / Cheat Sheet 1 Randomized Algorithm Expectation: For a random variable X with domain, the discrete set S, E [X] = s S P [X = s]
Likelihood Analysis of Gaussian Graphical Models
 Faculty of Science Likelihood Analysis of Gaussian Graphical Models Ste en Lauritzen Department of Mathematical Sciences Minikurs TUM 2016 Lecture 2 Slide 1/43 Overview of lectures Lecture 1 Markov Properties
Faculty of Science Likelihood Analysis of Gaussian Graphical Models Ste en Lauritzen Department of Mathematical Sciences Minikurs TUM 2016 Lecture 2 Slide 1/43 Overview of lectures Lecture 1 Markov Properties
Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining 1 (VO) ( )
 Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining 1 (VO) (707.003) Review of Linear Algebra Denis Helic KTI, TU Graz Oct 9, 2014 Denis Helic (KTI, TU Graz) KDDM1 Oct 9, 2014 1 / 74 Big picture: KDDM Probability Theory
Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining 1 (VO) (707.003) Review of Linear Algebra Denis Helic KTI, TU Graz Oct 9, 2014 Denis Helic (KTI, TU Graz) KDDM1 Oct 9, 2014 1 / 74 Big picture: KDDM Probability Theory
Linear Algebra Review
 January 29, 2013 Table of contents Metrics Metric Given a space X, then d : X X R + 0 and z in X if: d(x, y) = 0 is equivalent to x = y d(x, y) = d(y, x) d(x, y) d(x, z) + d(z, y) is a metric is for all
January 29, 2013 Table of contents Metrics Metric Given a space X, then d : X X R + 0 and z in X if: d(x, y) = 0 is equivalent to x = y d(x, y) = d(y, x) d(x, y) d(x, z) + d(z, y) is a metric is for all
Math Camp II. Basic Linear Algebra. Yiqing Xu. Aug 26, 2014 MIT
 Math Camp II Basic Linear Algebra Yiqing Xu MIT Aug 26, 2014 1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations 2 Vectors and Vector Spaces 3 Matrices 4 Least Squares Systems of Linear Equations Definition A linear
Math Camp II Basic Linear Algebra Yiqing Xu MIT Aug 26, 2014 1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations 2 Vectors and Vector Spaces 3 Matrices 4 Least Squares Systems of Linear Equations Definition A linear
Recall the convention that, for us, all vectors are column vectors.
 Some linear algebra Recall the convention that, for us, all vectors are column vectors. 1. Symmetric matrices Let A be a real matrix. Recall that a complex number λ is an eigenvalue of A if there exists
Some linear algebra Recall the convention that, for us, all vectors are column vectors. 1. Symmetric matrices Let A be a real matrix. Recall that a complex number λ is an eigenvalue of A if there exists
MATRICES ARE SIMILAR TO TRIANGULAR MATRICES
 MATRICES ARE SIMILAR TO TRIANGULAR MATRICES 1 Complex matrices Recall that the complex numbers are given by a + ib where a and b are real and i is the imaginary unity, ie, i 2 = 1 In what we describe below,
MATRICES ARE SIMILAR TO TRIANGULAR MATRICES 1 Complex matrices Recall that the complex numbers are given by a + ib where a and b are real and i is the imaginary unity, ie, i 2 = 1 In what we describe below,
Lecture 18. Ramanujan Graphs continued
 Stanford University Winter 218 Math 233A: Non-constructive methods in combinatorics Instructor: Jan Vondrák Lecture date: March 8, 218 Original scribe: László Miklós Lovász Lecture 18 Ramanujan Graphs
Stanford University Winter 218 Math 233A: Non-constructive methods in combinatorics Instructor: Jan Vondrák Lecture date: March 8, 218 Original scribe: László Miklós Lovász Lecture 18 Ramanujan Graphs
Exercise Sheet 1.
 Exercise Sheet 1 You can download my lecture and exercise sheets at the address http://sami.hust.edu.vn/giang-vien/?name=huynt 1) Let A, B be sets. What does the statement "A is not a subset of B " mean?
Exercise Sheet 1 You can download my lecture and exercise sheets at the address http://sami.hust.edu.vn/giang-vien/?name=huynt 1) Let A, B be sets. What does the statement "A is not a subset of B " mean?
Lecture 23: Trace and determinants! (1) (Final lecture)
 Lecture 23: Trace and determinants! (1) (Final lecture) Travis Schedler Thurs, Dec 9, 2010 (version: Monday, Dec 13, 3:52 PM) Goals (2) Recall χ T (x) = (x λ 1 ) (x λ n ) = x n tr(t )x n 1 + +( 1) n det(t
Lecture 23: Trace and determinants! (1) (Final lecture) Travis Schedler Thurs, Dec 9, 2010 (version: Monday, Dec 13, 3:52 PM) Goals (2) Recall χ T (x) = (x λ 1 ) (x λ n ) = x n tr(t )x n 1 + +( 1) n det(t
Lecture 1 Review: Linear models have the form (in matrix notation) Y = Xβ + ε,
 2. REVIEW OF LINEAR ALGEBRA 1 Lecture 1 Review: Linear models have the form (in matrix notation) Y = Xβ + ε, where Y n 1 response vector and X n p is the model matrix (or design matrix ) with one row for
2. REVIEW OF LINEAR ALGEBRA 1 Lecture 1 Review: Linear models have the form (in matrix notation) Y = Xβ + ε, where Y n 1 response vector and X n p is the model matrix (or design matrix ) with one row for
2. Linear algebra. matrices and vectors. linear equations. range and nullspace of matrices. function of vectors, gradient and Hessian
 FE661 - Statistical Methods for Financial Engineering 2. Linear algebra Jitkomut Songsiri matrices and vectors linear equations range and nullspace of matrices function of vectors, gradient and Hessian
FE661 - Statistical Methods for Financial Engineering 2. Linear algebra Jitkomut Songsiri matrices and vectors linear equations range and nullspace of matrices function of vectors, gradient and Hessian
MATH 583A REVIEW SESSION #1
 MATH 583A REVIEW SESSION #1 BOJAN DURICKOVIC 1. Vector Spaces Very quick review of the basic linear algebra concepts (see any linear algebra textbook): (finite dimensional) vector space (or linear space),
MATH 583A REVIEW SESSION #1 BOJAN DURICKOVIC 1. Vector Spaces Very quick review of the basic linear algebra concepts (see any linear algebra textbook): (finite dimensional) vector space (or linear space),
Lecture 1 and 2: Random Spanning Trees
 Recent Advances in Approximation Algorithms Spring 2015 Lecture 1 and 2: Random Spanning Trees Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan March 31st Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny
Recent Advances in Approximation Algorithms Spring 2015 Lecture 1 and 2: Random Spanning Trees Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan March 31st Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Our starting point consists of T observations from N variables, which will be arranged in an T N matrix R,
 Principal Component Analysis (PCA) PCA is a widely used statistical tool for dimension reduction. The objective of PCA is to find common factors, the so called principal components, in form of linear combinations
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) PCA is a widely used statistical tool for dimension reduction. The objective of PCA is to find common factors, the so called principal components, in form of linear combinations
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Economics Statistics. Lecture Notes on Matrix Algebra
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Economics 14.381 Statistics Guido Kuersteiner Lecture Notes on Matrix Algebra These lecture notes summarize some basic results on matrix algebra used
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Economics 14.381 Statistics Guido Kuersteiner Lecture Notes on Matrix Algebra These lecture notes summarize some basic results on matrix algebra used
33AH, WINTER 2018: STUDY GUIDE FOR FINAL EXAM
 33AH, WINTER 2018: STUDY GUIDE FOR FINAL EXAM (UPDATED MARCH 17, 2018) The final exam will be cumulative, with a bit more weight on more recent material. This outline covers the what we ve done since the
33AH, WINTER 2018: STUDY GUIDE FOR FINAL EXAM (UPDATED MARCH 17, 2018) The final exam will be cumulative, with a bit more weight on more recent material. This outline covers the what we ve done since the
Dimension. Eigenvalue and eigenvector
 Dimension. Eigenvalue and eigenvector Math 112, week 9 Goals: Bases, dimension, rank-nullity theorem. Eigenvalue and eigenvector. Suggested Textbook Readings: Sections 4.5, 4.6, 5.1, 5.2 Week 9: Dimension,
Dimension. Eigenvalue and eigenvector Math 112, week 9 Goals: Bases, dimension, rank-nullity theorem. Eigenvalue and eigenvector. Suggested Textbook Readings: Sections 4.5, 4.6, 5.1, 5.2 Week 9: Dimension,
(a) If A is a 3 by 4 matrix, what does this tell us about its nullspace? Solution: dim N(A) 1, since rank(a) 3. Ax =
 . (5 points) (a) If A is a 3 by 4 matrix, what does this tell us about its nullspace? dim N(A), since rank(a) 3. (b) If we also know that Ax = has no solution, what do we know about the rank of A? C(A)
. (5 points) (a) If A is a 3 by 4 matrix, what does this tell us about its nullspace? dim N(A), since rank(a) 3. (b) If we also know that Ax = has no solution, what do we know about the rank of A? C(A)
Online Exercises for Linear Algebra XM511
 This document lists the online exercises for XM511. The section ( ) numbers refer to the textbook. TYPE I are True/False. Lecture 02 ( 1.1) Online Exercises for Linear Algebra XM511 1) The matrix [3 2
This document lists the online exercises for XM511. The section ( ) numbers refer to the textbook. TYPE I are True/False. Lecture 02 ( 1.1) Online Exercises for Linear Algebra XM511 1) The matrix [3 2
Stat260: Bayesian Modeling and Inference Lecture Date: February 10th, Jeffreys priors. exp 1 ) p 2
 Stat260: Bayesian Modeling and Inference Lecture Date: February 10th, 2010 Jeffreys priors Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Timothy Hunter 1 Priors for the multivariate Gaussian Consider a multivariate
Stat260: Bayesian Modeling and Inference Lecture Date: February 10th, 2010 Jeffreys priors Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Timothy Hunter 1 Priors for the multivariate Gaussian Consider a multivariate
A = 1 6 (y 1 8y 2 5y 3 ) Therefore, a general solution to this system is given by
 Mid-Term Solutions 1. Let A = 3 1 2 2 1 1 1 3 0. For which triples (y 1, y 2, y 3 ) does AX = Y have a solution? Solution. The following sequence of elementary row operations: R 1 R 1 /3, R 1 2R 1 + R
Mid-Term Solutions 1. Let A = 3 1 2 2 1 1 1 3 0. For which triples (y 1, y 2, y 3 ) does AX = Y have a solution? Solution. The following sequence of elementary row operations: R 1 R 1 /3, R 1 2R 1 + R
Notes on Random Vectors and Multivariate Normal
 MATH 590 Spring 06 Notes on Random Vectors and Multivariate Normal Properties of Random Vectors If X,, X n are random variables, then X = X,, X n ) is a random vector, with the cumulative distribution
MATH 590 Spring 06 Notes on Random Vectors and Multivariate Normal Properties of Random Vectors If X,, X n are random variables, then X = X,, X n ) is a random vector, with the cumulative distribution
Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 361 / 761 Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane.
 Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 361 / 761 Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane c Sateesh R. Mane 2018 8 Lecture 8 8.1 Matrices July 22, 2018 We shall study
Queens College, CUNY, Department of Computer Science Numerical Methods CSCI 361 / 761 Spring 2018 Instructor: Dr. Sateesh Mane c Sateesh R. Mane 2018 8 Lecture 8 8.1 Matrices July 22, 2018 We shall study
Algebra II. Paulius Drungilas and Jonas Jankauskas
 Algebra II Paulius Drungilas and Jonas Jankauskas Contents 1. Quadratic forms 3 What is quadratic form? 3 Change of variables. 3 Equivalence of quadratic forms. 4 Canonical form. 4 Normal form. 7 Positive
Algebra II Paulius Drungilas and Jonas Jankauskas Contents 1. Quadratic forms 3 What is quadratic form? 3 Change of variables. 3 Equivalence of quadratic forms. 4 Canonical form. 4 Normal form. 7 Positive
Basic Concepts in Matrix Algebra
 Basic Concepts in Matrix Algebra An column array of p elements is called a vector of dimension p and is written as x p 1 = x 1 x 2. x p. The transpose of the column vector x p 1 is row vector x = [x 1
Basic Concepts in Matrix Algebra An column array of p elements is called a vector of dimension p and is written as x p 1 = x 1 x 2. x p. The transpose of the column vector x p 1 is row vector x = [x 1
Decomposable Graphical Gaussian Models
 CIMPA Summerschool, Hammamet 2011, Tunisia September 12, 2011 Basic algorithm This simple algorithm has complexity O( V + E ): 1. Choose v 0 V arbitrary and let v 0 = 1; 2. When vertices {1, 2,..., j}
CIMPA Summerschool, Hammamet 2011, Tunisia September 12, 2011 Basic algorithm This simple algorithm has complexity O( V + E ): 1. Choose v 0 V arbitrary and let v 0 = 1; 2. When vertices {1, 2,..., j}
x. Figure 1: Examples of univariate Gaussian pdfs N (x; µ, σ 2 ).
 .8.6 µ =, σ = 1 µ = 1, σ = 1 / µ =, σ =.. 3 1 1 3 x Figure 1: Examples of univariate Gaussian pdfs N (x; µ, σ ). The Gaussian distribution Probably the most-important distribution in all of statistics
.8.6 µ =, σ = 1 µ = 1, σ = 1 / µ =, σ =.. 3 1 1 3 x Figure 1: Examples of univariate Gaussian pdfs N (x; µ, σ ). The Gaussian distribution Probably the most-important distribution in all of statistics
Mathematical Methods wk 2: Linear Operators
 John Magorrian, magog@thphysoxacuk These are work-in-progress notes for the second-year course on mathematical methods The most up-to-date version is available from http://www-thphysphysicsoxacuk/people/johnmagorrian/mm
John Magorrian, magog@thphysoxacuk These are work-in-progress notes for the second-year course on mathematical methods The most up-to-date version is available from http://www-thphysphysicsoxacuk/people/johnmagorrian/mm
MAS223 Statistical Inference and Modelling Exercises
 MAS223 Statistical Inference and Modelling Exercises The exercises are grouped into sections, corresponding to chapters of the lecture notes Within each section exercises are divided into warm-up questions,
MAS223 Statistical Inference and Modelling Exercises The exercises are grouped into sections, corresponding to chapters of the lecture notes Within each section exercises are divided into warm-up questions,
INTRODUCTION TO LIE ALGEBRAS. LECTURE 1.
 INTRODUCTION TO LIE ALGEBRAS. LECTURE 1. 1. Algebras. Derivations. Definition of Lie algebra 1.1. Algebras. Let k be a field. An algebra over k (or k-algebra) is a vector space A endowed with a bilinear
INTRODUCTION TO LIE ALGEBRAS. LECTURE 1. 1. Algebras. Derivations. Definition of Lie algebra 1.1. Algebras. Let k be a field. An algebra over k (or k-algebra) is a vector space A endowed with a bilinear
1. Select the unique answer (choice) for each problem. Write only the answer.
 MATH 5 Practice Problem Set Spring 7. Select the unique answer (choice) for each problem. Write only the answer. () Determine all the values of a for which the system has infinitely many solutions: x +
MATH 5 Practice Problem Set Spring 7. Select the unique answer (choice) for each problem. Write only the answer. () Determine all the values of a for which the system has infinitely many solutions: x +
Bayesian Model Comparison
 BS2 Statistical Inference, Lecture 11, Hilary Term 2009 February 26, 2009 Basic result An accurate approximation Asymptotic posterior distribution An integral of form I = b a e λg(y) h(y) dy where h(y)
BS2 Statistical Inference, Lecture 11, Hilary Term 2009 February 26, 2009 Basic result An accurate approximation Asymptotic posterior distribution An integral of form I = b a e λg(y) h(y) dy where h(y)
Math 520 Exam 2 Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xiao/Dumas/Liaw) Spring 2008
 Math 520 Exam 2 Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xiao/Dumas/Liaw) Spring 2008 Exam 2 will be held on Tuesday, April 8, 7-8pm in 117 MacMillan What will be covered The exam will cover material from the lectures
Math 520 Exam 2 Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xiao/Dumas/Liaw) Spring 2008 Exam 2 will be held on Tuesday, April 8, 7-8pm in 117 MacMillan What will be covered The exam will cover material from the lectures
forms Christopher Engström November 14, 2014 MAA704: Matrix factorization and canonical forms Matrix properties Matrix factorization Canonical forms
 Christopher Engström November 14, 2014 Hermitian LU QR echelon Contents of todays lecture Some interesting / useful / important of matrices Hermitian LU QR echelon Rewriting a as a product of several matrices.
Christopher Engström November 14, 2014 Hermitian LU QR echelon Contents of todays lecture Some interesting / useful / important of matrices Hermitian LU QR echelon Rewriting a as a product of several matrices.
Principal Component Analysis
 Principal Component Analysis Laurenz Wiskott Institute for Theoretical Biology Humboldt-University Berlin Invalidenstraße 43 D-10115 Berlin, Germany 11 March 2004 1 Intuition Problem Statement Experimental
Principal Component Analysis Laurenz Wiskott Institute for Theoretical Biology Humboldt-University Berlin Invalidenstraße 43 D-10115 Berlin, Germany 11 March 2004 1 Intuition Problem Statement Experimental
1. Let m 1 and n 1 be two natural numbers such that m > n. Which of the following is/are true?
 . Let m and n be two natural numbers such that m > n. Which of the following is/are true? (i) A linear system of m equations in n variables is always consistent. (ii) A linear system of n equations in
. Let m and n be two natural numbers such that m > n. Which of the following is/are true? (i) A linear system of m equations in n variables is always consistent. (ii) A linear system of n equations in
MIMO Capacities : Eigenvalue Computation through Representation Theory
 MIMO Capacities : Eigenvalue Computation through Representation Theory Jayanta Kumar Pal, Donald Richards SAMSI Multivariate distributions working group Outline 1 Introduction 2 MIMO working model 3 Eigenvalue
MIMO Capacities : Eigenvalue Computation through Representation Theory Jayanta Kumar Pal, Donald Richards SAMSI Multivariate distributions working group Outline 1 Introduction 2 MIMO working model 3 Eigenvalue
Math Camp Lecture 4: Linear Algebra. Xiao Yu Wang. Aug 2010 MIT. Xiao Yu Wang (MIT) Math Camp /10 1 / 88
 Math Camp 2010 Lecture 4: Linear Algebra Xiao Yu Wang MIT Aug 2010 Xiao Yu Wang (MIT) Math Camp 2010 08/10 1 / 88 Linear Algebra Game Plan Vector Spaces Linear Transformations and Matrices Determinant
Math Camp 2010 Lecture 4: Linear Algebra Xiao Yu Wang MIT Aug 2010 Xiao Yu Wang (MIT) Math Camp 2010 08/10 1 / 88 Linear Algebra Game Plan Vector Spaces Linear Transformations and Matrices Determinant
Linear Algebra Review. Vectors
 Linear Algebra Review 9/4/7 Linear Algebra Review By Tim K. Marks UCSD Borrows heavily from: Jana Kosecka http://cs.gmu.edu/~kosecka/cs682.html Virginia de Sa (UCSD) Cogsci 8F Linear Algebra review Vectors
Linear Algebra Review 9/4/7 Linear Algebra Review By Tim K. Marks UCSD Borrows heavily from: Jana Kosecka http://cs.gmu.edu/~kosecka/cs682.html Virginia de Sa (UCSD) Cogsci 8F Linear Algebra review Vectors
Exam 2. Jeremy Morris. March 23, 2006
 Exam Jeremy Morris March 3, 006 4. Consider a bivariate normal population with µ 0, µ, σ, σ and ρ.5. a Write out the bivariate normal density. The multivariate normal density is defined by the following
Exam Jeremy Morris March 3, 006 4. Consider a bivariate normal population with µ 0, µ, σ, σ and ρ.5. a Write out the bivariate normal density. The multivariate normal density is defined by the following
Chapter 17: Undirected Graphical Models
 Chapter 17: Undirected Graphical Models The Elements of Statistical Learning Biaobin Jiang Department of Biological Sciences Purdue University bjiang@purdue.edu October 30, 2014 Biaobin Jiang (Purdue)
Chapter 17: Undirected Graphical Models The Elements of Statistical Learning Biaobin Jiang Department of Biological Sciences Purdue University bjiang@purdue.edu October 30, 2014 Biaobin Jiang (Purdue)
Lecture 11: Regression Methods I (Linear Regression)
 Lecture 11: Regression Methods I (Linear Regression) Fall, 2017 1 / 40 Outline Linear Model Introduction 1 Regression: Supervised Learning with Continuous Responses 2 Linear Models and Multiple Linear
Lecture 11: Regression Methods I (Linear Regression) Fall, 2017 1 / 40 Outline Linear Model Introduction 1 Regression: Supervised Learning with Continuous Responses 2 Linear Models and Multiple Linear
The Wishart distribution Scaled Wishart. Wishart Priors. Patrick Breheny. March 28. Patrick Breheny BST 701: Bayesian Modeling in Biostatistics 1/11
 Wishart Priors Patrick Breheny March 28 Patrick Breheny BST 701: Bayesian Modeling in Biostatistics 1/11 Introduction When more than two coefficients vary, it becomes difficult to directly model each element
Wishart Priors Patrick Breheny March 28 Patrick Breheny BST 701: Bayesian Modeling in Biostatistics 1/11 Introduction When more than two coefficients vary, it becomes difficult to directly model each element
ELE/MCE 503 Linear Algebra Facts Fall 2018
 ELE/MCE 503 Linear Algebra Facts Fall 2018 Fact N.1 A set of vectors is linearly independent if and only if none of the vectors in the set can be written as a linear combination of the others. Fact N.2
ELE/MCE 503 Linear Algebra Facts Fall 2018 Fact N.1 A set of vectors is linearly independent if and only if none of the vectors in the set can be written as a linear combination of the others. Fact N.2
STAT 309: MATHEMATICAL COMPUTATIONS I FALL 2013 PROBLEM SET 2
 STAT 309: MATHEMATICAL COMPUTATIONS I FALL 2013 PROBLEM SET 2 1. You are not allowed to use the svd for this problem, i.e. no arguments should depend on the svd of A or A. Let W be a subspace of C n. The
STAT 309: MATHEMATICAL COMPUTATIONS I FALL 2013 PROBLEM SET 2 1. You are not allowed to use the svd for this problem, i.e. no arguments should depend on the svd of A or A. Let W be a subspace of C n. The
Background Mathematics (2/2) 1. David Barber
 Background Mathematics (2/2) 1 David Barber University College London Modified by Samson Cheung (sccheung@ieee.org) 1 These slides accompany the book Bayesian Reasoning and Machine Learning. The book and
Background Mathematics (2/2) 1 David Barber University College London Modified by Samson Cheung (sccheung@ieee.org) 1 These slides accompany the book Bayesian Reasoning and Machine Learning. The book and
Multivariate Analysis and Likelihood Inference
 Multivariate Analysis and Likelihood Inference Outline 1 Joint Distribution of Random Variables 2 Principal Component Analysis (PCA) 3 Multivariate Normal Distribution 4 Likelihood Inference Joint density
Multivariate Analysis and Likelihood Inference Outline 1 Joint Distribution of Random Variables 2 Principal Component Analysis (PCA) 3 Multivariate Normal Distribution 4 Likelihood Inference Joint density
Multivariate Statistical Analysis
 Multivariate Statistical Analysis Fall 2011 C. L. Williams, Ph.D. Lecture 4 for Applied Multivariate Analysis Outline 1 Eigen values and eigen vectors Characteristic equation Some properties of eigendecompositions
Multivariate Statistical Analysis Fall 2011 C. L. Williams, Ph.D. Lecture 4 for Applied Multivariate Analysis Outline 1 Eigen values and eigen vectors Characteristic equation Some properties of eigendecompositions
Boolean Inner-Product Spaces and Boolean Matrices
 Boolean Inner-Product Spaces and Boolean Matrices Stan Gudder Department of Mathematics, University of Denver, Denver CO 80208 Frédéric Latrémolière Department of Mathematics, University of Denver, Denver
Boolean Inner-Product Spaces and Boolean Matrices Stan Gudder Department of Mathematics, University of Denver, Denver CO 80208 Frédéric Latrémolière Department of Mathematics, University of Denver, Denver
Part IB Statistics. Theorems with proof. Based on lectures by D. Spiegelhalter Notes taken by Dexter Chua. Lent 2015
 Part IB Statistics Theorems with proof Based on lectures by D. Spiegelhalter Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
Part IB Statistics Theorems with proof Based on lectures by D. Spiegelhalter Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
ELEC E7210: Communication Theory. Lecture 10: MIMO systems
 ELEC E7210: Communication Theory Lecture 10: MIMO systems Matrix Definitions, Operations, and Properties (1) NxM matrix a rectangular array of elements a A. an 11 1....... a a 1M. NM B D C E ermitian transpose
ELEC E7210: Communication Theory Lecture 10: MIMO systems Matrix Definitions, Operations, and Properties (1) NxM matrix a rectangular array of elements a A. an 11 1....... a a 1M. NM B D C E ermitian transpose
Part 6: Multivariate Normal and Linear Models
 Part 6: Multivariate Normal and Linear Models 1 Multiple measurements Up until now all of our statistical models have been univariate models models for a single measurement on each member of a sample of
Part 6: Multivariate Normal and Linear Models 1 Multiple measurements Up until now all of our statistical models have been univariate models models for a single measurement on each member of a sample of
Linear Regression. In this problem sheet, we consider the problem of linear regression with p predictors and one intercept,
 Linear Regression In this problem sheet, we consider the problem of linear regression with p predictors and one intercept, y = Xβ + ɛ, where y t = (y 1,..., y n ) is the column vector of target values,
Linear Regression In this problem sheet, we consider the problem of linear regression with p predictors and one intercept, y = Xβ + ɛ, where y t = (y 1,..., y n ) is the column vector of target values,
MATH 307 Test 1 Study Guide
 MATH 37 Test 1 Study Guide Theoretical Portion: No calculators Note: It is essential for you to distinguish between an entire matrix C = (c i j ) and a single element c i j of the matrix. For example,
MATH 37 Test 1 Study Guide Theoretical Portion: No calculators Note: It is essential for you to distinguish between an entire matrix C = (c i j ) and a single element c i j of the matrix. For example,
Bare minimum on matrix algebra. Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models
 Bare minimum on matrix algebra Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models Matrix multiplication 2 Consider three notations for linear combinations y11 y1 m x11 x 1p b11 b 1m y y x x b b n1
Bare minimum on matrix algebra Psychology 588: Covariance structure and factor models Matrix multiplication 2 Consider three notations for linear combinations y11 y1 m x11 x 1p b11 b 1m y y x x b b n1
Review of Linear Algebra
 Review of Linear Algebra Definitions An m n (read "m by n") matrix, is a rectangular array of entries, where m is the number of rows and n the number of columns. 2 Definitions (Con t) A is square if m=
Review of Linear Algebra Definitions An m n (read "m by n") matrix, is a rectangular array of entries, where m is the number of rows and n the number of columns. 2 Definitions (Con t) A is square if m=
TEST FOR INDEPENDENCE OF THE VARIABLES WITH MISSING ELEMENTS IN ONE AND THE SAME COLUMN OF THE EMPIRICAL CORRELATION MATRIX.
 Serdica Math J 34 (008, 509 530 TEST FOR INDEPENDENCE OF THE VARIABLES WITH MISSING ELEMENTS IN ONE AND THE SAME COLUMN OF THE EMPIRICAL CORRELATION MATRIX Evelina Veleva Communicated by N Yanev Abstract
Serdica Math J 34 (008, 509 530 TEST FOR INDEPENDENCE OF THE VARIABLES WITH MISSING ELEMENTS IN ONE AND THE SAME COLUMN OF THE EMPIRICAL CORRELATION MATRIX Evelina Veleva Communicated by N Yanev Abstract
Matrices A brief introduction
 Matrices A brief introduction Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Semester 1, 2014-15 B. Bona (DAUIN) Matrices Semester 1, 2014-15 1 / 41 Definitions Definition A matrix is a set of N real or complex
Matrices A brief introduction Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Semester 1, 2014-15 B. Bona (DAUIN) Matrices Semester 1, 2014-15 1 / 41 Definitions Definition A matrix is a set of N real or complex
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder. Canberra February June 2017
 Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2017 (Many figures from C. M. Bishop, "Pattern Recognition and ") 1of 141 Part III
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2017 (Many figures from C. M. Bishop, "Pattern Recognition and ") 1of 141 Part III
Lecture 10 - Eigenvalues problem
 Lecture 10 - Eigenvalues problem Department of Computer Science University of Houston February 28, 2008 1 Lecture 10 - Eigenvalues problem Introduction Eigenvalue problems form an important class of problems
Lecture 10 - Eigenvalues problem Department of Computer Science University of Houston February 28, 2008 1 Lecture 10 - Eigenvalues problem Introduction Eigenvalue problems form an important class of problems
PRACTICE FINAL EXAM. why. If they are dependent, exhibit a linear dependence relation among them.
 Prof A Suciu MTH U37 LINEAR ALGEBRA Spring 2005 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Are the following vectors independent or dependent? If they are independent, say why If they are dependent, exhibit a linear dependence
Prof A Suciu MTH U37 LINEAR ALGEBRA Spring 2005 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Are the following vectors independent or dependent? If they are independent, say why If they are dependent, exhibit a linear dependence
Lecture 15: Multivariate normal distributions
 Lecture 15: Multivariate normal distributions Normal distributions with singular covariance matrices Consider an n-dimensional X N(µ,Σ) with a positive definite Σ and a fixed k n matrix A that is not of
Lecture 15: Multivariate normal distributions Normal distributions with singular covariance matrices Consider an n-dimensional X N(µ,Σ) with a positive definite Σ and a fixed k n matrix A that is not of
1 2 2 Circulant Matrices
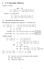 Circulant Matrices General matrix a c d Ax x ax + cx x x + dx General circulant matrix a x ax + x a x x + ax. Evaluating the Eigenvalues Find eigenvalues and eigenvectors of general circulant matrix: a
Circulant Matrices General matrix a c d Ax x ax + cx x x + dx General circulant matrix a x ax + x a x x + ax. Evaluating the Eigenvalues Find eigenvalues and eigenvectors of general circulant matrix: a
Math 18, Linear Algebra, Lecture C00, Spring 2017 Review and Practice Problems for Final Exam
 Math 8, Linear Algebra, Lecture C, Spring 7 Review and Practice Problems for Final Exam. The augmentedmatrix of a linear system has been transformed by row operations into 5 4 8. Determine if the system
Math 8, Linear Algebra, Lecture C, Spring 7 Review and Practice Problems for Final Exam. The augmentedmatrix of a linear system has been transformed by row operations into 5 4 8. Determine if the system
Problem # Max points possible Actual score Total 120
 FINAL EXAMINATION - MATH 2121, FALL 2017. Name: ID#: Email: Lecture & Tutorial: Problem # Max points possible Actual score 1 15 2 15 3 10 4 15 5 15 6 15 7 10 8 10 9 15 Total 120 You have 180 minutes to
FINAL EXAMINATION - MATH 2121, FALL 2017. Name: ID#: Email: Lecture & Tutorial: Problem # Max points possible Actual score 1 15 2 15 3 10 4 15 5 15 6 15 7 10 8 10 9 15 Total 120 You have 180 minutes to
More Linear Algebra. Edps/Soc 584, Psych 594. Carolyn J. Anderson
 More Linear Algebra Edps/Soc 584, Psych 594 Carolyn J. Anderson Department of Educational Psychology I L L I N O I S university of illinois at urbana-champaign c Board of Trustees, University of Illinois
More Linear Algebra Edps/Soc 584, Psych 594 Carolyn J. Anderson Department of Educational Psychology I L L I N O I S university of illinois at urbana-champaign c Board of Trustees, University of Illinois
A Quick Tour of Linear Algebra and Optimization for Machine Learning
 A Quick Tour of Linear Algebra and Optimization for Machine Learning Masoud Farivar January 8, 2015 1 / 28 Outline of Part I: Review of Basic Linear Algebra Matrices and Vectors Matrix Multiplication Operators
A Quick Tour of Linear Algebra and Optimization for Machine Learning Masoud Farivar January 8, 2015 1 / 28 Outline of Part I: Review of Basic Linear Algebra Matrices and Vectors Matrix Multiplication Operators
Math 21b Final Exam Thursday, May 15, 2003 Solutions
 Math 2b Final Exam Thursday, May 5, 2003 Solutions. (20 points) True or False. No justification is necessary, simply circle T or F for each statement. T F (a) If W is a subspace of R n and x is not in
Math 2b Final Exam Thursday, May 5, 2003 Solutions. (20 points) True or False. No justification is necessary, simply circle T or F for each statement. T F (a) If W is a subspace of R n and x is not in
Lecture 11: Regression Methods I (Linear Regression)
 Lecture 11: Regression Methods I (Linear Regression) 1 / 43 Outline 1 Regression: Supervised Learning with Continuous Responses 2 Linear Models and Multiple Linear Regression Ordinary Least Squares Statistical
Lecture 11: Regression Methods I (Linear Regression) 1 / 43 Outline 1 Regression: Supervised Learning with Continuous Responses 2 Linear Models and Multiple Linear Regression Ordinary Least Squares Statistical
Chapter 4 - MATRIX ALGEBRA. ... a 2j... a 2n. a i1 a i2... a ij... a in
 Chapter 4 - MATRIX ALGEBRA 4.1. Matrix Operations A a 11 a 12... a 1j... a 1n a 21. a 22.... a 2j... a 2n. a i1 a i2... a ij... a in... a m1 a m2... a mj... a mn The entry in the ith row and the jth column
Chapter 4 - MATRIX ALGEBRA 4.1. Matrix Operations A a 11 a 12... a 1j... a 1n a 21. a 22.... a 2j... a 2n. a i1 a i2... a ij... a in... a m1 a m2... a mj... a mn The entry in the ith row and the jth column
MATH 320: PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR THE FINAL AND SOLUTIONS
 MATH 320: PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR THE FINAL AND SOLUTIONS There will be eight problems on the final. The following are sample problems. Problem 1. Let F be the vector space of all real valued functions on
MATH 320: PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR THE FINAL AND SOLUTIONS There will be eight problems on the final. The following are sample problems. Problem 1. Let F be the vector space of all real valued functions on
YORK UNIVERSITY. Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH M Test #1. July 11, 2013 Solutions
 YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 222 3. M Test # July, 23 Solutions. For each statement indicate whether it is always TRUE or sometimes FALSE. Note: For
YORK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH 222 3. M Test # July, 23 Solutions. For each statement indicate whether it is always TRUE or sometimes FALSE. Note: For
The Matrix-Tree Theorem
 The Matrix-Tree Theorem Christopher Eur March 22, 2015 Abstract: We give a brief introduction to graph theory in light of linear algebra. Our results culminates in the proof of Matrix-Tree Theorem. 1 Preliminaries
The Matrix-Tree Theorem Christopher Eur March 22, 2015 Abstract: We give a brief introduction to graph theory in light of linear algebra. Our results culminates in the proof of Matrix-Tree Theorem. 1 Preliminaries
Chapter 6. Eigenvalues. Josef Leydold Mathematical Methods WS 2018/19 6 Eigenvalues 1 / 45
 Chapter 6 Eigenvalues Josef Leydold Mathematical Methods WS 2018/19 6 Eigenvalues 1 / 45 Closed Leontief Model In a closed Leontief input-output-model consumption and production coincide, i.e. V x = x
Chapter 6 Eigenvalues Josef Leydold Mathematical Methods WS 2018/19 6 Eigenvalues 1 / 45 Closed Leontief Model In a closed Leontief input-output-model consumption and production coincide, i.e. V x = x
STAT200C: Review of Linear Algebra
 Stat200C Instructor: Zhaoxia Yu STAT200C: Review of Linear Algebra 1 Review of Linear Algebra 1.1 Vector Spaces, Rank, Trace, and Linear Equations 1.1.1 Rank and Vector Spaces Definition A vector whose
Stat200C Instructor: Zhaoxia Yu STAT200C: Review of Linear Algebra 1 Review of Linear Algebra 1.1 Vector Spaces, Rank, Trace, and Linear Equations 1.1.1 Rank and Vector Spaces Definition A vector whose
Problem Set (T) If A is an m n matrix, B is an n p matrix and D is a p s matrix, then show
 MTH 0: Linear Algebra Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology - Kanpur Problem Set Problems marked (T) are for discussions in Tutorial sessions (T) If A is an m n matrix,
MTH 0: Linear Algebra Department of Mathematics and Statistics Indian Institute of Technology - Kanpur Problem Set Problems marked (T) are for discussions in Tutorial sessions (T) If A is an m n matrix,
. a m1 a mn. a 1 a 2 a = a n
 Biostat 140655, 2008: Matrix Algebra Review 1 Definition: An m n matrix, A m n, is a rectangular array of real numbers with m rows and n columns Element in the i th row and the j th column is denoted by
Biostat 140655, 2008: Matrix Algebra Review 1 Definition: An m n matrix, A m n, is a rectangular array of real numbers with m rows and n columns Element in the i th row and the j th column is denoted by
APPENDIX A. Background Mathematics. A.1 Linear Algebra. Vector algebra. Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components x 1 x 2.
 APPENDIX A Background Mathematics A. Linear Algebra A.. Vector algebra Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components 0 x x 2 B C @. A x n Definition 6 (scalar product). The scalar product
APPENDIX A Background Mathematics A. Linear Algebra A.. Vector algebra Let x denote the n-dimensional column vector with components 0 x x 2 B C @. A x n Definition 6 (scalar product). The scalar product
Orthogonal decompositions in growth curve models
 ACTA ET COMMENTATIONES UNIVERSITATIS TARTUENSIS DE MATHEMATICA Volume 4, Orthogonal decompositions in growth curve models Daniel Klein and Ivan Žežula Dedicated to Professor L. Kubáček on the occasion
ACTA ET COMMENTATIONES UNIVERSITATIS TARTUENSIS DE MATHEMATICA Volume 4, Orthogonal decompositions in growth curve models Daniel Klein and Ivan Žežula Dedicated to Professor L. Kubáček on the occasion
Miderm II Solutions To find the inverse we row-reduce the augumented matrix [I A]. In our case, we row reduce
![Miderm II Solutions To find the inverse we row-reduce the augumented matrix [I A]. In our case, we row reduce Miderm II Solutions To find the inverse we row-reduce the augumented matrix [I A]. In our case, we row reduce](/thumbs/88/117490958.jpg) Miderm II Solutions Problem. [8 points] (i) [4] Find the inverse of the matrix A = To find the inverse we row-reduce the augumented matrix [I A]. In our case, we row reduce We have A = 2 2 (ii) [2] Possibly
Miderm II Solutions Problem. [8 points] (i) [4] Find the inverse of the matrix A = To find the inverse we row-reduce the augumented matrix [I A]. In our case, we row reduce We have A = 2 2 (ii) [2] Possibly
ANALYTICAL MATHEMATICS FOR APPLICATIONS 2018 LECTURE NOTES 3
 ANALYTICAL MATHEMATICS FOR APPLICATIONS 2018 LECTURE NOTES 3 ISSUED 24 FEBRUARY 2018 1 Gaussian elimination Let A be an (m n)-matrix Consider the following row operations on A (1) Swap the positions any
ANALYTICAL MATHEMATICS FOR APPLICATIONS 2018 LECTURE NOTES 3 ISSUED 24 FEBRUARY 2018 1 Gaussian elimination Let A be an (m n)-matrix Consider the following row operations on A (1) Swap the positions any
Least-Squares Rigid Motion Using SVD
 Least-Squares igid Motion Using SVD Olga Sorkine Abstract his note summarizes the steps to computing the rigid transformation that aligns two sets of points Key words: Shape matching, rigid alignment,
Least-Squares igid Motion Using SVD Olga Sorkine Abstract his note summarizes the steps to computing the rigid transformation that aligns two sets of points Key words: Shape matching, rigid alignment,
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Rigid Body Motion Introduction + Math Review
 1 PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics Rigid Body Motion Introduction + Math Review 2 How to describe a rigid body? Rigid Body - a system of point particles fixed in space i r ij j subject to a holonomic constraint:
1 PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics Rigid Body Motion Introduction + Math Review 2 How to describe a rigid body? Rigid Body - a system of point particles fixed in space i r ij j subject to a holonomic constraint:
MATRIX ALGEBRA. or x = (x 1,..., x n ) R n. y 1 y 2. x 2. x m. y m. y = cos θ 1 = x 1 L x. sin θ 1 = x 2. cos θ 2 = y 1 L y.
 as Basics Vectors MATRIX ALGEBRA An array of n real numbers x, x,, x n is called a vector and it is written x = x x n or x = x,, x n R n prime operation=transposing a column to a row Basic vector operations
as Basics Vectors MATRIX ALGEBRA An array of n real numbers x, x,, x n is called a vector and it is written x = x x n or x = x,, x n R n prime operation=transposing a column to a row Basic vector operations
Linear algebra I Homework #1 due Thursday, Oct Show that the diagonals of a square are orthogonal to one another.
 Homework # due Thursday, Oct. 0. Show that the diagonals of a square are orthogonal to one another. Hint: Place the vertices of the square along the axes and then introduce coordinates. 2. Find the equation
Homework # due Thursday, Oct. 0. Show that the diagonals of a square are orthogonal to one another. Hint: Place the vertices of the square along the axes and then introduce coordinates. 2. Find the equation
MATH 431: FIRST MIDTERM. Thursday, October 3, 2013.
 MATH 431: FIRST MIDTERM Thursday, October 3, 213. (1) An inner product on the space of matrices. Let V be the vector space of 2 2 real matrices (that is, the algebra Mat 2 (R), but without the mulitiplicative
MATH 431: FIRST MIDTERM Thursday, October 3, 213. (1) An inner product on the space of matrices. Let V be the vector space of 2 2 real matrices (that is, the algebra Mat 2 (R), but without the mulitiplicative
1 Principal component analysis and dimensional reduction
 Linear Algebra Working Group :: Day 3 Note: All vector spaces will be finite-dimensional vector spaces over the field R. 1 Principal component analysis and dimensional reduction Definition 1.1. Given an
Linear Algebra Working Group :: Day 3 Note: All vector spaces will be finite-dimensional vector spaces over the field R. 1 Principal component analysis and dimensional reduction Definition 1.1. Given an
Testing a Normal Covariance Matrix for Small Samples with Monotone Missing Data
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 3, 009, no 54, 695-70 Testing a Normal Covariance Matrix for Small Samples with Monotone Missing Data Evelina Veleva Rousse University A Kanchev Department of Numerical
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 3, 009, no 54, 695-70 Testing a Normal Covariance Matrix for Small Samples with Monotone Missing Data Evelina Veleva Rousse University A Kanchev Department of Numerical
AMS526: Numerical Analysis I (Numerical Linear Algebra)
 AMS526: Numerical Analysis I (Numerical Linear Algebra) Lecture 1: Course Overview & Matrix-Vector Multiplication Xiangmin Jiao SUNY Stony Brook Xiangmin Jiao Numerical Analysis I 1 / 20 Outline 1 Course
AMS526: Numerical Analysis I (Numerical Linear Algebra) Lecture 1: Course Overview & Matrix-Vector Multiplication Xiangmin Jiao SUNY Stony Brook Xiangmin Jiao Numerical Analysis I 1 / 20 Outline 1 Course
Econ Slides from Lecture 8
 Econ 205 Sobel Econ 205 - Slides from Lecture 8 Joel Sobel September 1, 2010 Computational Facts 1. det AB = det BA = det A det B 2. If D is a diagonal matrix, then det D is equal to the product of its
Econ 205 Sobel Econ 205 - Slides from Lecture 8 Joel Sobel September 1, 2010 Computational Facts 1. det AB = det BA = det A det B 2. If D is a diagonal matrix, then det D is equal to the product of its
