Decibels and Acoustical Engineering
|
|
|
- Elmer Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Decibels and Acoustical Engineering
2 What is Sound? Sound is the movement of energy through substances in longitudinal (compression/rarefaction) waves. Sound is produced when a force causes an object or substance to vibrate the energy is transferred through the substance in a wave.
3 The diagram below shows how a sound wave is represented:
4 Sound is created by a vibration A vibration is a slight shaking movement that goes back and forth. Example: When a person hits a cymbal with a drumstick, it causes the cymbal to vibrate, which makes the sound! -w
5 Sound travels in waves Sound (energy) leaves an object and travels through air as a wave until it hits your ear. As sound waves move forward, they push the air together (compressions) and pull the air apart (rarefaction).
6 Sound needs a medium Medium : the material or substance that carries a sound wave from one place to another. Examples: 1. Solids: When you connect two cups with string, you can actually hear each other! How? 2. Liquids: When you yell underwater at the pool, you can hear your friend! Sound can travel through different liquids. 3. Gases: This is hard for us to see with our eyes but with a special tool you can see it. Check this out!
7 Sound can be absorbed Absorb: To take in or suck up like a sponge. Just like a sponge takes in water, a material can take in sound. If you didn t hear your brother calling you because you are playing a videogame, you could say you were absorbed in the game. The sound then becomes quieter! SHHHHH.
8 Sound can be reflected Reflection : when a sound wave bounces back off of a material and back to the person or object creating the sound. This causes something called an echo. Think about when you are in the gym or a long hallway and you make a noise. It repeats after you multiple times when the sound waves are reflected off of the material.
9 Decibel A unit to measure sound
10 Vocabulary absorption acoustic decibel medium oscillation reflection sound transmit soundproof vibration wave Word Word Definitio Definition The process by which a material, structure, or object takes in sound energy when sound waves are encountered, as opposed to reflecting the energy. The branch of physics that deals with the study of all mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound, and infrasound. A unit of measurement used to express the intensity of a sound, or the power level of an electrical signal by comparing it with a given level on a logarithmic scale. A material substance that can help move energy waves (such as sound) along. Also known as a transmission medium. The repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. The term vibration is precisely used to describe mechanical oscillation. The change in direction of a wave at the fact of a medium so that the wave returns to where it originated. A vibration that manifests itself as a wave of pressure and can be perceived by humans (depending on the frequency) via the ear. Humans can hear soundwaves when the frequency lies between 20Hz and 20 khz. In acoustics, sound passing from one area to another, normally through air or through a material constructed by some other medium. The means of preventing sound by constructing material that prevents its passage and reflection. In mechanics, an oscillation of the parts of a fluid or an elastic solid whose equilibrium has been disturbed, or of an electromagnetic wave. A wave of compression by which sound is propagated in an elastic medium such as air.
11 What Soundproofing Material Works Best? Each group will be testing a box filled with a different material to see if the decibel reading becomes lower (is absorbed) or if the decibel reading increases/does not absorb (is reflected). a. Group 1: Felt b. Group 2: Popsicle sticks c. Group 3: Styrofoam d. Group 4: Paper e. Group 5: Foil f. Group 6: Plastic plates We will test the box first without any materials to get your initial reading, then we will test the box again when you have your material inside the box.
12 Creating your box Tips and tricks: Place your materials down so that they are one layer surrounding the box Don t just stuff the materials in the box and then test! If you need to cut materials to make them flat against the surface you can You may use tape or glue to secure the materials to the box
13 Motivational activity Students, today you will have QUIZ! Each table group will be given one reading and only one student will read in each group. You will need to make sure you hear all of the information they are reading because you will be quizzed right after. Make sure you are listening! Article : World s largest Marsupial
14 Whole class discussion How would you feel if you had to listen to these loud noises each time you were trying to read a book or article? Would this affect your concentration? How would your grades be affected from the constant noise?
15 Designing a Soundproof Room Your new school is under construction and the architect accidentally put the music room next to the library. You need to design a room that will absorb the most amount of sound, so that the music room s sound does not disturb the library. You will be given a box and will need to create a design for the inside of the box that will decrease the sound decibel s that are being measured from the outside of the box. To measure this challenge, there will be a speaker within the box and an app to measure the sound decibels from the outside.
16 The store Each material you can buy for your soundproof room is within our classroom store Each item has a price and there is a limit on how many items you can buy per group You also have a budget that you MUST stay within: $15 Choose your materials wisely!
Sound Waves SOUND VIBRATIONS THAT TRAVEL THROUGH THE AIR OR OTHER MEDIA WHEN THESE VIBRATIONS REACH THE AIR NEAR YOUR EARS YOU HEAR THE SOUND.
 SOUND WAVES Objectives: 1. WHAT IS SOUND? 2. HOW DO SOUND WAVES TRAVEL? 3. HOW DO PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF A MEDIUM AFFECT THE SPEED OF SOUND WAVES? 4. WHAT PROPERTIES OF WAVES AFFECT WHAT WE HEAR? 5. WHAT
SOUND WAVES Objectives: 1. WHAT IS SOUND? 2. HOW DO SOUND WAVES TRAVEL? 3. HOW DO PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF A MEDIUM AFFECT THE SPEED OF SOUND WAVES? 4. WHAT PROPERTIES OF WAVES AFFECT WHAT WE HEAR? 5. WHAT
Matter and Sound. UNIT 8 Student Reader. E5 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 8 Page KnowAtom TM
 Matter and Sound UNIT 8 Student Reader E5 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 8 Page 1 2017 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The front cover shows a photograph of three students practicing in a band. E5 Student Reader v.
Matter and Sound UNIT 8 Student Reader E5 Student Reader v. 9 Unit 8 Page 1 2017 KnowAtom TM Front Cover: The front cover shows a photograph of three students practicing in a band. E5 Student Reader v.
How can we model sound waves?
 Guiding Question How can we model sound waves? Activity 2: Making Sound 1 Key Vocabulary Key Vocabulary } audiogram } compression } frequency } function } hertz } pattern } rarefaction } sound intensity
Guiding Question How can we model sound waves? Activity 2: Making Sound 1 Key Vocabulary Key Vocabulary } audiogram } compression } frequency } function } hertz } pattern } rarefaction } sound intensity
Homework #4 Reminder Due Wed. 10/6
 Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Due Wed. 10/6 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating
Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Due Wed. 10/6 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating
1. How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear?
 1. How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear? The vibrating object produces a series of compressions and rarefactions, one after the other in the medium. These pulses
1. How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear? The vibrating object produces a series of compressions and rarefactions, one after the other in the medium. These pulses
the ability to do work or cause change (work is force exerted on an object causing it to move a distance)
 Vocabulary Terms - Energy energy the ability to do work or cause change (work is force exerted on an object causing it to move a distance) heat Heat is a form of energy that flows between two substances
Vocabulary Terms - Energy energy the ability to do work or cause change (work is force exerted on an object causing it to move a distance) heat Heat is a form of energy that flows between two substances
Chapter 8: Wave Motion. Homework #4 Reminder. But what moves? Wave properties. Waves can reflect. Waves can pass through each other
 Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating disturbance
Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating disturbance
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
Page # Physics 103: Lecture 26 Sound. Lecture 26, Preflight 2. Lecture 26, Preflight 1. Producing a Sound Wave. Sound from a Tuning Fork
 Physics 103: Lecture 6 Sound Producing a Sound Wave Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave A tuning fork will produce
Physics 103: Lecture 6 Sound Producing a Sound Wave Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave A tuning fork will produce
Energy - Heat, Light, and Sound
 Energy - Heat, Light, and Sound Source: Utah State Office of Education A two-year-old has plenty of it, and the sun has a bunch of it. Do you know what it is? If not, let me give you a definition: A source
Energy - Heat, Light, and Sound Source: Utah State Office of Education A two-year-old has plenty of it, and the sun has a bunch of it. Do you know what it is? If not, let me give you a definition: A source
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES
 Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Wave Motions and Sound
 EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
Energy - the ability to do work or cause change. 1 point
 Energy and Waves Energy - the ability to do work or cause change Work - the transfer of energy Work = Force X Distance Power - the rate at which work is done Power = Work Time Kinetic Energy - the energy
Energy and Waves Energy - the ability to do work or cause change Work - the transfer of energy Work = Force X Distance Power - the rate at which work is done Power = Work Time Kinetic Energy - the energy
Stage 7J Current electricity 7K Forces 7L Sound 7I Energy
 Year 7 Physics Stage 7J Current electricity 7K Forces 7L Sound 7I Energy Pink I can Problem solve using the skills I have acquired. AND Describe how voltage is divided between the components in a series
Year 7 Physics Stage 7J Current electricity 7K Forces 7L Sound 7I Energy Pink I can Problem solve using the skills I have acquired. AND Describe how voltage is divided between the components in a series
3/9/2011. Outline Chapter 7 Waves Water Waves Water Waves. Water waves are really circular. They are an example of Mechanical waves.
 Outline Chapter 7 Waves 7-1. Water Waves 7-2. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves 7-3. Describing Waves 7-4. Standing Waves 7-5. Sound 7-6. Doppler Effect 7-7. Musical Sounds 7-8. Electromagnetic Waves 7-9.
Outline Chapter 7 Waves 7-1. Water Waves 7-2. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves 7-3. Describing Waves 7-4. Standing Waves 7-5. Sound 7-6. Doppler Effect 7-7. Musical Sounds 7-8. Electromagnetic Waves 7-9.
Learning Goal: By the end of today, I will be familiar with the following concepts: Demo Newton's Cradle Tuning Forks. Section 8.
 Section 8.1 Vibrations Learning Goal: By the end of today, I will be familiar with the following concepts: Vibrations and Mechanical waves The cyclical motion about an equilibrium point is called a vibration.
Section 8.1 Vibrations Learning Goal: By the end of today, I will be familiar with the following concepts: Vibrations and Mechanical waves The cyclical motion about an equilibrium point is called a vibration.
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 13 Sound
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 13 Sound Sound Sounds waves are an important example of wave motion Sound is central to hearing, speech, music and many other daily activities
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 13 Sound Sound Sounds waves are an important example of wave motion Sound is central to hearing, speech, music and many other daily activities
Introduction to Acoustics. Phil Joseph
 Introduction to Acoustics Phil Joseph INTRODUCTION TO ACOUSTICS Sound and Noise Sound waves Frequency, wavelength and wavespeed Point sources Sound power and intensity Wave reflection Standing waves Measures
Introduction to Acoustics Phil Joseph INTRODUCTION TO ACOUSTICS Sound and Noise Sound waves Frequency, wavelength and wavespeed Point sources Sound power and intensity Wave reflection Standing waves Measures
42 TRAVELING WAVES (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G)
 42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220. Final Exam. Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total)
 Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
due to striking, rubbing, Any vibration of matter spinning, plucking, etc. Find frequency first, then calculate period.
 Equilibrium Position Disturbance Period (T in sec) # sec T = # cycles Frequency (f in Hz) f = # cycles # sec Amplitude (A in cm, m or degrees [θ]) Other Harmonic Motion Basics Basic Definitions Pendulums
Equilibrium Position Disturbance Period (T in sec) # sec T = # cycles Frequency (f in Hz) f = # cycles # sec Amplitude (A in cm, m or degrees [θ]) Other Harmonic Motion Basics Basic Definitions Pendulums
Physics Worksheet Sound and Light Section: Name:
 Do Now: What is common between sound and light? What are the differences between sound and light? Sound Waves 1. Define Sound Waves from three different perspectives 6. Speed of sound =. Formula: v =.
Do Now: What is common between sound and light? What are the differences between sound and light? Sound Waves 1. Define Sound Waves from three different perspectives 6. Speed of sound =. Formula: v =.
TYPES OF WAVES. 4. Waves and Sound 1
 TYPES OF WAVES Consider a set of playground swings attached by a rope from seat to seat If you sit in the first swing and begin oscillating, this disturbs the equilibrium The connecting ropes cause the
TYPES OF WAVES Consider a set of playground swings attached by a rope from seat to seat If you sit in the first swing and begin oscillating, this disturbs the equilibrium The connecting ropes cause the
Chapter 6. Wave Motion. Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
 Chapter 6 Waves We know that when matter is disturbed, energy emanates from the disturbance. This propagation of energy from the disturbance is know as a wave. We call this transfer of energy wave motion.
Chapter 6 Waves We know that when matter is disturbed, energy emanates from the disturbance. This propagation of energy from the disturbance is know as a wave. We call this transfer of energy wave motion.
Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves. What is a wave?
 Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance or vibration that carries energy from one location to another. Some waves require a medium to transmit the energy whereas others can travel
Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance or vibration that carries energy from one location to another. Some waves require a medium to transmit the energy whereas others can travel
SoundWaves. Lecture (2) Special topics Dr.khitam Y, Elwasife
 SoundWaves Lecture (2) Special topics Dr.khitam Y, Elwasife VGTU EF ESK stanislovas.staras@el.vgtu.lt 2 Mode Shapes and Boundary Conditions, VGTU EF ESK stanislovas.staras@el.vgtu.lt ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI
SoundWaves Lecture (2) Special topics Dr.khitam Y, Elwasife VGTU EF ESK stanislovas.staras@el.vgtu.lt 2 Mode Shapes and Boundary Conditions, VGTU EF ESK stanislovas.staras@el.vgtu.lt ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI
KEY TERMS. compression rarefaction pitch Doppler effect KEY TERMS. intensity decibel resonance KEY TERMS
 CHAPTER 12 SECTION 1 Sound Waves Summary The frequency of a sound wave determines its pitch. The speed of sound depends on the medium. The relative motion between the source of waves and an observer creates
CHAPTER 12 SECTION 1 Sound Waves Summary The frequency of a sound wave determines its pitch. The speed of sound depends on the medium. The relative motion between the source of waves and an observer creates
Revision checklist SP4 5. SP4 Waves. SP4a Describing waves. SP4b Wave speeds. SP4c Refraction
 SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency, wavelength, amplitude, period and velocity. Describe
SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency, wavelength, amplitude, period and velocity. Describe
Producing a Sound Wave. Chapter 14. Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a Sound Wave. Using a Tuning Fork, cont.
 Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Lecture 18: Reflection and Impedance
 Lecture 18: Reflection and Impedance Let us look again at the question of what happens when a sound wave in the air runs into the surface of a body of water (or a wall, or glass, or whatever). How much
Lecture 18: Reflection and Impedance Let us look again at the question of what happens when a sound wave in the air runs into the surface of a body of water (or a wall, or glass, or whatever). How much
Schedule for the remainder of class
 Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
SOUND. Representative Sample Physics: Sound. 1. Periodic Motion of Particles PLANCESS CONCEPTS
 Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
Lecture 23 Sound Beats Sound Solids and Fluids
 Lecture 23 Sound Beats Sound Solids and Fluids To round out our discussion of interference and waves, we should talk about beats. When you combine two waves (sound is a good example), if the frequencies
Lecture 23 Sound Beats Sound Solids and Fluids To round out our discussion of interference and waves, we should talk about beats. When you combine two waves (sound is a good example), if the frequencies
2016 AP Physics Unit 6 Oscillations and Waves.notebook December 09, 2016
 AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
Physics General Physics. Lecture 25 Waves. Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
PHYSICS. Chapter 16 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
Revision checklist. Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it! Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it!
 SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency,
SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency,
Chapter 2 SOUND WAVES
 Chapter SOUND WAVES Introduction: A sound wave (or pressure or compression wave) results when a surface (layer of molecules) moves back and forth in a medium producing a sequence of compressions C and
Chapter SOUND WAVES Introduction: A sound wave (or pressure or compression wave) results when a surface (layer of molecules) moves back and forth in a medium producing a sequence of compressions C and
Section 6: Waves. The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Physics TAC (c).
 Section 6: Waves The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Physics TAC 112.39(c). 6.01 Classifications of Waves Physics (7)(A) Physics (7)(B) 6.02 Properties
Section 6: Waves The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Physics TAC 112.39(c). 6.01 Classifications of Waves Physics (7)(A) Physics (7)(B) 6.02 Properties
Chapter 16 Traveling Waves
 Chapter 16 Traveling Waves GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms as it is used in physics,
Chapter 16 Traveling Waves GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms as it is used in physics,
Announcements 2 Dec 2014
 Announcements 2 Dec 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 3 going on a. Covers Ch 9-12, HW 18-24 b. Late fee on Wed Dec 3, 3 pm c. Closes on Thursday Dec 4, 3 pm 3. Photo contest submissions due Friday Dec 5, midnight
Announcements 2 Dec 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 3 going on a. Covers Ch 9-12, HW 18-24 b. Late fee on Wed Dec 3, 3 pm c. Closes on Thursday Dec 4, 3 pm 3. Photo contest submissions due Friday Dec 5, midnight
1.32 Sound Waves. Chapter 1. Energy
 1.32 Sound Waves Define sound. Describe sound waves and how they are generated. Identify media through which sound waves can travel. Crack! Crash! Thud! That s what you d hear if you were in the forest
1.32 Sound Waves Define sound. Describe sound waves and how they are generated. Identify media through which sound waves can travel. Crack! Crash! Thud! That s what you d hear if you were in the forest
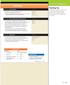
f 1/ T T 1/ f Formulas Fs kx m T s 2 k l T p 2 g v f
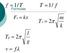 f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
Mechanical Waves. 3: Mechanical Waves (Chapter 16) Waves: Space and Time
 3: Mechanical Waves (Chapter 6) Phys3, A Dr. Robert MacDonald Mechanical Waves A mechanical wave is a travelling disturbance in a medium (like water, string, earth, Slinky, etc). Move some part of the
3: Mechanical Waves (Chapter 6) Phys3, A Dr. Robert MacDonald Mechanical Waves A mechanical wave is a travelling disturbance in a medium (like water, string, earth, Slinky, etc). Move some part of the
Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section
 Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section Claudio Campagnari Lecture 3: 30 Sep. 2004 Web page: http://hep.ucsb.edu/people/claudio/ph3-04/ 1 Sound Sound = longitudinal wave in a medium. The medium can be anything:
Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section Claudio Campagnari Lecture 3: 30 Sep. 2004 Web page: http://hep.ucsb.edu/people/claudio/ph3-04/ 1 Sound Sound = longitudinal wave in a medium. The medium can be anything:
Performance script for sixth graders By Thomas Kuo and Kimberly Kline LEAPS Fellows, University of California, Santa Barbara
 Performance script for sixth graders By Thomas Kuo and Kimberly Kline LEAPS Fellows, 2007-08 University of California, Santa Barbara [Remember to get answers from a wide variety of students in the audience.
Performance script for sixth graders By Thomas Kuo and Kimberly Kline LEAPS Fellows, 2007-08 University of California, Santa Barbara [Remember to get answers from a wide variety of students in the audience.
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal compression waves that propagate through a medium gas, liquid, or solid. Sound Waves in Air:
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal compression waves that propagate through a medium gas, liquid, or solid. Sound Waves in Air: Pressure and density vary sinusoidally. PheT The speed of sound in
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal compression waves that propagate through a medium gas, liquid, or solid. Sound Waves in Air: Pressure and density vary sinusoidally. PheT The speed of sound in
Physics 207 Lecture 28
 Goals: Lecture 28 Chapter 20 Employ the wae model Visualize wae motion Analyze functions of two ariables Know the properties of sinusoidal waes, including waelength, wae number, phase, and frequency. Work
Goals: Lecture 28 Chapter 20 Employ the wae model Visualize wae motion Analyze functions of two ariables Know the properties of sinusoidal waes, including waelength, wae number, phase, and frequency. Work
Ch Guided Reading Sound and Light
 Name Date Hour Chapter 15 Answer Key Ch.15-18 Guided Reading Sound and Light 1. Compare the speed of sound as it travels within a liquid, a solid, and a gas. Why does the speed of sound differ? Sound travels
Name Date Hour Chapter 15 Answer Key Ch.15-18 Guided Reading Sound and Light 1. Compare the speed of sound as it travels within a liquid, a solid, and a gas. Why does the speed of sound differ? Sound travels
APPENDIX B. Noise Primer
 APPENDIX B Noise Primer NOISE PRIMER TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. BASIC SOUND PRINCIPLES...1 2.1. SOUND AS A WAVE...1 2.2. SOUND PRESSURE LEVEL...2 2.2.1. Decibel Math...4 2.2.2. Descriptive
APPENDIX B Noise Primer NOISE PRIMER TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. BASIC SOUND PRINCIPLES...1 2.1. SOUND AS A WAVE...1 2.2. SOUND PRESSURE LEVEL...2 2.2.1. Decibel Math...4 2.2.2. Descriptive
Physics Mechanics. Lecture 34 Waves and sound II
 1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 34 Waves and sound II 2 Sound Waves Sound waves are pressure waves in solids, liquids, and gases. They are longitudinal in liquids and gases, and may have transverse components
1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 34 Waves and sound II 2 Sound Waves Sound waves are pressure waves in solids, liquids, and gases. They are longitudinal in liquids and gases, and may have transverse components
Work. Work and Energy Examples. Energy. To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or:
 Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
4. What is the speed (in cm s - 1 ) of the tip of the minute hand?
 Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Welcome to Year 4 Sound
 Welcome to www.year4sound.com Orange Group Red Group Green Group Purple Group Black Group Year 4 Sound On the next few pages you will learn about the exciting experiments the children in Year 4 have been
Welcome to www.year4sound.com Orange Group Red Group Green Group Purple Group Black Group Year 4 Sound On the next few pages you will learn about the exciting experiments the children in Year 4 have been
What is mechanical energy? How do we use it? Energy Energy
 You probably already have some idea what energy is. is easy to recognize. Yet it can be hard to describe. Where do you think you ve seen energy today? How do you think you will use energy tomorrow? Let
You probably already have some idea what energy is. is easy to recognize. Yet it can be hard to describe. Where do you think you ve seen energy today? How do you think you will use energy tomorrow? Let
Lecture 5 Notes: 07 / 05. Energy and intensity of sound waves
 Lecture 5 Notes: 07 / 05 Energy and intensity of sound waves Sound waves carry energy, just like waves on a string do. This energy comes in several types: potential energy due to the compression of the
Lecture 5 Notes: 07 / 05 Energy and intensity of sound waves Sound waves carry energy, just like waves on a string do. This energy comes in several types: potential energy due to the compression of the
Sound Waves 5 Spelling List
 Sound 5 Spelling List Free PDF ebook Download: Sound 5 Spelling List Download or Read Online ebook sound waves 5 spelling list in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database 7 days ago - list and to Ang
Sound 5 Spelling List Free PDF ebook Download: Sound 5 Spelling List Download or Read Online ebook sound waves 5 spelling list in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database 7 days ago - list and to Ang
Announcements 5 Dec 2013
 Announcements 5 Dec 2013 1. Photo contest submissions due tomorrow night! 2. Online course evaluations due Sun, Dec. 15 http://studentratings.byu.edu Please take both the ratings and the comments seriously.
Announcements 5 Dec 2013 1. Photo contest submissions due tomorrow night! 2. Online course evaluations due Sun, Dec. 15 http://studentratings.byu.edu Please take both the ratings and the comments seriously.
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects.
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Exercises The Origin of Sound (page 515) 26.2 Sound in Air (pages ) 26.3 Media That Transmit Sound (page 517)
 Exercises 26.1 The Origin of (page 515) Match each sound source with the part that vibrates. Source Vibrating Part 1. violin a. strings 2. your voice b. reed 3. saxophone c. column of air at the mouthpiece
Exercises 26.1 The Origin of (page 515) Match each sound source with the part that vibrates. Source Vibrating Part 1. violin a. strings 2. your voice b. reed 3. saxophone c. column of air at the mouthpiece
PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section VIII
 PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section VIII Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and
PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section VIII Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and
Y7 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Keywords
 Y7 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Biology Cells. Cells as the fundamental unit of living organisms, including how to observe cell structure using a light microscope. The functions of the cell wall,
Y7 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Biology Cells. Cells as the fundamental unit of living organisms, including how to observe cell structure using a light microscope. The functions of the cell wall,
PHYSICS 220. Lecture 21. Textbook Sections Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 220 1
 PHYSICS 220 Lecture 21 Sound Textbook Sections 13.1 13.7 Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Overview Last Lecture Interference and Diffraction Constructive, destructive Diffraction: bending of
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 21 Sound Textbook Sections 13.1 13.7 Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Overview Last Lecture Interference and Diffraction Constructive, destructive Diffraction: bending of
Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is energy? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: What is work? Q: Potential Energy
 Q: What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is work? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: Potential Energy The energy of an object due to its position, shape, or condition
Q: What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is work? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: Potential Energy The energy of an object due to its position, shape, or condition
Transfer of Energy in Collision
 Energy can be moved from place to place by moving objects through sound, light, or electric currents. Most energy must have a medium through which to travel. The transfer of this energy changes the way
Energy can be moved from place to place by moving objects through sound, light, or electric currents. Most energy must have a medium through which to travel. The transfer of this energy changes the way
The Nature of Sound Waves
 The Nature of Sound Waves Read from Lesson 1 of the Sound and Music chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/sound/u11l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/sound/u11l1b.html
The Nature of Sound Waves Read from Lesson 1 of the Sound and Music chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/sound/u11l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/sound/u11l1b.html
Fundamentals of Acoustics
 Fundamentals of Acoustics Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research of the Polish Academy of Sciences
Fundamentals of Acoustics Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research of the Polish Academy of Sciences
Name: Section: Forms of Energy Practice Test
 Name: Section: Forms of Energy Practice Test Directions: For each of the questions or incomplete statements below, choose the best of the answer choices given and write your answer on the line. 1. What
Name: Section: Forms of Energy Practice Test Directions: For each of the questions or incomplete statements below, choose the best of the answer choices given and write your answer on the line. 1. What
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
Marble Roller Coaster
 Marble Roller Coaster Topic Area(s) Cost Time Grade Level Supplies Gravity Potential/Kinetic energy Design Process Structures Friction $1.00/Child 30 min 6-12 Stopwatch or phone timer Scissors/utility
Marble Roller Coaster Topic Area(s) Cost Time Grade Level Supplies Gravity Potential/Kinetic energy Design Process Structures Friction $1.00/Child 30 min 6-12 Stopwatch or phone timer Scissors/utility
What is a wave? Waves
 What is a wave? Waves Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance that carries energy from one place to another. Classifying waves 1. Mechanical Waves - e.g., water waves, sound waves, and waves on strings.
What is a wave? Waves Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance that carries energy from one place to another. Classifying waves 1. Mechanical Waves - e.g., water waves, sound waves, and waves on strings.
9.1 Harmonic Motion. Motion in cycles. linear motion - motion that goes from one place to another without repeating.
 9.1 Harmonic Motion A bicyclist pedaling past you on the street moves in linear motion. Linear motion gets us from one place to another (Figure 9.1A). This chapter is about another kind of motion called
9.1 Harmonic Motion A bicyclist pedaling past you on the street moves in linear motion. Linear motion gets us from one place to another (Figure 9.1A). This chapter is about another kind of motion called
Lecture 21: Decay of Resonances
 Lecture 21: Decay of Resonances Recall that a resonance involves energy bouncing back and forth between two means of storage. In air resonances in cavities, energy is going back and forth between being
Lecture 21: Decay of Resonances Recall that a resonance involves energy bouncing back and forth between two means of storage. In air resonances in cavities, energy is going back and forth between being
Southern Nevada Regional Professional Development Program. What happens when water changes to a solid?
 3-5 Physical Science What happens when water changes to a solid? Two large soft vials with caps One plastic 50 ml syringe Plastic ice tray Water Freezer compartment 1. Completely fill the ice tray and
3-5 Physical Science What happens when water changes to a solid? Two large soft vials with caps One plastic 50 ml syringe Plastic ice tray Water Freezer compartment 1. Completely fill the ice tray and
Longitudinal Waves. waves in which the particle or oscillator motion is in the same direction as the wave propagation
 Longitudinal Waves waves in which the particle or oscillator motion is in the same direction as the wave propagation Longitudinal waves propagate as sound waves in all phases of matter, plasmas, gases,
Longitudinal Waves waves in which the particle or oscillator motion is in the same direction as the wave propagation Longitudinal waves propagate as sound waves in all phases of matter, plasmas, gases,
Lecture 18. Waves and Sound
 Lecture 18 Waves and Sound Today s Topics: Nature o Waves Periodic Waves Wave Speed The Nature o Sound Speed o Sound Sound ntensity The Doppler Eect Disturbance Wave Motion DEMO: Rope A wave is a traveling
Lecture 18 Waves and Sound Today s Topics: Nature o Waves Periodic Waves Wave Speed The Nature o Sound Speed o Sound Sound ntensity The Doppler Eect Disturbance Wave Motion DEMO: Rope A wave is a traveling
Unit 4 Waves and Sound Waves and Their Properties
 Lesson35.notebook May 27, 2013 Unit 4 Waves and Sound Waves and Their Properties Today's goal: I can explain the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves and their properties. Waves are a disturbances
Lesson35.notebook May 27, 2013 Unit 4 Waves and Sound Waves and Their Properties Today's goal: I can explain the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves and their properties. Waves are a disturbances
21. Earthquakes I (p ; 306)
 21. Earthquakes I (p. 296-303; 306) How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the last 4,000 years? How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the past century? What two recent earthquakes
21. Earthquakes I (p. 296-303; 306) How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the last 4,000 years? How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the past century? What two recent earthquakes
INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPT. OF PHYSICS P105, Basic Physics of Sound, Spring 2010
 Name: Joe E. Physics ID#: 999 999 999 INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPT. OF PHYSICS P105, Basic Physics of Sound, Spring 2010 Midterm Exam #1 Thursday, 11 Feb. 2010, 7:30 9:30 p.m. Closed book. You are allowed
Name: Joe E. Physics ID#: 999 999 999 INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPT. OF PHYSICS P105, Basic Physics of Sound, Spring 2010 Midterm Exam #1 Thursday, 11 Feb. 2010, 7:30 9:30 p.m. Closed book. You are allowed
Section 1: The Science of Energy¹
 SECTION1: THE SCIENCE OF ENERGY Section 1: The Science of Energy¹ What Is Energy? Energy is the ability to do work or the ability to make a change. Everything that happens in the world involves the exchange
SECTION1: THE SCIENCE OF ENERGY Section 1: The Science of Energy¹ What Is Energy? Energy is the ability to do work or the ability to make a change. Everything that happens in the world involves the exchange
EngrTEAMS 12/13/2017. Set up the first page of your EngrTEAMS notebook with a TABLE OF CONTENTS page.
 TABLE OF CONTENTS EngrTEAMS Ecuadorian Fishermen Set up the first page of your EngrTEAMS notebook with a TABLE OF CONTENTS page. VOCABULARY On the next to last page, write Vocabulary across the top of
TABLE OF CONTENTS EngrTEAMS Ecuadorian Fishermen Set up the first page of your EngrTEAMS notebook with a TABLE OF CONTENTS page. VOCABULARY On the next to last page, write Vocabulary across the top of
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Physics Paper 2
 4.5.1 Forces and their interactions 4.5.2 Work done and energy AQA Physics (8463) from 2016 Topics P4.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and vector quantities
4.5.1 Forces and their interactions 4.5.2 Work done and energy AQA Physics (8463) from 2016 Topics P4.5. Forces Topic Student Checklist R A G Identify and describe scalar quantities and vector quantities
Sound Waves. Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium
 Chapter 16 Sound Waves Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium An example of a compressional wave Waves can spread out in all directions Their speed depends on its medium
Chapter 16 Sound Waves Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium An example of a compressional wave Waves can spread out in all directions Their speed depends on its medium
What does the speed of a wave depend on?
 Today s experiment Goal answer the question What does the speed of a wave depend on? Materials: Wave on a String PHeT Simulation (link in schedule) and Wave Machine Write a CER in pairs. Think about the
Today s experiment Goal answer the question What does the speed of a wave depend on? Materials: Wave on a String PHeT Simulation (link in schedule) and Wave Machine Write a CER in pairs. Think about the
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
Final Exam Concept Map
 Final Exam Concept Map Rule of thumb to study for any comprehensive final exam - start with what you know - look at the quiz problems. If you did not do well on the quizzes, you should certainly learn
Final Exam Concept Map Rule of thumb to study for any comprehensive final exam - start with what you know - look at the quiz problems. If you did not do well on the quizzes, you should certainly learn
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
1. A wave is a traveling disturbance. 2. A wave carries energy from place to place.
 v = fλ 1. A wave is a traveling disturbance. 2. A wave carries energy from place to place. Transverse Wave Longitudinal Wave How is a guitar made to create different notes/pitches/frequencies? A wave s
v = fλ 1. A wave is a traveling disturbance. 2. A wave carries energy from place to place. Transverse Wave Longitudinal Wave How is a guitar made to create different notes/pitches/frequencies? A wave s
v wave Here F is the tension and µ is the mass/length.
 Main points of today s lecture: Transverse and longitudinal waves traveling waves v wave = Wave speed for a string fλ v = F µ Here F is the tension Intensity of sound I = and µ is the mass/length. P =
Main points of today s lecture: Transverse and longitudinal waves traveling waves v wave = Wave speed for a string fλ v = F µ Here F is the tension Intensity of sound I = and µ is the mass/length. P =
IDS 102: Electromagnetic Radiation and the Nature of Light
 IDS 102: Electromagnetic Radiation and the Nature of Light Major concepts we will cover in this module are: electromagnetic spectrum; wave intensity vs. wavelength, and the difference between light reflection,
IDS 102: Electromagnetic Radiation and the Nature of Light Major concepts we will cover in this module are: electromagnetic spectrum; wave intensity vs. wavelength, and the difference between light reflection,
Energy stored in a mechanical wave
 Waves 3 1. Energy stored in a mechanical wave. Wave equation revisited - separation of variables 3. Wave on string with fied ends 4. Waves at boundaries 5. mpedance 6. Other eamples: - Lossless transmission
Waves 3 1. Energy stored in a mechanical wave. Wave equation revisited - separation of variables 3. Wave on string with fied ends 4. Waves at boundaries 5. mpedance 6. Other eamples: - Lossless transmission
Forces and Motion: Accelerate your Mass of Students
 FORCES AND MOTION 60 Minute Physical Science Lesson Science-to-Go! Program Grades: 1-5 TEACHER GUIDE Forces and Motion: Accelerate your Mass of Students Description Make sure you have plenty of room for
FORCES AND MOTION 60 Minute Physical Science Lesson Science-to-Go! Program Grades: 1-5 TEACHER GUIDE Forces and Motion: Accelerate your Mass of Students Description Make sure you have plenty of room for
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
Chapter 17: Waves II. Sound waves are one example of Longitudinal Waves. Sound waves are pressure waves: Oscillations in air pressure and air density
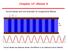 Sound waves are one example of Longitudinal Waves Sound waves are pressure waves: Oscillations in air pressure and air density Before we can understand pressure waves in detail, we need to understand what
Sound waves are one example of Longitudinal Waves Sound waves are pressure waves: Oscillations in air pressure and air density Before we can understand pressure waves in detail, we need to understand what
Electricity, Magnetism and Waves. Physical Science Unit 5
 Electricity, Magnetism and Waves Physical Science Unit 5 4/14/16 Entry Task Besides tensile strength, what other needs of society might determine which plastic is used? HW Read pages 382-388, answer #
Electricity, Magnetism and Waves Physical Science Unit 5 4/14/16 Entry Task Besides tensile strength, what other needs of society might determine which plastic is used? HW Read pages 382-388, answer #
Physics Unit: Force & Motion
 Physics Unit: Force & Motion What is physical science? A. Physical science is a field of science that studies matter and energy. B. Physical science has 2 main branches: 1. PHYSICS: the study of how matter
Physics Unit: Force & Motion What is physical science? A. Physical science is a field of science that studies matter and energy. B. Physical science has 2 main branches: 1. PHYSICS: the study of how matter
Conceptual Physics Final Exam Review
 Useful Information Work and Energy W = F x W = work [J] F = force [N] x = displacement [m] U g = mgh U g = gravitational potential energy [J] m = mass [kg] h = height [m] g = 10 m/s 2 DC Circuits I =!!
Useful Information Work and Energy W = F x W = work [J] F = force [N] x = displacement [m] U g = mgh U g = gravitational potential energy [J] m = mass [kg] h = height [m] g = 10 m/s 2 DC Circuits I =!!
Sample Pages from. Leveled Texts for Science: Physical Science
 Sample Pages from Leveled Texts for Science: Physical Science The following sample pages are included in this download: Table of Contents Readability Chart Sample Passage For correlations to Common Core
Sample Pages from Leveled Texts for Science: Physical Science The following sample pages are included in this download: Table of Contents Readability Chart Sample Passage For correlations to Common Core
Physics 221: Optical and Thermal Physics Exam 1, Sec. 500, 14 Feb Please fill in your Student ID number (UIN): IMPORTANT
 Physics 221: Optical and Thermal Physics Exam 1, Sec. 500, 14 Feb. 2005 Instructor: Dr. George R. Welch, 415 Engineering-Physics, 845-7737 Print your name neatly: Last name: First name: Sign your name:
Physics 221: Optical and Thermal Physics Exam 1, Sec. 500, 14 Feb. 2005 Instructor: Dr. George R. Welch, 415 Engineering-Physics, 845-7737 Print your name neatly: Last name: First name: Sign your name:
