INTEGRAL SOUND HEALING: SCIENCE, ART & ALCHEMY PART 2
|
|
|
- Jeremy Sims
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTEGRAL SOUND HEALING: SCIENCE, ART & ALCHEMY PART 2
2 The fairest thing we can experience is the mysterious. It is the fundamental emotion which stands at the cradle of true art and true science. Albert Einstein, from What I believe, Forum and Century 84 (1930), p
3 What we ll cover: Bio-energy fields: electromagnetic, scalar & sound Mechanical and quantum physics perspectives of sound Bio-sound energy healing - cellular / connective tissue / living matrix Healing with musical intervals, triads and modes - the art of integral sound healing Integral Sound Transformation Crucible - the alchemical process of sound healing
4 3 Forms of Bio-Energy identified by quantum physicists 1. Sound (phonons) 2. Light (photons) 3. Scalar energy
5
6 Dynamic Bio-Energy Field 3 forms of bio-energy exist within each atom, DNA and cell and are emitted by them - they travel outwards from our bodies into the environment - they can be measured and assessed for disturbances 3 forms of bio-energy exist in our environment and influence our cells and DNA - they travel inwards from the environment into our bodies and can optimise health and wellness
7
8 Dynamic Bio-Energy Field 3 forms of bio-energy exist within each atom, DNA and cell and are emitted by them - they travel outwards from our bodies into the environment - they can be measured and assessed for disturbances 3 forms of bio-energy exist in our environment and influence our cells and DNA - they travel inwards from the environment into our bodies and can optimise health and wellness
9 Electro-Magnetic Energy Electromagnetic energy is familiar to most people as light and heat, but it can take many other forms, such as radio waves and X-rays. Electromagnetic radiation is a transverse wave, meaning that its oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer and travel. Unlike sound waves, electromagnetic waves do not require a medium through which to move and can travel across empty space. The full range of wavelengths is known as the electromagnetic spectrum, of which visible light forms only a small part. Despite the observed wave-like character of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), it can also behave as if it's composed of tiny particles, known as photons.
10
11 photons: light energy - aura
12 heart field entrainment... Institute of HeartMath
13 activating low frequency, low intensity EMFs
14 activating low frequency, low intensity EMFs
15 what is scalar energy?
16 Non-Hertzian Quantum Fields 1980 & 1990s Glen Rein conducted a series of in vitro cellular experiments, with control groups, designed to reduce the influence of a possible placebo effect. Used devices with self-cancelling EM coils with unique winding geometry (caduceus) to generate quantum fields Demonstrate that quantum fields: inhibit neurotransmitter uptake into nerve cells stimulate the growth of human lymphocytes (white blood cells) alter the absorption of UV light of water treated with quantum fields. In all cases quantum fields produce larger biological responses than classical EM force fields Published in: Frontier Perspectives Vol. 7: 16-23, 1998 Biological Effects of Quantum Fields and Their Role in the Natural Healing Process Glen Rein, PhD Quantum Biology Research Lab, NY.
17 Properties of bio-scalar energy No measurable frequency Expansive Healing Valerie Hunt, Professor Emeritus of Physiological Science at UCLA Bioscalar - The Primary Healing Energy
18 Bio-scalar energy Bio-scalar energy exists in the environment and in all living things. It is ''a source of energy that directly influences all body tissue,'' Through meditative techniques, it can be tapped into by bioenergy healers and focused upon a client for specific healing purpose. It also can be tapped into by the individual healee' and focused on particular areas of his or her own body for healing and energy balancing. Bio-scalar energy can ''eliminate pain, heal traumatized tissue, destroy disease, and eliminate tumour growths.''
19 activating bio-scalar energy
20 activating bio-scalar energy
21 what is sound? mechanical physics Sound is the energy things produce when they vibrate (move back and forth quickly). If you bang a drum, you make the tight skin vibrate at very high speed (it's so fast that you can't usually see it), forcing the air all around it to vibrate as well. As the air moves, it carries energy out from the drum in all directions. Eventually, even the air inside your ears starts vibrating and that's when you begin to perceive the vibrating drum as a sound. We can also experience the sound vibrations directly through our skin and tissues in our body.
22 As the air moves, it carries energy out from the source of the sound in all directions
23 what is sound? Sound always has to have something to travel through (known as a medium), such as air, water, glass or metal. As a sound wave moves forward, it makes the air bunch together in some places and spread out in others. This creates an alternating pattern of squashed-together areas (known as compressions) and stretched-out areas (known as a rarefactions). In other words, sound pushes and pulls the air back and forth. Sound waves thump energy through the body of the air. Sound waves are compression waves. They're also called longitudinal waves because the air vibrates along the same direction as the wave travels.
24 Sound waves are longitudinal waves: the air moves back and forth along the same line as the wave travels, making alternate patterns of compressions and rarefactions
25 measuring sound Amplitude As waves travel, they set up patterns of disturbance. The amplitude of a wave is its maximum disturbance from its undisturbed position. Big sounds waves have high amplitude and we hear them as loud sounds. Wavelength The wavelength of a wave is the distance between a point on one wave and the same point on the next wave. It is often easiest to measure this from the crest of one wave to the crest of the next wave, but it doesn't matter where as long as it is the same point in each wave. Frequency The frequency of a wave is the number of waves produced by a source each second. It is also the number of waves that pass a certain point each second. The unit of frequency is the hertz (Hz).
26 measuring sound
27 measuring sound
28 frequency ranges...
29 infra & ultra sound...
30 ultrasound - baby scans
31 ears: first sense organ to fully develop in foetus - by 20 weeks
32 high intensity focused ultrasound: fibroids; prostate cancer
33 infrasound lithotripsy: kidney stones 1-2 Hz
34 sound medicine... Sounds are being used for medical diagnosis and treatment April 2015 researchers at MIT report: sound waves to detect rare cancer cells Acoustic device can rapidly isolate circulating tumour cells from patient blood samples
35 recording sounds There are now devices that can record and interpret: the sounds from space (e.g. NASA plasma wave antenna - vibrations caused by interaction between solar winds & planets) cells in our bodies (Bioscope Atomic Force Microscopy - singing cells) quantum particles (phonons)
36 recording the sound of quantum particles CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY. GOTHENBURG, SWEDEN
37 quantum particles: photons and phonons A phonon is a definite discrete unit or quantum of vibrational mechanical energy, just as a photon is a quantum of electromagnetic or light energy. Encyclopaedia Brittanica
38 Self-Field Theory Anthony Flemming DNA can be controlled via delivery of energy of appropriate discrete frequencies involved in the cell cycle. One way is via externally applied photons (EM) of precise frequency. Another technique is to use acoustic (phonon) energy instead of EM. The phonon has the advantage of being able to penetrate far deeper into biological tissues than EM radiation.
39 bio-sound energy healing Our cells emit and absorb sounds We can work with the natural acoustic sounds of some instruments and our voices to assess and harmonise imbalances in our bio-sound field and directly influence cell functioning
40 cell membrane receptors
41 how do cells respond to sounds? In addition to receiving and responding to physical molecules, receptors on cell membranes have antennas can read vibrational energy fields such as light and sound. The antennas vibrate like tuning forks. If an energy vibration in the environment resonate with a receptor s antenna, it will alter the protein s charge, causing the receptor to change shape. Biological behaviour can be controlled by sound as well as by physical molecules like penicillin. Bruce Lipton The Biology of Belief
42 cellular matrix
43 extracellular matrix: connective tissue - liquid crystal lattice
44 living matrix bio-energy, including sound, flows through it James Oschman Energy Medicine The Scientific Basis
45 music medicine... Music is an art form whose medium is sound and silence Rhythm: Medicine for the Body Melody: Medicine for the Heart Silence: Medicine for the Mind Harmony: Medicine for the Soul Inner Music: Medicine for the Spirit Christine Stevens Music Medicine: The Science and Spirit of Healing Yourself with Sound
46 musical intervals Difference in frequency between 2 notes 2 types of intervals
47 musical intervals Different intervals have different healing effects Some create harmony and balance - good for triggering the relaxation effect - e.g. Perfect 5th, notes C & G Some create dissonance - good for triggering the release of suppressed emotions - e.g. Major Seventh, notes C & B
48 musical triads Triple sounds for healing Major key triads - manifest your own inner strengths and express yourself solidly in the world Minor key triads - processing within what you have learned and created in the world around you
49 musical modes Modes - originate from Greece - Pythagoras Modes affect moods & moods affect our entire being - physical, emotional, mental, spiritual Modes can help the process of healing (becoming whole) 7 Healing Modes - western musical scale - 12 steps in octave Indian Ragas - based on modes - 22 microtones in octave
50
51 Integral Sound Transformation Crucible Taoist External Alchemy
52 Integral Sound Transformation Crucible Taoist Internal Alchemy
53 Integral Sound Transformation Crucible Alchemical Singing Bowls
54 Integral Sound Transformation Crucible Mentally rehearse every moment of it with all your senses Visualise, in vivid detail, your intention as established fact as the positive outcome of the healing While working with healing sounds, keep firmly in mind the desired outcome and do not allow yourself to think of failure Move aside surrender to the power of the universe and let go of the outcome
55 Integral Sound Transformation Crucible Cultivate and enter into an intentional healing space Power up your intention through deep breathing and meditation, to slow your brain waves to an alpha state (8 13 hertz) Move into peak focus through mindful awareness of the present, noticing the feelings and sensations in your body Trigger unconditional love and compassion in your heart (and if working with a client, make a meaningful empathetic connection, through conversation and touch) Clearly state the intention for healing and make it specific
56 what is integral sound healing? Integral Sound Healing integrates modern science, ancient wisdom, music and the healing arts. Healing with sound has been widely used throughout the world for thousands of years. It's a form of vibrational medicine that helps to balance all aspects of your being - physical, emotional, mental and spiritual. When you're out of balance, that's when aches, pains, illness and disease happens. So by fine tuning your system with sounds we can restore balance and activate your body's natural healing abilities."
57 Do What You Love! Make A Difference! Help Others With Healing Sounds Today! colourofsound.org academyofsoundhealing.com
Globe Institute- October 2016 CRYSTALS HEALING & VIBRATION
 Globe Institute- October 2016 CRYSTALS HEALING & VIBRATION I. Introductory notes: Every living thing on this planet has a life force of energy. Energy in its simplest form is vibration. This vibration
Globe Institute- October 2016 CRYSTALS HEALING & VIBRATION I. Introductory notes: Every living thing on this planet has a life force of energy. Energy in its simplest form is vibration. This vibration
Name Class Date. What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic spectrum? How can electromagnetic waves be used?
 CHAPTER 16 12 SECTION Sound and Light The Nature of Light KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic
CHAPTER 16 12 SECTION Sound and Light The Nature of Light KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What two models do scientists use to describe light? What is the electromagnetic
Energy - the ability to do work or cause change. 1 point
 Energy and Waves Energy - the ability to do work or cause change Work - the transfer of energy Work = Force X Distance Power - the rate at which work is done Power = Work Time Kinetic Energy - the energy
Energy and Waves Energy - the ability to do work or cause change Work - the transfer of energy Work = Force X Distance Power - the rate at which work is done Power = Work Time Kinetic Energy - the energy
Physics Worksheet Sound and Light Section: Name:
 Do Now: What is common between sound and light? What are the differences between sound and light? Sound Waves 1. Define Sound Waves from three different perspectives 6. Speed of sound =. Formula: v =.
Do Now: What is common between sound and light? What are the differences between sound and light? Sound Waves 1. Define Sound Waves from three different perspectives 6. Speed of sound =. Formula: v =.
Learning Goal: By the end of today, I will be familiar with the following concepts: Demo Newton's Cradle Tuning Forks. Section 8.
 Section 8.1 Vibrations Learning Goal: By the end of today, I will be familiar with the following concepts: Vibrations and Mechanical waves The cyclical motion about an equilibrium point is called a vibration.
Section 8.1 Vibrations Learning Goal: By the end of today, I will be familiar with the following concepts: Vibrations and Mechanical waves The cyclical motion about an equilibrium point is called a vibration.
Work. Work and Energy Examples. Energy. To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or:
 Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Page # Physics 103: Lecture 26 Sound. Lecture 26, Preflight 2. Lecture 26, Preflight 1. Producing a Sound Wave. Sound from a Tuning Fork
 Physics 103: Lecture 6 Sound Producing a Sound Wave Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave A tuning fork will produce
Physics 103: Lecture 6 Sound Producing a Sound Wave Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave A tuning fork will produce
Frequency: the number of complete waves that pass a point in a given time. It has the symbol f. 1) SI Units: Hertz (Hz) Wavelength: The length from
 Frequency: the number of complete waves that pass a point in a given time. It has the symbol f. 1) SI Units: Hertz (Hz) Wavelength: The length from the one crest of a wave to the next. I. Electromagnetic
Frequency: the number of complete waves that pass a point in a given time. It has the symbol f. 1) SI Units: Hertz (Hz) Wavelength: The length from the one crest of a wave to the next. I. Electromagnetic
Producing a Sound Wave. Chapter 14. Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a Sound Wave. Using a Tuning Fork, cont.
 Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Light is an electromagnetic wave (EM)
 What is light? Light is a form of energy. Light travels in a straight line Light speed is 3.0 x 10 8 m/s Light is carried by photons Light can travel through a vacuum Light is a transverse wave Light is
What is light? Light is a form of energy. Light travels in a straight line Light speed is 3.0 x 10 8 m/s Light is carried by photons Light can travel through a vacuum Light is a transverse wave Light is
due to striking, rubbing, Any vibration of matter spinning, plucking, etc. Find frequency first, then calculate period.
 Equilibrium Position Disturbance Period (T in sec) # sec T = # cycles Frequency (f in Hz) f = # cycles # sec Amplitude (A in cm, m or degrees [θ]) Other Harmonic Motion Basics Basic Definitions Pendulums
Equilibrium Position Disturbance Period (T in sec) # sec T = # cycles Frequency (f in Hz) f = # cycles # sec Amplitude (A in cm, m or degrees [θ]) Other Harmonic Motion Basics Basic Definitions Pendulums
the ability to do work or cause change (work is force exerted on an object causing it to move a distance)
 Vocabulary Terms - Energy energy the ability to do work or cause change (work is force exerted on an object causing it to move a distance) heat Heat is a form of energy that flows between two substances
Vocabulary Terms - Energy energy the ability to do work or cause change (work is force exerted on an object causing it to move a distance) heat Heat is a form of energy that flows between two substances
Revision checklist. Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it! Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it!
 SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency,
SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency,
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
The grand theory of astrology
 Astrology for Aquarius Sharing our Knowledge Hermetic astrology The grand theory of astrology The Brotherhood of Light The grand theory of astrology The Brotherhood of Light 1 Introduction Astrology was
Astrology for Aquarius Sharing our Knowledge Hermetic astrology The grand theory of astrology The Brotherhood of Light The grand theory of astrology The Brotherhood of Light 1 Introduction Astrology was
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
Being a Physicist Unit 5. Summary Sheets. Gleniffer High School
 Being a Physicist Unit 5 Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 Experiences & Outcomes I can explain how sound vibrations are carried by waves through air, water and other materials SCN 2-11a By exploring
Being a Physicist Unit 5 Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 Experiences & Outcomes I can explain how sound vibrations are carried by waves through air, water and other materials SCN 2-11a By exploring
CAMI - Science. CAPS - Physics Links Grade 10
 CAMI - Science CAPS - Physics Links Grade 10 TERM 1 TOPICS CONTENT, CONCEPTS & SKILLS CAMI - KEYSTROKES Transverse pulses on a string or spring Pulse, amplitude Define a pulse Define a transverse pulse
CAMI - Science CAPS - Physics Links Grade 10 TERM 1 TOPICS CONTENT, CONCEPTS & SKILLS CAMI - KEYSTROKES Transverse pulses on a string or spring Pulse, amplitude Define a pulse Define a transverse pulse
Photochemical principles
 Chapter 1 Photochemical principles Dr. Suzan A. Khayyat 1 Photochemistry Photochemistry is concerned with the absorption, excitation and emission of photons by atoms, atomic ions, molecules, molecular
Chapter 1 Photochemical principles Dr. Suzan A. Khayyat 1 Photochemistry Photochemistry is concerned with the absorption, excitation and emission of photons by atoms, atomic ions, molecules, molecular
Physics Common Assessment Unit 5-8 3rd Nine Weeks
 1) What is the direction of the force(s) that maintain(s) circular motion? A) one force pulls the object inward toward the radial center while another force pushes the object at a right angle to the first
1) What is the direction of the force(s) that maintain(s) circular motion? A) one force pulls the object inward toward the radial center while another force pushes the object at a right angle to the first
Wave Motions and Sound
 EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
Focusing on Light What is light? Is it a particle or a wave? An age-old debate that has persisted among scientists is related to the question, "Is
 Focusing on Light What is light? Is it a particle or a wave? An age-old debate that has persisted among scientists is related to the question, "Is light a wave or a stream of particles?" Very noteworthy
Focusing on Light What is light? Is it a particle or a wave? An age-old debate that has persisted among scientists is related to the question, "Is light a wave or a stream of particles?" Very noteworthy
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES
 Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Science 30 Unit C Review Outline GCCHS. Negatively charged Positively charged Coulomb Conductor Electric potential difference
 Science 30 Unit C Review Outline GCCHS Negatively charged Positively charged Coulomb Conductor Electric potential difference volt voltage Insulator Test body Gravitational field Field lines Solar wind
Science 30 Unit C Review Outline GCCHS Negatively charged Positively charged Coulomb Conductor Electric potential difference volt voltage Insulator Test body Gravitational field Field lines Solar wind
What is a wave? Waves
 What is a wave? Waves Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance that carries energy from one place to another. Classifying waves 1. Mechanical Waves - e.g., water waves, sound waves, and waves on strings.
What is a wave? Waves Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance that carries energy from one place to another. Classifying waves 1. Mechanical Waves - e.g., water waves, sound waves, and waves on strings.
3/9/2011. Outline Chapter 7 Waves Water Waves Water Waves. Water waves are really circular. They are an example of Mechanical waves.
 Outline Chapter 7 Waves 7-1. Water Waves 7-2. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves 7-3. Describing Waves 7-4. Standing Waves 7-5. Sound 7-6. Doppler Effect 7-7. Musical Sounds 7-8. Electromagnetic Waves 7-9.
Outline Chapter 7 Waves 7-1. Water Waves 7-2. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves 7-3. Describing Waves 7-4. Standing Waves 7-5. Sound 7-6. Doppler Effect 7-7. Musical Sounds 7-8. Electromagnetic Waves 7-9.
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
Homework #4 Reminder Due Wed. 10/6
 Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Due Wed. 10/6 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating
Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Due Wed. 10/6 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating
Sound Waves SOUND VIBRATIONS THAT TRAVEL THROUGH THE AIR OR OTHER MEDIA WHEN THESE VIBRATIONS REACH THE AIR NEAR YOUR EARS YOU HEAR THE SOUND.
 SOUND WAVES Objectives: 1. WHAT IS SOUND? 2. HOW DO SOUND WAVES TRAVEL? 3. HOW DO PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF A MEDIUM AFFECT THE SPEED OF SOUND WAVES? 4. WHAT PROPERTIES OF WAVES AFFECT WHAT WE HEAR? 5. WHAT
SOUND WAVES Objectives: 1. WHAT IS SOUND? 2. HOW DO SOUND WAVES TRAVEL? 3. HOW DO PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF A MEDIUM AFFECT THE SPEED OF SOUND WAVES? 4. WHAT PROPERTIES OF WAVES AFFECT WHAT WE HEAR? 5. WHAT
TYPES OF WAVES. 4. Waves and Sound 1
 TYPES OF WAVES Consider a set of playground swings attached by a rope from seat to seat If you sit in the first swing and begin oscillating, this disturbs the equilibrium The connecting ropes cause the
TYPES OF WAVES Consider a set of playground swings attached by a rope from seat to seat If you sit in the first swing and begin oscillating, this disturbs the equilibrium The connecting ropes cause the
Chapter 8: Wave Motion. Homework #4 Reminder. But what moves? Wave properties. Waves can reflect. Waves can pass through each other
 Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating disturbance
Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating disturbance
Physical Science DCI Progression Chart
 DCI Progression Chart PS1: Matter and Its Interactions Grade Bands PS1.A Structure & Properties of Matter Grades K-2 Grades 3-5 Grades 6-8 Grades 9-12 Second Grade * Different kinds of matter exist and
DCI Progression Chart PS1: Matter and Its Interactions Grade Bands PS1.A Structure & Properties of Matter Grades K-2 Grades 3-5 Grades 6-8 Grades 9-12 Second Grade * Different kinds of matter exist and
PHYSICS. Chapter 16 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST
 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Physics (J249) from 2016 Topic P1: Matter P1.1 Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time Describe the structure of the atom and discuss the charges
GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Physics (J249) from 2016 Topic P1: Matter P1.1 Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time Describe the structure of the atom and discuss the charges
RADIATION and the EM Spectrum
 RADIATION and the EM Spectrum Radioactivity is the of high-energy particles and/or of energy from a substance as a result of of its atoms. There are several types of radiation. Radiation from the sun is
RADIATION and the EM Spectrum Radioactivity is the of high-energy particles and/or of energy from a substance as a result of of its atoms. There are several types of radiation. Radiation from the sun is
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR)
 Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) It is kind of energy with wave character ( exactly as sea waves ) that can be characterized by : Wavelength ( ) : The distance between two identical points on the wave.
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) It is kind of energy with wave character ( exactly as sea waves ) that can be characterized by : Wavelength ( ) : The distance between two identical points on the wave.
Sound Waves. Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium
 Chapter 16 Sound Waves Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium An example of a compressional wave Waves can spread out in all directions Their speed depends on its medium
Chapter 16 Sound Waves Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium An example of a compressional wave Waves can spread out in all directions Their speed depends on its medium
Revision checklist SP4 5. SP4 Waves. SP4a Describing waves. SP4b Wave speeds. SP4c Refraction
 SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency, wavelength, amplitude, period and velocity. Describe
SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency, wavelength, amplitude, period and velocity. Describe
LECTURE 1: ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION
 LECTURE 1: ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION 1.0 -- PURPOSE OF UNIT The purpose of this unit is to identify and describe some of the basic properties common to all forms of electromagnetic radiation and to identify
LECTURE 1: ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION 1.0 -- PURPOSE OF UNIT The purpose of this unit is to identify and describe some of the basic properties common to all forms of electromagnetic radiation and to identify
Name Date Class _. Please turn to the section titled The Nature of Light.
 Please turn to the section titled The Nature of Light. In this section, you will learn that light has both wave and particle characteristics. You will also see that visible light is just part of a wide
Please turn to the section titled The Nature of Light. In this section, you will learn that light has both wave and particle characteristics. You will also see that visible light is just part of a wide
Schedule for the remainder of class
 Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1. Higher Level. Waves Atoms & Space
 Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Waves Atoms & Space Moulsham High School 1 1. Part of the electromagnetic spectrum is shown below. gamma rays X-rays A visible light infra-red
Year 11 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION QUESTIONS PAPER 1 Higher Level Waves Atoms & Space Moulsham High School 1 1. Part of the electromagnetic spectrum is shown below. gamma rays X-rays A visible light infra-red
Chapter 6. Wave Motion. Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
 Chapter 6 Waves We know that when matter is disturbed, energy emanates from the disturbance. This propagation of energy from the disturbance is know as a wave. We call this transfer of energy wave motion.
Chapter 6 Waves We know that when matter is disturbed, energy emanates from the disturbance. This propagation of energy from the disturbance is know as a wave. We call this transfer of energy wave motion.
Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves. What is a wave?
 Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance or vibration that carries energy from one location to another. Some waves require a medium to transmit the energy whereas others can travel
Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance or vibration that carries energy from one location to another. Some waves require a medium to transmit the energy whereas others can travel
Chapter 4 - Light. Name: Block:
 Chapter 4 Notes: Light Name: Block: Properties of Waves Waves are a repeating disturbance or movement that energy through matter or space without causing any displacement of material Features of a wave:
Chapter 4 Notes: Light Name: Block: Properties of Waves Waves are a repeating disturbance or movement that energy through matter or space without causing any displacement of material Features of a wave:
Electromagnetic Waves
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 23 Electromagnetic Waves Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Electromagnetic Theory Theoretical understanding of electricity and magnetism
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 23 Electromagnetic Waves Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Electromagnetic Theory Theoretical understanding of electricity and magnetism
SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER
 SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER Light Waves Light is a type of energy that travels as waves. Light is different than other waves because it does not need matter to travel. Light waves
SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER Light Waves Light is a type of energy that travels as waves. Light is different than other waves because it does not need matter to travel. Light waves
Properties of Waves. Before You Read. What are the features of a wave?
 Properties of Waves Textbook pages 134 143 Before You Read Section 4.1 Summary In this section, you will find out about waves, such as water waves, sound waves, and radio waves. On the lines below, list
Properties of Waves Textbook pages 134 143 Before You Read Section 4.1 Summary In this section, you will find out about waves, such as water waves, sound waves, and radio waves. On the lines below, list
Matter and Sound. UNIT 8 Student Reader. E5 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 8 Page KnowAtom TM
 Matter and Sound UNIT 8 Student Reader E5 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 8 Page 1 2017 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The front cover shows a photograph of three students practicing in a band. E5 Student Reader v.
Matter and Sound UNIT 8 Student Reader E5 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 8 Page 1 2017 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The front cover shows a photograph of three students practicing in a band. E5 Student Reader v.
The Nature of Light and Matter 1 Light
 The Nature of Light and Matter 1 Light ASTR 103 4/06/2016 1 Basic properties: The Nature of Light Light travels in a straight line. Most surfaces reflect light. Amount of reflection depends on the medium.
The Nature of Light and Matter 1 Light ASTR 103 4/06/2016 1 Basic properties: The Nature of Light Light travels in a straight line. Most surfaces reflect light. Amount of reflection depends on the medium.
Physics Unit: Force & Motion
 Physics Unit: Force & Motion What is physical science? A. Physical science is a field of science that studies matter and energy. B. Physical science has 2 main branches: 1. PHYSICS: the study of how matter
Physics Unit: Force & Motion What is physical science? A. Physical science is a field of science that studies matter and energy. B. Physical science has 2 main branches: 1. PHYSICS: the study of how matter
Electromagnetic radiation simply a stream of photons (a bundle of energy) What are photons???
 Electromagnetic radiation simply a stream of photons (a bundle of energy) What are photons??? no mass travel in a wave like pattern move at the speed of light contain a certain amount (or bundle) of energy
Electromagnetic radiation simply a stream of photons (a bundle of energy) What are photons??? no mass travel in a wave like pattern move at the speed of light contain a certain amount (or bundle) of energy
10/27/2017 [pgs ]
![10/27/2017 [pgs ] 10/27/2017 [pgs ]](/thumbs/82/85139288.jpg) Objectives SWBAT explain the relationship between energy and frequency. SWBAT predict the behavior of and/or calculate quantum and photon energy from frequency. SWBAT explain how the quantization of energy
Objectives SWBAT explain the relationship between energy and frequency. SWBAT predict the behavior of and/or calculate quantum and photon energy from frequency. SWBAT explain how the quantization of energy
Decibels and Acoustical Engineering
 Decibels and Acoustical Engineering What is Sound? Sound is the movement of energy through substances in longitudinal (compression/rarefaction) waves. Sound is produced when a force causes an object or
Decibels and Acoustical Engineering What is Sound? Sound is the movement of energy through substances in longitudinal (compression/rarefaction) waves. Sound is produced when a force causes an object or
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 13 Sound
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 13 Sound Sound Sounds waves are an important example of wave motion Sound is central to hearing, speech, music and many other daily activities
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 13 Sound Sound Sounds waves are an important example of wave motion Sound is central to hearing, speech, music and many other daily activities
Preparing for your mock exams - AQA P1
 Name Topic title 1.1 Infrared radiation and surfaces Preparing for your mock exams - AQA P1 Know that all materials emit and absorb infrared radiation. Understand that the hotter an object is, the higher
Name Topic title 1.1 Infrared radiation and surfaces Preparing for your mock exams - AQA P1 Know that all materials emit and absorb infrared radiation. Understand that the hotter an object is, the higher
Lecture III : Jan 30, 2017
 Lecture III : Jan 30, 2017 Prequantum Era Particles & Waves Reading Assignment: Chapter 2 and 3 from Quantum Physics for Poets. Summarize your thoughts with some questions/comments. ( One page writeup
Lecture III : Jan 30, 2017 Prequantum Era Particles & Waves Reading Assignment: Chapter 2 and 3 from Quantum Physics for Poets. Summarize your thoughts with some questions/comments. ( One page writeup
Light and Geometric Optics
 By the end of this week I will be able to... label a diagram of a wave Solve word problems using the wave equation identify the types of radiation on the EM spectrum explain how light behaves like a wave
By the end of this week I will be able to... label a diagram of a wave Solve word problems using the wave equation identify the types of radiation on the EM spectrum explain how light behaves like a wave
Radiation - Electromagnetic Waves (EMR): wave consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that move at the speed of light through space.
 Radiation - Electromagnetic Waves (EMR): wave consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that move at the speed of light through space. Photon: a quantum of light or electromagnetic wave. Quantum:
Radiation - Electromagnetic Waves (EMR): wave consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that move at the speed of light through space. Photon: a quantum of light or electromagnetic wave. Quantum:
f 1/ T T 1/ f Formulas Fs kx m T s 2 k l T p 2 g v f
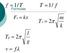 f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
Origin of Sound. Those vibrations compress and decompress the air (or other medium) around the vibrating object
 Sound Each celestial body, in fact each and every atom, produces a particular sound on account of its movement, its rhythm or vibration. All these sounds and vibrations form a universal harmony in which
Sound Each celestial body, in fact each and every atom, produces a particular sound on account of its movement, its rhythm or vibration. All these sounds and vibrations form a universal harmony in which
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 12 Electricity and Magnetism 1. AC circuits and EM waves The Electromagnetic Spectrum The Doppler Effect 6/20/2007 Modern Physics 1. Relativity Galilean Relativity Speed
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 12 Electricity and Magnetism 1. AC circuits and EM waves The Electromagnetic Spectrum The Doppler Effect 6/20/2007 Modern Physics 1. Relativity Galilean Relativity Speed
1. How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear?
 1. How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear? The vibrating object produces a series of compressions and rarefactions, one after the other in the medium. These pulses
1. How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear? The vibrating object produces a series of compressions and rarefactions, one after the other in the medium. These pulses
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Physics Paper 2
 4.5.1 Forces and their interactions 4.5.2 Work done and energy AQA Physics (8463) from 2016 Topics P4.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and vector quantities
4.5.1 Forces and their interactions 4.5.2 Work done and energy AQA Physics (8463) from 2016 Topics P4.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and vector quantities
Arvind Borde / PHY 12, Week 7: Electromagnetic Radiation
 Arvind Borde / PHY 12, Week 7: Electromagnetic Radiation 1 3 What do you know so far? (1) What in the name of electricity creates electric fields? Electric charges. (2) What in the name of magnetism creates
Arvind Borde / PHY 12, Week 7: Electromagnetic Radiation 1 3 What do you know so far? (1) What in the name of electricity creates electric fields? Electric charges. (2) What in the name of magnetism creates
Chapter 5 Light and Matter
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter Stars and galaxies are too far for us to send a spacecraft or to visit (in our lifetimes). All we can receive from them is light But there is much we can learn (composition,
Chapter 5 Light and Matter Stars and galaxies are too far for us to send a spacecraft or to visit (in our lifetimes). All we can receive from them is light But there is much we can learn (composition,
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal compression waves that propagate through a medium gas, liquid, or solid. Sound Waves in Air:
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal compression waves that propagate through a medium gas, liquid, or solid. Sound Waves in Air: Pressure and density vary sinusoidally. PheT The speed of sound in
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal compression waves that propagate through a medium gas, liquid, or solid. Sound Waves in Air: Pressure and density vary sinusoidally. PheT The speed of sound in
-Electromagnetic. Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical.
 Waves Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical requires a medium -Electromagnetic no medium required Mechanical waves: sound, water, seismic.
Waves Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical requires a medium -Electromagnetic no medium required Mechanical waves: sound, water, seismic.
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
Lecture 23 Sound Beats Sound Solids and Fluids
 Lecture 23 Sound Beats Sound Solids and Fluids To round out our discussion of interference and waves, we should talk about beats. When you combine two waves (sound is a good example), if the frequencies
Lecture 23 Sound Beats Sound Solids and Fluids To round out our discussion of interference and waves, we should talk about beats. When you combine two waves (sound is a good example), if the frequencies
Electromagnetic spectrum Electromagnetic radiation
 Chapter 4 Section 1 Electromagnetic spectrum includes all the different wave lengths of radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave like behavior as it travels through space.
Chapter 4 Section 1 Electromagnetic spectrum includes all the different wave lengths of radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave like behavior as it travels through space.
YEAR 11- Physics Term 1 plan
 YEAR 11- Physics Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes Week 1 5.1.2 Nucleus of the Atom Describe the composition of the nucleus in terms of protons and neutrons State the charges of protons
YEAR 11- Physics Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes Week 1 5.1.2 Nucleus of the Atom Describe the composition of the nucleus in terms of protons and neutrons State the charges of protons
ALBERT EINSTEIN AND THE FABRIC OF TIME by Gevin Giorbran
 ALBERT EINSTEIN AND THE FABRIC OF TIME by Gevin Giorbran Surprising as it may be to most non-scientists and even to some scientists, Albert Einstein concluded in his later years that the past, present,
ALBERT EINSTEIN AND THE FABRIC OF TIME by Gevin Giorbran Surprising as it may be to most non-scientists and even to some scientists, Albert Einstein concluded in his later years that the past, present,
Physics General Physics. Lecture 25 Waves. Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Introduction The Components The Technology (MRI) Physics behind MR Most slides taken from http:// www.slideworld.org/ viewslides.aspx/magnetic- Resonance-Imaging- %28MRI%29-MR-Imaging-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Introduction The Components The Technology (MRI) Physics behind MR Most slides taken from http:// www.slideworld.org/ viewslides.aspx/magnetic- Resonance-Imaging- %28MRI%29-MR-Imaging-
The Spectral Differences in Sounds and Harmonics. Through chemical and biological processes, we, as humans, can detect the movement and
 John Chambers Semester Project 5/2/16 The Spectral Differences in Sounds and Harmonics Through chemical and biological processes, we, as humans, can detect the movement and vibrations of molecules through
John Chambers Semester Project 5/2/16 The Spectral Differences in Sounds and Harmonics Through chemical and biological processes, we, as humans, can detect the movement and vibrations of molecules through
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Laser & Opto-Electronic Eng. Dept rd YEAR. The Electromagnetic Waves
 Spectroscopy Interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter yields that energy is absorbed or emitted by matter in discrete quantities (quanta). Measurement of the frequency or (wave length) of the
Spectroscopy Interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter yields that energy is absorbed or emitted by matter in discrete quantities (quanta). Measurement of the frequency or (wave length) of the
Planetary Science: Investigations 9-10 I-Check Quiz STUDY GUIDE Name HR Date
 1. How are different types of radiation arranged along the electromagnetic spectrum? A. By how fast they travel incorrect answer B. By their sources incorrect answer C. By the amount of energy they carry
1. How are different types of radiation arranged along the electromagnetic spectrum? A. By how fast they travel incorrect answer B. By their sources incorrect answer C. By the amount of energy they carry
Lecture 1 Bioradiation
 1 1 Radiation definition: Radiation, when broadly defined, includes the entire spectrum of electromagnetic waves : radiowaves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, and x-rays and particles.
1 1 Radiation definition: Radiation, when broadly defined, includes the entire spectrum of electromagnetic waves : radiowaves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, and x-rays and particles.
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects.
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Physics: Waves, Sound/Light, Electromagnetic Waves, Magnetism, Mains Electricity and the National Grid
 6.7 Describe the method to measure the speed of sound in air and the speed of ripples on the water surface 7.5 Link the properties of EM waves to their practical application 7.6 Apply knowledge of reflection,
6.7 Describe the method to measure the speed of sound in air and the speed of ripples on the water surface 7.5 Link the properties of EM waves to their practical application 7.6 Apply knowledge of reflection,
Section 1: The Science of Energy¹
 SECTION1: THE SCIENCE OF ENERGY Section 1: The Science of Energy¹ What Is Energy? Energy is the ability to do work or the ability to make a change. Everything that happens in the world involves the exchange
SECTION1: THE SCIENCE OF ENERGY Section 1: The Science of Energy¹ What Is Energy? Energy is the ability to do work or the ability to make a change. Everything that happens in the world involves the exchange
Introduction. Introduction. Forces An. Forces An. Forces in Action. Forces in Action. Pressure and Pressure. Pressure and Pressure.
 Forces An Introduction A force is a vector quantity. What does this mean? Forces An Introduction A vector quantity, such as force, has a direction as well as a magnitude. 1 1 Forces in Action The moment
Forces An Introduction A force is a vector quantity. What does this mean? Forces An Introduction A vector quantity, such as force, has a direction as well as a magnitude. 1 1 Forces in Action The moment
progressive electromagnetic wave
 LECTURE 11 Ch17 A progressive electromagnetic wave is a self-supporting, energy-carrying disturbance that travels free of its source. The light from the Sun travels through space (no medium) for only 8.3
LECTURE 11 Ch17 A progressive electromagnetic wave is a self-supporting, energy-carrying disturbance that travels free of its source. The light from the Sun travels through space (no medium) for only 8.3
Electromagnetic Waves
 Big Bang Theory OUTLINE First 25 minutes of the video Notes on waves, Doppler effect, and red/blue shift Mini lab on spectrums and how they are used to understand red and blue shift Mini lab on the expanding
Big Bang Theory OUTLINE First 25 minutes of the video Notes on waves, Doppler effect, and red/blue shift Mini lab on spectrums and how they are used to understand red and blue shift Mini lab on the expanding
Radiation Awareness Training. Stephen Price Office of Research Safety
 Radiation Awareness Training Stephen Price Office of Research Safety Purpose This training is intended for Clemson University Faculty, Staff or Students who do not work directly with radioactive materials
Radiation Awareness Training Stephen Price Office of Research Safety Purpose This training is intended for Clemson University Faculty, Staff or Students who do not work directly with radioactive materials
Technical University of Denmark
 Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 11 pages Written test, 9 December 2010 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: none. "Weighting": All problems weight equally.
Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 11 pages Written test, 9 December 2010 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: none. "Weighting": All problems weight equally.
National 3 Waves and Radiation
 What is a wave? National 3 Waves and Radiation 1. Wave Properties The basic definition Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We
What is a wave? National 3 Waves and Radiation 1. Wave Properties The basic definition Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We
Chapter 34. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves Waves If we wish to talk about electromagnetism or light we must first understand wave motion. If you drop a rock into the water small ripples are seen on the surface of
Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves Waves If we wish to talk about electromagnetism or light we must first understand wave motion. If you drop a rock into the water small ripples are seen on the surface of
Topic 6: Transferring Energy
 Topic 6: Transferring Energy Transferring Energy Thermal energy can be transferred 3 ways: 1) Radiation 2) Conduction 3) Convection 1) RADIATIONTRANSFERS ENERGY Use p. 226 to answer the following questions
Topic 6: Transferring Energy Transferring Energy Thermal energy can be transferred 3 ways: 1) Radiation 2) Conduction 3) Convection 1) RADIATIONTRANSFERS ENERGY Use p. 226 to answer the following questions
Lesson 13. Basic Concepts in Architectural Acoustics INTRODUCTION
 Lesson 13 Basic Concepts in Architectural Acoustics 13.1 Introduction. 13.2 The nature of sound. 13.3 Properties of sound. 13.4 Propagation of sound. 13.5 Sound power and sound intensity. 13.6 Effect of
Lesson 13 Basic Concepts in Architectural Acoustics 13.1 Introduction. 13.2 The nature of sound. 13.3 Properties of sound. 13.4 Propagation of sound. 13.5 Sound power and sound intensity. 13.6 Effect of
Subject Link to prior learning: Term Duration (approx.) Module
 . Cells and organisation Cells as the fundamental unit of living organisms, including how to observe, interpret and record cell structure using a light microscope. The functions of the cell wall, cell
. Cells and organisation Cells as the fundamental unit of living organisms, including how to observe, interpret and record cell structure using a light microscope. The functions of the cell wall, cell
KS3 Science PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST. YEAR 7 CONTENT Use this document to monitor your revision and target specific areas.
 KS3 Science PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST YEAR 7 CONTENT Use this document to monitor your revision and target specific areas. Topic Name BIOLOGY Historical ideas about living things Content Cells as the
KS3 Science PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST YEAR 7 CONTENT Use this document to monitor your revision and target specific areas. Topic Name BIOLOGY Historical ideas about living things Content Cells as the
Year 7 Physics Learning Cycle 4 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: How has our understanding of waves changed the life of the average English person?
 Year 7 Physics Learning Cycle 4 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: How has our understanding of waves changed the life of the average English person? Line of enquiry 1: Hypothesis 1: Hypothesis 2: Hypothesis
Year 7 Physics Learning Cycle 4 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: How has our understanding of waves changed the life of the average English person? Line of enquiry 1: Hypothesis 1: Hypothesis 2: Hypothesis
Imaging Chain. Imaging Chain. Imaging Chain. 1. Light source. 2. Object interactions. 3. Propagation & Collection: optics (lenses & mirrors)
 1. Light source λ [nm] sunset blue sky 2. Object interactions 3. Propagation & Collection: optics (lenses & mirrors) 1 Optics: Lenses Objects Images Optics: Mirrors Object Image 4. Detector or Sensor Photographic
1. Light source λ [nm] sunset blue sky 2. Object interactions 3. Propagation & Collection: optics (lenses & mirrors) 1 Optics: Lenses Objects Images Optics: Mirrors Object Image 4. Detector or Sensor Photographic
Lesson Propagation of sound Sound fields Spherical, cylindrical and perpendicular wave fronts.
 Lesson 13 Basic Concepts in Architectural Acoustics 13.1 Introduction. 13.2 The nature of sound. 13.2.1. Sound waves. 13.2.2. Frequency range of sound. 13.2.3. The audible range of sound. 13.3 Properties
Lesson 13 Basic Concepts in Architectural Acoustics 13.1 Introduction. 13.2 The nature of sound. 13.2.1. Sound waves. 13.2.2. Frequency range of sound. 13.2.3. The audible range of sound. 13.3 Properties
Wave Motion and Sound
 Wave Motion and Sound 1. A back and forth motion that repeats itself is a a. Spring b. Vibration c. Wave d. Pulse 2. The number of vibrations that occur in 1 second is called a. A Period b. Frequency c.
Wave Motion and Sound 1. A back and forth motion that repeats itself is a a. Spring b. Vibration c. Wave d. Pulse 2. The number of vibrations that occur in 1 second is called a. A Period b. Frequency c.
The Intersection of Chemistry and Biology: An Interview with Professor W. E. Moerner
 The Intersection of Chemistry and Biology: An Interview with Professor W. E. Moerner Joseph Nicolls Stanford University Professor W.E Moerner earned two B.S. degrees, in Physics and Electrical Engineering,
The Intersection of Chemistry and Biology: An Interview with Professor W. E. Moerner Joseph Nicolls Stanford University Professor W.E Moerner earned two B.S. degrees, in Physics and Electrical Engineering,
Electrocution (large quantities of charge flow through the body to earth) Insulating mats or shoes
 P4 in 30 minutes P4a: Sparks Like charges repel and unlike charges attract. a positive charge due to lack of electrons a negative charge due to an excess of electrons. Atoms or molecules that have become
P4 in 30 minutes P4a: Sparks Like charges repel and unlike charges attract. a positive charge due to lack of electrons a negative charge due to an excess of electrons. Atoms or molecules that have become
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Physics Paper 2
 4.5.1 Forces and their interactions 4.5.2 Work done and energy transfer AQA Physics (8463) from 2016 Topics P4.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and vector
4.5.1 Forces and their interactions 4.5.2 Work done and energy transfer AQA Physics (8463) from 2016 Topics P4.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and vector
