Origins of Probability Theory
|
|
|
- Oswin Gordon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 : INTRODUCTION Theory and Tools of Probability required to analyze and design systems subject to uncertain outcomes/unpredictability/randomness. Such systems more generally referred to as Experiments. Need for probabilistic approaches arises for several reasons Insufficient knowledge about processes contributing to the dynamics of systems that may well be deterministic. The cumulative effect of a large number of processes that individually may have subdominant effects on the system
2 2 Origins of Probability Theory Started in France in 1650 s in context of characterizing outcomes of gambling Classical principles formulated by Blaire Pascal and Pierre de Fermat Huygens in 1657 published first book on probability Bernoulli (Law of Large Numbers ) and De Moivre contributors in 18th century This period saw the origin of statistical theory Groundwork for Modern Approach to Probability: Fisher and Von Mises in 1920 s: Statistical theory of probability 1930 s Andrei Kolmogorov: Published axiomatic theory of probability: Basis of modern approach
3 3 Objectives Develop and understand general laws of probability, construct theoretical models and apply these models in various fields of engineering interest Consider primarily physical or statistical probability concepts where probabilities do not rely on judgements but on outcomes of the experiment Develop skills in handling large amounts of data/measurements generated by experiments with randomness through application of statistical reasoning and inference Keep an intuitive interpretation of probability to gain operational meaning in some applications.
4 4 Some Applications... Design of Communication Systems and Networks subject to: Random patterns of arrivals that utilize the resource Ex: Telephone Calls Initiated at a Local Exchange Switch, Packets arriving at a network router Random holding times of the resource Ex: Telephone call durations, Packet sizes and transmission times and Uncertainty in availability and quality of the resource Ex: Wireless channels that fade, effect of noise in transmission and changes
5 5 Experiment, Sample Space, Events and Fields H: Random Experiment Ω: Sample Space consisting of all outcomes or observations of H Set: Collection of Objects Set of all objects under discussion: Universal Set Events: Subsets of Ω : Compound or Simple Events Impossible (Null) Event: ; Certain Event: Ω Ω may consist of finite, countably finite or not countably finite number of elements Note: If Ω consists of N elements: Total of 2 N number of subsets can exist; All subsets of Ω need not be events
6 6 Set Algebra ζ Ω : ζ is an element of Ω or belongs to set Ω. (Elementary Event) Union of two sets E 1 and E 2 : E 1 E 2 or E 1 + E 2 Set of all elements in at least one of the sets E 1 or E 2. E 1 E 2 : (ζ : ζ E 1 or ζ E 2 ) Or ( ζ lies in both E 1 and E 2 ) E 1 is subset of E 2 : E 1 E 2. Then: E 1 E 2 = E 2. Intersection of E 1 and E 2 : E 1 E 2 or E 1 E 2 Set of all elements that are common to both E 1 and E 2 E 1 E 2 = (ζ : ζ E 1 and ζ E 2 ). Complement of E : E c. Set of elements not in E. Note: E E c = Ω.
7 7 Set Algebra Contd. Reduction of E 1 by E 2 : E 1 E 2 Set of elements in E 1 that are not in E 2 E 1 E 2 = E 1 E c 2 In general E 1 E 2 E 2 E 1. Exclusive-Or : E 1 E 2 : Set of elements in E 1 or E 2 but not both. E 1 E 2 = (E 1 E 2 ) (E 2 E 1 ) Disjoint sets E 1 and E 2 if E 1 E 2 =. No elements in common. Mutually Exclusive n-partition of E : Sequence of sets E i i = 1,.., n such that: E i E, N i=1 E i = E and E i E j =.
8 8 E F E F E E U F EF E complement F E E E F F E F F E E ex or F Venn Diagrams
9 9 DeMorgan s Laws Given sets E 1,...E n n [ E i] c = n i=1 n [ E i] c = n i=1 i=1 Ec i (1) i=1 Ec i
10 10 EVENTS Events of the experiment may be defined as subsets of Ω. Consider events A and B. Consider also the events A B, A B and A c. 1. A B : A or B 2. A B: A and B 3. A c : not A
11 11 FIELDS Consider C as a collection of subsets of the universal set Ω. This collection forms a field M if : if (A, B) M, then A B M if A M, then A c M. Any collection M of subsets of Ω that satisfy the above conditions is called a field. From the above properties it can be shown that A B M ; Ω M; M M is closed under finite unions and intersections. Iff (A 1, A 2,,,, A n ) M then n i=1 A i M.
12 12 σ FIELDS If Ω is an infinite set define a σ field as: M, Ω M if (A 1, A 2,...) M then i=1 A i M if A M, then A c M. A σ-field is closed under any countable set of unions, intersections and combinations. If E 1,..E n belong to M : i=1e i M and i=1e i M,
13 13 SUMMARY Given an experiment, associate a pair (Ω,M) Ω is the set of all possible outcomes or elementary events M is the σ-field of subsets of Ω M contains events whose occurrences are of interest Reference to A being an event is equivalent to A belongs to the σ-field in question. Note: If Ω is not countable, such as in the case of a real line, not every subset of Ω will be assigned a probability and called an event. The smaller collection of subsets that are events consistent with the axioms forms a σ-field and on the real line this is called the Borel field of events.
14 14 Probability Given [ H, Ω, F ] where Ω has countable number of elements Every subset of Ω can be assigned a probability consistent with the axioms of Kolmogorov Class of all subsets make up F : σ-field of events Each subset is an event Axiomatic Theory of Probability : (Ω,F, P) P is the probability measure. set function P[.] that assigns to every event A F, a number P[A] called probability
15 15 Probability Measure P P[A] 0 P[Ω] = 1 P[A B] = P[A] + P[B] if AB = The above establish the following results: P[ ] = 0 P[AB c ] = P[A] P[AB] where A F B F P[A] = 1 P[A c ] P[A B] = P[A] + P[B] P[AB]
16 16 Conditional Probabilities Consider two events A and B that are outcomes of an experiment Repeat experiment N times N B number of occurrences of B Consider only observations when B occurred Number of trials in which A also occurred be N (A B). N (A B) N B = N (A B)/N N B /N Interpreting these ratios as probabilities, P(A B) P(B) is the probability that A occurs given that B has occurred. If P(B) > 0, conditional probability that A occurs given that B has occurred is : (3) P(A B) = P(A B) P(B) = P(AB) P(B) (4)
17 17 The above probability is referred to as the probability of A given B or the probability of A conditioned (or conditional) on B. Note that P(AB) is also the joint probability of events A and B.
18 18 Unconditional (Total) Probability Define set of mutually exclusive events A 1, A 2,...A n : U n i=1a i = Ω Note: A i s are exhaustive Event B is defined over the probability space of the A i s. With P[A i ] 0 for all i: P(B) = P(B A 1 )P(A 1 ) + P(B A 2 )P(A 2 ) +...P(B A n )P(A n ) (5) P(B) is called the total or average probability of B.
19 19 Independence Define events A F and B F P(A) > 0 and P(B) > 0 Events A and B said to be independent iff P(AB) = P(A)P(B) Occurrence of event B does not change probability of another event A. Note: P(AB) = P(B A)P(A) in general. For independence P(B A) = P(B) and P(A B) = P(A).
20 20 Bayes Theorem A i i = 1,...n : set of disjoint and exhaustive events and P(A i ) 0 n i=1a i = Ω A i A j =. B any event with P(B) > 0 P(A j B) = P(B A j )P(A j ) n i=1 P(B A i )P(A i ) (6) Proof is shown by application of conditional probability to P(B A j ) in the numerator and total probability expression in the denominator.
21 21 Summary P[A j B]: Posteriori probability of A j given B P[B A j ]: Apriori probability of B given A j P[A j ]: Causal or apriori probability of A j Apriori probabilities: Estimated from past measurements or known from experience Aposteriori probabilities: Measured/Computed from observations
22 : EXAMPLES Fair coin flipped three times. Outcomes are heads (H) or tails (T). Find probability of obtaining two heads and one tail. Experiment consists of drawing two balls without replacement from a box containing six balls numbered 1 to 6. Desribe sample space Ω. How does Ω change if the ball is replaced before the second is drawn? A card is selected from a deck of 52 cards. Let A be event of selecting an ace and B be the event of selecting a red card. There are 4 aces and 26 red cards in the deck. Are events A and B independent?
23 23 Experiment is rolling two dice. Dice identified by colors red (R) and blue (B). Observations are pair of numbers shown on upper faces. Each outcome assumed equiprobable. State sample space of problem; Find probability R shows even and B shows odd numbers; Are events R even and B odd independent? Find probability that sum of numbers shown by R and B is 11 and R 5. Are these two events independent?
24 24 1. Consider a sample space Ω : {c, d, g, p}. The following probabilities are given: P[{c, d}] = 0.9, P[{g, p}] = 0.1 P[p] = 0.1, P[d] = 0.5. Determine all of the subsets (16) of Ω and their probabilities. 2. In Problem 1, the information given is reduced such that, P[{c, d}] = 0.9, P[{g, p}] = 0.1 and P[d] = 0.5. In this case, the subset {g, p} is to be taken as a single element, resulting in 8 subsets of Ω. Find the probabilites of the field in this case. 3. You have a choice of leasing two machines C i, i = 1, 2 each at 50 dollars a month or a single better machine N 1 at 100 dollars a month. Machines C 1, C 2 fail 40 percent of the time whereas machine N 1 fails 20 percent of the time. Assume each machine costs the same to repair. (a) If having at least one machine working is the priority which option would be best? (b) If cost of repairs is to be minimized which option would you choose?
LECTURE 1. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
 LECTURE 1 1 Introduction The first part of our adventure is a highly selective review of probability theory, focusing especially on things that are most useful in statistics. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
LECTURE 1 1 Introduction The first part of our adventure is a highly selective review of probability theory, focusing especially on things that are most useful in statistics. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
Axioms of Probability
 Sample Space (denoted by S) The set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment is called the Sample Space of the experiment, and is denoted by S. Example 1.10 If the experiment consists of tossing
Sample Space (denoted by S) The set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment is called the Sample Space of the experiment, and is denoted by S. Example 1.10 If the experiment consists of tossing
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability. Elements of Probability. Conditional probability. Sequential Calculation of Probability
 Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability Set Theory Elements of Probability Conditional probability Sequential Calculation of Probability Total Probability and Bayes Rule Independence Counting EE 178/278A: Basic
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Probability Set Theory Elements of Probability Conditional probability Sequential Calculation of Probability Total Probability and Bayes Rule Independence Counting EE 178/278A: Basic
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications Elementary Set Theory Random
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Probability Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications Elementary Set Theory Random
Introduction to Probability
 Introduction to Probability Gambling at its core 16th century Cardano: Books on Games of Chance First systematic treatment of probability 17th century Chevalier de Mere posed a problem to his friend Pascal.
Introduction to Probability Gambling at its core 16th century Cardano: Books on Games of Chance First systematic treatment of probability 17th century Chevalier de Mere posed a problem to his friend Pascal.
EE 178 Lecture Notes 0 Course Introduction. About EE178. About Probability. Course Goals. Course Topics. Lecture Notes EE 178
 EE 178 Lecture Notes 0 Course Introduction About EE178 About Probability Course Goals Course Topics Lecture Notes EE 178: Course Introduction Page 0 1 EE 178 EE 178 provides an introduction to probabilistic
EE 178 Lecture Notes 0 Course Introduction About EE178 About Probability Course Goals Course Topics Lecture Notes EE 178: Course Introduction Page 0 1 EE 178 EE 178 provides an introduction to probabilistic
Probability Theory Review
 Cogsci 118A: Natural Computation I Lecture 2 (01/07/10) Lecturer: Angela Yu Probability Theory Review Scribe: Joseph Schilz Lecture Summary 1. Set theory: terms and operators In this section, we provide
Cogsci 118A: Natural Computation I Lecture 2 (01/07/10) Lecturer: Angela Yu Probability Theory Review Scribe: Joseph Schilz Lecture Summary 1. Set theory: terms and operators In this section, we provide
Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes
 Chapter 6 Probability the study of randomness Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run, but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long
Chapter 6 Probability the study of randomness Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run, but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long
Fundamentals of Probability CE 311S
 Fundamentals of Probability CE 311S OUTLINE Review Elementary set theory Probability fundamentals: outcomes, sample spaces, events Outline ELEMENTARY SET THEORY Basic probability concepts can be cast in
Fundamentals of Probability CE 311S OUTLINE Review Elementary set theory Probability fundamentals: outcomes, sample spaces, events Outline ELEMENTARY SET THEORY Basic probability concepts can be cast in
Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna 1
 Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna 1 Introduction Probability theory was originated from gambling theory Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna 2 History of Probability Galileo
Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna 1 Introduction Probability theory was originated from gambling theory Probability Dr. Manjula Gunarathna 2 History of Probability Galileo
Why study probability? Set theory. ECE 6010 Lecture 1 Introduction; Review of Random Variables
 ECE 6010 Lecture 1 Introduction; Review of Random Variables Readings from G&S: Chapter 1. Section 2.1, Section 2.3, Section 2.4, Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.5, Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section
ECE 6010 Lecture 1 Introduction; Review of Random Variables Readings from G&S: Chapter 1. Section 2.1, Section 2.3, Section 2.4, Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.5, Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section
Deep Learning for Computer Vision
 Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Probabilistic models
 Probabilistic models Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became
Probabilistic models Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became
Random Signals and Systems. Chapter 1. Jitendra K Tugnait. Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering. James B Davis Professor.
 Random Signals and Systems Chapter 1 Jitendra K Tugnait James B Davis Professor Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Auburn University 2 3 Descriptions of Probability Relative frequency approach»
Random Signals and Systems Chapter 1 Jitendra K Tugnait James B Davis Professor Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Auburn University 2 3 Descriptions of Probability Relative frequency approach»
2011 Pearson Education, Inc
 Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 3 Probability Contents 1. Events, Sample Spaces, and Probability 2. Unions and Intersections 3. Complementary Events 4. The Additive Rule and Mutually Exclusive
Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 3 Probability Contents 1. Events, Sample Spaces, and Probability 2. Unions and Intersections 3. Complementary Events 4. The Additive Rule and Mutually Exclusive
Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Fall 2015
 L645 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Fall 2015 1 / 34 To start out the course, we need to know something about statistics and This is only an introduction; for a fuller understanding, you would
L645 Dept. of Linguistics, Indiana University Fall 2015 1 / 34 To start out the course, we need to know something about statistics and This is only an introduction; for a fuller understanding, you would
Statistical Inference
 Statistical Inference Lecture 1: Probability Theory MING GAO DASE @ ECNU (for course related communications) mgao@dase.ecnu.edu.cn Sep. 11, 2018 Outline Introduction Set Theory Basics of Probability Theory
Statistical Inference Lecture 1: Probability Theory MING GAO DASE @ ECNU (for course related communications) mgao@dase.ecnu.edu.cn Sep. 11, 2018 Outline Introduction Set Theory Basics of Probability Theory
Chapter 1 Axioms of Probability. Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao University
 Chapter 1 Axioms of Probability Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao University What is probability? A branch of mathematics that deals with calculating the likelihood of a given event
Chapter 1 Axioms of Probability Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao University What is probability? A branch of mathematics that deals with calculating the likelihood of a given event
Properties of Probability
 Econ 325 Notes on Probability 1 By Hiro Kasahara Properties of Probability In statistics, we consider random experiments, experiments for which the outcome is random, i.e., cannot be predicted with certainty.
Econ 325 Notes on Probability 1 By Hiro Kasahara Properties of Probability In statistics, we consider random experiments, experiments for which the outcome is random, i.e., cannot be predicted with certainty.
MATH MW Elementary Probability Course Notes Part I: Models and Counting
 MATH 2030 3.00MW Elementary Probability Course Notes Part I: Models and Counting Tom Salisbury salt@yorku.ca York University Winter 2010 Introduction [Jan 5] Probability: the mathematics used for Statistics
MATH 2030 3.00MW Elementary Probability Course Notes Part I: Models and Counting Tom Salisbury salt@yorku.ca York University Winter 2010 Introduction [Jan 5] Probability: the mathematics used for Statistics
Sample Space: Specify all possible outcomes from an experiment. Event: Specify a particular outcome or combination of outcomes.
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Probability 2.1 Probability Model Probability concerns about the chance of observing certain outcome resulting from an experiment. However, since chance is an abstraction of something
Chapter 2 Introduction to Probability 2.1 Probability Model Probability concerns about the chance of observing certain outcome resulting from an experiment. However, since chance is an abstraction of something
Chapter 2 Classical Probability Theories
 Chapter 2 Classical Probability Theories In principle, those who are not interested in mathematical foundations of probability theory might jump directly to Part II. One should just know that, besides
Chapter 2 Classical Probability Theories In principle, those who are not interested in mathematical foundations of probability theory might jump directly to Part II. One should just know that, besides
Venn Diagrams; Probability Laws. Notes. Set Operations and Relations. Venn Diagram 2.1. Venn Diagrams; Probability Laws. Notes
 Lecture 2 s; Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 2.4 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models January 8, 2014 s; Whitney Huang Purdue University 2.1 Agenda s; 1 2 2.2 Intersection: the intersection
Lecture 2 s; Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 2.4 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models January 8, 2014 s; Whitney Huang Purdue University 2.1 Agenda s; 1 2 2.2 Intersection: the intersection
Lecture Notes 1 Probability and Random Variables. Conditional Probability and Independence. Functions of a Random Variable
 Lecture Notes 1 Probability and Random Variables Probability Spaces Conditional Probability and Independence Random Variables Functions of a Random Variable Generation of a Random Variable Jointly Distributed
Lecture Notes 1 Probability and Random Variables Probability Spaces Conditional Probability and Independence Random Variables Functions of a Random Variable Generation of a Random Variable Jointly Distributed
Chapter 1 Axioms of Probability. Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao University
 Chapter 1 Axioms of Probability Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao University Introduction Luca Paccioli(1445-1514), Studies of chances of events Niccolo Tartaglia(1499-1557) Girolamo
Chapter 1 Axioms of Probability Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao University Introduction Luca Paccioli(1445-1514), Studies of chances of events Niccolo Tartaglia(1499-1557) Girolamo
Notes Week 2 Chapter 3 Probability WEEK 2 page 1
 Notes Week 2 Chapter 3 Probability WEEK 2 page 1 The sample space of an experiment, sometimes denoted S or in probability theory, is the set that consists of all possible elementary outcomes of that experiment
Notes Week 2 Chapter 3 Probability WEEK 2 page 1 The sample space of an experiment, sometimes denoted S or in probability theory, is the set that consists of all possible elementary outcomes of that experiment
Module 1. Probability
 Module 1 Probability 1. Introduction In our daily life we come across many processes whose nature cannot be predicted in advance. Such processes are referred to as random processes. The only way to derive
Module 1 Probability 1. Introduction In our daily life we come across many processes whose nature cannot be predicted in advance. Such processes are referred to as random processes. The only way to derive
PROBABILITY THEORY 1. Basics
 PROILITY THEORY. asics Probability theory deals with the study of random phenomena, which under repeated experiments yield different outcomes that have certain underlying patterns about them. The notion
PROILITY THEORY. asics Probability theory deals with the study of random phenomena, which under repeated experiments yield different outcomes that have certain underlying patterns about them. The notion
Lecture Notes 1 Probability and Random Variables. Conditional Probability and Independence. Functions of a Random Variable
 Lecture Notes 1 Probability and Random Variables Probability Spaces Conditional Probability and Independence Random Variables Functions of a Random Variable Generation of a Random Variable Jointly Distributed
Lecture Notes 1 Probability and Random Variables Probability Spaces Conditional Probability and Independence Random Variables Functions of a Random Variable Generation of a Random Variable Jointly Distributed
Presentation on Theo e ry r y o f P r P o r bab a il i i l t i y
 Presentation on Theory of Probability Meaning of Probability: Chance of occurrence of any event In practical life we come across situation where the result are uncertain Theory of probability was originated
Presentation on Theory of Probability Meaning of Probability: Chance of occurrence of any event In practical life we come across situation where the result are uncertain Theory of probability was originated
Probability COMP 245 STATISTICS. Dr N A Heard. 1 Sample Spaces and Events Sample Spaces Events Combinations of Events...
 Probability COMP 245 STATISTICS Dr N A Heard Contents Sample Spaces and Events. Sample Spaces........................................2 Events........................................... 2.3 Combinations
Probability COMP 245 STATISTICS Dr N A Heard Contents Sample Spaces and Events. Sample Spaces........................................2 Events........................................... 2.3 Combinations
2. AXIOMATIC PROBABILITY
 IA Probability Lent Term 2. AXIOMATIC PROBABILITY 2. The axioms The formulation for classical probability in which all outcomes or points in the sample space are equally likely is too restrictive to develop
IA Probability Lent Term 2. AXIOMATIC PROBABILITY 2. The axioms The formulation for classical probability in which all outcomes or points in the sample space are equally likely is too restrictive to develop
I - Probability. What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring. 1classical probability. 2empirical probability. 3subjective probability
 What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring eg 1classical probability 2empirical probability 3subjective probability Section 2 - Probability (1) Probability - Terminology random (probability)
What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring eg 1classical probability 2empirical probability 3subjective probability Section 2 - Probability (1) Probability - Terminology random (probability)
CIVL 7012/8012. Basic Laws and Axioms of Probability
 CIVL 7012/8012 Basic Laws and Axioms of Probability Why are we studying probability and statistics? How can we quantify risks of decisions based on samples from a population? How should samples be selected
CIVL 7012/8012 Basic Laws and Axioms of Probability Why are we studying probability and statistics? How can we quantify risks of decisions based on samples from a population? How should samples be selected
STT When trying to evaluate the likelihood of random events we are using following wording.
 Introduction to Chapter 2. Probability. When trying to evaluate the likelihood of random events we are using following wording. Provide your own corresponding examples. Subjective probability. An individual
Introduction to Chapter 2. Probability. When trying to evaluate the likelihood of random events we are using following wording. Provide your own corresponding examples. Subjective probability. An individual
the time it takes until a radioactive substance undergoes a decay
 1 Probabilities 1.1 Experiments with randomness Wewillusethetermexperimentinaverygeneralwaytorefertosomeprocess that produces a random outcome. Examples: (Ask class for some first) Here are some discrete
1 Probabilities 1.1 Experiments with randomness Wewillusethetermexperimentinaverygeneralwaytorefertosomeprocess that produces a random outcome. Examples: (Ask class for some first) Here are some discrete
Lecture 1: Probability Fundamentals
 Lecture 1: Probability Fundamentals IB Paper 7: Probability and Statistics Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge January 22nd, 2008 Rasmussen (CUED) Lecture 1: Probability
Lecture 1: Probability Fundamentals IB Paper 7: Probability and Statistics Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge January 22nd, 2008 Rasmussen (CUED) Lecture 1: Probability
Mathematics for Informatics 4a
 Mathematics for Informatics 4a José Figueroa-O Farrill Lecture 1 18 January 2012 José Figueroa-O Farrill mi4a (Probability) Lecture 1 1 / 23 Introduction Topic: Probability and random processes Lectures:
Mathematics for Informatics 4a José Figueroa-O Farrill Lecture 1 18 January 2012 José Figueroa-O Farrill mi4a (Probability) Lecture 1 1 / 23 Introduction Topic: Probability and random processes Lectures:
Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness
 Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness 6.1 The Idea of Probability 6.2 Probability Models 6.3 General Probability Rules 1 Simple Question: If tossing a coin, what is the probability of the coin
Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness 6.1 The Idea of Probability 6.2 Probability Models 6.3 General Probability Rules 1 Simple Question: If tossing a coin, what is the probability of the coin
Chap 1: Experiments, Models, and Probabilities. Random Processes. Chap 1 : Experiments, Models, and Probabilities
 EE8103 Random Processes Chap 1 : Experiments, Models, and Probabilities Introduction Real world word exhibits randomness Today s temperature; Flip a coin, head or tail? WalkAt to a bus station, how long
EE8103 Random Processes Chap 1 : Experiments, Models, and Probabilities Introduction Real world word exhibits randomness Today s temperature; Flip a coin, head or tail? WalkAt to a bus station, how long
What is Probability? Probability. Sample Spaces and Events. Simple Event
 What is Probability? Probability Peter Lo Probability is the numerical measure of likelihood that the event will occur. Simple Event Joint Event Compound Event Lies between 0 & 1 Sum of events is 1 1.5
What is Probability? Probability Peter Lo Probability is the numerical measure of likelihood that the event will occur. Simple Event Joint Event Compound Event Lies between 0 & 1 Sum of events is 1 1.5
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.436J/15.085J Fall 2008 Lecture 3 9/10/2008 CONDITIONING AND INDEPENDENCE
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.436J/15.085J Fall 2008 Lecture 3 9/10/2008 CONDITIONING AND INDEPENDENCE Most of the material in this lecture is covered in [Bertsekas & Tsitsiklis] Sections 1.3-1.5
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.436J/15.085J Fall 2008 Lecture 3 9/10/2008 CONDITIONING AND INDEPENDENCE Most of the material in this lecture is covered in [Bertsekas & Tsitsiklis] Sections 1.3-1.5
Probability and distributions. Francesco Corona
 Probability Probability and distributions Francesco Corona Department of Computer Science Federal University of Ceará, Fortaleza Probability Many kinds of studies can be characterised as (repeated) experiments
Probability Probability and distributions Francesco Corona Department of Computer Science Federal University of Ceará, Fortaleza Probability Many kinds of studies can be characterised as (repeated) experiments
Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics
 Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics Lecture 2 Probability Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 3-1 3.1 Definition Random Experiment a process leading to an uncertain
Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics Lecture 2 Probability Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 3-1 3.1 Definition Random Experiment a process leading to an uncertain
Probability theory basics
 Probability theory basics Michael Franke Basics of probability theory: axiomatic definition, interpretation, joint distributions, marginalization, conditional probability & Bayes rule. Random variables:
Probability theory basics Michael Franke Basics of probability theory: axiomatic definition, interpretation, joint distributions, marginalization, conditional probability & Bayes rule. Random variables:
Lecture 8: Probability
 Lecture 8: Probability The idea of probability is well-known The flipping of a balanced coin can produce one of two outcomes: T (tail) and H (head) and the symmetry between the two outcomes means, of course,
Lecture 8: Probability The idea of probability is well-known The flipping of a balanced coin can produce one of two outcomes: T (tail) and H (head) and the symmetry between the two outcomes means, of course,
Probability Theory for Machine Learning. Chris Cremer September 2015
 Probability Theory for Machine Learning Chris Cremer September 2015 Outline Motivation Probability Definitions and Rules Probability Distributions MLE for Gaussian Parameter Estimation MLE and Least Squares
Probability Theory for Machine Learning Chris Cremer September 2015 Outline Motivation Probability Definitions and Rules Probability Distributions MLE for Gaussian Parameter Estimation MLE and Least Squares
The enumeration of all possible outcomes of an experiment is called the sample space, denoted S. E.g.: S={head, tail}
 Random Experiment In random experiments, the result is unpredictable, unknown prior to its conduct, and can be one of several choices. Examples: The Experiment of tossing a coin (head, tail) The Experiment
Random Experiment In random experiments, the result is unpredictable, unknown prior to its conduct, and can be one of several choices. Examples: The Experiment of tossing a coin (head, tail) The Experiment
Preliminary Statistics Lecture 2: Probability Theory (Outline) prelimsoas.webs.com
 1 School of Oriental and African Studies September 2015 Department of Economics Preliminary Statistics Lecture 2: Probability Theory (Outline) prelimsoas.webs.com Gujarati D. Basic Econometrics, Appendix
1 School of Oriental and African Studies September 2015 Department of Economics Preliminary Statistics Lecture 2: Probability Theory (Outline) prelimsoas.webs.com Gujarati D. Basic Econometrics, Appendix
Review Basic Probability Concept
 Economic Risk and Decision Analysis for Oil and Gas Industry CE81.9008 School of Engineering and Technology Asian Institute of Technology January Semester Presented by Dr. Thitisak Boonpramote Department
Economic Risk and Decision Analysis for Oil and Gas Industry CE81.9008 School of Engineering and Technology Asian Institute of Technology January Semester Presented by Dr. Thitisak Boonpramote Department
Chapter 2.5 Random Variables and Probability The Modern View (cont.)
 Chapter 2.5 Random Variables and Probability The Modern View (cont.) I. Statistical Independence A crucially important idea in probability and statistics is the concept of statistical independence. Suppose
Chapter 2.5 Random Variables and Probability The Modern View (cont.) I. Statistical Independence A crucially important idea in probability and statistics is the concept of statistical independence. Suppose
Chapter ML:IV. IV. Statistical Learning. Probability Basics Bayes Classification Maximum a-posteriori Hypotheses
 Chapter ML:IV IV. Statistical Learning Probability Basics Bayes Classification Maximum a-posteriori Hypotheses ML:IV-1 Statistical Learning STEIN 2005-2017 Area Overview Mathematics Statistics...... Stochastics
Chapter ML:IV IV. Statistical Learning Probability Basics Bayes Classification Maximum a-posteriori Hypotheses ML:IV-1 Statistical Learning STEIN 2005-2017 Area Overview Mathematics Statistics...... Stochastics
STAT 430/510 Probability
 STAT 430/510 Probability Hui Nie Lecture 3 May 28th, 2009 Review We have discussed counting techniques in Chapter 1. Introduce the concept of the probability of an event. Compute probabilities in certain
STAT 430/510 Probability Hui Nie Lecture 3 May 28th, 2009 Review We have discussed counting techniques in Chapter 1. Introduce the concept of the probability of an event. Compute probabilities in certain
ECE353: Probability and Random Processes. Lecture 2 - Set Theory
 ECE353: Probability and Random Processes Lecture 2 - Set Theory Xiao Fu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Oregon State University E-mail: xiao.fu@oregonstate.edu January 10, 2018 Set
ECE353: Probability and Random Processes Lecture 2 - Set Theory Xiao Fu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Oregon State University E-mail: xiao.fu@oregonstate.edu January 10, 2018 Set
Chapter 2 Class Notes
 Chapter 2 Class Notes Probability can be thought of in many ways, for example as a relative frequency of a long series of trials (e.g. flips of a coin or die) Another approach is to let an expert (such
Chapter 2 Class Notes Probability can be thought of in many ways, for example as a relative frequency of a long series of trials (e.g. flips of a coin or die) Another approach is to let an expert (such
UNIT Explain about the partition of a sampling space theorem?
 UNIT -1 1. Explain about the partition of a sampling space theorem? PARTITIONS OF A SAMPLE SPACE The events B1, B2. B K represent a partition of the sample space 'S" if (a) So, when the experiment E is
UNIT -1 1. Explain about the partition of a sampling space theorem? PARTITIONS OF A SAMPLE SPACE The events B1, B2. B K represent a partition of the sample space 'S" if (a) So, when the experiment E is
4. Probability of an event A for equally likely outcomes:
 University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Probability Probability: A measure of the chance that something will occur. 1. Random experiment:
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Probability Probability: A measure of the chance that something will occur. 1. Random experiment:
Recitation 2: Probability
 Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15. Lecture 2: Random Experiments. Prof. Vince Calhoun
 ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15 Lecture 2: Random Experiments Prof. Vince Calhoun Reading This class: Section 2.1-2.2 Next class: Section 2.3-2.4 Homework: Assignment 1: From the
ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15 Lecture 2: Random Experiments Prof. Vince Calhoun Reading This class: Section 2.1-2.2 Next class: Section 2.3-2.4 Homework: Assignment 1: From the
Topic 3: Introduction to Probability
 Topic 3: Introduction to Probability 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Simple Definitions 3. Types of Probability 4. Theorems of Probability 5. Probabilities under conditions of statistically independent events
Topic 3: Introduction to Probability 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Simple Definitions 3. Types of Probability 4. Theorems of Probability 5. Probabilities under conditions of statistically independent events
Probabilistic models
 Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became the definitive formulation
Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became the definitive formulation
Lecture notes for probability. Math 124
 Lecture notes for probability Math 124 What is probability? Probabilities are ratios, expressed as fractions, decimals, or percents, determined by considering results or outcomes of experiments whose result
Lecture notes for probability Math 124 What is probability? Probabilities are ratios, expressed as fractions, decimals, or percents, determined by considering results or outcomes of experiments whose result
Compound Events. The event E = E c (the complement of E) is the event consisting of those outcomes which are not in E.
 Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events for which it
Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events for which it
Single Maths B: Introduction to Probability
 Single Maths B: Introduction to Probability Overview Lecturer Email Office Homework Webpage Dr Jonathan Cumming j.a.cumming@durham.ac.uk CM233 None! http://maths.dur.ac.uk/stats/people/jac/singleb/ 1 Introduction
Single Maths B: Introduction to Probability Overview Lecturer Email Office Homework Webpage Dr Jonathan Cumming j.a.cumming@durham.ac.uk CM233 None! http://maths.dur.ac.uk/stats/people/jac/singleb/ 1 Introduction
STAT:5100 (22S:193) Statistical Inference I
 STAT:5100 (22S:193) Statistical Inference I Week 3 Luke Tierney University of Iowa Fall 2015 Luke Tierney (U Iowa) STAT:5100 (22S:193) Statistical Inference I Fall 2015 1 Recap Matching problem Generalized
STAT:5100 (22S:193) Statistical Inference I Week 3 Luke Tierney University of Iowa Fall 2015 Luke Tierney (U Iowa) STAT:5100 (22S:193) Statistical Inference I Fall 2015 1 Recap Matching problem Generalized
HW MATH425/525 Lecture Notes 1
 HW MATH425/525 Lecture Notes 1 Definition 4.1 If an experiment can be repeated under the same condition, its outcome cannot be predicted with certainty, and the collection of its every possible outcome
HW MATH425/525 Lecture Notes 1 Definition 4.1 If an experiment can be repeated under the same condition, its outcome cannot be predicted with certainty, and the collection of its every possible outcome
Probability & Random Variables
 & Random Variables Probability Probability theory is the branch of math that deals with random events, processes, and variables What does randomness mean to you? How would you define probability in your
& Random Variables Probability Probability theory is the branch of math that deals with random events, processes, and variables What does randomness mean to you? How would you define probability in your
Review of Basic Probability Theory
 Review of Basic Probability Theory James H. Steiger Department of Psychology and Human Development Vanderbilt University James H. Steiger (Vanderbilt University) 1 / 35 Review of Basic Probability Theory
Review of Basic Probability Theory James H. Steiger Department of Psychology and Human Development Vanderbilt University James H. Steiger (Vanderbilt University) 1 / 35 Review of Basic Probability Theory
CS626 Data Analysis and Simulation
 CS626 Data Analysis and Simulation Instructor: Peter Kemper R 104A, phone 221-3462, email:kemper@cs.wm.edu Today: Probability Primer Quick Reference: Sheldon Ross: Introduction to Probability Models 9th
CS626 Data Analysis and Simulation Instructor: Peter Kemper R 104A, phone 221-3462, email:kemper@cs.wm.edu Today: Probability Primer Quick Reference: Sheldon Ross: Introduction to Probability Models 9th
ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page α 2 θ 1 u 3. wear coat. θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ 1 = cold u 3 = brrr!
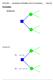 ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 2-01 Probability Decision trees u 1 u 2 α 2 θ 1 u 3 θ 2 u 4 Example 2.01 θ 1 = cold u 1 = snug! α 1 wear coat θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ
ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 2-01 Probability Decision trees u 1 u 2 α 2 θ 1 u 3 θ 2 u 4 Example 2.01 θ 1 = cold u 1 = snug! α 1 wear coat θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ
Statistical Theory 1
 Statistical Theory 1 Set Theory and Probability Paolo Bautista September 12, 2017 Set Theory We start by defining terms in Set Theory which will be used in the following sections. Definition 1 A set is
Statistical Theory 1 Set Theory and Probability Paolo Bautista September 12, 2017 Set Theory We start by defining terms in Set Theory which will be used in the following sections. Definition 1 A set is
Relative Risks (RR) and Odds Ratios (OR) 20
 BSTT523: Pagano & Gavreau, Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6: Probability slide: Definitions (6.1 in P&G) 2 Experiments; trials; probabilities Event operations 4 Intersection; Union; Complement Venn diagrams Conditional
BSTT523: Pagano & Gavreau, Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6: Probability slide: Definitions (6.1 in P&G) 2 Experiments; trials; probabilities Event operations 4 Intersection; Union; Complement Venn diagrams Conditional
Recap. The study of randomness and uncertainty Chances, odds, likelihood, expected, probably, on average,... PROBABILITY INFERENTIAL STATISTICS
 Recap. Probability (section 1.1) The study of randomness and uncertainty Chances, odds, likelihood, expected, probably, on average,... PROBABILITY Population Sample INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Today. Formulation
Recap. Probability (section 1.1) The study of randomness and uncertainty Chances, odds, likelihood, expected, probably, on average,... PROBABILITY Population Sample INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Today. Formulation
ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Experiments, Models, and Probabilities
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Experiments, Models, and Probabilities Dr. Jing Yang jingyang@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 1 Experiments, Models, and Probabilities Dr. Jing Yang jingyang@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Applications
Chapter 3 : Conditional Probability and Independence
 STAT/MATH 394 A - PROBABILITY I UW Autumn Quarter 2016 Néhémy Lim Chapter 3 : Conditional Probability and Independence 1 Conditional Probabilities How should we modify the probability of an event when
STAT/MATH 394 A - PROBABILITY I UW Autumn Quarter 2016 Néhémy Lim Chapter 3 : Conditional Probability and Independence 1 Conditional Probabilities How should we modify the probability of an event when
God doesn t play dice. - Albert Einstein
 ECE 450 Lecture 1 God doesn t play dice. - Albert Einstein As far as the laws of mathematics refer to reality, they are not certain; as far as they are certain, they do not refer to reality. Lecture Overview
ECE 450 Lecture 1 God doesn t play dice. - Albert Einstein As far as the laws of mathematics refer to reality, they are not certain; as far as they are certain, they do not refer to reality. Lecture Overview
PROBABILITY CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES UNIT OVERVIEW
 CHAPTER 16 PROBABILITY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Concept of probability is used in accounting and finance to understand the likelihood of occurrence or non-occurrence of a variable. It helps in developing financial
CHAPTER 16 PROBABILITY LEARNING OBJECTIVES Concept of probability is used in accounting and finance to understand the likelihood of occurrence or non-occurrence of a variable. It helps in developing financial
(6, 1), (5, 2), (4, 3), (3, 4), (2, 5), (1, 6)
 Section 7.3: Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events
Section 7.3: Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events
Chapter 2. Conditional Probability and Independence. 2.1 Conditional Probability
 Chapter 2 Conditional Probability and Independence 2.1 Conditional Probability Example: Two dice are tossed. What is the probability that the sum is 8? This is an easy exercise: we have a sample space
Chapter 2 Conditional Probability and Independence 2.1 Conditional Probability Example: Two dice are tossed. What is the probability that the sum is 8? This is an easy exercise: we have a sample space
Conditional Probability
 Conditional Probability Idea have performed a chance experiment but don t know the outcome (ω), but have some partial information (event A) about ω. Question: given this partial information what s the
Conditional Probability Idea have performed a chance experiment but don t know the outcome (ω), but have some partial information (event A) about ω. Question: given this partial information what s the
Math 3338: Probability (Fall 2006)
 Math 3338: Probability (Fall 2006) Jiwen He Section Number: 10853 http://math.uh.edu/ jiwenhe/math3338fall06.html Probability p.1/8 Chapter Two: Probability (I) Probability p.2/8 2.1 Sample Spaces and
Math 3338: Probability (Fall 2006) Jiwen He Section Number: 10853 http://math.uh.edu/ jiwenhe/math3338fall06.html Probability p.1/8 Chapter Two: Probability (I) Probability p.2/8 2.1 Sample Spaces and
CS4705. Probability Review and Naïve Bayes. Slides from Dragomir Radev
 CS4705 Probability Review and Naïve Bayes Slides from Dragomir Radev Classification using a Generative Approach Previously on NLP discriminative models P C D here is a line with all the social media posts
CS4705 Probability Review and Naïve Bayes Slides from Dragomir Radev Classification using a Generative Approach Previously on NLP discriminative models P C D here is a line with all the social media posts
4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio
 4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Wrong is right. Thelonious Monk 4.1 Three Definitions of
4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Wrong is right. Thelonious Monk 4.1 Three Definitions of
Probability Theory. Fourier Series and Fourier Transform are widely used techniques to model deterministic signals.
 Probability Theory Introduction Fourier Series Fourier Transform are widely used techniques to model deterministic signals. In a typical communication system, the output of an information source (e.g.
Probability Theory Introduction Fourier Series Fourier Transform are widely used techniques to model deterministic signals. In a typical communication system, the output of an information source (e.g.
Axiomatic Foundations of Probability. Definition: Probability Function
 Chapter 1 sections We will SKIP a number of sections Set theory SKIP Real number uncountability Definition of probability Finite sample spaces Counting methods Combinatorial methods SKIP tennis tournament
Chapter 1 sections We will SKIP a number of sections Set theory SKIP Real number uncountability Definition of probability Finite sample spaces Counting methods Combinatorial methods SKIP tennis tournament
 CHAPTER - 16 PROBABILITY Random Experiment : If an experiment has more than one possible out come and it is not possible to predict the outcome in advance then experiment is called random experiment. Sample
CHAPTER - 16 PROBABILITY Random Experiment : If an experiment has more than one possible out come and it is not possible to predict the outcome in advance then experiment is called random experiment. Sample
Probability Review I
 Probability Review I Harvard Math Camp - Econometrics Ashesh Rambachan Summer 2018 Outline Random Experiments The sample space and events σ-algebra and measures Basic probability rules Conditional Probability
Probability Review I Harvard Math Camp - Econometrics Ashesh Rambachan Summer 2018 Outline Random Experiments The sample space and events σ-algebra and measures Basic probability rules Conditional Probability
Lecture 10: Probability distributions TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 19, 2019
 Lecture 10: Probability distributions DANIEL WELLER TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 19, 2019 Agenda What is probability? (again) Describing probabilities (distributions) Understanding probabilities (expectation) Partial
Lecture 10: Probability distributions DANIEL WELLER TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 19, 2019 Agenda What is probability? (again) Describing probabilities (distributions) Understanding probabilities (expectation) Partial
Lecture 1 : The Mathematical Theory of Probability
 Lecture 1 : The Mathematical Theory of Probability 0/ 30 1. Introduction Today we will do 2.1 and 2.2. We will skip Chapter 1. We all have an intuitive notion of probability. Let s see. What is the probability
Lecture 1 : The Mathematical Theory of Probability 0/ 30 1. Introduction Today we will do 2.1 and 2.2. We will skip Chapter 1. We all have an intuitive notion of probability. Let s see. What is the probability
Discrete Random Variables
 CPSC 53 Systems Modeling and Simulation Discrete Random Variables Dr. Anirban Mahanti Department of Computer Science University of Calgary mahanti@cpsc.ucalgary.ca Random Variables A random variable is
CPSC 53 Systems Modeling and Simulation Discrete Random Variables Dr. Anirban Mahanti Department of Computer Science University of Calgary mahanti@cpsc.ucalgary.ca Random Variables A random variable is
Chapter Learning Objectives. Random Experiments Dfiii Definition: Dfiii Definition:
 Chapter 2: Probability 2-1 Sample Spaces & Events 2-1.1 Random Experiments 2-1.2 Sample Spaces 2-1.3 Events 2-1 1.4 Counting Techniques 2-2 Interpretations & Axioms of Probability 2-3 Addition Rules 2-4
Chapter 2: Probability 2-1 Sample Spaces & Events 2-1.1 Random Experiments 2-1.2 Sample Spaces 2-1.3 Events 2-1 1.4 Counting Techniques 2-2 Interpretations & Axioms of Probability 2-3 Addition Rules 2-4
Probability the chance that an uncertain event will occur (always between 0 and 1)
 Quantitative Methods 2013 1 Probability as a Numerical Measure of the Likelihood of Occurrence Probability the chance that an uncertain event will occur (always between 0 and 1) Increasing Likelihood of
Quantitative Methods 2013 1 Probability as a Numerical Measure of the Likelihood of Occurrence Probability the chance that an uncertain event will occur (always between 0 and 1) Increasing Likelihood of
Probability. 25 th September lecture based on Hogg Tanis Zimmerman: Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.)
 Probability 25 th September 2017 lecture based on Hogg Tanis Zimmerman: Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.) Properties of Probability Methods of Enumeration Conditional Probability Independent
Probability 25 th September 2017 lecture based on Hogg Tanis Zimmerman: Probability and Statistical Inference (9th ed.) Properties of Probability Methods of Enumeration Conditional Probability Independent
Statistics 1 - Lecture Notes Chapter 1
 Statistics 1 - Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Caio Ibsen Graduate School of Economics - Getulio Vargas Foundation April 28, 2009 We want to establish a formal mathematic theory to work with results of experiments
Statistics 1 - Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Caio Ibsen Graduate School of Economics - Getulio Vargas Foundation April 28, 2009 We want to establish a formal mathematic theory to work with results of experiments
Basic Concepts of Probability
 Probability Probability theory is the branch of math that deals with random events Probability is used to describe how likely a particular outcome is in a random event the probability of obtaining heads
Probability Probability theory is the branch of math that deals with random events Probability is used to describe how likely a particular outcome is in a random event the probability of obtaining heads
Week 2. Section Texas A& M University. Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station 22 January-24 January 2019
 Week 2 Section 1.2-1.4 Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station 22 January-24 January 2019 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week2 1
Week 2 Section 1.2-1.4 Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station 22 January-24 January 2019 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week2 1
Topic 5 Basics of Probability
 Topic 5 Basics of Probability Equally Likely Outcomes and the Axioms of Probability 1 / 13 Outline Equally Likely Outcomes Axioms of Probability Consequences of the Axioms 2 / 13 Introduction A probability
Topic 5 Basics of Probability Equally Likely Outcomes and the Axioms of Probability 1 / 13 Outline Equally Likely Outcomes Axioms of Probability Consequences of the Axioms 2 / 13 Introduction A probability
Foundations of Probability Theory
 1 Foundations of Probability Theory For centuries, mankind lived with the idea that uncertainty was the domain of the gods and fell beyond the reach of human calculation. Common gambling led to the first
1 Foundations of Probability Theory For centuries, mankind lived with the idea that uncertainty was the domain of the gods and fell beyond the reach of human calculation. Common gambling led to the first
Randomized Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker
 Randomized Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker Randomized Algorithms A randomized algorithm is an algorithm that makes random choices during its execution. A randomized algorithm uses values generated by a
Randomized Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker Randomized Algorithms A randomized algorithm is an algorithm that makes random choices during its execution. A randomized algorithm uses values generated by a
