Chapter 8 Vectors and Parametric Equations
|
|
|
- Steven Garrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 8 Vectors and Parametrc Eqatons 8- Geometrc Vectors Page 9 Check for Understandng. Sample answer: a a b b Draw a. Then draw b so that ts ntal pont (tp) s on the termnal pont (tal) of a. Draw a dashed lne from the ntal pont of a to the termnal pont of b. The dashed lne s the resltant.. Sample answer: A vector has magntde and drecton. A lne segment has onl length. A vector can be represented b a drected lne segment.. Sample answer: the veloctes of an arplane and a wnd crrent. No, the are oppostes. -. Answers ma var slghtl... cm, 6..9 cm, 7.. cm, cm,. h.9 cos v.9 sn h.66 cm v.8 cm a. b. Use the Pthagorean Theorem. c a b c () () c, c, or abot. m/s Pages 9 9 Eercses..6 cm, 8.. cm, 6.. cm, 7.. cm, 8-. Answers ma var slghtl. 8. r s cm.9 cm. cm r s 9..6 cm 7. cm, 7 cm, 9. s. cm s t t. cm,. s..6 cm, 9.8 cm, 9.8 cm s.9 cm.9 cm, Chapter 8
2 . 6. t r. cm r. cm r t.. cm, r t.9 cm r r 7.. cm, r s. cm s r.9 cm,. t. cm, 8. s r. cm. cm, 8. s. cm,. 8. cm, r s. cm 8. cm 8 s s 8. cm, 8 9. Draw to scale: t s. cm,. Draw to scale: t. cm s r. cm r t 7.7 cm, 7. h.6 cos 8 v.6 sn 8 h.6 cm v. cm. h. cos v. sn h.99 cm v.99 cm. h. cos v. sn h. cm v. cm r r t s.7 cm Chapter 8 6
3 . h. cos v. sn h.8 cm v. cm. c a b c (9.) (.) c 9.68 c or abot.7 m 6. The dfference of the vectors; sample answer: The other dagonal wold be the sm of one of the vectors and the opposte of the other vector, so t wold be the dfference. 7. Yes; sample answer: s. h 7 cos v 7 sn h 6 mph v mph. It s tre when k or when a s the ero vector.. c a b c () () c or abot 7 lb. a 6 6 b 6. cm r 8. 6 N s r s s r N r N a b eqlateral trangle a b lb. The orgn s not n the nteror of the acte angle. d d d or ) ( d or ( ) ( ) ( ) s 6. csc v cos v tan v s cos v c n v s n v sn v c os v cos v n v os v n where n s an nteger 8. 6 N, north of east 9. Sometmes; a b a b a b..7, scl b [, ] scl, for 9. tan 8 9. b b. tan 8 9 b 9.9 cm sn 8 9 h a b a a b. a b..7 h sn 8 9 h.8 cm b a. v. sn h. cos v.8 N h.9 N b. h. cos 78 v. sn 78 h. N v.7 N 7 Chapter 8
4 . v o volme of orgnal bo v n volme of new bo v o o w o h o (w ) w w (w )w w w v n n w n h n (w ) (w ) (w ) (w w )(w ) w 8w w w 8w w 6 w w o o w or 6 h o w or So, the dmensons of the orgnal bo are ft ft 6 ft. g() ( )( ) vertcal: As approaches and, the epresson approaches or. So, and are vertcal asmptotes. horontal: As ncreases postvel or negatvel, the epresson approaches. So, s a horontal asmptote.. Let,, and be consectve odd ntergers. ( ) 8 The correct answer. 8- Algebrac Vectors Pages Check for Understandng. Sample answer: a 8, 6, b 6, 8; eqal vectors have the same magntde and drecton.. Use XY ( ) ( ) and replace the vales for and. (, 6), (, ) XY [ )] ( [6)] ( (8) () 6 or 68. Jacq s correct. The representaton s ncorrect.,, s not eqal to, (),. The correct epresson s j.. MP, () or, MP () () or nts. MP, 6 or, MP () ) ( 6 nts 6. MP (9), or, MP () () nts 7. t v,,, () or, 8. t v,,,,, () or, 9. t 6 v, 6,, 6 8, 8, 6 () or,. t 8 8, 8(), 8() or 8,. 8, 6 86) ( or 8 6j. 7, (7) ) ( 7 7 j. Let T represent the force Terrell eerts. Let W represent the force Mr. Walker eerts. T cos 6 W 6 cos 69.. T sn 6 W 6 sn T 69., 6., W., 6.8 T W 6.6, 96. T W (6. 6) ) ( N Pages Eercses. YZ, 8 or, 6 YZ () 6 or Chapter 8 8
5 . YZ (), 7 or, YZ ) ( 6. YZ (), or, YZ ) ( 7. YZ, or, 7 YZ () ) ( YZ, or, YZ () 8 or 9. YZ (), 9 or, 7 YZ 7 7. YZ 7, 6 or, 6 YZ 6 or. YZ, () or 9, 9 YZ or 9. AB 6, () or, AB ) ( 69 or. a b c 6,, 8 6 (), 8 or,. a b c 6,, 8, 6, 8 (), 6 8 or 8,. a b c 6,, 8 6, 8, 6 6 (8), 6 or, 9 6. a b c 6,, 8, 6, (), 6 or, 7. a b c 6,, 8 6, 6, 6 (6), or, 9 8. a b c 6,, 8 6, 8, 6 6 (8), (6) or, 9. a b 6, 6, or 8, 9. a c, 8 (), 8 or,. a 6b c 66,, 8 6, 8 6, 6 (6), 8 or,. a.b.c.6,., 8.,..8, 9.6. (.8),. 9.6 or 7., 8.. a (b c ) (6,, 8) (, 6, ) ( (), 6 ), or,. a (b c ) b 6,, 8 6, 8, 9 (, 8, 8 (), 9 8 or,. m.n, [, 8,. [ (), 8 (.,. 6., or j 7., ) ( j 8. 6, (6) ) ( 7 6 j 9.., (.) 6. or.. j., () 7 j. 6, (6) ) ( or 6 j. ST (9), or, j. Stdent needs to show that ( v v ) v v ( v v ) ( v v ) v [a, b c, d] e, f a c, b d e, f a c e, b d f a c e, b d f a, b c e, d f a, b [c, d e, f] v ( v v ) a. N F b. sn F F sn N F 9 Chapter 8
6 a. Shore b. sn V k V k sn mph 6a. Snce QR ST, QR ST. So, the are oppostes. 6b. QR and ST have the same magntde, bt opposte drecton. So, the are parallel. Qadrlateral QRST s a parallelogram. 7a. t d r m m/ s V k or s 7b. d rt (. m/s)( s) or m 7c. V B V C.. 6 or abot. m/s 8. cos v ( ) ( ) v cos v v ) V sn v ( v ( ) v sn v 9. PQ 8, (7), PQ () RS 7 8, (7), 7 RS () 7 none. d A B C A B () 7() Srfer V s d 7) ( d or abot. 8. sn sn ( ) sn cos cos sn 6. A sn (k c) A: A 7 A 7 or 7 k: k k 8 c c: 6 k. Let a, b 6, C 6. c 6 ()(6) cos 6. c c P a b c 6 ft s (a b c) s () or 77 k s(s a)(s b)(s c) k 77(7 7 )(7 7 6)(7 7 ) k 7,,766, 79 k 86,7 sq ft. Sample answer:. 6. f() r 9 f() r [, ] scl b [, ] scl ma: (, ), mn: (.67,.8) f() f(), 99,97, 997, 97 7,,,,,, An pper bond s. Alower bond s. as, as Ths statement s tre regardless of the vale of, so t s tre for all real vales of. The correct choce s A. c 6 8 c 8 7 sn (8 8 ) Chapter 8
7 8- Vectors n Three-Dmensonal Space Pages Check for Understandng. Sample answer: sketch a coordnate sstem wth the -aes on the horontal, and the -as pontng p. Then, vector s two nts along the -as, vector j s three nts along the -as, and vector k s for nts along the -as. Draw broken lnes to represent three planes.. Sample answer: To fnd the components of the vector, o wll need the drecton (angle) wth the horontal as. Usng trgonometr, o can obtan the components of the vector.. Sample answer: Nether s correct. The sgn for the j -term mst be the same (), and the coeffcent for the k -term s, so the correct wa to epress the vector as a sm of nt vectors s j.. G(,, 7) OG ) ( RS (), 9, 8 or,, RS ) ( 6 or 9 6. RS, 7, () or 7,, RS 7 ) ( 7 or 9 7. a f g,, 8, 9,, 9,, 9,, 9 9, () or 6,, 8. a g f, 9,,, 8 6, 8,,, 6, 8 (), () or,, 8 9. EF 6 (), 6 (), 6,, j k. EF (), 7, (9),, j k.,,,97, 7 N Pages.. Eercses B(,,) OB ) ( 6 B(7,, ) OB B(,,) OB (). TM,, or,, 8 TM ) ( (8) 8 or 9 6. TM (),, 7 or,, TM () () 7 or 7. TM,, or,, TM ) ( () 8. TM, (), 6 or, 6, TM () 6 () 68 or 7 9. TM (), 8, 6 or, 9, 9 TM 9) ( (9) 7 or 9 Chapter 8
8 . TM, 6, or,, 6 TM ) ( (6). CJ (),, or, 8, ) CJ 8) ( ) ( 76 or 69. 6w 6, 6,,,, 6, 6 6,, 8 8, 6,. v w,,, 6,,,,,, 6, 6,, 8 6, 7,. v w,,, 6,, 9,, 6,, 8,. v w,,, 6,,,, 9,,, 6,, 8 6,, 6..7v. w.7,,., 6,,.,.7.,.,..,.7,. 7. w, 6,,, 8,, (,,,, 8 8. f g h,.,,, 6 6,,,, 6,, ,,, 6, 6 9. LB, 6, 7 or, 8, 8j k. LB (6),, or,, j k. LB 7 9, 7, () or,, 9 j 9k. LB 8, 7, 6 or,, j k. LB 8 (),, () or 7,, 6 7 j 6 k. LB 6 (9),, () or, 7, 7j. G G ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) G G becase ( ) ( ) for all real nmbers and. 6. If m m, m, m, then m (m ) ) (m (m. ) If m m, m, m, then m (m ) m ( ) ) (m. Snce m (m ), m (m ), and m (m ), m m. 7.,, 6,, F O 9,, 9 F O F 9,, 9 or 9,, 9 8. m (,, ) (,, 6 ) (6, 8, 8) (,, ) 9a. OK,, or,, j 9b. TK,, or,,. c b a c,,,, c,, a. 6 O 6 6 b. Fnd dstance between (,, ) and (,, ). d ( ) ( ) ( ) 67 or abot 6 feet c. sn v 6 v sn 6 7 v.. AB ( ) () ( ) or BC ( ) 6 6 or.69 AC ( ) or. No, the dstances between the ponts are not eqal. A and B are nts apart, B and C are.69 nts apart, and A and C are. nts apart..,, (),, 7 Chapter 8
9 . AB, or 8, CD d, d or d, d AB CD 8, d, d D (8, ) sn X. cos X cot X sn X cos X cos X sn X 6. cos v sn X cos X sn X c os X sn X cot X cot X cot X cot X cot X sn v cos v sn v 9 sn v 9 sn v 7. 6 sn v ampltde 6 or 6 perod k rad or rev 8. 6 m n mn rev 6 sec 8 radans per second 9. Yes, becase sbstttng 7 for and for reslts n the neqalt 8 whch s tre. (7) (7) 8. So, A, C, and D are not correct. So, B s not correct. The correct choce s E. 8- Perpendclar Vectors Pages 8 9 Check for Understandng. Sample answer: Vector v w s the negatve of vector w v. j k v w 6 7j k j k j k v w 6 7j k j k j k. a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a (a a a a ) (a a a a )j j k (a a a a ) k j k,,. Sample answer: No, becase a vector cannot be perpendclar to tself..,, 7 () (7), no. 8,., 8 8(.) (8) 6 6, es 6., 9, 8,, () 9() 8() 8 6, no j k 7.,,,, j k or,,, es,,,, () () ()(),,,, () () ()() 6 j k j k 8. 6,,,, j 6 k j k or 8,,, es 8,, 6,, 8(6) ()() ()() 8 8 8,,,, 9 8() ()() ()(9) 8 9. Sample answer: Let T(,, ), U(,, ), and V(,, ) TU,, UV,, TU UV j k 8j k or, 8, j k Chapter 8
10 . AB (.6,,.) (,, ).6,,. F,, T AB F j k j k. j k T.8 ( ).8 foot-ponds.6. Pages 9 Eercses..8 6, (6) 8(), es.,, () (), no.,, 6 () ()(6) 6, no. 7,, 7() (), no. 8, (, 8() () 6 6, no 6., 9, 6, 7, (6) 9(7) ()() 6, no 7.,,, 8, () (8) () , no 8.,, 8 6,, (6) () 8() 6 6, es 9. 7,,, 8, 7() ()(8) () 6 9, no. a b, 8,, es b c 8,, 8, no a c,, 9, no j k.,,,, j k j k or,,, es,,,, () () ()(),,,, () () ()() j k.,,,, j k 6j 9k or, 6, 9, es, 6, 9,, ()() (6)() 9() 7 87, 6, 9,, ()() (6)() 9() j k.,,,, j k j k or,,, es,,,, () () (),,,, () () () j k.,,,, j 6k or,, 6, es,, 6,, () () 6() 6,, 6,, () () 6() j k j k.,,,, 8 8j 6k or 8, 8, 6, es 8, 8, 6,, 8() 8() 6() 8 8, 8, 6,, 8() 8() 6() j k Chapter 8
11 j k 6.,, 7,, j k or,,, es,,,, () () () 8 8,, 7,, (7) () () 7. Sample answer: Let v v, v, v and v v, v, v j k j k v (v ) v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v j k j k 8. a (b c ) a a a (b c ) (b c ) (b c ) a (b c ) a (b c ) a (b c ) a (b c ) a [a (b k (b (b c ) a (b c c ) )] [a (b c ) a (b c )]j [a (b c ) a (b c )]k [(a b a c ) (a b a c )] [(a b a c ) (a b a c )]j [(a b a c ) (a b a c )]k [(a b a b ) (a c a c )] [(a b a b ) (a c a c )]j [(a b a b ) (a c a c )]k (a b a b ) (a c a c ) (a b a b )j (a c a c ) j (a b a b )k (a c a c )k [(a b a b ) (a b a b )j (a b a b )k ] [(a c a c ) (a c a c )j (a c a c )k ] a b a a b b a j a b b a k b j k j a b a b a b a b a b a b j k a a a a j a a k c c c c c c ( a b ) ( a c ) 9. Sample answer: Let T(,, ), U(,, ), and V(,, ) TU,, UV,, j k TU UV j k 7j k or, 7,. Sample answer: Let T(,, ), U(,, ), and V(,, ). TU,, UV 8,, j k TU UV 8 j k 8 8 j 6k or,, 6. Sample answer: Let T(,, ), U(,, ), and V(,, ). TU,, UV,, j k TU UV j k j k or,,. The epresson s false. m n and n m have the same magntde bt are opposte n drecton. a. forearm b. T AB F AB. cos ( ),,. sn ( ).(),,. F,, 6 j k AB F.. 6 j k T AB F or abot N-m j k. 8j k A (8) () j k 6 N. m elbow a. o,, 6 c 9, 8, b. o c (9) (8) 6() $, Chapter 8
12 6a. F 6b. W F d cos v W cos W 9 ft-lb 7a. X,, or,, ) Y,, or,, j k X Y j k 8 7j 9k or 8, 7, 9 7b. The cross prodct of two vectors s alwas a vector perpendclar to the two vectors and the plane n whch the le. 8a. v p (q r ) j k q r j k j k or,, p (q r ),,,, () () ()() or nts 8b. () or nts The are the same. 9. Need (kv w ). [k,, ], [k, k, ], k, k, (k ) (k ) k k 9k 9 k 9 9. BA a b a b cos v (a b ) (a b ) a a b b a b a b cos v (a b ) (a b ) a a b b a a b b cos v a a b b a a b b a a b b a b a b cos v a b a b a b a b cos v a b a b a a b b cos v a b a b a b cos v a b a b cos v. AB,, () or,,. D(8, ) E(, ) DE 8, ) or 8, DE (8) ) ( A B or p nts 7 sn f 7 7 cos f 7 7 tan f f. A 6, b, and c 6 a b c bc cos A a 6 ()(6) cos 6 a 8.9 sn s n B n 6 B sn s 8. 9 B 9. or 9 C C 8.9 or 8. tan 7 h cos 7 tan 7 h cos 7. h;. m.7 m ( ) or ( ) 9 So 6 8 The correct choce s B. Chapter 8 6
13 Page. Md-Chapter Q 8-B Graphng Calclator Eploraton: Fndng Cross Prodcts. cm 6 F. cos 6 F. sn 6.6 cm.7 cm..7 cm F 7 cos F 7 sn. mm. mm. CD (9), or, CD ) ( or. CD, 7 7, () or,, CD. r t s 6,, 6, 8, 6 6 8, 6 or, 8 6. r v,, 8, 9,, 9,, 9,, 9 9, () or 6,, 7., 6, () 6() ; es 8.,,,, () ()() () 8 ; no 9.,,,, j k j k j 7k or,, 7, es,, 7,, ()() () (7)(),, 7,, ()() () (7)() 7. Let X(,, ) and Y(7,, 6). XY (7 ) ( ) (6) or abot 6.7 m Page. 9,. 68, 96, 76.,,.,,.,, 7 6.,, 7. 6, 6, v 6 6 ) ( 6 8. v,, v ) ( ) ( 7 9. Sample answer: Insert the followng lnes after the last lne of the gven program. :Dsp LENGTH IS :Dsp ((BZ CY) (CX AZ) (AY BX) ) 8- Applcatons wth Vectors Pages 6 7 Check for Understandng. Sample answer: Pshng an object p the slope reqres less force becase the component of the weght of the object n the drecton of moton s mg sn v. Ths s less than the weght mg of the object, whch s the force that mst be eerted to lft the object straght p.. The tenson ncreases.. Sample answer: Forces are n eqlbrm f the resltant force s O.. Crrent knots. F F (7 cos ) (7 sn )j F F ( os 7 c ) 7 (sn ).9 N tan v 7 7 sn 7 cos v tan 7 sn 7 cos 6. F F j F F.8 N tan v or v tan horontal 8 cos.79 N vertcal 8 sn.7 N 7 Chapter 8
14 8. F ( cos 9 ) ( sn 9 )j or j F ( cos 6 ) ( sn 6 )j or j F F ( ) 7 N tan v or v tan 7 Aforce wth magntde 7 N and drecton 7 8 or wll prodce eqlbrm. 9a. mph 9 lb lb 9b. If v s the angle between the resltant path of the ferr and the lne between the landngs, then sn v or. So v sn, or abot 9.. Pages 7 9 Eercses... N mph. F F 9j F F N tan v 9 or v tan v 6 v ( cos ) ( sn )j or j v v 9 () mph tan v 9 or 8 8 Wnd 7 6 mph v tan Apostve vale for v s abot... v ( cos 6 ) ( sn 6 )j or j v ( cos ) ( sn )j or j v v () 99.9 km/h Snce tan v s ndefned and the vertcal component s postve, v The force mst be at least as great as the component of the weght of the object n the drecton of the ramp. Ths s sn, or abot 7.6 lb. 7. F F ( cos ) ( sn )j F F ( os c ) (sn ) 9.87 N tan v sn cos sn cos v tan 6.7. F (7 cos ) (7 sn )j or j F ( cos ) ( sn )j or j F (6 cos ) (6 sn )j or j tan v sn sn cos cos v tan 7. F F F ( ) ( ) 8.6 lb. F ( cos 6 ) ( sn 6 )j F v tan.6 8. F w sn v. 7 sn v. sn v 7. sn 7 v v 9. F ( cos ) ( sn )j F ( cos ) ( sn )j F F ( os c cos ) n ( s sn ). lb sn sn tan v cos cos or..j ( cos ) ( sn )j or..j F F ) ( 9.8 N Snce tan v s ndefned and the vertcal component s postve, v 9. A force wth magntde 9.8 N and drecton 9 8 or 7 wll prodce eqlbrm. Chapter 8 8
15 . a g sn sn.6 ft/s. F (6 cos ) (6 sn )j F (8 cos (8 sn )j F F (6 s co s 8 co) 6 ( sn 8 ) sn 9.9 N 6 sn 8 sn tan v 6 cos 8 cos v tan 6 sn 8 sn 6 cos 8 cos 6.7 or. west of soth a. lb 6 lb 7 b. F 7 F ( cos 6 ) ( sn 6 )j F F F (7 os c 6 ) cos n ( s 6 ) sn. lb sn 6 sn tan v 7 cos 6 cos v tan sn 6 sn 7 cos 6 cos 8.7 or 8.7 soth of west Snce F F F, the vectors are not n eqlbrm.. W F d [(6 cos ) (6 sn )j ] (6 cos )() (6 sn )(),,69 N-m 6a. Sample answer: The horontal forward force s F cos v. Yo can ncrease the horontal forward force b decreasng the angle v between the handle and the lawn. 6b. Sample answer: Pshng the lawnmower at a lower angle ma case back pan. 7a. tan v 8 or 6 v tan 6 9. soth of east 7b. s 8 8. mph 8. F cos v cos 9.6 N 9. F cos 7. F cos 6. F sn 7. F sn 6. The frst eqaton gves F co s 7. cos 6. F. Sbsttte nto the second eqaton. cos 7. sn 6. cos 6. 7 lb F sn 7. F F 76 lb F co s 7. cos 6. F 76 lb. Sample answer: Method b s better. Let F be the force eerted b the tractor, T be the tenson n the two halves of the rope, and v be the angle between the orgnal lne of the rope and half of the rope after t s plled. At eqlbrm, F T sn v F, or T s n. v So, f v, the force appled to the stmp sng method b s greater than the force eerted b the tractor.. Let T be the tenson n each towlne and sppose the as of the shp s the vertcal drecton. T sn 7 6 T s 6 n 7 9. tons. Let T be the tenson n each wre. The halves of the wre make angles of and wth the horontal. T sn T sn T T T lb. v 9() () () The vectors are not perpendclar snce v.. AB, (), 8, 6,. d v g sn v cos v sn 6 cos 6 9. ft 6. Sample answer: A plot of the data sggests a qadratc fncton. Performng a qadratc regresson and rondng the coeffcents gves b. p. b p.66 b p b..... O. sn 7. cos 7. tan 6. (.,.) (.,.) (.,.6) (.,.) The vertces are at (.,.), (.,.), (.,.) and (.,.6). cost fncton C(p, b) 9p b ( p b) 8p 8b C(.,.) 8(.) 8(.) or 76 C(.,.) 8(.) 8(.) or 8.8 C(.,.) 8(.) 8(.) or C(.,.6) 8(.) 8(.6) or 9.8 The mnmm cost s $76, sng % beef and % pork. p... F (sn 7. cos 7. tan 6. ) 9 Chapter 8
16 8. * *() ( ) [() ()] 6 () 8 The correct choce s A. Vectors and Parametrc Eqatons Pages Check for Understandng. When t, and. When t, 7 and. The graph s a lne throgh (, ) and (7, ).. Sample answer: For ever sngle nt ncrement of t, ncreases nt and ncreases nts. Then, the parametrc eqatons of the lne are t, 6 t.. When t, and, so the lne passes throgh (, ). When t, and, so the lne passes throgh (, ), ts -ntercept. The slope of the lne s or.. (), t, 8, t, 8 t 8t t 8t., t7, 7t t 7t t t t t t 8. t 9. 9t t 9 t t t. 8-6 t 9 9 t 6 a. recever: t t t O defensve plaer:.9t.7t.9t.7t b. t t t When t, the coordnates of the defensve plaer are (.9(),.7()) or (.,.), so the defensve plaer has not et caght the recever. Eercses., 7 t, t 7 t t 7. (), t6,, t6, 6t t 6t t. (6), t, 6, t, 6 t t 6 t t., t7, 7t t 7t t 6., t,, t, t t t 7., () t,, t, t t t t 8. t t t t t 9t. t t. t t. t t The slope s. ( ) 6 t t 6 Chapter 8 6
17 . t t t 7. t t t t 9. t t t t 7. Regardless of the vale of t, s alwas 8, so the parametrc eqatons represent the vertcal lne wth eqaton 8. a., () t, 7, t, 7 b. t 7t t 7t c. t t. t 7t [, ] Tstep [, ] Xscl [, ] Yscl 6. 7 t 7 t t t ( ) 6 8. t 8 8 t t t. [, ] Tstep [, ] Xscl [, ] Yscl. [, ] Tstep [, ] Xscl [, ] Yscl a. t and 7t If t, then and, so the part of the lne to the rght of pont (, ) s obtaned. b. t t t 6. cos t sn t cos t and sn t, so the graph s the segment of the lne wth eqaton from (, ) to (, ). (, ) 6 Chapter 8
18 7a. target drone: ()t t t mssle: t t 7b. t t t t When t, the mssle has a -coordnate of, not, so t does not ntercept the drone. 8a. Ceres: t, t, t Pallas: 7 t, 6 t, t 8b. Addng the eqatons for and for Ceres gves. Sbtractng the eqatons for and for Pallas reslts n. The solton of ths sstem s and. Elmnatng t from the eqatons for and reslts n the sstem 7, whch has solton and. Hence, the paths cross at (,, ). 8c. t v t 7 t v t Ceres s at (,, ) when t bt Pallas s at (,, ) when t. The asterods wll not collde. 9. The lne s parallel to the vector,, 8 or,, 9. The vector eqaton of the lne s,, t,, 9 or,, t,, 9. t t t t 9t 9t. v ( cos ) ( sn )j v ( cos ) ( sn )j v v ( os c ) cos ( sn sn ) 6. km/h sn sn tan v cos cos v tan sn sn cos cos 7 or 7 soth of east.,, () () Snce the nner prodct s not, the vectors are not perpendclar.. Snce A 9, a b, and a b sn A, no solton ests.. A graphng calclator ndcates that there s one real ero and that t s close to. f(), so the ero s eactl... The slope s. [ ()] 6. The lnear veloct of the belt arond the larger plle s ( rpm) 9 n./rev 8 n./mn. The lnear veloct arond the smaller plle mst be the same, so ts anglar veloct s (8 n./mn) rev n. 8 rpm. The correct choce s D. 8-6B Graphng Calclator Eploraton: Modelng wth Parametrc Eqatons Page t 8.(t.8) 8.7t 8.t t.789 t hr or.7 mn. d rt m. The tme for plane to fl mles s 8..7 The tme for plane s Sppose the speed of plane s ncreased b a mph a 8.7 a a mph Modelng Moton Usng Parametrc Eqatons Page Check for Understandng. Sample answer: a rocket lanched at 9 to the horontal; tp-off n basketball. Eqal magntde wth opposte drecton.. The greater the angle of the head of the golf clb, the greater the angle of ntal veloct of the ball.. v v sn v. v v cos v sn cos. ft/s.86 m/s 6. v v cos v v v sn v cos sn 8.6 ft/s.8 ft/s 7. v v cos v v v sn v 7. cos 7. sn 7. m/s.7 m/s Chapter 8 6
19 8 ft h 6 8a. mph mle s ft/s t v cos v t() cos t t v sn v gt h t() sn ()t 6t 8b. Sample graph: Heght (feet) 6 Horontal Dstance (feet) 8c. 6t 6t t 6 t 6 t.8 s 8d. t (.8) 6 ft Pages Eercses 9. v v cos v v v sn v 6 cos 6 6 sn 6. ft/s 6.9 ft/s. v v cos v v v sn v 7 cos.7 7 sn m/s 8.7 m/s. v v cos v v v sn v cos sn ft/s 8.96 ft/s. v v cos v v v sn v 7 cos 8 7 sn 8. ft/s 7.98 ft/s. v v cos v v v sn v 69 cos 7 69 sn 7. d/s. d/s. v v cos v v v sn v 6 cos 9 6 sn 9.9 km/h.98 km/h a. t v cos v t v sn v gt 7t cos 7t sn 6t b. 7t sn 6t t(7 sn 6t) 7 sn 6t 7 sn 6t 7 s n 6 t 7t cos 7 7 s n 6 cos 899. ft or d 6. To fnd the tme the projectle stas n the ar, set and solve for t. t v sn v gt t( v sn v gt) v sn v gt v sn v gt v sn v g t The greater the angle, the greater the tme the projectle stas n the ar. To fnd the horontal dstance covered, sbsttte the epresson for t n the eqaton for. t v cos v v sn v g v g sn v g v cos v As the angle ncreases from to, the horontal dstance ncreases. As the angle ncreases from to 9, the horontal dstance decreases. 7a. when t 7 7 v sn 78 ()7 7 v sn v sn 78 8 v 8 7s n 78 v 8. ft/s 7b. t v cos v d (7)(8.) cos 78 7 d 8. t v cos v t v cos v t v sn v gt v sn v g v v cos v cos v tan v v gcos v The presence of the -term (de to the force of gravt) means that s a qadratc fncton of. Therefore, the path of a projectle s a parabolc arc. 9. To fnd the tme the projectle stas n the ar f the ntal veloct s v, set and solve for t. t v sn v gt t v sn v gt v sn v gt v sn v gt v sn v g t t To fnd the range, sbsttte ths epresson for t n the eqaton for. t v cos v v sn v g v sn v g v cos v 6 Chapter 8
20 If the magntde of the ntal veloct s dobled to v, the range becomes ( v ) sn v g or v sn v g. The projectle wll travel for tmes as far. m h 6 a. 8 km/h km s. m/s t v cos v. t cos t v sn v gt.t sn (9.8)t.t sn.9t The negatve coeffcent n the t-term n the eqaton for ndcates that the arcraft s descendng. The negatve coeffcent n the eqaton for s arbtrar. b..t sn.9t.(.) sn.9 (.). The arcraft has descended abot. m. c.. m. s 69 m/s or 69 m/s km m 6 s h 8 ft h 6 s 68. km/h a. 7 mph m ft/s sn 6t t 8 8 sn 8 sn (6) t t.8 s t v cos v. ft b. 8 8 sn 6t 8 t 6t t 8 sn t t.7 s t v cos v. ft c. From the calclatons n part b, the tme s abot.7s. a. 8 8 sn 8 n s 6) ( b. a. when t.8.8 v sn 8 ()(.8).8 v sn v sn 8 v.7 ft/s b. t v cos v. d a. t v cos v t v sn v gt h t cos t sn 6t b. t cos t cos t sn 6t cos sn 6 cos 6. ft Snce 6., the ball wll clear the fence. c. t sn 6t sn ( n s) (6) t t.68 s t v cos v 8.86 ft. t t t 8 6t 8 6( ) 6 8 6a. mg sn v (9.8) sn. N 6b. mg cos v (9.8) cos 7.9 N 7. cos A A cos A 7 O t Chapter 8 6
21 8. ( ) ()..7 ( ) (). 6. ( ) (.7) (.).7 (.) The correct choce s B. Page stada Hstor of Mathematcs (), stada,(),, ft,, 8,67 m The actal crcmference of Earth s abot,9. mles.. See stdents work. No solton ests.. See stdents work. 8-8 Transformaton Matrces n Three-Dmensonal Space Pages 9 Check for Understandng. Matr T mltples -coordnates b and - and -coordnates b, so t prodces a reflecton over the -plane and ncreases the dmensons two-fold.. CC 8 6, 8 7, or,, The matr s.. VU are the same. T, so the transformatons a. BE,, or,, A(, (), ) A(,, ) C( (),, ) C(,, ) D( (), (), ) D(,, ) F(, (), ) F(,, ) G(,, ) G(,, ) H( (),, ) H(,, ) The matr s. b. () () () () () () () c. G B A H F C E O D () The mage s the reflecton over the -plane. d. The dmensons of the resltng fgre are half the orgnal. 6a. The scale factor of the dlaton s. The translaton ncreases -coordnates b. The matrces are D and T. a-c. Transformaton Orentaton Ste Shape Reflecton es no no Translaton no no no Dlaton no es no 6 Chapter 8
22 6b. Sample answer: If the orgnal prsm has vertces A(,, ) B(,, ), C(,, ), D(,, ), E(,, ), F(,, ), G(,, ), and H(,, ), then the mage has vertces A(,, ), B(,, ), C(,, ), D(,, ), E(,, ), F(,, ), G(,, ), and H(,, ). G H C D C G D F F H E E Pages Eercses 7. FB, 7, or, 6, A(,, (6), ) A(,, C(, 7 (6), ) C(,, ) The matr s AH (), (), or 7,, B(,, ) B(,, ) C(,, ()) C(,, ) D(,, ()) D(,, ) E( 7,, ()) E(,, ) F( 7,, ) F(,, ) G( 7,, ) G(,, ) The matr s 9. CF 6, (), or,, D(,, ()) D(,, ) E(,, ()) E(,, ) 6 The matr s.. () () () () () () () () B A B A D F H A E The reslt s a translaton of nts along the - as and nts along the -as.. () () E G O C B () () () () () () () () () () () () () () The reslt s a translaton of nt along the - as, nts along the -as, and nts along the -as.. () D F G A H () () 8 C B 8 D F A E () () C G B H () () 8 () The reslts s a translaton of nt along the - as, nts along the -as, and nts along the -as. 8 Chapter 8 66
23 . The transformaton does not change the fgre O A 6 B E D H. F The transformaton reslts n reflectons over the and -planes.. C D F E A H B G G G E A F D C B H C The transformaton reslts n reflectons over all three coordnate planes. 6. The matr reslts n a dlaton of scale factor, so the fgre s twce the orgnal se. 7., so the fgre s three tmes the orgnal se and reflected over the -plane , so the fgre s three-forths.7 the orgnal ste and reflected over all three coordnate planes., so the transformaton can 9a. be represented b the matr. 9b. The transformaton wll magnf the - and -dmensons two-fold, and the -dmenson -fold a b c. The reslt s a translaton.6 nts along the -as and 7 nts along the -as.. The matr wold reflect the prsm. over the -plane. The matr.. wold redce ts dmensons b half a. Placng a non ero element n the frst row and thrd colmn wll skew the cbe so that the top s no longer drectl above the bottom. Sample answer: b. Sample graphs: C D G H B A F E C G B H F E D A 67 Chapter 8
24 . The frst transformaton reflects the fgre over all three coordnate planes. The second transformaton stretches the dmensons along the - and -aes and skews t along the -plane. (The frst row of T changes the -coordnate of (,, ) to.). To mltpl the -coordnate b, the frst row of the matr mst be. Snce the -coordnate s mltpled b, the second row s. To convert a -coordnate to, se a thrd row of. The matr s. a. The -coordnates are nchanged, the -coordnates ncrease, and the -coordnates decrease, so the movement s dp-slp b a. La Shawna Jame t 6t 6t 6t 6t 6 6 t t.6 t t 6 7 ft 6b. Snce the stones have the same parametrc eqatons for, the land at the same tme. In part a, t was calclated that the elapsed tme s abot.6 seconds. 7. t t t t A graphng calclator ndcates that there s a solton between and. B Descartes Rle of Sgns, t s the onl solton. When., and when., So the solton to the nearest tenth s... Dvde each sde of the eqatons b,,, and 6, respectvel, so that the left sde s. I. II. III. IV. 8 Onl I and II are eqvalent, so the correct choce s A. Chapter 8 Std Gde and Assessment Page Understandng and Usng the Vocablar. resltant. nt. magntde. cross. nner 6. vector 7. parallel 8. standard 9. drecton. components 6 Sklls and Concepts.. cm,..9 cm,. q p q p. cm,. p. cm,. p q. cm q q. cm p q 8. sec cos coscos. cm 98 p. cm, 98 Chapter 8 68
25 6. p q. cm 8 q p. cm, 8 7. h. cos v. sn h.8 cm v cm 8. h.9 cos v.9 sn h.9 cm v. cm 9. CD 7, or, CD 69 or. CD (), 8 or 6, CD 6 or. CD, 9 () or, CD () 8 or 7. CD (6), or, 8 CD 8) ( 6. v w,,, () or, 6. v w,,, () or,. v w,, 6, 6, 6 6, () or, 7 6. v w,, 6, 6, 6 6, () or, 7. EF 6, (), or,, EF ) ( () 6 8. EF 9, 8, or,, 6 EF () ) (6 9. EF (), (), 7 ) or 6,, 7 EF EF, 7, (8) or 7, 7, EF (7) ) (7 67. w v,,, 7, 8,, (,, 8 (),, (), 7,..v.w., 7,.,,.,.7,.6,.,..6,.7 (.),.,.,.,, 6 () ()6 6 6; no., 6, () 6() 6 8; no.,,,, () () () 8 ; es 6.,, 6,, (6) ()() () 8; no 7.,,,, () () ()() 8 ; no j k 8.,,,, j k 6 j k or 6,, 6,,,, 6() () ()() 6,,,, 6() () ()() ,,,, 9 6j k or 9, 6, 9, 6,,, 9() (6)() () 8 8 9, 6,,, 9() (6)() () 8 8 j k j k 69 Chapter 8
26 .,,,, j k j k 8 9j k or 8, 9, 8, 9,,, (8)() 9()()() 8 8 8, 9,,, (8)() 9() ()() 8. 7,,,, j k j k 9j k or, 9,, 9, 7,, (7) (9) () 7 (8), 9,,, () (9) () (9) 9. Sample answer: Let (,, ), (,, ) and (,, ),, or,, (),, () or 9,,,, 9,, j k 9 j k j 9 k 9 or,,. F F 6j F F 6. N tan v 6 or 6 v tan v j v ( cos 6 ) ( sn 6 )j v v ( s co ) 6 ( 6 ) sn m/s tan v sn 6 cos 6 v tan cos , () t,, t, t t t t 6. (), 9 t7,, 9 t7, 7t 9 t 7t 9 t sn 6 7., t, 6, t, 6 t t 8. t 8t 7 7 8t 6t 9. t t. v v cos v v v sn v cos sn 8.6 ft/s.9 ft/s. v v cos v v v sn v. cos 66. sn 66.7 ft/s.6 ft/s. v v cos v v v sn v 8 cos 8 8 sn 8.89 m/s 8. m/s. CH,, () or 7, 6, A(, (6), ) A(,, ) B(, (6), ) B(,, ) D(,, ) D(,, ) E( (7),, ) E(,, ) F( (7),, ) F(,, ) G( (7), (6), ) G(,, ) The matr for the fgre s. The matr for the translated fgre s. A B H G D C The fgre moves nts along the -as and nts along the -as. E F Chapter 8 7
27 . D C E m The fgre s reflected over the -plane. Page 7 Applcatons and Problem Solvng. AB cos,, sn or,, F,, T AB F ft j k j k j k or,, T ) ( lb-ft 6. t v sn v gt h.(8) sn ()(.). ft 7a. 6 km/h km/h b (6 cos )c (6 sn )j c j b c (6 s co ) 6 ( sn ).7 km/h sn 7b. 6 6 cos sn 6 cos F A O B 6 7. m H G lb 6 8. F 9 F (7 cos ) (7 sn )j or j F F (9 ).6 N 7 tan v or v tan Page 7 Open-Ended Assessment a. Sample answer: X(, ), Y(, ) XY, () or, b. XY () or The magntde of XY onl depends on the dfferences of the coordnates of X and Y, not the actal coordnates. a. Sample answer: P(, ), Q(, ), R(, ), S(, ) PQ, or, RS, or, PQ and RS are parallel becase the have the same drecton. In fact, the are the same vector. b. Sample answer: a 8,, b, 6 a b 8() ()6 or a and b are perpendclar becase ther nner prodct s. Chapter 8 SAT & ACT Preparaton Page 9 SAT and ACT Practce. Recall that the formla for the area of a parallelogram s base tmes heght. Yo know the base s, bt o don t know the heght. Don t be fooled b the segment BD; t s not the heght of the parallelogram. Tr another method to fnd the area. The parallelogram s made p of two trangles. Fnd the area of each trangle. Snce ABCD s a parallelogram, AB DC and AD BC. The two trangles are both rght trangles, and the share a common sde, BD. B SAS, the two trangles are congrent. So o can fnd the area of one trangle and mltpl b. The hpotense of the trangle s and one sde s. Use the Pthagorean Theorem to fnd the other sde. b 9 b 6 b b The heght s. Use the formla for the area of a trangle. A bh A ()() or 6 Snce the parallelogram conssts of two trangles, the area of the parallelogram s 6 or. The correct choce s A. 7 Chapter 8
28 . In order to wrte the eqaton of a crcle, o need to know the coordnates of the center and the length of the rads. The general eqaton for a crcle s ( h) ( k) r, where the center s (h, k) and the rads s r. From the coordnates of ponts A and B, o know the length of the sde s. So the center Q, has coordnates (, ). To calclate the length of the rads, draw the rads OB. Ths creates a - -9 rght trangle. The two legs each have length. The hpotense has length. ( ) ( ) () ( ) () ( ) 8 The correct choce s B.. Wrte the eqaton for the permeter of a rectangle. then replace wth ts vale n terms of. Solve the eqaton for. p p p p p The correct choce s B.. Recall the trangle Ineqalt Theorem: the sm of the lengths of an two sdes of a trangle s greater than the length of the thrd sde. Let represent the length of the thrd sde. 8 8 Snce mst be greater than, cannot be eqal to. The correct choce s A. To check or answer, notce that the other answer choces are greater than and less than, so the are all possble vales for.. Snce the answer choces have fractonal eponents of, start b rewrtng the epresson wth fractonal eponents. Smplf the fractons and se the rles for eponents to combne terms. 9 9 ( ) or The correct choce s E. 6. Ths fgre looks more comple than t s. A semcrcle s jst one half of a crcle. Notce that the answer choces nclde, so don t convert to decmals. Fnd the rads of each sem-crcle. Calclate the area of each sem-crcle. The area of the shaded regon s the area of the large sem-crcle mns the area of the medm sem-crcle pls the area of the small sem-crcle. Large sem-crcle area 9 Medm sem-crcle area Small sem-crcle area Shaded area 9 6 The correct choce s A. 7. The onl vales for whch a ratonal fncton s ndefned are vales whch make the denomnator. Snce f(), the denomnator s onl when or. The correct choce s D. 8. Start b sketchng a dagram of the conter Use or calclator to fnd the area of the whole conter and then sbtract the area of the whte tles n the center. The whte tles cover an area of ( )( ) or (8)(8). ()() (8)(8) 6 Red tles 6 6 The correct choce s B. 9. Frst, fnd the slope of the lne contanng the ponts (, 6) and (, ). m 6 m 9 6 or 8 8 The pont-slope form of the lne s 6 ( ). 6 So the -ntercept of the lne s. The correct choce s B. Chapter 8 7
29 . Wrte an epresson for the sm of the areas of the two trangles. Recall the area of a trangle s one half the base tmes the heght. (AC)(AB) (CE)(ED) From the fgre, o know that ABC and CDE are both sosceles, becase of the angles marked and becase BCD s a lne segment. These two trangles have eqal correspondng angles. Snce the are sosceles trangles, AC AB and CE ED. Use these eqvalent lengths n the epressons for the area sm. (AC)(AB) (CE)(ED) (AC) (CE) [(AC) (CE) ] Usng the Pthagorean Theorem for ACE, o know that (AC) (CE) (AE) or. So the sm of the two areas s (). Yo can grd the answer ether as. or as. 7 Chapter 8
Physics 2A Chapter 3 HW Solutions
 Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Objective To use the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra to solve polynomial equations with complex solutions
 5-6 The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Content Standards N.CN.7 Solve quadratc equatons wth real coeffcents that have comple solutons. N.CN.8 Etend polnomal denttes to the comple numbers. Also N.CN.9,
5-6 The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Content Standards N.CN.7 Solve quadratc equatons wth real coeffcents that have comple solutons. N.CN.8 Etend polnomal denttes to the comple numbers. Also N.CN.9,
Unit 5: Quadratic Equations & Functions
 Date Perod Unt 5: Quadratc Equatons & Functons DAY TOPIC 1 Modelng Data wth Quadratc Functons Factorng Quadratc Epressons 3 Solvng Quadratc Equatons 4 Comple Numbers Smplfcaton, Addton/Subtracton & Multplcaton
Date Perod Unt 5: Quadratc Equatons & Functons DAY TOPIC 1 Modelng Data wth Quadratc Functons Factorng Quadratc Epressons 3 Solvng Quadratc Equatons 4 Comple Numbers Smplfcaton, Addton/Subtracton & Multplcaton
Section 8.1 Exercises
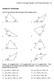 Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Solutions to Selected Exercises
 6 Solutons to Selected Eercses Chapter Secton.. a. f ( 0) b. Tons of garbage per week s produced by a cty wth a populaton of,000.. a. In 99 there are 0 ducks n the lake b. In 000 there are 0 ducks n the
6 Solutons to Selected Eercses Chapter Secton.. a. f ( 0) b. Tons of garbage per week s produced by a cty wth a populaton of,000.. a. In 99 there are 0 ducks n the lake b. In 000 there are 0 ducks n the
For all questions, answer choice E) NOTA" means none of the above answers is correct.
 0 MA Natonal Conventon For all questons, answer choce " means none of the above answers s correct.. In calculus, one learns of functon representatons that are nfnte seres called power 3 4 5 seres. For
0 MA Natonal Conventon For all questons, answer choce " means none of the above answers s correct.. In calculus, one learns of functon representatons that are nfnte seres called power 3 4 5 seres. For
Complex Numbers Practice 0708 & SP 1. The complex number z is defined by
 IB Math Hgh Leel: Complex Nmbers Practce 0708 & SP Complex Nmbers Practce 0708 & SP. The complex nmber z s defned by π π π π z = sn sn. 6 6 Ale - Desert Academy (a) Express z n the form re, where r and
IB Math Hgh Leel: Complex Nmbers Practce 0708 & SP Complex Nmbers Practce 0708 & SP. The complex nmber z s defned by π π π π z = sn sn. 6 6 Ale - Desert Academy (a) Express z n the form re, where r and
Bruce A. Draper & J. Ross Beveridge, January 25, Geometric Image Manipulation. Lecture #1 January 25, 2013
 Brce A. Draper & J. Ross Beerdge, Janar 5, Geometrc Image Manplaton Lectre # Janar 5, Brce A. Draper & J. Ross Beerdge, Janar 5, Image Manplaton: Contet To start wth the obos, an mage s a D arra of pels
Brce A. Draper & J. Ross Beerdge, Janar 5, Geometrc Image Manplaton Lectre # Janar 5, Brce A. Draper & J. Ross Beerdge, Janar 5, Image Manplaton: Contet To start wth the obos, an mage s a D arra of pels
AE/ME 339. K. M. Isaac. 8/31/2004 topic4: Implicit method, Stability, ADI method. Computational Fluid Dynamics (AE/ME 339) MAEEM Dept.
 AE/ME 339 Comptatonal Fld Dynamcs (CFD) Comptatonal Fld Dynamcs (AE/ME 339) Implct form of dfference eqaton In the prevos explct method, the solton at tme level n,,n, depended only on the known vales of,
AE/ME 339 Comptatonal Fld Dynamcs (CFD) Comptatonal Fld Dynamcs (AE/ME 339) Implct form of dfference eqaton In the prevos explct method, the solton at tme level n,,n, depended only on the known vales of,
COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
 COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS INTRODUCTION We know that x 0 for all x R e the square of a real number (whether postve, negatve or ero) s non-negatve Hence the equatons x, x, x + 7 0 etc are not
COMPLEX NUMBERS AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS INTRODUCTION We know that x 0 for all x R e the square of a real number (whether postve, negatve or ero) s non-negatve Hence the equatons x, x, x + 7 0 etc are not
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
SCALARS AND VECTORS All physical quantities in engineering mechanics are measured using either scalars or vectors.
 SCALARS AND ECTORS All phscal uanttes n engneerng mechancs are measured usng ether scalars or vectors. Scalar. A scalar s an postve or negatve phscal uantt that can be completel specfed b ts magntude.
SCALARS AND ECTORS All phscal uanttes n engneerng mechancs are measured usng ether scalars or vectors. Scalar. A scalar s an postve or negatve phscal uantt that can be completel specfed b ts magntude.
Math1110 (Spring 2009) Prelim 3 - Solutions
 Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
BAR & TRUSS FINITE ELEMENT. Direct Stiffness Method
 BAR & TRUSS FINITE ELEMENT Drect Stness Method FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS INTRODUCTION TO FINITE ELEMENT METHOD What s the nte element method (FEM)? A technqe or obtanng approxmate soltons
BAR & TRUSS FINITE ELEMENT Drect Stness Method FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS AND APPLICATIONS INTRODUCTION TO FINITE ELEMENT METHOD What s the nte element method (FEM)? A technqe or obtanng approxmate soltons
ˆ (0.10 m) E ( N m /C ) 36 ˆj ( j C m)
 7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
= 1.23 m/s 2 [W] Required: t. Solution:!t = = 17 m/s [W]! m/s [W] (two extra digits carried) = 2.1 m/s [W]
![= 1.23 m/s 2 [W] Required: t. Solution:!t = = 17 m/s [W]! m/s [W] (two extra digits carried) = 2.1 m/s [W] = 1.23 m/s 2 [W] Required: t. Solution:!t = = 17 m/s [W]! m/s [W] (two extra digits carried) = 2.1 m/s [W]](/thumbs/78/76802454.jpg) Secton 1.3: Acceleraton Tutoral 1 Practce, page 24 1. Gven: 0 m/s; 15.0 m/s [S]; t 12.5 s Requred: Analyss: a av v t v f v t a v av f v t 15.0 m/s [S] 0 m/s 12.5 s 15.0 m/s [S] 12.5 s 1.20 m/s 2 [S] Statement:
Secton 1.3: Acceleraton Tutoral 1 Practce, page 24 1. Gven: 0 m/s; 15.0 m/s [S]; t 12.5 s Requred: Analyss: a av v t v f v t a v av f v t 15.0 m/s [S] 0 m/s 12.5 s 15.0 m/s [S] 12.5 s 1.20 m/s 2 [S] Statement:
CHAPTER 4. Vector Spaces
 man 2007/2/16 page 234 CHAPTER 4 Vector Spaces To crtcze mathematcs for ts abstracton s to mss the pont entrel. Abstracton s what makes mathematcs work. Ian Stewart The man am of ths tet s to stud lnear
man 2007/2/16 page 234 CHAPTER 4 Vector Spaces To crtcze mathematcs for ts abstracton s to mss the pont entrel. Abstracton s what makes mathematcs work. Ian Stewart The man am of ths tet s to stud lnear
EQUATION CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1STRAIN IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM
 EQUTION HPTER SETION STRIN IN ONTINUOUS MEIUM ontent Introdcton One dmensonal stran Two-dmensonal stran Three-dmensonal stran ondtons for homogenety n two-dmensons n eample of deformaton of a lne Infntesmal
EQUTION HPTER SETION STRIN IN ONTINUOUS MEIUM ontent Introdcton One dmensonal stran Two-dmensonal stran Three-dmensonal stran ondtons for homogenety n two-dmensons n eample of deformaton of a lne Infntesmal
9. Complex Numbers. 1. Numbers revisited. 2. Imaginary number i: General form of complex numbers. 3. Manipulation of complex numbers
 9. Comple Numbers. Numbers revsted. Imagnar number : General form of comple numbers 3. Manpulaton of comple numbers 4. The Argand dagram 5. The polar form for comple numbers 9.. Numbers revsted We saw
9. Comple Numbers. Numbers revsted. Imagnar number : General form of comple numbers 3. Manpulaton of comple numbers 4. The Argand dagram 5. The polar form for comple numbers 9.. Numbers revsted We saw
Section 8.3 Polar Form of Complex Numbers
 80 Chapter 8 Secton 8 Polar Form of Complex Numbers From prevous classes, you may have encountered magnary numbers the square roots of negatve numbers and, more generally, complex numbers whch are the
80 Chapter 8 Secton 8 Polar Form of Complex Numbers From prevous classes, you may have encountered magnary numbers the square roots of negatve numbers and, more generally, complex numbers whch are the
MEMBRANE ELEMENT WITH NORMAL ROTATIONS
 9. MEMBRANE ELEMENT WITH NORMAL ROTATIONS Rotatons Mst Be Compatble Between Beam, Membrane and Shell Elements 9. INTRODUCTION { XE "Membrane Element" }The comple natre of most bldngs and other cvl engneerng
9. MEMBRANE ELEMENT WITH NORMAL ROTATIONS Rotatons Mst Be Compatble Between Beam, Membrane and Shell Elements 9. INTRODUCTION { XE "Membrane Element" }The comple natre of most bldngs and other cvl engneerng
C PLANE ELASTICITY PROBLEM FORMULATIONS
 C M.. Tamn, CSMLab, UTM Corse Content: A ITRODUCTIO AD OVERVIEW mercal method and Compter-Aded Engneerng; Phscal problems; Mathematcal models; Fnte element method. B REVIEW OF -D FORMULATIOS Elements and
C M.. Tamn, CSMLab, UTM Corse Content: A ITRODUCTIO AD OVERVIEW mercal method and Compter-Aded Engneerng; Phscal problems; Mathematcal models; Fnte element method. B REVIEW OF -D FORMULATIOS Elements and
1 Matrix representations of canonical matrices
 1 Matrx representatons of canoncal matrces 2-d rotaton around the orgn: ( ) cos θ sn θ R 0 = sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the x-axs: R x = 1 0 0 0 cos θ sn θ 0 sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the y-axs:
1 Matrx representatons of canoncal matrces 2-d rotaton around the orgn: ( ) cos θ sn θ R 0 = sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the x-axs: R x = 1 0 0 0 cos θ sn θ 0 sn θ cos θ 3-d rotaton around the y-axs:
Mathematics Intersection of Lines
 a place of mnd F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Currculum and Pedagog Mathematcs Intersecton of Lnes Scence and Mathematcs Educaton Research Group Supported b UBC Teachng and Learnng Enhancement
a place of mnd F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Currculum and Pedagog Mathematcs Intersecton of Lnes Scence and Mathematcs Educaton Research Group Supported b UBC Teachng and Learnng Enhancement
Pre-Calculus Summer Assignment
 Pre-Calculus Summer Assgnment Dear Future Pre-Calculus Student, Congratulatons on our successful completon of Algebra! Below ou wll fnd the summer assgnment questons. It s assumed that these concepts,
Pre-Calculus Summer Assgnment Dear Future Pre-Calculus Student, Congratulatons on our successful completon of Algebra! Below ou wll fnd the summer assgnment questons. It s assumed that these concepts,
Gravitational Acceleration: A case of constant acceleration (approx. 2 hr.) (6/7/11)
 Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
PHYS 1101 Practice problem set 12, Chapter 32: 21, 22, 24, 57, 61, 83 Chapter 33: 7, 12, 32, 38, 44, 49, 76
 PHYS 1101 Practce problem set 1, Chapter 3: 1,, 4, 57, 61, 83 Chapter 33: 7, 1, 3, 38, 44, 49, 76 3.1. Vsualze: Please reer to Fgure Ex3.1. Solve: Because B s n the same drecton as the ntegraton path s
PHYS 1101 Practce problem set 1, Chapter 3: 1,, 4, 57, 61, 83 Chapter 33: 7, 1, 3, 38, 44, 49, 76 3.1. Vsualze: Please reer to Fgure Ex3.1. Solve: Because B s n the same drecton as the ntegraton path s
The Bellman Equation
 The Bellman Eqaton Reza Shadmehr In ths docment I wll rovde an elanaton of the Bellman eqaton, whch s a method for otmzng a cost fncton and arrvng at a control olcy.. Eamle of a game Sose that or states
The Bellman Eqaton Reza Shadmehr In ths docment I wll rovde an elanaton of the Bellman eqaton, whch s a method for otmzng a cost fncton and arrvng at a control olcy.. Eamle of a game Sose that or states
Formulas for the Determinant
 page 224 224 CHAPTER 3 Determnants e t te t e 2t 38 A = e t 2te t e 2t e t te t 2e 2t 39 If 123 A = 345, 456 compute the matrx product A adj(a) What can you conclude about det(a)? For Problems 40 43, use
page 224 224 CHAPTER 3 Determnants e t te t e 2t 38 A = e t 2te t e 2t e t te t 2e 2t 39 If 123 A = 345, 456 compute the matrx product A adj(a) What can you conclude about det(a)? For Problems 40 43, use
Chapter 3. r r. Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Revisited
 Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
Q1: Calculate the mean, median, sample variance, and standard deviation of 25, 40, 05, 70, 05, 40, 70.
 Q1: Calculate the mean, medan, sample varance, and standard devaton of 5, 40, 05, 70, 05, 40, 70. Q: The frequenc dstrbuton for a data set s gven below. Measurements 0 1 3 4 Frequenc 3 5 8 3 1 a) What
Q1: Calculate the mean, medan, sample varance, and standard devaton of 5, 40, 05, 70, 05, 40, 70. Q: The frequenc dstrbuton for a data set s gven below. Measurements 0 1 3 4 Frequenc 3 5 8 3 1 a) What
International Mathematical Olympiad. Preliminary Selection Contest 2012 Hong Kong. Outline of Solutions
 Internatonal Mathematcal Olympad Prelmnary Selecton ontest Hong Kong Outlne of Solutons nswers: 7 4 7 4 6 5 9 6 99 7 6 6 9 5544 49 5 7 4 6765 5 6 6 7 6 944 9 Solutons: Snce n s a two-dgt number, we have
Internatonal Mathematcal Olympad Prelmnary Selecton ontest Hong Kong Outlne of Solutons nswers: 7 4 7 4 6 5 9 6 99 7 6 6 9 5544 49 5 7 4 6765 5 6 6 7 6 944 9 Solutons: Snce n s a two-dgt number, we have
Supplemental Instruction sessions next week
 Homework #4 Wrtten homework due now Onlne homework due on Tue Mar 3 by 8 am Exam 1 Answer keys and scores wll be posted by end of the week Supplemental Instructon sessons next week Wednesday 8:45 10:00
Homework #4 Wrtten homework due now Onlne homework due on Tue Mar 3 by 8 am Exam 1 Answer keys and scores wll be posted by end of the week Supplemental Instructon sessons next week Wednesday 8:45 10:00
Experimental Errors and Error Analysis
 Expermental Errors and Error Analss Rajee Prabhakar Unerst of Texas at Astn, Astn, TX Freeman Research Grop Meetng March 10, 004 Topcs coered Tpes of expermental errors Redcng errors Descrbng errors qanttatel
Expermental Errors and Error Analss Rajee Prabhakar Unerst of Texas at Astn, Astn, TX Freeman Research Grop Meetng March 10, 004 Topcs coered Tpes of expermental errors Redcng errors Descrbng errors qanttatel
Delhi School of Economics Course 001: Microeconomic Theory Solutions to Problem Set 2.
 Delh School of Economcs Corse 00: Mcroeconomc Theor Soltons to Problem Set.. Propertes of % extend to and. (a) Assme x x x. Ths mples: x % x % x ) x % x. Now sppose x % x. Combned wth x % x and transtvt
Delh School of Economcs Corse 00: Mcroeconomc Theor Soltons to Problem Set.. Propertes of % extend to and. (a) Assme x x x. Ths mples: x % x % x ) x % x. Now sppose x % x. Combned wth x % x and transtvt
Please review the following statement: I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: Instructor s Name and Secton: (Crcle Your Secton) Sectons:
Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: Instructor s Name and Secton: (Crcle Your Secton) Sectons:
Chapter 8. Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
 Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton of Energy In ths chapter we wll ntroduce the followng concepts: Potental Energy Conservatve and non-conservatve forces Mechancal Energy Conservaton of Mechancal
Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton of Energy In ths chapter we wll ntroduce the followng concepts: Potental Energy Conservatve and non-conservatve forces Mechancal Energy Conservaton of Mechancal
Kinematics in 2-Dimensions. Projectile Motion
 Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton A medeval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.net.net.au/~rmne/ht/ht0.html#5 Readng Assgnment: Chapter 4, Sectons -6 Introducton: In medeval das, people had
Knematcs n -Dmensons Projectle Moton A medeval trebuchet b Kolderer, c1507 http://members.net.net.au/~rmne/ht/ht0.html#5 Readng Assgnment: Chapter 4, Sectons -6 Introducton: In medeval das, people had
Statistics MINITAB - Lab 2
 Statstcs 20080 MINITAB - Lab 2 1. Smple Lnear Regresson In smple lnear regresson we attempt to model a lnear relatonshp between two varables wth a straght lne and make statstcal nferences concernng that
Statstcs 20080 MINITAB - Lab 2 1. Smple Lnear Regresson In smple lnear regresson we attempt to model a lnear relatonshp between two varables wth a straght lne and make statstcal nferences concernng that
= = = (a) Use the MATLAB command rref to solve the system. (b) Let A be the coefficient matrix and B be the right-hand side of the system.
 Chapter Matlab Exercses Chapter Matlab Exercses. Consder the lnear system of Example n Secton.. x x x y z y y z (a) Use the MATLAB command rref to solve the system. (b) Let A be the coeffcent matrx and
Chapter Matlab Exercses Chapter Matlab Exercses. Consder the lnear system of Example n Secton.. x x x y z y y z (a) Use the MATLAB command rref to solve the system. (b) Let A be the coeffcent matrx and
PHYSICS 203-NYA-05 MECHANICS
 PHYSICS 03-NYA-05 MECHANICS PROF. S.D. MANOLI PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY CHAMPLAIN - ST. LAWRENCE 790 NÉRÉE-TREMBLAY QUÉBEC, QC GV 4K TELEPHONE: 48.656.69 EXT. 449 EMAIL: smanol@slc.qc.ca WEBPAGE: http:/web.slc.qc.ca/smanol/
PHYSICS 03-NYA-05 MECHANICS PROF. S.D. MANOLI PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY CHAMPLAIN - ST. LAWRENCE 790 NÉRÉE-TREMBLAY QUÉBEC, QC GV 4K TELEPHONE: 48.656.69 EXT. 449 EMAIL: smanol@slc.qc.ca WEBPAGE: http:/web.slc.qc.ca/smanol/
Affine transformations and convexity
 Affne transformatons and convexty The purpose of ths document s to prove some basc propertes of affne transformatons nvolvng convex sets. Here are a few onlne references for background nformaton: http://math.ucr.edu/
Affne transformatons and convexty The purpose of ths document s to prove some basc propertes of affne transformatons nvolvng convex sets. Here are a few onlne references for background nformaton: http://math.ucr.edu/
Physics 114 Exam 3 Spring Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam 3 Sprng 015 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem 4. Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse
Physcs 114 Exam 3 Sprng 015 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem 4. Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse
Important Dates: Post Test: Dec during recitations. If you have taken the post test, don t come to recitation!
 Important Dates: Post Test: Dec. 8 0 durng rectatons. If you have taken the post test, don t come to rectaton! Post Test Make-Up Sessons n ARC 03: Sat Dec. 6, 0 AM noon, and Sun Dec. 7, 8 PM 0 PM. Post
Important Dates: Post Test: Dec. 8 0 durng rectatons. If you have taken the post test, don t come to rectaton! Post Test Make-Up Sessons n ARC 03: Sat Dec. 6, 0 AM noon, and Sun Dec. 7, 8 PM 0 PM. Post
Line Drawing and Clipping Week 1, Lecture 2
 CS 43 Computer Graphcs I Lne Drawng and Clppng Week, Lecture 2 Davd Breen, Wllam Regl and Maxm Peysakhov Geometrc and Intellgent Computng Laboratory Department of Computer Scence Drexel Unversty http://gcl.mcs.drexel.edu
CS 43 Computer Graphcs I Lne Drawng and Clppng Week, Lecture 2 Davd Breen, Wllam Regl and Maxm Peysakhov Geometrc and Intellgent Computng Laboratory Department of Computer Scence Drexel Unversty http://gcl.mcs.drexel.edu
One Dimensional Axial Deformations
 One Dmensonal al Deformatons In ths secton, a specfc smple geometr s consdered, that of a long and thn straght component loaded n such a wa that t deforms n the aal drecton onl. The -as s taken as the
One Dmensonal al Deformatons In ths secton, a specfc smple geometr s consdered, that of a long and thn straght component loaded n such a wa that t deforms n the aal drecton onl. The -as s taken as the
Modeling curves. Graphs: y = ax+b, y = sin(x) Implicit ax + by + c = 0, x 2 +y 2 =r 2 Parametric:
 Modelng curves Types of Curves Graphs: y = ax+b, y = sn(x) Implct ax + by + c = 0, x 2 +y 2 =r 2 Parametrc: x = ax + bxt x = cos t y = ay + byt y = snt Parametrc are the most common mplct are also used,
Modelng curves Types of Curves Graphs: y = ax+b, y = sn(x) Implct ax + by + c = 0, x 2 +y 2 =r 2 Parametrc: x = ax + bxt x = cos t y = ay + byt y = snt Parametrc are the most common mplct are also used,
Physics 40 HW #4 Chapter 4 Key NEATNESS COUNTS! Solve but do not turn in the following problems from Chapter 4 Knight
 Physcs 40 HW #4 Chapter 4 Key NEATNESS COUNTS! Solve but do not turn n the ollowng problems rom Chapter 4 Knght Conceptual Questons: 8, 0, ; 4.8. Anta s approachng ball and movng away rom where ball was
Physcs 40 HW #4 Chapter 4 Key NEATNESS COUNTS! Solve but do not turn n the ollowng problems rom Chapter 4 Knght Conceptual Questons: 8, 0, ; 4.8. Anta s approachng ball and movng away rom where ball was
Motion in One Dimension
 Moton n One Dmenson Speed ds tan ce traeled Aerage Speed tme of trael Mr. Wolf dres hs car on a long trp to a physcs store. Gen the dstance and tme data for hs trp, plot a graph of hs dstance ersus tme.
Moton n One Dmenson Speed ds tan ce traeled Aerage Speed tme of trael Mr. Wolf dres hs car on a long trp to a physcs store. Gen the dstance and tme data for hs trp, plot a graph of hs dstance ersus tme.
Please review the following statement: I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 ME 270 Summer 2014 Fnal Exam NAME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS
ME 270 Summer 2014 Fnal Exam NAME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations. Homework 4: Work, Energy and Linear Momentum Due Friday March 1 st
 EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
EN40: Dynamcs and bratons Homework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Momentum Due Frday March 1 st School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The fgure (from ths publcaton) shows the energy per unt area requred to
Solutions to selected problems from homework 1.
 Jan Hagemejer 1 Soltons to selected problems from homeork 1. Qeston 1 Let be a tlty fncton hch generates demand fncton xp, ) and ndrect tlty fncton vp, ). Let F : R R be a strctly ncreasng fncton. If the
Jan Hagemejer 1 Soltons to selected problems from homeork 1. Qeston 1 Let be a tlty fncton hch generates demand fncton xp, ) and ndrect tlty fncton vp, ). Let F : R R be a strctly ncreasng fncton. If the
12. The Hamilton-Jacobi Equation Michael Fowler
 1. The Hamlton-Jacob Equaton Mchael Fowler Back to Confguraton Space We ve establshed that the acton, regarded as a functon of ts coordnate endponts and tme, satsfes ( ) ( ) S q, t / t+ H qpt,, = 0, and
1. The Hamlton-Jacob Equaton Mchael Fowler Back to Confguraton Space We ve establshed that the acton, regarded as a functon of ts coordnate endponts and tme, satsfes ( ) ( ) S q, t / t+ H qpt,, = 0, and
Problem Do any of the following determine homomorphisms from GL n (C) to GL n (C)?
 Homework 8 solutons. Problem 16.1. Whch of the followng defne homomomorphsms from C\{0} to C\{0}? Answer. a) f 1 : z z Yes, f 1 s a homomorphsm. We have that z s the complex conjugate of z. If z 1,z 2
Homework 8 solutons. Problem 16.1. Whch of the followng defne homomomorphsms from C\{0} to C\{0}? Answer. a) f 1 : z z Yes, f 1 s a homomorphsm. We have that z s the complex conjugate of z. If z 1,z 2
ESS 265 Spring Quarter 2005 Time Series Analysis: Error Analysis
 ESS 65 Sprng Qarter 005 Tme Seres Analyss: Error Analyss Lectre 9 May 3, 005 Some omenclatre Systematc errors Reprodcbly errors that reslt from calbraton errors or bas on the part of the obserer. Sometmes
ESS 65 Sprng Qarter 005 Tme Seres Analyss: Error Analyss Lectre 9 May 3, 005 Some omenclatre Systematc errors Reprodcbly errors that reslt from calbraton errors or bas on the part of the obserer. Sometmes
1. Estimation, Approximation and Errors Percentages Polynomials and Formulas Identities and Factorization 52
 ontents ommonly Used Formulas. Estmaton, pproxmaton and Errors. Percentages. Polynomals and Formulas 8. Identtes and Factorzaton. Equatons and Inequaltes 66 6. Rate and Rato 8 7. Laws of Integral Indces
ontents ommonly Used Formulas. Estmaton, pproxmaton and Errors. Percentages. Polynomals and Formulas 8. Identtes and Factorzaton. Equatons and Inequaltes 66 6. Rate and Rato 8 7. Laws of Integral Indces
Lecture 12: Discrete Laplacian
 Lecture 12: Dscrete Laplacan Scrbe: Tanye Lu Our goal s to come up wth a dscrete verson of Laplacan operator for trangulated surfaces, so that we can use t n practce to solve related problems We are mostly
Lecture 12: Dscrete Laplacan Scrbe: Tanye Lu Our goal s to come up wth a dscrete verson of Laplacan operator for trangulated surfaces, so that we can use t n practce to solve related problems We are mostly
Week 11: Chapter 11. The Vector Product. The Vector Product Defined. The Vector Product and Torque. More About the Vector Product
 The Vector Product Week 11: Chapter 11 Angular Momentum There are nstances where the product of two vectors s another vector Earler we saw where the product of two vectors was a scalar Ths was called the
The Vector Product Week 11: Chapter 11 Angular Momentum There are nstances where the product of two vectors s another vector Earler we saw where the product of two vectors was a scalar Ths was called the
Chapter 8: Further Applications of Trigonometry
 Secton 8. Polar Form of Complex Numbers 1 Chapter 8: Further Applcatons of Trgonometry In ths chapter, we wll explore addtonal applcatons of trgonometry. We wll begn wth an extenson of the rght trangle
Secton 8. Polar Form of Complex Numbers 1 Chapter 8: Further Applcatons of Trgonometry In ths chapter, we wll explore addtonal applcatons of trgonometry. We wll begn wth an extenson of the rght trangle
Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 11
 Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
More metrics on cartesian products
 More metrcs on cartesan products If (X, d ) are metrc spaces for 1 n, then n Secton II4 of the lecture notes we defned three metrcs on X whose underlyng topologes are the product topology The purpose of
More metrcs on cartesan products If (X, d ) are metrc spaces for 1 n, then n Secton II4 of the lecture notes we defned three metrcs on X whose underlyng topologes are the product topology The purpose of
Chapter 9: Statistical Inference and the Relationship between Two Variables
 Chapter 9: Statstcal Inference and the Relatonshp between Two Varables Key Words The Regresson Model The Sample Regresson Equaton The Pearson Correlaton Coeffcent Learnng Outcomes After studyng ths chapter,
Chapter 9: Statstcal Inference and the Relatonshp between Two Varables Key Words The Regresson Model The Sample Regresson Equaton The Pearson Correlaton Coeffcent Learnng Outcomes After studyng ths chapter,
5.76 Lecture #21 2/28/94 Page 1. Lecture #21: Rotation of Polyatomic Molecules I
 5.76 Lecture # /8/94 Page Lecture #: Rotaton of Polatomc Molecules I A datomc molecule s ver lmted n how t can rotate and vbrate. * R s to nternuclear as * onl one knd of vbraton A polatomc molecule can
5.76 Lecture # /8/94 Page Lecture #: Rotaton of Polatomc Molecules I A datomc molecule s ver lmted n how t can rotate and vbrate. * R s to nternuclear as * onl one knd of vbraton A polatomc molecule can
Navier Stokes Second Exact Transformation
 Unversal Jornal of Appled Mathematcs (3): 136-140, 014 DOI: 1013189/jam01400303 http://wwwhrpborg Naver Stokes Second Eact Transformaton Aleandr Koachok Kev, Ukrane *Correspondng Athor: a-koachok1@andea
Unversal Jornal of Appled Mathematcs (3): 136-140, 014 DOI: 1013189/jam01400303 http://wwwhrpborg Naver Stokes Second Eact Transformaton Aleandr Koachok Kev, Ukrane *Correspondng Athor: a-koachok1@andea
Solutions to Homework 7, Mathematics 1. 1 x. (arccos x) (arccos x) 1
 Solutons to Homework 7, Mathematcs 1 Problem 1: a Prove that arccos 1 1 for 1, 1. b* Startng from the defnton of the dervatve, prove that arccos + 1, arccos 1. Hnt: For arccos arccos π + 1, the defnton
Solutons to Homework 7, Mathematcs 1 Problem 1: a Prove that arccos 1 1 for 1, 1. b* Startng from the defnton of the dervatve, prove that arccos + 1, arccos 1. Hnt: For arccos arccos π + 1, the defnton
Physics 2A Chapter 9 HW Solutions
 Phscs A Chapter 9 HW Solutons Chapter 9 Conceptual Queston:, 4, 8, 13 Problems: 3, 8, 1, 15, 3, 40, 51, 6 Q9.. Reason: We can nd the change n momentum o the objects b computng the mpulse on them and usng
Phscs A Chapter 9 HW Solutons Chapter 9 Conceptual Queston:, 4, 8, 13 Problems: 3, 8, 1, 15, 3, 40, 51, 6 Q9.. Reason: We can nd the change n momentum o the objects b computng the mpulse on them and usng
Finite Difference Method
 7/0/07 Instructor r. Ramond Rump (9) 747 698 rcrump@utep.edu EE 337 Computatonal Electromagnetcs (CEM) Lecture #0 Fnte erence Method Lecture 0 These notes ma contan coprghted materal obtaned under ar use
7/0/07 Instructor r. Ramond Rump (9) 747 698 rcrump@utep.edu EE 337 Computatonal Electromagnetcs (CEM) Lecture #0 Fnte erence Method Lecture 0 These notes ma contan coprghted materal obtaned under ar use
Work is the change in energy of a system (neglecting heat transfer). To examine what could
 Work Work s the change n energy o a system (neglectng heat transer). To eamne what could cause work, let s look at the dmensons o energy: L ML E M L F L so T T dmensonally energy s equal to a orce tmes
Work Work s the change n energy o a system (neglectng heat transer). To eamne what could cause work, let s look at the dmensons o energy: L ML E M L F L so T T dmensonally energy s equal to a orce tmes
Module 14: THE INTEGRAL Exploring Calculus
 Module 14: THE INTEGRAL Explorng Calculus Part I Approxmatons and the Defnte Integral It was known n the 1600s before the calculus was developed that the area of an rregularly shaped regon could be approxmated
Module 14: THE INTEGRAL Explorng Calculus Part I Approxmatons and the Defnte Integral It was known n the 1600s before the calculus was developed that the area of an rregularly shaped regon could be approxmated
MTH 263 Practice Test #1 Spring 1999
 Pat Ross MTH 6 Practce Test # Sprng 999 Name. Fnd the area of the regon bounded by the graph r =acos (θ). Observe: Ths s a crcle of radus a, for r =acos (θ) r =a ³ x r r =ax x + y =ax x ax + y =0 x ax
Pat Ross MTH 6 Practce Test # Sprng 999 Name. Fnd the area of the regon bounded by the graph r =acos (θ). Observe: Ths s a crcle of radus a, for r =acos (θ) r =a ³ x r r =ax x + y =ax x ax + y =0 x ax
So far: simple (planar) geometries
 Physcs 06 ecture 5 Torque and Angular Momentum as Vectors SJ 7thEd.: Chap. to 3 Rotatonal quanttes as vectors Cross product Torque epressed as a vector Angular momentum defned Angular momentum as a vector
Physcs 06 ecture 5 Torque and Angular Momentum as Vectors SJ 7thEd.: Chap. to 3 Rotatonal quanttes as vectors Cross product Torque epressed as a vector Angular momentum defned Angular momentum as a vector
UNIT 3 EXPRESSIONS AND EQUATIONS Lesson 4: Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Instruction. Guided Practice Example 1
 Guded Practce 3.4. Example 1 Instructon For each equaton, state the number and type of solutons by frst fndng the dscrmnant. x + 3x =.4x x = 3x = x 9x + 1 = 6x 1. Fnd the dscrmnant of x + 3x =. The equaton
Guded Practce 3.4. Example 1 Instructon For each equaton, state the number and type of solutons by frst fndng the dscrmnant. x + 3x =.4x x = 3x = x 9x + 1 = 6x 1. Fnd the dscrmnant of x + 3x =. The equaton
SE Story Shear Frame. Final Project. 2 Story Bending Beam. m 2. u 2. m 1. u 1. m 3. u 3 L 3. Given: L 1 L 2. EI ω 1 ω 2 Solve for m 2.
 SE 8 Fnal Project Story Sear Frame Gven: EI ω ω Solve for Story Bendng Beam Gven: EI ω ω 3 Story Sear Frame Gven: L 3 EI ω ω ω 3 3 m 3 L 3 Solve for Solve for m 3 3 4 3 Story Bendng Beam Part : Determnng
SE 8 Fnal Project Story Sear Frame Gven: EI ω ω Solve for Story Bendng Beam Gven: EI ω ω 3 Story Sear Frame Gven: L 3 EI ω ω ω 3 3 m 3 L 3 Solve for Solve for m 3 3 4 3 Story Bendng Beam Part : Determnng
C PLANE ELASTICITY PROBLEM FORMULATIONS
 C M.. Tamn, CSMLab, UTM Corse Content: A ITRODUCTIO AD OVERVIEW mercal method and Compter-Aded Engneerng; Phscal problems; Mathematcal models; Fnte element method. B REVIEW OF -D FORMULATIOS Elements and
C M.. Tamn, CSMLab, UTM Corse Content: A ITRODUCTIO AD OVERVIEW mercal method and Compter-Aded Engneerng; Phscal problems; Mathematcal models; Fnte element method. B REVIEW OF -D FORMULATIOS Elements and
I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 ME 270 Fall 2012 Fnal Exam Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem
ME 270 Fall 2012 Fnal Exam Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS Begn each problem
Physics 207: Lecture 20. Today s Agenda Homework for Monday
 Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
Physcs 207: Lecture 20 Today s Agenda Homework for Monday Recap: Systems of Partcles Center of mass Velocty and acceleraton of the center of mass Dynamcs of the center of mass Lnear Momentum Example problems
This model contains two bonds per unit cell (one along the x-direction and the other along y). So we can rewrite the Hamiltonian as:
 1 Problem set #1 1.1. A one-band model on a square lattce Fg. 1 Consder a square lattce wth only nearest-neghbor hoppngs (as shown n the fgure above): H t, j a a j (1.1) where,j stands for nearest neghbors
1 Problem set #1 1.1. A one-band model on a square lattce Fg. 1 Consder a square lattce wth only nearest-neghbor hoppngs (as shown n the fgure above): H t, j a a j (1.1) where,j stands for nearest neghbors
Report on Image warping
 Report on Image warpng Xuan Ne, Dec. 20, 2004 Ths document summarzed the algorthms of our mage warpng soluton for further study, and there s a detaled descrpton about the mplementaton of these algorthms.
Report on Image warpng Xuan Ne, Dec. 20, 2004 Ths document summarzed the algorthms of our mage warpng soluton for further study, and there s a detaled descrpton about the mplementaton of these algorthms.
Problem Points Score Total 100
 Physcs 450 Solutons of Sample Exam I Problem Ponts Score 1 8 15 3 17 4 0 5 0 Total 100 All wor must be shown n order to receve full credt. Wor must be legble and comprehensble wth answers clearly ndcated.
Physcs 450 Solutons of Sample Exam I Problem Ponts Score 1 8 15 3 17 4 0 5 0 Total 100 All wor must be shown n order to receve full credt. Wor must be legble and comprehensble wth answers clearly ndcated.
Computer Graphics. Curves and Surfaces. Hermite/Bezier Curves, (B-)Splines, and NURBS. By Ulf Assarsson
 Compter Graphcs Crves and Srfaces Hermte/Bezer Crves, (B-)Splnes, and NURBS By Ulf Assarsson Most of the materal s orgnally made by Edward Angel and s adapted to ths corse by Ulf Assarsson. Some materal
Compter Graphcs Crves and Srfaces Hermte/Bezer Crves, (B-)Splnes, and NURBS By Ulf Assarsson Most of the materal s orgnally made by Edward Angel and s adapted to ths corse by Ulf Assarsson. Some materal
MOUNT SAINT JOSEPH MILPERRA
 Student Name : MOUNT SAINT JOSEPH MILPERRA MOUNT SAINT JOSEPH I YEAR 8 MATHEMATICS 17th November 2006 70 MINUTES (plus 5 mnutes readng tme)... :... INSTRUCTIONS: > WRITE IN BLUE OR BLACK PEN ONLY > ALL
Student Name : MOUNT SAINT JOSEPH MILPERRA MOUNT SAINT JOSEPH I YEAR 8 MATHEMATICS 17th November 2006 70 MINUTES (plus 5 mnutes readng tme)... :... INSTRUCTIONS: > WRITE IN BLUE OR BLACK PEN ONLY > ALL
UNIT 4 EXTENDING THE NUMBER SYSTEM Lesson 3: Operating with Complex Numbers Instruction
 Prerequste Sklls Ths lesson requres the use of the followng sklls: understandng that multplyng the numerator and denomnator of a fracton by the same quantty produces an equvalent fracton multplyng complex
Prerequste Sklls Ths lesson requres the use of the followng sklls: understandng that multplyng the numerator and denomnator of a fracton by the same quantty produces an equvalent fracton multplyng complex
SIMPLE LINEAR REGRESSION
 Smple Lnear Regresson and Correlaton Introducton Prevousl, our attenton has been focused on one varable whch we desgnated b x. Frequentl, t s desrable to learn somethng about the relatonshp between two
Smple Lnear Regresson and Correlaton Introducton Prevousl, our attenton has been focused on one varable whch we desgnated b x. Frequentl, t s desrable to learn somethng about the relatonshp between two
Physics 2A Chapters 6 - Work & Energy Fall 2017
 Physcs A Chapters 6 - Work & Energy Fall 017 These notes are eght pages. A quck summary: The work-energy theorem s a combnaton o Chap and Chap 4 equatons. Work s dened as the product o the orce actng on
Physcs A Chapters 6 - Work & Energy Fall 017 These notes are eght pages. A quck summary: The work-energy theorem s a combnaton o Chap and Chap 4 equatons. Work s dened as the product o the orce actng on
1 i. δ ε. so all the estimators will be biased; in fact, the less correlated w. (i.e., more correlated to ε. is perfectly correlated to x 4 i.
 Specal Topcs I. Use Instrmental Varable to F Specfcaton Problem (e.g., omtted varable 3 3 Assme we don't have data on If s correlated to,, or s mssng from the regresson Tradtonal Solton - pro varable:
Specal Topcs I. Use Instrmental Varable to F Specfcaton Problem (e.g., omtted varable 3 3 Assme we don't have data on If s correlated to,, or s mssng from the regresson Tradtonal Solton - pro varable:
Correlation and Regression. Correlation 9.1. Correlation. Chapter 9
 Chapter 9 Correlaton and Regresson 9. Correlaton Correlaton A correlaton s a relatonshp between two varables. The data can be represented b the ordered pars (, ) where s the ndependent (or eplanator) varable,
Chapter 9 Correlaton and Regresson 9. Correlaton Correlaton A correlaton s a relatonshp between two varables. The data can be represented b the ordered pars (, ) where s the ndependent (or eplanator) varable,
Week 9 Chapter 10 Section 1-5
 Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Please review the following statement: I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam.
 ME 270 Sprng 2014 Fnal Exam NME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS
ME 270 Sprng 2014 Fnal Exam NME (Last, Frst): Please revew the followng statement: I certfy that I have not gven unauthorzed ad nor have I receved ad n the completon of ths exam. Sgnature: INSTRUCTIONS
First Law: A body at rest remains at rest, a body in motion continues to move at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force.
 Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
Spring 2002 Lecture #13
 44-50 Sprng 00 ecture # Dr. Jaehoon Yu. Rotatonal Energy. Computaton of oments of nerta. Parallel-as Theorem 4. Torque & Angular Acceleraton 5. Work, Power, & Energy of Rotatonal otons Remember the md-term
44-50 Sprng 00 ecture # Dr. Jaehoon Yu. Rotatonal Energy. Computaton of oments of nerta. Parallel-as Theorem 4. Torque & Angular Acceleraton 5. Work, Power, & Energy of Rotatonal otons Remember the md-term
Chapter Twelve. Integration. We now turn our attention to the idea of an integral in dimensions higher than one. Consider a real-valued function f : D
 Chapter Twelve Integraton 12.1 Introducton We now turn our attenton to the dea of an ntegral n dmensons hgher than one. Consder a real-valued functon f : R, where the doman s a nce closed subset of Eucldean
Chapter Twelve Integraton 12.1 Introducton We now turn our attenton to the dea of an ntegral n dmensons hgher than one. Consder a real-valued functon f : R, where the doman s a nce closed subset of Eucldean
Section 3.6 Complex Zeros
 04 Chapter Secton 6 Comple Zeros When fndng the zeros of polynomals, at some pont you're faced wth the problem Whle there are clearly no real numbers that are solutons to ths equaton, leavng thngs there
04 Chapter Secton 6 Comple Zeros When fndng the zeros of polynomals, at some pont you're faced wth the problem Whle there are clearly no real numbers that are solutons to ths equaton, leavng thngs there
First Year Examination Department of Statistics, University of Florida
 Frst Year Examnaton Department of Statstcs, Unversty of Florda May 7, 010, 8:00 am - 1:00 noon Instructons: 1. You have four hours to answer questons n ths examnaton.. You must show your work to receve
Frst Year Examnaton Department of Statstcs, Unversty of Florda May 7, 010, 8:00 am - 1:00 noon Instructons: 1. You have four hours to answer questons n ths examnaton.. You must show your work to receve
WINTER 2017 EXAMINATION
 (ISO/IEC - 700-00 Certfed) WINTER 07 EXAMINATION Model wer ject Code: Important Instructons to Eamners: ) The answers should be eamned by key words and not as word-to-word as gven n the model answer scheme.
(ISO/IEC - 700-00 Certfed) WINTER 07 EXAMINATION Model wer ject Code: Important Instructons to Eamners: ) The answers should be eamned by key words and not as word-to-word as gven n the model answer scheme.
Physics 4B. A positive value is obtained, so the current is counterclockwise around the circuit.
 Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
Correction key. Example of an appropriate method. be the wind vector x = 120 and x = y = 160 and y = 10.
 Correction key 1 D Example of an appropriate method /4 Let x, y be the wind vector (km) y 100, 150 x, y 10, 160 100 x, 150 y 10, 160 100 withot wind with wind 100 + x = 10 and x = 0 150 + y = 160 and y
Correction key 1 D Example of an appropriate method /4 Let x, y be the wind vector (km) y 100, 150 x, y 10, 160 100 x, 150 y 10, 160 100 withot wind with wind 100 + x = 10 and x = 0 150 + y = 160 and y
Four Bar Linkages in Two Dimensions. A link has fixed length and is joined to other links and also possibly to a fixed point.
 Four bar lnkages 1 Four Bar Lnkages n Two Dmensons lnk has fed length and s oned to other lnks and also possbly to a fed pont. The relatve velocty of end B wth regard to s gven by V B = ω r y v B B = +y
Four bar lnkages 1 Four Bar Lnkages n Two Dmensons lnk has fed length and s oned to other lnks and also possbly to a fed pont. The relatve velocty of end B wth regard to s gven by V B = ω r y v B B = +y
UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 TOPIC Non-lnear relatonshps. Overvew.. Introducton Most people use socal meda. If we were to graph the number of hours after a message or rumour had begun aganst the number of people who had seen or read
TOPIC Non-lnear relatonshps. Overvew.. Introducton Most people use socal meda. If we were to graph the number of hours after a message or rumour had begun aganst the number of people who had seen or read
5 The Rational Canonical Form
 5 The Ratonal Canoncal Form Here p s a monc rreducble factor of the mnmum polynomal m T and s not necessarly of degree one Let F p denote the feld constructed earler n the course, consstng of all matrces
5 The Ratonal Canoncal Form Here p s a monc rreducble factor of the mnmum polynomal m T and s not necessarly of degree one Let F p denote the feld constructed earler n the course, consstng of all matrces
Rigid body simulation
 Rgd bod smulaton Rgd bod smulaton Once we consder an object wth spacal etent, partcle sstem smulaton s no longer suffcent Problems Problems Unconstraned sstem rotatonal moton torques and angular momentum
Rgd bod smulaton Rgd bod smulaton Once we consder an object wth spacal etent, partcle sstem smulaton s no longer suffcent Problems Problems Unconstraned sstem rotatonal moton torques and angular momentum
