3 Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion
|
|
|
- Paula McDaniel
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 1 SECTION Matter in Motion 3 Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is friction? How does friction affect motion? What are the types of friction? How can friction be changed? National Science Education Standards PS 2c What Causes Friction? Suppose you are playing soccer and you kick the ball far from you. You know that the ball will slow down and eventually stop. This means that the velocity of the ball will decrease to 0. You also know that an unbalanced force is needed to change the velocity of objects. So, what force is stopping the ball? Friction is the force that opposes the motion between two surfaces that touch. Friction causes the ball to slow down and then stop. What causes friction? The surface of any object is rough. Even an object that feels smooth is covered with very tiny hills and valleys. When two surfaces touch, the hills and valleys of one surface stick to the hills and valleys of the other. This contact between surfaces causes friction. If a force pushes two surfaces together even harder, the hills and valleys come closer together. This increases the friction between the surfaces. STUDY TIP Imagine As you read, think about the ways that friction affects your life. Make a list of things that might happen, or not happen, if friction did not exist. READING CHECK 1. Describe What is friction? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why can t you see the hills and valleys without a close-up view of the objects? Interactive Textbook 11 Matter in Motion
2 SECTION 3 Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion continued STANDARDS CHECK PS 2c If more than one force acts on an object along a straight line, then the forces reinforce or cancel one another, depending on their direction and magnitude. Unbalanced forces will cause changes in the speed or direction of an object s motion. 3. Identify Two identical balls begin rolling next to each other at the same velocity. One is on a smooth surface and one is on a rough surface. Which ball will stop first? Why? What Affects the Amount of Friction? Imagine that a ball is rolled over a carpeted floor and another ball is rolled over a wood floor. Which surface affects a ball more? The smoothness of the surfaces of the objects affects how much friction exists. Friction is usually greater between materials that have rough surfaces than materials that have smooth surfaces. The carpet has greater friction than the wood floor, so the ball on the carpet stops first. What Types of Friction Exist? There are two types of friction: kinetic friction and static friction. Kinetic friction occurs when force is applied to an object and the object moves. When a cat slides along a countertop, the friction between the cat and the countertop is kinetic friction. The word kinetic means moving. The amount of kinetic friction between moving surfaces depends partly on how the surfaces move. In some cases, the surfaces slide past each other like pushing a box on the floor. In others, one surface rolls over another like a moving car on a road. There is usually less friction between surfaces that roll than between surfaces that slide. Static friction occurs when force applied to an object does not cause the object to move. When you try to push a piece of furniture that will not move, the friction observed is static friction. TAKE A LOOK 4. Describe When does static friction become kinetic friction? a b c There is no friction between the block and the table when no force is applied to the block. If a small force (dark gray arrow) is applied to the block, the block does not move. The force of static friction (light gray arrow) balances the force applied. When the force applied to the block is greater than the force of static friction, the block starts moving. When the block starts moving, kinetic friction (light gray arrow) replaces all of the static friction and opposes the force applied. Interactive Textbook 12 Matter in Motion
3 SECTION 3 Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion continued How Can Friction Be Decreased? To reduce the amount of friction, you can apply a lubricant between two surfaces. A lubricant is a substance that reduces the friction between surfaces. Motor oil, wax, and grease are examples of lubricants. You can also reduce friction by rolling, rather than sliding, an object. A refrigerator on rollers is much easier to move than one that just slides. Another way of reducing friction is to smooth the surfaces that rub against each other. Skiers have their skis sanded down to make them smoother. This makes it easier for the skis to slide over the snow. Critical Thinking 5. Infer How does a lubricant reduce the amount of friction? If you work on a bicycle, you may get dirty from the chain oil. This lubricant reduces friction between sections of the chain. How Can Friction Be Increased? Increasing the amount of friction between surfaces can be very important. For example, when the tires of a car grip the road better, the car stops and turns corners much better. Friction causes the tires to grip the road. Without friction, a car could not start moving or stop. On icy roads, sand can be used to make the road surface rougher. Friction increases as surfaces are made rougher. You can also increase friction by increasing the force between the two objects. Have you ever cleaned a dirty pan in the kitchen sink? You may have found that cleaning the pan with more force allows you to increase the amount of friction. This makes it easier to clean the pan. TAKE A LOOK 6. Identify Why is it important to put oil on a bicycle chain? READING CHECK 7. Identify Name two things that can be done to increase the friction between surfaces. Interactive Textbook 13 Matter in Motion
4 Section 3 NSES PS 2c SECTION VOCABULARY friction a force that opposes the motion between two surfaces that are in contact 1. Describe What effect does friction have when you are trying to move an object at rest? 2. Compare Explain the difference between static friction and kinetic friction. Give an example of each. 3. Compare The figure on the left shows two surfaces up close. On the right, draw a sketch. Show what the surfaces of two objects that have less friction between them might look like. 4. Analyze Name three common lubricants and describe why they are used. 5. Analyze In what direction does friction always act? 6. Identify A car is driving on a flat road. When the driver hits the brakes, the car slows down and stops. What would happen if there were no friction between the tires and the road? Explain your answer. Interactive Textbook 14 Matter in Motion
5 M Forces, Motion, and Energy Answer Key Chapter 1 Matter in Motion SECTION 1 MEASURING MOTION 1. When an object changes position over time in relation to a reference point, the object is in motion. 2. the mountain 3. Owen s desk 4. one positive unit on the y-axis and then one positive unit on the x-axis, or one positive unit on the x-axis and then one positive unit on the y-axis 5. Average speed does not mean constant speed. At times the bird flies faster, and at times it flies more slowly. 6. average speed total distance total time average speed 10 m 2.5 s 4 m/s 7. a straight diagonal line from 0,0 to the point 10 s, 7 m 8. No, velocity needs a direction. 9. Situation What changes Raindrop falling faster and faster Runner going around a turn on a track Car taking an exit off a highway Train arriving at a station Baseball being caught by a catcher Baseball hit by a batter Answers will vary. speed direction speed and direction speed speed speed and direction speed and direction 10. Yes, his speed is increasing. 11. It slows down. 12. positive for increasing speed, negative for decreasing speed 1. Speed is the rate at which an object moves, but velocity is the rate at which an object moves in a particular direction. 2. From left to right: at rest, positive acceleration, constant velocity, deceleration 3. The skateboard starts at rest and speeds up for 15 s. It stops for 5 s. It speeds up for 10 s. Then it turns around and speeds back to its starting point. 4. average speed total distance traveled total time average speed 80 m 40 s 2 m/s SECTION 2 WHAT IS A FORCE? 1. direction and size 2. balanced forces 3. Arrow pointing right is the size of both small arrows combined. 4. The rope would not move. The forces would be balanced. 5. The motion of the object will not change. 6. It will change its motion. 1. Net force is the total force acting on an object. If all of the forces balance each other out, there is no net force. 2. You push down on pedals, you push the handle bars in either direction, and your weight pushes down on the seat N to the right, 13 N down 4. The object on the left will move or accelerate to the right. The object on the right will move or accelerate down. 5. Balanced forces have a net force of 0 N, and the object will not change its motion. If the net force is other than 0, the force is unbalanced and the object will change its motion. SECTION 3 FRICTION: A FORCE THAT OPPOSES MOTION 1. Friction is a force that opposes the motion between two surfaces that touch. 2. Usually, the hills and valleys are very tiny. 3. The ball on the rough surface will stop first because of greater friction, or a greater unbalanced force. 4. when the force that is applied to an object at rest causes the object to move 5. A lubricant makes the surfaces smoother by filling up the valleys and coating the hills. 6. to reduce friction 7. Make surfaces rougher and increase the force between two surfaces. Interactive Textbook Answer Key 81 Forces, Motion, and Energy
6 M Forces, Motion, and Energy Answer Key continued 1. Friction makes it harder to get objects moving and keep them moving. 2. Static friction is friction between two surfaces that are not moving. Kinetic friction is between moving surfaces. Possible examples: Friction between the floor and a refrigerator that is being pushed but is not moving is static friction. Friction between the floor and a refrigerator that has started to slide is an example of kinetic friction. 3. Sketch should show smoother surfaces; peaks and valleys have less relief. 4. Grease, oil, and wax are lubricants. They reduce the friction between surfaces that touch. 5. Friction always acts in a direction opposite the direction of motion. 6. The car would not stop. Friction between the tires and the road is needed to start or stop. 7. The forces must be unbalanced, because the object starts moving (it is accelerating). SECTION 4 GRAVITY: A FORCE OF ATTRACTION 1. force of attraction between objects caused by their masses 2. Their masses are small, so they don t have much gravity. 3. All objects in the universe attract each other because of gravitational force. 4. masses of objects, distance between objects 5. gravity 6. Gravitational force is greater between objects with large masses N 8. We are on Earth, but the sun is very, very far away. 9. As the distance between two objects increases, the gravitational force decreases. As the distance between two objects decreases, the gravitational force increases. 10. Mass is the amount of matter in an object, but weight is the amount of gravitational force on an object ,588 N on Earth, 271 N on the moon 12. Gravity pulls down, and the shelf pushes up. 1. Gravity is a force of attraction between objects. It is determined by the masses of objects and the distance between them. 2. It will get larger. 3. The astronaut has the same mass on Earth and the moon, but the astronaut has a greater weight on Earth than the moon. The mass does not change, because it is the amount of matter in the astronaut. The weight is greater on Earth because Earth s gravity is greater. 4. Earth Planet X Mass of astronaut Weight of astronaut 80 kg 80kg 784 N 1,568 N 5. Student should circle the first pair. The reason given should be that the spheres are the largest pair of masses separated by the smallest distance. Chapter 2 Forces and Motion SECTION 1 GRAVITY AND MOTION 1. The cannonballs hit the ground at the same time. 2. Golf ball should be drawn at the same heights as the table tennis ball m/s; after the third second, the ball is moving 9.8 m/s faster than it was at the end of the second second. Then, 19.6 m/s 9.8 m/s 29.4 m/s. 4. final g t final 9.8 m/s s 2 s 19.6 m/s 5. t final g t 98 m/s 10 s 9.8 m/s s 6. the flat paper 7. The crumpled paper has a greater net force acting on it. 8. when the force of air resistance equals the force of gravity Interactive Textbook Answer Key 82 Forces, Motion, and Energy
BEFORE YOU READ. Forces and Motion Gravity and Motion STUDY TIP. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 2 1 SECTION Forces and Motion Gravity and Motion BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does gravity affect objects? How does air resistance
CHAPTER 2 1 SECTION Forces and Motion Gravity and Motion BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does gravity affect objects? How does air resistance
Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion
 3 What You Will Learn The magnitude of the force of can vary. Kinetic is a force that, when unbalanced, can change the velocity of a moving object. Static balances an applied force and can prevent motion.
3 What You Will Learn The magnitude of the force of can vary. Kinetic is a force that, when unbalanced, can change the velocity of a moving object. Static balances an applied force and can prevent motion.
Chapter 5. Preview. Section 1 Measuring Motion. Section 2 What Is a Force? Section 3 Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion
 Matter in Motion Preview Section 1 Measuring Motion Section 2 What Is a Force? Section 3 Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion Section 4 Gravity: A Force of Attraction Concept Mapping Section 1 Measuring
Matter in Motion Preview Section 1 Measuring Motion Section 2 What Is a Force? Section 3 Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion Section 4 Gravity: A Force of Attraction Concept Mapping Section 1 Measuring
Forces and Newton s Laws
 chapter 3 section 1 Forces Forces and Newton s Laws What You ll Learn how force and motion are related what friction is between objects the difference between mass and weight Before You Read When you hit
chapter 3 section 1 Forces Forces and Newton s Laws What You ll Learn how force and motion are related what friction is between objects the difference between mass and weight Before You Read When you hit
Section 3: Motion and Force. Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Fundamental Forces Balanced and Unbalanced Forces The Force of Friction Friction and Motion
 : Motion and Force Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Fundamental Forces Balanced and Unbalanced Forces The Force of Friction Friction and Motion Key Ideas What do scientists identify as the fundamental forces
: Motion and Force Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Fundamental Forces Balanced and Unbalanced Forces The Force of Friction Friction and Motion Key Ideas What do scientists identify as the fundamental forces
Force Test Review. 1. Give two ways to increase acceleration. You can increase acceleration by decreasing mass or increasing force.
 Force Test Review 1. Give two ways to increase acceleration. You can increase acceleration by decreasing mass or increasing force. 2. Define weight. The force of gravity on an object at the surface of
Force Test Review 1. Give two ways to increase acceleration. You can increase acceleration by decreasing mass or increasing force. 2. Define weight. The force of gravity on an object at the surface of
Forces. Net force is the combination all of the forces acting on an object. All forces have both size and direction.
 Objectives Forces Describe forces, and explain how forces act on objects. Determine the net force when more than one force is acting on an object. Compare balanced and unbalanced forces. Describe ways
Objectives Forces Describe forces, and explain how forces act on objects. Determine the net force when more than one force is acting on an object. Compare balanced and unbalanced forces. Describe ways
Directed Reading A. Section: Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion THE SOURCE OF FRICTION. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. (pp. 350 355) 1. Which of the following is a force that
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. (pp. 350 355) 1. Which of the following is a force that
The Laws of Motion. Gravity and Friction
 The Laws of Motion Gravity and Friction Types of Forces Think about all the things you pushed or pulled today. You might have pushed toothpaste out of a tube. Maybe you pulled out a chair to sit down.
The Laws of Motion Gravity and Friction Types of Forces Think about all the things you pushed or pulled today. You might have pushed toothpaste out of a tube. Maybe you pulled out a chair to sit down.
Name Class Date. What are the four fundamental forces in nature? How can forces affect the motion of an object? Why is friction sometime necessary?
 CHAPTER 11 SECTION Motion 3 Motion and Force KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are the four fundamental forces in nature? How can forces affect the motion of an object?
CHAPTER 11 SECTION Motion 3 Motion and Force KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are the four fundamental forces in nature? How can forces affect the motion of an object?
What Causes Friction?
 What Causes Friction? Friction is the force that opposes the motion between two surfaces that touch (parallel to the surface). The surface of any object is rough. Even an object that feels smooth is covered
What Causes Friction? Friction is the force that opposes the motion between two surfaces that touch (parallel to the surface). The surface of any object is rough. Even an object that feels smooth is covered
Chapter: Newton s Laws of Motion
 Table of Contents Chapter: Newton s Laws of Motion Section 1: Motion Section 2: Newton s First Law Section 3: Newton s Second Law Section 4: Newton s Third Law 1 Motion What is motion? Distance and Displacement
Table of Contents Chapter: Newton s Laws of Motion Section 1: Motion Section 2: Newton s First Law Section 3: Newton s Second Law Section 4: Newton s Third Law 1 Motion What is motion? Distance and Displacement
If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not move. If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not stop. The List:
 If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not move. If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not stop. The List: No Push No Go No Push No Stop No Push No Speed Up No Push No Slow Down
If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not move. If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not stop. The List: No Push No Go No Push No Stop No Push No Speed Up No Push No Slow Down
Section 1: Measuring Motion. Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Observing Motion Speed and Velocity Calculating Speed Math Skills Graphing Motion
 Section 1 Section 1: Measuring Motion Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Observing Motion Speed and Velocity Calculating Speed Math Skills Graphing Motion Section 1 Key Ideas How is a frame of reference used
Section 1 Section 1: Measuring Motion Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Observing Motion Speed and Velocity Calculating Speed Math Skills Graphing Motion Section 1 Key Ideas How is a frame of reference used
Forces. Unit 2. Why are forces important? In this Unit, you will learn: Key words. Previously PHYSICS 219
 Previously Remember From Page 218 Forces are pushes and pulls that can move or squash objects. An object s speed is the distance it travels every second; if its speed increases, it is accelerating. Unit
Previously Remember From Page 218 Forces are pushes and pulls that can move or squash objects. An object s speed is the distance it travels every second; if its speed increases, it is accelerating. Unit
Motion and Forces. Forces
 CHAPTER 8 Motion and LESSON 3 What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D
CHAPTER 8 Motion and LESSON 3 What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D
Isaac Newton was a British scientist whose accomplishments
 E8 Newton s Laws of Motion R EA D I N G Isaac Newton was a British scientist whose accomplishments included important discoveries about light, motion, and gravity. You may have heard the legend about how
E8 Newton s Laws of Motion R EA D I N G Isaac Newton was a British scientist whose accomplishments included important discoveries about light, motion, and gravity. You may have heard the legend about how
Physical Science Forces and Motion Study Guide ** YOU MUST ALSO USE THE NOTES PROVIDED IN CLASS TO PREPARE FOR THE TEST **
 Physical Science Forces and Motion Study Guide ** YOU MUST ALSO USE THE NOTES PROVIDED IN CLASS TO PREPARE FOR THE TEST ** 1. What is a force? A push or a pull on an object. Forces have size and direction.
Physical Science Forces and Motion Study Guide ** YOU MUST ALSO USE THE NOTES PROVIDED IN CLASS TO PREPARE FOR THE TEST ** 1. What is a force? A push or a pull on an object. Forces have size and direction.
Chapter 3, Section 3
 Chapter 3, Section 3 3 What is force? Motion and Forces A force is a push or pull. Sometimes it is obvious that a force has been applied. But other forces aren t as noticeable. What Is a Force? A force......
Chapter 3, Section 3 3 What is force? Motion and Forces A force is a push or pull. Sometimes it is obvious that a force has been applied. But other forces aren t as noticeable. What Is a Force? A force......
Force - a push or a pull A force described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts The SI unit for force is the newton (N)
 Forces Force - a push or a pull A force described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts The SI unit for force is the newton (N) The direction and strength of forces can be represented by
Forces Force - a push or a pull A force described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts The SI unit for force is the newton (N) The direction and strength of forces can be represented by
5 th Grade Force and Motion Study Guide
 Name: Date of Test: Vocabulary 5 th Grade Force and Motion Study Guide Motion- a change in position relative to a point of reference, a change in speed, or a change in distance. Point of Reference (Reference
Name: Date of Test: Vocabulary 5 th Grade Force and Motion Study Guide Motion- a change in position relative to a point of reference, a change in speed, or a change in distance. Point of Reference (Reference
Chapter 5 Matter in Motion Focus Notes
 Chapter 5 Matter in Motion Focus Notes Section 1 Define the following terms: Motion, Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration Motion: an object s change in position relative to a reference point. Speed: the distance
Chapter 5 Matter in Motion Focus Notes Section 1 Define the following terms: Motion, Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration Motion: an object s change in position relative to a reference point. Speed: the distance
The Laws of Motion. Gravity and Friction
 The Laws of Motion Gravity and Friction What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
The Laws of Motion Gravity and Friction What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
Unit 4 Forces (Newton s Laws)
 Name: Pd: Date: Unit Forces (Newton s Laws) The Nature of Forces force A push or pull exerted on an object. newton A unit of measure that equals the force required to accelerate kilogram of mass at meter
Name: Pd: Date: Unit Forces (Newton s Laws) The Nature of Forces force A push or pull exerted on an object. newton A unit of measure that equals the force required to accelerate kilogram of mass at meter
What is force? A force is a push or pull. Sometimes it is obvious that a force has been applied. But other forces aren t as noticeable.
 Chapter 3, Sec-on 3 3 What is force? Motion and Forces A force is a push or pull. Sometimes it is obvious that a force has been applied. But other forces aren t as noticeable. What Is a Force? A force......
Chapter 3, Sec-on 3 3 What is force? Motion and Forces A force is a push or pull. Sometimes it is obvious that a force has been applied. But other forces aren t as noticeable. What Is a Force? A force......
How Do Objects Move? Describing Motion. Different Kinds of Motion
 How Do Objects Move? Describing Motion Different Kinds of Motion Motion is everywhere. The planets are in motion around the Sun. Cars are in motion as they are driven down the street. There s even motion
How Do Objects Move? Describing Motion Different Kinds of Motion Motion is everywhere. The planets are in motion around the Sun. Cars are in motion as they are driven down the street. There s even motion
Chapter 6 Study Questions Name: Class:
 Chapter 6 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A feather and a rock dropped at the same time from
Chapter 6 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A feather and a rock dropped at the same time from
FORCES AND THE LAWS OF MOTION
 FORCES AND THE LAWS OF MOTION FORCE A force is the cause of an acceleration, or the change in an object s velocity (speed or direction). Forces are usually thought of as a push or a pull. The SI unit of
FORCES AND THE LAWS OF MOTION FORCE A force is the cause of an acceleration, or the change in an object s velocity (speed or direction). Forces are usually thought of as a push or a pull. The SI unit of
7.2. Assessment in Diploma Program Physics 281
 7.2. Assessment in Diploma Program Physics 281 figures in 100 kmh 1, we round the answer to two significant figures. Note that we have to use at least one significant figure more than the final result
7.2. Assessment in Diploma Program Physics 281 figures in 100 kmh 1, we round the answer to two significant figures. Note that we have to use at least one significant figure more than the final result
Chapter 12 Study Guide
 Chapter 12 Study Guide Key Concepts 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 A force can cause a resting object to move, or it can accelerate a moving object by changing the object s speed or direction. When the forces on
Chapter 12 Study Guide Key Concepts 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 A force can cause a resting object to move, or it can accelerate a moving object by changing the object s speed or direction. When the forces on
Force, Friction & Gravity Notes
 Force, Friction & Gravity Notes Key Terms to Know Speed: The distance traveled by an object within a certain amount of time. Speed = distance/time Velocity: Speed in a given direction Acceleration: The
Force, Friction & Gravity Notes Key Terms to Know Speed: The distance traveled by an object within a certain amount of time. Speed = distance/time Velocity: Speed in a given direction Acceleration: The
Newton s Third Law KEY IDEAS READING TOOLBOX. As you read this section keep these questions in mind: Name Class Date
 CHAPTER 12 Forces 3 SECTION KEY IDEAS Newton s Third Law As you read this section keep these questions in mind: What happens when one object exerts a force on another object? How can you calculate the
CHAPTER 12 Forces 3 SECTION KEY IDEAS Newton s Third Law As you read this section keep these questions in mind: What happens when one object exerts a force on another object? How can you calculate the
7. Two forces are applied to a 2.0-kilogram block on a frictionless horizontal surface, as shown in the diagram below.
 1. Which statement about the movement of an object with zero acceleration is true? The object must be at rest. The object must be slowing down. The object may be speeding up. The object may be in motion.
1. Which statement about the movement of an object with zero acceleration is true? The object must be at rest. The object must be slowing down. The object may be speeding up. The object may be in motion.
SPS8. STUDENTS WILL DETERMINE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG FORCE, MASS, AND MOTION.
 MOTION & FORCES SPS8. STUDENTS WILL DETERMINE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG FORCE, MASS, AND MOTION. A. CALCULATE VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION. B. APPLY NEWTON S THREE LAWS TO EVERYDAY SITUATIONS BY EXPLAINING THE
MOTION & FORCES SPS8. STUDENTS WILL DETERMINE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG FORCE, MASS, AND MOTION. A. CALCULATE VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION. B. APPLY NEWTON S THREE LAWS TO EVERYDAY SITUATIONS BY EXPLAINING THE
P11 Dynamics 1 Forces and Laws of Motion Bundle.notebook October 14, 2013
 Dynamics 1 Definition of Dynamics Dynamics is the study of why an object moves. In order to understand why objects move, we must first study forces. Forces A force is defined as a push or a pull. Forces
Dynamics 1 Definition of Dynamics Dynamics is the study of why an object moves. In order to understand why objects move, we must first study forces. Forces A force is defined as a push or a pull. Forces
Newton s Laws Student Success Sheets (SSS)
 --- Newton s Laws unit student success sheets--- Page 1 Newton s Laws Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-PS2-1 HS-PS2-2 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Physics Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
--- Newton s Laws unit student success sheets--- Page 1 Newton s Laws Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-PS2-1 HS-PS2-2 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Physics Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course
 Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C ONTENT S TANDARDS Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of 1.1
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C ONTENT S TANDARDS Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of 1.1
Newton s Laws of Motion
 3 Newton s Laws of Motion Key Concept Newton s laws of motion describe the relationship between forces and the motion of an object. What You Will Learn Newton s first law of motion states that the motion
3 Newton s Laws of Motion Key Concept Newton s laws of motion describe the relationship between forces and the motion of an object. What You Will Learn Newton s first law of motion states that the motion
Section 4: Newton s Laws and Momentum
 Section 4: Newton s Laws and Momentum The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Physics TAC 112.39(c). 4.01 Newton s First Law Physics (4)(D) 4.02 Newton
Section 4: Newton s Laws and Momentum The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Physics TAC 112.39(c). 4.01 Newton s First Law Physics (4)(D) 4.02 Newton
Review 3: Forces. 1. Which graph best represents the motion of an object in equilibrium? A) B) C) D)
 1. Which graph best represents the motion of an object in equilibrium? A) B) C) D) 2. A rock is thrown straight up into the air. At the highest point of the rock's path, the magnitude of the net force
1. Which graph best represents the motion of an object in equilibrium? A) B) C) D) 2. A rock is thrown straight up into the air. At the highest point of the rock's path, the magnitude of the net force
3rd Grade Motion and Stability
 Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction from patterns
Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction from patterns
Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces
 Chapter 3 Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Describing Motion Distance and time are
Chapter 3 Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Describing Motion Distance and time are
Forces. Video Demos. Graphing HW: October 03, 2016
 Distance (m or km) : Create a story using the graph. Describe what will be happening at each point during the day (A-D). Example: Trump has a busy day. He is currently at Trump Tower in NY. A- Trump jumps
Distance (m or km) : Create a story using the graph. Describe what will be happening at each point during the day (A-D). Example: Trump has a busy day. He is currently at Trump Tower in NY. A- Trump jumps
9/27/12. Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces. Motion and Position. Motion. Distance. Relative Motion
 9/7/ Table of Contents Chapter: Motion,, and Forces Section : Chapter Section : Section : Motion Distance and time are important. In order to win a race, you must cover the distance in the shortest amount
9/7/ Table of Contents Chapter: Motion,, and Forces Section : Chapter Section : Section : Motion Distance and time are important. In order to win a race, you must cover the distance in the shortest amount
6. Which graph best represents the motion of an object that is not in equilibrium as it travels along a straight line? A) B)
 1. The data table below lists the mass and speed of four different objects. 6. Which graph best represents the motion of an object that is not in equilibrium as it travels along a straight line? Which
1. The data table below lists the mass and speed of four different objects. 6. Which graph best represents the motion of an object that is not in equilibrium as it travels along a straight line? Which
Friction Can Be Rough
 8.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Friction Can Be Rough Perform the following experiment: Rest a brick on a rough surface. Tie a string around the brick and attach a large spring scale to it. Pull the scale
8.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Friction Can Be Rough Perform the following experiment: Rest a brick on a rough surface. Tie a string around the brick and attach a large spring scale to it. Pull the scale
Go on to the next page.
 Chapter 10: The Nature of Force Force a push or a pull Force is a vector (it has direction) just like velocity and acceleration Newton the SI unit for force = kg m/s 2 Net force the combination of all
Chapter 10: The Nature of Force Force a push or a pull Force is a vector (it has direction) just like velocity and acceleration Newton the SI unit for force = kg m/s 2 Net force the combination of all
Chapter 2. Forces & Newton s Laws
 Chapter 2 Forces & Newton s Laws 1st thing you need to know Everything from chapter 1 Speed formula Acceleration formula All their units There is only 1 main formula, but some equations will utilize previous
Chapter 2 Forces & Newton s Laws 1st thing you need to know Everything from chapter 1 Speed formula Acceleration formula All their units There is only 1 main formula, but some equations will utilize previous
Force, Friction, Gravity and Newton s Laws. Chapter 3 Lessons 4-6
 Force, Friction, Gravity and Newton s Laws Chapter 3 Lessons 4-6 I can... identify when forces add or subtract. calculate the Net Force. explain the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces. force:
Force, Friction, Gravity and Newton s Laws Chapter 3 Lessons 4-6 I can... identify when forces add or subtract. calculate the Net Force. explain the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces. force:
acceleration weight load
 Instructions for Vocabulary Cards: Please photocopy the following pages onto heavy card stock (back to back, so the word is printed on the back side of the matching definition). Then, laminate each page.
Instructions for Vocabulary Cards: Please photocopy the following pages onto heavy card stock (back to back, so the word is printed on the back side of the matching definition). Then, laminate each page.
Page 1. Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work!
 Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work! 7164-1 - Page 1 1) A car travels at constant speed around a section of horizontal, circular track. On the diagram provided
Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work! 7164-1 - Page 1 1) A car travels at constant speed around a section of horizontal, circular track. On the diagram provided
Making Things Move. Very often, we want to make something move, for example: Opening a door Opening a drawer
 Forces Making Things Move Very often, we want to make something move, for example: Opening a door Opening a drawer To open a drawer, we must pull, to open a door, we must push or pull. Pushes and pulls
Forces Making Things Move Very often, we want to make something move, for example: Opening a door Opening a drawer To open a drawer, we must pull, to open a door, we must push or pull. Pushes and pulls
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course
 Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C O N T E N T S T A N D A R D S Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C O N T E N T S T A N D A R D S Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion
Forces Homework Booklet
 Forces Homework Booklet Name: Class: Homework Number % Mark Parental Signature 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Homework 1. Use the proper layout, and show all your working to answer the following questions. 1. Calculate
Forces Homework Booklet Name: Class: Homework Number % Mark Parental Signature 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Homework 1. Use the proper layout, and show all your working to answer the following questions. 1. Calculate
Force - a push or a pull The SI unit for force is the newton (N)
 Forces Force - a push or a pull The SI unit for force is the newton (N) Arrows are used to show the strength of a force and the direction in which it acts; the longer the arrow, the stronger the force
Forces Force - a push or a pull The SI unit for force is the newton (N) Arrows are used to show the strength of a force and the direction in which it acts; the longer the arrow, the stronger the force
+F N = -F g. F g = m٠a g
 Force Normal = F N Force Normal (or the Normal Force, abbreviated F N ) = F N = The contact force exerted by a surface on an object. The word Normal means perpendicular to Therefore, the Normal Force is
Force Normal = F N Force Normal (or the Normal Force, abbreviated F N ) = F N = The contact force exerted by a surface on an object. The word Normal means perpendicular to Therefore, the Normal Force is
Friction, Inclined Planes, Forces Practice
 Name: Date: 1. The diagram below shows a 4.0-kilogram object accelerating at 10. meters per second 2 on a rough horizontal surface. 4. n 8.0-newton block is accelerating down a frictionless ramp inclined
Name: Date: 1. The diagram below shows a 4.0-kilogram object accelerating at 10. meters per second 2 on a rough horizontal surface. 4. n 8.0-newton block is accelerating down a frictionless ramp inclined
Newton s Contributions. Calculus Light is composed of rainbow colors Reflecting Telescope Laws of Motion Theory of Gravitation
 Newton s Contributions Calculus Light is composed of rainbow colors Reflecting Telescope Laws of Motion Theory of Gravitation Newton s First Law (law of inertia) An object at rest tends to stay at rest
Newton s Contributions Calculus Light is composed of rainbow colors Reflecting Telescope Laws of Motion Theory of Gravitation Newton s First Law (law of inertia) An object at rest tends to stay at rest
Motion *All matter in the universe is constantly at motion Motion an object is in motion if its position is changing
 Aim: What is motion? Do Now: Have you ever seen a race? Describe what occurred during it. Homework: Vocabulary Define: Motion Point of reference distance displacement speed velocity force Textbook: Read
Aim: What is motion? Do Now: Have you ever seen a race? Describe what occurred during it. Homework: Vocabulary Define: Motion Point of reference distance displacement speed velocity force Textbook: Read
Name: Class: Date: GRAVITY. 1. Gravity is the force of between all objects. It increases when items are or together.
 Name: Class: Date: GRAVITY 1. Gravity is the force of between all objects. It increases when items are or together. 2. The moon has the gravity of Earth. Jupiter has the gravity of Earth. 3. List these
Name: Class: Date: GRAVITY 1. Gravity is the force of between all objects. It increases when items are or together. 2. The moon has the gravity of Earth. Jupiter has the gravity of Earth. 3. List these
Unit 6: Forces II PRACTICE PROBLEMS
 Regents Physics Mrs. Long Unit 6: Forces II PRACTICE PROBLEMS Essential Understanding for the Unit: The net force can be determined by using force diagrams in order to show all forces acting, and thereby
Regents Physics Mrs. Long Unit 6: Forces II PRACTICE PROBLEMS Essential Understanding for the Unit: The net force can be determined by using force diagrams in order to show all forces acting, and thereby
Section 2: Friction, Gravity, and Elastic Forces
 Chapter 10, Section 2 Friction, Gravity, & Elastic Forces Section 2: Friction, Gravity, and Elastic Forces What factors determine the strength of the friction force between two surfaces? What factors affect
Chapter 10, Section 2 Friction, Gravity, & Elastic Forces Section 2: Friction, Gravity, and Elastic Forces What factors determine the strength of the friction force between two surfaces? What factors affect
Unit 6 Forces and Pressure
 Unit 6 Forces and Pressure Lesson Objectives: Mass and weight Gravitational field and field strength describe the effect of balanced and unbalanced forces on a body describe the ways in which a force may
Unit 6 Forces and Pressure Lesson Objectives: Mass and weight Gravitational field and field strength describe the effect of balanced and unbalanced forces on a body describe the ways in which a force may
Broughton High School of Wake County
 Name: Section: 1 Section 1: Which picture describes Newton s Laws of Motion? 5. Newton s Law 1. Newton s Law 2. Newton s Law 6. Newton s Law 3. Newton s Law 7. Newton s Law 4. Newton s Law 8. Newton s
Name: Section: 1 Section 1: Which picture describes Newton s Laws of Motion? 5. Newton s Law 1. Newton s Law 2. Newton s Law 6. Newton s Law 3. Newton s Law 7. Newton s Law 4. Newton s Law 8. Newton s
3. The diagram shows two bowling balls, A and B, each having a mass of 7.00 kilograms, placed 2.00 meters apart.
 1. Which statement describes the gravitational force and the electrostatic force between two charged particles? A) The gravitational force may be either attractive or repulsive, whereas the electrostatic
1. Which statement describes the gravitational force and the electrostatic force between two charged particles? A) The gravitational force may be either attractive or repulsive, whereas the electrostatic
NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION. Review
 NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION Review BACKGROUND Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician famous for his discovery of the law of gravity also discovered the three laws of motion. He
NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION Review BACKGROUND Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician famous for his discovery of the law of gravity also discovered the three laws of motion. He
Directed Reading A. Section: Gravity: A Force of Attraction. force of. THE EFFECTS OF GRAVITY ON MATTER. of.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Gravity: A Force of Attraction 1. The force of attraction between two objects that is due to their masses is the force of. 2. Why do astronauts on the moon
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Gravity: A Force of Attraction 1. The force of attraction between two objects that is due to their masses is the force of. 2. Why do astronauts on the moon
A force is could described by its magnitude and by the direction in which it acts.
 8.2.a Forces Students know a force has both direction and magnitude. P13 A force is could described by its magnitude and by the direction in which it acts. 1. Which of the following could describe the
8.2.a Forces Students know a force has both direction and magnitude. P13 A force is could described by its magnitude and by the direction in which it acts. 1. Which of the following could describe the
3.3 Acceleration An example of acceleration Definition of acceleration Acceleration Figure 3.16: Steeper hills
 3.3 Acceleration Constant speed is easy to understand. However, almost nothing moves with constant speed for long. When the driver steps on the gas pedal, the speed of the car increases. When the driver
3.3 Acceleration Constant speed is easy to understand. However, almost nothing moves with constant speed for long. When the driver steps on the gas pedal, the speed of the car increases. When the driver
Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review
 Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review 1600 kg 800 kg 9 m/s truck with mass 1600 kg collides with a car with mass 800 kg at rest. They stick together and continue to move to the right. 1. What is
Honors Physics Semester 2 Final Exam Review 1600 kg 800 kg 9 m/s truck with mass 1600 kg collides with a car with mass 800 kg at rest. They stick together and continue to move to the right. 1. What is
Chapter 2. Force and Newton s Laws
 Chapter 2 Force and Newton s Laws 2 1 Newton s First Law Force Force A push or pull that one body exerts on another body. Examples : 2 Categories of Forces Forces Balanced Forces Unbalanced Forces Balanced
Chapter 2 Force and Newton s Laws 2 1 Newton s First Law Force Force A push or pull that one body exerts on another body. Examples : 2 Categories of Forces Forces Balanced Forces Unbalanced Forces Balanced
3rd Grade. Forces and Motion Review. Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106. Slide 4 / 106. Slide 3 / 106. Slide 5 / 106. Slide 6 / 106. Motion and Stability
 Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Slide 4 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction
Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Slide 4 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction
Matter, Atoms & Molecules
 Matter, Atoms & Molecules Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms, which are too small to see with the naked eye. Matter Matter is anything
Matter, Atoms & Molecules Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms, which are too small to see with the naked eye. Matter Matter is anything
Assignment 4.2 Frictional Forces CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is the SI unit of the coefficient of friction (μ s or μ k )?
 CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is the SI unit of the coefficient of friction (μ s or μ k )? 2. Tennis is played on clay, grass, and hard surfaces. Please explain why you think tennis players have or don
CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is the SI unit of the coefficient of friction (μ s or μ k )? 2. Tennis is played on clay, grass, and hard surfaces. Please explain why you think tennis players have or don
Isaac Newton was a British scientist whose accomplishments
 E8 Newton s Laws of Motion R EA D I N G Isaac Newton was a British scientist whose accomplishments included important discoveries about light, motion, and gravity. You may have heard the legend about how
E8 Newton s Laws of Motion R EA D I N G Isaac Newton was a British scientist whose accomplishments included important discoveries about light, motion, and gravity. You may have heard the legend about how
Dynamics-Friction. 1. Which vector diagram best represents a cart slowing down as it travels to the right on a horizontal surface?
 1. Which vector diagram best represents a cart slowing down as it travels to the right on a horizontal surface? Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the information A student and the waxed skis she
1. Which vector diagram best represents a cart slowing down as it travels to the right on a horizontal surface? Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the information A student and the waxed skis she
Friction (static & Kinetic) Review
 Friction (static & Kinetic) Review 1. Sand is often placed on an icy road because the sand A) decreases the coefficient of friction between the tires of a car and the road B) increases the coefficient
Friction (static & Kinetic) Review 1. Sand is often placed on an icy road because the sand A) decreases the coefficient of friction between the tires of a car and the road B) increases the coefficient
1. Two forces are applied to a wooden box as shown below. Which statement best describes the effect these forces have on the box?
 1. Two forces are applied to a wooden box as shown below. Which statement best describes the effect these forces have on the box? A. The box does not move. B. The box moves to the right. C. The box moves
1. Two forces are applied to a wooden box as shown below. Which statement best describes the effect these forces have on the box? A. The box does not move. B. The box moves to the right. C. The box moves
Chapter: The Laws of Motion
 Table of Contents Chapter: The Laws of Motion Section 1: Newton s Second Law Section 2: Gravity Section 3: The Third Law of Motion 1 Newton s Second Law Force, Mass, and Acceleration Newton s first law
Table of Contents Chapter: The Laws of Motion Section 1: Newton s Second Law Section 2: Gravity Section 3: The Third Law of Motion 1 Newton s Second Law Force, Mass, and Acceleration Newton s first law
Do Now: Why are we required to obey the Seat- Belt law?
 Do Now: Why are we required to obey the Seat- Belt law? Newton s Laws of Motion Newton s First Law An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction.
Do Now: Why are we required to obey the Seat- Belt law? Newton s Laws of Motion Newton s First Law An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction.
I. What are forces? A. Characteristics:
 Chapter 5: forces I. What are forces? A. Characteristics: 1. Forces result from the interaction of objects. A FORCE is a push or a pull that one object exerts on another. 2. How are forces measured: a.
Chapter 5: forces I. What are forces? A. Characteristics: 1. Forces result from the interaction of objects. A FORCE is a push or a pull that one object exerts on another. 2. How are forces measured: a.
SCI-4 Kaechele_Dix_4.2 force,energy,motion Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 SCI-4 Kaechele_Dix_4.2 force,energy,motion Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:21HKN0 1 Speed is a measure of A motion B force C science D solid 2 A boy helped his neighbors pack
SCI-4 Kaechele_Dix_4.2 force,energy,motion Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:21HKN0 1 Speed is a measure of A motion B force C science D solid 2 A boy helped his neighbors pack
Sir Isaac Newton ( ) One of the world s greatest scientists Developed the 3 Laws of Motion
 Motion and Forces Sir Isaac Newton (1643 1727) One of the world s greatest scientists Developed the 3 Laws of Motion Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law Law of Inertia 2 nd Law Force = Mass x Acceleration
Motion and Forces Sir Isaac Newton (1643 1727) One of the world s greatest scientists Developed the 3 Laws of Motion Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law Law of Inertia 2 nd Law Force = Mass x Acceleration
Chapter 4 Force and Motion
 Chapter 4 Force and Motion Units of Chapter 4 The Concepts of Force and Net Force Inertia and Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion More on Newton s Laws:
Chapter 4 Force and Motion Units of Chapter 4 The Concepts of Force and Net Force Inertia and Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion More on Newton s Laws:
The Laws of Motion. Gravity and Friction
 CHAPTER 3 The Laws of Motion LESSON 1 Gravity and Friction What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
CHAPTER 3 The Laws of Motion LESSON 1 Gravity and Friction What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
KEY NNHS Introductory Physics: MCAS Review Packet #1 Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course
 Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C ONTENT S TANDARDS Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of 1.1
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C ONTENT S TANDARDS Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of 1.1
Marr College Science. Forces. Learning Outcomes and Summary Notes
 Marr College Science Forces Learning Outcomes and Summary Notes Learning Intentions By the end of this unit I will be able to 1. Describe a force as a push or a pull. 2. Describe the effects of forces
Marr College Science Forces Learning Outcomes and Summary Notes Learning Intentions By the end of this unit I will be able to 1. Describe a force as a push or a pull. 2. Describe the effects of forces
Lecture Notes Chapter 5 Friction
 Lecture Notes Chapter 5 Friction NORMAL FORCES When an object rests on a surface, the surface exerts a normal force on the object, keeping it from accelerating downward. A normal force is perpendicular
Lecture Notes Chapter 5 Friction NORMAL FORCES When an object rests on a surface, the surface exerts a normal force on the object, keeping it from accelerating downward. A normal force is perpendicular
Lesson 14: Friction. a) Fill in the table that follows by constructing a force diagram for the block (the system) for these five situations.
 Lesson 14: Friction 14.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Perform the following experiment: Rest a wooden block (or some other object, like your shoe) on a table. Attach a large spring scale to a string attached
Lesson 14: Friction 14.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Perform the following experiment: Rest a wooden block (or some other object, like your shoe) on a table. Attach a large spring scale to a string attached
Driveway Races Acceleration
 Driveway Races Acceleration You may notice that when things move they rarely move at the same speed all the time. Especially when you drive, you can see right away that your speed is constantly changing.
Driveway Races Acceleration You may notice that when things move they rarely move at the same speed all the time. Especially when you drive, you can see right away that your speed is constantly changing.
PYP 001 FIRST MAJOR EXAM CODE: TERM: 151 SATURDAY, OCTOBER 17, 2015 PAGE: 1
 TERM: 151 SATURDAY, OCTOBER 17, 2015 PAGE: 1 *Read the following (20) questions and choose the right answer: 1 The figure below represents the speed-time graph for the motion of a vehicle during a 7.0-minute
TERM: 151 SATURDAY, OCTOBER 17, 2015 PAGE: 1 *Read the following (20) questions and choose the right answer: 1 The figure below represents the speed-time graph for the motion of a vehicle during a 7.0-minute
Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion
 Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion Lesson 1 Gravity and Friction Force - A push or pull we pull on a locker handle push a soccer ball or on the computer keys Contact force - push or pull on one object by another
Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion Lesson 1 Gravity and Friction Force - A push or pull we pull on a locker handle push a soccer ball or on the computer keys Contact force - push or pull on one object by another
Forces. A Force is a push or a pull on an object. Forces can cause a resting object to move
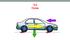 13.2 Forces Forces A Force is a push or a pull on an object Forces can cause a resting object to move Forces can cause a moving object to accelerate by changing its speed or its direction Measuring Force
13.2 Forces Forces A Force is a push or a pull on an object Forces can cause a resting object to move Forces can cause a moving object to accelerate by changing its speed or its direction Measuring Force
Applying Newton s Laws
 Applying Newton s Laws Free Body Diagrams Draw and label the forces acting on the object. Examples of forces: weight, normal force, air resistance, friction, applied forces (like a push or pull) Velocity
Applying Newton s Laws Free Body Diagrams Draw and label the forces acting on the object. Examples of forces: weight, normal force, air resistance, friction, applied forces (like a push or pull) Velocity
What does the lab partner observe during the instant the student pushes off?
 Motion Unit Review State Test Questions 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer.
Motion Unit Review State Test Questions 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer.
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at a constant velocity,
Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at a constant velocity,
8. The graph below shows a beetle s movement along a plant stem.
 Name: Block: Date: Introductory Physics: Midyear Review 1. Motion and Forces Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. 1.1 Compare and contrast
Name: Block: Date: Introductory Physics: Midyear Review 1. Motion and Forces Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. 1.1 Compare and contrast
Galileo & Friction 2000 yrs prior to inertia idea, the popular belief was that all objects want to come to a rest. BUT 1600's: Galileo reasoned that
 Galileo & Friction 2000 yrs prior to inertia idea, the popular belief was that all objects want to come to a rest. BUT 1600's: Galileo reasoned that moving objects eventually stop only because of a force
Galileo & Friction 2000 yrs prior to inertia idea, the popular belief was that all objects want to come to a rest. BUT 1600's: Galileo reasoned that moving objects eventually stop only because of a force
Name Class Date. height. Which ball would land first according to Aristotle? Explain.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Gravity and Motion 1. Suppose a baseball and a marble are dropped at the same time from the same height. Which ball would land first according to Aristotle?
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Gravity and Motion 1. Suppose a baseball and a marble are dropped at the same time from the same height. Which ball would land first according to Aristotle?
