Handbook of Stochastic Methods
|
|
|
- Wesley May
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C. W. Gardiner Handbook of Stochastic Methods for Physics, Chemistry and the Natural Sciences Third Edition With 30 Figures Springer
2 Contents 1. A Historical Introduction Motivation I 1.2 Some Historical Examples Brownian Motion Langevin's Equation Birth-Death Processes Noise in Electronic Systems Shot Noise Autocorrelation Functions and Spectra Fourier Analysis of Fluctuating Functions: Stationary Systems Johnson Noise and Nyquist's Theorem Probability Concepts Events, and Sets of Events Probabilities Probability Axioms The Meaning of P(A) The Meaning of the Axioms Random Variables Joint and Conditional Probabilities: Independence Joint Probabilities Conditional Probabilities Relationship Between Joint Probabilities of Different Orders Independence Mean Values and Probability Density Determination of Probability Density by Means of Arbitrary Functions Sets of Probability Zero Mean Values Moments, Correlations, and Covariances The Law of Large Numbers Characteristic Function Cumulant Generating Function: Correlation Functions and Cumulants Example: Cumulant of Order 4: ((^X.X^)) Significance of Cumulants Gaussian and Poissonian Probability Distributions The Gaussian Distribution 36
3 XII Contents Central Limit Theorem The Poisson Distribution Limits of Sequences of Random Variables Almost Certain Limit Mean Square Limit (Limit in the Mean) Stochastic Limit, or Limit in Probability Limit in Distribution Relationship Between Limits Markov Processes Stochastic Processes Markov Process Consistency the Chapman-Kolmogorov Equation Discrete State Spaces More General Measures Continuity in Stochastic Processes Mathematical Definition of a Continuous Markov Process Differential Chapman-Kolmogorov Equation Derivation of the Differential Chapman-Kolmogorov Equation Status of the Differential Chapman-Kolmogorov Equation Interpretation of Conditions and Results Jump Processes: The Master Equation Diffusion Processes the Fokker-Planck Equation Deterministic Processes Liouville's Equation General Processes Equations for Time Development in Initial Time Backward Equations Stationary and Homogeneous Markov Processes Ergodic Properties Homogeneous Processes Approach to a Stationary Process Autocorrelation Function for Markov Processes Examples of Markov Processes The Wiener Process The Random Walk in One Dimension Poisson Process The Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Process Random Telegraph Process The Ito Calculus and Stochastic Differential Equations Motivation Stochastic Integration Definition of the Stochastic Integral Example j W(t')dW{t') 84
4 Contents XIII The Stratonovich Integral Nonanticipating Functions Proof that dw(tf = dt and dw(t) 2+N = O Properties of the Ito Stochastic Integral Stochastic Differential Equations (SDE) Ito Stochastic Differential Equation: Definition Markov Property of the Solution of an Ito Stochastic Differential Equation Change of Variables: Ito's Formula Connection Between Fokker-Planck Equation and Stochastic Differential Equation Multivariable Systems Stratonovich's Stochastic Differential Equation Dependence on Initial Conditions and Parameters Some Examples and Solutions Coefficients Without x Dependence Multiplicative Linear White Noise Process Complex Oscillator with Noisy Frequency Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Process Conversion from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates Multivariate Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Process The General Single Variable Linear Equation Multivariable Linear Equations Time-Dependent Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Process The Fokker-Planck Equation Background Fokker-Planck Equation in One Dimension Boundary Conditions Stationary Solutions for Homogeneous Fokker-Planck Equations Examples of Stationary Solutions Boundary Conditions for the Backward Fokker-Planck Equation Eigenfunction Methods (Homogeneous Processes) Examples First Passage Times for Homogeneous Processes Probability of Exit Through a Particular End of the Interval Fokker-Planck Equations in Several Dimensions Change of Variables Boundary Conditions Stationary Solutions: Potential Conditions Detailed Balance Consequences of Detailed Balance Examples of Detailed Balance in Fokker-Planck Equations 155
5 XIV Contents Eigenfunction Methods in Many Variables Homogeneous Processes First Exit Time from a Region (Homogeneous Processes) Solutions of Mean Exit Time Problems Distribution of Exit Points Approximation Methods for Diffusion Processes Small Noise Perturbation Theories Small Noise Expansions for Stochastic Differential Equations Validity of the Expansion Stationary Solutions (Homogeneous Processes) Mean, Variance, and Time Correlation Function Failure of Small Noise Perturbation Theories Small Noise Expansion of the Fokker-Planck Equation Equations for Moments and Autocorrelation Functions Example Asymptotic Method for Stationary Distributions Adiabatic Elimination of Fast Variables Abstract Formulation in Terms of Operators and Projectors Solution Using Laplace Transform Short-Time Behaviour Boundary Conditions Systematic Perturbative Analysis White Noise Process as a Limit of Nonwhite Process Generality of the Result More General Fluctuation Equations Time Nonhomogencous Systems Effect of Time Dependence in L, Adiabatic Elimination of Fast Variables: The General Case Example: Elimination of Short-Lived Chemical Intermediates Adiabatic Elimination in Haken's Model Adiabatic Elimination of Fast Variables: A Nonlinear Case An Example with Arbitrary Nonlinear Coupling Master Equations and Jump Processes Birth-Death Master Equations One Variable Stationary Solutions Example: Chemical Reaction X ^± A A Chemical Bistable System Approximation of Master Equations by Fokker-Planck Equations Jump Process Approximation of a Diffusion Process The Kramers-Moyal Expansion Van Kampen's System Size Expansion 250
6 Contents XV Kurtz's Theorem Critical Fluctuations Boundary Conditions for Birth-Death Processes Mean First Passage Times Probability of Absorption Comparison with Fokker-Planck Equation Birth-Death Systems with Many Variables Stationary Solutions when Detailed Balance Holds Stationary Solutions Without Detailed Balance (Kirchoffs Solution) System Size Expansion and Related Expansions Some Examples X + A^±2X X^±Y^A Prey-Predator System Generating Function Equations The Poisson Representation Kinds of Poisson Representations Real Poisson Representations Complex Poisson Representations The Positive Poisson Representation Time Correlation Functions Trimolecular Reaction Third-Order Noise Spatially Distributed Systems Background Functional Fokker-Planck Equations Multivariate Master Equation Description Diffusion Continuum Form of Diffusion Master Equation Reactions and Diffusion Combined Poisson Representation Methods Spatial and Temporal Correlation Structures Reaction X^ Y Reactions B + X C,A+X 2X A Nonlinear Model with a Second-Order Phase Transition Connection Between Local and Global Descriptions Explicit Adiabatic Elimination of Inhomogeneous Modes Phase-Space Master Equation Treatment of Flow Flow as a Birth-Death Process Inclusion of Collisions the Boltzmann Master Equation Collisions and Flow Together 339
7 XVI Contents 9. Bistability, Metastability, and Escape Problems Diffusion in a Double-Well Potential (One Variable) Behaviour for D = Behaviour if/) is Very Small Exit Time Splitting Probability Decay from an Unstable State Equilibration of Populations in Each Well Kramers' Method Example: Reversible Denaturation of Chymotrypsinogen Bistability with Birth-Death Master Equations (One Variable) Bistability in Multivariable Systems Distribution of Exit Points Asymptotic Analysis of Mean Exit Time Kramers'Method in Several Dimensions Example: Brownian Motion in a Double Potential Simulation of Stochastic Differential Equations The One Variable Taylor Expansion Euier Methods Higher Orders Multiple Stochastic Integrals The Euler Algorithm Milstein Algorithm The Meaning of Weak and Strong Convergence Stability Consistency Implicit and Semi-implicit Algorithms Vector Stochastic Differential Equations Formulae and Notation Multiple Stochastic Integrals The Vector Euler Algorithm The Vector Milstein Algorithm The Strong Vector Semi-implicit Algorithm The Weak Vector Semi-implicit Algorithm Higher Order Algorithms Stochastic Partial Differential Equations Fourier Transform Methods The Interaction Picture Method Software Resources 391 References 393 Bibliography 399
8 Contents XVII Symbol Index 403 Author Index 407 Subject Index 409
Handbook of Stochastic Methods
 Springer Series in Synergetics 13 Handbook of Stochastic Methods for Physics, Chemistry and the Natural Sciences von Crispin W Gardiner Neuausgabe Handbook of Stochastic Methods Gardiner schnell und portofrei
Springer Series in Synergetics 13 Handbook of Stochastic Methods for Physics, Chemistry and the Natural Sciences von Crispin W Gardiner Neuausgabe Handbook of Stochastic Methods Gardiner schnell und portofrei
STOCHASTIC PROCESSES IN PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY
 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES IN PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY Third edition N.G. VAN KAMPEN Institute for Theoretical Physics of the University at Utrecht ELSEVIER Amsterdam Boston Heidelberg London New York Oxford Paris
STOCHASTIC PROCESSES IN PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY Third edition N.G. VAN KAMPEN Institute for Theoretical Physics of the University at Utrecht ELSEVIER Amsterdam Boston Heidelberg London New York Oxford Paris
Table of Contents [ntc]
![Table of Contents [ntc] Table of Contents [ntc]](/thumbs/93/114200514.jpg) Table of Contents [ntc] 1. Introduction: Contents and Maps Table of contents [ntc] Equilibrium thermodynamics overview [nln6] Thermal equilibrium and nonequilibrium [nln1] Levels of description in statistical
Table of Contents [ntc] 1. Introduction: Contents and Maps Table of contents [ntc] Equilibrium thermodynamics overview [nln6] Thermal equilibrium and nonequilibrium [nln1] Levels of description in statistical
Elementary Applications of Probability Theory
 Elementary Applications of Probability Theory With an introduction to stochastic differential equations Second edition Henry C. Tuckwell Senior Research Fellow Stochastic Analysis Group of the Centre for
Elementary Applications of Probability Theory With an introduction to stochastic differential equations Second edition Henry C. Tuckwell Senior Research Fellow Stochastic Analysis Group of the Centre for
Control Theory in Physics and other Fields of Science
 Michael Schulz Control Theory in Physics and other Fields of Science Concepts, Tools, and Applications With 46 Figures Sprin ger 1 Introduction 1 1.1 The Aim of Control Theory 1 1.2 Dynamic State of Classical
Michael Schulz Control Theory in Physics and other Fields of Science Concepts, Tools, and Applications With 46 Figures Sprin ger 1 Introduction 1 1.1 The Aim of Control Theory 1 1.2 Dynamic State of Classical
Applied Probability and Stochastic Processes
 Applied Probability and Stochastic Processes In Engineering and Physical Sciences MICHEL K. OCHI University of Florida A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS New York - Chichester Brisbane
Applied Probability and Stochastic Processes In Engineering and Physical Sciences MICHEL K. OCHI University of Florida A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS New York - Chichester Brisbane
EQUATION LANGEVIN. Physics, Chemistry and Electrical Engineering. World Scientific. With Applications to Stochastic Problems in. William T.
 SHANGHAI HONG WorlrfScientific Series krtonttimfjorary Chemical Physics-Vol. 27 THE LANGEVIN EQUATION With Applications to Stochastic Problems in Physics, Chemistry and Electrical Engineering Third Edition
SHANGHAI HONG WorlrfScientific Series krtonttimfjorary Chemical Physics-Vol. 27 THE LANGEVIN EQUATION With Applications to Stochastic Problems in Physics, Chemistry and Electrical Engineering Third Edition
STOCHASTIC PROCESSES FOR PHYSICISTS. Understanding Noisy Systems
 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES FOR PHYSICISTS Understanding Noisy Systems Stochastic processes are an essential part of numerous branches of physics, as well as biology, chemistry, and finance. This textbook provides
STOCHASTIC PROCESSES FOR PHYSICISTS Understanding Noisy Systems Stochastic processes are an essential part of numerous branches of physics, as well as biology, chemistry, and finance. This textbook provides
An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications
 An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications WILLIAM FELLER (1906-1970) Eugene Higgins Professor of Mathematics Princeton University VOLUME II SECOND EDITION JOHN WILEY & SONS Contents I
An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications WILLIAM FELLER (1906-1970) Eugene Higgins Professor of Mathematics Princeton University VOLUME II SECOND EDITION JOHN WILEY & SONS Contents I
NPTEL
 NPTEL Syllabus Nonequilibrium Statistical Mechanics - Video course COURSE OUTLINE Thermal fluctuations, Langevin dynamics, Brownian motion and diffusion, Fokker-Planck equations, linear response theory,
NPTEL Syllabus Nonequilibrium Statistical Mechanics - Video course COURSE OUTLINE Thermal fluctuations, Langevin dynamics, Brownian motion and diffusion, Fokker-Planck equations, linear response theory,
Random Vibrations & Failure Analysis Sayan Gupta Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Random Vibrations & Failure Analysis Sayan Gupta Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture 1: Introduction Course Objectives: The focus of this course is on gaining understanding on how to make an
Random Vibrations & Failure Analysis Sayan Gupta Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture 1: Introduction Course Objectives: The focus of this course is on gaining understanding on how to make an
Lecture 4: Introduction to stochastic processes and stochastic calculus
 Lecture 4: Introduction to stochastic processes and stochastic calculus Cédric Archambeau Centre for Computational Statistics and Machine Learning Department of Computer Science University College London
Lecture 4: Introduction to stochastic processes and stochastic calculus Cédric Archambeau Centre for Computational Statistics and Machine Learning Department of Computer Science University College London
M4A42 APPLIED STOCHASTIC PROCESSES
 M4A42 APPLIED STOCHASTIC PROCESSES G.A. Pavliotis Department of Mathematics Imperial College London, UK LECTURE 1 12/10/2009 Lectures: Mondays 09:00-11:00, Huxley 139, Tuesdays 09:00-10:00, Huxley 144.
M4A42 APPLIED STOCHASTIC PROCESSES G.A. Pavliotis Department of Mathematics Imperial College London, UK LECTURE 1 12/10/2009 Lectures: Mondays 09:00-11:00, Huxley 139, Tuesdays 09:00-10:00, Huxley 144.
Statistical Mechanics
 Franz Schwabl Statistical Mechanics Translated by William Brewer Second Edition With 202 Figures, 26 Tables, and 195 Problems 4u Springer Table of Contents 1. Basic Principles 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2
Franz Schwabl Statistical Mechanics Translated by William Brewer Second Edition With 202 Figures, 26 Tables, and 195 Problems 4u Springer Table of Contents 1. Basic Principles 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2
Path integrals for classical Markov processes
 Path integrals for classical Markov processes Hugo Touchette National Institute for Theoretical Physics (NITheP) Stellenbosch, South Africa Chris Engelbrecht Summer School on Non-Linear Phenomena in Field
Path integrals for classical Markov processes Hugo Touchette National Institute for Theoretical Physics (NITheP) Stellenbosch, South Africa Chris Engelbrecht Summer School on Non-Linear Phenomena in Field
1 Elementary probability
 1 Elementary probability Problem 1.1 (*) A coin is thrown several times. Find the probability, that at the n-th experiment: (a) Head appears for the first time (b) Head and Tail have appeared equal number
1 Elementary probability Problem 1.1 (*) A coin is thrown several times. Find the probability, that at the n-th experiment: (a) Head appears for the first time (b) Head and Tail have appeared equal number
Probability and Stochastic Processes
 Probability and Stochastic Processes A Friendly Introduction Electrical and Computer Engineers Third Edition Roy D. Yates Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey David J. Goodman New York University
Probability and Stochastic Processes A Friendly Introduction Electrical and Computer Engineers Third Edition Roy D. Yates Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey David J. Goodman New York University
ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS MATLAB
 ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS WITH MATLAB THIRD EDITION Dean G. Duffy Contents Dedication Contents Acknowledgments Author Introduction List of Definitions Chapter 1: Complex Variables 1.1 Complex Numbers
ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS WITH MATLAB THIRD EDITION Dean G. Duffy Contents Dedication Contents Acknowledgments Author Introduction List of Definitions Chapter 1: Complex Variables 1.1 Complex Numbers
Monte Carlo Methods. Handbook of. University ofqueensland. Thomas Taimre. Zdravko I. Botev. Dirk P. Kroese. Universite de Montreal
 Handbook of Monte Carlo Methods Dirk P. Kroese University ofqueensland Thomas Taimre University ofqueensland Zdravko I. Botev Universite de Montreal A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION Preface Acknowledgments
Handbook of Monte Carlo Methods Dirk P. Kroese University ofqueensland Thomas Taimre University ofqueensland Zdravko I. Botev Universite de Montreal A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION Preface Acknowledgments
C.W. Gardiner. P. Zoller. Quantum Nois e. A Handbook of Markovian and Non-Markovia n Quantum Stochastic Method s with Applications to Quantum Optics
 C.W. Gardiner P. Zoller Quantum Nois e A Handbook of Markovian and Non-Markovia n Quantum Stochastic Method s with Applications to Quantum Optics 1. A Historical Introduction 1 1.1 Heisenberg's Uncertainty
C.W. Gardiner P. Zoller Quantum Nois e A Handbook of Markovian and Non-Markovia n Quantum Stochastic Method s with Applications to Quantum Optics 1. A Historical Introduction 1 1.1 Heisenberg's Uncertainty
An Introduction to Stochastic Modeling
 F An Introduction to Stochastic Modeling Fourth Edition Mark A. Pinsky Department of Mathematics Northwestern University Evanston, Illinois Samuel Karlin Department of Mathematics Stanford University Stanford,
F An Introduction to Stochastic Modeling Fourth Edition Mark A. Pinsky Department of Mathematics Northwestern University Evanston, Illinois Samuel Karlin Department of Mathematics Stanford University Stanford,
A Short Introduction to Diffusion Processes and Ito Calculus
 A Short Introduction to Diffusion Processes and Ito Calculus Cédric Archambeau University College, London Center for Computational Statistics and Machine Learning c.archambeau@cs.ucl.ac.uk January 24,
A Short Introduction to Diffusion Processes and Ito Calculus Cédric Archambeau University College, London Center for Computational Statistics and Machine Learning c.archambeau@cs.ucl.ac.uk January 24,
Stochastic Processes. Theory for Applications. Robert G. Gallager CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Stochastic Processes Theory for Applications Robert G. Gallager CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xv Swgg&sfzoMj ybr zmjfr%cforj owf fmdy xix Acknowledgements xxi 1 Introduction and review
Stochastic Processes Theory for Applications Robert G. Gallager CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xv Swgg&sfzoMj ybr zmjfr%cforj owf fmdy xix Acknowledgements xxi 1 Introduction and review
Session 1: Probability and Markov chains
 Session 1: Probability and Markov chains 1. Probability distributions and densities. 2. Relevant distributions. 3. Change of variable. 4. Stochastic processes. 5. The Markov property. 6. Markov finite
Session 1: Probability and Markov chains 1. Probability distributions and densities. 2. Relevant distributions. 3. Change of variable. 4. Stochastic processes. 5. The Markov property. 6. Markov finite
PROBABILITY AND STOCHASTIC PROCESSES A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers
 PROBABILITY AND STOCHASTIC PROCESSES A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates Rutgers, The State University ofnew Jersey David J. Goodman Rutgers, The State University
PROBABILITY AND STOCHASTIC PROCESSES A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates Rutgers, The State University ofnew Jersey David J. Goodman Rutgers, The State University
HANDBOOK OF APPLICABLE MATHEMATICS
 HANDBOOK OF APPLICABLE MATHEMATICS Chief Editor: Walter Ledermann Volume II: Probability Emlyn Lloyd University oflancaster A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester - New York - Brisbane
HANDBOOK OF APPLICABLE MATHEMATICS Chief Editor: Walter Ledermann Volume II: Probability Emlyn Lloyd University oflancaster A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester - New York - Brisbane
5 Applying the Fokker-Planck equation
 5 Applying the Fokker-Planck equation We begin with one-dimensional examples, keeping g = constant. Recall: the FPE for the Langevin equation with η(t 1 )η(t ) = κδ(t 1 t ) is = f(x) + g(x)η(t) t = x [f(x)p
5 Applying the Fokker-Planck equation We begin with one-dimensional examples, keeping g = constant. Recall: the FPE for the Langevin equation with η(t 1 )η(t ) = κδ(t 1 t ) is = f(x) + g(x)η(t) t = x [f(x)p
Probability for Statistics and Machine Learning
 ~Springer Anirban DasGupta Probability for Statistics and Machine Learning Fundamentals and Advanced Topics Contents Suggested Courses with Diffe~ent Themes........................... xix 1 Review of Univariate
~Springer Anirban DasGupta Probability for Statistics and Machine Learning Fundamentals and Advanced Topics Contents Suggested Courses with Diffe~ent Themes........................... xix 1 Review of Univariate
Different approaches to model wind speed based on stochastic differential equations
 1 Universidad de Castilla La Mancha Different approaches to model wind speed based on stochastic differential equations Rafael Zárate-Miñano Escuela de Ingeniería Minera e Industrial de Almadén Universidad
1 Universidad de Castilla La Mancha Different approaches to model wind speed based on stochastic differential equations Rafael Zárate-Miñano Escuela de Ingeniería Minera e Industrial de Almadén Universidad
Long-Range Dependence and Self-Similarity. c Vladas Pipiras and Murad S. Taqqu
 Long-Range Dependence and Self-Similarity c Vladas Pipiras and Murad S. Taqqu January 24, 2016 Contents Contents 2 Preface 8 List of abbreviations 10 Notation 11 1 A brief overview of times series and
Long-Range Dependence and Self-Similarity c Vladas Pipiras and Murad S. Taqqu January 24, 2016 Contents Contents 2 Preface 8 List of abbreviations 10 Notation 11 1 A brief overview of times series and
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CONTENTS. Preface Preface to the First Edition
 Preface Preface to the First Edition xi xiii 1 Basic Probability Theory 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Sample Spaces and Events 3 1.3 The Axioms of Probability 7 1.4 Finite Sample Spaces and Combinatorics 15
Preface Preface to the First Edition xi xiii 1 Basic Probability Theory 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Sample Spaces and Events 3 1.3 The Axioms of Probability 7 1.4 Finite Sample Spaces and Combinatorics 15
Continuum Limit of Forward Kolmogorov Equation Friday, March 06, :04 PM
 Continuum Limit of Forward Kolmogorov Equation Friday, March 06, 2015 2:04 PM Please note that one of the equations (for ordinary Brownian motion) in Problem 1 was corrected on Wednesday night. And actually
Continuum Limit of Forward Kolmogorov Equation Friday, March 06, 2015 2:04 PM Please note that one of the equations (for ordinary Brownian motion) in Problem 1 was corrected on Wednesday night. And actually
Local vs. Nonlocal Diffusions A Tale of Two Laplacians
 Local vs. Nonlocal Diffusions A Tale of Two Laplacians Jinqiao Duan Dept of Applied Mathematics Illinois Institute of Technology Chicago duan@iit.edu Outline 1 Einstein & Wiener: The Local diffusion 2
Local vs. Nonlocal Diffusions A Tale of Two Laplacians Jinqiao Duan Dept of Applied Mathematics Illinois Institute of Technology Chicago duan@iit.edu Outline 1 Einstein & Wiener: The Local diffusion 2
Introduction to Stochastic SIR Model
 Introduction to Stochastic R Model Chiu- Yu Yang (Alex), Yi Yang R model is used to model the infection of diseases. It is short for Susceptible- Infected- Recovered. It is important to address that R
Introduction to Stochastic R Model Chiu- Yu Yang (Alex), Yi Yang R model is used to model the infection of diseases. It is short for Susceptible- Infected- Recovered. It is important to address that R
First Passage Time Calculations
 First Passage Time Calculations Friday, April 24, 2015 2:01 PM Homework 4 will be posted over the weekend; due Wednesday, May 13 at 5 PM. We'll now develop some framework for calculating properties of
First Passage Time Calculations Friday, April 24, 2015 2:01 PM Homework 4 will be posted over the weekend; due Wednesday, May 13 at 5 PM. We'll now develop some framework for calculating properties of
07. Stochastic Processes: Applications
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Nonequilibrium Statistical Physics Physics Course Materials 10-19-2015 07. Stochastic Processes: Applications Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Nonequilibrium Statistical Physics Physics Course Materials 10-19-2015 07. Stochastic Processes: Applications Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu
Introduction to nonequilibrium physics
 Introduction to nonequilibrium physics Jae Dong Noh December 18, 2016 Preface This is a note for the lecture given in the 2016 KIAS-SNU Physics Winter Camp which is held at KIAS in December 17 23, 2016.
Introduction to nonequilibrium physics Jae Dong Noh December 18, 2016 Preface This is a note for the lecture given in the 2016 KIAS-SNU Physics Winter Camp which is held at KIAS in December 17 23, 2016.
Stochastic differential equation models in biology Susanne Ditlevsen
 Stochastic differential equation models in biology Susanne Ditlevsen Introduction This chapter is concerned with continuous time processes, which are often modeled as a system of ordinary differential
Stochastic differential equation models in biology Susanne Ditlevsen Introduction This chapter is concerned with continuous time processes, which are often modeled as a system of ordinary differential
PRINCIPLES OF NONLINEAR OPTICAL SPECTROSCOPY
 PRINCIPLES OF NONLINEAR OPTICAL SPECTROSCOPY Shaul Mukamel University of Rochester Rochester, New York New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1995 Contents 1. Introduction 3 Linear versus Nonlinear Spectroscopy
PRINCIPLES OF NONLINEAR OPTICAL SPECTROSCOPY Shaul Mukamel University of Rochester Rochester, New York New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS 1995 Contents 1. Introduction 3 Linear versus Nonlinear Spectroscopy
Contents. 1 Preliminaries 3. Martingales
 Table of Preface PART I THE FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES page xv 1 Preliminaries 3 2 Martingales 9 2.1 Martingales and examples 9 2.2 Stopping times 12 2.3 The maximum inequality 13 2.4 Doob s inequality 14
Table of Preface PART I THE FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES page xv 1 Preliminaries 3 2 Martingales 9 2.1 Martingales and examples 9 2.2 Stopping times 12 2.3 The maximum inequality 13 2.4 Doob s inequality 14
Stochastic Methods. John R. Boccio
 Stochastic Methods John R. Boccio November 20, 2012 Contents 1 A Historical Introduction 1 1.1 Motivation.............................. 1 1.2 Some Historical Examples...................... 2 1.2.1 Brownian
Stochastic Methods John R. Boccio November 20, 2012 Contents 1 A Historical Introduction 1 1.1 Motivation.............................. 1 1.2 Some Historical Examples...................... 2 1.2.1 Brownian
GENERATION OF COLORED NOISE
 International Journal of Modern Physics C, Vol. 12, No. 6 (2001) 851 855 c World Scientific Publishing Company GENERATION OF COLORED NOISE LORENZ BARTOSCH Institut für Theoretische Physik, Johann Wolfgang
International Journal of Modern Physics C, Vol. 12, No. 6 (2001) 851 855 c World Scientific Publishing Company GENERATION OF COLORED NOISE LORENZ BARTOSCH Institut für Theoretische Physik, Johann Wolfgang
Preface. Preface to the Third Edition. Preface to the Second Edition. Preface to the First Edition. 1 Introduction 1
 xi Contents Preface Preface to the Third Edition Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition v vii viii ix 1 Introduction 1 I GENERAL THEORY OF OPEN QUANTUM SYSTEMS 5 Diverse limited approaches:
xi Contents Preface Preface to the Third Edition Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition v vii viii ix 1 Introduction 1 I GENERAL THEORY OF OPEN QUANTUM SYSTEMS 5 Diverse limited approaches:
Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models
 Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models Statistical regularity Properties of relative frequency
Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models Statistical regularity Properties of relative frequency
Table of contents Lecture 1: Discrete-valued random variables. Common probability distributions and their properties. Bernoulli trials. Binomial, dist
 NPTEL COURSE PHYSICAL APPLICATIONS OF STOCHASTIC PROCESSES V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 600 036, India This course comprises 9 lectures. The notes
NPTEL COURSE PHYSICAL APPLICATIONS OF STOCHASTIC PROCESSES V. Balakrishnan Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 600 036, India This course comprises 9 lectures. The notes
Gillespie s Algorithm and its Approximations. Des Higham Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Strathclyde
 Gillespie s Algorithm and its Approximations Des Higham Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Strathclyde djh@maths.strath.ac.uk The Three Lectures 1 Gillespie s algorithm and its relation
Gillespie s Algorithm and its Approximations Des Higham Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Strathclyde djh@maths.strath.ac.uk The Three Lectures 1 Gillespie s algorithm and its relation
Lecture 12: Detailed balance and Eigenfunction methods
 Miranda Holmes-Cerfon Applied Stochastic Analysis, Spring 2015 Lecture 12: Detailed balance and Eigenfunction methods Readings Recommended: Pavliotis [2014] 4.5-4.7 (eigenfunction methods and reversibility),
Miranda Holmes-Cerfon Applied Stochastic Analysis, Spring 2015 Lecture 12: Detailed balance and Eigenfunction methods Readings Recommended: Pavliotis [2014] 4.5-4.7 (eigenfunction methods and reversibility),
TIME SERIES ANALYSIS. Forecasting and Control. Wiley. Fifth Edition GWILYM M. JENKINS GEORGE E. P. BOX GREGORY C. REINSEL GRETA M.
 TIME SERIES ANALYSIS Forecasting and Control Fifth Edition GEORGE E. P. BOX GWILYM M. JENKINS GREGORY C. REINSEL GRETA M. LJUNG Wiley CONTENTS PREFACE TO THE FIFTH EDITION PREFACE TO THE FOURTH EDITION
TIME SERIES ANALYSIS Forecasting and Control Fifth Edition GEORGE E. P. BOX GWILYM M. JENKINS GREGORY C. REINSEL GRETA M. LJUNG Wiley CONTENTS PREFACE TO THE FIFTH EDITION PREFACE TO THE FOURTH EDITION
The Smoluchowski-Kramers Approximation: What model describes a Brownian particle?
 The Smoluchowski-Kramers Approximation: What model describes a Brownian particle? Scott Hottovy shottovy@math.arizona.edu University of Arizona Applied Mathematics October 7, 2011 Brown observes a particle
The Smoluchowski-Kramers Approximation: What model describes a Brownian particle? Scott Hottovy shottovy@math.arizona.edu University of Arizona Applied Mathematics October 7, 2011 Brown observes a particle
Introduction to Computational Stochastic Differential Equations
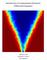 Introduction to Computational Stochastic Differential Equations Gabriel J. Lord Catherine E. Powell Tony Shardlow Preface Techniques for solving many of the differential equations traditionally used by
Introduction to Computational Stochastic Differential Equations Gabriel J. Lord Catherine E. Powell Tony Shardlow Preface Techniques for solving many of the differential equations traditionally used by
APPLIED PARTIM DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS with Fourier Series and Boundary Value Problems
 APPLIED PARTIM DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS with Fourier Series and Boundary Value Problems Fourth Edition Richard Haberman Department of Mathematics Southern Methodist University PEARSON Prentice Hall PEARSON
APPLIED PARTIM DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS with Fourier Series and Boundary Value Problems Fourth Edition Richard Haberman Department of Mathematics Southern Methodist University PEARSON Prentice Hall PEARSON
Numerical Integration of SDEs: A Short Tutorial
 Numerical Integration of SDEs: A Short Tutorial Thomas Schaffter January 19, 010 1 Introduction 1.1 Itô and Stratonovich SDEs 1-dimensional stochastic differentiable equation (SDE) is given by [6, 7] dx
Numerical Integration of SDEs: A Short Tutorial Thomas Schaffter January 19, 010 1 Introduction 1.1 Itô and Stratonovich SDEs 1-dimensional stochastic differentiable equation (SDE) is given by [6, 7] dx
Stochastic Integration (Simple Version)
 Stochastic Integration (Simple Version) Tuesday, March 17, 2015 2:03 PM Reading: Gardiner Secs. 4.1-4.3, 4.4.4 But there are boundary issues when (if ) so we can't apply the standard delta function integration
Stochastic Integration (Simple Version) Tuesday, March 17, 2015 2:03 PM Reading: Gardiner Secs. 4.1-4.3, 4.4.4 But there are boundary issues when (if ) so we can't apply the standard delta function integration
Lessons in Estimation Theory for Signal Processing, Communications, and Control
 Lessons in Estimation Theory for Signal Processing, Communications, and Control Jerry M. Mendel Department of Electrical Engineering University of Southern California Los Angeles, California PRENTICE HALL
Lessons in Estimation Theory for Signal Processing, Communications, and Control Jerry M. Mendel Department of Electrical Engineering University of Southern California Los Angeles, California PRENTICE HALL
PROBABILITY: LIMIT THEOREMS II, SPRING HOMEWORK PROBLEMS
 PROBABILITY: LIMIT THEOREMS II, SPRING 218. HOMEWORK PROBLEMS PROF. YURI BAKHTIN Instructions. You are allowed to work on solutions in groups, but you are required to write up solutions on your own. Please
PROBABILITY: LIMIT THEOREMS II, SPRING 218. HOMEWORK PROBLEMS PROF. YURI BAKHTIN Instructions. You are allowed to work on solutions in groups, but you are required to write up solutions on your own. Please
Time Series: Theory and Methods
 Peter J. Brockwell Richard A. Davis Time Series: Theory and Methods Second Edition With 124 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition vn ix CHAPTER 1 Stationary
Peter J. Brockwell Richard A. Davis Time Series: Theory and Methods Second Edition With 124 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface to the First Edition vn ix CHAPTER 1 Stationary
DATA-DRIVEN TECHNIQUES FOR ESTIMATION AND STOCHASTIC REDUCTION OF MULTI-SCALE SYSTEMS
 DATA-DRIVEN TECHNIQUES FOR ESTIMATION AND STOCHASTIC REDUCTION OF MULTI-SCALE SYSTEMS A Dissertation Presented to the Faculty of the Department of Mathematics University of Houston In Partial Fulfillment
DATA-DRIVEN TECHNIQUES FOR ESTIMATION AND STOCHASTIC REDUCTION OF MULTI-SCALE SYSTEMS A Dissertation Presented to the Faculty of the Department of Mathematics University of Houston In Partial Fulfillment
Mathematical Theory of Control Systems Design
 Mathematical Theory of Control Systems Design by V. N. Afarias'ev, V. B. Kolmanovskii and V. R. Nosov Moscow University of Electronics and Mathematics, Moscow, Russia KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS DORDRECHT
Mathematical Theory of Control Systems Design by V. N. Afarias'ev, V. B. Kolmanovskii and V. R. Nosov Moscow University of Electronics and Mathematics, Moscow, Russia KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS DORDRECHT
Dynamical Analysis of Complex Systems 7CCMCS04
 Dynamical Analysis of Complex Systems 7CCMCS04 A Annibale Department of Mathematics King s College London January 2011 2 Contents Introduction and Overview 7 0.1 Brownian Motion....................................
Dynamical Analysis of Complex Systems 7CCMCS04 A Annibale Department of Mathematics King s College London January 2011 2 Contents Introduction and Overview 7 0.1 Brownian Motion....................................
Modeling with Itô Stochastic Differential Equations
 Modeling with Itô Stochastic Differential Equations 2.4-2.6 E. Allen presentation by T. Perälä 27.0.2009 Postgraduate seminar on applied mathematics 2009 Outline Hilbert Space of Stochastic Processes (
Modeling with Itô Stochastic Differential Equations 2.4-2.6 E. Allen presentation by T. Perälä 27.0.2009 Postgraduate seminar on applied mathematics 2009 Outline Hilbert Space of Stochastic Processes (
The Kramers problem and first passage times.
 Chapter 8 The Kramers problem and first passage times. The Kramers problem is to find the rate at which a Brownian particle escapes from a potential well over a potential barrier. One method of attack
Chapter 8 The Kramers problem and first passage times. The Kramers problem is to find the rate at which a Brownian particle escapes from a potential well over a potential barrier. One method of attack
Extreme Value Theory An Introduction
 Laurens de Haan Ana Ferreira Extreme Value Theory An Introduction fi Springer Contents Preface List of Abbreviations and Symbols vii xv Part I One-Dimensional Observations 1 Limit Distributions and Domains
Laurens de Haan Ana Ferreira Extreme Value Theory An Introduction fi Springer Contents Preface List of Abbreviations and Symbols vii xv Part I One-Dimensional Observations 1 Limit Distributions and Domains
Population Games and Evolutionary Dynamics
 Population Games and Evolutionary Dynamics William H. Sandholm The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England in Brief Series Foreword Preface xvii xix 1 Introduction 1 1 Population Games 2 Population
Population Games and Evolutionary Dynamics William H. Sandholm The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England in Brief Series Foreword Preface xvii xix 1 Introduction 1 1 Population Games 2 Population
Langevin Methods. Burkhard Dünweg Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research Ackermannweg 10 D Mainz Germany
 Langevin Methods Burkhard Dünweg Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research Ackermannweg 1 D 55128 Mainz Germany Motivation Original idea: Fast and slow degrees of freedom Example: Brownian motion Replace
Langevin Methods Burkhard Dünweg Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research Ackermannweg 1 D 55128 Mainz Germany Motivation Original idea: Fast and slow degrees of freedom Example: Brownian motion Replace
06. Stochastic Processes: Concepts
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Nonequilibrium Statistical Physics Physics Course Materials 2015 06. Stochastic Processes: Concepts Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Nonequilibrium Statistical Physics Physics Course Materials 2015 06. Stochastic Processes: Concepts Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu
Approximation of Top Lyapunov Exponent of Stochastic Delayed Turning Model Using Fokker-Planck Approach
 Approximation of Top Lyapunov Exponent of Stochastic Delayed Turning Model Using Fokker-Planck Approach Henrik T. Sykora, Walter V. Wedig, Daniel Bachrathy and Gabor Stepan Department of Applied Mechanics,
Approximation of Top Lyapunov Exponent of Stochastic Delayed Turning Model Using Fokker-Planck Approach Henrik T. Sykora, Walter V. Wedig, Daniel Bachrathy and Gabor Stepan Department of Applied Mechanics,
1/f Fluctuations from the Microscopic Herding Model
 1/f Fluctuations from the Microscopic Herding Model Bronislovas Kaulakys with Vygintas Gontis and Julius Ruseckas Institute of Theoretical Physics and Astronomy Vilnius University, Lithuania www.itpa.lt/kaulakys
1/f Fluctuations from the Microscopic Herding Model Bronislovas Kaulakys with Vygintas Gontis and Julius Ruseckas Institute of Theoretical Physics and Astronomy Vilnius University, Lithuania www.itpa.lt/kaulakys
Example 4.1 Let X be a random variable and f(t) a given function of time. Then. Y (t) = f(t)x. Y (t) = X sin(ωt + δ)
 Chapter 4 Stochastic Processes 4. Definition In the previous chapter we studied random variables as functions on a sample space X(ω), ω Ω, without regard to how these might depend on parameters. We now
Chapter 4 Stochastic Processes 4. Definition In the previous chapter we studied random variables as functions on a sample space X(ω), ω Ω, without regard to how these might depend on parameters. We now
INTRODUCTION TO о JLXJLA Из А lv-/xvj_y JrJrl Y üv_>l3 Second Edition
 INTRODUCTION TO о JLXJLA Из А lv-/xvj_y JrJrl Y üv_>l3 Second Edition Kerson Huang CRC Press Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group an Informa
INTRODUCTION TO о JLXJLA Из А lv-/xvj_y JrJrl Y üv_>l3 Second Edition Kerson Huang CRC Press Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group an Informa
16. Working with the Langevin and Fokker-Planck equations
 16. Working with the Langevin and Fokker-Planck equations In the preceding Lecture, we have shown that given a Langevin equation (LE), it is possible to write down an equivalent Fokker-Planck equation
16. Working with the Langevin and Fokker-Planck equations In the preceding Lecture, we have shown that given a Langevin equation (LE), it is possible to write down an equivalent Fokker-Planck equation
Independent Component Analysis. Contents
 Contents Preface xvii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Linear representation of multivariate data 1 1.1.1 The general statistical setting 1 1.1.2 Dimension reduction methods 2 1.1.3 Independence as a guiding principle
Contents Preface xvii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Linear representation of multivariate data 1 1.1.1 The general statistical setting 1 1.1.2 Dimension reduction methods 2 1.1.3 Independence as a guiding principle
Stochastic Integration and Stochastic Differential Equations: a gentle introduction
 Stochastic Integration and Stochastic Differential Equations: a gentle introduction Oleg Makhnin New Mexico Tech Dept. of Mathematics October 26, 27 Intro: why Stochastic? Brownian Motion/ Wiener process
Stochastic Integration and Stochastic Differential Equations: a gentle introduction Oleg Makhnin New Mexico Tech Dept. of Mathematics October 26, 27 Intro: why Stochastic? Brownian Motion/ Wiener process
Quantum Dissipation: A Primer
 Quantum Dissipation: A Primer P. Hänggi Institut für Physik Universität Augsburg NOISE-INDUCED ESCAPE Reaction-rate theory: fifty years after Kramers CONTENTS Peter Hanggi Lehrstuhl fur Theoretische
Quantum Dissipation: A Primer P. Hänggi Institut für Physik Universität Augsburg NOISE-INDUCED ESCAPE Reaction-rate theory: fifty years after Kramers CONTENTS Peter Hanggi Lehrstuhl fur Theoretische
The dynamics of small particles whose size is roughly 1 µmt or. smaller, in a fluid at room temperature, is extremely erratic, and is
 1 I. BROWNIAN MOTION The dynamics of small particles whose size is roughly 1 µmt or smaller, in a fluid at room temperature, is extremely erratic, and is called Brownian motion. The velocity of such particles
1 I. BROWNIAN MOTION The dynamics of small particles whose size is roughly 1 µmt or smaller, in a fluid at room temperature, is extremely erratic, and is called Brownian motion. The velocity of such particles
PROBABILITY: LIMIT THEOREMS II, SPRING HOMEWORK PROBLEMS
 PROBABILITY: LIMIT THEOREMS II, SPRING 15. HOMEWORK PROBLEMS PROF. YURI BAKHTIN Instructions. You are allowed to work on solutions in groups, but you are required to write up solutions on your own. Please
PROBABILITY: LIMIT THEOREMS II, SPRING 15. HOMEWORK PROBLEMS PROF. YURI BAKHTIN Instructions. You are allowed to work on solutions in groups, but you are required to write up solutions on your own. Please
Accelerator Physics. Tip World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI HONG KONG TAIPEI BANGALORE. Second Edition. S. Y.
 Accelerator Physics Second Edition S. Y. Lee Department of Physics, Indiana University Tip World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI HONG KONG TAIPEI BANGALORE Contents Preface Preface
Accelerator Physics Second Edition S. Y. Lee Department of Physics, Indiana University Tip World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI HONG KONG TAIPEI BANGALORE Contents Preface Preface
Lecture 12: Detailed balance and Eigenfunction methods
 Lecture 12: Detailed balance and Eigenfunction methods Readings Recommended: Pavliotis [2014] 4.5-4.7 (eigenfunction methods and reversibility), 4.2-4.4 (explicit examples of eigenfunction methods) Gardiner
Lecture 12: Detailed balance and Eigenfunction methods Readings Recommended: Pavliotis [2014] 4.5-4.7 (eigenfunction methods and reversibility), 4.2-4.4 (explicit examples of eigenfunction methods) Gardiner
The Boltzmann Equation and Its Applications
 Carlo Cercignani The Boltzmann Equation and Its Applications With 42 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo CONTENTS PREFACE vii I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF THE KINETIC
Carlo Cercignani The Boltzmann Equation and Its Applications With 42 Illustrations Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo CONTENTS PREFACE vii I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF THE KINETIC
Homogenization with stochastic differential equations
 Homogenization with stochastic differential equations Scott Hottovy shottovy@math.arizona.edu University of Arizona Program in Applied Mathematics October 12, 2011 Modeling with SDE Use SDE to model system
Homogenization with stochastic differential equations Scott Hottovy shottovy@math.arizona.edu University of Arizona Program in Applied Mathematics October 12, 2011 Modeling with SDE Use SDE to model system
The Diffusion Approximation for Markov Processes
 The Diffusion Approximation for Markov Processes N. G. van Kampen Warem willest du dich von uns allen Und unsrer Meinung entfernen? Ich schreibe nicht, euch zu gefallen, Ihr sollt was lernen! Goethe Markov
The Diffusion Approximation for Markov Processes N. G. van Kampen Warem willest du dich von uns allen Und unsrer Meinung entfernen? Ich schreibe nicht, euch zu gefallen, Ihr sollt was lernen! Goethe Markov
Statistical Mechanics
 Statistical Mechanics Entropy, Order Parameters, and Complexity James P. Sethna Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics Cornell University, Ithaca, NY OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of figures
Statistical Mechanics Entropy, Order Parameters, and Complexity James P. Sethna Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics Cornell University, Ithaca, NY OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of figures
Tyn Myint-U Lokenath Debnath. Linear Partial Differential Equations for Scientists and Engineers. Fourth Edition. Birkhauser Boston Basel Berlin
 Tyn Myint-U Lokenath Debnath Linear Partial Differential Equations for Scientists and Engineers Fourth Edition Birkhauser Boston Basel Berlin Preface to the Fourth Edition Preface to the Third Edition
Tyn Myint-U Lokenath Debnath Linear Partial Differential Equations for Scientists and Engineers Fourth Edition Birkhauser Boston Basel Berlin Preface to the Fourth Edition Preface to the Third Edition
1 Introduction. 2 Diffusion equation and central limit theorem. The content of these notes is also covered by chapter 3 section B of [1].
![1 Introduction. 2 Diffusion equation and central limit theorem. The content of these notes is also covered by chapter 3 section B of [1]. 1 Introduction. 2 Diffusion equation and central limit theorem. The content of these notes is also covered by chapter 3 section B of [1].](/thumbs/73/68456615.jpg) 1 Introduction The content of these notes is also covered by chapter 3 section B of [1]. Diffusion equation and central limit theorem Consider a sequence {ξ i } i=1 i.i.d. ξ i = d ξ with ξ : Ω { Dx, 0,
1 Introduction The content of these notes is also covered by chapter 3 section B of [1]. Diffusion equation and central limit theorem Consider a sequence {ξ i } i=1 i.i.d. ξ i = d ξ with ξ : Ω { Dx, 0,
Biology in Time and Space: A Partial Differential Equation Approach. James P. Keener University of Utah
 Biology in Time and Space: A Partial Differential Equation Approach James P. Keener University of Utah 26 December, 2015 2 Contents I The Text 9 1 Introduction 11 2 Conservation 13 2.1 The Conservation
Biology in Time and Space: A Partial Differential Equation Approach James P. Keener University of Utah 26 December, 2015 2 Contents I The Text 9 1 Introduction 11 2 Conservation 13 2.1 The Conservation
Stochastic Partial Differential Equations with Levy Noise
 Stochastic Partial Differential Equations with Levy Noise An Evolution Equation Approach S..PESZAT and J. ZABCZYK Institute of Mathematics, Polish Academy of Sciences' CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents
Stochastic Partial Differential Equations with Levy Noise An Evolution Equation Approach S..PESZAT and J. ZABCZYK Institute of Mathematics, Polish Academy of Sciences' CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents
Lecture 21: Physical Brownian Motion II
 Lecture 21: Physical Brownian Motion II Scribe: Ken Kamrin Department of Mathematics, MIT May 3, 25 Resources An instructie applet illustrating physical Brownian motion can be found at: http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/jaa/gas2d/gas2d.html
Lecture 21: Physical Brownian Motion II Scribe: Ken Kamrin Department of Mathematics, MIT May 3, 25 Resources An instructie applet illustrating physical Brownian motion can be found at: http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/jaa/gas2d/gas2d.html
Mathematical Methods for Neurosciences. ENS - Master MVA Paris 6 - Master Maths-Bio ( )
 Mathematical Methods for Neurosciences. ENS - Master MVA Paris 6 - Master Maths-Bio (2014-2015) Etienne Tanré - Olivier Faugeras INRIA - Team Tosca November 26th, 2014 E. Tanré (INRIA - Team Tosca) Mathematical
Mathematical Methods for Neurosciences. ENS - Master MVA Paris 6 - Master Maths-Bio (2014-2015) Etienne Tanré - Olivier Faugeras INRIA - Team Tosca November 26th, 2014 E. Tanré (INRIA - Team Tosca) Mathematical
Fundamentals of Applied Probability and Random Processes
 Fundamentals of Applied Probability and Random Processes,nd 2 na Edition Oliver C. Ibe University of Massachusetts, LoweLL, Massachusetts ip^ W >!^ AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS
Fundamentals of Applied Probability and Random Processes,nd 2 na Edition Oliver C. Ibe University of Massachusetts, LoweLL, Massachusetts ip^ W >!^ AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS
Exact power spectra of Brownian motion with solid friction
 Exact power spectra of Brownian motion with solid friction Touchette, H; Prellberg, T; Just, W For additional information about this publication click this link. http://qmro.qmul.ac.uk/jspui/handle/13456789/999
Exact power spectra of Brownian motion with solid friction Touchette, H; Prellberg, T; Just, W For additional information about this publication click this link. http://qmro.qmul.ac.uk/jspui/handle/13456789/999
Boundary-Layer Theory
 Hermann Schlichting Klaus Gersten Boundary-Layer Theory With contributions from Egon Krause and Herbert Oertel Jr. Translated by Katherine Mayes 8th Revised and Enlarged Edition With 287 Figures and 22
Hermann Schlichting Klaus Gersten Boundary-Layer Theory With contributions from Egon Krause and Herbert Oertel Jr. Translated by Katherine Mayes 8th Revised and Enlarged Edition With 287 Figures and 22
Boundary. DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS with Fourier Series and. Value Problems APPLIED PARTIAL. Fifth Edition. Richard Haberman PEARSON
 APPLIED PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS with Fourier Series and Boundary Value Problems Fifth Edition Richard Haberman Southern Methodist University PEARSON Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco
APPLIED PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS with Fourier Series and Boundary Value Problems Fifth Edition Richard Haberman Southern Methodist University PEARSON Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco
Inverse Langevin approach to time-series data analysis
 Inverse Langevin approach to time-series data analysis Fábio Macêdo Mendes Anníbal Dias Figueiredo Neto Universidade de Brasília Saratoga Springs, MaxEnt 2007 Outline 1 Motivation 2 Outline 1 Motivation
Inverse Langevin approach to time-series data analysis Fábio Macêdo Mendes Anníbal Dias Figueiredo Neto Universidade de Brasília Saratoga Springs, MaxEnt 2007 Outline 1 Motivation 2 Outline 1 Motivation
M5A42 APPLIED STOCHASTIC PROCESSES
 M5A42 APPLIED STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Professor G.A. Pavliotis Department of Mathematics Imperial College London, UK LECTURE 1 06/10/2016 Lectures: Thursdays 14:00-15:00, Huxley 140, Fridays 10:00-12:00,
M5A42 APPLIED STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Professor G.A. Pavliotis Department of Mathematics Imperial College London, UK LECTURE 1 06/10/2016 Lectures: Thursdays 14:00-15:00, Huxley 140, Fridays 10:00-12:00,
Systems Driven by Alpha-Stable Noises
 Engineering Mechanics:A Force for the 21 st Century Proceedings of the 12 th Engineering Mechanics Conference La Jolla, California, May 17-20, 1998 H. Murakami and J. E. Luco (Editors) @ASCE, Reston, VA,
Engineering Mechanics:A Force for the 21 st Century Proceedings of the 12 th Engineering Mechanics Conference La Jolla, California, May 17-20, 1998 H. Murakami and J. E. Luco (Editors) @ASCE, Reston, VA,
08. Brownian Motion. University of Rhode Island. Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island,
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Nonequilibrium Statistical Physics Physics Course Materials 1-19-215 8. Brownian Motion Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu Follow this
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Nonequilibrium Statistical Physics Physics Course Materials 1-19-215 8. Brownian Motion Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu Follow this
Appendix A Definitions and Solution Techniques of SDEs
 Appendix A Definitions and Solution Techniques of SDEs Here we summarize the mathematical machinery we needed in Chapter 5. This material is from [15]. 1. Mathematical Preliminaries DEFINITION A.1 lf0.
Appendix A Definitions and Solution Techniques of SDEs Here we summarize the mathematical machinery we needed in Chapter 5. This material is from [15]. 1. Mathematical Preliminaries DEFINITION A.1 lf0.
Chapter Three Theoretical Description Of Stochastic Resonance 24
 Table of Contents List of Abbreviations and Symbols 5 Chapter One Introduction 8 1.1 The Phenomenon of the Stochastic Resonance 8 1.2 The Purpose of the Study 10 Chapter Two The Experimental Set-up 12
Table of Contents List of Abbreviations and Symbols 5 Chapter One Introduction 8 1.1 The Phenomenon of the Stochastic Resonance 8 1.2 The Purpose of the Study 10 Chapter Two The Experimental Set-up 12
AD-A1GS 323 FIRST PASSAGE TIMES IN STOCHASTIC DIFFERENTIAL - 71 EQUATIONS OF NATHENATICAL..(U) NORTHWMESTERN UNIV EVANSTON IL DEPT OF ENGINEERING
 AD-A1GS 323 FIRST PASSAGE TIMES IN STOCHASTIC DIFFERENTIAL - 71 EQUATIONS OF NATHENATICAL..(U) NORTHWMESTERN UNIV EVANSTON IL DEPT OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AIND.. UNCLASSIFIED 9 J MATKOMSKY APR 85 RFOSR-TR-85-6767
AD-A1GS 323 FIRST PASSAGE TIMES IN STOCHASTIC DIFFERENTIAL - 71 EQUATIONS OF NATHENATICAL..(U) NORTHWMESTERN UNIV EVANSTON IL DEPT OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AIND.. UNCLASSIFIED 9 J MATKOMSKY APR 85 RFOSR-TR-85-6767
Problems 5: Continuous Markov process and the diffusion equation
 Problems 5: Continuous Markov process and the diffusion equation Roman Belavkin Middlesex University Question Give a definition of Markov stochastic process. What is a continuous Markov process? Answer:
Problems 5: Continuous Markov process and the diffusion equation Roman Belavkin Middlesex University Question Give a definition of Markov stochastic process. What is a continuous Markov process? Answer:
Ergodicity for Infinite Dimensional Systems
 London Mathematical Society Lecture Note Series. 229 Ergodicity for Infinite Dimensional Systems G. DaPrato Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa J. Zabczyk Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw If CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
London Mathematical Society Lecture Note Series. 229 Ergodicity for Infinite Dimensional Systems G. DaPrato Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa J. Zabczyk Polish Academy of Sciences, Warsaw If CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
