COMPUTATION OF SMOKE SPREAD IN A BUILDING FIRE BY MULTI-LAYER ZONE MODEL
|
|
|
- Rosaline McCormick
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMPUTATION OF SMOKE SPREAD IN A BUILDING FIRE BY MULTI-LAYER ZONE MODEL K. Suzuki Institute of Technology, Shiizu Construction Corporation Etchuia Koto-ku, Tokyo , Japan T. Tanaka Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University, Gokasho, Ui, Kyoto 6-, Japan K. Harada Departent of Architecture and Architectural Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering Kyoto University, Katsura Capus C2-46, Nishikyo-ku, Kyoto , Japan ABSTRACT The ulti-layer zone fire soke oveent siulation odel (called as MLZ odel), a new zone odeling approach, was addressed to predict vertical distributions of the physical properties, such as teperature and cheical species concentration in a building fire. The odel still retains the advantage of other zone odels in ters of light coputational load, so it is expected to be useful for a practical application for fire safety design of a building. In this study, the verification against a fire experient in a ulti-roo area is presented. As the result, the predicted teperatures and gas velocity generally show satisfactory agreeent. Additionally, a GUI tool which decreases the user s load for calculation settings and which displays calculation results by color on a two-diensional plane was introduced. KEYWORDS: Multi-layer zone odel, Soke oveent, Fire experient, GUI tool INTRODUCTION A ulti-layer zone odel, a new zone odeling approach, was applied to predict vertical distributions of the physical properties in a building fire. As illustrated in Fig., the space volue of each roo is divided into an arbitrary nuber of ultiple layers as the control volues in which the physical properties are assued to be unifor. The boundary walls are also divided into segents in accordance with the layer divisions, and the convection and radiation heat transfer aong the layers and the wall segents are calculated. In this way, the vertical distributions of the physical properties in each roo are calculated. However the odel still retains the advantage of two-layer zone odels, such as CFAST and BRI22, in ters of light coputational load, so it is expected to be useful for a practical application for fire safety design of buildings. These basic concepts of the MLZ odel for a single roo and for a tunnel were introduced 2,3. In this study, the odel is extended to a ulti-roo configuration and iproveents are ade on the influence of ventilation flow to fire plue, the prediction of the ceiling et, the entrainent of the opening et plue and the radiation heat transfer fro the flae. The results of the validation against a fire experient in a building are deonstrated. THE MODEL The iage of the fluid oveent in the MLZ odel is deonstrated in Fig.. One of the notable differences of the concept fro the existing two-layer zone odels is that the fire plue flow does not ix with the upper layer the instant it penetrates the layer interface but continues to rise until it hits the Copyright International Association for Fire Safety Science
2 ceiling, after which it pushes down the gases in the top layer while flowing horizontally as a ceiling et. The iage of teperature prediction in a fire roo by the MLZ odel relative to that by a two-layer zone odel is on the left side of Fig.. The two-layer zone odel predicts the layer interface height and only two teperature values, i.e. those of upper and lower layers. In the case of the MLZ odel, the distribution of teperature can be predicted by calculating the teperatures of the ultiple layers of which positions are arbitrarily pre-fixed. () Governing Equation for Zone Properties The zone governing equation for the teperature of each layer is derived fro the conservation equations of ass and internal energy for each horizontal layer as follows: dti, = hi, + hi, Cpl,, i + Ti, + Cpl,, i Ti, + hop,, i + h, i + Qcw,, i + Q rl,, i dt C ρ V p i, i, [] h i, ( l,, i ) ( l,, i ) C p li,, Ti, = C p li,, Ti, < [2] where li,, and h i, are the vertical ass and enthalpy flow rate through the boundary between the th layer and the (+) th layer outside of the fire plue, respectively. Q cw,, i is the convection heat gain fro wall and Q rl,, i is the net radiation heat gain. Subscript i eans roo i. The enthalpy of the fire plue, h, i, is added only when entering the top layer of the fire roo, and in the other layer it equals zero. The enthalpies of ventilation flow are transferred to the ceiling or floor by buoyancy through the opening et plue, then the enthalpy of it, h op,, i, is added only to the layer in which the opening et plue reached. Likewise, the zone governing equations for ass fraction of species l (i.e. CO 2 ) in each layer can be derived. FIGURE. Iage of MLZ odel (a graph of left side shows coparison with teperature prediction iage of MLZ and 2-layer zone) 2
3 (2) Flow through the Openings Suing up the energy conservation equations in each roo of the atospheric pressure, the following equation could be written, x x x x C p T T Q Q Q nb i, nb, i nb, i, + cw,, i + + = rl,, i c nb = nb = = = [3] where Q c, the convective heat fro the fire source, which equals zero except for in the fire roo. The horizontal ass flow rates through the openings, i and nb, nb, are calculated fro Eq. [4] and i, Eq. [5]. ( ) ( ) = α B Δz 2ρ P P P P v i nb, i nb, i, i, nb, i, nb, ( ) = α B Δz 2 ρ ( P P ) P P < v nb i, i nb, nb, nb, i, i, nb, [4] i, i, i, k k = P = P g ρ Δz [5] Here, Eq. [3] can be solved for the value of the pressure of roo i at the floor height, P i,, by an appropriate iteration ethod, because it includes P i, iplicitly, i.e. starting fro an initial value of P i, and calculating i and nb, nb by Eq. [4], next substituting the into the left hand side of i, Eq. [3], then odifying P i, iteratively until the value of the left hand side of Eq. [3] becoes close enough to zero. This process is repeated to all roos by the Gauss-Seidel ethod, thus P i, of all roos and horizontal ass flow rates are calculated iplicitly. The flows that have passed through openings becoe opening et plues by buoyancy. They change direction upward or downward, depending on their teperature relative to the environent, entraining the gas around it. The teperature, the velocity, the half-width and the trace of the axis are calculated by arranging the conservation equations of ass, energy, and oent for two-direction. (3) Fire Plue Entrainent The ass entrainent rate into the fire plue fro the th layer,, and the enthalpy transported through fire plue into the top layer, h fp, are assued to be given 4 : ( ) /3 5/3 5/3 e, c = C Q z z [6] where the entrainent coefficient of fire plue, C e,, is estiated as 8 in the windless condition, while the value increases by the influence of the draft fro the openings on the fire plue. The plots in Fig. 2 shows the relation of the ratio of divided by the entrained ass flow rate in windless condition,, and the ratio of the ventilation velocity, U, divided by the velocity of the fuel, w* 5. Thus in this study, shown as the thick line in Fig. 2, it is assued to have a linear relation in * 833 U W.25 as follows: U = [7] 8.33 * w 3
4 Qg C w* = DρTC [8] p * Fro Eqs. [6], [7] and [8], the equation for C e, is given as 8 2U W. When U is too * * high, U W >.25, or U is too low, U W < 833, then C e, is decided as.24 and 8, respectively. C U * W U U = 8 2 < 2 3 * W < W U e, * 8 2 * W [9] Upper liit windless condition lower liit FIGURE 2. Relation of horizontal flow and entrainent increase rate (4) Teperature of Ceiling Jet FC The teperature rise of ceiling et under an unconfined ceiling under cal conditions, Δ T c, and Δ, can be calculated by the following equations 6 : FC T c, r 2/3 FC FC Q c, c, 5/3 r Δ T T T = [] H H 2/3 2/3 FC FC Q r r c, r c, r = < 5/3 Δ T T T [] H H H To apply Eqs. [] and [] to a fire in a copartent with a confined ceiling, consideration should be ade of the following issues: a) the entrainent of a fire plue increases by the draft fro openings as discussed in section (2), b) the enthalpy of the fire plue increases due to the entrainent of the hotter gas fro the layers at elevated teperature and c) the enthalpy into the ceiling et increases by 4
5 the sae reason. Hence, the calculation ethod for the teperature rise of ceiling et in a copartent fire, Δ T c, and Δ T c, r, is introduced as follows: a) Increase of the fire plue entrainent by draft The teperature rise of ceiling et adapted for the increase of the ass flow rate fro to, FC by draft, T FC Δ, and Δ T,, can be obtained as follows: letting the adusted ceiling height, or c entrainent height H be: c r fp 3/5 x x H = H = = [2] Substituting H for H in Eqs. [] and [] yields: 2/3 FC Q r c, = /3 Δ T [3] H H 2/3 2/3 FC Q r r c, r = /3 < Δ T H H H [4] b) Influence of plue entrainent fro layers at elevated teperature into the fire plue Fro the energy conservation of the fire plue, Δ T c, is calculated as: x = ( ) Tf, T FC = r Δ Tc, =Δ T c, +.8 x H [5] c) Influence of hot gas entrained into the ceiling et Considering the energy conservation for the ceiling et under unconfined ceiling without wind, the ass flow rate entrained by the ceiling et at radial distance r fro the ipinging point, c, r, is found to be: ΔT FC x 2/3 x c, r c, r = = 3.4 FC ΔT c, r = H = [6] Assuing that c, r can be obtained by Eq. [6] in an unconfined ceiling configuration, the equation for Δ T c, r is obtained by cobining the energy conservation of the ceiling et and Eq. [6] as follows: 5
6 x ( ) Tf, T c, r ( T FC f, x T = ) r Δ Tc, r =Δ T c, r + + >.8 x x H + + c, r c, r = = [7] (5) Radiation Heat Transfer In the odel, the radiation heat flux is assued to consist of three directional coponents between layers or layer and wall, i.e. the upward, the downward and the horizontal one fro each layer. The upward, downward and horizontal heat fluxes, q& ru,, i, q& rd,, i and q& rw,, i are calculated as follows: ( ) ( ) ( ) { } q& = α F q& + α σt + α F α q& + α σt [8] 4 4 ru,, i g,, i LU,, i ru,, i g,, i i, g,, i WU,, i w,, i rw,, i w,, i ws,, i ( ) + ( ) ( ) { } q& = α F q& + α σt + α F α q& + α σt [9] 4 4 rd,, i g,, i UL,, i rd,, i g,, i i, g,, i WL,, i w,, i rw,, i w,, i ws,, i 4 ( α )( + ) α σ q& = F q& + F q& + T + Q A [2] rw,, i g,, i LW,, i ru,, i UW,, i rd,, i g,, i i, rfw, w,, i where α wi,, are the radiation absorptivity, which is the sae as the eissivity, of the wall surface. Only in the fire roo, radiation fro the flae of the fire source to walls, partially absorbed in layers, is considered, as shown as broken lines in Fig. 3. The fraction of radiation heat fro the flae directing to the surface of the th wall segent, Q rf,, is given as: Q = Q F [2] rf, r FW, where Q r is the radiation heat eitted fro the fire source and FW, F is the ratio of radiation heat fro the fire source directing to the th wall. The fraction of Q rf, reached th, Q rfw,, is calculated by Eq. [22,] subtracted the radiation heat absorbed by the layers ( st - th ) fro Q rf, : Q ( α )( α ) ( α ) = L Q [22] rfw, g, f, g, f, g, f, rf, where α gi,,, the radiation absorptivity of the th layer of the i th roo, changes according to the gas teperature and ass fractions of CO 2, H 2 O and soot, of which the spectra are not unifor. In this odel, the Fortran progra ABSORB, developed by Modak 7, is used to calculate α gi,,. In the other hand, the total radiation absorbed in the th layer fro the fire point, Q x ( ) ( ) = α α L α Q [23] rfl, f, f, f, rf, k k= Thus the net radiation heat gain of the th layer of the i th roo, Q rl,, i, is: (& & ) ( & & + + ) 4 {( α ) & α σ } Q = A q q + A q + q rl,, i f,, i ru,, i rd,, i f,, i ru,, i rd,, i + A q& q + T + Q wi,, rwi,, wi,, rwi,, wi,, wi,, rfl, [24] 6
7 (6) Calculation Flow Fig. 4 shows the flow chart of this odel. (-α w,f, )q rw,f, +α w,f, σ(τ ws,f, ) 4 q rw,f, Q rfl, q rd,f,+ + layer T ws,f, q ru,f, T f, q rd,f, layer Wall - layer Q rfw, Q rf, fire q ru,f,- Point q rd,f,2 2 layer q rw,f, T ws,f, Q rfw, q ru,f, T f, q rd,f, layer Q rf, T ws,f, q ru,f, Area f FIGURE 3. Iage of radiation transfer in fire roo Reading setting file Initial condition t=t+δt t= Heat release rate Cobustion gas calc. Opening flow and pressure calc. Opening et plue calc. Fire plue calc. Ceiling et calc. Vertical flow calc. Radiation heat transfer calc. Convective heat transfer calc. Wall teperature calc. Gas teperature calc. Gas concentration calc. Output data no Tie finish? yes end FIGURE 4. Flow chart 7
8 COMPARISON WITH EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS () Experiental Data In this section, the results of teperature and velocity easureents in 4 cases of the fire experients are copared with the predictions by the odel for validation. The experiental setup of the roo of the fire origin, the plane of the whole experiental structure layout and a picture of the fire roo are shown in Figs. 5, 6 and 7, respectively. The experiental fields, adusted by the openings, and the fire source conditions are shown in Table. The total heat release rate data of the fire sources was obtained by easuring the weight loss of the fuel (n-heptane) and ultiplying the heat of cobustion per unit fuel (44.4 MJ/kg), as shown in Fig. 8. The vertical distributions of gas and wall surface teperature were easured by therocouples and the velocity distributions at the openings were easured by Pitot tubes and differential pressure gauges. As the ceiling et, the teperature at the point 2 below the ceiling at 2 distance fro the center of the fire source was easured by therocouple. FIGURE 5. Scheatic of fire roo FIGURE 6. Plane of experient field 8
9 FIGURE 7. A picture of fire roo 4 total h.r.r 3 2 CASE3 CASE4 CASE2 CASE tie[s] FIGURE 8. Total heat release rate TABLE. Suary of experiental conditions (4 cases) Case Case 2 Case 3 Case 4 doain fire roo fire roo fire roo+ corridor fire roo+corridor + non-fire roo opening (height-width[] ) opening (.6x.4) opening (.6x.4) opening2(2.x.8) opening3(x.8) opening2(2.x.8) opening3(x.8) opening4(2.x.8) Firepan (area) pan (. 2 ) 2 pans (.22 2 ) 2 pans (.22 2 ) 2 pans (.22 2 ) peak H.H.R. 2 kw 32 kw 35 kw 3 kw (2) Condition of the Calculation The calculation doain consists of 4 spaces, i.e., the two roos and the corridor that is virtually divided into two at the center for better precision of the prediction. Each space is divided into 2 horizontal layers of equal thickness. The conditions, such as the areas of roos, the ceiling height, the 9
10 initial air teperature and the total heat release rate were deterined basically according to the experiental conditions for each case. In the experient, ost of the partition walls were assebly walls with 24 plaster board on both sides and 5 glass wool in between. However, in the calculation the walls were siplified as 48 plaster boards. The property of the ceiling and the floor were set as 2 plaster board and concrete according to the conditions of the experient. The calculation tie step was s. The flow coefficient, α v, was set to.7 on the openings and.95 on the virtual boundary of the center of the corridor. (3) Coputer Load The CPU tie of the calculation for each case was within 3 s for coputing 24 s by a PC with Pentiu4 2.4 GHz, hence it could be found that this odel has the advantage of coputing load. (4) Results and Discussion Fig. 9 shows the coparison between the experients and the calculations of the vertical distribution of the teperature in the fire roo, the corridor (case 3 and 4 only) and the non-fire roo (case 4 only) at 6, 2 and 8 s. The calculations in the fire roo generally show satisfactory agreeent with the experients. However, they were a little lower at.3 to.2 fro the floor, and especially at 6 s in case 4 the calculation was fairly lower. The ain reasons are suspected to be that the total heat release rate easured in the experient ight not be so accurate and that the experients are influenced by radiation heat of the flae. The calculations in the corridor were higher at.9 to.4 fro the floor in case 3 and at.2 to.4 fro the floor in case 4, because the influence of the diffusion and the entrainent into the opening et ight be calculated less. Fig. shows the coparison with the teperature on the wall surface in the fire roo and the sae conclusion can be found with Fig gas tep.[ ] gas tep[ ] gas tep.[ ] gas tep.[ ] Case (Fire roo) Case 2 (Fire roo) Case 3 (Fire roo) Case 3(Corridor) gas tep.[ ] gas tep.[ ] gas tep.[ ] Case 4 (Fire roo) Case 4 (Corridor) Case 4 (Non-fire roo) cal 2s cal 8s exp 6s 5 52 exp 2s exp 温度 8s [ ] 床面高さ []cal 6s FIGURE 9. Gas teperature in fire roo, corridor and non-fire roo
11 時間 [ 秒 ] Fig. shows the coparison of the teperatures easured under the ceiling and the ceiling et teperature predicted by Eq. [7], and for reference by Eq. [5] (r = ) and Eq. [] (r = 2, original Alpert s equation). Within 6 s in case to 3, the calculations were high. The reason is unclear, but Eq. [] was tuned for steady condition, hence the applicability ight be beyond the range for the quick increase of the heat release. In the other, the coparisons were slightly high. Fig. 2 shows the coparison with the velocity through the opening. The calculations were roughly coincident with the experients, but soe of the neutral heights were different. It sees that the experients were easured only along the centerline of the opening so they were different with the average value of the opening area. The influence of entering wind fro outside could also be considered. GUI TOOL FOR PRE AND POST PROCESS For quick and easy aking of setting files and iproveent of visibility of the result, the pre-post GUI (Grafic User Interface) tool of the MLZ odel was developed, referring to CFD software on the arket. Fig. 3 shows the flow of process for the prediction including the pre-post tool. hegiht[] wall surface tep.[ ] wall surface tep.[ ] wall surface tep.[ ] wall surface tep.[ ] Case Case 2 Case 3 Case 4 FIGURE. Wall surface teperature in fire roo 温度 [ ] cal 2 eq.7 exp 2 cal f.c. eq. eq.5 cal Ceilinget Tep.[ 3 2 Ceilinget tep.[ 3 2 Ceiling et tep. 3 2 Ceiliget tep.[ tie[sec] tie[sec] ti e[sec] ti e[sec] Case Case 2 Case 3 Case 4 FIGURE. Gas teperature under ceiling in fire roo
12 fire roo.6 outdoor fire roo.6 outdoor fire roo corridor.8 corridor 2.8 outdoor opening.4 opening.4 OPENING 2 2. opening velocity[/s] -2-2 velocity[/s] -2-2 velocity[/s] -2-2 velocity[/s] Case Opening Case 2 Opening Case 3 Opening 2 Case 3 Opening 3 fire roo corridor.8 opening 2 2. corridor 2.8 opening 3.96 outdoor cal 2s cal 8s exp 6s 5 52 exp 2s exp 温度 8s [ ] 床面高さ []cal 6s velocity[/s] velocity[/s] Case 4 Opening 2 Case 4 Opening 3 FIGURE 2. Gas velocity through openings Pre process Reading picture of plan Setting space condition Setting wall condition Setting openings condition Setting soke control condition Setting fire detections Setting fire sources Output setting file MLZ progra Calculation Post process Reading calculation result Displaying teperature on plan Displaying teperature on section FIGURE 3. Process of prediction 2
13 Firstly, the pre tool helps aking a setting file. Boundaries of roos are drawn by click and snap of ouse operation above an iage file of a plane of an obect space. Soe other conditions such as the heat release rate of a fire source, an opening type, walls type can be set by selection fro a pull-down box or by nueric input with key. Fig. 4 shows an iage where input of a shape and soe conditions of calculation area and a fire scenario was finished. As a suppleent, the default values were inputted as a heat release rate and an exhaust gas flow rate in the standard fire safety design of Japan, and it is possible to plan coparatively early and quickly. After the calculation of the MLZ progra using the setting file, the post tool can display the calculation results visually. Fig. 5 shows an exaple of visualizing horizontal gas teperature data by color. Any height and any tie can be selected or changed progressively like an aniation. Fig. 6 shows a vertical distribution of gas teperature on a section, which is selected fro any plane. In this version, only gas teperature and gas concentrations can be displayed by color. FIGURE 4. Drawing the boundaries of roos (pre) FIGURE 5. Display of gas teperature on the plane (post) 3
14 FIGURE 6. Display of teperature distribution on the section (post) CONCLUSION In this study, the forulation of a MLZ odel was extended to ulti-roo configuration, and also the refineents were ade of the coponent odels such as fire plue, opening et plue, ceiling et and radiation heat transfer. The validation was ade against the full-scale fire experient. Considerably satisfactory results were obtained fro the validation, so the odel present is considered to be a useful tool for fire protection design. However there is still roo for further study on coparison with various experients and confiration of accuracy and applicability. ACKNOWDGEMENT This study has been carried out by the support of the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (No ). The authors thank Dr. Shigeru Yaada, Dr. Jun-ichi Watanabe, Dr Yuki Akizuki and Mitsuo Kadoya, Yoshitoo Kanai for their help and advice. REFERENCES. Tanaka, T. and Nakaura, K., Model for Predicting Soke Transport in Buildings - Base on Two Layer Zone Concept, Building Research Institute, No. 23, BRI, MOC, K. Suzuki, K. Harada and T. Tanaka, A Multi-Layer Zone Model for Predicting Fire Behavior in a Single roo, The 7th Syposiu of IAFSS, Jun, Suzuki, K., Harada, K. Tanaka, T. and Yoshida, H., An Application of a Multi-Layer Zone Model to a Tunnel Fire, 6th Asia-Oceania Syposiu on Fire Science and Technology, Zukoski, E.E., Soke Moveent and Mixing in Two-Layer Fire Models, The 8th UJNR Joint Panel Meeting on Fire Research and Safety, Tsukuba, May, J. G. Quintiere, The Effect of Roo Openings on Fire Plue Entrainent, Cobustion Science and Technology, Alpert, R.L., Calculation of Response Tie of Ceiling-Mounted Fire Detectors, Fire Technology, Modak, A.T., Radiation fro Products of Cobustion, Fire Research,, 978/79. 4
BALLISTIC PENDULUM. EXPERIMENT: Measuring the Projectile Speed Consider a steel ball of mass
 BALLISTIC PENDULUM INTRODUCTION: In this experient you will use the principles of conservation of oentu and energy to deterine the speed of a horizontally projected ball and use this speed to predict the
BALLISTIC PENDULUM INTRODUCTION: In this experient you will use the principles of conservation of oentu and energy to deterine the speed of a horizontally projected ball and use this speed to predict the
Data-Driven Imaging in Anisotropic Media
 18 th World Conference on Non destructive Testing, 16- April 1, Durban, South Africa Data-Driven Iaging in Anisotropic Media Arno VOLKER 1 and Alan HUNTER 1 TNO Stieltjesweg 1, 6 AD, Delft, The Netherlands
18 th World Conference on Non destructive Testing, 16- April 1, Durban, South Africa Data-Driven Iaging in Anisotropic Media Arno VOLKER 1 and Alan HUNTER 1 TNO Stieltjesweg 1, 6 AD, Delft, The Netherlands
Faraday's Law Warm Up
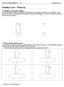 Faraday's Law-1 Faraday's Law War Up 1. Field lines of a peranent agnet For each peranent agnet in the diagra below draw several agnetic field lines (or a agnetic vector field if you prefer) corresponding
Faraday's Law-1 Faraday's Law War Up 1. Field lines of a peranent agnet For each peranent agnet in the diagra below draw several agnetic field lines (or a agnetic vector field if you prefer) corresponding
Ocean 420 Physical Processes in the Ocean Project 1: Hydrostatic Balance, Advection and Diffusion Answers
 Ocean 40 Physical Processes in the Ocean Project 1: Hydrostatic Balance, Advection and Diffusion Answers 1. Hydrostatic Balance a) Set all of the levels on one of the coluns to the lowest possible density.
Ocean 40 Physical Processes in the Ocean Project 1: Hydrostatic Balance, Advection and Diffusion Answers 1. Hydrostatic Balance a) Set all of the levels on one of the coluns to the lowest possible density.
ABSTRACT. A new scaling technique based on the hypothesis that flows in a compartment fire are
 ABSTRACT Title of Thesis: SCALE MODELING OF THE TRANSIENT BEHAVIOR OF HEAT FLUX IN ENCLOSURE FIRES Peter Surendran Veloo, Master of Science, 26 Directed By: John L. Bryan Chair Professor Jaes G. Quintiere
ABSTRACT Title of Thesis: SCALE MODELING OF THE TRANSIENT BEHAVIOR OF HEAT FLUX IN ENCLOSURE FIRES Peter Surendran Veloo, Master of Science, 26 Directed By: John L. Bryan Chair Professor Jaes G. Quintiere
Physically Based Modeling CS Notes Spring 1997 Particle Collision and Contact
 Physically Based Modeling CS 15-863 Notes Spring 1997 Particle Collision and Contact 1 Collisions with Springs Suppose we wanted to ipleent a particle siulator with a floor : a solid horizontal plane which
Physically Based Modeling CS 15-863 Notes Spring 1997 Particle Collision and Contact 1 Collisions with Springs Suppose we wanted to ipleent a particle siulator with a floor : a solid horizontal plane which
INVESTIGATION INTO RISE TIME OF BUOYANT FIRE PLUME FRONTS
 , Volume 2, Number, p.4-25, 2000 INVESTIGATION INTO RISE TIME OF BUOYANT FIRE PLUME FRONTS T. Tanaka isaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University, Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto, 6-00 Japan T. Fujita Shimizu
, Volume 2, Number, p.4-25, 2000 INVESTIGATION INTO RISE TIME OF BUOYANT FIRE PLUME FRONTS T. Tanaka isaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University, Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto, 6-00 Japan T. Fujita Shimizu
THE EFFECT OF SOLID PARTICLE SIZE UPON TIME AND SEDIMENTATION RATE
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering Vol. 5 (54) No. 1-1 THE EFFECT OF SOLID PARTICLE SIZE UPON TIME AND SEDIMENTATION RATE
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering Vol. 5 (54) No. 1-1 THE EFFECT OF SOLID PARTICLE SIZE UPON TIME AND SEDIMENTATION RATE
The Development of a Generalised Jet Mixing Model for the Derivation of Exclusion Zones in Hazardous Area Classification
 The Developent of a Generalised Jet Mixing Model for the Derivation of Exclusion Zones in Hazardous Area Classification Katherine McCobe, Peter Tait, Jason Whitley LogiCas Ltd. 33 Boundary Street, Spring
The Developent of a Generalised Jet Mixing Model for the Derivation of Exclusion Zones in Hazardous Area Classification Katherine McCobe, Peter Tait, Jason Whitley LogiCas Ltd. 33 Boundary Street, Spring
Chapter 4: Hypothesis of Diffusion-Limited Growth
 Suary This section derives a useful equation to predict quantu dot size evolution under typical organoetallic synthesis conditions that are used to achieve narrow size distributions. Assuing diffusion-controlled
Suary This section derives a useful equation to predict quantu dot size evolution under typical organoetallic synthesis conditions that are used to achieve narrow size distributions. Assuing diffusion-controlled
Department of Building Science, Tsinghua University, Beijing , China
 Supporting Inforation A SPME based C a -history ethod for easuring SVOC diffusion coefficients in clothing aterial Jianping Cao 1,, Ningrui Liu 1,, Yinping Zhang 1,,* 1 Departent of Building Science, Tsinghua
Supporting Inforation A SPME based C a -history ethod for easuring SVOC diffusion coefficients in clothing aterial Jianping Cao 1,, Ningrui Liu 1,, Yinping Zhang 1,,* 1 Departent of Building Science, Tsinghua
Accuracy of the Scaling Law for Experimental Natural Frequencies of Rectangular Thin Plates
 The 9th Conference of Mechanical Engineering Network of Thailand 9- October 005, Phuket, Thailand Accuracy of the caling Law for Experiental Natural Frequencies of Rectangular Thin Plates Anawat Na songkhla
The 9th Conference of Mechanical Engineering Network of Thailand 9- October 005, Phuket, Thailand Accuracy of the caling Law for Experiental Natural Frequencies of Rectangular Thin Plates Anawat Na songkhla
REPRODUCING KERNEL PARTICLE METHOD FOR CONDUCTION RADIATION INTERACTION IN 3D PARTICIPATING MEDIA
 Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Theral Sciences 2017, 1st ACTS March 26-30, 2017, Jeu Island, Korea ACTS-P00337 REPRODUCING KERNEL PARTICLE METHOD FOR CONDUCTION RADIATION INTERACTION IN 3D PARTICIPATING
Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Theral Sciences 2017, 1st ACTS March 26-30, 2017, Jeu Island, Korea ACTS-P00337 REPRODUCING KERNEL PARTICLE METHOD FOR CONDUCTION RADIATION INTERACTION IN 3D PARTICIPATING
Chapter 8 Deflection. Structural Mechanics 2 Dept of Architecture
 Chapter 8 Deflection Structural echanics Dept of rchitecture Outline Deflection diagras and the elastic curve Elastic-bea theory The double integration ethod oent-area theores Conjugate-bea ethod 8- Deflection
Chapter 8 Deflection Structural echanics Dept of rchitecture Outline Deflection diagras and the elastic curve Elastic-bea theory The double integration ethod oent-area theores Conjugate-bea ethod 8- Deflection
Chapter 10 Atmospheric Forces & Winds
 Chapter 10 Atospheric Forces & Winds Chapter overview: Atospheric Pressure o Horizontal pressure variations o Station vs sea level pressure Winds and weather aps Newton s 2 nd Law Horizontal Forces o Pressure
Chapter 10 Atospheric Forces & Winds Chapter overview: Atospheric Pressure o Horizontal pressure variations o Station vs sea level pressure Winds and weather aps Newton s 2 nd Law Horizontal Forces o Pressure
e-companion ONLY AVAILABLE IN ELECTRONIC FORM
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH doi 10.1287/opre.1070.0427ec pp. ec1 ec5 e-copanion ONLY AVAILABLE IN ELECTRONIC FORM infors 07 INFORMS Electronic Copanion A Learning Approach for Interactive Marketing to a Custoer
OPERATIONS RESEARCH doi 10.1287/opre.1070.0427ec pp. ec1 ec5 e-copanion ONLY AVAILABLE IN ELECTRONIC FORM infors 07 INFORMS Electronic Copanion A Learning Approach for Interactive Marketing to a Custoer
PHY 171. Lecture 14. (February 16, 2012)
 PHY 171 Lecture 14 (February 16, 212) In the last lecture, we looked at a quantitative connection between acroscopic and icroscopic quantities by deriving an expression for pressure based on the assuptions
PHY 171 Lecture 14 (February 16, 212) In the last lecture, we looked at a quantitative connection between acroscopic and icroscopic quantities by deriving an expression for pressure based on the assuptions
The Effects of External Parallel Direct Current Magnetic Field on a Cold Atmospheric Pressure Argon Plasma Jet
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 014 Available online at www.irjabs.co ISSN 51-838X / Vol, 8 (7): 895-903 Science Explorer Publications The Effects of External Parallel Direct
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 014 Available online at www.irjabs.co ISSN 51-838X / Vol, 8 (7): 895-903 Science Explorer Publications The Effects of External Parallel Direct
26 Impulse and Momentum
 6 Ipulse and Moentu First, a Few More Words on Work and Energy, for Coparison Purposes Iagine a gigantic air hockey table with a whole bunch of pucks of various asses, none of which experiences any friction
6 Ipulse and Moentu First, a Few More Words on Work and Energy, for Coparison Purposes Iagine a gigantic air hockey table with a whole bunch of pucks of various asses, none of which experiences any friction
Supplementary Information for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polymer Actuators
 Suppleentary Inforation for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polyer Actuators Bavani Balakrisnan, Alek Nacev, and Elisabeth Sela University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 074 1 Analytical
Suppleentary Inforation for Design of Bending Multi-Layer Electroactive Polyer Actuators Bavani Balakrisnan, Alek Nacev, and Elisabeth Sela University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland 074 1 Analytical
MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on Deceber 15, 2014 Partners Naes: Grade: EXPERIMENT 8 Electron Beas 0. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. Nae the 2 forces that are equated in order to derive the charge to
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on Deceber 15, 2014 Partners Naes: Grade: EXPERIMENT 8 Electron Beas 0. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. Nae the 2 forces that are equated in order to derive the charge to
Kinetic Theory of Gases: Elementary Ideas
 Kinetic Theory of Gases: Eleentary Ideas 17th February 2010 1 Kinetic Theory: A Discussion Based on a Siplified iew of the Motion of Gases 1.1 Pressure: Consul Engel and Reid Ch. 33.1) for a discussion
Kinetic Theory of Gases: Eleentary Ideas 17th February 2010 1 Kinetic Theory: A Discussion Based on a Siplified iew of the Motion of Gases 1.1 Pressure: Consul Engel and Reid Ch. 33.1) for a discussion
EVALUATION OF THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY IN PITCH- BASED CARBON FIBER REINFORCED PLASTICS
 16 TH INTERNATIONA CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIAS EVAUATION OF THERMA CONDUCTIVITY IN PITCH- BASED CARBON FIBER REINFORCED PASTICS Shinji Ogihara*, Makoto Yaaguchi**, Takahito Chiba**, Junichi Shiizu****,
16 TH INTERNATIONA CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIAS EVAUATION OF THERMA CONDUCTIVITY IN PITCH- BASED CARBON FIBER REINFORCED PASTICS Shinji Ogihara*, Makoto Yaaguchi**, Takahito Chiba**, Junichi Shiizu****,
Theory and Applications of the Indoor Noise Module (VDI 3760)
 Fullerton, CA 9835 USA Theory and Applications of the Indoor Noise Module (VDI 3760) The following Technical Note suarizes the atheatical concepts used in the SoundPLAN Indoor Factory Noise Module. 1.
Fullerton, CA 9835 USA Theory and Applications of the Indoor Noise Module (VDI 3760) The following Technical Note suarizes the atheatical concepts used in the SoundPLAN Indoor Factory Noise Module. 1.
Feature Extraction Techniques
 Feature Extraction Techniques Unsupervised Learning II Feature Extraction Unsupervised ethods can also be used to find features which can be useful for categorization. There are unsupervised ethods that
Feature Extraction Techniques Unsupervised Learning II Feature Extraction Unsupervised ethods can also be used to find features which can be useful for categorization. There are unsupervised ethods that
The Thermal Dependence and Urea Concentration Dependence of Rnase A Denaturant Transition
 The Theral Dependence and Urea Concentration Dependence of Rnase A Denaturant Transition Bin LI Departent of Physics & Astronoy, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15260, U.S.A Feb.20 th, 2001 Abstract:
The Theral Dependence and Urea Concentration Dependence of Rnase A Denaturant Transition Bin LI Departent of Physics & Astronoy, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15260, U.S.A Feb.20 th, 2001 Abstract:
CONTINUOUS THERMODYNAMICS FINITE DIFFUSION MODEL FOR MULTICOMPONENT FUEL SPRAY EVAPORATION
 CONTINUOUS THERMODYNAMICS FINITE DIFFUSION MODEL FOR MULTICOMPONENT FUEL SPRAY EVAPORATION Dongyao Wang 1 and Chia-fon F. Lee Departent of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics 1 Departent of Mechanical and
CONTINUOUS THERMODYNAMICS FINITE DIFFUSION MODEL FOR MULTICOMPONENT FUEL SPRAY EVAPORATION Dongyao Wang 1 and Chia-fon F. Lee Departent of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics 1 Departent of Mechanical and
3D acoustic wave modeling with a time-space domain dispersion-relation-based Finite-difference scheme
 P-8 3D acoustic wave odeling with a tie-space doain dispersion-relation-based Finite-difference schee Yang Liu * and rinal K. Sen State Key Laboratory of Petroleu Resource and Prospecting (China University
P-8 3D acoustic wave odeling with a tie-space doain dispersion-relation-based Finite-difference schee Yang Liu * and rinal K. Sen State Key Laboratory of Petroleu Resource and Prospecting (China University
Kinetic Theory of Gases: Elementary Ideas
 Kinetic Theory of Gases: Eleentary Ideas 9th February 011 1 Kinetic Theory: A Discussion Based on a Siplified iew of the Motion of Gases 1.1 Pressure: Consul Engel and Reid Ch. 33.1) for a discussion of
Kinetic Theory of Gases: Eleentary Ideas 9th February 011 1 Kinetic Theory: A Discussion Based on a Siplified iew of the Motion of Gases 1.1 Pressure: Consul Engel and Reid Ch. 33.1) for a discussion of
Kinematics and dynamics, a computational approach
 Kineatics and dynaics, a coputational approach We begin the discussion of nuerical approaches to echanics with the definition for the velocity r r ( t t) r ( t) v( t) li li or r( t t) r( t) v( t) t for
Kineatics and dynaics, a coputational approach We begin the discussion of nuerical approaches to echanics with the definition for the velocity r r ( t t) r ( t) v( t) li li or r( t t) r( t) v( t) t for
CHAPTER ONE. Physics and the Life Sciences
 Solution anual for Physics for the Life Sciences 2nd Edition by Allang Link download full: http://testbankair.co/download/solution-anual-forphysics-for-the-life-sciences-2nd-edition-by-allang/ CHAPTER
Solution anual for Physics for the Life Sciences 2nd Edition by Allang Link download full: http://testbankair.co/download/solution-anual-forphysics-for-the-life-sciences-2nd-edition-by-allang/ CHAPTER
A Pulley System Apparatus for a Laboratory Experience in Dynamics
 A Pulley Syste Apparatus for a Laboratory Experience in Dynaics Chris J. Kobus and Yin-Ping Chang Oakland University, Rochester, MI 48309-4478 Eail: cjkobus@oakland.edu Abstract This paper describes a
A Pulley Syste Apparatus for a Laboratory Experience in Dynaics Chris J. Kobus and Yin-Ping Chang Oakland University, Rochester, MI 48309-4478 Eail: cjkobus@oakland.edu Abstract This paper describes a
Assessment of wind-induced structural fatigue based on joint probability density function of wind speed and direction
 The 1 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environental, and Materials Research (ACEM 1) eoul, Korea, August 6-3, 1 Assessent of wind-induced structural fatigue based on oint probability density function
The 1 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environental, and Materials Research (ACEM 1) eoul, Korea, August 6-3, 1 Assessent of wind-induced structural fatigue based on oint probability density function
Modelling of the Through-air Bonding Process
 Modelling of the Through-air Bonding Process M. Hossain 1, M. Acar, Ph.D. 2, W. Malalasekera 2 1 School of Engineering, The Robert Gordon University, Aberdeen, UNITED KINDOM 2 Mechanical and Manufacturing
Modelling of the Through-air Bonding Process M. Hossain 1, M. Acar, Ph.D. 2, W. Malalasekera 2 1 School of Engineering, The Robert Gordon University, Aberdeen, UNITED KINDOM 2 Mechanical and Manufacturing
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF COLD AIR JET ATTACHMENT TO NON ADIABATIC WALLS
 Eleventh International IBPSA Conference Glasgow, Scotland July 27-30, 2009 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF COLD AIR JET ATTACHMENT TO NON ADIABATIC WALLS Nikola Mirkov 1, Žana Stevanović 1, and Žarko Stevanović
Eleventh International IBPSA Conference Glasgow, Scotland July 27-30, 2009 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF COLD AIR JET ATTACHMENT TO NON ADIABATIC WALLS Nikola Mirkov 1, Žana Stevanović 1, and Žarko Stevanović
ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECT OF THE CHEMICAL SPECIES CONCENTRATIONS ON THE RADIATION HEAT TRANSFER IN PARTICIPATING GASES USING A MONTE CARLO METHODOLOGY
 Proceedings of the 11 th Brazilian Congress of Theral Sciences and Engineering -- ECIT 2006 Braz. Soc. of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering -- ABCM, Curitiba, Brazil,- Dec. 5-8, 2006 Paper CIT06-0366
Proceedings of the 11 th Brazilian Congress of Theral Sciences and Engineering -- ECIT 2006 Braz. Soc. of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering -- ABCM, Curitiba, Brazil,- Dec. 5-8, 2006 Paper CIT06-0366
National 5 Summary Notes
 North Berwick High School Departent of Physics National 5 Suary Notes Unit 3 Energy National 5 Physics: Electricity and Energy 1 Throughout the Course, appropriate attention should be given to units, prefixes
North Berwick High School Departent of Physics National 5 Suary Notes Unit 3 Energy National 5 Physics: Electricity and Energy 1 Throughout the Course, appropriate attention should be given to units, prefixes
8.1 Force Laws Hooke s Law
 8.1 Force Laws There are forces that don't change appreciably fro one instant to another, which we refer to as constant in tie, and forces that don't change appreciably fro one point to another, which
8.1 Force Laws There are forces that don't change appreciably fro one instant to another, which we refer to as constant in tie, and forces that don't change appreciably fro one point to another, which
SIMULATION OF THE HEATING STEP WITHIN THE THERMOFORMING PROCESS USING THE FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD
 SIMULATION OF THE HEATING STEP WITHIN THE THERMOFORMING PROCESS USING THE FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD A. Fertschej 1 *, G.R. Langecker 1 University of Leoben artur.fertschej@u-leoben.at; Franz-Josef Strasse
SIMULATION OF THE HEATING STEP WITHIN THE THERMOFORMING PROCESS USING THE FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD A. Fertschej 1 *, G.R. Langecker 1 University of Leoben artur.fertschej@u-leoben.at; Franz-Josef Strasse
COS 424: Interacting with Data. Written Exercises
 COS 424: Interacting with Data Hoework #4 Spring 2007 Regression Due: Wednesday, April 18 Written Exercises See the course website for iportant inforation about collaboration and late policies, as well
COS 424: Interacting with Data Hoework #4 Spring 2007 Regression Due: Wednesday, April 18 Written Exercises See the course website for iportant inforation about collaboration and late policies, as well
External Transverse Direct Current Magnetic Field Effect On Optical Emission Of a Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Argon Plasma Jet
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 014 Available online at www.irjabs.co ISSN 51-838X / Vol, 8 (7): 944-950 Science Explorer Publications External Transverse Direct Current Magnetic
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 014 Available online at www.irjabs.co ISSN 51-838X / Vol, 8 (7): 944-950 Science Explorer Publications External Transverse Direct Current Magnetic
A MODEL OF SMOKE MOVEMENT IN STAIR SHAFTS
 A MODEL OF SMOKE MOVEMENT IN STAIR SHAFTS Daisaku Nii 1,4, Noe Takehira 1, Kazunori Harada 1,, Yoshifumi Ohmiya 2, Toshio Yamana 3 and Ichiro Hagiwara 3 1 Department of Architecture and Environmental Design,
A MODEL OF SMOKE MOVEMENT IN STAIR SHAFTS Daisaku Nii 1,4, Noe Takehira 1, Kazunori Harada 1,, Yoshifumi Ohmiya 2, Toshio Yamana 3 and Ichiro Hagiwara 3 1 Department of Architecture and Environmental Design,
MODIFIED SERIES RESISTANCE MODEL - DETERMINATION OF MEAN CONCENTRATION BY INTEGRAL TRANSFORMATION
 MODIFIED SERIES RESISTANCE MODEL - DETERMINATION OF MEAN CONCENTRATION BY INTEGRAL TRANSFORMATION A. L. Venezuela a, R. F. Cantão a, R. S. Ongaratto b, and R. N. Haneda c a Universidade Federal de São
MODIFIED SERIES RESISTANCE MODEL - DETERMINATION OF MEAN CONCENTRATION BY INTEGRAL TRANSFORMATION A. L. Venezuela a, R. F. Cantão a, R. S. Ongaratto b, and R. N. Haneda c a Universidade Federal de São
Modelling diabatic atmospheric boundary layer using a RANS-CFD code with a k-ε turbulence closure F. VENDEL
 Modelling diabatic atospheric boundary layer using a RANS-CFD code with a k-ε turbulence closure F. VENDEL Florian Vendel 1, Guillevic Laaison 1, Lionel Soulhac 1, Ludovic Donnat 2, Olivier Duclaux 2,
Modelling diabatic atospheric boundary layer using a RANS-CFD code with a k-ε turbulence closure F. VENDEL Florian Vendel 1, Guillevic Laaison 1, Lionel Soulhac 1, Ludovic Donnat 2, Olivier Duclaux 2,
Celal S. Konor Release 1.1 (identical to 1.0) 3/21/08. 1-Hybrid isentropic-sigma vertical coordinate and governing equations in the free atmosphere
 Celal S. Konor Release. (identical to.0) 3/2/08 -Hybrid isentropic-siga vertical coordinate governing equations in the free atosphere This section describes the equations in the free atosphere of the odel.
Celal S. Konor Release. (identical to.0) 3/2/08 -Hybrid isentropic-siga vertical coordinate governing equations in the free atosphere This section describes the equations in the free atosphere of the odel.
THERMAL ENDURANCE OF UNREINFORCED UNSATURATED POLYESTERS AND VINYL ESTER RESINS = (1) ln = COMPOSITES & POLYCON 2009
 Aerican Coposites Manufacturers Association January 15-17, 29 Tapa, FL USA Abstract THERMAL ENDURANCE OF UNREINFORCED UNSATURATED POLYESTERS AND VINYL ESTER RESINS by Thore M. Klaveness, Reichhold AS In
Aerican Coposites Manufacturers Association January 15-17, 29 Tapa, FL USA Abstract THERMAL ENDURANCE OF UNREINFORCED UNSATURATED POLYESTERS AND VINYL ESTER RESINS by Thore M. Klaveness, Reichhold AS In
2 Q 10. Likewise, in case of multiple particles, the corresponding density in 2 must be averaged over all
 Lecture 6 Introduction to kinetic theory of plasa waves Introduction to kinetic theory So far we have been odeling plasa dynaics using fluid equations. The assuption has been that the pressure can be either
Lecture 6 Introduction to kinetic theory of plasa waves Introduction to kinetic theory So far we have been odeling plasa dynaics using fluid equations. The assuption has been that the pressure can be either
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Wave Resistance Prediction of a Cataaran by Linearised Theory M.INSEL Faculty of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, Istanbul Technical University, TURKEY A.F.MOLLAND, J.F.WELLICOME Departent of
Wave Resistance Prediction of a Cataaran by Linearised Theory M.INSEL Faculty of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, Istanbul Technical University, TURKEY A.F.MOLLAND, J.F.WELLICOME Departent of
Uniaxial compressive stress strain model for clay brick masonry
 Uniaxial copressive stress strain odel for clay brick asonry Heant B. Kaushik, Durgesh C. Rai* and Sudhir K. Jain Departent of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, Kanpur 208 016,
Uniaxial copressive stress strain odel for clay brick asonry Heant B. Kaushik, Durgesh C. Rai* and Sudhir K. Jain Departent of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, Kanpur 208 016,
Title. Author(s)Izumida, Yuki; Okuda, Koji. CitationPhysical review E, 80(2): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type.
 Title Onsager coefficients of a finite-tie Carnot cycle Author(s)Izuida, Yuki; Okuda, Koji CitationPhysical review E, 80(2): 021121 Issue Date 2009-08 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/39348 Rights 2009
Title Onsager coefficients of a finite-tie Carnot cycle Author(s)Izuida, Yuki; Okuda, Koji CitationPhysical review E, 80(2): 021121 Issue Date 2009-08 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/39348 Rights 2009
OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION
 M7 Chapter 3 Section 1 OBJECTIVES Suarize data using easures of central tendency, such as the ean, edian, ode, and idrange. Describe data using the easures of variation, such as the range, variance, and
M7 Chapter 3 Section 1 OBJECTIVES Suarize data using easures of central tendency, such as the ean, edian, ode, and idrange. Describe data using the easures of variation, such as the range, variance, and
Name: Partner(s): Date: Angular Momentum
 Nae: Partner(s): Date: Angular Moentu 1. Purpose: In this lab, you will use the principle of conservation of angular oentu to easure the oent of inertia of various objects. Additionally, you develop a
Nae: Partner(s): Date: Angular Moentu 1. Purpose: In this lab, you will use the principle of conservation of angular oentu to easure the oent of inertia of various objects. Additionally, you develop a
Study of radiation in spherical media using moment method
 Aerican Journal of Physics and Applications 03; (): 5-3 Published online July 0, 03 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.co/j/ajpa) doi: 0.648/j.ajpa.0300.5 Study of radiation in spherical edia using oent
Aerican Journal of Physics and Applications 03; (): 5-3 Published online July 0, 03 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.co/j/ajpa) doi: 0.648/j.ajpa.0300.5 Study of radiation in spherical edia using oent
2002 University of Porto, Faculty of Engineering (FEUP)
 Holberg H, Ahtila P. Drying phenoenon in a fixed bed under the bio fuel ulti stage drying. In: Oliveira A, Afonso C, Riffat S, editors. Proceedings of the st International Conference on Sustainable Energy
Holberg H, Ahtila P. Drying phenoenon in a fixed bed under the bio fuel ulti stage drying. In: Oliveira A, Afonso C, Riffat S, editors. Proceedings of the st International Conference on Sustainable Energy
Farid Samara 1, Dominic Groulx 1 and Pascal H. Biwole 2 1
 Farid Saara 1, Doinic Groulx 1 and Pascal H. Biwole 2 1 Departent of Mechanical Engineering, Dalhousie University 2 Departent of Matheatics and Interactions, Université of Nice Sophia-Antipolis Excerpt
Farid Saara 1, Doinic Groulx 1 and Pascal H. Biwole 2 1 Departent of Mechanical Engineering, Dalhousie University 2 Departent of Matheatics and Interactions, Université of Nice Sophia-Antipolis Excerpt
CFD SIMULATION OF A MEMBRANE DISTILLATION MODULE CHANNEL
 CFD SIMULATION OF A MEMBRANE DISTILLATION MODULE CHANNEL A. Cipollina *, A. Di Miceli *, J. Koschikowski, G. Micale *, L. Rizzuti * * Dipartiento di Ingegneria Chiica dei Processi e dei Materiali, Università
CFD SIMULATION OF A MEMBRANE DISTILLATION MODULE CHANNEL A. Cipollina *, A. Di Miceli *, J. Koschikowski, G. Micale *, L. Rizzuti * * Dipartiento di Ingegneria Chiica dei Processi e dei Materiali, Università
Problem T1. Main sequence stars (11 points)
 Proble T1. Main sequence stars 11 points Part. Lifetie of Sun points i..7 pts Since the Sun behaves as a perfectly black body it s total radiation power can be expressed fro the Stefan- Boltzann law as
Proble T1. Main sequence stars 11 points Part. Lifetie of Sun points i..7 pts Since the Sun behaves as a perfectly black body it s total radiation power can be expressed fro the Stefan- Boltzann law as
An earlier article in this column considered the problem
 --- CALC CORNER Estiating nternal Air Cooling Teperature Reduction in a Closed Box Utilizing Theroelectrically Enhanced Heat Rejection Previously published in February, 2013 Bob Sions BM Retired The following
--- CALC CORNER Estiating nternal Air Cooling Teperature Reduction in a Closed Box Utilizing Theroelectrically Enhanced Heat Rejection Previously published in February, 2013 Bob Sions BM Retired The following
Hysteresis model for magnetic materials using the Jiles-Atherton model
 Hysteresis odel for agnetic aterials using the Jiles-Atherton odel Predrag Petrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, pegi@ei.yu Nebojsa itrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, itar@tfc.tfc.kg.ac.yu
Hysteresis odel for agnetic aterials using the Jiles-Atherton odel Predrag Petrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, pegi@ei.yu Nebojsa itrovic Technical faculty Svetog Save 65 32 Cacak, itar@tfc.tfc.kg.ac.yu
HALF-LIFE TIME FOR VOC EMISSION AND SORPTION OF POROUS BUILDING MATERIALS
 HAF-IFE TIME FOR VOC EMISSION AND SORPTION OF POROUS BUIDING MATERIAS C.-S. ee is Ph.D. Candidate, Departent of Building, Civil, and Environental Engineering; F. Haghighat is Professor, Departent of Building,
HAF-IFE TIME FOR VOC EMISSION AND SORPTION OF POROUS BUIDING MATERIAS C.-S. ee is Ph.D. Candidate, Departent of Building, Civil, and Environental Engineering; F. Haghighat is Professor, Departent of Building,
An Approximate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity Increase in the Intermediate Ballistics Period
 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction of the Velocity... 77 Central European Journal of Energetic Materials, 205, 2(), 77-88 ISSN 2353-843 An Approxiate Model for the Theoretical Prediction
Measuring orbital angular momentum superpositions of light by mode transformation
 CHAPTER 7 Measuring orbital angular oentu superpositions of light by ode transforation In chapter 6 we reported on a ethod for easuring orbital angular oentu (OAM) states of light based on the transforation
CHAPTER 7 Measuring orbital angular oentu superpositions of light by ode transforation In chapter 6 we reported on a ethod for easuring orbital angular oentu (OAM) states of light based on the transforation
Time-of-flight Identification of Ions in CESR and ERL
 Tie-of-flight Identification of Ions in CESR and ERL Eric Edwards Departent of Physics, University of Alabaa, Tuscaloosa, AL, 35486 (Dated: August 8, 2008) The accuulation of ion densities in the bea pipe
Tie-of-flight Identification of Ions in CESR and ERL Eric Edwards Departent of Physics, University of Alabaa, Tuscaloosa, AL, 35486 (Dated: August 8, 2008) The accuulation of ion densities in the bea pipe
The Thermal Conductivity Theory of Non-uniform Granular Flow and the Mechanism Analysis
 Coun. Theor. Phys. Beijing, China) 40 00) pp. 49 498 c International Acadeic Publishers Vol. 40, No. 4, October 5, 00 The Theral Conductivity Theory of Non-unifor Granular Flow and the Mechanis Analysis
Coun. Theor. Phys. Beijing, China) 40 00) pp. 49 498 c International Acadeic Publishers Vol. 40, No. 4, October 5, 00 The Theral Conductivity Theory of Non-unifor Granular Flow and the Mechanis Analysis
Daniel López Gaxiola 1 Student View Jason M. Keith
 Suppleental Material for Transport Process and Separation Process Principles Chapter Principles of Moentu Transfer and Overall Balances In fuel cells, the fuel is usually in gas or liquid phase. Thus,
Suppleental Material for Transport Process and Separation Process Principles Chapter Principles of Moentu Transfer and Overall Balances In fuel cells, the fuel is usually in gas or liquid phase. Thus,
Modeling of the Turbulence in the Water Column under Breaking Wind Waves
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 59, pp. 1 to 41, Modeling of the Turbulence in the Water Colun under Breaking Wind Waves HONG ZHANG* and ENG-SOON CHAN Tropical Marine Science Institute, National University
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 59, pp. 1 to 41, Modeling of the Turbulence in the Water Colun under Breaking Wind Waves HONG ZHANG* and ENG-SOON CHAN Tropical Marine Science Institute, National University
Optimization of ripple filter for pencil beam scanning
 Nuclear Science and Techniques 24 (2013) 060404 Optiization of ripple filter for pencil bea scanning YANG Zhaoxia ZHANG Manzhou LI Deing * Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Acadey of Sciences,
Nuclear Science and Techniques 24 (2013) 060404 Optiization of ripple filter for pencil bea scanning YANG Zhaoxia ZHANG Manzhou LI Deing * Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Acadey of Sciences,
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(2): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.co Journal of Cheical and Pharaceutical Research, 214, 6(2):77-82 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Design of experients of electroigration reliability for
Available online www.jocpr.co Journal of Cheical and Pharaceutical Research, 214, 6(2):77-82 Research Article ISSN : 975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Design of experients of electroigration reliability for
CFD SIMULATION OF PRESSURE LOSS IN HVDC TRANSFORMER WINDING
 Journal of Energy VOLUME 63 2014 journal hoepage: http://journalofenergy.co/ Ralf Wittaack Sieens AG, Nürnberg, Gerany Ralf.Wittaack@Sieens.co CFD SIMULATION OF PRESSURE LOSS IN HVDC TRANSFORMER WINDING
Journal of Energy VOLUME 63 2014 journal hoepage: http://journalofenergy.co/ Ralf Wittaack Sieens AG, Nürnberg, Gerany Ralf.Wittaack@Sieens.co CFD SIMULATION OF PRESSURE LOSS IN HVDC TRANSFORMER WINDING
12 Towards hydrodynamic equations J Nonlinear Dynamics II: Continuum Systems Lecture 12 Spring 2015
 18.354J Nonlinear Dynaics II: Continuu Systes Lecture 12 Spring 2015 12 Towards hydrodynaic equations The previous classes focussed on the continuu description of static (tie-independent) elastic systes.
18.354J Nonlinear Dynaics II: Continuu Systes Lecture 12 Spring 2015 12 Towards hydrodynaic equations The previous classes focussed on the continuu description of static (tie-independent) elastic systes.
Variation of the Frost Boundary below Road and Railway Embankments in Permafrost Regions in Response to Solar Irradiation and Winds
 Excerpt fro the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 009 Milan Variation of the Frost Boundary below Road and Railway Ebankents in Perafrost Regions in Response to Solar Irradiation and Winds N.I. Köle
Excerpt fro the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 009 Milan Variation of the Frost Boundary below Road and Railway Ebankents in Perafrost Regions in Response to Solar Irradiation and Winds N.I. Köle
Numerical Modeling of Self-Compacting Mortar Flow Using Discrete Element Method
 Nuerical Modeling of Self-Copacting Flow Using Discrete Eleent Method - Technical Paper - Miansong HUANG *1, Xuehui AN *, Takayuki OBARA *3 and Masahiro OUCHI *4 ABSTRACT A nuerical odeling of Self-Copacting
Nuerical Modeling of Self-Copacting Flow Using Discrete Eleent Method - Technical Paper - Miansong HUANG *1, Xuehui AN *, Takayuki OBARA *3 and Masahiro OUCHI *4 ABSTRACT A nuerical odeling of Self-Copacting
In this lecture... Axial flow turbine Impulse and reaction turbine stages Work and stage dynamics Turbine blade cascade
 Lect- 0 1 Lect-0 In this lecture... Axial flow turbine Ipulse and reaction turbine stages Work and stage dynaics Turbine blade cascade Lect-0 Axial flow turbines Axial turbines like axial copressors usually
Lect- 0 1 Lect-0 In this lecture... Axial flow turbine Ipulse and reaction turbine stages Work and stage dynaics Turbine blade cascade Lect-0 Axial flow turbines Axial turbines like axial copressors usually
A remark on a success rate model for DPA and CPA
 A reark on a success rate odel for DPA and CPA A. Wieers, BSI Version 0.5 andreas.wieers@bsi.bund.de Septeber 5, 2018 Abstract The success rate is the ost coon evaluation etric for easuring the perforance
A reark on a success rate odel for DPA and CPA A. Wieers, BSI Version 0.5 andreas.wieers@bsi.bund.de Septeber 5, 2018 Abstract The success rate is the ost coon evaluation etric for easuring the perforance
Thermal processes in industrial furnaces. doc. Ing. Pavel Šonovský, CSc.
 Theral processes in industrial furnaces doc. Ing. Pavel Šonovsý, CSc. STUDY INSTRUCTIONS Theral processes in industrial furnaces For the subject of the 10th seester of the study branch Metallurgical technology,
Theral processes in industrial furnaces doc. Ing. Pavel Šonovsý, CSc. STUDY INSTRUCTIONS Theral processes in industrial furnaces For the subject of the 10th seester of the study branch Metallurgical technology,
SIMULATION OF SOIL TEMPERATURE VARIATION FOR GEOTHERMAL APPLICATIONS
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volue 8, Issue 2, February 2017, pp. 167 175 Article ID: IJMET_08_02_020 Available online at http://www.iaee.co/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=2
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volue 8, Issue 2, February 2017, pp. 167 175 Article ID: IJMET_08_02_020 Available online at http://www.iaee.co/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=2
16.512, Rocket Propulsion Prof. Manuel Martinez-Sanchez Lecture 30: Dynamics of Turbopump Systems: The Shuttle Engine
 6.5, Rocket Propulsion Prof. Manuel Martinez-Sanchez Lecture 30: Dynaics of Turbopup Systes: The Shuttle Engine Dynaics of the Space Shuttle Main Engine Oxidizer Pressurization Subsystes Selected Sub-Model
6.5, Rocket Propulsion Prof. Manuel Martinez-Sanchez Lecture 30: Dynaics of Turbopup Systes: The Shuttle Engine Dynaics of the Space Shuttle Main Engine Oxidizer Pressurization Subsystes Selected Sub-Model
Neural Network Identifier with Iterative Learning for Turbofan Engine Rotor Speed Control System
 Neural Network Identifier with Iterative earning for Turbofan Engine Rotor Speed Control Syste QIAN Kun PANG Xiangping I Bangyuan Departent of Aerial Instruent and Electric Engineering The First Aeronautical
Neural Network Identifier with Iterative earning for Turbofan Engine Rotor Speed Control Syste QIAN Kun PANG Xiangping I Bangyuan Departent of Aerial Instruent and Electric Engineering The First Aeronautical
CFD-Parametric Study in Stator Heat Transfer of an Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Machine
 World Acadey of Science, Engineering and Technology CFD-Paraetric Study in Stator Heat Transfer of an Axial Flux Peranent Magnet Machine Alireza Rasekh, Peter Sergeant, Jan Vierendeels Abstract This paper
World Acadey of Science, Engineering and Technology CFD-Paraetric Study in Stator Heat Transfer of an Axial Flux Peranent Magnet Machine Alireza Rasekh, Peter Sergeant, Jan Vierendeels Abstract This paper
USEFUL HINTS FOR SOLVING PHYSICS OLYMPIAD PROBLEMS. By: Ian Blokland, Augustana Campus, University of Alberta
 1 USEFUL HINTS FOR SOLVING PHYSICS OLYMPIAD PROBLEMS By: Ian Bloland, Augustana Capus, University of Alberta For: Physics Olypiad Weeend, April 6, 008, UofA Introduction: Physicists often attept to solve
1 USEFUL HINTS FOR SOLVING PHYSICS OLYMPIAD PROBLEMS By: Ian Bloland, Augustana Capus, University of Alberta For: Physics Olypiad Weeend, April 6, 008, UofA Introduction: Physicists often attept to solve
REDUCTION OF FINITE ELEMENT MODELS BY PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION
 ISSN 139 14X INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND CONTROL, 008, Vol.37, No.3 REDUCTION OF FINITE ELEMENT MODELS BY PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION Riantas Barauskas, Vidantas Riavičius Departent of Syste Analysis, Kaunas
ISSN 139 14X INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY AND CONTROL, 008, Vol.37, No.3 REDUCTION OF FINITE ELEMENT MODELS BY PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION Riantas Barauskas, Vidantas Riavičius Departent of Syste Analysis, Kaunas
Dynamics of Bass Reflex Loudspeaker Systems (3)
 MCAP5E Dynaics of Bass Refle Loudspeaker Systes (3) Deriving Equations of Motion of Bass Refle Speaker Systes 3. Deriving Equations of Motion Shigeru Suzuki Released in May 5th, 8 in Japanese Released
MCAP5E Dynaics of Bass Refle Loudspeaker Systes (3) Deriving Equations of Motion of Bass Refle Speaker Systes 3. Deriving Equations of Motion Shigeru Suzuki Released in May 5th, 8 in Japanese Released
Development of point source method and its practical significance
 Water Science and Engineering, 9, (): 19-31 doi:1.388/j.issn.1674-37.9..3 http://kkb.hhu.edu.cn e-ail: wse@hhu.edu.cn Developent of point source ethod and its practical significance Bidya Sagar PANI* Civil
Water Science and Engineering, 9, (): 19-31 doi:1.388/j.issn.1674-37.9..3 http://kkb.hhu.edu.cn e-ail: wse@hhu.edu.cn Developent of point source ethod and its practical significance Bidya Sagar PANI* Civil
EVAPORATION EFFECT IN NONLINEAR PENETRATION OF HIGH ENERGY BEAM DRILLING
 1 Journal of Marine Science and echnology, Vol. 17, No., pp. 1-17 (9) EVAPORAION EFFEC IN NONLINEAR PENERAION OF HIGH ENERGY BEAM DRILLING Je-Ee Ho* and Chen-Lung Yen** Key words: enthalpy ethod. ABSRAC
1 Journal of Marine Science and echnology, Vol. 17, No., pp. 1-17 (9) EVAPORAION EFFEC IN NONLINEAR PENERAION OF HIGH ENERGY BEAM DRILLING Je-Ee Ho* and Chen-Lung Yen** Key words: enthalpy ethod. ABSRAC
1 Brownian motion and the Langevin equation
 Figure 1: The robust appearance of Robert Brown (1773 1858) 1 Brownian otion and the Langevin equation In 1827, while exaining pollen grains and the spores of osses suspended in water under a icroscope,
Figure 1: The robust appearance of Robert Brown (1773 1858) 1 Brownian otion and the Langevin equation In 1827, while exaining pollen grains and the spores of osses suspended in water under a icroscope,
Optical Properties of Plasmas of High-Z Elements
 Forschungszentru Karlsruhe Techni und Uwelt Wissenschaftlishe Berichte FZK Optical Properties of Plasas of High-Z Eleents V.Tolach 1, G.Miloshevsy 1, H.Würz Project Kernfusion 1 Heat and Mass Transfer
Forschungszentru Karlsruhe Techni und Uwelt Wissenschaftlishe Berichte FZK Optical Properties of Plasas of High-Z Eleents V.Tolach 1, G.Miloshevsy 1, H.Würz Project Kernfusion 1 Heat and Mass Transfer
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations, Simple Harmonic Motion
 Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
Lecture #8-3 Oscillations Siple Haronic Motion So far we have considered two basic types of otion: translation and rotation. But these are not the only two types of otion we can observe in every day life.
Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyramidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular Cross-Sectional Area
 Proceedings of the 006 WSEAS/IASME International Conference on Heat and Mass Transfer, Miai, Florida, USA, January 18-0, 006 (pp13-18) Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyraidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular
Proceedings of the 006 WSEAS/IASME International Conference on Heat and Mass Transfer, Miai, Florida, USA, January 18-0, 006 (pp13-18) Spine Fin Efficiency A Three Sided Pyraidal Fin of Equilateral Triangular
A Numerical Investigation of Turbulent Magnetic Nanofluid Flow inside Square Straight Channel
 A Nuerical Investigation of Turbulent Magnetic Nanofluid Flow inside Square Straight Channel M. R. Abdulwahab Technical College of Mosul, Mosul, Iraq ohaedalsafar2009@yahoo.co Abstract A nuerical study
A Nuerical Investigation of Turbulent Magnetic Nanofluid Flow inside Square Straight Channel M. R. Abdulwahab Technical College of Mosul, Mosul, Iraq ohaedalsafar2009@yahoo.co Abstract A nuerical study
Curious Bounds for Floor Function Sums
 1 47 6 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 1 (018), Article 18.1.8 Curious Bounds for Floor Function Sus Thotsaporn Thanatipanonda and Elaine Wong 1 Science Division Mahidol University International
1 47 6 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 1 (018), Article 18.1.8 Curious Bounds for Floor Function Sus Thotsaporn Thanatipanonda and Elaine Wong 1 Science Division Mahidol University International
A Simplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the Weaving Machines with Automatic Filling Repair
 Proceedings of the 6th SEAS International Conference on Siulation, Modelling and Optiization, Lisbon, Portugal, Septeber -4, 006 0 A Siplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the eaving
Proceedings of the 6th SEAS International Conference on Siulation, Modelling and Optiization, Lisbon, Portugal, Septeber -4, 006 0 A Siplified Analytical Approach for Efficiency Evaluation of the eaving
A Two-zone fire growth and smoke movement model for multi-compartment buildings. Fu, Z.; Hadjisophocleous, G. V.
 A Two-zone fire rowth and soke oveent odel for ulti-copartent buildins u, Z.; Hadjisophocleous, G. V. NR- A version of this paper is published in / Une version de ce docuent se trouve dans : ire Safety
A Two-zone fire rowth and soke oveent odel for ulti-copartent buildins u, Z.; Hadjisophocleous, G. V. NR- A version of this paper is published in / Une version de ce docuent se trouve dans : ire Safety
are equal to zero, where, q = p 1. For each gene j, the pairwise null and alternative hypotheses are,
 Page of 8 Suppleentary Materials: A ultiple testing procedure for ulti-diensional pairwise coparisons with application to gene expression studies Anjana Grandhi, Wenge Guo, Shyaal D. Peddada S Notations
Page of 8 Suppleentary Materials: A ultiple testing procedure for ulti-diensional pairwise coparisons with application to gene expression studies Anjana Grandhi, Wenge Guo, Shyaal D. Peddada S Notations
Two Dimensional Consolidations for Clay Soil of Non-Homogeneous and Anisotropic Permeability
 Two Diensional Consolidations for Clay Soil of Non-Hoogeneous and Anisotropic Pereability Ressol R. Shakir, Muhaed Majeed Thiqar University, College of Engineering, Thiqar, Iraq University of Technology,
Two Diensional Consolidations for Clay Soil of Non-Hoogeneous and Anisotropic Pereability Ressol R. Shakir, Muhaed Majeed Thiqar University, College of Engineering, Thiqar, Iraq University of Technology,
A NEW MODEL FOR ESTIMATING NEUTRAL PLANE IN FIRE SITUATION
 A NEW MODEL FOR ESTIMATING NEUTRAL PLANE IN FIRE SITUATION JY Zhang¹,*, Jane WZ Lu² and R Huo¹ 1 PhD student, State Key Laboratory of Fire Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei,
A NEW MODEL FOR ESTIMATING NEUTRAL PLANE IN FIRE SITUATION JY Zhang¹,*, Jane WZ Lu² and R Huo¹ 1 PhD student, State Key Laboratory of Fire Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei,
Bayesian Approach for Fatigue Life Prediction from Field Inspection
 Bayesian Approach for Fatigue Life Prediction fro Field Inspection Dawn An and Jooho Choi School of Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering, Korea Aerospace University, Goyang, Seoul, Korea Srira Pattabhiraan
Bayesian Approach for Fatigue Life Prediction fro Field Inspection Dawn An and Jooho Choi School of Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering, Korea Aerospace University, Goyang, Seoul, Korea Srira Pattabhiraan
A New Algorithm for Reactive Electric Power Measurement
 A. Abiyev, GAU J. Soc. & Appl. Sci., 2(4), 7-25, 27 A ew Algorith for Reactive Electric Power Measureent Adalet Abiyev Girne Aerican University, Departernt of Electrical Electronics Engineering, Mersin,
A. Abiyev, GAU J. Soc. & Appl. Sci., 2(4), 7-25, 27 A ew Algorith for Reactive Electric Power Measureent Adalet Abiyev Girne Aerican University, Departernt of Electrical Electronics Engineering, Mersin,
ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND PARAMETRIC STUDY OF LATERAL IMPACT BEHAVIOR OF PRESSURIZED PIPELINES AND INFLUENCE OF INTERNAL PRESSURE
 DRAFT Proceedings of the ASME 014 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition IMECE014 Noveber 14-0, 014, Montreal, Quebec, Canada IMECE014-36371 ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND PARAMETRIC
DRAFT Proceedings of the ASME 014 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition IMECE014 Noveber 14-0, 014, Montreal, Quebec, Canada IMECE014-36371 ANALYTICAL INVESTIGATION AND PARAMETRIC
Simplified Explicit Model to Measure Transient Heat Transfer in Foamcrete Panel System
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 77: -, ISSN 99-878 Siplified Eplicit Model to Measure ransient Heat ransfer in Foacrete Panel Syste Md Azree Othuan Mydin School of Housing, Building and
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 77: -, ISSN 99-878 Siplified Eplicit Model to Measure ransient Heat ransfer in Foacrete Panel Syste Md Azree Othuan Mydin School of Housing, Building and
Darcy s law describes water flux determined by a water potential gradient: q w = k dψ dx
 6 Hydraulic Properties The soil hydraulic properties are of utost iportance for a large variety of soil processes and in particular for soil water flow. The two ost coon hydraulic properties are the soil
6 Hydraulic Properties The soil hydraulic properties are of utost iportance for a large variety of soil processes and in particular for soil water flow. The two ost coon hydraulic properties are the soil
