Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie. Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks
|
|
|
- Toby Preston
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie (Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks) is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial 3.0 United States License. All content provided in this work are originally developed by the Georgia Department of Education with all rights reserved as of June All work must be reproduced in its entirety with the exception of Warm-up sections which are attributed to David Rennie. Additional copyright attributes cited where appropriate.
2 Jaden s Phone Plan Mathematical Goals Create one-variable linear equations and inequalities from contextual situations. Solve and interpret the solution to multi-step linear equations and inequalities in context. Common Core State Standards MCC9 12.A.REI.1: Explain each step in solving a simple equation as following from the equality of numbers asserted at the previous step, starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Construct a viable argument to justify a solution method. MCC9 12.A.REI.3: Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters. Standards for Mathematical Practice (1) Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (2) Reason abstractly and quantitatively. (3) Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. (4) Model with mathematics. Introduction In this task, students will solve a series of linear equations and inequality word problems to help Jaden choose a cell phone plan. In order to help Jaden, students must explain in detail each step of the problem and justify the answer. Materials Paper Pencil GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 2 of 39
3 Jaden s Phone Plan Warm-up A phone company charges 25 cents for each picture message received by an individual caller while text messages cost only 2 cents per message received. For each of the following situations, find the total cost each caller must pay given the number of messages received. For the last problem, find the number of text messages received. 1. Sarah got 2 picture messages and 100 text messages. 2. Kevin received 25 picture messages and 17 text messages. 3. Brianna paid $7.50 in message charges. She knows she received 12 picture messages. How many text messages were received by Brianna? The Task (Part 1) Jaden has a prepaid phone plan (Plan A) that charges 15 cents for each text sent and 10 cents per minute for calls. 1. If Jaden uses only text, write an equation for the cost C of sending t texts. (a) How much will it cost Jaden to send 15 texts? Justify your answer. (b) If Jaden has $6, how many texts can he send? Justify your answer. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 3 of 39
4 2. If Jaden only uses the talking features of his plan, write an equation for the cost C of talking m minutes. (a) How much will it cost Jaden to talk for 15 minutes? Justify your answer. (b) If Jaden has $6, how many minutes can he talk? Justify your answer. 3. If Jaden uses both talk and text, write an equation for the cost C of sending t texts and talking m minutes. (a) How much will it cost Jaden to send 7 texts and talk for 12 minutes? Justify your answer. (b) If Jaden wants to send 21 texts and only has $6, how many minutes can he talk? (c) Will Jaden use all of his money in part (b)? If not, will how much money will he have left? Justify your answer. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 4 of 39
5 The Task (Part 2) Jaden discovers another prepaid phone plan (Plan B) that charges a flat fee of $15 per month, then $.05 per text sent or minute used. 1. Write an equation for the cost of Plan B. Assume that in an average month, Jaden sends 200 texts and talks for 100 minutes. 2. Which plan will cost Jaden the least amount of money (Plan A from Part 1 or Plan B from Part 2)? Justify your answer. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 5 of 39
6 Solving Systems of Equations Algebraically Mathematical Goals Model and write an equation in one variable and solve a problem in context. Create one-variable linear equations and inequalities from contextual situations. Represent constraints with inequalities. Solve word problems where quantities are given in different units that must be converted to understand the problem. Common Core State Standards MCC9 12.A.REI.5: Prove that, given a system of two equations in two variables, replacing one equation by the sum of that equation and a multiple of the other produces a system with the same solutions. MCC9 12.A.REI.6: Solve systems of linear equations exactly and approximately (e.g., with graphs), focusing on pairs of linear equations in two variables. Standards for Mathematical Practice (1) Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (2) Reason abstractly and quantitatively. (3) Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. (4) Model with mathematics. Introduction In this task, students justify the solution to a system of equations by both graphing and substituting values into the system. Students will then show that multiplying one or both equations in a system of equations by a constant creates a new system with the same solutions as the original. This task will lead into using the elimination method for solving a system of equations algebraically. Materials Ruler Calculator Notebook paper Pencil GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 6 of 39
7 Solving Systems of Equations Algebraically Warm-up You are given the following system of two equations: x+2 y=16 3 x 4 y= 2 1. One common practice in mathematics when working with a system of equations is to label the equations. Normally this is done by writing the label in parentheses to the left of the equation. An example might look like the example to the right where the equation is the first line is called Equation A and the equation in the second line is called Equation B. Take a moment to label the equations given to you in this warm-up. (eq A):x+7=9 (eq B):2 x+14=18 Example 1: Linear Equations Labeled Does it matter which equation is labeled equation A and which one is labeled equation B? 2. What are some ways to show that the coordinate (6,5) is a solution to the system of equations given above? The Task (Part 1) 1. Using graph paper, prove that (6, 5) is a solution to the system by graphing both equations in the system on the same grid. 2. Using algebraic techniques, prove that (6, 5) is a solution to the system by substituting the coordinate values in for both equations. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 7 of 39
8 3. Multiply both sides of the equation x+2 y=16 by the constant 7. The initial setup is shown for you. Be sure to show all your work. 7 ( x +2 y)=7 16 New Equation: (a) Does the new equation still have a solution of (6, 5)? Justify your answer. (b) Why do you think the solution to the equation (did/did not) changed when you multiplied by the 7? 4. Multiply the equation x+2 y =16 by three other numbers. Recording the resulting equations. (a) (b) (c) 5. For each of the equations found in problem (6), is the coordinate (6,5) still a solution? Justify your answer. 6. Multiply the equation 3 x 4 y= 2 by 7 and record the equation. Prove that (6,5) is a solution to the resulting equation you recorded. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 8 of 39
9 7. Multiply the equation 3 x 4 y = 2 by three different numbers and record the resulting equations. (a) (b) (c) 8. Is the coordinate (6,5) a solution to the equations found in problem (9)? Justify your answer. 9. Summarize any finds/new learnings made during this activity so far. Closing 1. What is the solution to a system of equations and how can you prove it is the solution? 2. Does the solution change when you multiply one of the equations by a constant? 3. Does the value of the constant you multiply by matter? 4. Does it matter which equation you multiply by the constant? GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 9 of 39
10 Solving Systems of Equations Algebraically The Task (Part 2) Consider the following system of equations: 5 x+6 y=9 4 x+3 y=0 1. Show by substituting in the values that ( 3,4) is a solution to the system of equations. 2. Multiply 4 x+3 y=0 by 5. Then add your answer to 5 x+6 y=9. Record your answer and label as a new equation. Show your work below. SETUP: 5 (4 x+3 y)=(0) 5 (ANSWER) + 5 x + 6 y = 9 (New Equation) 3. Is ( 3,4) still a solution to the new equation in part (2)? Justify your answer. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 10 of 39
11 4. Using the same setup and steps from part (2), Multiply the equation 4 x+3 y=0 by 2. Then add your answer to 5 x+6 y=9. (a) What happened to the y variable in this new equation? (b) Solve the new equation for the variable x. (c) What is the value of x that solves this equation? (d) Does the value of x found in part (4c) agree with the value you already new to be a solution? 5. How could you use the value of x from part (4c) to find a value for y from one of the original equations from the system of equations? GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 11 of 39
12 The method you just used in problems (4) and (5) is called The Elimination Method for solving a system of equations. When using the Elimination Method, one of the original variables is eliminated from the system by adding the two equations together (sometimes after multiplying one or both of the equations by a constant on both sides). Use the Elimination Method to solve the following system of equations: 6. 3 x+2 y= 6 5 x 2 y= x+7 y=11 5 x+3y=19 GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 12 of 39
13 Solving Systems of Equations Algebraically The Task (Part 3) When using the Elimination Method, one of the original variables is eliminated from the system by adding the two equations together. Sometimes it is necessary to multiply one or both of the original equations by a constant. The equations are then added together and one of the variables is eliminated. Use the Elimination Method to solve the following system of equations: (Equation 1) 4 x+3 y = 14 (Equation 2) 2 x+ y = 8 1. Your choice of which variable to eliminate will change the steps you choose to take. First focus on eliminating the x variable. (a) The coefficients of x are 4 and 2. If you want to eliminate the x variable, you should multiply Equation 2 by what constant? (b) Multiply Equation 2 by the constant from part (1a). Add the resulting new equation to Equation 1. Record your answer after showing all of your steps. (c) What happened to the x variable? (d) Solve the resulting equation from (1b) for any variable that is remaining. Show all of your work and record the answer when done. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 13 of 39
14 (e) Substitute the value from (1d) into Equation 1 and solve for any remaining variable. Show all of your work and record your answer. (f) Using your answers from (1d) and (1e) you should have a solution to the system of equations. What is the solution to the system of equations? 2. Given the solution you obtained in (1f), do you think you would have obtained the same answer if the y variable had been eliminated? Justify your answer. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 14 of 39
15 3. Consider focusing on Equation 1 and Equation2 again but paying attention to the y variable this time. (a) The coefficients of y are 3 and 1. If you want to eliminate the y term, you should multiply Equation 2 by what constant? (b) Multiply Equation 2 by the constant from (3a). Then add your answer equation to Equation 1. Recording your answer after showing all of your work. (c) What happened to the y variable? (d) Solve the resulting equation from (3b) for any variable that is remaining. Show all of your work and record the answer when done. (e) Substitute the value from (1d) into Equation 1 and solve for any remaining variable. Show all of your work and record your answer. (f) Using your answers from (3d) and (3e) you should have a solution to the system of equations. What is the solution to the system of equations? GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 15 of 39
16 Use your findings from problem 1 and problem 3 to answer the following questions in sentence form. 4. Do you need to eliminate both variables to solve a system of equations? 5. What are some things you should consider when deciding which variable to eliminate? Is there a wrong variable to eliminate? 6. Verify that the solution you found in Problem 1 and Problem 3 is a solution to both Equation 1 and Equation 2 using substitution. Be sure to show all your work. Closing Use your findings from problem 1 and problem 3 to answer the following questions in sentence form. 1. Is the ordered pair solution the same for either variable that is eliminated? Justify your answer. 2. Would you need to eliminate both variables to solve the problem? Justify your answer. 3. What are some things you should consider when deciding which variable to eliminate? Is there a wrong variable to eliminate? 4. How do you decide what constant to multiply by in order to make the chosen variable eliminate? GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 16 of 39
17 Solving Systems of Equations Algebraically Homework 1. 3 x+2 y = 6 6 x 3 y = x+ 5 y = 4 7 x 10 y = x+ 6 y = 16 2 x+10 y = 5 GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 17 of 39
18 Summer Job Mathematical Goals Model and write an inequality in two variables and solve a problem in context. Create two-variable linear equations and inequalities from contextual situations. Solve word problems involving inequalities. Represent constraints with inequalities. Common Core State Standards MCC9 12.A.REI.12: Graph the solutions to a linear inequality in two variables as a half plane (excluding the boundary in the case of a strict inequality), and graph the solution set to a system of linear inequalities in two variables as the intersection of the corresponding half planes. Standards for Mathematical Practice (1) Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (2) Reason abstractly and quantitatively. (4) Model with mathematics. (5) Use appropriate tools strategically. (6) Attend to precision. Introduction In this task, students will write a model for an inequality from the context of a word problem using real life situations. The students will then graph the inequality in two variables and analyze the solution. Students will reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems. Materials Graph paper Notebook paper Ruler Pencil Colored Pencils GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 18 of 39
19 Summer Job Warm-up In order to raise money, you are planning to work during the summer babysitting and cleaning houses. You earn $10 per hour while babysitting and $20 per hour while cleaning houses. You need to earn at least $1000 during the summer. 1. Write an expression to represent the amount of money earned while babysitting. Be sure to choose a variable to represent the number of hours spent babysitting. 2. Write an expression to represent the amount of money earned while cleaning houses. 3. Does the amount of money you earned over the summer need to be exactly $1000? Justify your answer. The Task (Part 1) 1. Suppose all of the information from the Warm-up is still valid. Write a mathematical formula that relates the total amount of money earned over the summer ( T ) to the number of hours spent cleaning ( c ) and the number of hours spent babysitting ( b ). 2. Write a mathematical relationship between the total money earned over the summer and the goal of $1000. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 19 of 39
20 3. Complete the following table based on your formula from part(2). Hours Spent Babysitting Hours Spent Cleaning Total Money Earned 0 $ $ $ $1000 $1000 $ Is there more than one way to earn $1100? Justify your answer. 5. Consider making a graph that would model this situation provided in the table. Use the provided graph as a guide. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 20 of 39
21 6. Use the graph to answer the following questions (a) Why does the graph only fall in the 1 st Quadrant? (b) Is it acceptable to earn exactly $1000? (c) What are some possible combinations of outcomes that equal exactly $1000? (d) Where do all of the outcomes that total $1000 lie on the graph? (e) Is it acceptable to earn more than $1000? (f) What are some possible combinations of outcomes that total more than $1000? (g) Where do all of these outcomes fall on the graph? GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 21 of 39
22 7. Use the graph to answer the following (a) Is it acceptable to work 10 hours babysitting and 10 hours cleaning houses? Why or why not? (b) Where does the combination of 10 hours babysitting and 10 hours cleaning houses fall on the graph? (c) Are combinations that fall in this area a solution to the mathematical model? Why or why not? 8. How would the model change if you had to earn more than $1000? (a) Write a new model to represent needing to earn more than $1000. (b) How would this change the graph of the model? (c) Would the line still be part of the solution? (d) How would you change the line to show this? GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 22 of 39
23 9. Graph the new model from part (8) GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 23 of 39
24 Summer Job The Task (Part 2) You plan to use part of the money you earned from your summer job to buy jeans and shirts for school. Jeans cost $40 per pair and shirts are $20 each. You want to spend less than $400 of your money on these items. 1. Write a mathematical model representing the amount of money spent on jeans and shirts. Be sure to clearly identify the variables used in this model. 2. Graph the model defined above. Place the number of jeans on the x-axis and the number of shirts on the y-axis. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 24 of 39
25 3. Use the graph to answer the following questions (a) Why does the graph only fall in the 1 st Quadrant? (b) Is it acceptable to spend less than $400? (c) What are some possible combinations of outcomes that spend less than $400? (d) Where do all of the combinations that spend less than $400 fall on the graph? (e) Is it acceptable to spend exactly $400? (f) List at least three combinations of shirts and jeans that cost exactly $400. (g) Where do all of the combinations that spend exactly $400 fall on the graph? (h) Is it acceptable to spend more than $400? (i) List out at least three combination of shirts and jeans that cost more than $400. (j) Where do all of the combinations that spend more than $400 fall on the graph? GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 25 of 39
26 Summer Job Closing Summarize your knowledge of graphing inequalities in two variables by answering the following questions in sentence form: 1. Explain the difference between a solid line and a broken line when graphing inequalities. (a) How can you determine from the model whether the line will be solid or broken? (b) How can you look at the graph and know if the line is part of the solution? 2. How do you determine which area of the graph of an inequality to shade? (a) What is special about the shaded area of an inequality? (b) What is special about the area that is not shaded? GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 26 of 39
27 Graphing Inequalities Mathematical Goals Model and write an inequality in two variables and solve a problem in context. Create two-variable linear equations and inequalities from contextual situations. Solve word problems involving inequalities. Represent constraints with inequalities. Common Core State Standards MCC9 12.A.REI.12: Graph the solutions to a linear inequality in two variables as a half plane (excluding the boundary in the case of a strict inequality), and graph the solution set to a system of linear inequalities in two variables as the intersection of the corresponding half planes. Standards for Mathematical Practice (1) Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (2) Reason abstractly and quantitatively. (4) Model with mathematics. (5) Use appropriate tools strategically. (6) Attend to precision. Introduction In this task, students will graph two separate inequalities in two variables and analyze the graph for solutions to each. The students will then graph the two inequalities in two variables on the same coordinate system to show that the solution to both inequalities is the area where the graphs intersect. Materials Colored pencils Pencil Calculator Paper Ruler GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 27 of 39
28 Graphing Inequalities Warm-up 1. Graph the inequality y> 1 x+5. List out at least 2 three solutions to this inequality. 2. Graph the inequality y<x+2. List out at least three solutions to this inequality. The Task 1. Look at the two graphs from the Warm-up. (a) There are solutions that work for both inequalities. List out three examples of these solutions. (b) There are solutions that work for 1 inequality but not the other? Give 3 examples and show which inequality each example works for. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 28 of 39
29 2. On grid paper, graph both inequalities. Use a different color to shade each inequality. (a) Look at the region that is shaded in both colors. What does this region represent? (b) Look at the regions that are shaded in only 1 color. What do these regions represent? (c) Look at the region that is not shaded. What does this region represent? 3. Graph the following system on the same coordinate grid. Use a different color for each. x+y 3 y x+5 (a) Give three coordinates that are solutions to the system. (b) Give three coordinates that are not solutions to the system. (c) Is a coordinate on either line a solution to the system? Justify your answer. (d) How would you change the inequality x+ y 3 so that it would shade below the line? (e) How would you change the inequality y x+5 so that it would shade above the line? GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 29 of 39
30 4. Graph the new inequalities from part (3f) and (3e) on the same coordinate grid (creating a new system of inequalities). Use blue to shade the solution set for one inequality and red for the other inequality. (a) What do the coordinates in blue represent? (b) What do the coordinates in red represent? (c) Why do the colors not overlap this time? Homework Graph each of the following systems on the same coordinate grid and give 3 solutions for each system x+3 y<6 x+5 y>5 y 1 2 x 1 y 1 4 x x 4 y>5 y> 3 4 x+1 GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 30 of 39
31 Family Outing Mathematical Goals Model and write an inequality in two variables and solve a problem in context. Create two-variable linear equations and inequalities from contextual situations. Solve word problems involving inequalities. Represent constraints with inequalities. Common Core State Standards MCC9 12.A.REI.1: Explain each step in solving a simple equation as following from the equality of numbers asserted at the previous step, starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Construct a viable argument to justify a solution method. MCC9 12.A.REI.3: Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters. MCC9 12.A.REI.5: Prove that, given a system of two equations in two variables, replacing one equation by the sum of that equation and a multiple of the other produces a system with the same solutions. MCC9 12.A.REI.6: Solve systems of linear equations exactly and approximately (e.g., with graphs), focusing on pairs of linear equations in two variables. MCC9 12.A.REI.12: Graph the solutions to a linear inequality in two variables as a half plane (excluding the boundary in the case of a strict inequality), and graph the solution set to a system of linear inequalities in two variables as the intersection of the corresponding half planes. MCC9 12.A.REI.12: Graph the solutions to a linear inequality in two variables as a half plane (excluding the boundary in the case of a strict inequality), and graph the solution set to a system of linear inequalities in two variables as the intersection of the corresponding half planes. Standards for Mathematical Practice (1) Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (2) Reason abstractly and quantitatively. (4) Model with mathematics. (5) Use appropriate tools strategically. (6) Attend to precision. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 31 of 39
32 Introduction In this task, students will write a model for an inequality from the context of a word problem using real life situations. The students will then graph the inequality in two variables and analyze the solution. Students will reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems. Materials Pencil Colored Pencils Ruler Calculator GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 32 of 39
33 Family Outing Warm-up You and your family are planning to rent a van for a 1 day trip to Family Fun Amusement Park in Friendly Town. For the van your family wants, the Wheels and Deals Car Rental Agency charges $25 per day plus 50 cents per mile to rent the van. The Cars R Us Rental Agency charges $40 per day plus 25 cents per mile to rent the same type van. List out any key information that is important for this scenario. The Task (Part 1) 1. Write a mathematical model to represent the cost of renting a van from the Wheels and Deals Agency for 1 day. (a) Do the units matter for this equation? (b) Use the equation to determine the cost for renting the van from this agency for 1 day and driving 40 miles. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 33 of 39
34 2. Write a mathematical model to represent the cost of renting from the Cars R Us Agency for 1 day. (a) Do the units for this equation match the units for the equation in problem 1? (b) Does this matter when comparing the 2 equations? (c) Use the equation from section (2) to determine the cost for renting the van from Cars R Us for 1 day and driving 40 miles. 3. Graph the 2 models from section(1) and section (2) on the same coordinate system. Be sure to extend the lines until they intersect. (a) Where do the 2 lines intersect? (b) What does the point of intersection represent? (c) When is it cheaper to rent from Wheels and Deals? (d) When is it cheaper to rent from Cars R Us? GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 34 of 39
35 4. Friendly Town is approximately 80 miles from your home town. Which agency should you choose to rent a vehicle? Justify your answer. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 35 of 39
36 Family Outing The Task (Part 2) When you leave the car rental agency, your father goes to the Fill er Up Convenience Store for gas. The gas hand indicates the van is on empty, so your father plans to fill the tank. Gas at the station is $3.49 per gallon. 1. If your father spends $78 on gas, approximately how many gallons did he purchase? Be sure to show all work to justify your answer. While in the store, your father purchases drinks for the six people in your van. Part of your family wants coffee and the rest want a soda. 2. Coffee in the store costs $.49 per cup and sodas are $1.29 each. The cost of the drinks before tax was $6.14. (a) Write a mathematical model that represents the total number of cups of coffee and sodas. (b) Write a mathematical model that represents the cost of the coffee and soda. (c) Solve the system of equations using the elimination method. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 36 of 39
37 When you arrive in Friendly Town at the Family Fun Amusement Park, the 6 people in your family pair up to enter the park. You and your brother decide to enter and ride together. The cost to enter the park is $10, with each ride costing $2. 3. You bring $55 to the park. You must pay to enter the park and you budget an additional $10 for food. Write and solve an inequality to determine the maximum number of rides you can ride. Explain your answer. 4. Your brother brings $70 to the park and budgets $12 for food. How many more rides can he ride than you? Explain your answer. Inside the park, there are 2 vendors that sell popcorn and cotton candy. Jiffy Snacks sells both for $2.50 per bag. Quick Eats has cotton candy for $4 per bag and popcorn for $2 per bag. 5. If you use the $10 you budgeted for food, write an inequality to model the possible combinations of popcorn and cotton candy you can purchase from Jiffy Snacks. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 37 of 39
38 6. Write an inequality to model the possible combinations of popcorn and cotton candy you can purchase from Quick Eats. 7. Graph a system of inequalities from sections (5) and (6). Give two combinations that work for both vendors. 8. Assuming you purchase at least one bag of each snack, what is the maximum number of bags of cotton candy and popcorn that work for both equations? GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 38 of 39
39 Family Outing The Task (Part 3) Assume that the information from The Task (Part 2) is still true for the remainder of Part 3. When you leave the park, your father notices that you have used tank of gas you purchased before you left. 3 4 of the 1. Do you have enough gas to get home? Justify your answer. 2. Your father wants to purchase enough gas to get home, but not leave extra in the tank when the van is returned to the rental agency. Approximately how many more gallons should he purchase? Justify your answer. GADOE unless otherwise noted on the information page of each section. PAGE: 39 of 39
Mathematics. Unit 2: Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities
 CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics CCGPS Coordinate Algebra Unit 2: Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics CCGPS Coordinate Algebra Unit 2: Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute
SOLVING LINEAR INEQUALITIES
 Topic 15: Solving linear inequalities 65 SOLVING LINEAR INEQUALITIES Lesson 15.1 Inequalities on the number line 15.1 OPENER Consider the inequality x > 7. 1. List five numbers that make the inequality
Topic 15: Solving linear inequalities 65 SOLVING LINEAR INEQUALITIES Lesson 15.1 Inequalities on the number line 15.1 OPENER Consider the inequality x > 7. 1. List five numbers that make the inequality
Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics GSE Coordinate Algebra Unit 2: Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities Unit 2 Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities Table of Contents OVERVIEW...
Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics GSE Coordinate Algebra Unit 2: Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities Unit 2 Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities Table of Contents OVERVIEW...
28 (Late Start) 7.2a Substitution. 7.1b Graphing with technology Feb 2. 4 (Late Start) Applications/ Choosing a method
 Unit 7: Systems of Linear Equations NAME: The calendar and all assignments are subject to change. Students will be notified of any changes during class, so it is their responsibility to pay attention and
Unit 7: Systems of Linear Equations NAME: The calendar and all assignments are subject to change. Students will be notified of any changes during class, so it is their responsibility to pay attention and
Serena: I don t think that works because if n is 20 and you do 6 less than that you get 20 6 = 14. I think we should write! 6 > 4
 24 4.6 Taking Sides A Practice Understanding Task Joaquin and Serena work together productively in their math class. They both contribute their thinking and when they disagree, they both give their reasons
24 4.6 Taking Sides A Practice Understanding Task Joaquin and Serena work together productively in their math class. They both contribute their thinking and when they disagree, they both give their reasons
Chapter 4: Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter 4: Systems of Equations and Inequalities 4.1 Systems of Equations A system of two linear equations in two variables x and y consist of two equations of the following form: Equation 1: ax + by =
Chapter 4: Systems of Equations and Inequalities 4.1 Systems of Equations A system of two linear equations in two variables x and y consist of two equations of the following form: Equation 1: ax + by =
ALGEBRA UNIT 5 LINEAR SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1)
 ALGEBRA UNIT 5 LINEAR SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1) System: Solution to Systems: Number Solutions Exactly one Infinite No solution Terminology Consistent and Consistent and Inconsistent
ALGEBRA UNIT 5 LINEAR SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1) System: Solution to Systems: Number Solutions Exactly one Infinite No solution Terminology Consistent and Consistent and Inconsistent
Final Exam Study Guide
 Algebra 2 Alei - Desert Academy 2011-12 Name: Date: Block: Final Exam Study Guide 1. Which of the properties of real numbers is illustrated below? a + b = b + a 2. Convert 6 yards to inches. 3. How long
Algebra 2 Alei - Desert Academy 2011-12 Name: Date: Block: Final Exam Study Guide 1. Which of the properties of real numbers is illustrated below? a + b = b + a 2. Convert 6 yards to inches. 3. How long
UNIT 5 INEQUALITIES CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher:
 UNIT 5 INEQUALITIES 2015-2016 CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher: Topic(s) Page(s) Unit 5 Vocabulary 2 Writing and Graphing Inequalities 3 8 Solving One-Step Inequalities 9 15 Solving Multi-Step Inequalities
UNIT 5 INEQUALITIES 2015-2016 CCM6+/7+ Name: Math Teacher: Topic(s) Page(s) Unit 5 Vocabulary 2 Writing and Graphing Inequalities 3 8 Solving One-Step Inequalities 9 15 Solving Multi-Step Inequalities
ALGEBRA UNIT 5 -SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1)
 ALGEBRA UNIT 5 -SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1) System: Solution to Systems: Number Solutions Exactly one Infinite No solution Terminology Consistent and Consistent and Inconsistent independent
ALGEBRA UNIT 5 -SYSTEMS SOLVING SYSTEMS: GRAPHICALLY (Day 1) System: Solution to Systems: Number Solutions Exactly one Infinite No solution Terminology Consistent and Consistent and Inconsistent independent
UNIT 2: REASONING WITH LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES. Solving Equations and Inequalities in One Variable
 UNIT 2: REASONING WITH LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES This unit investigates linear equations and inequalities. Students create linear equations and inequalities and use them to solve problems. They
UNIT 2: REASONING WITH LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES This unit investigates linear equations and inequalities. Students create linear equations and inequalities and use them to solve problems. They
Algebra 1 Fall Review
 Name Algebra 1 Fall Review 2013-2014 Date 1. Write an inequality to best represent the graph shown at right. (A.1.D.) m: b: inequality: 2. Write an inequality to best describe the graph shown at right.
Name Algebra 1 Fall Review 2013-2014 Date 1. Write an inequality to best represent the graph shown at right. (A.1.D.) m: b: inequality: 2. Write an inequality to best describe the graph shown at right.
TASK: WHEN IS IT NOT EQUAL?
 TASK: WHEN IS IT NOT EQUAL? ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What strategies can I use to help me understand and represent real situations using inequalities? How can I write, interpret and manipulate inequalities?
TASK: WHEN IS IT NOT EQUAL? ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What strategies can I use to help me understand and represent real situations using inequalities? How can I write, interpret and manipulate inequalities?
Lesson 8: Representing Proportional Relationships with Equations
 Lesson 8: Representing Proportional Relationships with Equations Student Outcomes Students use the constant of proportionality to represent proportional relationships by equations in real world contexts
Lesson 8: Representing Proportional Relationships with Equations Student Outcomes Students use the constant of proportionality to represent proportional relationships by equations in real world contexts
Algebra I Practice Exam
 Algebra I This practice assessment represents selected TEKS student expectations for each reporting category. These questions do not represent all the student expectations eligible for assessment. Copyright
Algebra I This practice assessment represents selected TEKS student expectations for each reporting category. These questions do not represent all the student expectations eligible for assessment. Copyright
Sample: Do Not Reproduce LF6 STUDENT PAGES LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 6: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS. Name Period Date
 Name Period Date LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 6: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS LF6.1 LF6.2 LF6.3 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Understand the definition of a system of linear equations Understand
Name Period Date LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 6: SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS LF6.1 LF6.2 LF6.3 Introduction to Systems of Linear Equations Understand the definition of a system of linear equations Understand
Name. Check with teacher. equation: a. Can you find. a. (-2, -3) b. (1, 3) c. (2, 5) d. (-2, -6) a. (-2, 6) b. (-1, 1) c. (1, 3) d. (0, 0) Explain why
 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations: Graphing Name Part I - Warm Up with ONE EQUATION: a. Which of the following is a solution to the equation: y 3x 1? a. (-2, -3) b. (1, 3) c. (2, 5) d. (-2, -6) Partt II
7.1 Solving Systems of Equations: Graphing Name Part I - Warm Up with ONE EQUATION: a. Which of the following is a solution to the equation: y 3x 1? a. (-2, -3) b. (1, 3) c. (2, 5) d. (-2, -6) Partt II
Define the word inequality
 Warm Up: Define the word inequality Agenda: Objective- Students can solve linear inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters. Define Inequalities One & Two
Warm Up: Define the word inequality Agenda: Objective- Students can solve linear inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters. Define Inequalities One & Two
Simple Inequalities Involving Addition and Subtraction. Unit 3 Inequalities.notebook. November 18, Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Simple Inequalities Addition/Subtraction Simple Inequalities Multiplication/Division Two-Step and Multiple-Step Inequalities Solving Compound Inequalities Special Cases of Compound Inequalities
Table of Contents Simple Inequalities Addition/Subtraction Simple Inequalities Multiplication/Division Two-Step and Multiple-Step Inequalities Solving Compound Inequalities Special Cases of Compound Inequalities
Expressions and Equations
 Name Expressions and Equations 6.EE Common Core Cluster Apply and extend previous understanding of arithmetic to algebraic expressions. Mathematically proficient students communicate precisely by engaging
Name Expressions and Equations 6.EE Common Core Cluster Apply and extend previous understanding of arithmetic to algebraic expressions. Mathematically proficient students communicate precisely by engaging
Writing and Solving Equations
 Writing and Solving Equations Melody s Music Solution Lesson 6-1 Modeling and Writing Two-Step Equations ACTIVITY 6 Learning Targets: Use variables to represent quantities in real-world problems. Model
Writing and Solving Equations Melody s Music Solution Lesson 6-1 Modeling and Writing Two-Step Equations ACTIVITY 6 Learning Targets: Use variables to represent quantities in real-world problems. Model
3.1 NOTES Solving Systems of Linear Equations Graphically
 3.1 NOTES Solving Systems of Linear Equations Graphically A system of two linear equations in two variables x and y consist of two equations of the following form: Ax + By = C Equation 1 Dx + Ey = F Equation
3.1 NOTES Solving Systems of Linear Equations Graphically A system of two linear equations in two variables x and y consist of two equations of the following form: Ax + By = C Equation 1 Dx + Ey = F Equation
More with Systems of Equations
 More with Systems of Equations In 2008, 4.7 million Americans went on a rafting expedition. In Georgia, outfitters run whitewater expeditions for ages 8 and up on the Chattooga River. 12.1 Systems of Equations
More with Systems of Equations In 2008, 4.7 million Americans went on a rafting expedition. In Georgia, outfitters run whitewater expeditions for ages 8 and up on the Chattooga River. 12.1 Systems of Equations
Name: Systems 2.1. Ready Topic: Determine if given value is a solution and solve systems of equations
 Name: Systems 2.1 Ready, Set, Go! Ready Topic: Determine if given value is a solution and solve systems of equations TE-16 1. Graph both equations on the same axes. Then determine which ordered pair is
Name: Systems 2.1 Ready, Set, Go! Ready Topic: Determine if given value is a solution and solve systems of equations TE-16 1. Graph both equations on the same axes. Then determine which ordered pair is
Foundations of Algebra. Learning Goal 3.1 Algebraic Expressions. a. Identify the: Variables: Coefficients:
 Learning Goal 3.1 Algebraic Expressions What you need to know & be able to do 1. Identifying Parts of Algebraic Expressions 3.1 Test Things to remember Identify Parts of an expression Variable Constant
Learning Goal 3.1 Algebraic Expressions What you need to know & be able to do 1. Identifying Parts of Algebraic Expressions 3.1 Test Things to remember Identify Parts of an expression Variable Constant
Algebra 1 Unit 3 Practice
 Lesson 1-1 Use the table for Items 1 and. Canoe Rental Days Cost ($) 1 5 3 78 5 1 7 13 1. Use function notation to write a linear function that gives the cost C in dollars of renting a canoe for t days.
Lesson 1-1 Use the table for Items 1 and. Canoe Rental Days Cost ($) 1 5 3 78 5 1 7 13 1. Use function notation to write a linear function that gives the cost C in dollars of renting a canoe for t days.
Foundations of Math. Chapter 3 Packet. Table of Contents
 Foundations of Math Chapter 3 Packet Name: Table of Contents Notes #43 Solving Systems by Graphing Pg. 1-4 Notes #44 Solving Systems by Substitution Pg. 5-6 Notes #45 Solving by Graphing & Substitution
Foundations of Math Chapter 3 Packet Name: Table of Contents Notes #43 Solving Systems by Graphing Pg. 1-4 Notes #44 Solving Systems by Substitution Pg. 5-6 Notes #45 Solving by Graphing & Substitution
Evaluate algebraic expressions and use exponents. Translate verbal phrases into expressions.
 Algebra 1 Notes Section 1.1: Evaluate Expressions Section 1.3: Write Expressions Name: Hour: Objectives: Section 1.1: (The "NOW" green box) Section 1.3: Evaluate algebraic expressions and use exponents.
Algebra 1 Notes Section 1.1: Evaluate Expressions Section 1.3: Write Expressions Name: Hour: Objectives: Section 1.1: (The "NOW" green box) Section 1.3: Evaluate algebraic expressions and use exponents.
Chapter 4 - Writing Linear Functions
 Chapter 4 - Writing Linear Functions Write an equation of the line with the given slope and y-intercept. 1. slope: 3 y-intercept: 6 a. y = 6x + 3 c. y = 6x 3 b. y = 3m + 6 d. y = 3x 6 2. D REF: Algebra
Chapter 4 - Writing Linear Functions Write an equation of the line with the given slope and y-intercept. 1. slope: 3 y-intercept: 6 a. y = 6x + 3 c. y = 6x 3 b. y = 3m + 6 d. y = 3x 6 2. D REF: Algebra
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES. ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 OVERVIEW Algebra I Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 OVERVIEW Algebra I Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
Math Chapter 5: Linear Relations, Equations, and Inequalities. Goal: Use symbols to describe a pattern that changes at a constant rate.
 Math 9-14 Chapter 5: Linear Relations, Equations, and Inequalities 5.1 (Part 1) Describing Relations Algebraically Goal: Use symbols to describe a pattern that changes at a constant rate. Relation: Ex
Math 9-14 Chapter 5: Linear Relations, Equations, and Inequalities 5.1 (Part 1) Describing Relations Algebraically Goal: Use symbols to describe a pattern that changes at a constant rate. Relation: Ex
Topic 1. Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. Solve the following equation
 Topic 1. Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. Solve the following equation Algebraically 2( x 3) = 12 Graphically 2( x 3) = 12 2. Solve the following equations algebraically a. 5w 15 2w = 2(w 5) b. 1
Topic 1. Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. Solve the following equation Algebraically 2( x 3) = 12 Graphically 2( x 3) = 12 2. Solve the following equations algebraically a. 5w 15 2w = 2(w 5) b. 1
4. The table shows the number of toll booths driven through compared to the cost of using a Toll Tag.
 ALGEBRA 1 Fall 2016 Semester Exam Review Name 1. According to the data shown below, which would be the best prediction of the average cost of a -bedroom house in Georgetown in the year 2018? Year Average
ALGEBRA 1 Fall 2016 Semester Exam Review Name 1. According to the data shown below, which would be the best prediction of the average cost of a -bedroom house in Georgetown in the year 2018? Year Average
Unit 5. Linear equations and inequalities OUTLINE. Topic 13: Solving linear equations. Topic 14: Problem solving with slope triangles
 Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Algebra Practice Set. *Evaluate number and algebraic expressions using rational numbers and Order of Operations
 Algebra Practice Set Expressions *Evaluate number and algebraic expressions using rational numbers and Order of Operations *Translate algebraic expressions into words using appropriate language *Write
Algebra Practice Set Expressions *Evaluate number and algebraic expressions using rational numbers and Order of Operations *Translate algebraic expressions into words using appropriate language *Write
Houston County School System Mathematics
 Student Name: Teacher Name: Grade: 6th Unit #: 4b Unit Title: Analyzing Quantitative Relationships Approximate Start Date of Unit: January 4 Approximate End Date (and Test Date) of Unit: January 19 I can
Student Name: Teacher Name: Grade: 6th Unit #: 4b Unit Title: Analyzing Quantitative Relationships Approximate Start Date of Unit: January 4 Approximate End Date (and Test Date) of Unit: January 19 I can
Algebra I Solving & Graphing Inequalities
 Slide 1 / 182 Slide 2 / 182 Algebra I Solving & Graphing Inequalities 2016-01-11 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 182 Table of Contents Simple Inequalities Addition/Subtraction click on the topic to go to that
Slide 1 / 182 Slide 2 / 182 Algebra I Solving & Graphing Inequalities 2016-01-11 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 182 Table of Contents Simple Inequalities Addition/Subtraction click on the topic to go to that
ALGEBRA 1 SEMESTER 1 INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS Courses: Algebra 1 S1 (#2201) and Foundations in Algebra 1 S1 (#7769)
 Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Ramal goes to the grocery store and buys pounds of apples and pounds of bananas. Apples cost dollars per
Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Ramal goes to the grocery store and buys pounds of apples and pounds of bananas. Apples cost dollars per
Algebra 2 Level 2 Summer Packet
 Algebra Level Summer Packet This summer packet is for students entering Algebra Level for the Fall of 01. The material contained in this packet represents Algebra 1 skills, procedures and concepts that
Algebra Level Summer Packet This summer packet is for students entering Algebra Level for the Fall of 01. The material contained in this packet represents Algebra 1 skills, procedures and concepts that
Expressions & Equations Chapter Questions. 6. What are two different ways to solve equations with fractional distributive property?
 Expressions & Equations Chapter Questions 1. Explain how distribution can simplify a problem. 2. What are like terms? 3. How do you combine like terms? 4. What are inverse operations? Name them. 5. How
Expressions & Equations Chapter Questions 1. Explain how distribution can simplify a problem. 2. What are like terms? 3. How do you combine like terms? 4. What are inverse operations? Name them. 5. How
Name Period Date DRAFT
 Name Period Date Equations and Inequalities Student Packet 4: Inequalities EQ4.1 EQ4.2 EQ4.3 Linear Inequalities in One Variable Add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers. Write expressions, equations,
Name Period Date Equations and Inequalities Student Packet 4: Inequalities EQ4.1 EQ4.2 EQ4.3 Linear Inequalities in One Variable Add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers. Write expressions, equations,
Section 2.2 Objectives
 Section 2.2 Objectives Solve multi-step equations using algebra properties of equality. Solve equations that have no solution and equations that have infinitely many solutions. Solve equations with rational
Section 2.2 Objectives Solve multi-step equations using algebra properties of equality. Solve equations that have no solution and equations that have infinitely many solutions. Solve equations with rational
Houston County School System Mathematics
 Student Name: Teacher Name: Grade: 6th Unit #: 4b Unit Title: Analyzing Quantitative Relationships Approximate Start Date of Unit: Approximate End Date (and Test Date) of Unit: The following Statements
Student Name: Teacher Name: Grade: 6th Unit #: 4b Unit Title: Analyzing Quantitative Relationships Approximate Start Date of Unit: Approximate End Date (and Test Date) of Unit: The following Statements
Chapter 4.1 Introduction to Relations
 Chapter 4.1 Introduction to Relations The example at the top of page 94 describes a boy playing a computer game. In the game he has to get 3 or more shapes of the same color to be adjacent to each other.
Chapter 4.1 Introduction to Relations The example at the top of page 94 describes a boy playing a computer game. In the game he has to get 3 or more shapes of the same color to be adjacent to each other.
Algebra I Notes Linear Inequalities in One Variable and Unit 3 Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
 PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students must have a clear understanding of signed numbers and their operations students must understand meaning of operations and how they relate to one another students must be able
PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students must have a clear understanding of signed numbers and their operations students must understand meaning of operations and how they relate to one another students must be able
Introduction to Systems of Equations
 Systems of Equations 1 Introduction to Systems of Equations Remember, we are finding a point of intersection x 2y 5 2x y 4 1. A golfer scored only 4 s and 5 s in a round of 18 holes. His score was 80.
Systems of Equations 1 Introduction to Systems of Equations Remember, we are finding a point of intersection x 2y 5 2x y 4 1. A golfer scored only 4 s and 5 s in a round of 18 holes. His score was 80.
Unit 5. Linear equations and inequalities OUTLINE. Topic 13: Solving linear equations. Topic 14: Problem solving with slope triangles
 Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Unit 5 Linear equations and inequalities In this unit, you will build your understanding of the connection between linear functions and linear equations and inequalities that can be used to represent and
Math 3 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities
 Math 3 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities 1 MATH 1 REVIEW SOLVING AN ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATION Absolute value is a measure of distance; how far a number is from zero. In practice,
Math 3 Variable Manipulation Part 7 Absolute Value & Inequalities 1 MATH 1 REVIEW SOLVING AN ABSOLUTE VALUE EQUATION Absolute value is a measure of distance; how far a number is from zero. In practice,
Section 4 Topic 1 Arithmetic Sequences
 Section 4 Topic 1 Arithmetic Sequences Let s look at the following sequence of numbers: 3, 8, 13, 18, 23,.... Ø Ø Ø The at the end means that this sequence goes on forever. 3, 8, 13, 18, and 23 are the
Section 4 Topic 1 Arithmetic Sequences Let s look at the following sequence of numbers: 3, 8, 13, 18, 23,.... Ø Ø Ø The at the end means that this sequence goes on forever. 3, 8, 13, 18, and 23 are the
Part 1: You are given the following system of two equations: x + 2y = 16 3x 4y = 2
 Solving Systems of Equations Algebraically Teacher Notes Comment: As students solve equations throughout this task, have them continue to explain each step using properties of operations or properties
Solving Systems of Equations Algebraically Teacher Notes Comment: As students solve equations throughout this task, have them continue to explain each step using properties of operations or properties
PreAP Algebra I Problems for the First Semester Exam
 This is not a semester exam, but problems that you could use on a semester exam that are similar to some of the problems from the unit quizzes 1. Stephanie left home at 8:30 and rode her bicycle at a steady
This is not a semester exam, but problems that you could use on a semester exam that are similar to some of the problems from the unit quizzes 1. Stephanie left home at 8:30 and rode her bicycle at a steady
4) Solve for this system using your graphing
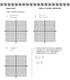 Algebra Unit 5 HW Day 1 SOLVING GRAPHICALLY Graph the following systems: 1) x 2y 12 y 2x 6 2) y x 2 6x 2y 10 ) x y 9 4) Solve for this system using your graphing x calculator. [You will still need to put
Algebra Unit 5 HW Day 1 SOLVING GRAPHICALLY Graph the following systems: 1) x 2y 12 y 2x 6 2) y x 2 6x 2y 10 ) x y 9 4) Solve for this system using your graphing x calculator. [You will still need to put
Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Focus on Modeling
 Name Class 5-6 Date Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Focus on Modeling Essential question: How can you use systems of linear equations or inequalities to model and solve contextual problems? N-Q.1.1*,
Name Class 5-6 Date Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Focus on Modeling Essential question: How can you use systems of linear equations or inequalities to model and solve contextual problems? N-Q.1.1*,
b. In the situation described above, what is the value of y?
 1 Algebra I Chapter 6 Test Review Standards/Goals: D.1.g: I can solve systems of equations in a variety of methods, including: graphing, substitution and elimination. A.REI.12.: I can graph the solution
1 Algebra I Chapter 6 Test Review Standards/Goals: D.1.g: I can solve systems of equations in a variety of methods, including: graphing, substitution and elimination. A.REI.12.: I can graph the solution
Grade 8 Systems of Linear Equations 8.EE.8a-c
 THE NEWARK PUBLIC SCHOOLS THE OFFICE OF MATHEMATICS Grade 8 Systems of Linear Equations 8.EE.8a-c 2012 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS ALIGNED MODULES 2012 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS ALIGNED MODULES THE NEWARK
THE NEWARK PUBLIC SCHOOLS THE OFFICE OF MATHEMATICS Grade 8 Systems of Linear Equations 8.EE.8a-c 2012 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS ALIGNED MODULES 2012 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS ALIGNED MODULES THE NEWARK
Systems of Equations. Red Company. Blue Company. cost. 30 minutes. Copyright 2003 Hanlonmath 1
 Chapter 6 Systems of Equations Sec. 1 Systems of Equations How many times have you watched a commercial on television touting a product or services as not only the best, but the cheapest? Let s say you
Chapter 6 Systems of Equations Sec. 1 Systems of Equations How many times have you watched a commercial on television touting a product or services as not only the best, but the cheapest? Let s say you
ACCELERATED ALGEBRA ONE SEMESTER ONE REVIEW. Systems. Families of Statistics Equations. Models 16% 24% 26% 12% 21% 3. Solve for y.
 ACCELERATED ALGEBRA ONE SEMESTER ONE REVIEW NAME: The midterm assessment assesses the following topics. Solving Linear Systems Families of Statistics Equations Models and Matrices Functions 16% 24% 26%
ACCELERATED ALGEBRA ONE SEMESTER ONE REVIEW NAME: The midterm assessment assesses the following topics. Solving Linear Systems Families of Statistics Equations Models and Matrices Functions 16% 24% 26%
Complete Week 6 Package
 Complete Week 6 Package HighSchoolMathTeachers@2018 Table of Contents Unit 2 Pacing Chart -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Day 26 Bellringer
Complete Week 6 Package HighSchoolMathTeachers@2018 Table of Contents Unit 2 Pacing Chart -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Day 26 Bellringer
constant matrix Study Guide and Review - Chapter 3
 Choose the term from above to complete each sentence. 1. A feasible region that is open and can go on forever is called. unbounded 2. To means to seek the best price or profit using linear programming.
Choose the term from above to complete each sentence. 1. A feasible region that is open and can go on forever is called. unbounded 2. To means to seek the best price or profit using linear programming.
Section 2 Equations and Inequalities
 Section 2 Equations and Inequalities The following Mathematics Florida Standards will be covered in this section: MAFS.912.A-SSE.1.2 Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. MAFS.912.A-REI.1.1
Section 2 Equations and Inequalities The following Mathematics Florida Standards will be covered in this section: MAFS.912.A-SSE.1.2 Use the structure of an expression to identify ways to rewrite it. MAFS.912.A-REI.1.1
Review for the Algebra EOC
 Review for the Algebra EOC The test is Thursday, January 26 th, 2017 The answer key for this review booklet can be found at: www.mrshicklin.pbworks.com 1. A 1,500-gallon tank contains 200 gallons of water.
Review for the Algebra EOC The test is Thursday, January 26 th, 2017 The answer key for this review booklet can be found at: www.mrshicklin.pbworks.com 1. A 1,500-gallon tank contains 200 gallons of water.
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT
 HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT 8 th Grade Math Third Quarter Unit 3: Equations Topic C: Equations in Two Variables and Their Graphs (Continued) This topic focuses on extending the
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT 8 th Grade Math Third Quarter Unit 3: Equations Topic C: Equations in Two Variables and Their Graphs (Continued) This topic focuses on extending the
Tennessee Comprehensive Assessment Program TCAP. Algebra I Practice Test Subpart 1, Subpart 2, & Subpart 3. Student Name.
 Tennessee Comprehensive Assessment Program TCAP Algebra I Practice Test Subpart 1, Subpart 2, & Subpart 3 Student Name Teacher Name r2 Published under contract with the Tennessee Department of Education
Tennessee Comprehensive Assessment Program TCAP Algebra I Practice Test Subpart 1, Subpart 2, & Subpart 3 Student Name Teacher Name r2 Published under contract with the Tennessee Department of Education
Unit 4 Linear Relationships
 Unit 4 Linear Relationships Standards: 8.EE.5 8.EE.6 8.EE.7 8.F.1 8.F.2 8.F.3 8.F.4 8.F.5 Domain and Standards Overview Expressions and Equations Understand the connections between proportional relationships,
Unit 4 Linear Relationships Standards: 8.EE.5 8.EE.6 8.EE.7 8.F.1 8.F.2 8.F.3 8.F.4 8.F.5 Domain and Standards Overview Expressions and Equations Understand the connections between proportional relationships,
OTHER METHODS FOR SOLVING SYSTEMS
 Topic 18: Other methods for solving systems 175 OTHER METHODS FOR SOLVING SYSTEMS Lesson 18.1 The substitution method 18.1 OPENER 1. Evaluate ab + 2c when a = 2, b = 3, and c = 5. 2. Following is a set
Topic 18: Other methods for solving systems 175 OTHER METHODS FOR SOLVING SYSTEMS Lesson 18.1 The substitution method 18.1 OPENER 1. Evaluate ab + 2c when a = 2, b = 3, and c = 5. 2. Following is a set
Linear Equations Revisited Four Important Formulas: Math 8. Slope: Slope-Intercept Form: y mx b. Standard:
 Linear Equations Revisited Four Important Formulas: Slope: m x x Slope-Intercept Form: mx b Standard: Ax B C Point-Slope: m x ) ( x You should be able to convert equations easil. Example: Convert to slope-intercept
Linear Equations Revisited Four Important Formulas: Slope: m x x Slope-Intercept Form: mx b Standard: Ax B C Point-Slope: m x ) ( x You should be able to convert equations easil. Example: Convert to slope-intercept
1-1 Practice. Patterns and Expressions. Describe each pattern using words. Draw the next figure in each pattern.
 1-1 Practice Patterns and Expressions Describe each pattern using words. Draw the next figure in each pattern. 1. 2. 3. Copy and complete each table. Include a process column. 4. 5. 6. Input Output Input
1-1 Practice Patterns and Expressions Describe each pattern using words. Draw the next figure in each pattern. 1. 2. 3. Copy and complete each table. Include a process column. 4. 5. 6. Input Output Input
CCSS MIDDLE SCHOOL PROPORTIONAL REASONING: IT S A BIG DEAL
 CCSS MIDDLE SCHOOL PROPORTIONAL REASONING: IT S A BIG DEAL Presented by Cynthia Raff cynthia@mathandteaching.org Mark Goldstein mark@mathandteaching.org The Center for Mathematics and Teaching, Inc. www.mathandteaching.org
CCSS MIDDLE SCHOOL PROPORTIONAL REASONING: IT S A BIG DEAL Presented by Cynthia Raff cynthia@mathandteaching.org Mark Goldstein mark@mathandteaching.org The Center for Mathematics and Teaching, Inc. www.mathandteaching.org
ALGEBRA I END-of-COURSE PRACTICE
 1. Which graph is the solution to the inequality A. 2 x 6 B. C. D. 2. Which of the following tables does not represent a functional relationship? Division of Mathematics, Science, and Advanced Academic
1. Which graph is the solution to the inequality A. 2 x 6 B. C. D. 2. Which of the following tables does not represent a functional relationship? Division of Mathematics, Science, and Advanced Academic
ACTIVITY 3. Learning Targets: 38 Unit 1 Equations and Inequalities. Solving Inequalities. continued. My Notes
 Learning Targets: Write inequalities to represent real-world situations. Solve multi-step inequalities. SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Create Representations, Guess and Check, Look for a Pattern, Think-Pair-Share,
Learning Targets: Write inequalities to represent real-world situations. Solve multi-step inequalities. SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Create Representations, Guess and Check, Look for a Pattern, Think-Pair-Share,
Unit Test Linear equations and Inequalities
 Unit Test Linear equations and Inequalities Name: Date: Directions: Select the best answer for the following questions. (2 points each) 7L 1. The steps for solving are: 1) Read the problem and label variables,
Unit Test Linear equations and Inequalities Name: Date: Directions: Select the best answer for the following questions. (2 points each) 7L 1. The steps for solving are: 1) Read the problem and label variables,
constant matrix Study Guide and Review - Chapter 3
 Choose the term from above to complete each sentence. 1. A feasible region that is open and can go on forever is called. unbounded 2. To means to seek the best price or profit using linear programming.
Choose the term from above to complete each sentence. 1. A feasible region that is open and can go on forever is called. unbounded 2. To means to seek the best price or profit using linear programming.
2.5 Solving Compound Inequalities 2017 ink.notebook. October 03, page 70. page 69. page Compound Inequalities
 2.5 Solving Compound Inequalities 2017 ink.notebook page 70 page 69 page 68 2.5 Compound Inequalities Lesson Objectives Standards Standards 2.5 Solving Compound Inequalities N.Q.3 A.CED.1 A.CED.3 A.CED.3
2.5 Solving Compound Inequalities 2017 ink.notebook page 70 page 69 page 68 2.5 Compound Inequalities Lesson Objectives Standards Standards 2.5 Solving Compound Inequalities N.Q.3 A.CED.1 A.CED.3 A.CED.3
Equations can be classified according to the types of operations and quantities involved. Important types include:
 UNIT 5. EQUATIONS AND SYSTEM OF EQUATIONS EQUATIONS An equation is a mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions. In modern notation, this is written by placing the expressions
UNIT 5. EQUATIONS AND SYSTEM OF EQUATIONS EQUATIONS An equation is a mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions. In modern notation, this is written by placing the expressions
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Assessment: 07 Mathematics Mathematics Interim 2
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Assessment: 07 Mathematics Mathematics Interim 2 Description: Mid-Year 2014 - Grade 7 Mathematics Form: 201 1. Which statement describes
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Assessment: 07 Mathematics Mathematics Interim 2 Description: Mid-Year 2014 - Grade 7 Mathematics Form: 201 1. Which statement describes
Summer Prep Work for Students Entering Geometry
 Summer Prep Work for Students Entering Geometry Operations, Expressions, and Equations 4 1. Evaluate when a =, b = 0.5, c =, d = (cd) + ab. The expression x(x + ) is the same as: a.) x + b.) x + c.) x
Summer Prep Work for Students Entering Geometry Operations, Expressions, and Equations 4 1. Evaluate when a =, b = 0.5, c =, d = (cd) + ab. The expression x(x + ) is the same as: a.) x + b.) x + c.) x
Equations & Inequalities Chapter Questions. 3. What are two different ways to solve equations with fractional distributive property?
 Equations & Inequalities Chapter Questions 1. What are inverse operations? Name them. 2. How do you solve equations? 3. What are two different ways to solve equations with fractional distributive property?
Equations & Inequalities Chapter Questions 1. What are inverse operations? Name them. 2. How do you solve equations? 3. What are two different ways to solve equations with fractional distributive property?
To determine the slope or rate of change of a linear function, use m =, positive slopes, rises from left to right, negative
 Common Core Regents Review Linear Functions The standard form for a linear equation is y = mx + b, where m represents the slope and b represents the y-intercept. To determine the slope or rate of change
Common Core Regents Review Linear Functions The standard form for a linear equation is y = mx + b, where m represents the slope and b represents the y-intercept. To determine the slope or rate of change
WRITING EQUATIONS through 6.1.3
 WRITING EQUATIONS 6.1.1 through 6.1.3 An equation is a mathematical sentence that conveys information to the reader. It uses variables and operation symbols (like +, -, /, =) to represent relationships
WRITING EQUATIONS 6.1.1 through 6.1.3 An equation is a mathematical sentence that conveys information to the reader. It uses variables and operation symbols (like +, -, /, =) to represent relationships
On Your Own. Applications. Unit 1. 1 p = 7.5n - 55, where n represents the number of car washes and p represents the profit in dollars.
 Applications 1 p = 7.5n - 55, where n represents the number of car washes and p represents the profit in dollars. 2 t = 0.5 + 2a, where a represents the area of the grass and t represents the time in hours
Applications 1 p = 7.5n - 55, where n represents the number of car washes and p represents the profit in dollars. 2 t = 0.5 + 2a, where a represents the area of the grass and t represents the time in hours
2(m + 3) + 5 = 7(4 m) 5m Simplify both sides of the equation using order of operations. Solution
 Unit 2, Activity 2, Split-Page Notetaking Example 2(m + 3) + 5 = 7(4 m) 5m Simplify both sides of the equation using order of operations. 2m + 6 + 5 = 28 7m 5m 2m + 11 = 28 12m +12m +12m 14m + 11 = 28-11
Unit 2, Activity 2, Split-Page Notetaking Example 2(m + 3) + 5 = 7(4 m) 5m Simplify both sides of the equation using order of operations. 2m + 6 + 5 = 28 7m 5m 2m + 11 = 28 12m +12m +12m 14m + 11 = 28-11
Linear Models Practice EOC Practice Standard A-CED.2
 Linear Models Practice EOC Practice Standard A-CED.2 6. An ice cream shop charges $1 for a cone and $2 per scoop of ice cream. Which equation models the cost of an ice cream cone, y, with x scoops of ice
Linear Models Practice EOC Practice Standard A-CED.2 6. An ice cream shop charges $1 for a cone and $2 per scoop of ice cream. Which equation models the cost of an ice cream cone, y, with x scoops of ice
Algebra. Chapter 6: Systems of Equations and Inequalities. Name: Teacher: Pd:
 Algebra Chapter 6: Systems of Equations and Inequalities Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents Chapter 6-1: SWBAT: Identify solutions of systems of linear equations in two variables; Solve systems of linear
Algebra Chapter 6: Systems of Equations and Inequalities Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents Chapter 6-1: SWBAT: Identify solutions of systems of linear equations in two variables; Solve systems of linear
Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations. Unit Calendar
 Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations Unit Calendar Date Topic Homework Nov 5 (A ) 6.1 Solving Linear Inequalities +/- 6.2 Solving Linear Inequalities x/ 6.3 Solving
Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations Unit Calendar Date Topic Homework Nov 5 (A ) 6.1 Solving Linear Inequalities +/- 6.2 Solving Linear Inequalities x/ 6.3 Solving
Solving and Graphing Linear Inequalities Chapter Questions. 2. Explain the steps to graphing an inequality on a number line.
 Solving and Graphing Linear Inequalities Chapter Questions 1. How do we translate a statement into an inequality? 2. Explain the steps to graphing an inequality on a number line. 3. How is solving an inequality
Solving and Graphing Linear Inequalities Chapter Questions 1. How do we translate a statement into an inequality? 2. Explain the steps to graphing an inequality on a number line. 3. How is solving an inequality
Algebra 1 STAAR Review Name: Date:
 Algebra 1 STAAR Review Name: Date: 1. Which graph does not represent y as a function of x? I. II. III. A) I only B) II only C) III only D) I and III E) I and II 2. Which expression is equivalent to? 3.
Algebra 1 STAAR Review Name: Date: 1. Which graph does not represent y as a function of x? I. II. III. A) I only B) II only C) III only D) I and III E) I and II 2. Which expression is equivalent to? 3.
COLLEGE ALGEBRA. Linear Functions & Systems of Linear Equations
 COLLEGE ALGEBRA By: Sister Mary Rebekah www.survivormath.weebly.com Cornell-Style Fill in the Blank Notes and Teacher s Key Linear Functions & Systems of Linear Equations 1 2 Slope & the Slope Formula
COLLEGE ALGEBRA By: Sister Mary Rebekah www.survivormath.weebly.com Cornell-Style Fill in the Blank Notes and Teacher s Key Linear Functions & Systems of Linear Equations 1 2 Slope & the Slope Formula
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition. Mathematics. 8 th Grade Unit 4: Functions
 CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics 8 th Grade Unit 4: Functions These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. The contents
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics 8 th Grade Unit 4: Functions These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. The contents
The steps in Raya s solution to 2.5 (6.25x + 0.5) = 11 are shown. Select the correct reason for line 4 of Raya s solution.
 A.CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear functions. Unit 2: Reasoning with Linear Equations and Inequalities The perimeter
A.CED.1 Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear functions. Unit 2: Reasoning with Linear Equations and Inequalities The perimeter
Lesson 5: Solving Linear Systems Problem Solving Assignment solutions
 Write inequalities to represent the following problem, and then solve to answer the question. 1. The Rent-A-Lemon Car Rental Company charges $60 a day to rent a car and an additional $0.40 per mile. Alex
Write inequalities to represent the following problem, and then solve to answer the question. 1. The Rent-A-Lemon Car Rental Company charges $60 a day to rent a car and an additional $0.40 per mile. Alex
Section 4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities
 Section 4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality? Question 2 How do you graph a system of linear inequalities? Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality?
Section 4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality? Question 2 How do you graph a system of linear inequalities? Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality?
Math 7 Homework # 46 M3 L1
 Name Date Math 7 Homework # 46 M3 L1 Lesson Summary Terms that contain exactly the same variable symbol can be combined by addition or subtraction because the variable represents the same number. Any order,
Name Date Math 7 Homework # 46 M3 L1 Lesson Summary Terms that contain exactly the same variable symbol can be combined by addition or subtraction because the variable represents the same number. Any order,
CHAPTER 2: INTRODUCTION TO VARIABLES AND PROPERTIES OF ALGEBRA
 CHAPTER 2: INTRODUCTION TO VARIABLES AND PROPERTIES OF ALGEBRA Chapter Objectives By the end of this chapter, students should be able to: Interpret different meanings of variables Evaluate algebraic expressions
CHAPTER 2: INTRODUCTION TO VARIABLES AND PROPERTIES OF ALGEBRA Chapter Objectives By the end of this chapter, students should be able to: Interpret different meanings of variables Evaluate algebraic expressions
3-1 Solving Systems of Equations. Solve each system of equations by using a table. 1. ANSWER: (3, 5) ANSWER: (2, 7)
 Solve each system of equations by using a table. 1. 9. CCSS MODELING Refer to the table below. (3, 5) 2. (2, 7) Solve each system of equations by graphing. 3. a. Write equations that represent the cost
Solve each system of equations by using a table. 1. 9. CCSS MODELING Refer to the table below. (3, 5) 2. (2, 7) Solve each system of equations by graphing. 3. a. Write equations that represent the cost
Section 2.1 Exercises
 Section. Linear Functions 47 Section. Exercises. A town's population has been growing linearly. In 00, the population was 45,000, and the population has been growing by 700 people each year. Write an equation
Section. Linear Functions 47 Section. Exercises. A town's population has been growing linearly. In 00, the population was 45,000, and the population has been growing by 700 people each year. Write an equation
Name Class Date. Describe each pattern using words. Draw the next figure in each pattern Input Output
 1-1 Practice Patterns and Expressions Form G Describe each pattern using words. Draw the next figure in each pattern. 1. 2. 3. Copy and complete each table. Include a process column. 4. 5. 6. Input Output
1-1 Practice Patterns and Expressions Form G Describe each pattern using words. Draw the next figure in each pattern. 1. 2. 3. Copy and complete each table. Include a process column. 4. 5. 6. Input Output
Unit 7 Systems and Linear Programming
 Unit 7 Systems and Linear Programming PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to solve linear equations students should be able to graph linear equations students should be able to create linear equations
Unit 7 Systems and Linear Programming PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to solve linear equations students should be able to graph linear equations students should be able to create linear equations
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. Linear Equations & Graphs 1. A line has a y intercept of and a slope of. Find the equation of the line. A. B. C. D. Evaluate Functions 2. The graph of the function
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. Linear Equations & Graphs 1. A line has a y intercept of and a slope of. Find the equation of the line. A. B. C. D. Evaluate Functions 2. The graph of the function
Name Algebra 1 Midterm Review Period. = 10 4x e) x ) Solve for y: a) 6x 3y = 12 b) 4y 8x = 16
 Name Algebra 1 Date Midterm Review Period 1) Solve each equation: a) x 2x + 2 = 3 b) 5 5 + 9 = 13 c) 64 = 9x +1 d) x 7 2 = 10 4x e) x + 2 3 = 3x 2) Solve for y: a) 6x 3y = 12 b) 4y 8x = 16 3) Solve and
Name Algebra 1 Date Midterm Review Period 1) Solve each equation: a) x 2x + 2 = 3 b) 5 5 + 9 = 13 c) 64 = 9x +1 d) x 7 2 = 10 4x e) x + 2 3 = 3x 2) Solve for y: a) 6x 3y = 12 b) 4y 8x = 16 3) Solve and
Winter-Break Packet 7 th grade mathematics
 M.S. 181 PABLO CASALS CHRISTOPHER WARNOCK, PRINCIPAL 800 BAYCHESTER AVENUE, BRONX, NY 10475 PHONE: 718-904-5600 Conceive, it, Believe it, Achieve it! Winter-Break Packet 7 th grade mathematics Student:
M.S. 181 PABLO CASALS CHRISTOPHER WARNOCK, PRINCIPAL 800 BAYCHESTER AVENUE, BRONX, NY 10475 PHONE: 718-904-5600 Conceive, it, Believe it, Achieve it! Winter-Break Packet 7 th grade mathematics Student:
